- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

Narrative Nonfiction Books: Definition and Examples

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is narrative nonfiction, narrative nonfiction examples, how prowritingaid can help you write narrative nonfiction.
There are countless types of nonfiction books that you can consider writing. One popular genre you might have heard of is narrative nonfiction.
So, what exactly is narrative nonfiction?
The short answer is that narrative nonfiction is any true story written in the style of a fiction novel.
Read on to learn more about what narrative nonfiction looks like as well as some examples of bestselling narrative nonfiction books.
Let’s start with a quick overview of what narrative nonfiction means.
Narrative Nonfiction Definition
Narrative nonfiction, which is also sometimes called literary nonfiction or creative nonfiction, is a subgenre of nonfiction . This subgenre includes any true story that’s written in the style of a novel.

It’s easy to understand this term if you break it down into its component parts. The first word, narrative, means story. The second word, nonfiction , means writing that’s based on fact rather than imagination.
So, if you put those two words together, it’s clear that narrative nonfiction refers to true events that are written in the style of a story.
Narrative Nonfiction Meaning
You can think of narrative nonfiction as a genre that focuses both on conveying the truth and on telling a good story.
Everything in a narrative nonfiction book should be an accurate portrayal of true events. However, those events are told using techniques that are often used in fiction.
For example, narrative nonfiction writers might consider writing craft elements such as plot structure, character development, and effective world-building to craft a compelling story.
Most narrative nonfiction books include the following elements:
A protagonist (either the author themselves or the core subject of the story)
A cast of characters (who are real people)
Immersive, fleshed-out scenes
A plot arc similar to the plot arcs found in fiction novels
Use of literary devices such as metaphors, symbols, and flashbacks
Some narrative nonfiction writers also play with more creative elements to make the story more intriguing, such as multiple POVs, alternating timelines, and even the inclusion of emails, diary entries, and text messages.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
At the end of the day, though, narrative nonfiction is still a form of nonfiction. That means it’s important to try to be as accurate as possible.
Authors writing in this genre need extensive research skills, whether that means combing through historical records or interviewing experts. It’s impossible to create a completely accurate representation of any true story, so it’s fine to take some creative license when writing narrative nonfiction, but most authors still do as much research as they can to make sure they’re correctly depicting what happened.
Which Genres Count as Narrative Nonfiction?
It’s hard to draw a clear line around what counts as narrative nonfiction since many works of writing blur the lines between subgenres.
Two genres that commonly intersect with narrative nonfiction are memoir and autobiography, which are terms that apply when an author tells the story of their own life. When these stories are told in a narrative style, some people consider that to be narrative nonfiction or literary nonfiction, while others believe memoir and autobiography should be a separate category.
Most journalism and biographies aren’t included under the narrative nonfiction umbrella, since they usually focus more on reporting than on telling a story. Still, a form of journalism called literary journalism deliberately aims to tell personal stories in a more creative way, and there are also biographies that do the same.
Some books in other nonfiction subgenres, such as travel writing, true crime, and even food writing, can also be told in a way that resembles narrative nonfiction. In fact, more and more nonfiction books these days are using literary techniques to hook readers in.
Narrative nonfiction books can focus on just about any topic as long as they use literary styles to tell true stories. If you’re writing nonfiction, you can definitely consider incorporating literary elements to craft a compelling narrative around your topic.
The best way to understand a genre of writing is by reading examples within that genre. Here are ten of the best narrative nonfiction books to add to your reading list.
In Cold Blood by Truman Capote (1965)
Truman Capote, best known for his novella Breakfast at Tiffany’s, started out as a fiction writer. When he wrote In Cold Blood , he famously called it a “nonfiction novel,” which introduced that term into the popular consciousness for the first time.
In Cold Blood tells the story of a brutal quadruple murder that took place in 1959 in Holcomb, Kansas. The book describes the details of the murder, the ensuing investigation, and the eventual arrest of the murderers.
In many ways, In Cold Blood defined the narrative nonfiction genre. It was one of the first times an author had written journalism in the structure of a novel, and it inspired many future writers to try creative nonfiction too.
Into Thin Air by Jon Krakauer (1997)
Jon Krakauer is a journalist and a mountaineer who summited Mt. Everest on the day a terrible storm hit the mountain. That storm ended up claiming five lives and leaving Krakauer himself ridden with guilt.
Into Thin Air is Krakauer’s account of his adventure and its deadly aftermath. It portrays the entire cast of characters that accompanied him up the mountain and also shows the character growth Krakauer experienced as a result.
This book is a famous example of a memoir that reads like an adventure novel. The American Academy of Arts and Letters gave this book an Academy Award in Literature in 1999 and described it as combining “the finest tradition of investigative journalism with the stylish subtlety and profound insight of the born writer.”
Seabiscuit: An American Legend by Laura Hillenbrand (1999)
Seabiscuit was a California racehorse in the 1930s. Because of his crooked leg, he was never expected to win.
However, when Seabiscuit was bought by Charles Howard and ridden by a jockey named Red Pollard, he rose to unexpected success. Now, Seabiscuit is remembered as one of the most iconic racehorses of all time.
Laura Hillenbrand, an equestrian writer, tells Seabiscuit’s story in this classic work of narrative nonfiction. Charles Howard, Red Pollard, and all the other characters involved in Seabiscuit’s life are researched and portrayed in a masterful way.

Reading Lolita in Tehran: A Memoir in Books by Azar Nafisi (2003)
From 1995 to 1997, Nafisi led a secret book club at her house in Tehran. Every Thursday, she met with her most dedicated female student to read banned Western classics together, from Pride and Prejudice to Lolita.
In Reading Lolita in Tehran , Nafisi describes her experiences throughout the Iranian revolution. It’s a gripping book that provides rare and extraordinary insight into what it was like to be a woman in Tehran in the late 1990s.
Like all great narrative nonfiction, this book would be a compelling novel even if you didn’t know it was a true story, but the fact that it’s all true makes it even more powerful.
The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks by Rebecca Skloot (2010)
Henrietta Lacks was a Black woman whose cells were taken by medical researchers in 1951 without her knowledge or consent. Ever since then, her cells, now known as HeLa cells, have been kept alive for medical uses.
HeLa cells have been essential for researching diseases, creating the polio vaccination, and making other medical breakthroughs. And yet, her family never benefited from or consented to their use.
Rebecca Skloot’s bestselling book The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks tells Lacks’ story in a thoughtful and illuminating way, weaving in research on the unjust intersection of medicine and race. The book won many awards and was later made into an HBO movie.
Hidden Figures by Margot Lee Shetterly (2016)
America’s achievements in space could never have happened without the contributions of Black female mathematicians at NASA, known as “human computers.” Before modern computers existed, these women used pen and paper to perform the calculations that launched rockets into space.
Shetterly’s book tells the stories of four of these brilliant women: Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson, Katherine Johnson, and Christine Darden. The story follows them for over three decades as they overcame racial and gender prejudices to help shape American history.
This work of literary nonfiction is well-researched, informative, and powerful. It was also made into a major motion picture by Twentieth Century Fox.
When Breath Becomes Air by Paul Kalanithi (2016)
Paul Kalanithi, a Stanford neurosurgeon, was only 36 years old when he received his Stage IV lung cancer diagnosis. He went from treating patients to becoming the patient in such a short span of time that he had to quickly learn how to accept his own mortality.
Kalanithi wrote this medical memoir during the last years of his life, describing how he came to terms with his diagnosis. When Breath Becomes Air tells Kalanithi’s story in a poignant and unforgettable way.
Killers of the Flower Moon: The Osage Murders and the Birth of the FBI by David Grann (2017)
Killers of the Flower Moon is a true crime murder mystery about a terrible crime in the 1920s, when members of the Osage Indian nation in Oklahoma started getting killed one by one. Anyone who tried to investigate was in danger of getting murdered too until the death toll rose to over two dozen.
When the truth was finally uncovered, it turned out to be a chilling conspiracy bolstered by prejudice against Indigenous people.
Journalist David Grann tells the story of this shocking crime in this narrative nonfiction book, which is soon to be made into a major motion picture.
I’ll Be Gone in the Dark: One Woman’s Obsessive Search for the Golden State Killer by Michelle McNamara (2018)
The Golden State Killer was a serial killer who raped and murdered dozens of people in the 1970s and 1980s. Michelle McNamara was a true crime journalist who coined the name “Golden State Killer” in 2013 when she was poring over police records, determined to figure out the killer’s identity.
I’ll Be Gone in the Dark, which was still in the process of being written when McNamara died, blurs the genres between nonfiction, memoir, and crime fiction. The book eventually helped lead to the killer’s capture.
Facing the Mountain: A True Story of Japanese American Heroes in WWII by Daniel James Brown (2021)
After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, Japanese Americans faced suspicion and systemic prejudice from their own country. In spite of the injustices they faced over the next several years, many Japanese Americans still signed up to fight for the US in World War II.
In Facing the Mountain , Daniel James Brown tells the stories of four Japanese American heroes: Rudy Tokiwa, Kats Miho, Gordon Hirabayashi, and Fred Shiosaki. The book follows these four men and their families and communities, who were irreversibly impacted by the events of the war.

Writing narrative nonfiction can be incredibly rewarding, but it can also be unusually tricky because you have to accomplish two goals at once. Unlike other nonfiction, which aims to inform, or most fiction, which aims to entertain, narrative nonfiction seeks to inform and entertain at the same time.
To inform, you’ll need your writing to be clear and easily readable. To entertain, you’ll need it to be gripping and active.
ProWritingAid can help with both of those goals. At the most basic level, the AI-powered grammar checker will make sure your writing is free of grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes. At a more sophisticated level, it will also make sure you’re hooking your reader in by using the active voice, precise word choices, and varied sentence lengths.
In addition, you can also use ProWritingAid to make sure you’re writing in the right tone and for the right reading level. Running your narrative nonfiction manuscript through ProWritingAid will ensure your writing truly shines.
There you have it—our complete guide to narrative nonfiction.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Join the Mailing List
Search the blog.
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Alyssa Teaches
an Upper Elementary Blog
Teaching Narrative Nonfiction

I remember when I first saw the term “narrative nonfiction” in my state’s reading standards and honestly, I didn’t know what it meant! If you’re new to teaching literary nonfiction, I hope this post will give you a good overview to get you started!
What Is Narrative Nonfiction?
Narrative nonfiction, or literary nonfiction, is nonfiction text that uses a storytelling structure to present information about a topic, such as a real person or event. It’s different than expository text, which simply presents the facts.
Since the facts are written in a narrative format with characters, a setting, a plot, etc., it can be a more engaging and memorable way for students to learn about the world.

It’s kind of tricky to differentiate between narrative nonfiction and historical fiction. To me, narrative nonfiction is more about presenting facts through a story, and historical fiction is more about telling a story that is based on some facts. Clear as mud, lol.
Biographies, autobiographies, and memoirs are definitely part of the narrative nonfiction genre, but it can also include texts based on historical events or other topics like animals. The good news is that there’s a huge variety of texts that will attract readers with different interests in your classroom.
Introducing Narrative Nonfiction
One way to kick off this unit is to put out a selection of nonfiction, fiction, and literary nonfiction books for students to explore. You can have them work in small groups to discuss what they notice about the formats of the books and maybe sort them into groups.
They’ll start to see that expository nonfiction books have text features and mostly stick to the facts, but narrative nonfiction books look a lot more like fiction and often contain dialogue. I like to create an anchor chart as groups share the characteristics they notice.
Another option to introduce literary nonfiction is to start with a mentor text read-aloud and ask students to identify the author’s purpose. This leads to great discussions and helps students see that it’s kind of the best of both worlds. Scroll down for some of my recommendations for books to use!
Book Pairings
Another way to teach students the difference between expository texts and narrative nonfiction texts is to pair literary nonfiction books with nonfiction books on the same topic. Students can compare and contrast the structures and details of the two books. I ask students to discuss which type is the most efficient to use if you need to find a fact quickly, and I also have them share which type they prefer. You can also try using shorter passages , which are great for reading groups.
Here are some examples of book pairings:
The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind [picture book] by William Kamkwamba and Wind Power: Alternative Energy by Matthew Ziem

I, Fly: The Buzz About Flies and How Awesome They Are by Bridget Heos and Flies by Larry Dane Brimner

Similarly, you can compare narrative nonfiction books or passages with fiction by asking students to highlight the facts they find it in each. This is a great way to reinforce author’s purpose for this unit – while they’re being entertained, they are also being hit with lots of facts!
Literary Nonfiction Skills and Standards
There are tons of reading skills that you can weave into a literary nonfiction unit, including:
- summarizing the events and supporting details (and sequencing, too)
- drawing conclusions and making inferences
- identifying the conflict and resolution
- analyzing the author’s word choice (i.e., figurative language, descriptive words, vocabulary)
- identifying cause and effect relationships
- inferring character traits
- identifying the narrator of the story
- describing how the language, characters, and setting contribute to the plot
- explaining the author’s purpose
- synthesizing the main idea of the text (i.e., what are this person’s contributions/why is this event significant?)
My fourth graders were struggling one year with summarizing the events of a text. I read aloud Only Passing Through: The Story of Sojourner Truth by Anne Rockwell. We identified the major events in the story as a class and then I assigned partners one event to illustrate and write in their own words. We put them together to create our own timeline of the book and it made a really nice display.
This genre is a perfect one to dive deep into character analysis and have students infer character traits using evidence from the text. They can practice making conclusions about that person’s contributions or the event’s significance. I’ve also had some great conversations with my students about what might have happened to the character(s) if they’d lived in a different place or time.
My Favorite Narrative Nonfiction Books
Here are a few narrative nonfiction mentor texts that I recommend for 3rd-6th grades! Click on the titles for more info!
- Finding Winnie: The True Story of the World’s Most Famous Bear by Lindsay Mattick
- Pop!: The Invention of Bubble Gum by Meghan McCarthy
- We Are the Ship: The Story of Negro League Baseball by Kadir Nelson
- The Boston Tea Party by Russell Freedman
- One Plastic Bag: Isatou Ceesay and the Recycling Women of the Gambia by Miranda Paul
- Owen & Mzee: The True Story of a Remarkable Friendship by Isabella Hatkoff
- Mr. Ferris and His Wheel by Kathryn Gibbs Davis
- Separate is Never Equal by Duncan Tonatiuh
- The Marvelous Thing that Came From a Spring by Gilbert Ford
- Mesmerized: How Ben Franklin Solved a Mystery That Baffled All of France by Mara Rockliff
- Henry’s Freedom Box by Levine Ellen
- Ivan: The Remarkable True Story of the Shopping Mall Gorilla by Katherine Applegate
- Nya’s Long Walk: A Step at a Time by Linda Sue Park
- Balloons Over Broadway by Melissa Sweet
- One Tiny Turtle by Nicola Davies
Scholastic News and Time for Kids are some other good places to look for short narrative nonfiction articles.
I think narrative nonfiction is a really engaging and fun genre to teach. It definitely makes informational text more accessible for reluctant readers! It’s also fun to have students write their own pieces after researching a person or topic of interest to them. What tips do you have for teaching a literary nonfiction unit?
This post contains affiliate links; I earn a small commission from products purchased through these links.

