Extended essay
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper.
One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students.
Read about the extended essay in greater detail.
You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for the extended essay , find examples of extended essay titles from previous DP students and learn about the world studies extended essay .
Learn more about the extended essay in a DP workshop for teachers .

DP subject briefs
Find out about what each subject offers within the Diploma Programme (DP).
Our DP subject briefs—for both standard and higher level—contain information about core requirements, aims and assessment.
- Explore the DP subject briefs

We use cookies on this site. By continuing to use this website, you consent to our use of these cookies. Read more about cookies

IB Study Resources
September 14, 2021
A Definitive Guide to the IB Extended Essay (EE)
The Extended Essay (EE) is an independent, self-directed academic research, presented in the form of a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. The final work is given a grade from E to A, and makes up part of each student’s final IB score. These are our thoughts on how to do well in the EE:
Step 1: Choosing a Extended Essay (EE) topic
Choosing a good topic for your extended essay can make a huge difference on your final score. Firstly, you should always choose a topic that you are interested in! The writing process becomes much more engaging, and will also be good content you can write in your personal statement for your university applications.
Always be creative and original when choosing your research topic. Think about how you can make your research question and the way you communicate your academic research unique. In addition, if you wish to explore a multidisciplinary field , you could consider writing a World Studies extended essay . This research is analysed through at least two disciplines, encouraging students to apply their knowledge to a problem with global significance. For example, you may want to consider the effects of an electric vehicle subsidy on climate change. This is an exciting opportunity and provides a good insight to an interdisciplinary university degree such as PPE.
Step 2: Framing your research question
Once you know your extended essay subject, your next step is to choose a question. Often, questions will be framed as “To what extent does…”. Exploring multiple perspectives, and critically analysing each of these, are key to success. Therefore, try and shape your question so that more than one point of view can be explored.
Similarly, make sure your question is specific ! Having a focused question will guide your research and show that you can explore one area in detail. For example, here are 2 examples of Economics extended essay questions:
- To what extent do smartphone companies compete with each other?
- To what extent do Apple and Samsung operate in a duopoly in the global smartphone market?
The second research question is more focused, allowing for greater in-depth research into which areas they are competing over. You can use secondary data from both companies’ annual reports, competitor websites, and undertake primary research (such as through an Economic survey or personal interview) – Having a research question that allows you to explore a specific area critically will definitely help you to score highly.

Step 3: Meeting your supervisor to establish specific targets
We recommend meeting with your supervisor as early as possible to check whether your research question is appropriate. If it is, this is a great opportunity to explore potential avenues of research. For example, a Physics extended essay on the path of a bowling bowl may look to incorporate several different features, such as force, weight, and air resistance into a model. Whichever subject area you choose, your supervisor is usually your first port of call for any questions you have.
During the meeting, it will be good to establish a timeline for your extended essay. Although this may only be rough, this will give you deadlines to work towards (much like you will need to do for university essays). Similarly, setting specific targets for your next meeting, such as writing an introduction or doing your survey, will also give you definitive targets to meet. Make sure at the end of this meeting you have clear goals to achieve and by your next meeting.
Furthermore, make sure that you are keeping a record of all of your meetings with your extended essay supervisor. 6 of the 36 marks for the EE are from your Reflections on Planning and Progress Form (RPPF) where you reflect on the meetings you have had with your supervisor. These should show that you are engaged with your topic, so discuss the ideas you have considered in response to setbacks whilst writing your extended essay and make sure to use personal pronouns (I, my) to convey your engagement. Detail any changes you made to your research method and demonstrate how you have taken a creative approach to your topic, as these will highlight what you have done to stand out.
Step 4: Starting your EE research
Following the meeting with your supervisor, it is time to begin researching your topic! This does not have to be too detailed to begin with, and we recommend aiming to research enough to write an introduction to your essay. This introduction should outline the main themes you will explore and your line of argument. To reiterate, your main argument may change as your essay develops, so do not worry if it is not perfect when you begin.
Some useful sources of information are your school library or Jstor. Your school librarian may be able to suggest some good books or articles to start reading, whilst using academic sources like Jstor or Google scholar gives you access to a wide range of academic material. When reading books or journal articles, you do not have to read them cover to cover! In fact, you should only read the sections that are relevant to your topic, and reading the introduction and conclusion will often tell you whether a journal article is relevant.
When reading, consistently keep in mind your essay title as this will help you to focus your reading on key sections of texts. For instance, highlight the key sections of the texts to review later. Alternatively, you could make notes in a separate word document; such as Googledocs; or with pen and paper. It is useful to keep everything you do in the same format, however, so you can easily collate it.
Step 5: Writing the essay’s first draft
The most difficult part with the EE is getting the first draft down. Many students struggle o to write the perfect introduction and methodology, and get stuck for weeks in the process. Your introduction and first draft do not have to be perfect but should form the base of your essay moving forward. It is often good to form a plan from your research that contains the key elements of each paragraph. Once you are confident with this and have filled it in with more research, you can turn this into a fully operational first draft.
We recommend breaking down the writing stage into several paragraphs, setting yourself mini-goals to achieve. This will help you to move along faster and make the seemingly daunting task of a 4,000-word essay a lot simpler. Similarly, you should use the research you have to support your ideas. Your research might consist of facts to back up your analysis or other writers’ opinions that agree with your own. Furthermore, you can also use this research to explore multiple points of view, coming to a conclusion as to which one is most appropriate. However, save yourself time whilst doing this by including links to the original article, rather than full references, as it is likely you may change the content of your essay and the references you use as you progress.
Make sure you save your extended essay frequently and to an accessible platform such Dropbox or Google Drive so that if your computer were to crash your progress will be stored!
Step 6: Reviewing your first draft
Your aim when meeting with your supervisor this time is to look over your first draft to see which parts are excellent, which can be explored further and which need to be rethought. This can be split into a number of meetings; for example, I looked at my introduction, then at the 4 sections of my main body, and finally at my conclusion. This reshaped the goals that I had moving forward and gave me specific subsections to work on.
Whilst editing your first draft, do not be afraid to delete, reword or move some parts that you have written, as this will help you shape your extended essay into the finished article. You can, if needed, even slightly alter your question. I changed my question at the start of April, with a June deadline for my essay. However, changing my essay question did not leave me with a whole new essay to write, as I was able to use most of what I had already written, adapting it to focus on the new question. Whatever changes you have to make, they are all moving you towards a complete final version, so stay positive!
Step 7: Refining your Extended Essay
After your meeting, review the changes you have to make to your methodology and research process. You should consider whether you have critically investigated the variables in your RQ and whether it is backed up by a solid methodology. For instance, are there any counter arguments you have not considered? Does your research process flow? Always draw links to each paragraph, so that your essay has a logical flow from its introduction to its argument, counter arguments, responses, and conclusion.
When researching areas in more detail, make use of what you have learnt from your current research. For instance, look at the suggested reading or references in books that you have read or look at articles from the same journal. Furthermore, stay up to date with the news in case you can include new research in your extended essay.
When editing, it is useful to save a new copy of your extended essay (for example, EE draft 2) so that you can track any changes that you make. Also, if anything were to happen to your new copy, you always have the previous copy and notes from the meeting to re-do any changes. We recommend doing this on Googledocs whether changes are saved real-time on the servers so you don’t lose precious work if your computer crashes.
Step 8: Final Notes
Once you are done with your initial drafts, ensure that you have professional presentation, consistent formatting, and proper citations. Make sure that you have included page numbers and a bibliography (if required). Additionally, make the layout justified, font and size, as well as double spaced as per IB requirements. You have to include a cover page with a title, your research question, word count and subject. You also have to meet your supervisor the final time to fill out your viva voce (oral) section of the RPPF before the final submission.
Step 9: Final Submission
When submitting your extended essay, ensure that your name, candidate number and your school’s name are not on the document. This will ensure that your EE is marked fairly without prejudice. Your EE is electronically stamped and the IB can track who it belongs to, as is your RPPF.
We wish you the best of luck with your extended essay and hope you enjoy the process. If you would like help with your extended essay, please take a look at our courses or contact us for more information. We also offer IB tuition for various subjects and University applications mentoring and are more than happy to tailor our classes to your needs and requirements!
Related Posts

The English IA: Tips for a successful presentation

How to prepare for the Singapore Medical School applications

Ace Your Biology IA (HL): A How-to Guide

How to Ace your Business Management Internal Assessment (HL)
Contact Info
545 Orchard Road #14-06/09 Singapore 238882
(+65) 61009338
QE_Singapore
Mondays to Fridays: 10am to 7pm
Quick Links
Join Our Mailing List
© 2024 Quintessential Education™

- Westbourne Voices
- Awards and Affiliations
- Virtual Tour
- Admissions Overview
- School Admissions Process
- Nursery Admissions Process
- International Student Admissions
- Visits & Open Days
- Welcome to Nursery
- Nursery Life
- Nursery Curriculum
- Nursery Sessions
- Nursery Fees and Applications
- Stepping up to Prep School
- Welcome to Prep School
- Prep Academic Curriculum
- Prep Co-Curricular
- Prep School Case Studies
- Stepping up to Senior School
- Welcome to Senior School
- GCSE Subjects
- Senior Co-curricular
- Stepping Up to Sixth Form
- Welcome to Sixth Form
- IB Subjects
- IB Inner Core
- Oxbridge and Russell Group
- Careers Guidance
- Super Curriculum
- Sixth Form Case Studies
- Westbourne Life
- Welcome to Boarding
- Boarding Options
- Boarding Life
- Boarding FAQs
- Boarding Case Studies
- Future Leaders Lab
- School Uniform
- School Transport
- Visiting Information

How To Write The Extended Essay (With Topics and Examples)
This comprehensive guide navigates through every aspect of the EE, from selecting a topic and developing a research question to conducting in-depth research and writing a compelling essay. It offers practical strategies, insights, and tips to help students craft a piece of work that not only meets the rigorous standards of the IB but also reflects their academic passion and curiosity. Join us as we explore the keys to success in the Extended Essay, preparing you for an intellectually rewarding experience.
Posted: 13th February 2024
Section jump links:
Section 1: Understanding the IB Extended Essay
Section 2: the importance of the extended essay, section 3: selecting a topic, section 4: developing your research question, section 5: research methodology and theoretical frameworks, section 6: evaluating sources and data, section 7: integrating evidence and analysis, section 8: writing and structuring the extended essay, section 9: reflection and the rppf, section 10: the significance of academic discipline in the ee, section 11: good practice in extended essay writing, section 12: managing the extended essay process, section 13: collaboration and feedback, section 14: avoiding plagiarism, section 15: emphasising original thought, section 16: final presentation and viva voce, section 17: beyond the extended essay, what is the ib extended essay.
The International Baccalaureate (IB) Extended Essay (EE) is a cornerstone of the IB Diploma Programme . It’s an independent, self-directed piece of research, culminating in a 4,000-word paper. This project offers students an opportunity to investigate a topic of their own choice, bridging the gap between classwork and the kind of research required at the university level.
Key Objectives and the Role of the EE in the IB Curriculum
The Extended Essay has several key objectives:
- To provide students with the chance to engage in an in-depth study of a question of interest within a chosen subject.
- To develop research, thinking, self-management, and communication skills.
- To introduce students to the excitement and challenges of academic research.
The EE plays a critical role in the IB curriculum by:
- Encouraging intellectual discovery and creativity.
- Facilitating academic growth and personal development through research and writing.
- Preparing students for the rigours of higher education.
Extended Essay Word Count and Requirements
The EE has a maximum word count of 4,000 words. This does not include the abstract, contents page, bibliography, or footnotes (which must be used sparingly). Here are some essential requirements:
- Research Question: Your essay must be focused on a clear, concise research question. You should aim to provide a comprehensive answer to this question through your research and writing.
- Subject : The EE can be written in one of the student’s six chosen subjects for the IB diploma or in a subject recognized by the IB.
- Supervision : Each student is assigned a supervisor (usually a teacher in their school) who provides guidance and support throughout the research and writing process.
- Assessment: The essay is externally assessed by the IB, contributing up to three points towards the total score for the IB diploma, depending on the grade achieved and the performance in the Theory of Knowledge course.
The Extended Essay is not just an academic requirement but a unique opportunity to explore a topic of personal interest in depth. This can be an incredibly rewarding experience, providing valuable skills and insights that will serve you well in your future academic and professional endeavours.

The EE is more than just a requirement for the IB Diploma. It’s an essential part of the IB experience , offering profound benefits for students. Let’s explore why the EE holds such significance.
Academic and Personal Development Benefits
Skill enhancement:.
The EE fosters a range of academic skills crucial for success in higher education and beyond. It teaches students how to:
- Conduct comprehensive research
- Develop a coherent argument
- Write extensively on a subject
- Manage time effectively
Personal Growth:
Beyond academic prowess, the EE encourages personal development. Students learn to:
- Pursue their interests deeply
- Overcome challenges independently
- Reflect on their learning process
- Enhance their curiosity and creativity
Contribution to University Admissions
Standout applications:.
The EE can be a significant advantage in university applications . It demonstrates a student’s ability to undertake serious research projects and commit to an intensive academic task. Universities value this dedication, seeing it as indicative of a student’s readiness for undergraduate studies.
Showcase of Skills:
The EE allows students to showcase their research, writing, and analytical skills. It provides concrete evidence of their academic abilities and their capacity to engage deeply with a topic of interest.
Skill Development: Research, Writing, and Critical Thinking
Research Skills:
Students learn to navigate academic literature, evaluate sources, and gather relevant data. This process sharpens their research skills, laying a solid foundation for future academic endeavours.
Writing Skills:
Crafting a 4,000-word essay challenges students to express their ideas clearly and persuasively. It hones their writing skills, teaching them the art of structured and focused academic writing.
Critical Thinking:
The EE encourages students to analyse information critically, assess arguments, and develop their viewpoints. This critical engagement fosters a sophisticated level of thought, beneficial in both academic and real-world contexts.
In conclusion, the Extended Essay is a pivotal element of the IB Diploma Programme. It’s an invaluable opportunity for intellectual and personal growth, preparing students for the challenges of higher education and beyond. With its emphasis on independent research and writing, the EE equips students with the skills and confidence to navigate their future academic journeys successfully.

Choosing a topic for your Extended Essay is the first step in a journey towards developing a deep understanding of a specific area of interest. It’s crucial to select a topic that is not only academically viable but also personally engaging. Here’s how to navigate this critical phase.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Your EE Topic
Interest and passion:.
Select a topic that fascinates you. Your interest will sustain motivation over the months of research and writing.
Availability of Resources:
Ensure there are enough resources available on your chosen topic. Access to libraries, databases, and experts in the field is essential for comprehensive research.
Scope and Focus:
The topic should be narrow enough to allow for in-depth study yet broad enough to find sufficient research material. Balancing specificity with resource availability is key.
IB Subject Areas:
Your topic must align with one of the subjects you are studying in the IB Diploma Programme or an approved subject area. Familiarity with the subject’s methodology and criteria is crucial for success.
How to Align Your Interests with the IB Subjects
Explore the syllabus:.
Review the syllabus of your IB subjects to identify topics that interest you. This can provide a framework for your EE.
Consult with Teachers:
Teachers can offer insights into feasible topics that align with the IB criteria and offer guidance on how to approach them.
Consider Interdisciplinary Topics:
Some of the most engaging EEs explore the intersection between different subjects. If this interests you, ensure your approach meets the criteria for an interdisciplinary essay under the IB’s World Studies EE option.
Extended Essay Topics: Examples Across Various Disciplines
- Sciences: How does the introduction of non-native plant species affect biodiversity in your local ecosystem?
- History : What was the impact of Winston Churchill’s leadership on Britain’s role in World War II?
- English: How does the use of unreliable narrators influence the reader’s perception in Ian McEwan’s novels?
- Mathematics: Investigating the application of the Fibonacci sequence in predicting stock market movements.
- Visual Arts: Exploring the influence of Japanese art on Claude Monet’s painting style.
Selecting the right topic is foundational to your EE journey. It shapes your research direction, influences your engagement with the essay, and ultimately contributes to the satisfaction and success of your EE experience. Take your time, consult widely, and choose a topic that you are eager to explore in depth.

Crafting a focused and clear research question is a pivotal element of your Extended Essay. This question not only guides your research but also frames your essay’s entire structure. It’s the question to which your essay will provide an answer, and as such, it requires thoughtful consideration and precision.
A well-developed research question should be specific, relevant, and challenging. It should invite analysis, discussion, and the exploration of significant academic literature. Here’s a deeper look into formulating a robust research question for your EE.
Characteristics of a Strong Research Question
The hallmark of a strong research question is its specificity. It shouldn’t be too broad, as this could lead to a superficial treatment of the topic.
Conversely, a question that’s too narrow might not allow for comprehensive exploration or significant discussion. Finding a balance is key. The question should also be focused on a particular aspect of a subject area, enabling in-depth analysis within the word count limit.
Another important characteristic is the question’s alignment with available resources. Before finalising your question, ensure that you have access to sufficient data and scholarly research to support your investigation. This might involve preliminary searches in academic databases, libraries, or consultation with your supervisor.
Tips for Refining Your Research Question
Start by brainstorming broad topic areas that interest you. Once you’ve identified a general area of interest, begin narrowing down by asking yourself specific questions about the topic. What aspects of this topic are unexplored or underexplored? What specific angle can I take that will make my research unique?
It’s also beneficial to review past EEs or academic journals for inspiration. Seeing how others have structured their research questions can provide valuable insight into crafting your own. However, ensure your question remains original and tailored to your interests.
Examples of Effective Research Questions
To give you an idea of what a well-formulated research question looks like, here are a few examples:
- Biology: How does the concentration of a specific nutrient affect the growth rate of plant species X in a hydroponic setup compared to soil-based growth?
- History: To what extent did the public speeches of Martin Luther King Jr. influence the public’s perception of the Civil Rights Movement in the United States between 1963 and 1968?
- Economics: How significant is the impact of recent economic policies on small businesses in [specific location] during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- English Literature: How does the use of magical realism in Gabriel García Márquez’s ‘One Hundred Years of Solitude’ reflect the political and social issues of post-colonial Latin America?
Developing your research question is an iterative process. It may evolve as you delve deeper into your research. Be open to refining your question based on the information you discover and discussions with your supervisor. A well-crafted research question will not only guide your research effectively but also engage your interest throughout the writing process, leading to a more meaningful and insightful Extended Essay.

