- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
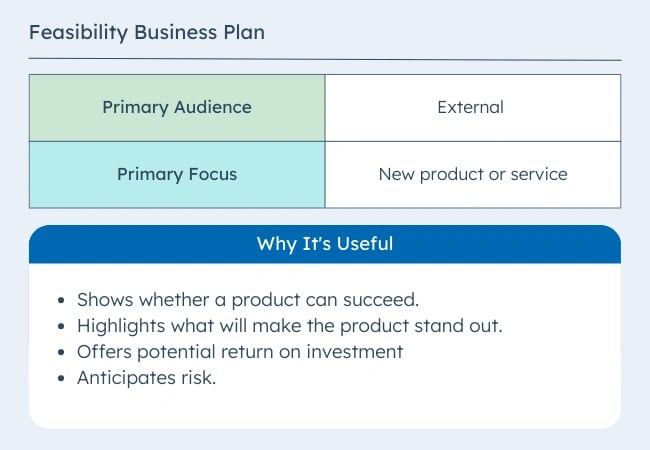
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![definition and types of business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![definition and types of business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![definition and types of business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
Business Plan: What It Is + How to Write One
Discover what a business plan includes and how writing one can foster your business’s development.
![definition and types of business plan [Featured image] Woman showing a business plan to a man at a desk](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/8jaIrEmfb9uCidnAGOr2F/c551eade2b440294787de7afd2acb369/GettyImages-1127726432__1_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning.
In your research into business plans, you may come across different formats, and you might be wondering which kind will work best for your purposes.
Let’s define two main types of business plans , the traditional business pla n and the lean start-up business plan . Both types can serve as the basis for developing a thriving business, as well as exploring a competitive market analysis, brand strategy , and content strategy in more depth. There are some significant differences to keep in mind [ 1 ]:
The traditional business plan is a long document that explores each component in depth. You can build a traditional business plan to secure funding from lenders or investors.
The lean start-up business plan focuses on the key elements of a business’s development and is shorter than the traditional format. If you don’t plan to seek funding, the lean start-up plan can serve mainly as a document for making business decisions and carrying out tasks.
Now that you have a clear business plan definition , continue reading to begin writing a detailed plan that will guide your journey as an entrepreneur.
How to write a business plan
In the sections below, you’ll build the following components of your business plan:
Executive summary
Business description
Products and services
Competitor analysis
Marketing plan and sales strategies
Brand strategy
Financial planning
Explore each section to bring fresh inspiration to the surface and reveal new possibilities for developing your business. You may choose to adapt the sections, skip over some, or go deeper into others, depending on which format you’re using. Consider your first draft a foundation for your efforts and one that you can revise, as needed, to account for changes in any area of your business.
Read more: What Is a Marketing Plan? And How to Create One
1. Executive summary
This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful. If you are seeking funding, summarize the basics of the financial plan.
2. Business description
Use this section to provide detailed information about your company and how it will operate in the marketplace.
Mission statement: What drives your desire to start a business? What purpose are you serving? What do you hope to achieve for your business, the team, your customers?
Revenue streams: From what sources will your business generate revenue? Examples include product sales, service fees, subscriptions, rental fees, license fees, and more.
Leadership: Describe the leaders in your business, their roles and responsibilities, and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design, product development, or sales.
Legal structure: If you’ve incorporated your business or registered it with your state as a legal entity such as an S-corp or LLC, include the legal structure here and the rationale behind this choice.
3. Competitor analysis
This section will include an assessment of potential competitors, their offers, and marketing and sales efforts. For each competitor, explore the following:
Value proposition: What outcome or experience does this brand promise?
Products and services: How does each one solve customer pain points and fulfill desires? What are the price points?
Marketing: Which channels do competitors use to promote? What kind of content does this brand publish on these channels? What messaging does this brand use to communicate value to customers?
Sales: What sales process or buyer’s journey does this brand lead customers through?
Read more: What Is Competitor Analysis? And How to Conduct One
4. Products and services
Use this section to describe everything your business offers to its target market . For every product and service, list the following:
The value proposition or promise to customers, in terms of how they will experience it
How the product serves customers, addresses their pain points, satisfies their desires, and improves their lives
The features or outcomes that make the product better than those of competitors
Your price points and how these compare to competitors
5. Marketing plan and sales strategies
In this section, you’ll draw from thorough market research to describe your target market and how you will reach them.
Who are your ideal customers?
How can you describe this segment according to their demographics (age, ethnicity, income, location, etc.) and psychographics (beliefs, values, aspirations, lifestyle, etc.)?
What are their daily lives like?
What problems and challenges do they experience?
What words, phrases, ideas, and concepts do consumers in your target market use to describe these problems when posting on social media or engaging with your competitors?
What messaging will present your products as the best on the market? How will you differentiate messaging from competitors?
On what marketing channels will you position your products and services?
How will you design a customer journey that delivers a positive experience at every touchpoint and leads customers to a purchase decision?
Read more: Market Analysis: What It Is and How to Conduct One
6. Brand strategy
In this section, you will describe your business’s design, personality, values, voice, and other details that go into delivering a consistent brand experience.
What are the values that define your brand?
What visual elements give your brand a distinctive look and feel?
How will your marketing messaging reflect a distinctive brand voice, including the tone, diction, and sentence-level stylistic choices?
How will your brand look and sound throughout the customer journey?
Define your brand positioning statement. What will inspire your audience to choose your brand over others? What experiences and outcomes will your audience associate with your brand?
Read more: What Is a Brand Strategy? And How to Create One
7. Financial planning
In this section, you will explore your business’s financial future. If you are writing a traditional business plan to seek funding, this section is critical for demonstrating to lenders or investors that you have a strategy for turning your business ideas into profit. For a lean start-up business plan, this section can provide a useful exercise for planning how you will invest resources and generate revenue [ 2 ].
Use any past financials and other sections of this business plan, such as your price points or sales strategies, to begin your financial planning.
How many individual products or service packages do you plan to sell over a specific time period?
List your business expenses, such as subscribing to software or other services, hiring contractors or employees, purchasing physical supplies or equipment, etc.
What is your break-even point, or the amount you have to sell to cover all expenses?
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) – (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast
Quantify how much capital you have on hand.
When writing a traditional business plan to secure funding, you may choose to append supporting documents, such as licenses, permits, patents, letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you’ve received, and media mentions and appearances.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices
Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors.
Keep these best practices in mind:
Your business plan should evolve as your business grows. Return to it periodically, such as every quarter or year, to update individual sections or explore new directions your business can take.
Make sure everyone on your team has a copy of the business plan and welcome their input as they perform their roles.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs for feedback on your business plan and look for opportunities to strengthen it, from conducting more market and competitor research to implementing new strategies for success.
Start your business with Coursera
Ready to start your business? Watch this video on the lean approach from the Entrepreneurship Specialization :
Article sources
1. US Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan , https://www.sba.gov/business-guide/plan-your-business/write-your-business-plan." Accessed April 19, 2022.
2. Inc. " How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan , https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html." Accessed April 14, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

How To Get A Business License In North Dakota (2024)
How To Write An Effective Business Proposal
Best New Hampshire Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Employer Staffing Solutions Group Review 2024: Features, Pricing & More
How To Sell Clothes Online In 2024
2024 SEO Checklist
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. Before joining the team, she was a Content Producer at Fit Small Business where she served as an editor and strategist covering small business marketing content. She is a former Google Tech Entrepreneur and she holds an MSc in International Marketing from Edinburgh Napier University. Additionally, she is a Columnist at Inc. Magazine.
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
7 types of business plans every entrepreneur should know
- Amanda Bellucco Chatham
- Aug 3, 2023

What’s the difference between a small business that achieves breakthrough growth and one that fizzles quickly after launch? Oftentimes, it’s having a solid business plan.
Business plans provide you with a roadmap that will take you from wantrepreneur to entrepreneur. It will guide nearly every decision you make, from the people you hire and the products or services you offer, to the look and feel of the business website you create.
But did you know that there are many different types of business plans? Some types are best for new businesses looking to attract funding. Others help to define the way your company will operate day-to-day. You can even create a plan that prepares your business for the unexpected.
Read on to learn the seven most common types of business plans and determine which one fits your immediate needs.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your company’s goals and explains how you will achieve them. Putting this information down on paper brings valuable benefits. It gives you insight into your competitors, helps you develop a unique value proposition and lets you set metrics that will guide you to profitability. It’s also a necessity to obtain funding through banks or investors.
Keep in mind that a business plan isn’t a one-and-done exercise. It’s a living document that you should update regularly as your company evolves. But which type of plan is right for your business?
7 common types of business plans
Startup business plan
Feasibility business plan
One-page business plan
What-if business plan
Growth business plan
Operations business plan
Strategic business plan