Related posts

Must-Have Summer Narrative Nonfiction Books for Kids

Teaching Headings and Subheadings

Teaching Fact and Opinion in Upper Elementary
30 comments.
Hey there – I was wondering if you had a link to the anchor chart you used? So glad I found your site and TPT – need more VA TPT teachers 🙂
Hi Rachel, I’m glad you’re finding the content helpful! Please email me through the Contact page and I can send it to you!
I would love to have the anchor chart that you used! I’ll be using your guidance as I teach this for the first time! So great!
I was searching for additional work on narrative nonfiction. I found this very attractive and informative for fourth graders in this virtual learning era. I will definitely use the image as my introduction.
I was thinking of how to teach Nonfiction and came across your post. Thank you so much for posting it. I found it very useful.
I subscribed but I was never sent these anchor charts.
Hi April, thanks for subscribing! You should receive an email asking you to confirm your subscription. Please check for that in your spam folder!
I subscribed but was never sent the anchor chart.
Hi Erin, thanks for subscribing! You should receive a confirmation email asking you to confirm your subscription, and then you’ll get a second email with the download. Please reach out again if you don’t see it!
Thank you for the post. I also subscribed with the hopes of receiving the anchor chart but it hasn’t come through yet.
Hi Leslie, thanks for subscribing! If you used your work email address, it may have been blocked or gone to your spam folder. Can you please try again with a personal email?
Could you please share your anchor chart? Thanks!
Hi there! If you use the link at the bottom of the post to enter your email, it will automatically be sent to you!
Thank you for sharing!
Hello. I subscribed, but alas no anchor chart. I did check all mail including spam and did use a personal email address. Thanks for your help.
Sending you an email, Kimberly!
Hi there, I did subscribe like the others but did not receive the anchor chart. I checked my spam folder as well.
I’ll send it your way, Lisa!
Hello! I did subscribe to follow your work, though I did not a chart. How would I go about being able to get one? Thank you!
Hi Jill! Did you receive a confirmation email? Let me know if you haven’t gotten access to the PDF yet!
Hello Alyssa. Great website and resources! I just wanted to let you know that I have subscribed and checked my spam folder, but I have received no confirmation email and anchor charts. I would love the PDF if possible. Thank you so much!
Hi Euan! Did the download go through for you?
Hello! I subscribed and received the confirmation email, but did not receive the anchor chart. I would love to use the anchor chart with my students. Thannks!
Hi Sherri! Did the download go through for you?
Hi, I subscribed and did not receive the anchor chart. Are you able to email to me or send a pdf?
Hi, I’m not sure what’s going on with this download lately! Did you receive a confirmation email?
I subscribed and didn’t get the narrative nonfiction anchor chart.
Hi there! Did you confirm your subscription in the initial email? Let me know if you still don’t see it!
Did you ever post the anchor chart? and yes, I would love to see the mini-lessons you taught with this unit. My 11th grade students are interviewing someone over Christmas break in anticipation of writing a 1000-word nonfiction narrative. The collection will be published by our local newspaper into a hard-bound book. I’m excited to get rolling after Christmas. We’ve been reading memoirs and collecting beautiful sentences.
What an amazing project! I did something similar in 8th grade and interviewed my grandmother! You can access the anchor chart by subscribing to my weekly newsletter at the end of the blog post!
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Join the mailing list for tips, ideas, and freebies.
- Mentor Teacher
- Organization
- Social Studies
- Teacher Tips
- Virginia Studies
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
The Creative Penn
Writing, self-publishing, book marketing, making a living with your writing
How To Write Narrative Non-Fiction With Matt Hongoltz-Hetling
posted on August 24, 2020
Podcast: Download (Duration: 1:04:14 — 52.2MB)
Subscribe: Spotify | TuneIn | RSS | More
What is narrative non-fiction and how do you write a piece so powerful it is nominated for a Pulitzer? In this interview, Matt Hongoltz-Hetling talks about his process for finding stories worth writing about and how he turns them into award-winning articles.

In the intro, I talk about Spotify (possibly) getting into audiobooks and Amazon (possibly) getting into podcasts as reported on The Hotsheet , and the New Publishing Standard . David Gaughran's How to Sell Books in 2020 ; a college student who used GPT3 to reach the top of Hacker News with an AI-generated blog post [ The Verge ]; and ALLi on Is Copyright Broken? Artificial Intelligence and Author Copyright . Plus, synchronicity in book research, and my personal podcast episode on Druids, Freemasons, and Frankenstein: The Darker Side of Bath, England (where I live!)

