How to Write Critical Reviews
When you are asked to write a critical review of a book or article, you will need to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. In other words, you will be examining another person’s thoughts on a topic from your point of view.
Your stand must go beyond your “gut reaction” to the work and be based on your knowledge (readings, lecture, experience) of the topic as well as on factors such as criteria stated in your assignment or discussed by you and your instructor.
Make your stand clear at the beginning of your review, in your evaluations of specific parts, and in your concluding commentary.
Remember that your goal should be to make a few key points about the book or article, not to discuss everything the author writes.

Understanding the Assignment
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work–deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole.
Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain points and prevent you from merely summarizing what the author says. Assuming the role of an analytical reader will also help you to determine whether or not the author fulfills the stated purpose of the book or article and enhances your understanding or knowledge of a particular topic.
Be sure to read your assignment thoroughly before you read the article or book. Your instructor may have included specific guidelines for you to follow. Keeping these guidelines in mind as you read the article or book can really help you write your paper!
Also, note where the work connects with what you’ve studied in the course. You can make the most efficient use of your reading and notetaking time if you are an active reader; that is, keep relevant questions in mind and jot down page numbers as well as your responses to ideas that appear to be significant as you read.
Please note: The length of your introduction and overview, the number of points you choose to review, and the length of your conclusion should be proportionate to the page limit stated in your assignment and should reflect the complexity of the material being reviewed as well as the expectations of your reader.
Write the introduction
Below are a few guidelines to help you write the introduction to your critical review.
Introduce your review appropriately
Begin your review with an introduction appropriate to your assignment.
If your assignment asks you to review only one book and not to use outside sources, your introduction will focus on identifying the author, the title, the main topic or issue presented in the book, and the author’s purpose in writing the book.
If your assignment asks you to review the book as it relates to issues or themes discussed in the course, or to review two or more books on the same topic, your introduction must also encompass those expectations.
Explain relationships
For example, before you can review two books on a topic, you must explain to your reader in your introduction how they are related to one another.
Within this shared context (or under this “umbrella”) you can then review comparable aspects of both books, pointing out where the authors agree and differ.
In other words, the more complicated your assignment is, the more your introduction must accomplish.
Finally, the introduction to a book review is always the place for you to establish your position as the reviewer (your thesis about the author’s thesis).
As you write, consider the following questions:
- Is the book a memoir, a treatise, a collection of facts, an extended argument, etc.? Is the article a documentary, a write-up of primary research, a position paper, etc.?
- Who is the author? What does the preface or foreword tell you about the author’s purpose, background, and credentials? What is the author’s approach to the topic (as a journalist? a historian? a researcher?)?
- What is the main topic or problem addressed? How does the work relate to a discipline, to a profession, to a particular audience, or to other works on the topic?
- What is your critical evaluation of the work (your thesis)? Why have you taken that position? What criteria are you basing your position on?
Provide an overview
In your introduction, you will also want to provide an overview. An overview supplies your reader with certain general information not appropriate for including in the introduction but necessary to understanding the body of the review.
Generally, an overview describes your book’s division into chapters, sections, or points of discussion. An overview may also include background information about the topic, about your stand, or about the criteria you will use for evaluation.
The overview and the introduction work together to provide a comprehensive beginning for (a “springboard” into) your review.
- What are the author’s basic premises? What issues are raised, or what themes emerge? What situation (i.e., racism on college campuses) provides a basis for the author’s assertions?
- How informed is my reader? What background information is relevant to the entire book and should be placed here rather than in a body paragraph?
Write the body
The body is the center of your paper, where you draw out your main arguments. Below are some guidelines to help you write it.
Organize using a logical plan
Organize the body of your review according to a logical plan. Here are two options:
- First, summarize, in a series of paragraphs, those major points from the book that you plan to discuss; incorporating each major point into a topic sentence for a paragraph is an effective organizational strategy. Second, discuss and evaluate these points in a following group of paragraphs. (There are two dangers lurking in this pattern–you may allot too many paragraphs to summary and too few to evaluation, or you may re-summarize too many points from the book in your evaluation section.)
