- Information for: Future Student Current Student Graduate Student Faculty/Staff Alumni and Donors
- Life at WOU

College of Education
Home » Academics title_li= Alumni & Students title_li= Early Childhood title_li= Education & Leadership » Early childhood studies senior class of 2020 present diverse capstone projects
Early childhood studies senior class of 2020 present diverse capstone projects
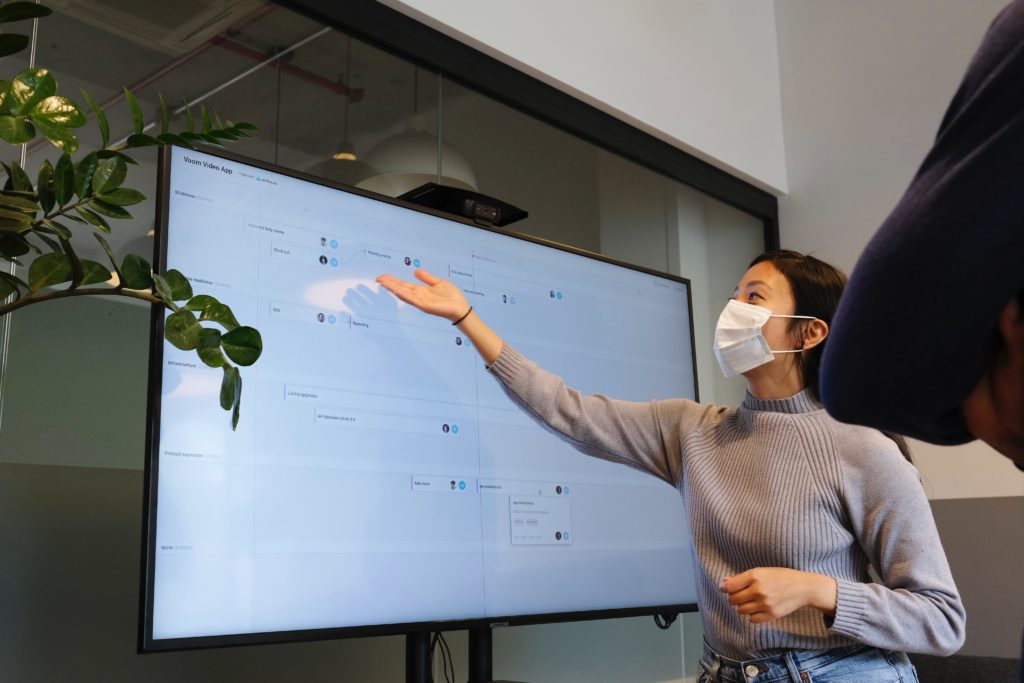
Exam week of Spring 2020 was bittersweet for the early childhood studies senior cohort. After working on their capstone projects for three terms and persisting through a challenging Spring term at home, they presented their capstone work in a Zoom gathering with faculty, peers, family, and friends.
There were wishes to be together in person as well as calls for social justice in early education. But as soon as the presentations began, it was clear that hope was present as the graduating class of Early Childhood Studies demonstrated the readiness to face the challenges that lay ahead.
The Early Childhood Studies Class of 2020
Breanna beebe, andrea trujillo, faith van putten, mary mahoney, cara o’brien, christina carney, brianna lundgren.
The students’ projects range from developing a training for trauma-informed care to a teaching portfolio from a toddler classroom. These deliverables were as diverse as the topics spanning integrated inclusive classrooms to drawing as a form of early compositional writing.
Early childhood studies seniors complete a capstone project as the culminating assignment for their degree. The capstone project empowers students to select their own topic and project outcome based on their interests.
Some of the 2020 Seniors were inspired by their placements.
Cara O’Brien presented “Positive Impacts of Teen Parent Programs on Young Families: The Perspective of Parents” after doing her clinical placement in the Salem-Keizer Teen Parent infant/toddler classroom and working closely with teen parents to form supportive home-school connections.
Brianna Lundgren chose to write a research article drawing on the most recent literature and her personal experiences working in a residential setting for young children’s mental health entitled, “Trauma-Informed Care In Early Childhood.”
Other students became curious about a topic based on an interaction that occurred in their placement but required focused research and reflection to unpack. This is an incredible opportunity for seniors to deepen their commitment to and expertise in a particular topic in early childhood (birth to age 8).
The Zoom presentations closed with a quote from Martin Luther King Jr. “Take the first step in faith. You don’t have to see the whole staircase, just take the first step.”
These capstone presentations mark the end of our students’ preparation and the start of a new chapter in their journey as lifelong learners. We trust that the variety displayed in areas of interests represent the unique strengths they bring to the field of early childhood education.
Congratulations to the Early Childhood Studies Class of 2020 and to all Western Oregon University 2020 graduates!

Western Oregon University Recipient of Prestigious Award
The coe mathematics department receives a new grant.

Welcome New Faculty Member Dr. Annie Delbridge
- Alumni & Students
- Bilingual Teacher Scholars
- Community Health
- Deaf Studies & Professional Studies
- Early Childhood
- Education & Leadership
- Exercise Science
- Faculty & Staff
- Health & Exercise Science
- Teacher Licensure
- Uncategorized
Richard Woodcock Education Center
Phone: (503) 838-8471
Email: [email protected]
ACADEMIC DIVISIONS
Offices and centers.
- Dean’s Office
- Office of Justice, Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Office of Clinical Practice & Licensure
- Office of Assessment & Data Management
- Center for the Advancement of Paraprofessionals
- Research and Resource Center with Deaf* Communities
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

WESTERN OREGON UNIVERSITY 345 Monmouth Ave. N. Monmouth OR 97361
503-838-8000 | 1-877-877-1593
Campus Maps Canvas Find People Portal WOU Email Technical Support
A-Z Index Accessibility Academic Calendar Class Schedule Jobs at WOU Partnerships Student Services
Western Oregon University’s Land Acknowledgement Western Oregon University in Monmouth, OR is located within the traditional homelands of the Luckiamute Band of Kalapuya. Following the Willamette Valley Treaty of 1855 (Kalapuya etc. Treaty), Kalapuya people were forcibly removed to reservations in Western Oregon. Today, living descendants of these people are a part of the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde Community of Oregon and the Confederated Tribes of the Siletz Indians .
Accessibility Public Records Privacy Student Consumer Information
WOU prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, color, sex, national or ethnic origin, age, religion, marital status, disability, veteran status, sexual orientation, gender identity, and gender expression in all programs, activities and employment practices as required by Title IX, other applicable laws, and policies. Retaliation is prohibited by WOU.

- Spanish – español
Project Examples
By sharing documentation of their experiences implementing the Project Approach, Illinois teachers can help each other learn new strategies and ideas for implementation.
Educators are invited to submit simple documentation of project work from their classrooms. Check out our Guidelines for Submitting a Project to IEL for suggestions on how to submit a project example. Once you’ve submitted a project, IEL staff will help edit and publish your project.
Once you’ve decided to submit project example, contact our project director, Emily Dorsey, via email – [email protected] , to let us know your submission is ready. We will create a Box folder for you and give you instructions on uploading your materials. Please note that due to the higher volume of project submissions, not all projects will be published on the website. If your project is selected, IEL staff will help edit and publish your project.
Browse our Project Examples Table . It organizes projects according to the type of classroom setting where they were completed.

Here a Chick, There a Chick!

The Car Project

The Teeth Project

A Community Service Project

The Beach Project

The Bat Project

The Cleaning Project

The Baby Project

Pasta, Pasta!

Farm Implements: Learning About Tractors and Combines

Recipes for Learning: A Baking Project

The Squirrel Project

Voting Project

Carson’s Fishing Project

The Sharing Pizza Project

The Baking Project

“Where Does the Water Go?” Investigating Pipes and Plumbing

The Pizza Project: A Delicious Learning Opportunity

The Pumpkin Project

The Tractor Project: Noisy Neighbors Lead to Investigation

Discovering the World of Insects on the Playground

How Do People Celebrate Birthdays?

Garden Project Sprouts From Simple Question: “What’s That?”

The Worm Project

The Combine Project: Using a Museum Experience to Enrich Project Work

The Tamale Project

Cooking with Spinach

Tools People Use

The Cow Project

Up Up and Away: The Airplane Project

One Fish, Two Fish, Red Fish…NEW Fish: A Preschool Fish Project

Cracks and Holes Project

The House Project

The Music Project

The Horse Project
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer

Center for Engaged Learning
Capstone experiences.

Capstone experiences aim to facilitate students’ sense-making of their growth and development across their major or general educational studies and have been a hallmark of undergraduate education in one form or another for at least as long as higher education has existed in the United States (Levine 1998). Historically, capstone experiences took the form of a culminating examination, testing a student’s accumulated knowledge. In the 1800s, a seminar model emerged, often taught by the college president (Levine 1998). Beginning in the early 1900s, course-based capstone experiences became a final opportunity to instill university values and reinforce learning (Kinzie 2013). They continue to be integrative and transformative learning experiences that mark the transitional nature of the final year (Kinzie 2013; Levine 1998).
Capstone experiences can take the form of:
- A problem-based learning experience in which students work to apply their knowledge in a discipline to a problem (e.g., Brooks, Benton-Kupper, and Slayton 2004; Butler et al. 2017; Dunlap 2005).
- An undergraduate research experience sometimes but not always structured as the writing of a thesis (e.g., Julien et al. 2012; Nelson-Hurwitz and Tagorda 2015; Upson-Saia 2013).
- A service-learning or community-based learning approach in which students work with community members to put into action the skills and knowledge they acquired over their college career (e.g., Collier 2000; Nelson-Hurwitz and Tagorda 2015).
- A collaborative learning approach in which students tackle problems and apply their learning in groups, simultaneously navigating interpersonal challenges and learning from one another (e.g., Brooks et al. 2004; Collier 2000; Julien et al. 2012; Upson-Saia 2013).
Capstone experiences may even be developed as some combination of the above practices.
Even within a single university, the range of practice in capstones can be significant, and for good reason. Capstone experiences may occur as the culmination of a disciplinary major or mark the integration of interdisciplinary learning across a core curriculum. In either case, there is no universal way students might synthesize and apply their learning. In a study across capstone experiences at University of La Verne, Peggy Redman (2013) shares some examples:

The marketing student may identify growth through the complexities of developing a marketing plan in partnership with a local business or nonprofit organization. The education student sees learning in the development of a unit including lessons that cut across many disciplines, preparing him or her for the multiple-subject classroom.

A student in psychology completes a senior project that takes the student and faculty member to a conference where they are major presenters. All of these pathways can be part of the capstone, a critical force in integrating classroom learning and practical application. (Heading 6, par. 1)
Back to Top
What makes it a high-impact practice?
Capstone experiences are designed to “provide students a host of opportunities to be engaged in educationally purposeful practice” (Kinzie 2013). Much of that design incorporates the qualities Kuh, O’Donnell, and Schneider (2017) specify as essential elements of High Impact Practices (HIPs). The following section reviews these elements in the specific context of capstone experiences.
Performance expectations set at appropriately high levels . Strong capstone experiences recognize the deep learning students have done over time and continue to challenge students in their application of those skills and sets of knowledge. One example of this is Julien et al.’s (2012) assessment of capstone courses in which students participated in “authentic research experiences” in advanced physiology so as to be prepared for future study or work in health sciences.
Significant investment of concentrated effort by students over an extended period of time. The semester-long class can harness this element of HIPs by structuring students’ development of a common goal or focus over the entire course. Projects in which students develop and conduct their own research are good examples of this. But extended capstone structures that carry over multiple semesters or even years (Nelson-Hurwitz and Tagorda 2015; Rash and Weld 2013; Redman 2013) could potentially be even more impactful for students.