01. Startup business plan
The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company’s success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan.
Startup plans serve two purposes: internally, they provide a step-by-step guide that you and your team can use to start a business and generate results on day one. Externally, they prove the validity of your business concept to banks and investors, whose capital you’ll likely need to make your entrepreneurial dreams a reality.
Elements of a startup business plan should include the following steps:
Executive summary : Write a brief synopsis of your company’s concept, potential audience, product or services, and the amount of funding required.
Company overview: Go into detail about your company’s location and its business goals. Be sure to include your company’s mission statement , which explains the “why” behind your business idea.
Products or services: Explain exactly what your business will offer to its customers. Include detailed descriptions and pricing.
Situation analysis: Use market research to explain the competitive landscape, key demographics and the current status of your industry.
Marketing plan: Discuss the strategies you’ll use to build awareness for your business and attract new customers or clients.
Management bios: Introduce the people who will lead your company. Include bios that detail their industry-specific background.
Financial projections: Be transparent about startup costs, cash flow projections and profit expectations.
Don’t be afraid to go into too much detail—a startup business plan can often run multiple pages long. Investors will expect and appreciate your thoroughness. However, if you have a hot new product idea and need to move fast, you can consider a lean business plan. It’s a popular type of business plan in the tech industry that focuses on creating a minimum viable product first, then scaling the business from there.
02. Feasibility business plan
Let’s say you started a boat rental company five years ago. You’ve steadily grown your business. Now, you want to explore expanding your inventory by renting out jet skis, kayaks and other water sports equipment. Will it be profitable? A feasibility business plan will let you know.
Often called a decision-making plan, a feasibility business plan will help you understand the viability of offering a new product or launching into a new market. These business plans are typically internal and focus on answering two questions: Does the market exist, and will you make a profit from it? You might use a feasibility plan externally, too, if you need funding to support your new product or service.
Because you don’t need to include high-level, strategic information about your company, your feasibility business plan will be much shorter and more focused than a startup business plan. Feasibility plans typically include:
A description of the new product or service you wish to launch
A market analysis using third-party data
The target market , or your ideal customer profile
Any additional technology or personnel needs required
Required capital or funding sources
Predicted return on investment
Standards to objectively measure feasibility
A conclusion that includes recommendations on whether or not to move forward
03. One-page business plan
Imagine you’re a software developer looking to launch a tech startup around an app that you created from scratch. You’ve already written a detailed business plan, but you’re not sure if your strategy is 100% right. How can you get feedback from potential partners, customers or friends without making them slog through all 32 pages of the complete plan?
That’s where a one-page business plan comes in handy. It compresses your full business plan into a brief summary. Think of it as a cross between a business plan and an elevator pitch—an ideal format if you’re still fine-tuning your business plan. It’s also a great way to test whether investors will embrace your company, its mission or its goals.
Ideally, a one-page business plan should give someone a snapshot of your company in just a few minutes. But while brevity is important, your plan should still hit all the high points from your startup business plan. To accomplish this, structure a one-page plan similar to an outline. Consider including:
A short situation analysis that shows the need for your product or service
Your unique value proposition
Your mission statement and vision statement
Your target market
Your management team
The funding you’ll need
Financial projections
Expected results
Because a one-page plan is primarily used to gather feedback, make sure the format you choose is easy to update. That way, you can keep it fresh for new audiences.

04. What-if business plan
Pretend that you’re an accountant who started their own financial consulting business. You’re rapidly signing clients and growing your business when, 18 months into your new venture, you’re given the opportunity to buy another established firm in a nearby town. Is it a risk worth taking?
The what-if business plan will help you find an answer. It’s perfect for entrepreneurs who are looking to take big risks, such as acquiring or merging with another company, testing a new pricing model or adding an influx of new staff.
A what-if plan is additionally a great way to test out a worst-case scenario. For example, if you’re in the restaurant business, you can create a plan that explores the potential business repercussions of a public health emergency (like the COVID-19 pandemic), and then develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
You can share your what-if plan internally to prepare your leadership team and staff. You can also share it externally with bankers and partners so that they know your business is built to withstand any hard times. Include in your plan:
A detailed description of the business risk or other scenario
The impact it will have on your business
Specific actions you’ll take in a worst-case scenario
Risk management strategies you’ll employ
05. Growth business plan
Let’s say you’re operating a hair salon (see how to create a hair salon business plan ). You see an opportunity to expand your business and make it a full-fledged beauty bar by adding skin care, massage and other sought-after services. By creating a growth business plan, you’ll have a blueprint that will take you from your current state to your future state.
Sometimes called an expansion plan, a growth business plan is something like a crystal ball. It will help you see one to two years into the future. Creating a growth plan lets you see how far—and how fast—you can scale your business. It lets you know what you’ll need to get there, whether it’s funding, materials, people or property.
The audience for your growth plan will depend on your expected sources of capital. If you’re funding your expansion from within, then the audience is internal. If you need to attract the attention of outside investors, then the audience is external.
Much like a startup plan, your growth business plan should be rather comprehensive, especially if the people reviewing it aren’t familiar with your company. Include items specific to your potential new venture, including:
A brief assessment of your business’s current state
Information about your management team
A thorough analysis of the growth opportunity you’re seeking
The target audience for your new venture
The current competitive landscape
Resources you’ll need to achieve growth
Detailed financial forecasts
A funding request
Specific action steps your company will take
A timeline for completing those action steps
Another helpful thing to include in a growth business plan is a SWOT analysis . SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis will help you evaluate your performance, and that of your competitors. Including this type of in-depth review will show your investors that you’re making an objective, data-driven decision to expand your business, helping to build confidence and trust.
06. Operations business plan
You’ve always had a knack for accessories and have chosen to start your own online jewelry store. Even better, you already have your eCommerce business plan written. Now, it’s time to create a plan for how your company will implement its business model on a day-to-day basis.
An operations business plan will help you do just that. This internal-focused document will explain how your leadership team and your employees will propel your company forward. It should include specific responsibilities for each department, such as human resources, finance and marketing.
When you sit down to write an operations plan, you should use your company’s overall goals as your guide. Then, consider how each area of your business will contribute to those goals. Be sure to include:
A high-level overview of your business and its goals
A clear layout of key employees, departments and reporting lines
Processes you’ll use (i.e., how you’ll source products and fulfill orders)
Facilities and equipment you’ll need to conduct business effectively
Departmental budgets required
Risk management strategies that will ensure business continuity
Compliance and legal considerations
Clear metrics for each department to achieve
Timelines to help you reach those metrics
A measurement process to keep your teams on track
07. Strategic business plan
Say you open a coffee shop, but you know that one store is just the start. Eventually, you want to open multiple locations throughout your region. A strategic business plan will serve as your guide, helping define your company’s direction and decision-making over the next three to five years.
You should use a strategic business plan to align all of your internal stakeholders and employees around your company’s mission, vision and future goals. Your strategic plan should be high-level enough to create a clear vision of future success, yet also detailed enough to ensure you reach your eventual destination.
Be sure to include:
An executive summary
A company overview
Your mission and vision statements
Market research
A SWOT analysis
Specific, measurable goals you wish to achieve
Strategies to meet those goals
Financial projections based on those goals
Timelines for goal attainment
Related Posts
What is a target market and how to define yours
21 powerful mission statement examples that stand out
Free business plan template for small businesses
Was this article helpful?
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

