
MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
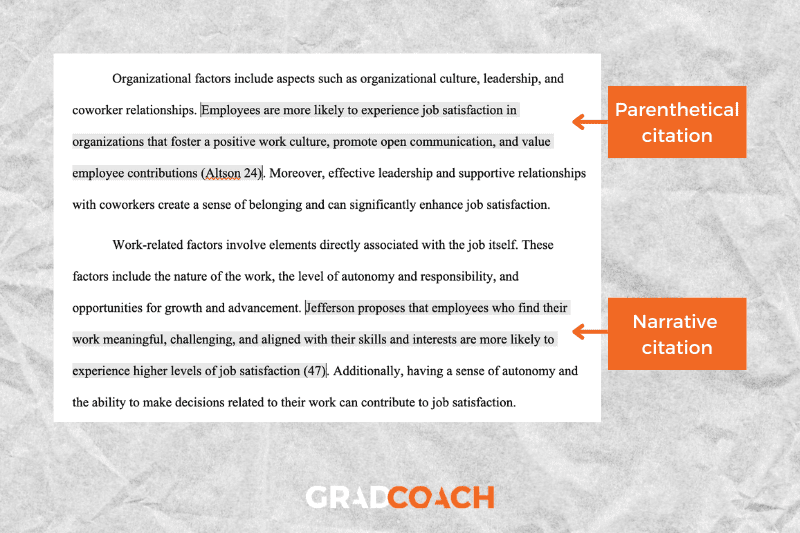
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
You Might Also Like:

Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

MLA Style Guide, 8th & 9th Editions: Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Works Cited entries: What to Include
- Title of source
- Title of container
- Contributors
- Publication date
- Supplemental Elements
- Book with Personal Author(s)
- Book with Organization as Author
- Book with Editor(s)
- Parts of Books
- Government Publication
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Multivolume Works
- Newspaper Article
- Other Formats
- Websites, Social Media, and Email
- About In-text Citations
- In-text Examples
- How to Paraphrase and Quote
- Citing Poetry
- Formatting Your MLA Paper
- Formatting Your Works Cited List
- MLA Annotated Bibliography
- MLA 9th Edition Quick Guide
- Submit Your Paper for MLA Style Review
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman font or another readable typeface (e.g. serif ).
Line Spacing & Margins
Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper.
Leave 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and each side.
Indent the first line of each paragraph half an inch from the left margin.
Quotes longer than 4 lines should be written as a block of text a half an inch from the left margin.
Heading and Title
An MLA research paper does not need a title page, but your instructor may require one. If no instructions are given, follow the MLA guidelines below:
Type the following one inch from the top of the first page, flush with the left margin (double spacing throughout).
Your Instructor's Name
Course Number or Name
Center the title on the next line. Follow the rules for capitalization. Do not italicize, underline, or bold the title. An exception is when your title includes a title. Example: The Attitude toward Violence in A Clockwork Orange
Indent the next line and begin typing your text.
Include your last name and page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The page numbers will be one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. If your instructor prefers no page number on the first page, begin numbering from 2 on the second page.
Sample Papers from MLA
There are sample papers available in the MLA Style Center. Check them out to see the correct formatting.
Styling Headings and Subheadings
According to the MLA Style Center website, writers should avoid using headings in shorter papers. If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center :
"Levels
The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent.
Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence. After the first level, the other headings are subheadings—that is, they are subordinate. Font styling and size are used to signal prominence. In general, a boldface, larger font indicates prominence; a smaller font, italics, and lack of bold can be used to signal subordination. For readability, don’t go overboard: avoid using all capital letters for headings (in some cases, small capitals may be acceptable):
Heading Level 1
Heading Level 2
Heading Level 3
Note that word-processing software often has built-in heading styles.
Consistency
Consistency in the styling of headings and subheadings is key to signaling to readers the structure of a research project. That is, each level 1 heading should appear in the same style and size, as should each level 2 heading, and so on. Generally, avoid numbers and letters to designate heads unless you are working in a discipline where doing so is conventional. Note that a heading labeled “1” requires a subsequent heading labeled “2,” and a heading labeled “a” requires a subsequent heading labeled “b.”
In a project that is not professionally designed and published, headings should be flush with the left margin, to avoid confusion with block quotations. (The exception is the paper or chapter title, which is centered in MLA style.)
For readability, it is helpful to include a line space above and below a heading, as shown in this post.
No internal heading level should have only one instance. For example, if you have one level 1 heading, you need to have a second level 1 heading. (The exceptions are the paper or chapter title and the headings for notes and the list of works cited.) You should also generally have text under each heading.
Capitalization
Capitalize headings like the titles of works, as explained in section 1.2 of the MLA Handbook.
The shorter, the better."
Modern Language Association. "How Do I Style Headings and Subheadings in a Research Paper?" MLA Style Center., 13 December 2018, style.mla.org/styling-headings-and-subheadings .
MLA Style Paper Template
- MLA 9th Edition Paper Template This template was created and saved as a Word template for Microsoft Word 2016. The process for saving and using the template is the same for the instructions given above for 2013.
You can save a personal template in Microsoft Word (IRSC students, download Office for free, see a librarian if you need help). Above is a template you can use every time you need to set-up a research paper using MLA style format. Simply open the template and type your own information every time you need to write an MLA style paper. Microsoft Word will allow you to save personal templates. Once you have the template opened in Word
Click "Save as"
Give the file a name
Under "Save as type", select Word Template

Then when you open Word, you will be able to choose a template rather than a blank document. You might have to select Personal to find your template.

Sample MLA Paper

How to Use the MLA Style Template
Formatting Group Project Papers
For a research paper written collaboratively by several students, such as for a group project, create a title page instead of listing all authors in the header on page 1 of the essay. On the title page, list each student's full name, placing one name on each double-spaced line. After the final student name, enter the professor's name. After the professor's name, give the course name. The last line of the heading will be the date in 5 August 2021 format. Press Enter a few times to move down the page then give the paper title, centered.

- << Previous: Citing Poetry
- Next: Formatting Your Works Cited List >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 11:37 AM
- URL: https://irsc.libguides.com/mla
- Writing Center
MLA Style Guide – 9th Edition
Click here to download a .pdf copy of our MLA Style Guide !
Last updated : October 7, 2023
Consider keeping a printed copy to have when writing and revising your resume! If you have any additional questions, make an appointment or email us at [email protected] !
Source Attribution : Information in this handout is adapted from the Modern Language Association Handbook, Ninth Edition (2021).
Reference Entry : Adapted from Modern Language Association. MLA Handbook. 9th ed . The Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
MLA Style Guide - 9th Edition
Basics of formatting with mla style.
The Modern Language Association style, commonly referred to as MLA style, is a system of documentation generally used in the humanities, such as language arts and history. MLA documentation requires in-text citations for brief references to sources used in the body of the text and a works cited page featuring full citation information for all of your sources. In this style, writers create citations by listing all the core elements of a source.
Margins are 1 inch on all sides of the page.
Standard font is 12-point Times New Roman. For other fonts, MLA recommends a font that when the word is italicized the difference is clear. Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks.
Paragraph and line spacing:
Indent the first line of each paragraph 0.5 in. Text is double-spaced. No extra spaces before or after headings or between paragraphs.
First page:
In the upper left hand corner of the first page, write your name, professor’s title and last name, the course title and number, and then the date (Day Month Year) on separate lines. On a new line, create a title (in Title Case) centered on the page. List your last name and page number in the top right corner of every page.
Section headings:
Section headings are used to divide major sections of a paper. MLA does not require specific formatting for section headings. The general rule is to maintain consistency in the use of bold, italics, and alignment when creating levels. Topics of equal importance share the same level heading throughout the document.
In-text citations are used to credit the work of others and refer readers to the source on your Works Cited page. Parenthetical citations include the author’s last name and page numbers. Enclose citations in parentheses and follow by a period.
Works Cited:
Begin a new page. Title as “Works Cited” centered on the top of the page. List all sources used alphabetically.
Sample First Page
MLA title page begins on the first page of the paper with the paper text beginning after the title. The following example depicts a common MLA title page and a description of the elements within.

- Header : The header lists your last name and the page number. Align to the right.
- Author : List your first and last name. If there are multiple contributors, provide each of the names a separate line then continue with the rest of the requirements discussed here.
- Professor : Include your instructor’s name. It’s most universally accepted to put professor before their last name, unless otherwise requested (for example, a professor may request to be called Dr. Harmon).
- Class : List the course and course number. It’s most universally accepted to put the full subject name over the abbreviation (for example, English 101 instead of ENGL 101).
- Date : Format the date as Month Day Year. List the assignment due date, not when the document was originally created or last updated.
- Title : Hit enter and create a space between the header and the first line of the text. Make sure it’s in the center of the page. Do not underline, italicize, or add quotations around the title except if referring to other works within the title.
MLA In-Text Citations
Citing in the text.
In MLA, every time you use the work or thoughts of another, you need to cite the original author. The use of others’ work or thoughts includes summary, paraphrase, and direct quotations. To cite the source, you will need an in-text citation, which typically consists of the author’s last name and the page number where the material comes from. In-text citations are enclosed in parentheses and followed by a period.
Single Author
If introducing the author in the text, use their first name and last name the first time it is used and then use only the surname thereafter. If introducing the author in the parenthetical citation, list only the author’s last name followed by the page number.
Single Author Example
The text portrays the mindset of millennials through lines like this: “[Alice thinks] of the twentieth century as one long question, and in the end we got the answer wrong” (Rooney 101).
Two Authors
If a source has two authors, list the authors’ names in the parenthetical citation or in the text and connect them with an ‘and’:
Two Authors Example
The first time the character Viktor is introduced, he’s described as “[…]the lowliest of the lot” (Charaipotra and Clayton 18).
Three or More Authors
List the first author’s last name followed by the abbreviation “et al.” (and others)
Three or More Authors Example
Heat is a significant symbol in the book Blackout. The very first page discussed how “tensions matching the temperature make people do stupid things in a city full of millions” (Clayton et al. 1).
Organization or Group Author
If no author is listed and/or the source is published by an organization or group, list the group’s full name in the text or citation (with the page number), followed by the abbreviation if well known. Use the acronym for every subsequent citation. If no known acronym is given, shorten the organization name to the shortest noun phrase within the parenthetical citation.
Organization or Group Author Example
According to The Modern Language Association (MLA), “whenever you use the title of a source in your writing, take the title from an authoritative location in the work” (53).
Narrative Citation
If you introduce the author before quoting, summarizing, or paraphrasing, then only the page number is included in the in-text citation:
Narrative Citation Example
According to music critic Mark Prindle, Minneapolis rock combo The Cows are an acquired taste (259).
Unknown Author
If the author’s name is unknown, and there is no group author, include a shortened version of the publication title in quotations if it’s a short work or italics if it’s a longer work. Include a page number if it’s available.
Unknown Author Example
When thinking about what kind of photography to use, it’s important to consider that, “[d]igital photography is more eco-friendly than traditional photography” (Eco-tography 119).
Block Quotations
When using a direct quotation that runs four or more lines long, the quotation is introduced by a colon, set off from the main text, and indented an extra half inch from the left margin. Do not indent the first line, add quotation marks not present in the original, or adjust the line spacing. Include the parenthetical citation after the final period or punctuation mark of the block quote.
Block Quotations Example
Fitzgerald movingly describes how the personality traits of Gatsby:
Only in Gatsby, the man who gives his name to this book, was exempt from my reaction—Gatsby who represented everything for which I have an unaffected scorn. If personality is an unbroken series of successful gestures, there was something gorgeous about him, some heightened sensitivity to the promises of life, as if he were related to one of those intricate machines that register earthquakes ten thousand miles away. (Fitzgerald 6)
Omissions or Alterations to Quotations
Place an ellipsis (…) where parts of a quote were omitted in the middle of the sentence (e.g. “Grammar… is the study of writing techniques”). Ellipses are not necessary to indicate the first part of a phrase was omitted. Put brackets [text] around necessary alterations made to quotations for clarity, as in “[They] said…”
Common Knowledge
Facts or information that you already know, is widely available, and undisputed is considered common knowledge, which does not require an in-text citation. Common knowledge includes biographical information, dates of historical events, and other information that reasonable readers would accept as fact.
Common Knowledge Example
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th president of the United States.
More Information for In-Text Citations
Primary and secondary sources:.
If you quote an author’s quotation of another author’s work, put the phrase “qtd. in” (short for “quoted in”) in the parenthetical citation, followed by the secondary source (e.g. qtd. in Jacobson). The abbreviation isn’t necessary if it’s made clear in prose it’s an indirect quote. Always try to find the direct source if you can!
Timed media:
For timed media such as videos or songs, cite the time in parentheses (e.g. Eilish 2:57-3:15).
Multiple sources:
In-text citations with multiple sources are separated by a semicolon. The order should correspond with the order of the research (e.g. Offerman, 52; Yong, 33). However, if delineating the specific attribution is needed, avoid combining the citations and instead separate each source into its own sentence.
Multiple works by one author:
Include the title of the work within the in-text citation (with a comma before it) or in prose (e.g. Tolkien, The Hobbit 237).
Consecutive use of one or more sources:
When referencing one source multiple times consecutively, you can avoid multiple parenthetical citations by first introducing the source. Refer to the author in text using the known-new contract, adding page numbers for quotes where needed.
Personal communication:
If citing a personal communication such as an email, interview, or telephone conversation, include the name of the person, the date, and the type of communication. If citing a lecture, include the subject of the lecture. Where possible, include the author’s name in a narrative citation to avoid the long parenthetical entry.
Works Cited Entries
Writing bibliography entries.
Disclaimer : Our WordPress does not allow for “hanging indents,” therefore the following bibliography entries are not formatted with hanging indents. Check out the .pdf guide for a more accurate view!
MLA style requires a works cited page that includes full citation information for each source. Begin by starting on another page titled “Works Cited” centered in the page. Alphabetize each entry by the last name of the first author listed. Hanging indents are an important characteristic of work cited pages. To make a hanging indent, The second and following lines are indented 1/2 inch after the first line. MLA style customizes entries for each type of source, meaning that each citation will be unique.
Webpage from a Website
Website citations follow a basic format for all types of websites. For sources without authors, list the group or organization as the author. If no group or organization is given, move the website name to the author position.
Webpage from a Website Example
Author Last Name, Author First Name. “Article Title.” Publisher , Day Month Year, URL.
Boise State University Writing Center. “Welcome to the Writing Center.” Boise State University . https://www.boisestate.edu/writingcenter/. Accessed 9 Sep. 2022.
List the author, the title, the publisher, and the year it was published. Include the editor/translator/any other type of contributor before the publisher if it can be found. The title can start the citation:
Book Example
Author Last Name, Author First Name. Book Title. Publisher, Year Published.
Pratchett, Terry. Guards! Guards! Gollancz, 1989.
Work from a Collection
The type of works in this category may include an essay in an edited collection/anthology or a chapter of a book. Here’s the basic form:
Work from a Collection Example
Last Name, First Name. “Chapter Title.” Title of Book, edited by Editor’s Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page Range.
Kinsella, Sophie. “Seven.” The Party Crasher, edited by Kara Cesare et. al., The Dial Press, 2021, pp. 95-119.
Journal Article
Journal articles, or periodicals, are print and electronic sources issued within larger journals:
Journal Article Example
Author(s). “Article Title.” Journal Title, Volume (vol. #), Issue Number (no. #), Year, Page Range (pp.). DOI if available
Hollingdale, Jack et. al. “Impact of COVID-19 for people living and working with ADHD: A brief review of the literature.” AIMS Public Health , vol. 8, no. 4, 2021, pp. 581–597. DOI: 10.3934/publichealth.2021047
Newspaper Article
Newspaper and magazine articles are two other types of periodicals. Include volume, issue, and/or page number(s) if available:
Newspaper Article Example
Last name, First Name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Day Month Year, pages (if print). URL (if digital)
Mitchell, Jessi. “New public health laboratory breaks ground in Harlem.” CBS NEW YORK, 06 July 2022, https://www.cbsnews.com/newyork/news/harlem-public-health-laboratory/
YouTube Video
Including the author/creator/publisher is optional, you could just go into the title. If you bring up a name in your paper or want to emphasize a participant in the video, it would be a good idea to include it.
YouTube Video Example
Last Name, First Name. “Video Title.” Streaming Service , uploaded by Username, Day Month Year, URL
Smith, Clint. “Marsha P. Johnson and the Stonewall Rebellion.” YouTube , uploaded by CrashCourse, 29 June 2022, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ftcvaJCKVjs
Podcast Episode
Citing a podcast differs from the typical way of citing in MLA in that the title of the episode is listed first, followed by the name of the series in italics. Make sure to include where it was published, who it’s hosted by, and that it’s the podcast edition of the recording.
Podcast Episode Example
“Episode Name” Name of series from Publisher, hosted by Host Name, Podcast Number, Day Month Year. URL
“The Mysterious Disappearance of Brittanee Drexel.” Morbid from Amazon Music , hosted by Alaina Urquhart and Ashleigh Kelley, episode 203, 23 January 2021. music.amazon.com/podcasts/30381209-4d12-4c82-ba16-5bde361156c9/episodes/40756d04-f27a-4723-b036-8a3d3083f508/morbidepisode203themysteriousdisappearanceofbrittaneedrexel
More Information for Works Cited Entries
Multiple authors:.
With sources that have three or more authors, follow the first author’s name with a comma and the abbreviation ‘et al.’ (“and others”).
Online handles:
Supply the author’s handle in square brackets with the name [@handle] if the handle differs from the author’s account name.
Organization or group author:
In instances where an organization or group authored the work, spell out the full name of the group but omit initial articles (e.g. a, an, the). If the author is the publisher, skip the author element and begin the entry with the title.
In a reference entry for a work with no author, move the title of the work to the author position.
If no publication date is available, include the date you accessed the source at the end, e.g. Boise State University. https://www.boisestate.edu/writingcenter/. Accessed 9 Sep. 2022.
Publishers’ names are given in full; however, do not give words indicating business structure, like Ltd. or LLC. Terms like Press and Books should be included.
Sample MLA Works Cited Page
MLA works cited begin on a new page. “Works Cited” title is centered. On the left-hand margin are titles that explain the type of citation used in the corresponding reference entry. Each entry is formatted with a hanging indent and alphabetised.

