

APA Referencing Guide (Avoiding Common Mistakes): 7th edition
- Referencing
- 7th edition
- Common Mistakes
- Conference Proceedings
- Theses and Dissertations
- Online Content
- Media Resources
- Laws and Executive Orders
- Student Works

- Include any edition information in parentheses after the title, without italics.
- If the book includes a DOI, include the DOI in the reference after the publisher name.
- Do not include the publisher location.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/book-references

- If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference. Include “https” at the beginning of doi.
- If the journal article does not have a DOI but does have a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online journal that is not part of a database), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the journal article has an article number instead of a page range, include the word “Article” and then the article number instead of the page range.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/journal-article-references

- The format for conference proceedings published as an edited book chapter is the same as for edited book chapters.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/conference-proceeding-references

- A dissertation or thesis is considered published when it is available from a database such as ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global or PDQT Open, an institutional repository, or an archive.
- Include the description “Doctoral dissertation” or “Master’s thesis” followed by a comma and the name of the institution that awarded the degree. Place this information in square brackets after the dissertation or thesis title and any publication number.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/published-dissertation-references

- Provide the writer as the author.
- Provide the specific date the story was published.
- Provide the title of the news story in italic sentence case.
- List the name of the news website in the source element of the reference.
- End the reference with the URL.
- The words ‘Retrieved from’ for online resources are no longer needed.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/webpage-website-references

- Include the description “[Video]” in square brackets after the title.
- Provide the site name (YouTube) and URL of the video.
- Please refer to this link for more information: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/#online-media

- Please refer to this link for more information: https://libguides.css.edu/APA7thEd/Legal
- Please refer to this link for referencing report by a government agency: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/report-government-agency-references

- Works not formally published including student works can use this format.
- More examples from Morling College , Walden University , James Cook University and UCL Institute of Education .
Basics of APA Explained
General notes
In APA 7th edition, please remember the following when writing your reference list:
- The place of publication is omitted.
- The list may contain up to 20 authors.
- The DOI format shall include https in the beginning. The format is now: https://doi.org/10.xxxx
The 7th edition also accepts the following font sizes aside from Times New Roman size 12pt: Calibri size 11pt, Arial 11pt, Lucida Sans Unicode 10pt, and Georgia 11pt as allowed fonts.
You may also refer to:
- Comprehensive examples can be found here: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/examples/
- Other examples: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/c.php?g=27779&p=170330
- New & Notable Changes in APA 7th edition on https://libguides.ecu.edu/c.php?g=982594&p=7316507
- << Previous: Referencing
- Next: Common Mistakes >>
- Updated: Dec 26, 2023 2:31 PM
- URL: https://nu.kz.libguides.com/APA_guide
- +44 7897 053596
- [email protected]

Get an experienced writer start working
Review our examples before placing an order, learn how to draft academic papers, mastering harvard style referencing for your thesis: expert tips and techniques.

How to Overcome the Feeling of Failure after Missing a Dissertation Deadline

How Long is a Literature Review for a Dissertation?

The Harvard system is another name for the Author-Date referencing style and citation . A Harvard referencing thesis uses the Harvard referencing system to cite sources. Developed at Harvard University in the USA, this is probably Australia's most commonly used referencing system, especially in the sciences. If studying law, OSCOLA (Oxford University Standard for Citation of Legal Authorities) is the most appropriate choice.
In this article, I will share Harvard referencing thesis examples for your inspiration.
Harvard Referencing thesis Examples;
- Example 1: Internet Censorship in the UAE: Freedom of the Internet
- Example 2: Development of Sustainable Homes Through Renewable Energy Sources
- Example 3: The Importance of Procurement Strategy & Impact on Construction Projects
3-Step Dissertation Process!

Get 3+ Topics

Dissertation Proposal

Get Final Dissertation
What is harvard referencing style, and why should you use it.
Harvard referencing style is a widely used system for citing sources in academic writing. This referencing style is typically used in the academic community and professional settings. It can help to ensure that research materials are properly cited and referenced throughout your work.
By using Harvard referencing, you demonstrate study breadth and respect for cited academics. It ensures proper source listing and formatting, portraying you as a reliable researcher following academic norms. Employing Harvard referencing in your thesis showcases your competence and gains reader appreciation.
How to Use Harvard Referencing Style in Thesis or Dissertation in
Harvard referencing system is an Author-Date system. When citing a thesis in Harvard style, two elements are very important:
- The author’s last name and first initials
- The year the thesis was published
This basic format can be used for both online and offline sources. While referencing an online thesis , you must include the URL or DOI (Digital Object Identifier). For an offline source, you will need to include the name of the institution where the thesis was published.
In-Text Citations in Harvard Referencing Thesis
Citing others' work is essential. It's called citing or quoting references. Consistency and precision help readers locate the information (e.g., Smith 2020 ). Include page numbers when quoting directly (e.g., Smith 2020, p. 23 ).
Reference List
The reference list should be arranged alphabetically by the author's last name. If an author has written more than one thesis, they should be listed from oldest to newest. Thesis reference entry should include:
- Author’s last name and first initials
- Year of publication (in brackets)
- Title of thesis (in italics)
- Type of thesis [PhD, Masters]
- Name of institution where located [if offline source] OR URL/DOI [if online source]
Examples of How to Reference a Thesis in Harvard Style
Here is an example of reference list entry in Harvard Style:
Smith, J. (2020). The impact of social media on society. PhD thesis, University of Miami. https://doi.org/10.1123/abc123456
Smith, J. (2020). The impact of social media on society [PhD thesis]
Testimonials
Very satisfied students
This is our reason for working. We want to make all students happy, every day. Review us on Sitejabber
Tips for Avoiding Common Mistakes When Referencing a Thesis in Harvard Style
1. citing the author.
When referencing a thesis in Harvard style, citing the work's author is important. It can be done by including the author's last name and the year of publication in parentheses after the quote or paraphrase.
For example: (Smith, 2020).
2. Citing the Title
In addition to citing the author, it is also important to include the title of the work referenced. This can be done by including the title in quotation marks after the author's last name and publication year.
For example: (Smith, 2020, "Thesis Title").
3. Citing the Date of Publication
Including the publication date when referencing a thesis in Harvard style is also important. It can be done by including the year of publication in parentheses after the author's last name and title.
4. Citing the URL
When referencing a thesis that is available online, it is important to include the URL of the website where it can be found. It can be done by including the URL in parentheses after the author's last name, publication date, and title.
For example: (Smith, 2020, "Thesis Title," http://www.example.com).
5. Citing Page Numbers
When quoting or paraphrasing specific passages from a thesis, it is important to include page numbers in citations. This can be done by including the page number or range of pages in parentheses after the author's last name, date of publication, and title.
For example: (Smith, 2020, "Thesis Title," p. 12).
6. Creating a Reference List
In Harvard style, reference a thesis with a final reference list. Include all cited works, alphabetized by author's last name. Entries should provide author, publication date, title, and URL if relevant.
7. Formatting
When writing a paper in Harvard style, it is important to format it correctly. This includes using 12-point Times New Roman font and 1-inch margins on all sides of your paper.
How Does It Work ?

Fill the Form
Please fill the free topic form and share your requirements

Writer Starts Working
The writer starts to find a topic for you (based on your requirements)

3+ Topics Emailed!
The writer shared custom topics with you within 24 hours
Mistakes to Avoid
As a student writing a Harvard Referencing thesis, you must be mindful of following mistakes that can ruin your research work.
1. Not Citing All Sources
A major student blunder is not citing all sources used. Remember to cite direct quotes, paraphrased, and summarized content to avoid plagiarism claims.
2. Incorrectly Citing Sources
Another error is wrong source citing, often due to format uncertainty or careless data entry. This causes confusion and potential plagiarism allegations .
3. Not Updating the Reference List
As students continue to work on their thesis, they will inevitably use new sources of information. It is important to add these new sources to the reference list as they are used; otherwise, the reference list will become outdated and inaccurate.
4. Using Unreliable Sources
Students should only use reliable sources of information. Unreliable sources include websites that are not reputable, personal blogs, and social media posts. Using unreliable sources could lead to incorrect or misleading information being included in the thesis.
5. Failing to Proofread the Reference List
Once the reference list has been completed, it is important to proofread it carefully to ensure that all information is accurate and correctly formatted. Any errors in the reference list could reflect poorly on the student’s attention to detail and organizational skills.
6. Including Too Much Detail in the Reference List
Students should only include relevant and necessary information when adding citations to the reference list. Including too much detail could make a list difficult to read and understand and lead to accusations of plagiarism.
Referencing a thesis in Harvard style is simple when you grasp key elements. In-text, cite author's last name, initials, publication year, and thesis title. For the reference list, alphabetize by author's last name. Include details like thesis type and institution name (if offline).
Check these examples to see how to use the Harvard referencing style professionally in your thesis writing .
Get 3+ Free Dissertation Topics within 24 hours?
Your Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Masters PhD
Area of Research
Get an Immediate Response
Discuss your requirments with our writers
admin farhan
Related posts.