- Alternatively, you can summarize and evaluate the major points you have chosen from the book in a point-by-point schema. That means you will discuss and evaluate point one within the same paragraph (or in several if the point is significant and warrants extended discussion) before you summarize and evaluate point two, point three, etc., moving in a logical sequence from point to point to point. Here again, it is effective to use the topic sentence of each paragraph to identify the point from the book that you plan to summarize or evaluate.
Questions to keep in mind as you write
With either organizational pattern, consider the following questions:
- What are the author’s most important points? How do these relate to one another? (Make relationships clear by using transitions: “In contrast,” an equally strong argument,” “moreover,” “a final conclusion,” etc.).
- What types of evidence or information does the author present to support his or her points? Is this evidence convincing, controversial, factual, one-sided, etc.? (Consider the use of primary historical material, case studies, narratives, recent scientific findings, statistics.)
- Where does the author do a good job of conveying factual material as well as personal perspective? Where does the author fail to do so? If solutions to a problem are offered, are they believable, misguided, or promising?
- Which parts of the work (particular arguments, descriptions, chapters, etc.) are most effective and which parts are least effective? Why?
- Where (if at all) does the author convey personal prejudice, support illogical relationships, or present evidence out of its appropriate context?
Keep your opinions distinct and cite your sources
Remember, as you discuss the author’s major points, be sure to distinguish consistently between the author’s opinions and your own.
Keep the summary portions of your discussion concise, remembering that your task as a reviewer is to re-see the author’s work, not to re-tell it.
And, importantly, if you refer to ideas from other books and articles or from lecture and course materials, always document your sources, or else you might wander into the realm of plagiarism.
Include only that material which has relevance for your review and use direct quotations sparingly. The Writing Center has other handouts to help you paraphrase text and introduce quotations.
Write the conclusion
You will want to use the conclusion to state your overall critical evaluation.
You have already discussed the major points the author makes, examined how the author supports arguments, and evaluated the quality or effectiveness of specific aspects of the book or article.
Now you must make an evaluation of the work as a whole, determining such things as whether or not the author achieves the stated or implied purpose and if the work makes a significant contribution to an existing body of knowledge.
Consider the following questions:
- Is the work appropriately subjective or objective according to the author’s purpose?
- How well does the work maintain its stated or implied focus? Does the author present extraneous material? Does the author exclude or ignore relevant information?
- How well has the author achieved the overall purpose of the book or article? What contribution does the work make to an existing body of knowledge or to a specific group of readers? Can you justify the use of this work in a particular course?
- What is the most important final comment you wish to make about the book or article? Do you have any suggestions for the direction of future research in the area? What has reading this work done for you or demonstrated to you?

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews
How to Write an Article Review
Last Updated: September 8, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,089,979 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Things You Should Know
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information. [1] X Research source
Preparing to Write Your Review

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.
Writing the Article Review

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [10] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.
Sample Article Reviews

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Oct 25, 2023
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
%20(2).webp)

Book Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. It offers a process and suggests some strategies for writing book reviews.
What is a review?
A review is a critical evaluation of a text, event, object, or phenomenon. Reviews can consider books, articles, entire genres or fields of literature, architecture, art, fashion, restaurants, policies, exhibitions, performances, and many other forms. This handout will focus on book reviews. For a similar assignment, see our handout on literature reviews .
Above all, a review makes an argument. The most important element of a review is that it is a commentary, not merely a summary. It allows you to enter into dialogue and discussion with the work’s creator and with other audiences. You can offer agreement or disagreement and identify where you find the work exemplary or deficient in its knowledge, judgments, or organization. You should clearly state your opinion of the work in question, and that statement will probably resemble other types of academic writing, with a thesis statement, supporting body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Typically, reviews are brief. In newspapers and academic journals, they rarely exceed 1000 words, although you may encounter lengthier assignments and extended commentaries. In either case, reviews need to be succinct. While they vary in tone, subject, and style, they share some common features:
- First, a review gives the reader a concise summary of the content. This includes a relevant description of the topic as well as its overall perspective, argument, or purpose.