The Writing Center
Search Modern Language Association
Log in to Modern Language Association
- Annual Report
- MLA News Digest Archive
- Mission and Strategic Priorities
- Advertising
- Join the MLA Mailing List
- The MLA Staff
- Delegate Assembly
- Executive Council
- Related Organizations
- Donate to the MLA
- Leading Contributors to the MLA
- ADE-ALD Summer Seminar and MAPS Leadership Institute
- MLA Webinars Site
- 2025 Convention Program Forms
- Presidential Theme for the 2025 Convention
- A Letter from MLA Executive Director Paula M. Krebs Urging Support of Convention Attendance
- MLA Exhibit Hall
- Access Guidelines for MLA Convention Session Organizers and Presenters
- Calls for Papers
- Policies for Forums and Allied Organizations
- Procedures for Organizing Convention Meetings
- Exhibiting at the 2025 MLA Convention
- Sponsorship and Marketing
- Convention History
- Appropriate Conduct at the MLA Annual Convention
- Membership Benefits
- Join the MLA
- MLA Academic Program Services
- MLA Newsletter
- MLA Strategic Partnership Network
- Member Resources
- Member Search
- Renew Your Membership
MLA Handbook Plus
- Buy the MLA Handbook
- MLA Style Support
Publications
- Backlist Titles
- Forthcoming Titles
- Library Subscriptions
- What We Publish
- What We Value
- How to Propose a Volume
- Contribute to a Book in Development
- Request Your Complimentary MLA Handbook
- About the MLA International Bibliography
- Free Online Course
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Submitting Work to the MLA International Bibliography
- Tutorial Videos
- Using the MLA International Bibliography
- A Video from Paula Krebs about Humanities Successes
- Executive Council Actions
- MLA Pathways
- Resources on Academic Freedom, Free Speech, and the Right to Protest
- Resources on Collective Action
- Career Resources
- Conferences, Fellowships, and Announcements
- MLA Grants and Awards
- MLA Professional Development Webinars
- MLA Sit and Write Sessions
- MLA Webinars on the Public Humanities
- Reimagining Humanities Coursework for Career Readiness: A Workshop
- MLA Language Map
- Reports and Professional Guidelines

Request Your Free Member Copy

Buy the MLA Handbook

The MLA Style Center
What is mla style.
Building confidence in the information and ideas we share with one another is perhaps more important today than ever before, and for nearly a century it has been the driving principle behind MLA style, a set of standards for writing and documentation used by writers to find and evaluate information, alert their audience to the trustworthiness of their findings through citation, and shape the expression of their ideas in conversation with others.
Resources for MLA Style
Our new, subscription-based digital platform, MLA Handbook Plus is
- Trusted: The only authorized subscription-based digital resource featuring the latest edition of the MLA Handbook is available for unlimited simultaneous users.
- Evolving: Get the same content as the print edition, plus seamless annual updates and forthcoming additional resources such as videos and companion titles.
- Dynamic: Features an easy-to-search interface, cross-linking of related material, and a split view that lets students see illustrations while reading corresponding content.
- Flexible: Whether on campus, at home, or in a coffee shop, students can access the platform from anywhere—perfect for remote or hybrid learning environments.
- Affordable: Tiered pricing model based on full-time undergraduate enrollments in US higher education institutions (with custom pricing options for secondary schools, consortia, international schools, campus systems, and other organizations).
- Accessible: Meets current accessibility standards—ensuring that learning MLA style is available to all.
Contact [email protected] for more info.
MLA Handbook , 9th Edition
The ninth edition of the MLA Handbook , published in spring 2021, builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements—facts common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date—that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal articles in databases to song lyrics, online images, social media posts, dissertations, and more. With this focus on source evaluation as the cornerstone of citation, MLA style promotes the skills of information and digital literacy so crucial today. The new edition offers
- New chapters on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, spelling, numbers, italics, abbreviations, and principles of inclusive language
- Guidelines on setting up research papers in MLA format with updated advice on headings, lists, and title pages for group projects
- Revised, comprehensive, step-by-step instructions for creating a list of works cited in MLA format that are easier to learn and use than ever before
- A new appendix with hundreds of example works-cited-list entries by publication format, including websites, YouTube videos, interviews, and more
- Detailed examples of how to find publication information for a variety of sources
- Newly revised explanations of in-text citations, including comprehensive advice on how to cite multiple authors of a single work
- Detailed guidance on using notes in MLA style
- Instructions on quoting, paraphrasing, summarizing, and avoiding plagiarism
- Annotated bibliography examples
- Numbered sections throughout for quick navigation
- Advanced tips for professional writers and scholars
The MLA Style Center offers free online resources on MLA style, including an interactive MLA format template, answers to common questions on Ask the MLA, advice from the MLA editors, and more. Get updates by signing up for The Source newsletter, and follow us on Twitter @MLAstyle .

MLA Format Guide - 9th edition
- Essay Formatting
How to Create a Header
- To add your header, either double-click in the top inch of the page or select the "Insert" tab in Microsoft Word, navigate to the "Header & Footer" section, select "Header," and click the first option titled "Blank."
- When editing your header, navigate to the "Design" tab and check the box beside "Different First Page" as every heading after your first page should only include the page number.
- Still in the design tab under the "Header & Footer" section, select "Page Number." In the drop-down box, select the first option, labeled "Top of Page," then select the third option labeled "Plain Number 3." Add your last name in front of the page number, and change the font settings to match that of the rest of your paper.
- On the next line, set the text alignment to align your text to the left side of the page (under the "Paragraph" section of the "Home" tab) and on four different lines type your first and last name, your instructor's name, the course the assignment is for, and the date in the format DD Month YYYY.
- On the next line, center the text (under the "Paragraph" section of the "Home" tab) and type the title of your paper.
An example of an MLA formatted header is included below.

How to Create a Works Cited Page
You can create your Works Cited page before, during, or after you write your essay. If you do not create it before, be sure to document the sources you used, including any website links, so you can go back and create your citations later. Citation format will be discussed in a later section, but this section will detail how to create a Works Cited Page.
- At the end of your essay, insert a page break (found under the "Insert" tab) and center the words "Works Cited" at the top of your page (not in the header). If there is only one source being cited, type "Work Cited".
- Insert your citations in alphabetical order in the subsequent lines. Make sure they are left aligned.
- If your citation is more than one line, apply the hanging indent feature to everything after the first line for each individual entry. You can do this by selecting the second line of the entry, navigating to the "Home" tab in Microsoft Word, selecting the arrow at the bottom right in the "Paragraph" section to open up the "Paragraph Settings" box, and under the "Indentation" section, select the drop-down box labeled "Special," and choose "Hanging". This will move everything but the first line of your citation slightly to the right.

Other essay formatting notes
When formatting your essay, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Use the correct font as listed under the "Home" tab of this guide. Double-space your text, use 12 pt font, and use a legible font style, such as Times New Roman, Ariel, Calibri, etc., ensuring that the regular and italic font styles are distinct.
- After the first page, only include your last name and the page number in the top right corner of the header.
- Change the paragraph options to remove space before and after all paragraphs. Select the entire essay (you can use the Ctrl + A feature), and in the "Paragraph" section of the "Home" tab, select the drop-down arrow where you can adjust the line spacing and make sure both selections at the bottom of the drop-down box read "Add Space Before Paragraph" and "Add Space After Paragraph". If they say "Remove Space Before Paragraph" and/or "Remove Space After Paragraph," click to remove the space.
- On the last page, include a Works Cited page with your citations listed in alphabetical order.
- Last Updated: Oct 13, 2023 9:40 AM
- URL: https://uaccm.libguides.com/what_is_MLA_style
Research: Documentation
Mla general format.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability to their source material. Most importantly, the use of MLA style can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the purposeful or accidental uncredited use of source material by other writers.
If you are asked to use MLA format, be sure to consult the MLA Handbook (8th edition). Publishing scholars and graduate students should also consult the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3rd edition). The MLA Handbook is available in most writing centers and reference libraries; it is also widely available in bookstores, libraries, and at the MLA web site. See the Additional Resources section of this handout for a list of helpful books and sites about using MLA style.
Paper Format
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA style is covered in chapter four of the MLA Handbook, and chapter four of the MLA Style Manual . Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style.
General Guidelines
- Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Double-space the text of your paper, and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are recognizable one from another. The font size should be 12 pt.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks (unless otherwise instructed by your instructor).
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Indent the first line of paragraphs one half-inch from the left margin. MLA recommends that you use the Tab key as opposed to pushing the Space Bar five times.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor may ask that you omit the number on your first page. Always follow your instructor’s guidelines.)
- Use italics throughout your essay for the titles of longer works and, only when absolutely necessary, providing emphasis.
- If you have any endnotes, include them on a separate page before your Works Cited page. Entitle the section Notes (centered, unformatted).
Formatting the First Page of Your Paper
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically requested.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor’s name, the course, and the date. Again, be sure to use double-spaced text.
- Double space again and center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks; write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
- Use quotation marks and/or italics when referring to other works in your title, just as you would in your text: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas as Morality Play; Human Weariness in “After Apple Picking”
- Double space between the title and the first line of the text.
- Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space with a page number; number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor or other readers may ask that you omit last name/page number header on your first page. Always follow instructor guidelines.)
Here is a sample of the first page of a paper in MLA style:

The First Page of an MLA Paper
Section Headings
Writers sometimes use Section Headings to improve a document’s readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay.
MLA recommends that when you divide an essay into sections that you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
- Early Writings
- The London Years
- Traveling the Continent
- Final Years
MLA does not have a prescribed system of headings for books (for more information on headings, please see page 146 in the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , 3rd edition). If you are only using one level of headings, meaning that all of the sections are distinct and parallel and have no additional sections that fit within them, MLA recommends that these sections resemble one another grammatically. For instance, if your headings are typically short phrases, make all of the headings short phrases (and not, for example, full sentences). Otherwise, the formatting is up to you. It should, however, be consistent throughout the document.
If you employ multiple levels of headings (some of your sections have sections within sections), you may want to provide a key of your chosen level headings and their formatting to your instructor or editor.
Sample Section Headings
The following sample headings are meant to be used only as a reference. You may employ whatever system of formatting that works best for you so long as it remains consistent throughout the document.
- Water Conservation
- Energy Conservation
Formatted, unnumbered:
Level 1 Heading: bold, flush left
Level 2 Heading: italics, flush left
Level 3 Heading: centered, bold
Level 4 Heading: centered, italics
Level 5 Heading: underlined, flush left
- MLA General Format. Provided by : OWL Purdue. Located at : https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/purdue_owl.html . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Educational Use