Understanding TOK Concepts: A Beginner’s Guide

Research Hypotheses: Directional vs. Non-Directional Hypotheses

Is AP Psychology Hard? Exploring the Challenges and Rewards
Comments are closed.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
In this citation guide, you will learn how to reference and cite an undergraduate thesis, master’s thesis, or doctoral dissertation. This guide will also review the differences between a thesis or dissertation that is published and one that has remained unpublished. The guidelines below come from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (2020a), pages 333 and 334. Please note that the association is not affiliated with this guide.
Alternatively, you can visit EasyBib.com for helpful citation tools to cite your thesis or dissertation .
Guide Overview
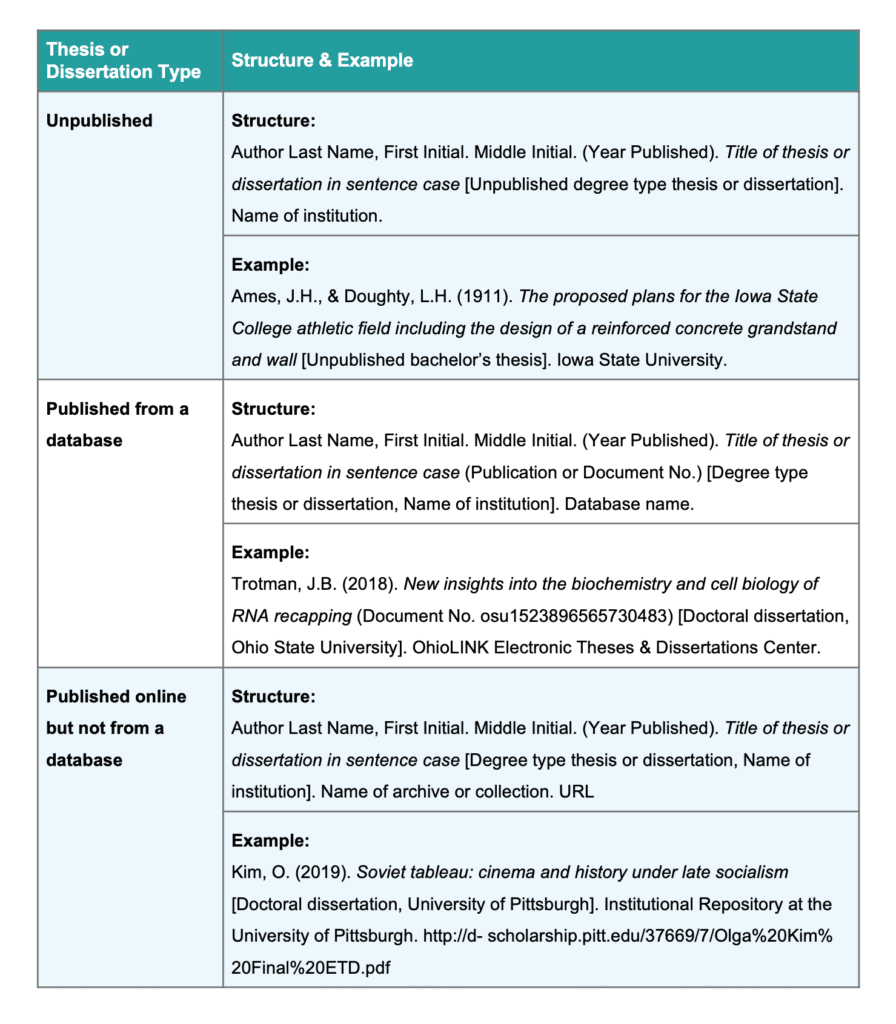
Citing an unpublished thesis or dissertation, citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation: reference overview, what you need.
Since unpublished theses can usually only be sourced in print form from a university library, the correct citation structure includes the university name where the publisher element usually goes.
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution.
Ames, J. H., & Doughty, L. H. (1911). The proposed plans for the Iowa State College athletic field including the design of a reinforced concrete grandstand and wall [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University.
In-text citation example:
- Parenthetical : (Ames & Doughty, 1911)
- Narrative : Ames & Doughty (1911)
If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It’s similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences:
- The institution is presented in brackets after the title
- The archive or database name is included
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name.
Examples 1:
Knight, K. A. (2011). Media epidemics: Viral structures in literature and new media (Accession No. 2013420395) [Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Santa Barbara]. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.