A critical component of your Extended Essay is selecting an appropriate research methodology and theoretical framework. These elements are foundational to conducting your research and crafting your argument, influencing how you collect, analyse, and interpret data.
Understanding Research Methodologies
Research methodology refers to the systematic approach you take to investigate your research question. It encompasses the methods and procedures you use to collect and analyse data. Your chosen methodology should align with the nature of your research question and the objectives of your essay.
In the sciences, for example, your methodology might involve experiments, observations, or simulations to gather empirical data. In the humanities, you may lean towards content analysis, comparative analysis, or historical investigation, relying on textual or archival sources.
Selecting the right methodology is crucial. It should provide a clear path to answering your research question, considering the resources available and the scope of your essay. It’s also important to justify your choice of methodology in your essay, explaining why it’s appropriate for your research question and how it will help you achieve your objectives.
Applying Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks provide a lens through which your research is conducted and interpreted. They offer a structured way to understand and analyse your findings, grounding your study in existing knowledge and theories.
Choosing a theoretical framework involves identifying relevant theories, models, or concepts that apply to your topic. For instance, if you’re exploring media representation of gender, you might utilise feminist theory as a framework to analyse your findings. In economics, you might apply game theory to understand competitive behaviours in a market.
The framework should guide your analysis, providing a coherent basis for interpreting your data. It helps to structure your argument, offering a deeper insight into the significance of your findings within the broader academic discourse.
Integrating Methodology and Frameworks into Your Research
Successfully integrating your chosen methodology and theoretical framework involves a few key steps:
- Clarify the Scope: Ensure your research question, methodology, and theoretical framework align in scope and focus. They should work together seamlessly to guide your research.
- Justify Your Choices: Explain the rationale behind your chosen methodology and framework. Discuss why they are suitable for your research question and how they will support your investigation.
- Apply Consistently: Use your methodology and framework consistently throughout your research and analysis. This consistency strengthens the coherence and academic rigour of your essay.
Reflecting on these components during the planning stage can enhance the quality of your research and the clarity of your argument. Your methodology and theoretical framework are not just academic requirements; they’re tools that shape the direction and depth of your inquiry, enabling a more structured and insightful exploration of your topic.

In the journey of crafting an Extended Essay (EE), the ability to critically evaluate sources and data stands as a fundamental skill. This evaluation is crucial in establishing the credibility and reliability of the information that forms the backbone of your research. Understanding how to discern the quality and relevance of your sources ensures that your EE is built on a solid foundation of trustworthy information.
Criteria for Selecting Credible and Relevant Sources
Authority: Consider the source’s authorship. Look for works by experts in the field, academic institutions, or reputable organisations. The author’s qualifications and affiliations can significantly impact the reliability of the information.
Accuracy: The information should be supported by evidence, referenced appropriately, and free from factual errors. Reliable sources often undergo a peer-review process, ensuring that the content is scrutinised and validated by other experts in the field.
Currency: The relevance of information can diminish over time, especially in fields that evolve rapidly, such as science and technology. Ensure that the sources you use are up-to-date, reflecting the latest research and developments.
Purpose: Understand the purpose behind the information. Is it to inform, persuade, entertain, or sell? Recognising the intent can help you assess potential biases, which is particularly important when dealing with controversial topics.
Techniques for Evaluating the Reliability and Validity of Data
Cross-Verification: Cross-check information across multiple sources to verify its accuracy and reliability. Consistency among various sources can be a good indicator of the information’s validity.
Statistical Analysis: When dealing with numerical data, consider its statistical significance and the methodology used in its collection. Reliable data should be gathered using sound scientific methods and accurately represent the population or phenomena studied.
Source Evaluation Tools: Utilise tools and checklists designed to evaluate the credibility of sources. These can provide a structured approach to assessing the quality of your research materials.
Incorporating Primary vs. Secondary Sources Effectively
Primary Sources: These are firsthand accounts or direct evidence concerning the topic you’re researching. They include interviews, surveys, experiments, and historical documents. Primary sources offer original insights and data, allowing for a deeper and more personal engagement with your subject.
Secondary Sources: These sources analyse, interpret, or summarise information from primary sources. They include textbooks, articles, and reviews. Secondary sources can provide context, background, and a broader perspective on your topic.
Balancing primary and secondary sources enriches your research, providing both the raw data and the interpretations that help frame your analysis. By rigorously evaluating sources and data, you ensure that your Extended Essay rests on a foundation of credible and relevant information, enhancing the depth and rigour of your investigation.

The heart of a compelling Extended Essay (EE) lies in the seamless integration of evidence and analysis. This integration not only supports and substantiates your arguments but also demonstrates your ability to critically engage with your research topic. Here’s how to weave evidence and analysis together in a way that enhances the strength and persuasiveness of your EE.
Strategies for Integrating Evidence Seamlessly into Your Argument
Directly Link Evidence to Your Thesis: Every piece of evidence you include should directly support or relate to your thesis statement. This ensures that all the information contributes to building your argument coherently.
Use Evidence to Illustrate Points: Utilise examples, data, quotes, and case studies as concrete evidence to illustrate your points. This makes abstract concepts more tangible and convincing to the reader.
Analyse, Don’t Just Present: For every piece of evidence, provide analysis and interpretation. Explain how it supports your argument, what it demonstrates, and its implications for your research question.
Balancing Descriptive and Analytical Writing
Avoid Over-Description: While some description is necessary to set the context, avoid dedicating too much space to merely describing your evidence. The focus should be on analysis.
Develop a Critical Voice: Cultivate a critical approach to your evidence. This means evaluating its reliability, considering its limitations, and discussing its relevance to your argument.
Synthesise Information: Aim to synthesise evidence from multiple sources to support your points. This demonstrates comprehensive understanding and the ability to draw connections across your research.
How to Critically Analyse Sources and Data Within Your Essay
Question the Source: Consider the source’s origin, purpose, and potential bias. How might these factors influence the information presented?
Evaluate Methodology: If the evidence comes from a study or experiment, evaluate the methodology used. Is it sound and appropriate for the research question?
Consider the Broader Context: Place your evidence within the broader scholarly conversation on your topic. How does it fit with, challenge, or expand existing knowledge?
By thoughtfully integrating evidence and providing in-depth analysis, you can create a nuanced and compelling EE that goes beyond mere description to offer original insights into your topic. This approach not only strengthens your argument but also showcases your critical thinking and analytical skills, essential qualities for success in the IB Diploma Programme and beyond.
The Extended Essay presents an opportunity for IB students to engage deeply with a topic of their choice. However, to effectively communicate your research and insights, your essay must be well-structured and clearly written.
This section provides guidance on how to write and structure your EE, ensuring your work is coherent, persuasive, and academically rigorous.
Outline of the Extended Essay Structure
A well-organised structure is crucial for the readability and coherence of your EE. Typically, an Extended Essay includes the following components:
- Title Page: Displays the essay title, research question, subject the essay is registered in, and word count.
- Abstract: A concise summary of the essay, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusion (Note: For essays submitted in 2018 and forward, the IB no longer requires an abstract, so check the most current guidelines).
- Contents Page: Lists the sections and subsections of your essay with page numbers.
- Introduction: Introduces the research question and your essay’s purpose, outlining the scope of the investigation.
- Body : The main section of your essay, divided into clearly titled subsections, each addressing specific aspects of the research question. It’s where you present your argument, supported by evidence.
- Conclusion: Summarises the findings, discusses the implications, and reflects on the research’s limitations and potential areas for further study.
- References/Bibliography: Lists all sources used in the essay in a consistent format, following the chosen citation style.
- Appendices: (If necessary) Contains supplementary material that is relevant to the research but not essential to its explanation.
Detailed Breakdown of Each Section
Introduction:
The introduction sets the stage for your research. It should clearly state your research question and explain the significance of the topic. Briefly outline the theoretical framework and methodology, and provide an overview of the essay’s structure.
The body is the heart of your essay. It should be logically organised to build your argument step by step. Each paragraph should start with a clear topic sentence, followed by evidence and analysis. Use subheadings to divide the sections thematically or methodologically, ensuring each part contributes to answering the research question.
- Developing Arguments: Present and critique different perspectives, systematically leading the reader through your analytical process.
- Using Evidence: Incorporate relevant data, quotes, and examples to support your arguments. Ensure all sources are appropriately cited.
- Analysis and Discussion: Go beyond describing your findings; analyse and interpret them in the context of your research question and theoretical framework.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should not introduce new information. Instead, it should synthesise your findings, highlighting how they contribute to understanding the research question. Reflect on the research process, acknowledging any limitations and suggesting areas for further investigation.
Importance of Coherence and Logical Flow
Maintaining coherence and a logical flow throughout your EE is essential. Transition sentences between paragraphs and sections can help link ideas smoothly, guiding the reader through your argument. A coherent structure ensures that your essay is accessible and persuasive, making a strong impression on the reader.
A well-written and structured EE is a testament to your understanding of the research process and your ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. By adhering to a clear structure and focusing on coherence and logical progression, you can craft an essay that is engaging, insightful, and academically rigorous.

A unique and integral component of the IB Extended Essay (EE) process is the Reflections on Planning and Progress Form (RPPF). The RPPF serves as a personal and academic exploration tool, guiding students through the planning, research, and writing phases of their EE. It encourages students to reflect on their learning journey, documenting insights gained, challenges encountered, and the evolution of their thinking.
The Role of Reflection in the EE Process
Reflection is at the heart of the EE, enabling students to engage critically with their own learning processes. It helps in:
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging students to consider their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Skill Development: Facilitating a deeper understanding of the research and writing skills developed during the EE process.
- Critical Thinking: Promoting an evaluative approach to the research process, allowing students to make informed decisions about their methodologies, sources, and arguments.
How to Effectively Complete the RPPF
Completing the RPPF involves three formal reflection sessions, which are crucial milestones in the EE journey:
- Initial Reflection: Focuses on the selection of the topic and formulation of the research question. Students should discuss their motivations, initial ideas, and anticipated challenges.
- Interim Reflection: Occurs midway through the process. Students reflect on the progress made, adjustments to their research plan, and any challenges they’ve faced. It’s an opportunity to reassess the direction of the EE and make necessary modifications.
- Final Reflection: After completing the EE, students reflect on their overall experience, the skills they’ve developed, and the knowledge they’ve gained. This reflection should also consider the impact of the research process on their personal and academic growth.
In each reflection, students should be honest and critical, providing insights into their learning journey. The reflections are not just about documenting successes but also about understanding the learning process, including setbacks and how they were overcome.
Examples of Reflective Questions and Insightful Responses
Initial reflection:.
Question: “What excites me about my chosen topic?”
Insightful Response: Discuss the personal or academic interest in the topic, any prior knowledge, and what you hope to discover through your research.
Interim Reflection:
Question: “What challenges have I encountered in my research, and how have I addressed them?”
Insightful Response: Describe specific obstacles, such as difficulty accessing resources or refining the research question, and the strategies employed to overcome them.
Final Reflection:
Question: “How has my understanding of the topic evolved through the research process?”
Insightful Response: Reflect on how the research challenged or confirmed initial assumptions and what was learned about the topic and the research process itself.
The RPPF is not just a formal requirement but a valuable component of the EE that enriches the student’s learning experience. By fostering reflection, the RPPF helps students to articulate their journey, offering insights into the complexities of research and the personal growth that accompanies the creation of an extended academic work.

The Extended Essay allows students to explore a topic of interest within the framework of an IB subject. The choice of academic discipline not only shapes the content and focus of the essay but also influences the methodologies and theoretical frameworks that students may employ. Understanding and adhering to the conventions and requirements of the chosen discipline is crucial for the success of the EE.
Adhering to Disciplinary Conventions and Guidelines
Each academic discipline has its own set of conventions regarding research methodologies, writing styles, and citation formats. For example, a science EE might require empirical research and quantitative analysis, whereas an essay in the humanities might focus on qualitative analysis and critical interpretation of texts.
Key considerations include:
- Methodology: The choice of methodology should align with disciplinary norms. Science EEs might involve experiments, whereas essays in history might rely on primary source analysis.
- Structure: While the basic structure of the EE remains consistent across subjects, the presentation of arguments and evidence might vary. Essays in the arts and humanities might follow a thematic structure, while those in the sciences might be organised around experimental findings.
- Citation Style: Different disciplines prefer specific citation styles. For instance, APA might be favoured in psychology, while MLA is commonly used in literature essays. Adhering to the appropriate style is crucial for academic integrity.
How Different Disciplines Influence the Approach to Research and Writing
The academic discipline not only dictates the formal aspects of the EE but also influences the approach to research and writing. For instance, an EE in Visual Arts would require a different analytical lens compared to an EE in Economics. The former might analyse the impact of cultural contexts on artistic expressions, while the latter could evaluate economic theories through case studies.
Disciplinary perspectives also affect:
- Argumentation : The way arguments are constructed and evidenced can differ. In the sciences, arguments are often built around data and logical reasoning, while in the humanities, they might be more interpretative, drawing on various theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Engagement: The extent and nature of critical engagement with sources can vary. In subjects like History or English, a critical analysis of diverse interpretations is fundamental, whereas in the Sciences, the focus might be on empirical evidence and hypothesis testing.
Examples of Disciplinary Perspectives in Extended Essay Examples
- Biology EE: An investigation into the effects of environmental changes on local biodiversity, employing scientific methods for data collection and analysis.
- Economics EE: An analysis of the impact of a specific economic policy on a local economy, using economic theories and models to interpret data.
- English Literature EE: A comparative study of the theme of alienation in two novels, using literary theories to explore the authors’ narrative techniques.
Understanding the significance of academic discipline in the EE ensures that students approach their research with the appropriate methodologies and analytical frameworks. It encourages respect for the depth and breadth of the subject area, contributing to a more nuanced and informed exploration of the chosen topic.

Writing an Extended Essay involves more than just conducting research and presenting findings; it requires careful planning, effective engagement with your supervisor, and a critical approach to your sources. Here are some best practices to help you navigate the EE writing process successfully.
Time Management and Planning
Time management is crucial in the EE process. The project spans several months, so it’s essential to break down the work into manageable stages. Create a timeline early in the process, including key milestones such as completing the research, drafting sections, and finalising the essay. Allocate time for unexpected challenges and ensure you have buffer periods for revision and feedback.
Planning Tips:
- Set Goals: Establish clear, achievable goals for each phase of your EE journey.
- Use Tools: Leverage planning tools or software to organise your tasks and deadlines.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review your progress against your plan and adjust as necessary.
Engaging with Supervisors Effectively:Your supervisor is a valuable resource throughout the EE process. They can provide guidance on your research question, methodology, and essay structure, as well as feedback on your drafts.
Maximising Supervisor Engagement:
- Prepare for Meetings: Come to each meeting with specific questions or sections of your essay you want feedback on.
- Be Open to Feedback: Constructive criticism is essential for improvement. Listen to your supervisor’s suggestions and consider how to incorporate them into your work.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep your supervisor informed of your progress and any challenges you encounter.
Critical Engagement with Sources
A critical approach to the sources you use is fundamental to a high-quality EE. Evaluate the reliability, relevance, and bias of your sources to ensure your essay is grounded in credible evidence.
Strategies for Source Evaluation:
- Source Variety: Use a range of sources, including academic journals, books, and reputable online resources, to provide a balanced perspective on your topic.
- Critical Analysis : Don’t just summarise sources. Analyse their arguments, identify limitations, and consider how they contribute to your research question.
- Citation and Paraphrasing: Accurately cite all sources to avoid plagiarism. When paraphrasing, ensure you’re genuinely rephrasing ideas in your own words while still crediting the original author.
Good practice in EE writing is not just about adhering to academic standards; it’s about engaging deeply with your topic, embracing the research process, and developing skills that will serve you well in your academic and professional future. By managing your time effectively, leveraging the support of your supervisor, and critically engaging with sources, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also personally rewarding.

Successfully navigating the Extended Essay process requires more than just academic skill; it demands effective project management. This encompasses planning, organising, and executing your EE from initial conception to final submission. Here are strategies to help you manage the EE process, ensuring a smooth journey and a rewarding outcome.
Planning and Time Management Strategies Specific to the EE
Develop a Detailed Plan: Start by breaking down the EE process into stages: topic selection, research, drafting, and revising. Assign deadlines to each stage based on the final submission date, allowing extra time for unforeseen delays.
Use a Calendar or Planner: Keep track of deadlines, meetings with your supervisor, and other important dates. Digital tools can be particularly useful, offering reminders and helping you stay organised.
Set Regular Milestones: Milestones offer checkpoints to assess your progress. These could be completing the research phase, finishing a first draft, or finalising your citations. Celebrate these achievements to stay motivated.
Milestones and Checklists to Keep You on Track
Create Checklists: For each phase of the EE process, develop a checklist of tasks. This could include conducting initial research, writing specific sections of the essay, or completing rounds of revision.
Regular Progress Reviews: Schedule weekly or bi-weekly reviews of your progress against your plan. Adjust your plan as needed based on these reviews.
Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adapt your plan. Research might take longer than expected, or you might decide to change your focus slightly after discussing with your supervisor.
Dealing with Challenges and Setbacks During the EE Journey
Anticipate Potential Issues: Think ahead about what might go wrong and how you would address it. Having contingency plans can reduce stress and keep you on track.
Seek Support When Needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out to your supervisor, peers, or other mentors if you encounter obstacles. They can offer advice, support, and perspective.
Maintain a Positive Attitude: Challenges are part of the learning process. View setbacks as opportunities to improve your problem-solving and resilience skills.
Managing the EE process effectively is about more than just completing a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an exercise in self-management and personal growth. By carefully planning your work, setting and celebrating milestones, and being prepared to tackle challenges, you can navigate the EE process with confidence and achieve a result that reflects your hard work and dedication.