Privacy Policy
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida , Barbara McLain - The Out-of-Door Academy , Jennifer Janechek - IBM Quantum
What is MLA Format?
MLA Format refers to the formatting guidelines published by the MLA (Modern Language Association) for writers of research papers (see MLA Handbook, 9th Edition ).
Related Concepts: Annotated Bibliography ; Intellectual Property ; Page Design ; Plagiarism
Select a readable font such as Times New Roman, and an easily legible font size (usually 10- to 12-point font).
MLA Page Layout
For the entire paper, set all margins at 1” and double-space throughout.
Each new paragraph should be indented. There should be no extra spaces anywhere, from the first line of your heading, all the way to the last line of your text.
MLA First Page
Course information.
On separate lines, type
- Your first and last name
- Your instructor’s name
- The course title
- Day month year.
Items in the heading should be double-spaced, in the same 12-point font as the rest of the paper.
MLA Page Header
Using the automatic header feature of your word processor, set a running head .5” from the top of the page with your last name and the automatic page number feature.
Each page of your MLA formatted paper, including page one, should have a header in the upper right margin. The header should include your first name followed by the page number:
MLA Block Quotations
If you are quoting a selection that is longer than 3 typed lines, MLA requires that you block the quotation. This means introducing the quote as you normally do, but starting the quote on a new line. The entire quote will still be double spaced, but also indented.
Note that block quotations do not have quotation marks around them and that the citation comes after the punctuation.
MLA Headings and Subheadings
Section headings and subheadings are styled according to prominence, and the MLA designates 5 levels:
Here is what a heading looks like in the text of a paper:
MLA Works Cited
The header will continue on to the works cited page in the upper right corner. The title (Works Cited) should be centered at the top of the page. Your bibliographic entries should be alphabetized according to the first item in each entry, double-spaced, with a hanging indentation. There are no extra spaces between entries.

MLA Annotated Bibliography
The formatting of an annotated bibliography will be similar to a works cited page. The bibliographic entries will be identical, but annotations will be added. Start the annotation on a new line, and indent again. The entire annotation should be indented.
Note: If the annotated bibliography is a stand alone assignment, you should begin with a header, title, and heading, just as you would for an essay.
MLA Footnotes – MLA Endnotes
There are two types of information that can be included in footnotes and endnotes:
- at the bottom of the page
- at the end of the document, as an endnote.
MLA footnotes and MLA Endnotes MLA discourages the use of footnotes and endnotes for lengthy asides, but does have rules in the event that these notes are needed.
To format a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number following the sentence that requires either explanation or citation. Most word-processing programs will automatically create a corresponding place for an entry at the foot of the page or the end of the document. You only need to place your cursor where you want to superscript number to go, click on “insert,” and then select footnote or endnote.
Footnotes themselves will be single-spaced with an extra space between entries.
MLA Format Example
The following is a full essay in MLA format:

MLA Checklist
General Formatting
1. Is the heading in the upper left-hand corner of the first page?
2. Does the heading include:
- Your Instructor’s name?
- The course name?
3. Does the paper have an original title (other than something like “Final Paper”)? Is the title presented without being bolded, italicized, or placed in quotation marks?
4. Does the paper have 1″ margins on all sides?
5. Is the paper written in Times New Roman (or another standard font your professor allows) and in 12-pt. font?
6. Is everything double-spaced (including any notes and the works cited page)?
7. Are your last name and the page number in the upper right-hand corner of each page (0.5″ from the top, or inserted using the “header” function in Word)?
Formatting Evidence
8. Are all direct quotes in quotation marks?
9. Does all paraphrase and summary clearly indicate that it comes from other sources?
10. Does each in-text reference include a parenthetical citation that includes the author’s last name (unless it is obvious from the context of the sentence who you are referencing) and the page number from which the information was taken?
11. If a quotation is 4 lines or more, is it block-quoted? (i.e. double-spaced, indented 1 inch from the left margin)
12. Have you clearly indicated where you found all information you did not previously know?
Formatting the Works Cited
13. If you’ve used outside sources, do you have a works cited page?
14. Is it titled “Works Cited” (without the quotation marks)?
15. Does it have a header?
16. Are the entries in your list of works cited in alphabetical order?
17. Are the entries double-spaced, with no extra spaces in between entries?
18. Does each entry include a hanging indentation?
19. Does each source have an entry on the works cited page?
MLA Template
The following is an MLA template for Microsoft Word. Feel free to use it to ensure that you’re properly formatting your papers.
Related Articles:

MLA Format Example: Sample MLA Format Essay
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Barbara McLain
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know Here
Welcome to an overview of “What is MLA Format?” in relation to paper formatting. You’ll find in-depth guidelines, examples, and visual samples to help you easily format your paper. This guide does not serve as a reference for MLA citation format.
For help determining the proper structure for citing, refer to the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here is another informative site which may help with further understanding of MLA citation format.
Guidelines for Formatting a Paper in MLA
- Use white 8 ½ x 11” paper.
- Make 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides.
- The first word in every paragraph should be indented one half inch.
- Indent set-off or block quotations one half inch from the left margin.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman. Make sure that italics look different from the regular typeface.
- Use 12-point size.
- Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page.
- Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces.
These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center’s web page “Formatting a Research Paper.”
MLA Guide Overview
There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper.
This guide includes the following sections:
- Format background
- General paper formatting
- MLA heading format & title page instructions
- Running head & page numbers
- Paraphrases
- Abbreviations
- Numbers (includes the use of numbers in MLA outline format)
- Images, tables, and musical scores
- MLA works cited format
- MLA citation format (for in-depth citation rules visit this MLA citation guide or MLA in-text citation guide)
- Edits & proofreading
If you need more guidance, a website like EasyBib.com usually has guides and tools to help you out. There’s also resources on other styles, like our guide on “ APA reference page ”, otherwise known as a “References” page.
MLA Format Background
The Modern Language Association (MLA) is an organization responsible for developing MLA format. It was developed as a means for researchers, students, and scholars in the literature and language fields to uniformly format their papers and assignments. This uniform, or consistent, method to developing a paper or assignment allows for easy reading. Today, MLA is not only used in literature and language subject areas; many others have adopted it as well.
The Modern Language Association released the 9th and most current edition of their MLA Handbook in April 2021. The Handbook provides thorough instructions on citing, as well as guidelines for submitting work that adheres to the Modern Language Association’s rules and standards. Although we’re not affiliated with the MLA, our citation specialists bring you this thoughtful and informative guide on the format.
Looking for information about previous editions to the Handbook ? Want to learn more about the origin of “What is MLA format?” Click here to learn about the previous editions to the Handbook .
Actually, are you looking for help on using another style? See how to cite an APA journal , learn to create an APA book citation , and more!
Formatting the Header in MLA
To create a header for your first page, follow these steps:
- Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin.
- Type your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
- Double space once more and center the title. Do NOT underline, bold, or type the title in all capital letters. Only italicize words that would normally be italicized in the text. Example: Character Development in The Great Gatsby
- Do not place a period after the title or after any headings
- Double space between the title and first lines of the text

General Paper Formatting
Paper choice.
While many professors, instructors, and publications allow electronic submission, some prefer printed, hard copies of papers. This section focuses on the type of paper to use for printed submission.
If you choose to print your paper, use white paper only. Do not use ivory, off-white, or any other shades or colors.
Choose a standard, high quality paper to print your project on. Do not use cardstock. It is not necessary to use resum é paper. Use typical, high quality printer or copy paper.
When it comes to size, 8 ½-by-11-inch paper is the recommended size. If you’d like to use a different size, ask your teacher prior to submission.
Use One-Inch Margins in MLA
Use one-inch margins around the entire page. The running head should be the only item seen in the one inch margin (see below for more on running heads).
Most word processing programs automatically default to using one inch margins. Check the page settings section of the program to locate the margin size.
Indenting Paragraphs in MLA
Indent the first word in every paragraph. Sentences should begin one half inch from the left margin.
It is not necessary to manually measure half an inch. Use the “tab” button on the keyboard to create a half inch space.
Double Space Paragraphs in MLA
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page.
While it may seem tempting to place a few extra lines between the heading, title, and beginning of the paper, lines should all be double spaced.
Font and Font Size in MLA
In an MLA paper, it is acceptable to use any font type that is easy to read. Many source types, such as books and articles, use fonts that are easy to read, so if you’re seeking an appropriate font style, look at other sources for guidance. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Arial and Times New Roman.
It is important for the reader to be able to distinguish the difference between italicized and regular font, so if you choose a font style different than Arial or Times New Roman, make sure the difference between the two type styles is evident.
The use of a 12-point font size is recommended as this is the default size for many word processing programs. It is acceptable to use another standard size, such as 11-point or 11.5-point.
Some professors or instructors will provide guidance on how to secure hard copies of projects. If your instructor does not provide you with any expectations or guidance, a simple staple in the top left corner should suffice. If a stapler is not available, some instructors allow paper or binder clips.
Do not fold the top left corner down to secure the pages together. The page could easily unfold, causing a mess of papers. While binders and plastic holders are cute, in reality, they add bulk to a professor or instructor who may like to take the papers home for grading purposes. Keep the binding simple and clean. Staples work best, and binder and paper clips are the next best option.
As always, follow any instructions your professor or teacher may provide. The guidelines found here are simply recommendations.
MLA Heading & Title Page Instructions
The web page “Formatting a Research Paper” gives two options when it comes to creating the header for your project:
- An MLA format heading can be placed at the top of the first page
- A title page can grace the front of the assignment. If you choose to create a title page, keep in mind that there aren’t any official title page or cover page guidelines in MLA format. See more information below.
If choosing option one, creating an MLA heading, you’ll need to include four main components:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The name and number of the course or class
- The assignment’s due date
The first item typed on the paper should be your full name.
- Position your name one inch from the top and left margins of the page.
- Add a double space beneath your name, and type the name of your instructor.
- Below the professor or instructor’s name should be a double space, followed by the name of the course, class, or section number (if available).
- Below it, include another double space and add the assignment’s due date (Day Month Year).
Here’s an example:

The assignment’s title should be placed below the due date, after a double space. Align the title so it sits in the center of the MLA format paper. The title should be written in standard lettering, without underlines, bold font, italicized font, or any quotation marks. Only include italics or quotation marks if your title includes the title of another source.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment:
Neal E. Bibdarsh
Professor Haujeemoto
English 201
The Trials and Tribulations of Lincoln’s Reciting of “The Gettysburg Address”
*Note: The quotation marks here are around the title of a speech included in the paper’s title.
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
If your teacher or professor requires a standalone title page, but has not provided any guidance or specifications, here are a few suggestions from EasyBib.com and this MLA guide :
- Center and double space all of the text on your page.
- Place the name of your school at the top of the page.
- Skip down to about the center of the page and type the title of your paper. Do not bold the title, italicize the entire title, place quotation marks around it, or type the title out in capital letters.
- Use italics for the titles of any sources in the title of your paper. Example: An Analysis of Mythical Creatures in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
- first letter of the title
- first letter of the last word
- first letter of any adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs
- If your paper has a subtitle, include on the next line below your title.
- Skip down to the bottom third of the page and add your name, the the name of your instructor, the name/number of the course or class, and the assignment’s due date on four separate lines.
- Keep the font size at 12 pt., or a size close to it, to make it look professional.
- Use the same font as the text of the paper. The Modern Language Association recommends any font that is easy to read and has a clear distinction between italics and standard font. Times New Roman and Arial are recommended, but many other fonts work as well.
- Include a page number in the top right corner of the paper. For more information on how to style page numbers, check out the next section, “Running Head and Page Numbers.”
- We do not recommend adding any images or cover art to the title page.
Click additional information about essays to see an example of a formatted header.
You can either create a title page using the EasyBib Title Page creator or omit the title page completely and use a header.
Running Head & Page Numbers in MLA
A running head is a brief heading that is placed in the top right corner of every page in a project. The Modern Language Association Style Center (online) states that the running head consists of:
- Last name of the paper’s author
- Page number
General tips to keep in mind:
- The running head is placed in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin of the page.
- Type your last name before the page number.
- The last name and page number should be separated by a single space.
- Do not place the word “page” or use an abbreviation, such as p. or pg., before the page number.
- Quite often, the running head begins on the second page, but your instructor may ask you to include the running head on the first page of the assignment. As always, if your instructor provides you with specific directions, follow his or her guidelines.