Trotman, J.B. (2018). New insights into the biochemistry and cell biology of RNA recapping (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center.
In the example given above, the dissertation is presented with a Document Number (Document No.). Sometimes called a database number or publication number, this is the identifier that is used by the database’s indexing system. If the database you are using provides you with such a number, then include it directly after the work’s title in parentheses.
If you are interested in learning more about how to handle works that were accessed via academic research databases, see Section 9.3 of the Publication Manual.
In-text citation examples :
- Parenthetical citation : (Trotman, 2018)
- Narrative citation : Trotman (2018)
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year Published). Title in sentence case [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL
Kim, O. (2019). Soviet tableau: cinema and history under late socialism [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. https://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf
Stiles, T. W. (2001). Doing science: Teachers’ authentic experiences at the Lone Star Dinosaur Field Institute [Master’s thesis, Texas A&M University]. OAKTrust. https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-2001-THESIS-S745
It is important to note that not every thesis or dissertation published online will be associated with a specific archive or collection. If the work is published on a private website, provide only the URL as the source element.
In-text citation examples:
- Parenthetical citation : (Kim, 2019)
- Narrative citation : Kim (2019)
- Parenthetical citation : (Stiles, 2001)
- Narrative citation : Stiles (2001)
We hope that the information provided here will serve as an effective guide for your research. If you’re looking for even more citation info, visit EasyBib.com for a comprehensive collection of educational materials covering multiple source types.
If you’re citing a variety of different sources, consider taking the EasyBib citation generator for a spin. It can help you cite easily and offers citation forms for several different kinds of sources.
To start things off, let’s take a look at the different types of literature that are classified under Chapter 10.6 of the Publication Manual :
- Undergraduate thesis
- Master’s thesis
- Doctoral dissertation
You will need to know which type you are citing. You’ll also need to know if it is published or unpublished .
When you decide to cite a dissertation or thesis, you’ll need to look for the following information to use in your citation:
- Author’s last name, and first and middle initials
- Year published
- Title of thesis or dissertation
- If it is unpublished
- Publication or document number (if applicable; for published work)
- Degree type (bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral)
- Thesis or dissertation
- Name of institution awarding degree
- DOI (https://doi.org/xxxxx) or URL (if applicable)
Since theses and dissertations are directly linked to educational degrees, it is necessary to list the name of the associated institution; i.e., the college, university, or school that is awarding the associated degree.
To get an idea of the proper form, take a look at the examples below. There are three outlined scenarios:
- Unpublished thesis or dissertation
- Published thesis or dissertation from a database
- Thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database
American Psychological Association. (2020a). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
American Psychological Association. (2020b). Style-Grammar-Guidelines. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/basic-principles/parenthetical-versus-narrative
Published August 10, 2012. Updated March 24, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite a published thesis in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, publication year, title of the thesis, institute name, archive name, and URL (uniform resource locator). The templates for an in-text citation and reference list entry of a thesis, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Use the author surname and the publication year in the in-text citation.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Cartmel (2007)
Parenthetical:
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Cartmel, 2007)
Reference list entry template and example:
The title of the thesis is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose the thesis and the institute awarding the degree inside brackets following the publication year. Then add the name of the database followed by the URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the thesis [Master’s thesis, Institute Name]. Name of the Database. URL
Cartmel, J. (2007). Outside school hours care and schools [Master’s thesis, Queensland University of Technology]. EPrints. http://eprints.qut.edu.au/17810/1/Jennifer_Cartmel_Thesis.pdf
To cite an unpublished dissertation in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, year, title of the dissertation, and institute name. The templates for in-text citation and reference list entry of an online thesis, along with examples, are given below:
Author Surname (Year)
Averill (2009)
(Author Surname, Year)
(Averill, 2009)
The title of the dissertation is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose “Unpublished doctoral dissertation” inside brackets following the year. Then add the name of the institution awarding the degree.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the dissertation [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Name of the Institute.
Averill, R. (2009). Teacher–student relationships in diverse New Zealand year 10 mathematics classrooms: Teacher care [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Victoria University of Wellington.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Mastering Your Dissertation pp 123–130 Cite as
How Do I Reference?
Referencing and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
- First Online: 19 October 2023
208 Accesses
References are an important part of your dissertation, and you may need anywhere between 20 and 200 references, possibly more depending on the length of your thesis. But it is important that you reference appropriately and correctly, whether this is in the in-text citations or the list of references at the end of your thesis. This chapter explains the differences between a reference list and a bibliography. You will also want to avoid the risk of plagiarism, and this is explained, to help you ensure that you write your dissertation entirely in your own words.
- Reference management
- Referencing style
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Cottrell S (2008) The study skills handbook. Palgrave Macmillan, London
Google Scholar
Lindahl JF, Grace D (2018) Students' and supervisors' knowledge and attitudes regarding plagiarism and referencing. Research Integrity and Peer Review 3:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-018-0054-2
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Neville C (2010) The complete guide to referencing and avoiding plagiarism. Open University Press, London
Perry B (2010) Exploring academic misconduct: some insights into student behaviour. Act Learn High Educ 11:97–108
Article Google Scholar
Rumsey S (2008) How to find information, a guide for researchers. Open University Press, London
Reeves S, Jeanes Y (2022) The study skills handbook for nutritionists and dietitians. Open University Press, London
Further Reading
Neville C (2010) The Complete Guide to Referencing and Avoiding Plagiarism. Open University Press, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Reference?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_11
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- How it works
How to Best Use References in a Dissertation
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
“In a dissertation, references refer to the sources and citations used to support and validate the research.”
They provide evidence, scholarly context, and acknowledgment of the works consulted during the study. References typically include books, journal articles, websites, and other relevant publications cited in the dissertation.
Writing a dissertation can be challenging especially if you haven’t had the chance to write a dissertation before. You need to look into relevant literature, analyze past researches, conduct surveys, interviews, etc. and also reference and cite information that you’ve gathered from different sources.
Many students are usually confused regarding which sources should be mentioned and which be omitted. This confusion arises because they are unaware of the fact as to which sources are credible, reliable, and authentic and which are not.
Thus, the question always remains ‘How to Best Use References in a Dissertation’?
While there is no single way to best use references in a dissertation, students should have a clear understanding of the concept of the use of credible and reliable sources in their dissertation paper.
In today’s world where changes take place frequently, some newspaper articles published online are also categorized as authentic and credible sources.
Information and/or data can be extracted from these articles and included in dissertations with proper use of a citation.
To make sure that references are used appropriately in dissertations, here are a few ways that you can follow:
Research Relevant Studies
Depending on the topic of your dissertation , make sure to research and look into similar researches that have been conducted in the past. In addition to this, you could also read, analyze and review researches that have utilized the same model or talk about the same theory as you are applying in your dissertation.
Doing so will add a lot of value to your dissertation and you will be able to include models and theories with correct references and citations.
Include Recent Researches
As important as relevant studies are for your dissertation, including recent studies only is equally important. Using reference in a dissertation that belong to the past five to ten years are acceptable; however, using references of the 1980s or 1990s is not recommended.
The main reason being changes in time, settings, environment, participants, etc. All these factors contribute a lot towards accurate conclusions, thus they are regarded as essential when using a study for reference purposes.
Also, writing a dissertation in the current setting, considering the current environment, only recent researches must be included in the dissertation. This gives readers the idea that the research that has been conducted is recent.
Also Read: How to avoid plagiarism in an academic paper
Stuck on a difficult dissertation? We can help!
Our dissertation Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