Mastering the art of collaboration and effectively incorporating feedback are pivotal aspects of crafting a high-calibre Extended Essay (EE). These processes enrich your work, offering new perspectives and insights that can significantly enhance the depth and quality of your research and writing. Let’s delve into how to navigate these collaborative interactions and integrate feedback productively.
Effective Collaboration with Your Supervisor
Your supervisor is a key ally in your EE journey, providing guidance, support, and expert insight into your chosen topic. Building a productive relationship with your supervisor involves clear communication, active engagement, and receptiveness to their advice.
- Prepare for Meetings: Maximise the value of your meetings by preparing questions and topics for discussion. This shows initiative and helps you focus on areas where you need the most guidance.
- Be Open to Suggestions: Your supervisor brings a wealth of experience and knowledge. Being open to their suggestions can unlock new avenues of inquiry and refine your research focus.
- Follow Up: After meetings, review the guidance provided and take action. Following up on suggestions and demonstrating progress is key to a fruitful collaboration.
Incorporating Feedback Constructively
Feedback is a gift, offering you fresh eyes on your work and highlighting areas for improvement. Whether it comes from your supervisor, peers, or other mentors, constructive feedback is instrumental in elevating the quality of your EE.
- Critically Evaluate Feedback: Not all feedback will be equally applicable or helpful. Assess suggestions critically and decide which ones align with your research goals and vision for your EE.
- Implement Changes Thoughtfully: When integrating feedback, do so thoughtfully and systematically. Consider how each piece of advice enhances your argument or strengthens your analysis.
- Maintain Your Own Voice: While it’s important to consider feedback, your EE should ultimately reflect your ideas, analysis, and voice. Balance the input from others with your own scholarly insights.
Balancing Independent Research with Guidance
Navigating the balance between independent research and the guidance received is a delicate aspect of the EE process. While the EE is your project, drawing on the expertise and feedback of others can significantly enhance its depth and scope.
- Value Independence: Embrace the opportunity to conduct independent research, making your EE a true reflection of your interests and intellectual curiosity.
- Seek Guidance Wisely: Utilise your supervisor and other resources judiciously. They can provide clarity, offer new perspectives, and help you navigate complex aspects of your research.
- Synthesise Input: Integrate the guidance and feedback you receive in a way that complements your research, ensuring that your EE remains a coherent and cohesive piece of scholarly work.
The interplay between collaboration, feedback, and independent research is central to the EE process. By engaging effectively with your supervisor, thoughtfully incorporating feedback, and maintaining a balance between guidance and your own scholarly pursuits, you can craft an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also a true testament to your growth as a learner.
Plagiarism is a critical concern in academic writing, including the Extended Essay. It involves using someone else’s work without proper acknowledgment, which can compromise the integrity of your essay and result in severe penalties. Understanding what constitutes plagiarism and how to avoid it is essential for maintaining academic honesty and ensuring the credibility of your research.
Understanding What Constitutes Plagiarism
Plagiarism can take many forms, from directly copying text without quotation marks to paraphrasing someone else’s ideas without proper citation. It also includes using images, charts, or data without acknowledging the source. Even unintentional plagiarism, where sources are not deliberately misrepresented but are inadequately cited, can have serious consequences.
How to Properly Cite Sources and Paraphrase
Citing Sources : Every time you use someone else’s words, ideas, or data, you must cite the source. This not only includes quotes and paraphrases but also data, images, and charts. Familiarise yourself with the citation style recommended for your subject area, whether it be APA, MLA, Chicago, or another, and apply it consistently throughout your essay.
Paraphrasing: Paraphrasing involves rewording someone else’s ideas in your own words. It’s essential to do more than just change a few words around; you need to completely rewrite the concept, ensuring you still cite the original source. Good paraphrasing demonstrates your understanding of the material and integrates it seamlessly into your argument.
Using Plagiarism Detection Tools
Many schools and students use plagiarism detection tools to check the originality of their work before submission. These tools compare your essay against a vast database of published material and other student submissions to identify any matches. Utilising these tools can help you identify areas of your essay that need better paraphrasing or citation.
Avoiding plagiarism in the EE involves diligent research, careful writing, and thorough citation. It’s about respecting the intellectual property of others while demonstrating your own understanding and analysis of the topic. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your EE is both original and academically honest, reflecting the hard work and integrity that define the IB learner profile.

In the Extended Essay, showcasing original thought is not just encouraged; it’s a cornerstone of what makes an EE stand out. Originality in this context means more than just avoiding plagiarism; it involves presenting unique perspectives, developing novel arguments, or exploring new areas within a subject. Here’s how you can emphasise original thought in your EE.
The Value of Originality and Creativity
Originality and creativity in the EE demonstrate your ability to think independently and engage critically with your subject. It shows that you’re not just capable of summarising existing knowledge but also contributing to the conversation in your discipline. This level of engagement is what the IB looks for in assessing the EE, as it reflects a deeper understanding and application of the subject matter.
Balancing Academic Rigour with Personal Voice and Analysis
While it’s important to ground your EE in academic research and follow disciplinary conventions, finding a balance with your personal voice and analysis is key to originality. Here are ways to achieve this balance:
- Personal Insight : Inject your essay with your insights, interpretations, and conclusions based on the research. This personal engagement with the topic distinguishes your EE from a mere literature review.
- Critical Analysis: Go beyond describing what others have said. Critique the arguments, identify gaps in the research, and propose new ways of understanding the subject.
- Innovative Approach: Consider addressing less explored aspects of your topic or applying theories and methodologies from other disciplines to bring fresh perspectives.
Strategies for Developing and Showcasing Original Thought
Question Assumptions: Start by questioning the prevailing assumptions or widely held beliefs in your subject area. This critical stance can open up avenues for original analysis.
Interdisciplinary Connections: Drawing connections between different disciplines can reveal new insights and approaches that enrich your essay.
Reflect on Your Learning: Use the insights gained from your coursework and personal interests to inform your approach. Often, your unique educational and life experiences can inspire original perspectives.
Emphasising original thought in your EE is about striking a balance between demonstrating your mastery of the subject and pushing beyond the boundaries of existing knowledge. It involves a blend of thorough research, critical thinking, and creative engagement with the topic. By fostering a unique perspective and injecting your personal voice into your analysis, you can create an EE that is not only academically rigorous but also distinctly yours, leaving a lasting impression on your readers.

The culmination of the Extended Essay process includes the final presentation and the Viva Voce, a concluding interview between the student and their supervisor. These components serve not only as a summation of your EE journey but also as an opportunity to reflect on your learning and the skills you’ve developed. Understanding the significance and how to prepare for these elements is crucial for a successful EE completion.
Preparing for the Final Presentation
The final presentation is an opportunity to share the highlights of your EE journey, including your research question, methodology, key findings, and any challenges you overcame. It’s a moment to showcase the depth of your research and the personal growth you experienced throughout the process.
Key Elements to Include:
- Overview of Your Research: Briefly summarise your research question and why you chose it, highlighting your methodology and the scope of your investigation.
- Significant Findings: Share the key insights and discoveries you made during your research. This is a chance to underscore the original contributions of your EE.
- Challenges and Solutions : Discuss any significant obstacles you faced and how you addressed them. Reflecting on these challenges shows your problem-solving skills and resilience.
- Reflections on the Process: Share what you’ve learned about yourself as a learner, the skills you’ve developed, and how the EE has impacted your academic and personal growth.
Tips for a Successful Viva Voce
The Viva Voce is a short interview with your supervisor after you’ve submitted your EE. It’s an integral part of the reflection process, allowing you to discuss the successes and challenges of your research journey.
To Prepare for the Viva Voce:
- Review Your EE: Be familiar with your essay’s content, as you’ll discuss your work in detail. Be ready to explain your research decisions and reflect on your learning process.
- Anticipate Questions: Your supervisor might ask about how you selected your topic, the development of your research question, your approach to research and writing, and the skills you’ve developed.
- Reflect on Your Learning: Think about the entire EE process, including what you learned, how you’ve grown, and how the experience might influence your future academic or career goals.
How the Viva Voce Contributes to Your Overall EE Assessment
While the Viva Voce doesn’t directly affect your EE grade, it plays a crucial role in the holistic assessment of your IB Diploma. It demonstrates the authenticity of your work and your engagement with the EE process, providing insights into your approach, dedication, and intellectual growth.
The final presentation and Viva Voce are essential milestones that mark the completion of your EE journey. They offer a platform to reflect on the challenges you’ve navigated, the knowledge you’ve gained, and the skills you’ve honed. Preparing thoroughly for these elements ensures you can confidently articulate your research journey, showcasing the depth of your inquiry and your development as an IB learner.

The journey through the Extended Essay is more than an academic exercise; it’s a transformative experience that equips IB Diploma students with skills and insights that extend far beyond the programme.
Reflecting on how the EE prepares you for future academic and professional endeavours can highlight the lasting value of this rigorous project.
How the Skills Developed During the EE Can Benefit You in Future Academic and Professional Endeavours
Research and Analytical Skills: The EE demands a high level of research and analysis, teaching students how to gather, assess, and interpret data. These skills are invaluable in higher education and many professional fields, where evidence-based decision-making is crucial.
Critical Thinking: Crafting an EE requires students to evaluate sources critically, consider multiple perspectives, and develop well-reasoned arguments. This ability to think critically is highly sought after in both academia and the workplace.
Project Management: Completing an EE involves planning, organisation, time management, and problem-solving. Managing such a long-term project successfully can boost your confidence in handling complex tasks and projects in the future.
Communication: Writing the EE enhances your ability to communicate complex ideas clearly and effectively, a skill that is essential in any professional setting. Additionally, the final presentation and Viva Voce develop your verbal communication and presentation skills.
Examples of How the EE Has Helped Alumni in Their Post-IB Journeys
Many IB alumni attribute their success in university and their careers to the foundation laid by their EE experience. For instance, alumni often report that the EE made the transition to university-level research and writing much smoother. Others have found that the skills developed through the EE, such as critical thinking and project management, have set them apart in job interviews and workplace projects.
Encouragement to View the EE as a Stepping Stone to Lifelong Learning
The EE is not just a requirement for the IB Diploma; it’s an introduction to a lifelong journey of inquiry and discovery. It encourages a mindset of curiosity and a habit of continuous learning that can enrich both your personal and professional life. Viewing the EE through this lens can transform it from a daunting task into an exciting opportunity to explore your passions and develop essential skills for the future.
The Extended Essay is a hallmark of the IB Diploma Programme, embodying the essence of inquiry, critical thinking, and scholarly engagement. From selecting a topic and formulating a research question to conducting in-depth research and presenting findings, the EE challenges students to transcend the boundaries of traditional learning, fostering skills and insights that extend far beyond the confines of the classroom.
This comprehensive guide has navigated the critical aspects of the EE process, offering strategies for managing time, engaging with supervisors, and ensuring academic integrity. It has underscored the importance of original thought, the role of academic discipline, and the value of reflection, aiming to equip students with the tools they need to succeed in this rigorous academic endeavour.
The Extended Essay is a testament to your dedication, intellectual curiosity, and academic prowess. Embrace this opportunity to shine, to explore, and to make your mark on the world of knowledge.
How can we help?
The IB Extended Essay Explained

What is the Extended Essay?
The Extended Essay ( ‘EE’), together with CAS and TOK, is a core component of the International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme. It is mandatory for all students, regardless of the subjects they are taking. The aim of the EE is to provide students with the opportunity to research a topic of their interest. It is also an opportunity for students to showcase their knowledge and reading beyond the classroom syllabus. During the EE students will acquire some of the essential skills for researching and writing university theses.
Students usually start their essay in the second term of the first year of their IB Diploma Programme, around January time. They will need a supervisor (one of the teachers at their school). They will meet regularly with them to help structure their research questions and guide them in writing the paper. The programme allows for one draft to be handed in to the supervisor for feedback. The second version is the final version. The Essay should be no longer than 4000 words, with a short viva voce at the end. The process takes around a year.
Approaching the IB Extended Essay
How to choose a topic for the extended essay.
The topic must be related to one of the six topics that the student is taking for their Diploma. Students can also take an interdisciplinary ‘world studies’ issue that relates to two of their subjects. This requires a global issue to be looked at through a local lens. For example, how wider climate change, cultural, terrorism, technology or health trends are manifested in a specific context or place.
It is generally best for students to choose a topic that they are passionate about. Not least because they will have to work on it for a year! One way to choose is to take something that they recently questioned.
Examples of the The IB Extended Essay
For example, a Physics student watching the film ‘The Martian’, which was filmed in the Namibia desert, might have found it very surprising that Earth bears such a resemblance to Mars, and they could set about researching certain communalities and differences between these two planets. An English student might want to take a couple of poems and compare how the writers use a particular literary style. In Economics, a student might analyse the dynamics of a specific market (such as shoes, cars, finance, a food-type), against a particular theory. A History student might look at how the rules of two different dictators can be viewed through a certain ideology.
It is normal to be overwhelmed by having too much choice for the topic. Brainstorming about the subject they most enjoy or are good at, and thinking more specifically about why they enjoy it can help generate ideas. Taking two related things they are interested in (historic events, technologies, inventions, books, poems, geographies, markets, planets, experiments and so on) and comparing them against a related concept can also be a good model to start with.
The topic needs to be approved by the IBO, which the school will help with.
How to choose a research question for the Extended Essay
Once students have chosen their topic, they need to decide on a research question. A wrongly formulated research question will turn this learning experience into a stressful one. It is essential that the question is relevant, focused. The answer should not be a simple yes or no, but should also actually be answerable. It is not necessary to prove the research question right – disagreeing with the initial hypothesis is perfectly fine. Questions will fall broadly into two categories. Either they will be aimed at solving a problem, for example, through conducting an experiment. Or, they will lead to a research or study around the topic.

The question should not necessarily start with words like, ‘ Does’, ‘Will’ or ‘Is’ . Simply stating that ‘ yes, it is true’ or ‘ no, it is not true’ is insufficient. For this reason the highest scoring essays usually have a research question that start with, ‘ To what extent’ , ‘A study of’, ‘An analysis of’, or ‘ How far ’, or could even just be a statement to analyse.
Students often set a question without contemplating if they are capable of answering it. It is important to evaluate how the relevant data can be collected, as an essay that includes both primary and secondary research will be well supported. However, it should be noted that in some cases it is only possible to use secondary data. This is fine, but it is good to state why. If thinking around the question has started early enough, if there are too many barriers to collecting the data, it may be best to alter the question with the supervisor’s help before getting stuck in.
The body of the essay: investigating, analysing and writing
Once the research question has been set and tested, it’s time to start collecting primary and secondary data. Keeping a log of the data is a good idea. The results of the research can be put in an appendix and, where appropriate, referred to in the text. In the essay itself the data can be summarised in charts and tables.
Once all the data has been collected, it can be analysed. The outcomes of this should be evaluated against relevant concepts and reading in the chosen subject.
It’s a good idea to write out the arguments, structure, and headings before beginning writing so the essay is presented clearly and logically, using any terminology correctly.
The introduction and conclusion
A rough draft of the introduction can be written at an early stage. After having collected, analysed and evaluated the data, the introduction can be adjusted to fit the essay. The introduction should explain why the research question is worth investigating, and how it relates to the subject, in other words, it should set the academic context for the essay.
The conclusion should be written at the end, and should not include any additional research or analysis. It should summarise what has already been stated. Examiners carefully look at this.
The abstract and final sections of the Extended Essay
At the end of writing, the student needs to write the abstract, which is a 300-word summary of the essay. It should include the research question, a very short summary of the analysis and the answer to the research question. Students also need a title page, contents page, references and bibliography, and any appendices (for example, containing any data). All of these things must be included in the word limit.
Deadlines for the IB Extended Essay
The official IB deadline is different for every school, and schools will let students know. 4000 words cannot all be written the weekend before the deadline. Therefore, careful planning is needed to avoid a last minute crunch. After all, it would be a shame to waste the amazing research and ideas by running out of writing time. Schools tend to set their own internal deadlines for their students to have completed different sections of the project. Therefore it is good to be in constant communication with supervisors and relevant subject teachers. This will allow you to make sure each section is completed along the way.
The viva voce interview
The viva voce is essentially a short interview with the supervisor, in which they ask students to reflect on the strengths and successes of their findings. Also, they could look at any areas that caused unexpected problems, and what can be learned from the research report. It’s nothing to worry about. It’s just something that can be greatly enhanced with preparation and thinking beforehand. They are also making sure that the report hasn’t been plagiarised!
A word of advice
Students often make the mistake of deciding on an easier, less interesting field of research. It would be much better to take on a more complex topic that fascinates them. If there is a subject that they are considering studying at university, now is a good time to really get into that subject. The finished product could help with the university application and interview. As long as the question can be tested with data and the student and supervisor think it is plausible, it is best to go for the more exciting option. The disciplines learnt during the EE are useful for approaching real-life problems, and knowing this can help keep motivation up. Learning to ask, “ Do I have enough data about a given situation?”, or “What does this data allow me to conclude for the moment?” is never a bad thing!
Official IBO assessment criteria for the IB Extended Essay can be found here .
More from International School Parent
Find more articles like this here: www.internationalschoolparent.com/articles/
Want to write for us? If so, you can submit an article here: www.internationalschoolparent.submittable.com
Explore international schools
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
- View all schools
Explore international camps
- View all camps

Read our latest magazine for free
Also available in our apps.
What is the IB Program Extended Essay?
Why is the ib extended essay important, writing the extended essay, how can i choose a topic, how can i best prepare for the extended essay, final thoughts.
Published November 26, 2023
The Ultimate Guide to IB Extended Essays