8 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
We get this question a lot, mainly because there are so many different things labelled as business plans: strategic plans, annual plans, operational plans, feasibility plans, and, of course, what most people think of, business plans for startups seeking investment. And also, what real business owners want—lean business plans for better management.
In this article, we’re going to help you figure out which plan is the one for you.
- Start with this: Form follows function
Put all business plans into this basic principle: form follows function . What do you want your business plan to do for you? That business objective should determine what kind of a plan you need.
All businesses start with a lean plan
These are things that every business owner needs to do in order to run the business effectively. They apply to all businesses, large or small, startup or not:
- Develop and execute strategy
- Set priorities
- Allocate efforts and resources according to priorities
- Establish tasks, responsibilities, and performance expectations
- Track results and compare them to expectations
- Manage cash flow
- Budget sales and spending
So, every business is better off with a lean plan.
It’s a short, effective collection of bullet points, lists, and forecasts, covering all of the functions above:
- It starts with bullet points for strategy. This isn’t text for outsiders. It’s not explanations; it’s reminders, for the entrepreneur and her team, of the major strategy points. Strategy is focus, so it’s a reminder of the target market, the product (or service), and the business identity. Sometimes it also includes a definition of success. It’s important, but just the bullet point reminders.
- Then come tactics. Strategy is useless without tactics. These are also bullet points. They are the important decisions made regarding key points of a marketing plan, product plan, financial plan, recruitment plan … not explanations or details for outsiders, but just the main points for you and your team. Think about pricing, channels, social media, launch dates, products, services, features, and so forth.
- Third part is concrete specifics. That includes a list of assumptions, important milestones, tasks, deadlines, responsibilities, and measurable performance expectations.
- The fourth and final part is budgets. That’s sales forecast, spending budget, and cash flow.
Make this the lean plan and add a regular process of review and revision to keep it fresh. You can download a free template for a lean business plan here . Can you imagine any business that isn’t better off for having at least this kind of planning in place, even if they don’t need an elaborate business plan? I can’t.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Lean plan for startups:
All startups can benefit from the lean plan above plus one extra ingredient: starting costs, and starting plans.
Starting costs
Starting costs are a matter of two lists: one for starting expenses, the other for starting assets.
The first list includes expenses like legal costs, logo, initial website, fixing up a location, and similar expenses that a startup business incurs once; and in some cases the expense of running expenses, such as rent and payroll, that have to start before launch for practical reasons.
The second includes assets required at start. These are items like starting inventory, equipment, and starting cash.
Startup plan
Keep it simple like the tactics in the normal lean plan, but add some bullets and concrete specifics for tasks and timing to get a startup going. These are items like choosing the location, setting up initial branding and website, accounts for social media, and launch events.
- A plan for the SBA, banks, investors, buyers, and partners
If you need to present a business plan to your bank or prospective investors, start with your latest revised lean business plan as the first draft. The lean plan is just for management. Dress that up to include the additional content that outsiders will want and need.
Add summaries and explanations
Add a very strong executive summary because some of your outsider target readers will read only that. Keep it short and make it fit the need. Often there’s a selling-the-idea or selling-the-potential purpose to a written plan, and in that case you make the summary include the highlights you want those readers to see to pique their interest.
Your lean plan doesn’t include details about your strategy, your company, your market, or your product. It has just summary tactics for marketing plan, product plan, financial plan, and management plan. Think of your readers—outsiders looking in—and help them understand the business. Achieve the specific goal of this dressed-up business plan.
Add formal financial projections
While the lean plan might be fine with just sales forecast, expense budget, and cash management, a business plan for a business plan event normally has to include formal financial projections that respect finance and accounting standards and include Profit and Loss, Cash Flow, and Balance Sheet. Banks will want to see projections of key ratios as well, and investors will like a Use of Funds table and sometimes a Break-even Analysis.
Stay mindful of the business purpose
We call it the business plan event—that’s the specific business need for a dressed-up plan. Form follows function here too.
A plan for investors will emphasize different elements than a plan for a bank loan. The investors want to see product-market fit; potential growth; something proprietary and protectable like technology, patents, trade secrets, or so-called secret sauce; and potential investor exit in a few years. The bank wants to see stability, credit history, collateral, and guarantees. A business broker or business buyer wants to see what can be most useful under new ownership.
Plan, pitch, and summary memo go together
Some business plan events require some special variations of your plan output. These days investors expect to see a short summary memo first. That’s a two to five page summary of your plan, a lot like your executive summary, but it stands alone. Then, if they like what they see from the summary, investors will want a pitch presentation. That’s a 20-40 minute slide presentation that backs up a verbal presentation, you with investors.
Neither summary memo nor pitch deck stand alone. They have to be summaries of your underlying plan. A pitch presentation is only really successful if it summarizes a real plan with a lot of concrete details on financials, milestones, traction, and next steps. Don’t get caught without a plan you can dig into when investors start asking more questions.
- Business plans have lots of different names
Shakespeare wrote, “a rose by any other name would smell as sweet.” I say a plan by any other name is still a plan. Here are some common varieties and business plan vocabulary.
Most lean plans are also internal plans
An operations plan—also called an annual plan—is a type of internal plan. An operations plan includes specific implementation milestones, project deadlines, and responsibilities of team members and managers. This is the plan used for staying on track to meet your goals as a business. Planning for your goals as a business allows your company to assign priorities, focus on results, and track your progress. Your operations plan covers the inner workings of your business. It outlines the specifics of who should be doing what, and when they should be doing it.
Of course, cash flow figures prominently here as well. For example, your milestones will need to have sufficient funding for their implementation, and you’ll need to track your progress so you know how much you’re spending.
A growth or expansion plan focuses on a specific area of a business, or a subset of the business. For example, a plan for the creation of a new product is a growth plan. These plans could be internal plans or not, depending on whether they are being linked to loan applications or new investment. An expansion plan requiring new outside investment would include full company descriptions and background on the management team, just the same as a standard plan for investors would. Loan applications would require this much detail as well.
However, an internal plan used to set up the steps for growth or expansion that is funded internally could skip these descriptions. It might not be necessary to include detailed financial projections for the company overall, but it should at least include detailed forecasts of sales and expenses for the new venture or product.
What’s a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is another kind of internal plan. A strategic plan incorporates the financial information and milestones of an operations plan, but focuses more on setting company-wide priorities. As you build the strategy for your company and decide how to implement it, you will want to examine your strengths and weaknesses as a business. What does your company do well? As your company grows, you want to play to your strengths. Strategy is often a matter of selecting the right opportunities. Resources should be funneled strategically to the areas where they will provide the biggest overall benefits.
Once you have an idea of your strategy, you must have a plan for implementing it. This is where the milestones portion of the plan becomes key. To effectively execute your strategies, it’s critical to assign responsibilities and have a schedule for following through. The implementation tactics you use will actively move you in the right direction toward achieving your goals.
Resources for moving forward
Reading about the different types of business plans is a good jumping-off point in the process of creating a business plan. If you’re looking for more information about business plans and how to write them, you’ll find our business planning tutorials and sample business plan library to be helpful resources.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

14 Min. Read
How to Write a Five-Year Business Plan

11 Min. Read
Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan

6 Min. Read
Differences Between Single-Use and Standing Plans Explained
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- HR & Payroll

Business Plan: A Beginner’s Guide with Types and Templates

Setting up your own company, business, or startup could be an overwhelming process. It involves a variety of operations that need to be carried out in areas such as legal, financial, sales, among others. All these operations are a part of the Business Plan. The question here is what is a business plan and how do you go about writing it?