Cite/Reference while Writing
Many of us are guilty of extracting information from various sources when writing without noting down the reference. As a result, we lose track of that particular reference and end up spending hours looking for that specific article or research.
Thus, you should always note down the reference as soon as you refer to it in your dissertation or when you include data or information. In this manner, you will have a complete list of references that you’ve used when you’ve finished writing your dissertation.
Also, doing so will save you a lot of your time, and you will be able to finish your dissertation without any delays.
Know when and where to Cite
Remember the hours you spent looking for the statistics or the specific piece of information that you mentioned in your dissertation, but forgot to cite? This usually happens when the deadline is nearing, and we’re in a hurry to complete our dissertation.
However, you should always keep in mind that when you rush things, you tend to spend a lot more time than needed. Thus, whenever you’re mentioning a fact, statistics, or a particular piece of information that is exact and accurate, always cite it.
Not doing so will keep your readers in doubt whether the statistic or number mentioned is accurate or not. On the other hand, if you cite those exact numbers, readers will have the impression that you have done your research, and they can even crosscheck it by referring to your citation.
Choose the Correct Referencing Style
There are various referencing styles. Depending on your university and other requirements, the right referencing style is chosen and conveyed to you.
What you should make sure of is understanding the required referencing style, so you can cite accurately. A Harvard style referencing style example includes a reference list with the name of authors, the journal or book name, the publisher’s name, and the date and the page number.
When citing the exact words of an author or when defining a theory or model, make sure that you include the page number as they are required for direct quotations.
If, in case you do not understand any of the referencing styles, you should either follow the guidelines provided by your tutor or you can also search the internet for your required referencing style.
With time, new editions of referencing styles have been introduced to make sure that all thesis and dissertations follow the same pattern. Thus, make it a practice to crosscheck your referencing style from the internet to make sure that you’re following the latest format and edition.
Proofread your Reference List
This is one of the most important, but often most ignored aspects when looking at how to use references correctly. Your reference list should be sorted as soon as you finish writing your dissertation.
For instance, it should be alphabetically arranged, the number of references should be appropriate for the dissertation, and should be free from all types of errors such as formatting, grammatical and style .
The correct style should be followed, the reference list should be properly formatted and proofread to eliminate all errors. An ideal list of reference examples includes correct mention of the author name, year of publication, and name of the book.
The publisher’s name should be italicized and the page number should also be mentioned. For academic journals, mentioning volume and issue number is mandatory. All these aspects should be considered to make sure that an accurate reference list is prepared for your dissertation.
Crosscheck your Citations
When citing your dissertation, you need to make sure that your text corresponds with the in-text citation that you’re including. Not doing so will make your research unreliable and unauthentic.
Readers will get an impression that the in-text citations have been included just for the sake of it, instead of being related to the text and information that is being mentioned.
Thus, the best in-text citation example includes the name of the author along with the year of publication. If there is a direct quote or a definition included in the exact words of the author, then the page number must be also indicated while citing.
Make sure that all your in-text citations are in line with the information that has been presented and discussed in the paper.
Number of References to be Used
‘How many references should I use for my dissertation? This is a question that most students face. They usually get confused when it comes to the number of references that should be used in a dissertation. There’s no right number of references that should be used in a dissertation.
It depends on the topic, the academic level of the dissertation, and the literature review that is being presented.
Also, the models and theories used in the paper contribute to the total number of references. Ideally, it is recommended that every paragraph of 100 words or more should have a reference; however, this is not required and mandatory in all cases.
The literature review is usually the chapter that uses the most references. This helps in formulating a dissertation that is not only informative but is backed by credible resources as well.
Referencing a dissertation is an easy task if done in the right manner. To answer the question, ‘how to best use references in a dissertation, you need to make sure that you’ve collected the right sources and are referring to credible and reliable information only.
Once you’ve sorted your references, you’re on your way to right an authentic dissertation. The literature review is an important aspect of every dissertation for mentioning relevant theories, models, and information. Thus, this section is critical when it comes to referencing. You should make sure that the models and theories are referenced appropriately, and all references are recent.
If you’re still unsure of whether you’re using references in the right manner or not, or you’re seeking help with referencing your dissertation, get in touch with our professional dissertation writing services .
At ResearchProspect, we make sure that your dissertation is properly referenced and accurately cited. All our information is up to date, and we make sure that only recent references are included in the dissertation to leave a lasting impression on the readers. Contact us today and leave your referencing worries to us!
FAQs About References in a Dissertation
Can i cite old research papers in my dissertation.
Old papers are usually outdated in terms of significance and impact. Therefore, you must look for recent papers to cite in your dissertation.
Why is it important to cite/ reference while writing?
Without citation, it looks like you are presenting someone else’s words as your views idea, which will eventually count as plagiarism .
Moreover, the citations increase the credibility and accuracy of the information presented in the paper.
Which is the correct referencing style?
There are many referencing styles available to pick from, such as MLA, APA, Harvard referencing style , etc. You must check with your university preferences to choose one. However, most UK universities prefer Harvard referencing style.
You May Also Like
Not sure how to start your dissertation and get it right the first time? Here are some tips and guidelines for you to kick start your dissertation project.
This brief introductory section aims to deal with the definitions of two paradigms, positivism and post-positivism, as well as their importance in research.
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
APA 7th Edition Citation Examples
- Volume and Issue Numbers
- Page Numbers
- Undated Sources
- Citing a Source Within a Source
- In-Text Citations
- Academic Journals
- Encyclopedia Articles
- Book, Film, and Product Reviews
- Online Classroom Materials
- Conference Papers
- Technical + Research Reports
- Court Decisions
- Treaties and Other International Agreements
- Federal Regulations: I. The Code of Federal Regulations
- Federal Regulations: II. The Federal Register
- Executive Orders
- Charter of the United Nations
- Federal Statutes
Format for dissertations and theses
Dissertations and theses database.
- Interviews, E-mail Messages + Other Personal Communications
- Social Media
- Business Sources
- PowerPoints
- AI: ChatGPT, etc.
Author last name, first initial. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No.) [Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis, University]. Database. URL
- Author: List the last name, followed by the first initial (and second initial). See Authors for more information.
- Year: List the year between parentheses, followed by a period.
- Title of dissertation/thesis: In italics. Capitalize the first word of the title, subtitle, and proper nouns.
- Publication number: Can be found in Dissertations and Theses database, listed in the item record as “Dissertation/thesis number.”
- Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis: List whether it is a dissertation or a thesis.
- University: List the university associated with the dissertation/thesis.
- Database: List database the dissertation/thesis was found in, if found in a database.
- URL: List URL if found on the free Web rather than in a database.
See specific examples below.
Dissertations:
Pecore, J. T. (2004). Sounding the spirit of Cambodia: The living tradition of Khmer music and dance-drama in a Washington, DC community (Publication No. 3114720) [Doctoral dissertation, University of Maryland]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
Master's Theses:
Hollander, M. M. (2017). Resitance to authority: Methodological innovations and new lessons from the Milgram experiment (Publication No. 10289373) [Master's thesis, University of Wisconsin - Madison]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
APA calls for the citation to include a unique identifying number for the dissertation, labeling it “Publication No.” That number can be found in Dissertations and Theses database, listed in the item record as “Dissertation/thesis number.”
Karamanos, X. (2020). The influence of professional development models on student mathematics performance in New Jersey public elementary schools [Doctoral dissertation, Seton Hall University]. Seton Hall University Dissertations and Theses (ETDs). https://scholarship.shu.edu/dissertations/2732
Bordo, V. C. (2011). Making a case for the use of foreign language in the educational activities of nonprofit arts organizations [Master's thesis, University of Akron]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=akron1311135640
Caprette, C. L. (2005). Conquering the cold shudder: The origin and evolution of snake eyes [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University].
Angelova, A. N. (2004). Data pruning [Master's thesis, California Institute of Technology].
See Publication Manual , 10.6.
- << Previous: Federal Statutes
- Next: Images >>
- Last Updated: Mar 18, 2024 12:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/apa-examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
Published on June 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on November 7, 2022.
A citation style is a set of guidelines on how to cite sources in your academic writing . You always need a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize a source to avoid plagiarism . How you present these citations depends on the style you follow. Scribbr’s citation generator can help!
Different styles are set by different universities, academic associations, and publishers, often published in an official handbook with in-depth instructions and examples.
There are many different citation styles, but they typically use one of three basic approaches: parenthetical citations , numerical citations, or note citations.
Parenthetical citations
- Chicago (Turabian) author-date
CSE name-year
Numerical citations
CSE citation-name or citation-sequence
Note citations
- Chicago (Turabian) notes and bibliography

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Types of citation: parenthetical, note, numerical, which citation style should i use, parenthetical citation styles, numerical citation styles, note citation styles, frequently asked questions about citation styles.
The clearest identifying characteristic of any citation style is how the citations in the text are presented. There are three main approaches:
- Parenthetical citations: You include identifying details of the source in parentheses in the text—usually the author’s last name and the publication date, plus a page number if relevant ( author-date ). Sometimes the publication date is omitted ( author-page ).
- Numerical citations: You include a number in brackets or in superscript, which corresponds to an entry in your numbered reference list.
- Note citations: You include a full citation in a footnote or endnote, which is indicated in the text with a superscript number or symbol.
Citation styles also differ in terms of how you format the reference list or bibliography entries themselves (e.g., capitalization, order of information, use of italics). And many style guides also provide guidance on more general issues like text formatting, punctuation, and numbers.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
In most cases, your university, department, or instructor will tell you which citation style you need to follow in your writing. If you’re not sure, it’s best to consult your institution’s guidelines or ask someone. If you’re submitting to a journal, they will usually require a specific style.
Sometimes, the choice of citation style may be left up to you. In those cases, you can base your decision on which citation styles are commonly used in your field. Try reading other articles from your discipline to see how they cite their sources, or consult the table below.
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) recommends citing your sources using Chicago author-date style . AAA style doesn’t have its own separate rules. This style is used in the field of anthropology.
APA Style is defined by the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . It was designed for use in psychology, but today it’s widely used across various disciplines, especially in the social sciences.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
The citation style of the American Political Science Association (APSA) is used mainly in the field of political science.
The citation style of the American Sociological Association (ASA) is used primarily in the discipline of sociology.
Chicago author-date
Chicago author-date style is one of the two citation styles presented in the Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition). It’s used mainly in the sciences and social sciences.
The citation style of the Council of Science Editors (CSE) is used in various scientific disciplines. It includes multiple options for citing your sources, including the name-year system.
Harvard style is often used in the field of economics. It is also very widely used across disciplines in UK universities. There are various versions of Harvard style defined by different universities—it’s not a style with one definitive style guide.
Check out Scribbr’s Harvard Reference Generator
MLA style is the official style of the Modern Language Association, defined in the MLA Handbook (9th edition). It’s widely used across various humanities disciplines. Unlike most parenthetical citation styles, it’s author-page rather than author-date.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
The American Chemical Society (ACS) provides guidelines for a citation style using numbers in superscript or italics in the text, corresponding to entries in a numbered reference list at the end. It is used in chemistry.
The American Medical Association ( AMA ) provides guidelines for a numerical citation style using superscript numbers in the text, which correspond to entries in a numbered reference list. It is used in the field of medicine.
CSE style includes multiple options for citing your sources, including the citation-name and citation-sequence systems. Your references are listed alphabetically in the citation-name system; in the citation-sequence system, they appear in the order in which you cited them.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE ) provides guidelines for citing your sources with IEEE in-text citations that consist of numbers enclosed in brackets, corresponding to entries in a numbered reference list. This style is used in various engineering and IT disciplines.
The National Library of Medicine (NLM) citation style is defined in Citing Medicine: The NLM Style Guide for Authors, Editors, and Publishers (2nd edition).
Vancouver style is also used in various medical disciplines. As with Harvard style, a lot of institutions and publications have their own versions of Vancouver—it doesn’t have one fixed style guide.
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It’s widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines.
Chicago notes and bibliography
Chicago notes and bibliography is one of the two citation styles presented in the Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition). It’s used mainly in the humanities.
The Oxford University Standard for the Citation of Legal Authorities ( OSCOLA ) is the main legal citation style in the UK (similar to Bluebook for the US).
There are many different citation styles used across different academic disciplines, but they fall into three basic approaches to citation:
- Parenthetical citations : Including identifying details of the source in parentheses —usually the author’s last name and the publication date, plus a page number if available ( author-date ). The publication date is occasionally omitted ( author-page ).
- Numerical citations: Including a number in brackets or superscript, corresponding to an entry in your numbered reference list.
- Note citations: Including a full citation in a footnote or endnote , which is indicated in the text with a superscript number or symbol.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
A scientific citation style is a system of source citation that is used in scientific disciplines. Some commonly used scientific citation styles are:
- Chicago author-date , CSE , and Harvard , used across various sciences
- ACS , used in chemistry
- AMA , NLM , and Vancouver , used in medicine and related disciplines
- AAA , APA , and ASA , commonly used in the social sciences
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles. Scribbr. Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/citation-styles/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa vs. mla | the key differences in format & citation, the basics of in-text citation | apa & mla examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