Interactions with faculty and peers about substantive matters. Many of the examples of capstones involve collaborative learning among students (e.g., Brooks et al. 2004; Julien et al. 2012). It is worth noting the significance of student-faculty interactions within capstones as well. The most successful capstones embrace this key opportunity for students and faculty to reshape their relationship by “reframing the faculty–student relationship such that faculty become mentors, and students are both comfortable with coaching and highly motivated as they take on primary responsibility for their work” (Paris and Ferren 2013, Heading 2, par. 1; see also Rash and Weld 2013). Research suggests the relationships developed in college, especially with faculty, are one of the most significant and potentially transformative elements of higher education (Felten et al. 2016).
Experiences with diversity; wherein students are exposed to and must contend with people and circumstances that differ from those with which the students are familiar. Many capstones involve some kind of service-learning, community-based learning, or internship experience (Butler et al. 2017; Collier 2000; Nelson-Hurwitz and Tagorda 2015). These are not only grounded opportunities to apply learning, but they are also often good opportunities for students to interact in meaningful ways across difference. Even capstones with collaborative learning without this experiential component show evidence of improving students’ interpersonal skills (Brooks et al. 2004), which may be connected with students working in diverse groups.
Opportunities to discover relevance of learning to real-world applications. This feature is most apparent in capstone experiences that involve service-learning, community-based learning, or internship experiences (Butler et al. 2017; Collier 2000; Nelson-Hurwitz and Tagorda 2015). The relevance of learning to real-world applications can also come in carefully structured undergraduate research experiences. Brooks et al. (2004) in particular found that capstones structured as student-led multi-disciplinary team projects were especially well equipped to help students bridge their personal, professional, and public worlds.
Public demonstration of competence. Several capstone experience examples include oral presentation components (e.g., Brooks et al. 2004), and Redman gives one example of a student who shares research with her professor as a major conference (2013). Half of the thesis examples in Upson-Saia’s (2013) study require some kind of public presentation or defense. However, an in-class presentation is very different from contributing to a disciplinary conference. It is unclear from this research how significant a public demonstration needs to be to have a positive impact on a student. It would also be worth exploring the impact of this practice in capstones that offer more creative or flexible forms of public demonstration of confidence, such as curating a gallery, leading a teach-in, or performing creatively.
Periodic, structured opportunities to reflect and integrate learning . There are multiple examples that explicitly highlight reflection and reflective activities or projects as a key element of the capstone experience (e.g., Brooks et al. 2004; Butler et al. 2017; and Redman 2013). Reflection provides an opportunity to synthesize and, as in one example, ask the key questions: “Who am I?, How can I know?, and What should I do?” (Brooks et al. 2004, 283). However, reflection must be intentionally facilitated, rather than assumed as a natural element of capstones. The examples that best showed students making gains in their reflective learning were those like Brooks et al. (2004) that included reflection as a driving goal of the capstone course.
Research-Informed Practices
Upson-Saia (2013, 12-15) offers three overarching suggestions for the development of capstones:
- Think locally
- Think holistically
- Reassess periodically
While her recommendations were written following study of discipline-specific capstone experiences (in her case, in religious studies), they are broad enough to be both relevant and highly applicable to interdisciplinary capstones as well.
Think Locally: Upson-Saia (2013) describes the first recommendation as a reminder that capstones should be context specific. In the case of disciplinary capstones, this means the capstone should be tightly woven with departmental missions. Even for interdisciplinary capstones, focusing on just one culminating goal will give the capstone direction and focus (2013). A backwards approach to design, keeping one top priority in mind for what students will accomplish or take away from the experience, will help the experience be most impactful for students. Lee and Loton’s (2017) study of capstone purposes across disciplines may help those designing capstones prioritize goals. This focused and context-specific approach to design can help reign in the overwhelming possibilities as well as reinforce courses and projects that feature a significant investment of effort by students over an extended period of time (Kuh et al. 2017).
Think holistically: This recommendation addresses the institutional factors that will make or break capstones. With the number of features HIPs need to include, and the goals some researchers have suggested of shifting the role of teaching to mentoring (Paris and Ferren 2013; Rash and Weld 2013), instructors have a difficult job facilitating successful capstone courses. Several researchers emphasize that the time and resources required are substantial, and they suggest administrators acknowledge and support faculty in this work (Lee and Loton 2017; Upson-Saia 2013). In addition, Lee and Loton (2017) describe capstones as “high risk activities” due to the high expectations both students and faculty place on these experiences. These expectations make administrative support imperative, but it also means that if an instructor wishes to deviate their capstone structure from the institutional norm, they will need to offer substantial justification due to the existing pressure on these courses and projects.
Reassess periodically: Upson-Saia reminds us that because there is such a wide variety of possibilities, the form of capstone an instructor settles on may not remain appropriate as departmental cultures, curricular structures, and students all change and evolve over time. She describes the special topics seminar form of some capstones in her study as minimally different from other upper-level courses in the department and a holdover from the senior seminars of the 1800s (Upson-Saia 2013) and questions whether that model is still the most appropriate way to culminate a student’s experience. It is worth checking in and evaluating the efficacy of a program or project no matter what. Brooks et al. (2004) offer a helpful example of how to assess a capstone experience; they found that while their capstone did not meet some goals they assumed it would, it was successful in a number of other areas and did broader curricular work for the department that was otherwise missing. Without pausing to assess their program, they would not have understood whether its form was successful for their departmental goals.
Embedded and Emerging Questions for Research, Practice, and Theory
Several characteristics of high impact practices need to be researched more deeply in the context of capstone experiences, including in particular: interaction with faculty and peers about substantive matters, public demonstration of competence, and frequent and timely feedback. Recent research has revealed the mentored relationship to be one of the most impactful of a student’s undergraduate experience (Lambert, Husser, and Felten 2018). Writings on capstones recommend spending time developing these mentored relationships in the capstone, but few explore the particular impact of relationship and mentorship in capstone experiences. Future research on this topic could contribute enormously to scholarly conversations about course-embedded mentorship and relationship building. Current research doesn’t specify how public demonstration of competence need be to make a capstone high impact. It would be worth exploring, for example, the impact of the demonstration of competence in capstones which have more creative forms such as curating a gallery, leading a teach-in, or performing creatively. Finally, frequent, timely, and constructive feedback—a key element of high impact practices—remains unexplored in the context of capstones and could make a valuable new direction for research.
Like the qualities of high impact practices, writing about the benefits of capstones often doesn’t do enough to highlight the unique impacts of the qualities of capstones. Research on capstones highlighting their benefits often center on elements of capstones that are other HIPs—such as collaborative learning, problem-based learning, service- or community-based learning, or undergraduate research. This practice makes distinguishing the benefits of capstones from the known benefits associated with these other HIPs nearly impossible. And this challenge raises an important question: would a capstone without these elements be equally successful in promoting deep and engaged learning?
While capstones share admirable goals and purposes, it has been more difficult to tell how much they are actually meeting those goals. Some interesting analysis of capstones has emerged of late that found that capstones were a significant positive predictor for only one element of liberal learning (“need for cognition”—or one’s propensity to engage in lifelong learning) and in fact was a significant negative predictor for critical thinking (Kilgo et al. 2015). The authors of this study specify that more research on capstones is needed, but a previous 2004 case study found similar results (Brooks et al. 2004). In Brooks, Benton-Kupper, and Slayton’s (2004) assessment of a university (interdisciplinary) capstone, they were surprised to find that though they expected the university capstone to significantly support students’ critical thinking development, “the students did not identify the course as meeting those common threads of the University’s goals to a great or moderate degree” (Brooks et al. 2004, 281). Instead, students who took a discipline-specific capstone reported higher levels of critical thinking development. Both of these studies noted a number of other strong benefits to capstones—so it may be that in conjunction with the other coursework students engage in, they do not need to have a strong critical thinking focus. It is also possible that capstones that look different from these—perhaps those with more of an undergraduate research focus—may do a better job developing this skill. More research is needed in this area to make sense of these findings.
Key Scholarship
Butler, Des, Sandra Coe, Rachael Field, Judith McNamara, Sally Kift, and Catherine Brown. 2017. “Embodying Life-Long Learning: Transition and Capstone Experiences.” Oxford Review of Education 43 (2): 194-208. https://doi.org/10.1080/03054985.2016.1270199 .
About this Journal Article:
This case study describes the first of six principles , which informed the development of a capstone design for Australian legal education, and according to the authors, should inform the development of any capstone. The authors focus on Transition–the first of their selected principles–as a theoretical framework for the pedagogical design they develop. They extend Kift’s Transition Pedagogy, an adaptation of Schlossberg that focuses on first year students, to inform final year practices—viewing final year students as students in transition, too. The authors identify three areas in which the incorporation of transition pedagogy can enhance a capstone experience and help students manage uncertainty, complexity, and change; develop a professional identity; and career plan. While the case study doesn’t cover the implementation of the capstone design, the study can offer a useful model for capstone development. Additionally, the transition framework does a helpful job of linking student development theory (and Schlossberg’s theory of t ransition) with pedagogy and ends with qualitative data from students as evidence of the necessity of the framework.
Collier, Peter J. 2000. “The Effects of Completing a Capstone Course on Student Identity.” Sociology of Education 73 (4): 285-299. https://doi.org/10.2307/2673235 .
Collier’s article studies the effect of participation in a capstone experience on undergraduate students’ identification as a college student. He proposes that the increased identification with this role by capstone students over time indicate capstones’ effectiveness in socialization. Using different identity theories around role identities and role-identity acquisition as theoretical frameworks, Collier developed a longitudinal study of 26 senior capstone students (multidisciplinary and across the university) of one year’s capstone at a university, with a nonequivalent control group (n=26). Using pre- and post-measurements, Collier found that the nature of the capstone as a grounded and experiential course contributed to its transformative impact on students. Students connecting with the community in a capstone context were pushed to work more collaboratively, and this social aspect of their learning and work helped them to associate more strongly with the role of a college student. The development of identity as a student is a potential strength of capstones. However, Collier fails to discuss why developing a student identity–especially in the senior year–is a worthwhile or positive practice, nor does he discuss how that student identity intersects with other social identities a student may hold. Collier does offer several practical implications for curriculum and specifically capstone development.
Dunlap, Joanna C. 2005. “Problem-Based Learning and Self-Efficacy: How a Capstone Course Prepares Students for a Profession.” Educational Technology Research and Development 53 (1): 65-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02504858 .
Dunlap employed a mixed methods approach to study the self-efficacy of 31 students in a required undergraduate capstone course. She analyzed guided journal submissions and triangulated those responses with student responses to a survey tool called the General Perceived Self-Efficacy Scale, a 10-item scale that “assesses optimistic self-beliefs to cope with a variety of difficult demands in life” (73). Her findings — that students’ participation in a p roblem- b ased l earning environment impacts students’ sense of capability, especially looking forward to career prospects and their sense of professional identity — offer data to support why capstones serve as a powerful facilitator of transition for students. While her findings are most specific to problem-based learning, a related high impact practice, their basis in a capstone context may help support the development of positively impactful capstone experiences.
Julien, Brianna L, Louise Lexis, Johannes Schuijers, Tom Samiric, and Stuart McDonald. 2012. “Using Capstones to Develop Research Skills and Graduate Capabilities: A Case Study from Physiology.” Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice 9 (3): 58-73. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.9.3.6 .
This case study describes two physiology capstones that culminate the Bachelor of Health Science at La Trobe University. The authors describe the student assessments involved in the capstones and evaluate the program itself based on student performance, student feedback, and faculty perceptions of the course. The authors found that final grades for students were significantly higher in 2011 , following the implementation of the capstone course than final grades in the previous two years. Students reported positive skill development and satisfaction, and instructors noticed a higher degree of student-centered learning along with a “vastly increased workload” and “greater need for infrastructure services” (11). The value of this case study is not only the model it provides for capstone development, but also the consideration of staffing and resource needs to support strong capstone experiences. Other institutions looking to launch or revise capstone experiences would do well to recognize this resource challenge.
Ketcham , Caroline J, Anthony G Weaver, and Jessie L Moore. 2023. Cultivating Capstones: Designing High-Quality Culminating Experiences for Student Learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
About this Book:
Cultivating Capstones introduces higher education faculty and administrators to the landscape of capstone experiences, offers research-informed models that institutions could adapt for their own contextual goals, and suggests faculty development strategies to support implementation of high-quality student learning experiences. The edited collection draws primarily from multi-year, multi-institutional, and mixed-methods studies conducted by participants in the 2018-2020 Center for Engaged Learning research seminar on Capstone Experiences; this work is complemented by chapters by additional scholars focused on culminating experiences.
The collection is divided into three sections. Part one offers typographies of capstones, illustrating the diversity of experiences included in this high-impact practice while also identifying essential characteristics that contribute to high-quality culminating experiences for students. Part two shares specific culminating experiences (e.g., seminar courses in general education curricula, capstone experiences in the major, capstone research projects in a multi-campus early college program, capstone ePortfolios, etc.), with examples from multiple institutions and strategies for adapting them for readers’ own campus contexts. Part three offers research-informed strategies for professional development to support implementation of high-quality student learning experiences across a variety of campus contexts.
Learn more at Cultivating Capstones – Center for Engaged Learning
Kilgo, Cindy A, Jessica K Ezell Sheets, and Ernest T Pascarella. 2014. “The Link between High-Impact Practices and Student Learning: Some Longitudinal Evidence.” Higher Education 69 (4): 509-525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-014-9788-z .
This study used pre- and post-tests to estimate the efficacy of the 10 high impact practices supported by AAC&U and found that overall, the high impact practices do, in fact, support student learning. They found that active , collaborative learning and undergraduate research were especially effective in promoting critical thinking, cognition, and intercultural effectiveness, while capstones (among other HIP s ) had more mixed effects. For capstones in particular, the authors found a negative link to critical thinking, “but positive net association with four-year gains in need for cognition” (519). The authors highlight several other specific positive gains in student learning as a result of capstones, and this data can be especially helpful in advocating not only for the value of capstones themselves, but in the value of intentionally designed capstones. The multi-institutional results help generalize the benefits, and even more importantly point to areas where negative links occurred, suggesting that administration and facilitation are key in capstones actually having high (positive) impact.
Lee, Nicolette, and Daniel Loton. 2017. “Capstone Purposes across Disciplines.” Studies in Higher Education 44 (1): 134-50. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2017.1347155 .
This literature review analyzes the purposes of capstones as presented by faculty involved in capstone design and instruction. This review is valuable in offering a broad overview of capstone literature and present understandings— for example, capstones are frequently linked to development of employability skills and personal student attributes. In addition to a review of the literature, Lee and Loton conducted an online survey of 216 capstone educators internationally (with just over three – quarters originating from Australia, the authors’ base). Here, they found the 20 most highly rated purposes for capstones were similarly rated across disciplinary groups — implying they serve a common purpose regardless of discipline. The survey responses echoed what has been focused on broadly in the literature and adds some nuance that will be useful to readers seeking to understand capstones at an introductory level. Finally, the purposes raised may help designers of capstones identify shared purposes from which to backward design the capstone experience.
Paris, David, and Ann Ferren. 2013. “How Students, Faculty, and Institutions Can Fulfill the Promise of Capstones.” Peer Review 15 (4). https://www.aacu.org/publications-research/periodicals/how-students-faculty-and-institutions-can-fulfill-promise .
This article offers a useful analysis of the capstone experience broadly, offering some recent historical context for capstones as well as recommendations for where they are headed today based on practice examples found across the United States. For American readers in particular, this analysis will offer some helpful comparisons to programs in a more familiar context. Unlike some of the heavier and formal research-centered pieces, another benefit of this article is its accessibility, due in large part because it serves to introduce a whole issue of Peer Review focused on capstone experiences. Paris and Ferren’s focus on the faculty-student relationship within capstones may be especially useful to readers, as it’s a lens of capstones not frequently seen in other literature and may be a key element in what makes capstones a high impact practice.
Rash, Agnes, and Kathryn Weld. 2013. “The Capstone Course: Origins, Goals, Methods, and Issues.” PRIMUS 23 (4): 291-96. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511970.2013.775203 .
This is an introduction to a special issue on capstone courses, which describes a range of models, common goals across capstones, popular teaching methods used in capstones, the value of capstones as a way to assess a curricular program, and issues related to faculty development. The curricular focus, mathematics, is somewhat unique and so may be especially useful for instructors who come with a strong disciplinary connection and are unsure of how capstones may fit into or enhance the content they hope to impart on students. An interesting and also unique aspect of this piece is the acknowledgement of capstones’ value in program assessment. For administrators in particular, this may be a helpful argument for an added benefit of capstones beyond student learning directly associated with the course. This article , as with several others, is explicit in framing the teaching of capstones as more of a mentorship relationship–an idea that would be worth following up on in future research.
Redman, Peggy. 2013. “Going beyond the Requirement: The Capstone Experience.” Peer Review 15 (4). https://www.aacu.org/publications-research/periodicals/going-beyond-requirement-capstone-experience .
This case study describes capstones across the curriculum and educational levels (bachelors, master’s, and doctoral) at the University of La Verne in southern California. By looking at the 127 capstone projects that students produced (41 undergraduate), Redman analyzed student writing and learning. As a result of the findings associated with this analysis, the university adapted a more integrated and reflective process across all four years to prepare students for their final capstone. This piece serves as a valuable model for thoughtfully embedding and scaffolding the capstone experience not only in the final year, but from a student’s first experience on campus. Additionally, the piece offers innovative ideas for linking capstones to other high impact practices such as community partnerships (service-learning) and ePortfolios .
Upson-Saia, Kristi. 2013. “The Capstone Experience for the Religious Studies Major.” Teaching Theology & Religion 16 (1): 3-17. https://doi.org/10.1111/teth.12001 .
This study examines capstone experiences for religious studies majors at 29 different U.S. institutions. Upson-Saia not only explores the strengths across these experiences, and the factors that set apart especially successful programs, but also takes an explicit focus on “the most frustrating aspects of the capstone” and “how some departments avoid such frustrations” (4). Unlike Lee and Loton (2017), who found strong consensus among the top purposes of capstones, Upson-Saia found little consensus among religious studies capstones beyond “culmination” in their educational objectives. This may be a difference in scale–on a smaller scale, more variation is visible–or in context . P erhaps authors have similar ideas about what should be talked about in published articles, but in practice , there may be more variation in purpose. Interestingly, Upson-Saia discusses one of the themes Lee and Loton raised about the pressures put on the capstone: suggesting that frustrations about the capstone as not going well , or doing as much as it could , stem from those pressures for capstone to be doing everything. She takes a historical lens in her response to this, exploring the evolution of capstones and their purposes through history to think through how capstones may be positioned today. Her resulting list of best practices for religious studies capstones may be adapted across disciplinary contexts and offer a useful starting point for people designing and developing capstones.
Young, Dallin George, Jasmin K Chung, Dory E Hoffman, and Ryan Bronkema. 2017. 2016 National Survey of Senior Capstone Experiences: Expanding our Understanding of Culminating Experiences. Columbia, SC: National Resource Center for the First-Year Experience and Students in Transition.
This publication reports on the 2016 National Survey of Senior Capstone Experiences conducted by the National Resource Center for The First-Year Experience and Students in Transition. The survey previously was administered in 1999 and 2011. It reports on capstones in curricular and co-curricular higher education programs, including objectives for the capstone experiences, types of capstone by field of study, and percentage of seniors participating in capstones.
See all Capstone Experiences entries
Model Programs
The University of Oregon has several strong capstone examples based around community engaged learning. Their Environmental Leadership Program (ELP) serves as the capstone experience for environmental studies majors and other interested students, and involves matching student “teams with non-profit organizations, governmental agencies, and businesses to address local environmental needs” ( Lynch and Boulay 2011 ). Similarly, the University of Oregon’s Master of Public Administration program matches students to local clients to “solve real-world policy and management problems” ( IPRE Blog 2020 ). In 2020, students in this program focused on supporting vulnerable populations, developing resilience, and supporting sustainability. The real-world and problem-based nature of these capstone experiences allow students to apply their learning to projects that matter.
The University of Leeds has a culminating research experience as the capstone for its honors bioscience students. The department specifies that “all honors degree students are expected to have some personal experience of the approach to practice and evaluation of scientific research,” and that “it is expected to include an element of novelty satisfied by work that is hypothesis-driven or which leads to formation of an hypothesis” ( University of Leeds and D.I. Lewis 2019 ).
The College of Wooster in Ohio has a robust final year research project as its culminating experience. Wooster works to set the foundation for this work early, through opportunities like the Sophomore Research Program , which funds students as paid research assistants to Wooster faculty and encourages students to connect with faculty on independent research projects in other spaces as well. The final capstone experience is called the Independent Study , and pairs every student with a professor for a one-on-one mentored experience. This deep, synthesizing, sustained, and highly mentored experience checks off each of the key qualities of high impact practices.
Additional programs are featured in Cultivating Capstones (forthcoming from Stylus Publishing).
Related Blog Posts
Designing an interdisciplinary capstone, part 1: faculty perspectives.
Limed: Teaching with a TwistSeason 2, Episode 7 Designing an interdisciplinary capstone course is a challenging task that presents an opportunity to innovate. Lina Kuhn and Kai Swanson from Elon University join the show to get some advice on how…
ePortfolios as Capstone Experience
Making College “Worth It” – Season 1, Episode 7 In this episode, we visit with Carol Van Zile-Tamsen, associate vice provost for curriculum, assessment, and teaching transformation at the University at Buffalo, about UB’s ePortfolio capstone requirement for general education….
Capitalizing on Capstone Experiences
Making College “Worth It” – Season 1, Episode 4 Caroline Ketcham and Tony Weaver, co-editors of Cultivating Capstones: Designing High-Quality Culminating Experiences for Student Learning, share strategies for faculty and students to make the most of these high-impact opportunities for…
View All Related Blog Posts
Featured Resources
Elon statement on capstone experiences.
From 2018 to 2020, twenty-two scholars participated in the Center for Engaged Learning research seminar on Capstone Experiences, co-led by Caroline Ketcham (Elon University), Jillian Kinzie (Indiana University), and Tony Weaver (Elon University). The seminar fostered international, multi-institutional research on capstone…
“2020 Capstone and Oregon Policy Lab Project Launch.” Web log. IPRE Blog (blog). University of Oregon, February 20, 2020. https://blogs.uoregon.edu/cscenter/2020/01/28/2020-capstone-and-oregon-policy-lab-project-launch/.
Brooks, Randy, Jodi Benton-Kupper, and Deborah Slayton. “Curricular Aims: Assessment of a University Capstone Course.” The Journal of General Education 53, no. 3/4 (2004): 275–87. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27797996.
Covington, Owen, Leo M Lambert, Jason Husser, and Peter Felton. “The Conversation: Mentors Play Critical Role in Quality of College Experience.” Today at Elon. The Conversation, August 22, 2018. https://www.elon.edu/u/news/2018/08/22/the-conversation-mentors-play-critical-role-in-quality-of-college-experience/.
Felten, Peter, John N Gardner, Charles C Schroeder, Leo M Lambert, and Betsy O Barefoot. The Undergraduate Experience: Focusing Institutions on What Matters Most . Wiley, 2016.
Kinzie, J. “Taking Stock of Capstones and Integrative Learning.” 2013. Peer Review; Washington 15, no. 4: 27–30.
Kuh, George, Ken O’Donnell, and Carol Geary Schneider. “Hips at Ten.” 2017. Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning 49, no. 5: 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/00091383.2017.1366805.
Lynch, Kathryn A., and Margaret C. Boulay. 2011. “Promoting Civic Engagement: The Environmental Leadership Program at the University of Oregon.” Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences 1, no. 3: 189–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13412-011-0028-x.
Levine, Arthur. 1998. “A President’s Personal and Historical Perspective.” In The Senior Year Experience: Facilitating Reflection, Integration, Closure and Transition, ed. John N. Gardner, Gretchen Van der Veer, and Associates. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
“Microbiology Society.” Homepage | Microbiology Society. PIXL 8 Group, 2021. https://microbiologysociety.org/.
Nelson-Hurwitz, Denise C., and Michelle Tagorda. 2015. “Developing an Undergraduate Applied Learning Experience.” Frontiers in Public Health 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2015.00002.
The Center thanks Sophia Abbot, our 2018-2020 graduate apprentice, for contributing the initial content for this resource.