This article takes you on a detailed journey of writing a business plan apart from the following points:
- Understanding a business plan
- Elements of a business plan
- Types of business plans
- We also see why making a business plan is important
- How to write a step-by-step business plan?
- We also look into why some business plans fail.
- Business plans FAQ
What Is a Business Plan?
The startup of a company requires knowing and addressing many problems — legal issues, finance, sales and commercialization, protection of intellectual property, protection of liability, and more.
A business plan is defined as a written document that comprises business details, the company’s goals, and methods to achieve these goals. A business plan contains a comprehensive framework for the company in terms of marketing, finance, and operations.
Business plans serve a significant purpose. They are documents that can assist in inviting potential investment before a substantiated record of success has been ascertained. It helps create a good platform for businesses to continue to pursue targets.
Drafting a business plan is specifically useful for a startup or new enterprise. Optimally, the plan will be periodically restructured to see if objectives have been achieved or changed throughout the years. The companies may also decide after some time to redraw and upgrade the business plan to give a new direction after establishment.
Understanding Business Plans
Fundamentally, a business plan is a key document that must be put in place before start-up activities. Therefore, before new companies can provide their capital, banks and risk-capital companies often make a viable business plan a necessary precondition.
It is highly advisable to define a business plan before commencing any operations of the business. There have been examples of companies not lasting long without a competent business plan. It helps the businesses take decisions on matters of investments, learn about potential risks and adapt to new trends.
A strong business plan defines a company's identity, what it does, how it does it, and where it's headed. It is easier to grasp a company plan if you keep this history in mind. The core team or the people in a company's internal dynamics shapes its policies and objectives, or participates in the capital budgeting process must be able to comprehend a business plan.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to understanding the complicated and detailed document.
Executive Summary
Being the first section in a business plan, it comprises the summary of the entire strategy of the company. This 2 to 3-page summary presents the vision statement and brings into perspective the rest of the strategy.
Table of Contents
This comes after the executive summary. This should be looked into carefully to know if there are any particular aspects you would want to know the details about.
The next few sections can tell you a lot about who the adversaries are and what sort of products and services does the company offer. Any kind of issues that the company faces or even its capabilities are mentioned in this section.
Look for Management Capabilities
Within these sections, there would be information about the people playing key roles in the company. You can know about their qualifications and expertise from the document. These spaces will also consist of the description of the location of the company. It would be good to know about it to assess if it is strategically situated.
Operations Section
This section comprehensively describes the manufacturing, marketing, selling of products carried out by the business. Its customer support and other services can be assessed from this section.
Finances and Forecast Section
This could be helpful in understanding the revenue, expenditure, and other critical financial aspects of the organization. A complete chart of costs, risk analyses, and earnings estimates can be accessed through this section. This space also provides details about how these important digits were arrived at.
Final Section
This helps you understand the company’s targets and projections and the measures they wish to take for accomplishing the same. This will also share a glimpse of the ways in which the resources or funds from the investors will be used.
Elements of a Business Plan
Typically, a 20-25 page document, business plan varies hugely based on the type and size of the business. The details or the depth of the plan could be diverse and entail different kinds of elements. However, there are some crucial elements that come under the main plan and are also a part of the appendices.
Although, business plans are different, here are some common critical elements that are included in all the plans. Let’s look at them one by one:
This is the point that elaborately explains the mission of the company. Besides, it also includes information about the company’s management leaders, employees, functions.
Products and Services
This point includes all the products or services that the company is offering. Apart from the names of these products, services, it also comprises the details pertaining to the product such as the pricing, longevity, and benefits that the customers can avail of from its services.
Other information that could be a part of this point, includes production and manufacturing processes. It may also showcase any patents or proprietary technology that the company has acquired. A research and development report is also a part of this element.
Market Analysis
A company must have a thorough understanding of its sector as well as its intended audience. A market analysis will show you the expected demand for the products that the company sells. It will also help you know what difficulties you could face from the competitors. This will also assist you with an insight into the expertise of the contemporaries along with their strengths and drawbacks.
Marketing Strategy
This section explains how the organization plans to recruit and retain customers, as well as how it plans to reach out to them. This necessitates the creation of a distinct distribution channel. It will also detail branding, brand awareness and email marketing campaign plans , as well as the forms of media via which such efforts will be carried out.
Financial Planning
The organization should incorporate its financial planning and future estimates in order to persuade the other parties to review its business plan. The established companies may include income statements , balance sheets, and so on; On the other hand, new enterprises will include objectives and projections for the initial years of operation, as well as venture capitalists.
Every good business should have a budget in place. This comprises expenses such as employment, innovation, production, advertising, and any other business-related expenditure.
Types of Business Plans
The company management and investors can use business plans to help them start and grow their company. A company prepares a business plan to describe the objectives that will forecast and organize for expansion and to understand each area of the firm. A business plan is written by competent entrepreneurs to direct management and attract investment funds.
Business plans are drawn based on the requirements of the company. With this in mind, there are the following types of business plans:
Business Plans for Startups
A start-up business plan should outline the actions necessary to launch a new firm. It also includes a financial study with spreadsheets that describe financial concepts such as income, profit, and cash flow estimates. This may also be used by potential investors to gain an insight into the financial status of the startup. The startup business plans give clarity on market analysis, the product or service that the startup will provide besides the set goals.
Internal Business Plans
Internal plans detail project marketing, staffing, and technology costs. This document will summarise the company's present situation, including administrative performance and profitability, before determining whether and how the company would repay any project-related cash. These are written for a limited audience within the company, such as the marketing team evaluating a proposed initiative. They usually comprise a market study that shows the intended audience, competitive landscape, and the market's beneficial impact on corporate profits.
Business Plans for Strategic Business Development
A strategic business plan lays out a structural plan by providing a high-level picture of the company's objectives and how it moves to achieve them. While the framework of a strategic business plan varies per firm, typically contain five elements:
- The vision statement
- The mission statement
- Defining the key performance factors
- tactics for accomplishing objectives
- Timeframe for implementation
A strategic business plan engages personnel at all levels of the organization in the big picture, motivating them to collaborate to achieve the company's objectives
Business Plans for Scalability
A feasibility or scalability business plan considers two key issues regarding a planned business endeavor:
- If there will be buyers for the products or services that the company intends to sell.
- Whether or not the enterprise will be profitable.
This plan highlights the details of the demand of the product or service and the associated target audience for the said product. A feasibility study typically concludes by providing recommendations for the future.
Business Plans for Operations
These include features regarding the operations of the company and hence, the name. The plan specifies the deployment benchmarks and timelines for the future year. It also entails employee responsibilities.
Business Plans for Growth
These are also known as the plans for expansion and are created for both, internal as well as external use. This plan features the details around the following points:
- Detailed and specific highlights about the company
- Details of officials as the company
It is important to chalk out this plan and give the relevant corporate details to convince the potential investors.
The Importance of Making a Business Plan
Entrepreneurs frequently utilize business plans. It is doable to travel without a business strategy, but doing so will simply raise the chances of wandering aimlessly along the trip. This helps them to steer clear of any potential problems and putting themselves in a situation where they may have to keep asking for directions.
Therefore, business plans are necessary to help business owners in observing the broader picture, planning for the future, making critical decisions, and increasing their overall chances of success.
Defining organizational goals
A small business, a startup, an established business; all need a business plan. When it comes to small businesses, the business plans can be helpful in structuring the goals of the organization. It can allow you to monitor and govern everything you've strived to produce if you use it correctly and use it on a frequent basis. Finally, it can serve as a reliable tool for management to stay on track with administrative milestones.
To assist you in making important decision
The fundamental objective of a good business plan is to assist business owners in making better decisions. Companies don't always have the opportunity to take time and analyzing all of the implications of a decision. A company plan can help with this. Management frequently deals with a never-ending exercise in making decisions and dealing with crises. Developing a business plan involves estimating the outcome with some of the most important company actions.
Minimize Risks
Handling the operations of a business can involve risky steps, but it tends to become much more sustainable with a well-thought business strategy. Developing accounting period predictions, logistics planning, and a thorough knowledge of the future outlook can assist with mitigating the risk of a job that is intrinsically insecure.
A business plan makes it easier to find better solutions, leads to better decisions, and see a clearer picture of the organizational future.
Obtain Funding
While there are multiple activities for which a business plan is required, a major reason why you may need it is to secure funding from venture capitalists. The most effective means of demonstrating your competence is through a business plan, which is usually a prerequisite for anyone seeking outside funding. And anyway, anyone considering investing in your company will want to know it's in fantastic form and will be profitable in the long run.
To serve as a resource for service providers
Contractors, freelancers, and other experts are commonly a part of an organization. They are important people as they help with some of the crucial duties such as bookkeeping, legal aid, consulting, and so on. Having a business plan in place will help them get a fair idea of the key portions of areas where they are required.
To prevent unnecessary blunders
A business plan can help understand the reasons and avoid potential mistakes and blunders. Some of the most commonly observed mistakes could be:
- Capital troubles: Cash flow troubles or just running out of money are both examples of a lack of capital.
- No Appreciation: Nobody buys what you're selling since there isn't a market for it.
- Insufficient team: This emphasizes the significance of employing the correct personnel to assist you in running your company.
- Excessive competition: It's difficult to make a consistent profit when there's huge competition.
5 Quick and Easy Ways to Create an Excellent Business Plan
Let's speak about certain guidelines that will make the entire company planning process more efficient before you start writing your business plan. We have put together the following points to direct you towards writing a goal-oriented business plan.
Keep it concise
A long business plan which has over 50 pages will not only consume a lot of time in drafting but may not essentially be efficient in the long run. The foundation of writing a business plan is to quickly write it and move on with the tasks defined in it.
Moreover, it is a tool to help the company grow; it will require to be fine-tuned continuously, and therefore, it is best to keep it short and precise.