High School Sophomore from West Virginia, Avid Classics Enthusiast, Marketing Intern and Blog Writer at Knowt :)
For high school students taking part in the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, the Extended Essay is a substantial academic endeavor that deserves careful consideration. Not doing well on this essay might lose you your IB diploma. It represents an opportunity to dive deeply into a subject of personal interest, showcasing not only one's research and writing abilities but also a commitment to scholarly exploration. In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive understanding of what the essay entails, its significance within the program, the sequential stages involved in its completion, and how students can effectively navigate this substantial academic challenge. Whether you are embarking on this intellectual journey or seeking to gain insight into this fundamental component of the IB curriculum, our guide intends to shed light on the purpose, process, and educational impact of the essay in a formal and informative manner.
The IB Extended Essay is a rigorous independent research project at the heart of the IB Diploma Programme. It challenges high school students to dive into a chosen subject of personal interest in a structured and scholarly manner. The Extended Essay requires students to engage in extensive research, develop a clear research question or hypothesis, and produce a substantial written essay of up to 4,000 words. This endeavor is designed to cultivate essential skills, including critical thinking, research methodology, and effective communication, while encouraging students to explore their passions and pursue academic excellence. The Extended Essay not only serves as a capstone achievement in the programbut also provides a valuable opportunity for students to develop the intellectual independence and research skills needed for success in higher education and beyond.
The IB Extended Essay holds paramount significance within the International Baccalaureate (IB) program for several compelling reasons. Firstly, it fosters intellectual independence and critical thinking, as students are tasked with formulating their research questions, conducting thorough investigations, and presenting their findings in a scholarly manner. This process not only hones their research skills but also nurtures a passion for academic inquiry. Additionally, the Extended Essay equips students with valuable research methodologies, analytical abilities, and effective communication skills, all of which are indispensable for success in higher education and future careers. Furthermore, it offers an opportunity for students to explore their interests deeply, cultivating a lifelong love for learning. Ultimately, the Extended Essay is not merely an academic exercise but a transformative experience that prepares students for the challenges of university studies and instills a sense of intellectual curiosity and rigor that extends far beyond their academic journey.
Topic Selection: Begin by selecting a subject area and a specific topic that genuinely interests you. Ensure that it aligns with one of the approved IB subject areas and is sufficiently focused.
Formulate a Research Question: Develop a clear and concise research question or hypothesis that will serve as the central focus of your essay. Ensure that your question is researchable and open to investigation.
Conduct In-Depth Research: Dive into extensive research, gathering a variety of sources relevant to your topic. This includes books, academic articles, primary sources, and data, if applicable. Keep detailed notes and organize your sources systematically.
Create an Outline: Outline the structure of your essay, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Establish a logical flow for your arguments and evidence. You can use Knowt's AI to help structure your essay as well!
Write the First Draft: Begin writing your essay based on your outline. Ensure that your arguments are well-structured, supported by evidence, and directly related to your research question. Adhere to the word limit and proper citation style.
Revise and Refine: Review your first draft critically. Check for clarity, coherence, and conciseness in your writing. Revise and refine your arguments, and make sure your essay flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback: Share your draft with teachers, peers, or mentors for constructive feedback. Consider their suggestions and make necessary revisions.
Finalize Your Essay: After incorporating feedback, finalize your essay, paying meticulous attention to grammar, spelling, and formatting. Ensure that your citations and bibliography follow the prescribed citation style.
Abstract and Table of Contents: Write a clear and concise abstract that summarizes your essay's key points. Create a table of contents to provide readers with a roadmap of your essay's structure.
Proofread: Proofread your essay carefully to eliminate any errors or inconsistencies. Consider seeking assistance from a trusted proofreader to catch any overlooked mistakes.
Submit Your Essay: Submit your final essay to your IB coordinator, adhering to the submission deadline and any specific formatting requirements.
Reflect on the Process: Take time to reflect on your journey, the challenges you encountered, and the skills you developed. Consider how your research contributed to your understanding of the subject.
Looking over your subject matter, or notes, to see if there is a particular part of the class that you would like to explore further is one way to start. Look for a subject that you find particularly interesting and would like to explore further. You will be spending quite a bit of time with your research topic, so make sure it is something you enjoy! If your notes are not very detailed and need more information, check out these free IB resources , which include study guides and notes from HL Latin to SL Biology to HL/SL Computer Science . We have it all.
Preparing effectively for the IB Extended Essay involves a combination of careful planning and consistent effort. Start by selecting a topic that genuinely interests you, as passion for your subject matter will sustain your motivation throughout the project. Next, create a detailed timeline that outlines specific milestones, research periods, and writing deadlines to ensure you stay on track. Familiarize yourself with the Extended Essay guide from various IB resources and assessment criteria to understand what is expected. Seek guidance and feedback from your EE supervisor and teachers, and don't hesitate to ask questions when you encounter challenges. Prioritize thorough research, utilize credible sources, and keep meticulous notes to ease the writing process. Stay organized, manage your time wisely, and allocate dedicated study sessions for your EE. Finally, embrace revisions and feedback as opportunities for improvement and consider seeking external guidance or resources if needed. With careful planning, dedication, and a proactive approach to research and writing, you'll be well-prepared to excel in your Extended Essay project.
Overall, the IB Extended Essay is an exciting journey that invites you to explore your interests deeply and cultivate a genuine passion for learning. It's a chance to take your academic skills to the next level, fostering critical thinking, research prowess, and effective communication—all of which will serve you well in future endeavors. Embrace this opportunity with enthusiasm, knowing that your dedication and curiosity will lead you to discoveries beyond the confines of your essay. While the path may have its challenges, remember that with determination and support, you can not only succeed but also find fulfillment in the pursuit of knowledge. So, embark on this adventure with confidence, for the Extended Essay is your platform to make a meaningful contribution to the world of ideas and scholarship. Your journey is bound to be rewarding, and your growth as a student and thinker, truly remarkable.

Everything You Need To Get A 7 in IB Theatre
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Theatre exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Theatre test prep so with the right strategies and IB Theatre resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Theatre Resources!! Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Theatre! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Theatre exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Theatre exam tips created by fellow students that will help y...

Everything You Need to Get a 7 on IB Economics
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Economics exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Economics test prep so with the right strategies and IB Economics resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Economics Resources!! Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Economics! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Economics exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Economics exam tips created by fellow students th...

Everything You Need to Get a 7 on IB Computer Science
Hey there! This article is all about our tips for how to study for the IB Computer Science exam to get a solid 7. I'll break down the tricks, and IB Computer Science test prep so with the right strategies and IB Computer Science resources, nailing the exam is totally doable! Free IB Computer Science resources Hey, no worries if you're in a last-minute cramming session for IB Computer Science! We totally get it, and trust me, we've all been there too! So, if you're wondering how to ace the IB Computer Science exam when you're running out of time, here are some awesome resources and IB Computer ...
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
What Is an IB Extended Essay and How to Write It?
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker

You may also like

If topics seem too complex, turn to our top essay writers. They will accomplish any IB assignment in the best way your professor can evaluate it!
Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
The IB extended essay is a paper of up to 4,000 words that is required for students enrolled in the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program. The extended essay allows students to engage in independent research on a topic within one of the available subject areas.
The extended essay should be an original piece of academic writing that demonstrates the following student's abilities:
Check out this article by StudyCrumb to discover how to write an IB extendend essay properly. We will give you a complete writing guide and critical tips you need for this essay type.
An extended essay is independent research. Usually students choose a topic in consultation with a mentor. It is an integral part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) degree program. This means that you won't receive a degree without a successfully written paper. It requires 4,000-word study on a chosen narrow topic. To get a high score, you should meet all required structure and formatting standards. This is the result of approximately 40 working hours. Its purpose is giving you the opportunity to try independent research writing. It's approved that these skills are critical for student success at university. The following sections explain how to write an extended article with examples. So keep reading!
IB extended essay guidelines require supervisor meetings, totaling 3-5 hours. They include three critical reflections. A mentor won't write a paper instead of you but can help adjust it. So it is important to consult with them, but no one will proofread or correct actual research for you. In general, initially treat an essay as an exclusively individual work. So your role and contribution are maximal.
Let's take a look at how to write an extended essay outline. In this part, you organize yourself so that your work develops your idea. So we especially recommend you work out this step with your teacher. You can also find any outline example for essay . In your short sketch, plan a roadmap for your thoughts. Think through and prepare a summary of each paragraph. Then, expand annotation of each section with a couple more supporting evidence. Explain how specific examples illustrate key points. Make it more significant by using different opinions on general issues.
After you chose an extended essay topic and made an outline, it's time to start your research. Start with a complete Table of Contents and make a choice of a research question. Select the subject in which you feel most confident and which is most interesting for you. For example, if at school you are interested in natural science, focus on that. If you have difficulties choosing a research question, rely on our essay topic generator .
In the introduction of an extended essay, present a thesis statement. But do it in such a way that your readers understand the importance of your research. State research question clearly. That is the central question that you are trying to answer while writing. Even your score depends on how you develop your particular research question. Therefore, it is essential to draw it up correctly. Gather all relevant information from relevant sources. Explain why this is worth exploring. Then provide a research plan, which you will disclose further.
In accordance with extended essay guidelines, it's mandatory to choose and clearly state a methodological approach. So, it will be apparent to your examiner how you answered your research question. Include your collection methods and tools you use for collection and analysis. Your strategies can be experimental or descriptive, quantitative or qualitative. Research collection tools include observations, questionnaires, interviews, or background knowledge.
Well, here we come to the most voluminous part of the extended essay for IB! In every essay body paragraph , you reveal your research question and discuss your topic. Provide all details of your academic study. But stay focused and do it without dubious ideas. Use different sources of information to provide supporting arguments and substantial evidence. This will impress professors. For this section, 3 main paragraphs are enough. Discuss each idea or argument in a separate paragraph. You can even use supporting quotes where appropriate. But don't overcomplicate. Make your extended essay easy to read and logical. It's critical to stay concise, so if you aren't sure how to make your text readable, use our tool to get a readbility test . Following the plan you outlined earlier is very important. Analyze each fact before including it in your writing. And don't write unnecessary information.
Now let's move on to the final part of IB extended essay guidelines. In conclusion, focus on summarizing the main points you have made. No new ideas or information can be introduced in this part. Use conclusion as your last chance to impress your readers. Reframe your own strong thesis. Here you must show all key points. Do not repeat absolutely every argument. Better try to make this part unique. This will show that you have a clear understanding of the topic you have chosen. And even more professional will be recommendations of new areas for future research. One good paragraph may be enough here. Although in some cases, two or three paragraphs may be required.
To write an impressive extended essay, you should focus on appropriate information. You must create a separate page for bibliography with all sources you used. Tip from us: start writing this page with the first quote you use. Don't write this part last or postpone. In turn, appendices are not an essential section. Examiners will not pay much attention to this part. Therefore, include all information directly related to analysis and argumentation in the main body. Include raw data in the appendix only if it is really urgently needed. Moreover, it is better not to refer to appendices in text itself. This can disrupt the narrative of the essay.
We have prepared a good example of an extended essay. You can check it by downloading it for free. You can use it as a template. However, pay attention that your paper is required to be unique. Don't be afraid to present all the skills you gained during your IB.
In this article, we presented detailed IB extended essay guidelines. An extended essay is a daunting academic challenge to write. It is a research paper with a deep thematic analysis of information. But we have described several practical and straightforward tips. Therefore, we are sure that you will succeed!
- Formulating a research question
- Conductig independent investigation
- Presenting key findings in a scholarly format.
IB Extended Essay: What Is It?
Choosing a mentor for extended essay, extended essay outline, extended essay: getting started, extended essay introduction, extended essay methodology, extended essay main body, extended essay conclusion, extended essay bibliography & appendices, extended essay examples, final thoughts on ib extended essay.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
What is the IB Extended Essay?
What’s covered:, overview of the ib program, what is the extended essay (ee), what is the extended essay supervisor, when is the extended essay due.
- How is The Extended Essay Scored?
The International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme (IB or IBDP) is a curriculum with examinations and assessments to test students’ knowledge. Understanding IB as a curriculum is imperative to learning more about the extended essay (EE), the research paper required to earn the diploma.
IB is scored out of a total of 45 attainable points, with 42 being from six subjects, each worth a maximum of seven points. Those seven points are attained from a combination of internal and external assessments and numerous papers for each subject. The remaining three points come from what IB calls its “core,” which is the extended essay, theory of knowledge, and CAS (creativity, activity, and service). Passing the core is essential to receiving the diploma, even if you have a good score without the extra three points.
The extended essay is a mandatory component of the core, but it’s more like a practical approach to undergraduate-level research papers, giving students a chance to research any of the six subjects they’ve selected in their IB journey to a greater degree.
Students spend the first few weeks of their IB curriculum choosing a subject to write their EE on. For the sake of examples, let’s break down the EE in the perspective of a student who had chosen Chemistry HL (Higher Level).
You’d start by choosing a topic to analyze for your EE. Topics should focus on a very specific application of knowledge, making the paper as detailed as possible. For example, a topic could be “The effects of sugar-free gum on the pH of saliva in the mouth.” The idea is to create a specific topic that allows you to not only stand out from other IB candidates, but to also help you explore something you’d personally want to invest time into. Your topic is also your title for the EE.
After creating a descriptive focal point for your EE, the next step is collecting data and carrying out the scientific process of forming a hypothesis just like any other research paper. Collecting data that is irrelevant to your experiment/research and goes unused is actually harmful to the scoring of your EE, so make sure you stay on track of what you need and don’t.
After collecting data, compiling into the 4000 word essay is difficult but can be an enjoyable process if you let it be. Finding creative ways to present your findings using graphs and media can be not only great ways to earn extra points but also teach you more about how to create a quality research paper. After all, the point of the EE is to prepare you for college-level research paper writing. Make sure to structure the essay in a way where the body of the essay constitutes the majority, discussing and referencing back to a research question and your data throughout the paper.
For a better understanding of the timeline for your EE, refer to the following:
Note that this isn’t the only usable timeline, just an example, as there isn’t a due date set by the IB Board themselves.
You’ll receive support and guidance from an appointed EE supervisor. This person is usually a teacher for the subject you’ve selected. In the case of our previous example, it’d be your chemistry teacher. There are also mandatory reflection sessions, where students log their progress in their work and prove gradual completion of their EE over time.
Consistent checking for plagiarism is also done by the supervisor. The final session is called a viva voce and it’s an interview that will be recorded and sent to the IB Board for inspection. Your viva voce is considered when grading your EE. Your supervisor is someone you’ll be in constant, back and forth communication with, so choosing an advisor you know wants the best for you is important.
The EE doesn’t come with an externally set due date from the Board. Instead, the school creates and sets it for students. It’s important to understand that IB takes and considers the school’s due date, so make sure to adhere to it. Failing to meet your school’s due date could result in an instant fail from the board. As for a school’s selection for the date, it varies, but you can use the timeline above and make sure to adjust relative to a planned due date and you’ll be fine!
No matter the date, make sure to start as early as possible because IB consists of difficult and long tasks other than the EE, like theory of knowledge and even occasional internal exams. Starting early relieves you of stress in the long-term, and will definitely prove to be beneficial!
How is the Extended Essay Scored?
IB is scored out of a total of 34 points, with there being five letter grades attributed to a boundary. The following table details the boundaries as of 2021, but new boundaries may be released, so it’s important to refer to the IB board or your school for updates.
With the EE comes CAS and theory of knowledge, the other components of the core. Scoring well in the core’s three points is important to getting the diploma and passing IB as well, the following table details the scoring procedure for the core of IB.
While IB scores are important to receive the diploma, it’s good to know your actual scores don’t determine your chances of college admissions as much as you might think. It’s actually more important to take the IB classes pertaining to your future major, and show work ethic by signing up for difficult courses. For more insight into college admissions and your chances, use CollegeVine’s admissions calculator !
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

International Baccalaureate/Extended Essay Tips
- 1.1 Recommendations
- 1.2.1.1 Essay Competitions
- 1.3.1 Citing Sources
- 1.3.2 Organization
- 1.3.3 IBO Official Guide
Introduction and Getting Started!
Start Working NOW!
The Extended Essay (EE) is one of the requirements of the IB Diploma Programme. It provides students with an opportunity to conduct independent research on a topic of interest to them. It is written on a freely-chosen topic as long as there is a subject teacher in school, as the candidate must have a subject supervisor.

Recommendations
The IBO recommends that candidates spend approximately 40 hours in total on their extended essays, and if you put it off until that last weekend, your work won't be nearly as good as it can be. Talk to your IB school supervisor, as it is his or her job to set internal school deadlines (i.e. choosing a topic, formulating an outline, rough draft, final draft, etc).
Getting Started
- Firstly, find a topic you're actually interested in, or you'll never work on it.
- Don't stress. After doing all your research 4,000 words is nothing (your first draft could be 6,000-8,000 words). While the Extended Essay has the potential to make you hate your own topic (as many academic assignments do), an interest in the topic can motivate you to pull through in the end.
- Many students are appalled at the sheer number of words that this task requires. But by following the guidelines set out for you, you'll quickly realize how hard pressed you will be to contain your work to the limit.
- Make sure that your focus is somewhat specific, or that you have a specific topic in mind (instead of just a general subject area).
- Example : Your final essay title should be somewhat similar to the style used in the Internal Assessments for the 20th Century World Issues course - specific and focused with some form of cause and effect. Check the official Extended Essay guidelines for more on this - it offers sample essay titles (along with title choosing advice and essay titles to avoid) for each subject area.
- If the above example does not apply to you, perhaps ask your IB Coordinator for examples from students past. Many of them keep a record of every essay, mainly to ensure there is no plagiarism.
- Make sure you stay on top of the work.
- Look over the guidelines and the explanations.
To get a diploma, you need to complete the TOK Essay and the Extended Essay. At best, you can achieve 3 bonus points towards your IB diploma, so don't ignore your schoolwork, as your courses are worth much more. The point matrix is outlined in the "Diploma Points Matrix for the Extended Essay and TOK" grid in the IBO form. You can still get your diploma if you get a "Mediocre" on one and an "Elementary" on another. NOTE: As of May 2010, an 'Elementary' on both TOK and Extended essay is an automatic fail, but you may still pass with an 'Elementary' on either one, just not both. An 'Elementary' on either is a so called 'failing condition' which requires a minimum 28 points rather than the usual 24 to obtain your diploma.
However, you can make a very good essay, provided you allot yourself enough time to write about something you are interested in. The IBO knows that you are between 16 and 18 years old and thus does not require a perfect essay or a groundbreaking new discovery. They just want to see that you can work on and complete a big project.
Picking a Topic
You'll want to write about a topic or subject you're fairly familiar with. For instance, if you've nailed the process of writing labs, do a science investigation. It'll be just like a big lab write-up, and writing the method, materials, qualitative/quantitative observations are all part of the word count, and take up a significant amount of words.
Essay Competitions
Find out if there are competitions or scholarship opportunities in which you can enter your essay. Why not kill two birds with one stone and head off to university with a scholarship? If you don't win, at least you'll get feedback, something the IBO neglects to give.
Writing a Good Extended Essay
Everyone wants to write a good Extended Essay, but just remember that it's really not as overwhelming as it sounds. Some candidates will find their first drafts are in the 6,000 to 8,000 range, while others will reach about 2800-3500. In fact, keep in mind that 4,000 words is the maximum word count and not where you must get to. While most essays have a word count in the 3,900 range, it is perfectly acceptable to submit an essay that is 3,500 words. While there is no actual minimum word count, you would probably want to write over 3,000 words, since a short essay might imply that the topic was not investigated thoroughly enough. However, some topics - mathematics among them - may require only 2,000 words to fully investigate them.
Citing Sources
Keep legible, consistent and accurate notes that include bibliographic information. There's nothing more annoying than browsing through a 1200 page book looking for where that key quotation came from. Cite your sources in a consistent manner (either in MLA or APA format, or some other recognized format). IBO is very strict with plagiarism, so remember that the text has to be your own and do not forget to make references. You will have to sign an IBO form certifying that your EE is your own, and has no unsourced material in it, before they will even read your essay. Failure to submit an Extended Essay will result in no diploma being awarded.
Use the internet to find information but do include books in your research especially if your essay is not on the Sciences. Be skeptical in your use of the internet. Anyone can post anything, so read with a critical eye. Generally, university and academic websites are good sources to refer to. News sources are generally reliable, but be sure to stay away from "gossip" media which often contorts the truth.
Keep in mind that a general guide line used in many schools is 5 sources minimum for the IA in History, so if you are doing a History paper aim to have as close to ten sources as possible if not more for the EE.
Organization
Once you have researched your topic, you should spend a lot of time structuring and organizing your essay. Make sure your essay has a clear introduction, research question/focus (i.e. what you will be investigating), body, and conclusion. A poorly organized or unclear essay will hurt the assessment of your essay. You should also spend some time making sure that your 300-word abstract is clear and succinct in summarizing your essay. An unclear abstract will make your essay difficult to understand and will also hurt the assessment of your essay.
Although this is stated in the "General Requirements" for the Extended Essay, I feel it is necessary to repeat: if you are doing a paper in a subject not offered at your school, be very careful , especially if doing your paper in World Religions. You might want to either reconsider your choice of topic, or make sure you have several people with good credibility in that topic reading your paper. If you don't, especially in World Religions, you could end up offending your reader, and I promise you, you do not want to do that.
You can do your extended essay on any topic for which an IB class exists - i.e. something like Islamic History, which only about 100 candidates a year write about. However, you cannot do your extended essay in Theory of Knowledge, most pilot subjects and school-based syllabus subjects (check with your IB coordinator). Bear in mind that getting a good score in your extended essay, combined with your score for your Theory of Knowledge essay, may reward you with up to 3 bonus points. So aim high!
IBO Official Guide
The IBO's official guide to writing the Extended Essay can be found here: http://xmltwo.ibo.org/publications/DP/Group0/d_0_eeyyy_gui_1012_1/html/production-app3.ibo.org/publication/258/part/1/chapter/1.html
The above site is quite useful in perusing tips and hints for writing the essay, in addition to viewing the IBO standards for the essay. Note that the above link is for consideration purposes only.
"three: The Ultimate Student's Guide to Acing the Extended Essay and Theory of Knowledge" by Alexander Zouev - a book full of tips and time savers for IB EE.
- Book:International Baccalaureate
Navigation menu
- – Curriculum Overview
- – IB Middle Years, 11-16
- – IB Diploma, 16-18
- – Personal Learning
- – Digital Leadership
- —> IB Science
- —> IB Mathematics
- —> IB Arts
- —> IB Design
- —> IB Individuals and Societies
- —> IB PHE
- —> IB Language and Literature
- – Student Life
- – Extra-Curricular Activities
- – Explorations
- – Wellbeing
- – Lunch at Halcyon
- – Graduate Destinations
- – Our Alumni Programme
- – University and Careers Counselling
- Meet the Team
- Join the Team
- – Apply
- – Fees
- – Bursary
- Visit Halcyon
- Support the Bursary Programme
- Matched Funding Campaign 2024
- Term Dates & Calendar
Why the IB Extended Essay is so important – and why all students should do one
What is the purpose of education? The International Baccalaureate Organisation (IBO) aims, through its educational programmes, to create well-rounded citizens: to provide frameworks that allow students to learn through thinking, experiencing, and doing. This approach nurtures young people to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and planning skills - all key to the future of our students. What role does the Extended Essay play in this?
While classroom lessons and IB exams can nurture and measure these faculties with greater success than other curricula, conducting a full assessment of young peoples’ ability to plan, research, investigate, and come to complex conclusions - especially when they approach university - requires a purpose-built assessment. It is this kind of assessment that is missing from our national curriculum. However, students of the IB Diploma Programme (aged 16-18), must complete an Extended Essay to graduate. We spoke to our Extended Essay Project Coordinator, Sonja Bartholomew, and IB DP Coordinator, Lori Fritz, to find out why this is such an essential step in our students’ academic development.
Here’s why all students should complete an Extended Essay.