- Second, and more importantly, a review offers a critical assessment of the content. This involves your reactions to the work under review: what strikes you as noteworthy, whether or not it was effective or persuasive, and how it enhanced your understanding of the issues at hand.
- Finally, in addition to analyzing the work, a review often suggests whether or not the audience would appreciate it.
Becoming an expert reviewer: three short examples
Reviewing can be a daunting task. Someone has asked for your opinion about something that you may feel unqualified to evaluate. Who are you to criticize Toni Morrison’s new book if you’ve never written a novel yourself, much less won a Nobel Prize? The point is that someone—a professor, a journal editor, peers in a study group—wants to know what you think about a particular work. You may not be (or feel like) an expert, but you need to pretend to be one for your particular audience. Nobody expects you to be the intellectual equal of the work’s creator, but your careful observations can provide you with the raw material to make reasoned judgments. Tactfully voicing agreement and disagreement, praise and criticism, is a valuable, challenging skill, and like many forms of writing, reviews require you to provide concrete evidence for your assertions.
Consider the following brief book review written for a history course on medieval Europe by a student who is fascinated with beer:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600, investigates how women used to brew and sell the majority of ale drunk in England. Historically, ale and beer (not milk, wine, or water) were important elements of the English diet. Ale brewing was low-skill and low status labor that was complimentary to women’s domestic responsibilities. In the early fifteenth century, brewers began to make ale with hops, and they called this new drink “beer.” This technique allowed brewers to produce their beverages at a lower cost and to sell it more easily, although women generally stopped brewing once the business became more profitable.
The student describes the subject of the book and provides an accurate summary of its contents. But the reader does not learn some key information expected from a review: the author’s argument, the student’s appraisal of the book and its argument, and whether or not the student would recommend the book. As a critical assessment, a book review should focus on opinions, not facts and details. Summary should be kept to a minimum, and specific details should serve to illustrate arguments.
Now consider a review of the same book written by a slightly more opinionated student:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 was a colossal disappointment. I wanted to know about the rituals surrounding drinking in medieval England: the songs, the games, the parties. Bennett provided none of that information. I liked how the book showed ale and beer brewing as an economic activity, but the reader gets lost in the details of prices and wages. I was more interested in the private lives of the women brewsters. The book was divided into eight long chapters, and I can’t imagine why anyone would ever want to read it.
There’s no shortage of judgments in this review! But the student does not display a working knowledge of the book’s argument. The reader has a sense of what the student expected of the book, but no sense of what the author herself set out to prove. Although the student gives several reasons for the negative review, those examples do not clearly relate to each other as part of an overall evaluation—in other words, in support of a specific thesis. This review is indeed an assessment, but not a critical one.
Here is one final review of the same book:
One of feminism’s paradoxes—one that challenges many of its optimistic histories—is how patriarchy remains persistent over time. While Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 recognizes medieval women as historical actors through their ale brewing, it also shows that female agency had its limits with the advent of beer. I had assumed that those limits were religious and political, but Bennett shows how a “patriarchal equilibrium” shut women out of economic life as well. Her analysis of women’s wages in ale and beer production proves that a change in women’s work does not equate to a change in working women’s status. Contemporary feminists and historians alike should read Bennett’s book and think twice when they crack open their next brewsky.
This student’s review avoids the problems of the previous two examples. It combines balanced opinion and concrete example, a critical assessment based on an explicitly stated rationale, and a recommendation to a potential audience. The reader gets a sense of what the book’s author intended to demonstrate. Moreover, the student refers to an argument about feminist history in general that places the book in a specific genre and that reaches out to a general audience. The example of analyzing wages illustrates an argument, the analysis engages significant intellectual debates, and the reasons for the overall positive review are plainly visible. The review offers criteria, opinions, and support with which the reader can agree or disagree.