Audience-centric
Make your business plan by keeping in mind the audience who would be referring to it for accomplishing their goals. An example is if the business plan is aimed at readers that consist of investors as the primary audience, it would be wise to draft it in a language that would be comprehended by them.
Test viability of your business
The more tests you conduct for the elements mentioned in your plan, the better the business plan. Elements of a business plan, as we know now, could include anything from mission and vision statement to products and services. It is recommended you get approval or feedback on the elements included in your business plan.
Determine your aims and objectives
You should have a clear idea of what you want to obtain out of your company from the start. Determine if you are looking for a complete overhaul of your business? Or if you are aiming to expand your employee base? Knowing what you want to achieve can help you design a company plan that is tailored to these objectives.
Don’t Get Discouraged
You might be a new entrepreneur who has just started to look for setting up a business plan. No matter, how daunting this may seem in the beginning, it is good you do not get intimidated by the process.
Although initially writing a business plan may seem difficult, all you need is to be confident and expert in your field. If you're an expert in your field and know everything there is to know about it, then this is all that takes to establish a business strategy.
With this information, we move on to the main section of this article which explains a step-by-step process to write a business plan.
Download Business Plan Template
How to write a business plan, step by step.
While writing a business plan, there could be two scenarios that could be considered:
- Traditional Business Plan
- Lean Startup Plan
Let’s look at each of these in detail:
Traditional Business Plan Format
If you're particularly looking for specifics, want a complete plan, or plan to seek funding from conventional sources, you could choose a typical business plan structure. Instead of following the conventional model, focus on the portions that are most relevant to your business and needs. You could use a combination of the sections in the conventional plan to describe how your company can benefit the reader.
Executive Summary: Points that can go here are:
- Mission statement
- Talk about your products and services
- Information regarding the key personnel, employees
- Location of the company
- Also, some high-level plans for growth, in case you wish to seek funds.
Company Details: This includes all the minute details of your company. Talk about what kind of solutions your company provides. Points to be included here are:
- Problems that you can solve
- Enlist your consumers or businesses you wish to serve
- Mention the distinguishing feature or the USP of your company
- Mention the expertise held by the key people involved
- Include a complete overview of the strengths of your company
Market Analysis: You must closely understand your business perspective and the target market. Through thorough competitive analysis, you could assess the market trends and seek answers to the following questions:
- What are the current trends in the market?
- What are the success mantras of other companies?
- Will you be able to achieve what they are doing?
- Do you need more expertise to do it better?
Company and Management: This section is about informing your audience about how and who is in charge of the business. This would be an apt space to describe the points mentioned:
- Company’s legal structure.
- Declare of your company is a general or limited partnership.
- Determine if you want your business to be a C or S corporation
- Also, state if you are the only proprietor or a Limited Liability company.
Products and Services: This section explain the products and services that you wish to sell. Include these under this section:
- Let your audience know of your planning to get a patent, intellectual property, or copyright fr your products.
- Explain the R&D process undertaken with regards to a particular product or service.
- Also, describe the product lifecycle and the benefits of your product.
Marketing and Sales: With the varying requirements per company, the marketing strategies can be unique to all. Based on your domain and industry, you must explain the following points in this section:
- Describe the appeal and retention of customers
- How a sale really is going to take place
- Make revenue projections and forecasts
Funding Application/Request: This area will explain your funding requirements in case you apply for funding. You should also make these points clear:
- How often and how much funding you shall require
- Explain how you plan to use it over the years (providing the number of years would be appropriate)
- Mention the terms and conditions agreeable by you
- If you would want to take a debt or an equity
- Explain your expenses like your bills, employee salaries, purchase of new equipment, etc.
- Always mention your debt repayment strategies.
Financial/Revenue Projections: This goes hand-in-hand with your funding request. It brings forth your company’s stability, sustainability, and growth prospects. Here’s what should go in this section:
- All the revenue reports, balance, and income statements for the past 5 years in case yours is an established company.
- Enlist any guarantees you can levy against a loan
- Explain your financial growth plan for the next 5 years.
- Income forecasts, expenditures, and budgets
- Present a graphical analysis through charts to depict your monthly/quarterly growth plan.
Appendix: This section could be used to attach other essential documents such as:
- Legal documents
- Product pictures, if demanded.
- Credit history
- Licenses, etc.
Let’s look at the startup business plan and its design.
Startup Business Plan
Although all the business plans comprise of the nice segments, the startup business plan can touch upon each one of those without going much into the details. Moreover, as compared to the traditional plan, this one provides you a lot more agility in terms of making amendments. This would be beneficial as a startup frequently undergoes a lot of changes in its initial years.
Let’s look at the components you’ll be adding to your startup business plan:
Customer Segment: This section explains who your target customers or audience will be. While there could be numerous segments enlisted in this section, it would be wise to identify the ones that your business will most appeal to. Identifying them and naming them here is crucial.
Value Proposition: This is intended for the different audiences your business wishes to serve, The value your business holds or offers to them can be different. In this section, you describe how and what value proposition you will be making for each of those businesses/customers. It is important to figure this out and write it down here as that indicates the value-add your company holds.
Channels: This displays the communication channels you will be using to covey your propositions to your customers.
Customer Relationships: This will highlight your ways of maintaining communication with your customers. You can list down the ways through which you shall be communicating: whether they will be informed through automated emails or will you be connecting with them personally, all goes in here.
Revenue Streams: This point elaborates on where your revenue or income is coming from. An already established business may have multiple sources of income but if yours is a startup, then it may have only one. Nevertheless, you must identify and mention it here.
Key Resources: The resources in your company need to be mentioned here; this includes but is not limited to your employees, key personnel, infrastructure, among others.
Activities: Details of all the crucial activities that strengthen your business or lead it to a meritorious milestone need to go in here.
Important Partnerships: Most of the new businesses invite partnerships and have shared resources. There are certainly some other entities or businesses involved and they must find a mention in this section. These include all your vendors, suppliers, manufacturers, or other people you are working with.
Cost Structure: Once you have identified and defined your business’s requirements and infrastructure, it is time to get the details of the costs of your business. You can also give away the plans or strategies you have to optimize those associated costs.
Why do Business Plans Fail?
While there are numerous business plans drafted each year, only a few of these companies make it to the success ladder. While such business plans can include good suggestions, they fall short. The company’s projects also tend to meet the same fate; despite the brilliant ideas, the project collapses. The reasons for this failure could be many. Wouldn’t it be great if we could foresee them and avoid them before they cause failure?
Here are some reasons that could lead to a failed business plan:
Unreal objectives and ambitions
It may not always be a great idea to reach out for the highest goals in the realm of the business plan. Although high goals are important, the path to reach these goals must be realistic and achievable. You might aspire to make a grand sale of say, thousands of your products in a month but that may not always be attainable. It s, therefore, important to work out a business plan to make it realistic to avoid failures in the future.
Lack of Motivation
Businesses are driven on tonnes of motivation, which in turn is effective on the productivity of the company. The entrepreneurs with a solid determination and motivated team have been great examples of turning their ventures into grand success stories in a relatively short time. Not only does the leader need to be motivated, but the motivation also needs to flow on to his team and all employees to make a difference to the overall output. A company where the leaders lack motivation could be walking slowly towards failure.
Lack of Proper Budgeting
Budgeting is a vital aspect of a business, and a lack of real-world budgeting is a factor to avoid. It is not advisable to always go for a loan to launch the company every time. Unless you can get your theory to move in the right direction, your financial support may evaporate. Therefore, the cost of building a company must be determined and maintained through the first year. All the cost factors should be worked out much in advance to keep away disappointments in the later stages of development.
Inadequate Market Research
Market research is all about acquiring enough information and understanding the current trends in the market. Your plan should be aligned with the kind of market research you have done. Being a vital part of a new company’s business plan, market research needs to provide you a competent data to battle out the odds that you may face. Sufficient information in this regard will help you establish a plan that’s effective. Not doing so may lead you to scrap it and restart the work with greater amounts of time and effort.
Business Plans FAQ
Now that you have a fair idea of how to go about writing a business plan, let’s look around at some of the frequently asked questions:
Do I have to include all the sections?
A clear answer is No. You need not include all the sections, but work out only those that are relevant to your company and business. With the nine sections, you are trying to give away maximum relevant information in the plan; however, not all of the sections would need to be addressed.
How long should the plan be?
Your plan only needs to have all the information composed well into one document. There is no specific length or the number of pages that it should have. When you are sure that it mentions all the required information, you are good to go.
Would be a good idea to start a business in an economically challenged scenario?
Although economic ups and downs could be dissuading, especially while starting a new business. Our take is that any business that can compete well with the existing prices and offers great value to customers can make it big.
How can Deskera Help You with Your Business Plan?
Deskera offers you to learn the concepts of business and get acquainted with the top software applications for startups and can also help with accounting for startups . You may refer to Deskera’s blogs to get a better grip over business topics such as How to understand a balance sheet , Main financial statements , Why are income statements important .
Besides, you may also learn a lot from the Best Marketing Blogs 2020 and the user-friendly CRM , Business Expense , Accounting Cycles .
Take your business to the next level with Deskera All-in-One . It is a platform that offers Invoicing, Accounting, Inventory, CRM, HR & Payroll all under one roof. With Deskera Books , you can avail of online invoicing, accounting & inventory software to boost your business. It covers all the significant aspects of business such as billing, payments, warehouse management, Credit &Debit Notes, financial reports, an elaborate business dashboard apart from many other features.
Key Takeaways
Let’s look at the key points from the document:
- A business plan is a written document that describes the functional areas, goals, and the way in which a company aims to address its objectives.
- In order to attract external investors startups utilize business plans.
- Companies can develop a longer traditional business plan or a shorter startup or small business plan.
- Executive summaries, distribution channels, promotional strategies, and analytical information, wealth management, and budget should include good business plans.
- Business plans could be drafted for Startups, internal business, strategic business development, scalability, and operations.
- There are 2 major types of business plans: Traditional business plans and startup business plans.
- Unreal objectives, lack of motivation, and market research could be the reasons for the failure of a business plan
Related Links
10 Tips for CFOs to Navigate Growth Complexities