271+ Most Creative Capstone Project Ideas for Students
Looking for the most creative Capstone project ideas? That provides an opportunity to apply knowledge and skills gained throughout their studies to real-world challenges.
If yes, these capstone projects often demand creativity, innovation, and problem-solving abilities. If you’re a student seeking inspiration for your capstone project or an educator looking to suggest ideas, we’ve compiled a list of 271+ creative capstone project ideas across various fields of study.
You can use these simple capstone project ideas to get more creative and make your overall creativity more good.
what is a capstone project
Table of Contents
A capstone project ideas is an academic undertaking, typically completed in the final year of a program, where students integrate and apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their studies. It serves as a culmination of their educational journey, requiring students to tackle complex real-world problems or challenges within their field of study.
These projects often involve independent research, creativity, or practical application of concepts and theories. Capstone projects vary in format, which may include research papers, creative works, software development, engineering prototypes, business plans, and more. Students are typically evaluated on their ability to demonstrate mastery of the subject matter, critical thinking skills, and effective communication of their findings.
Successful completion of capstone project ideas can serve as a testament to a student’s readiness for employment or further academic pursuits, making it a significant component of their educational experience.
how to do a capstone project
These steps will help you to make the best capstone project, let’s follow them.
- Select a Topic : Choose a specific and relevant project topic that aligns with your field of study and interests.
- Define Objectives : Clearly outline the goals and objectives you aim to achieve through your capstone project.
- Research and Literature Review : Conduct thorough research and review relevant literature to inform your project.
- Develop a Plan : Create a detailed project plan, including timelines, tasks, and resource requirements.
- Execute the Project : Implement your plan by conducting experiments, collecting data, or completing the creative work, depending on your project type.
- Analyze and Evaluate : Analyze the data or outcomes and evaluate your project’s success in meeting its objectives.
- Communicate Results : Present your findings or project outcomes through a written report, presentation, or creative display, emphasizing the significance of your work and its contribution to your field.
Most Creative Capstone Project Ideas for Students
These are the following great capstone project ideas are given below for every field student.
Engineering and Technology Capstone Project Ideas
- Solar-Powered Water Desalination System : Design a sustainable solution to convert seawater into freshwater using solar energy.
- Autonomous Drone for Environmental Monitoring : Develop a drone equipped with sensors to monitor air and water quality, wildlife, or deforestation.
- Smart Traffic Management System : Create an AI-driven traffic management system that optimizes traffic flow and reduces congestion.
- Robotic Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation : Design a wearable exoskeleton to assist patients with mobility impairments during rehabilitation.
- Energy-Efficient Home Automation : Build a home automation system that optimizes energy usage, reducing electricity bills and carbon footprint.
- 3D Printing in Medicine : Investigate and create 3D-printed medical devices or prosthetics customized to patients’ needs.
- Autonomous Agricultural Robot : Develop a robot capable of autonomously planting, monitoring, and harvesting crops.
- Drone-Based Firefighting : Design a drone system to aid in firefighting efforts, including fire detection and containment.
- Smart Wearables for Healthcare : Create wearable devices that monitor health parameters and provide real-time feedback to users and healthcare providers.
- Virtual Reality Therapy : Develop immersive virtual reality environments for therapy and rehabilitation purposes.
Capstone Project Ideas For Computer Science and Software Development
- AI-Powered Personal Assistant : Build an intelligent personal assistant capable of managing tasks, and schedules, and providing personalized recommendations.
- Natural Language Processing Chatbot : Create a chatbot using NLP techniques for customer support, information retrieval, or language learning.
- Blockchain-Based Voting System : Develop a secure and transparent voting system using blockchain technology.
- Predictive Analytics for Disease Outbreaks : Create a predictive model to forecast disease outbreaks based on historical data and environmental factors.
- Augmented Reality Educational Apps : Design AR applications to enhance classroom learning experiences.
- E-commerce Recommendation Engine : Build a recommendation system that suggests products to users based on their preferences and browsing behavior.
- Social Media Sentiment Analysis : Develop a tool for sentiment analysis on social media data to gauge public opinion on various topics.
- Cybersecurity Solutions : Design and implement cybersecurity tools or protocols to protect data and networks from cyber threats.
- AI-Generated Art : Explore the intersection of art and AI by generating creative artworks using neural networks.
- Video Game Development : Create an original video game, from concept to playable prototype.
Business and Entrepreneurship Capstone Project Ideas
- Market Entry Strategy for a New Product : Analyze market trends and competition to develop an effective strategy for introducing a new product or service.
- Small Business Sustainability Plan : Develop a sustainability plan for a small business, focusing on reducing environmental impact and increasing profitability.
- Impact Investing Portfolio : Build a portfolio of impact investments, evaluating financial returns alongside social and environmental impact.
- E-commerce Business Optimization : Optimize an e-commerce business by improving website design , user experience, and marketing strategies.
- Startup Incubator : Establish a startup incubator program to support and mentor aspiring entrepreneurs in your community.
- Financial Literacy App : Create an educational app to improve financial literacy among young adults.
- Marketplace for Local Artisans : Develop an online platform to connect local artisans with customers interested in handmade products.
- Sustainable Tourism Initiative : Design a sustainable tourism program that preserves natural and cultural resources while boosting local economies.
- Food Delivery Service Optimization : Optimize food delivery services by reducing delivery times, costs, and environmental impact.
- Green Supply Chain Management : Develop a sustainable supply chain management strategy for a company to reduce waste and emissions.
Capstone Project Ideas In Health and Medicine
- Telemedicine Platform : Create a telemedicine platform that connects patients with healthcare providers for remote consultations.
- Medical Record Blockchain : Implement a blockchain-based system for secure and interoperable medical records.
- Personalized Nutrition App : Develop an app that offers personalized dietary recommendations based on users’ health data and goals.
- Mental Health Chat Support : Build an AI-driven chat support system for individuals seeking mental health assistance.
- Medical Imaging AI : Train AI algorithms to assist radiologists in diagnosing medical conditions from imaging data.
- Healthcare Data Analytics : Analyze healthcare data to identify trends, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes.
- Health Monitoring Wearables : Design wearable devices that continuously monitor health parameters and provide real-time alerts.
- Biodegradable Medical Implants : Create biodegradable medical implants that reduce the need for additional surgeries.
- Nutraceutical Product Development : Develop innovative nutraceutical products with health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
- AI-Enhanced Drug Discovery : Use AI algorithms to accelerate drug discovery and development processes.
Environmental Science and Sustainability Capstone Projects
- Plastic Waste Reduction : Develop a solution to reduce plastic waste in oceans, rivers, or landfills.
- Carbon Footprint Tracker : Create an app that helps individuals and businesses track and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Renewable Energy Optimization : Optimize the efficiency and output of renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines.
- Eco-Friendly Design : Design sustainable and biodegradable packaging design solutions for consumer products.
- Urban Green Spaces : Plan and implement green spaces within urban areas to improve air quality and biodiversity.
- Water Quality Monitoring System : Build a system that continuously monitors water quality in lakes, rivers, or reservoirs.
- Waste-to-Energy Conversion : Develop technologies to convert organic waste into renewable energy sources.
- Community Recycling Initiatives : Create a community-based recycling program to encourage responsible waste disposal.
- Climate Change Education Platform : Build an educational platform to raise awareness about climate change and its impacts.
- Bee Conservation : Develop strategies and technologies to support bee populations and pollination efforts.
topics for the capstone project In Social Sciences and Psychology
- Online Mental Health Support Community : Create an online platform where individuals can connect and provide emotional support to others.
- Behavioral Economics Study : Conduct experiments and research on how cognitive biases influence decision-making.
- Criminal Justice Reform Proposal : Develop a comprehensive proposal for criminal justice reform, addressing issues such as mass incarceration and police brutality.
- Homelessness Intervention Program : Design an intervention program to provide housing and support for homeless individuals.
- Youth Empowerment Workshops : Organize workshops and mentoring programs to empower disadvantaged youth.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation : Digitize and preserve cultural heritage through virtual museums and interactive exhibits.
- Domestic Violence Prevention : Create educational materials and campaigns to prevent domestic violence and support survivors.
- Human Rights Advocacy : Develop advocacy campaigns and platforms to raise awareness of human rights violations.
- Community Policing Initiatives : Implement community policing strategies to improve police-community relations.
- Elderly Care and Isolation Reduction : Develop programs and technologies to reduce social isolation among the elderly.
Capstone Project Ideas For High School
- Online Language Learning Platform : Build an interactive platform for learning languages through gamification and AI-driven lessons.
- STEM Education for Underprivileged Youth : Create STEM education programs for underserved communities to bridge the educational gap.
- EdTech Assessment Tools : Develop tools for educators to assess and track student progress effectively.
- Virtual Science Labs : Create virtual labs that allow students to conduct experiments and explore scientific concepts remotely.
- Digital Storytelling for Education : Design a platform that enables students and teachers to create interactive digital stories for learning.
- Interactive History Lessons : Develop immersive historical experiences through augmented or virtual reality.
- Financial Literacy Curriculum : Create a comprehensive financial literacy curriculum for high school students.
- Inclusive Educational Games : Design educational games that cater to diverse learning styles and abilities.
- Teacher Professional Development Platform : Build a platform that offers ongoing professional development resources for educators.
- Peer Tutoring Network : Establish a peer tutoring network where students can help each other in various subjects.
Art and Design Capstone Project Ideas
- Interactive Art Installations : Create interactive art installations that engage viewers and explore societal themes.
- Artificial Intelligence in Art : Explore the use of AI in generating, enhancing, or critiquing art.
- Wearable Art : Design wearable art pieces that incorporate technology or unconventional materials.
- Virtual Art Gallery : Create a virtual platform for artists to showcase their work and engage with a global audience.
- Sustainable Fashion Collection : Design a sustainable fashion collection using eco-friendly materials and ethical production methods.
- Digital Sculpture : Explore digital sculpting techniques and create 3D printed sculptures.
- Community Murals : Collaborate with a community to create public art murals that reflect its identity and values.
- Art Therapy Workshops : Organize art therapy workshops for individuals facing mental health challenges.
- Animated Short Film : Produce an animated short film that conveys a powerful message or story.
- Interactive Graphic Novels : Combine storytelling and interactivity in the form of digital graphic novels.
Capstone Project Ideas For Media and Communication
- Podcast Series on Social Issues : Create a podcast series that explores and discusses pressing social issues.
- Documentary on Cultural Heritage : Produce a documentary film highlighting the cultural heritage of a specific region or community.
- Virtual Reality Journalism : Use VR technology to deliver immersive news stories and experiences.
- Youth Empowerment Magazine : Launch a magazine dedicated to empowering and showcasing the talents of young individuals.
- Interactive Web Series : Develop an interactive web series where viewers can influence the storyline’s direction.
- Local News Aggregator App : Create an app that aggregates local news sources for easy access and community engagement.
- Digital Marketing Campaign : Plan and execute a digital marketing campaign for a nonprofit organization or local business.
- Social Media Analytics Tool : Build a tool that provides insights into social media trends and engagement metrics.
- Multilingual Translation Service : Create a platform that offers real-time multilingual translation services for video content.
- Sci-Fi Audio Drama : Produce a science fiction audio drama series with immersive soundscapes and storytelling.
Agriculture & Food Science Capstone Project Ideas
- Precision Agriculture Solutions : Develop technology and systems for precision farming to optimize crop yields.
- Food Traceability Platform : Create a blockchain-based platform for tracking the origin and journey of food products.
- Urban Vertical Farming : Design vertical farming systems for urban environments to promote local food production.
- Aquaponics Farming : Build an aquaponics system that combines fish farming with hydroponics for sustainable food production.
- Food Waste Reduction App : Develop an app that connects consumers with surplus food from restaurants and grocery stores .
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives : Create innovative plant-based meat substitutes using novel ingredients and technologies.
- Smart Greenhouses : Design automated greenhouses with sensors and AI for optimal crop growth.
- Farm-to-Table Delivery Service : Establish a farm-to-table delivery service that connects consumers with local producers.
- Food Allergen Detection : Develop a portable device for detecting food allergens in real-time.
- Edible Insect Farming : Explore the feasibility of farming edible insects as a sustainable protein source.
Capstone Project Ideas For Architecture and Urban Planning
- Sustainable Housing Designs : Create architectural designs for eco-friendly and energy-efficient housing solutions.
- Public Space Redesign : Transform public spaces to improve accessibility, aesthetics, and functionality.
- Historical Building Restoration : Restore and preserve historical buildings while making them suitable for modern use.
- Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure : Design infrastructure and buildings that can withstand natural disasters.
- Affordable Housing Models : Develop innovative housing models to address affordable housing shortages in urban areas.
- Smart City Initiatives : Plan and implement smart city projects that enhance urban living through technology.
- Urban Mobility Solutions : Propose solutions to improve transportation and reduce traffic congestion in urban areas.
- Green Building Certification : Create a certification program for environmentally friendly construction practices.
- Community Garden Spaces : Design community gardens that promote urban agriculture and community engagement.
- Accessible Playgrounds : Create inclusive playgrounds designed for children of all abilities.
Music and Performing Arts Capstone Project Ideas
- Virtual Choir Performance : Coordinate and produce a virtual choir performance with participants from around the world.
- Music Therapy Program : Develop a music therapy program for individuals with cognitive, emotional, or physical challenges.
- Interactive Dance Performance : Create an interactive dance performance where the audience’s participation influences the choreography.
- Music Production Software : Design user-friendly software for music producers and musicians.
- Digital Artistic Collaborations : Collaborate with artists from different disciplines to create multimedia performances.
- Music Education App : Create an app that teaches music theory, composition, and instrument skills in an engaging way.
- Soundscapes for Healing : Design soothing soundscapes and environments for healthcare facilities and relaxation.
- Theatrical Set Design : Create innovative set designs for theater productions that challenge traditional norms.
- Film Score Composition : Compose original film scores that enhance storytelling and emotional impact.
- Street Art and Performance Festival : Organize a festival that celebrates street art, music, and live performances.
Capstone Project Ideas For Science and Astronomy
- Astrophotography Project : Capture and analyze stunning astronomical images using telescopes and cameras.
- Satellite Tracking Software : Develop software to track and predict the movements of satellites in Earth’s orbit.
- Space Colonization Simulation : Create a realistic simulation of a space colony, considering life support systems and sustainability.
- Citizen Science Initiative : Organize a project that encourages citizen scientists to contribute to scientific research.
- Mars Rover Simulation : Build a functional Mars rover prototype capable of navigating challenging terrain.
- Astronomy Education Planetarium : Establish a portable planetarium for educational outreach in schools and communities.
- Ocean Exploration Robot : Design a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) for deep-sea exploration.
- Microgravity Experiments : Plan and execute experiments to investigate the effects of microgravity on various organisms and materials.
- Weather Prediction AI : Develop an AI system for more accurate and timely weather predictions.
- Interactive Science Museum Exhibit : Create an interactive exhibit that explains complex scientific concepts in a fun and engaging way.
best Capstone Project Ideas For Sports and Fitness
- Virtual Reality Sports Training : Develop VR simulations for sports training, enhancing skills and strategy.
- Sports Injury Prevention App : Create an app that helps athletes prevent injuries through personalized workouts and assessments.
- Sports Analytics Platform : Build a platform that provides in-depth analytics for improving team performance.
- Fitness Gamification : Design fitness games that motivate users to stay active and achieve their fitness goals.
- Accessible Sports Equipment : Create adaptive sports equipment to enable individuals with disabilities to participate in sports.
- Sports Nutrition App : Develop an app that offers personalized nutrition plans for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
- E-sports Tournament Organizer : Organize and host e-sports tournaments for popular online games.
- Athlete Mental Health Support : Create a platform that offers mental health resources and support for athletes.
- Sports Event Management System : Design a comprehensive system for managing and promoting sports events.
- Sports Rehabilitation Tools : Develop innovative tools and devices for sports injury rehabilitation.
Great Capstone Projects For Psychology and Neuroscience
- Neurofeedback Training App : Create an app that provides neurofeedback training to improve cognitive functions and mental well-being.
- Memory Enhancement Game : Develop a game or app that enhances memory and cognitive skills.
- Stress Management App : Design an app that offers stress-reduction techniques, meditation, and relaxation exercises.
- Neuromarketing Research : Conduct neuromarketing studies to understand consumer behavior and preferences.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation Tools : Create tools and exercises to aid in the cognitive rehabilitation of individuals with brain injuries.
- Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy : Use VR technology to treat phobias, PTSD, and anxiety disorders through exposure therapy.
- Mindfulness and Meditation Platform : Build a platform that promotes mindfulness and meditation practices.
- Sleep Quality Monitoring Device : Develop a wearable device that monitors and improves sleep quality.
- Emotion Recognition Software : Create software that accurately recognizes and analyzes human emotions from facial expressions.
- Childhood Development Program : Design an early childhood development program that enhances cognitive, social, and emotional skills.
Capstone Project Ideas For Robotics and Automation
- Humanoid Robot Assistant : Build a humanoid robot capable of assisting humans in daily tasks.
- Robotics in Agriculture : Create robots for planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops in agricultural settings.
- Autonomous Delivery Vehicles : Develop self-driving vehicles for last-mile delivery of goods and packages.
- Robotics for Disaster Response : Design robots that can assist in search and rescue operations during natural disasters.
- Telepresence Robot : Build a telepresence robot for remote communication and interaction.
- Robotic Prosthetics : Develop advanced robotic prosthetic limbs with natural movement and sensory feedback.
- Underwater Exploration Robot : Create a remotely operated underwater robot for exploring deep-sea environments.
- Robotic Pet Companions : Design robots that provide companionship and support for individuals with disabilities or loneliness.
- AI-Powered Cleaning Robot : Build a smart cleaning robot that autonomously cleans homes or offices.
- Robotics Education Kits : Develop educational kits for teaching robotics and programming to students of all ages.
Interesting Capstone Project Ideas For Mathematics and Statistics
- Math Learning Game : Create an interactive game that makes learning mathematics fun and engaging for students.
- Statistical Analysis Software : Develop user-friendly software for statistical analysis and data visualization.
- Mathematical Modeling for Epidemiology : Build models to predict disease spread and evaluate intervention strategies.
- Cryptocurrency Price Prediction : Develop AI algorithms to predict cryptocurrency price movements.
- Interactive Geometry Visualization : Create tools that visualize geometric concepts to aid in learning.
- Number Theory Explorer : Design an interactive platform for exploring number theory concepts and conjectures.
- Math Assessment and Tutoring App : Build an app that assesses students’ math skills and provides personalized tutoring.
- Machine Learning for Financial Forecasting : Develop models for predicting stock prices, market trends, and financial risks.
- Graph Theory Applications : Explore practical applications of graph theory in various domains.
- Mathematical Puzzle Solver : Create a tool that solves complex mathematical puzzles and challenges.

Capstone Project Ideas For History and Archaeology
- Virtual Historical Tours : Develop virtual tours of historical sites, allowing users to explore ancient civilizations.
- Interactive Archaeological Digs : Create a digital experience that simulates archaeological excavations and artifact analysis.
- Historical Document Digitization : Digitize and preserve historical documents, manuscripts, and records.
- Ancient Language Translation Tool : Build a tool that translates ancient or extinct languages into modern languages.
- History-Based Educational Games : Develop educational games that immerse players in historical events and decision-making.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation : Collaborate with local communities to preserve and document their cultural heritage.
- Archaeological Site Reconstruction : Use 3D modeling to reconstruct and visualize ancient cities and structures.
- Oral History Collection : Record and archive oral histories from individuals with unique life experiences.
- Historical Costume Reproduction : Create historically accurate clothing replicas for museums and reenactments.
- Digital History Exhibits : Design digital exhibits that explore historical themes and narratives.
Good Capstone Project Ideas For Environmental Engineering
- Bioremediation of Contaminated Sites : Develop bioremediation strategies to clean up polluted soil and water.
- Waste-to-Energy Conversion : Investigate technologies for converting waste materials into renewable energy.
- Green Infrastructure Planning : Plan and design green infrastructure projects to manage stormwater and enhance urban ecosystems.
- Air Quality Monitoring Network : Create a network of air quality monitoring stations to track pollutants and inform public health decisions.
- Microplastics Detection : Develop tools for detecting and quantifying microplastics in aquatic environments.
- Environmental Impact Assessment : Conduct assessments of proposed development projects to evaluate their environmental impact.
- Habitat Restoration : Restore and rehabilitate natural habitats to support biodiversity conservation.
- Sustainable Water Management : Implement sustainable water management practices to conserve and protect freshwater resources.
- Renewable Energy Integration : Investigate methods for integrating renewable energy sources into existing power grids.
- Eco-Friendly Transportation Solutions : Develop and promote eco-friendly transportation options, such as electric vehicles and public transit.
Political Science and International Relations
- International Conflict Resolution Simulation : Create a simulation to model and explore diplomatic negotiations in international conflicts.
- Public Policy Analysis Tool : Develop a tool that assists policymakers in analyzing the potential impacts of policy decisions.
- Human Rights Database : Build a comprehensive database of human rights violations and abuses worldwide.
- Political Campaign Strategy Platform : Create a platform that helps political campaigns with voter outreach, data analysis, and messaging.
- Foreign Policy Simulator : Design a simulator that allows users to navigate complex international relations scenarios.
- Legislative Transparency App : Develop an app that provides transparency and updates on legislative activities.
- Political Participation Initiative : Organize programs and initiatives to encourage voter registration and civic engagement.
- Government Performance Assessment : Develop metrics and tools to assess the performance and efficiency of government agencies.
- Election Security Protocols : Propose and implement security measures to protect election integrity.
- Diplomatic Crisis Management : Create strategies and frameworks for managing diplomatic crises and conflicts.
Capstone Project Ideas For Geology and Earth Sciences
- Geological Hazard Prediction : Develop predictive models for earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides.
- Climate Change Impact Assessment : Assess the local impacts of climate change on ecosystems, agriculture, and communities.
- Geological Mapping Software : Create software for geological mapping and analysis of rock formations.
- Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring : Utilize satellite imagery and remote sensing data to monitor changes in the Earth’s surface.
- Mineral Exploration Algorithms : Develop algorithms to assist in the discovery of mineral deposits and resources.
- Geological Virtual Field Trips : Design virtual field trips that allow students and researchers to explore geological sites remotely.
- Geoheritage Conservation : Promote the preservation and recognition of geological heritage sites.
- Geothermal Energy Feasibility Study : Evaluate the potential for harnessing geothermal energy in specific regions.
- Hydrological Modeling : Create models to predict and manage water flow in river systems and watersheds.
- Geological Time Scale Interactive Tool : Develop an interactive tool for understanding and visualizing geological time periods.
Culinary Arts and Food Service
- Food Waste Reduction Program : Implement strategies to reduce food waste in commercial kitchens and restaurants.
- Gourmet Pop-Up Restaurant : Organize a pop-up restaurant featuring gourmet dishes and unique dining experiences.
- Culinary Innovation Lab : Establish a culinary lab for experimenting with new recipes, techniques, and ingredients.
- Farm-to-Table Cooking Classes : Offer cooking classes that teach participants how to prepare meals with local and seasonal ingredients.
- Sustainable Menu Design : Create sustainable menus for restaurants that emphasize locally sourced, eco-friendly ingredients.
- Culinary Tourism Promotion : Develop campaigns and materials to promote culinary tourism in a specific region.
- Food Allergy-Friendly Recipes : Create a collection of recipes tailored for individuals with food allergies or dietary restrictions.
- Food Photography and Styling : Explore the art of food photography and styling to create visually appealing dishes.
- Food History Research : Investigate the historical origins and evolution of specific dishes or culinary traditions.
- Cookbook for Sustainable Eating : Author a cookbook that focuses on sustainable and ethical eating choices.
Capstone Project Ideas For Literature and Writing
- Interactive Literature App : Design an app that allows users to interact with classic literature through immersive experiences.
- Creative Writing Workshop Series : Organize workshops and events to inspire creativity and improve writing skills.
- Digital Poetry Journal : Create an online platform for poets to share their work and engage with readers.
- Literary Analysis Tool : Develop software that assists in the analysis of literary texts and themes.
- Bilingual Literature Project : Translate and publish literature in multiple languages to promote cross-cultural understanding.
- Literary Podcast Series : Produce a podcast series that explores and discusses classic and contemporary literary works.
- Author’s Archive Preservation : Digitize and archive the works and writings of lesser-known authors.
- Interactive Storytelling Games : Design interactive games that allow players to influence the narrative and characters’ choices.
- Literary Magazine Publication : Launch a literary magazine to showcase the work of emerging writers and poets.
- Virtual Writing Retreats : Offer virtual writing retreats and workshops for aspiring authors.
Film and Media Production Capstone Projects
- Short Film on Social Issues : Produce a short film that raises awareness of important social issues.
- Interactive Web Series : Create an interactive web series where viewers can make decisions that impact the storyline.
- Film Production for Nonprofits : Collaborate with nonprofit organizations to produce promotional videos and documentaries.
- Virtual Reality Film : Develop a VR film experience that immerses viewers in a narrative or documentary.
- Film Score Composition : Compose original scores for films, enhancing the emotional impact of the story.
- Documentary Series on Environmental Conservation : Produce a documentary series highlighting efforts to protect the environment.
- Music Video Production : Direct and produce music videos for emerging artists and musicians.
- Film Festival Organization : Organize a film festival that showcases independent and international films.
- Stop-Motion Animation Project : Create a stop-motion animation film using innovative techniques and storytelling.
- Film Restoration and Preservation : Restore and preserve classic films to ensure they are accessible to future generations.
Top Capstone Project Ideas For Physics and Astronomy
- Particle Physics Experiments : Conduct experiments to explore subatomic particles and their interactions.
- Astrophysics Research : Investigate phenomena in the cosmos, such as black holes, neutron stars, and dark matter.
- Quantum Computing Algorithms : Develop algorithms and applications for quantum computers.
- Laser Technology Applications : Explore applications of laser technology in fields like communications, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Astronomical Spectroscopy Analysis : Analyze astronomical spectra to gain insights into celestial objects.
- Physics Education App : Create an app that offers interactive physics simulations and educational materials.
- Advanced Materials for Energy Storage : Research and develop materials for more efficient energy storage devices.
- Nuclear Fusion Experiments : Participate in experiments related to nuclear fusion as a potential future energy source.
- Gravitational Wave Detection : Contribute to the detection and analysis of gravitational waves from cosmic events.
- Nanotechnology for Medicine : Investigate nanoscale materials and devices for medical applications.
Mechanical Engineering Capstone Project Ideas
- Biomimetic Robotics : Design robots inspired by nature, mimicking the movements and capabilities of animals.
- Renewable Energy Harvesting : Develop innovative methods for harnessing renewable energy from the environment.
- Mechanical Prosthetic Limbs : Create advanced prosthetic limbs with enhanced mobility and dexterity.
- Advanced Materials Testing : Conduct experiments to test the properties and durability of new materials.
- Mechanical System Optimization : Optimize mechanical systems to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
- Aerospace Engineering Design : Design and prototype aerospace components or vehicles.
- Robotics for Elderly Care : Create robots that assist elderly individuals with daily tasks and companionship.
- Bioinspired Transportation : Design transportation systems inspired by natural organisms, such as birds and fish.
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicles : Build AUVs for underwater exploration, data collection, and marine research.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques : Explore cutting-edge manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing and nanomanufacturing.
Simple Capstone Project Ideas For Economics and Finance
- Economic Impact Assessment : Analyze the economic impact of policy changes, events, or investments.
- Financial Forecasting Models : Develop models for predicting financial trends, stock market movements, and economic indicators.
- Behavioral Economics Experiments : Conduct experiments to study how individuals make economic decisions.
- Economic Development Strategies : Propose strategies to promote economic growth in a specific region or community.
- Blockchain-Based Financial Services : Create blockchain solutions for secure and transparent financial transactions.
- Impact Investing Portfolio : Build a portfolio of investments that prioritize both financial returns and social impact.
- Financial Literacy Program : Develop educational programs and resources to improve financial literacy among different demographics.
- Cryptocurrency and Fintech : Research and innovate in the fields of cryptocurrency and financial technology.
- Healthcare Economics Analysis : Analyze the economic aspects of healthcare systems and policies.
- International Trade Simulation : Create a simulation to model international trade scenarios and trade agreements.
- Sustainable Finance Initiatives : Develop strategies and products that promote sustainable and ethical investment practices.
Conclusion – Capstone Project Ideas
So, these are the 271+ creative and senior capstone project ideas that span a wide range of disciplines. It provides ample inspiration for students looking to make a meaningful impact in their respective fields. Remember to choose a project that aligns with your interests and passions, as the journey toward completing a capstone project ideas can be a rewarding one. Good luck with your capstone project examples, and may it lead to innovative solutions and valuable contributions to your chosen field of study!
What is an example of a capstone project Ideas?
Capstone projects come in all shapes and sizes, including research papers, case studies, creative works, internships, and field placement projects.
Are capstone project Ideas hard?
Taking on a big, longer-term academic or professional project can be very challenging.
Do colleges look at capstone?
Many colleges and universities offer credit and/or placement for a qualifying score in AP Seminar, AP Research, or both.
Similar Articles

