- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Descriptive Research: Definition, Characteristics, Methods + Examples

Suppose an apparel brand wants to understand the fashion purchasing trends among New York’s buyers, then it must conduct a demographic survey of the specific region, gather population data, and then conduct descriptive research on this demographic segment.
The study will then uncover details on “what is the purchasing pattern of New York buyers,” but will not cover any investigative information about “ why ” the patterns exist. Because for the apparel brand trying to break into this market, understanding the nature of their market is the study’s main goal. Let’s talk about it.
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method describing the characteristics of the population or phenomenon studied. This descriptive methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research subject than the “why” of the research subject.
The method primarily focuses on describing the nature of a demographic segment without focusing on “why” a particular phenomenon occurs. In other words, it “describes” the research subject without covering “why” it happens.
Characteristics of descriptive research
The term descriptive research then refers to research questions, the design of the study, and data analysis conducted on that topic. We call it an observational research method because none of the research study variables are influenced in any capacity.
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment’s nature.
- Uncontrolled variables: In it, none of the variables are influenced in any way. This uses observational methods to conduct the research. Hence, the nature of the variables or their behavior is not in the hands of the researcher.
- Cross-sectional studies: It is generally a cross-sectional study where different sections belonging to the same group are studied.
- The basis for further research: Researchers further research the data collected and analyzed from descriptive research using different research techniques. The data can also help point towards the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
Applications of descriptive research with examples
A descriptive research method can be used in multiple ways and for various reasons. Before getting into any survey , though, the survey goals and survey design are crucial. Despite following these steps, there is no way to know if one will meet the research outcome. How to use descriptive research? To understand the end objective of research goals, below are some ways organizations currently use descriptive research today:
- Define respondent characteristics: The aim of using close-ended questions is to draw concrete conclusions about the respondents. This could be the need to derive patterns, traits, and behaviors of the respondents. It could also be to understand from a respondent their attitude, or opinion about the phenomenon. For example, understand millennials and the hours per week they spend browsing the internet. All this information helps the organization researching to make informed business decisions.
- Measure data trends: Researchers measure data trends over time with a descriptive research design’s statistical capabilities. Consider if an apparel company researches different demographics like age groups from 24-35 and 36-45 on a new range launch of autumn wear. If one of those groups doesn’t take too well to the new launch, it provides insight into what clothes are like and what is not. The brand drops the clothes and apparel that customers don’t like.
- Conduct comparisons: Organizations also use a descriptive research design to understand how different groups respond to a specific product or service. For example, an apparel brand creates a survey asking general questions that measure the brand’s image. The same study also asks demographic questions like age, income, gender, geographical location, geographic segmentation , etc. This consumer research helps the organization understand what aspects of the brand appeal to the population and what aspects do not. It also helps make product or marketing fixes or even create a new product line to cater to high-growth potential groups.
- Validate existing conditions: Researchers widely use descriptive research to help ascertain the research object’s prevailing conditions and underlying patterns. Due to the non-invasive research method and the use of quantitative observation and some aspects of qualitative observation , researchers observe each variable and conduct an in-depth analysis . Researchers also use it to validate any existing conditions that may be prevalent in a population.
- Conduct research at different times: The analysis can be conducted at different periods to ascertain any similarities or differences. This also allows any number of variables to be evaluated. For verification, studies on prevailing conditions can also be repeated to draw trends.
Advantages of descriptive research
Some of the significant advantages of descriptive research are:

- Data collection: A researcher can conduct descriptive research using specific methods like observational method, case study method, and survey method. Between these three, all primary data collection methods are covered, which provides a lot of information. This can be used for future research or even for developing a hypothesis for your research object.
- Varied: Since the data collected is qualitative and quantitative, it gives a holistic understanding of a research topic. The information is varied, diverse, and thorough.
- Natural environment: Descriptive research allows for the research to be conducted in the respondent’s natural environment, which ensures that high-quality and honest data is collected.
- Quick to perform and cheap: As the sample size is generally large in descriptive research, the data collection is quick to conduct and is inexpensive.
Descriptive research methods
There are three distinctive methods to conduct descriptive research. They are:
Observational method
The observational method is the most effective method to conduct this research, and researchers make use of both quantitative and qualitative observations.
A quantitative observation is the objective collection of data primarily focused on numbers and values. It suggests “associated with, of or depicted in terms of a quantity.” Results of quantitative observation are derived using statistical and numerical analysis methods. It implies observation of any entity associated with a numeric value such as age, shape, weight, volume, scale, etc. For example, the researcher can track if current customers will refer the brand using a simple Net Promoter Score question .
Qualitative observation doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead just monitoring characteristics. In this case, the researcher observes the respondents from a distance. Since the respondents are in a comfortable environment, the characteristics observed are natural and effective. In a descriptive research design, the researcher can choose to be either a complete observer, an observer as a participant, a participant as an observer, or a full participant. For example, in a supermarket, a researcher can from afar monitor and track the customers’ selection and purchasing trends. This offers a more in-depth insight into the purchasing experience of the customer.
Case study method
Case studies involve in-depth research and study of individuals or groups. Case studies lead to a hypothesis and widen a further scope of studying a phenomenon. However, case studies should not be used to determine cause and effect as they can’t make accurate predictions because there could be a bias on the researcher’s part. The other reason why case studies are not a reliable way of conducting descriptive research is that there could be an atypical respondent in the survey. Describing them leads to weak generalizations and moving away from external validity.
Survey research
In survey research, respondents answer through surveys or questionnaires or polls . They are a popular market research tool to collect feedback from respondents. A study to gather useful data should have the right survey questions. It should be a balanced mix of open-ended questions and close ended-questions . The survey method can be conducted online or offline, making it the go-to option for descriptive research where the sample size is enormous.
Examples of descriptive research
Some examples of descriptive research are:
- A specialty food group launching a new range of barbecue rubs would like to understand what flavors of rubs are favored by different people. To understand the preferred flavor palette, they conduct this type of research study using various methods like observational methods in supermarkets. By also surveying while collecting in-depth demographic information, offers insights about the preference of different markets. This can also help tailor make the rubs and spreads to various preferred meats in that demographic. Conducting this type of research helps the organization tweak their business model and amplify marketing in core markets.
- Another example of where this research can be used is if a school district wishes to evaluate teachers’ attitudes about using technology in the classroom. By conducting surveys and observing their comfortableness using technology through observational methods, the researcher can gauge what they can help understand if a full-fledged implementation can face an issue. This also helps in understanding if the students are impacted in any way with this change.
Some other research problems and research questions that can lead to descriptive research are:
- Market researchers want to observe the habits of consumers.
- A company wants to evaluate the morale of its staff.
- A school district wants to understand if students will access online lessons rather than textbooks.
- To understand if its wellness questionnaire programs enhance the overall health of the employees.
FREE TRIAL LEARN MORE
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 8 Best Digital Experience Platforms in 2024
Mar 15, 2024

Top 10 Patient Experience Software to Shape Modern Healthcare
Mar 14, 2024

Email List Building Tool: Choose The Best From These 9 Tools
Exploring Top 15 Data Analysis Tools to Elevate Your Insights
Mar 13, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Descriptive Research Design
Definition:
Descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied.
Descriptive research design does not attempt to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables or make predictions about future outcomes. Instead, it focuses on providing a detailed and accurate representation of the data collected, which can be useful for generating hypotheses, exploring trends, and identifying patterns in the data.
Types of Descriptive Research Design
Types of Descriptive Research Design are as follows:
Cross-sectional Study
This involves collecting data at a single point in time from a sample or population to describe their characteristics or behaviors. For example, a researcher may conduct a cross-sectional study to investigate the prevalence of certain health conditions among a population, or to describe the attitudes and beliefs of a particular group.
Longitudinal Study
This involves collecting data over an extended period of time, often through repeated observations or surveys of the same group or population. Longitudinal studies can be used to track changes in attitudes, behaviors, or outcomes over time, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
This involves an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, or situation to gain a detailed understanding of its characteristics or dynamics. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and business to explore complex phenomena or to generate hypotheses for further research.
Survey Research
This involves collecting data from a sample or population through standardized questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can be used to describe attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or demographic characteristics of a group, and can be conducted in person, by phone, or online.
Observational Research
This involves observing and documenting the behavior or interactions of individuals or groups in a natural or controlled setting. Observational studies can be used to describe social, cultural, or environmental phenomena, or to investigate the effects of interventions or treatments.
Correlational Research
This involves examining the relationships between two or more variables to describe their patterns or associations. Correlational studies can be used to identify potential causal relationships or to explore the strength and direction of relationships between variables.
Data Analysis Methods
Descriptive research design data analysis methods depend on the type of data collected and the research question being addressed. Here are some common methods of data analysis for descriptive research:
Descriptive Statistics
This method involves analyzing data to summarize and describe the key features of a sample or population. Descriptive statistics can include measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (e.g., range, standard deviation).
Cross-tabulation
This method involves analyzing data by creating a table that shows the frequency of two or more variables together. Cross-tabulation can help identify patterns or relationships between variables.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing qualitative data (e.g., text, images, audio) to identify themes, patterns, or trends. Content analysis can be used to describe the characteristics of a sample or population, or to identify factors that influence attitudes or behaviors.
Qualitative Coding
This method involves analyzing qualitative data by assigning codes to segments of data based on their meaning or content. Qualitative coding can be used to identify common themes, patterns, or categories within the data.
Visualization
This method involves creating graphs or charts to represent data visually. Visualization can help identify patterns or relationships between variables and make it easier to communicate findings to others.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing data across different groups or time periods to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can help describe changes in attitudes or behaviors over time or differences between subgroups within a population.
Applications of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has numerous applications in various fields. Some of the common applications of descriptive research design are:
- Market research: Descriptive research design is widely used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes. This helps companies to develop new products and services, improve marketing strategies, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is used in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population. This helps healthcare providers to develop prevention and treatment strategies.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs. This helps educators to improve teaching methods and develop effective educational programs.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs. This helps researchers to understand social behavior and develop effective policies.
- Public opinion research: Descriptive research design is used in public opinion research to understand the opinions and attitudes of the general public on various issues. This helps policymakers to develop effective policies that are aligned with public opinion.
- Environmental research: Descriptive research design is used in environmental research to describe the environmental conditions of a particular region or ecosystem. This helps policymakers and environmentalists to develop effective conservation and preservation strategies.
Descriptive Research Design Examples
Here are some real-time examples of descriptive research designs:
- A restaurant chain wants to understand the demographics and attitudes of its customers. They conduct a survey asking customers about their age, gender, income, frequency of visits, favorite menu items, and overall satisfaction. The survey data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to describe the characteristics of their customer base.
- A medical researcher wants to describe the prevalence and risk factors of a particular disease in a population. They conduct a cross-sectional study in which they collect data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to identify patterns in the prevalence and risk factors of the disease.
- An education researcher wants to describe the learning outcomes of students in a particular school district. They collect test scores from a representative sample of students in the district and use descriptive statistics to calculate the mean, median, and standard deviation of the scores. They also create visualizations such as histograms and box plots to show the distribution of scores.
- A marketing team wants to understand the attitudes and behaviors of consumers towards a new product. They conduct a series of focus groups and use qualitative coding to identify common themes and patterns in the data. They also create visualizations such as word clouds to show the most frequently mentioned topics.
- An environmental scientist wants to describe the biodiversity of a particular ecosystem. They conduct an observational study in which they collect data on the species and abundance of plants and animals in the ecosystem. The data is analyzed using descriptive statistics to describe the diversity and richness of the ecosystem.
How to Conduct Descriptive Research Design
To conduct a descriptive research design, you can follow these general steps:
- Define your research question: Clearly define the research question or problem that you want to address. Your research question should be specific and focused to guide your data collection and analysis.
- Choose your research method: Select the most appropriate research method for your research question. As discussed earlier, common research methods for descriptive research include surveys, case studies, observational studies, cross-sectional studies, and longitudinal studies.
- Design your study: Plan the details of your study, including the sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis plan. Determine the sample size and sampling method, decide on the data collection tools (such as questionnaires, interviews, or observations), and outline your data analysis plan.
- Collect data: Collect data from your sample or population using the data collection tools you have chosen. Ensure that you follow ethical guidelines for research and obtain informed consent from participants.
- Analyze data: Use appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis methods to analyze your data. As discussed earlier, common data analysis methods for descriptive research include descriptive statistics, cross-tabulation, content analysis, qualitative coding, visualization, and comparative analysis.
- I nterpret results: Interpret your findings in light of your research question and objectives. Identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, and describe the characteristics of your sample or population.
- Draw conclusions and report results: Draw conclusions based on your analysis and interpretation of the data. Report your results in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate tables, graphs, or figures to present your findings. Ensure that your report follows accepted research standards and guidelines.
When to Use Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used in situations where the researcher wants to describe a population or phenomenon in detail. It is used to gather information about the current status or condition of a group or phenomenon without making any causal inferences. Descriptive research design is useful in the following situations:
- Exploratory research: Descriptive research design is often used in exploratory research to gain an initial understanding of a phenomenon or population.
- Identifying trends: Descriptive research design can be used to identify trends or patterns in a population, such as changes in consumer behavior or attitudes over time.
- Market research: Descriptive research design is commonly used in market research to understand consumer preferences, behavior, and attitudes.
- Health research: Descriptive research design is useful in health research to describe the prevalence and distribution of a disease or health condition in a population.
- Social science research: Descriptive research design is used in social science research to describe social phenomena such as cultural norms, values, and beliefs.
- Educational research: Descriptive research design is used in educational research to describe the performance of students, schools, or educational programs.
Purpose of Descriptive Research Design
The main purpose of descriptive research design is to describe and measure the characteristics of a population or phenomenon in a systematic and objective manner. It involves collecting data that describe the current status or condition of the population or phenomenon of interest, without manipulating or altering any variables.
The purpose of descriptive research design can be summarized as follows:
- To provide an accurate description of a population or phenomenon: Descriptive research design aims to provide a comprehensive and accurate description of a population or phenomenon of interest. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon.
- To identify trends and patterns: Descriptive research design can help researchers to identify trends and patterns in the data, such as changes in behavior or attitudes over time. This can be useful for making predictions and developing strategies.
- To generate hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- To establish a baseline: Descriptive research design can establish a baseline or starting point for future research. This can be useful for comparing data from different time periods or populations.
Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several key characteristics that distinguish it from other research designs. Some of the main characteristics of descriptive research design are:
- Objective : Descriptive research design is objective in nature, which means that it focuses on collecting factual and accurate data without any personal bias. The researcher aims to report the data objectively without any personal interpretation.
- Non-experimental: Descriptive research design is non-experimental, which means that the researcher does not manipulate any variables. The researcher simply observes and records the behavior or characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Quantitative : Descriptive research design is quantitative in nature, which means that it involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. This helps to provide a more precise and accurate description of the population or phenomenon.
- Cross-sectional: Descriptive research design is often cross-sectional, which means that the data is collected at a single point in time. This can be useful for understanding the current state of the population or phenomenon, but it may not provide information about changes over time.
- Large sample size: Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Systematic and structured: Descriptive research design involves a systematic and structured approach to data collection, which helps to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This involves using standardized procedures for data collection, such as surveys, questionnaires, or observation checklists.
Advantages of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design has several advantages that make it a popular choice for researchers. Some of the main advantages of descriptive research design are:
- Provides an accurate description: Descriptive research design is focused on accurately describing the characteristics of a population or phenomenon. This can help researchers to develop a better understanding of the subject of interest.
- Easy to conduct: Descriptive research design is relatively easy to conduct and requires minimal resources compared to other research designs. It can be conducted quickly and efficiently, and data can be collected through surveys, questionnaires, or observations.
- Useful for generating hypotheses: Descriptive research design can be used to generate hypotheses or research questions that can be tested in future studies. For example, if a descriptive study finds a correlation between two variables, this could lead to the development of a hypothesis about the causal relationship between the variables.
- Large sample size : Descriptive research design typically involves a large sample size, which helps to ensure that the data is representative of the population of interest. A large sample size also helps to increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Can be used to monitor changes : Descriptive research design can be used to monitor changes over time in a population or phenomenon. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns, and for making predictions about future behavior or attitudes.
- Can be used in a variety of fields : Descriptive research design can be used in a variety of fields, including social sciences, healthcare, business, and education.
Limitation of Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design also has some limitations that researchers should consider before using this design. Some of the main limitations of descriptive research design are:
- Cannot establish cause and effect: Descriptive research design cannot establish cause and effect relationships between variables. It only provides a description of the characteristics of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited generalizability: The results of a descriptive study may not be generalizable to other populations or situations. This is because descriptive research design often involves a specific sample or situation, which may not be representative of the broader population.
- Potential for bias: Descriptive research design can be subject to bias, particularly if the researcher is not objective in their data collection or interpretation. This can lead to inaccurate or incomplete descriptions of the population or phenomenon of interest.
- Limited depth: Descriptive research design may provide a superficial description of the population or phenomenon of interest. It does not delve into the underlying causes or mechanisms behind the observed behavior or characteristics.
- Limited utility for theory development: Descriptive research design may not be useful for developing theories about the relationship between variables. It only provides a description of the variables themselves.
- Relies on self-report data: Descriptive research design often relies on self-report data, such as surveys or questionnaires. This type of data may be subject to biases, such as social desirability bias or recall bias.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Qualitative Research Methods

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Descriptive Research | Definition, Types, Methods & Examples
Descriptive Research | Definition, Types, Methods & Examples
Published on May 15, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what , where , when and how questions , but not why questions.
A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables . Unlike in experimental research , the researcher does not control or manipulate any of the variables, but only observes and measures them.
Table of contents
When to use a descriptive research design, descriptive research methods, other interesting articles.
Descriptive research is an appropriate choice when the research aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories.
It is useful when not much is known yet about the topic or problem. Before you can research why something happens, you need to understand how, when and where it happens.
Descriptive research question examples
- How has the Amsterdam housing market changed over the past 20 years?
- Do customers of company X prefer product X or product Y?
- What are the main genetic, behavioural and morphological differences between European wildcats and domestic cats?
- What are the most popular online news sources among under-18s?
- How prevalent is disease A in population B?
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research , though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable .
Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analyzed for frequencies, averages and patterns. Common uses of surveys include:
- Describing the demographics of a country or region
- Gauging public opinion on political and social topics
- Evaluating satisfaction with a company’s products or an organization’s services
Observations
Observations allow you to gather data on behaviours and phenomena without having to rely on the honesty and accuracy of respondents. This method is often used by psychological, social and market researchers to understand how people act in real-life situations.
Observation of physical entities and phenomena is also an important part of research in the natural sciences. Before you can develop testable hypotheses , models or theories, it’s necessary to observe and systematically describe the subject under investigation.
Case studies
A case study can be used to describe the characteristics of a specific subject (such as a person, group, event or organization). Instead of gathering a large volume of data to identify patterns across time or location, case studies gather detailed data to identify the characteristics of a narrowly defined subject.
Rather than aiming to describe generalizable facts, case studies often focus on unusual or interesting cases that challenge assumptions, add complexity, or reveal something new about a research problem .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Descriptive Research | Definition, Types, Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/descriptive-research/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, correlational research | when & how to use, descriptive statistics | definitions, types, examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Join thousands of product people at Insight Out Conf on April 11. Register free.
Insights hub solutions
Analyze data
Uncover deep customer insights with fast, powerful features, store insights, curate and manage insights in one searchable platform, scale research, unlock the potential of customer insights at enterprise scale.
Featured reads
Product updates
Dovetail retro: our biggest releases from the past year
Tips and tricks
How to affinity map using the canvas

Dovetail in the Details: 21 improvements to influence, transcribe, and store
Events and videos
© Dovetail Research Pty. Ltd.
- What is descriptive research?
Last updated
5 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Descriptive research is a common investigatory model used by researchers in various fields, including social sciences, linguistics, and academia.
Read on to understand the characteristics of descriptive research and explore its underlying techniques, processes, and procedures.
Analyze your descriptive research
Dovetail streamlines analysis to help you uncover and share actionable insights
Descriptive research is an exploratory research method. It enables researchers to precisely and methodically describe a population, circumstance, or phenomenon.
As the name suggests, descriptive research describes the characteristics of the group, situation, or phenomenon being studied without manipulating variables or testing hypotheses . This can be reported using surveys , observational studies, and case studies. You can use both quantitative and qualitative methods to compile the data.
Besides making observations and then comparing and analyzing them, descriptive studies often develop knowledge concepts and provide solutions to critical issues. It always aims to answer how the event occurred, when it occurred, where it occurred, and what the problem or phenomenon is.
- Characteristics of descriptive research
The following are some of the characteristics of descriptive research:
Quantitativeness
Descriptive research can be quantitative as it gathers quantifiable data to statistically analyze a population sample. These numbers can show patterns, connections, and trends over time and can be discovered using surveys, polls, and experiments.
Qualitativeness
Descriptive research can also be qualitative. It gives meaning and context to the numbers supplied by quantitative descriptive research .
Researchers can use tools like interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies to illustrate why things are what they are and help characterize the research problem. This is because it’s more explanatory than exploratory or experimental research.
Uncontrolled variables
Descriptive research differs from experimental research in that researchers cannot manipulate the variables. They are recognized, scrutinized, and quantified instead. This is one of its most prominent features.
Cross-sectional studies
Descriptive research is a cross-sectional study because it examines several areas of the same group. It involves obtaining data on multiple variables at the personal level during a certain period. It’s helpful when trying to understand a larger community’s habits or preferences.
Carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive studies are usually carried out in the participants’ everyday environment, which allows researchers to avoid influencing responders by collecting data in a natural setting. You can use online surveys or survey questions to collect data or observe.
Basis for further research
You can further dissect descriptive research’s outcomes and use them for different types of investigation. The outcomes also serve as a foundation for subsequent investigations and can guide future studies. For example, you can use the data obtained in descriptive research to help determine future research designs.
- Descriptive research methods
There are three basic approaches for gathering data in descriptive research: observational, case study, and survey.
You can use surveys to gather data in descriptive research. This involves gathering information from many people using a questionnaire and interview .
Surveys remain the dominant research tool for descriptive research design. Researchers can conduct various investigations and collect multiple types of data (quantitative and qualitative) using surveys with diverse designs.
You can conduct surveys over the phone, online, or in person. Your survey might be a brief interview or conversation with a set of prepared questions intended to obtain quick information from the primary source.
Observation
This descriptive research method involves observing and gathering data on a population or phenomena without manipulating variables. It is employed in psychology, market research , and other social science studies to track and understand human behavior.
Observation is an essential component of descriptive research. It entails gathering data and analyzing it to see whether there is a relationship between the two variables in the study. This strategy usually allows for both qualitative and quantitative data analysis.
Case studies
A case study can outline a specific topic’s traits. The topic might be a person, group, event, or organization.
It involves using a subset of a larger group as a sample to characterize the features of that larger group.
You can generalize knowledge gained from studying a case study to benefit a broader audience.
This approach entails carefully examining a particular group, person, or event over time. You can learn something new about the study topic by using a small group to better understand the dynamics of the entire group.
- Types of descriptive research
There are several types of descriptive study. The most well-known include cross-sectional studies, census surveys, sample surveys, case reports, and comparison studies.
Case reports and case series
In the healthcare and medical fields, a case report is used to explain a patient’s circumstances when suffering from an uncommon illness or displaying certain symptoms. Case reports and case series are both collections of related cases. They have aided the advancement of medical knowledge on countless occasions.
The normative component is an addition to the descriptive survey. In the descriptive–normative survey, you compare the study’s results to the norm.
Descriptive survey
This descriptive type of research employs surveys to collect information on various topics. This data aims to determine the degree to which certain conditions may be attained.
You can extrapolate or generalize the information you obtain from sample surveys to the larger group being researched.
Correlative survey
Correlative surveys help establish if there is a positive, negative, or neutral connection between two variables.
Performing census surveys involves gathering relevant data on several aspects of a given population. These units include individuals, families, organizations, objects, characteristics, and properties.
During descriptive research, you gather different degrees of interest over time from a specific population. Cross-sectional studies provide a glimpse of a phenomenon’s prevalence and features in a population. There are no ethical challenges with them and they are quite simple and inexpensive to carry out.
Comparative studies
These surveys compare the two subjects’ conditions or characteristics. The subjects may include research variables, organizations, plans, and people.
Comparison points, assumption of similarities, and criteria of comparison are three important variables that affect how well and accurately comparative studies are conducted.
For instance, descriptive research can help determine how many CEOs hold a bachelor’s degree and what proportion of low-income households receive government help.
- Pros and cons
The primary advantage of descriptive research designs is that researchers can create a reliable and beneficial database for additional study. To conduct any inquiry, you need access to reliable information sources that can give you a firm understanding of a situation.
Quantitative studies are time- and resource-intensive, so knowing the hypotheses viable for testing is crucial. The basic overview of descriptive research provides helpful hints as to which variables are worth quantitatively examining. This is why it’s employed as a precursor to quantitative research designs.
Some experts view this research as untrustworthy and unscientific. However, there is no way to assess the findings because you don’t manipulate any variables statistically.
Cause-and-effect correlations also can’t be established through descriptive investigations. Additionally, observational study findings cannot be replicated, which prevents a review of the findings and their replication.
The absence of statistical and in-depth analysis and the rather superficial character of the investigative procedure are drawbacks of this research approach.
- Descriptive research examples and applications
Several descriptive research examples are emphasized based on their types, purposes, and applications. Research questions often begin with “What is …” These studies help find solutions to practical issues in social science, physical science, and education.
Here are some examples and applications of descriptive research:
Determining consumer perception and behavior
Organizations use descriptive research designs to determine how various demographic groups react to a certain product or service.
For example, a business looking to sell to its target market should research the market’s behavior first. When researching human behavior in response to a cause or event, the researcher pays attention to the traits, actions, and responses before drawing a conclusion.
Scientific classification
Scientific descriptive research enables the classification of organisms and their traits and constituents.
Measuring data trends
A descriptive study design’s statistical capabilities allow researchers to track data trends over time. It’s frequently used to determine the study target’s current circumstances and underlying patterns.
Conduct comparison
Organizations can use a descriptive research approach to learn how various demographics react to a certain product or service. For example, you can study how the target market responds to a competitor’s product and use that information to infer their behavior.
- Bottom line
A descriptive research design is suitable for exploring certain topics and serving as a prelude to larger quantitative investigations. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the “what” of the group or thing you’re investigating.
This research type acts as the cornerstone of other research methodologies . It is distinctive because it can use quantitative and qualitative research approaches at the same time.
What is descriptive research design?
Descriptive research design aims to systematically obtain information to describe a phenomenon, situation, or population. More specifically, it helps answer the what, when, where, and how questions regarding the research problem rather than the why.
How does descriptive research compare to qualitative research?
Despite certain parallels, descriptive research concentrates on describing phenomena, while qualitative research aims to understand people better.
How do you analyze descriptive research data?
Data analysis involves using various methodologies, enabling the researcher to evaluate and provide results regarding validity and reliability.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 September 2023
Last updated: 14 February 2024
Last updated: 17 February 2024
Last updated: 19 November 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2024
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Just one more step to your free trial.
.surveysparrow.com
Already using SurveySparrow? Login
By clicking on "Get Started", I agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms of Service .
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Enterprise Survey Software
Enterprise Survey Software to thrive in your business ecosystem
NPS Software
Turn customers into promoters
Offline Survey
Real-time data collection, on the move. Go internet-independent.
360 Assessment
Conduct omnidirectional employee assessments. Increase productivity, grow together.
Reputation Management
Turn your existing customers into raving promoters by monitoring online reviews.
Ticket Management
Build loyalty and advocacy by delivering personalized support experiences that matter.
Chatbot for Website
Collect feedback smartly from your website visitors with the engaging Chatbot for website.
Swift, easy, secure. Scalable for your organization.
Executive Dashboard
Customer journey map, craft beautiful surveys, share surveys, gain rich insights, recurring surveys, white label surveys, embedded surveys, conversational forms, mobile-first surveys, audience management, smart surveys, video surveys, secure surveys, api, webhooks, integrations, survey themes, accept payments, custom workflows, all features, customer experience, employee experience, product experience, marketing experience, sales experience, hospitality & travel, market research, saas startup programs, wall of love, success stories, sparrowcast, nps benchmarks, learning centre, apps & integrations.
Our surveys come with superpowers ⚡
Blog General
Descriptive Research 101: Definition, Methods and Examples
Parvathi vijayamohan.
18 October 2023
Table Of Contents
- Descriptive Research 101: The Definitive Guide
What is Descriptive Research?
Key characteristics of descriptive research.
- Descriptive Research Methods: The 3 You Need to Know!
Observation
Case studies, 7 types of descriptive research, descriptive research: examples to build your next study, tips to excel at descriptive research.
Imagine you are a detective called to a crime scene. Your job is to study the scene and report whatever you find: whether that’s the half-smoked cigarette on the table or the large “RACHE” written in blood on the wall. That, in a nutshell, is descriptive research .
Researchers often need to do descriptive research on a problem before they attempt to solve it. So in this guide, we’ll take you through:
- What is descriptive research + characteristics
- Descriptive research methods
- Types of descriptive research
- Descriptive research examples
- Tips to excel at the descriptive method
Click to jump to the section that interests you.
Definition: As its name says, descriptive research describes the characteristics of the problem, phenomenon, situation, or group under study.
So the goal of all descriptive studies is to explore the background, details, and existing patterns in the problem to fully understand it. In other words, preliminary research.
However, descriptive research can be both preliminary and conclusive . You can use the data from a descriptive study to make reports and get insights for further planning.
What descriptive research isn’t: Descriptive research finds the what/when/where of a problem, not the why/how .
Because of this, we can’t use the descriptive method to explore cause-and-effect relationships where one variable (like a person’s job role) affects another variable (like their monthly income).
- Answers the “what,” “when,” and “where” of a research problem. For this reason, it is popularly used in market research , awareness surveys , and opinion polls .
- Sets the stage for a research problem. As an early part of the research process, descriptive studies help you dive deeper into the topic.
- Opens the door for further research. You can use descriptive data as the basis for more profound research, analysis and studies.
- Qualitative and quantitative . It is possible to get a balanced mix of numerical responses and open-ended answers from the descriptive method.
- No control or interference with the variables . The researcher simply observes and reports on them. However, specific research software has filters that allow her to zoom in on one variable.
- Done in natural settings . You can get the best results from descriptive research by talking to people, surveying them, or observing them in a suitable environment. For example, suppose you are a website beta testing an app feature. In that case, descriptive research invites users to try the feature, tracking their behavior and then asking their opinions .
- Can be applied to many research methods and areas. Examples include healthcare, SaaS, psychology, political studies, education, and pop culture.
Descriptive Research Methods: The Top Three You Need to Know!
In short, survey research is a brief interview or conversation with a set of prepared questions about a topic.
So you create a questionnaire, share it, and analyze the data you collect for further action. Learn about the differences between surveys and questionnaires here .
You can access free survey templates , over 20+ question types , and pass data to 1,500+ applications with survey software, like SurveySparrow . It enables you to create surveys, share them and capture data with very little effort.
Sign up today to launch stunning surveys for free.
Please enter a valid Email ID.
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit Card Required • No Strings Attached
- Surveys can be hyper-local, regional, or global, depending on your objectives.
- Share surveys in-person, offline, via SMS, email, or QR codes – so many options !
- Easy to automate if you want to conduct many surveys over a period.
The observational method is a type of descriptive research in which you, the researcher, observe ongoing behavior.
Now, there are several (non-creepy) ways you can observe someone. In fact, observational research has three main approaches:
- Covert observation: In true spy fashion, the researcher mixes in with the group undetected or observes from a distance.
- Overt observation : The researcher identifies himself as a researcher – “The name’s Bond. J. Bond.” – and explains the purpose of the study.
- Participatory observation : The researcher participates in what he is observing to understand his topic better.
- Observation is one of the most accurate ways to get data on a subject’s behavior in a natural setting.
- You don’t need to rely on people’s willingness to share information.
- Observation is a universal method that can be applied to any area of research.
In the case study method, you do a detailed study of a specific group, person, or event over a period.
This brings us to a frequently asked question: “What’s the difference between case studies and longitudinal studies?”
A case study will go very in-depth into the subject with one-on-one interviews, observations, and archival research. They are also qualitative, though sometimes they will use numbers and stats.
An example of longitudinal research would be a study of the health of night shift employees vs. general shift employees over a decade. An example of a case study would involve in-depth interviews with Casey, an assistant director of nursing who’s handled the night shift at the hospital for ten years now.
- Due to the focus on a few people, case studies can give you a tremendous amount of information.
- Because of the time and effort involved, a case study engages both researchers and participants.
- Case studies are helpful for ethically investigating unusual, complex, or challenging subjects. An example would be a study of the habits of long-term cocaine users.
1. Case Study: Airbnb’s Growth Strategy
In an excellent case study, Tam Al Saad, Principal Consultant, Strategy + Growth at Webprofits, deep dives into how Airbnb attracted and retained 150 million users .
“What Airbnb offers isn’t a cheap place to sleep when you’re on holiday; it’s the opportunity to experience your destination as a local would. It’s the chance to meet the locals, experience the markets, and find non-touristy places.
Sure, you can visit the Louvre, see Buckingham Palace, and climb the Empire State Building, but you can do it as if it were your hometown while staying in a place that has character and feels like a home.” – Tam al Saad, Principal Consultant, Strategy + Growth at Webprofits
2. Observation – Better Tech Experiences for the Elderly
We often think that our elders are so hopeless with technology. But we’re not getting any younger either, and tech is changing at a hair trigger! This article by Annemieke Hendricks shares a wonderful example where researchers compare the levels of technological familiarity between age groups and how that influences usage.
“It is generally assumed that older adults have difficulty using modern electronic devices, such as mobile telephones or computers. Because this age group is growing in most countries, changing products and processes to adapt to their needs is increasingly more important. “ – Annemieke Hendricks, Marketing Communication Specialist, Noldus
3. Surveys – Decoding Sleep with SurveySparrow
SRI International (formerly Stanford Research Institute) – an independent, non-profit research center – wanted to investigate the impact of stress on an adolescent’s sleep. To get those insights, two actions were essential: tracking sleep patterns through wearable devices and sending surveys at a pre-set time – the pre-sleep period.
“With SurveySparrow’s recurring surveys feature, SRI was able to share engaging surveys with their participants exactly at the time they wanted and at the frequency they preferred.”
Read more about this project : How SRI International decoded sleep patterns with SurveySparrow
1: Answer the six Ws –
- Who should we consider?
- What information do we need?
- When should we collect the information?
- Where should we collect the information?
- Why are we obtaining the information?
- Way to collect the information
#2: Introduce and explain your methodological approach
#3: Describe your methods of data collection and/or selection.
#4: Describe your methods of analysis.
#5: Explain the reasoning behind your choices.
#6: Collect data.
#7: Analyze the data. Use software to speed up the process and reduce overthinking and human error.
#8: Report your conclusions and how you drew the results.
Wrapping Up
That’s all, folks!
Growth Marketer at SurveySparrow
Fledgling growth marketer. Cloud watcher. Aunty to a naughty beagle.
You Might Also Like
How to respond to negative feedback, 70 best employee onboarding survey questions for new hires, how an nps detractor can help your business.
Leave us your email, we wont spam. Promise!
Start your free trial today
No Credit Card Required. 14-Day Free Trial
Request a Demo
Want to learn more about SurveySparrow? We'll be in touch soon!
Scale up your descriptive research with the best survey software
Build surveys that actually work. give surveysparrow a free try today.
14-Day Free Trial • No Credit card required • 40% more completion rate
Hi there, we use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience and to analyze site traffic. By continuing to use our website, you consent to the use of these cookies. Learn More
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what , where , when , and how questions , but not why questions.
A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables . Unlike in experimental research , the researcher does not control or manipulate any of the variables, but only observes and measures them.
Table of contents
When to use a descriptive research design, descriptive research methods.
Descriptive research is an appropriate choice when the research aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories.
It is useful when not much is known yet about the topic or problem. Before you can research why something happens, you need to understand how, when, and where it happens.
- How has the London housing market changed over the past 20 years?
- Do customers of company X prefer product Y or product Z?
- What are the main genetic, behavioural, and morphological differences between European wildcats and domestic cats?
- What are the most popular online news sources among under-18s?
- How prevalent is disease A in population B?
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Descriptive research is usually defined as a type of quantitative research , though qualitative research can also be used for descriptive purposes. The research design should be carefully developed to ensure that the results are valid and reliable .
Survey research allows you to gather large volumes of data that can be analysed for frequencies, averages, and patterns. Common uses of surveys include:
- Describing the demographics of a country or region
- Gauging public opinion on political and social topics
- Evaluating satisfaction with a company’s products or an organisation’s services
Observations
Observations allow you to gather data on behaviours and phenomena without having to rely on the honesty and accuracy of respondents. This method is often used by psychological, social, and market researchers to understand how people act in real-life situations.
Observation of physical entities and phenomena is also an important part of research in the natural sciences. Before you can develop testable hypotheses , models, or theories, it’s necessary to observe and systematically describe the subject under investigation.
Case studies
A case study can be used to describe the characteristics of a specific subject (such as a person, group, event, or organisation). Instead of gathering a large volume of data to identify patterns across time or location, case studies gather detailed data to identify the characteristics of a narrowly defined subject.
Rather than aiming to describe generalisable facts, case studies often focus on unusual or interesting cases that challenge assumptions, add complexity, or reveal something new about a research problem .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 12 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/descriptive-research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, correlational research | guide, design & examples, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods.
- Descriptive Research Designs: Types, Examples & Methods