Total Quality Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Quality Control Techniques

How can Firms Manage Quality Control while Scaling?
Hey! Try Deskera Now!
Everything to Run Your Business
Get Accounting, CRM & Payroll in one integrated package with Deskera All-in-One .

Business Plan Development
Masterplans experts will help you create business plans for investor funding, bank/SBA lending and strategic direction
Investor Materials
A professionally designed pitch deck, lean plan, and cash burn overview will assist you in securing Pre-Seed and Seed Round funding
Immigration Business Plans
A USCIS-compliant business plan serves as the foundation for your E-2, L-1A, EB-5 or E-2 visa application
Customized consulting tailored to your startup's unique challenges and goals
Our team-based approach supports your project with personal communication and technical expertise.
Pricing that is competitive and scalable for early-stage business services regardless of industry or stage.
Client testimonials from just a few of the 18,000+ entrepreneurs we've worked with over the last 20 years
Free tools, research, and templates to help with business plans & pitch decks
What Is A Business Plan (& Do I Really Need One?)
The term "business plan" is a familiar one, often bandied about in entrepreneurial circles. Yet, despite its ubiquity, it's remarkable how much mystery and confusion can surround this essential business tool.
What exactly is a business plan? What purpose does it serve? How is it structured? This article aims to lift the veil, demystifying the business plan and revealing its multifaceted nature.
Business Plan Definition
A business plan is a document that describes a company's objectives and its marketing, financial, and operational strategies for achieving them. It's more than a mere document; it's a structured communication tool designed to articulate the vision of the business, allowing stakeholders to easily find the information they seek.
The business plan is a tangible reflection of the strategic planning that has gone into the business's future. While the plan is a static document, the planning is a dynamic process, capturing the strategic thinking and decision-making that shape the business's direction.
Purposes of a Business Plan
1. attracting funding opportunities.
A well-crafted business plan illustrates the company's potential for growth and profitability. It outlines the company's vision, mission, and strategies, providing a clear roadmap for success. A potential investor, whether venture capitalists or angel investors, can see how capital will be utilized, fostering trust and confidence in the business venture. A bank or financial institution can assess your company's ability to meet debt service obligations and compliance with strict financial accounting to meet underwriting requirements.
2. Aligning Organizational Objectives
A business plan acts as a unifying document that aligns the team with the company's goals and strategies. It ensures that everyone is on the same page, working towards common objectives. This alignment fosters collaboration and efficiency, driving the business towards its targets.
3. Validating the Business Concept
Before launching, a business plan helps in validating the feasibility of the business idea. It's a rigorous process that tests the concept against real-world scenarios, ensuring that the idea is not only innovative but also practical and sustainable. This validation builds credibility and prepares the business for the challenges ahead. For an existing business, a business plan can help address a possible merger and acquisition (M&A), rolling out a new business product or location, or expanding the target market.
4. Facilitating Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Whether it's securing a visa for international operations or meeting other regulatory requirements, a business plan can be an essential tool. It provides the necessary information in a structured format, demonstrating compliance with legal and regulatory standards. This can streamline processes and prevent potential legal hurdles.
5. Articulating and Formalizing the Business Vision
The business plan is more than a set of numbers and projections; it's the embodiment of the business vision. It communicates the essence of the business to stakeholders, turning abstract ideas into a concrete operational plan. It's a vital tool for leadership to articulate and formalize the vision, setting the stage for strategic execution.
Identifying the Right Type of Business Plan
Once you understand who your business plan is for and what specific needs it must address, you can identify the type of plan that best suits your situation. Business plans can be categorized into two main types: traditional and lean, each serveing its own unique purpose.
Traditional Business Plan
The Traditional Business Plan is a detailed and comprehensive document, often used by a new business, especially those seeking significant funding. It provides a complete picture of the company's vision, strategies, and operations. A traditional business plan leaves no stone unturned, offering a robust tool that communicates the business's entire vision and plan to stakeholders.
Lean Business Plan
In contrast, the Lean Business Plan is an abbreviated structure that still emphasizes the key elements of a Traditional Business Plan, but in less detail. It's suitable for early-stage startups, small businesses, or situations where agility and speed are essential. The Lean Business Plan focuses on the essentials, providing a quick overview without overwhelming details. It's a flexible and adaptable tool that can evolve with the business. One of the primary distinctions between it and a Traditional Business Plan is that a Lean Business Plan does not typically include financial planning, or if it does, it's a simple financial forecast or cash burn.
Components of a Business Plan
There are many places online where you can buy a business plan template. Often, those documents are just an outline of the sections of the business plan and what is included in each. If that's what you're looking for, here's a good business plan outline:
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary is the first section read but often the last written, as it encapsulates the entire plan. If the company has a mission statement, it's typically included here. When used for funding, it includes the ask or uses of funds, and for investment, it may contain an investor proposition. It's a concise overview that sets the tone, summarizing each section that follows.
Company Overview
The Company Overview is the foundation of the business, articulating how it operates, generates revenue, and delivers unique value to its customers. This section defines products and/or service the business sells, as well as the company’s business model and unique value proposition. It covers key partners, pricing strategy, revenue model, and other essential business activities.
Market Analysis Summary
The Market Analysis is the business intelligence portion of the plan. It comprises an industry analysis, market segments, target customers, competitive analysis, competitive advantage. This section provides insights into the market landscape, identifying opportunities, challenges, and how the business positions itself uniquely within the industry.
Strategy & Implementation Summary
Here, the business plan should outline the short-term and long-term objectives, marketing strategy and sales approach. It's a roadmap that details how the business will achieve its goals, including tactical steps, timelines, and resources. In a business plan for investors, the inclusion of an exit strategy can provide a vision for the future, considering various potential outcomes.
Management Summary
The Management Summary offers profiles of key personnel, their qualifications, roles, and plans to fill talent gaps. It's a snapshot of the leadership team, providing assurance that the right people are in place to execute the business plan successfully.
Financial Projections
This section includes standard financial statements like the profit & loss statement (P&L), the balance sheet, and the cash flow statement. It offers a detailed financial blueprint, illustrating the company’s revenue drivers and unit assumptions, income statement, a break-even analysis, and a sensitivity analysis to examine how changes in variables affect outcomes. For businesses with complex structures, framing the revenue in terms of market share can offer additional insight into the viability and feasibility of the financial projections.
The Appendices often include year 1 and year 2 monthly financial statements, intellectual property like patents and trademarks, construction blueprints, and other essential documentation. It's a repository for supporting information that adds depth and context to the main sections of the plan.
Do I Need a Business Plan?
The question "Do I need a business plan?" is one that many entrepreneurs and business leaders grapple with. The answer, however, is not as straightforward as it might seem. While not every business requires a traditional business plan, the strategic planning process is essential for all.
In some cases, a traditional business plan is required. Applying for a Small Business Administration (SBA) loan , obtaining a entrepreneurship visa , or meeting specific investor requirements may mandate a comprehensive business plan.
However a traditional business plan isn’t always necessary. For example, in early-stage investor funding, particularly in industries like SaaS, a lean business plan accompanied by a pitch deck presentation will often suffice. The focus here is on agility and essential information rather than exhaustive detail.
Every Business Needs Business Planning
Unlike the traditional business plan, which may or may not be required depending on the situation, business planning as a process is indispensable for every business, regardless of size or stage.
Business planning is a dynamic, continuous process. It's not confined to a single document but evolves with the business, adapting to changes, challenges, and opportunities. Effective strategic planning ensures internal alignment with both long-term vision and short-term objectives. It's a holistic approach that guides business goal-setting decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic direction. It often serves as the basis for a fully developed marketing plan.
Every business, from a small startup to a large corporation, benefits from strategic planning. It's a practice that fosters growth, innovation, and resilience, providing a roadmap for success.
Not every business needs a traditional business plan as a document, but all businesses need to engage in business planning as a process. While the traditional business plan serves specific purposes and audiences, business planning is a universal practice that guides and grows the business.
Entrepreneurs and business leaders must assess their specific needs, recognizing that the traditional business plan is just one tool among many. The true value of the business plan lies in continuous planning, adapting, and aligning with the unique vision and goals of the business.