Top 19 Tips & Tricks On How To Improve Grades?
Do you want to improve your grades? If yes, then don’t worry! In this blog, I have provided 19 tips…

How To Study For Final Exam – 12 Proven Tips You Must Know
How To Study For Final Exam? Studying for the final exam is very important for academic success because they test…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Early & Elementary Education
Seven innovative ideas for prek-3rd education: will these projects be funded, laura bornfreund, july 13, 2010.
With nearly 1700 school districts and non-profit organizations vying for the U.S. Department of Education’s Investing in Innovation (i3) grants, it’s encouraging to see that 384 of them are putting a focus on early learning -- and at least seven of them are proposing programs that recognize the continuum of learning from birth or pre-K up through third grade.
The grants come from $650 million provided to the Education Department after the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. The i3 program emphasizes the same priorities as the Race to the Top grant program:
- Effective teachers and leaders,
- Use of data,
- High standards and high-quality assessments, and
- Persistently low-performing schools.
(a) improving young children’s school readiness (including social, emotional, and cognitive readiness) so that children are prepared for success in core academic subjects (as defined in section 9101(11) of the ESEA); (b) improving developmental milestones and standards and aligning them with appropriate outcome measures; and (c) improving alignment, collaboration, and transitions between early learning programs that serve children from birth to age three, in preschools, and in kindergarten through third grade.
- The Hartford School District in Connecticut requested $3,354,073 to develop the Betances Early Reading Lab Prek-3 Lab School , which would “create an innovative learning community by joining together two powerful components.” The first component of this project is the Pre-k – 3rd school structure. The second piece is the establishment of an early literacy professional development center, housed in the school, that would foster a learning community of teachers and staff who use data collaboratively and effectively to maximize student learning.
- The New School Foundation in Seattle submitted an application for $20,760,468 in collaboration with Bremerton School District, located in a working-class town; Toppenish School District, a predominantly Latino and Native American district; and Seattle School District, the state's largest district to validate its Pre-K-3rd Quality and Alignment Model (P3QAM) . According to the project’s description, P3QAM links preschool programs to elementary school programs by using aligned high standards, curricula and instruction combined with high quality assessments. The applicants intend to validate that this approach increases third grade academic achievement, accelerates academic growth in the Pre-K - 3rd years, reduces achievement gaps, reduces supplemental services for students and improves the social/emotional status for children.
- The Bank Street College of Education in New York submitted an application in partnership with the Memphis City Schools for $3,951,419 to develop the Project Teacher Leaders for the Pre-K Continuum (Project TLC) . The project’s goal is to support improved outcomes for all pre-K - 3rd grade children attending school in the district, with more intensive efforts in the city’s lowest-performing (striving) schools. Project TLC includes six activities: 1) a comprehensive and intensive teacher advisement program in striving schools; 2) on-site support for school leadership teams; 3) on-site and online professional development for teachers & leaders in striving schools; 4) visitations to higher performing (Paragon) schools; 5) a professional development video library and guide for district-wide use; and 6) annual citywide conferences.
- Building Tomorrow's Scholars Today is a project proposed by the Bridgeport Public Schools in Connecticut. The district requested almost $5 million to build on an existing Early Reading First Project. This pre-K – 2 nd grade literacy initiative comprises a job-embedded coaching model and targeted professional development for classroom teachers and paraprofessionals. A multi-disciplinary literacy team, including a speech/language pathologist, would provide regular support to teachers and students as well as parent trainings. Additionally, teachers would be trained to work with parents to establish home-school connections intended to support children’s language and literacy development. Teachers who participate in the project would also have the opportunity to take three on-site graduate level courses delivered by Fairfield University.
- The Life Services System of Ottawa County in Holland, Michigan – in partnership with eight school districts – submitted a proposal to validate its project Parents and Communities United for Success . They requested $21,938,400 over five years. According to the project summary, this birth to 3rd grade initiative combines several strategies that create a continuum of support for children and their families from birth through 3rd grade. Strategies include extending learning time for core academic content; integrating support services; parent engagement activities; establishing a protocol for schools and parents to work together on an educational plan for their student/child; and securing the private sector's support and understanding of the importance of early childhood learning.
- McMinnville School District in Oregon submitted a proposal requesting about $3 million to develop a Birth through 3rd Grade Project . MSD’s plans is to build a bridge to graduation and postsecondary completion by increasing school readiness and ensuring that every child enters kindergarten with skills at or above age five, fostering early school success, and increasing the percentage of students performing at or above grade level in reading and math by the end of third grade. MSD would establish a mobile child development center to provide curriculum resources, modeling, and coaching to parents of high-needs young children. MSD would also provide preschool for high-needs children; Kinder-Plus (enrichment) for high-needs students; and an extended day/year and supplemental support for high-needs students in kindergarten through third grade.
- ServeMinnesota, along with a consortium of several schools, submitted a validation proposal for its Age 3 to Grade 3 Reading Proficiency: A Scalable Model for Individualized Interventions Harnessing the Power of Americorps to Deliver Accelerated Results . The applicants requested $20,232,904 over five years to validate the potential for AmeriCorps to “serve as the vehicle for implementing the use of an individualized data based problem solving model as a proven, effective methodology for helping age 3 to grade 3 children achieve reading proficiency by 3rd grade on a national, unprecedented scale.”
- Our Mission
Bringing Project-Based Learning to Preschool
Young children’s natural curiosity lends itself well to PBL—and with the right supports, these projects can be extremely effective.

Project-based learning (PBL) provides an interesting challenge for preschool teachers because it extends beyond early-childhood education mainstays such as teacher-directed themed crafts and short daily lessons.
PBL, which focuses on children learning through investigating a topic or answering a question, is an involved process that could last for as long as the children show interest. Facilitating PBL is easier when teachers pick something to explore based on the children’s interests and implement their ideas in the project. When children are engaged in the process, they naturally develop skills they can apply later in life.
Young Filmmakers
While teaching preschool in Seattle, my co-teacher and I observed some children playing cats and dogs in the drama area. We sat with that small group of children and talked about their play. The children expressed that they wanted to make cat and dog masks.
To honor their request, we propped up real pictures of cats and dogs and gave the children a variety of materials. While we filmed the children with their masks, they asked to make a movie! At first, I didn’t know how to make that happen, which led to the question, “How do we make a movie?”
During free choice, we pulled the small group of children for 15 minutes a day and asked them for ideas. They made the script and chose the film location outside. They even picked the title, A Dog’s Story: A Dog’s Life. The sessions grew longer as the children worked on their costumes and did rehearsals.
After two weeks of prepping, filming day finally came. We put a camera on a tripod, and the children took turns filming. They acted out their scenes and said their lines, which we read aloud and they repeated. I put together the final scenes with their choice of music. The children made movie premier posters and wrote invitations for families. They picked the snacks and set up the viewing area.
From an adult’s viewpoint, it was quite a bizarre movie with an odd plot of masked children jumping out of bushes and saying funny things. The ending was everyone on all fours meowing and barking. However, the children were so proud when their families came and watched the movie. Our final step was to create a learning story showing how we touched on all learning domains (math, literacy, language, social and emotional, drama, etc.).
4 Keys to Effective PBL in Preschool
1. Teachers create the opportunities. One way to start setting up PBL is to create a classroom culture of innovation. A teacher’s viewpoint on children’s capabilities is important. The children are inventors, architects, actors, artists, scientists, or engineers. They are capable of doing amazing things with the right space, materials, tools, and time, which is why creating indoor and outdoor spaces with a variety of open materials is so crucial.
2. Observe the children to find your topic or question. Once the environment is established, a teacher needs to intentionally watch and listen. This can be during large group, free choice, and outside time. It’s capturing an experience, seeing recurring play, or noticing a comment. How can we make our hot wheels go faster? How do birds make nests? How do you make a rocket ship?
3. Teachers are the project managers. Once a teacher picks a question or topic, they need to see themselves as a facilitator and organizer of the children’s plans. Young children have minimal experience and limited access to resources, materials, and information. They’re still learning how to get along with others. Teachers will need to model the process and maybe even take on some of the work that’s outside of preschool students’ abilities, such as conducting online research and using tools like glue guns.
4. Children generate the ideas. To start the project, the teachers can have an open discussion on the topic and write down all the children’s responses. What do we know? What do we want to know? How will we learn it? What steps do we need to take? What materials do we need? If the children are stumped, it’s OK to make suggestions for them to consider. Posting the children’s ideas shows them that their thoughts and concepts have value. The teacher’s next job is to make the children’s plans come to life—no matter how it may look at the end!
We tend to think PBL is better suited for older children, but preschool-age children are very capable. They just need opportunity. Children are eager to be a part of something big by creating things and solving problems. As a teacher models project planning, they show children how to work as a team, create a plan, and execute collaborative ideas. The focus should be on the process rather than the final product. Our dog movie may not be Academy Award worthy, but the skills and confidence gained by the children were the true gift. It will always be one of my favorite (and most hilarious) moments in teaching.
tag manager container
- Employee Hub
- Directories
Early Childhood Education Institute
Research Topics | Early Childhood Education Institute