One of the components of research is getting enough information about the research problem—the what, how, when and where answers, which is why descriptive research is an important type of research. It is very useful when conducting research whose aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, correlations, and categories.
This research method takes a problem with little to no relevant information and gives it a befitting description using qualitative and quantitative research method s. Descriptive research aims to accurately describe a research problem.
In the subsequent sections, we will be explaining what descriptive research means, its types, examples, and data collection methods.
What is Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why.
This is mainly because it is important to have a proper understanding of what a research problem is about before investigating why it exists in the first place.
For example, an investor considering an investment in the ever-changing Amsterdam housing market needs to understand what the current state of the market is, how it changes (increasing or decreasing), and when it changes (time of the year) before asking for the why. This is where descriptive research comes in.
What Are The Types of Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research is classified into different types according to the kind of approach that is used in conducting descriptive research. The different types of descriptive research are highlighted below:
- Descriptive-survey
Descriptive survey research uses surveys to gather data about varying subjects. This data aims to know the extent to which different conditions can be obtained among these subjects.
For example, a researcher wants to determine the qualification of employed professionals in Maryland. He uses a survey as his research instrument , and each item on the survey related to qualifications is subjected to a Yes/No answer.
This way, the researcher can describe the qualifications possessed by the employed demographics of this community.
- Descriptive-normative survey
This is an extension of the descriptive survey, with the addition being the normative element. In the descriptive-normative survey, the results of the study should be compared with the norm.
For example, an organization that wishes to test the skills of its employees by a team may have them take a skills test. The skills tests are the evaluation tool in this case, and the result of this test is compared with the norm of each role.
If the score of the team is one standard deviation above the mean, it is very satisfactory, if within the mean, satisfactory, and one standard deviation below the mean is unsatisfactory.
- Descriptive-status
This is a quantitative description technique that seeks to answer questions about real-life situations. For example, a researcher researching the income of the employees in a company, and the relationship with their performance.
A survey will be carried out to gather enough data about the income of the employees, then their performance will be evaluated and compared to their income. This will help determine whether a higher income means better performance and low income means lower performance or vice versa.
- Descriptive-analysis
The descriptive-analysis method of research describes a subject by further analyzing it, which in this case involves dividing it into 2 parts. For example, the HR personnel of a company that wishes to analyze the job role of each employee of the company may divide the employees into the people that work at the Headquarters in the US and those that work from Oslo, Norway office.
A questionnaire is devised to analyze the job role of employees with similar salaries and who work in similar positions.
- Descriptive classification
This method is employed in biological sciences for the classification of plants and animals. A researcher who wishes to classify the sea animals into different species will collect samples from various search stations, then classify them accordingly.
- Descriptive-comparative
In descriptive-comparative research, the researcher considers 2 variables that are not manipulated, and establish a formal procedure to conclude that one is better than the other. For example, an examination body wants to determine the better method of conducting tests between paper-based and computer-based tests.
A random sample of potential participants of the test may be asked to use the 2 different methods, and factors like failure rates, time factors, and others will be evaluated to arrive at the best method.
- Correlative Survey
Correlative surveys are used to determine whether the relationship between 2 variables is positive, negative, or neutral. That is, if 2 variables say X and Y are directly proportional, inversely proportional or are not related to each other.
Examples of Descriptive Research
There are different examples of descriptive research, that may be highlighted from its types, uses, and applications. However, we will be restricting ourselves to only 3 distinct examples in this article.
- Comparing Student Performance:
An academic institution may wish 2 compare the performance of its junior high school students in English language and Mathematics. This may be used to classify students based on 2 major groups, with one group going ahead to study while courses, while the other study courses in the Arts & Humanities field.
Students who are more proficient in mathematics will be encouraged to go into STEM and vice versa. Institutions may also use this data to identify students’ weak points and work on ways to assist them.
- Scientific Classification
During the major scientific classification of plants, animals, and periodic table elements, the characteristics and components of each subject are evaluated and used to determine how they are classified.
For example, living things may be classified into kingdom Plantae or kingdom animal is depending on their nature. Further classification may group animals into mammals, pieces, vertebrae, invertebrae, etc.
All these classifications are made a result of descriptive research which describes what they are.
- Human Behavior
When studying human behaviour based on a factor or event, the researcher observes the characteristics, behaviour, and reaction, then use it to conclude. A company willing to sell to its target market needs to first study the behaviour of the market.
This may be done by observing how its target reacts to a competitor’s product, then use it to determine their behaviour.
What are the Characteristics of Descriptive Research?
The characteristics of descriptive research can be highlighted from its definition, applications, data collection methods, and examples. Some characteristics of descriptive research are:
- Quantitativeness
Descriptive research uses a quantitative research method by collecting quantifiable information to be used for statistical analysis of the population sample. This is very common when dealing with research in the physical sciences.
- Qualitativeness
It can also be carried out using the qualitative research method, to properly describe the research problem. This is because descriptive research is more explanatory than exploratory or experimental.
- Uncontrolled variables
In descriptive research, researchers cannot control the variables like they do in experimental research.
- The basis for further research
The results of descriptive research can be further analyzed and used in other research methods. It can also inform the next line of research, including the research method that should be used.
This is because it provides basic information about the research problem, which may give birth to other questions like why a particular thing is the way it is.
Why Use Descriptive Research Design?
Descriptive research can be used to investigate the background of a research problem and get the required information needed to carry out further research. It is used in multiple ways by different organizations, and especially when getting the required information about their target audience.
- Define subject characteristics :
It is used to determine the characteristics of the subjects, including their traits, behaviour, opinion, etc. This information may be gathered with the use of surveys, which are shared with the respondents who in this case, are the research subjects.
For example, a survey evaluating the number of hours millennials in a community spends on the internet weekly, will help a service provider make informed business decisions regarding the market potential of the community.
- Measure Data Trends
It helps to measure the changes in data over some time through statistical methods. Consider the case of individuals who want to invest in stock markets, so they evaluate the changes in prices of the available stocks to make a decision investment decision.
Brokerage companies are however the ones who carry out the descriptive research process, while individuals can view the data trends and make decisions.
Descriptive research is also used to compare how different demographics respond to certain variables. For example, an organization may study how people with different income levels react to the launch of a new Apple phone.
This kind of research may take a survey that will help determine which group of individuals are purchasing the new Apple phone. Do the low-income earners also purchase the phone, or only the high-income earners do?
Further research using another technique will explain why low-income earners are purchasing the phone even though they can barely afford it. This will help inform strategies that will lure other low-income earners and increase company sales.
- Validate existing conditions
When you are not sure about the validity of an existing condition, you can use descriptive research to ascertain the underlying patterns of the research object. This is because descriptive research methods make an in-depth analysis of each variable before making conclusions.
- Conducted Overtime
Descriptive research is conducted over some time to ascertain the changes observed at each point in time. The higher the number of times it is conducted, the more authentic the conclusion will be.
What are the Disadvantages of Descriptive Research?
- Response and Non-response Bias
Respondents may either decide not to respond to questions or give incorrect responses if they feel the questions are too confidential. When researchers use observational methods, respondents may also decide to behave in a particular manner because they feel they are being watched.
- The researcher may decide to influence the result of the research due to personal opinion or bias towards a particular subject. For example, a stockbroker who also has a business of his own may try to lure investors into investing in his own company by manipulating results.
- A case-study or sample taken from a large population is not representative of the whole population.
- Limited scope:The scope of descriptive research is limited to the what of research, with no information on why thereby limiting the scope of the research.
What are the Data Collection Methods in Descriptive Research?
There are 3 main data collection methods in descriptive research, namely; observational method, case study method, and survey research.
1. Observational Method
The observational method allows researchers to collect data based on their view of the behaviour and characteristics of the respondent, with the respondents themselves not directly having an input. It is often used in market research, psychology, and some other social science research to understand human behaviour.
It is also an important aspect of physical scientific research, with it being one of the most effective methods of conducting descriptive research . This process can be said to be either quantitative or qualitative.
Quantitative observation involved the objective collection of numerical data , whose results can be analyzed using numerical and statistical methods.
Qualitative observation, on the other hand, involves the monitoring of characteristics and not the measurement of numbers. The researcher makes his observation from a distance, records it, and is used to inform conclusions.
2. Case Study Method
A case study is a sample group (an individual, a group of people, organizations, events, etc.) whose characteristics are used to describe the characteristics of a larger group in which the case study is a subgroup. The information gathered from investigating a case study may be generalized to serve the larger group.
This generalization, may, however, be risky because case studies are not sufficient to make accurate predictions about larger groups. Case studies are a poor case of generalization.
3. Survey Research
This is a very popular data collection method in research designs. In survey research, researchers create a survey or questionnaire and distribute it to respondents who give answers.
Generally, it is used to obtain quick information directly from the primary source and also conducting rigorous quantitative and qualitative research. In some cases, survey research uses a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
Survey research can be carried out both online and offline using the following methods
- Online Surveys: This is a cheap method of carrying out surveys and getting enough responses. It can be carried out using Formplus, an online survey builder. Formplus has amazing tools and features that will help increase response rates.
- Offline Surveys: This includes paper forms, mobile offline forms , and SMS-based forms.
What Are The Differences Between Descriptive and Correlational Research?
Before going into the differences between descriptive and correlation research, we need to have a proper understanding of what correlation research is about. Therefore, we will be giving a summary of the correlation research below.
Correlational research is a type of descriptive research, which is used to measure the relationship between 2 variables, with the researcher having no control over them. It aims to find whether there is; positive correlation (both variables change in the same direction), negative correlation (the variables change in the opposite direction), or zero correlation (there is no relationship between the variables).
Correlational research may be used in 2 situations;
(i) when trying to find out if there is a relationship between two variables, and
(ii) when a causal relationship is suspected between two variables, but it is impractical or unethical to conduct experimental research that manipulates one of the variables.
Below are some of the differences between correlational and descriptive research:
- Definitions :
Descriptive research aims is a type of research that provides an in-depth understanding of the study population, while correlational research is the type of research that measures the relationship between 2 variables.
- Characteristics :
Descriptive research provides descriptive data explaining what the research subject is about, while correlation research explores the relationship between data and not their description.
- Predictions :
Predictions cannot be made in descriptive research while correlation research accommodates the possibility of making predictions.
Descriptive Research vs. Causal Research
Descriptive research and causal research are both research methodologies, however, one focuses on a subject’s behaviors while the latter focuses on a relationship’s cause-and-effect. To buttress the above point, descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular or specific population or situation.
It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of an already existing state of affairs between variables. Descriptive research answers the questions of “what,” “where,” “when,” and “how” without attempting to establish any causal relationships or explain any underlying factors that might have caused the behavior.
Causal research, on the other hand, seeks to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It aims to point out the factors that influence or cause a particular result or behavior. Causal research involves manipulating variables, controlling conditions or a subgroup, and observing the resulting effects. The primary objective of causal research is to establish a cause-effect relationship and provide insights into why certain phenomena happen the way they do.
Descriptive Research vs. Analytical Research
Descriptive research provides a detailed and comprehensive account of a specific situation or phenomenon. It focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or attempting to explain underlying factors or the cause of the factor.
It is primarily concerned with providing an accurate and objective representation of the subject of research. While analytical research goes beyond the description of the phenomena and seeks to analyze and interpret data to discover if there are patterns, relationships, or any underlying factors.
It examines the data critically, applies statistical techniques or other analytical methods, and draws conclusions based on the discovery. Analytical research also aims to explore the relationships between variables and understand the underlying mechanisms or processes involved.
Descriptive Research vs. Exploratory Research
Descriptive research is a research method that focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. This type of research describes the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context without looking for an underlying cause.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting and analyzing quantitative or qualitative data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. Exploratory research differs from descriptive research because it aims to explore and gain firsthand insights or knowledge into a relatively unexplored or poorly understood topic.
It focuses on generating ideas, hypotheses, or theories rather than providing definitive answers. Exploratory research is often conducted at the early stages of a research project to gather preliminary information and identify key variables or factors for further investigation. It involves open-ended interviews, observations, or small-scale surveys to gather qualitative data.
Read More – Exploratory Research: What are its Method & Examples?
Descriptive Research vs. Experimental Research
Descriptive research aims to describe and document the characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena of a particular population or situation. It focuses on providing an accurate and detailed account of the existing state of affairs.
Descriptive research typically involves collecting data through surveys, observations, or existing records and analyzing the data to generate descriptive statistics or narratives. It does not involve manipulating variables or establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
Experimental research, on the other hand, involves manipulating variables and controlling conditions to investigate cause-and-effect relationships. It aims to establish causal relationships by introducing an intervention or treatment and observing the resulting effects.
Experimental research typically involves randomly assigning participants to different groups, such as control and experimental groups, and measuring the outcomes. It allows researchers to control for confounding variables and draw causal conclusions.
Related – Experimental vs Non-Experimental Research: 15 Key Differences
Descriptive Research vs. Explanatory Research
Descriptive research focuses on providing a detailed and accurate account of a specific situation, group, or phenomenon. It aims to describe the characteristics, behaviors, or relationships within the given context.
Descriptive research is primarily concerned with providing an objective representation of the subject of study without explaining underlying causes or mechanisms. Explanatory research seeks to explain the relationships between variables and uncover the underlying causes or mechanisms.
It goes beyond description and aims to understand the reasons or factors that influence a particular outcome or behavior. Explanatory research involves analyzing data, conducting statistical analyses, and developing theories or models to explain the observed relationships.
Descriptive Research vs. Inferential Research
Descriptive research focuses on describing and summarizing data without making inferences or generalizations beyond the specific sample or population being studied. It aims to provide an accurate and objective representation of the subject of study.
Descriptive research typically involves analyzing data to generate descriptive statistics, such as means, frequencies, or percentages, to describe the characteristics or behaviors observed.
Inferential research, however, involves making inferences or generalizations about a larger population based on a smaller sample.
It aims to draw conclusions about the population characteristics or relationships by analyzing the sample data. Inferential research uses statistical techniques to estimate population parameters, test hypotheses, and determine the level of confidence or significance in the findings.
Related – Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples
Conclusion
The uniqueness of descriptive research partly lies in its ability to explore both quantitative and qualitative research methods. Therefore, when conducting descriptive research, researchers have the opportunity to use a wide variety of techniques that aids the research process.
Descriptive research explores research problems in-depth, beyond the surface level thereby giving a detailed description of the research subject. That way, it can aid further research in the field, including other research methods .
It is also very useful in solving real-life problems in various fields of social science, physical science, and education.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- descriptive research
- descriptive research method
- example of descriptive research
- types of descriptive research
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Type I vs Type II Errors: Causes, Examples & Prevention
This article will discuss the two different types of errors in hypothesis testing and how you can prevent them from occurring in your research

Extrapolation in Statistical Research: Definition, Examples, Types, Applications
In this article we’ll look at the different types and characteristics of extrapolation, plus how it contrasts to interpolation.
Acceptance Sampling: Meaning, Examples, When to Use
In this post, we will discuss extensively what acceptance sampling is and when it is applied.
Cross-Sectional Studies: Types, Pros, Cons & Uses
In this article, we’ll look at what cross-sectional studies are, how it applies to your research and how to use Formplus to collect...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Descriptive Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Descriptive research: what it is and how to use it.
8 min read Understanding the who, what and where of a situation or target group is an essential part of effective research and making informed business decisions.
For example you might want to understand what percentage of CEOs have a bachelor’s degree or higher. Or you might want to understand what percentage of low income families receive government support – or what kind of support they receive.
Descriptive research is what will be used in these types of studies.
In this guide we’ll look through the main issues relating to descriptive research to give you a better understanding of what it is, and how and why you can use it.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a research method used to try and determine the characteristics of a population or particular phenomenon.
Using descriptive research you can identify patterns in the characteristics of a group to essentially establish everything you need to understand apart from why something has happened.
Market researchers use descriptive research for a range of commercial purposes to guide key decisions.
For example you could use descriptive research to understand fashion trends in a given city when planning your clothing collection for the year. Using descriptive research you can conduct in depth analysis on the demographic makeup of your target area and use the data analysis to establish buying patterns.
Conducting descriptive research wouldn’t, however, tell you why shoppers are buying a particular type of fashion item.
Descriptive research design
Descriptive research design uses a range of both qualitative research and quantitative data (although quantitative research is the primary research method) to gather information to make accurate predictions about a particular problem or hypothesis.
As a survey method, descriptive research designs will help researchers identify characteristics in their target market or particular population.
These characteristics in the population sample can be identified, observed and measured to guide decisions.
Descriptive research characteristics
While there are a number of descriptive research methods you can deploy for data collection, descriptive research does have a number of predictable characteristics.
Here are a few of the things to consider:
Measure data trends with statistical outcomes
Descriptive research is often popular for survey research because it generates answers in a statistical form, which makes it easy for researchers to carry out a simple statistical analysis to interpret what the data is saying.
Descriptive research design is ideal for further research
Because the data collection for descriptive research produces statistical outcomes, it can also be used as secondary data for another research study.
Plus, the data collected from descriptive research can be subjected to other types of data analysis .
Uncontrolled variables
A key component of the descriptive research method is that it uses random variables that are not controlled by the researchers. This is because descriptive research aims to understand the natural behavior of the research subject.
It’s carried out in a natural environment
Descriptive research is often carried out in a natural environment. This is because researchers aim to gather data in a natural setting to avoid swaying respondents.
Data can be gathered using survey questions or online surveys.
For example, if you want to understand the fashion trends we mentioned earlier, you would set up a study in which a researcher observes people in the respondent’s natural environment to understand their habits and preferences.
Descriptive research allows for cross sectional study
Because of the nature of descriptive research design and the randomness of the sample group being observed, descriptive research is ideal for cross sectional studies – essentially the demographics of the group can vary widely and your aim is to gain insights from within the group.
This can be highly beneficial when you’re looking to understand the behaviors or preferences of a wider population.
Descriptive research advantages
There are many advantages to using descriptive research, some of them include:
Cost effectiveness
Because the elements needed for descriptive research design are not specific or highly targeted (and occur within the respondent’s natural environment) this type of study is relatively cheap to carry out.
Multiple types of data can be collected
A big advantage of this research type, is that you can use it to collect both quantitative and qualitative data. This means you can use the stats gathered to easily identify underlying patterns in your respondents’ behavior.
Descriptive research disadvantages
Potential reliability issues.
When conducting descriptive research it’s important that the initial survey questions are properly formulated.
If not, it could make the answers unreliable and risk the credibility of your study.
Potential limitations
As we’ve mentioned, descriptive research design is ideal for understanding the what, who or where of a situation or phenomenon.
However, it can’t help you understand the cause or effect of the behavior. This means you’ll need to conduct further research to get a more complete picture of a situation.
Descriptive research methods
Because descriptive research methods include a range of quantitative and qualitative research, there are several research methods you can use.
Use case studies
Case studies in descriptive research involve conducting in-depth and detailed studies in which researchers get a specific person or case to answer questions.
Case studies shouldn’t be used to generate results, rather it should be used to build or establish hypothesis that you can expand into further market research .
For example you could gather detailed data about a specific business phenomenon, and then use this deeper understanding of that specific case.
Use observational methods
This type of study uses qualitative observations to understand human behavior within a particular group.
By understanding how the different demographics respond within your sample you can identify patterns and trends.
As an observational method, descriptive research will not tell you the cause of any particular behaviors, but that could be established with further research.
Use survey research
Surveys are one of the most cost effective ways to gather descriptive data.
An online survey or questionnaire can be used in descriptive studies to gather quantitative information about a particular problem.
Survey research is ideal if you’re using descriptive research as your primary research.
Descriptive research examples
Descriptive research is used for a number of commercial purposes or when organizations need to understand the behaviors or opinions of a population.
One of the biggest examples of descriptive research that is used in every democratic country, is during elections.
Using descriptive research, researchers will use surveys to understand who voters are more likely to choose out of the parties or candidates available.
Using the data provided, researchers can analyze the data to understand what the election result will be.
In a commercial setting, retailers often use descriptive research to figure out trends in shopping and buying decisions.
By gathering information on the habits of shoppers, retailers can get a better understanding of the purchases being made.
Another example that is widely used around the world, is the national census that takes place to understand the population.
The research will provide a more accurate picture of a population’s demographic makeup and help to understand changes over time in areas like population age, health and education level.
Where Qualtrics helps with descriptive research
Whatever type of research you want to carry out, there’s a survey type that will work.
Qualtrics can help you determine the appropriate method and ensure you design a study that will deliver the insights you need.
Our experts can help you with your market research needs , ensuring you get the most out of Qualtrics market research software to design, launch and analyze your data to guide better, more accurate decisions for your organization.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Child Care and Early Education Research Connections
Descriptive research studies.
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group. For example, descriptive studies might be used to answer questions such as: What percentage of Head Start teachers have a bachelor's degree or higher? What is the average reading ability of 5-year-olds when they first enter kindergarten? What kinds of math activities are used in early childhood programs? When do children first receive regular child care from someone other than their parents? When are children with developmental disabilities first diagnosed and when do they first receive services? What factors do programs consider when making decisions about the type of assessments that will be used to assess the skills of the children in their programs? How do the types of services children receive from their early childhood program change as children age?
Descriptive research does not answer questions about why a certain phenomenon occurs or what the causes are. Answers to such questions are best obtained from randomized and quasi-experimental studies . However, data from descriptive studies can be used to examine the relationships (correlations) among variables. While the findings from correlational analyses are not evidence of causality, they can help to distinguish variables that may be important in explaining a phenomenon from those that are not. Thus, descriptive research is often used to generate hypotheses that should be tested using more rigorous designs.
A variety of data collection methods may be used alone or in combination to answer the types of questions guiding descriptive research. Some of the more common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, case studies, and portfolios. The data collected through these methods can be either quantitative or qualitative. Quantitative data are typically analyzed and presenting using descriptive statistics . Using quantitative data, researchers may describe the characteristics of a sample or population in terms of percentages (e.g., percentage of population that belong to different racial/ethnic groups, percentage of low-income families that receive different government services) or averages (e.g., average household income, average scores of reading, mathematics and language assessments). Quantitative data, such as narrative data collected as part of a case study, may be used to organize, classify, and used to identify patterns of behaviors, attitudes, and other characteristics of groups.
Descriptive studies have an important role in early care and education research. Studies such as the National Survey of Early Care and Education and the National Household Education Surveys Program have greatly increased our knowledge of the supply of and demand for child care in the U.S. The Head Start Family and Child Experiences Survey and the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study Program have provided researchers, policy makers and practitioners with rich information about school readiness skills of children in the U.S.
Each of the methods used to collect descriptive data have their own strengths and limitations. The following are some of the strengths and limitations of descriptive research studies in general.
Study participants are questioned or observed in a natural setting (e.g., their homes, child care or educational settings).
Study data can be used to identify the prevalence of particular problems and the need for new or additional services to address these problems.
Descriptive research may identify areas in need of additional research and relationships between variables that require future study. Descriptive research is often referred to as "hypothesis generating research."
Depending on the data collection method used, descriptive studies can generate rich datasets on large and diverse samples.
Limitations:
Descriptive studies cannot be used to establish cause and effect relationships.
Respondents may not be truthful when answering survey questions or may give socially desirable responses.
The choice and wording of questions on a questionnaire may influence the descriptive findings.
Depending on the type and size of sample, the findings may not be generalizable or produce an accurate description of the population of interest.

What is Descriptive Research and How is it Used?

Introduction
What does descriptive research mean, why would you use a descriptive research design, what are the characteristics of descriptive research, examples of descriptive research, what are the data collection methods in descriptive research, how do you analyze descriptive research data, ensuring validity and reliability in the findings.
Conducting descriptive research offers researchers a way to present phenomena as they naturally occur. Rooted in an open-ended and non-experimental nature, this type of research focuses on portraying the details of specific phenomena or contexts, helping readers gain a clearer understanding of topics of interest.
From businesses gauging customer satisfaction to educators assessing classroom dynamics, the data collected from descriptive research provides invaluable insights across various fields.
This article aims to illuminate the essence, utility, characteristics, and methods associated with descriptive research, guiding those who wish to harness its potential in their respective domains.