Matt Hongoltz-Hetling is a Pulitzer finalist and award-winning investigative journalist. He's also the author of A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear .
You can listen above or on your favorite podcast app or read the notes and links below. Here are the highlights and the full transcript below.
- From writing for pennies an article to writing a Pulitzer – nominated article
- What is narrative non-fiction?
- How does narrative non-fiction differ from fiction?
- Where ideas come from and how to begin forming a story idea
- The necessity of being respectful of the real lives being examined and written about
- Portraying interview subjects with shades of grey
- Turning hours of source material into something coherent
- Finding the balance between story structure and meaning
- Knowing when an idea is appropriate for a book
You can find Matt Hongoltz-Hetling at matt-hongoltzhetling.com and on Twitter @hh_matt
Transcript of Interview with Matt Hongoltz-Hetling
Joanna: Matt Hongoltz-Hetling is a Pulitzer finalist and award-winning investigative journalist. He's also the author of A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear . Welcome, Matt.
Matt: Hey, thanks for having me on, Joanna.
Joanna: It's great to have you on the show.
First up, tell us a bit more about you and how you got into writing.
Matt: I got into writing when I was eight years old and I wrote this amazing book. I don't want to brag, but I wrote this book about an elf that was fighting in a dungeon, and this elf had some items of a magical persuasion and used them to defeat all sorts of monsters. So, that was pretty awesome. And I've been writing stuff ever since.
I grew up knowing that I wanted to write, loving to read, all that. And then my career path never really seemed to go that way. I actually started a student newspaper when I was in college in the hopes that that would be primarily a writing occupation, but I found very quickly that it was more small business skills that were needed.
I was selling advertisements much more so than writing to fill the newspaper sadly. And so, at some point I had just got the pile of rejection slips that I think we're all familiar with. I just didn't really know how to go about getting into the industry.
I was literally writing articles for, like, 25 cents an article, these, like, ‘How do you fix an engine?' or not even an engine, nothing that complicated, but, ‘How do you clean a window?'
Joanna: Content farms.
Matt: Yes, right. Content farms. Yes. Thank you. But I was writing.
My wife encouraged me to submit an article for my local weekly newspaper in a small town in the state of Maine. And that led to me being able to write more articles, still for very small amounts, 30 bucks an article. And that led to me getting a full-time job as a journalist at a weekly newspaper in rural Maine.
And even though that was fantastically exciting for me, I always knew that I wanted to do more. And so, I was always pushing, looking for that next level that would allow me to write more of the stuff that I wanted to write. And so, that led to larger newspapers, and then magazine opportunities, and then magazine opportunities led to a book opportunity. Now, I'm happy that I am just on the cusp of publishing my first book. I'm very excited about that.
Joanna: We're going to get into that in a second, but I just wonder because this is so fascinating.
How many years was it between writing for a content farm to being a Pulitzer finalist?
Matt: That was actually the shortest journey that you can imagine. Within, let's say, two years of my first newspaper article. I wrote the article that led to my highest-profile resume point which was that Pulitzer finalist status. And that article was about substandard housing conditions in the federal Section 8 program. It's federally subsidized housing and it's meant to be kept up to a certain standard, and the article which I wrote with a writing partner demonstrated that it was not and that there were a lot of people at fault.
What really elevated that article, it was a good article and all of that, but what really got it that level of recognition was that it also turned out to be an impactful article. It happened to come at a time when other people were looking at the housing authority for various reasons. It really struck a nerve and our Senator, Republican Susan Collins of Maine, she took a very avid interest in our reporting and was motivated to encourage reforms of the national Section 8 system.
She was in a political position to do that because she held the purse strings for the housing authorities. And so, it happened to have this very disproportionate impact and because it led to a positive change for the Section 8 housing program in the United States.
I think the people in the Pulitzer committee must've loved the idea that this tiny little rural weekly newspaper where we had three reporter desks, one of which was perennially vacant, had managed to write a story that was really relevant to the national scene.
Joanna: Absolutely fascinating. And I hope that encourages people listening who might feel that they're in a place in their writing career where they're not feeling very successful and yet you bootstrapped your way up there to something really impactful, as you say.
We're going to come back to the craft of writing, but let's just define ‘narrative nonfiction.' Your book, A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear , which is a great title.
What is narrative nonfiction and where's the line between that and fiction or straight nonfiction?
Matt: Narrative nonfiction, the way that I think of it is i t's basically just like any other fiction book, or novel, or piece that you might pick up except for the events described in it actually happened .
When I think of the difference, it just seems, to me, to be such a small, tiny little difference between fiction and nonfiction because when you write fiction, you're starting with an infinite number of possible events to write about. And when you're writing nonfiction, you're starting with a universe of events.
You're starting with everything that ever happened in the entire universe. That's the material that you can draw on. It is so close to infinite that really, it's just a method of curation. You're going to select some of these facts and arrange them in an order that will create the same exact experience as a powerful piece of fiction writing.
A narrative piece emphasizes the same things that a fiction story would in terms of there's character arcs, there are transformations, there's setting. We want a climax, we want everything that you would want when you're writing a fiction piece.
Joanna: Interesting. And you said at the beginning that it's a tiny difference between fiction and nonfiction. And I'm like, ‘No, surely, this is the biggest separation.' So, I feel like people would have quite a different view on that, but it's interesting because you said there, ‘a method of curation,' and you select the facts, whereas with fiction, obviously, you make it up.
How can you curate truth in a way that serves your story but doesn't distort what really happened?
Matt: That's an excellent question. And I think you do have to be careful to keep things in perspective.
So, I was thinking, ‘What if I was writing about someone in the aeronautics industry or who was an astronaut or maybe someone else within the industry who is motivated by this idea that people want to,' or yeah, ‘that he would like people to colonize the stars?' That's, I think, a very common sci-fi-type theme, and it's also very apparent in the people who go into those fields.
And so, you might take a set of facts. I would ask that person, ‘What are some of the seminal moments in your career? What were the turning points? What were the important things that shaped you as a person?' And this was just an idea that I had, I would look at the amount of cosmic matter in our atmosphere. So, every time a meteor hits the atmosphere, we know it burns up, dust rains down on the earth and that dust becomes part of us. We breathe it in.
Then I would try to draw a timeline between some natural spike in the amount of cosmic dust in the air that might've gone into our subject's body, and that person's decision to get into aeronautics. So, you maybe get to describe that this fantastic spectacular event of a comet the size of a blue whale entering the atmosphere, burning up, raining dust down on, let's say, North America.
And this aeronautics person is 12 years old at the time, he's thinking about baseball, but then he goes to a museum two weeks later and he's breathing in more cosmic dust on that day than he would on an average day, and then he decides to become an astronaut.
You can paint a very poetic scene with that, but it's also very important that you're not actually suggesting or theorizing that the cosmic dust had anything to do with that person's decision.
It's a way to wax poetically about this character and to maybe access a greater idea which is that we all want to go colonize the stars to some extent. That's a very human thing. It appears in our very earliest writings on both fictional and non-fictional.
And you can talk about this amazing spectacular event, you can talk about this person's decision, and if you do it right, the audience will understand that you've just used this as a jumping-off point to explore some of these bigger concepts and cool narrative opportunities without actually saying in a false way that cosmic dust is what makes us want to go out there. So, I'm just saying that you can arrange those events in a way that gives it life, and vibrancy, and maybe some creativity.
Joanna: I like that example. And you brought up so many things that I'm thinking about there.
First of all is using the individual to highlight the universal. If you wrote a piece about how big the universe is or whatever, that's not narrative nonfiction. That might be one of your how-to articles back in the day. So, you've used someone's experience to highlight something universal.
Where do you start? Because this is a question that fiction writers think about all the time. Do you start with the theme of, say, space? Do you start with a character, say you met someone and you want to interview them, or are you starting with, in your case, I guess, a commission or are you starting with just your own curiosity and following where it goes? So, I guess, as you said, that you could write about anything in the whole world.
How do you decide what to write?
Matt: I've spent a lot of my freelance writing career trying to craft pitches that will convince editors to give me a green light and offer me compensation in exchange for a piece of writing. And so, that undergirding structure allows for all those sorts of scenarios that you posit.
I'm always keeping my eye out for things when something interests me and lights me up, then I try to think about how I can make that subject or person who has just lit me up into a pitch that is marketable. I saw a freestyle street rapper a few weeks ago and I was really into what he was doing. I just thought he was amazing because his shtick was that he would incorporate things about the world around him into his rhymes really seamlessly.
I thought, ‘Oh, this guy has got this really amazing talent.' And so then you start thinking like, ‘Is this something that I would pitch to maybe a magazine about rhyme and rhyme structure or is this something that might be more like…is this a cognitive or a neurological skill that he's developed and how might that fit into maybe more of a neuroscience type magazine or is this just a guy who's got the great American story of, he developed a skill on the streets as it were, and then launched it into a career, in which case, we have maybe more of a universal story that could appear in any major market magazine?'
I suppose usually what sparks my interest is a person but it's not at all uncommon for my interest to also be sparked by just a topic. And then I'm searching for those characters who can exemplify that topic.
Joanna: Your writing does focus very much on people and all characters, as you say, but I'm wondering where do you take it from then? How do you tease out the story? Do you interview them?
And again, when you have this material about that person, how do you highlight your story, but also respect the person because you might say that, so, you've got the pitch with the neurological aspect. So, you think, ‘Okay. I want to write about how his brain works differently to someone else, how he can do that,' but then you find out some awful thing and you think that, ‘Okay. How do I respect this person, but how do I also deliver on my pitch?'
How do we ask the right questions to make our characters real, but also be respectful, because this is real life you're writing about?
Matt: My own inclination and approach is typically to just jump in and that's often great because it allows me to maintain forward momentum and use real wishful positive thinking to just hope that everything's going to pan out.
But sometimes its failing is that I will go very confidently striding down what turns out to be a dead end. And so, maybe I pitch this thing as a neurological sciencey story, and then a magazine editor says, ‘Yes, let's do this.' And so then I go back to the subject and I say, ‘I'd like to interview you,' and tell them what's going on.
And in the course of the interview, it turns out that they are not at all representative of the category of box that I want to put them into. And then I've suddenly got this big, awkward problem where I am looking for a different subject to satisfy the magazine editor and trying to get value out of my initial subject and my interview with him by placing him into something that is more appropriate for him. But when I get to that interview phase, I typically like to already have a commission in place before I do that because it's quite a time investment.
When I do interview someone, I like to make them very lengthy, in-depth interviews. Rarely do I talk to someone for less than two or three hours. And in the course of that two or three hours, my interview style is to not necessarily focus too much on asking the right questions so much as just unlocking how they see themselves and what is important to them, and get them talking about what lights them up.
And by not having a very firm idea of where I want to lead a subject, and being flexible in what they can say, what I find is that I often wind up with a really interesting story that maybe doesn't quite fit the mold precisely for where I thought it would go, but it's close enough that I can bridge that gap and the narrative is so compelling and good that nobody cares if there's maybe a slight sidetrack, a slight departure.
And as far as what if you find out something bad about someone while you're in the course of that interview? You're interviewing a person and they suddenly put the interview on pause and speak very sharply or meanly to their spouse or child and suddenly you get the feeling like, ‘You know what, this isn't really actually a very good person.' So, what do you do there?
I think it is very important to acknowledge the bad in people. And it's almost a necessary component. If I am not writing something both bad and good about a person that I'm writing about, then I know I'm not really doing a very good job because I don't know any people who are 100% good and I don't know any people who are 100% bad.
Oftentimes, if I'm talking to someone who we might think of as the hero of a narrative, they're doing good work, we're spotlighting them because of some amazing accomplishment they've done, I think it's really important to throw in a couple of negative character traits or details that will add a note of reality to your writing.
And conversely, if I'm interviewing someone who has committed murder or if I'm interviewing them because they're a bad person, then I'm always really looking for that redeeming quality because some murderers have just had a very bad day or gone through a very bad period in their life and maybe had some disadvantages in the first place.
Even though they've done this terrible, awful thing, there's still some context that you can provide that humanizes them. I think that most of my subjects, I think, appreciate that. Certainly, I've written about some people who've been very unhappy with how they've been portrayed. But I think most people appreciate it when you portray enough facets of their character that their true personality comes through.
Joanna: I've not done this kind of writing. So, I find it fascinating. I've been doing this podcast for 12 years and I have many, many, many hours and a lot of transcripts of material and I've thought many times, ‘It'd be great if I could go through and find all these snippets and turn this into something.' Working with transcripts is really hard. You just mentioned, you have a three-hour interview. So, presumably, you're recording this and you're taking notes as well.
How do you turn all this source material into an article? What's your curation and what's that process?
Matt: I am the kind of person who hates to throw things out. My wife will tell you that that can drive her nuts. And the same is true of my writing. I like to start with everything that has been said, even in a three-hour interview, and then just slowly apply criteria that squeezed some things out.
I always wind up with more material than will fit in the space that I have allotted. And then that encourages me to try to cram more words and more facts into smaller spaces and that results in this real efficient distillation. I think that's another good thing maybe about not being too goal-oriented when you write.
What I typically do is I'll interview someone, we'll have the three-hour interview. I've got copious notes, I got an audio transcript. If I am feeling up to it, I will transcribe every word of that audio interview which is grueling. Sometimes I will use one of those online programs that will convert it and spit out a transcript for you. And that transcript is never perfect, but you can make it perfect by listening and going through. And then I just slowly go through and clean it up.
Often, it's not like writing at all. It's like just fixing things. I might go through it and just correct all the typos in my transcription. And then I might go through and remove all the garble and then I might go through and anything that seems like a cohesive thought, I might put quotation marks around and put on the, ‘he said,' or the, ‘she said.'
Then I will maybe strip out, I'll say, ‘Oh, here, this person talked for 10 minutes about their mother and they were actually quite redundant, but here, this one time they said it, it was the most striking of the eight times they said the same thing.' And so, I will move those other seven iterations down to a notes section at the bottom.
And in this way, I am slowly shrinking and squeezing the text that is there. And if there are things that they've said, points they've made that are important, but that they didn't say it particularly well, then I might write a paraphrase and put the originals down in my notes section.
And then at some point, I will create a series of categories that represent different areas of the story, and then I will sort all of their quotes into those different categories. And all of this stuff that I've just talked about is very mechanical. So, even if you're not feeling particularly inspired, you can go through this rote, brute-force process and nibble away, and nibble away, and nibble away.
What you find at the end is that you actually have the bones of a story.
Often, the story will also involve going through the same process with multiple people and other sources of information, but once you've arranged all that stuff under the subheadings, and then you start to rearrange things within those sections, you find that you are suddenly, magically two-thirds of the way there.
Joanna: That's fascinating. I want to ask about this Pulitzer thing because I know everyone's so interested. And really, this is one of those prizes that is, for many people, a life goal, and you've actually won other awards. You're a multi-award-winning writer.
What's interesting to me is you talked about a story that made an impact. Substandard housing conditions is not the most inspirational thing for most people, but it's interesting. Presumably, you're not winning these prizes for your beautiful sentence structure.
For those authors who obsess with grammar and exact sentences, where's the line between that and story and meaning?
Matt: I think it is all-important including the sentence structure. I always take the position that grammar, and grammar is not really all that important other than in the service of making points very clearly. I really tend to take these very esoteric grammar points and just chuck them out the window because I want somebody to be able to understand what I'm saying.
Oftentimes, adhering very strictly to the rules of grammar impedes the knowledge of the layperson who I want to be able to read, and digest, and appreciate my article . I don't want to poo-poo sentence structure too much. I think there are so many articles written that you're trying to break through the noise of, and stand out in some way. I think the stories that I've been awarded from various organizations and for various things, they've all gone through the same basic process as many of my stories that have not been so recognized and have not turned out necessarily all that good.
But for whatever reason, there was a perfect alignment where the person that I happened to be talking to happened to exemplify that issue just right and the setting happened to work out and the climax of their personal story… there's a lot of just happenstance, I suppose, in that once you've been commissioned to write a story, you're writing that story.
And sometimes the material will support a real cracker-jack breakout story. What's more often is that as you go through the process, you hit an obstacle that you have to smooth over in some way and you turn in a very serviceable, perfectly good story.
But the things that I think really allow it to break through and get head and shoulders above tend to be things that are out of your control. You're going to do your very best job of research, you're going to do your very best job of writing, you're going to use all the good phrases, you're going to exert full control of your mastery of time and space, you're going to jump around in the narrative if that's in the timeline rather, if that's what the narrative calls for.
If you want to focus on the beating of a fly's wings, for some reason, you will do that. If you want to jump back into prehistory, you'll do that. And after you've employed all of those tricks and techniques to craft the very best story that you possibly can from the material, sometimes the material itself will just harmonize perfectly and get you to that place to achieve that potential that you hoped that you could. It's a little bit of luck and magic, I suppose. We can't always summon it or bottle it.
Joanna: Coming to the book, A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear , which, again, I love the title. It's great. What was it about this idea that made you decide to turn this story into a book-length project rather than a long-form article?
How did you know, ‘Right, I'm going to write a book about this?'
Matt: I was first commissioned for an article on the same topic. The story for those who don't know, it's about a group of libertarians which is a fringe political movement within the United States and their emphasis is on personal freedoms and personal rights.
This national group of libertarians decided to come to one small town, and just take over the town, and turn it into their utopia. Soon after they tried to enact this kind of crazy heist of the town, the town started experiencing bear problems. And so, the book is about how those things are connected.
I was initially commissioned to write an article based on the unusual bear activity that was seen in that town. I was interviewing a woman for my local newspaper about her difficulties in accessing VA benefits. And she was what we stereotype as a crazy cat lady. She was a little bit of a shut-in, she had a bunch of cats milling around, and I asked her about her cats because it's a good icebreaker, and I like cats.
She said, ‘I used to let them outside, but that was before the bears came.' I was like, ‘Oh, well, that sounds really interesting. Forget about the VA. Tell me about bears.' She just started talking about how a bear had eaten two of her cats and how the bears had become very bold and aggressive and were doing weird things.
I started asking around town, asking other people if they had also had bear experiences that seemed unusual. And when I had a feeling for what was going on in that town, I pitched the magazine article and I was really excited to get this magazine article. I really wanted to do a great job on it because ‘The Atavist Magazine' is a good platform and I knew that it would help me to make the case to other magazines that I could write really good narrative stuff.
I went back to town and went through all the interview process and all of that. And when I wrote my first draft for that magazine article, it was 32,000 words. And they would have accepted 4,000 words. So, the article, which I was very happy with, was still very much of a compromise of what I wanted to say about this bizarre situation involving libertarians and bears in this town.
I got in a couple of the best anecdotes including a situation where a bear fights a llama, but there was so much left unsaid, so many colorful things. In that case, I just had this massive trove of colorful materials sitting in my pocket. I knew that there was a very large narrative there because I had already written probably half of the book-length on it. So, it just seemed very natural to write a book about it.
Joanna: Is it a comedy?
Matt: I would call it a dark comedy. There is a lot of very funny stuff, I think, and I do stray into the comedic quite a bit. But there are also some very, kind of, weighty issues. A woman gets attacked by a bear. That's not funny, but there's also just all sorts of goofy stuff.
The llama thing is great. There's one situation where there are two old women who live next door to each other on a hill, and one of them is absolutely terrified of bears. Every time she cooks steak inside, she won't go outside for a day because she's afraid that the bears will smell the steak on her. And meanwhile, her neighbor has been feeding the bears doughnuts for 20 years and has a crowd of bears sitting outside her home waiting for her to come out with doughnuts and buckets of grain twice a day.
There's just a lot of really absurd situations that I was privy to. And I milk them for all I've got.
Joanna: That's so funny. It's so funny there because, of course, the truth can sometimes be stranger than fiction. And I guess that's what you're doing with narrative nonfiction is you are finding these stories.
We're almost out of time, but I do want to ask you because in your original email to me, you said, ‘I think a lot of writers start off like I started out, isolated and bereft of helpful connections and not the person who is going to schmooze at an event or something.'
How you have managed to do these things and even interview these people and get over those initial issues?
Matt: I think for most of my life, even while being very passionate about writing, I never felt like I was plugged into the writing community. I feel like everyone who went to get an advanced degree in writing, their professor could hook them up and their former colleagues would go out and join the industry and in places that would be helpful to them.
I just felt, like, really locked out of all of that. And schmoozing is definitely helpful, but, Joanna, I know that there's a certain component of your audience that is never going to schmooze because it's not their thing, and if they try really hard to force themselves to schmooze, they will sound like they're someone who's trying really hard to schmooze, right? It's just not going to be in everyone's nature and it wasn't in my nature.
I think even though the non-schmoozers have a disadvantage relative to the schmoozers, the non-schmoozers can get by on the basis of purely professional relationships which is what I did. As a journalist, I did develop a certain skill set in talking to people, but I've never been the guy at the cocktail party of other writers and editors who is like, ‘Hey, hire me for your next opportunity.'
I think for me, the key was to always I started small, I started writing for newspapers. I sent endless pitches and queries with different ideas and I slowly got better at sending those pitches . And every time a story of mine turned out that was something that I was proud of, that turned out pretty good, I added that to my portfolio.
And when one editor gives you a chance, lends you that sympathetic ear and gives you a chance to write for the next tier of publication that you're interested in, if you satisfy that editor, you may not have schmoozed them, but you have a working relationship with them. If they're happy with your work, that's all you need.
If you don't have the ability to schmooze your way into that, you still have an editor that you're working with. And perhaps you can ask that editor if they have other people in the industry who might also be willing to look favorably upon a submission from you where you're not just in the slush pile.
And you go through that process 100 or 1,000 times, and if you pay attention while you do it, you walk out of it with a group of a dozen editors that you can send a pitch to who have some idea of who you are and whether or not they like your work and your writing. And you're just always working to increase that circle of editors who look on you favorably.
Over the years, what I found and was very happy about was that those editors also bounce around from one position to another. Every time someone you know moves from one publication to the other, you want to try to maintain some contact with their initial publication and approach them in their new position and see if that might allow you to expand your horizons a little bit.
It's an iterative, slow process. It's not as easy as going to a cocktail party or a bar and palling around with the people who hold the reins to these publications, but it does get you there.
Joanna: That's great advice because I know I'm an introvert, many people listening are introverts, and knowing that the long-term professional approach is great. I think that's true if it's people submitting to short stories or if people want to get into traditional publishing, then all of that's quite true.
Where can people find you and your work and everything you do online?
Matt: Oh, thank you so much for asking. You can find me on Twitter @hh_matt . If you Google my name, you'll get to my website at matt-hongoltzhetling.com , and you can find my book, A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear , on Amazon, any major online retailer, and through the publisher which is PublicAffairs, a subsidiary of Hachette.
Joanna: Fantastic. Well, thanks so much for your time, Matt. That was great.
Matt: Joanna, thank you so much. This has been fantastic.

Reader Interactions
August 24, 2020 at 4:19 am
You always ask great questions Joanna but you outdid yourself this time on a topic I knew nothing about. That bear book sounds fascinating!
August 24, 2020 at 8:47 am
Thanks, Julie! Glad you found it interesting 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Connect with me on social media
Sign up for your free author blueprint.

Thanks for visiting The Creative Penn!
What is Narrative Nonfiction?