Research Topics
Adoption/fostering.
Benton, A. L. (2020). An Autoethnographic Tale of One Louisiana Mother’s Personal Journey of Fostering and Adopting: The Impact of the Fostering Process Versus the Fostering Process in Classrooms. Journal of Foster Care, 1(1), 23-35.
DiCarlo, C. & Ota, C. (2017). Advocacy in early childhood teacher preparation (Chapter 5). In Advocacy in Academia and the Role of Teacher Preparation Programs (Thomas, U. Ed). IGI Global.
Reames, H. Sistrunk, C., Prejean, J., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2016). Advocating for recess: Preservice teachers perspectives on the advocacy process. Journal for Service-Learning, Leadership, and Social Change.
Attention/Engagement
DiCarlo, C., Baumgartner, J., Ota, C., & Brooksher, M. (in review). Recommended practice in whole-group instruction: Increasing child attention. International Journal of Early Years Education.
DiCarlo, C., Deris, A., & Deris, T. (in review). mLearning versus paper & pencil practice for telling time: Impact for attention & accuracy. Journal of Elementary Education.
DiCarlo C. F., Baumgartner, J. J., Ota, C.L., Deris, A.R. & Brooksher, M.H. (2020) Recommended practice in whole-group instruction: Increasing child attention. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, DOI: 10.1080/00168890.2020.184840
DiCarlo, C.F., Baumgartner, J., Ota, C., & Geary, K. (2016). Child sustained attention in preschool-aged children. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 30(2), 143-152.
DiCarlo, C.F., Geary, K. E., & Ota, C.L. (2016). The impact of choice on child sustained attention in the preschool classroom. Journal of Research Childhood Education.
DiCarlo, C.F., Baumgartner, J., Pierce, S.H., Harris, M.E., & Ota, C. (2012). Whole group instruction practices and young children’s attention: A preliminary report. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 26(2), 154-168.
DiCarlo, C., Pierce, S., Baumgartner, J.J., Harris, M., & Ota, C. (2012). Whole-group instruction practices and children’s attention: A preliminary report. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 26(2), 154-168.
DiCarlo, C., Baumgartner, J., Schellhaas, A., & Pierce,S., (2012). Using Structured Choice to Increase Child Engagement in Low Preference Centers. Early Child Development & Care, 183(1), 109-124.
Isbell, D. (2019). Intermediate and High School Band. In Conway, C., Stanley, A., Pelligrino, K., and West, C. (Eds.), Handbook of Preservice Music Teacher Education. Oxford Publishing
Isbell, D. and Stanley, A. M. (2011). Keeping instruments out of the attic: The concert band experiences of the non-music major. Music Education Research International,5, 22-32
Isbell, D. (2006). The Steamboat Springs high school ski band 1935-2005. Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, 28(1), 21-37.
Caregiver Health and Identity
Baumgartner, J., Carson, R., Ota, C., DiCarlo, C., Bauer, R. (in review). Using Ecological Momentary Assessment to Examine the Relationship Between Childcare Teachers’ Stress, Classroom Behaviors, and Afterhours Professionalism Activities. Early Child Development and Care.
Bergen, D., Lee, L., Dicarlo, C. & Burnett, G. (2020). Enhancing Young Children’s Brain Development in Infants and Young Children: Strategies for Caregivers and Educators. New York, NY: Teacher’s College Press.
DiCarlo, C., Meaux, A., & LaBiche - Hebert, E. (in press). The impact of mindfulness practices on classroom climate and perceived teacher stress. Early Childhood Education Journal.
Chiang, C.J.,Jonson-Reid, M., & Drake, B. (2020). Caregiver physical health and child maltreatment reports and re-reports. Children and Youth Services Review, 108, 104671.
Baumgartner, J., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2013). Reducing workplace stress. Childcare Exchange. May/June, 60-63.
Ota, C.L., Baumgartner, J.J., & Austin, A.M.B. (2013). Provider stress and children's active engagement. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 27, 1-13. doi: 10.1080/02568543.2012.739588
Baumgartner, J., DiCarlo, C., & Apavaloie, L. (2011). Finding more joy in teaching children. Dimensions, 39(2), 34-38.
Isbell, D. (2008) Musicians and Teachers: The Socialization and Occupational Identity of Preservice Music Teachers. Journal of Research in Music Education, 56(2). 162-178.
Child Health
Shon, E., Choe, S, Lee, L., & Ki, Y. (In Press). Influenza Vaccination among U.S. College or University Students: A Systematic Review. American Journal of Health Promotion.
Fowler L.A., Grammer A.C., Staiano A.E., Fitzsimmons-Craft E.E., Chen L., Yaeger L.H., & Wilfley D.E. (2021). Harnessing technological innovations for childhood obesity prevention and treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of current applications. International Journal of Obesity.
Kepper M.M., Walsh-Bailey C., Staiano A.E., Fowler L., Gacad A., Blackwood A., Fowler S., & Kelley M. (2021). Health Information Technology use among healthcare providers treating children and adolescents with obesity: A systematic review. Current Epidemiology Reports.
Staiano, A.E., Shanley, J.R., Kihm, H., Hawkins, K.R., Self-Brown, S., Hӧchsmann, C., Osborne, M., LeBlanc, M.M., Apolzan, J.W., & Martin, C.K. (2021). Digital tools to support family-based weight management for children: Mixed methods pilot and feasibility study. Pediatrics and Parenting. 4(1) doi: 10.2196/24714 PMID: 33410760
Antczak, D., Lonsdale, C., Lee, J., Hilland, T., Duncan, M.J., del Pozo Cruz, B., Hulteen, R.M., Parker, P. and Sanders, T. (2020). Physical Activity and Sleep are Weakly Related in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 51, doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101278
Olson KL, Neiberg R, Espeland M, Johnson K, Knowler W, Pi-Sunyer X, Staiano AE, Wagenknecht L, & Wing RR. (2020) Waist circumference change during intensive lifestyle intervention and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Look AHEAD trial. Obesity.
Kracht CL, Katzmarzyk PT, & Staiano AE. (2020) Comparison of abdominal visceral adipose tissue measurements in adolescents between magnetic resonance imaging and dual energy x-ray absorptiometry. International Journal of Obesity.
Kracht CL, Webster E, & Staiano AE. (2020). A natural experiment of state-level physical activity and screen-time policy changes: Early childhood education (ECE) centers and child physical activity. BMC Public Health.
Fearnbach SN, Johannsen NM, Martin CK, Beyl RA, Hsia DS, Carmichael CT, & Staiano AE. (2020) A pilot study of cardiorespiratory fitness, adiposity, and cardiometabolic health in youth with overweight and obesity. Pediatric Exercise Science.
Webster E, & Staiano AE. (2020) Extended heavy television viewing may impact weight long-term in adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health.
Kepper MM, Staiano AE, Katzmarzyk PT, Reis RS, Eyler AA, Griffith DM, KendallML, ElBanna B, Denstel KD, & Broyles ST. (2020). Using mixed methods to understand women’s parenting practices related to their child’s outdoor play and physical activity among families living in diverse neighborhood environments. Health and Place.
Kracht CL, Joseph ED, & Staiano AE. (2020). Video games, obesity, and children. Current Obesity Reports.
Kracht CL, Champagne CM, Hsia DS, Martin CK, Newton RL, Katzmarzyk PT, & Staiano AE. (2020). Association between meeting physical activity, sleep, and dietary guidelines and cardiometabolic risk factors and adiposity in adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health.
Hulteen, R.M., Waldhauser, K.J. and Beauchamp, M.R. (2019). Promoting Health-Enhancing Physical Activity: A State-of-the-Art Review of Peer-Delivered Interventions. Current Obesity Reports, 8, 341-353. doi: 10.1007/s13679-019-00366-w (invited)
Kracht CL, Chaput JP, Martin CK, Champagne CM, Katzmarzyk PT, & Staiano AE. (2019). Associations of sleep with food cravings, diet, and obesity in adolescence. Nutrients.
Joseph E, Kracht CL, St. Romain J, Allen AT, Barbaree C, Martin CK, & Staiano AE. (2019). Young children’s screen-time and physical activity: Perspectives of parents and early care and education center providers. Global Pediatric Health.
Staiano AE, Adams MA, & Norman GJ. (2019). Motivation for Exergame Play Inventory: Construct validity and test-retest reliability. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace.
Hawkins KR, Apolzan JW, Staiano AE, Shanley JR, & Martin CK. (2019). Efficacy of a home-based parent training-focused weight management intervention for preschool children: The DRIVE randomized controlled pilot trial. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior.
Sandoval P, Staiano AE, & Kihm H. (2019). The influence of visual and auditory stimuli on intensity of physical activity in school-aged children. The Physical Educator.
Webster EK, Martin CK, & Staiano AE. (2019) Fundamental motor skills, physical activity, and screen-time in preschoolers. Journal of Sport and Health Science.
Staiano AE, Beyl RA, Hsia DS, Katzmarzyk PT, & Newton R.L. (2018). A 12-week randomized controlled pilot study of dance exergaming in a group: Influence on psychosocial factors in adolescent girls. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace.
Katzmarzyk PT, Denstel KD, Beals K, Carlson J, Crouter SE, McKenzie TL, Pate RR, Sisson SB, Staiano AE,Stanish H, Ward DS, Whitt-Glover M, & Wright C. (2018). Results from the United States 2018 Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth. Journal of Physical Activity & Health.
Staiano AE, Kihm H, & Sandoval P. (2018). The use of competition to elicit high intensity physical activity during children’s exergame play. Journal of Family & Consumer Sciences.
Flynn, R.M.,Staiano, A.E., Beyl, R., Richert, R.A., Wartella, E. & Calvert, S.L. (2018). The influence of active gaming on cardiorespiratoryfitness in Black and Hispanic youth. Journal of School Health.
Staiano, A.E., Webster, E.K., Allen, A.T., Jarrell, A.R., & Martin, C.K. (2018). Screen-time policies and practices in early care and education centers in relationship to child physical activity. Childhood Obesity.
Staiano, A.E., Martin, C.K., Champagne, C.M., Rood, J.C., & Katzmarzyk, P.T. (2018). Sedentary time, physical activity, and adiposity in a longitudinal cohort of non-obese young adults. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Staiano, A.E., Beyl, R.A., Guan, W., Hendrick, C.A., Hsia, D.S., & Newton, R.L. (2018). Home-based exergaming among children with overweight and obesity: A randomized clinical trial. Pediatric Obesity.
Staiano, A.E., Allen, A.T., Fowler, W., Gustat, J., Kepper, M.M., Lewis, L., Martin, C.K., St. Romain, J., & Webster, E.K. (2018). State licensing regulations on screen-time in childcare centers: An impetus for participatory action research. Progress in Community Health Partnerships: Research, Education, and Action.
Heerman, W.J., Bennett, W.L., Kraschnewski, J.L., Nauman, E., Staiano, A.E., & Wallston, K.A. (2018) Willingness to participate in weight-related research among patients in PCORnet Clinical Data Research Networks. BMC Obesity.
Cohen, K.E., Morgan, P.J., Plotnikoff, R.C., Hulteen, R.M. and Lubans, D.R. Psychological, social and physical environmental mediators of the SCORES intervention on physical activity among children living in low-income communities. (2017). Psychology of Sport & Exercise, 32, 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2017. 05.001
Katzmarzyk, P.T., & Staiano, A.E. (2017). Relationship between meeting 24-hour movement guidelines and cardiometabolic risk factors in children. Journal of Physical Activity & Health.
Staiano, A.E., Beyl, R.A., Hsia, D.S., Katzmarzyk, P.T., Mantzor, S., Newton, R.L., Jarrell, A., & Tyson, P. (2017). Step tracking with goals increases children’s weight loss in a behavioral intervention. Childhood Obesity
Staiano, A.E., Marker, A.M., Liu, M., Hayden, E., Hsia, D.S., & Broyles, S.T. (2017). Childhood obesity screening and treatment practices of pediatric healthcare providers. Journal of the Louisiana State Medical Society
Baranowski, T., Blumberg, F., Gao, Z., Kato, P.M., Kok, G., Lu, A.S., Lyons, E.J., Morrill, B.A., Peng, W., Prins, P.J., Snyder, L., Staiano, A.E., & Thompson, D. (2017) Getting research on games for health funded. Games for Health Journal.
Wilfley, D.E., Staiano, A.E., Altman, M., Lindros, J., Lima, A., Hassink, S.G., Dietz, W.H., & Cook, S. (2017). Improving Access and Systems of Care for Evidence-Based Childhood Obesity Treatment Conference W. Improving access and systems of care for evidence-based childhood obesity treatment: Conference key findings and next steps. Obesity.
Kihm H, Staiano AE, & Sandoval P. (2017) Project IPAL: To enhance the well-being of elementary school children. Journal of Family & Consumer Sciences 109(1) 54-56.
Staiano AE, Marker AM, Beyl RA, Hsia DS, Katzmarzyk PT, & Newton RL. (2017). A randomized controlled trial of dance exergaming for exercise training in overweight and obese adolescent girls. Pediatric Obesity. 12(2) 120-128.
Staiano AE, Marker AM, Frelier JM, Hsia DS, & Broyles ST. (2017). Family-based behavioral treatment for childhood obesity: Parent-reported barriers and facilitators. The Ochsner Journal. 17(1):83-92.
Staiano AE, Beyl RA, Hsia DS, Katzmarzyk PT, & Newton RL. (2017). Twelve weeks of dance exergaming in overweight and obese adolescent girls: Transfer effects on physical activity, screen time, and self-efficacy. Journal of Sport and Health Science.
Katzmarzyk PT, Denstel KD, Beals K, Bolling C, Wright C, Crouter SE, McKenzie TL, Pate RR, Saelens BE, Staiano AE, Stanish HI, & Sisson SB. (2016). Results from the United States of America's 2016 report card on physical activity for children and youth. Journal of Physical Activity and Health.
Staiano AE, Morrell M, Hsia DS, Hu G, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2016) The burden of obesity, elevated blood pressure, and diabetes in uninsured and underinsured adolescents. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders. 14(9), 437-441.
Staiano AE, Marker AM, Martin CK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2016). Physical activity, mental health, and weight gain in a longitudinal observational cohort of nonobese young adults. Obesity, 24(9), 1969-1975.
Staiano AE, Marker AM, Frelier JM, Hsia DS, & Martin CK. (2016). Influence of screen-based peer modeling on preschool children's vegetable consumption and preferences. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, 48(5), 331-335
Mackintosh KA, Standage M, Staiano AE, Lester L, & McNarry MA. (2016). Investigating the physiological and psychosocial responses of single-and dual-player exergaming in young adults. Games for Health Journal, 5(6), 375-381
Baranowski T, Blumberg F, Buday R, DeSmet A, Fiellin LE, Green CS, Kato PM, Lu AS, Maloney AE, Mellecker R, Morrill BA, Peng W, Shegog R, Simons M, Staiano AE, Thompson D, & Young K. (2016). Games for health for children-current status and needed research. Games for Health Journal, 5(1), 1-12.
Michel, G. F., Marcinowski, E. C., Babik, I., Nelson, E. L., & Campbell, J. M. (2015). An Interdisciplinary Biopsychosocial Perspective on Infant Development. In S. Calkins (Ed.) Handbook of Infant Development: A Biopsychosocial Perspective, 427-446.
Staiano AE, Broyles ST, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2015). School term vs. school holiday: Associations with children's physical activity, screen-time, diet and sleep. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(8), 8861-8870.
Staiano AE, Harrington DM, Johannsen NM, Newton RL, Jr., Sarzynski MA, Swift DL, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2015). Uncovering physiological mechanisms for health disparities in type 2 diabetes. Ethnicity and Disease, 25(1), 31-37.
Marker AM, & Staiano AE. (2015) Better together: Outcomes ofcooperation versus competition in social exergaming. Games for Health Journal, 4(1), 25-30.
Carson V, Staiano AE, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2015). Physical activity, screen time, and sitting among U.S. adolescents. Pediatric Exercise Science, 27(1), 151-159.
Pere, C., Ginn, R., Hill, N., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2015). Childhood Obesity prevention: A service-learning advocacy project. Journal for Service-Learning, Leadership, and Social Change.
Harshaw, C., Marcinowski, E. C., & Campbell, J. M. (2014). Communicating Developmental Psychobiology to the Masses: Why Psychobiologists Should Contribute to Wikipedia. Developmental Psychobiology, 56 (7), 1439-1441.
Staiano AE, & Flynn R. (2014). Therapeutic uses of active videogames: A systematic review. Games for Health Journal, 3(6), 351-365.
Staiano AE. (2014). Learning by playing: Video gaming in education-a cheat sheet for games for health designers. Games for Health Journal, 3(5), 319-321.
Flynn RM, Richert RA, Staiano AE, Wartella E, & Calvert SL. (2014). Effects of exergame playon EF in children and adolescents at a summer camp for low income youth. Journal of Educational and Developmental Psychology, 4(1), 209-225.
Katzmarzyk PT, Barlow S, Bouchard C, Catalano PM, Hsia DS, Inge TH, Lovelady C, Raynor H, Redman LM, Staiano AE, Spruijt-Metz D, Symonds ME, Vickers M, Wilfley D, & Yanovski JA. (2014). An evolving scientific basis for the prevention and treatment of pediatric obesity. International Journal of Obesity, 38(7), 887-905.
Staiano AE, Gupta AK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2014). Cardiometabolic risk factors and fat distribution in children and adolescents. Journal of Pediatrics, 164(3), 560-565.
Baranowski T, Adamo KB, Hingle M, Maddison R, Maloney A, Simons M, & Staiano AE. (2013). Gaming, adiposity, and obesogenic behaviors among children. Games for Health Journal, 2(3), 119-126.
Michel, G. F., Babik, I., Nelson, E. L., Campbell, J. M., & Marcinowski, E. C. (2013). How the development of handedness could contribute to the development of language. Developmental Psychobiology, 55(6), 608-20.
Staiano AE, Broyles ST, Gupta AK, Malina RM, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013). Maturity-associated variation in total and depot-specific body fat in children and adolescents. American Journal of Human Biology, 25(4), 473-479.
Staiano AE, Broyles ST, Gupta AK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013) Ethnic and sex differences in visceral, subcutaneous, and total body fat in children and adolescents. Obesity, 21(6), 1251-1255.
Harrington DM, Staiano AE, Broyles ST, Gupta AK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013). BMI percentiles for the identification ofabdominal obesity and metabolic risk in children and adolescents: Evidence in support of the CDC 95th percentile. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 67(2), 218-222.
Staiano AE, Harrington DM, Broyles ST, Gupta AK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013). Television, adiposity, and cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 44(1), 40-47.
Calvert SL, Staiano AE, & Bond BJ. (2013). Electronic gaming and the obesity crisis. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, 139,51-57.
Harrington DM, Staiano AE, Broyles ST, Gupta AK, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013). Waist circumference measurement site does not affect relationships with visceral adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children. Pediatric Obesity, 8(3), 199-206.
Barreira TV, Staiano AE, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2013). Validity assessment of a portable bioimpedance scale to estimate body fat percentage in white and African-American children and adolescents. Pediatric Obesity, 8(2), 29-32.
Staiano AE, Abraham AA, & Calvert SL. (2012). The Wii Club: Gaming for weight loss in overweight and obese youth. Games for Health Journal, 1(5), 377-380.
Broyles ST, Staiano AE, Drazba KT, Gupta AK, Southern M, & Katzmarzyk PT. (2012). Elevated C-reactive protein in children from risky neighborhoods: Evidence for a stress pathway linking neighborhoods and inflammation in children. PloS One, 7(9)
Staiano AE, Katzmarzyk PT. (2012). Ethnic and sex differences in body fat and visceral and subcutaneous adiposity in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity, 36(10), 1261-1269.
Staiano AE, & Calvert SL. (2012). Digital gaming and pediatric obesity: At the intersection of science and social policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 6(1), 54-81.
Staiano AE, & Calvert SL. (2011). Exergames for physical education courses: Physical, social, and cognitive benefits. Child Development Perspectives, 5(2),93-98.
Child Trauma
Kim, H., Jonson-Reid, M., Kohl, P., Chiang, C. J., Drake, B., Brown, D., McBride, T., & Guo, S. (2020).Latent class analysis risk profiles: An effective method to predict a first re-report of maltreatment. Evaluation and Program Planning, 101792.
Jonson-Reid, M., Chiang, C.J., Kohl, P., Drake, B., Brown, D., Guo, S., & McBride, T. (2019). Repeat reports among cases reported for child neglect: A scoping review. Child Abuse & Neglect, 92, 43-65.
Chiang, C. J.,& Ma, T. J. (2013). Working experiences with children witnessed domestic homicide, Taiwanese Social Work, 11, 115-144
Lee, L., Miller, C., & Caballero, J, (In Progress). Community-based, social justice-oriented experiences in ethnically, socio-economically diverse preschools: Early childhood pre-service teachers’ perspectives.
Drake, B., Jonson-Reid, M., Kim, H., Chiang, C. J., & Davalishvili, D. (2021) Disproportionate Need as a Factor Explaining Racial Disproportionality in the CW System. In Racial Disproportionality and Disparities in the Child Welfare System (pp. 159-176). Springer, Cham.
Kracht CL, Webster EK, & Staiano AE. (2019). Sociodemographic differences in young children meeting 24-hour movement guidelines. Journal of Physical Activity & Health.
Lee, L. (2018). Korean mode of color-blind perspectives on ethnic diversity: A case study of Korean Elementary teachers. International Journal of Diversity of Education, 18(1), 27-38.
Lee, L. (2016, Summer). A learning journey with Latino immigrant children: An American low-income preschool project. Childhood Explorer, 3.
Lee, L., & Misco, T. (2014). All for one or one for all: An analysis of the concepts of patriotism and others in multicultural Korea through elementary moral education textbooks. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher. 23(1), 2-10.
Misco, T., & Lee, L. (2013). “There is no such thing as being Guamanian”: Controversial Issues in the context of Guam. Theory and Research in Social Education, 42(3), 414-439.
Misco, T.,& Lee, L. (2012).1Multiple and overlapping identities: The case study of Guam. Multicultural Education, 20(1), 23-32.
Lee, L. (2011). Language and identity in the moral domains: Minority children in education. Focus on Elementary, 23(3). 3-6.
Lee. L. (2011). Cultural awareness in beliefs and practice: An elementary teacher’s perspective on Korean children and their culture. Focus on Teacher Education, 11(2), 4-10.
ECE Professional Attrition
Chiang, C.J., Jonson-Reid, M., Kim. H., Drake. B., Pons. L., Kohl. P., Constantino. J., & Auslander. W., (2018) Service engagement and retention: Lessons from the Early Childhood Connections Program. Children and Youth Services Review, 88, 114-127. DOI: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.02.028
Carson, R. L., Baumgartner, J. J., Ota, C.L., Pulling Kuhn, A. C., & Durr, A. (2016). An ecological momentary assessment of burnout, rejuvenation strategies, job satisfaction, and quitting intentions in childcare teachers. Early Childhood Education Journal, 1-8.
Educational Leadership
Nelson-Smith, K. (2009). Building Opportunities through Leadership Development (BOLD). A curriculum.
Jonson-Reid, M., & Chiang, C. J.(2019). Problems in Understanding Program Efficacy in Child Welfare. In Re-Visioning Public Health Approaches for Protecting Children (pp. 349-377). Springer, Cham.
Environment (Classroom)
Deris, A., DiCarlo, C., Wagner, D. & Krick-Oborn, K. (in press). Using environmental modification and teacher mediation to increase literacy behaviors in inclusive preschool settings. Infants & Young Children
Reames, H. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2016). Creating a learner-centered classroom. Focus on PK/K, Early Years Bulletin, 3(3), 1-3, 7.
Guan, X. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2009). Minimizing stressors in the early childhood classroom. Collaborations, 2, 22-23.
Wayne, A., DiCarlo, C., Burts, D., & Benedict, J. (2007). Increasing the literacy behaviors of preschool children through environmental modifications. The Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 22(1), 5-16.
DiCarlo, C.F., Stricklin, S., & Reid, D.H. (2006). Increasing toy play among toddlers with and without disabilities by modifying structural quality of the classroom environment. National Head Start Association Dialog, 9(1)49-62.
Behavior Guidance
Reames, H. & DiCarlo, C. (2018). Using positive reinforcement to increase attentive behavior and correct task performance for preschoolers during extra curricular activities. Journal of Teacher Action Research, 4(2), 1-9.
DiCarlo, C.F., Baumgartner, J., & Ourso, J. & Powers, C. (2016). Using least-to-most assistive prompt hierarchy to increase child compliance with teacher directives in preschool classroom. Early Childhood Education Journal, 44(6) 1-10.doi:10.1007/s10643- 016-0825-7.
DiCarlo, C. & Baumgartner, J. (2011). Promoting Positive Behavior in the Preschool Classroom. Focus on Pre-K and K, 24(1), 4-7.
Torres, A., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2008). Positive Guidance. Collaborations. 3, 14-15.
Literacy and Language
Terrusi, M. (2020). Illustrated books without words for inclusion: Method reflections on reading, between form and metaphor. In E.A. Emili & V. Macchia (Eds.), Reading the inclusion: Picture books and books for one and all (pp. 77-88). ETS Editions.
Terrusi, M. (2018). Silent Books. Wonder, Silence and Other Metamorphosis in Wordless Picture Books. Proceedings, 1(9), 1 – 12. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1090879
Terrusi, M. (2017). Child portraits. Representations of the child body in children's illustration and literature: Some interpretative categories. Magazine of history of education, 4(1), 183 – 210. http://dx.doi.org/10.4454/rse.v4i1.28
Terrusi, M. (2017). Constellation of early childhood, Gugu's firmament. A portrait of Augusta Rasponi del Sale (Ravenna 1864-1942), author of picture book. Research of education and education, 12(2), 71 – 88. http://dx.doi.org/10.6092/issn.1970-2221/7082
Terrusi, M. (2017). Eternals, children, winged: Neoteny, lightness and literature for children. Training Studies, 20(2), 387 – 408. http://dx.doi.org/10.13128/Studi_Formaz-22195
Terrusi, M. (2017). Mute wonders: Silent book and children's literature. Carocci.
Beach, D., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2016). Can I play, again? Using a literacy ipad app to increase letter recognition & phonemic awareness. Journal of Teacher Action Research,2(2), 70-76.
Terrusi, M. (2016). Children read great. In C.I. Salviati (Ed.), In vitro: An experimental project to promote reading (pp. 18-21). Center for Literature and Reading. MIBAC Ministry of Artistic and Cultural Heritage.
Terrusi, M. (2016). The possible, the visible, the questionable: Unexpected (or wordless) books at school. In E. A. Emili (Ed.), Languages for an inclusive school (pp. 51-66). Free Books.
Grilli, G. & Terrusi, M. (2014). A (Visual) Journey to Italy. In E. Arizpe, T. Colomer, & C. Martinez-Roldan (Eds.), Visual Journeys Through Wordless Narratives (pp. 217-238). Bloomsbury Academic.
Grilli, G. & Terrusi, M. (2014). Migrant readers and wordless books: Visual narratives' inclusive experience. Encyclopaideia, 18(38), 67 – 90. http://dx.doi.org/10.6092/issn.1825-8670/4508
Ota, C. L. & Austin, A.M. (2013). Training and mentoring: Family child care providers’ use of linguistic inputs in conversations with children. Early Childhood Research Quarterly 28(4), 972-983
Terrusi, M. (2013). The room of children's literature: Educators, teachers and storytellers. In C. Panciroli & F. D. Pizzigoni (Eds.), The museum as a workshop of experiences with heritage: The example of the Mode (pp. 1-199). Quiedit.
Terrusi, M. (2013). The life of children in the figures: Gugú, a forgotten author. Childhood, 6(1), 335-339.
Terrusi, M. (2012). Illustrated books: Read, look, name the world in children's books. Carocci
Brintazzoli, G. & Terrusi, M. (2011). At the edge of the page. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 92(1), 50 – 52.
Terrusi, M. (2011). Read the visible. The world pictured in the pages. Form and poetics of early childhood books. In E. Beseghi & G. Grilli (Eds.), The invisible literature: Childhood and children's books (pp. 143-164). Carocci.
Chung, M. & Lee, L. (2009). Critical literacy theories for media literacy education. Academic Exchange Quarterly, 13(4), 121-127.
Lee, L. (2009). Media literacy. Academic Exchange Quarterly, 13(4), 10.
Terrusi, M. (2009). Classic fairy tales with contemporary design, interview with Steven Guarnaccia. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 82(1), 60 – 61.
Terrusi, M. (2009). The art of the three little pigs. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 82(1), 59 – 63.
Terrusi, M. (2007). Philosophers animals: whether they are feathered canids or felines, we can consider them Masters. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 74(1), 30 – 31.
Terrusi, M. (2007). Families and new conformisms: The challenge of the bourgeois mentality seen through the complex father-son dialectic: Holidays with the father by Marcello Argilli. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 73(1), 44-45.
Terrusi, M. (2007). Books on the road. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 76(1), 54 – 55.
Terrusi, M. (2006). Andersen Press turns 30: from the voice of its founder, Klaus Flugge, the story of the famous English publishing house. Andersen, 224(1), 31 – 35.
Mathematics
Hendershot, S., Austin, A. M. B., Blevins-Knabe, B., & Ota, C.L. (2015). Young children’s mathematics references during free play in family child care settings. Early Child Development and Care. 186(7), 1126-1141.
Misco, T., Lee, L., & Malone, K. Goley, S., & Seabolt, P. (2012).*Using the idea of insurance to develop mathematical skills and democratic dispositions. Interdisciplinary Journal of Teaching and Learning, 2(2), 78-89.
Austin, A.M., Blevins-Knabe, B., Ota, C., Rowe, T., & Knudsen Lindauer, S. (2011). Mediators of preschoolers’ early mathematics concepts. Early Child Development and Care, 181(9), 1181-1198.
Motor Skills
Molinini, R. M., Koziol, Marcinowski, E. C., Tripathi, T., Hsu, L.-Y., Harbourne, R. T., Lobo, M. A., McCoy, S. W., Bovaird, J., & Dusing, S. C. (2021). Early motor skills predict the developmental trajectory of problem solving skills in young children with motor impairments. Developmental Psychobiology. [Early View]
Barnett, L.M., Stodden, D.F., Hulteen, R.M. and Sacko, R. (2020). Motor Proficiency Assessment. In T. Brusseau, S. Fairclough & D. Lubans (Eds.), The Routledge Handbook of Youth Physical Activity.
Gonzalez, S. L., Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., Michel, G. F., Coxe, S., & Nelson, E. L. (2020). Preschool language ability is predicted by toddler hand preference trajectories. Developmental Psychology, 56(4), 699-709.
Hulteen, R.M., Barnett, L.M. True, L., Lander, N., Cruz, B.P. and Lonsdale, C. (2020). Validity and Reliability Evidence for Motor Competence Assessments in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Journal of Sports Sciences, 38(15), 1717-1798, doi: 10.1080/02640414.2020.1756674
Hulteen, R.M., True, L., and Pfeiffer, K. (2020). Differences in Associations of Product- and Process-Oriented Motor Competence Assessments with Physical Activity in Children. Journal of Sports Sciences, 38(4), 375-382. doi:10.1080/02640414.2019.17 02279
Webster, E.K., Kracht, C.L., Newton, R.L., Beyl, R.A., & Staiano, A.E. (2020). Intervention to improve preschoolers’ fundamental motor skills: Protocol of a parent-focused, mobile app-based comparative effectiveness trial. Research Protocols, 9(10):e19943.
Fearnbach, S.N., Martin, C.K., Heymsfield, S.B., Staiano, A.E., Newton, R.L., Garn, A.C., Johannsen, N.M., Hsia, D.S., Carmichael, O.T., Murray, K.B., Ramakrisnapillai, S., Murray, K.B., Blundell, J.E., & Finlayson, G.S. (2020) Validation of the Activity Preference Assessment: A tool for quantifying children’s implicit preferences for sedentary and physical activities. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity
Kracht, C.L., Webster, E.K., & Staiano, A.E. (2020) Relationship between the 24-hour movement guidelines and fundamental motor skills in preschoolers. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.
Marcinowski, E. C., Tripathi, T., Hsu, L.-Y., McCoy, S. W., & Dusing, S. C. (2019). Sitting skill and the emergence of arms‐free sitting affects the frequency of object looking and exploration. Developmental Psychobiology, 61 (7), 1035-47.
Marcinowski, E. C., Nelson, E. L., Campbell, J. M., & Michel, G. F. (2019). The development of object construction from infancy through toddlerhood. Infancy, 24(3), 368-391.
Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., & Michel, G. F. (2018). The Development of Neuromotor Skills and Hand Preference During Infancy. Developmental Psychobiology, 60(2), 165-175.
lteen, R.M., Morgan, P.J., Barnett, L.M., Robinson, L.E. Barton, C., Wrotniak, B., and Lubans, D.R. (2018). Initial Predictive Validity of the Lifelong Physical Activity Skills Battery. Journal of Motor Learning and Development, 6(2), 301-314. doi: 10.1123/jmld.2017-0036
Michel, G. F., Babik, I., Nelson, E. L., Campbell, J. M., & Marcinowski, E. C. (2018). Evolution and Development of Handedness: An Evo-Devo Approach. In G. Forrester, W. D. Hopkins, K. Hudry, & A. K. Lindell (Eds.), Cerebral Lateralization and Cognition: Evolutionary and Developmental Investigations of Motor Biases. Elsevier Inc.: Academic Press. 347-374.
Hulteen, R.M., Morgan, P.J., Barnett, L.M., Stodden, D.F. and Lubans, D.R. Development of Foundational Motor Skills: A Conceptual Model for Physical Activity Across the Lifespan. (2018). Sports Medicine, 48(7), 1533-1540. doi: 10.1007/s4029-018-0892-6
Marcinowski, E. C., & Campbell, J. M. (2017). Building on what you have learned: Constructing skill during infancy influences the development of spatial relation words. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 41(3), 341-349. doi:10.1177/0165025416635283
Nelson, E. L., Gonzalez, S., Coxe, S., Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., & Michel, G. F. (2017). Toddler hand preference trajectories predict 3-year language outcome. Developmental Psychobiology, 59(7), 876-887.
Nathan, N., Cohen, K., Beauchamp, M. W.L., Hulteen, R.M., Babic, M. and Lubans, D.R. Feasibility and Efficacy of the Greater Leaders Active StudentS (GLASS) Program on Improving Children’s Fundamental Movement Skills: A Pilot Study. (2017). Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 20(12), 1081-1086. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2017.04.016
Johnson, T.M., Ridgers, N.D. Hulteen, R.M., Mellecker, R.R. and Barnett, L.M. (2016). Does Playing a Sports Active Video Game Improve Young Children’s Ball Skill Competence? Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 19(5), 432-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2015.05.002
Marcinowski, E. C., Campbell, J. M., Faldowski, R. A., & Michel, G. F. (2016). Do hand preferences predict stacking skill during infancy? Developmental Psychobiology, 58(8), 958-967.
Michel, G. F., Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., Nelson, E. L., & Babik, I. (2016). Infant Hand Preference and the Development of Cognitive Abilities. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 410. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00410
Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., Babik, I., & Michel, G. F. (2015). The influence of a hand preference for acquiring objects on the development of a hand preference for unimanual manipulation from 6 to 14 months. Infant Behavior and Development, 39, 107-117.
Campbell, J. M., Marcinowski, E. C., Latta, J. A., & Michel, G. F. (2015). Different assessment tasks produce different estimates of handedness stability during the 8 to 14 month age period. Infant Behavior and Development, 39, 67-80.
Hulteen, R.M., Johnson, T.M., Ridgers, N.D., Mellecker, R.R. and Barnett, L.M. (2015). Children’s Movement Skills When Playing Active Video Games. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 121(3), 1-24. doi: 10.2466/25.10.PMS.121c24x5
Michel, G. F., Nelson, E. L., Babik, I., Campbell, J. M., & Marcinowski, E. C. (2013). Multiple trajectories in the developmental psychobiology of human handedness. In R. M. Lerner, & J. B. Benson (Eds.), Embodiment and epigenesis: Theoretical and methodological issues in understanding the role of biology within the relational developmental system Part B: Ontogenetic Dimensions. Elsevier Inc.: Academic Press, 227-260.
Music Education
Isbell, D. (2018). Music educators consider musical futures. Contributions in Music Education. 43(1). 39-58.
Isbell, D. S., & Stanley, A. M. (2018). Code-switching musicians: an exploratory study. Music Education Research,20(2), 145-162.
Isbell, D. (2015). My Music and School Music: Formal and Informal Music Experiences. In Burton, S. and Snell, A. (Eds.), Engaging Musical Practices: A Sourcebook for Instrumental Music. Rowman and Littlefield Education Publishers, Inc.
Isbell, D. and Stanley, A. (2015) Are you a musical code-switcher?Polyphonic.org: The Orchestra Music Forum. http://www.polyphonic.org/2015/06/22/are-you-a-musical-code-switcher/.
Isbell, D. (2015)Apprehensive and excited: Music education students ’ encounter vernacular musicianship. Journal of Music Teacher Education. doi:10.1177/1057083714568020.
Isbell, D. (2014). The socialization and identity of undergraduate music teachers: A review of literature. Update: Applications for Research in Music Education.doi: 10.1177/8755123314547912.
Isbell, D. (2012). Learning theories: Insights for music educators. General Music Today 25(2). 9-23.
Isbell, D. (2009). Understanding Socialization and Occupational Identity among Preservice Music Teachers. In M. Schmidt (Ed.), Collaborative action for change:Selected proceedings from the 2007 symposium on music teacher education. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
Isbell, D. (2007). Popular music and the public school music classroom. Update: Applications for Research in Music Education.26(1).
Bowers, J., Cassellberry, J., Isbell, D., Kyakuwa, J., Li, Y., Mercado, E., and Wallace, E.(2019) A Descriptive Study of the Use of Music During Naptime in Louisiana Child Care Centers. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 33(2). doi: 10.1080/02568543.2019.1577770.
National Disasters
DiCarlo, C.F., Burts, D., Buchanan, T., Aghayan, C., & Benedict, J. (2007). Making Lemonade from Lemons: Early Childhood Teacher Educators’ Programmatic Responses to Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education, 28 (1), 61-68.
Outdoor Education
Terrusi, M. (2020). Children's books and outdoor education imagery: Stories and figures to tell each other. In S. Meo & M. Ognissanti (Eds.), From risk to opportunity: Outdoor education experiences in childcare and primary school services (pp. 115-118). Junior- Children Editions.
Farné, R., Bortolotti, A., Terrusi, M. (2018) Introduction: Natural educational needs. In R. Farné, A. Bortolotti, & M. Terrusi (Eds.), Outdoor education: Theoretical perspectives and good practices (pp. 13-24). Carocci.
Terrusi, M. (2018). Children's literature and natural imaginary. In R. Farné, A. Bortolotti, & M. Terrusi (Eds.), Outdoor education: Theoretical perspectives and good practices (pp. 183- 200). Carocci.
Terrusi, M. (2015). The green ship: natural education and reading for children. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 106(2), 40 – 42.
Terrusi, M. (2015). The teacher's shelf. Childhood, 1(4), 334 – 336.
Terrusi, M. (2014). Children's literature and natural narratives. In R. Farné & F. Agostini (Eds.) Outdoor education: Education takes care of outdoors (pp. 69-74). Junior-Spaggiari.
Grantham-Caston, M., & Perry, M. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2019). Playful Reggio Emilia. International Play Association, Spring-Fall, 20-25.
Dicarlo, C.F., Baumgartner, J.J., Ota, C.L. & Jensen, C. (2015). Preschool teachers’ perceptions of rough and tumble play vs. aggression in preschool-aged boys. Early Child Development and Care, 185(5), 779-790.
Carson, R., Lima, M. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2015). Play On! Playground learning activities for youth fitness (2nd edition). Reston, VA: American Association for Physical Activity and Recreation.
Casey, E. M. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2015). Play traditions in the Garifuna culture of Belize. International Play Association eJournal, www.Ipausa.org.
DiCarlo, C.F. & Vagianos, L.A. (2009). Preferences and play. Young Exceptional Children, 12(4), 31-39.
Popular Culture
Lee, L. (2012). Conceptualizing childhood in Korean Educational Broadcasting System (EBS): Critical analysis of Popular Picture Book, Pororo. In V. Cvetkovic & D. Olsen (Eds.), Fleeting Images: A Childhood Studies Examination of Children in Popular Culture (pp. 85-100). Lexington Press.
Lee, L. (2012). "That's a great idea but I will think about it later": Early childhood pre-service Teachers' perceptions about popular culture in Teaching. Teacher Education and Practice, 25(1), 87-99.
Lee, L. (2010). Disney in Korea: A socio-cultural context of children’s popular culture. Red Feather Journal: An International Journal of Children’s Visual Culture, 1(2), 41-45.
Lee, L.,& Goodman, J. (2010). Romantic love and sexuality in Disney: A study of young, Korean immigrant girls’ perspectives. Education and Society, 28(1), 25-47.
Lee, L. & Goodman, J. (2009). Traversing the challenges of conducting research with young immigrant children: The case of Korean children. Interchange, 40(2), 225–244.
Lee, L. (2009). American immigrant girls’ perceptions about female body image in Disney: A critical analysis of young Korean girls. European Early Childhood Education Research Journal, 17(3), 363-375.
Lee, L. (2009). Marry the prince or stay with family—That is the question: A perspective of young Korean immigrant girls on Disney’s marriages in the United States. Australian Journal of Early Childhood, 34(2), 39-46.
Lee, L. (2009). Young American immigrant children’s interpretations of royalty in popular culture: A case study of Korean girls’ perspectives. Journal of Early Childhood Research, 7(2), 200-215.
Lee, L. (2008). Issues of popular culture and young children in American society: A Critical perspective. Academic Exchange Quarterly, 12(4),49-53.
Lee, L. (2008). Understanding gender through Disney’s marriages: A study of young Korean immigrant girls. Early Childhood Education Journal, 36(1), 11-18.
Parents in Education
Kepper MM, Staiano AE,Katzmarzyk PT, Reis R, Eyler A, Griffith DM, Kendall M, ElBanna B, Denstel KD, & Broyles ST (2019). Neighborhood influences on women’s parenting practices for adolescents’ outdoor play: A qualitative study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Baumgartner, J., McBride, B., Ota, C.L., & DiCarlo, C., (2016). How much do they need to be the same? What parents believe about continuity between home and childcare environments. Early Child Development and Care, 187(7), 1184-1193.
Professional Development
Bowers, J., Isbell, D., Stanley, A., and West, J. (in press). Attrition, (De)motivation, and “Effective” Music Teacher Professional Development: An Instrumental Case Study. Bulletin of the Council for Research in Music Education.
Grantham-Caston, M. & DiCarlo, C. (2019). Lights! Camera! Action! Improving your teaching through video self-reflection. Young Children, 74(4)
Grantham-Caston, M. & DiCarlo, C. (2019). The impact of video self-reflection on teacher practice. National Head Start Association Dialog, 22(2), 61-75.
Grantham-Caston, M. & DiCarlo, C. (2019). Video self-reflection. Dialog, 22(2), 99-102.
Isbell, D. and Russell, J. (2009). Perceptions of Music Educators Regarding the Practice, Impact, and Outcomes of Professional Development. Southern Music Education Journal.
Physical Education
Ferkel, R.C.. Allen, H.R., True, L. and Hulteen, R.M. (2018). Split-Week Programming for Secondary Physical Education: Inducing Behavioral Change for Lifetime Fitness. Journal of Physical Education, Recreation and Dance, 89(8), 11-22. doi: 10.1080/07303084.2018.1503118
Hulteen, R.M., Morgan, P.J., Barnett, L.M., Barton, C., Wrotniak, B., Robinson, L.E. and Lubans, D.R. (2018). Development, Content Validity and Test-Retest Reliability of the Lifelong Physical Activity Skills Battery in Adolescents. Journal of Sports Sciences, 36(20), 2358-2367. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2018.1458392
Hulteen, R. M., Smith, J.J., Morgan, P.J., Barnett, L.M, Hallal, P.C., Colyvas, K. and Lubans, D.R. (2017). Global Sport and Leisure-Time Physical Activities Participation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Preventive Medicine, 95, 14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.11.027
Hulteen, R.M., Lander, N.J., Morgan, P.J., Barnett, L.M., Robertson, S.J. and Lubans, D.R. (2015). Validity and Reliability of Field-Based Measures for Assessing Movement Skill Competency in Lifelong Physical Activities: A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine, 45(10), 1443-54. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0357-0
Physical Therapy
Harbourne, R. T., Dusing, S. C., Lobo, M. A., McCoy, S. W., Koziol, N. A., Hsu, L.-Y., Willett, S., Marcinowski, E. C., Babik, I., Cunha, A. B., An, M., Chang, H.-J., Bovaird, J. A., Sheridan S. M. (2020). START-Play physical therapy intervention impacts motor and cognitive outcomes in infants with neuromotor disorders: A multisite randomized clinical trial. Physical Therapy, 101(2), 1-11.
Dusing, S. C., Harbourne, R. T., Lobo, M. A., Westcott-McCoy, S., Bovaird, J., Kane, A. E., Syed, G., Marcinowski, E. C., Koziol, N., Brown, S. E. (2019). A physical therapy intervention to advance cognitive skills a young child with cerebral palsy: A single subject with severe motor impairments. Pediatric Physical Therapy, 31(4), 347-352.
Dusing, S. C., Marcinowski, E. C., Tripathi, T., Rocha, A., & Brown, S. (2018). A perspective on the importance of assessing parent-child interaction in rehabilitation using high or low tech methods. Physical Therapy Journal, 99(6), 658-665.
Harbourne, R. T., Dusing, S. C., Lobo, M. A., McCoy, S. W., Bovaird, J., Sheridan, S., Galloway, J. C., Chang, H.-J., Hsu, L.-Y., Koziol, N., Marcinowski, E. C., & Babik, I. (2018). Sitting Together and Reaching to Play (START-Play): Protocol for a multisite randomized controlled efficacy trial on intervention for infants with neuromotor disorders. Physical Therapy, 76(1), 1-31.
Dusing, S. C., Tripathi, T., Marcinowski, E. C., Thacker, L., Brown, L., & Hendricks-Munoz, K. (2018). Supporting Play Exploration and Early Developmental Intervention versus usual care to enhance developmental outcomes during the transition from the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit to home: A pilot randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatrics, 18(46), 1-12.
Social-Emotional
DiCarlo, C. F., Ota, C., & Deris, A. (under revision). Social behavior in kindergarten. Journal of Early Childhood Research.
DiCarlo, C., Hebert, E. & Meaux, A. (in review). Finding the “om” in your ABCs: Mindfulness in the classroom. Child Care Exchange.
Chiang, C.J., Chen, Y. C., Wei, H. S., & Jonson-Reid, M. (2020). Social bonds and profiles of delinquency among adolescents: Differential effects by gender and age. Children and Youth Services Review, 104751
Benton, A., & DiCarlo, C. F. The impact of social stories on compliance and aggression in a kindergarten aged child. The Journal of Teacher Action Research, 4(3), 55 – 67.
DiCarlo, C.F, Ota, C.L., & Deris, A. (2020). An ecobehavioral analysis of social behavior across learning contexts in kindergarten. Early Childhood Education Journal, DOI 10.1007/s10643-020-01103-y
DiCarlo, C.F., & Melikyan, S. (2016). Increasing the communicative behaviors of children with low levels of communicative initiations in an inclusive preschool classroom. Literacy Experiences Special Interest Group (LESIG), 46(1) 14-35.
Beckert, T., Lee, C., & Ota, C.L. (2015). Correlates of psychosocial development for Taiwanese youth. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 46(6), 837-855.
DiCarlo, C.F., Onwujuba, C., & Baumgartner, J.J. (2014). Infant Communicative Behaviors and Maternal Responsiveness. Child and Youth Care Forum, 43(2), 195-209.
Deris, A. R., DiCarlo, C., Flynn, L. L., Ota, C.L., & O’Hanlon, A. (2012). Importance of social supports of parents of children with autism. International Journal of Early Childhood Special Education, 4(1), 17-31.
Baumgartner, J., Burnett, L., DiCarlo, C. & Buchanan, T. (2012). An inquiry of children’s social support networks using eco-maps. Child and Youth Care Forum, doi: 10.1007/s10566-011-9166-2
Deris, A. R., DiCarlo, C. F., & Deris, T. P. (2012). Evidence-based practices: Using story-based interventions to improve social behavior in the general education setting. Focus on Inclusive Education, 10(1), 5-8.
Social Studies
Casey, E., DiCarlo, C., & *Sheldon, K. (2019). Growing democratic citizenship competencies: Fostering social studies understandings through inquiry learning in the preschool garden. The Journal of Social Studies Research. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jssr.2018.12.001
Casey, E. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2016). Social studies surprises found in the garden. Focus on PK/K, Early Years Bulletin, 4(2), 7-10. http://www.acei.org/sites/default/files/eybwinter2016.pdf
Lee, L., & Misco, T. (2016). Seeking moral autonomy in a Chinese context: A study of elementary moral education standards. Journal of International Social Studies, 6(2), 84 95.
Special Education
Deris, A., & DiCarlo, C.F. (2015). Effects of using a weighted or pressure vest for a child with autism. Autonomy, the critical journal of interdisciplinary Autism studies, 1(4).
Deris, A. R., & DiCarlo, C. F. (2013). Working with young children with autism in inclusive classrooms. Support for Learning, 28(2), 52-56.
Deris, A. R., DiCarlo, C., Flynn, L. L., Ota, C., & O’Hanlon, A. (2012). Investigation of social supports for parents of children with autism. International Journal of Early Childhood Special Education, 4(1), 17-32.
Sola, S. & Terrusi, M. (2010). Just like us. Li.Ber books for children and boys, 87(1), 50 – 51.
DiCarlo, C.F., Schepis, M., & Flynn, L. (2009). Embedding sensory preferences in toys to enhance toy play in toddlers with disabilities. Infants and Young Children, 22(3), 187-199.
Flynn-Wilson, L, & DiCarlo, C.F. (2009). Transdisciplinary intervention: What does it look like in community-based child care? Collaborations, 1, 30-32.
Sola, S. & Terrusi, M. (2009). The difference is not a subtraction: Books for children and disabilities. Lapis.
DiCarlo, C.F., Benedict, J., & Aghayan, C. (2008). Social proximity of preschoolers with disabilities in an inclusive classroom. The Journal of Early Childhood Education and Family Review
Terrusi, M. (2008). All uses of the book at all. Childhood, 4(1), 46-49.
DiCarlo, C.F., & Reid, D.H. (2004). Increasing pretend toy play among 2-year-old children with disabilities in an inclusive setting. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis. 37, 197-207.
Reid, D.H., DiCarlo, C.F., Schepis, M.M., Hawkins, J., & Stricklin, S.B. (2003). Observational assessment of toy preferences among young children with disabilities in inclusive settings: Efficiency analysis and comparison with staff opinion. Behavior Modification, 27(2), 233-250.
Banajee, M., DiCarlo, C., & Stricklin, S. (2003). Core vocabulary determination for toddlers. Augmentative/Alternative Communication, 19, 67-73.
DiCarlo, C.F., Reid, D.H., & Stricklin, S. (2003). Increasing toy play among toddlers with multiple disabilities in an inclusive classroom: A more-to-less, child-directed intervention continuum. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 24, 195-209.
DiCarlo, C.F., Stricklin, S., Banajee, M., & Reid, D. (2001). Effects of manual signing on communicative vocalizations by toddlers with and without disabilities in inclusive classrooms. The Journal of the Association for Persons with Severe Handicaps, 26(2), 1-7.
DiCarlo, C.F., & Banajee, M. (2000). Using voice output devices to initiations among children with disabilities. Journal of Early Intervention, 23(3), 191-199. http://jei.sagepub.com/content/23/3/191.full.pdf+html
DiCarlo, C.F., Banajee, M., Stricklin, S. (2000). Circle time: Embedding augmentative communication into routine activities. Young Exceptional Children, 3, 18-26.
Teacher Education
Baumgartner, J., DiCarlo, C.F., & Casbergue, R. (in press). Service-learning in early childhood education: The Intersection of modeling developmentally appropriate teacher education & the P.A.R.E. model. Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education.
Isbell, D. S. (2020). Early Socialization and Opinions of Musicianship Among Preservice Music Teachers. Journal of Music Teacher Education,29(3), 62-76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1057083720928496
Lee, L. (2016). Infant-toddler field experience design: A developmentally and culturally relevant approach in restrictive reality. Early Years Bulletin, 4(1), 7-11.
Isbell, D. (2009) Understanding Music Teacher Preparation. Saarbrucken, Germany: VDM, Verlag Publishing, Inc
Isbell, D. (2009). Role Models and Career Commitment Among Music Education Undergraduate Students. Music Education Research International, 3.13-27
Lee, L. & McMullen, M. B. (2006). Social ideology and early childhood education: A comparative analysis of Korean early childhood teacher education textbooks written in 1993 and 2003. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood, 7(2), 119-129.
Ota, C.,DiCarlo, C.F.,Burts,D., Laird, R., & Gioe, C. (2006). Training and the needs of adult learners. Journal of Extension, 44(6), Article 6TOT5.
Ota, C.,DiCarlo, C.F.,Burts,D., Laird, R., & Gioe, C. (2006). The impact of training on caregiver responsiveness. The Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education, 27(2), 149-160
Teaching Practices
Hulin, C., DiCarlo, C., & Grantham-Caston, M. (in review). The Impact of responsive partnership strategies on the satisfaction of co-teaching relationships in early childhood classrooms. NHSA Dialog: The Research-to-Practice Journal for the Early Childhood Field.
Watson, K.J. & DiCarlo, C.F. (2015). Increasing completion of classroom routines through the use of picture activity schedules. Early Childhood Education Journal. DOI 10.1007/s10643-015-0697-2
DiCarlo, C.F. & Haney, L. (2014). Action research/evidence-based practice in early childhood. Focus on Infants & Toddlers, 1(4), 11-14.
Flynn, L., & DiCarlo, C., (2009). Using a transdisciplinary teaming service delivery approach in preschools. Focus on Inclusive Education, 6(4), 2-3.
VanDerHeyden, A., Snyder, P., DiCarlo, C.F., Stricklin, S.B., & Vagianos, L.A. (2002). Comparison of within-stimulus and extra-stimulus prompts to increase targeted play behaviors in an inclusive early intervention program. The Behavior Analyst Today, 3 (2), 189.
Teaching Adults
Ota, C., DiCarlo, C.F., Burts, D., Laird, R., & Gioe, C. (2006). Training and the needs of adult learners. Journal of Extension, 44(6) [Article No. 6TOT5].
Lee, L. (2020). Technology-augmented play materials. In D. Bergen (Ed.), Handbook of Developmentally Appropriate Toys. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
Lee, L. (2019). When technology met real-life experiences; Science curriculum project with technology for low-income Latino preschoolers. In N. Kucirkova & J. Rowsell (Eds.), International Handbook of Learning with Technology in Early Childhood Theory and Method (pp. 338-348). New York: Routledge.
Tu, X., & Lee, L. (2019). Integrating digital media in early childhood education: A case study of using iPad in American Mid-Western preschools. Journal of Studies in Chinese Early Childhood Education. [Chinese], 54-59.
Clark, S., & Lee, L. (2018). Technology Enhanced Classroom for Low-Income Children’s Mathematical Content Learning: A Case Study. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 9(1), 66-69.
Lee, L. & Tu, X. (2016). Digital media for low-income preschoolers’ effective science learning: A case study of iPads with a social development approach. Computer in the Schools, 33(4), 1-14.
Lee, L., & Tu, X. (2016). Mathematical learning with digital media for low income preschool children: A case study of ELL and Non-ELL. International Journal of Early Childhood Learning, 23(3), 1-10.
Lee, L. (2015). Digital media for supporting young children’s learning: A case study of American preschool children and their uses of iPads. International Journal of Information and Education Technology, 5(12), 947-950.
Lee, L. (2015). Young children, play, and technology: Meaningful ways of using technology and digital media. In D. P. Fromberg & D. Bergen (Eds.) (3rd), Play from Birth to Twelve: Contexts, Perspectives, and Meanings (pp. 217-224). New York: Routledge
Lee, L. (2012). “It is a learning Journey for all”: A lesson from American elementary teachers who used a classroom Wiki. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 11(3).
Types of Schools (Charter, urban, rural, laboratory)
Nelson-Smith, K. & Gunn, B. (2019). Determining the Perception and Necessity for a Child Development Laboratory in Local Communities. Journal of Education and Human Development, 8(4), pgs. 1-7.
Nelson-Smith, K. (2014). Charter Schools and the Corporate Makeover of Public Education: What’s at Stake? Journal of Negro Education. Book Review. Volume 83(3).
Andrews, N., Houston, W. R., Tobe, P. F., Zhang, A., & Powers, K. (2013). United Way Bright Beginnings Program Evaluation 2012. A program of the United Way of Greater Houston and ExxonMobil. Institute for Urban Education, University of Houston.
Houston, W. R.; Tobe, P. F., Zhang, A., Francis, T. P., & Stallings, T. (2012). United Way Bright Beginnings Program Evaluation, January 2011-January 2012. A program of the United Way of Greater Houston and ExxonMobil. Institute for Urban Education, University of Houston.
Houston, W. R., Tobe, P. F., Dixon, J., & Zhang, A. (2011). United Way Bright Beginnings Program Evaluation, January 2010-January 2011. A program of the United Way of the Texas Gulf Coast and ExxonMobil. Institute for Urban Education, University of Houston.
Nelson-Smith, K. (2011). Extension Role in Urban Education: Why Aren’t We Involved? Journal of Extension,49(4). Can be found at: http://www.joe.org/joe/2011august/comm1.php
Isbell, D. (2005). Music education in rural areas: A few keys to success. Music Educators Journal, 92(2), 30-34.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
50 Senior Project Ideas That Will Inspire You
Senior project is a long-awaited experience for many high schoolers. The anticipation can lead to a lot of uncertainty on what exactly to do, however. After years of looking forward to this opportunity, many students get so caught up in looking for the perfect idea that they can’t make a decision.
If you’re looking for original and inspiring senior project ideas, this is just the place for you. Read on for suggestions related to a wide variety of interests, from medicine to marketing to environmentalism.
What is a Senior Project?
A senior project allows high school students to explore whatever interests them through experiential learning. Students normally design and implement their own projects from start to finish. These projects often occur in the second semester of senior year, and can involve time off from regular classes.
Senior project ideas include everything from future careers to special talents to community service projects, and can range from research to hands-on activities. One of the great benefits of senior projects is that students can apply their acquired skills and knowledge to a project they’re passionate about, while also gaining greater insight into their particular interest.
High schoolers can also build essential life skills by participating in a senior project, such as long-term planning and time management.
50 Inspiring Senior Project Ideas
While many schools will have a list of suggested senior project ideas, they don’t always have one that lines up with a student’s interests, and the best senior projects generally involve a subject or area the student is enthusiastic about. If you’re looking for an engaging and exciting senior project idea, look no further—below are 50 senior project ideas spread across 11 areas of interest to inspire you.
- Volunteer on the campaign of a local political candidate, or work in the office of a local representative.
- Write op-eds and articles for your local newspaper on issues you truly care about.
- Start a mock senate to give your fellow students a simulated experience with the business of the U.S. Senate and a better understanding of how a bill becomes a law.
- Define a local problem, the political situation around it, what interest groups and lobbyists have a stake in it and what their positions are. Then, discuss potential solutions, or what it would take for there to be progress on the issue.
Virtual Arts
- Organize the creation of a mural at your school or local community to highlight a memorable moment in local history.
- Take portraits of meaningful life milestones (engagement, wedding, senior photos) for low-income families who might otherwise not be able to afford it.
- Start a painting class for kids from low-income homes who may not have easy access to art supplies.
- Make a documentary about a lesser-known part of local history.
- Put on a production of a play you wrote yourself to call attention to issues such as racial discrimination and body image.
- Create a curriculum for teaching seniors how to use a computer/internet and circulate it to local nursing homes and retirement communities.
- Organize volunteers to mentor adults without high school diplomas and help them graduate.
- Work with local business people to create a series of workshops teaching vital job skills to people out of work.
- Construct a “ Little Free Library Box ” in a neighborhood where access to libraries and books is limited.
- Go through the process of changing a school policy that many students disagree with.
- Work with your local senior center or retirement home to teach a foreign language to their members/residents—you’re never too old to learn!
- Volunteer to assist in an ESL (English as a second language) class, or mentor non-native speakers one-on-one.
- Develop a website or app where people can find language partners to practice with.
- Act as a translator at school or in a local business, or translate documents/media that are read by a significant immigrant population
- If your school serves a large percentage of non-English or non-native English speakers, petition your school to become more inclusive by also providing documents in the predominant language spoken.
- Help translate for patients at a doctor’s office with a significant immigrant population.
- Define a community health problem and develop solutions, working with local officials and medical professionals (for example, obesity, diabetes, drug use, etc.).
- Coordinate a free health screening event with medical professionals for at-risk and underserved community members.
- Investigate the accessibility of healthcare in your community by interviewing a diverse selection of residents, and writing a paper on your findings, or creating a documentary.
- Work with a local nonprofit or business to better understand what it takes to thrive in today’s economy.
- Start a business—conduct market research, develop a product or service, and sell it.
- Identify a local economic issue and develop solutions, working with local representatives and organizations who can make a difference (for example, homelessness, hunger, inaccessible healthcare, low minimum wage, etc.)
- Help a local business with their accounting or record keeping. Tech-savvy students might even upgrade an old business, transferring them from pen-and-paper bookkeeping to a program like Quickbooks.