At its core, descriptive research refers to a systematic approach used by researchers to collect, analyze, and present data about real-life phenomena to describe it in its natural context. It primarily aims to describe what exists, based on empirical observations .
Unlike experimental research, where variables are manipulated to observe outcomes, descriptive research deals with the "as-is" scenario to facilitate further research by providing a framework or new insights on which continuing studies can build.
Definition of descriptive research
Descriptive research is defined as a research method that observes and describes the characteristics of a particular group, situation, or phenomenon.
The goal is not to establish cause and effect relationships but rather to provide a detailed account of the situation.
The difference between descriptive and exploratory research
While both descriptive and exploratory research seek to provide insights into a topic or phenomenon, they differ in their focus. Exploratory research is more about investigating a topic to develop preliminary insights or to identify potential areas of interest.
In contrast, descriptive research offers detailed accounts and descriptions of the observed phenomenon, seeking to paint a full picture of what's happening.
The evolution of descriptive research in academia
Historically, descriptive research has played a foundational role in numerous academic disciplines. Anthropologists, for instance, used this approach to document cultures and societies. Psychologists have employed it to capture behaviors, emotions, and reactions.
Over time, the method has evolved, incorporating technological advancements and adapting to contemporary needs, yet its essence remains rooted in describing a phenomenon or setting as it is.
Descriptive research serves as a cornerstone in the research landscape for its ability to provide a detailed snapshot of life. Its unique qualities and methods make it an invaluable method for various research purposes. Here's why:
Benefits of obtaining a clear picture
Descriptive research captures the present state of phenomena, offering researchers a detailed reflection of situations. This unaltered representation is crucial for sectors like marketing, where understanding current consumer behavior can shape future strategies.
Facilitating data interpretation
Given its straightforward nature, descriptive research can provide data that's easier to interpret, both for researchers and their audiences. Rather than analyzing complex statistical relationships among variables, researchers present detailed descriptions of their qualitative observations . Researchers can engage in in depth analysis relating to their research question , but audiences can also draw insights from their own interpretations or reflections on potential underlying patterns.
Enhancing the clarity of the research problem
By presenting things as they are, descriptive research can help elucidate ambiguous research questions. A well-executed descriptive study can shine light on overlooked aspects of a problem, paving the way for further investigative research.
Addressing practical problems
In real-world scenarios, it's not always feasible to manipulate variables or set up controlled experiments. For instance, in social sciences, understanding cultural norms without interference is paramount. Descriptive research allows for such non-intrusive insights, ensuring genuine understanding.
Building a foundation for future research
Often, descriptive studies act as stepping stones for more complex research endeavors. By establishing baseline data and highlighting patterns, they create a platform upon which more intricate hypotheses can be built and tested in subsequent studies.
Descriptive research is distinguished by a set of hallmark characteristics that set it apart from other research methodologies . Recognizing these features can help researchers effectively design, implement , and interpret descriptive studies.
Specificity in the research question
As with all research, descriptive research starts with a well-defined research question aiming to detail a particular phenomenon. The specificity ensures that the study remains focused on gathering relevant data without unnecessary deviations.
Focus on the present situation
While some research methods aim to predict future trends or uncover historical truths, descriptive research is predominantly concerned with the present. It seeks to capture the current state of affairs, such as understanding today's consumer habits or documenting a newly observed phenomenon.
Standardized and structured methodology
To ensure credibility and consistency in results, descriptive research often employs standardized methods. Whether it's using a fixed set of survey questions or adhering to specific observation protocols, this structured approach ensures that data is collected uniformly, making it easier to compare and analyze.
Non-manipulative approach in observation
One of the standout features of descriptive research is its non-invasive nature. Researchers observe and document without influencing the research subject or the environment. This passive stance ensures that the data gathered is a genuine reflection of the phenomenon under study.
Replicability and consistency in results
Due to its structured methodology, findings from descriptive research can often be replicated in different settings or with different samples. This consistency adds to the credibility of the results, reinforcing the validity of the insights drawn from the study.
Analyze data quickly and efficiently with ATLAS.ti
Download a free trial to see how you can make sense of complex qualitative data.
Numerous fields and sectors conduct descriptive research for its versatile and detailed nature. Through its focus on presenting things as they naturally occur, it provides insights into a myriad of scenarios. Here are some tangible examples from diverse domains:
Conducting market research
Businesses often turn to data analysis through descriptive research to understand the demographics of their target market. For instance, a company launching a new product might survey potential customers to understand their age, gender, income level, and purchasing habits, offering valuable data for targeted marketing strategies.
Evaluating employee behaviors
Organizations rely on descriptive research designs to assess the behavior and attitudes of their employees. By conducting observations or surveys , companies can gather data on workplace satisfaction, collaboration patterns, or the impact of a new office layout on productivity.
Understanding consumer preferences
Brands aiming to understand their consumers' likes and dislikes often use descriptive research. By observing shopping behaviors or conducting product feedback surveys , they can gauge preferences and adjust their offerings accordingly.
Documenting historical patterns
Historians and anthropologists employ descriptive research to identify patterns through analysis of events or cultural practices. For instance, a historian might detail the daily life in a particular era, while an anthropologist might document rituals and ceremonies of a specific tribe.
Assessing student performance
Educational researchers can utilize descriptive studies to understand the effectiveness of teaching methodologies. By observing classrooms or surveying students, they can measure data trends and gauge the impact of a new teaching technique or curriculum on student engagement and performance.
Descriptive research methods aim to authentically represent situations and phenomena. These techniques ensure the collection of comprehensive and reliable data about the subject of interest.
The most appropriate descriptive research method depends on the research question and resources available for your research study.
Surveys and questionnaires
One of the most familiar tools in the researcher's arsenal, surveys and questionnaires offer a structured means of collecting data from a vast audience. Through carefully designed questions, researchers can obtain standardized responses that lend themselves to straightforward comparison and analysis in quantitative and qualitative research .
Survey research can manifest in various formats, from face-to-face interactions and telephone conversations to digital platforms. While surveys can reach a broad audience and generate quantitative data ripe for statistical analysis, they also come with the challenge of potential biases in design and rely heavily on respondent honesty.
Observations and case studies
Direct or participant observation is a method wherein researchers actively watch and document behaviors or events. A researcher might, for instance, observe the dynamics within a classroom or the behaviors of shoppers in a market setting.
Case studies provide an even deeper dive, focusing on a thorough analysis of a specific individual, group, or event. These methods present the advantage of capturing real-time, detailed data, but they might also be time-intensive and can sometimes introduce observer bias .
Interviews and focus groups
Interviews , whether they follow a structured script or flow more organically, are a powerful means to extract detailed insights directly from participants. On the other hand, focus groups gather multiple participants for discussions, aiming to gather diverse and collective opinions on a particular topic or product.
These methods offer the benefit of deep insights and adaptability in data collection . However, they necessitate skilled interviewers, and focus group settings might see individual opinions being influenced by group dynamics.
Document and content analysis
Here, instead of generating new data, researchers examine existing documents or content . This can range from studying historical records and newspapers to analyzing media content or literature.
Analyzing existing content offers the advantage of accessibility and can provide insights over longer time frames. However, the reliability and relevance of the content are paramount, and researchers must approach this method with a discerning eye.
Descriptive research data, rich in details and insights, necessitates meticulous analysis to derive meaningful conclusions. The analysis process transforms raw data into structured findings that can be communicated and acted upon.
Qualitative content analysis
For data collected through interviews , focus groups , observations , or open-ended survey questions , qualitative content analysis is a popular choice. This involves examining non-numerical data to identify patterns, themes, or categories.
By coding responses or observations , researchers can identify recurring elements, making it easier to comprehend larger data sets and draw insights.
Using descriptive statistics
When dealing with quantitative data from surveys or experiments, descriptive statistics are invaluable. Measures such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and frequency distributions help summarize data sets, providing a snapshot of the overall patterns.
Graphical representations like histograms, pie charts, or bar graphs can further help in visualizing these statistics.
Coding and categorizing the data
Both qualitative and quantitative data often require coding. Coding involves assigning labels to specific responses or behaviors to group similar segments of data. This categorization aids in identifying patterns, especially in vast data sets.
For instance, responses to open-ended questions in a survey can be coded based on keywords or sentiments, allowing for a more structured analysis.
Visual representation through graphs and charts
Visual aids like graphs, charts, and plots can simplify complex data, making it more accessible and understandable. Whether it's showcasing frequency distributions through histograms or mapping out relationships with networks, visual representations can elucidate trends and patterns effectively.
In the realm of research , the credibility of findings is paramount. Without trustworthiness in the results, even the most meticulously gathered data can lose its value. Two cornerstones that bolster the credibility of research outcomes are validity and reliability .
Validity: Measuring the right thing
Validity addresses the accuracy of the research. It seeks to answer the question: Is the research genuinely measuring what it aims to measure? In descriptive research, where the objective is to paint an authentic picture of the current state of affairs, ensuring validity is crucial.
For instance, if a study aims to understand consumer preferences for a product category, the questions posed should genuinely reflect those preferences and not veer into unrelated territories. Multiple forms of validity, including content, criterion, and construct validity, can be examined to ensure that the research instruments and processes are aligned with the research goals.
Reliability: Consistency in findings
Reliability, on the other hand, pertains to the consistency of the research findings. When a study demonstrates reliability, this suggests that others could repeat the study and the outcomes would remain consistent across repetitions.
In descriptive research, factors like the clarity of survey questions , the training of observers , and the standardization of interview protocols play a role in enhancing reliability. Techniques such as test-retest and internal consistency measurements can be employed to assess and improve reliability.

Make your research happen with ATLAS.ti
Analyze descriptive research with our powerful data analysis interface. Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti.

Marketing91
Descriptive Research – Characteristics, Methods, Examples, Advantages
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Descriptive research is a type of research that provides an in-depth description of the phenomenon or population under study. Descriptive research is neither in the category of qualitative research nor in the class of quantitative research, but it uses the features of both types of research.
Descriptive research emphasizes what kind of question to be asked in the research study. The descriptive research provides the answer to the “what” part of a research and does not answer the questions why/when/how.
Descriptive research is a suitable choice if you want to learn about the trends of a particular field or the frequency of an event. This research is also an appropriate option when you do not have any information about the research problem, and primary information gathering is required to establish a hypothesis. In this article, you will learn about the characteristics, methods, examples, advantages, and disadvantages of descriptive research.
Table of Contents
Characteristics of Descriptive Research

1. Statistical Outcome
Descriptive research answers the “what” questions in statistical form. As the output is in emphasizes form, it is easy for the researcher to deduce results and implement them. Because of this characteristic of descriptive research, it is popularly used in market researches.
2. The basis for secondary research
The results obtained from descriptive research is in statistical form. Therefore, it can also be used as secondary data for similar research problems. In addition to this, different research techniques can be applied to the data for the analysis of various factors of the research problem.
3. Unrestrained variable
Random variables are used in descriptive research. Therefore, it is not in the hands of researchers to control the variables of descriptive research. In descriptive research, the natural behavior of participants is observed to learn about them.
4. Natural setting
Descriptive researches are usually conducted in natural settings. For example, you can distribute questionnaires of surveys among random people, or in an observational method, you can observe the behavior of people in a particular environment. For example, if you want to learn about the buying behavior of people, then you can go to a supermarket and observe people.
5. Cross-sectional study
In descriptive research, different aspects of a single group are studied and compared to gain a different insight into the group.
Methods of Descriptive Research

There are three methods of descriptive research
1. Case study method
The case study method refers to the in-depth and detailed study of the subject, person or case, which is to be studied. A case study involves a formal research method to carry out the research. Using the outcomes obtained from the case study research hypothesis can be established, which can be used to expand the horizons of research.
However, case study research is not suitable to determine the relationship between cause and effect as it does not provide accurate results. Moreover, the outcome of the case study method is relevant to that particular case and similar cases and can’t be generalised. Case studies are focused on interesting and unusual cases that are complex and challenging and provide additional information about a particular case.
For example, in a medical case study, researchers study a rare medical case to get more knowledge about the medical case. Similarly, case study methods are used by scientists to learn about unusual phenomenon.

2. Observational Method
Observational research is a type of non- experimental research . Observational research can be defined as a type of research where the researcher observes the ongoing behaviors of the subject being studied. Observational research is majorly used in the marketing and social science fields. In observational research, the researcher finds the actions of subjects under study in their natural setting.
Observational methods are different from experimental research methods because, in experimental research methods, an artificial environment is created for the subjects under study. An observational study can be of two types, naturalistic observation or participant observation. A naturalistic observation study means the study of subjects when they are at their natural behavior.
In participant observation, people being observed in the research study are aware of the observation. They are asked to take part in the observation study. Observational research methods are suitable for studying the behavior of subjects under the study. However, this research is incapable of providing information about the actual cause of the behaviours of subjects under study.
3. Survey Research
Survey research is one of the most popular and easy forms of research to obtain information or to collect data. A questionnaire is prepared to contain questions related to the research problem either on paper or in any digital format. These questionnaires are distributed among random people in the hope of getting their accurate opinion.
The survey research method is popularly used in University researches and business researches. Survey research is also called primary research and can be used with other research methods to obtain accurate outcomes.
Moreover, data collected from survey research can be used as secondary research data by other researchers.
Examples of descriptive research

Let us take the case of a sports clothing brand . The sports brand wants to set up a business in selling gym gears. They want to know about in detail about the kind of clothes people want to wear while exercising in the gym. To get in-depth information about the preference of people, they adopted two descriptive methods one is naturalistic observation, and the other is a survey.
In naturalistic observation, they started observing people at different gyms and silently learn about the kind of clothes they prefer to wear. To know more about their choices, they conducted a survey and distributed questionnaire containing questions like How much would they like to spend on a sports track pant?
What color of gym gear do they prefer to wear while working out? Answer to these questions will provide them the knowledge that was difficult to obtain through observing.
A restaurant planned to start to serve continental food to its customers. Therefore, to learn about the choice of people in flavor and taste, they an observation method to learn about what kind of spreads, herbs, and meat preferred by people.
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Descriptive Research.
Advantages of descriptive research

- Data collected from descriptive research is helpful in important decision-making because the data is obtained from a large population. Because using the descriptive survey method, statistical information can be obtained, and analysis of that data can be made to deduce desired results.
- A variety of data can be obtained using different descriptive research methods like surveys, observation, and vase study. These three research methods provide different type of data which can be used to analysis for a research problem. For example, using the case study research method can be used to develop a hypothesis about a research problem.
- One advantage of descriptive research over other research methods is that it is cheap and quick to conduct descriptive research. You don’t require having a great place dedicated only to research. Descriptive research like observation research can be held in natural settings, and you can distribute surveys to people online or get them answered by random people at your business place or other public places.
- Descriptive research provides both quantitative and qualitative data. The variety of data provides a holistic understanding of the research problem.
- Descriptive research can be conducted in natural settings. There is no need to have a designated space to conduct research using any of the descriptive research methods.
Disadvantages of descriptive research
- Descriptive methods only provide the answers for “what” and do not answer the why and how. Therefore, descriptive research methods are not suitable for determining cause and effect relationships.
- Descriptive methods mainly depend on the responses of people. There are chances that people might not act their true selves if they know they are being observed. In the case of the survey method, there are chances that some people don’t answer the questions honestly, which makes the output of the descriptive research study invalid. Because the results derived from this type of data will not be accurate.
- Another problem associated with descriptive research is the halo effect. A researcher might get partial if he knows the participant personally. The observations made in this way would be considered invalid.
- In descriptive research methods, participants are picked randomly. The randomness of the sample can’t represent the whole population accurately.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- What is Behavioral research? Importance, Methods & Examples
- Field Research – Reasons And Methods
- Research Methodology – Overview, Types and Methods
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- What is Advertising? Advertising Methods and Advantages
- 11 Characteristics of Qualitative Research
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Characteristics of Qualitative Descriptive Studies: A Systematic Review
MSN, CRNP, Doctoral Candidate, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
Justine S. Sefcik
MS, RN, Doctoral Candidate, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
Christine Bradway
PhD, CRNP, FAAN, Associate Professor of Gerontological Nursing, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
Qualitative description (QD) is a term that is widely used to describe qualitative studies of health care and nursing-related phenomena. However, limited discussions regarding QD are found in the existing literature. In this systematic review, we identified characteristics of methods and findings reported in research articles published in 2014 whose authors identified the work as QD. After searching and screening, data were extracted from the sample of 55 QD articles and examined to characterize research objectives, design justification, theoretical/philosophical frameworks, sampling and sample size, data collection and sources, data analysis, and presentation of findings. In this review, three primary findings were identified. First, despite inconsistencies, most articles included characteristics consistent with limited, available QD definitions and descriptions. Next, flexibility or variability of methods was common and desirable for obtaining rich data and achieving understanding of a phenomenon. Finally, justification for how a QD approach was chosen and why it would be an appropriate fit for a particular study was limited in the sample and, therefore, in need of increased attention. Based on these findings, recommendations include encouragement to researchers to provide as many details as possible regarding the methods of their QD study so that readers can determine whether the methods used were reasonable and effective in producing useful findings.
Qualitative description (QD) is a label used in qualitative research for studies which are descriptive in nature, particularly for examining health care and nursing-related phenomena ( Polit & Beck, 2009 , 2014 ). QD is a widely cited research tradition and has been identified as important and appropriate for research questions focused on discovering the who, what, and where of events or experiences and gaining insights from informants regarding a poorly understood phenomenon. It is also the label of choice when a straight description of a phenomenon is desired or information is sought to develop and refine questionnaires or interventions ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sullivan-Bolyai et al., 2005 ).
Despite many strengths and frequent citations of its use, limited discussions regarding QD are found in qualitative research textbooks and publications. To the best of our knowledge, only seven articles include specific guidance on how to design, implement, analyze, or report the results of a QD study ( Milne & Oberle, 2005 ; Neergaard, Olesen, Andersen, & Sondergaard, 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 , 2010 ; Sullivan-Bolyai, Bova, & Harper, 2005 ; Vaismoradi, Turunen, & Bondas, 2013 ; Willis, Sullivan-Bolyai, Knafl, & Zichi-Cohen, 2016 ). Furthermore, little is known about characteristics of QD as reported in journal-published, nursing-related, qualitative studies. Therefore, the purpose of this systematic review was to describe specific characteristics of methods and findings of studies reported in journal articles (published in 2014) self-labeled as QD. In this review, we did not have a goal to judge whether QD was done correctly but rather to report on the features of the methods and findings.
Features of QD
Several QD design features and techniques have been described in the literature. First, researchers generally draw from a naturalistic perspective and examine a phenomenon in its natural state ( Sandelowski, 2000 ). Second, QD has been described as less theoretical compared to other qualitative approaches ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ), facilitating flexibility in commitment to a theory or framework when designing and conducting a study ( Sandelowski, 2000 , 2010 ). For example, researchers may or may not decide to begin with a theory of the targeted phenomenon and do not need to stay committed to a theory or framework if their investigations take them down another path ( Sandelowski, 2010 ). Third, data collection strategies typically involve individual and/or focus group interviews with minimal to semi-structured interview guides ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 ). Fourth, researchers commonly employ purposeful sampling techniques such as maximum variation sampling which has been described as being useful for obtaining broad insights and rich information ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 ). Fifth, content analysis (and in many cases, supplemented by descriptive quantitative data to describe the study sample) is considered a primary strategy for data analysis ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 ). In some instances thematic analysis may also be used to analyze data; however, experts suggest care should be taken that this type of analysis is not confused with content analysis ( Vaismoradi et al., 2013 ). These data analysis approaches allow researchers to stay close to the data and as such, interpretation is of low-inference ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ), meaning that different researchers will agree more readily on the same findings even if they do not choose to present the findings in the same way ( Sandelowski, 2000 ). Finally, representation of study findings in published reports is expected to be straightforward, including comprehensive descriptive summaries and accurate details of the data collected, and presented in a way that makes sense to the reader ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 ).
It is also important to acknowledge that variations in methods or techniques may be appropriate across QD studies ( Sandelowski, 2010 ). For example, when consistent with the study goals, decisions may be made to use techniques from other qualitative traditions, such as employing a constant comparative analytic approach typically associated with grounded theory ( Sandelowski, 2000 ).
Search Strategy and Study Screening
The PubMed electronic database was searched for articles written in English and published from January 1, 2014 to December 31, 2014, using the terms, “qualitative descriptive study,” “qualitative descriptive design,” and “qualitative description,” combined with “nursing.” This specific publication year, “2014,” was chosen because it was the most recent full year at the time of beginning this systematic review. As we did not intend to identify trends in QD approaches over time, it seemed reasonable to focus on the nursing QD studies published in a certain year. The inclusion criterion for this review was data-based, nursing-related, research articles in which authors used the terms QD, qualitative descriptive study, or qualitative descriptive design in their titles or abstracts as well as in the main texts of the publication.
All articles yielded through an initial search in PubMed were exported into EndNote X7 ( Thomson Reuters, 2014 ), a reference management software, and duplicates were removed. Next, titles and abstracts were reviewed to determine if the publication met inclusion criteria; all articles meeting inclusion criteria were then read independently in full by two authors (HK and JS) to determine if the terms – QD or qualitative descriptive study/design – were clearly stated in the main texts. Any articles in which researchers did not specifically state these key terms in the main text were then excluded, even if the terms had been used in the study title or abstract. In one article, for example, although “qualitative descriptive study” was reported in the published abstract, the researchers reported a “qualitative exploratory design” in the main text of the article ( Sundqvist & Carlsson, 2014 ); therefore, this article was excluded from our review. Despite the possibility that there may be other QD studies published in 2014 that were not labeled as such, to facilitate our screening process we only included articles where the researchers clearly used our search terms for their approach. Finally, the two authors compared, discussed, and reconciled their lists of articles with a third author (CB).
Study Selection
Initially, although the year 2014 was specifically requested, 95 articles were identified (due to ahead of print/Epub) and exported into the EndNote program. Three duplicate publications were removed and the 20 articles with final publication dates of 2015 were also excluded. The remaining 72 articles were then screened by examining titles, abstracts, and full-texts. Based on our inclusion criteria, 15 (of 72) were then excluded because QD or QD design/study was not identified in the main text. We then re-examined the remaining 57 articles and excluded two additional articles that did not meet inclusion criteria (e.g., QD was only reported as an analytic approach in the data analysis section). The remaining 55 publications met inclusion criteria and comprised the sample for our systematic review (see Figure 1 ).