What is the IB Extended Essay?
The IB Extended Essay is a 4000 word essay, completed during the IB Diploma Programme, which lasts between the ages of 16-18 (Year 12-13/Grade 11-12).
An Extended Essay begins from a question, posed and selected by the student, that involves looking at a topic from a theoretical angle, in addition to: “extensive research, thorough investigation, scientific assessment, or an in-depth exploration of secondary resources,” explained Sonja Bartholomew.
Whilst challenging, students find that the Extended Essay is a greatly enjoyable opportunity to focus on one of their interests while acquiring practical skills that they can directly apply in their their future careers. Students pursue a topic that relates to one of their chosen six subjects - or, if a student find that their interests are especially disciplinary, they can choose to ‘world studies’, which is a combined topic related to two of their subject choices.
An extended project: the only way to assess a range of skills
We asked our IB DP Coordinator Lori Fritz why the IB Extended Essay has remained at the core of the IB Diploma Programme since 1978.
“Having a mandatory longer piece of work in the curriculum, such an Extended Essay, is essential so that educators are able to formally assess skills that aren’t just based on students’ ability to fulfil an exam syllabus,” Lori shared.
We can see why the inclusion of the Extended Essay allows the International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme to produce a fully well-rounded education for its students, and why a similar requirement in other curricula - such as the national curriculum, which lacks any assessment of critical thinking throughout - should be considered.

Extended Essays and the future: gaining real-life career knowledge and skills
Beyond supporting Diploma students in developing the general skillset they will need for university and beyond, the IB Extended Essay encourages students to think about the specific skills and knowledge that they might need for the career or academic discipline they aspire to pursue.
Completing an Extended Essay in medicine, for example, not only allows students to embark on research in that field at a young age, but provides them with an opportunity to “learn and practice scientific skills and gain experience in medical citation patterns”, as Lori Fritz explained.
At Halcyon, our students have engaged in research with real-world implications for their Extended Essays, developing skills that will take them far into the future in the process. One student, for example, studied how we can predict the movement of plastics through seas with the assistance of Markov Chains (a mathematical model) to make predictions about the aquatic environment. Another conducted a dual environmental and economic study of wind farms in Grimsby, measuring the physical output of energy that they created and providing an economic justification for their proliferation.
Sonja Bartholomew explained, the EPQ, or Extended Project Qualification, which is an extended piece often taken alongside A-Levels, may “allow students to explore something they are interested in, but it is optional. A-Level students are not required to seriously think about how they might want to take their interests to the next level through academia or beyond.”
Why students should study the IB Diploma Programme
“Arguably, other curricula should have a mandatory assessed piece of longer work to ensure students are developing these crucial skills, but the International Baccalaureate is the only curriculum that has such a future-facing philosophy at its core,” explained Lori Fritz. The IB’s mission - to “develop inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people who help to create a better and more peaceful world” - has created a robust, educational framework that prepares our students for the future. In that sense, it is like no other, and Halcyon is proud to be an IB-accredited international school in London.
IB Student Profile: Lola, Grade 12, on the Diploma Programme
3 ways in which the IB prepares students for Oxbridge: an interview with Cambridge graduates
How the IB prepares students for university: an interview with Asil Al-Shammari
Breaking Down the Extended Essay: Guidance and Support from IB Tutors
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program is a hallmark of rigorous academic standards, emphasizing critical thinking, inquiry, and interdisciplinary learning. Central to the IB diploma i s the Extended Essay (EE), a substantial piece of independent research and writing undertaken by students under the guidance of a supervisor. This blog delves into the various facets of the Extended Essay, its purpose, components, and significance within the IB curriculum.
- Introduction to the Extended Essay
- Purpose of the Extended Essay
- Components of the Extended Essay
- Selecting a Perfect Topic for IB Extended Essays
- Importance of Writing an Extended Essay for an IB Diploma
- The Role of IB Tutors in Supporting Extended Essays
- Addressing Common Concerns in the Extended Essay Process
- Tips for Writing an Extended Essay
- How to Find the Best IB Tutors for Guidance
What are extended essays for IB diploma?
The Extended Essay serves as a cornerstone of the IB diploma, providing students with an opportunity to engage in in-depth inquiry and research on a topic of their choice. At its core, the Extended Essay is an exercise in independent study, where students develop essential skills such as critical thinking, research methodology, and academic writing.
Unlike standard academic essays, the Extended Essay demands more intellectual engagement and originality. It encourages students to explore topics beyond the confines of the classroom curriculum, fostering intellectual curiosity and a passion for learning.
What is the purpose of an extended essay?
The primary purpose of the Extended Essay is multifaceted:
- Academic Exploration: It allows students to delve into a subject area of personal interest, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the chosen topic.
- Research Skills Development: Through the Extended Essay process, students hone their research skills, including information gathering, analysis, and synthesis, preparing them for higher education and beyond.
- Critical Thinking and Reflection: The Extended Essay encourages students to critically evaluate sources, analyze information, and present coherent arguments, fostering a habit of critical inquiry and reflection.
- Preparation for University-Level Study: Engaging in an extended research project equips students with the academic skills and resilience needed for success in tertiary education.
Also read, A Beginner’s Guide to the International Baccalaureate (IB) in High School | Rostrum Education
What do we have to write in an extended essay?
In an extended essay for the IB diploma, students are required to write a formal academic research paper on a topic of their choice within one of the subjects offered by the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. The extended essay should demonstrate the student’s ability to engage in independent research, analyze information critically, and present coherent arguments supported by evidence. Key components of an extended essay include:
- Title Page: The title page includes essential information such as the essay title, the student’s name, the candidate number, the subject in which the essay is registered, and the session (month and year) of the examination.
- Abstract: The abstract provides a concise summary of the essay, outlining the research question, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. It typically does not exceed 300 words.
- Table of Contents: The table of contents lists the various sections and subsections of the essay, along with corresponding page numbers, facilitating navigation and accessibility.
- Introduction: The introduction sets the context for the research, presents the research question or hypothesis, and outlines the scope and structure of the essay.
- Main Body: The main body of the essay encompasses the core content, including a literature review, analysis, discussion of findings, and critical evaluation of sources.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the key findings, restates the research question, and reflects on the implications of the research.
- References and Bibliography: The references section lists all sources cited in the essay, following a specific citation style (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago). The bibliography includes additional sources consulted during the research process.
How to select a perfect topic for IB extended essays?
Selecting a suitable topic for an IB extended essay is crucial for a successful research endeavor. Here are some tips to help students choose a perfect topic:
- Personal Interest: Choose a topic that genuinely interests you and aligns with your passions, hobbies, or academic pursuits. Your enthusiasm for the topic will fuel your motivation throughout the research process.
- Narrow Focus: Select a topic that is specific enough to allow for in-depth analysis within the word limit of the extended essay. Narrowing down the scope of your topic will help you explore it comprehensively and avoid being too broad or vague.
- Feasibility: Consider the availability of resources, access to relevant information, and the feasibility of researching your chosen topic. Ensure that you can access credible sources, data, and materials to support your research.
- Relevance to Subject: Your topic should be relevant to one of the subjects offered in the IB program. Choose a subject area where you have a strong foundation of knowledge and understanding, and where you can apply critical thinking skills to explore complex issues.
- Researchable Question : Formulate a clear and focused research question that can be effectively investigated through research and analysis. Your research question should be open-ended, allowing for the exploration and interpretation of different perspectives and arguments.
- Consultation : Seek guidance from your IB supervisor, teachers, or subject experts when selecting a topic. They can provide valuable insights, suggest potential research questions, and help you refine your topic based on feasibility and academic rigor.
- Originality : Aim for originality and innovation in your topic selection. Consider exploring emerging trends, interdisciplinary connections, or unexplored areas within your subject of interest.
Importance of Topic Selection and Research Question Formulation
Central to the success of the Extended Essay is the selection of a relevant and engaging research topic. The process of topic selection is both challenging and rewarding, requiring students to consider their interests, academic strengths, and the availability of credible sources.
A well-formulated research question serves as the guiding beacon of the Extended Essay, directing the trajectory of the research and shaping the subsequent analysis and discussion. A compelling research question is:
- Focused: It addresses a specific issue or problem within the chosen subject area, avoiding overly broad or vague topics.
- Feasible: It can be adequately explored within the scope of the essay, considering time constraints and resource availability.
- Significant: It explores a topic of genuine interest and relevance, contributing to existing scholarly discourse or addressing real-world challenges.
- Open to Interpretation: It invites critical inquiry and analysis, allowing multiple perspectives and interpretations.
In essence, topic selection and research question formulation is a critical first step in the Extended Essay journey, laying the foundation for meaningful inquiry and scholarly exploration.
Why do we need to write an extended essay for an IB diploma? Why is it important?
Writing an extended essay is a crucial component of the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program, and it serves several important purposes:
- Developing Research Skills: The extended essay provides students with an opportunity to engage in independent research and inquiry-based learning. It helps students develop critical thinking skills, research methodologies, and the ability to analyze and evaluate complex issues.
- Preparation for Higher Education: The skills acquired through the extended essay, such as research, analysis, and writing, are highly valued in higher education. Completing an extended essay prepares students for the academic rigor of university-level studies and enhances their ability to undertake independent research projects.
- Exploration of Personal Interests: The extended essay allows students to explore topics of personal interest within their chosen subject area. It encourages students to pursue their passions, delve deeper into specific areas of study, and develop a deeper understanding of topics beyond the standard curriculum.
- Demonstrating Intellectual Curiosity: Engaging in the extended essay demonstrates a student’s intellectual curiosity, initiative, and commitment to academic excellence. It showcases a student’s ability to formulate research questions, gather and analyze data, and communicate findings in a coherent and structured manner.
- Holistic Assessment: The extended essay is one of the core components of the IB diploma program and is assessed according to established criteria. It contributes to the holistic assessment of students’ academic abilities and is considered alongside other components such as internal assessments, external examinations, and the Theory of Knowledge (TOK) essay.
- Encouraging Critical Reflection: Through the process of writing the extended essay, students engage in critical reflection on their own learning journey, research methodologies, and academic achievements. It fosters self-awareness, self-assessment, and a deeper understanding of the research process.
Here’s an interesting read: Cracking the Code: What IB Score Opens the Doors to Oxbridge Admission – Rostrumedu
Challenges Faced by Students
Undertaking the Extended Essay presents a unique set of challenges for students within the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. From the initial stages of topic selection to the final submission of the completed essay, students encounter various hurdles that demand resilience, critical thinking, and effective time management. This section explores the common challenges faced by students throughout the Extended Essay process and offers insights into overcoming these obstacles.
Identifying Suitable Research Topics
One of the initial hurdles students encounter is the daunting task of identifying a suitable research topic for their Extended Essay. The process of topic selection requires careful consideration of personal interests, academic strengths, and the availability of credible sources. However, students often struggle with:
- Narrowing Down Broad Interests: Many students possess diverse interests across multiple subject areas, making it challenging to narrow down a research topic that aligns with their passions and academic strengths.
- Navigating Complex Subject Matter: Certain subject areas, such as history or economics, encompass vast and complex topics, making it difficult for students to identify specific research questions that are both manageable and meaningful.
- Balancing Personal Interest and Academic Rigor: While it is essential to choose a topic that resonates with personal interests, students must also consider the academic rigor and relevance of their research question within the context of the Extended Essay.
Formulating a Clear Research Question
At the heart of the Extended Essay lies the research question—a succinct and focused inquiry that guides the trajectory of the student’s investigation. However, formulating a clear and compelling research question poses significant challenges, including:
- Clarity and Specificity: Crafting a research question that is clear, specific, and narrowly defined can be challenging, especially when navigating complex subject matter or interdisciplinary topics.
- Achieving Balance: Striking the right balance between breadth and depth is crucial. A research question that is too broad may lack focus and coherence, while one that is too narrow may limit the scope of inquiry and available resources.
- Aligning with Assessment Criteria: Students must ensure that their research question aligns with the assessment criteria outlined by the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO), including relevance, academic rigor, and the ability to engage critically with the chosen topic.
Managing Time Effectively
The Extended Essay is a long-term project that unfolds over several months, requiring students to manage their time effectively and adhere to deadlines. However, time management remains a significant challenge for many students, manifesting in:
- Procrastination and Time Pressure: Procrastination often leads to last-minute rushes and heightened stress levels, compromising the quality of research and writing.
- Balancing Academic and Extracurricular Commitments: IB students juggle multiple academic subjects, extracurricular activities, and personal responsibilities, making it challenging to allocate sufficient time and energy to the Extended Essay.
- Navigating Unforeseen Challenges: Unexpected setbacks, such as technical issues, illness, or changes in personal circumstances, can disrupt the Extended Essay timeline, requiring students to adapt and readjust their schedules accordingly.
Handling Research Methodologies and Sources
Conducting rigorous and methodical research is a fundamental aspect of the Extended Essay process. However, students often encounter challenges related to research methodologies and sources, including:
- Navigating Information Overload: The abundance of information available in digital databases, scholarly journals, and online repositories can be overwhelming, requiring students to develop discernment and critical evaluation skills.
- Ensuring Academic Integrity: Students must adhere to principles of academic integrity, including proper citation practices, avoidance of plagiarism, and ethical use of sources.
- Accessing Credible Sources: Access to relevant and credible sources may vary depending on the subject area and the availability of resources in the student’s geographical location, posing challenges in conducting comprehensive research.
Role of IB Tutors
In the complex landscape of the International Baccalaureate (IB) program, IB tutors play a pivotal role in guiding and supporting students through the Extended Essay (EE) process. As mentors, facilitators, and subject matter experts, IB tutors offer invaluable assistance and expertise, empowering students to navigate the challenges of independent research and academic writing. This section examines the multifaceted role of IB tutors and their significance in facilitating student success in the Extended Essay.
Role of IB Tutors in the Extended Essay Process
IB tutors serve as experienced guides and mentors who provide personalized support and guidance to students undertaking the Extended Essay. Their role encompasses various responsibilities, including:
- Providing Subject-Specific Expertise: IB tutors possess specialized knowledge and expertise in their respective subject areas, allowing them to offer targeted guidance and feedback tailored to the requirements of the Extended Essay.
- Offering Academic Support: Tutors assist students in clarifying research topics, formulating research questions, developing research methodologies, and refining academic writing skills.
- Navigating Assessment Criteria: IB tutors help students understand and navigate the assessment criteria outlined by the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO), ensuring that their Extended Essays meet the required standards of academic rigor and excellence.
- Fostering Critical Thinking: Tutors encourage students to engage critically with their chosen topics, challenge assumptions, explore alternative perspectives, and develop analytical reasoning skills.
- Providing Emotional Support: Beyond academic guidance, tutors offer emotional support and encouragement, helping students navigate the highs and lows of the Extended Essay journey with resilience and confidence.
Also check out Rostrum offers IB tutoring for international admissions.
Providing Guidance on Topic Selection and Research Question Formulation
One of the primary functions of IB tutors is to assist students in selecting suitable research topics and formulating clear and focused research questions. Tutors support students by:
- Facilitating Brainstorming Sessions: Tutors engage students in brainstorming sessions to explore potential research topics, identify areas of interest, and narrow down viable research questions.
- Offering Feedback and Suggestions: Tutors provide constructive feedback and suggestions to help students refine their research topics, ensuring alignment with academic interests, feasibility, and academic rigor.
- Guiding Literature Review: Tutors guide students in conducting preliminary literature reviews, identifying key scholarly sources, and evaluating the relevance and credibility of existing research within their chosen field of inquiry.
Assisting with the Development of Research Methodologies
Developing a robust research methodology is essential for the success of the Extended Essay. IB tutors support students by:
- Exploring Research Approaches: Tutors introduce students to various research methodologies, including qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method approaches, helping them select the most appropriate methods for their research questions.
- Providing Methodological Guidance: Tutors offer guidance on data collection techniques, sampling methods, data analysis procedures, and ethical considerations, ensuring methodological rigor and integrity.
- Facilitating Access to Resources: Tutors assist students in accessing relevant research materials, databases, and scholarly journals, helping them navigate the complexities of academic research and information retrieval.
Offering Feedback and Support Throughout the Writing Process
As students progress through the Extended Essay journey, IB tutors offer ongoing feedback and support to facilitate continuous improvement and refinement. Tutors:
- Review Drafts and Provide Feedback: Tutors review draft chapters, sections, and outlines of the Extended Essay, offering feedback on clarity, coherence, structure, argumentation, and adherence to academic conventions.
- Facilitate Revision and Editing: Tutors guide students through the process of revising and editing their work, helping them strengthen arguments, refine language, and polish their writing style.
- Addressing Challenges and Obstacles: Tutors provide guidance and support to students facing challenges or obstacles during the writing process, offering strategies for problem-solving, time management, and stress reduction.
Helping Students Understand and Meet Assessment Criteria
Understanding and meeting the assessment criteria outlined by the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO) is essential for achieving success in the Extended Essay. IB tutors:
- Clarify Assessment Expectations: Tutors help students understand the assessment criteria, including criteria for research, analysis, presentation, and reflection, ensuring alignment with academic standards.
- Provide Exemplars and Examples: Tutors share exemplar Extended Essays and examples of high-quality work, helping students gain insights into effective approaches, structures, and presentation formats.
- Offer Strategies for Meeting Criteria: Tutors offer practical strategies and tips for meeting the assessment criteria, emphasizing the importance of coherence, depth of analysis, originality, and academic integrity.
In essence, IB tutors play a central role in supporting students throughout the Extended Essay process, offering guidance, expertise, and encouragement at every stage of the journey. Through their mentorship and support, tutors empower students to navigate the complexities of independent research and academic writing with confidence and competence, fostering intellectual growth and academic excellence within the IB program.
Addressing Common Concerns
As students embark on the challenging journey of the Extended Essay (EE), it is essential to address common concerns that may arise during the research and writing process.
Balancing Academic Integrity with Support from Tutors
- Clarifying Academic Integrity Expectations: Communicate the expectations regarding academic integrity to both students and IB tutors. Emphasize the importance of originality and the prohibition of plagiarism while encouraging collaboration within ethical boundaries.
- Educating Tutors on Ethical Guidelines: Guide IB tutors on the ethical guidelines and expectations set by the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO). Ensure that tutors are aware of their role in supporting students while upholding academic integrity.
- Encouraging Transparent Collaboration: Foster an environment where students feel comfortable discussing their collaboration with IB tutors openly. Encourage them to document the nature of the support received in their reflections, ensuring transparency in the Extended Essay process.
Academic Resources and Material Accessibility
- Digital Resource Accessibility: In an increasingly digital world, ensure that students have access to online academic resources and databases. Collaborate with the school’s library and administration to provide digital subscriptions and ensure that students can navigate online research effectively.
- Library and Physical Resources: Recognize that not all students may have equal access to physical resources, such as a well-equipped library. Implement measures to address this, such as extending library hours, creating resource-sharing platforms, or providing alternative access points.
What are some tips for writing an extended essay?
- Choose a topic you are passionate about and genuinely interested in exploring further.
- Start your research early to allow for sufficient time to gather information, analyze sources, and refine your ideas.
- Develop a clear research question that is specific, focused, and allows for in-depth investigation.
- Create a well-organized outline or plan to structure your essay and ensure a logical flow of ideas.
- Use a variety of credible sources, including books, academic journals, primary documents, and reputable websites.
- Maintain academic integrity by accurately citing all sources and avoiding plagiarism.
- Engage in critical analysis and evaluation of sources and arguments to develop your own perspective.
- Revise and edit your essay carefully to improve clarity, coherence, and overall quality of writing.
- Seek feedback from your supervisor or peers to gain different perspectives and identify areas for improvement.
- Stay focused and manage your time effectively to meet deadlines and produce a high-quality essay.
Also read, How to crack IB Exam – Rostrumedu
How do I find the best IB tutors for guidance?
Finding the best IB tutors for guidance in your extended essay and other aspects of the IB program requires careful consideration and research. Here are some steps to help you find suitable IB tutors:
- Ask for Recommendations: Seek recommendations from teachers, classmates, or friends who have experience with IB tutors. They can provide valuable insights into the quality of tutoring services and the effectiveness of individual tutors.
- Online Platforms: Explore online tutoring platforms and websites that specialize in connecting students with qualified tutors. Look for platforms that specifically cater to IB students and offer tutors with expertise in IB subjects and extended essay.
- IB Community Forums: Join online forums, discussion boards, or social media groups dedicated to the IB program. Engage with fellow students and alumni to ask for recommendations or insights on reputable IB tutors in your area or online.
- Check Credentials: When evaluating potential IB tutors, review their credentials, qualifications, and teaching experience. Look for tutors who have a strong background in the IB curriculum, subject expertise, and a track record of helping students achieve academic success.
- Interview Potential Tutors: Take the time to interview potential tutors to assess their teaching style, approach to tutoring, and compatibility with your learning needs and preferences. Ask about their experience working with IB students, their tutoring methods, and their availability for regular sessions.
- Trial Sessions: Consider scheduling trial sessions with different tutors to gauge their teaching effectiveness and rapport with you. Use these sessions to assess the tutor’s ability to explain concepts clearly, provide constructive feedback, and support your academic goals.
- Feedback and Reviews: Seek feedback and reviews from previous students or parents who have worked with the tutor. Positive testimonials and reviews can provide valuable insights into the tutor’s teaching style, communication skills, and ability to support students throughout the IB program.
By following these steps and conducting thorough research, you can find the best IB tutors who can provide personalized guidance, support, and mentorship to help you excel in your IB studies, including your extended essay. Rostrum connects students with experienced and qualified tutors specializing in the IB curriculum. These tutors have a deep understanding of the specific requirements and challenges of the IB diploma program, including the extended essay. They can offer personalized guidance, share effective study strategies, and provide constructive feedback on the extended essay, contributing to a student’s overall success in the IB program.
JOIN THE ROSTRUM COMMUNITY
Contact us today.