The (free) course to get you started
Take the first step towards crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project with our free mini-course .
– 100% free – there’s absolutely no cost to enroll – Easy to understand explanations and examples – Extensive video , audio and text-based content – Free downloadable templates and tools
The Perfect Starting Point
This flexible mini-course is built from a carefully curated selection of our best video and text content. Working through the course content, you’ll learn:
- How to find a high-quality research topic
- How to develop a convincing research proposal
- How to craft a high-quality introduction and literature review
- How to choose a suitable methodology and present your results
- How to polish your dissertation or thesis for the highest marks
You can start wherever makes sense for you, and you can work at your own pace. While you will get the maximum benefit from working through all the content in order, you’re welcome to skip around.
What It Covers
Below you’ll find an overview of the course curriculum. To view more detail, simply click to expand the respective section.
Part 1: Topic Ideation & Proposal
In this section, we lay the foundations for a strong dissertation by exploring the topic ideation and proposal development stages.
- Dissertation 101: What you need to know
- Topic ideation and refinement: 5 time-saving tips
- Research aims, objectives and questions (the golden thread)
- Research proposal 101: What you need to know
- How to write a research proposal
- Common mistakes in the proposal stage
- Research proposal template (Download)
Part 2: Starting Your Dissertation Or Thesis
In this section, we move onto the dissertation/thesis document itself. We consider the broader structure of the document, as well as the first chapter – the introduction.
- How to structure your dissertation or thesis
- Introduction chapter 101 – Why, what and how
- Delimitations and limitations
- Common mistakes in the introduction chapter
- Dissertation/thesis template (Download)
Part 3: Crafting Your Literature Review
In this section, we explore the all-important literature review chapter, as well as the broader literature review process.
- Literature review 101: What you need to know
- How to write a literature review: big-picture process
- How to find high-quality literature (quickly)
- How to review journal articles efficiently
- Literature review Excel template (Download)
- How to structure the literature review chapter
- Literature review chapter template (Download)
- Common mistakes in the literature review
- Tips & tools to fast-track your literature review
Part 4: Designing Your Methodology
In this section, we dive into the complex world of research methodology to demystify this often-intimidating aspect of research.
- Research methodology & design 101
- Qualitative vs quantitative research
- How to choose a research methodology
- Saunder’s research onion: Overview
- How to write the methodology chapter/section
- Sampling methods and strategies
- Qualitative data collection and analysis
- Quantitative data collection and analysis
- How to write the methodology chapter
- Methodology chapter template (Download)
- Common mistakes in the methodology chapter
- Avoiding bias in your research
Part 5: Presenting Your Results
With the methodology out of the way, we move onto the results and discussion chapters in this section. We consider important matters for both qualitative and quantitative projects.
- The results chapter: Qualitative
- The results chapter: Quantitative
- Common mistakes in the results chapter
- The discussion chapter 101: What, why & how
- Common mistakes in the discussion chapter
- Discussion chapter template (Download)
Part 6: Wrapping Up
In this section, we move on to the final chapter in the typical dissertation – the conclusion chapter. We also discuss some other important considerations to help ensure that you present a strong document.
- The conclusion chapter 101: What, why and how
- Research limitations and implications
- Common mistakes in the conclusion chapter
- Conclusion chapter template (Download)
- The abstract 101: What, why and how
- Writing the abstract: 5 common mistakes to avoid
- Defending your dissertation or thesis
- Referencing: How to use Mendeley & Zotero
- Referencing: 7 common mistakes to avoid
Part 7: General Tips & Tools
In this final section, we discuss a mixed bag to help you approach your dissertation/thesis writing in the most efficient way possible.
- Essential apps for the research journey
- Descriptive vs analytical writing
- How to reduce word count
- How to craft strong arguments in your dissertation
- How to choose the right charts and graphs
- Academic misconduct
Join Now (Instant Access)
Enter your details to join the course (100% free)

Frequently Asked Questions
Is this course really free.
Yes. There is no cost to enroll in the course or use any of the course resources. All content is free to access, whenever you need it.
Is there a set schedule for the course?
No. You can complete the course at your own pace and select whichever lessons are most relevant to you.
Does this course involve tests and/or exams?
No. As a flexible mini-course, there are no tests or exams. Please consider our paid courses if you are looking for an assessed course.
Can I get a certificate of completion?
No. Since the mini-course is completely flexible and there are no tests/assessments, we cannot issue a certificate of completion. If you’re looking for a certificate program, please consider our paid courses .
Can I access the templates without doing the course?
Yes. You can access the templates here .
Is this the same as the "Work Smarter Not Harder" ebook?
We unbundled the ebook a few years ago to make the content more accessible and digestible for first-time researchers. This course draws on much of the original content and is far more comprehensive than the ebook.