Before adding this information manually onto every single page, check to see if the word processor you’re using has the capability to automatically add this information for you. Try looking in the settings area where page numbers or headers can be added or modified.
Google Docs: Adding a header
- Go to the menu section “Insert.”
- Select “Page numbers” and select the option that places the page number in the upper-right corner.
- A page number will appear; your cursor will blink next to it.
- Move your cursor to the left of the page number.
- Type your last name. Add a space between your name and the page number.
- You should now have a properly formatted header on every page!
Microsoft Word Document: Adding a header
- Double-click in the space at the top of the page (where the page number is).
- OR Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Header,” and select “Edit Header.”
- Type your last name next to page number. If it isn’t already right-aligned, go to the “Home” menu and right-align your name.
Quotations in MLA
Quotes are added into assignments to help defend an argument, prove a point, add emphasis, or simply liven up a project.
Quotes should not take up the majority of your paper or assignment. Quotes should be sprinkled sparingly throughout, and quotes longer than 4 lines should be formatted as MLA block quotes . Use direct quotes from outside sources to enhance and expand on your own writing and ideas.
Words from quotes belong to the individual who spoke or wrote them, so it is essential to credit that individual’s work. Credit him or her by adding what is called an “in-text citation” into the body of the project.
There are three ways to add quotes: 1. With the author’s name in the sentence (a citation in prose).
Dan Gutman shares a glimpse into the overall plot by stating, “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman is the author of the book that this quote is pulled from.
2. Without the author’s name in the sentence (a parenthetical citation).
The main character’s confusing experience is realized and explained when he states “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (Gutman 5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman’s name isn’t included in the sentence. It’s included in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. This is an example of a proper MLA style citation in the body of a project.
3. In a block quote, which is used when a large quote, of 4 lines or more, is added into a project.
Using footnotes and endnotes
The Modern Language Association generally promotes the use of references as described in the sections above, but footnotes and endnotes are also acceptable forms of references to use in your paper.
Footnotes and endnotes are helpful to use in a variety of circumstances. Here are a few scenarios when it may seem appropriate to use this type of referencing:
- When you are referring to a number of various sources, by various authors, in a section of your paper. In this situation, it is a good idea to use a footnote or endnote to share information for parenthetical references. This will encourage the reader to stay focused on the text of the research paper, instead of having to read through all of the reference information.
- When you are sharing additional information that doesn’t quite fit into the scope of the paper, but is beneficial for the reader. These types of footnotes and endnotes are helpful when explaining translations, adding background information, or sharing counterexamples to research.
To include a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number at the end of the sentence the footnote or endnote refers to. They can be included mid-sentence if necessary, but be sure to add it after any punctuation, such as commas or periods. Find a location that doesn’t distract the reader from the content and flow of the paper.
Within the text example:
Numerous well-known children’s books include characters from a wide range of races and ethnicities, thus promoting diversity and multiculturalism.¹
At the bottom of the page (footnote) or at the end of the section (endnote):
¹See Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez. While Parr’s work features characters of various colors, such as pink or blue, children easily correlate it with individuals of different races and ethnicities.
On the last page of the assignment, the writer includes the full references for the books by Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez.
For more on block quotes and a further, detailed explanation on the use of quotes, including MLA footnotes, refer to our MLA In-Text Citation and Parenthetical Citations Guide. In this guide you’ll find further information including directions for the use of quotes without an author, page numbers, and how to properly credit work from electronic sources.
For guides on citations in another style, check out APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation .
Paraphrases in MLA
Paraphrases are created when text or speech from another source are added into a project, but the writer chooses to summarize them and weave in his or her own writing and writing style.
Even though the writer modifies the information from another source, it is still necessary to credit the source using proper format ( Handbook 98). Paraphrased information uses the same MLA reference format as stated in the section directly above this one.
Here is an acceptable paraphrase:
Original text:
“Stay hungry. Stay foolish.” Steve Jobs
Paraphrase:
Steve Jobs encouraged students at Stanford to continue with their determination, drive, and ambitious behavior. They should never be simply satisfied with the status quo. They should continue to push themselves despite possible obstacles and failures.
To develop a well-written paraphrase, follow these simple, step-by-step instructions.
- Find a phrase, sentence, paragraph, or section of original text you’d like to turn into a paraphrase.
- Read the text carefully and make sure you fully comprehend its meaning. A writer can only develop a well-written paraphrase if the information has been fully grasped and understood. If you’re having difficulty understanding the information, take a few minutes to read up on tricky words and background information. If all else fails, ask a friend to see if they’re able to make sense of the concepts.
- After analyzing and completely understanding the original text, put it to the side. Take a moment to think about what you’ve read and connect the idea to your own assignment.
- Now that the information is completely understood, take a moment to rewrite what you’ve read, in your own words and writing style. Do not simply substitute words in the original text with synonyms. That’s plagiarism! Show off and demonstrate your ability to process the original information, connect it to the content in your paper, and write it in your own individual and unique writing style.
- Include an in-text reference next to the paraphrase. All paraphrases include references, similar to direct quotes. See the “Quotations” section of this guide to learn how to properly attribute your paraphrased information.
- Give yourself a pat on the back! Paraphrasing is an important part of the research and writing process.
Wondering if it’s better to quote or paraphrase?
An essential part of the research process involves adding direct quotes and paraphrases into projects. Direct quotes provide word-for-word evidence and allow writers to use another author’s eloquent words and language in their own projects. When it comes to paraphrases, writers are able to take a block of text and shrink the scope of it into the their papers. Paper writers can also use paraphrases to demonstrate their ability to analyze and reiterate information in a meaningful and relevant way.
If you’re wondering which one is better to consistently use, quotes or paraphrases, there’s a clear winner. Paraphrases come out on top. Sure, direct quotes are incredibly beneficial, but copying and pasting too many of these into a project can cause a reader to lose sight of the writer’s own voice. Mixing your own voice with another author’s too much can make for choppy and disjointed reading.
The ultimate goal of a research project is to have your voice and research merged together as one. Paraphrases allow just that. When you combine information from outside sources with your own writing style, it demonstrates your ability as a researcher to showcase your understanding and analyzation of a topic.
Remember, whether you’re adding direct quotes or paraphrases into a project, both types of additions need references. References are placed after the quotes and paraphrases, and also at the end of an assignment.
If you’re looking for additional help with your punctuation or grammar, check out the EasyBib plagiarism checker !
Using Abbreviations in MLA
Abbreviations are commonly used in many source types including websites, blog posts, books, and journal articles. It is acceptable to use abbreviations in all of these sources.
When it comes to school and research assignments, however, the MLA Handbook states that abbreviations should be used rarely in the prose of your paper (293). Spelling out abbreviations into their full words and meanings is recommended. This ensures understanding and avoids any confusion from your reader.
There are times when you may feel it is perfectly acceptable to use an abbreviation rather than its typed out counterpart in a paper. If you do abbreviate, be sure you are using commonly accepted abbreviations, which you can find in the dictionary. You can also review Appendix 1 in the MLA Handbook .
General Abbreviation Tips
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be abbreviated to HIV, not H.I.V.
- United States should be US, not U.S.
- Digital video disc should be DVD, not D.V.D.
- For lower case abbreviations, it is acceptable to include periods between the letters.
- The abbreviation, “For example” = e.g.
- If there is a mix of lower case and upper case letters, do not use periods if the majority of the letters are upper case. Examples include PhD and EdD
Abbreviating Months
Type out entire month names when being used in the body of a research paper or assignment.
She rented out the beach house from May through September
When it comes to references, MLA bibliography format requires months longer than four letters to be abbreviated.
- July = July
- November = Nov.
Other abbreviations that are perfectly acceptable to use in a bibliography (not the body of a project) include:
- p. or pp. for page and page numbers
- ch. for chapter
- ed. for edition
- trans. for translation or translated
- vol. for volume
- no. for number
- rev. for revised
Again, these abbreviations should only be used in the final page(s) of a project, the MLA Works Cited list. They should not be used in the body of a project.
For more information on bibliographies, see our MLA format Works Cited List page.
Abbreviating Publishers
One of the quirkiest things about this particular style is how publisher names are structured on the final page of references. Certain words are abbreviated, some words are omitted, and other words are written in full.
Words describing what type of business the publisher is are omitted from the works cited. Here’s a breakdown of the words that should be excluded:
- Co. (Company)
- Corp. (Corporation)
- Inc. (Incorporated)
- Ltd. (Limited)
- The (when at the beginning of the name)
If a publisher’s name contains the words “University” and “Press” (or the equivalent in another language), the words should be abbreviated to the letters “U” and “P” in your citation. But if only one of the words appears, it should be written out normally.
Here are a few examples:
- University of Delaware
- U College of London P
All other words related to the names of publishers should be written out in full.
Abbreviating Titles
Certain classical and biblical works are abbreviated in a bibliography, but also in any parenthetical references in the text.
The official handbook provides a lengthy list, spanning over multiple pages, of the preferred abbreviations to use for classical and biblical works ( Handbook 295-301), but here’s a quick snapshot of some of the commonly used ones:
Hebrew Bible or Old Testament = OT
- Deut. = Deuteronomy
- Gen. = Genesis
- Lev. = Leviticus
- Num. = Numbers
- Ps. = Psalms
New Testament = NT
- 1 Cor. = 1 Corinthians
- Jas. = James
- Matt. = Matthew
Shakespeare:
- Ado = Much Ado about Nothing
- 3H6 = Henry VI, Part 3
- JC = Julius Caesar
- Mac. = Macbeth
- MND = A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Oth. = Othello
- Rom. = Romeo and Juliet
Again, the titles above are allowed to be abbreviated both in references in parentheses in the body of a project and also on the final page of references. If you’re wondering why, it’s because they’re cited often and it’s unnecessary to type out the entire title names.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
Use of numerals.
If the project calls for frequent use of numbers (such as a scientific study or statistics), use numerals that precede measurements.
- 247 milligrams
Other items to keep in mind:
In divisions, use numbers, ex: In page 5 of the study
Arabic Numbers
When including a number in a paper, spell out the number if it can be written as one word (such as six ) or two words (such as sixty-two ). For fractions, decimals, or longer numbers, type them out using digits. For larger numbers, write the number itself ( Handbook 82-84).
- twenty-seven
- one hundred
If the number comes before a unit of measurement or label, type the number using digits.
- 8 tablespoons
- 3 July 2018
- 25 King Street
More on Numbers
Starting a sentence with a number is generally frowned upon. Try modifying the sentence so that the number, or number word, is found elsewhere.
Instead of:
225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Use this sentence:
A total of 225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
If modifying the sentence is not possible or does not work well with the flow of the assignment or paper, type out the written number:
Two hundred twenty five children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Do not include any ISBN numbers in your paper.
Outline Format
The Modern Language Association does not have any requirements regarding the structure of an outline. If your teacher asks you to create an MLA outline, we recommend using roman numerals, capital and lowercase letters, and numbers.
Here is an example of a recommended outline structure:

In addition to outlines, use roman numerals for suffixes.
- King George IV
Using Images, Tables, & Musical Scores in MLA
Photographs, data sets, tables, graphs, and other images are often added into projects or papers to promote or aid understanding. They provide meaningful visuals for the reader. If the illustration or visual image does not enhance the quality of the paper, do not include it in the project.
Tables and illustrations should be placed as close as possible to the text that they most closely refer to.
For an image to be significant and easily identifiable, place it as close as possible to the text in the project where it is discussed.
It is not acceptable to simply place an image in a project without including identifiable information. All images must include information about its origin.
Here are the directions to properly attribute an image:
- Assign an Arabic number. The image closest to the beginning of the project should be labeled as Fig. 1. The next image in the project should be Fig. 2. and so on.
- Provide a caption. The caption should be a brief explanation or the title of the contents of the image. Place the caption directly next to the label.
- Immediately following the caption, it is acceptable to include attribution information. If the image is not discussed further in the rest of the paper or project, it is acceptable to include the MLA bibliography format citation below the image and omit it from the bibliography or MLA format works cited page.
In the text of the project or paper where the figure is discussed, include the label in parentheses to ensure the reader knows where to find the figure in your paper.
In the text:
Sarah’s tattoo design was filled with two of her favorite flowers: lilies and daffodils along a thinly curved vine (fig. 1).
Image formatting:
(Image Would Be Here) Fig. 1. Sarah’s Tattoo. barneyWILLIAMSable, Deviant Art , 2011, barneywilliamsable.deviantart.com/art/Sarah-s-Tattoo-design-193048938.

Fig. 1. White Studio. “Houdini and Jennie, the Elephant, Performing at the Hippodrome, New York.” Library of Congress , www.loc.gov/item/96518833/.
When adding a table or data set into a project, it is formatted a little differently. Above the data set, include the label “Table” with an Arabic numeral, and title it. The table number and title should be located flush left and on separate lines. The first table seen in the project is labeled as Table 1. The second table in the project is Table 2, and so on. The table’s title should be written in title case form (the first letter of each word is capitalized, except for small, insignificant words).
Underneath the table, provide the source and any notes. Notes should be labeled with a letter, rather than a numeral, so the reader is able to differentiate between the notes of the text and the notes of the table.
International Scholars from India Enrolled at Yale University a
Source: “International Scholars Academic Year 2015-2016.” Yale University , Office of International Students and Scholars, yale.app.box.com/v/scholar-2015-2016. a. The numbers reflect students who are enrolled full-time.
The information included above and below any images or table should be double spaced, similar to the rest of the project or paper.
Musical Scores
Musical scores need to be labeled as well. When including a musical score in a project, label musical scores with “Ex.” which is short for example. This label should be placed below the musical score. Next to the abbreviation “Ex.”, assign the score an Arabic numeral. The first musical score in the project should be labeled as Ex. 1. The second musical score found in an assignment should be labeled as Ex. 2., and so on.
If possible, provide a caption after to the label. If the caption below the sheet music includes enough information about the source, it is not necessary to include the full reference at the end of the assignment.
Here is an example of a possible label and caption:
Ex. 4. Scott Joplin, The Entertainer, piano, C major.
Another example:

Here’s more on tables and illustrations.
Using Lists in MLA
It’s appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional vertical style.
Often, you will use a colon between the introductory sentence and the list. But you should not include a colon if the first item in the list is part of the sentence.
List Example #1
Here is an example of how a list may look incorporated into the prose of a research project or assignment:
William Shakespeare wrote numerous plays, many of which were considered tragedies: Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear .
List Example #2 Here is an example of how a list may look in a research project or assignment when the list is part of the introductory sentence:
Many of William Shakespeare’s were tragedies. Some of his most popular tragedies include Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear.
MLA Works Cited Format
EasyBib.com has a full, comprehensive guide to creating a proper works cited MLA format , but here are a few items to keep in mind when developing this portion of a project:
- The list of citations should be the very last page of a research project or essay.
- The top of the page should include the running head and the page number.
- All entries should be placed in alphabetical order by the first item in the MLA format citation.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
For more detailed information, make sure to check out the EasyBib guide to MLA format Works Cited pages.
MLA Citation Format
The majority of this guide focuses on MLA formatting in regards to MLA paper format rules and guidelines. If you’re seeking information related to the proper formatting of an MLA citation, refer to our individual pages and posts on various types of citations.
If you’re simply looking for the general structure for full references, which are found on the final pages of projects, here’s the proper order:
Author’s Last name, Author’s First name. “Title of Source.”* Title of Container , Names of other contributors along with their specific roles, version of the source (if it differs from the original or is unique), any key numbers associated with the source that aren’t dates (such as journal issue numbers or volume numbers), Name of the Publisher, publication date, location (such as the URL or page numbers).
*Note: A title may be in italics instead of quotation marks, depending of the type of source. The general rule is that works that are self-contained (like books, journals, or television shows) are formatted in italics. Works that are part of a larger work (like articles, chapters, or specific episodes) are formatting in quotation marks.
MLA Format Citing FAQs:
“What in the world are containers?”
Containers are what hold the source. If you’re creating a reference for a chapter in a book, the title of the chapter is the title of the source , and the container is the title of the book . The book holds the chapter, so it’s the container. If you’re searching for how to cite a website, here’s a tip: the title of the source is the name of the individual page and the title of the container is the name of the full website.
“This seems like a lot of information for a reference. Is it all necessary?”
The short answer is “No!” When citing, only include the components that help the reader locate the exact same source themselves.
It isn’t necessary to go digging for items such as numbers, version types, or names of other individuals or contributors associated with the source if they aren’t applicable. If you think it’s beneficial for the reader, then include it.
Related to citations, here are helpful pages on:
- MLA citation website format
- Citing a book
- Citing a journal
- What is a DOI ?
- More on PDFs
If you’re looking for an MLA citation generator, head to the EasyBib homepage. Our formatter will help you create citations quickly and easily!
Need APA, too? There are also EasyBib tools and an APA citation website reference guide to help you learn the basics.
Edits and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading your assignment prior to submission is an incredibly important step in the research process. Editing involves checking the paper for the following items:
- Spelling : Are all words spelled correctly? Review all proper names, places, and other unique words to ensure correct spelling. When finished, run the project through a spell checker. Many word processing programs, such as Microsoft Word and Google Drive, provide a free spell checking feature. While spell checks are beneficial, they do not always spot every mistake, so make sure you take the time to read through the assignment carefully. If you’re still not sure if your project contains proper spelling, ask a friend to read through it. They may find a mistake you missed!
- Grammar : Check your assignment to make sure you’ve included proper word usage. There are numerous grammar checkers available to review your project prior to submission. Again, take the time to review any recommendations from these programs prior to accepting the suggestions and revisions.
- Punctuation : Check to make sure the end of every sentence has an ending punctuation mark. Also make sure commas, hyphens, colons, and other punctuation marks are placed in the appropriate places.
- Attribution : Do all quotes and paraphrases include a citation? Did you create an in-text citation for each individual piece of information?
Smart idea: running your paper through a paper checker before you turn it in. EasyBib Plus offers a checker that scans for grammar errors and unintentional plagiarism.
Check out our MLA sample papers . Also, check out the EasyBib MLA Annotated Bibliography Guide.
Don’t forget to use the EasyBib citation generator to develop your Modern Language Association style references.EasyBib.com also has helpful guides on APA format and more styles . Lastly, stay up-to-date on what’s coming by following our EasyBib Twitter account.
Works Cited
“Formatting a Research Paper.” The MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association of America, style.mla.org/formatting-papers/.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. You can find her here on Twitter. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The works-cited list provides the reader full information so that a reader can locate the source for further use.
Basic formatting
The works-cited list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
Page margins
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Running head
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. For example, Times New Roman font set to 12 points.
Formatting entries
Entries should be double-spaced, including a double-space between the heading and the first entry. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Formatting the title
The title should be “Works Cited.” Center the title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title. If you cite only one source in the list, the title should be “Work Cited.” If you include sources that you only consulted and didn’t cite directly, the title should be changed accordingly to “Works Cited and Consulted.”
Arranging works cited
Works-cited-list entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name (or the editor’s last name for entire edited collections). Double-space all entries. Begin each entry flush with the left margin. If any entry runs over more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin (sometimes called a hanging indent).
Example works cited
Damasio, Antonio. The Feeling of What Happens: Body, Emotion and the Making of Consciousness . Vintage, 2000.
Hill, R. T. “Legitimizing Colonial Privilege: Native Americans at a Quincentenary of Discourse.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 16, no. 1, 1996, pp. 92–100.
MacDonald, Shauna M. “Performance as Critical Posthuman Pedagogy.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 164–81.
Zilio, M. “Canada Will Not Move Embassy to Jerusalem, Federal Government Says.” The Globe and Mail . 7 Sept. 2017, www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/canada-will-not-move-embassy-to-jerusalem-federal-government-says/article37219576/ .
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed in the text. It is styled in two ways: a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when directly quoting text from the source being cited. When including a page number, do not include a comma or any other punctuation mark between the author’s surname and the page number.
Parenthetical citations usually add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Sometimes they include a page number or other locator. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The spiritual geography of the landscape is explained (Cooper).
If you want to cite a chapter number, a scene, or a line number, follow the abbreviation guidelines below:
When including a more specific locator number rather than a page number, place a comma between the author’s surname and the label.
(Cooper, ch. 2).
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for sources with different numbers or types of authors:
Use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations. If you want to add a page number (or another indicator of the place in a work), add it after the author’s surname without any punctuation between the surname and the page number.
(Abraham 7).
Two authors
Add only the surnames of the authors. Use “and” to separate the two authors.
(Langmuir and Einstein).
Three or more authors
Add only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
(Low et al.).
Corporate author
Shorten the organization name wherever possible, excluding any initial articles and using the shortest noun phrase (e.g., shorten Literary Society of Tamil Culture to Literary Society).
(Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s surname.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is shortened to Fantastic Beasts .
( Fantastic Beasts 160).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- Creating an MLA header
Creating an MLA Header | What to Include & How to Format It
Published on August 22, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024.
The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The course name and number
- The date of submission
After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special styling, and should be the same font and size as the rest of the paper.
MLA style does not require a separate title page , but one may be included if your instructor requires it or if the paper is a group project. Usually, though, the main body of your paper just starts on the same page, directly under the title.
Include your name and the page number right-aligned in the running head on every page.
MLA header template (Word) MLA header template (Google Docs)
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Mla header format, mla running head, frequently asked questions about mla format.
The MLA header follows the same format as the rest of an MLA paper:
- 1-inch margins
- Double-spaced
- Left-aligned
- 12 point standard font (e.g. Times New Roman)
Put each piece of information on a separate line, and don’t use periods or other punctuation at the end of each line. The header and title should be in plain text, without any styling.
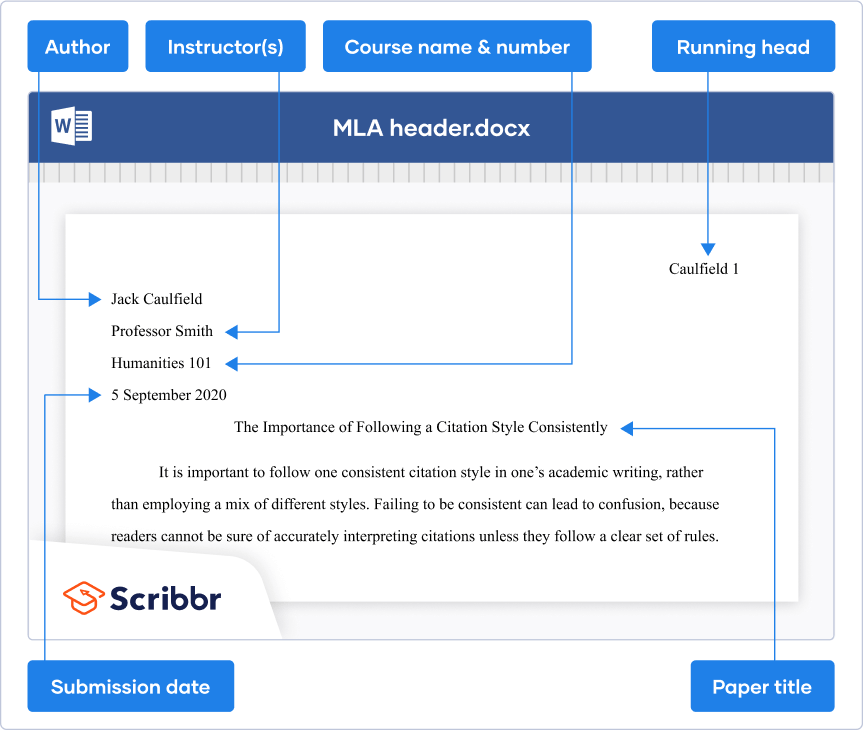
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
On each page of your paper, include a right-aligned running head with your last name and the page number. Don’t use any punctuation or styling.
Most word processing programs will allow you to automatically add page numbers. In Microsoft Word, you can do this by selecting the “Insert” menu and clicking on “Page Number”.
Make sure the running head is in the same font as the rest of your paper.
Creating an MLA running head in Word
If you’re working on a group project and therefore need to list multiple authors for your paper , MLA recommends against including a normal header . Instead, create a separate title page .
On the title page, list each author on a separate line, followed by the other usual information from the header: Instructor, course name and number, and submission date. Then write the title halfway down the page, centered, and start the text of the paper itself on the next page.
Usually, no title page is needed in an MLA paper . A header is generally included at the top of the first page instead. The exceptions are when:
- Your instructor requires one, or
- Your paper is a group project
In those cases, you should use a title page instead of a header, listing the same information but on a separate page.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
MLA recommends using 12-point Times New Roman , since it’s easy to read and installed on every computer. Other standard fonts such as Arial or Georgia are also acceptable. If in doubt, check with your supervisor which font you should be using.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). Creating an MLA Header | What to Include & How to Format It. Scribbr. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/header/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, creating an mla title page, mla format for academic papers and essays, how to format your mla works cited page, what is your plagiarism score.
Ask the MLA
Search our list of frequently asked questions.
Haven't found what you're looking for? Submit a question .
Browse Questions
Questions about works-cited lists, questions about using sources, questions about in-text citations, questions about writing tips, questions about titles of works, questions about punctuation, questions about quotations, questions about formatting a paper, questions about digital sources, questions about names, questions about works-cited list, questions about websites, questions about capitalization, questions about dates, questions about books, questions about italics, questions about abbreviations, questions about page numbers, questions about images, questions about notes, questions about poetry, questions about social media, questions about spelling, questions about one author, questions about foreign language, questions about urls, questions about grammar, questions about numbers, questions about videos, questions about translations, questions about journal articles, questions about movies, questions about artworks, questions about interviews, questions about two authors, questions about captions, questions about essays, questions about dramatic works, questions about alphabetization, questions about paraphrases, questions about more than two authors, questions about republished works, questions about musical works, questions about usage, questions about newspapers, questions about live presentations, questions about credits, questions about photographs, questions about songs, questions about unpublished works, questions about edited collections, questions about television shows, questions about hb9, questions about performances, questions about anthologies, questions about anonymous works, questions about magazines, questions about letters, questions about dictionaries, questions about data, questions about databases, questions about mla style, questions about dissertations, questions about tables, questions about advertisements, questions about apps, questions about editions, questions about corporate authors, questions about speeches, questions about e-mail, questions about lists, questions about appendixes, questions about multivolume works, questions about museums, questions about headings, questions about dois, questions about legal works, questions about conference presentations, questions about word choice, questions about theses, questions about pdfs, questions about textbooks, questions about sound recordings, questions about profiles, questions about containers, questions about introductions, questions about comics, questions about exhibits, questions about e-books, questions about reference works, questions about personal communications, questions about short stories, questions about encyclopedias, questions about transliteration, questions about scripture, questions about lectures, questions about government publications, questions about reports, questions about text messages, questions about podcasts, questions about publishers, questions about news services, questions about maps, questions about annotated bibliographies, questions about use of italics, questions about reviews, questions about special features, questions about radio programs, questions about audiobooks, questions about slide presentations, questions about plays, questions about video games, questions about prefaces, questions about qur'an, questions about summaries, questions about typography, questions about formatting an essay, questions about bible, questions about surveys, questions about blog posts, question about digital archives, question about teaching tips, question about research, question about quotation, question about software, question about formatting, question about citation styles, question about song lyrics, question about writing, question about translation, question about archives, question about science writing, question about foreign languages, question about manuscripts, question about pdf, question about brochures, question about plagiarism, question about article, question about handbook corrections, question about ai, question about working papers, question about afterwords, question about book series, popular questions, how do i cite several e-mails sent on the same day to the same correspondent, what should i do if an author’s last name is not provided in a source, how do i cite one person’s testimony in a congressional hearing, how do i cite a video game, in a quotation from a play, how do i show that material has been omitted, how do i cite a source that uses “supplement” as part of its number element, how do i cite a debate, when altering a quotation in a language other than english, should the alteration be in the language of the quotation, how do i cite a selfie, how do i alter a quotation using square brackets if the quotation already contains bracketed words, how do i cite a commentator’s handwritten notes on a work, should i reproduce a quotation in all caps in my essay, how do i cite audio commentary for a movie or tv show, how do i cite a state law, where should the original author’s name appear when citing indirect sources.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
Health Inc.
- Public Health
Health industry struggles to recover from cyberattack on a unit of UnitedHealth
Darius Tahir
Bernard J. Wolfson
Daniel Chang

Dr. Margaret Parsons, one of three dermatologists at a 20-person practice in Sacramento, California, is in a bind.
Since a Feb. 21 cyberattack on a previously obscure medical payment processing company, Change Healthcare, Parsons said, she and her colleagues haven't been able to electronically bill for their services.
She heard Noridian Healthcare Solutions , California's Medicare payment processor, was not accepting paper claims as of earlier this week, she said. And paper claims can take 3-6 months to result in payment anyway, she estimated.
"We will be in trouble in very short order, and are very stressed," she said in an interview with KFF Health News.
The hacked company handles "14 billion clinical, financial, and operational transactions annually," according to its website .
A California Medical Association spokesperson said March 7 that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services had agreed in a meeting to encourage payment processors like Noridian to accept paper claims. A Noridian spokesperson referred questions to CMS.
The American Hospital Association calls the suspected ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a unit of insurance giant UnitedHealth Group's Optum division, "the most significant and consequential incident of its kind against the U.S. health care system in history." While doctors' practices, hospital systems, and pharmacies struggle to find workarounds, the attack is exposing the health system's broad vulnerability to hackers, as well as shortcomings in the Biden administration's response.