Marketing/Media
- Create a social marketing campaign for your local animal shelter to raise awareness and find homes for pets.
- Start your own blog on a topic that you’re passionate about and write SEO-optimized content, or start a blog for a local business or non-profit.
- Intern for a local magazine or newspaper.
- Research the impact of the media on your community during a local or national election.
- Work with your high school Amnesty International Club to create materials like pamphlets and posters to raise awareness of human rights issues.
Environmentalism
- Work with the local government to create a space for a community garden.
- Create a documentary to teach people about environmental issues in your community.
- Work with your school cafeteria to implement changes that reduce food waste, like introducing compost or switching to biodegradable trays.
- Organize an event to clean up a local park or woodland (you can take it a step further and even make it a hike or a run to pick up trash; there’s actually a trend called “plogging” when you jog and pick up trash)
- Work in the lab of a local professor to research a topic that you’re passionate about.
- Develop an app for simplifying school communication.
- Act as a teaching assistant for your STEM teacher at school, helping students during labs, developing supplemental materials, or holding review sessions.
- Build a website that changes an industry—Facebook, WordPress, and Dell were all founded by undergraduates, and Google began as a Ph.D. research program.
- Develop a plan for building mountain bike trails, organize volunteers, and demonstrate the economic impact they’ll have on the community.
- Organize a new club for an unrepresented sport at your school, like rock climbing or fencing.
- Offer a service that pairs high-energy dogs whose owners can’t give them enough exercise with runners looking for a canine training partner.
- Volunteer to coach a Special Olympics team.
- Found a group that exposes athletic opportunities to people who might otherwise not experience them—for example, taking inner-city kids backpacking.
- Take your love of shopping and do good by organizing a squad of shoppers that picks up groceries and medicine for the elderly.
- Gather a group to make and distribute holiday gifts for kids in the hospital.
- Set up a ride service that takes the elderly to and from doctors’ appointments.
- Serve meals at the local homeless shelter, or work with a local restaurant to help feed the homeless.
- Plan and put on a low-key party for children on the autism spectrum who can find some festivities overwhelming.
Curious about your chances of acceptance to your dream school? Our free chancing engine uses factors like GPA, test scores, extracurriculars to predict your odds of acceptance at over 500 colleges across the U.S. It also lets you know how you stack up against other applicants and how you can improve your profile. Sign up for your free CollegeVine account today to get started!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Playful learning creates multigenerational opportunities with intergenerational impacts
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, irv katz and irv katz senior fellow - generations united hailey m. gibbs hailey m. gibbs senior policy analyst in early childhood policy - center for american progress @haileymgibbs.
January 30, 2023
Play is an important part of children’s learning and development. While it generally evokes a picture of a small child running, jumping, and shouting, the benefits that play offers in promoting early development and better health outcomes extend far beyond childhood. In fact, playful learning—an area of research that examines how children learn best through playful exchanges—shares many of the same core foundations as the study of intergenerational learning—a body of research involving older and younger generations coming together in the service of mutually-beneficial learning experiences.
As the COVID-19 pandemic introduced new layers to our understanding of the importance of social connection for a range of outcomes, researchers have an opportunity to look to the future of the playful learning and intergenerational learning movements together—what they share and how they can be leveraged jointly to support social interactions that foster well-being throughout life.
Playful Learning Landscapes support enriching interactions and promote learning
As a natural medium for fostering rich interactions, play creates opportunities for children to develop language skills , engage in collaboration , test theories about how the world works, and even develop better self-regulation . Child development experts, recreation and play professionals, and educators have long examined the connection between play and learning—and, more recently, how the kinds of enriching interactions that take place during play can be fostered through the built environment.
Enter Playful Learning Landscapes : a growing movement of community-based research partnerships across a number of cities in the U.S. and abroad, including in Brazil, Israel, and South Africa, that morph public spaces in places that foster interaction, learning, and joy (see illustrative photo below). By reimagining everyday environments in ways that encourage play while embedding a targeted learning goal, the movement fosters a learning model known as playful learning , in which children build content knowledge while simultaneously playing freely. Playful learning research has not only generated improvements to children’s language and literacy , numeracy, spatial reasoning, and executive functioning —all skills that set the foundation for later development and school readiness—but also strong civic engagement, increased ownership of communal spaces, enriched interactions between children and their caregivers, and a deeper understanding among caregivers of the role of play in their children’s learning.