Developing an assessment: before you write
There is no definitive method to writing a review, although some critical thinking about the work at hand is necessary before you actually begin writing. Thus, writing a review is a two-step process: developing an argument about the work under consideration, and making that argument as you write an organized and well-supported draft. See our handout on argument .
What follows is a series of questions to focus your thinking as you dig into the work at hand. While the questions specifically consider book reviews, you can easily transpose them to an analysis of performances, exhibitions, and other review subjects. Don’t feel obligated to address each of the questions; some will be more relevant than others to the book in question.
- What is the thesis—or main argument—of the book? If the author wanted you to get one idea from the book, what would it be? How does it compare or contrast to the world you know? What has the book accomplished?
- What exactly is the subject or topic of the book? Does the author cover the subject adequately? Does the author cover all aspects of the subject in a balanced fashion? What is the approach to the subject (topical, analytical, chronological, descriptive)?
- How does the author support their argument? What evidence do they use to prove their point? Do you find that evidence convincing? Why or why not? Does any of the author’s information (or conclusions) conflict with other books you’ve read, courses you’ve taken or just previous assumptions you had of the subject?
- How does the author structure their argument? What are the parts that make up the whole? Does the argument make sense? Does it persuade you? Why or why not?
- How has this book helped you understand the subject? Would you recommend the book to your reader?
Beyond the internal workings of the book, you may also consider some information about the author and the circumstances of the text’s production:
- Who is the author? Nationality, political persuasion, training, intellectual interests, personal history, and historical context may provide crucial details about how a work takes shape. Does it matter, for example, that the biographer was the subject’s best friend? What difference would it make if the author participated in the events they write about?
- What is the book’s genre? Out of what field does it emerge? Does it conform to or depart from the conventions of its genre? These questions can provide a historical or literary standard on which to base your evaluations. If you are reviewing the first book ever written on the subject, it will be important for your readers to know. Keep in mind, though, that naming “firsts”—alongside naming “bests” and “onlys”—can be a risky business unless you’re absolutely certain.
Writing the review
Once you have made your observations and assessments of the work under review, carefully survey your notes and attempt to unify your impressions into a statement that will describe the purpose or thesis of your review. Check out our handout on thesis statements . Then, outline the arguments that support your thesis.
Your arguments should develop the thesis in a logical manner. That logic, unlike more standard academic writing, may initially emphasize the author’s argument while you develop your own in the course of the review. The relative emphasis depends on the nature of the review: if readers may be more interested in the work itself, you may want to make the work and the author more prominent; if you want the review to be about your perspective and opinions, then you may structure the review to privilege your observations over (but never separate from) those of the work under review. What follows is just one of many ways to organize a review.
Introduction
Since most reviews are brief, many writers begin with a catchy quip or anecdote that succinctly delivers their argument. But you can introduce your review differently depending on the argument and audience. The Writing Center’s handout on introductions can help you find an approach that works. In general, you should include:
- The name of the author and the book title and the main theme.
- Relevant details about who the author is and where they stand in the genre or field of inquiry. You could also link the title to the subject to show how the title explains the subject matter.
- The context of the book and/or your review. Placing your review in a framework that makes sense to your audience alerts readers to your “take” on the book. Perhaps you want to situate a book about the Cuban revolution in the context of Cold War rivalries between the United States and the Soviet Union. Another reviewer might want to consider the book in the framework of Latin American social movements. Your choice of context informs your argument.
- The thesis of the book. If you are reviewing fiction, this may be difficult since novels, plays, and short stories rarely have explicit arguments. But identifying the book’s particular novelty, angle, or originality allows you to show what specific contribution the piece is trying to make.
- Your thesis about the book.
Summary of content
This should be brief, as analysis takes priority. In the course of making your assessment, you’ll hopefully be backing up your assertions with concrete evidence from the book, so some summary will be dispersed throughout other parts of the review.