Health care company ties Russian-linked cybercriminals to prescriptions breach
To date, government has relied on more voluntary standards to protect the health care system's networks, Beau Woods, a co-founder of the cyber advocacy group I Am The Cavalry, said. But "the purely optional, do-this-out-of-the-goodness-of-your-heart model clearly is not working," he said. The federal government needs to devote greater funding, and more focus, to the problem, he said.
The crisis will take time to resolve. Comparing the Change attack to others against parts of the health care system, "we have seen it generally takes a minimum of 30 days to restore core systems," said John Riggi , the hospital association's national adviser on cybersecurity.
In a March 7 statement, UnitedHealth Group said two services — related to electronic payments and medical claims — would be restored later in the month. "While we work to restore these systems, we strongly recommend our provider and payer clients use the applicable workarounds we have established," the company said.
"We're determined to make this right as fast as possible," said company CEO Andrew Witty.
Providers and patients are meanwhile paying the price. Reports of people paying out-of-pocket to fill vital prescriptions have been common. Independent physician practices are particularly vulnerable.
"How can you pay staff, supplies, malpractice insurance — all this — without revenue?" said Dr. Stephen Sisselman, an independent primary care physician on Long Island in New York. "It's impossible."
Jackson Health System, in Miami-Dade County, Florida, may miss out on as much as $30 million in payments if the outage lasts a month, said Myriam Torres , its chief revenue officer. Some insurers have offered to mail paper checks.
Relief programs announced by both UnitedHealth and the federal government have been criticized by health providers, especially hospitals. Sisselman said Optum offered his practice, which he said has revenue of hundreds of thousands of dollars a month, a loan of $540 a week. Other providers and hospitals interviewed by KFF Health News said their offers from the insurer were similarly paltry.
In its March 7 statement, the company said it would offer new financing options to providers.
Providers pressure government to act
On March 5, almost two weeks after Change first reported what it initially called a cybersecurity "issue," the Health and Human Services Department announced several assistance programs for health providers.
One recommendation is for insurers to advance payments for Medicare claims — similar to a program that aided health systems early in the pandemic. But physicians and others are worried that would help only hospitals, not independent practices or providers.
Anders Gilberg , a lobbyist with the Medical Group Management Association, which represents physician practices, posted on X , formerly known as Twitter, that the government "must require its contractors to extend the availability of accelerated payments to physician practices in a similar manner to which they are being offered to hospitals."
HHS spokesperson Jeff Nesbit said the administration "recognizes the impact" of the attack and is "actively looking at their authority to help support these critical providers at this time and working with states to do the same." He said Medicare is pressing UnitedHealth Group to "offer better options for interim payments to providers."
Another idea from the federal government is to encourage providers to switch vendors away from Change. Sisselman said he hoped to start submitting claims through a new vendor within 24 to 48 hours. But it's not a practicable solution for everyone.
Torres said suggestions from UnitedHealth and regulators that providers change clearinghouses, file paper claims, or expedite payments are not helping.
"It's highly unrealistic," she said of the advice. "If you've got their claims processing tool, there's nothing you can do."
Mary Mayhew , president of the Florida Hospital Association, said her members have built up sophisticated systems reliant on Change Healthcare. Switching processes could take 90 days — during which they'll be without cash flow, she said. "It's not like flipping a switch."
Nesbit acknowledged switching clearinghouses is difficult, "but the first priority should be resuming full claims flow," he said. Medicare has directed its contractors and advised insurers to ease such changes, he added.
Health care leaders including state Medicaid directors have called on the Biden administration to treat the Change attack similarly to the pandemic — a threat to the health system so severe that it demands extraordinary flexibility on the part of government insurance programs and regulators.
Beyond the money matters — critical as they are — providers and others say they lack basic information about the attack. UnitedHealth Group and the American Hospital Association have held calls and published releases about the incident; nevertheless, many still feel they're in the dark.
Riggi of the AHA wants more information from UnitedHealth Group. He said it's reasonable for the conglomerate to keep some information closely held, for example if it's not verified or to assist law enforcement. But hospitals would like to know how the breach was perpetrated so they can reinforce their own defenses.
"The sector is clamoring for more information, ultimately to protect their own organizations," he said.
Rumors have proliferated.
"It gets a little rough: Any given day you're going to have to pick and choose who to believe," Saad Chaudhry, an executive at Maryland hospital system Luminis Health, told KFF Health News. "Do you believe these thieves? Do you believe the organization itself, that has everything riding on their public image, who have incentives to minimize this kind of thing?"
What happens next?
Wired Magazine reported that someone paid the ransomware gang believed to be behind the attack $22 million in bitcoin. If that was indeed a ransom intended to resolve some aspect of the breach, it's a bonanza for hackers.
Cybersecurity experts say some hospitals that have suffered attacks have faced ransom demands for as little as $10,000 and as much as $10 million . A large payment to the Change hackers could incentivize more attacks.
"When there's gold in the hills, there's a gold rush," said Josh Corman , another co-founder of I Am The Cavalry and a former federal cybersecurity official.
Longer-term, the attack intensifies questions about how the private companies that comprise the U.S. health system and the government that regulates them are defending against cyberthreats. Attacks have been common: Thieves and hackers, often believed to be sponsored or harbored by countries like Russia and North Korea, have knocked down systems in the United Kingdom's National Health Service, pharma giants like Merck, and numerous hospitals.
The FBI reported 249 ransomware attacks against health care and public health organizations in 2023, but Corman believes the number is higher.
Federal efforts to protect the health system are a patchwork, according to cybersecurity experts. While it's not yet clear how Change was hacked, experts have warned a breach can occur through a phishing link in an email or more exotic pathways. That means regulators need to consider hardening all kinds of products.
One example of the slow-at-best efforts to mend these defenses concerns medical devices. Devices with outdated software could provide a pathway for hackers to get into a hospital network or simply degrade its functioning.
The FDA recently gained more authority to assess medical devices' digital defenses and issue safety communications about them. But that doesn't mean vulnerable machines will be removed from hospitals. Products often linger because they're expensive to take out of service or replace.
Senator Mark Warner (D-Va.) has previously proposed a "Cash for Clunkers"-type program to pay hospitals to update the cybersecurity of their old medical devices, but it was "never seriously pursued," Warner spokesperson Rachel Cohen said. Riggi said such a program might make sense, depending on how it's implemented.
Weaknesses in the system are widespread and often don't occur to policymakers immediately. Even something as prosaic as a heating and air conditioning system can, if connected to a hospital's internet network, be hacked and allow the institution to be breached.
But erecting more defenses requires more people and resources — which often aren't available. In 2017, Woods and Corman assisted on an HHS report surveying the digital readiness of the health care sector. As part of their research, they found a slice of wealthier hospitals had the information technology staff and resources to defend their systems — but the vast majority had no dedicated security staff. Corman calls them "target-rich but cyber-poor."
"The desire is there. They understand the importance," Riggi said. "The issue is the resources."
HHS has proposed requiring minimum cyberdefenses for hospitals to participate in Medicare, a vital source of revenue for the entire industry. But Riggi says the AHA won't support it.
"We oppose unfunded mandates and oppose the use of such a harsh penalty," he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF .
- health care billing
- health care data
- United HealthCare
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
No More No. 2 Pencils: The SAT Goes Fully Digital
The new format cuts nearly an hour out of the exam and has shorter reading passages.

By Dana Goldstein
With adolescent anxiety surging and attention spans challenged, high school students will take a revamped version of the SAT on Saturday, which has been designed in part to reduce stress, according to the College Board, which administers the test.
The exam will be briefer — two hours and 14 minutes instead of three hours — and students will have more time for each question. The reading passages will be much shorter, and test-takers will now be able to use an online graphing calculator for the entire math section of the exam.
Listen to this article with reporter commentary
Open this article in the New York Times Audio app on iOS.
And after 98 years of students scratching answers on paper, the SAT will now be fully digital for the remote-learning generation.
The College Board said its piloting of the exam showed it was just as rigorous as the paper test, but less intimidating for students. And those with A.D.H.D. and dyslexia, as well as those learning English, reported that they were “better able to maintain their focus” on the digital test, compared with the earlier format, said Jaslee Carayol, director of communications for the College Board.
Delivering the test digitally will also reduce the possibility of cheating, the College Board said, because few students will receive the exact same exam. In both reading and math, test-takers who perform well early in the exam will receive harder questions as they go along . (The College Board says scores will be accurate, regardless of the difficulty of questions.)
There are critics, though. The switch to shorter reading passages has not been universally celebrated by English teachers, many of whom believe that in the face of constant distractions from technology, students need to develop greater reading stamina.
The latest overhaul of the exam comes at a fraught moment for the standardized testing industry, in which most colleges have dropped testing requirements.
According to data from Common App , the number of college applicants submitting SAT or ACT scores plummeted from 76 percent in the 2019-2020 admissions cycle to 45 percent this year.

Here’s What It’s Like to Take the New SAT
Students will take a new SAT on Saturday. It’s all digital, and the reading and writing sections do away with page-long reading excerpts with eight to 11 questions.
Even though Yale , Dartmouth and Brown recently made waves by reinstating standardized test requirements, saying the scores are the best predictor of academic success, it is unlikely that most colleges, which are far less selective, will follow suit, said Mary L. Churchill, associate dean at the Boston University Wheelock College of Education and Human Development.
The average acceptance rate among four-year institutions is 73 percent , and most colleges do not face the challenge of having to draw fine-grained distinctions between huge swaths of highly qualified students. Indeed, with some smaller colleges facing under-enrollment and at risk of shutting down, many admissions directors see test-optional policies as a way to encourage more applications, Dr. Churchill said.
Amid this changing landscape, the College Board has successfully promoted the SAT to state policymakers as an integral part of the high school experience, and 16 states now require or encourage students to take the test during the school day, regardless of their plans for life after high school.
In total, 1.9 million students took the SAT in the high school class of 2023, with two-thirds taking the exam during the school day, often for free. In the 2019 class, there were 2.2 million test-takers.
Students will take the exam on an app called Bluebook. In some ways, it tries to recreate the experience of working with paper. There are tools to make highlights and annotations, and to cross out multiple-choice responses students think are wrong.
Test-takers will no longer need to flip back and forth between long reading passages and pages of accompanying questions. Instead, they will tackle a string of much shorter passages — some just one paragraph — each associated with a single question.
Yoon S. Choi, chief executive of CollegeSpring, a nonprofit that provides in-school test prep to low-income students, said the new format was a boon to many, especially English language learners.
But others — including some educators who work with that same population of students — expressed skepticism about the College Board’s revision.
“It seems to me like they are maybe trying to cater to this generation that is doing a lot of reading on the internet, bouncing around from one place to the next,” said Ariel Sacks, a New York City public school English teacher and author of a book arguing for the importance of assigning full novels. “But I don’t think that’s setting a high or even effective expectation for what students should be doing as juniors in high school.”
Ms. Carayol of the College Board acknowledged that reading stamina was important, but said the paper SAT also had not been a good test of that skill.
“Long test passages force students to race through text hunting for answers instead of reading carefully,” she wrote in an email. “There’s a huge benefit for a student by having these shorter passages. If they get uncomfortable or disoriented by a passage, they can skip it and return, rather than having eight to 11 questions tied to each passage.”
At North Houston Early College High School, Adair Rivera, a 17-year-old junior, will take the SAT in the School Day program. He hopes to become the first member of his immediate family to attend college, to study computer science.
Adair said he is earning higher scores on digital practice tests than when he took the paper SAT. He hopes to attend M.I.T. or Yale, which require test scores, or the University of Pennsylvania, which does not.
“It’s a game changer,” he said of the shorter reading passages and shorter exam time. “It doesn’t wear out students as fast.”
Audio produced by Sarah Diamond .
Dana Goldstein covers education and families for The Times. More about Dana Goldstein
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.
Supreme Betrayal
A requiem for Section 3 of the Fourteenth Amendment