Extended Essay: Purpose
- Extended Essay- The Basics
- Step 1. Choose a Subject
- Step 2. Educate yourself!
- Using Brainstorming and Mind Maps
- Identify Keywords
- Do Background Reading
- Define Your Topic
- Conduct Research in a Specific Discipline
- Step 5. Draft a Research Question
- Step 6. Create a Timeline
- Find Articles
- Find Primary Sources
- Get Help from Experts
- Search Engines, Repositories, & Directories
- Databases and Websites by Subject Area
- Create an Annotated Bibliography
- Advice (and Warnings) from the IB
- Chicago Citation Syle
- MLA Works Cited & In-Text Citations
- Step 9. Set Deadlines for Yourself
- Step 10. Plan a structure for your essay
- Evaluate & Select: the CRAAP Test
- Conducting Secondary Research
- Conducting Primary Research
- Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Presentation Requirements
- Evaluating Your Work
The CRAAP Test - Purpose
Purpose: the reason the information exists.
- What is the purpose of the information? Is it to inform, teach, sell, entertain or persuade?
- Do the authors and/or sponsors make their intentions or purpose clear?
- Is the information fact, opinion or propaganda?
- Does the point of view appear objective and impartial?
- Are there political, ideological, cultural, religious, institutional or personal biases?
On this page you can learn:
Why you need to check for objectivity - and how to do it How to think about the intentions and purpose of a website (an example) How to think about the purpose and bias of the information on a website (two examples)
Checking for Objectivity

- Does the information show a minimum of bias?
- Is the page designed to sway opinion?
- Is there any advertising on the page?
Why? Because:
- Frequently the goals of the sponsors and/or authors are not clearly stated.
- Often the Web serves as a virtual "soap box" where the speaker stands and delivers an appeal, speech, or rant on some political topic
Do the Authors Make Their Purpose Clear?
Sometimes you will need to dig beneath the surface to find the purpose of a website.
The Life Happens website, for example, describes itself as a nonprofit organization that can help consumers make smart insurance decisions. It does provide a lot of information on different types of insurance, but as you explore the site you will find it also provides links to the insurance agents who belong to the insurance groups who finance the site.
So, what do you think - is the purpose of this site to inform, teach, sell, entertain or persuade?
A good resource should make it's intentions and purpose clear.

Is There Any Bias to the Information?
When you find resources, it is important to understand the purpose of the information.
Is the information aiming to inform, teach, sell, entertain or persuade?
Organizations (their web address may end .org) often have a purpose or a mission so their information may be biased. Bias is not necessarily a negative factor, you just need to be aware of it.
Both the websites below have very different purposes and a different bias but they are both valid sites and could both contain useful information for a project or essay.

- << Previous: Accuracy
- Next: Step 12. Do the Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 2, 2024 1:39 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westsoundacademy.org/ee
Extended Essay Writers

How to Write an Introduction for Your IB Extended Essay?

Luke MacQuoid
I’ve seen my fair share of Extended Essays (EE) as a seasoned IB writer. The IB Extended Essay introduction, in particular, can be a make-or-break element. So, let’s get right into the art of EE introduction crafting, a skill crucial for any aspiring IB student.
The Purpose of the IB Extended Essay Introduction
The purpose of the IB Extended Essay introduction goes much further than just starting your paper. As an experienced IB writer, I can confidently say that this part is crucial to capturing your reader’s interest and setting the tone for your entire essay. It’s your first opportunity to make an impression and pique your reader’s curiosity.
In EE introduction writing, your primary objective is to present your research question and thesis in a clear, concise, and intriguing manner. It is where you lay the groundwork for your argument and outline the scope of your investigation. It’s about framing your research to make your reader think, “This is a path I want to take.”
Moreover, the introduction should establish the relevance of your topic. Why is this research important? How does it contribute to the field? In the IB Extended Essay, where independent research plays a central role, showing the significance of your work is crucial. Your introduction should echo the importance of your topic and its contribution to your field of study.
Tips on How to Write IB Extended Essay Introduction
Writing an introduction for your IB Extended Essay is like laying the foundation for a captivating story. In my extensive experience with the IB curriculum, I’ve identified several key components that make up a compelling introduction. These elements combine to grab the reader’s attention, set the stage for your research, and present a concise argument. Let’s break these down.

1. Start with a Hook
The very first sentences of your essay should serve as the hook. It is the element designed to capture the reader’s interest immediately. It could be a surprising fact, a provocative question, or an intriguing statement related to your topic. The purpose of the hook is to pique curiosity and encourage the reader to continue. For example, if your essay is about environmental policies, you might start with a startling statistic about climate change.
2. Providing Context
Once you’ve hooked your reader, the next step is to provide context. It involves setting the background or framework for your research. Here, you can briefly discuss the broader topic before narrowing it down to your specific area of interest. This part of the introduction should inform the reader about the general field of study, historical background, or current trends related to your topic. It helps situate your research question within a larger conversation or academic discourse.
3. Stating the Research Question
A clear and concise research question is a must in your introduction. It is a focused question that your essay intends to answer. It guides your research and writing, and it should be directly related to the topic you are investigating. The research question sets the direction and purpose of your essay, making it clear to the reader what you are investigating.
4. Thesis Statement
Following the research question, your introduction should include a thesis statement. It is a crucial element where you state your main argument or position in the essay. The thesis statement should be specific, debatable, and supported by your research. It acts as a roadmap for your essay, outlining the major points or arguments you will develop throughout the paper.
5. Significance and Rationale
It’s essential to explain why your research topic and question are significant. It can involve discussing the implications of your research, its relevance to the field, or its contribution to existing knowledge. This part of the introduction helps the reader understand the importance of your work and why it is worth reading.
6. Outline of the Essay Structure
Briefly outlining the structure of your essay can be a helpful component of the introduction. It doesn’t have to be a detailed roadmap, but a quick overview of each section of your essay can give your reader a sense of direction and how your argument will unfold.
7. Engaging and Accessible Language
The tone and style of your introduction should be engaging yet academic. Use clear, accessible language that appeals to your audience. Avoid jargon or overly complex sentences, as the introduction should be understandable to readers who may not be experts in your field of study.
8. Personal Touch
Finally, adding a personal touch to your introduction can make it more engaging. It could briefly mention what inspired your interest in the topic or why you find it significant. This personal connection can make your essay more relatable to your reader.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in EE Introduction Writing
Over the years, I have observed several common mistakes students make while writing the introduction for their IB Extended Essay. Learning how to avoid these pitfalls can significantly enhance the quality of your paper:
- Being Too Vague . To avoid this, ensure you clearly understand your research question and thesis statement before you begin writing. Be precise about what your essay will investigate and your stance.
- Overloading with Details . To prevent this, provide just enough background to set the stage for your research, but save the detailed evidence and in-depth discussion for the subsequent sections of your essay.
- Lack of a Strong Thesis Statement . Your thesis should be a clear, concise statement that presents your main argument. Spend time refining your thesis to ensure it accurately reflects your essay’s content and direction.
- Neglecting the Hook . It could be an intriguing fact, a provocative question, or a compelling quote. Consider what aspect of your topic is most fascinating and use that to draw the reader in.
- Inconsistent Tone and Style . If your introduction is overly formal or informal compared to the subsequent sections, it can create a jarring experience for the reader. Aim for a consistent voice that reflects the academic nature of the IB program.
- Writer’s Block . Get your ideas down on paper and then refine them. Sometimes, it’s easier to write the introduction after completing the body of your essay, as you’ll have a clearer understanding of your overall argument and main points.
- Ignoring the Scope and Limitations . Be clear about what your essay will and will not cover. It sets realistic expectations for the reader and helps to focus your research and writing.
- Failing to Proofread . Always proofread your introduction for errors and clarity. Getting feedback from mentors or teachers might also be helpful.
Remember, this is your first opportunity to make an impression on your reader. By avoiding these common mistakes and focusing on presenting a clear, engaging, and well-structured introduction, you set the stage for a compelling and insightful Extended Essay.

Need help with your IB extended essay?
From research and analysis to structuring and editing, our skilled mentors will be by your side, helping you write an exceptional extended essay that meets the word count and stringent IB criteria and reflects your passion for the selected IB group .
Tailoring Your Extended Essay Introduction to Different Subjects
Let me share some insights on how to adapt your introduction in the Extended Essay based on different subject areas.
Biology, Chemistry, and Physics essays often benefit from a direct, precise approach. Start with a clear statement of your research question or hypothesis. If your essay revolves around an experiment, briefly mentioning the experiment’s outcome or significance in the introduction can be effective. Use factual and straightforward language, and outline the scientific context of your research.
Mathematics
In Mathematics, your introduction should immediately convey the problem or theorem you are addressing. Be clear and concise in defining terms and setting up the problem. You can include a brief overview of the methods you will use to approach the problem, which helps establish your essay’s scope.
History, Geography, and Languages essays often benefit from a more narrative style. Starting with a historical backdrop or a provocative question can be very effective. Your introduction should set your study’s cultural, historical, or social context and outline the central argument or thesis.
For essays in the Visual Arts, Music, or Theatre Studies, analyzing a particular piece of work, an artist, or a movement central to your topic can be a good approach. An engaging story or description can draw the reader into the more abstract aspects of your analysis later on.
In literature essays, beginning with a quote from the work you are analyzing or a brief analysis of a critical theme can be very engaging. Your introduction should hint at the novel, play, or poem’s broader significance and how your essay will contribute to its understanding.
Social Sciences
Essays in Psychology, Economics, and Business Management should start with the broader context of the issue or theory you are examining. A relevant statistic or a brief case study can effectively set the stage for data analysis . Be sure to clearly state your research question and how it relates to the field.
World Studies
For a World Studies EE , which is inherently interdisciplinary, start by explaining the global significance of your topic. Provide a brief overview of how you will integrate different disciplines to address your research question. This type of essay benefits from a clear statement of the real-world implications of your study.
So, writing an IB extended essay introduction is about striking a balance between informative content and engaging writing. From my experience, it sets the tone for your entire essay. Keep your reader intrigued, present your argument clearly, and you’re on your way to an excellent EE.
Remember, practice makes perfect. Keep refining your skills in EE introduction writing, and you’ll see your efforts pay off in your final essay. Also, our Extended Essay Writers are always ready to help.
Luke MacQuoid has extensive experience teaching English as a foreign language in Japan, having worked with students of all ages for over 12 years. Currently, he is teaching at the tertiary level. Luke holds a BA from the University of Sussex and an MA in TESOL from Lancaster University, both located in England. As well to his work as an IB Examiner and Master Tutor, Luke also enjoys sharing his experiences and insights with others through writing articles for various websites, including extendedessaywriters.com blog

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
IB Business Management Extended Essay: The Complete Guide
by Antony W
October 28, 2023