Narrative nonfiction infuses true-life accounts with the storytelling techniques of your favorite fictional narratives. From mind-boggling scientific odysseys and eye-opening historical reports to nerve-jangling true crime investigations, the genre has something for everyone. But what is narrative nonfiction, and how is it different from other literary genres? Buckle up as we journey into the history and controversies of narrative nonfiction, where we’ll discover some captivating reads that are anything but dull.
What Is Narrative Nonfiction?
Sometimes referred to as literary nonfiction or creative nonfiction, narrative nonfiction draws on the literary methods of fiction writing to present well-researched information. It’s a flexible term that can be applied to various works and styles, including memoir , history , investigative journalism , current affairs , and scientific accounts. What sets the genre apart from more traditional nonfiction is that narrative nonfiction aims to entertain as much as inform by building a compelling story around its central subject.
As such, some of the most popular narrative nonfiction books center on groundbreaking discoveries, ripped-from-the-headlines investigations, or major historical events. Recent examples include Paul Kix’s You Have to Be Prepared to Die Before You Can Begin to Live , which chronicles a crucial moment in the Civil Rights Movement, and Elon Green’s Edgar Award–winning true crime book Last Call , which examines a harrowing murder case from 1980s and ’90s New York. Narrative nonfiction also excels at telling quieter human stories that connect to deep social issues. One such example is Brothers on Three by journalist Abe Streep. The award-winning nonfiction book follows a group of young basketball players from Montana’s Flathead Indian Reservation as they embark on their final year of high school. What begins as a seemingly straightforward sports book about a championship season soon blossoms into a moving examination of identity, community, and growing up under the weight of generational trauma.
The appeal of narrative nonfiction is that it invites us to learn about real-life people and events in a way that’s both edifying and enthralling. By enhancing factual accounts with literary techniques like world-building, character development, rising action, and compelling dialogue, authors of narrative nonfiction connect with their readers on multiple levels — and, ideally, help them gain a more thorough understanding of the topic at hand. The key, of course, is applying these narrative enhancements without damaging factual accuracy.
What Are the Origins of Narrative Nonfiction?
Perhaps you noticed that a number of the authors mentioned thus far are journalists . In fact, the origins of narrative nonfiction can be traced back to the New Journalism movement of the 1960s, which sought to infuse nonfiction reporting with literary sensibilities. Traditional journalism typically featured reporters who delivered the news with impartial authority. New Journalists, in contrast, saw personal transparency, subjective reporting, and uniqueness of voice as keys to capturing a moment and connecting with an audience. Leaders of the New Journalism movement included Tom Wolfe, Truman Capote , Joan Didion , Hunter S. Thompson , and Norman Mailer . While their works differed in tone and format — for instance, Tom Wolfe’s Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test and Norman Mailer’s Armies of the Night tended toward novelistic memoir, while Truman Capote’s In Cold Blood was an innovative true crime book — they all pushed back at the notion that neutrality was necessary for impactful and effective journalism.
Are There Controversies About Narrative Nonfiction?
When you test the limits of nonfiction, you inevitably run into thorny issues about the truth. After all, how much creative license are you allowed to take before your true-life account crosses into fiction? As a result, narrative nonfiction has had its share of controversies. Throughout his career, Capote faced questioning about the veracity of certain scenes and dialogue from In Cold Blood. Janet Malcolm, an author and a New Yorker journalist who frequently explored issues of journalistic objectivity in her work, was sued for libel by a subject of her 1984 book In the Freud Archives . She later provoked debate in 1990 with The Journalist and the Murderer, which delves into the ethics of journalism and the troubled relationship between an author and their subject. Perhaps the most high-profile narrative nonfiction controversy centers on James Frey’s 2003 book A Million Little Pieces . While the work was marketed as a memoir, it was later revealed to contain multiple alterations and outright fabrications . The revelation sparked a heated conversation over what constitutes a memoir and led to a notoriously tense interview with Oprah Winfrey just weeks after she had picked the book for her book club.
What Are Some Different Styles of Narrative Nonfiction?
As discussed, narrative nonfiction covers an array of subjects, styles, and authorial positions. Here are just a few of the most popular subgenres of narrative nonfiction.
Historical Nonfiction
Historical nonfiction books investigate the chapters of the past from a lively perspective, bringing yesteryear to life and often drawing parallels to present-day events. Popular works include In the Garden of Beasts by Erik Larson and Isabel Wilkerson’s The Warmth of Other Suns, an award-winning account of Black migration in America. Another excellent example of historical nonfiction is You Have to Be Prepared to Die Before You Can Begin to Live by journalist Paul Kix. In it, Kix vividly chronicles Project C, the 10-week 1963 Civil Rights campaign to desegregate Birmingham, Alabama, that was led by Martin Luther King, Jr., Wyatt Walker, Fred Shuttlesworth, and James Bevel. Kix’s gripping prose and fine eye for detail transport readers back to this crucial moment in history, guiding us through the campaign and tracing a clear line from the events of 1963 to today’s continuing fight against discrimination and racial inequality .
True crime is a popular literary genre that traces back through history but reached a new level of readership with the 1966 publication of Truman Capote’s In Cold Blood . The influential work centers on the 1959 murder of the Clutter family in Kansas. Capote spent years researching the murders, gathering accounts from locals, and interviewing the convicted killers before crafting his account. The resulting narrative was a national bestseller that read more like a novel than a work of reporting — indeed, Capote himself viewed In Cold Blood as a “ nonfiction novel .” Today it stands as a landmark of true crime and narrative nonfiction. A modern-day example of exceptional true crime is Elon Green’s Last Call : A True Story of Love, Lust, and Murder in Queer New York . The Edgar Award–winning book examines the lesser-known case of the Last Call Killer, a serial murderer who targeted gay men in New York City in the 1980s and ’90s, at the height of the AIDS epidemic. Green’s book not only recounts the investigation but condemns the entrenched intolerance that allowed these killings to go overlooked for years, and it champions the strength of the gay community in the face of violence, persecution, and sustained social ostracization.
Investigative Journalism
In many ways, investigative journalism is an ideal form of narrative nonfiction: Each account examines a harrowing real-life event from a deeply personal perspective, often with the journalist at the center of their own story. All the President’s Men by Carl Bernstein and Bob Woodward is a seminal work. More recent examples include Beth Macy’s Dopesick, which examines the opioid crisis in America, and She Said by Jodi Kantor and Megan Twohey, which recounts the sexual harassment investigation that sparked the #MeToo reckoning. In Bad City: Peril and Power in the City of Angels , Pulitzer Prize–winning journalist Paul Pringle combines investigative reporting with personal narrative to compelling effect. The nonfiction thriller takes readers along for the ride as Pringle and his colleagues at the L.A. Times unearth a web of criminality at the University of Southern California and root out corruption across Los Angeles. Rather than writing an impartial report, Pringle chronicles the investigation from his perspective, beat by beat. As a result, Bad City reads like a noir novel come to life, merging true crime and investigative reporting with the shocking twists of an L.A. mystery .
We’ve only just begun to scratch the surface of narrative nonfiction, and there’s a vast world to explore. Whether you’re looking to dive deep into the past, learn about scientific breakthroughs, or lose yourself in a true-life story, there’s a perfect nonfiction book out there that will open your eyes and keep you enthralled until the last page is turned.
Share with your friends
Related articles.

10 Evocative Literary Fiction Books Set in Small Towns

11 Must-Read Books About Dogs

What We’re Reading: Spring 2024
Celadon delivered.
Subscribe to get articles about writing, adding to your TBR pile, and simply content we feel is worth sharing. And yes, also sign up to be the first to hear about giveaways, our acquisitions, and exclusives!
" * " indicates required fields
Connect with
Sign up for our newsletter to see book giveaways, news, and more.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction
Most of your familiarity with essays probably comes from your own coursework. When you are assigned an essay for a class, perhaps you’ve been assigned an expository essay or a persuasive essay. In other words, you may have been assigned an essay with a clear purpose.
Literary essays are an exciting departure from those essays that many of us have been assigned. Employing techniques akin to those used by novelists, poets, and short story writers, essayists work to explore an idea. In fact, the word “essay” is etymologically linked to the notion of experimenting, weighing, or testing out. Essayists rarely produce straightforward manifestos or polemics. Instead, they entice the reader to care or understand or learn by using elements and techniques common to and found in literature. The more adept you are at recognizing those elements, the better you’ll be able to appreciate a work of creative nonfiction.
In order to analyze creative nonfiction, you should be aware of the different rhetorical structures writers use. Most of these structures will be familiar to you. What is important to consider, though, is how creative nonfiction writers use literary structures and techniques to achieve a particular effect.
Analyzing Nonfiction
Analysis of Nonfiction
Like analysis of fiction, poetry, and drama, analysis of a nonfiction requires more than understanding the point or the content of a nonfiction text. It requires that we go beyond what the text says explicitly and look at such factors as implied meaning, intended purpose and audience, the context in which the text was written, and how the author presents his/her argument. Before you can analyze, however, you must first comprehend the text and be able to provide an objective summary.
When working with a complex text, it is best to start with short excerpts, go through several reads of the piece if possible, and focus on moving from basic comprehension on the first read, to deeper, more complex understandings with each subsequent reading. For an example of an effective strategy, use the “SOAPSTone” strategy, which consists of a series of questions that provide a basis for analysis. Remember that regardless of analysis strategy, you must always provide evidence taken directly from the text to prove their point.
Subject: What is the subject? This is the general topic, content, and ideas contained in the text. Try to state the subject in only a few words or a short phrase so as to concisely summarize the topic for your own comprehension purposes.
Occasion: What is the occasion? It is the time and place of the piece; the context that encouraged the writing to happen. This can be a large occasion (an environment of ideas and emotions that swirl around a broad issue) or an immediate occasion or specific event.
Audience: Who is the audience? The audience is the group of readers to whom the piece is directed. The audience may be an individual, a small group, or a large group of people. It may be specific or more general.
Purpose: What is the purpose? It is the reason behind the text. What does the author want the audience to think or do as a result of this text? Does the author call for some specific action or is the purpose to convince the reader to think, feel or believe in a certain way? Too often readers do not consider this question, yet understanding the purpose of a nonfiction text is crucial in order to critically analyze the text.
Speaker: Who is the speaker? This is the voice that tells the story. What is their background? Is there a bias? Does that impact how the text is written and the points being made? Typically in nonfiction, the speaker and the author are the same; however, when we approach fiction, we must realize that the speaker and the author are often NOT the same. In fiction the author may choose to tell the story from any number of different points of view. In fact, the method of narration and the character of the speaker may be a crucial piece in understanding the work, particularly in satire. However, in nonfiction, the speaker and the author of the text are most likely going to be the same, which allows us a different avenue for analysis, as we can critique a text alongside what we know about the author.
Tone: What is the tone? This is the attitude a writer takes towards the subject or character: It can be serious, humorous, sarcastic, or even objective. Examine the author’s choice of words, sentence structure, and imagery. Consider providing students with a list of tone words to help them find the exact word. Often in informational text, the tone is objective because the author is simply relaying information and is not trying to sway the audience; however, in literary nonfiction as with fiction, the author may want his/her audience to feel a certain way about the situation, characters, etc.
“Text-Dependent Analysis: Nonfiction.” Licensed under Standard Youtube License https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VzMzHrroZGM
“Analyzing Nonfiction.” Licensed under Standard Youtube License https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f_k6RXWMHas
“How to Analyze Non-Fiction.” Licensed under CC BY SA 4.0 http://www.rpdp.net/literacyFiles/literacy_101.pdf
The world of creative nonfiction is broad, but learning to analyze the techniques used by literary and personal essayists is a good way to understand how much crafting goes into making a true story, told well. And though the word “essay” may have once been associated with homework assignments and tests, rest assured, there’s much more to the form.
Like fiction, creative nonfiction relies on the careful choices made by a writer. What separates creative nonfiction from fiction, of course, is the writer’s tacit promise to be conveying a story or set of events that is purported to be true. In order to accentuate that truth or present it in its most compelling fashion, creative nonfiction writers use a variety of literary elements and techniques. Everything from the structure of an essay to its shape to its tone influences how a reader makes sense of the content.
ENG134 – Literary Genres Copyright © by The American Women's College and Jessica Egan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Table of Contents
What is narrative writing?
- First-person versus third-person narrative
- How to get out of your own way & write
- Examples of great narrative writing
How to improve your narrative writing
What is narrative writing (& how to use it in a nonfiction book).