Flow Diagram of Study Selection
Of the 55 publications, 23 originated from North America (17 in the United States; 6 in Canada), 12 from Asia, 11 from Europe, 7 from Australia and New Zealand, and 2 from South America. Eleven studies were part of larger research projects and two of them were reported as part of larger mixed-methods studies. Four were described as a secondary analysis.
Quality Appraisal Process
Following the identification of the 55 publications, two authors (HK and JS) independently examined each article using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) qualitative checklist ( CASP, 2013 ). The CASP was chosen to determine the general adequacy (or rigor) of the qualitative studies included in this review as the CASP criteria are generic and intend to be applied to qualitative studies in general. In addition, the CASP was useful because we were able to examine the internal consistency between study aims and methods and between study aims and findings as well as the usefulness of findings ( CASP, 2013 ). The CASP consists of 10 main questions with several sub-questions to consider when making a decision about the main question ( CASP, 2013 ). The first two questions have reviewers examine the clarity of study aims and appropriateness of using qualitative research to achieve the aims. With the next eight questions, reviewers assess study design, sampling, data collection, and analysis as well as the clarity of the study’s results statement and the value of the research. We used the seven questions and 17 sub-questions related to methods and statement of findings to evaluate the articles. The results of this process are presented in Table 1 .
CASP Questions and Quality Appraisal Results (N = 55)
Note . The CASP questions are adapted from “10 questions to help you make sense of qualitative research,” by Critical Appraisal Skills Programme, 2013, retrieved from http://media.wix.com/ugd/dded87_29c5b002d99342f788c6ac670e49f274.pdf . Its license can be found at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Once articles were assessed by the two authors independently, all three authors discussed and reconciled our assessment. No articles were excluded based on CASP results; rather, results were used to depict the general adequacy (or rigor) of all 55 articles meeting inclusion criteria for our systematic review. In addition, the CASP was included to enhance our examination of the relationship between the methods and the usefulness of the findings documented in each of the QD articles included in this review.
Process for Data Extraction and Analysis
To further assess each of the 55 articles, data were extracted on: (a) research objectives, (b) design justification, (c) theoretical or philosophical framework, (d) sampling and sample size, (e) data collection and data sources, (f) data analysis, and (g) presentation of findings (see Table 2 ). We discussed extracted data and identified common and unique features in the articles included in our systematic review. Findings are described in detail below and in Table 3 .
Elements for Data Extraction
Data Extraction and Analysis Results
Note . NR = not reported
Quality Appraisal Results
Justification for use of a QD design was evident in close to half (47.3%) of the 55 publications. While most researchers clearly described recruitment strategies (80%) and data collection methods (100%), justification for how the study setting was selected was only identified in 38.2% of the articles and almost 75% of the articles did not include any reason for the choice of data collection methods (e.g., focus-group interviews). In the vast majority (90.9%) of the articles, researchers did not explain their involvement and positionality during the process of recruitment and data collection or during data analysis (63.6%). Ethical standards were reported in greater than 89% of all articles and most articles included an in-depth description of data analysis (83.6%) and development of categories or themes (92.7%). Finally, all researchers clearly stated their findings in relation to research questions/objectives. Researchers of 83.3% of the articles discussed the credibility of their findings (see Table 1 ).
Research Objectives
In statements of study objectives and/or questions, the most frequently used verbs were “explore” ( n = 22) and “describe” ( n = 17). Researchers also used “identify” ( n = 3), “understand” ( n = 4), or “investigate” ( n = 2). Most articles focused on participants’ experiences related to certain phenomena ( n = 18), facilitators/challenges/factors/reasons ( n = 14), perceptions about specific care/nursing practice/interventions ( n = 11), and knowledge/attitudes/beliefs ( n = 3).
Design Justification
A total of 30 articles included references for QD. The most frequently cited references ( n = 23) were “Whatever happened to qualitative description?” ( Sandelowski, 2000 ) and “What’s in a name? Qualitative description revisited” ( Sandelowski, 2010 ). Other references cited included “Qualitative description – the poor cousin of health research?” ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ), “Reaching the parts other methods cannot reach: an introduction to qualitative methods in health and health services research” ( Pope & Mays, 1995 ), and general research textbooks ( Polit & Beck, 2004 , 2012 ).
In 26 articles (and not necessarily the same as those citing specific references to QD), researchers provided a rationale for selecting QD. Most researchers chose QD because this approach aims to produce a straight description and comprehensive summary of the phenomenon of interest using participants’ language and staying close to the data (or using low inference).
Authors of two articles distinctly stated a QD design, yet also acknowledged grounded-theory or phenomenological overtones by adopting some techniques from these qualitative traditions ( Michael, O'Callaghan, Baird, Hiscock, & Clayton, 2014 ; Peacock, Hammond-Collins, & Forbes, 2014 ). For example, Michael et al. (2014 , p. 1066) reported:
The research used a qualitative descriptive design with grounded theory overtones ( Sandelowski, 2000 ). We sought to provide a comprehensive summary of participants’ views through theoretical sampling; multiple data sources (focus groups [FGs] and interviews); inductive, cyclic, and constant comparative analysis; and condensation of data into thematic representations ( Corbin & Strauss, 1990 , 2008 ).
Authors of four additional articles included language suggestive of a grounded-theory or phenomenological tradition, e.g., by employing a constant comparison technique or translating themes stated in participants’ language into the primary language of the researchers during data analysis ( Asemani et al., 2014 ; Li, Lee, Chen, Jeng, & Chen, 2014 ; Ma, 2014 ; Soule, 2014 ). Additionally, Li et al. (2014) specifically reported use of a grounded-theory approach.
Theoretical or Philosophical Framework
In most (n = 48) articles, researchers did not specify any theoretical or philosophical framework. Of those articles in which a framework or philosophical stance was included, the authors of five articles described the framework as guiding the development of an interview guide ( Al-Zadjali, Keller, Larkey, & Evans, 2014 ; DeBruyn, Ochoa-Marin, & Semenic, 2014 ; Fantasia, Sutherland, Fontenot, & Ierardi, 2014 ; Ma, 2014 ; Wiens, Babenko-Mould, & Iwasiw, 2014 ). In two articles, data analysis was described as including key concepts of a framework being used as pre-determined codes or categories ( Al-Zadjali et al., 2014 ; Wiens et al., 2014 ). Oosterveld-Vlug et al. (2014) and Zhang, Shan, and Jiang (2014) discussed a conceptual model and underlying philosophy in detail in the background or discussion section, although the model and philosophy were not described as being used in developing interview questions or analyzing data.
Sampling and Sample Size
In 38 of the 55 articles, researchers reported ‘purposeful sampling’ or some derivation of purposeful sampling such as convenience ( n = 10), maximum variation ( n = 8), snowball ( n = 3), and theoretical sampling ( n = 1). In three instances ( Asemani et al., 2014 ; Chan & Lopez, 2014 ; Soule, 2014 ), multiple sampling strategies were described, for example, a combination of snowball, convenience, and maximum variation sampling. In articles where maximum variation sampling was employed, “variation” referred to seeking diversity in participants’ demographics ( n = 7; e.g., age, gender, and education level), while one article did not include details regarding how their maximum variation sampling strategy was operationalized ( Marcinowicz, Abramowicz, Zarzycka, Abramowicz, & Konstantynowicz, 2014 ). Authors of 17 articles did not specify their sampling techniques.
Sample sizes ranged from 8 to 1,932 with nine studies in the 8–10 participant range and 24 studies in the 11–20 participant range. The participant range of 21–30 and 31–50 was reported in eight articles each. Six studies included more than 50 participants. Two of these articles depicted quite large sample sizes (N=253, Hart & Mareno, 2014 ; N=1,932, Lyndon et al., 2014 ) and the authors of these articles described the use of survey instruments and analysis of responses to open-ended questions. This was in contrast to studies with smaller sample sizes where individual interviews and focus groups were more commonly employed.
Data Collection and Data Sources
In a majority of studies, researchers collected data through individual ( n = 39) and/or focus-group ( n = 14) interviews that were semistructured. Most researchers reported that interviews were audiotaped ( n = 51) and interview guides were described as the primary data collection tool in 29 of the 51 studies. In some cases, researchers also described additional data sources, for example, taking memos or field notes during participant observation sessions or as a way to reflect their thoughts about interviews ( n = 10). Written responses to open-ended questions in survey questionnaires were another type of data source in a small number of studies ( n = 4).
Data Analysis
The analysis strategy most commonly used in the QD studies included in this review was qualitative content analysis ( n = 30). Among the studies where this technique was used, most researchers described an inductive approach; researchers of two studies analyzed data both inductively and deductively. Thematic analysis was adopted in 14 studies and the constant comparison technique in 10 studies. In nine studies, researchers employed multiple techniques to analyze data including qualitative content analysis with constant comparison ( Asemani et al., 2014 ; DeBruyn et al., 2014 ; Holland, Christensen, Shone, Kearney, & Kitzman, 2014 ; Li et al., 2014 ) and thematic analysis with constant comparison ( Johansson, Hildingsson, & Fenwick, 2014 ; Oosterveld-Vlug et al., 2014 ). In addition, five teams conducted descriptive statistical analysis using both quantitative and qualitative data and counting the frequencies of codes/themes ( Ewens, Chapman, Tulloch, & Hendricks, 2014 ; Miller, 2014 ; Santos, Sandelowski, & Gualda, 2014 ; Villar, Celdran, Faba, & Serrat, 2014 ) or targeted events through video monitoring ( Martorella, Boitor, Michaud, & Gelinas, 2014 ). Tseng, Chen, and Wang (2014) cited Thorne, Reimer Kirkham, and O’Flynn-Magee (2004)’s interpretive description as the inductive analytic approach. In five out of 55 articles, researchers did not specifically name their analysis strategies, despite including descriptions about procedural aspects of data analysis. Researchers of 20 studies reported that data saturation for their themes was achieved.
Presentation of Findings
Researchers described participants’ experiences of health care, interventions, or illnesses in 18 articles and presented straightforward, focused, detailed descriptions of facilitators, challenges, factors, reasons, and causes in 15 articles. Participants’ perceptions of specific care, interventions, or programs were described in detail in 11 articles. All researchers presented their findings with extensive descriptions including themes or categories. In 25 of 55 articles, figures or tables were also presented to illustrate or summarize the findings. In addition, the authors of three articles summarized, organized, and described their data using key concepts of conceptual models ( Al-Zadjali et al., 2014 ; Oosterveld-Vlug et al., 2014 ; Wiens et al., 2014 ). Martorella et al. (2014) assessed acceptability and feasibility of hand massage therapy and arranged their findings in relation to pre-determined indicators of acceptability and feasibility. In one longitudinal QD study ( Kneck, Fagerberg, Eriksson, & Lundman, 2014 ), the researchers presented the findings as several key patterns of learning for persons living with diabetes; in another longitudinal QD study ( Stegenga & Macpherson, 2014 ), findings were presented as processes and themes regarding patients’ identity work across the cancer trajectory. In another two studies, the researchers described and compared themes or categories from two different perspectives, such as patients and nurses ( Canzan, Heilemann, Saiani, Mortari, & Ambrosi, 2014 ) or parents and children ( Marcinowicz et al., 2014 ). Additionally, Ma (2014) reported themes using both participants’ language and the researcher’s language.
In this systematic review, we examined and reported specific characteristics of methods and findings reported in journal articles self-identified as QD and published during one calendar year. To accomplish this we identified 55 articles that met inclusion criteria, performed a quality appraisal following CASP guidelines, and extracted and analyzed data focusing on QD features. In general, three primary findings emerged. First, despite inconsistencies, most QD publications had the characteristics that were originally observed by Sandelowski (2000) and summarized by other limited available QD literature. Next, there are no clear boundaries in methods used in the QD studies included in this review; in a number of studies, researchers adopted and combined techniques originating from other qualitative traditions to obtain rich data and increase their understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. Finally, justification for how QD was chosen and why it would be an appropriate fit for a particular study is an area in need of increased attention.
In general, the overall characteristics were consistent with design features of QD studies described in the literature ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 , 2010 ; Vaismoradi et al., 2013 ). For example, many authors reported that study objectives were to describe or explore participants’ experiences and factors related to certain phenomena, events, or interventions. In most cases, these authors cited Sandelowski (2000) as a reference for this particular characteristic. It was rare that theoretical or philosophical frameworks were identified, which also is consistent with descriptions of QD. In most studies, researchers used purposeful sampling and its derivative sampling techniques, collected data through interviews, and analyzed data using qualitative content analysis or thematic analysis. Moreover, all researchers presented focused or comprehensive, descriptive summaries of data including themes or categories answering their research questions. These characteristics do not indicate that there are correct ways to do QD studies; rather, they demonstrate how others designed and produced QD studies.
In several studies, researchers combined techniques that originated from other qualitative traditions for sampling, data collection, and analysis. This flexibility or variability, a key feature of recently published QD studies, may indicate that there are no clear boundaries in designing QD studies. Sandelowski (2010) articulated: “in the actual world of research practice, methods bleed into each other; they are so much messier than textbook depictions” (p. 81). Hammersley (2007) also observed:
“We are not so much faced with a set of clearly differentiated qualitative approaches as with a complex landscape of variable practice in which the inhabitants use a range of labels (‘ethnography’, ‘discourse analysis’, ‘life history work’, narrative study’, ……, and so on) in diverse and open-ended ways in order to characterize their orientation, and probably do this somewhat differently across audiences and occasions” (p. 293).
This concept of having no clear boundaries in methods when designing a QD study should enable researchers to obtain rich data and produce a comprehensive summary of data through various data collection and analysis approaches to answer their research questions. For example, using an ethnographical approach (e.g., participant observation) in data collection for a QD study may facilitate an in-depth description of participants’ nonverbal expressions and interactions with others and their environment as well as situations or events in which researchers are interested ( Kawulich, 2005 ). One example found in our review is that Adams et al. (2014) explored family members’ responses to nursing communication strategies for patients in intensive care units (ICUs). In this study, researchers conducted interviews with family members, observed interactions between healthcare providers, patients, and family members in ICUs, attended ICU rounds and family meetings, and took field notes about their observations and reflections. Accordingly, the variability in methods provided Adams and colleagues (2014) with many different aspects of data that were then used to complement participants’ interviews (i.e., data triangulation). Moreover, by using a constant comparison technique in addition to qualitative content analysis or thematic analysis in QD studies, researchers compare each case with others looking for similarities and differences as well as reasoning why differences exist, to generate more general understanding of phenomena of interest ( Thorne, 2000 ). In fact, this constant comparison analysis is compatible with qualitative content analysis and thematic analysis and we found several examples of using this approach in studies we reviewed ( Asemani et al., 2014 ; DeBruyn et al., 2014 ; Holland et al., 2014 ; Johansson et al., 2014 ; Li et al., 2014 ; Oosterveld-Vlug et al., 2014 ).
However, this flexibility or variability in methods of QD studies may cause readers’ as well as researchers’ confusion in designing and often labeling qualitative studies ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ). Especially, it could be difficult for scholars unfamiliar with qualitative studies to differentiate QD studies with “hues, tones, and textures” of qualitative traditions ( Sandelowski, 2000 , p. 337) from grounded theory, phenomenological, and ethnographical research. In fact, the major difference is in the presentation of the findings (or outcomes of qualitative research) ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ; Sandelowski, 2000 ). The final products of grounded theory, phenomenological, and ethnographical research are a generation of a theory, a description of the meaning or essence of people’s lived experience, and an in-depth, narrative description about certain culture, respectively, through researchers’ intensive/deep interpretations, reflections, and/or transformation of data ( Streubert & Carpenter, 2011 ). In contrast, QD studies result in “a rich, straight description” of experiences, perceptions, or events using language from the collected data ( Neergaard et al., 2009 ) through low-inference (or data-near) interpretations during data analysis ( Sandelowski, 2000 , 2010 ). This feature is consistent with our finding regarding presentation of findings: in all QD articles included in this systematic review, the researchers presented focused or comprehensive, descriptive summaries to their research questions.
Finally, an explanation or justification of why a QD approach was chosen or appropriate for the study aims was not found in more than half of studies in the sample. While other qualitative approaches, including grounded theory, phenomenology, ethnography, and narrative analysis, are used to better understand people’s thoughts, behaviors, and situations regarding certain phenomena ( Sullivan-Bolyai et al., 2005 ), as noted above, the results will likely read differently than those for a QD study ( Carter & Little, 2007 ). Therefore, it is important that researchers accurately label and justify their choices of approach, particularly for studies focused on participants’ experiences, which could be addressed with other qualitative traditions. Justifying one’s research epistemology, methodology, and methods allows readers to evaluate these choices for internal consistency, provides context to assist in understanding the findings, and contributes to the transparency of choices, all of which enhance the rigor of the study ( Carter & Little, 2007 ; Wu, Thompson, Aroian, McQuaid, & Deatrick, 2016 ).
Use of the CASP tool drew our attention to the credibility and usefulness of the findings of the QD studies included in this review. Although justification for study design and methods was lacking in many articles, most authors reported techniques of recruitment, data collection, and analysis that appeared. Internal consistencies among study objectives, methods, and findings were achieved in most studies, increasing readers’ confidence that the findings of these studies are credible and useful in understanding under-explored phenomenon of interest.
In summary, our findings support the notion that many scholars employ QD and include a variety of commonly observed characteristics in their study design and subsequent publications. Based on our review, we found that QD as a scholarly approach allows flexibility as research questions and study findings emerge. We encourage authors to provide as many details as possible regarding how QD was chosen for a particular study as well as details regarding methods to facilitate readers’ understanding and evaluation of the study design and rigor. We acknowledge the challenge of strict word limitation with submissions to print journals; potential solutions include collaboration with journal editors and staff to consider creative use of charts or tables, or using more citations and less text in background sections so that methods sections are robust.
Limitations
Several limitations of this review deserve mention. First, only articles where researchers explicitly stated in the main body of the article that a QD design was employed were included. In contrast, articles labeled as QD in only the title or abstract, or without their research design named were not examined due to the lack of certainty that the researchers actually carried out a QD study. As a result, we may have excluded some studies where a QD design was followed. Second, only one database was searched and therefore we did not identify or describe potential studies following a QD approach that were published in non-PubMed databases. Third, our review is limited by reliance on what was included in the published version of a study. In some cases, this may have been a result of word limits or specific styles imposed by journals, or inconsistent reporting preferences of authors and may have limited our ability to appraise the general adequacy with the CASP tool and examine specific characteristics of these studies.
Conclusions
A systematic review was conducted by examining QD research articles focused on nursing-related phenomena and published in one calendar year. Current patterns include some characteristics of QD studies consistent with the previous observations described in the literature, a focus on the flexibility or variability of methods in QD studies, and a need for increased explanations of why QD was an appropriate label for a particular study. Based on these findings, recommendations include encouragement to authors to provide as many details as possible regarding the methods of their QD study. In this way, readers can thoroughly consider and examine if the methods used were effective and reasonable in producing credible and useful findings.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the John A. Hartford Foundation’s National Hartford Centers of Gerontological Nursing Excellence Award Program.
Hyejin Kim is a Ruth L. Kirschstein NRSA Predoctoral Fellow (F31NR015702) and 2013–2015 National Hartford Centers of Gerontological Nursing Excellence Patricia G. Archbold Scholar. Justine Sefcik is a Ruth L. Kirschstein Predoctoral Fellow (F31NR015693) through the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Nursing Research.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Contributor Information
Hyejin Kim, MSN, CRNP, Doctoral Candidate, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing.
Justine S. Sefcik, MS, RN, Doctoral Candidate, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing.
Christine Bradway, PhD, CRNP, FAAN, Associate Professor of Gerontological Nursing, University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing.
- Adams JA, Anderson RA, Docherty SL, Tulsky JA, Steinhauser KE, Bailey DE., Jr Nursing strategies to support family members of ICU patients at high risk of dying. Heart & Lung. 2014; 43 (5):406–415. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahlin J, Ericson-Lidman E, Norberg A, Strandberg G. Care providers' experiences of guidelines in daily work at a municipal residential care facility for older people. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 2014; 28 (2):355–363. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Al-Zadjali M, Keller C, Larkey L, Evans B. GCC women: causes and processes of midlife weight gain. Health Care for Women International. 2014; 35 (11–12):1267–1286. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asemani O, Iman MT, Moattari M, Tabei SZ, Sharif F, Khayyer M. An exploratory study on the elements that might affect medical students' and residents' responsibility during clinical training. Journal of Medical Ethics and History of Medicine. 2014; 7 :8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Atefi N, Abdullah KL, Wong LP, Mazlom R. Factors influencing registered nurses perception of their overall job satisfaction: a qualitative study. International Nursing Review. 2014; 61 (3):352–360. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ballangrud R, Hall-Lord ML, Persenius M, Hedelin B. Intensive care nurses' perceptions of simulation-based team training for building patient safety in intensive care: a descriptive qualitative study. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing. 2014; 30 (4):179–187. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benavides-Vaello S, Katz JR, Peterson JC, Allen CB, Paul R, Charette-Bluff AL, Morris P. Nursing and health sciences workforce diversity research using. PhotoVoice: a college and high school student participatory project. Journal of Nursing Education. 2014; 53 (4):217–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bernhard C, Zielinski R, Ackerson K, English J. Home birth after hospital birth: women's choices and reflections. Journal of Midwifery and Women's Health. 2014; 59 (2):160–166. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borbasi S, Jackson D, Langford RW. Navigating the maze of nursing research: An interactive learning adventure. 2nd. New South Wales, Australia: Mosby/Elsevier; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradford B, Maude R. Fetal response to maternal hunger and satiation - novel finding from a qualitative descriptive study of maternal perception of fetal movements. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2014; 14 :288. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burns N, Grove SK. The practice of nursing research: Conduct, critique, & utilization. 5th. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Canzan F, Heilemann MV, Saiani L, Mortari L, Ambrosi E. Visible and invisible caring in nursing from the perspectives of patients and nurses in the gerontological context. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 2014; 28 (4):732–740. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carter SM, Littler M. Justifying knowledge, justifying methods, taking action: Epistemologies, methodologies, and methods in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research. 2007; 17 (10):1316–1328. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP 2013) 10 questions to help you make sense of qualitative research. Oxford: CASP; 2013. Retrieved from http://media.wix.com/ugd/dded87_29c5b002d99342f788c6ac670e49f274.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Chan CW, Lopez V. A qualitative descriptive study of risk reduction for coronary disease among the Hong Kong Chinese. Public Health Nursing. 2014; 31 (4):327–335. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen YJ, Tsai YF, Lee SH, Lee HL. Protective factors against suicide among young-old Chinese outpatients. BMC Public Health. 2014; 14 :372. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cleveland LM, Bonugli R. Experiences of mothers of infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome in the neonatal intensive care unit. Journal of Obstetric Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing. 2014; 43 (3):318–329. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corbin J, Strauss A. Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 3rd. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corbin JM, Strauss A. Grounded theory research: Procedures, canons and evaluation criteria. Qualitative Sociology. 1990; 13 (1):3–21. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeBruyn RR, Ochoa-Marin SC, Semenic S. Barriers and facilitators to evidence-based nursing in Colombia: perspectives of nurse educators, nurse researchers and graduate students. Investigación y Educación en Enfermería. 2014; 32 (1):9–21. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. The Discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. Handbook of qualitative research. 2nd. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2000. pp. 1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ewens B, Chapman R, Tulloch A, Hendricks JM. ICU survivors' utilisation of diaries post discharge: a qualitative descriptive study. Australian Critical Care. 2014; 27 (1):28–35. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fantasia HC, Sutherland MA, Fontenot H, Ierardi JA. Knowledge, attitudes and beliefs about contraceptive and sexual consent negotiation among college women. Journal of Forensic Nursing. 2014; 10 (4):199–207. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friman A, Wahlberg AC, Mattiasson AC, Ebbeskog B. District nurses' knowledge development in wound management: ongoing learning without organizational support. Primary Health Care Research & Development. 2014; 15 (4):386–395. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaughan V, Logan D, Sethna N, Mott S. Parents' perspective of their journey caring for a child with chronic neuropathic pain. Pain Management Nursing. 2014; 15 (1):246–257. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education. 2007; 30 (3):287–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hart PL, Mareno N. Cultural challenges and barriers through the voices of nurses. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2014; 23 (15–16):2223–2232. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hasman K, Kjaergaard H, Esbensen BA. Fathers' experience of childbirth when non-progressive labour occurs and augmentation is established. A qualitative study. Sexual & Reproductive HealthCare. 2014; 5 (2):69–73. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Higgins I, van der Riet P, Sneesby L, Good P. Nutrition and hydration in dying patients: the perceptions of acute care nurses. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2014; 23 (17–18):2609–2617. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Holland ML, Christensen JJ, Shone LP, Kearney MH, Kitzman HJ. Women's reasons for attrition from a nurse home visiting program. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing. 2014; 43 (1):61–70. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johansson M, Hildingsson I, Fenwick J. 'As long as they are safe--birth mode does not matter' Swedish fathers' experiences of decision-making around caesarean section. Women and Birth. 2014; 27 (3):208–213. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kao MH, Tsai YF. Illness experiences in middle-aged adults with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: findings from a qualitative study. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2014; 70 (7):1564–1572. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kawulich BB. Participant observation as a data collection method. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2005; 6 (2) Art. 43. Retrieved from http://www.qualitative-research.net/index.php/fqs/article/view/466/997 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kerr D, McKay K, Klim S, Kelly AM, McCann T. Attitudes of emergency department patients about handover at the bedside. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2014; 23 (11–12):1685–1693. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kneck A, Fagerberg I, Eriksson LE, Lundman B. Living with diabetes - development of learning patterns over a 3-year period. International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being. 2014; 9 :24375. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krippendorf K. Content analysis: An introduction to its methodology. 2nd. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Larocque N, Schotsman C, Kaasalainen S, Crawshaw D, McAiney C, Brazil E. Using a book chat to improve attitudes and perceptions of long-term care staff about dementia. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2014; 40 (5):46–52. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li IC, Lee SY, Chen CY, Jeng YQ, Chen YC. Facilitators and barriers to effective smoking cessation: counselling services for inpatients from nurse-counsellors' perspectives--a qualitative study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11 (5):4782–4798. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lux KM, Hutcheson JB, Peden AR. Ending disruptive behavior: staff nurse recommendations to nurse educators. Nurse Education in Practice. 2014; 14 (1):37–42. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lyndon A, Zlatnik MG, Maxfield DG, Lewis A, McMillan C, Kennedy HP. Contributions of clinical disconnections and unresolved conflict to failures in intrapartum safety. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing. 2014; 43 (1):2–12. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma F, Li J, Liang H, Bai Y, Song J. Baccalaureate nursing students' perspectives on learning about caring in China: a qualitative descriptive study. BMC Medical Education. 2014; 14 :42. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma L. A humanbecoming qualitative descriptive study on quality of life with older adults. Nursing Science Quarterly. 2014; 27 (2):132–141. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marcinowicz L, Abramowicz P, Zarzycka D, Abramowicz M, Konstantynowicz J. How hospitalized children and parents perceive nurses and hospital amenities: A qualitative descriptive study in Poland. Journal of Child Health Care. 2014 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Martorella G, Boitor M, Michaud C, Gelinas C. Feasibility and acceptability of hand massage therapy for pain management of postoperative cardiac surgery patients in the intensive care unit. Heart & Lung. 2014; 43 (5):437–444. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McDonough A, Callans KM, Carroll DL. Understanding the challenges during transitions of care for children with critical airway conditions. ORL Head and Neck Nursing. 2014; 32 (4):12–17. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McGilton KS, Boscart VM, Brown M, Bowers B. Making tradeoffs between the reasons to leave and reasons to stay employed in long-term care homes: perspectives of licensed nursing staff. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2014; 51 (6):917–926. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Michael N, O'Callaghan C, Baird A, Hiscock N, Clayton J. Cancer caregivers advocate a patient- and family-centered approach to advance care planning. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2014; 47 (6):1064–1077. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller WR. Patient-centered outcomes in older adults with epilepsy. Seizure. 2014; 23 (8):592–597. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Milne J, Oberle K. Enhancing rigor in qualitative description: a case study. Journal of Wound Ostomy & Continence Nursing. 2005; 32 (6):413–420. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Neergaard MA, Olesen F, Andersen RS, Sondergaard J. Qualitative description - the poor cousin of health research? BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2009; 9 :52. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- O'Shea MF. Staff nurses' perceptions regarding palliative care for hospitalized older adults. The American Journal of Nursing. 2014; 114 (11):26–34. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oosterveld-Vlug MG, Pasman HR, van Gennip IE, Muller MT, Willems DL, Onwuteaka-Philipsen BD. Dignity and the factors that influence it according to nursing home residents: a qualitative interview study. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2014; 70 (1):97–106. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oruche UM, Draucker C, Alkhattab H, Knopf A, Mazurcyk J. Interventions for family members of adolescents with disruptive behavior disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing. 2014; 27 (3):99–108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parse RR. Qualitative inquiry: The path of sciencing. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Barlett; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peacock SC, Hammond-Collins K, Forbes DA. The journey with dementia from the perspective of bereaved family caregivers: a qualitative descriptive study. BMC Nursing. 2014; 13 (1):42. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peterson WE, Sprague AE, Reszel J, Walker M, Fell DB, Perkins SL, Johnson M. Women's perspectives of the fetal fibronectin testing process: a qualitative descriptive study. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. 2014; 14 :190. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Nursing research: principles and methods. 7. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Polit DF, Beck CT. International differences in nursing research, 2005–2006. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2009; 41 (1):44–53. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Nursing research: generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. 9. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Essentials of Nursing Research: Appraising Evidence for Nursing Practice. 8. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health; Lippincott Willians & Wilkins; 2014. Supplement for Chapter 14: Qualitative Descriptive Studies. Retrieved from http://downloads.lww.com/wolterskluwer_vitalstream_com/sample-content/9781451176797_Polit/samples/CS_Chapter_14.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Mays N. Qualitative research in health care. 3rd. Victoria, Australia: Blackwell Publishing; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Mays N. Reaching the parts other methods cannot reach: an introduction to qualitative methods in health and health services research. BMJ. 1995; 311 (6996):42–45. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Raphael D, Waterworth S, Gott M. The role of practice nurses in providing palliative and end-of-life care to older patients with long-term conditions. International Journal of Palliative Nursing. 2014; 20 (8):373–379. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Saldana J. Longitudinal qualitative research: Analyzing change through time. Walnut Creek, CA: AltaMira Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. Whatever happened to qualitative description? Research in Nursing & Health. 2000; 23 (4):334–340. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M. What's in a name? Qualitative description revisited. Research in Nursing & Health. 2010; 33 (1):77–84. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santos HP, Jr, Sandelowski M, Gualda DM. Bad thoughts: Brazilian women's responses to mothering while experiencing postnatal depression. Midwifery. 2014; 30 (6):788–794. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharp R, Grech C, Fielder A, Mikocka-Walus A, Cummings M, Esterman A. The patient experience of a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC): A qualitative descriptive study. Contemporary Nurse. 2014; 48 (1):26–35. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Soule I. Cultural competence in health care: an emerging theory. ANS Advances in Nursing Science. 2014; 37 (1):48–60. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stegenga K, Macpherson CF. "I'm a survivor, go study that word and you'll see my name": adolescent and cancer identity work over the first year after diagnosis. Cancer Nursing. 2014; 37 (6):418–428. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Streubert HJ, Carpenter DR. Qualitative research in nursing: Advancing the humanistic imperative. 5th. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sturesson A, Ziegert K. Prepare the patient for future challenges when facing hemodialysis: nurses' experiences. International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being. 2014; 9 :22952. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sullivan-Bolyai S, Bova C, Harper D. Developing and refining interventions in persons with health disparities: the use of qualitative description. Nursing Outlook. 2005; 53 (3):127–133. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sundqvist AS, Carlsson AA. Holding the patient's life in my hands: Swedish registered nurse anaesthetists' perspective of advocacy. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. 2014; 28 (2):281–288. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomson Reuters. EndNote X7. 2014 Retrieved from http://endnote.com/product-details/x7 .
- Thorne S. Data analysis in qualitative research. Evidence Based Nursing. 2000; 3 :68–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne S, Reimer Kirkham S, O’Flynn-Magee K. The analytic challenge in interpretive description. International Journal of Qualitative Methods. 2004; 3 (1):1–11. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tseng YF, Chen CH, Wang HH. Taiwanese women's process of recovery from stillbirth: a qualitative descriptive study. Research in Nursing & Health. 2014; 37 (3):219–228. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vaismoradi M, Jordan S, Turunen H, Bondas T. Nursing students' perspectives of the cause of medication errors. Nurse Education Today. 2014; 34 (3):434–440. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vaismoradi M, Turunen H, Bondas T. Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nursing & Health Sciences. 2013; 15 (3):398–405. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valizadeh L, Zamanzadeh V, Fooladi MM, Azadi A, Negarandeh R, Monadi M. The image of nursing, as perceived by Iranian male nurses. Nursing & Health Sciences. 2014; 16 (3):307–313. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Villar F, Celdran M, Faba J, Serrat R. Barriers to sexual expression in residential aged care facilities (RACFs): comparison of staff and residents' views. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2014; 70 (11):2518–2527. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiens S, Babenko-Mould Y, Iwasiw C. Clinical instructors' perceptions of structural and psychological empowerment in academic nursing environments. Journal of Nursing Education. 2014; 53 (5):265–270. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Willis DG, Sullivan-Bolyai S, Knafl K, Zichi-Cohen M. Distinguishing Features and Similarities Between Descriptive Phenomenological and Qualitative Description Research. West J Nurs Res. 2016 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu YP, Thompson D, Aroian KJ, McQuaid EL, Deatrick JA. Commentary: Writing and Evaluating Qualitative Research Reports. J Pediatr Psychol. 2016; 41 (5):493–505. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang H, Shan W, Jiang A. The meaning of life and health experience for the Chinese elderly with chronic illness: a qualitative study from positive health philosophy. International Journal of Nursing Practice. 2014; 20 (5):530–539. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]

Descriptive Research: Methods And Examples
A research project always begins with selecting a topic. The next step is for researchers to identify the specific areas…

A research project always begins with selecting a topic. The next step is for researchers to identify the specific areas of interest. After that, they tackle the key component of any research problem: how to gather enough quality information. If we opt for a descriptive research design we have to ask the correct questions to access the right information.
For instance, researchers may choose to focus on why people invest in cryptocurrency, knowing how dynamic the market is rather than asking why the market is so shaky. These are completely different questions that require different research approaches. Adopting the descriptive method can help capitalize on trends the information reveals. Descriptive research examples show the thorough research involved in such a study.
Get to know more about descriptive research design .
Descriptive Research Meaning
Features of descriptive research design, types of descriptive research, descriptive research methods, applications of descriptive research, descriptive research examples.
A descriptive method of research is one that describes the characteristics of a phenomenon, situation or population. It uses quantitative and qualitative approaches to describe problems with little relevant information. Descriptive research accurately describes a research problem without asking why a particular event happened. By researching market patterns, the descriptive method answers how patterns change, what caused the change and when the change occurred, instead of dwelling on why the change happened.
Descriptive research refers to questions, study design and analysis of data conducted on a particular topic. It is a strictly observational research methodology with no influence on variables. Some distinctive features of descriptive research are:
- It’s a research method that collects quantifiable information for statistical analysis of a sample. It’s a quantitative market research tool that can analyze the nature of a demographic
- In a descriptive method of research , the nature of research study variables is determined with observation, without influence from the researcher
- Descriptive research is cross-sectional and different sections of a group can be studied
- The analyzed data is collected and serves as information for other search techniques. In this way, a descriptive research design becomes the basis of further research
To understand the descriptive research meaning , data collection methods, examples and application, we need a deeper understanding of its features.
Different ways of approaching the descriptive method help break it down further. Let’s look at the different types of descriptive research :
Descriptive Survey
Descriptive normative survey, descriptive status.
This type of research quantitatively describes real-life situations. For example, to understand the relation between wages and performance, research on employee salaries and their respective performances can be conducted.
Descriptive Analysis
This technique analyzes a subject further. Once the relation between wages and performance has been established, an organization can further analyze employee performance by researching the output of those who work from an office with those who work from home.
Descriptive Classification
Descriptive classification is mainly used in the field of biological science. It helps researchers classify species once they have studied the data collected from different search stations.
Descriptive Comparative
Comparing two variables can show if one is better than the other. Doing this through tests or surveys can reveal all the advantages and disadvantages associated with the two. For example, this technique can be used to find out if paper ballots are better than electronic voting devices.
Correlative Survey
The researcher has to effectively interpret the area of the problem and then decide the appropriate technique of descriptive research design .
A researcher can choose one of the following methods to solve research problems and meet research goals:
Observational Method
With this method, a researcher observes the behaviors, mannerisms and characteristics of the participants. It is widely used in psychology and market research and does not require the participants to be involved directly. It’s an effective method and can be both qualitative and quantitative for the sheer volume and variety of data that is generated.
Survey Research
It’s a popular method of data collection in research. It follows the principle of obtaining information quickly and directly from the main source. The idea is to use rigorous qualitative and quantitative research methods and ask crucial questions essential to the business for the short and long term.
Case Study Method
Case studies tend to fall short in situations where researchers are dealing with highly diverse people or conditions. Surveys and observations are carried out effectively but the time of execution significantly differs between the two.
There are multiple applications of descriptive research design but executives must learn that it’s crucial to clearly define the research goals first. Here’s how organizations use descriptive research to meet their objectives:
- As a tool to analyze participants : It’s important to understand the behaviors, traits and patterns of the participants to draw a conclusion about them. Close-ended questions can reveal their opinions and attitudes. Descriptive research can help understand the participant and assist in making strategic business decisions
- Designed to measure data trends : It’s a statistically capable research design that, over time, allows organizations to measure data trends. A survey can reveal unfavorable scenarios and give an organization the time to fix unprofitable moves
- Scope of comparison: Surveys and research can allow an organization to compare two products across different groups. This can provide a detailed comparison of the products and an opportunity for the organization to capitalize on a large demographic
- Conducting research at any time: An analysis can be conducted at any time and any number of variables can be evaluated. It helps to ascertain differences and similarities
Descriptive research is widely used due to its non-invasive nature. Quantitative observations allow in-depth analysis and a chance to validate any existing condition.
There are several different descriptive research examples that highlight the types, applications and uses of this research method. Let’s look at a few:
- Before launching a new line of gym wear, an organization chose more than one descriptive method to gather vital information. Their objective was to find the kind of gym clothes people like wearing and the ones they would like to see in the market. The organization chose to conduct a survey by recording responses in gyms, sports shops and yoga centers. As a second method, they chose to observe members of different gyms and fitness institutions. They collected volumes of vital data such as color and design preferences and the amount of money they’re willing to spend on it .
- To get a good idea of people’s tastes and expectations, an organization conducted a survey by offering a new flavor of the sauce and recorded people’s responses by gathering data from store owners. This let them understand how people reacted, whether they found the product reasonably priced, whether it served its purpose and their overall general preferences. Based on this, the brand tweaked its core marketing strategies and made the product widely acceptable .
Descriptive research can be used by an organization to understand the spending patterns of customers as well as by a psychologist who has to deal with mentally ill patients. In both these professions, the individuals will require thorough analyses of their subjects and large amounts of crucial data to develop a plan of action.
Every method of descriptive research can provide information that is diverse, thorough and varied. This supports future research and hypotheses. But although they can be quick, cheap and easy to conduct in the participants’ natural environment, descriptive research design can be limited by the kind of information it provides, especially with case studies. Trying to generalize a larger population based on the data gathered from a smaller sample size can be futile. Similarly, a researcher can unknowingly influence the outcome of a research project due to their personal opinions and biases. In any case, a manager has to be prepared to collect important information in substantial quantities and have a balanced approach to prevent influencing the result.
Harappa’s Thinking Critically program harnesses the power of information to strengthen decision-making skills. It’s a growth-driven course for young professionals and managers who want to be focused on their strategies, outperform targets and step up to assume the role of leader in their organizations. It’s for any professional who wants to lay a foundation for a successful career and business owners who’re looking to take their organizations to new heights.
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as Main Objectives of Research , Examples of Experimental Research , Methods Of Ethnographic Research , and How To Use Blended Learning to upgrade your knowledge and skills.