Need hands-on help?
If you need personalised support for your research project, consider our private coaching service. As your research partner, we’ll hold your hand throughout the research journey, step by step .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
English Mistakes Commonly Made in a Dissertation | Examples
Published on 19 September 2022 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on 11 November 2022.
Students tend to make the same language mistakes over and over again in academic writing . Taking a careful look at these lists of mistakes that we often encounter may help you to break these habits. Avoiding them will set your writing apart and give it a more polished feel.
If you want to make sure your dissertation doesn’t contain any language errors, you could consider using a dissertation editing service .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Spelling mistakes, word choice, capitalisation, conjunctions and linking terms, nouns/noun phrases, prepositions/prepositional phrases, punctuating numbers, quantifiers, terms used in citations, verbs/phrasal verbs, words that are commonly confused.
Although spellcheck features catch many spelling mistakes, they cannot be relied on entirely. These words are still frequently misspelled in many theses.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Following these tips will help you to improve your written academic English in general. The next step is to fine-tune your writing depending on whether you are using American, British, or Australian English ! A grammar checker can also help you automatically fix mistakes you may have missed after proofreading.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Vinz, S. (2022, November 11). English Mistakes Commonly Made in a Dissertation | Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/english-language/common-mistakes-english/
Is this article helpful?
Sarah's academic background includes a Master of Arts in English, a Master of International Affairs degree, and a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science. She loves the challenge of finding the perfect formulation or wording and derives much satisfaction from helping students take their academic writing up a notch.
Other students also liked
What is a pronoun | definition, types & examples, how to tell if a noun is countable or uncountable | examples, what is an adjective | definition, types & examples.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.84(7); 2020 Jul
Manuscript Referencing Errors and Their Impact on Shaping Current Evidence
It is imperative that articles published in reputable peer-reviewed journals provide balanced, fair, objective, and accurate references. However, studies on the accuracy of references in various scientific disciplines demonstrate an error rate of 25%-54%. These errors can range from minor errors in citation accuracy to major errors that alter the original content and meaning of the material referenced. This article discusses importance of citation accuracy, reviews principles of good citation practices, and offers recommendations aimed to decrease citation error rates.
The pharmacy community relies on peer-reviewed articles in clinical and academic journals to maintain current knowledge and remain abreast of changes in specific areas of practice and pedagogy. Trust in the reliability of published literature is essential to a journal’s reputability. Central to substantiating an article’s findings are the introduction and discussion sections, which depend on the accurate review and summary of existing literature to frame new information. The overall expectation is that seasoned academicians and practitioners possess the requisite in-depth knowledge of their field and follow good practices in managing citations that both support and counter their research. However, several studies describe various issues that may arise when citing original research or reviews done by others. 1-3 While academics educate their students in how to properly cite research and reference appropriate sources, citation errors still occur in published manuscripts, even those written by expert researchers.
This is an important although not commonly discussed issue. Improper referencing can affect an individual article’s citation index, thereby exaggerating or diminishing the perceived impact of the authors’ research. This perceived impact can have several vital implications if this metric is used as a criterion for scholarship evaluation in promotion and tenure decisions. Another aspect is that erroneous or inaccurate quotations, if continually repeated, may turn inaccuracies into conventional knowledge. 4 As an example, a 2018 review article published in Environmental Research debated the alleged role of heavy metals, such as mercury, in increasing the risk of autism spectrum disorders. 5 The article cites another article that studied ethical controversies in published literature related to this subject. 6 However, the citation for that article is inaccurate: the numerical information reported in the Environmental Research article differs from that given in the source article. 6 More concerning (and perhaps ironic) is that the cited article was originally published online in 2015 and had been retracted for ethical conflicts and erroneous information in 2017. 7 Nevertheless, it was cited in 2018 review in Environmental Research , thereby propagating potentially invalid and biased information.
As illustrated by this example, referencing errors have serious implications and can affect an author’s reputation. Furthermore, and perhaps more importantly, decisions that have an impact on patient care or the education of future health practitioners are often based on information found in the published literature. The responsibility lies with authors, peer reviewers, and editors to deliver high-quality research articles that are balanced and unbiased, and include a fair evaluation of how the new research findings fit within current knowledge.
Several guidance documents are available to direct proper referencing. The Office of Research Integrity (ORI) within the Department of Health and Human Services provides an excellent education module regarding the ethical principles of proper citations practices. 8 Additionally, in 2002, in her insightful review of common referencing mistakes, Harzing proposed 12 straight-forward guidelines for good citation practices. 1 While her in-depth analysis offers a case study relevant to economics and commerce, these principles are easily applicable to other disciplines, including pharmacy practice and education. A literature search was conducted to identify relevant examples to support these principles. Reflections on some of the most important citation practices with applicable examples from the identified articles are presented below.
When working on a reference list, it is important to cite the correct reference s and provide complete and accurate information for each publication . 1 Several studies on the accuracy of references in various scientific disciplines demonstrate an error rate of 25%-54%. 2,9-11 Errors occur when there is incorrect or missing information, which hinders the identification of the correct reference. With wide use of reference management software applications, such as EndNote, Mendeley, or EasyBib, these types of errors are likely on the decline; however, they cannot be completely eliminated because of the author’s ability to manually enter some sources (such as conference proceedings, for example). Studies that evaluate the impact of these applications on referencing error rates are lacking.
Referring to an incorrect publication may occur when the citation may be accurate, but the intention was to cite a different article (eg, same author, different publication). Care must be taken to avoid this, as the software mentioned above would not be able to identify these types of errors.
Harzing proposed the term empty references 1 for publications that do not contain original research but rather refer to the original research done by other investigators. There are several problems with using empty references, for example, the increased opportunity for the introduction of erroneous information or misinterpretation. Copying references without reviewing the content of the articles and then offering an author’s own evaluation and interpretation of the findings is what Roig considers a “deceptive citation practice.” 8 It is difficult to know when this occurs; however, reader’s confidence is violated if authors summarize and offer their opinion on issues discussed in articles that they have not read. Additionally, using seemingly updated “empty” references with a later publication year can create the illusion of newer data being available even though the cited reference still goes back to the older, original data.
Another important guideline is for an author to use reliable sources when they are considering adding a reference to an article’s citation list. 1 Peer-reviewed articles are a cornerstone of academic publishing. While other sources of information, such as trade journals, newspapers, non-peer-reviewed articles, and media can add to the narrative, using these sources to solely support a research claim is likely not appropriate. An author should also make sure that the references they cited had not been amended or retracted after publication, such as in the mercury example discussed earlier. Several studies indicate that retracted articles remain to be actively cited even after published retraction, with most citing articles including a positive overview of retracted research. 12-16
Using very specific data and extrapolating the data to conditions or populations not studied leads to irrelevant interpretation and unintended, incorrect implications, violating the “using generalizable sources for generalized statements ” principle. 1 This also applies when using a small number of studies or studies of limited scope to imply generalizable conclusions.
Incorrect interpretation of the objectives, results, or implications of the referenced study is perhaps the most detrimental type of referencing error. 1 The ORI guidelines caution against using resources that are not thoroughly understood. 8 When scientists across various disciplines were asked how well they knew the content of the references they cited in their research papers, 40% reported that they knew them only “slightly well” or “not well at all.” Additionally, scientists admitted being influenced by a referenced paper’s citation index, being less familiar with the details of prominent papers than with less well-cited papers. This finding demonstrates that authors sometimes rely on a citation index, which can serve as a proxy for a papers’ reputation, more than they rely on their own review and evaluation of the article (preliminary data). 17
In their study of the accuracy of quotations and references in medical journals, de Lacey and colleagues found a 15% misquotation rate, 4 a statistic that was confirmed by a more recent study by Mogull. 3 The significance of these misquotes ranged from “trivial” to “seriously misleading,” with all six highly regarded journals included in this analysis having published from two to five seriously misleading quotations in 50 randomly selected articles. 4 Similar rates of misinterpreted citations were reported in a study examining citations of review articles in the ecology journals. 18
The problem of incorrect interpretation of the objectives, results, or implications published in a referenced study affects all journals, even the most reputable. In fact, while the intent of this article is not to evaluate misleading quotations in AJPE, this author’s own work was misquoted in several articles that were recently published in the Journal . 19,20 Comparing one’s study with the findings from other studies that had significantly different objectives would result in misinterpretation of the content of the referenced articles.
Citing contemporary references 1 is especially important in the field of healthcare, where advancements are fast-paced and the need to stay on top of the latest developments is self-evident. Of course, there are some landmark studies that may still be appropriate to cite. However, as mentioned before, using “empty” references to make a references list appear current is a discouraged practice.
Foregoing impartiality towards journals with high impact factor s is another principle of good referencing practice. 1 Recognizing an author’s biases is important in addressing them, and the perceived contribution of the study to the field is one of the common biases. One study found that researchers’ perception of a study’s validity, significance, and generalizability were significantly influenced by its citation index. 17
Finally , presenting balanced information, including potentially conflicting evidence or counter-evidence , 1 enriches the article and provides fair “food for thought” for readers. Searching for articles including the ones that support and others that contradict study findings should generate rich discussion points and provide objective points of view, considering all available evidence on the matter.
Recommendations
These recommendations to improve citation practices are directed at both authors and journals. 2 All authors (not just primary or corresponding authors) should review and approve all references; statements should be checked against the source manuscripts, and empty references should not be used. 2,21,22 To avoid incorrect implications, references should be cited next to the statement they support rather than grouped together at the end of the sentence or paragraph. Simultaneously, journal should require authors to provide an affidavit at the time of manuscript submission confirming that all references have been checked against the original works, along with full-text copies of all cited articles. 2,23
Journals should consider limiting the number of references permitted for various manuscript types. This will guide authors to select only the best references to support their statements, and give them more manageable ownership of their citations. 2,21,23 During the manuscript review process, editors and peer reviewers should conduct a random reference check to ensure citation accuracy. 24-26 The editorial office should convey to the authors that references will be evaluated and that accuracy is expected before a manuscript can be accepted for publication.
In summary, it is important to provide balanced, fair, objective, and accurate references that support research paper findings. Overlooking the principles of good practices in referencing can lead to disseminating incorrect information, inappropriately diminishing or exaggerating the author’s contributions to the field, and/or developing practices that, while being based on academic literature, are not based on good science.
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