Narrative writing isn’t just for fiction. Not by a long shot.
In fact, the art of storytelling in written form can make or break just about any book.
Why? Because books are long . They have to hold a reader’s attention over thousands of words, and nothing holds a reader’s attention like a good story.
Well-told stories can:
- grab and hold the reader’s attention
- illustrate new ideas in an entertaining way
- help readers relate those ideas to their own lives
If you want readers to love your book, to see themselves in it, and to recommend it to other readers, chances are you’ll need to tell a few good stories.
Narrative writing is any writing that tells a story.
The story can be fiction or nonfiction. It can be a full-length memoir (or novel) that tells one long story from start to finish, or it can be a quick anecdote in the middle of a how-to book.
No matter how long or short it is, whether it’s true or made up, every story in written form is narrative writing.
But here’s the good news: you don’t have to be a professional writer to write a good story .
Whether or not you’ve ever written even one story in your life, I’d bet good money that you’ve told a few.
In fact, you probably have a whole collection of stories. About the best and worst and craziest things that ever happened to you. Stories you’ve told a hundred times or more.
Narrative writing is just storytelling that’s written down.
First-person versus third-person narrative in nonfiction
There are two basic forms of storytelling: first-person and third-person.
One isn’t any better than the other, but first-person stories are the kind most people think of when they think about storytelling.
What is first-person narrative writing?
The first-person point of view uses “I” or “we” to tell a story.
The narrator is the main character, so the story is being told by the person who lived it.
“I’m finally on the road, heading for the convention, and I’m feeling pretty good. Despite the morning from hell, I hadn’t broken my neck, I hadn’t destroyed my marriage, and by some miracle, I’d managed to leave the house just 15 minutes behind schedule.
If I skipped lunch, I could still make it in time to give the keynote address.
This is what I was thinking, mentally patting myself on the back, when I suddenly realized I’d left my lunch on the counter, back in the kitchen, dropping it there during my meltdown.
Along with my speech.”
What is third-person narrative writing?
Third-person narrative writing uses “he,” “she,” or “they” to tell a story.
In nonfiction, third-person narration is often used to illustrate a point through a short story or case study.
“It was the worst setback the company had ever faced. The market for their revolutionary plastics had dried up overnight. And, given their recent expansion, the cash in the bank could only meet their payroll for about six more weeks.
The CEO called an executive meeting. Everyone assumed she was going to lay out a plan for a global shutdown. But what she proposed instead proved to be one of the greatest operational pivots in the history of manufacturing.”
Which one is better?
Like most writing, what’s best depends on the situation.
When the main character or actor in your story is someone else, third-person narrative is the obvious choice.
This is common in business books that include case studies, or in books by investigative journalists who track down stories about other people to learn about a given topic or idea.
When you’re writing a memoir, or when you’re writing a knowledge-share book that includes stories from your own experience, first-person narrative is extremely powerful.
But you don’t need to get bogged down in this kind of literary analysis.
Whether you’re writing a personal narrative or presenting a case study, just write it.
How to get out of your own way and write
Here’s the thing: you already know how to tell a story.
Don’t make the process of writing more complicated than it has to be.
Your book might jump back and forth between different points of view depending on what story you’re telling, but that isn’t something you’ll have to think about.
If you’re writing about something that happened to you, you’ll write “I” or “we” without paying any attention to it. It’s as natural as breathing.
If you’re writing about someone else, you’ll refer to them in the third person without any conscious effort.
The advice I am about to give you goes against most conventional writing wisdom:
People are natural-born storytellers. Trust yourself to tell the stories you need to tell.
What’s far more important is to think about how to tell the story. What should you focus on? What should you leave out?
Those decisions need to happen on a case-by-case basis, and the best way to learn how to make them is to see the results of good writing and editing in action.
Examples of great narrative writing in nonfiction books
Instead of getting hung up on literary terms like first-person or third-person narrative, great Authors worry about entertaining the reader.
No matter what kind of nonfiction you’re writing, people respond to stories, especially stories that start out with a problem.
Like these first paragraphs of Tiffany Haddish’s The Last Black Unicorn.
Tiffany Haddish: The Last Black Unicorn
“School was hard for me, for lots of reasons. One was I couldn’t read until, like, ninth grade. Also I was a foster kid for most of high school, and when my mom went nuts, I had to live with my grandma. That all sucked.
I got popular in high school, but before that, I wasn’t so popular. Kids would tease me all the time in elementary and middle school. They’d say I got flies on me and I smell like onions.
The flies thing came from the moles on my face. I got one under my eye, I had one on my chin, and so on. That was kind of mean.
The onions thing was because my mom used to make eggs in the morning with onions in them. Every damn morning, I had to eat eggs and onions. That would just make you stink. The whole house would stink.
Yeah, it was mean to say I stunk like onions, but…I did stink like onions.”
Story structure: why this is great
These opening paragraphs of Tiffany Haddish’s memoir grab the reader’s attention. Understanding how and why is the first step to strong narrative writing.
1. The style is conversational
There’s nothing formal or stilted about the writing. In fact, it reads like the Author is talking directly to the reader.
That’s the first key to writing narratives: write like you’re talking to someone. In fact, don’t even think of it as writing. Think of it as storytelling.
2. It starts with a highly relatable problem
School might have been hard for different people in different ways, but we’ve all been kids. And most of us had some kind of trouble with school at some point or another.
Opening with a universal problem gives readers something to relate to personally.
3. It gets personal and vulnerable quickly
If the first line of the book presents a problem almost everyone can relate to, the second line moves like lightning into the Author’s specific experience: “I couldn’t read until, like, ninth grade.”
Sharing a vulnerable and personal experience makes the story come alive. It’s straightforward, open, and honest, and admits something that most people would be far too ashamed to admit.
A lot of great writing comes down to the simplest writing lesson of all: be brutally honest about the things that feel the most private or make you feel the most vulnerable.
That’s virtually guaranteed to grab the reader’s attention.
4. It doesn’t over-explain things
In the first few lines, the reader learns that the Author couldn’t read until the ninth grade, that she was a foster kid, and that her mother “went nuts.” But we don’t get any details about any of those things.
At least, not yet.
By not explaining them here, the Author uses those revealed facts to invite the reader deeper into the story. The explanation can come later.
5. It offers the right sensory details
At the same time, the Author does explain some things.
Specifically, she tells the reader where her tormentors’ taunts came from. Details like the stink of onions are vivid in the reader’s imagination.
But these details aren’t just sensory. They’re intensely personal, which is the toughest part of the writing process.
Even in this very short piece of writing, the Author was willing to cut deep.
6. The reader’s interest drives the organization
When they first sit down to write, a lot of Authors feel compelled to present their story in chronological order. But the actual timing of events isn’t what drives a good story.
Instead, narrative text should be driven by the reader’s interest.
In three short paragraphs, the Author jumps from high school to middle school to serve the reader. She uses these miniature flashbacks to set the scene for the whole book.
She isn’t trying to present an ordered storyline.
She’s presenting new information in the order that will best draw the reader into the story. And it works brilliantly.
David Goggins: Can’t Hurt Me
“We found hell in a beautiful neighborhood. In 1981, Williamsville offered the tastiest real estate in Buffalo, New York. Leafy and friendly, its safe streets were dotted with dainty homes filled with model citizens. Doctors, attorneys, steel plant executives, dentists, and professional football players lived there with their adoring wives and their 2.2 kids. Cars were new, roads swept, possibilities endless. We’re talking about a living, breathing American Dream. Hell was a corner on Paradise Road.
That’s where we lived in a two-story, four-bedroom, white wooden home with four square pillars framing a front porch that led to the widest, greenest lawn in Williamsville. We had a vegetable garden out back and a two-car garage stocked with a 1962 Rolls Royce Silver Cloud, a 1980 Mercedes 450 SLC, and, in the driveway, a sparkling new 1981 black Corvette. Everyone on Paradise Road lived near the top of the food chain, and based on appearances, most of our neighbors thought that we, the so-called happy, well-adjusted Goggins family, were the tip of that spear. But glossy surfaces reflect much more than they reveal.”
Although the paragraph structure here is more like a narrative essay than a casual conversation, the writing skills are just as obvious.

1. It starts with a personal problem
Here, again, the very first line presents a problem. By using the first-person “we,” the Author makes the problem personal.
But, in this case, what draws the reader in isn’t relatability but curiosity about the unexpected.
“We found hell in a beautiful neighborhood.”
The juxtaposition between hell and a beautiful, presumably peaceful neighborhood catches the reader’s attention and holds their interest, making them want to know more.
2. It presents a powerful conflict
The opening line mentions hell. Then several sentences describe a beautiful neighborhood, but the paragraph ends with hell again.
One of the most basic facts about stories is that readers need conflict to stay interested.
Paradise, in and of itself, is boring.
Why? Because the human brain was built to solve problems. When we find one, we latch onto it.
Here, the Author paints the picture of an affluent American neighborhood but continues to touch on the idea of finding hell there, creating tension through foreshadowing.
“But glossy surfaces reflect much more than they reveal.”
3. It paints a picture with details
The Author could have simply said it was a wealthy neighborhood, but the writing paints a more vivid image by using just the right level of detail.
“Doctors, attorneys, steel plant executives, dentists, and professional football players lived there with their adoring wives and their 2.2 kids.”
By listing specific professions, the Author brings the street alive. These are real people.
At the same time, he shows the reader the facade they’re all hiding behind by using the phrase “2.2 kids.” There’s no such thing as two-tenths of a kid. The street is both real and fake at the same time.
Which is exactly the Author’s point, without having to say it directly.
The art of good storytelling is important, but you can’t get hung up on it while you’re trying to write your first draft.
Just write your book. And be as honest as you can while you’re doing it.
I can’t stress that enough.
All great books move through several rounds of editing before they’re published . They don’t come out looking perfect in the first round.
But the core value of a good book comes from being true to yourself when you’re writing it.
So, don’t worry about your writing style or choosing the right sensory details or any of that when you’re writing your rough draft.
Just get your truth down on the page.
Once your draft is finished, the polish comes in the editing . Hire a great editor , and trust them.
They’ll help you hone that draft until it grabs the reader’s attention and holds it until the end.
The Scribe Crew
Read this next.
Book Ghostwriters for Hire: Find the Perfect Writer
How to Use AI When Writing a Book
Why Work With a Memoir Ghostwriter?
The Finest Narrative Non-Fiction Essays
Narrative essays that I consider ideal models of the medium
- Linguistics
Authors like , , , , , and epitomise this way of writing.
I'm not a Writer , but I write to explore other things – anthropology, weird cultural quirks in the web development community, interaction design, and the rising field of " tools for thought ". These things are all factual and grounded in reality, but have interesting stories twisted around them. Ones I'm trying to tell in my little notes and essays.
Perhaps you're the same kind of non- Writer writer. The playful amateur kind who uses it to explore and communicate ideas, rather than making the medium part of your identity. But even amateurs want to be good. I certainly want to get good.
Knowing what you like is half the battle in liking what you create. In that spirit, I collect narrative non-fiction essays that I think are exceptional. They're worth looking at closely – their opening moves, sentence structure, turns of phrase, and narrative arcs.
The only sensible way to improve your writing is by echoing the work of other writers. Good artists copy and great artists steal quotes from Picasso.
You may want to start your own collection of lovely essays like this. There will certainly be some Real Writers who find my list trite and full of basic, mainstream twaddle. It probably is. I've done plenty of self-acceptance work and I'm okay with it.
Twaddle aside, the essays below are worth your attention.
by Paul Ford
Paul Ford explains code in 38,000 words and somehow makes it all accessible, technically accurate, narratively compelling, and most of all, culturally insightful and humanistic.
I have unreasonable feelings about this essay. It is, to me, perfect. Few essays take the interactive medium of the web seriously, and this one takes the cake. There is a small blue cube character, logic diagrams, live code snippets to run, GIFs, tangential footnotes, and a certificate of completion at the end.
by David Foster Wallace – Published under the title 'Shipping Out'
Forgive me for being a David Foster Wallace admirer. The guy had issues, but this account of his 7-day trip on a luxury cruiseliner expresses an inner monologue that is clarifying, rare and often side-splittingly hilarious.
He taught me it is 100% okay to write an entire side-novel in your footnotes if you need to.
by David Graeber
Graeber explores play and work from an anthropological perspective. He's a master of moving between the specific and the general. Between academic theory and personal storytelling. He's always ready with armfuls of evidence and citations but doesn't drown you in them.
by Malcolm Gladwell
This piece uses a typical Gladwellian style. He takes a fairly dull question – Why had ketchup stayed the same, while mustard comes in dozens of varieties? – and presents the case in a way that makes it reasonably intriguing. He's great at starting with specific characters, times and places to draw you in. There are always rich scenes, details, personal profiles, and a grand narrative tying it all together.
Some people find the classic New Yorker essay format overdone, but it relies on storytelling techniques that consistently work.
by Mark Slouka
by Joan Didion
1 Backlinks
On opening essays, conference talks, and jam jars.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.7: The Personal Narrative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40379

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Assignment TLDR;
This first essay assignment is a chance for me, the instructor and your peers to get to know you. It is also an opportunity to practice MLA formatting & understand basic concepts of storytelling/literature.
Below are the parts to help you scaffold this assignment:
- Personal Narrative Rough Draft
- Personal Narrative Peer Review
- Personal Narrative Final Draft
The following readings will help you with the technical aspects of the essay:
- The Writing Process
- MLA Formatting
The following readings are effective examples of personal narratives you can use to help you craft your essay:
- Creative Nonfiction Readings
- Student Sample Personal Narratives
The following activity will help you get started:
- Descriptive Imagery Worksheets
The in-depth essay directions follow.
Detailed Directions
For this writing assignment, students are to use what they have learned about Creative Nonfiction to write a personal narrative of their own.
To review, creative nonfiction tells a true story in an artistic -- or literary -- way. This means that the story has certain elements, such as descriptive imagery, setting, plot, conflict, characters, imagery, metaphors, and other literary devices. A personal narrative , then, is a work of creative nonfiction that is, well, personal . Usually, a personal narrative is narrated in first-person, though sometimes it can be written in third-person. Though writing about your personal experiences is often the subject of a personal narrative, if you are feeling self-conscious the story does not necessarily have to be about you: often writers will write about someone they love, an object, a place, or even a stranger with a remarkable story.
Scope, or how "big" of a story you choose to tell, is an important consideration for a personal narrative. Since you have limited time in your literature or writing class, you will probably not be able to write an autobiography or memoir. For 750-1500 words, it is best to focus on a single moment in time. An effective example of this might be "The Fourth of July" by Audre Lorde (Date unknown) or "The Death of the Moth" by Virginia Woolf (1942). But if you have a story that stretches over a few days rather than a few minutes or hours, journal entries or letters ( epistolary form) can be an effective method to tell a drawn-out story through a series of vignettes , or image-centric flashes of memory. Please see the story "Bajadas" by Francisco Cantu (2015) for an effective example of the epistolary form. Lastly, some authors choose to organize their essays with anchoring images or subheaders. For an effective example of this form of personal narrative, see "Girl" by Alexander Chee (2016). Take a look at the readings in this chapter to get some ideas about scope. After examining these professional examples, it's time to tell your story! So where is a good place to start? Think about a metamorphic moment in your life.
Metamorphic Moments

"Untitled" by morganglines , 17 June 2007, published on Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
What does metamorphic mean? Think of the caterpillar's metamorphosis into a butterfly while in the chrysalis. Similarly, a metamorphic moment is an intense moment or experience which profoundly impacts or changes a person. It could be the happiest moment of a person's life, such as a wedding, birth of a child, or graduation from college. It could be the worst moment of a person's life, like the moment they realized their dream job was not a good fit after all, the moment they realized racism was real, the moment they lost someone they loved, or the moment they realized their lifelong hero was a fraud. It could be a hilarious moment, a scary moment, an extremely embarrassing moment: essentially, it is a moment that made you see the world in a new way or transformed you from the person you were to the person you are .
Whatever the moment might be, the important idea to remember is to tell a story in a way which immerses the reader: that you make the reader feel like they are there by describing the moment in great detail using your five senses; that you use metaphors; that you have a setting, conflict, and some kind of character growth. A great essay makes a reader forget they are reading an essay. It transports them to your world. It forces them to see the world through your narrator's eyes. As one of my favorite mentors, Caroline Kremers, once said about engaging readers with your writing, "go for the jugular." (Note: please do not physically assault your readers. This is a metaphor.)
Descriptive Imagery: Showing vs. Telling

"moon" by George Lezenby , 14 Sep. 2017, published on Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
“Don't tell me the moon is shining; show me the glint of light on broken glass.” ― Anton Chekhov
Which of the above lakes would you want to visit? Which one paints a more immersive picture, making you feel like you are there? When writing a story, our initial instinct is usually to make a list of chronological moments: first I did this, then I did this, then I did that, it was neat-o. That might be factual, but it does not engage the reader or invite them into your world. It bores the reader. Ever been stuck listening to someone tell a story that seems like it will never end? It probably was someone telling you a story rather than using the five senses to immerse you . In the example above, the writer uses visual (sight), auditory (sound), olfactory (smell), tactile (touch), or gustatory (taste) imagery to help the reader picture the setting in their mind. By the final draft, the entire story should be compelling and richly detailed. While it's fine to have an outline or first draft that recounts the events of the story, the final draft should include dialogue, immersive description, plot twists, and metaphors to capture your reader's attention as you write.