Bridging the Gap: Overcome these 7 flaws in descriptive research design
Descriptive research design is a powerful tool used by scientists and researchers to gather information about a particular group or phenomenon. This type of research provides a detailed and accurate picture of the characteristics and behaviors of a particular population or subject. By observing and collecting data on a given topic, descriptive research helps researchers gain a deeper understanding of a specific issue and provides valuable insights that can inform future studies.
In this blog, we will explore the definition, characteristics, and common flaws in descriptive research design, and provide tips on how to avoid these pitfalls to produce high-quality results. Whether you are a seasoned researcher or a student just starting, understanding the fundamentals of descriptive research design is essential to conducting successful scientific studies.
Table of Contents
What Is Descriptive Research Design?
The descriptive research design involves observing and collecting data on a given topic without attempting to infer cause-and-effect relationships. The goal of descriptive research is to provide a comprehensive and accurate picture of the population or phenomenon being studied and to describe the relationships, patterns, and trends that exist within the data.
Descriptive research methods can include surveys, observational studies , and case studies, and the data collected can be qualitative or quantitative . The findings from descriptive research provide valuable insights and inform future research, but do not establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Importance of Descriptive Research in Scientific Studies
1. understanding of a population or phenomenon.
Descriptive research provides a comprehensive picture of the characteristics and behaviors of a particular population or phenomenon, allowing researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the topic.
2. Baseline Information
The information gathered through descriptive research can serve as a baseline for future research and provide a foundation for further studies.
3. Informative Data
Descriptive research can provide valuable information and insights into a particular topic, which can inform future research, policy decisions, and programs.
4. Sampling Validation
Descriptive research can be used to validate sampling methods and to help researchers determine the best approach for their study.
5. Cost Effective
Descriptive research is often less expensive and less time-consuming than other research methods , making it a cost-effective way to gather information about a particular population or phenomenon.
6. Easy to Replicate
Descriptive research is straightforward to replicate, making it a reliable way to gather and compare information from multiple sources.
Key Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design
The primary purpose of descriptive research is to describe the characteristics, behaviors, and attributes of a particular population or phenomenon.
2. Participants and Sampling
Descriptive research studies a particular population or sample that is representative of the larger population being studied. Furthermore, sampling methods can include convenience, stratified, or random sampling.
3. Data Collection Techniques
Descriptive research typically involves the collection of both qualitative and quantitative data through methods such as surveys, observational studies, case studies, or focus groups.
4. Data Analysis
Descriptive research data is analyzed to identify patterns, relationships, and trends within the data. Statistical techniques , such as frequency distributions and descriptive statistics, are commonly used to summarize and describe the data.
5. Focus on Description
Descriptive research is focused on describing and summarizing the characteristics of a particular population or phenomenon. It does not make causal inferences.
6. Non-Experimental
Descriptive research is non-experimental, meaning that the researcher does not manipulate variables or control conditions. The researcher simply observes and collects data on the population or phenomenon being studied.
When Can a Researcher Conduct Descriptive Research?
A researcher can conduct descriptive research in the following situations:
- To better understand a particular population or phenomenon
- To describe the relationships between variables
- To describe patterns and trends
- To validate sampling methods and determine the best approach for a study
- To compare data from multiple sources.
Types of Descriptive Research Design
1. survey research.
Surveys are a type of descriptive research that involves collecting data through self-administered or interviewer-administered questionnaires. Additionally, they can be administered in-person, by mail, or online, and can collect both qualitative and quantitative data.
2. Observational Research
Observational research involves observing and collecting data on a particular population or phenomenon without manipulating variables or controlling conditions. It can be conducted in naturalistic settings or controlled laboratory settings.
3. Case Study Research
Case study research is a type of descriptive research that focuses on a single individual, group, or event. It involves collecting detailed information on the subject through a variety of methods, including interviews, observations, and examination of documents.
4. Focus Group Research
Focus group research involves bringing together a small group of people to discuss a particular topic or product. Furthermore, the group is usually moderated by a researcher and the discussion is recorded for later analysis.
5. Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research involves conducting detailed observations of a particular culture or community. It is often used to gain a deep understanding of the beliefs, behaviors, and practices of a particular group.
Advantages of Descriptive Research Design
1. provides a comprehensive understanding.
Descriptive research provides a comprehensive picture of the characteristics, behaviors, and attributes of a particular population or phenomenon, which can be useful in informing future research and policy decisions.
2. Non-invasive
Descriptive research is non-invasive and does not manipulate variables or control conditions, making it a suitable method for sensitive or ethical concerns.
3. Flexibility
Descriptive research allows for a wide range of data collection methods , including surveys, observational studies, case studies, and focus groups, making it a flexible and versatile research method.
4. Cost-effective
Descriptive research is often less expensive and less time-consuming than other research methods. Moreover, it gives a cost-effective option to many researchers.
5. Easy to Replicate
Descriptive research is easy to replicate, making it a reliable way to gather and compare information from multiple sources.
6. Informs Future Research
The insights gained from a descriptive research can inform future research and inform policy decisions and programs.
Disadvantages of Descriptive Research Design
1. limited scope.
Descriptive research only provides a snapshot of the current situation and cannot establish cause-and-effect relationships.
2. Dependence on Existing Data
Descriptive research relies on existing data, which may not always be comprehensive or accurate.
3. Lack of Control
Researchers have no control over the variables in descriptive research, which can limit the conclusions that can be drawn.
The researcher’s own biases and preconceptions can influence the interpretation of the data.
5. Lack of Generalizability
Descriptive research findings may not be applicable to other populations or situations.
6. Lack of Depth
Descriptive research provides a surface-level understanding of a phenomenon, rather than a deep understanding.
7. Time-consuming
Descriptive research often requires a large amount of data collection and analysis, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
7 Ways to Avoid Common Flaws While Designing Descriptive Research

1. Clearly define the research question
A clearly defined research question is the foundation of any research study, and it is important to ensure that the question is both specific and relevant to the topic being studied.
2. Choose the appropriate research design
Choosing the appropriate research design for a study is crucial to the success of the study. Moreover, researchers should choose a design that best fits the research question and the type of data needed to answer it.
3. Select a representative sample
Selecting a representative sample is important to ensure that the findings of the study are generalizable to the population being studied. Researchers should use a sampling method that provides a random and representative sample of the population.
4. Use valid and reliable data collection methods
Using valid and reliable data collection methods is important to ensure that the data collected is accurate and can be used to answer the research question. Researchers should choose methods that are appropriate for the study and that can be administered consistently and systematically.
5. Minimize bias
Bias can significantly impact the validity and reliability of research findings. Furthermore, it is important to minimize bias in all aspects of the study, from the selection of participants to the analysis of data.
6. Ensure adequate sample size
An adequate sample size is important to ensure that the results of the study are statistically significant and can be generalized to the population being studied.
7. Use appropriate data analysis techniques
The appropriate data analysis technique depends on the type of data collected and the research question being asked. Researchers should choose techniques that are appropriate for the data and the question being asked.
Have you worked on descriptive research designs? How was your experience creating a descriptive design? What challenges did you face? Do write to us or leave a comment below and share your insights on descriptive research designs!
extremely very educative
Indeed very educative and useful. Well explained. Thank you
Simple,easy to understand
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Industry News
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

When should AI tools be used in university labs?
- Form Builder
- Survey Maker
- AI Form Generator
- AI Survey Tool
- AI Quiz Maker
- Store Builder
- WordPress Plugin
- Integrations
- Popular Forms
- Job Application Form Template
- Rental Application Form Template
- Hotel Accommodation Form Template
- Online Registration Form Template
- Employment Application Form Template
- Application Forms
- Booking Forms
- Consent Forms
- Contact Forms
- Donation Forms
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Evaluation Surveys
- Feedback Surveys
- Market Research Surveys
- Personality Quiz Template
- Geography Quiz Template
- Math Quiz Template
- Science Quiz Template
- Vocabulary Quiz Template
Try without registration Quick Start
HubSpot CRM
Google Sheets
Google Analytics
Microsoft Excel
Read engaging stories, how-to guides, learn about forms.app features.
Inspirational ready-to-use templates for getting started fast and powerful.
Spot-on guides on how to use forms.app and make the most out of it.
See the technical measures we take and learn how we keep your data safe and secure.
- Help Center
- Sign In Sign Up Free
- What is descriptive research: Methods & examples

Defne Çobanoğlu
Being able to observe and describe your surroundings successfully is very crucial when you are doing a study. But what does it really mean? Let us give an example;
You are watching a schoolyard and observing the kids interact with one another. Then, you make comments about their ages, sexes, and playing patterns. You write down how many children there are and how many have blond hair, brown eyes, and stuff like that. In this scenario, you are “describing” them according to your observation.
Have this concept on a much bigger scale, and you have descriptive research. But why would a researcher need to do this research? Let us see what it means, when to do it, and some real-life examples.🔎
- What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research is a type of research where researchers try to “describe” the characteristics of the problem, phenomenon, or subject.
The researcher studies the details and background information related to the subject. Therefore, this research type deals with the questions of what, when, and where and try to find answers to these questions.
However, it is important to keep in mind that this research type does not try to explore the cause-and-effect relationship of the aspects. So, this research type does not deal with questions of why and how.
- When to use descriptive research?
A researcher can use descriptive research for numerous reasons. As with all the research types, the researcher should want to answer some questions. In this method, the questions are basically, “ What are the elements that contribute to this phenomenon?” But let us make a list of reasons that may play a role in the researcher's mind. The researcher chooses to conduct descriptive research when he/she:
- Wants to understand a concept better than before. (This research method brings forward the hidden details and gives them a systematic form)
- Wishes to describe relationships between different concepts.
- Wants to explore patterns and trends.
- Wants to get into the core of the information for future studies.
- Decides to compare data from numerous sources.
- Wishes to explore the best approach for future studies.
- Characteristics of descriptive research
Descriptive research is characterized by several key features, and these aspects differentiate it from other research types. Now, let us see a list of the main characteristics of descriptive research:
- It answers W questions. Meaning what, when, who, and where. They give concrete answers that are useful for the whole study.
- It gives qualitative and quantitative results . The results of descriptive research can be both numerical and open-ended.
- Makes way for future research . The results collected via descriptive research make a good start for future studies. The researcher can simply take what is on hand and build on it.
- It is conducted in natural settings . As natural observation and surveying are two of the great methods of descriptive research, they provide unbiased information. Let us say you want to test the accessibility and effectiveness of children's playgrounds; you can observe daily and survey the parents, etc.
- It can be used in many areas. From marketing, medicine, and education to psychology, the results of descriptive research can be used in any field.
- Descriptive research methods

Descriptive research methodologies
In order to conduct descriptive research, the researchers can use one of the methods below or make a mix of all three. It depends on the researchers and the research problems. Now let us see the three descriptive research methods:
1. Observations
One of the best ways to collect real-life, accurate, and honest information about human behavior is through observations. The observational method is an essential part of descriptive research. There is no outside intervention to observations. However, the researcher can be part of the observation as an observer, participant as an observer, or a full participant.
2. Case study
A case study study is done by gathering a group of individuals as a sample group. The characteristics, details, and choices of this sample group are used to have a generalized idea to represent a bigger population. This generalization from a case study is actually risky as the data collected can be insufficient to make accurate predictions about larger groups.
3. Survey research
Surveys are where the researcher asks pre-determined questions to participants to collect information from them. The questions can be close-ended questions or open-ended questions where the answers are more free.
The survey can be done face-to-face, or it can be done online using a smart survey maker , such as forms.app. forms.app has more than 4000 ready-to-use templates, and it is free of charge.
- Real-life examples of descriptive research
The study type of descriptive research can be used in many areas, including psychology, medicine, marketing, business, and education. It mostly depends on your objective. However, it is almost always smart to start with descriptive research. Now, here are some descriptive research examples:
Descriptive research example #1
A school branch that wants to open a daycare in the district can look at the demographics in the area. They can make a list of the number of families with kids ages 1-6 and the percentages of working mothers. If there are other competitors, they can make informed analyses about them as well. After all this studying of the region, the school branch can make an informed decision about whether or not to open a daycare in the area.
Descriptive research example #2
A restaurant owner wants to figure out what areas need to be improved and what kind of problems the visitors face daily. In order to collect detailed and systematic data about the subject, it is smart to use a survey, such as a customer satisfaction survey or a feedback survey . The survey can help identify specific areas that need improvements, such as food quality, service speed, or cleanliness concerns. The main focus of the study is obtaining customer feedback without manipulating variables.
- Frequently asked questions about descriptive research
This research type has some similarities and differences with other research types and we have gathered some frequently asked questions about the subject. Let us see them:
What is the difference between descriptive and analytical research?
The methods used in descriptive research are surveys and observation. For analytical research, the researcher has to use facts already available and analyze them to make a critical evaluation.
What is the difference between qualitative and descriptive studies?
Descriptive research is usually described as quantitative research. The researcher doing a descriptive study defines the existing facts through observations and surveys. On the other hand, qualitative research aims to explore and answer the underlying meaning and context of subjects.
Can a study be both analytical and descriptive?
Yes, a study can be both analytical and descriptive. Researchers often use mixed methods to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of a concept. For example, particular research tries to analyze the characteristics of the youth population in a certain area (descriptive) and then examine how these characteristics are associated with alcohol abuse in the area (analytical).
What is the goal of descriptive research?
The aim of descriptive research is to accurately and systematically obtain information to summarize events, subjects, and concepts. The data collected using types of descriptive research methods can be used to describe the characteristics, patterns, and relationships within a specific context.
Why is descriptive research used in research?
Descriptive research is used to provide a detailed understanding of the elements of a specific subject, area, or concept in research. The findings of descriptive research work as a foundation for further investigations, hypothesis testing, and decision-making.
- Key points to take away
A descriptive research method is an important step when starting a research project. The result of such data can give detailed information on the population or the area of the subject. After all, knowing what you are working with is a crucial element. Therefore, as descriptive research is a good start to a study, it also opens the doors for future projects. Here are some key elements to take away about descriptive research:
- Descriptive research does not explore cause-and-effect relations but rather answers the questions of what, who, and when.
- It is used to define details and explore patterns.
- Gives both qualitative and quantitative results.
- The methods that can be used when doing descriptive research are case studies, observations, and surveys.
- Gives a good foundation for future research.
In conclusion, descriptive research is about being able to make an analysis that answers qualitative and quantitative questions. In this article, we mentioned when to use this research type, its characteristics, research methods, examples, and frequently asked questions. For so much more and all your research needs, visit forms.app today!
Defne is a content writer at forms.app. She is also a translator specializing in literary translation. Defne loves reading, writing, and translating professionally and as a hobby. Her expertise lies in survey research, research methodologies, content writing, and translation.
- Form Features
- Data Collection
Table of Contents
Related posts.
Diagnostic analysis: Definition, tools & examples

Best 360 degree feedback questions to use in your surveys
Şeyma Beyazçiçek

forms.app integrates with Slack: Get instant notifications now
- Descriptive research-definition, methodology, methods, characteristics, examples and advantages
On this Page
- Introduction
Descriptive research methodology
- Descriptive Research Methodology-Diagrammatic Approach
- Logical Steps; Descriptive Research Methodology
Descriptive research data collection methods
- Characteristics of descriptive research
Applicability of descriptive research
Disadvantages, descriptive research; definition; methodology; methods; characteristics; examples and advantages.
1.1 Definition
Descriptive research is a type of research Classified under “ purpose of research ” and it is the systematic process of establishing the features or characteristics that distinguish a particular nature or type of population from another. This research narrates the features or characteristics of a variable being observed. It is also referred to as observational research.
Descriptive research deals with analyzing of a character that does not change or vary with time and that’s why it focuses on subject matter such as demographic perspectives such as age, sex, level of education, and market share size etc.
2.1 Definition
Descriptive Research Methodology is the logical process or step by step outline on how to solve a research problem that entails a variable which cannot be manipulated such as age, sex or level of education etc. Descriptive Research methodology involves choosing a logical procedure on the topic to be studied. That is the research problem, how specific objectives and research hypotheses of the study will be identified/or formulated. Identification of knowledge gaps to be filled, the methods used in identification of the study population and sample size determination, type of data to be collected and how it will be collected and analyzed, data presentation and interpretations thereof and the reporting of the research findings.
The aforementioned description /definition on descriptive research methodology is in tandem with the argument of (Kothari, 1984) who hypothesized that research methodology is the reasoning behind the methods we use in the context of our research study. This provides a rationale as to why one is using a particular method or technique at a particular stage in the research process and not others so that research output is accomplished either by the researcher himself or by others.
2.1.1 Questions Descriptive Research Methodology tries to Answer
Descriptive research methodology answers the following questions;
Questions pertaining to a particular population or group. But it does not answer questions such as why?
A “WHAT” Question means the approach is limited in interrogating the variables under investigation. For example, the study simply wants to know “ what is the age range of girls in form one up to form four” in a certain country. You see, the researcher cannot manipulate the variable “AGE” for it is a matter of fact that after digging deeper, he/she will only work with the range available such as;
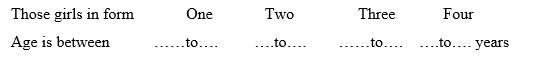
Another example of answering “ What ” question is when one is gathering opinion over a certain matter from respondents using a Likert scale.
Example of such questions is “what is your opinion as pertaining effectiveness of tackling of corruption issues by presidential candidate “Mr. XX” if he wins the USA General elections?”
From this statement, indicate by ticking the range of options given below.
Very Effective (VE)
Effective (E)
Neutral (N)
Not Effective (NE)
Not Effective at All (NA)
A “WHEN” Question means the approach is limited in interrogating the variables under investigation. For example, the study simply want to know “ When ” a certain event occurred.
For example, the researcher may be investigating the year in which African countries got their independence. So, it is a matter of fact as indicated in history or the secondary data.
Example, when did the East African countries get their independence?

The following matrix portrays the link between descriptive type of research and the type of research methodology adopted and then an explanation of the logical approach associated with this category and then in the last column, the research method(s) used in formulating the research problem as per Table 1.1.
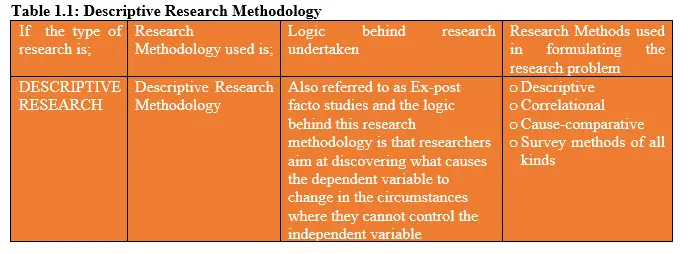
2.2 Descriptive Research Methodology-Diagrammatic Approach
The following diagram as per Figure 1.1 represents a summary of logical roadmap to be adhered to in descriptive research methodology.
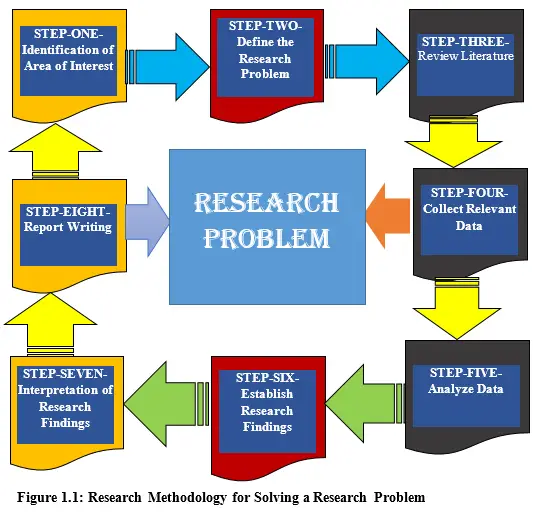
2.3 Logical Steps; Descriptive Research Methodology
The following logical steps describe the descriptive research methodology. From step one to eight, it represents a logical way of how systematically the matter at hand need to be dealt with. Remember that in this approach, the researcher only carries observations on the characteristic of the variable or the phenomenon being studied and cannot manipulate the variable or phenomenal state.
2.3.1 Step One; Identification of Area of Interest
This is the first step in descriptive research where by the researcher is venturing in observing the characteristic of the variable being studied. Once he/she narrows to that specific perspective, the researcher has to ask himself or herself the following questions;
Q1. Do I really have any interest in a certain TOPICAL Issue, let say Education Psychology where I have more knowledge in?
Q2. What are the thematic issues in this realm?
Q3. Am I motivated on some specific aspects in this realm?
Q4. Which specific variables are dominant in this area and are observable?
Therefore, descriptive research is governed by either of the following research questions;
You should note that these are the research questions which govern the researcher to identify the area of interest.
2.3.2 Step Two; Define the Research Problem
Under Descriptive research, formulation of research problem is on the basis of either a to c questions as indicated below;
a). Descriptive Question
For example, descriptive affiliated research questions assume the following form “what is the sales level of product Z in the market?”
“What is the buying or consumption trend of a certain story book amongst the youth in New York City?”
b). Correlational Questions
“To what extent does religious beliefs determine the kind of dressing an individual prefer to put on?” This is a question to do with the level of correlation between consumers’ beliefs and demand of a certain dress fashion. This is an example of a descriptive correlational study in which the researcher is primarily concerned with describing relationships between two variables, without seeking to establish a causal connection.
c). Cause-comparative Questions
The cause-effect research question focuses on influence of the predictor variable on the dependent variable where by the predictor variable is not manipulated. For instance,
“Does age level determine the food diet one uses in life?” this is an example of a descriptive causal-effect research in which the researcher is primarily interested in causal connection.
2.3.3 Step Three; Literature Review
Once the research problem has been identified, the next step is to undertake the necessary literature review to build the research gaps. The research gaps may either be of theoretical, methodological or contextual nature.
2.3.4 Step Four; Collect Relevant Data
In this step, the researcher is concerned with how to collect data relevant to guide him or her whether there exists any link of stated variables. Methods used include;
Observational methods- which is very much appropriate whereby they make use of both quantitative and qualitative observations. For quantitative, numbers are observed while for qualitative approach, characteristics are observed or monitored. The researcher watches the behavior of the respondents from far.
Survey method -data is collected by conducting a survey especially when the area of coverage is wide. Survey questions are set ad sent either physically or online for the respondents to reply. The questions should take care of all logistics such that both open ended and closed ended questionnaires should be used.
Case-study method -it is an in-depth study of individuals or groups. The method opens doors for further study of a phenomenon. But caution should be undertaken that the method should not be used in collecting data to test for cause-effect studies.
2.3.5 Step Five; Analyze Data
For descriptive research, the data analysis approach used is strictly descriptive in nature for it ought to explain the characteristics of a variable or a phenomenon. The relevant statistics used include those related to measures of central tendency such as mean, median and mode, measures of dispersion such as standard deviation, variance, range and quartiles just to mention but a few. It also entails summarization of data to interpretable status such as frequency and percentages. The descriptive data analysis will focus on variable trends or movements.
It should be noted that descriptive statistics are utilized to summarize data in an organized manner by describing the relationship between variables in a population or sample. Descriptive data analysis is the genesis of other advanced data analysis processes.
Under descriptive data analysis, the researcher should be in a position of identifying the diverse types of variables involved, which include, namely;
Categorical variables- variables which are qualitative in nature. Sometimes also referred to as discrete.
Categorical variables are further divided in to sub-classes namely;
i). Nominal sub-category -a scale in which numbers serve as “identifiers” or “markers” only, to identify or classify an object. For instance
1=Best situation;
2=Fair Situation;
3=Bad Situation and
4=Worsted Situation
ii). Ordinal sub-category -take more than two categories that can be ranked or ordered as in the case of Likert scale approach
iii). Dichotomous sub-category -DI means TWO. So, in this case, we have only two categories E.g., male or female or alive or dead options.
iii). Continuous Variable sub-category - Also known as quantitative or numerical) and they are further categorized as either interval or ratio.
You should note that the variables being studies are analyzed appropriately based on the sub-classification each one of them falls under.
2.3.6 Step Six; Establish Research Findings
With the new data, the researcher establishes the research findings which should be conclusive. The groups conducted or the surveys carried out will provide the researcher with feedback which can be reviewed for accuracy, viability, and topically relevant information in order to be incorporated into existing bodies of knowledge.
The research findings arrived at is a solution to the study. In other words, the findings should fill a certain research gap.
2.3.7 Step Seven; Interpretation of Research Findings
Interpretation of research findings is done by use of computer programs such as e-Views, R, C, STATA, SPSS and excel.
Once analysis of data is complete, the research findings are supposed to be properly interpreted and the findings be well tackled so that the researcher can be in a position to communicate to his/her audience. You should know that any wrong interpretation of the output will translate to no effective communication to the end users of the research findings and this will render the research endeavors futile.
For descriptive research finding interpretation, the following example can be used
Example (a past study extract), see Table 1.2 for the details
“The study sought to establish the influence of innovation on the sales level of SME projects in Kingpin City. Out of 221 respondents who participated in the study, 161(72.9%, i.e., 35.3+37.6%) felt that innovation fairly influenced sales levels of SME projects in Kingpin City. Whereas 20(9.2% i.e., 5+4.2%) disagreed and the other 40(18.1%) had no idea of the exact cause of changes in sales levels. As per Table 1.2, the responses realized a mean of 3.95 greater than the composite mean and SD=1.05. Hence innovation significantly contributed to positive change in sales levels and also the financial performance of the SME projects.”
Therefore, this Is How We Should Interpret Results of Descriptive Nature.
2.3.8 Step Eight; Report Writing
Based on the research findings gotten in step seven, the researcher prepares a report on the extent to which the research problem has been solved and the recommendations to be undertaken by the concerned parties. If the research was being conducted on behalf of the management of a particular business concern, then the researcher needs to advise the client according to the research findings. In the report, he/she should also portray generally the contribution of the research as pertains, policy, theory and practice.
Research methods are all the techniques that are utilized in all the stages of research processes. They are tools used to ensure the end results of research task are accomplished. These techniques vary from one stage of research process to another. These methods are further classified in to two categories, namely;
- a) Pre-Data analysis methods
- b) Data Analysis related methods
As per Table 1.1 in this article, the descriptive research methods indicated in that table (refer), namely; descriptive; correlational, cause-comparative and survey methods are for the purposes of formulating the research problem and are some of the methods which fall under pre-data analysis category. However, in this discussion of descriptive research, we will focus first on the THREE main methods of data collection which are also pre-data analysis in nature. That is; observation, survey and case study.
3.1 Observation Data Collection Method
It is an approach of collecting data in a more direct manner whereby the researcher physically watches a behavior being portrayed. This is a common approach in behavioral science. The researcher observes things as they happen live without directly asking the respondent to give an opinion. This method is more objective for this method is independent of respondents’ willingness to reply and as such is relatively less demanding of active collaboration on the part of respondents as it is in the case of interview or the questionnaire method.
- Simple to apply in research unlike other Methods
- Helps is Hypothesizing the research problem
- It is more accurate as compared to other approaches
- It is a universally accepted by most researchers hence its validity is high
- Objectivity-it is an objective method of collecting data for the data is collected from a scenario which is free from any human being interference.
- Not applicable in all cases. That is, some of the occurrences may not be fitted to observation. For instance, it is not ethical to collect data of one undergoing main operation in hospital theatre.
- Portraying of the wrong information by the respondent-when the respondent knows that he or she is being observed, there is high chances of portraying the wrong information for that is human nature. For example, if the researcher wants to learn the productivity level of workers in a factory. If the researcher or the investigator avails him/herself in person, every worker will pretend to be busy hence wrong conclusion is made.
- Difficulties in carrying out generalization after data collection. Due to biasness and prejudice of the researcher, it may proof to be harder to make a general conclusion on the population
3.2 Survey Data Collection Method
As the name suggests, survey method simply involves watching at a behavior or phenomenon in a more comprehensive way or manner. It entails a wide spectrum of methods which include; in-person and telephone interviews, mailed and online questionnaires as further explained below;
In-Person Interviews.
This approach is the most effective way of data collection for it involves actual interaction with the respondent. In other words, this is the most effective manner in which information or data is accessed from an individual.
Telephone interviews
The method relies on making free will calls to the respondents. The method involves the concerned party making calls to the targeted group or individual(s). The method is cheap although with increased frauds many respondents are skeptical when giving information.
Mailed Questionnaires
This method involves sending of written questionnaires to the respondents using their contacts who in turn fill and return the filled questionnaires within a specific period of time. Although it is a little bit expensive, more people may be reached by paper surveys than any other method.
Online Questionnaires
The online approach is a unique one for the same questionnaire is prepared by the researcher and sent digitally to the targeted respondents who answer the questions therein in an electronic manner and then they revert their answers to the sender. It should be noted that, online questionnaires are common amongst researchers and they are at least cheap. They also reach more respondents all over the globe.
Advantages of Survey Data Collection Method
1). Simple to use-it is not a complicated method to collect data.
2). It is a less time-consuming approach-the method is time saving for it just requires either facing the respondent directly in the case of face-to-face approach or sending the questionnaire
3). Cost effective-the approach is economically viable because when conducting survey, one need to pay for the production of the questionnaire materials that’s all.
4). Eliminates geographical barriers-if online approach is used the issue of mountainous or valley or geographical distance is eliminated and hence coverage is wider.
5). Large data is collected-a broad data size is collected by the researcher and this assures of validity.
6). Level of statistical significance is high-the sample size is reasonably good to be a true representation of the whole population and as a result, the research findings have a high chance of being significant.
Disadvantages of Survey Data Collection Method
1). The method is not flexible- that is, if in some circumstances it is not possible to rely on survey approach, it is not possible to replace this method with a more appropriate one.
2). Poor answering of questions in the questionnaire -now that these questionnaires are sent to the respondents who are away, no room to guide the respondents in case of errors or as pertains some areas requiring clarifications.
3). Dishonesty responses-questionnaires are very sensitive for the answers expected are highly influenced by one’s emotions hence missing objectivity of the inquiry.
4). Missing items-the questionnaire may have many unanswered gaps which may render the response futile hence thrown away.
3.3 Case Study Data Collection Method
This method entails in depth or very detailed collection of descriptive information about a particular entity, or a case, or a group. Then the data collected is tested for all aspects of the subject’s life and history so as to learn the pattern or trend dominating the group or subject matter. This helps the researcher to conclude on the behavior thereof or the causes of a certain behavior then generalize to other similar population. The results gotten are presented in a narrative manner.
Advantages of Case Study Data Collection Method
- Case study data collection method allows scenarios which were difficulty to be handled in a lab setting so as to be investigated.
- Help in hypothesis development by the researcher.
- It is in depth approach- that is, this method provides holistic investigation of a subject matter.
- No sample is required-since the researcher is dealing with only one unit of observation, sampling process which has high-cost implication is not required.
- Increased knowledge-the method is a tool useful in providing analytical approach in gaining new knowledge which is advantageous.
- Full understandability of the subject matter under interrogation-since the method is rigorous, it increases the researcher’s level of familiarizing with the subject matter.
Disadvantages of Data Collection Method
- Challenge of human biasness- since the researcher focuses on only one case at a time, chances are high that he/she may over do the observations resulting to one side’s conclusions. This makes the conclusions unreliable.
- Scientifically, the method is not rigorous as compared to other methods. You see, even the number of data points are very few.
- Not suitable for cause-effect conclusions. The playground to the researcher is limited to very few research participants and this makes the researcher not being in good position to conclude the causes of change of the dependent variable for the data is very small.
- No generalization-the information collected from the single identity may not be relied up on to generalize on the whole population.
Characteristics of descriptive research
How do we distinguish this type of research with other approaches? The following distinctive features separate descriptive research and other types of research;
- Deals with Quantitative perspective: Descriptive research attempts to collect information which is quantifiable in terms of numbers for data analysis reasons.
- No manipulation of independent variables: Descriptive research does not advocate for the changing of the characteristics of the study variable. E.g., cannot change respondent’s age or sex.
- Cross-sectional based: Descriptive research focuses studying different aspects or sections of the unit of observation to come up with diverse data. The researcher can enquire one’s age, sex, level of education and years of experience.
- Foundation for further research: Descriptive research is the basis for further detailed types of research by the researchers. This is because the descriptive data already collected can also aid in pinpointing the types of research methods used for the subsequent research.
- Precise- descriptive research is detailed for it provides good space to obtain more clear data about the subject matter under investigation.
- Generalization- results from descriptive research are easily generalizable to the whole population.
- Accommodative- descriptive research provides room for use of different techniques and instruments for data collection such as interviews, survey methods, documentation, participant observation.
Where does descriptive research apply in real life situation?
The following are some of the areas where the research apples well
1). It defines or describes the respondent’s characteristics in a holistic manner-when a closed ended questionnaire is used, it attempts to draw all aspects of the respondent such that the research is well informed of the patterns, traits, and behaviors of the respondents. Even respondents’ attitude or opinion is easy.
2). Used in measuring the variable trend or movements-it is possible for the researcher to understand the general movement of the study variable. Or let us put it this way that the researcher can use descriptive research to tell the data trends over time. For instance, he or she can tell the data trends over time.
3). Used for comparison purposes. Researchers can make use of descriptive research abilities to compare two variables as far as a particular perspective is concerned. For example, a researcher can use a descriptive research approach to demonstrate how different groups of respondents behave given a certain condition. For example, the question on age, income, gender, geographical location and political affiliation of an individual etc.
4). Validation of prevailing conditions: For underlying patterns of a study object matter, a researcher can prove or disapprove whether a certain state assumed by the study variable is due to the underlying circumstances or not using descriptive research.
5). Descriptive research is used in different time horizons to observe if the results are the same or vary due to time factor as it is in the case of cross-sectional analysis. The analysis can be conducted at different periods to ascertain any similarities or differences.
Advantages
- Decision-making. Data collected from descriptive research is used by management in resource allocations and in undertaking all the five functions of a manager. This is because the data is obtained from a large population.
- Help in precise answering of the research questions-descriptive research accommodates a variety of data through diverse descriptive research methods like surveys, observation, and case study. For instance, it is possible to develop a hypothesis using data from case study.
- Cost effective-descriptive research is cheaper over the other approaches used in research. For instance, when this research relies on observation method to collect data which is characterized by observation in natural settings, it turns out to be less costly.
- Double sword-Descriptive research provides both qualitative and quantitative information hence it all round informative to the researcher and other end users of research efforts.
- It answers limited questions of what and how but cannot explain “ why” a certain situation exists. Therefore, this method is not appropriate for establishing cause-effect association.
- Halo effect problem-data collected from respondents may be pegged on the psychological halo issues. Halo effect is the first physical assessment one makes on an individual depending on dressing or outward outlook. For instance, one may look presentable and so is assumed to give valid answers on the questionnaire. Which may not turn to be true.
- Descriptive research uses a sample which if not well selected and this approach may result to biased data, leading to misrepresentation of the whole population.