9 Common Citation Mistakes in Academic Studies
Being a proofreading and editing service provider, we often find researchers making common citation mistakes in their research papers. Well, making mistakes is normal, but repeating the same mistakes is not accepted. Recognizing the gravity of the situation, we here bring the list of common errors students and researchers make while citing sources.
This guide discusses the most common citation mistakes in academic studies. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
The study in any academic field is about authenticity. The reliability of information is the essence of any academic paper. Whether you are writing a research paper or an essay, keeping the information authentic enhances the acceptance of your article in any scholarly journal. One of the best ways to enhance the authenticity of your research paper is proper citation. Citation is the backbone of any academic writing process and strengthens the reliability of information used in a scholarly paper.
Being a proofreading and editing service provider, we often find researchers making common citation mistakes in their research papers. Well, making mistakes is normal, but repeating the same mistakes is not accepted. Recognizing the gravity of the situation, we here bring the list of common errors students or researchers make while citing sources.
1. Failing to build a correlation between citation and reference list
Understanding the contrast between citation and referencing is important. Citation can be used in the entire body of the research paper. However, the reference list is added at the end of the paper. However, researchers often make mistakes by removing some parts of references from the end, or sometimes, they attach more sources just to make the reference list lengthy. Take note that any reference or citation you use should complement each other. Failing to build a correlation between citation and reference refers to entire mismanagement in this part.
2. Making mistakes while inserting page numbers
When a student is quoting any information from somewhere, it is essential to put the page numbers in the bracket. Recording the page number in order helps researchers organize any information systematically. Suppose a reviewer wants to check the information or quotation you have mentioned; page numbers will help them to do so. Researchers or students should always keep their ground clear.
3. Using outdated or wrong information
Any information that might be true 20–30 years ago may not be appropriate for today’s society. The world is evolving every day. Therefore, the information gets updated regularly. Therefore, when a researcher is citing information, he or she must ensure that the information is recent, authentic, and relevant. We often notice that people cite from Wikipedia, but it can’t be considered a trusted source. Rather, you can use trusted databases such as Google Scholar , ScienceOpen , DOAJ . However, ensure that information is not outdated.
· 10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
· Top 5 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Academics
4. Not citing in alphabetical order
Citation used in an academic research paper must be put in alphabetical order. The reference list used at the end of your paper must be alphabetized like the citation used in the body. However, the condition may vary in the case of different referencing styles but using alphabetical order remains intact.
5. Merging different citation styles
In academic writing, there are different referencing styles such as Harvard, MLA, Chicago, APA . Every referencing style possesses its set of rules. Suppose your university specifically directs you to use MLA referencing style , your entire paper, including citations and references, should follow the MLA format. However, researchers often make common mistakes by mixing up two different styles that lead to complete mismanagement. Therefore, it is always a wise decision to get the entire paper checked by expert editors.
· Citation Styles | Which Citation Style Should I Use?
· Importance of Academic Referencing and Citing
· How to Cite Sources in APA Referencing Style | With APA 7th Edition Update
· APA Manual 7th Edition: The 9 Most Important Changes

6. Improper punctuation
In the previous paragraph, we have mentioned why it is necessary to use the right citation styles. However, the same goes for punctuation. Any errors in placing punctuation may violate the citation guidelines. Many examiners are strict about the use of punctuation marks. In this case, a professional proofreader can help you rectify any punctuation errors. Click here to see the most common punctuation errors in academic writing.
7. Making mistakes while using et al.
In academic writing, et al . is used to limit the usage of names of the multiple authors. Suppose an article or book is written by six authors, using all the names does not look good and moreover, it consumes more space. Therefore, if the numbers of authors exceed two, et al. needs to be used. However, the use of et al. may vary in different referencing styles. Make sure to follow the guidelines of the particular referencing styles instructed by the university or your target journal.
For instance, in APA style, for a source with three or more authors, list the first author’s last name and “et al.” for all citations, including the first citation. Note that this rule has changed from APA 6th Edition guidelines on using “et al.” which recommend listing all author names in the first citation up to five authors but then using “et al.” for the second and subsequent citations.
8. Lack of reference where it requires
Many parts of the academic essay or article require references. For example, suppose you are talking about a particular statement, you can’t leave the phrase like “According to the study…” or “Research proves...” without clarifying the ‘‘Studies’’ or ‘‘Research.’’ In such cases, please give proper references to justify the studies or research.
9. Avoiding experts’ assistance in proofreading and editing
Many students and researchers ignore this part, and as a result, they have to face rejection or poor grades. Gathering authentic information from scholarly journals and citing the information is a hectic job. Moreover, researchers need to make the right use of punctuation, proper referencing and citation style, and even grammar. In this case, consulting experienced proofreading and editing service like Best Edit & Proof can help you get an error-free academic paper from every aspect, including citation and referencing.
Do you need an expert to review and edit your manuscript?
Have you completed writing your manuscript? Do you want someone to review the entire article and make necessary changes if required? If yes, we bring the most trusted and efficient editing and proofreading services near you. At Best Edit & Proof, our experts will edit and proofread your papers to make necessary changes.
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering manuscripts with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized styles of writing. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English manuscript formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Kindly visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
If you need support for editing and proofreading services, contact us . You can also e-mail us or use the 24/7 live chat module to get direct support. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript. Alternatively, you can text us through our WhatsApp business support line.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
Do you like this article? Make sure to share and subscribe!
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Avoid Anthropomorphism in Your Dissertation?
How to Write a Research Methodology Section for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Theoretical Framework for a Dissertation and Thesis?
How to Write Literature Review for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Dissertation and Thesis Introduction
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Research databases are the foundation of any dissertation or research paper. Scanning through previous findings and research is a key factor while compiling your research proposal or a thesis. Here we discuss the top 5 free online journal and research databases for academics.

A good part of any research depends on the right questions asked. If you are asking wrong questions, your entire research may go off track. Therefore, understanding what questions you need to ask is essential for your research. If you are on the way to your research but don’t know how to start framing the right research questions, we have just the right information for you. This article discusses the process of formulating research questions.

Blog writing is an effective way to share your knowledge and ideas with your target group. Here you can dive deep and talk about your favorite topics, showcase your expertise and attract an audience or readers interested in your work. However, creating a perfect blog post can sometimes get overwhelming – from choosing the right topics to selecting the proper format for your articles to picking images that generate interest and engagement, it's no less than a task.

The first chapter of your thesis or dissertation includes the introduction. You should provide the reader with a solid start. Next is staging your research with an apparent focus, objective, and direction.

The central tendency, mean, median, and mode depict where most data points concentrate, while variability illustrates how far they are. It is exceedingly crucial because the amount of variability demonstrates the generalization one can make from the sample to the population. Low variability is desirable because it implies that predicting information about the population using sample data is well-justified. Contrarily, high variability illustrates decreased consistency, making data predictions harder.

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Common Mistakes in Academic Writing & How to Avoid Them
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Academic writing, while demanding, can be mastered with a good grasp of language rules and careful attention to common pitfalls. Mistakes ranging from structuring, style, to grammatical errors can distract from your argument and undermine the credibility of your work. Most of these common mistakes are avoidable, so it’s important to know which mistakes you’re likely to make. Explore our guide to transform these challenges into opportunities for improvement in your academic writing.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Common Mistakes – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Common mistakes
- 3 Common mistakes: British vs. American English
- 4 Common mistakes: Citation terms
- 5 Common mistakes: Quantifiers
- 6 Common mistakes: Nouns & plurals
- 7 Common mistakes: Punctuating numbers and dates
- 8 Common mistakes: Adjectives
- 9 Common mistakes: Verbs/phrasal verbs
- 10 Common mistakes: Words that are mixed up
- 11 Common mistakes: Conjunctions and prepositions
Common Mistakes – In a Nutshell
- There are many common mistakes in writing.
- Researchers can use British or American English in their work, although it must be consistent throughout.
- Students should ensure their work is free from any mistakes before submitting their work.
Definition: Common mistakes
Common mistakes are errors in academic writing that most students fail to notice in their research. There are different common mistakes ranging from inappropriate punctuation to improper sentence structure and more. Proofreading and editing your work is essential to correct language mistakes and other errors, as they can give you a lower score even if your research is well-structured.