"Eibsee Lake" by barnyz , 2 August 2011, published on Flickr CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Need a more specific prompt to get you inspired? Check out the 7 Personal Insight Questions from the University of California's Personal Statement Prompts for Transfer Students . Interested in transferring or applying to another college or scholarship? An effective personal statement is a story that captures the attention of your readers (the college admissions team) and shows them why you are a good fit for the school/scholarship.
Why Write A Personal Narrative, Anyway?
First of all, writing a piece of creative work will help students gain an appreciation for the skill and effort which goes into writing, and helps them recognize common literary devices. It will help you get acquainted with some of the basic elements of writing, such as specificity, writing process, and time management. It will also allow you to practice MLA formatting . This will come in handy for future essays. But personal narratives are not just for literature and creative writing classes!
Believe it or not, writing a personal narrative is an extremely useful skill for anyone to master. Besides helping you get into colleges and win scholarship money, you can use it to ace job interviews, get Instagram or YouTube followers, sell a product to customers through effective marketing, or share the most interesting parts of yourself with a new friend or romantic interest. In science? Telling the story of your research can help you get grants from the government. In the medical field? Listening to patient stories can help you better provide quality care. Small business owner? Personal narratives can help attract clients (think of the "About Us" section of websites!). Passionate about social justice? A powerful personal narrative can quite literally change the world. Whatever your future career or interests, effective storytelling can make a difference in your life. So what are you waiting for? Let's get writing!
Brainstorming
- First, write a list of as many "metamorphic moments" you can think of.
- Next, write a list of the most important or memorable places you have been.
- Lastly, write a list of objects which hold symbolic importance to you.
After you have written these lists, wait at least a day. Then come back and circle the 3 list items which you feel will make the best essay, or that you feel most strongly drawn to write about.
Once you find three moments, try making a brainstorming web. Write any associated words, objects, ideas, and descriptive imagery (all five senses) you associate with this moment, place, or object. Finally, pick the topic upon which you were able to generate the most ideas. This could be your essay topic!
Free Writing
Find a quiet place and set a timer for 10 minutes. Write as much as possible on your topic, as much as you can remember, in as vivid of detail as possible. Try to keep the pen moving on the page without stopping. Do not worry about grammar, spelling, punctuation, or that mean little critical voice in your head. Your job is just to get ideas down. Pretend you are trying to explain the memory to someone who has never met the people you are describing or has never been to the place where the story takes place. How would you describe the moment to an alien? That is usually a good way to ensure you are very detailed!
Other Generative Writing Ideas
- Find a picture that means a lot to you. While it is clear to you why this picture is important, it is likely not clear to a stranger. Try to describe to a stranger all the sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and feelings of the moment so that they understand why the picture is meaningful to you.
- Find an image, object, action, or place/scene that is important to you. Use this descriptive imagery worksheet by Shane Abrams to help you describe that object.
Learning Outcomes
- Analyze and employ logical and structural methods such as inductive and deductive reasoning, cause and effect, and logos, ethos, and pathos.
- Use style, diction, and tone appropriate to the academic community and the purpose of the specific writing task; proofread and edit essays for presentation so they exhibit no disruptive errors in English grammar, usage, or punctuation

- Scriptwriting
What is a Narrative Essay — Examples, Format & Techniques
I was in the Amazon jungle the first time I wrote a narrative essay, enlightened and enraptured by the influence of ayahuasca. That’s not true. I’ve never been to South America nor have I ever taken ayahuasca. The purpose of that opening is to show how to craft a narrative essay intro — hook, line, and sinker. Narrative essays rely on hooking the reader, and enticing them to read on. But what is a narrative essay? We’re going to break down everything you need to know about these essays — definition, examples, tips and tricks included. By the end, you’ll be ready to craft your own narrative essay for school or for publication.
What’s a Narrative Essay?
First, let’s define narrative essay.
Narrative essays share a lot of similarities with personal essays, but whereas the former can be fictional or non-fictional, the latter are strictly non-fictional. The goal of the narrative essay is to use established storytelling techniques, like theme , conflict , and irony , in a uniquely personal way.
The responsibility of the narrative essayist is to make the reader feel connected to their story, regardless of the topic. This next video explores how writers can use structural elements and techniques to better engage their readers.
Personal Narrative Essay Examples With Essay Pro
Narrative essays rely on tried and true structure components, including:
- First-person POV
- Personal inspiration
- Focus on a central theme
By keeping these major tenets in mind, you’ll be better prepared to recognize weaknesses and strengths in your own works.
NARRATIVE ESSAY DEFINITION
What is a narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that’s focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that’s personal to the writer. Everything in these essays should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Famous Narrative Essay Examples
- Ticker to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
- After Life by Joan Didion
- Here is a Lesson in Creative Writing by Kurt Vonnegut
Narrative Writing Explained
How to start a narrative essay.
When you go to sleep at night, what do you think of? Flying squirrels? Lost loved ones? That time you called your teacher ‘mom’? Whatever it is, that’s what you need to write about. There’s a reason those ideas and moments have stuck with you over time. Your job is to figure out why.
Once you realize what makes a moment important to you, it’s your job to make it important to the reader too. In this next video, Academy Award-nominated filmmaker J. Christian Jensen explains the power of the personal narrative.
Narrative Writing and the Personal Narrative Essay • Video by TEDx Talks
Anything and everything can be the topic of your essay. It could be as benign as a walk to school or as grandiose as a trip to the moon — so long as that narrative exists within reality. Give your thoughts and opinions on the matter too — don’t be afraid to say “this is what I think” so long as it’s supported by storytelling techniques. Remember, never limit yourself as a writer, just keep in mind that certain topics will be harder to make engaging than others.
Narrative Essay Outline
How to write a narrative essay.
First step, game plan. You’re going to want to map out the story from beginning to end, then mark major story beats in your document.
Like all stories, your narrative essay needs a clear beginning, middle, and end. Each section should generally conform to a specifically outlined structure. For reference, check out the outline below.
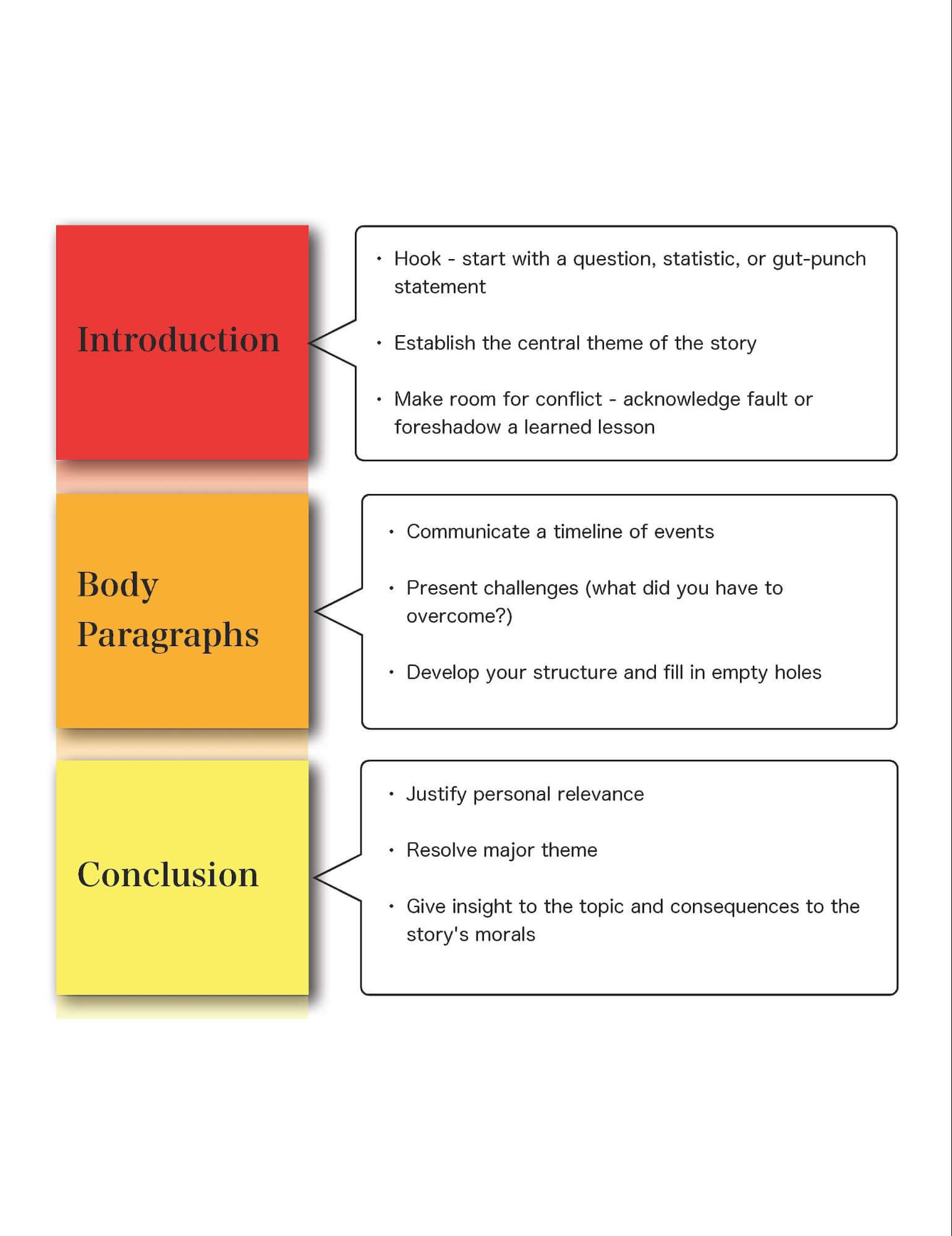
Narrative Essay Format • How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step
Make sure to reference back to this outline throughout the writing process to make sure you have all your major beats covered.
Purpose of narrative essay writing
Narrative essays give writers the ability to freely express themselves within the structure of a traditional story. Nearly all universities ask applicants to submit a narrative essay with their formal application. This is done for two reasons: they allow institutions to judge the linguistic and grammar capabilities of its applicants, as well as their raw creative side.
If you’re considering studying creative writing in an undergraduate or graduate program, then you’re going to write A LOT of narrative style essays. This process may seem indomitable; How am I supposed to write hundreds of pages about… me? But by the end, you’ll be a better writer and you’ll have a better understanding of yourself.
One thing that all successful essayists have in common is that they make radical, often defiant statements on the world at large. Think Ralph Waldo Emerson, Virginia Woolf, and Langston Hughes for example.
Being a professional essayist isn’t easy, and it’s near-impossible to be one who makes a lot of money. Many essayists work as professors, editors, and curriculum designers as well.
This next video features the late, award-winning essayist Brian Doyle. He explains all the things you need to hear when thinking about writing a story.
Narrative Essay Examples “Lecture” via Boston University
We can learn a lot from the way Doyle “opens” his stories. My favorite is how he begins with the statement, “I met the Dalai Lama once.” How can we not be interested in learning more?
This brings us all the way back to the beginning. Start with a hook, rattle off the line, then reel in the sinker. If you entice the reader, develop a personal plot, and finish with a resolute ending, you’ll have a lot of success in essay writing.
Up Next
Narrative essay topics.
We've curated a collection of narrative essay topics that will spark your creativity and bring your experiences to life. Dive into the rich tapestry of your memories, explore the unique threads of your life, and let your narrative unfold.
Up Next: Narrative Essay Topics →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What are the 12 Principles of Animation — Ultimate Guide
- What is Pacing in Writing — And Why It’s So Important
- What Does O.S. Mean in a Script & How to Use It
- What Does a Leadman Do in Film — Job Description Explained
- What is a Unit Production Manager — Job and Role Explained
- 1 Pinterest
Narrative Essay
Definition of narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a type of essay that has a single motif , or a central point, around which the whole narrative revolves. All incidents, happenings, and characters revolve around a single motif presented in the narrative. A narrative essay is similar to a simple five-paragraph essay, in that it has the same format. It is only different in that it is a narrative, having characters, incidents, and dialogues.
Difference Between a Narrative Essay and a Short Story
A narrative essay has a specific format, specific aspects to discover, and a specific motif. It revolves around that motif set by the writer prior to writing the essay. A short story , however, is different from a narrative essay in that it does not revolve around a pre-set motif, and that it does not have a specific format. Also, a short story always leaves readers at a critical juncture with the desire to discover more. In contrast , a narrative essay ends when the readers are fully satisfied. They do not wish to read anymore or do not want to discover anymore.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay has three required elements: character , theme , and dialogue :
Characters are an important part of a narrative essay. Even if the essay is autobiographical in nature, the person writing the essay is a character involving some other characters who act, behave, and do like all other characters presented in stories and novels .
Theme or Motif
A narrative essay revolves around a theme or a motif. This theme or motif is presented in its thesis statement, which breaks it down into three distinct pieces of evidence . These three distinct pieces of evidence are then further elaborated through characters in body paragraphs .
Dialogue is used to capture the conversation between characters. In a narrative essay, dialogue is the third important element, without which the characters lose their worth and liveliness.
How to Choose a Topic for Narrative Essay
There are four major steps to choosing the topic of a narrative essay:
- Choose a theme or thematic strand around which to weave a story.
- Outline the character, events, and happenings.
- Think about the conversation of the characters and place them in a setting and plot
- Synchronize the characters with the plot and the setting to see if they integrate with each other.
MLA and APA Formats in Narrative Essay
MLA and APA are used in all types of essays. However, APA is mostly used in social sciences, while MLA is used in humanities. Whereas the application of MLA in a narrative is concerned, it is used in the format, intext citation , and in the Works Cited page. The first page comprises the student’s name, class, tutor’s name, and date with the topic of the essay given after all of them. However, in APA, all this information appears on the cover page. Similarly, both MLA and APA differ in intext citation, with MLA having only the author’s name and page without any comma. In contrast, APA has the author’s name as well as page number with a comma and ‘p’ with a period before the number of the page, such as (Hardy, p. 45). Regarding the sources, MLA shows Works Cited page at the end, while APA shows Reference at the end.
Reflective Narrative Essay
As the name suggests, a reflection narrative is an essay that presents the reflections of a person who is writing that essay. He takes an incident from his life and gives it an organization on the pattern of an essay with a narrative having a beginning, middle, and an end. The essay may or may not have moral lessons, which does not make a lot of difference if the experiences carry the deeper meaning. What matters is that the writer reflects on his own life, taking out some significant moment to make it a storied essay or a narrative essay with a theme in it.
Examples of Narrative Essays in Literature
Example #1: new directions (by maya angelou).
“Annie, over six feet tall, big-boned, decided that she would not go to work as a domestic and leave her “precious babes” to anyone else’s care. There was no possibility of being hired at the town’s cotton gin or lumber mill, but maybe there was a way to make the two factories work for her. In her words, “I looked up the road I was going and back the way I come, and since I wasn’t satisfied, I decided to step off the road and cut me a new path.” She told herself that she wasn’t a fancy cook but that she could “mix groceries well enough to scare hungry away and keep from starving a man.”
This paragraph is an example from a narrative essay of Maya Angelou. She has described how a girl looks, and how she behaves. She has also written direct dialogues to show that it is a narrative.
Example #2: Saturday Evening Post (by Russell Baker)
“When I burst in that afternoon she was in conference with an executive of the Curtis Publishing Company. She introduced me. He bent low from the waist and shook my hand. Was it true as my mother had told him, he asked, that I longed for the opportunity to conquer the world of business? My Mother replied that I was blessed with a rare determination to make something of myself. ‘That’s right,’ I whispered. ‘But have you got the grit, the character, the never-say-quit spirit it takes to succeed in business?’ My Mother said I certainly did.”
In this piece from a narrative essay by Russell Baker of the famed Saturday Evening Post , the author has fully described the efforts of his mother by her dialogue. Both character and dialogue are very clear.
Example #3: Only Daughter (by Sandra Cisneros)
“Once several years ago, when I was just starting out my writing career, I was asked to write my own contributor’s note for an anthology I was part of, I wrote: ‘ I am the only daughter in a family of six sons. That explains everything.’ “Well, I’ve thought about that ever since, and yes, it explains a lot to me, but for the reader’s sake I should have written: ‘I am the only daughter in a Mexican family of six sons.’ Or even: ‘I am the only daughter of a Mexican father and a Mexican-American mother.’ Or: ‘I am the only daughter of a working-class family of nine.’ All of these had everything to do with who I am today.”
In this essay, the author has given a full description of a daughter – how she looks and how she behaves.
Function of Narrative Essay
A narrative essay describes people, presents their conversations, and narrates their experiences to teach lessons to readers. In fact, it is like a story, but different in that it is weaved around a motif. A motif is given before the incidents of the essay. Readers become aware of this single theme, central idea, or motif once they go through the essay. Its major aim is to provide information about life experiences and lessons learned from those experiences.
Synonyms of Narrative Essay
Some of the words closely related to the narrative essay are reflective account, chronicle, chronology , and historical narrative. However, these words cannot be interchangeably used to replace this title.
Related posts:
- Narrative Poem
- Elements of an Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Types of Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation

25 Great Nonfiction Essays You Can Read Online for Free
Alison Doherty
Alison Doherty is a writing teacher and part time assistant professor living in Brooklyn, New York. She has an MFA from The New School in writing for children and teenagers. She loves writing about books on the Internet, listening to audiobooks on the subway, and reading anything with a twisty plot or a happily ever after.
View All posts by Alison Doherty
I love reading books of nonfiction essays and memoirs , but sometimes have a hard time committing to a whole book. This is especially true if I don’t know the author. But reading nonfiction essays online is a quick way to learn which authors you like. Also, reading nonfiction essays can help you learn more about different topics and experiences.
Besides essays on Book Riot, I love looking for essays on The New Yorker , The Atlantic , The Rumpus , and Electric Literature . But there are great nonfiction essays available for free all over the Internet. From contemporary to classic writers and personal essays to researched ones—here are 25 of my favorite nonfiction essays you can read today.