This PLL installation, which is located in Philadelphia, is called Urban Thinkscape. Photographer credit: Sahar Coston-Hardy Photography.
But the benefits are not for children alone—playful interactions can also be a boon for older adults , supporting better health and social engagement, staving off cognitive decline, and creating multigenerational learning opportunities with intergenerational impacts.
Intergenerational research showcases benefits to, and contributions of, older adults
A century ago, multiple generations lived, worked, and played together. Today, much of our society treats young children and older adults as fundamentally different from one another—and, more likely than not, we live apart , sometimes a great distance, from even the closest generations of our own families. We now each belong to a separate “ named generation ” that reinforces generational differences, which may contribute to the persistent and widespread problem of ageism , that has well-documented negative effects on physical and mental health, economic well-being, and access to critical support services. Though the developmental literature acknowledges that many of our needs evolve as we age, the benefits we experience from rich social connections, learning opportunities that support cognitive function, and activity that promotes physical health remain constant throughout life.
The intergenerational movement , which has emerged over the past several decades and gained momentum in recent years, emphasizes the benefits of enriching interactions in mitigating social isolation—which became all the more critical in periods of isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic —creating health and learning opportunities for older adults, and promoting powerful community connections. Social service leaders, academic researchers, public officials, and others demonstrated that there are reciprocal benefits to children and older adults as a product of interacting and engaging with one another. In a 2021 review of intergenerational programs , Generations United and the RRF Foundation for Aging identified benefits of intergenerational programs for children at several different developmental periods, parents, and older adults—even those aged 100 and older.
Among the many positive outcomes, researchers found that children in preschool partnered with older adult volunteers show better socio-emotional outcomes (e.g., empathy and acceptance); elementary school children partnered with older adults show increased learning, reading comprehension, and improvement in writing; and older adults report less social isolation and a sense of connectedness and community when engaged with children and youth. This connectedness is a critical component for supporting both physical and mental health and well-being in older adults and for staving off some age-related declines in cognitive functioning.
Play is not just for the kids: Intergenerational learning has lifelong benefits
By bringing these two areas of study together—one based in a long history of intergenerational research, the other in a rich and growing playful learning movement—researchers and advocates can integrate and build on opportunities to engage adults and children in their day-to-day environments in ways that promote enriching and mutually-beneficial learning and health outcomes. This could include, for example, puzzles embedded in bus stops or at local parks, featuring iconic references from a grandparent’s generation that can promote both shape language that supports foundational math skills and storytelling that helps boost rich language interactions and gives older adults an opportunity to share their experiences. It could look like grocery store games, where older adults are prompted to discuss favorite foods and recipes from their childhood, or it could look like story fragments printed on the sidewalk outside of an elderly home that prompts older adults and young children to take it in turns to build out narratives together. Redesigning playful learning spaces with an intergenerational framework in mind can facilitate these kinds of rich interactions between young and old and lead to improvements in their respective well-being, bridge generational divides at the earliest stages of children’s lives, and strengthen community resilience across the lifespan.
Photographer credit for cover image: Saxum.
The authors thank Sarah Lyttle, Kathy Hirsh-Pasek, and Jennifer Vey for their reviews of this blog.
Related Content
Helen Shwe Hadani, Shwetha Parvathy
February 3, 2022
Helen Shwe Hadani, Jennifer S. Vey, Shwetha Parvathy, Kathy Hirsh-Pasek
October 19, 2021
Early Childhood Education K-12 Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
Darcy Hutchins, Emily Markovich Morris, Laura Nora, Carolina Campos, Adelaida Gómez Vergara, Nancy G. Gordon, Esmeralda Macana, Karen Robertson
March 28, 2024
Jennifer B. Ayscue, Kfir Mordechay, David Mickey-Pabello
March 26, 2024
Anna Saavedra, Morgan Polikoff, Dan Silver