The IB Business Management Extended Essay is an assessment designed to assess your ability to analyze and understand business activities at the different levels of the economy.
In this assignment, you have to:
- Choose an interesting topic to explore.
- Develop a research question .
- Do in-depth research on the issue.
- Write a critically analyzed argument.
- Present credible data and evidence for your work.
Help for Assessment offers professional EE writing service for all approved subjects, including Business Management. So if you have limited time, hire our service and get more flexibility to complete the paper on time.
IB Business Management Extended Essay Research Question
The research question is important in IB Business Management Extended Essay because the entire assignment hinges on it.
You want to make sure you EE in Business and Management meets the following conditions:
The term scope refers to how wide the topic you selected is. Don’t focus on a research question that lacks sufficient research material for the 4,000 words limit.
Instead, choose a topic that’s highly specific, one to which you can find sufficient information to cover more comprehensively.
2. Ability to Apply Concepts and Techniques Learned
Choose a research question that lets you apply business analysis methods, terminologies, and techniques that you’ve learned.
Not only should the question have a tight link to the syllabus, but also it should allow you to draw direct links to the theoretical concepts taught in the business management coursework.
Keep in mind the goal of the EE in business isn’t to show off your knowledge but to prove that you understand and can apply what you’ve already learned.
3. Availability of Research Material
A research question may look great, but it isn’t going to be worth focusing on if it lacks the depth of material and knowledge base to warrant the 4,000-word treatment.
If you can’t access records or useful research data for the research question, drop it.
4. Usefulness and Application
Your research question should be relevant and applicable to the current business environment.
You may draw your inspiration from journals and newspapers for current ideas.
5. Engaging
Don’t just develop an EE research question simply because you find it interesting. It has to be something that you’ve actually investigated or have always want to research.
That way, you’ll have an easy time pulling off the engagement part of the assessment criteria.
Check out our post on IB Business & Management EE Topics for some ideas that might be interesting to explore.
IB Business Management EE Outline to Use
The following is the structure of an IB Extended Essay for Business Management:
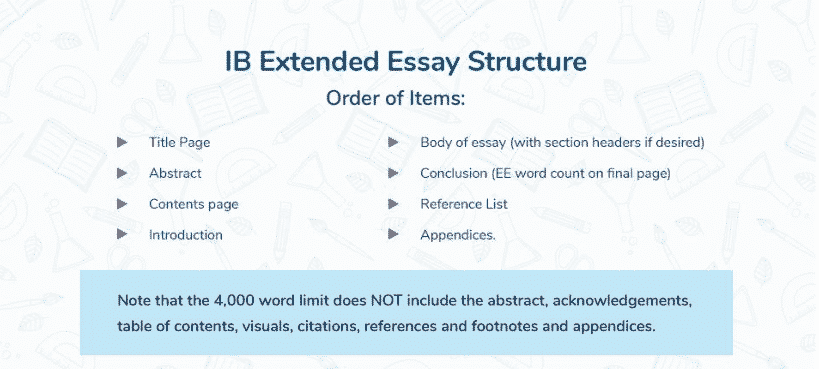
It’s the first page of your IB Business Management Extended essay. While it’s not included in your word count, it’s an important part of the assignment that includes the following information:
- Your Business Management EE Title: Should not be a question but a clear, summarized statement of your research question
- Your Research Question: Write your question in this section
- The Subject: The subject should be “Business Management”
- Word Count: This part should be your word count
You should not write your name, candidate name, date, or school name on the page title of the Extended Essay.
Table of Content
This part is also not included in your word count, but you must include it because it’s part of the assignment.
Include all parts of your IB Business Management Extended essay in this section. Don’t forget to include the page numbers.
Introduction (About 250 Words)
The introduction is a section where you provide a clear context for your research question.
Use this space to describe why your research is interesting and why it’s important to your audience.
Make sure your audience knows what you’ll be exploring, how you intend to explore your research question, and how valuable your research is to your audience.
Methodology (About 350 Words)
Have two parts for the methodology, one explaining your sources and the other one explaining your tools – with the limitations and drawbacks of each.
Methodology Part 1: Sources
State and explain primary and secondary sources for your research. Make sure to include the benefit and weaknesses of each source.
Some insightful sources include news articles, encyclopedias, company annual reports, and magazine articles.
These make good secondary sources, which is where majority of your research should come from.
Methodology Part 2: Tools
Here, state the tools you will use and make sure to include a brief description explaining why you’re going to use them in IB Business Management EE.
If you change your tools as you write your EE, mention those changes here.
Main Body (About 2800 Words)
The main body is the largest part of you IB Business Management Extended Essay.
In this section, you will share your research, analysis, discussion, and evaluation . You can divide the section into two, the first part for your tools and the second for your research.
In the first part, show your teacher that you know how to do what you’ve learned in the IB Business Management class.
The second part is where you make an impression with your research, which sometimes can go beyond what you’ve learned in the classroom.
As you work on the body part of the essay, make sure each paragraph relates to the research question. So make sure you include only the tools and research that answers the questions properly.
Tie everything together to show that what you’ve done so far fully answers your research question. You can also mention the limitations of your research.
Also, you can try to explain other unresolved questions, but don’t introduce any new idea in the essay.
Bibliography
This isn’t included in your word count, but aiming for at most 3 or 4 pages of sources should be fine for the assignment.
IB Business Management Extended Essay Rubric and Assessment Criteria
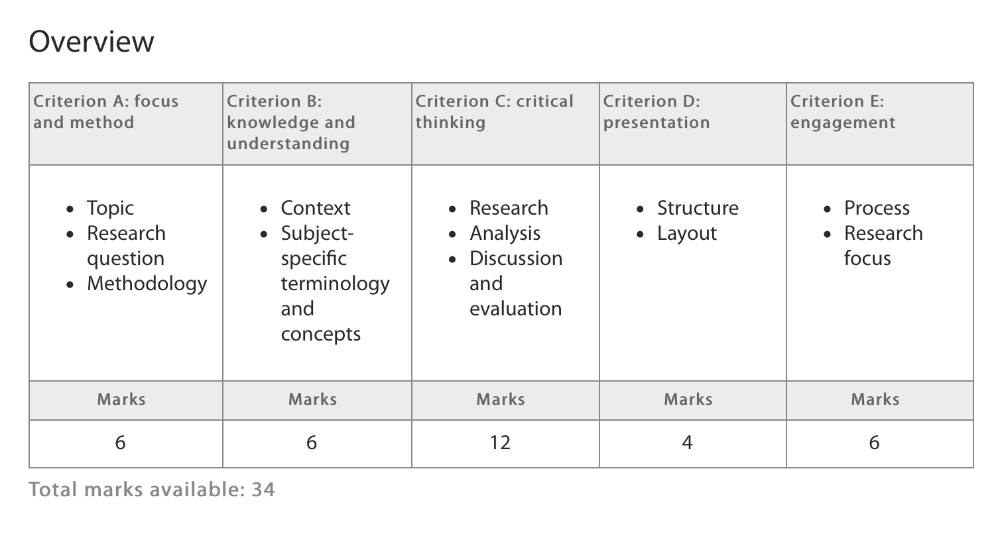
IB Business Management EE Rubric (Assessment Criteria)
IB evaluates business management extended essays based on the following 5 criteria:
- Focus and method
- Knowledge and understanding
- Critical thinking
- Presentation
The grades range from A to E, with the top grade having a maximum of 34 points and anything worse than a C being a fail.
While the professional judgment of selected instructors can affect your grades, these descriptors used to determine the actual grade that you get in the end.
Criterion A: Focus and Method
Criterion A examines how unique, focused, intelligent, and analytical you’re when using techniques learned in the course and outside the classroom.
Evaluators expect you to demonstrate your scholastic ability to apply theories in practical situations, come up with answers to you research issue, and offer a possible solution to the problem at hand.
To score a 6 for focus and method:
- Develop a clear, focused research question.
- Use secondary sources for topic research.
- Support your arguments with relevant, recent, and credible evidence or data.
- Develop a well-organized, logical methodology leading up to your conclusions.
Criteria B: Knowledge and Understanding
Knowledge and understanding focuses on not only how much you’ve learned in the course but also how well you can apply the concepts taught in class to the real world.
To show a business-oriented thinking, use business terminologies.
You can use abstract concepts in the paper, but you should also add thorough explanation your process using a simple language that readers can understand.
Diagrams and charts can help explain concepts that would be hard to explain in words, but it’s important to explain each so that your ideas are clear.
As you explain business trends linked to your research topic, ensure your ideas follow an analytical process while remaining grounded in the case you’re exploring.
Criteria C: Critical Thinking
To score high on this criterion, show a unique application of business concepts, technique, theories, and methods to analyze the problem under investigation.
- Back your argument with in-depth, credible research.
- Be self-critical, making sure you evaluate the accuracy and reliability of your sources.
- Comment on the gaps or weaknesses your arguments don’t solve and suggest what you think researchers can do to solve these issues.
- Use the analytical techniques learned in the course to follow up every point you make in your business management extended essay.
Criterion D: Presentation
The presentation criterion looks at how well you organize and communicate your ideas. The common academic standards evaluated include:
- A clear and easy to understand language
- Clearly labeled charts, graphs, figures, and images
- A well-structured essay with headings and subheadings
Criterion E: Engagement
Criterion E evaluates how you engage with the research topic based on the subject’s intersection in your life.
Avoid using a third-person perspective because doing so will earn you few points.
Quite instances of personal interactions instead, and show that the research question you choose is relevant to you and others.
IB Business Management Extended Essay Grade Descriptors

The following are the grade descriptors used for IB Business Management Extended Essay:
Descriptor A
To get an A, you must have a clear research question, conduct relevant research, and demonstrate expert knowledge and understanding of the materials taught in the classroom.
Also, show a comprehensive engagement to and explanation of the problem.
Your extended essay in business management should feature a logical, structural layout, include key reflections, and have relevant, accurate conclusions.
Descriptor B
To score a B, you need to demonstrate good knowledge of research, appropriate research skill, and a reasonable application of the business concepts and techniques learned in the classroom.
Also, offer a synthesis of an effective research question, a satisfactory presentation, and conclusion supported by evidence presented in the IB business management extended essay.
Descriptor C
Students who score a C for their extended essay in business management are those who display some knowledge and understanding of the key concepts involved, including reasonable application of the topic.
However, the essay fails to synthesize the research question, it offers descriptive instead of an evaluative discussion, there are errors in the arguments use, and structure used is poor.
Descriptor D
Business management extended essays that score a D reflect poor research that lead to a general focus.
Although the essay shows some relevant knowledge of the topic, the content is full of discrepancies and inaccuracies.
In addition to the lack of a logical structure and coherent readability, the essay lacks a critical evaluation of the topic and the conclusions are inconsistent.
Descriptor E
An E is the grade awarded to an unclear essay with an unsystematic approach. The essay lacks a clear focus because it portrays limited knowledge of key concept, not to mention it has an inconsistent analysis and an inaccurate conclusion.
Tips to Write a Compelling IB Business Management Extended Essay

1. Choose Your Research Question
The research question for your IB Business Management Extended essay should not be practical or actionable.
This is applicable only in the Internal Assessment.
Also, make your research question focused, not too broad and not to narrow. While you should be asking relatively simple questions, make sure they aren’t too obvious.
2. Formatting Your Work
Your IB teacher will also look into how you format your work. So it’s important to make sure you get this right from the start.
Use the Times New Roman font type and 12-point font size. Double space your work and make sure every page has a number.
3. Citing Sources
You need to cite all the sources you use in writing your IB Business Management Extended Essay. You can use any citation format, but it’s preferable to MLA.
And don’t worry if you find citing sources somewhat confusing. Our guide on sources and citation should be enough to point you in the right direction.
4. Sticking to the Word Count
Your piece of research should not exceed 4,000 words.
Even if you feel like you have a lot to write to make your ideas clear , you should trim down during revision if your work is more than 4,000 words already.
5. Write a Great Reflection
The reflection for your IB Business Management Extended essay is not only important as the other parts of the assignment.
It’s also about 18% of the total grade. So you should give it your best shot.
6. Edit Your Work Thoroughly
Reading a 4,000-word IB Business Management Extended Essay after spending so many hours writing it can be rather boring and much less time consuming.
But doing so is the only way to make sure your essay is good enough for submission and ready for marking.
- Look out for grammar and spelling mistakes and fix them. Use a tool such as Grammarly to make your work easier
- Rewrite longer sentences, making them short and concise.
- Don’t hesitate to trim down word count in a sentence if you can say the same thing but in fewer words
- Do parts of your essay sound redundant? Delete them, regardless of where they appear in the essay
- Have you used a source you haven’t cited? Go back and fix the error
Editing your work thoroughly isn’t the fun part of working on an IB Business Management Extended Essay. However, it goes a long way to make your essay read better.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
The Link Between the Resurrection and Elections

I went to a funeral recently. It was an old friend and former colleague . The big "C," diagnosed six years ago. He outlived the first diagnosis by five years but eventually it caught up. Splendid service, lovely music, fine sermon, many poignant moments. I met dozens of people I hadn’t seen for years. All as it should be.
Except for one thing. The service was billed as a "resurrection" celebration. The printed service paper said so. The preacher said so. Some of the hymns said so. But the resurrection itself—a new bodily life in God’s eventual new creation—was conspicuous by its all-but-absence. And that’s a problem. Not only because most people in our culture don’t know what "resurrection" means , but because they don’t know why it matters .
Resurrection matters because what you ultimately hope for affects the person you are right now. More particularly, it matters because people who really believe in resurrection have a different approach to all of life—including politics. Including issues of justice and mercy, at all levels. Including, dare I say, voting and elections. This affects all of us.
Read More: The Hidden History of Those Who Wrote the Christian Story
So what does "resurrection" mean? Most people today assume that it’s a fancy way of saying "life after death." That’s certainly what I would have picked up from that funeral service. But "resurrection" never meant "life after death," or "going to heaven." Plenty of people in Jesus’ day believed in "life after death," in some form, but were still shocked by talk of "resurrection." That’s because "resurrection" always meant people who had been physically dead coming back to a new life—a new bodily life. Whatever we might mean by "life after death" (the Bible actually says very little about that), "resurrection" is a further stage. It’s life after "life after death." Wherever Jesus was after his horrible death, he wasn’t raised again until the third day. "Resurrection" is the final stage in a two-stage post-mortem journey. With that, a new world is born, full of possibilities.
Jesus’ risen body was the first element in God’s long-promised "new creation." A little bit of God’s new world, coming forward from the ultimate future into our surprised and unready present time. And launching the project of new creation that continues to this day.
Most people in our world, including most churchgoers, have never heard this explained. This robs us, as individuals, of our ultimate hope, leaving us with "pie in the sky when you die," which was never the original Christian vision. In particular, it robs us of the motivation to work for God’s new creation in the present. And that means public life—justice, politics, voting—and all that goes with them.
Read More: The Bible’s Most Misunderstood Verse
Here's the point: Jesus’ resurrection doesn’t mean, "He’s gone to heaven, so we can go there too" (though you might be forgiven for thinking it meant that, granted the many sermons both at funerals and at Easter). It means, "In Jesus, God has launched his plan to remake creation as a whole, and if you are a follower of Jesus you get to be part of that right now." What God did for Jesus, close up and personal, is what he plans to do for the whole world. And the project is already under way.
How does this work? One way of putting it is to say that God intends to put the whole world right in the end. This will be a great act of total new creation, for which Jesus’ resurrection is the advance model. In the present time, though, God puts people right—women, men, children—by bringing them to faith in Jesus and shaping their lives by his spirit. And he does this so that they can, here and now, become "putting-right" people for the world. In the future, God will put the world right; in the present, God does put people right.
And the "put-right" people are called to be "putting-right" people, Sermon-on-the-Mount people, lovers of justice and peace, in and for God’s world. They are to be signs of the new creation which began with Jesus’ resurrection. They are to produce, here and now, further signs of that new world. The church as a whole, and every member, is called to become a small working model of new creation.
And that new creation includes (what we call) social reform. Check out the relevant biblical passages. The Psalms sketch the ideal society: in Psalm 72, the No.1 priority for God’s chosen king is to look after the weak, the poor and the helpless. The prophets add their dramatic pictures, as in Isaiah 11 where the wolf and the lamb will lie down together. (They tried that in a zoo in California, and it worked fine provided they put in a new lamb each day.) Already in Jesus’ day some Jewish teachers were interpreting Isaiah’s picture of the peaceable world in terms of warring nations finding reconciliation. Jesus announced that the time had come for this new way of peace. St Paul picked up that theme, seeing the church as, by definition, a multicultural, multi-ethnic society, without social class or gender hierarchy, as a sign and foretaste of the coming new creation of justice and peace.
The tragedy in the western churches is that, by misunderstanding "resurrection," both the "conservatives" and the "liberals" have robbed themselves of the whole message. The conservatives, eager to tell people how to go to heaven, regard any attempt to improve the present world as a distraction, not realizing that with Jesus’ resurrection the new creation has already been launched. The liberals, having long been taught that science has disproved Jesus’ resurrection, dismiss its importance and pursue their own vision of social improvement.
Hence the unholy stand-off: liberal Christians saying "justice and peace" but denying resurrection; conservative Christians saying "resurrection" but meaning "going to heaven." The problem is that trying to get the result (social justice) without the resource (Jesus’ resurrection) is building on sand. Just as a "heaven " that is not "a new creation" is vacuous (and unbiblical), a liberal agenda that is not rooted in the resurrection is rudderless. The 18th-century Enlightenment tried that experiment (reform without resurrection), and it clearly hasn’t worked. No: it is because God raised Jesus from the dead that ultimate new creation is promised, and present new creation becomes possible.
A true understanding of new creation, instead, starts with the Easter message about Jesus’ new bodily life, and the powerful gift of his spirit. It flows out into creative, healing, and restorative work in God’s world—including, of course, political and public life. That insight slices through our present culture wars, where bits of half-remembered "religion" get muddled up with bits of half-understood "politics." It’s time to reset the terms, both of debate and of action. Get resurrection right and political priorities, including wise voting, will rearrange themselves.
That is the hope. And, in the New Testament, "hope" doesn’t mean "optimism" or "always look on the bright side." It means Jesus.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Why We're Spending So Much Money Now
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- Breaker Sunny Choi Is Heading to Paris
- Why TV Can’t Stop Making Silly Shows About Lady Journalists
- The Case for Wearing Shoes in the House
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
You May Also Like
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission
- The Case for Marrying an Older Man
A woman’s life is all work and little rest. An age gap relationship can help.