“Beware of Feminist Lite” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
The author of We Should All Be Feminists writes a short essay explaining the danger of believing men and woman are equal only under certain conditions.
“It’s Silly to Be Frightened of Being Dead” by Diana Athill
A 96-year-old woman discusses her shifting attitude towards death from her childhood in the 1920s when death was a taboo subject, to World War 2 until the present day.
“Letter from a Region in my Mind” by James Baldwin
There are many moving and important essays by James Baldwin . This one uses the lens of religion to explore the Black American experience and sexuality. Baldwin describes his move from being a teenage preacher to not believing in god. Then he recounts his meeting with the prominent Nation of Islam member Elijah Muhammad.
“Relations” by Eula Biss
Biss uses the story of a white woman giving birth to a Black baby that was mistakenly implanted during a fertility treatment to explore racial identities and segregation in society as a whole and in her own interracial family.
“Friday Night Lights” by Buzz Bissinger
A comprehensive deep dive into the world of high school football in a small West Texas town.
“The Case for Reparations” by Ta-Nehisi Coates
Coates examines the lingering and continuing affects of slavery on American society and makes a compelling case for the descendants of slaves being offered reparations from the government.
“Why I Write” by Joan Didion
This is one of the most iconic nonfiction essays about writing. Didion describes the reasons she became a writer, her process, and her journey to doing what she loves professionally.
“Go Gentle Into That Good Night” by Roger Ebert
With knowledge of his own death, the famous film critic ponders questions of mortality while also giving readers a pep talk for how to embrace life fully.
“My Mother’s Tongue” by Zavi Kang Engles
In this personal essay, Engles celebrates the close relationship she had with her mother and laments losing her Korean fluency.
“My Life as an Heiress” by Nora Ephron
As she’s writing an important script, Ephron imagines her life as a newly wealthy woman when she finds out an uncle left her an inheritance. But she doesn’t know exactly what that inheritance is.
“My FatheR Spent 30 Years in Prison. Now He’s Out.” by Ashley C. Ford
Ford describes the experience of getting to know her father after he’s been in prison for almost all of her life. Bridging the distance in their knowledge of technology becomes a significant—and at times humorous—step in rebuilding their relationship.
“Bad Feminist” by Roxane Gay
There’s a reason Gay named her bestselling essay collection after this story. It’s a witty, sharp, and relatable look at what it means to call yourself a feminist.
“The Empathy Exams” by Leslie Jamison
Jamison discusses her job as a medical actor helping to train medical students to improve their empathy and uses this frame to tell the story of one winter in college when she had an abortion and heart surgery.
“What I Learned from a Fitting Room Disaster About Clothes and Life” by Scaachi Koul
One woman describes her history with difficult fitting room experiences culminating in one catastrophe that will change the way she hopes to identify herself through clothes.
“Breasts: the Odd Couple” by Una LaMarche
LaMarche examines her changing feelings about her own differently sized breasts.
“How I Broke, and Botched, the Brandon Teena Story” by Donna Minkowitz
A journalist looks back at her own biased reporting on a news story about the sexual assault and murder of a trans man in 1993. Minkowitz examines how ideas of gender and sexuality have changed since she reported the story, along with how her own lesbian identity influenced her opinions about the crime.
“Politics and the English Language” by George Orwell
In this famous essay, Orwell bemoans how politics have corrupted the English language by making it more vague, confusing, and boring.
“Letting Go” by David Sedaris
The famously funny personal essay author , writes about a distinctly unfunny topic of tobacco addiction and his own journey as a smoker. It is (predictably) hilarious.
“Joy” by Zadie Smith
Smith explores the difference between pleasure and joy by closely examining moments of both, including eating a delicious egg sandwich, taking drugs at a concert, and falling in love.
“Mother Tongue” by Amy Tan
Tan tells the story of how her mother’s way of speaking English as an immigrant from China changed the way people viewed her intelligence.
“Consider the Lobster” by David Foster Wallace
The prolific nonfiction essay and fiction writer travels to the Maine Lobster Festival to write a piece for Gourmet Magazine. With his signature footnotes, Wallace turns this experience into a deep exploration on what constitutes consciousness.
“I Am Not Pocahontas” by Elissa Washuta
Washuta looks at her own contemporary Native American identity through the lens of stereotypical depictions from 1990s films.
“Once More to the Lake” by E.B. White
E.B. White didn’t just write books like Charlotte’s Web and The Elements of Style . He also was a brilliant essayist. This nature essay explores the theme of fatherhood against the backdrop of a lake within the forests of Maine.
“Pell-Mell” by Tom Wolfe
The inventor of “new journalism” writes about the creation of an American idea by telling the story of Thomas Jefferson snubbing a European Ambassador.
“The Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf
In this nonfiction essay, Wolf describes a moth dying on her window pane. She uses the story as a way to ruminate on the lager theme of the meaning of life and death.

You Might Also Like

No one knows what ‘creative nonfiction’ is. That’s what makes it great.
In the first paragraph of “ The Fine Art of Literary Fist-Fighting ,” Lee Gutkind, the “Godfather” of the creative-nonfiction genre (a title used once to describe him in Vanity Fair in 1997 and since taken up repeatedly over the years, mostly by Gutkind himself, including in the bio on this book jacket), begins with a question he often receives: “‘What is creative nonfiction?’ Or, in some cases, ‘What the hell is creative nonfiction?’”
It’s a fitting sentiment for the genre, and for its longtime champion. This term, which others forgo in favor of “literary nonfiction” or “narrative nonfiction,” or simply “the essay,” as Gutkind writes, is a blanket that seeks to cover works from Joan Didion’s stylized journalistic chronicles of the ’60s to Mary Karr and the memoir boom of the ’90s to Annie Dillard’s nature writing, and everything in between that isn’t made up but also probably wouldn’t run in the newspaper. To practice or teach creative nonfiction (or whatever else you might want to call it) has been to operate from a defensive position. As Gutkind shows, this is a genre whose inception and growth were met with uncertainty, skepticism and in many cases disdain.
In trying to name, categorize, legitimize creative nonfiction, it’s hard not to feel that you’re being defined by what you are failing to do — it’s not creative in the eyes of fiction writers, or rigorously factual in the eyes of journalists, or properly literary in the eyes of academics. Here, Gutkind attempts to narrate the history of the genre, and that story is inevitably one of contestation and conflict — about what “creative nonfiction” even is, above all else, and just how “creative” writers can be before they’re no longer writing nonfiction. Those are familiar debates for some of us, and they haven’t stopped. I was in graduate school more than a decade ago, at one of the creative-nonfiction programs that Gutkind describes, and I was constantly getting into “Literary Fist-Fights,” though I imagine most of the people around me wanted to punch me for real.
Gutkind has been out there on those self-drawn front lines since the early ’70s. He’s a writer of numerous creative-nonfiction books (for which he immersed himself in topics ranging from the lives of those awaiting organ transplants, to the cutting-edge robotics program at Carnegie Mellon, to the ecosystem of a children’s hospital), a professor and an editor, all of these identities working toward a final form somewhere between evangelist and carnival barker. “I know that all of this scheming, all of these machinations, seem pretty crass and certainly not literary,” he writes about his efforts to get sustained funding for his seminal magazine, Creative Nonfiction. “I got a lot of heat from colleagues and other writers for being an unabashed promoter and even a self-promoter. Okay, maybe that was true — or partly true. But so what? It might work.”
It did work, and those of us who love the genre — many first drawn in by Gutkind’s magazine or his edited anthology — are grateful for it. These days, I don’t know if anyone would knock the hustle. Doomed hustling is the only literary mode left available, as so many great magazines, especially the kind that published the inventive, diverse work that we might call creative nonfiction, have fallen by the wayside — cut from shrinking university budgets, bought and gutted by venture-capital goons, scrubbed from the internet. The latest issue of Creative Nonfiction came out in 2022; there doesn’t seem to anything coming down the pike.
To look back, in these times of true literary and academic scarcity, the “fist-fighting” of grad program expansion and barbs exchanged between the tenured and endowed can seem like pretty enviable brawls. As much as anything, “The Fine Art of Literary Fist-Fighting” is a book about academia, a version of it that’s nearly extinct. Multiple scenes take place in panels at academic conferences, or during contentious department meetings; enemies are blazered, bloviating, Faulkner scholars who pound the table and refuse to let nonfiction writers into their ivory tower.
In the midst of all this, Gutkind, in his own telling, is the perma-rebel: a former hippie motorcycle man without a graduate degree, who doesn’t belong. He’s the scrappy kid from the real world, pushing himself through every door the fancier folk might want to slam in his face. But for most of the book, he’s ensconced within the literary and academic establishment, ultimately moving comfortably through the tenure track at a major research university in the city where he was born. I don’t mean to downplay Gutkind’s enormous accomplishments; only to say, as a fellow academic, that it’s easy to get caught up in the perceived intrigue of a meeting, to frame yourself only against those in your bubble, to lose sight of the fact that the art being discussed is a far more compelling subject than the minutiae of the discussion about it.
Gutkind is at his best in this book when he grudgingly becomes the type of memoirist that he usually writes about. The moments when he stops to look back on his own evolving perspective and investment are truly compelling — reflecting the continuing intellectual curiosity of someone who cares enough about this field to allow himself to change with it. He thinks back on essays that he rejected from the magazine that he might accept now, and shows us how dogmas seem indispensable until suddenly they’re old fashioned.
Most compellingly, he reflects upon his writing career, the choices he made within the murkily defined borders of creative nonfiction. He describes a scene from his second book, in which he sits outside a motel room to eavesdrop on a fight between two White baseball umpires and their crewmate, the first Black umpire in the National League. Decades on, he delves into not only what happened in the scene but his place as eavesdropper, the context leading up to the moment, the stylistic choices in not making up but certainly emphasizing the cruel language, and most of all, whether “in the end I actually hurt the man I was trying to help.” He puts himself, and us, right back in the moment — and the results are vivid, ambiguous, emotionally resonant, fascinating.
That is the enduring thrill of creative nonfiction — tiptoeing along the border between art and fact. It requires turning a critical eye on your own ambition, your care for others, the literal truth of what happened and the style with which you might express how it felt, as well as the question of whose story is being told and who has the right to tell it. It’s one that Gutkind chronicles as a reader, too, capturing the experience that we who love the genre have all had, coming upon a work that feels epiphanic with all these tensions and intimacies, even if you didn’t have the language to call what you were reading “creative nonfiction.” He writes of what it meant to a young journalist to encounter a piece that broke the rules, as he did when he first read Gay Talese’s “Frank Sinatra Has a Cold.” And he describes the awe he felt upon reading James Baldwin’s “Notes of a Native Son,” an essay that achieved so much . He captures this experience as an editor, too, when a then-unknown writer sent him her first manuscript and, decades into his career, he discovered that he could still be surprised.
This is, I think, what so often gets buried in discussions about creative nonfiction — including many of those documented in this book. The more one zeroes in on defining and defending, the more the writing can move away from whatever it is that makes the genre meaningful to so many people. Gutkind has given his life to this genre; I wish I knew more about what it means to him.
The Fine Art of Literary Fist-Fighting
How a Bunch of Rabble-Rousers, Outsiders, and Ne’er-Do-Wells Concocted Creative Nonfiction
By Lee Gutkind
Yale University Press. 292 pp. $35