- Survey Software The world’s leading omnichannel survey software
- Online Survey Tools Create sophisticated surveys with ease.
- Mobile Offline Conduct efficient field surveys.
- Text Analysis
- Close The Loop
- Automated Translations
- NPS Dashboard
- CATI Manage high volume phone surveys efficiently
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud on-premise dialer
- IVR Survey Software Boost productivity with automated call workflows.
- Analytics Analyze survey data with visual dashboards
- Panel Manager Nurture a loyal community of respondents.
- Survey Portal Best-in-class user friendly survey portal.
- Voxco Audience Conduct targeted sample research in hours.
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer 360
- Customer Loyalty
- Fraud & Risk Management
- AI/ML Enablement Services
- Credit Underwriting

Find the best survey software for you! (Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 100+ question types
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Skip logic and branching
- Multi-lingual survey
- Text piping
- Question library
- CSS customization
- White-label surveys
- Customizable ‘Thank You’ page
- Customizable survey theme
- Reminder send-outs
- Survey rewards
- Social media
- SMS surveys
- Website surveys
- Correlation analysis
- Cross-tabulation analysis
- Trend analysis
- Real-time dashboard
- Customizable report
- Email address validation
- Recaptcha validation
- SSL security
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Download feature sheet.
- Hospitality
- Financial Services
- Academic Research
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Product Experience
- Market Research
- Social Research
- Data Analysis
- Banking & Financial Services
- Retail Solution
- Risk Management
- Customer Lifecycle Solutions
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Behaviour Analytics
- Customer Segmentation
- Data Unification
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
Get a Quote
- NPS Calculator
- CES Calculator
- A/B Testing Calculator
- Margin of Error Calculator
- Sample Size Calculator
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Market Research Hub
- Patient Experience Hub
- Employee Experience Hub
- Market Research Guide
- Customer Experience Guide
- The Voxco Guide to Customer Experience
- NPS Knowledge Hub
- Survey Research Guides
- Survey Template Library
- Webinars and Events
- Feature Sheets
- Try a sample survey
- Professional services
- Blogs & White papers
- Case Studies
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.
Get the Guide Now

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Client Stories
- Voxco Reviews
- Why Voxco Research?
- Why Voxco Intelligence?
- Careers at Voxco
- Vulnerabilities and Ethical Hacking
Explore Regional Offices
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud & on-premise dialer
- Fraud & Risk Management
Get Buyer’s Guide
- Banking & Financial Services
Explore Voxco
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Blogs & White papers
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Our clients
- Client stories
- Featuresheets
Descriptive Research: Definition, Methods & Examples
- August 19, 2021
Voxco’s Descriptive Research guide helps uncover the how, when, what, and where questions in a research problem
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON

When you are a store manager in a convenience store, and you have to make a report. Any finding such as which product is selling most, what time of the day you have the most crowd, or which product customers are demanding most, all these observations and reporting is descriptive research.
It is often the first step of any research since the data you gather sets the stage for the research question. It is used to determine the problem you want to explore before fully realizing it. The information helps you identify the problem.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the characteristics, types, pros & cons, and three ways to conduct this research type to help you in your next market research.
What is descriptive research?
Descriptive research refers to the research method that describes the characteristics of the variables you are studying. This methodology focuses on answering questions to the “WHAT” than the “WHY” of the research question. The primary focus of this research method is to describe the nature of the demographics understudy instead of focusing on the “why”.
It is called an observational research method as none of the variables in the study are influenced during the research process.
For example, let’s assume that a UK-based brand is trying to establish itself in New York and wants to understand the demographics of the buyers who generally purchase from brands similar to it.
In descriptive research, the information gathered from the survey will only focus on the population’s demographics. It will uncover details on the buying patterns of different age cohorts in New York. It will not study why such patterns exist because the brand is trying to establish itself in New York.
They want to understand the buying behavior of the population, not why such associations exist. It is a part of quantitative market research or social research study, which involves conducting survey research using quantitative variables on a market research software or social research software .
Voxco’s omnichannel survey software helps you collect insights from multiple channels using a single platform.
See the true power of using an integrated survey platform to conduct online, offline, and phone surveys along with a built-in analytical suite.
What are the characteristics of descriptive research?
Among the many, the following are the main characteristics of this research type:
- Quantitative research
- Nature of variables
- Cross-sectional studies
- Directs future research
Let’s discuss these four characteristics in detail.
1. Quantitative research:
It is quantitative as it attempts to collect and statistically analyze information. This research type is a powerful research tool that permits a researcher to collect data and describe the demographics of the same with the help of statistical analysis. Thus, it is a quantitative research method .
2. Nature of variables:
The variables included in this research are uncontrolled. They are not manipulated in any way. Descriptive research mostly uses observational methods; thus, the researcher cannot control the nature and behavior of the variables under study.
3. Cross-sectional studies:
In this research type, different sections of the same group are studied. For instance, in order to study the fashion preferences of New York, the researcher can study Gen Z as well as Millennials from the same population in New York.
4. Directs future research:
Since this research identifies the patterns between variables and describes them, researchers can further study the data collected here. It guides researchers to discover further why such patterns have been found and their association. Hence, it gives researchers a direction toward insightful market research.
What are the methods of conducting descriptive research?
Primarily, there are three descriptive research methods:
- Observation,
- Survey, &
We have explained how you can conduct this research type in three different ways. Each method helps gather descriptive data and sets the scene for thorough research.
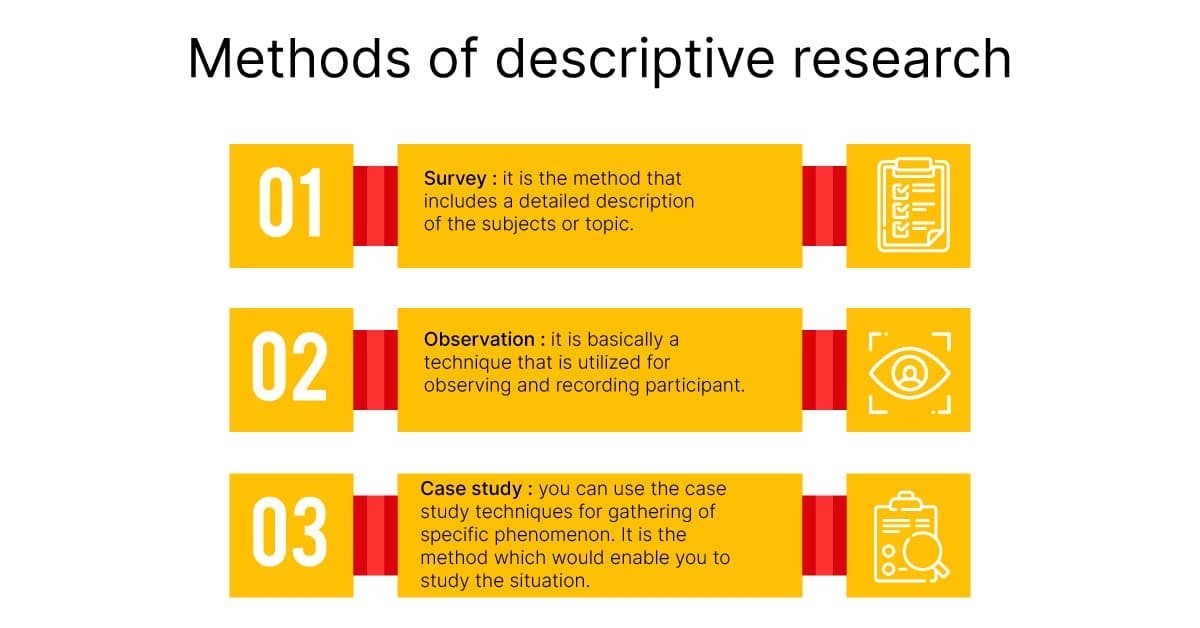
1. Observational method
All research has some component of observation, this observation can be quantitative or qualitative. A quantitative observation includes objectively collecting data that is primarily in numerical form.
The data collected should be related to or understood in terms of quantity.
Quantitative observations are analyzed with the help of survey analytics software .
Examples of quantitative observations include observation of any variable related to a numerical value such as age, shape, weight, height, scale, etc.
For example, a researcher can understand a customer’s satisfaction with their recent purchases by asking them to rate their satisfaction on a Likert scale ranging from 1 (extremely unsatisfied) to 7 (extremely satisfied).
Qualitative observations monitor the characteristics of a phenomenon and do not involve numerical measurements.
Using this type of descriptive research, you can observe respondents in a naturalistic environment from a distance. Since the respondents are in a natural environment, the observed characteristics enrich and offer more insights.
For instance, you can monitor and note down the observations of customers in a supermarket by observing their selection and purchasing patterns. This offers a detailed cognizance of the customer.
In any kind of research, you should ensure high survey response rates for improved quality of insights.
2. Survey method
The survey method includes recording the answers of respondents through surveys or questionnaires. Surveys can include polls as well. They are the most common tool for collecting market research data.
Surveys are generally used to collect feedback from the respondents. It should have a survey that taps into both open-ended and closed-ended questions .
The biggest advantage of the survey method is that it can be conducted using online or offline survey tools . One of the reasons why the survey method is the go-to option for descriptive research is that it entails the collection of large amounts of data in a limited span of time.
3. Case study method
The in-depth study of an individual or a group is known as a case study. Case studies usually lead to developing a hypothesis to explore a phenomenon further. Case studies are limited in their scope in that they don’t allow the researcher to make cause-effect conclusions or accurate predictions.
This is because these associations could reflect the bias on the researchers’ part instead of a naturally occurring phenomenon. Another reason why case studies are limited in scope is that they could just be reflecting an atypical respondent in the survey.
An atypical respondent refers to someone who is different from the average consumer, and if researchers make judgments about the entire target population based on this consumer, it can affect the external validity of the study.
[ Related read: Descriptive vs experimental research ]
Read how Voxco helped Brain Research improve research productivity by 60%.
“The platform extends our ability to productively manage our busy intercept survey projects, and the confidence to support major new clients.”
Laura Ruvalcaba, President & CEO, Brain Research
What are the types of descriptive research?
There are seven types of descriptive research based on when you conduct them and what type of data research you conduct. We have explained these seven types in brief with examples to help you better understand them.
1. Cross-sectional:
A descriptive method of studying a particular section of the target population at a specific point in time.
Example : Tracking the use of social media by Gen Z in the Netherlands.
2. Longitudinal:
This type of descriptive study is conducted for an extended period on a group of people.
Example : Monitoring changes in the volume of cyber-bullying among Millenials from 2022 to 2024.
3. Normative:
In this descriptive method, we compare the result of a study with an existing norm.
Example : Comparing legal verdicts in similar types of cases.
4. Relational/Correlational:
We investigate the type of relationships (correlation) between two variables in this type of descriptive research.
Example : Investigating the relationship between video games and mental health.
5. Comparative:
A descriptive study that compares two or more people, groups, or conditions based on a specific aspect.
Example : Comparing the salary of two employees in similar job roles from two companies.
6. Classification:
This type of research arranges collected data into classes based on specific criteria to analyze them.
Example : Classification of customers based on their buying behavior.
7. Archival:
A descriptive study where you search for past records and extract information.
Example : Tracking company’s sales data over the decade.
We have been discussing the descriptive method with examples. So now let’s see how you can use this research type in a real-world application.
Guide to Descriptive Research
Learn the key steps of conducting descriptive research to uncover breakthrough insights into your target market.
Examples of Descriptive Research Under Market Research
This research type helps you gather the necessary information you need to understand the problem. It sets the scene to conduct further research. But how can you use this research method in the real world?
We have explained its real-world application in three scenarios to help you determine where and where you want to use this research type.
1. Sales Studies
You can use this research type to analyze the potential of the market, what is currently trending in the market, and which products may perform well in terms of sales. You can also study what circumstances influence the market shares and when they are likely to increase or decrease.
This research type can help you gather the demographic data of the consumers.
2. Consumer Perception and Behavior Studies
You can use this research method to analyze what consumers think about the brand. You can evaluate their perceptions about the products sold by a particular brand and the uses of other competitive products.
Using descriptive research, you can also analyze what advertising strategies have worked to increase the positive perceptions of the brand. You can assess consumers’ consumption behavior and how it is influenced by product pricing.
3. Market Characteristics Studies
Another way you can use this research method is by analyzing the distribution of the products in the market. You can gather contextual data on questions such as “which countries have more sales”, “which countries have fewer products but the product is sold out quickly” , etc.
You can also analyze the brand management of competitors ; what strategy is working for them and what is not.
What are the applications of descriptive research?
This research method is used for a variety of reasons. Even after outlining survey goals, and survey designs as well as collecting information through surveys, there is no way of knowing whether or not the research you are conducting will meet the predictions that you have made.
Here are some popular ways in which organizations use this research type:
1. Defining the characteristics of respondents
Since most descriptive research methods use close-ended questions for the collection of data, it helps in drawing objective conclusions about the respondents.
It helps in deriving patterns, traits, and behaviors of respondents. It also aims to understand respondents’ attitudes and opinions about certain phenomena.
For instance , researchers can understand how many hours young adults spend on the internet, their opinions about social media platforms, and how important they consider these platforms to be. This information will help the company make informed decisions regarding its products and brands.
One-stop-shop to gather, measure, uncover, and act on insightful data.
Curious about the price? Click below to get a personalized quote.
2. Analyzing trends in data
You can use statistical data analysis to understand the trends in data over time.
For instance, consider an apparel company that drops a new line of clothing; they may research how Gen Z and Millennials react to the new launch. If they discover that the new range of clothes has worked effectively for one group (Gen Z) but not the other, the company may stop producing clothes for the other group.
Leverage a data analysis platform that allows you to conduct advanced statistical analysis and offers a data analytics dashboard to track real-time data.
3. Comparing different groups
Something closely knit to the previous point is also comparing different groups of customers based on their demographics. With descriptive research, you can study how different groups of people respond to specific services offered by a company.
For instance , what is the influence of income, age, gender, income, etc. influence the spending behaviors of consumers?
This research method helps companies understand what they should do to increase their brand appeal in different groups of the population.
4. Validating existing patterns of respondents
Since it is non-invasive and makes use of quantitative data (mostly), you can make observations about why the current patterns of purchasing exist in customers.
You can also use the findings as the basis of a more in-depth study in the future.
5. Conducting research at different times
Descriptive research can be conducted at different periods of time in order to see whether the patterns are similar or dissimilar at different points in time. You can also replicate the studies to verify the findings of the original study to draw accurate conclusions.
6. Finding correlations among variables
This method is also used to draw correlations between variables and the degree of association between the variables.
For instance, if the focus is on men’s age and expenditure.
There is a possibility of finding a negative correlation between the two variables, indicating that as the age of men increases, the less they spend on sports products.
Download Market Research Tool kit
5 MR templates + MR trends guide + Online survey guide + Agile MR guide
Descriptive research Examples
A descriptive method of research aims to gather answers for how, what, when, and where.
Let’s use some examples to understand how a descriptive method of research is used.
Before investing in housing at any location, you would want to conduct your own research to understand
- How is the market changing?
- When or at what time of year is it changing?
- Where would you make more profit?
This type of research is an example of a descriptive study.
A company studies the behavior of its customers to identify its target market before it launches a new product. This is another use case of how brands use descriptive research.
The company may conduct this research by observing the customer’s reaction and behavior toward a competitor’s product.
Or, they can also conduct surveys to ask customer opinions on the new product by the company before its launch.
A restaurant planning to open a branch in a new locality will research to understand the behavior of the people living there. They will survey the people to know their choice of flavor, taste, foods, drinks, and more.
Now that we’ve seen how you can use this research method for your research purpose, let’s also see the advantages & disadvantages of the research.
What Are the Advantages of Descriptive Research?
It is the preliminary research method. Most researchers use this method to discover the problem they should prioritize. Before diving into the experiments, let’s see some of the reasons why you should be conducting this research.
1. Primary data collection
In this type of descriptive research, the data is collected through primary data collection methods such as case studies, observational methods, and surveys. This kind of data collection provides us with rich information and can be used for future research as well. It can also be used for developing hypotheses or your research objective.
2. Multiple data collection
Descriptive research can also be conducted by collecting qualitative or quantitative data . Hence, it is more varied, flexible, and diverse and tends to be thorough and elaborate.
[ Related read: Data Collection: All you need to know! ]
3. Observational behavior
The observational method of this research allows researchers to observe the respondent’s behavior in natural settings. This also ensures that the data collected is high in quality and honest.
4. Cost-effective
It is cost-effective and the data collection of this research can be done quickly. You can conduct descriptive research using an all-in-one solution such as Voxco. Leverage a platform that gives you the capability of the best market research software to conduct customer, product, and brand research.
What Are the Disadvantages of Descriptive Research?
Descriptive research also has some disadvantages. Let’s learn about these cons so you can wisely decide when you should use this research to keep the disadvantages to a minimum.
1. Misleading information
Respondents can give misleading or incorrect responses if they feel that the questions are assessing intimate matters. Respondents can also be affected by the observer’s presence and may engage in pretending. This is known as the observer effect.
2. Biases in studies
The researchers’ own opinions of biases may affect the results of the study. This is known as the experimenter effect.
3. Representative issue
There is also the problem of data representativeness. It occurs when a case study or the data of a small sample does not adequately represent the whole population.
4. Limited scope
Descriptive research has limited scope, wherein it only analyzes the “what” of research, it does not evaluate the “why” or “how” questions of research.
Voxco is trusted by 500+ global brands and top 50 MR firms to gather insights and take actions.
See how Voxco can help enhance your research efficiency.
Wrapping up;
So that sums up our descriptive research guide. It is a wide concept that demands a conceptual framework for descriptive design and a thorough understanding of descriptive survey design .
Naturally, it becomes essential that you adopt online survey tools that facilitates all of the above and provides ample room for insightful research.
Voxco’s omnichannel survey software allows you to create interactive surveys, deploy them across multiple channels, and conduct data analysis in one platform.
This research method enables you to explain and describe the characteristics of a target population. The descriptive research method helps you uncover deeper insights into various aspects of the target population, such as who, what, when, where, and how.
There are many data collection methods you can use to collect descriptive research data. For example, you can perform the research via surveys (online, phone, or offline), case studies, observations, and archival research.
Here are some key characteristics of this research methodology:
This research type helps you describe the characteristics, behavior, opinions, and perspectives of the population or research subject.
The data gathered from descriptive research is a reliable and comprehensive source of explanation of the research subject.
In this methodology, the researcher focuses on observing and reporting on the natural relationship between the variables. There is no manipulation of variables or establishing a cause-and-effect relationship.
Descriptive research offers many advantages.
Descriptive research methods are simple and easy to design and conduct. You don’t need research expertise for this research design in comparison to conducting more complex research.
This research method is more cost-effective than other research methodologies, particularly experimental research designs.
The descriptive research method enables you to collect qualitative and quantitative data. The research data helps extract valuable insights and supports further root-cause analysis.
Descriptive research methodology also has some limitations, here are some of those:
Descriptive research data may generate insights specific to a population under study. This limits your ability to generalize the results to a wider population, which makes the data less representative.
The data collection approaches and observation biases can lead to bias in the research method, which can negatively impact the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
Join the network of 500+ happy survey creators.
Explore all the survey question types possible on Voxco
Explore Voxco Survey Software
+ Omnichannel Survey Software
+ Online Survey Software
+ CATI Survey Software
+ IVR Survey Software
+ Market Research Tool
+ Customer Experience Tool
+ Product Experience Software
+ Enterprise Survey Software
Multiple Choice Questions: A Guide
Multiple Choice Questions: A Guide SHARE THE ARTICLE ON See what question types are possible with a sample survey! Try a Sample Survey Table of

Hcahps survey questions: definition and questions
Hcahps survey questions: definition and questions SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Table of Contents What is Hcahps

Rating Scale
The Art of Leveraging Rating Scales Transform your insight generation process Use our in-depth online survey guide to create an actionable feedback collection survey process.

Interval Scale
SURVEY METHODOLOGIES Interval Scale Try a free Voxco Online sample survey! Unlock your Sample Survey SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is an

How to improve employee experience
How to improve employee experience SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is employee experience? Employee experience is defined as the totality of a