How to Write a Management Summary for Your Business Plan
Entrepreneurs are often celebrated for their uncanny ability to understand others – their customers, the market, and the ever-evolving global...

Understanding Venture Debt vs Venture Capital
Despite growth in sectors like artificial intelligence, venture capital funding has seen better days. After peaking at $347.5 billion in 2021, there...

Going Beyond Writing: The Multifaceted Role of Business Plan Consultants
Most people think of a professional business plan company primarily as a "business plan writer." However, here at Masterplans, we choose to approach...

Try for free
Business Plan
Who should write a business plan, pros and cons of a business plan, the anatomy of a business plan, .css-uphcpb{position:absolute;left:0;top:-87px;} what is a business plan, definition of a business plan.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and which tactics you plan to use to reach commercial success.
Whilst every enterprise should have a plan of some sort, a business plan is of particular importance during the investment process. Banks, venture capitalists, and angel investors alike will need to see a detailed plan in order to make sound investment decisions — think of your plan as a way of convincing them your idea is worth their resources.
Roadmapping From A to Z

Business plans can also be useful as a guide to keeping a new business on track, especially in the first few months or years when the road ahead isn’t too clear.
Starting a business isn’t an exact science. Some companies organically develop out of trial and error, while others are plotted out from start to finish.
So if you’re asking whether your company needs a lengthy business plan, the answer would be ‘no’. That said, there are definitely a few situations in which writing a plan makes sense and can help increase the chances of a business becoming successful:
In situations when the market is new and untested — or simply volatile — it can be very helpful to have a business plan to refer back to when the road ahead isn’t clear.
For those who have an exciting business idea but haven’t necessarily distilled it down into black-and-white. Writing a business plan is a great way to look at a concept from all angles and spot any potential pitfalls.
How to write a business plan?
The most important step in writing a business plan is to identify its purpose.
Who are you trying to attract with it, and why?
Here are a few key pointers for writing a business plan:
Are you looking to secure a bank loan, get funding from private investors, or to lure skilled professionals to join you?
Include a brief history of your business, the concept, and the products or services. Keep it professional and transparent.
Don’t exaggerate your experience or skills, and definitely don’t leave out information investors need to know. They’ll find out at some point, and if they discover you lied, they could break off their involvement. Trust is crucial.
Explain what the product or service your business offers in simplistic terms.
Watch out for complex language and do whatever you can to prevent readers from becoming confused.
Focus on the benefits the business offers, how it solves the core audience’s problem(s), and what evidence you have to prove that there is a space in the market for your idea. It’s important to touch on the market your business will operate in, and who your main competitors are.
Another essential aspect of writing an effective business plan is to keep it short and sweet. Just focus on delivering the crucial information the reader has to know in order to make a decision. They can always ask you to elaborate on certain points later.
Still, deciding whether or not a business plan will benefit you at this stage of your venture?
Let’s look at a few reasons why you might (or might not) want to write a business plan.
A business plan will help you to secure funding even when you have no trading history. At the seed stage, funding is all-important — especially for tech and SaaS companies. It’s here that a business plan can become an absolute lifesaver.
Your business plan will maintain a strategic focus as time goes on. If you’ve ever heard of “mission creep”, you’ll know how important an agreed can be — and your business plan serves exactly that purpose.
Having a plan down in black and white will help you get other people on board . Again, with no trading history, it can be hard to convince new partners that you know what you’re doing. A business plan elegantly solves this problem.
Your business plan can cause you to stop looking outward. Sometimes, especially in business, you need to be reactive to market conditions. If you focus too much on your original business plan, you might make mistakes that can be costly or miss golden opportunities because they weren’t in the plan.
A lot of time can be wasted analyzing performance. It’s easy to become too focused on the goals and objectives in your business plan — especially when you’re not achieving them. By spending too much time analyzing past performance and looking back, you may miss out on other ways to push the business forward.
A business plan is out of date as soon as it’s written. We all know how quickly market conditions change. And, unfortunately, certain elements in your business plan may have lost relevance by the time you’re ready to launch. But there is another way — by transferring your strategic plan into an actionable roadmap , you can get the best of both worlds. The business plan contains important detail that is less likely to change, such as your mission statement and target audience, and the roadmap clarifies a flexible, adaptable, route forward.
So, you’ve decided to write a business plan — a great choice!
But now comes the tricky task of actually writing it.
This part can be a little frustrating because there is no one-size-fits-all template appropriate for all business plans. The best approach, in fact, is to look at common ingredients of a business plan and pick out the ones that make sense for your venture.
The key elements of a great business plan include:
An overview of the business concept . This is sometimes referred to as an executive summary and it’s essentially the elevator pitch for your business.
A detailed description of the product or service. It’s here that you’ll describe exactly what your core offering will be — what’s your USP , and what value do you deliver?
An explanation of the target audience. You need a good understanding of who you’ll be selling your product or service to, backed up by recent market research.
Your sales and marketing strategy. Now that you know who you’re targeting, how do you plan to reach them? Here you can list primary tactics for finding and maintaining an engaged client base.
Your core team . This section is all about people: do you have a team behind you already? If not, how will you build this team and what will the timeline be? Why are you the right group of people to bring this idea to the market? This section is incredibly important when seeking external investment — in most cases, passion can get you much further than professional experience.
Financial forecasts . Some investors will skim the executive summary and skip straight to the finances — so expect your forecasts to be scrutinized in a lot of detail. Writing a business plan for your eyes only? That’s fine, but you should still take time to map out your financial requirements: how much money do you need to start? How do you plan to keep money coming in? How long will it take to break even ? Remember, cash is king. So you need a cash flow forecast that is realistic, achievable and keeps your business afloat, especially in the tricky first few years.

General FAQ
Glossary categories.

Feedback Management

Prioritization

Product Management

Product Strategy

Roadmapping
Build great roadmaps
Book a demo
Experience the new way of doing product management

- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
The Different Types of Business Plans

Free Business Plan Template
Ayush Jalan
- December 14, 2023
A business plan is a blueprint for your business. No matter if you’re running a startup or a well-established company, every entrepreneur needs to create a business plan . It helps you have a clear idea of your goals, and objectives, the execution of your strategies, and tracking progress.
Business plans come in all shapes and sizes.
You can create a plan based on your unique requirements and goals. Often, businesses require different types of plans for different situations and to tackle different problems. Having just one standard business plan is not enough.
A meticulously crafted business plan will efficiently serve its intended purpose . In fact, business plans are categorized based on the type of audience, the scope of the plan, and the purpose and format of the plan.
Understanding the basics of each type will help you pick out the right one for your business requirements. In this article, you will learn the different types of business plans and when and where they are used.
Based on Audience

Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience. They are:
- 1. Internal business plans: As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company’s goals, and the personnel and processes aimed to achieve them.
- 2. External business plans: On the contrary, external business plans are intended for people outside the company, such as investors, banks, partners, etc. These plans usually contain detailed information about the company’s background, finances, and overall operation of the business.
Based on the Scope