International Handbook of Early Childhood Education pp 1095–1111 Cite as
Tools of the Mind : A Vygotskian Early Childhood Curriculum
- Elena Bodrova 3 &
- Deborah J. Leong 3 , 4
12k Accesses
10 Citations
Part of the book series: Springer International Handbooks of Education ((SIHE))
Tools of the Mind is an early childhood curriculum based on the principles of cultural-historical psychology. The program was originally developed and pilot tested in Denver, Colorado, in the 1990s and since then has expanded to many other states and is currently serving over 30,000 children ages 3–6. The main goal of the program is to help children learn how to become – in Vygotsky’s words – “masters of their own behavior.” To accomplish this, Tools of the Mind engages young children in activities that promote their social, emotional, and cognitive self-regulation. Mature intentional make-believe play is one of the hallmarks of the program, and special instructional strategies are employed to scaffold play in children who enter preschool or kindergarten lacking mature play skills. In addition to supporting play, Tools teachers engage children in a variety of other activities and games that have children acquire early academic skills while at the same time practicing other-regulation and self-regulation.
Tools of the Mind gained attention in education community when a study published in the journal Science by one of the leading neuroscientists in the USA showed that Tools preschool children had higher levels of self-regulation than a control group. Several new studies are currently underway, and their preliminary results look promising. Tools represents innovative early childhood programs in the UNESCO’s international database INODATA and is listed among seven effective social-emotional learning programs in the 2013 Collaborative for Academic, Social and Emotional Learning Guide.
- Cultural-historical approach
- Early childhood education
- Make-believe play
- Scaffolding
- Early literacy instruction
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Barnett, W. S., Jung, K., Yarosz, D., Thomas, J., Hornbeck, A., Stechuk, R., & Burns, S. M. (2008). Educational effects of the tools of the mind curriculum: A randomized trial. Early Childhood Research Quarterly , 23 , 299–313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2008.03.001 .
Berk, L. E. (1992). Children’s private speech: An overview of theory and the status of research. In R. M. Diaz & L. E. Berk (Eds.), Private speech: From social interaction to self-regulation (pp. 17–53). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Google Scholar
Berk, L. E., & Winsler, A. (1995). Scaffolding children’s learning: Vygotsky and early childhood education , NAEYC research into practice series (Vol. 7). Washington, DC: National Association for the Education of Young Children.
Blair, C., & Raver, C. (2014). Closing the achievement gap through modification of neurocognitive and neuroendocrine function: Results from a cluster randomized controlled trial of an innovative approach to the education of children in kindergarten. PLOS ONE, 9 (11), e112393. doi: 10.1371/journal.phone.0112393 .
Article Google Scholar
Bodrova, E., & Leong, D. J. (1995). Scaffolding the writing process: The Vygotskian approach. Colorado Reading Council Journal, 6 , 27–29.
Bodrova, E., & Leong, D. J. (1998). Scaffolding emergent writing in the zone of proximal development. Literacy Teaching and Learning, 3 (2), 1–18.
Bodrova, E., & Leong, D. (2001). Tools of the mind: A case study of implementing the Vygotskian approach in American early childhood and primary classrooms (Innodata Monographs 7). Geneva: International Bureau of Education.
Bodrova, E., & Leong, D. J. (2007). Tools of the mind (2nd ed.). Columbus: Merrill/Prentice Hall.
Bodrova, E., Germeroth, C., & Leong, D. J. (2013). Play and self-regulation. American Journal of Play, 6 (1), 111–123.
Campione, J. C., & Brown, A. L. (1990). Guided learning and transfer. In N. Fredricksen, R. Glaser, A. Lesgold, & M. G. Shafto (Eds.), Diagnostic monitoring of skill and knowledge acquisition (pp. 141–172). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Chaiklin, S., Hedegaard, M., & Jensen, U. J. (Eds.). (1999). Activity theory and social practice: Cultural-historical approach . Aarhus: Aarhus University Press.
Clay, M. (1993). Reading recovery . Portsmouth: Heinemann.
Common Core State Standards Initiative. (2012). Common core state standards for English language arts . http://www.corestandards.org/ELA-Literacy/RL/K
Copple, C., & Bredekamp, S. (Eds.). (2009). Developmentally appropriate practice in early childhood programs serving children from birth to age 8 . Washington, DC: National Association for the Education of Young Children.
Davydov, V. V. (1990). Types of generalization in instruction . Reston: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics.
Diamond, A., Barnett, S., Thomas, J., & Munro, S. (2007). Preschool program improves cognitive control. Science, 318 , 1387–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.1151148 .
Domitrovich, C., Durlak, J., Goren, P., & Weissberg, R. (2013). Effective social and emotional learning programs: Preschool and elementary school edition. 2013 CASEL guide . Chicago: Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning.
Elkonin, D. (1977). Toward the problem of stages in the mental development of the child. In M. Cole (Ed.), Soviet developmental psychology (pp. 538–563). White Plains: M. E. Sharpe.
Elkonin, D. (1978). Psychologija igry [The psychology of play]. Moscow: Pedagogika.
Elkonin, D. B. (2005a). The psychology of play: Preface. Journal of Russian and East European Psychology, 43 (1), 11–21 (Original work published 1978).
Elkonin, D. B. (2005b). The psychology of play: Chapter I. Journal of Russian and East European Psychology, 43 (1), 22–48 (Original work published 1978).
Farran, D. C. (Chair). (2012) . Enhancing executive function and achievement in prekindergarten classrooms: The effectiveness of tools of the mind . Symposium conducted at the meeting of the Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness.
Farran, D. C., & Son-Yarbrough, W. (2001). Title I funded preschools as a developmental context for children’s play and verbal behaviors. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 16 , 245–262. doi: 10.1016/S0885–2006(01)00100-4 .
Gresham, F., & Elliot, S. (1990). Social skills rating scale . Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Gudareva, O. V. (2005). Psikhologicheskie osobennosti suzhetno-rolevoy igry sovremennykh doshkol’nikov [Psychological features of make-believe play in today’s preschoolers]. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Moscow City University for Psychology and Education, Moscow.
Hammond, S., Müller, U., Carpendale, J., Bibok, M., & Liebermann-Finestone, D. (2012). The effects of parental scaffolding on preschoolers’ executive function. Developmental Psychology, 48 (1), 271–281. doi: 10.1037/a0025519 .
Karpov, Y. V. (2005). The neo-Vygotskian approach to child development . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Leont’ev, A. (1978). Activity, consciousness, and personality . Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Levin, D. E. (2008). Problem solving deficit disorder: The dangers of remote controlled versus creative play. In E. Goodenough (Ed.), Where do children play? (pp. 137–140). Detroit: Wayne University Press.
Luria, A. R. (1969). Speech development and the formation of mental processes. In M. Cole & I. Maltzman (Eds.), Handbook of contemporary soviet psychology . New York: Basic Books.
Luria, A. R. (1983). The development of writing in the child. In M. Martlew (Ed.), The psychology of written language: Developmental and educational perspectives (pp. 237–277). Chichester: Wiley.
Miller, E., & Almon, J. (2009). Crisis in the kindergarten: Why children need play in school . College Park: Alliance for Childhood.
Newman, D., Griffin, P., & Cole, M. (1989). The construction zone: Working for cognitive change in school . Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press.
Rubtsov, V. (1991). Learning in children: Organization and development of cooperative actions . New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Rueda, M. R., Fan, J., McCandliss, B. D., Halparin, J. D., Gruber, D. B., Lercari, L. P., & Posner, M. I. (2004). Development of attentional networks in childhood. Neuropsychologia, 42 , 1029–1040.
Smirnova, E. O., & Gudareva, O. V. (2004). Igra i proizvol’nost u sovremennykh doshkol’nikov [Play and intentionality in modern preschoolers]. Voprosy Psychologii, 1 , 91–103.
Sophian, C. (2007). The origins of mathematical knowledge in childhood . London: Routledge.
Tharp, R. G., & Gallimore, R. (1989). Rousing minds to life: Teaching, learning and schooling in social context . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1956). Izbrannye psychologicheskije trudy [Selected psychological works]. Moscow: RSFSR Academy of Pedagogical Sciences
Vygotsky, L. S. (1967). Play and its role in the mental development of the child. Soviet Psychology, 5 (3), 6–18.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher mental processes . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1987). Thinking and Speech (N. Minick, Trans. Vol. 1). New York: Plenum Press.
Winsler, A., de Leon, J. R., Wallace, B. A., Carlton, M. P., & Willson-Quayle, A. (2003). Private speech in preschool children: Developmental stability and change, across-task consistency, and relations with classroom behaviour. Journal of Child Language, 30 , 583–608. doi: 10.1017/S0305000903005671 .
Wood, D., Bruner, J. C., & Ross, G. (1976). The role of tutoring in problem solving. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 17 , 89–100.
Zaporozhets, A. (1986). Izbrannye psychologicheskie trudy [Selected works]. Moscow: Pedagogika
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Tools of the Mind, Denver, CO, USA
Elena Bodrova & Deborah J. Leong ( Professor Emerita )
Department of Psychology, Metropolitan State University of Denver, Denver, CO, USA
Deborah J. Leong ( Professor Emerita )
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Elena Bodrova .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, Monash University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Marilyn Fleer
Department of Theory & Research in Education, VU Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Bert van Oers
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Bodrova, E., Leong, D.J. (2018). Tools of the Mind : A Vygotskian Early Childhood Curriculum. In: Fleer, M., van Oers, B. (eds) International Handbook of Early Childhood Education. Springer International Handbooks of Education. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-0927-7_56
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-0927-7_56
Publisher Name : Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN : 978-94-024-0925-3
Online ISBN : 978-94-024-0927-7
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store
At Home with Makerspaces

You are here
By Melissa Catena
The maker movement is clearly having its moment in the education world. Whether you call them makerspaces , hackerspaces, or DIY labs, the idea is the same—they’re places where kids can tinker, invent, and build to their heart's content. They are great for fostering creativity and hands-on learning. Makerspaces are popping up mainly in schools and libraries. But you can bring the fun into your home with your own box of maker tools and materials. A selection that includes both everyday and unexpected materials helps children’s imaginations run wild!
To get started on your makerspace, here are five types of household materials to collect:
1. Cardboard - Boxes, toilet paper and paper towel cylinders, egg cartons, and other miscellaneous cardboard scraps are easy to gather from around the house. They make great bases for many projects. Beyond cardboard, add molded styrofoam and shaped acrylic foam packaging. Don't forget to include different colored tapes to hold the pieces together.
2. Textiles - Fabric scraps, felt, mesh, ribbon, yarn, and string are perfect additions to a makerspace. No need to include a sewing machine—a simple needle and thread will work just fine. Glue guns are great to have and can be found at the dollar store.
3. Art and craft supplies - Paint, paintbrushes, wire, buttons, scissors, paper, old magazines to cut up, and other odds and ends provide endless possibilities for creative projects.
4. Building tools - Legos are a must-have for any makerspace. Screwdrivers, pliers, and a few other basic construction tools come in handy. Wood scraps, wooden dowels, and duct tape can be used to support handmade structures. (If the group includes children kindergarten age or younger, plan to be close by to supervise their use of some of the tools.)
5. Tech tools - You certainly don't need to buy a 3-D printer; but consider including broken technology items. Kids have fun disassembling old keyboards and using the keys in their projects. An old cell phone case could become something else entirely.
What next? Step back and let your minimakers do their thing. If children are really stumped, get their gears turning with some project ideas .
Once the creative juices start flowing, pat yourself on the back for building your very own screen-free play area. Oh, and don't be surprised if your makerspace becomes the new go-to place for children’s neighborhood get-togethers.
Melissa Catena is a freelance writer and former editor for educational publishers. She lives in the San Francisco Bay Area with her husband and two sons, ages two and four.
Creative Arts and Music

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Exam week of Spring 2020 was bittersweet for the early childhood studies senior cohort. After working on their capstone projects for three terms and persisting through a challenging Spring term at home, they presented their capstone work in a Zoom gathering with faculty, peers, family, and friends.
Podcasts Podcasts are a great way to explore early childhood education topics on the go. The Illinois Early Learning Project will continue to add new audio content that can be streamed or downloaded to your device. Standards & Guidelines. Illinois Early Learning Guidelines for Children Birth to Age 3; IELG Resources; 2013 Illinois Early ...
Part two shares specific culminating experiences (e.g., seminar courses in general education curricula, capstone experiences in the major, capstone research projects in a multi-campus early college program, capstone ePortfolios, etc.), with examples from multiple institutions and strategies for adapting them for readers' own campus contexts.
Technology and Innovation Capstone Project Ideas. The future of artificial intelligence and its societal impacts. Blockchain technology: Beyond cryptocurrency. The ethical implications of facial recognition technology. Virtual reality in education: Pros and cons. The rise of smart cities and privacy concerns.
Climate Change Education Platform: ... Childhood Development Program: Design an early childhood development program that enhances cognitive, social, and emotional skills. ... So, these are the 271+ creative and senior capstone project ideas that span a wide range of disciplines. It provides ample inspiration for students looking to make a ...
Explore key early childhood topics such Developmentally Appropriate Practice, play, and math. ... and math. Blog. Stay up-to-date on issues in early childhood education and hear perspectives from a wide range of educators. Position Statements. Learn about NAEYC's informed positions on significant issues affecting young children's education ...
NAEYC promotes high-quality early learning for all children, birth through age 8, by connecting practice, policy, and research. We advance a diverse early childhood profession and support all who care for, educate, and work on behalf of young children. Article. Young Children. June 1, 2021.
The new standards elevate the important infrastructure that needs to be in place for programs to effectively prepare early childhood educators. There are now six standards that address essential components of high-quality professional preparation programs: Standard A: Program Identity, Candidates, Organization, and Resources.
The Hartford School District in Connecticut requested $3,354,073 to develop the Betances Early Reading Lab Prek-3 Lab School, which would "create an innovative learning community by joining together two powerful components.". The first component of this project is the Pre-k - 3rd school structure. The second piece is the establishment of ...
McCallops, K., Karpyn, A., Klein, J., & Jelenewicz, S. (April 2021). 10 Current Trends in Early Childhood Education: Literature Review and Resources for Practitioners. (T21-008). Newark, DE: Center for Research in Education and Social Policy. Center for Research in Education and Social Policy/Page 3 of 20.
We begin by briefly reviewing the project approach (Helm & Katz, 2016) and its use in inclusive early childhood settings and review the literature examining project work in early childhood teacher education.We review the central role of high-quality field experiences and the need to partner with cooperating teachers, followed by a review of research on the use of project work in EC teacher ...
Project-based learning (PBL) provides an interesting challenge for preschool teachers because it extends beyond early-childhood education mainstays such as teacher-directed themed crafts and short daily lessons. PBL, which focuses on children learning through investigating a topic or answering a question, is an involved process that could last ...
Research Topics | Early Childhood Education Institute. Top. ... Project IPAL: To enhance the well-being of elementary school children. Journal of Family & Consumer Sciences 109(1) 54-56. Staiano AE, Marker AM, Beyl RA, Hsia DS, Katzmarzyk PT, & Newton RL. (2017). A randomized controlled trial of dance exergaming for exercise training in ...
A senior project allows high school students to explore whatever interests them through experiential learning. Students normally design and implement their own projects from start to finish. These projects often occur in the second semester of senior year, and can involve time off from regular classes. Senior project ideas include everything ...
This article examines the use of an observational approach in the form of Learning Stories, a narrative-based formative assessment created by New Zealand early childhood education leaders. By encouraging teachers to recognize children as competent explorers and learners at any given moment, Learning Stories provide a way to document children ...
Redesigning playful learning spaces with an intergenerational framework in mind can facilitate these kinds of rich interactions between young and old and lead to improvements in their respective ...
A senior project is a culminating academic experience that allows you to apply the skills and knowledge you have acquired throughout your high school education to a real-world project. It is typically a semester-long project that you undertake in your final year of high school.
Tools of the Mind is an early childhood curriculum based on the principles of cultural-historical psychology. The program was originally developed and pilot tested in Denver, Colorado, in the 1990s and since then has expanded to many other states and is currently serving over 30,000 children ages 3-6. The main goal of the program is to help ...
In this ECE online degree program, you will discover all the wonders of early childhood education as you learn ways to support children during a pivotal time of academic and personal growth. Accelerated 5- to 6-week courses. Transfer approved college credits toward your bachelor's program at UAGC. 1 course at a time. $0 Application Fee.
Explore key early childhood topics such Developmentally Appropriate Practice, play, and math. ... Stay up-to-date on issues in early childhood education and hear perspectives from a wide range of educators. Position Statements. Learn about NAEYC's informed positions on significant issues affecting young children's education and development.
There are 6 modules in this course. This course is targeted toward individuals wishing to operate a family day care center, and it covers topics including the fundamentals of early childhood development; the importance of play and Developmentally Appropriate Practice; and the significance of building strong family-educator relationships and how ...
Despite the challenges, Turkey's motivation to increase schooling and quality in early childhood education is still on the agenda. The targets were very clear in the Ninth Development Plan for Turkey: 50 % pre-schooling in 2012-2013 through public and private services countrywide.
3. Art and craft supplies - Paint, paintbrushes, wire, buttons, scissors, paper, old magazines to cut up, and other odds and ends provide endless possibilities for creative projects. 4. Building tools - Legos are a must-have for any makerspace. Screwdrivers, pliers, and a few other basic construction tools come in handy.