10 Best Customer Experience Survey Software
Exploring Top 10 Customer Experience Survey Software Customer Experience Ensuring an excellent customer experience can be tricky but an effective guide can help. Download Now
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
Looking for the best research tools?
Voxco offers the best online & offline survey research tools!
- Open access
- Published: 04 October 2023
A scoping review of the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services across regional, rural, and remote Australia
- Bianca E. Kavanagh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1656-2775 1 ,
- Kayla B. Corney 2 ,
- Hannah Beks ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2851-6450 1 ,
- Lana J. Williams ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1377-1272 2 ,
- Shae E. Quirk 2 , 3 , 4 &
- Vincent L. Versace ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8514-1763 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 23 , Article number: 1060 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
2801 Accesses
2 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Inadequate healthcare access and utilisation are implicated in the mental health burden experienced by those living in regional, rural, and remote Australia. Facilitators that better enable access and utilisation are also reported in the literature. To date, a synthesis on both the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services within the rural Australian context has not been undertaken. This scoping review aims to (1) synthesise the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services in regional, rural, and remote Australia, as identified using the Modified Monash Model; and (2) better understand the relationship between barriers and facilitators and their geographical context.
A systematic search of Medline Complete, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Scopus, and CINAHL was undertaken to identify peer-reviewed literature. Grey literature was collated from relevant websites. Study characteristics, including barriers and facilitators, and location were extracted. A descriptive synthesis of results was conducted.
Fifty-three articles were included in this scoping review. Prominent barriers to access and utilisation included: limited resources; system complexity and navigation; attitudinal and social matters; technological limitations; distance to services; insufficient culturally-sensitive practice; and lack of awareness. Facilitators included person-centred and collaborative care; technological facilitation; environment and ease of access; community supports; mental health literacy and culturally-sensitive practice. The variability of the included studies precluded the geographical analysis from being completed.
Both healthcare providers and service users considered a number of barriers and facilitators to mental health service access and utilisation in the regional, rural, and remote Australian context. Barriers and facilitators should be considered when re-designing services, particularly in light of the findings and recommendations from the Royal Commission into Victoria’s Mental Health System, which may be relevant to other areas of Australia. Additional research generated from rural Australia is needed to better understand the geographical context in which specific barriers and facilitators occur.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The mental health of Australians who live in regional, rural, and remote Australia is an ongoing concern [ 1 ]. Poor healthcare access is one of the key determinants of adverse mental health outcomes, with access issues being more pronounced in regional, rural, and remote Australia (hereafter referred to as rural , in line with the Australian Government’s definition under the Rural Health Multidisciplinary Training [RHMT] Program [ 2 ]), compared to metropolitan Australia [ 3 ]. People living in rural Australia often face difficulties in obtaining healthcare, and this care is often delayed and more expensive for the patient [ 4 ]. These difficulties in accessing and utilising healthcare are implicated in the higher mental disorder burden experienced by those living in rural Australia, shown by the higher rates of suicide, compared with major cities [ 5 ]. Moreover, this group is less likely than those living in major cities to take-up and complete mental health treatment [ 6 ]. Workforce maldistribution plays a role in these health inequalities [ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ], with more clinical full time equivalent (FTE) mental health professionals working in major cities, compared with rural areas (i.e., 92 vs. 30–80 mental health nurses, 15 vs. 2–6 psychiatrists, and 90 vs. 15–55 psychologists per 100,000/population) [ 3 ]. Other areas of the health workforce are similarly maldistributed across the country (i.e., 403 vs. 223–309 clinical FTE medical practitioners and 531 vs. 382–469 clinical FTE allied health professionals per 100,000/population in major cities versus rural areas) [ 11 ].
There are a number of factors that are implicated — both directly and indirectly — in the access and utilisation of mental health services, and these factors may be pertinent to the level of remoteness experienced. This includes particular aspatial (i.e., social) and spatial (i.e., geographical) dimensions [ 12 , 13 ]. Aspatial dimensions consist of the factors that affect the affordability , acceptability , accommodation , and awareness of healthcare access. In the rural context of Australia, this tends to relate to social matters [ 14 , 15 ] including stoicism, low help-seeking behaviours, and confidentiality concerns [ 16 ]. Spatial dimensions are concerned with the availability and accessibility of service access, including geographical isolation [ 14 ], service delivery capacity [ 17 ] [ 18 ], and dual-roles [ 14 ] (i.e., the intersection of professional and personal relationships) in rural areas. While here we define access as factors that pertain to the attributes/expectations of the individual and their alignment with the provider/services [ 12 ], other models conceptualise access as the opportunity to identify healthcare needs, seek services, reach resources, obtain or use services, and have the need for services fulfilled [ 19 ]. Utilisation refers to the generation of a healthcare plan throughout a healthcare encounter, as well as its implementation and follow-through [ 20 ].
Conceivably, mitigating the barriers and augmenting the facilitators to the utilisation of mental health services may be particularly important when considering the obstacles that people from rural areas face when accessing services. One previous study on rurally-based Australian adolescents suggested that barriers to accessing services, such as social exclusion and ostracism by members of their community, also likely prevented the continued utilisation of services and negatively affected treatment outcomes [ 21 ]. Cheesmond et al. [ 22 ], in a review of residents in rural Australia, Canada, and the United States of America, highlighted a link between sociocultural rurality, rural identity, and help-seeking behaviour. Cheesmond et al. [ 22 ] suggested that specific place-sensitive approaches are needed to overcome barriers to help-seeking, and that a greater understanding of help-seeking in the rural context is required. This includes further exploration of rurality as a concept, conducting research within diverse environments, allowing participants to contextualise barriers to help-seeking, and exploring the co-existence of multiple help-seeking barriers. Parallel to this, a paucity of research has focussed on the facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services in rural Australia.
To the authors’ knowledge, no previous reviews have specifically focussed on understanding the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services within the rural Australian context. A scoping review was chosen as the preferred approach to this work because of the emerging and cross-disciplined nature of the research. The aim of this scoping review is to: (1) explore the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services for Australians living in rural areas; and (2) better understand the relationship between barriers and facilitators and their geographical context.
This scoping review conforms to the guidelines put forward by Arksey and O’Malley [ 23 ], follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) [ 24 ], and a published protocol [ 25 ].
Eligibility criteria
The scope of this review was intentionally broad to allow explanation of the nature and extent of the literature describing the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services across regional, rural, and remote Australia. Articles were eligible for inclusion if they met the following criteria:
Included individuals with a diagnosed mental disorder, experienced mental health issues, or were part of a mental health community service; or included healthcare providers that provided diagnostic, assessment, or treatment services for mental health issues.
Explained obstacles that impeded the uptake, quality, or level of mental health services being accessed or described facilitators that allowed the uptake, quality, or level of mental health services being received.
Included service users, healthcare providers, or services that were based in regional, rural, or remote Australia according to the Modified Monash Model (MMM) 2–7 ( regional centres to very remote communities ) [ 4 ] (i.e. the current RHMT definition of rural).
The population/concept/context (PCC) framework was used to generate the eligibility criteria for this scoping review and is described in Table 1 . The eligibility criteria for this review varied slightly from the published protocol [ 25 ]. In this review, we included pharmacists as healthcare providers, as it was identified that pharmacists play a key role in mental health services in some rural areas. We excluded mental health programs and health promotion activities that were considered to be a “structured activity” delivered by a service, reviews, viewpoints, declarations, tailpieces, frameworks, and commentaries. We also excluded articles that did not provide sufficient detail to describe the barriers or facilitators to accessing or utilising services, as well as articles that pooled results across participants from metropolitan and regional/rural/remote areas. The only exception to this was when authors referred to the study setting as regional/rural/remote, but upon further investigation using the health workforce locator [ 26 ] (see Sect. 2.8 Geographical analysis ), the location was deemed to be metropolitan according to the MMM [ 4 ] — this exception was allowed due to the differences in geographical models applied to Australian health research [ 27 , 28 ]. Separately, we decided to include articles that reported on the barriers and/or facilitators of a specific rural mental health service implementation activity or service model, as we felt that these articles offered important insights that may be translated to new service initiatives or research activities.
Information sources
The following databases were systematically searched: Medline Complete, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Scopus, and Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL). Websites of the Australian federal and state government’s Department of Health, Primary Health Network (PHN), key rural and remote peak bodies/agencies known to the authors from their collective experience on the topic, and Google were also searched to ascertain grey literature. The search was performed on 11th January 2022 and a 2012-current date filter was employed using the ‘start’ and ‘end’ publication year functions. Additional sources were identified through ‘snowball’ searching of included studies. Where needed, additional location information was obtained via a study’s first or corresponding author.
The search strategy was developed in consultation with two scholarly services librarians (JS and BK) to identify peer-reviewed studies and grey literature records. Relevant keywords, search terms, and wildcard symbols were applied to each database. An adapted search string was searched in Google using the advanced search function. The “all these words” and “any of these words” search options were engaged, and PDF files were requested. All (n = 11) pages of the search results were assessed for eligibility by one reviewer (BEK), and the research term agreed on their inclusion.
The full search strategy and grey literature sources are presented in Additional Table 1 .
Selection of sources of evidence
One reviewer (BEK) applied the search strategy to the databases and websites. Two reviewers (BEK and KBC) independently screened all articles using Covidence [ 29 ]. Where discrepancies concerning the eligibility of an article occurred, a meeting was held to determine consensus; if consensus could not be reached, a third reviewer (LJW) was consulted to make the final decision.
Data charting process
To ensure that the data charting process was consistent with the research question, a charting form was developed and piloted by two authors (BEK and KBC). One author (BEK) then charted the data for each of the eligible articles, using Microsoft Excel.
The following data items were extracted from eligible studies: author and year, study objective, study design, location, sample size, characteristics of participants, mental health diagnosis/issue and assessment method, healthcare provider type/role, barriers, facilitators, mental health service, regional/rural/remote area of Australia, and summary of findings (Additional Table 2 ). For literature that included participants from both metropolitan and regional/rural/remote areas, only information that pertained to those from regional/rural/remote areas was extracted, except for instances where statistical differences between groups were reported for comparison. Likewise, in instances where articles included participants who were eligible (e.g., healthcare providers) as well as participants who were ineligible (e.g., no evidence of mental health diagnosis/engagement with services), only information from eligible participants was extracted. First or corresponding authors of studies that did not specifically state where the study was conducted were contacted to provide additional location information.
Synthesis of results
A descriptive synthesis was conducted by providing an overview of the included study characteristics, setting and target groups, and barries and facilitators. Links to aspatial and spatial access factors were also described, where relevant. The study characteristics are presented in Table 2 and the barriers and facilitators pertaining to each included study are presented in Additional Table 3 . A quality appraisal of the included studies was not undertaken as scoping reviews aim to offer an overview or map of the pertinent evidence [ 30 ].
Geographical analysis
Geographical coordinates provided by the health workforce locator [ 26 ] were used to determine the remoteness of the study locations according to the MMM categories. These data were inputted into STATA to determine the number and proportion of each of the MMM categories.
The database search yielded 1,278 articles, of which 555 articles were removed due to duplication. Subsequently, 723 titles and abstracts were screened, and 441 were excluded due to ineligibility. At the full text stage, 282 articles were screened, with 181 studies being excluded, resulting in 47 articles meeting the eligibility criteria. The grey literature search yielded 128 potentially relevant sources, of which six were eligible after removing three for duplication. In total, 53 articles were included in this scoping review. A snowball search of the references of included records was also conducted and two additional records were identified but were deemed ineligible as they reported on studies/samples that were already included in the review. Figure 1 displays the PRISMA flow throughout each screening stage.
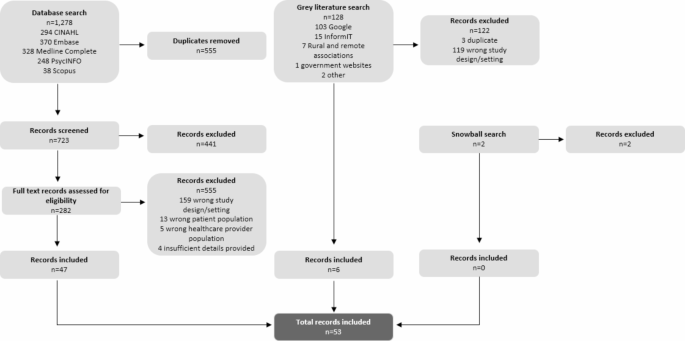
PRISMA flow diagram of studies considered in this review
Study characteristics
Of the 53 included studies, 25 articles described barriers and/or facilitators from the healthcare provider perspective, 13 were from the point of view of the service user, eight reported on combined perspectives of both the healthcare provider and service user, and seven reported on barriers/facilitators from neither the healthcare provider nor service user perspective directly but did consider the barriers/facilitators of the service environment (e.g., service evaluations).
Most studies (n = 29, 54.7%) employed qualitative methods, including interviews and/or focus groups; 12 studies utilised quantitative cross-sectional or longitudinal methods, seven were mixed-methods research designs, and two were service description and classification studies.
The highest proportion of studies were conducted in New South Wales (NSW) (n = 13) [ 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 ], followed by Australia broadly (n = 12) [ 33 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], South Australia (SA) (n = 10) [ 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 ], Victoria (VIC) (n = 6) [ 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 ], Queensland (QLD) (n = 5) [ 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 ], Western Australia (WA) (n = 3) [ 76 , 77 , 78 ], Tasmania (TAS) (n = 2) [ 79 , 80 ], and Northern Territory (NT) (n = 1) [ 81 ]. One study pertained to areas within NSW, QLD, and VIC [ 82 ], and another study concerned NSW and WA [ 83 ]. No studies were centred on Australian Capital Territory (ACT). Table 2 depicts the characteristics of the included studies.
Setting and target groups
Mental health service setting.
Fourteen studies reported on general or community-based mental health services [ 18 , 33 , 43 , 48 , 53 , 54 , 57 , 64 , 72 , 74 , 77 , 78 , 83 ]. Four studies described mental health services provided within emergency departments (EDs) and/or urgent care centres (UCCs) [ 40 , 41 , 46 , 65 ]. The remaining studies described mental health services provided by counsellors and GPs [ 38 ], nurses, peer-workers [ 71 ], personal helpers and mentors [ 35 ], pharmacists [ 47 ], and a combination of several healthcare providers [ 59 ]. Seven studies reported on technology-based or -enhanced mental health services [ 51 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 75 , 76 ].
Target groups
The population group focus of studies varied. Of the studies that commented on, or specified that they targeted specific subpopulations, four studies discussed care pertinent to Indigenous or Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander Peoples [ 66 , 67 , 68 , 81 ]. Four studies discussed mental health services for young people [ 55 , 63 , 73 , 82 ]. Three studies specifically included at least a proportion of service users who were under the age of 18 years old [ 55 , 61 , 79 ]. Two studies reported on mental health services for older people [ 50 , 58 ]. Other studies described barriers and or facilitators specific to sex workers [ 80 ], medical doctors [ 45 ], LGBTIQA + people [ 51 ], immigrants [ 49 ], and women [ 39 ] or men [ 70 ] with specific mental health issues. Three studies described mental health services that were specific for supporting people with depression [ 34 , 39 , 55 ]; two studies were focussed on suicide [ 68 , 70 ]; two studies described care for people with eating disorders [ 42 , 52 ]; and one study was centred on perinatal and infant support [ 75 ].
Barriers and facilitators
The included studies varied significantly. This included differences in the purpose and type of study, participant sample, and methodology, and reporting of findings. Barriers and facilitators were grouped into prominent concepts based on terminology used by the relevant literature and are presented in Table 3 . Barriers related to limited resources; system complexity and navigation; attitudinal and social matters; technological limitations; distance to services; insufficient culturally-sensitive practice; and lack of awareness. Facilitators related to person-centred and collaborative care; technological facilitation; environment and ease of access; community supports; mental health literacy; and culturally-sensitive practice.
Prominent barrier concepts
Barriers affecting healthcare providers and service users.
Limited resources. Across the studies, the most considerable barrier was limited resources [ 18 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 42 , 45 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 71 , 74 , 75 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 82 ]. This key concept considered limited resources at the healthcare provider and service user level. Notably, lack of available general and specialist services, limited service capacity, workforce shortages, difficulty attracting and retaining staff, and staff turnover were frequently reported as considerable spatial barriers to service delivery, hampering access to services. Moreover, financial costs, disadvantage, or appointment fees [ 34 , 37 , 52 , 53 , 61 , 62 , 78 ], and lack of transport [ 34 , 50 , 52 , 53 , 58 , 62 , 71 , 78 ] restricted access to mental health services for the service user. These issues reflect the lower relative socio-economic advantage seen in rural areas of Australia [ 2 ].
System complexity and navigation. The complexity in using and navigating the system was a common aspatial barrier [ 18 , 33 , 36 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 45 , 46 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 61 , 63 , 65 , 66 , 69 , 73 , 74 , 78 , 80 ], which affected healthcare providers in coordinating patient care and service users in utilising such care. These issues were most frequently reflected in reports on extended wait times and delays in assessment and diagnosis [ 34 , 40 , 46 , 53 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 62 , 66 , 78 , 80 ].
Attitudinal or social matters. Many studies reported that attitudinal or social matters were a barrier for the service user [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 43 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 70 , 78 , 80 , 81 ], particularily concerning privacy or confidentiality concerns [ 39 , 51 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 66 , 67 , 78 ], affecting aspatial access to care. The need to be stoic was reported as a barrier to seeking psychological help among regional medical doctors, relating to their perceptions of regional practitioner identity [ 45 ], and among service users [ 50 , 67 , 70 ].
Technological limitations. Several studies cited limitations to services delivered via technological means [ 51 , 53 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 64 , 78 ]. Some studies acknowledged that technology can enhance physical mental health services, but cannot replace them [ 62 , 64 ], particularly for specific client groups, including the older population and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people, who reportedly prefer face-to-face service delivery [ 78 ]. In addition, poor connectivity and high costs of technology use were reported as aspatial barriers to accessing technology-delivered mental health services and may also affect their utilisation [ 53 , 62 , 78 ].
Lack of awareness. Lack of awareness about mental health issues, needs, or services available was reported as an aspatial barrier in the current review [ 43 , 50 , 52 , 67 , 78 ]. This lack of awareness was reported at the healthcare provider level in one study, and was described as the healthcare provider having a limited understanding of the mental health needs in older people, resulting in a lack of referral to appropriate services [ 50 ]. At the service user level, a lack of awareness precluded individuals from recognising mental health problems [ 67 ], while a lack of awareness of services was a barrier to seeking help [ 52 , 78 ].
Barriers affecting service users
Distance to services. The spatial distance required to travel to physical services is a considerable issue for people residing in rural localities, and this distance has been shown to reduce service access and utilisation in the current review [ 52 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 67 , 71 , 78 ]. There is also an additional burden experienced by those with physical disability, or those who don’t have a support person to assist them [ 53 ].
Insufficient culturally-sensitive practice. A limited capacity to meet the needs of culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities was reported, affecting aspatial access and utilisation of services. This tended to be a result of service users not feeling culturally safe within the service environment, perceptions that health professionals had cultural assumptions about the service user, and inappropriate assessment tools [ 48 , 49 , 58 , 73 , 78 ].
Prominent facilitator concepts
Facilitators affecting healthcare providers and service users .
Person-centred and collaborative care. Many studies reported that person- (or client-) centred care that is non-judgemental and permits collaboration to be an important aspatial facilitator to mental health service access and utilisation [ 31 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 41 , 42 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 61 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 72 , 74 , 81 ]. It is noteworthy that person centred care was specifically reported in studies pertaining to the service user [ 61 ] and healthcare provider [ 63 , 64 ] in the current review, suggesting that this approach is recognised as important by both those delivering and using the service. Care that is regular and non-intrusive was seen as a way to facilitate service utilisation [ 34 , 57 ].
Technological facilitation. Technology-based services, including integrated mental health services, telehealth, live chat, SMS appointment reminders and coordination, and mental health web-pages, were reported to be useful in filling spatial and aspatial gaps in service delivery for physical services [ 51 , 53 , 58 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 75 , 76 , 78 ]. These services were reported to facilitate connection and information sharing [ 62 ], clinical supervision, contact with specialists [ 60 ], workforce upskilling, and security [ 75 ] for the healthcare provider. For the service user, technology-based services facilitated immediacy of consultations, cost savings, and anonymity, and reduced mental health hospitalisations and admissions, additional client appointments, the need to travel, stigma, and family stress [ 60 ].
Environment and ease of access. The mental health service environment and the ease of which one may access services — granted that all other access issues are overcome — were frequently reported as spatial facilitators [ 31 , 49 , 65 , 73 , 80 , 81 ]. Specifically, services that permitted a non-clinical and comfortable environment were deemed as important aspatial factors for young people [ 61 , 73 ]. Co-located services were also considered important for access, as this allows service integration and facilitated information sharing [ 31 , 41 , 63 ].
Community supports. The community was considered to be an important aspatial facilitator. This included healthcare providers being involved and connected with the community [ 56 , 65 , 66 ], as well as having a sense of community [ 59 ], as a way to facilitate care via information sharing, collaboration, and knowing community members and local issues. For the service user, community and place was seen as a source of strength as noted by one study [ 39 ].
Facilitators affecting service users
Mental health literacy. Several studies reported that having awareness of mental health issues and being confident in using services were aspatial facilitators to mental health service access and utilisation [ 52 , 57 , 59 , 66 , 70 ]. These factors are generally referred to as mental health literacy within the wider literature, which is a crucial component of healthcare [ 84 ].
Culturally-sensitive practice. Of the studies that reported on cultural elements of mental health service provision, it was noted that Indigenous and other culturally appropriate staff (i.e., a Koori Mental Health Liaison Officer or Aboriginal Mental Health Worker), as well as the involvement of Community Elders and spiritual healers [ 48 ] assisted with service access and utilisation [ 48 , 66 ]. Further, culturally appropriate décor and flexibility in meeting places [ 66 ], and the use of culturally acceptable models of mental health [ 48 ] were also seen as important aspatial dimensions.
Overall, thirty studies were described as being relevant to rural areas [ 18 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 42 , 43 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 53 , 57 , 58 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 73 , 76 , 78 , 83 ], three studies were pertinent to regional areas [ 39 , 56 , 79 ], two studies were concerned with remote areas [ 77 , 81 ], and the remaining studies involved combinations of regional/rural/remote populations of Australia [ 37 , 40 , 41 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 55 , 59 , 60 , 71 , 74 , 75 , 80 , 82 ]. Over one third of the studies (n = 21, 39.6%) reported or provided specific spatial data, which allowed the MMM [ 4 ] to be applied directly to the study location; n = 10 (47.6%) of these studies included multiple locations, resulting in a total of 41 MMM categories. Studies were conducted most frequently in MM5 small rural towns (n = 10, 24.4%) and MM3 large rural towns (n = 9, 22.0%) and least frequently in MM6 remote communities (n = 3, 7.3%). The first author’s location was used as a proxy location for 28 studies (52.8%). Of these studies, the most frequent location was MM1 metropolitan settings (n = 16, 57.1%), likely due to the high proportion of study locations being taken from the first author’s location, and that many universities and research centres are located in major cities. There were no studies conducted in MM5 small rural towns (n = 0, 0%). Three author locations (5.7%) could not be determined due to limited information provided. Table 4 displays details of the MMM categories according to spatial data reported or obtained and proxy locations. Due to the heterogeneity and lack of mutual exclusivity of the data, an analysis of the association between geographical area and specific barriers and facilitators was unable to be completed.
Discussion and implications
This scoping review identified the barriers and facilitators experienced by healthcare providers delivering mental health services and individuals accessing, or attempting to access mental health services in rural Australia. Prominent barriers included: limited resources; system complexity and navigation; attitudinal and social matters; technological limitations; distance to services; insufficient culturally-sensitive practice; and lack of awareness. Facilitators included person-centred and collaborative care; technological facilitation; environment and ease of access; community supports; mental health literacy and culturally-sensitive practice. We also aimed to understand these barriers and facilitators in relation to their geographical context; however, the variability in the data precluded the geographical analysis from being completed.
This study revealed a paucity of research conducted in MM6 remote and MM7 very remote communities in Australia when specific spatial data are considered, as well as in the ACT — however, it is noted that the majority of the ACT is classified as metropolitan, with 99.83% (387,887 residents) of the population residing in MM1 at the time of the 2016 census [ 2 ]. Moreover, when proxy study locations are used, many studies are conducted by researchers located in metropolitan areas. Only three studies specifically included service users who were under the age of 18 years old, representing a significant gap in understanding the mental health service needs of the younger population. Although it is acknowledged that there are considerable research ethics restrictions in place to protect children and young people, the onset of many mental health issues tends to occur between 14.5 and 18 years of age [ 85 ], highlighting the importance of understanding barriers and facilitators to accessing mental health services amongst the younger cohort. Due to the heterogeneity of the findings, the following discussion considers the most prominent barriers and facilitator concepts identified across the studies.
Review findings support limited resources as being one of the biggest restrictors of mental health service access and utilisation within rural Australia. Thes findings echo reports at the national scale, which show the mental health workforce is heavily concentrated in metropolitan areas compared to other remoteness areas, relative to the population [ 86 ]. Considerable efforts need to be made to reduce the resource inequalities, including the dearth of mental health professionals practicing outside of metropolitan cities. Recently, the National Mental Health Workforce Strategy Taskforce (the Strategy) was established to deliberate the quality, supply, distribution, structure, and methods to improve attracting, training, and retaining Australia’s mental health workforce [ 87 ]. The Consultation Draft of the Strategy highlights six objectives, including (1) careers in mental health are recognised as, attractive; (2) data underpins workforce planning; (3) the entire mental health workforce is utilised; (4) the mental health workforce is appropriately skilled; (5) the mental health workforce is retained in the sector; and (6) the mental health workforce is distributed to deliver support and treatment when and where consumers need it [ 88 ]. These objectives reflect the systemic resource issues cited in the current scoping review and emphasise the importance of a contemporary approach to increasing resources for mental health services in rural Australia. This contemporary approach is important, as it has previously been acknowledged that increasing graduates has not resolved workforce maldistribution in other areas of healthcare (i.e., medical physicians), but rather, an improved distribution of both human and other resources is needed [ 89 , 90 ].
For the service user, resource issues spanned both aspatial and spatial dimensions and include the affordability (i.e., perceived worth relative to cost) and accessibility of the service (i.e., the location of the service and ease of getting to that location) [ 12 , 13 ]. Transport issues were commonly reported to be a resource issue within the current review and the wider literature. Limited transport compounds access issues for specific subpopulations, such the elderly, particularly when they do not have personal transport and when there is no public transport available [ 50 ]. This issue is likely compounded by resource limitations, including the cost of travel, and is specifically related to spatial distance to services. Distance to services is a significant barrier to accessing healthcare. Wood et al. [ 91 ] in a systematic review, identified that there is a lack of research which measures spatial access specific to mental health services in Australia, and highlighted a need for consensus on what is reasonable access to healthcare services. Further, reports have noted that while distance alone is a significant barrier to accessing healthcare, accommodation may sometimes need to be sought depending on the time of the appointment, adding to the cost of attending the appointment [ 92 ] and further perpetuating the resource issues experienced by those living in rural areas of Australia. In addition, although not specifically reported in the current review, it is likely that the time required for traveling to and attending such appointments may require the individual to choose between tending to work or family needs or receiving the help needed.
Transport and other resource issues, as well as distance to services, may be mitigated through telehealth appointments, which have been central to the provision of healthcare since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the utilisation of telehealth requires many patients to have had a face-to-face consultation with their GP in the previous 12 months [ 93 ], which may preclude some Australians from rural areas from its use, considering the significant workforce maldistribution previously discussed. Moreover, rural areas of Australia also experience digital disadvantage as a result of lower internet connectivity — brought about by the high costs of installing internet infrastructure in rural and remote areas — and the socio-economic disadvantage experienced by those who live outside of metropolitan areas [ 94 ]. These issues are compounded by an ageing population, lower educational levels, a larger primary industry sector, a higher unemployment rate, and a higher Indigenous population in rural and remote Australia [ 94 ]. High cost, connectivity issues, and suitability for specific client groups should be key considerations in the delivery of technology-based mental health services. Notwithstanding these issues, the current review identified that technology-based services may be a useful adjunct to physical services, particularly in relation to reducing the need to travel, consultation immediacy, and clinician upskilling. This finding partially supports a recent systematic review, which found that youth located in rural and remote areas of Australia and Canada prefer to see mental health professionals in person, with telehealth provided as an additional option [ 95 ]. As such, the benefits and limitations to technology-based mental health services needs to be carefully considered by those designing services.
A key barrier to both access and utilisation in the current review was the complexity of using and navigating the mental health system. These issues typically occur at the system and organisation level and affect the way a service operates and its culture, making it challenging for service users to receive effective care. A complex mental health system and service fragmentation has been previously reported to lead to confusion and a lengthy amount time spent trying to navigate the system, with these issues being even greater amongst those who are younger, less autonomous, or who have less experience navigating the system [ 96 ]. System navigation initiatives may address this gap and have previously been implemented via the Partners in Recovery (PIR) program — established to facilitate care coordination for people with severe and persistent mental illness — with positive impacts for those who used the program [ 97 ]. However, the introduction of the National Disability Insurance Scheme has superseded the PIR program, and has rendered many former PIR program participants ineligible for support [ 98 , 99 ], representing a significant gap in mental health service navigation and care coordination support. Isaacs et al. [ 100 ], identified that it is more cost effective to support people with severe and persistent mental illness to access PIR supports than to not provide this support, due to the potential increased need for other services (e.g., hospital admissions, homelessness supports, residential supports). Indeed, the Australian Government’s Productivity Commission (Productivity Commission) recommended that life insurers should have greater flexibility to fund approved mental health services to reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation for mental health issues [ 101 ]. In addition, Isaacs et al. [ 100 ] reported that co-located services — which were reported as a facilitator in the current review — and the increased need of non-clinical support through mental health community support services, offered via non-governmental and not-for-profit organisations, were demonstrated to be important considerations for cost effective mental health care.
Attitudinal or social matters are frequently reported to be key barriers for rural Australians to accessing care and are considered to be an aspatial dimension [ 12 , 13 ]. These matters which include stigma, fear of judgement, stoicism, lack of trust, preference for keeping to oneself, and reluctance to seek help have been reported on the global scale as impacting upon help-seeking in rural areas in relation to rural identity [ 22 ]. Stoicism, in particular, is ordinarily viewed as a positive trait, with rural participants of a global review contextualising stoicism as an inflexible element to their core identity, however, this trait has repeatedly been reported as a barrier to the uptake of mental health services in this review [ 45 , 50 , 67 , 70 ] and in the wider literature [ 22 ]. In terms of addressing attitudinal and social matters, previous Australian research [ 16 ] has identified that intentions to seek help for a mental or emotional issue decreased with a higher classification of remoteness. Moreover, stoicism and attitudes towards seeking professional help were predictive of help-seeking intentions for participants from both rural and metropolitan areas, but sex, suicidality, and previous engagement with a mental health professional were additionally predictive of help-seeking intentions for rural Australians [ 16 ]. The current scoping review identified few studies that specifically reported on these issues in relation to barriers to accessing services [ 37 , 55 , 68 , 70 ], suggesting a need to increase research focus on these issues. Interestingly, Kaukiainen and Kõlves [ 16 ] study, found that attitudes towards seeking professional help mediated the relationship between stoicism and help-seeking intentions for participants from both rural and metropolitan locations, suggesting that attitudes towards seeking professional help may be a fruitful avenue to target to increase help-seeking intentions for all Australians [ 16 ]. Education programs delivered in secondary school or tertiary settings have been suggested as a way to improve attitudes towards help-seeking and stigma [ 102 ]. These avenues may also be useful to increase mental health literacy (i.e., the public knowledge and recognition of mental disorders and knowing where and how to seek help) [ 84 ] in the community, given that lack of awareness was a barrier and mental health literacy was a facilitator in the current review.