Listen to this article
Produced by ElevenLabs and News Over Audio (NOA) using AI narration.
The Supreme Court of the United States did a grave disservice to both the Constitution and the nation in Trump v. Anderson .
In a stunning disfigurement of the Fourteenth Amendment, the Court impressed upon it an ahistorical misinterpretation that defies both its plain text and its original meaning. Despite disagreement within the Court that led to a 5–4 split among the justices over momentous but tangential issues that it had no need to reach in order to resolve the controversy before it, the Court was disappointingly unanimous in permitting oath-breaking insurrectionists, including former President Donald Trump, to return to power. In doing so, all nine justices denied “We the People” the very power that those who wrote and ratified the Fourteenth Amendment presciently secured to us to save the republic from future insurrectionists—reflecting a lesson hard-learned from the devastation wrought by the Civil War.
Quinta Jurecic: The Supreme Court is not up to the challenge
For a century and a half before the Court’s decision, Section 3 of the Fourteenth Amendment was the Constitution’s safety net for America’s democracy, promising to automatically disqualify from public office all oath-breaking insurrectionists against the Constitution, deeming them too dangerous to entrust with power unless supermajorities of both houses of Congress formally remove their disability. This provision has been mistakenly described by some as “undemocratic” because it limits who may be elected to particular positions of power. But disqualification is not what is antidemocratic; rather, it is the insurrection that is antidemocratic, as the Constitution emphatically tells us.
In any event, all qualifications for office set by the Constitution limit who may be elected to particular positions of power. And no other of these disqualifications requires congressional legislation to become operative, as the Court now insists this one does. To be sure, the other qualifications—age, residence, natural-born citizenship—appear outside the Fourteenth Amendment, whose fifth section specifically makes congressional action to enforce its provisions available. But no such action is needed to enforce the rights secured to individuals by Section 1 of the same amendment, so deeming congressional action necessary to enforce Section 3 creates a constitutional anomaly in this case that the majority could not and did not explain. For that matter, no other provision of the other two Reconstruction amendments requires congressional enforcement either. As the concurring justices explained, the majority “simply [created] a special rule for the insurrection disability in Section 3.”
That the disqualification clause has not previously been invoked to keep traitors against the Constitution from having a second opportunity to fracture the framework of our republic reflects not its declining relevance but its success at deterring the most dangerous assaults on our government until now. Put simply, far from what some irresponsibly dismiss as an “obscure, almost discarded provision” of our legal and political system, this section of our Constitution has long been among its mightiest pillars, one that the Supreme Court itself has now all but destroyed.
What ought to have been, as a matter of the Constitution’s design and purpose, the climax of the struggle for the survival of America’s democracy and the rule of law instead turned out to be its nadir, delivered by a Court unwilling to perform its duty to interpret the Constitution as written. Desperate to assuage the growing sense that it is but a political instrument, the Court instead cemented that image into history. It did so at what could be the most perilous constitutional and political moment in our country’s history, when the nation and the Constitution needed the Court most—to adjudicate not the politics of law, but the law of the politics that is poisoning the lifeblood of America.
The issues before the Court were not difficult ones under the Constitution. As Chief Justice John Marshall once wrote of a considerably more challenging question, that of the Court’s own role in reviewing the constitutionality of government decisions, this was indeed “a question deeply interesting to the United States; but, happily, not of an intricacy proportional to its interest.” As the extraordinary array of amicus briefs filed in Trump v. Anderson made clear, the voluminous historical scholarship exploring the origins of the disqualification clause and its intended operation left no genuine doubt that the Colorado Supreme Court got it exactly right in its decision explaining why the former president was ineligible to “hold any office, civil or military, under the United States,” certainly including the presidency.
Perhaps some of the justices were untroubled by the consequences of disregarding both that scholarship and the plain language of the disqualification clause. Joining fully in the Court’s anonymous per curiam opinion that states cannot enforce the clause against federal (as opposed to state) officeholders and candidates would presumably have caused those justices no personal discomfort—apart, perhaps, from that of being seen as trying to square the ruling with their ostensible fidelity to textualism and their supposed belief in the binding force of original meaning.
Adam Serwer: The Supreme Court reveals once again the fraud of originalism
For Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan, and Ketanji Brown Jackson—who wrote a separate concurrence that in parts read more like a dissent—we can only surmise that any discomfort they felt was outweighed by the extra-constitutional allure of going along with the other justices on the decision’s bottom line and thus enabling the nation’s electorate to work its will, rather than the Constitution’s. Those three justices took the opportunity to distance themselves from at least part of what the Court’s majority did by criticizing its “attempts to insulate all alleged insurrectionists from future challenges to their holding federal office.” Sotomayor, Kagan, and Jackson convincingly dispatched as “inadequately supported as they are gratuitous” the majority’s unnecessary holdings that only Congress can enforce the disqualification clause and that Congress’s implementing legislation must satisfy the majority’s made-up insistence upon “congruence and proportionality.” Those three justices left in tatters much that all the other justices, with the exception of Amy Coney Barrett, wrote about the operation of the disqualification clause against federal officeholders, making plain that the majority’s “musings” simply cannot be reconciled with the Fourteenth Amendment’s language, structure, and history.
For her part, Justice Barrett lectured the country about the “message Americans should take home” from the decision, criticizing the majority for needlessly addressing “the complicated question whether federal legislation is the exclusive vehicle through which Section 3 can be enforced,” while simultaneously criticizing her three separately concurring colleagues for supposedly amplifying “disagreement with stridency,” despite the absence of a single strident word in their clarion warning.
What, then, accounted for the unanimous outcome in this case? All nine justices were persuaded by the appeal of a fatuous argument featured prominently in the briefs supporting the former president—the argument that no single state should be able to disqualify a candidate for the presidency.
But that argument, despite its prominence in many public discussions of this decision, was always utterly empty of constitutional substance. Anyone who knows anything about the United States Constitution and the way the judicial system operates—and that surely includes all nine Supreme Court justices—has to know that a single state could never have rendered a disqualification ruling that would bind the other 49 states, an admittedly untenable result. Here’s how Jason Murray, a counsel for the challengers, put the constitutional answer to that argument when he was pressed on this very question by Justice Kagan:
Ultimately, it’s this Court that’s going to decide that question of federal constitutional eligibility and settle the issue for the nation. And, certainly, it’s not unusual that questions of national importance come up through different states.
Although no justice mentioned this response, nobody should doubt that a state court’s determination of a federal constitutional question—such as Colorado’s that the former president had “engaged in an insurrection or rebellion” against the U.S. Constitution—is subject to review by the Supreme Court. If the Court upholds the state’s disqualification decision, then it will be binding nationwide, in the manner and to the extent decided by the Court. If the state’s disqualification is held to be invalid, then it will be invalid in that state, as well as nationwide. It’s as simple as that.
Nothing about letting an individual state initiate the disqualification process ever threatened to create what the unanimous Court called a “patchwork” of divergent state resolutions of the controlling federal questions of what constitutes a disqualifying “insurrection” and whether the former president had “engaged” in one. From the outset, the hand-wringing about how no state should be empowered to rule over its sister states on the national question as to who might run for president was all smoke and mirrors, manifestly predicated on a demonstrably false premise about the way our judicial system works.
So it’s little surprise that, built on that false premise, the opinion that emerged from the Court’s constitutional confusion was a muddled, nameless per curiam decree palpably contrary to the text, history, and purpose of the Fourteenth Amendment.
For no apparent reason other than to create the impression that it was leaving open the possibility that the former president might yet be disqualified pursuant to congressional legislation, the per curiam opinion went out of its way to mention that Congress, in legislation whose enactment predated Section 3, had indeed “effectively provided an additional procedure for enforcing disqualification” by making “engaging in insurrection or rebellion … a federal crime punishable by disqualification from holding office under the United States”; the opinion also noted that a “successor” to that legislation “remains on the books today.”
Many will no doubt catch the transparent implication that, if the former president or other future insurrectionists permanently escape disqualification, that result will be attributable to whoever controls the Justice Department at any given time, not to any action by the Court. But that intended implication overlooks the point that, were that statute all that mattered, a simple majority of Congress could remove the disqualification penalty from that criminal statute, leaving Section 3 unenforceable again. It also conveniently ignores the fact—not denied even by this majority—that Section 3 was specifically intended and written to make criminal conviction unnecessary for disqualifying an insurrectionist from seeking or holding office in the future.
There is, of course, no possibility whatsoever that the statute, 18 U.S. Code § 2383, will play any role in the former president’s eligibility in this election cycle. And the difficulty of enacting legislation of the sort the majority declared essential makes it exceedingly unlikely that anyone who engages in an insurrection against the U.S. Constitution after taking an oath as an officer to support it will ever be disqualified under the Fourteenth Amendment. Thus, as concurring Justices Sotomayor, Kagan, and Jackson damningly noted, the majority’s gratuitous resolution of “novel constitutional questions” about how Section 3 could be enforced in the future was plainly intended “to insulate this Court and [Trump] from future controversy” while insulating “all alleged insurrectionists from future challenges to their holding federal office.”
George T. Conway III: The Court’s Colorado decision wasn’t about the law
The five-justice majority came to its constitutionally unsupported view that states can disqualify insurrectionists from state, but not federal, office by pronouncing incongruous a conclusion that would find—nestled within a constitutional amendment that generally expanded “‘federal power at the expense of state autonomy’”—anything that would “give States new powers to determine who may hold the Presidency” or indeed any other federal office.
But, as many amicus briefs conclusively demonstrated, the Court’s description of how the Fourteenth Amendment altered the intricate relationship of state and federal powers was an absurdly oversimplified and ahistorical caricature. Among the Court’s most basic errors was that it described this state action to enforce Section 3 as a “new power” requiring an affirmative “delegation”—an explicit assignment of authority—elsewhere in the Constitution. If the Court had to identify such a delegation, which it did not, it need have looked no further than the elections and electors clauses of Articles I and II, respectively, which indisputably assign the determination of presidential qualification and disqualification to the states, at least in the first instance. Instead, the Court dismissed that constitutional assignment out of hand by asserting, with no explanation, that “there is little reason to think that these Clauses implicitly authorize the States to enforce Section 3 against federal officeholders and candidates.” Of course, no explanation could have sufficed, which is why none was offered. Under the Constitution, there is every reason to believe that these clauses in fact do authorize the states to enforce Section 3 against federal officeholders and candidates.
In the end, without even trying to address the compelling analysis of the three-justice concurrence, the majority violated the precept rightly insisted on by Chief Justice John Roberts in objecting to how far the Court had gone in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization two years earlier, which stated that, when “it is not necessary to decide more to dispose of a case, then it is necessary not to decide more.” The three justices—objecting that the Court had departed from that “vital principle” by “deciding not just this case, but challenges that might arise in the future”—quoted Justice Stephen Breyer’s dissent in Bush v. Gore : “What it does today, the Court should have left undone.” “In a sensitive case crying out for judicial restraint,” the concurring justices wrote , the majority simply “abandoned” all restraint.
But whatever praise the three justices deserve for distancing themselves from the majority’s extraordinary overreach, they cannot be excused for joining the majority in holding—wrongly, in light of the Supreme Court’s obvious power and responsibility to ensure uniformity—that the Court’s decision to disempower Colorado from playing its part in the ultimate determination was somehow necessary to prevent the emergence of “a chaotic state-by-state patchwork, at odds with our Nation’s federalism principles.” By insisting that states have no role to play in initiating the disqualification of insurrectionists from federal office even with the Supreme Court sitting to review what each state does so as to ensure nationwide consistency, all nine justices stood federalism on its head.
Whether born of a steeled determination not to disqualify the presumptive Republican nominee from the presidency, or of a debilitating fear of even deciding whether the Constitution disqualifies the presumptive Republican nominee precisely because he is the presumptive Republican nominee, this step that all nine justices took represents a constitutionally unforgivable departure from the fundamental truth of our republic that “no man is above the law.”
Nor can their action be explained, much less justified, by the converse truth that neither is any man beneath the law. If the process Colorado had followed to determine Trump’s disqualification could have been deemed constitutionally inadequate as a foundation for the Supreme Court to have affirmed the ruling of the state’s highest court and applied it to him nationwide, this would be a different case altogether. But nothing any of the justices said even hinted at such inadequacy. On the contrary, the week-long trial by the Colorado state court, which had indisputable jurisdiction to consider the matter, undoubtedly more than satisfied the constitutional requirements for disqualifying the former president under Section 3. At that trial, he was afforded every opportunity to defend himself against the charge that he had personally “engaged” in an “insurrection or rebellion” against the Constitution. Not a single justice suggested that the process was less than what the former president was due. That trial ended in a finding by “clear and convincing evidence” that he had not only engaged in that insurrection but had orchestrated the entire months-long effort to obstruct the joint session’s official proceeding, preventing the peaceful transfer of power for the first time in American history. Not a single justice suggested that a more stringent standard of proof was required or that the courts below applied an insufficiently rigorous definition of insurrection . No justice suggested that the First Amendment or anything else in the Constitution shielded the former president from the reach of Section 3.
Mark A. Graber: Of course presidents are officers of the United States
Nor did any justice offer any other reason to doubt the correctness of the conclusion by both courts below that the former president’s conduct was indeed the paradigm of an insurrection or a rebellion against the Constitution, disqualifying him from the presidency ever again. Nor, finally, is it easy to imagine a more thoroughgoing misinterpretation of the Fourteenth Amendment and scrambling of the division of responsibilities that the amendment carefully assigns. In supposedly following the blueprint of the amendment, which specifically provides a method for oath-breaking insurrectionists to be exempted from Section 3’s disqualification by joint action on the part of two-thirds of both houses of Congress, the Court’s majority decreed that mere inaction by Congress would suffice to lift that disqualification. Thus, by effectively flipping on its head the congressional power to remove disqualification, the Court seized for itself the role that the Fourteenth Amendment expressly and deliberately left to Congress—that of deciding whether a particular oath-breaking insurrectionist poses too little danger to the republic to be permanently barred from holding or seeking public office.
Far from preventing what it sought to depict as state usurpation of a federal responsibility, the Supreme Court itself usurped a congressional responsibility, and it did so in the name of protecting a congressional prerogative, that of enacting enforcement legislation under Section 5 of the Fourteenth Amendment.
Our highest court dramatically and dangerously betrayed its obligation to enforce what once was the Constitution’s safety net for America’s democracy. The Supreme Court has now rendered that safety net a dead letter, effectively rescinding it as if it had never been enacted.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Books