What is creative nonfiction? Despite its slightly enigmatic name, no literary genre has grown quite as quickly as creative nonfiction in recent decades. Literary nonfiction is now well-established as a powerful means of storytelling, and bookstores now reserve large amounts of space for nonfiction, when it often used to occupy a single bookshelf.
Like any literary genre, creative nonfiction has a long history; also like other genres, defining contemporary CNF for the modern writer can be nuanced. If you’re interested in writing true-to-life stories but you’re not sure where to begin, let’s start by dissecting the creative nonfiction genre and what it means to write a modern literary essay.
What Creative Nonfiction Is
Creative nonfiction employs the creative writing techniques of literature, such as poetry and fiction, to retell a true story.
How do we define creative nonfiction? What makes it “creative,” as opposed to just “factual writing”? These are great questions to ask when entering the genre, and they require answers which could become literary essays themselves.
In short, creative nonfiction (CNF) is a form of storytelling that employs the creative writing techniques of literature, such as poetry and fiction, to retell a true story. Creative nonfiction writers don’t just share pithy anecdotes, they use craft and technique to situate the reader into their own personal lives. Fictional elements, such as character development and narrative arcs, are employed to create a cohesive story, but so are poetic elements like conceit and juxtaposition.
The CNF genre is wildly experimental, and contemporary nonfiction writers are pushing the bounds of literature by finding new ways to tell their stories. While a CNF writer might retell a personal narrative, they might also focus their gaze on history, politics, or they might use creative writing elements to write an expository essay. There are very few limits to what creative nonfiction can be, which is what makes defining the genre so difficult—but writing it so exciting.
Different Forms of Creative Nonfiction
From the autobiographies of Mark Twain and Benvenuto Cellini, to the more experimental styles of modern writers like Karl Ove Knausgård, creative nonfiction has a long history and takes a wide variety of forms. Common iterations of the creative nonfiction genre include the following:
Also known as biography or autobiography, the memoir form is probably the most recognizable form of creative nonfiction. Memoirs are collections of memories, either surrounding a single narrative thread or multiple interrelated ideas. The memoir is usually published as a book or extended piece of fiction, and many memoirs take years to write and perfect. Memoirs often take on a similar writing style as the personal essay does, though it must be personable and interesting enough to encourage the reader through the entire book.
Personal Essay
Personal essays are stories about personal experiences told using literary techniques.
When someone hears the word “essay,” they instinctively think about those five paragraph book essays everyone wrote in high school. In creative nonfiction, the personal essay is much more vibrant and dynamic. Personal essays are stories about personal experiences, and while some personal essays can be standalone stories about a single event, many essays braid true stories with extended metaphors and other narratives.
Personal essays are often intimate, emotionally charged spaces. Consider the opening two paragraphs from Beth Ann Fennelly’s personal essay “ I Survived the Blizzard of ’79. ”
We didn’t question. Or complain. It wouldn’t have occurred to us, and it wouldn’t have helped. I was eight. Julie was ten.
We didn’t know yet that this blizzard would earn itself a moniker that would be silk-screened on T-shirts. We would own such a shirt, which extended its tenure in our house as a rag for polishing silver.
The word “essay” comes from the French “essayer,” which means “to try” or “attempt.” The personal essay is more than just an autobiographical narrative—it’s an attempt to tell your own history with literary techniques.
Lyric Essay
The lyric essay contains similar subject matter as the personal essay, but is much more experimental in form.
The lyric essay contains similar subject matter as the personal essay, with one key distinction: lyric essays are much more experimental in form. Poetry and creative nonfiction merge in the lyric essay, challenging the conventional prose format of paragraphs and linear sentences.
The lyric essay stands out for its unique writing style and sentence structure. Consider these lines from “ Life Code ” by J. A. Knight:
The dream goes like this: blue room of water. God light from above. Child’s fist, foot, curve, face, the arc of an eye, the symmetry of circles… and then an opening of this body—which surprised her—a movement so clean and assured and then the push towards the light like a frog or a fish.
What we get is language driven by emotion, choosing an internal logic rather than a universally accepted one.
Lyric essays are amazing spaces to break barriers in language. For example, the lyricist might write a few paragraphs about their story, then examine a key emotion in the form of a villanelle or a ghazal . They might decide to write their entire essay in a string of couplets or a series of sonnets, then interrupt those stanzas with moments of insight or analysis. In the lyric essay, language dictates form. The successful lyricist lets the words arrange themselves in whatever format best tells the story, allowing for experimental new forms of storytelling.
Literary Journalism
Much more ambiguously defined is the idea of literary journalism. The idea is simple: report on real life events using literary conventions and styles. But how do you do this effectively, in a way that the audience pays attention and takes the story seriously?
You can best find examples of literary journalism in more “prestigious” news journals, such as The New Yorker , The Atlantic , Salon , and occasionally The New York Times . Think pieces about real world events, as well as expository journalism, might use braiding and extended metaphors to make readers feel more connected to the story. Other forms of nonfiction, such as the academic essay or more technical writing, might also fall under literary journalism, provided those pieces still use the elements of creative nonfiction.
Consider this recently published article from The Atlantic : The Uncanny Tale of Shimmel Zohar by Lawrence Weschler. It employs a style that’s breezy yet personable—including its opening line.
So I first heard about Shimmel Zohar from Gravity Goldberg—yeah, I know, but she insists it’s her real name (explaining that her father was a physicist)—who is the director of public programs and visitor experience at the Contemporary Jewish Museum, in San Francisco.
How to Write Creative Nonfiction: Common Elements and Techniques
What separates a general news update from a well-written piece of literary journalism? What’s the difference between essay writing in high school and the personal essay? When nonfiction writers put out creative work, they are most successful when they utilize the following elements.
Just like fiction, nonfiction relies on effective narration. Telling the story with an effective plot, writing from a certain point of view, and using the narrative to flesh out the story’s big idea are all key craft elements. How you structure your story can have a huge impact on how the reader perceives the work, as well as the insights you draw from the story itself.
Consider the first lines of the story “ To the Miami University Payroll Lady ” by Frenci Nguyen:
You might not remember me, but I’m the dark-haired, Texas-born, Asian-American graduate student who visited the Payroll Office the other day to complete direct deposit and tax forms.
Because the story is written in second person, with the reader experiencing the story as the payroll lady, the story’s narration feels much more personal and important, forcing the reader to evaluate their own personal biases and beliefs.
Observation
Telling the story involves more than just simple plot elements, it also involves situating the reader in the key details. Setting the scene requires attention to all five senses, and interpersonal dialogue is much more effective when the narrator observes changes in vocal pitch, certain facial expressions, and movements in body language. Essentially, let the reader experience the tiny details – we access each other best through minutiae.
The story “ In Transit ” by Erica Plouffe Lazure is a perfect example of storytelling through observation. Every detail of this flash piece is carefully noted to tell a story without direct action, using observations about group behavior to find hope in a crisis. We get observation when the narrator notes the following:
Here at the St. Thomas airport in mid-March, we feel the urgency of the transition, the awareness of how we position our bodies, where we place our luggage, how we consider for the first time the numbers of people whose belongings are placed on the same steel table, the same conveyor belt, the same glowing radioactive scan, whose IDs are touched by the same gloved hand[.]
What’s especially powerful about this story is that it is written in a single sentence, allowing the reader to be just as overwhelmed by observation and context as the narrator is.
We’ve used this word a lot, but what is braiding? Braiding is a technique most often used in creative nonfiction where the writer intertwines multiple narratives, or “threads.” Not all essays use braiding, but the longer a story is, the more it benefits the writer to intertwine their story with an extended metaphor or another idea to draw insight from.
“ The Crush ” by Zsofia McMullin demonstrates braiding wonderfully. Some paragraphs are written in first person, while others are written in second person.
The following example from “The Crush” demonstrates braiding:
Your hair is still wet when you slip into the booth across from me and throw your wallet and glasses and phone on the table, and I marvel at how everything about you is streamlined, compact, organized. I am always overflowing — flesh and wants and a purse stuffed with snacks and toy soldiers and tissues.
The author threads these narratives together by having both people interact in a diner, yet the reader still perceives a distance between the two threads because of the separation of “I” and “you” pronouns. When these threads meet, briefly, we know they will never meet again.
Speaking of insight, creative nonfiction writers must draw novel conclusions from the stories they write. When the narrator pauses in the story to delve into their emotions, explain complex ideas, or draw strength and meaning from tough situations, they’re finding insight in the essay.
Often, creative writers experience insight as they write it, drawing conclusions they hadn’t yet considered as they tell their story, which makes creative nonfiction much more genuine and raw.
The story “ Me Llamo Theresa ” by Theresa Okokun does a fantastic job of finding insight. The story is about the history of our own names and the generations that stand before them, and as the writer explores her disconnect with her own name, she recognizes a similar disconnect in her mother, as well as the need to connect with her name because of her father.
The narrator offers insight when she remarks:
I began to experience a particular type of identity crisis that so many immigrants and children of immigrants go through — where we are called one name at school or at work, but another name at home, and in our hearts.
How to Write Creative Nonfiction: the 5 R’s
CNF pioneer Lee Gutkind developed a very system called the “5 R’s” of creative nonfiction writing. Together, the 5 R’s form a general framework for any creative writing project. They are:
- Write about r eal life: Creative nonfiction tackles real people, events, and places—things that actually happened or are happening.
- Conduct extensive r esearch: Learn as much as you can about your subject matter, to deepen and enrich your ability to relay the subject matter. (Are you writing about your tenth birthday? What were the newspaper headlines that day?)
- (W) r ite a narrative: Use storytelling elements originally from fiction, such as Freytag’s Pyramid , to structure your CNF piece’s narrative as a story with literary impact rather than just a recounting.
- Include personal r eflection: Share your unique voice and perspective on the narrative you are retelling.
- Learn by r eading: The best way to learn to write creative nonfiction well is to read it being written well. Read as much CNF as you can, and observe closely how the author’s choices impact you as a reader.
You can read more about the 5 R’s in this helpful summary article .
How to Write Creative Nonfiction: Give it a Try!
Whatever form you choose, whatever story you tell, and whatever techniques you write with, the more important aspect of creative nonfiction is this: be honest. That may seem redundant, but often, writers mistakenly create narratives that aren’t true, or they use details and symbols that didn’t exist in the story. Trust us – real life is best read when it’s honest, and readers can tell when details in the story feel fabricated or inflated. Write with honesty, and the right words will follow!
Ready to start writing your creative nonfiction piece? If you need extra guidance or want to write alongside our community, take a look at the upcoming nonfiction classes at Writers.com. Now, go and write the next bestselling memoir!
Sean Glatch
Thank you so much for including these samples from Hippocampus Magazine essays/contributors; it was so wonderful to see these pieces reflected on from the craft perspective! – Donna from Hippocampus
Absolutely, Donna! I’m a longtime fan of Hippocampus and am always astounded by the writing you publish. We’re always happy to showcase stunning work 🙂
[…] Source: https://www.masterclass.com/articles/a-complete-guide-to-writing-creative-nonfiction#5-creative-nonfiction-writing-promptshttps://writers.com/what-is-creative-nonfiction […]
So impressive
Thank you. I’ve been researching a number of figures from the 1800’s and have come across a large number of ‘biographies’ of figures. These include quoted conversations which I knew to be figments of the author and yet some works are lauded as ‘histories’.
excellent guidelines inspiring me to write CNF thank you
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The genre of narrative nonfiction requires heavy research, thorough exploration, and an aim to entertain while also sharing a true, compelling story. There are many ways to tell a story—some writers prefer to stick to the truth, some prefer to make up truths of their own, and some will settle somewhere in the middle. The genre of narrative ...
The best way to understand narrative nonfiction is by a list of examples of this type of literary work. Narrative nonfiction can include diaries, memoirs, personal essays, and literary journalism.
Narrative nonfiction, which is also sometimes called literary nonfiction or creative nonfiction, is a subgenre of nonfiction. This subgenre includes any true story that's written in the style of a novel. It's easy to understand this term if you break it down into its component parts. The first word, narrative, means story.
Introducing Narrative Nonfiction. One way to kick off this unit is to put out a selection of nonfiction, fiction, and literary nonfiction books for students to explore. You can have them work in small groups to discuss what they notice about the formats of the books and maybe sort them into groups. They'll start to see that expository ...
Transcript of Interview with Matt Hongoltz-Hetling. Joanna: Matt Hongoltz-Hetling is a Pulitzer finalist and award-winning investigative journalist. He's also the author of A Libertarian Walks Into a Bear. Welcome, Matt. Matt: Hey, thanks for having me on, Joanna. Joanna: It's great to have you on the show.
Narrative non-fiction brings to life true stories like historic events and personal experiences. It uses the techniques usually associated with fiction writing, such as plot, character, and detailed scene-setting.. This very popular genre informs the reader with facts and detailed accounts of real-life events, but is written in an engaging and dramatic way designed to grip the reader's ...
When applying for college, you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities. For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay. College application prompt. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure.
Sometimes referred to as literary nonfiction or creative nonfiction, narrative nonfiction draws on the literary methods of fiction writing to present well-researched information. It's a flexible term that can be applied to various works and styles, including memoir, history, investigative journalism, current affairs, and scientific accounts.
Narrative essays are always non-fiction and usually autobiographical. They are written with a more creative style versus the strictly objective, fact-based language of academic writing or journalism. Narrative essays are often part of the coursework in high school and during college admissions. Articles. Videos. Instructors.
The world of creative nonfiction is broad, but learning to analyze the techniques used by literary and personal essayists is a good way to understand how much crafting goes into making a true story, told well. And though the word "essay" may have once been associated with homework assignments and tests, rest assured, there's much more to ...
Creative nonfiction (also known as literary nonfiction, narrative nonfiction, literary journalism or verfabula) is a genre of writing that uses literary styles and techniques to create factually accurate narratives. Creative nonfiction contrasts with other nonfiction, such as academic or technical writing or journalism, which are also rooted in accurate fact though not written to entertain ...
Narrative writing is any writing that tells a story. The story can be fiction or nonfiction. It can be a full-length memoir (or novel) that tells one long story from start to finish, or it can be a quick anecdote in the middle of a how-to book. No matter how long or short it is, whether it's true or made up, every story in written form is ...
Narrative non-fiction is the catch-all term for factual writing that uses narrative, literary-like techniques to create a compelling story for the reader. It's non-fiction work that goes beyond presenting bland information in chronological order, and instead uses plot, character, structure, tension, and drama to make plain reality more ...
What Is Narrative Nonfiction? Narrative nonfiction is a fairly new term being introduced as a genre of writing, but its individual elements are not new at all.It blends factual events with entertainment, setting it apart from academic nonfiction and journalism, which are factual but not generally entertaining, and straight fiction, which is not based on any real event and is meant to be ...
A nonfiction essay is a short text dealing with a single topic. A classic essay format includes: An introductory paragraph, ending in a statement of thesis (that is, the purpose of the essay ...
To review, creative nonfiction tells a true story in an artistic -- or literary -- way. This means that the story has certain elements, such as descriptive imagery, setting, plot, conflict, characters, imagery, metaphors, and other literary devices. A personal narrative, then, is a work of creative nonfiction that is, well, personal. Usually, a ...
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. If you're new to the world of nonfiction writing, finding your footing can be a bit overwhelming. Use these techniques to guide your writing and demystify the nonfiction-writing process.
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that's focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that's personal to the writer. Everything in these essays should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
A narrative essay has three required elements: character, theme, and dialogue: Character. Characters are an important part of a narrative essay. Even if the essay is autobiographical in nature, the person writing the essay is a character involving some other characters who act, behave, and do like all other characters presented in stories and novels. ...
Now He's Out." by Ashley C. Ford. Ford describes the experience of getting to know her father after he's been in prison for almost all of her life. Bridging the distance in their knowledge of technology becomes a significant—and at times humorous—step in rebuilding their relationship.
This term, which others forgo in favor of "literary nonfiction" or "narrative nonfiction," or simply "the essay," as Gutkind writes, is a blanket that seeks to cover works from Joan ...
In creative nonfiction, the personal essay is much more vibrant and dynamic. Personal essays are stories about personal experiences, and while some personal essays can be standalone stories about a single event, many essays braid true stories with extended metaphors and other narratives. ... rite a narrative: Use storytelling elements ...