In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty, gratuitous heat — kicking up dust and languid debates over how we’d spend such an influx. I purchase scratch-offs, jackpot tickets, scraping the former with euro coins in restaurants too fine for that. I never cash them in, nor do I check the winning numbers. For I already won something like the lotto, with its gifts and its curses, when he married me.
He is ten years older than I am. I chose him on purpose, not by chance. As far as life decisions go, on balance, I recommend it.
When I was 20 and a junior at Harvard College, a series of great ironies began to mock me. I could study all I wanted, prove myself as exceptional as I liked, and still my fiercest advantage remained so universal it deflated my other plans. My youth. The newness of my face and body. Compellingly effortless; cruelly fleeting. I shared it with the average, idle young woman shrugging down the street. The thought, when it descended on me, jolted my perspective, the way a falling leaf can make you look up: I could diligently craft an ideal existence, over years and years of sleepless nights and industry. Or I could just marry it early.
So naturally I began to lug a heavy suitcase of books each Saturday to the Harvard Business School to work on my Nabokov paper. In one cavernous, well-appointed room sat approximately 50 of the planet’s most suitable bachelors. I had high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out. Apologies to Progress, but older men still desired those things.
I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence. Each time I reconsidered the project, it struck me as more reasonable. Why ignore our youth when it amounted to a superpower? Why assume the burdens of womanhood, its too-quick-to-vanish upper hand, but not its brief benefits at least? Perhaps it came easier to avoid the topic wholesale than to accept that women really do have a tragically short window of power, and reason enough to take advantage of that fact while they can. As for me, I liked history, Victorian novels, knew of imminent female pitfalls from all the books I’d read: vampiric boyfriends; labor, at the office and in the hospital, expected simultaneously; a decline in status as we aged, like a looming eclipse. I’d have disliked being called calculating, but I had, like all women, a calculator in my head. I thought it silly to ignore its answers when they pointed to an unfairness for which we really ought to have been preparing.
I was competitive by nature, an English-literature student with all the corresponding major ambitions and minor prospects (Great American novel; email job). A little Bovarist , frantic for new places and ideas; to travel here, to travel there, to be in the room where things happened. I resented the callow boys in my class, who lusted after a particular, socially sanctioned type on campus: thin and sexless, emotionally detached and socially connected, the opposite of me. Restless one Saturday night, I slipped on a red dress and snuck into a graduate-school event, coiling an HDMI cord around my wrist as proof of some technical duty. I danced. I drank for free, until one of the organizers asked me to leave. I called and climbed into an Uber. Then I promptly climbed out of it. For there he was, emerging from the revolving doors. Brown eyes, curved lips, immaculate jacket. I went to him, asked him for a cigarette. A date, days later. A second one, where I discovered he was a person, potentially my favorite kind: funny, clear-eyed, brilliant, on intimate terms with the universe.
I used to love men like men love women — that is, not very well, and with a hunger driven only by my own inadequacies. Not him. In those early days, I spoke fondly of my family, stocked the fridge with his favorite pasta, folded his clothes more neatly than I ever have since. I wrote his mother a thank-you note for hosting me in his native France, something befitting a daughter-in-law. It worked; I meant it. After graduation and my fellowship at Oxford, I stayed in Europe for his career and married him at 23.
Of course I just fell in love. Romances have a setting; I had only intervened to place myself well. Mainly, I spotted the precise trouble of being a woman ahead of time, tried to surf it instead of letting it drown me on principle. I had grown bored of discussions of fair and unfair, equal or unequal , and preferred instead to consider a thing called ease.
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon. When a 50-year-old man and a 25-year-old woman walk down the street, the questions form themselves inside of you; they make you feel cynical and obscene: How good of a deal is that? Which party is getting the better one? Would I take it? He is older. Income rises with age, so we assume he has money, at least relative to her; at minimum, more connections and experience. She has supple skin. Energy. Sex. Maybe she gets a Birkin. Maybe he gets a baby long after his prime. The sight of their entwined hands throws a lucid light on the calculations each of us makes, in love, to varying degrees of denial. You could get married in the most romantic place in the world, like I did, and you would still have to sign a contract.
Twenty and 30 is not like 30 and 40; some freshness to my features back then, some clumsiness in my bearing, warped our decade, in the eyes of others, to an uncrossable gulf. Perhaps this explains the anger we felt directed at us at the start of our relationship. People seemed to take us very, very personally. I recall a hellish car ride with a friend of his who began to castigate me in the backseat, in tones so low that only I could hear him. He told me, You wanted a rich boyfriend. You chased and snuck into parties . He spared me the insult of gold digger, but he drew, with other words, the outline for it. Most offended were the single older women, my husband’s classmates. They discussed me in the bathroom at parties when I was in the stall. What does he see in her? What do they talk about? They were concerned about me. They wielded their concern like a bludgeon. They paraphrased without meaning to my favorite line from Nabokov’s Lolita : “You took advantage of my disadvantage,” suspecting me of some weakness he in turn mined. It did not disturb them, so much, to consider that all relationships were trades. The trouble was the trade I’d made struck them as a bad one.
The truth is you can fall in love with someone for all sorts of reasons, tiny transactions, pluses and minuses, whose sum is your affection for each other, your loyalty, your commitment. The way someone picks up your favorite croissant. Their habit of listening hard. What they do for you on your anniversary and your reciprocal gesture, wrapped thoughtfully. The serenity they inspire; your happiness, enlivening it. When someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them.
When I think of same-age, same-stage relationships, what I tend to picture is a woman who is doing too much for too little.
I’m 27 now, and most women my age have “partners.” These days, girls become partners quite young. A partner is supposed to be a modern answer to the oppression of marriage, the terrible feeling of someone looming over you, head of a household to which you can only ever be the neck. Necks are vulnerable. The problem with a partner, however, is if you’re equal in all things, you compromise in all things. And men are too skilled at taking .
There is a boy out there who knows how to floss because my friend taught him. Now he kisses college girls with fresh breath. A boy married to my friend who doesn’t know how to pack his own suitcase. She “likes to do it for him.” A million boys who know how to touch a woman, who go to therapy because they were pushed, who learned fidelity, boundaries, decency, manners, to use a top sheet and act humanely beneath it, to call their mothers, match colors, bring flowers to a funeral and inhale, exhale in the face of rage, because some girl, some girl we know, some girl they probably don’t speak to and will never, ever credit, took the time to teach him. All while she was working, raising herself, clawing up the cliff-face of adulthood. Hauling him at her own expense.
I find a post on Reddit where five thousand men try to define “ a woman’s touch .” They describe raised flower beds, blankets, photographs of their loved ones, not hers, sprouting on the mantel overnight. Candles, coasters, side tables. Someone remembering to take lint out of the dryer. To give compliments. I wonder what these women are getting back. I imagine them like Cinderella’s mice, scurrying around, their sole proof of life their contributions to a more central character. On occasion I meet a nice couple, who grew up together. They know each other with a fraternalism tender and alien to me. But I think of all my friends who failed at this, were failed at this, and I think, No, absolutely not, too risky . Riskier, sometimes, than an age gap.
My younger brother is in his early 20s, handsome, successful, but in many ways: an endearing disaster. By his age, I had long since wisened up. He leaves his clothes in the dryer, takes out a single shirt, steams it for three minutes. His towel on the floor, for someone else to retrieve. His lovely, same-age girlfriend is aching to fix these tendencies, among others. She is capable beyond words. Statistically, they will not end up together. He moved into his first place recently, and she, the girlfriend, supplied him with a long, detailed list of things he needed for his apartment: sheets, towels, hangers, a colander, which made me laugh. She picked out his couch. I will bet you anything she will fix his laundry habits, and if so, they will impress the next girl. If they break up, she will never see that couch again, and he will forget its story. I tell her when I visit because I like her, though I get in trouble for it: You shouldn’t do so much for him, not for someone who is not stuck with you, not for any boy, not even for my wonderful brother.
Too much work had left my husband, by 30, jaded and uninspired. He’d burned out — but I could reenchant things. I danced at restaurants when they played a song I liked. I turned grocery shopping into an adventure, pleased by what I provided. Ambitious, hungry, he needed someone smart enough to sustain his interest, but flexible enough in her habits to build them around his hours. I could. I do: read myself occupied, make myself free, materialize beside him when he calls for me. In exchange, I left a lucrative but deadening spreadsheet job to write full-time, without having to live like a writer. I learned to cook, a little, and decorate, somewhat poorly. Mostly I get to read, to walk central London and Miami and think in delicious circles, to work hard, when necessary, for free, and write stories for far less than minimum wage when I tally all the hours I take to write them.
At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self, couldn’t imagine doing it in tandem with someone, two raw lumps of clay trying to mold one another and only sullying things worse. I’d go on dates with boys my age and leave with the impression they were telling me not about themselves but some person who didn’t exist yet and on whom I was meant to bet regardless. My husband struck me instead as so finished, formed. Analyzable for compatibility. He bore the traces of other women who’d improved him, small but crucial basics like use a coaster ; listen, don’t give advice. Young egos mellow into patience and generosity.
My husband isn’t my partner. He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did. Adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations. But his logistics ran so smoothly that he simply tacked mine on. I moved into his flat, onto his level, drag and drop, cleaner thrice a week, bills automatic. By opting out of partnership in my 20s, I granted myself a kind of compartmentalized, liberating selfishness none of my friends have managed. I am the work in progress, the party we worry about, a surprising dominance. When I searched for my first job, at 21, we combined our efforts, for my sake. He had wisdom to impart, contacts with whom he arranged coffees; we spent an afternoon, laughing, drawing up earnest lists of my pros and cons (highly sociable; sloppy math). Meanwhile, I took calls from a dear friend who had a boyfriend her age. Both savagely ambitious, hyperclose and entwined in each other’s projects. If each was a start-up , the other was the first hire, an intense dedication I found riveting. Yet every time she called me, I hung up with the distinct feeling that too much was happening at the same time: both learning to please a boss; to forge more adult relationships with their families; to pay bills and taxes and hang prints on the wall. Neither had any advice to give and certainly no stability. I pictured a three-legged race, two people tied together and hobbling toward every milestone.
I don’t fool myself. My marriage has its cons. There are only so many times one can say “thank you” — for splendid scenes, fine dinners — before the phrase starts to grate. I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that shapes the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him. He doesn’t have to hold it over my head. It just floats there, complicating usual shorthands to explain dissatisfaction like, You aren’t being supportive lately . It’s a Frenchism to say, “Take a decision,” and from time to time I joke: from whom? Occasionally I find myself in some fabulous country at some fabulous party and I think what a long way I have traveled, like a lucky cloud, and it is frightening to think of oneself as vapor.
Mostly I worry that if he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive, but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials, the way Renaissance painters hid in their paintings their faces among a crowd. I wonder if when they looked at their paintings, they saw their own faces first. But this is the wrong question, if our aim is happiness. Like the other question on which I’m expected to dwell: Who is in charge, the man who drives or the woman who put him there so she could enjoy herself? I sit in the car, in the painting it would have taken me a corporate job and 20 years to paint alone, and my concern over who has the upper hand becomes as distant as the horizon, the one he and I made so wide for me.
To be a woman is to race against the clock, in several ways, until there is nothing left to be but run ragged.
We try to put it off, but it will hit us at some point: that we live in a world in which our power has a different shape from that of men, a different distribution of advantage, ours a funnel and theirs an expanding cone. A woman at 20 rarely has to earn her welcome; a boy at 20 will be turned away at the door. A woman at 30 may find a younger woman has taken her seat; a man at 30 will have invited her. I think back to the women in the bathroom, my husband’s classmates. What was my relationship if not an inconvertible sign of this unfairness? What was I doing, in marrying older, if not endorsing it? I had taken advantage of their disadvantage. I had preempted my own. After all, principled women are meant to defy unfairness, to show some integrity or denial, not plan around it, like I had. These were driven women, successful, beautiful, capable. I merely possessed the one thing they had already lost. In getting ahead of the problem, had I pushed them down? If I hadn’t, would it really have made any difference?
When we decided we wanted to be equal to men, we got on men’s time. We worked when they worked, retired when they retired, had to squeeze pregnancy, children, menopause somewhere impossibly in the margins. I have a friend, in her late 20s, who wears a mood ring; these days it is often red, flickering in the air like a siren when she explains her predicament to me. She has raised her fair share of same-age boyfriends. She has put her head down, worked laboriously alongside them, too. At last she is beginning to reap the dividends, earning the income to finally enjoy herself. But it is now, exactly at this precipice of freedom and pleasure, that a time problem comes closing in. If she would like to have children before 35, she must begin her next profession, motherhood, rather soon, compromising inevitably her original one. The same-age partner, equally unsettled in his career, will take only the minimum time off, she guesses, or else pay some cost which will come back to bite her. Everything unfailingly does. If she freezes her eggs to buy time, the decision and its logistics will burden her singly — and perhaps it will not work. Overlay the years a woman is supposed to establish herself in her career and her fertility window and it’s a perfect, miserable circle. By midlife women report feeling invisible, undervalued; it is a telling cliché, that after all this, some husbands leave for a younger girl. So when is her time, exactly? For leisure, ease, liberty? There is no brand of feminism which achieved female rest. If women’s problem in the ’50s was a paralyzing malaise, now it is that they are too active, too capable, never permitted a vacation they didn’t plan. It’s not that our efforts to have it all were fated for failure. They simply weren’t imaginative enough.
For me, my relationship, with its age gap, has alleviated this rush , permitted me to massage the clock, shift its hands to my benefit. Very soon, we will decide to have children, and I don’t panic over last gasps of fun, because I took so many big breaths of it early: on the holidays of someone who had worked a decade longer than I had, in beautiful places when I was young and beautiful, a symmetry I recommend. If such a thing as maternal energy exists, mine was never depleted. I spent the last nearly seven years supported more than I support and I am still not as old as my husband was when he met me. When I have a child, I will expect more help from him than I would if he were younger, for what does professional tenure earn you if not the right to set more limits on work demands — or, if not, to secure some child care, at the very least? When I return to work after maternal upheaval, he will aid me, as he’s always had, with his ability to put himself aside, as younger men are rarely able.
Above all, the great gift of my marriage is flexibility. A chance to live my life before I become responsible for someone else’s — a lover’s, or a child’s. A chance to write. A chance at a destiny that doesn’t adhere rigidly to the routines and timelines of men, but lends itself instead to roomy accommodation, to the very fluidity Betty Friedan dreamed of in 1963 in The Feminine Mystique , but we’ve largely forgotten: some career or style of life that “permits year-to-year variation — a full-time paid job in one community, part-time in another, exercise of the professional skill in serious volunteer work or a period of study during pregnancy or early motherhood when a full-time job is not feasible.” Some things are just not feasible in our current structures. Somewhere along the way we stopped admitting that, and all we did was make women feel like personal failures. I dream of new structures, a world in which women have entry-level jobs in their 30s; alternate avenues for promotion; corporate ladders with balconies on which they can stand still, have a smoke, take a break, make a baby, enjoy themselves, before they keep climbing. Perhaps men long for this in their own way. Actually I am sure of that.
Once, when we first fell in love, I put my head in his lap on a long car ride; I remember his hands on my face, the sun, the twisting turns of a mountain road, surprising and not surprising us like our romance, and his voice, telling me that it was his biggest regret that I was so young, he feared he would lose me. Last week, we looked back at old photos and agreed we’d given each other our respective best years. Sometimes real equality is not so obvious, sometimes it takes turns, sometimes it takes almost a decade to reveal itself.
More From This Series
- Can You Still Sell Out in This Economy?
- 7 Stories of Dramatic Career Pivots
- My Mother’s Death Blew Up My Life. Opening a Book and Wine Store Helped My Grief
- newsletter pick
- first person
- relationships
- the good life
The Cut Shop
Most viewed stories.
- Madame Clairevoyant: Horoscopes for the Week of March 31–April 6
- What We Know About the Mommy Vlogger Accused of Child Abuse
- This Mercury Retrograde in Aries Will Be Peak Chaos
- When Your Kid Is the Classroom Problem Child
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
What is your email.
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.
Celtics aim to avenge early-season loss to Hornets
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

The Detroit Tigers saw some evidence their long rebuild might be nearing its completion during a season-opening sweep of the Chicago White Sox.
The last time the Texas Rangers came to Florida, they swept two games against the Tampa Bay Rays in an American League wild-card series en route to winning the World Series.

The Philadelphia Phillies will look for their second victory in a row when they open a three-game series against the Cincinnati Reds on Monday.
Baltimore pitchers will look to continue their strong start to the 2024 season when the Orioles open a three-game series against the visiting Kansas City Royals on Monday.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The extended essay is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. Read about the extended essay in greater detail. You can also read about how the IB sets deadlines for ...
References and bibliography. Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories, or IB subject groups, which are as follows: Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature. Group 2: Language Acquisition. Group 3: Individuals and Societies. Group 4: Sciences. Group 5: Mathematics.
The extended essay contributes to the overall diploma score through the award of points in conjunction with theory of knowledge. A maximum of three points are awarded according to a student's combined ... The purpose of this assignment is to lead you to the research question that will be at the heart of your extended essay. The research ...
The Extended Essay (EE) is an independent, self-directed academic research, presented in the form of a 4,000-word paper. One component of the International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) core, the extended essay is mandatory for all students. ... Your aim when meeting with your supervisor this time is to look over your first draft ...
The Extended Essay has several key objectives: To provide students with the chance to engage in an in-depth study of a question of interest within a chosen subject. To develop research, thinking, self-management, and communication skills. To introduce students to the excitement and challenges of academic research.
The Extended Essay ( 'EE'), together with CAS and TOK, is a core component of the International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme. It is mandatory for all students, regardless of the subjects they are taking. The aim of the EE is to provide students with the opportunity to research a topic of their interest. It is also an opportunity for ...
5. Novelty: Aim for a research question that offers a unique perspective or contributes to existing knowledge. Originality in your approach and analysis can make your Extended Essay stand out. 6. Consultation: Seek guidance from your teachers, mentors, or IB tutors.
The extended essay (often called the EE) is a 4000-word structured essay on a topic of your choice, which can take many different forms. Ultimately, what your EE ends up looking like depends on the topic that you choose. Some students choose to write their extended essay on an aspect of literature or
The Extended Essay requires students to engage in extensive research, develop a clear research question or hypothesis, and produce a substantial written essay of up to 4,000 words. This endeavor is designed to cultivate essential skills, including critical thinking, research methodology, and effective communication, while encouraging students ...
extended essay and theory of knowledge will fall into one of the five bands previously described in the criterion for each assessment. The total number of points awarded is determined by the combination of the performance levels achieved by the student in both the extended essay and theory of knowledge according to the following matrix. Changes ...
The IB extended essay is a paper of up to 4,000 words that is required for students enrolled in the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma program. The extended essay allows students to engage in independent research on a topic within one of the available subject areas. ... Its purpose is giving you the opportunity to try independent research ...
Just write. No one will see it but you. Exercise 2: Pick one of the three options above and try it: write your favourite 'piece' of the essay first, write as much as you can by hand in one writing sprint, or lose the grammar and just get the ideas down in the right order. 3. Perfect Your Extended Essay Language.
The extended essay is a mandatory component of the core, but it's more like a practical approach to undergraduate-level research papers, giving students a chance to research any of the six subjects they've selected in their IB journey to a greater degree. Students spend the first few weeks of their IB curriculum choosing a subject to write ...
The Extended Essay (EE) is one of the requirements of the IB Diploma Programme. It provides students with an opportunity to conduct independent research on a topic of interest to them. It is written on a freely-chosen topic as long as there is a subject teacher in school, as the candidate must have a subject supervisor.
The Extended Essay, abbreviated as EE, is an individual project that requires self-directed research. In an EE, you choose a topic, develop a research question, conduct independent research, and then write a report of your finding. You'll write an EE alongside other IB assignments, which are Internal Assessments at Standard and Higher Levels ...
The IB Extended Essay is a 4000 word essay, completed during the IB Diploma Programme, which lasts between the ages of 16-18 (Year 12-13/Grade 11-12). An Extended Essay begins from a question, posed and selected by the student, that involves looking at a topic from a theoretical angle, in addition to: "extensive research, thorough ...
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program is a hallmark of rigorous academic standards, emphasizing critical thinking, inquiry, and interdisciplinary learning. Central to the IB diploma is the Extended Essay (EE), a substantial piece of independent research and writing undertaken by students under the guidance of a supervisor. This blog delves into the various facets of the Extended Essay ...
A good resource should make it's intentions and purpose clear. A site with basic information about life insurance, and disability and long-term care insurance, 'calculators' for determining the amount needed for these types of coverage, and links to insurance providers. Life Happens receives financial support from more than 140 of the nation ...
The IB Extended Essay introduction, in particular, can be a make-or-break element. So, let's get right into the art of EE introduction crafting, a skill crucial for any aspiring IB student. The Purpose of the IB Extended Essay Introduction. The purpose of the IB Extended Essay introduction goes much further than just starting your paper.
October 28, 2023. The IB Business Management Extended Essay is an assessment designed to assess your ability to analyze and understand business activities at the different levels of the economy. In this assignment, you have to: Choose an interesting topic to explore. Develop a research question. Do in-depth research on the issue.
Here's the point: Jesus' resurrection doesn't mean, "He's gone to heaven, so we can go there too" (though you might be forgiven for thinking it meant that, granted the many sermons both at ...
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon.
April 1 - The Boston Celtics complete an extended road trip when they face the Charlotte Hornets on Monday night. Other than back-to-back, last-minute losses in Atlanta, the Celtics have had a ...