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
When you are gathering book sources, be sure to make note of the following bibliographic items: the author name(s), other contributors such as translators or editors, the book’s title, editions of the book, the publication date, the publisher, and the pagination.
The 8 th edition of the MLA handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
Please note these changes in the new edition:
- Commas are used instead of periods between Publisher, Publication Date, and Pagination.
- Medium is no longer necessary.
- Containers are now a part of the MLA process. Commas should be used after container titles.
- DOIs should be used instead of URLS when available.
- Use the term “Accessed” instead of listing the date or the abbreviation, “n.d."
Below is the general format for any citation:
Author. Title. Title of container (do not list container for standalone books, e.g. novels), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs URL or DOI). 2 nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Basic Book Format
The author’s name or a book with a single author's name appears in last name, first name format. The basic form for a book citation is:
Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . City of Publication, Publisher, Publication Date.
* Note: the City of Publication should only be used if the book was published before 1900, if the publisher has offices in more than one country, or if the publisher is unknown in North America.
Book with One Author
Gleick, James. Chaos: Making a New Science . Penguin, 1987.
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
Book with More Than One Author
When a book has two authors, order the authors in the same way they are presented in the book. Start by listing the first name that appears on the book in last name, first name format; subsequent author names appear in normal order (first name last name format).
Gillespie, Paula, and Neal Lerner. The Allyn and Bacon Guide to Peer Tutoring . Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
If there are three or more authors, list only the first author followed by the phrase et al. (Latin for "and others") in place of the subsequent authors' names. (Note that there is a period after “al” in “et al.” Also note that there is never a period after the “et” in “et al.”).
Wysocki, Anne Frances, et al. Writing New Media: Theory and Applications for Expanding the Teaching of Composition . Utah State UP, 2004.
Two or More Books by the Same Author
List works alphabetically by title. (Remember to ignore articles like A, An, and The.) Provide the author’s name in last name, first name format for the first entry only. For each subsequent entry by the same author, use three hyphens and a period.
Palmer, William J. Dickens and New Historicism . St. Martin's, 1997.
---. The Films of the Eighties: A Social History . Southern Illinois UP, 1993.
Book by a Corporate Author or Organization
A corporate author may include a commission, a committee, a government agency, or a group that does not identify individual members on the title page.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry.
American Allergy Association. Allergies in Children . Random House, 1998.
When the author and publisher are the same, skip the author, and list the title first. Then, list the corporate author only as the publisher.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.
Book with No Author
List by title of the book. Incorporate these entries alphabetically just as you would with works that include an author name. For example, the following entry might appear between entries of works written by Dean, Shaun and Forsythe, Jonathan.
Encyclopedia of Indiana . Somerset, 1993.
Remember that for an in-text (parenthetical) citation of a book with no author, you should provide the name of the work in the signal phrase and the page number in parentheses. You may also use a shortened version of the title of the book accompanied by the page number. For more information see the In-text Citations for Print Sources with No Known Author section of In-text Citations: The Basics .
A Translated Book
If you want to emphasize the work rather than the translator, cite as you would any other book. Add “translated by” and follow with the name(s) of the translator(s).
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . Translated by Richard Howard, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
If you want to focus on the translation, list the translator as the author. In place of the author’s name, the translator’s name appears. His or her name is followed by the label, “translator.” If the author of the book does not appear in the title of the book, include the name, with a “By” after the title of the book and before the publisher. Note that this type of citation is less common and should only be used for papers or writing in which translation plays a central role.
Howard, Richard, translator. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason . By Michel Foucault, Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Republished Book
Books may be republished due to popularity without becoming a new edition. New editions are typically revisions of the original work. For books that originally appeared at an earlier date and that have been republished at a later one, insert the original publication date before the publication information.
For books that are new editions (i.e. different from the first or other editions of the book), see An Edition of a Book below.
Butler, Judith. Gender Trouble . 1990. Routledge, 1999.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine . 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
An Edition of a Book
There are two types of editions in book publishing: a book that has been published more than once in different editions and a book that is prepared by someone other than the author (typically an editor).
A Subsequent Edition
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the number of the edition after the title.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students . 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
A Work Prepared by an Editor
Cite the book as you normally would, but add the editor after the title with the label "edited by."
Bronte, Charlotte. Jane Eyre, edited by Margaret Smith, Oxford UP, 1998.
Note that the format for citing sources with important contributors with editor-like roles follows the same basic template:
...adapted by John Doe...
Finally, in the event that the source features a contributor that cannot be described with a past-tense verb and the word "by" (e.g., "edited by"), you may instead use a noun followed by a comma, like so:
...guest editor, Jane Smith...
Anthology or Collection (e.g. Collection of Essays)
To cite the entire anthology or collection, list by editor(s) followed by a comma and "editor" or, for multiple editors, "editors." This sort of entry is somewhat rare. If you are citing a particular piece within an anthology or collection (more common), see A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection below.
Hill, Charles A., and Marguerite Helmers, editors. Defining Visual Rhetorics . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2004.
Peterson, Nancy J., editor. Toni Morrison: Critical and Theoretical Approaches . Johns Hopkins UP, 1997.
A Work in an Anthology, Reference, or Collection
Works may include an essay in an edited collection or anthology, or a chapter of a book. The basic form is for this sort of citation is as follows:
Last name, First name. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , edited by Editor's Name(s), Publisher, Year, Page range of entry.
Some examples:
Harris, Muriel. "Talk to Me: Engaging Reluctant Writers." A Tutor's Guide: Helping Writers One to One , edited by Ben Rafoth, Heinemann, 2000, pp. 24-34.
Swanson, Gunnar. "Graphic Design Education as a Liberal Art: Design and Knowledge in the University and The 'Real World.'" The Education of a Graphic Designer , edited by Steven Heller, Allworth Press, 1998, pp. 13-24.
Note on Cross-referencing Several Items from One Anthology: If you cite more than one essay from the same edited collection, MLA indicates you may cross-reference within your works cited list in order to avoid writing out the publishing information for each separate essay. You should consider this option if you have several references from a single text. To do so, include a separate entry for the entire collection listed by the editor's name as below:
Rose, Shirley K, and Irwin Weiser, editors. The Writing Program Administrator as Researcher . Heinemann, 1999.
Then, for each individual essay from the collection, list the author's name in last name, first name format, the title of the essay, the editor's last name, and the page range:
L'Eplattenier, Barbara. "Finding Ourselves in the Past: An Argument for Historical Work on WPAs." Rose and Weiser, pp. 131-40.
Peeples, Tim. "'Seeing' the WPA With/Through Postmodern Mapping." Rose and Weiser, pp. 153-67.
Please note: When cross-referencing items in the works cited list, alphabetical order should be maintained for the entire list.
Poem or Short Story Examples :
Burns, Robert. "Red, Red Rose." 100 Best-Loved Poems, edited by Philip Smith, Dover, 1995, p. 26.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories , edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
If the specific literary work is part of the author's own collection (all of the works have the same author), then there will be no editor to reference:
Whitman, Walt. "I Sing the Body Electric." Selected Poems, Dover, 1991, pp. 12-19.
Carter, Angela. "The Tiger's Bride." Burning Your Boats: The Collected Stories, Penguin, 1995, pp. 154-69.
Article in a Reference Book (e.g. Encyclopedias, Dictionaries)
For entries in encyclopedias, dictionaries, and other reference works, cite the entry name as you would any other work in a collection but do not include the publisher information. Also, if the reference book is organized alphabetically, as most are, do not list the volume or the page number of the article or item.
"Ideology." The American Heritage Dictionary. 3rd ed. 1997.
A Multivolume Work
When citing only one volume of a multivolume work, include the volume number after the work's title, or after the work's editor or translator.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
When citing more than one volume of a multivolume work, cite the total number of volumes in the work. Also, be sure in your in-text citation to provide both the volume number and page number(s) ( see "Citing Multivolume Works" on our in-text citations resource .)
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria . Translated by H. E. Butler, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980. 4 vols.
If the volume you are using has its own title, cite the book without referring to the other volumes as if it were an independent publication.
Churchill, Winston S. The Age of Revolution . Dodd, 1957.
An Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
When citing an introduction, a preface, a foreword, or an afterword, write the name of the author(s) of the piece you are citing. Then give the name of the part being cited, which should not be italicized or enclosed in quotation marks; in italics, provide the name of the work and the name of the author of the introduction/preface/foreword/afterword. Finish the citation with the details of publication and page range.
Farrell, Thomas B. Introduction. Norms of Rhetorical Culture , by Farrell, Yale UP, 1993, pp. 1-13.
If the writer of the piece is different from the author of the complete work , then write the full name of the principal work's author after the word "By." For example, if you were to cite Hugh Dalziel Duncan’s introduction of Kenneth Burke’s book Permanence and Change, you would write the entry as follows:
Duncan, Hugh Dalziel. Introduction. Permanence and Change: An Anatomy of Purpose, by Kenneth Burke, 1935, 3rd ed., U of California P, 1984, pp. xiii-xliv.
Book Published Before 1900
Original copies of books published before 1900 are usually defined by their place of publication rather than the publisher. Unless you are using a newer edition, cite the city of publication where you would normally cite the publisher.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Italicize “The Bible” and follow it with the version you are using. Remember that your in-text (parenthetical citation) should include the name of the specific edition of the Bible, followed by an abbreviation of the book, the chapter and verse(s). (See Citing the Bible at In-Text Citations: The Basics .)
The Bible. Authorized King James Version , Oxford UP, 1998.
The Bible. The New Oxford Annotated Version , 3rd ed., Oxford UP, 2001.
The New Jerusalem Bible. Edited by Susan Jones, Doubleday, 1985.
A Government Publication
Cite the author of the publication if the author is identified. Otherwise, start with the name of the national government, followed by the agency (including any subdivisions or agencies) that serves as the organizational author. For congressional documents, be sure to include the number of the Congress and the session when the hearing was held or resolution passed as well as the report number. US government documents are typically published by the Government Printing Office.
United States, Congress, Senate, Committee on Energy and Natural Resources. Hearing on the Geopolitics of Oil . Government Printing Office, 2007. 110th Congress, 1st session, Senate Report 111-8.
United States, Government Accountability Office. Climate Change: EPA and DOE Should Do More to Encourage Progress Under Two Voluntary Programs . Government Printing Office, 2006.
Cite the title and publication information for the pamphlet just as you would a book without an author. Pamphlets and promotional materials commonly feature corporate authors (commissions, committees, or other groups that does not provide individual group member names). If the pamphlet you are citing has no author, cite as directed below. If your pamphlet has an author or a corporate author, put the name of the author (last name, first name format) or corporate author in the place where the author name typically appears at the beginning of the entry. (See also Books by a Corporate Author or Organization above.)
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Your Rights Under California Welfare Programs . California Department of Social Services, 2007.
Dissertations and Master's Theses
Dissertations and master's theses may be used as sources whether published or not. Unlike previous editions, MLA 8 specifies no difference in style for published/unpublished works.
The main elements of a dissertation citation are the same as those for a book: author name(s), title (italicized) , and publication date. Conclude with an indication of the document type (e.g., "PhD dissertation"). The degree-granting institution may be included before the document type (though this is not required). If the dissertation was accessed through an online repository, include it as the second container after all the other elements.
Bishop, Karen Lynn. Documenting Institutional Identity: Strategic Writing in the IUPUI Comprehensive Campaign . 2002. Purdue University, PhD dissertation.
Bile, Jeffrey. Ecology, Feminism, and a Revised Critical Rhetoric: Toward a Dialectical Partnership . 2005. Ohio University, PhD dissertation.
Mitchell, Mark. The Impact of Product Quality Reducing Events on the Value of Brand-Name Capital: Evidence from Airline Crashes and the 1982 Tylenol Poisonings. 1987. PhD dissertation. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
List the names of corporate authors in the place where an author’s name typically appears at the beginning of the entry if the author and publisher are not the same.
Fair Housing—Fair Lending. Aspen Law & Business, 1985.

VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document's readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay. Essays. MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
This quick guide will help you set up your MLA format paper in no time. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Times New Roman 12. 1″ page margins. Double line spacing. ½" indent for new paragraphs. Title case capitalization for headings. For accurate citations, you can use our free MLA Citation Generator.
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
The Opening Section. While MLA-formatted papers typically don't require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page. Here's how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition. On the first line, write your full name (flush left) On a new line, write your professor or instructor's ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
If you are writing a longer research paper, you may want to include headings and subheadings to help organize the sections of your paper. Advice from the MLA Style Center: "Levels. The paper or chapter title is the first level of heading, and it must be the most prominent. Headings should be styled in descending order of prominence.
MLA Essay Template. For even experienced students, formatting a paper can be a daunting task. For that reason, the Excelsior Online Writing Lab created this template to give writers a foundation for formatting using the Modern Language Association guidelines. The template also references OWL sections that might be helpful when writing an essay.
Section headings: Section headings are used to divide major sections of a paper. MLA does not require specific formatting for section headings. The general rule is to maintain consistency in the use of bold, italics, and alignment when creating levels. Topics of equal importance share the same level heading throughout the document. Citations:
Guidelines on setting up research papers in MLA format with updated advice on headings, lists, and title pages for group projects; Revised, comprehensive, step-by-step instructions for creating a list of works cited in MLA format that are easier to learn and use than ever before ... Numbered sections throughout for quick navigation; Advanced ...
Citation format will be discussed in a later section, but this section will detail how to create a Works Cited Page. At the end of your essay, insert a page break (found under the "Insert" tab) and center the words "Works Cited" at the top of your page (not in the header). If there is only one source being cited, type "Work Cited".
This guide follows the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook, published by the Modern Language Association in 2021. To cite sources in MLA style, you need. In-text citations that give the author's last name and a page number. A list of Works Cited that gives full details of every source. Make sure your paper also adheres to MLA ...
Writers sometimes use Section Headings to improve a document's readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay. Essays. MLA recommends that when you divide an essay into sections that you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name. Early ...
Using the automatic header feature of your word processor, set a running head .5" from the top of the page with your last name and the automatic page number feature. Each page of your MLA formatted paper, including page one, should have a header in the upper right margin. The header should include your first name followed by the page number:
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
MLA Guide Overview. There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper. This guide includes the following sections: Format background; The header; General paper formatting; MLA heading format & title page instructions; Running head & page ...
High-level headings (e.g., heading level 1) are used to divide the paper into main sections, while low-level headings (e.g., heading level 3) are used to divide the main sections into smaller subsections. ... Main Section 2 [MLA heading level 1] Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore ...
Revised on March 5, 2024. The first page of your MLA format paper starts with a four-line left-aligned header containing: Your full name. Your instructor's name. The course name and number. The date of submission. After the header, the title of the paper is centred on a new line, in title case. The header and title do not take any special ...
MLA Style Center, the only authorized Web site on MLA style, provides free resources on research, writing, and documentation. ... Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style; Teaching. Submit a Resource; Teaching Resources; Ask The MLA; menu search. Search for posts, topics, or tags. Search.
And paper claims can take 3-6 months to result in payment anyway, she estimated. "We will be in trouble in very short order, and are very stressed," she said in an interview with KFF Health News.
Summary: MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Opinion Columnist. As of Monday, March 4, 2024, Section 3 of the 14th Amendment of the Constitution is essentially a dead letter, at least as it applies to candidates for federal office. Under the ...
And after 98 years of students scratching answers on paper, the SAT will now be fully digital for the remote-learning generation. The College Board said its piloting of the exam showed it was just ...
Guernica. The literary magazine Guernica's decision to retract an essay about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict reveals much about how the war is hardening human sentiment. In the days after ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Under section 524B(a) of the FD&C Act (21 U.S.C. 360n-2(a)), a person who submits a 510(k), premarket approval application (PMA), product development protocol (PDP), De Novo, or humanitarian device exemption (HDE) for a device that meets the definition of a cyber device, as defined under section 524B(c) of the FD&C Act, is required to submit ...
A requiem for Section 3 of the Fourteenth Amendment. Although no justice mentioned this response, nobody should doubt that a state court's determination of a federal constitutional question ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.