Providing person-centred and collaborative care was reported as a key facilitator in the current review. Person-centred care is generally defined as care that is holistic and incorporates the person’s context, individual expression, beliefs, and preferences, and includes families and caregivers, as well as prevention and promotion activities [ 103 ]. Indeed, person-centred care is a prominent practice model in mental health care, and this model of care may be particularly beneficial in rural Australia, given that it aims to decrease barriers between health service providers via shared knowledge. This model of care is collaborative by nature, although it should be noted that collaborative care is a distinct, though related model of care. Collaborative care refers to health professionals and patients working together to overcome a mental health problem [ 104 ]. This model of care has been shown to improve depression and anxiety outcomes across the short to long term (i.e., 0–24 months), and has benefits on medication use, patient satisfaction, and mental health quality of life [ 104 ]. The Productivity Commission recommended the trial of innovation funds to diffuse best practice in mental health service delivery and to eliminate practices that are no longer supported by evidence [ 101 ]. Such innovation funds may allow healthcare providers to maintain currency on practices such as person-centred and collaborative care. Importantly, the Royal Commission into Victoria’s Mental Health System (the Royal Commission) [ 90 ] identified person-centred care as a way to promote inclusion and prevent inequalities, and was specifically linked to providing culturally safe mental health care — which was noted as a facilitator to access and utilisation in the current review and has been highlighted as an important approach to eliminate health inequalities [ 105 ]. Moreover, the Royal Commission recommended the use of an integrated service approach — where service providers can work together to provide care [ 90 ]. This approach to care may mitigate service fragmentation and system complexity and navigation barriers, and also permit environments that are comfortable and allow ease of use — as identified as facilitators in the current review.
Community support, both in the sense of individuals feeling connected to the community and healthcare providers being seen within the community, was a key concept in the current review. For the service user, Johnson et al. [ 39 ] reported that accessing services under the scrutiny of the community was seen as a challenge, but that the community was also seen a source of strength. Crotty et al. [ 56 ] noted the duality for healthcare providers being involved with the community in both a social and professional sense, leading to both challenges and a feeling of togetherness. This sense of togetherness reflects the historical view that rural and remote communities have been connected over several generations [ 106 ]. Notably, in the current review, one study on healthcare provider perspectives on workforce retention reported that personal connections and a ‘natural’ connection to the community were key factors in the decision for staff working in remote areas to stay [ 33 ], suggesting the importance of embedded relationships in this setting. Preferences to stay in rural and remote towns have been associated with a sense of belonging and the quality of diverse and interesting activities, particularly for younger people [ 107 ], and these factors should be strengthened to permit the retention of the rural mental health workforce.
It is noteworthy that many of the studies were undertaken at metropolitan locations, suggesting that much of the research completed on rural locations was not necessarily conducted within this setting. However, it is acknowledged that many university locations are affiliated with major campuses, which are often located in metropolitan areas. Simultaneously, many rurally-based health and community services do not have the resources to undertake locally-generated research, and this consequently limits the evidence available for policymakers to make informed decisions regarding the health of the rural population — noting that place-based approaches are gaining traction [ 108 , 109 , 110 ]. This area is a key focus of the RHMT program [ 111 ]. The RHMT program aims to maximise investment in of Australia via academic networks, developing an evidence-base, and providing training in rural areas for health professionals. To date the RHMT program has seen that health graduates who undertook clinical placements in the most rural settings are working more in rural locations [ 112 ], and this is likely to have flow-on effects for healthcare providers to build connections to these areas, retain the workforce, and increase health outcomes for the community.
This review highlights the need for a contemporary approach to mental health services in rural Australia. This includes encouraging and educating the public about mental health issues and how to seek and engage in timely mental health care that is appropriate to one’s needs. Simultaneously, this review suggests a need to reconsider how the public navigates mental health services, and to redesign services that are easy to engage with, culturally safe, comfortable to use, and have technological capabilities. This may be more accurately achieved when services are designed with local issues and the community in mind via the integration of bottom-up place-based strategies and top-down place-sensitive approaches, particularly given that a one-size-fits-all approach to policy — and thus mental health service design — does not favour regions and localities [ 113 ]. It is critical that rural mental health services are invested in to remove barriers and improve health equity. The fiscal implications of such investment may be offset using this integrated approach, which leverages local and external assets, encourages workforce retention, and may reduce costs in other areas healthcare service delivery.
Strengths and limitations
The strengths of this scoping review include the use of peer-reviewed and grey literature, the full-span of the child-adult age range, and the wide variety of included studies. In addition, this scoping review applied a consistent approach to applying remoteness categories, albeit this application was not without issues. For example, Wand et al. [ 40 ] and Wand et al. [ 41 ] reports on work done in Maitland (MM1) and Dubbo (MM3). Maitland (NSW) is of particular interest in the context of remoteness settings as it has historically been described as a regional area. In the early 2000s when the Australian Bureau of Statistics was defining the most accessible category of the Accessibility/Remoteness Index of Australia (ARIA), Maitland (as well as other locations such as Wollongong, NSW and Geelong, Victoria) was included in the most accessible category [ 114 ].
Several limitations must also be considered. Firstly, many sources — particularly grey literature sources — included potentially relevant information; however, a lack of clear evidence that the data specifically pertained to those living in regional/rural/remote areas prevented many of these sources from being included. In addition, findings were limited by the available literature, especially among community service organisations, which have limited resources to generate research outputs. The search strategy was limited to 2012–2022 and did not include search terms specific to certain subgroups of the population who have been known to experience barriers to mental health services in rural areas (e.g., farmers and people from CALD backgrounds), and some search results may have been omitted as a result of this. It was not possible to discern whether findings related specifically to access or utilisation in many studies, and as such, a nuanced discussion of these dimensions is not provided. Further, the data were heterogeneous and results tended to be grouped across regional, rural, and/or remote contexts, precluding an analysis of the association between geographical area and barriers and facilitators from taking place. Future research may consider completing a comprehensive geographical analysis once additional data on the topic becomes available. Lastly, although data screening was completed by two reviewers, only one reviewer coded the extracted data into key concepts, and this may have introduced bias into the results, however the key concepts were agreed upon by the research team.
This scoping review found a number of barriers to accessing and utilising mental health services that may be overcome through initiatives that have been implemented or suggested by the government. Importantly, many of the spatial barriers associated with access and utilisation may be mitigated through innovative solutions, such as a combination of face-to-face and technology-based service provision, provided that careful consideration is given to the technological and resource limitations seen in the rural context of Australia. Parallel with this, several facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services were noted, some of which may already be prominent in the provision of services, but could be further strengthened through additional training, service re-design, and community initiatives.
The included studies varied in their aim, setting, and study design, and many studies were grouped across MMM categories, disallowing a nuanced understanding of how barriers and facilitators operate within specific geographical contexts. This, paired with the finding that many studies were conducted at a metropolitan location, highlights the importance of conducting research within the rural setting. Additional research generated from rural areas, as well as consideration for how remoteness is measured, would assist in providing a more comprehensive understanding of the barriers and facilitators to mental health services within the geographic contexts they occur.
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Australian Capital Territory
Accessibility/Remoteness Index of Australia
Culturally and linguistically diverse
Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature
Emergency department
Full time equivalent
General practitioner
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, intersex, queer/questioning, asexual
Modified Monash Model
Population/concept/context
Primary Health Network
Partners in Recovery
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for scoping reviews
New South Wales
Northern Territory
Rural Health Multidisciplinary Training
South Australia
Urgent care centre
Western Australia
5 References
Inder KJ, Berry H, Kelly BJ. Using cohort studies to investigate rural and remote mental health. Aust J Rural Health. 2011;19(4):171–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Versace VL, Skinner TC, Bourke L, Harvey P, Barnett T. National analysis of the modified Monash Model, population distribution and a socio-economic index to inform rural health workforce planning. Aust J Rural Health. 2021;29(5):801–10.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Mental health workforce 2023 [Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/mental-health/topic-areas/workforce ].
Australian Department of Health. Modified Monash Model 2019 [Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/modified-monash-model-fact-sheetaccess ].
Australian Government. Deaths by suicide by remoteness areas. In: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, editor.; 2021.
Rost K, Fortney J, Fischer E, Smith J. Use, quality, and outcomes of care for mental health: the rural perspective. Med Care Res Rev. 2002;59(3):231–65.
Fitzpatrick SJ, Perkins D, Luland T, Brown D, Corvan E. The effect of context in rural mental health care: understanding integrated services in a small town. Health Place. 2017;45:70–6.
Francis K. Health and health practice in rural Australia: where are we, where to from here? Online J Rural Nurs Health Care. 2012;5(1):28–36.
Article Google Scholar
Fuller J, Edwards J, Martinez L, Edwards B, Reid K. Collaboration and local networks for rural and remote primary mental healthcare in South Australia. Health Soc Care Commun. 2004;12(1):75–84.
Russell DJ, Humphreys JS, Ward B, Chisholm M, Buykx P, McGrail M, et al. Helping policy-makers address rural health access problems. Aust J Rural Health. 2013;21(2):61–71.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Health workforce 2023 [Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/workforce/health-workforce#rural ].
Penchansky R, Thomas JW. The concept of access: definition and relationship to consumer satisfaction. Med Care. 1981;19(2):127–40.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Khan AA. An integrated approach to measuring potential spatial access to health care services. Socio-Economic Plann Sci. 1992;26(4):275–87.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bourke L, Humphreys JS, Wakerman J, Taylor J. Understanding rural and remote health: a framework for analysis in Australia. Health Place. 2012;18(3):496–503.
Saurman E. Improving access: modifying Penchansky and Thomas’s theory of access. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2016;21(1):36–9.
Kaukiainen A, Kõlves K. Too tough to ask for help? Stoicism and attitudes to mental health professionals in rural Australia. Rural Remote Health. 2020;20(2):5399.
PubMed Google Scholar
Catherine C, Myfanwy M, Rafat H. Work challenges negatively affecting the job satisfaction of early career community mental health professionals working in rural Australia: findings from a qualitative study. J Mental Health Train Educ Pract. 2018;13(3):173–86.
Cosgrave C, Maple M, Hussain R. Work challenges negatively affecting the job satisfaction of early career community mental health professionals working in rural Australia: findings from a qualitative study. The Journal of Mental Health Training, Education and Practice; 2018.
Levesque J-F, Harris MF, Russell G. Patient-centred access to health care: conceptualising access at the interface of health systems and populations. Int J Equity Health. 2013;12(1):18.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liu C, Watts B, Litaker D. Access to and utilization of healthcare: the provider’s role. Expert Rev PharmacoEcon Outcomes Res. 2006;6(6):653–60.
Aisbett D, Boyd CP, Francis KJ, Newnham K. Understanding barriers to mental health service utilization for adolescents in rural Australia. Rural Remote Health. 2007;7(1):1–10.
Google Scholar
Cheesmond NE, Davies K, Inder KJ. Exploring the role of rurality and rural identity in mental health help-seeking behavior: a systematic qualitative review. J Rural Mental Health. 2019;43(1):45–59.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Kavanagh B, Beks H, Versace V, Quirk S, Williams L. Exploring the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services in regional, rural, and remote Australia: a scoping review protocol. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(12).
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. Health workforce locator 2022 [Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/resources/apps-and-tools/health-workforce-locator ].
Versace VL, Beks H, Charles J. Towards consistent geographic reporting of australian health research. Med J Australia. 2021;215(11):525.
Beks H, Walsh S, Alston L, Jones M, Smith T, Maybery D et al. Approaches used to describe, measure, and analyze place of practice in Dentistry, Medical, nursing, and Allied Health Rural Graduate Workforce Research in Australia: a systematic scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health [Internet]. 2022; 19(3).
Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence systematic review software, Melbourne, Australia [Available from: www.covidence.org.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Barraclough F, Longman J, Barclay L. Integration in a nurse practitioner-led mental health service in rural Australia. Aust J Rural Health. 2016;24(2):144–50.
Cosgrave C, Maple M, Hussain R. Work challenges negatively affecting the job satisfaction of early career community mental health professionals working in rural Australia: findings from a qualitative study. J Mental Health Train Educ Pract. 2018;13(3):173–86.
Cosgrave C, Hussain R, Maple M. Retention challenge facing Australia’s rural community mental health services: service managers’ perspectives. Austr J Rural Health. 2015;23(5):272–6.
De Silva T, Prakash A, Yarlagadda S, Johns MD, Sandy K, Hansen V et al. General practitioners’ experiences and perceptions of mild moderate depression management and factors influencing effective service delivery in rural Australian communities: A qualitative study. International Journal of Mental Health Systems. 2017;11(1).
Dunstan DA, Todd AK, Kennedy LM, Anderson DL. Impact and outcomes of a rural personal helpers and mentors service. Aust J Rural Health. 2014;22(2):50–5.
Evans J, Horn K, Cowan D, Brunero S. Development of a clinical pathway for screening and integrated care of eating disorders in a rural substance use treatment setting. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2020;29(5):878–87.
Handley TE, Kay-Lambkin FJ, Inder KJ, Lewin TJ, Attia JR, Fuller J et al. Self-reported contacts for mental health problems by rural residents: predicted service needs, facilitators and barriers. BMC Psychiatry. 2014;14.
Hussain R, Guppy M, Robertson S, Temple E. Physical and mental health perspectives of first year undergraduate rural university students. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:848.
Johnson S, Brough M, Darracott R. Unmasking depression: challenging structural oppression whilst recognising individual agency. Qualitative Social Work: Research and Practice. 2021;20(3):738–54.
Wand T, Collett G, Cutten A, Buchanan-Hagen S, Stack A, White K. Patient and staff experience with a new model of emergency department based mental health nursing care implemented in two rural settings. Int Emerg Nurs. 2021;57:N.PAG-N.PAG.
Wand T, Collett G, Keep J, Cutten A, Stack A, White K. Mental health nurses’ experiences of working in the emergency department of two rural australian settings. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2021.
Weber M, Davis K. Food for thought: enabling and constraining factors for effective rural eating disorder service delivery. Aust J Rural Health. 2012;20(4):208–12.
Wilson RL, Cruickshank M, Lea J. Experiences of families who help young rural men with emergent mental health problems in a rural community in New South Wales, Australia. Contemp Nurse. 2012;42(2):167–77.
Batterham PJ, Kazan D, Banfield M, Brown K. Differences in mental health service use between urban and rural areas of Australia. Australian Psychol. 2020;55(4):327–35.
Clough BA, March S, Leane S, Ireland MJ. What prevents doctors from seeking help for stress and burnout? A mixed-methods investigation among metropolitan and regional-based australian doctors. J Clin Psychol. 2019;75(3):418–32.
Duggan M, Harris B, Chislett W-K, Calder R. Nowhere else to go: Why Australia’s health system results in people with mental illness getting ‘stuck’in emergency departments. 2020.
Hays C, Sparrow M, Taylor S, Lindsay D, Glass B. Pharmacists’ full scope of practice: knowledge, attitudes and practices of rural and remote australian pharmacists. J Multidisciplinary Healthc. 2020;13:1781–9.
Mirza T. First Australians deserve first-class psychiatric care: towards a better sociocultural understanding. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53:66.
Mollah TN, Antoniades J, Lafeer FI, Brijnath B. How do mental health practitioners operationalise cultural competency in everyday practice? A qualitative analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):480.
Muir-Cochrane E, O’Kane D, Barkway P, Oster C, Fuller J. Service provision for older people with mental health problems in a rural area of Australia. Aging Ment Health. 2014;18(6):759–66.
Bowman S, Nic Giolla Easpaig B, Fox R. Virtually caring: a qualitative study of internet-based mental health services for LGBT young adults in rural Australia. Rural Remote Health. 2020;20(1):5448.
Butterfly Foundation. Maydays 2020 survey report: Barriers to accessing eating disorder healthcare & support. 2020. Available from: https://butterfly.org.au/get-involved/campaigns/maydays/
Mental Health Council of Tasmania. Submission to the Senate Community Affairs Reference Committee inquiry into accessibility and quality of mental health serices in rural and remote Australia. 2018.
National Rural Health Alliance. Mental health in rural and remote Australia. National Rural Health Alliance; 2017.
Black G, Roberts RM, Li-Leng T. Depression in rural adolescents: relationships with gender and availability of mental health services. Rural Remote Health. 2012;12(3):2092.
Crotty MM, Henderson J, Fuller JD. Helping and hindering: perceptions of enablers and barriers to collaboration within a rural South australian mental health network. Aust J Rural Health. 2012;20(4):213–8.
Dawson S, Gerace A, Muir-Cochrane E, O’Kane D, Henderson J, Lawn S, et al. Accessing mental health services for older people in rural South Australia. Australian Nurs Midwifery J. 2016;23(7):50.
Henderson J, Crotty MM, Fuller J, Martinez L. Meeting unmet needs? The role of a rural mental health service for older people. Adv Mental Health. 2014;12(3):182–91.
Henderson J, Dawson S, Fuller J, O’Kane D, Gerace A, Oster C, et al. Regional responses to the challenge of delivering integrated care to older people with mental health problems in rural Australia. Aging Ment Health. 2018;22(8):1025–31.
Newman L, Bidargaddi N, Schrader G. Service providers’ experiences of using a telehealth network 12 months after digitisation of a large australian rural mental health service. Int J Med Informatics. 2016;94:8–20.
Orlowski S, Lawn S, Antezana G, Venning A, Winsall M, Bidargaddi N, et al. A rural youth consumer perspective of technology to enhance face-to-face mental health services. J Child Fam stud. 2016;25(10):3066–75.
Orlowski S, Lawn S, Matthews B, Venning A, Wyld K, Jones G, et al. The promise and the reality: a mental health workforce perspective on technology-enhanced youth mental health service delivery. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:562.
Orlowski S, Lawn S, Matthews B, Venning A, Jones G, Winsall M, et al. People, processes, and systems: an observational study of the role of technology in rural youth mental health services. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2017;26(3):259–72.
Procter N, Ferguson M, Backhouse J, Cother I, Jackson A, Murison J, et al. Face to face, person to person: skills and attributes deployed by rural mental health clinicians when engaging with consumers. Aust J Rural Health. 2015;23(6):352–8.
Beks H, Healey C, Schlicht KG. When you’re it’: a qualitative study exploring the rural nurse experience of managing acute mental health presentations. Rural & Remote Health. 2018;18(3):1–11.
Isaacs AN, Maybery D, Gruis H. Mental health services for aboriginal men: mismatches and solutions. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2012;21(5):400–8.
Isaacs AN, Maybery D, Gruis H. Help seeking by Aboriginal men who are mentally unwell: a pilot study. Early Intervent Psychiatry. 2013;7(4):407–13.
Isaacs AN, Sutton K, Hearn S, Wanganeen G, Dudgeon P. Health workers’ views of help seeking and suicide among Aboriginal people in rural Victoria. Aust J Rural Health. 2017;25(3):169–74.
Kidd T, Kenny A, Meehan-Andrews T. The experience of general nurses in rural australian emergency departments. Nurse Educ Pract. 2012;12(1):11–5.
Trail K, Oliffe JL, Patel D, Robinson J, King K, Armstrong G, et al. Promoting healthier masculinities as a suicide Prevention intervention in a Regional Australian Community: a qualitative study of stakeholder perspectives. Front Sociol. 2021;6:728170.
Byrne L, Happell B, Reid-Searl K. Acknowledging rural disadvantage in Mental Health: views of peer workers. Perspect Psychiatr Care. 2017;53(4):259–65.
Knight D, Plumb T, Gorey C. A STARR is born! A shining example of Integrated Care. Int J Integr Care. 2018;18:1–2.
Malatzky C, Bourke L, Farmer J. I think we’re getting a bit clinical here’: a qualitative study of professionals’ experiences of providing mental healthcare to young people within an australian rural service. Health & Social Care in the Community; 2020.
Onnis L-A, Kinchin I, Pryce J, Ennals P, Petrucci J, Tsey K. Evaluating the implementation of a Mental Health Referral Service connect to Wellbeing: a Quality Improvement Approach. Front Public Health. 2020;8:585933.
Taylor M, Kikkawa N, Hoehn E, Haydon H, Neuhaus M, Smith AC, et al. The importance of external clinical facilitation for a perinatal and infant telemental health service. J Telemed Telecare. 2019;25(9):566–71.
Richardson L, Reid C, Dziurawiec S. Going the extra mile’: satisfaction and alliance findings from an evaluation of videoconferencing telepsychology in rural western Australia. Australian Psychol. 2015;50(4):252–8.
Salinas-Perez JA, Gutierrez-Colosia MR, Furst MA, Suontausta P, Bertrand J, Almeda N, et al. Patterns of mental health care in remote areas: Kimberley (Australia), Nunavik (Canada), and Lapland (Finland). Can J Psychiatry / La Revue canadienne de psychiatrie. 2020;65(10):721–30.
Consumers of Mental Health WA. Accessibility and quality of mental health services in rural and remote Australia Submission 31. 2018. Available from: https://comhwa.org.au/resources-publications
Bridgman H, Ashby M, Sargent C, Marsh P, Barnett T. Implementing an outreach headspace mental health service to increase access for disadvantaged and rural youth in Southern Tasmania. Aust J Rural Health. 2019;27(5):444–7.
Reynish TD, Hoang H, Bridgman H, Nic Giolla Easpaig B. Mental health and related service use by sex workers in rural and remote Australia: ‘there’s a lot of stigma in society’. Culture, Health & Sexuality. 2021:1–16.
Hinton R, Kavanagh DJ, Barclay L, Chenhall R, Nagel T. Developing a best practice pathway to support improvements in indigenous Australians’ mental health and well-being: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2015;5(8).
Ellem K, Baidawi S, Dowse L, Smith L. Services to young people with complex support needs in rural and regional Australia: beyond a metro-centric response. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2019;99:97–106.
van Spijker BA, Salinas-Perez JA, Mendoza J, Bell T, Bagheri N, Furst MA, et al. Service availability and capacity in rural mental health in Australia: Analysing gaps using an integrated mental health atlas. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53(10):1000–12.
Jorm AF. Mental health literacy: empowering the community to take action for better mental health. Am Psychol. 2012;67(3):231.
Solmi M, Radua J, Olivola M, Croce E, Soardo L, Salazar de Pablo G, et al. Age at onset of mental disorders worldwide: large-scale meta-analysis of 192 epidemiological studies. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(1):281–95.
Australian Government Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Mental health services in Australia 2022 [Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/mental-health-services/mental-health-services-in-australia/report-contents/mental-health-workforce ].
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. National Mental Health Workforce Strategy Taskforce 2021 [Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/committees-and-groups/national-mental-health-workforce-strategy-taskforce ].
ACIL Allen. National Mental Health Workforce Strategy consultation draft. 2021. Available from: https://acilallen.com.au/uploads/media/NMHWS-ConsultationDraftStrategy-040821-1628234534.pdf
May JA, Scott A. The road less travelled: supporting physicians to practice rurally. Med J Aust. 2021;215(1):29–30.
State of Victoria. Royal Commission into Victoria’s Mental Health System. 2021.
Wood SM, Alston L, Beks H, Mc Namara K, Coffee NT, Clark RA, et al. The application of spatial measures to analyse health service accessibility in Australia: a systematic review and recommendations for future practice. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):330.
Mental Health Council of Tasmania. Submission to Legislative Council Inquiry into Rural Health Services: Access to timely and appropriate mental health care in rural and remote Tasmanian communities. 2021.
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. Providing health care remotely during the COVID-19 pandemic 2022 [Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/health-alerts/covid-19/coronavirus-covid-19-advice-for-the-health-and-disability-sector/providing-health-care-remotely-during-the-covid-19-pandemic ].
Park S. Digital inequalities in rural Australia: a double jeopardy of remoteness and social exclusion. J Rural Stud. 2017;54:399–407.
Mseke EP, Jessup B, Barnett T. A systematic review of the preferences of rural and remote youth for mental health service access: Telehealth versus face-to‐face consultation. Aust J Rural Health. 2023.
Robards F, Kang M, Steinbeck K, Hawke C, Jan S, Sanci L, et al. Health care equity and access for marginalised young people: a longitudinal qualitative study exploring health system navigation in Australia. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):41.
Stewart V, Slattery M, Roennfeldt H, Wheeler AJ. Partners in recovery: paving the way for the National Disability Insurance Scheme. Aust J Prim Health. 2018;24(3):208–15.
Consortia HaLMMPiR. Submission to the joint standing committee on the NDIS: The provision of services under the NDIS for people with psychosocial disabilities related to mental health conditions. Joint submisson by the Hume and Loddon Mallee Murray Partners in Recovery Consortia. 2017.
Hancock N, Smith-Merry J, Gillespie JA, Yen I. Is the Partners in Recovery program connecting with the intended population of people living with severe and persistent mental illness? What are their prioritised needs? Aust Health Rev. 2016;41(5):566–72.
Isaacs AN, Dalziel K, Sutton K, Maybery D. Referral patterns and implementation costs of the Partners in Recovery initiative in Gippsland: learnings for the National Disability Insurance Scheme. Australasian Psychiatry. 2018;26(6):586–9.
Productivity Commission. 5-year Productivity Inquiry: Advancing Prosperity. Canberra., ; 2023. Contract No.: Inquiry Report no. 100. Available from: https://www.pc.gov.au/inquiries/completed/productivity/report
Mehta N, Clement S, Marcus E, Stona A-C, Bezborodovs N, Evans-Lacko S, et al. Evidence for effective interventions to reduce mental health-related stigma and discrimination in the medium and long term: systematic review. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(5):377–84.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Santana MJ, Manalili K, Jolley RJ, Zelinsky S, Quan H, Lu M. How to practice person-centred care: a conceptual framework. Health Expect. 2018;21(2):429–40.
Archer J, Bower P, Gilbody S, Lovell K, Richards D, Gask L et al. Collaborative care for depression and anxiety problems. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2012(10).
Curtis E, Jones R, Tipene-Leach D, Walker C, Loring B, Paine S-J, et al. Why cultural safety rather than cultural competency is required to achieve health equity: a literature review and recommended definition. Int J Equity Health. 2019;18(1):174.
Wainer J, Chesters J. Rural mental health: neither romanticism nor despair. Aust J Rural Health. 2000;8(3):141–7.
Pretty GH, Chipuer HM, Bramston P. Sense of place amongst adolescents and adults in two rural australian towns: the discriminating features of place attachment, sense of community and place dependence in relation to place identity. J Environ Psychol. 2003;23(3):273–87.
Alston L, Bourke L, Nichols M, Allender S. Responsibility for evidence-based policy in cardiovascular disease in rural communities: implications for persistent rural health inequalities. Aust Health Rev. 2020;44(4):527–34.
Alston L, Versace VL. Place-based research in small rural hospitals: an overlooked opportunity for action to reduce health inequities in Australia? Lancet Reg Health–Western Pac. 2023;30.
Alston L, Field M, Brew F, Payne W, Aras D, Versace VL. Addressing the lack of research in rural communities through building rural health service research: establishment of a research unit in Colac, a medium rural town. Aust J Rural Health. 2022;30(4):536.
Walsh S, Lyle DM, Thompson SC, Versace V, Browne LJ, Knight S et al. The role of national policies to address rural allied health, nursing and dentistry workforce maldistribution. 2020.
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. Rural Health Multidisciplinary Training (RHMT) program 2022 [Available from: https://www.health.gov.au/our-work/rhmt ].
Sotarauta M. Place-based policy, place sensitivity and place leadership. Working paper 46/2020: Tampere University; 2020.
Australian Bureau of Statistics. ABS views on remoteness 2001 2001 [Available from: https://www.ausstats.abs.gov.au/ausstats/free.nsf/0/FCC8158C 85424727CA256C0F000035 75/$File/12440_2001.pdf.
Batterham PJ, Calear AL, Christensen H, Carragher N, Sunderland M. Independent effects of mental disorders on suicidal behavior in the community. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior. 2018;48(5):512–21.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Emergency department care 2017–18: Australian hospital statistics Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; 2018 [Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/getmedia/9ca4c770-3c3b-42fe-b071-3d758711c23a/aihw-hse-216.pdf.aspx?inline=true ].
Mental Health Services Australia A. [Available from: https://mhsa.aihw.gov.au/services/medicare/ ].
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
BEK, HB, and VLV are funded by the Rural Health Multidisciplinary Training (RHMT) program. LJW is supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Emerging Leadership Fellowship [1174060].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Deakin Rural Health, School of Medicine, Deakin University, Princes Highway, Warrnambool, VIC, 3280, Australia
Bianca E. Kavanagh, Hannah Beks & Vincent L. Versace
Institute for Mental and Physical Health and Clinical Translation, School of Medicine, Deakin University, Barwon Health, Geelong, VIC, Australia
Kayla B. Corney, Lana J. Williams & Shae E. Quirk
Institute of Clinical Medicine, Psychiatry, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
Shae E. Quirk
Institute of Clinical Medicine, Kuopio Musculoskeletal Research Unit (KMRU), University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
BEK conceptualised the research question; completed the search, data screening, extraction, and analysis; and wrote the original draft of this manuscript. KBC contributed to data screening and extraction. HB and VLV assisted with the geographical analysis. All authors edited and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bianca E. Kavanagh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
As this scoping review utilised published literature only, ethics approval and consent to participate was not required.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional Table 1: Search strategy for Medline Complete via EBSCO
Additional table 2: charting form used for data extraction, 12913_2023_10034_moesm3_esm.docx.
Additional Table 3: Barriers and/or facilitators of access and/or utilisation factors in regional, rural, and remote Australia
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kavanagh, B.E., Corney, K.B., Beks, H. et al. A scoping review of the barriers and facilitators to accessing and utilising mental health services across regional, rural, and remote Australia. BMC Health Serv Res 23 , 1060 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-023-10034-4
Download citation
Received : 15 May 2023
Accepted : 14 September 2023
Published : 04 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-023-10034-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Rural health
- Mental health services
- Rural Health Services
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Some distinctive characteristics of descriptive research are: Quantitative research: It is a quantitative research method that attempts to collect quantifiable information for statistical analysis of the population sample. It is a popular market research tool that allows us to collect and describe the demographic segment's nature.
Descriptive research design is a type of research methodology that aims to describe or document the characteristics, behaviors, attitudes, opinions, or perceptions of a group or population being studied.
Descriptive research is an appropriate choice when the research aim is to identify characteristics, frequencies, trends, and categories. It is useful when not much is known yet about the topic or problem. Before you can research why something happens, you need to understand how, when and where it happens. Descriptive research question examples
The following are some of the characteristics of descriptive research: Quantitativeness Descriptive research can be quantitative as it gathers quantifiable data to statistically analyze a population sample. These numbers can show patterns, connections, and trends over time and can be discovered using surveys, polls, and experiments. Qualitativeness
Descriptive research is a methodological approach that seeks to depict the characteristics of a phenomenon or subject under investigation. In scientific inquiry, it serves as a foundational tool for researchers aiming to observe, record, and analyze the intricate details of a particular topic.
Definition: As its name says, descriptive research describes the characteristics of the problem, phenomenon, situation, or group under study. So the goal of all descriptive studies is to explore the background, details, and existing patterns in the problem to fully understand it. In other words, preliminary research.
Revised on 10 October 2022. Descriptive research aims to accurately and systematically describe a population, situation or phenomenon. It can answer what, where, when, and how questions, but not why questions. A descriptive research design can use a wide variety of research methods to investigate one or more variables.
Descriptive research is a type of research that describes a population, situation, or phenomenon that is being studied. It focuses on answering the how, what, when, and where questions If a research problem, rather than the why.
Descriptive research is mainly done when a researcher wants to gain a better understanding of a topic. That is, analysis of the past as opposed to the future. Descriptive research is the exploration of the existing certain phenomena. The details of the facts won't be known. The existing phenomena's facts are not known to the person.
Descriptive research is a research method used to try and determine the characteristics of a population or particular phenomenon. Using descriptive research you can identify patterns in the characteristics of a group to essentially establish everything you need to understand apart from why something has happened.
Descriptive research is a type of research that is used to describe the characteristics of a population. It collects data that are used to answer a wide range of what, when, and how questions pertaining to a particular population or group.
1. Purpose. The primary purpose of descriptive research is to describe the characteristics, behaviors, and attributes of a particular population or phenomenon. 2. Participants and Sampling. Descriptive research studies a particular population or sample that is representative of the larger population being studied.
Types of descriptive research. Observational method. Case studies. Surveys. Recap. Descriptive research methods are used to define the who, what, and where of human behavior and other ...
Definition of descriptive research. Descriptive research is defined as a research method that observes and describes the characteristics of a particular group, situation, or phenomenon. The goal is not to establish cause and effect relationships but rather to provide a detailed account of the situation.
Characteristics of a descriptive study design often include the following: To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account View Video Only Video Course 462K views What...
1. Statistical Outcome. Descriptive research answers the "what" questions in statistical form. As the output is in emphasizes form, it is easy for the researcher to deduce results and implement them. Because of this characteristic of descriptive research, it is popularly used in market researches. 2.
Qualitative description (QD) is a term that is widely used to describe qualitative studies of health care and nursing-related phenomena. However, limited discussions regarding QD are found in the existing literature. In this systematic review, we identified characteristics of methods and findings reported in research articles published in 2014 ...
Descriptive Research Meaning. A descriptive method of research is one that describes the characteristics of a phenomenon, situation or population. It uses quantitative and qualitative approaches to describe problems with little relevant information. Descriptive research accurately describes a research problem without asking why a particular ...
Key Characteristics of Descriptive Research Design When Can a Researcher Conduct Descriptive Research? Types of Descriptive Research Design Advantages of Descriptive Research Design Disadvantages of Descriptive Research Design 7 Ways to Avoid Common Flaws While Designing Descriptive Research What Is Descriptive Research Design?
Descriptive research is a type of research where researchers try to "describe" the characteristics of the problem, phenomenon, or subject. The researcher studies the details and background information related to the subject. Therefore, this research type deals with the questions of what, when, and where and try to find answers to these ...
Qualitative research collects data qualitatively, and the method of analysis is also primarily qualitative. This often involves an inductive exploration of the data to identify recurring themes, patterns, or concepts and then describing and interpreting those categories. Of course, in qualitative research, the data collected qualitatively can ...
Descriptive Research Methodology is the logical process or step by step outline on how to solve a research problem that entails a variable which cannot be manipulated such as age, sex or level of education etc. Descriptive Research methodology involves choosing a logical procedure on the topic to be studied. That is the research problem, how ...
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is descriptive research? What are the characteristics of descriptive research? What are the methods of conducting descriptive research? What are the types of descriptive research? Examples of Descriptive Research Under Market Research What are the applications of descriptive research?
Methods. A systematic search of Medline Complete, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Scopus, and CINAHL was undertaken to identify peer-reviewed literature. Grey literature was collated from relevant websites. Study characteristics, including barriers and facilitators, and location were extracted. A descriptive synthesis of results was conducted. Results
Methods: Data from a national chart review study of coroner and medical examiner data on ATDs that occurred in Canada between 2016 and 2017 were used to conduct descriptive analyses with proportions, mortality rates and proportionate mortality rates. Where possible, youth in the chart review study were compared with youth in the general ...