Similarly, business plans are classified into two types based on their size and the depth of information they encompass. They are:
1. Standard business plans
A standard business plan is a bulky document that contains every detail of the company. Most external plans slide into this category as they often need to be detailed for presentation to people outside the company.
A standard business plan contains these sections:
- Executive summary
- Company Overview
- Problem analysis
- Market analysis
- Customer analysis
- Competitive analysis
- SWOT analysis
- Marketing Plan
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Finances plan
- Supporting documentation
A standard plan is usually presented to banks and any potential investors as it provides a complete view of the company, and future financial projections , and helps attain funding. But oftentimes, drafting a traditional business plan can be a tedious task as it takes a lot of time and effort.
2. Lean business plans
A lean plan is a condensed version of the standard business plan. It includes the highlights of a standard business plan and summaries of all the sections. It is a compact document that emphasizes achieving milestones and tracking finances.
Drafting a lean business plan is easier, faster, and is considered to be more efficient compared to a standard plan. It is flexible and can be revised effortlessly as many times as needed, which provides room for adjusting milestones, and improvising.
A lean business plan is apt for situations where you are uncertain about the process of creating a business plan, and it can be the essential first draft for your business. Everything in a lean business plan should be concise and represented in bullet points or short texts.
These are the elements that a lean business plan focuses on:
Based on purpose and format.
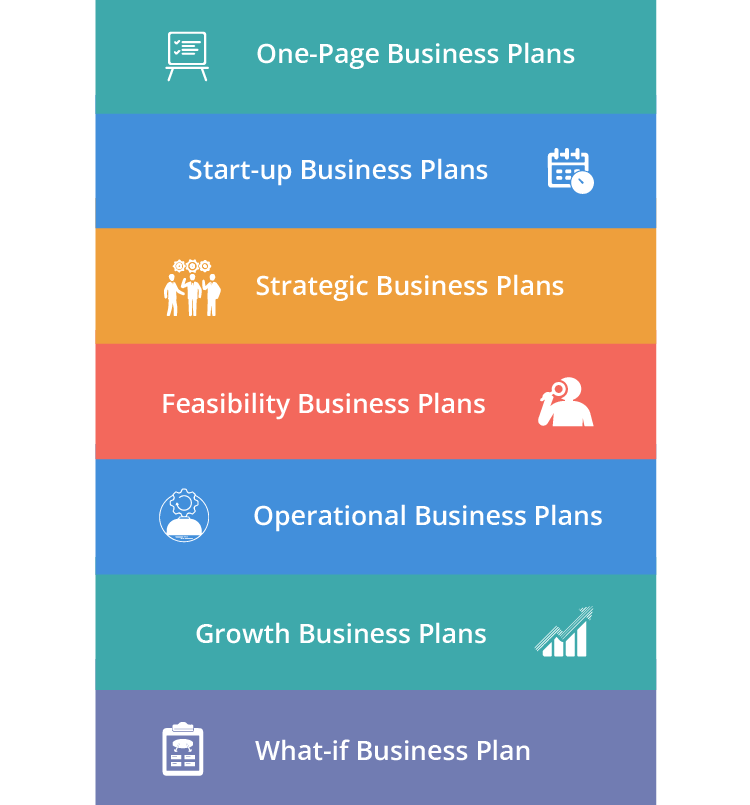
Business plans are further classified based on their purpose and format into seven types, they are:
1. One-page business plans
A one-page business plan can be described as an outline of a lean business plan . It is also called a business pitch or a quick summary. It is sometimes used to present a quick overview of your business to your vendors, partners, and employees and as a summary to banks and investors.
This encapsulates all the essential parts of a business plan on a single page. This summarizes the target market, business offering, main milestones, and essential sales forecast.
2. Startup business plans
A startup business plan can be defined as a lean plan with elements of a standard plan included to seek investors. The primary purpose of a startup plan is to put forth the steps required to get a business up and running. Later on, it should also serve as a plan that will help score investment.
The steps of establishing a new company include acquiring licenses and permits, setting up an office or store, getting equipment, and hiring and managing employees. All of these should be included in the startup business plan.
A startup plan should include information about the company, its products, and services, a detailed analysis of the industry, market, competition, SWOT, the bios of management, their responsibilities and roles, complete financial details and analysis, and projections of the usage of funding.
3. Strategic business plans
A strategic business plan is a lean business plan that contains details of the strategies and their implementation to achieve the goals and objectives of a company. These are internal plans that will focus entirely on the strategies with almost no inclusion of finances.
Conduct SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis to begin an effective strategic business plan. This will help you better understand the factors that play a role in the decision-making process of a business.
A SWOT analysis will help you decide the strategies that will best suit your company and accomplish the goals, utilizing the available resources. Every strategic plan should contain these five elements:
- Mission statement
- Vision statement
- Factors that determine success
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Implementation process
4. Feasibility business plans
You require a feasible plan in case the business is stepping into a new market or introducing a new product or service. It is more a decision-making plan than a business plan as it focuses on two primary concerns:
- Determining the existence of a market
- Determining the profits of the initiative
A feasibility plan is a quick analysis of the practicality of a business idea.
This type of business plan usually excludes all the other sections and solely focuses on the scope of the initiative, its profitability, analysis of the market and competition, and acquiring the funding for it.
It is mostly crafted for internal management and ends with recommendations on whether the decision of entering a new market or introducing a new product or service is viable or not.
5. Operational business plans
An operational plan is a type of lean plan that focuses on the implementation process, achieving milestones, project deadlines, and the responsibilities of management, departments, and employees. It also focuses on the funding required to accomplish the milestones.
This business plan is called an annual plan, as businesses often use it to plan and specify milestones and their implementation for the coming year.
Some of the key elements every operational plan should contain are:
- Objectives for the operations
- Activities required to achieve objectives
- Resources required
- Staffing requirements
- Deadlines for implementation
- Tracking progress
6. Growth business plans
Draft a growth business plan when a company looks to expand its business into new markets. It is essentially a startup plan for a new segment of your business. This is also known as an expansion plan as it focuses on the long-term goals of a business.
This business plan can be both external and internal.
An external growth plan includes complete financial details and a funding request. On the other hand, an internal one contains details of the forecast of sales and expenses of the upcoming venture.
7. What-if business plan
Use a what-if plan when a business is taking a risky decision and needs a plan if the outcome turns unfavorable. This plan is usually less formal unless a funding request is included.
It entails a contingency plan that considers the worst-case scenarios.
This plan provides a glimpse into the possible outcomes of taking that risky decision and its effects on the company. It makes sense when taking a major business decision, merging with another company, raising the prices of products, etc. These are all the different types of business plans from which you can hand-pick the best fit for your company.
A Plan for Every Priority
Planning is essential for every business, without one a business is not likely to sustain itself in the long run. Although daunting sometimes, choosing the right plan for your business requirement can help you achieve your goals faster and with smart use of resources.
Every situation needs a unique approach to tackle effectively. Fortunately, there’s a plan for every purpose to help your business stand the test of time. Feel free to pick one that suits your business the best. Make sure to update it regularly.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

Lean Business Planning: The Modern approach to Business Plan Writing
Table of Contents in Business Plan – Example, Template
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections.Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over ...
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
In my experience, some of the more common types of plans include: Startup Plan. • Audience: External. • Depth: Standard. • Purpose: Development of a blueprint for building a successful ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained. Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans, operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more. Different situations call for different types of plans. But what makes each type of plan unique?
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Growth business plan. Operations business plan. Strategic business plan. 01. Startup business plan. The startup business plan is a comprehensive document that will set the foundation for your company's success. It covers all aspects of a business, including a situation analysis, detailed financial information and a strategic marketing plan ...
All businesses start with a lean plan. These are things that every business owner needs to do in order to run the business effectively. They apply to all businesses, large or small, startup or not: Develop and execute strategy. Set priorities. Allocate efforts and resources according to priorities.
A business plan is defined as a written document that comprises business details, the company's goals, and methods to achieve these goals. A business plan contains a comprehensive framework for the company in terms of marketing, finance, and operations. Business plans serve a significant purpose.
The business plan is more than a set of numbers and projections; it's the embodiment of the business vision. It communicates the essence of the business to stakeholders, turning abstract ideas into a concrete operational plan. It's a vital tool for leadership to articulate and formalize the vision, setting the stage for strategic execution.
Clawback. v. t. e. A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it ...
Value proposition. Strategic marketing plan. Market evaluations. Projected startup costs. Cash flow projections and income and profit expectations. Within the financial section, a business also needs to explain the exit strategy for investors and how specifically the company plans to use investor money.
Creating a business plan is an indispensable part of any business. The main purpose of creating such a document is to attract prospective investors to provide capital to the enterprise. Therefore, the plan should cover all the important perspectives of a business - financial, operational, personnel, competition, etc. Table of contents.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them. In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and ...
Based on Audience. Business plans are broadly categorized into two types based on the type of audience. They are: 1. Internal business plans: As the name suggests, an internal business plan is solely for the people inside the company. These can be specific to certain departments such as marketing, HR, production, etc. Internal business plans focus primarily on the company's goals, and the ...
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
A business plan can help increase clarity within the company. It sets out the company's vision, mission and values. It also provides guidance on what the company wants to achieve and how to go about doing it. Such information help employees understand their roles and responsibilities within the company.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
An operations business plan defines the operating procedures and policies for the business. It Indicates the projected costs and revenues, objectives of each department, employees responsible, strategies to carry out the operations, deadlines and timelines. It includes steps to follow to achieve realistic projections and business goals.