Common mistakes: British vs. American English
British English and American English are the main languages used in academic writing by students and researchers. However, some words are spelled differently, and students should use the instructed language in their work to avoid common mistakes in language use.
Common mistakes: Citation terms
Terms used in a citation, including et al. are commonly miswritten as Et al or Et all. For example:
✘ The spread of the bubonic plague was largely influenced by trade and immigration (Gretel et all. , 1976)
✘ The spread of the bubonic plague was largely influenced by trade and immigration (Gretel et. al. , 1976)
✓ The spread of the bubonic plague was largely influenced by trade and immigration (Gretel et al. , 1976)
Common mistakes: Quantifiers
Common mistakes: nouns & plurals.
Some common mistakes in noun plurals include:
Common mistakes: Punctuating numbers and dates
Using commas correctly ensures proper punctuation of numbers, as follows:
Common mistakes: Adjectives
Students also make some common mistakes when using adjectives correctly. For instance:
Common mistakes: Verbs/phrasal verbs
Some common mistakes include:
Common mistakes: Words that are mixed up
It is common for students to mix up certain words, especially those that have similar pronunciations, such as:
- Effect – noun
- Affect – verb
The effect of the pandemic was widespread, it affected many people in the world.
- Personnel – noun
- Personal – adjective
The school’s personnel like to keep their personal items in their cars.
- Principal – adjective
- Principle – noun
The principal theme of the study draws on principles defined in the main source.
- Were – verb
- Where – adjective
They were found in the park where they like to play.
- Bear – verb
- Bare – adjective
The axle bears the load on a bare surface.
Common mistakes: Conjunctions and prepositions
Conjunctions and prepositions are used frequently in academic writing. Some common mistakes include the following:
What are the common mistakes in academic writing?
The most common mistakes in writing are grammatical errors from incorrect punctuation, spelling, and word groups. They also include misuse of phrases and confusing similar words.
How can you avoid common mistakes in your written work?
Proofreading and revising is the best way to find errors. Also, confirm the correct forms of words and spellings before using them.
What is the difference between American and British English?
There are different spellings for certain words in these forms of writing. For instance, the use of “s” and “z” may vary, such as analyse and analyze.
How do you punctuate numbers correctly?
Use a comma in the right place to show a number correctly. For instance 10,000 not 10.000.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
David and Ruth discuss how to handle references and citations in your dissertation or thesis. They explain 7 of the most commonly made mistakes in terms of r...
Referencing mistake in masters dissertation [duplicate] Closed 3 years ago. I handed in my masters dissertation a few weeks ago and I've now discovered a referencing mistake in my literature review. A medical publication I'd been citing has had a number of updates over the years and instead of citing the earlier year (2009) I've cited 2018.
Sources with multiple authors in the reference list. As with in-text citations, up to three authors should be listed; when there are four or more, list only the first author followed by ' et al. ': Number of authors. Reference example. 1 author. Davis, V. (2019) …. 2 authors. Davis, V. and Barrett, M. (2019) …. 3 authors.
A dissertation or thesis is considered published when it is available from a database such as ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global or PDQT Open, an institutional repository, or an archive. Include the description "Doctoral dissertation" or "Master's thesis" followed by a comma and the name of the institution that awarded the degree.
Tips for Avoiding Common Mistakes When Referencing a Thesis in Harvard Style 1. Citing the Author . When referencing a thesis in Harvard style, citing the work's author is important. It can be done by including the author's last name and the year of publication in parentheses after the quote or paraphrase. For example: (Smith, 2020). 2. Citing ...
To cite an unpublished dissertation (one you got directly from the author or university in print form), add "Unpublished" to the bracketed description, and list the university at the end of the reference, outside the square brackets. APA format. Author last name, Initials. ( Year ).
Citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database. If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It's similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences: Structure: Author's last name, F. M. (Year published).
APA Only • $9.95. Powered by advanced machine learning technology. Fix issues yourself with the help of automatically generated solutions. Receive your citation report within a few minutes. In-text citations and detects missing references. Access to helpful articles and videos about citing sources.
In Harvard, the following reference list entry format is used for the dissertation: Author Surname, Author Initials. (Year Published). Title of the dissertation in italics. Level. Institution Name. For example, reference list entry for the above source would be: Darius, H. (2014).
References are an important part of your dissertation, and you may need anywhere between 20 and 200 references, possibly more depending on the length of your thesis. But it is important that you reference appropriately and correctly, whether this is in the in-text citations or the list of references at the end of your thesis.
Using reference in a dissertation that belong to the past five to ten years are acceptable; however, using references of the 1980s or 1990s is not recommended. The main reason being changes in time, settings, environment, participants, etc. All these factors contribute a lot towards accurate conclusions, thus they are regarded as essential when ...
Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis: List whether it is a dissertation or a thesis. University: List the university associated with the dissertation/thesis. ... APA calls for the citation to include a unique identifying number for the dissertation, labeling it "Publication No." That number can be found in Dissertations and Theses database ...
4. Double-Check Citations for Accuracy: Before finalizing your dissertation, double-check all citations for accuracy and consistency.Verify that each citation includes all required information ...
Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles. Published on June 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on November 7, 2022. A citation style is a set of guidelines on how to cite sources in your academic writing.You always need a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize a source to avoid plagiarism.How you present these citations depends on the style you follow.
Published dissertation or thesis references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.6 and the Concise Guide Section 10.5. This guidance has been revised from the 6th edition. Date created: February 2020. Cite This Webpage. This page contains reference examples for published dissertations or ...
Step #2: Avoid common citation mistakes by selecting the appropriate citation style for your document. ... If you are writing a thesis, your university might actually have a guideline and requirement to use a specific referencing style. The same applies to academic journals. Please do check the guidelines for authors because they usually ...
Defending your dissertation or thesis; Referencing: How to use Mendeley & Zotero; Referencing: 7 common mistakes to avoid; Part 7: General Tips & Tools. In this final section, we discuss a mixed bag to help you approach your dissertation/thesis writing in the most efficient way possible.
The majority of failed Ph.D. dissertations are sloppily presented. They contain typos, grammatical mistakes, referencing errors and inconsistencies in presentation. Looking at some committee reports randomly, I note the following comments: "The thesis is poorly written.". "That previous section is long, badly written and lacks structure.".
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the 'Cite this Scribbr article' button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator. Vinz, S. (2022, November 11). English Mistakes Commonly Made in a Dissertation | Examples. Scribbr.
As illustrated by this example, referencing errors have serious implications and can affect an author's reputation. Furthermore, and perhaps more importantly, decisions that have an impact on patient care or the education of future health practitioners are often based on information found in the published literature. The responsibility lies ...
25. Generally no official action can or should be taken regarding errors in a dissertation (assuming they are not a sign of dishonesty or fraud). However, it could be worth pointing out errors to the author in case he/she is preparing a publication based on the dissertation. I wouldn't do this if it's from long ago or you see that the material ...
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, we here bring the list of common errors students or researchers make while citing sources. 1. Failing to build a correlation between citation and reference list. Understanding the contrast between citation and referencing is important. Citation can be used in the entire body of the research paper.
Common mistakes: Citation terms. Terms used in a citation, including et al. are commonly miswritten as Et al or Et all. For example: The spread of the bubonic plague was largely influenced by trade and immigration (Gretel et all., 1976) The spread of the bubonic plague was largely influenced by trade and immigration (Gretel et. al., 1976)
The reference to form instructions is not removed in 8 CFR(c)(7), on page 6391, first column, because the CNMI education funding fee will be included in the form instructions for Form I-129CW. ... This document corrects technical and typographic errors in the preamble (including tables) and regulatory text, but does not make substantive ...