The necessary amount of summary also depends on your audience. Graduate students, beware! If you are writing book reviews for colleagues—to prepare for comprehensive exams, for example—you may want to devote more attention to summarizing the book’s contents. If, on the other hand, your audience has already read the book—such as a class assignment on the same work—you may have more liberty to explore more subtle points and to emphasize your own argument. See our handout on summary for more tips.
Analysis and evaluation of the book
Your analysis and evaluation should be organized into paragraphs that deal with single aspects of your argument. This arrangement can be challenging when your purpose is to consider the book as a whole, but it can help you differentiate elements of your criticism and pair assertions with evidence more clearly. You do not necessarily need to work chronologically through the book as you discuss it. Given the argument you want to make, you can organize your paragraphs more usefully by themes, methods, or other elements of the book. If you find it useful to include comparisons to other books, keep them brief so that the book under review remains in the spotlight. Avoid excessive quotation and give a specific page reference in parentheses when you do quote. Remember that you can state many of the author’s points in your own words.
Sum up or restate your thesis or make the final judgment regarding the book. You should not introduce new evidence for your argument in the conclusion. You can, however, introduce new ideas that go beyond the book if they extend the logic of your own thesis. This paragraph needs to balance the book’s strengths and weaknesses in order to unify your evaluation. Did the body of your review have three negative paragraphs and one favorable one? What do they all add up to? The Writing Center’s handout on conclusions can help you make a final assessment.
Finally, a few general considerations:
- Review the book in front of you, not the book you wish the author had written. You can and should point out shortcomings or failures, but don’t criticize the book for not being something it was never intended to be.
- With any luck, the author of the book worked hard to find the right words to express her ideas. You should attempt to do the same. Precise language allows you to control the tone of your review.
- Never hesitate to challenge an assumption, approach, or argument. Be sure, however, to cite specific examples to back up your assertions carefully.
- Try to present a balanced argument about the value of the book for its audience. You’re entitled—and sometimes obligated—to voice strong agreement or disagreement. But keep in mind that a bad book takes as long to write as a good one, and every author deserves fair treatment. Harsh judgments are difficult to prove and can give readers the sense that you were unfair in your assessment.
- A great place to learn about book reviews is to look at examples. The New York Times Sunday Book Review and The New York Review of Books can show you how professional writers review books.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Drewry, John. 1974. Writing Book Reviews. Boston: Greenwood Press.
Hoge, James. 1987. Literary Reviewing. Charlottesville: University Virginia of Press.
Sova, Dawn, and Harry Teitelbaum. 2002. How to Write Book Reports , 4th ed. Lawrenceville, NY: Thomson/Arco.
Walford, A.J. 1986. Reviews and Reviewing: A Guide. Phoenix: Oryx Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
College admissions
Course: college admissions > unit 4.
- Writing a strong college admissions essay
- Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
- Brainstorming tips for your college essay
- How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
- Taking your college essay to the next level
Sample essay 1 with admissions feedback
- Sample essay 2 with admissions feedback
- Student story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
- Student story: Admissions essay about personal identity
- Student story: Admissions essay about community impact
- Student story: Admissions essay about a past mistake
- Student story: Admissions essay about a meaningful poem
- Writing tips and techniques for your college essay
Introduction
Sample essay 1, feedback from admissions.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
How to Revise an Essay in 3 Simple Steps
Published on December 2, 2014 by Shane Bryson . Revised on December 8, 2023 by Shona McCombes.
Revising and editing an essay is a crucial step of the writing process . It often takes up at least as much time as producing the first draft, so make sure you leave enough time to revise thoroughly. Although you can save considerable time using our essay checker .
The most effective approach to revising an essay is to move from general to specific:
- Start by looking at the big picture: does your essay achieve its overall purpose, and does it proceed in a logical order?
- Next, dive into each paragraph: do all the sentences contribute to the point of the paragraph, and do all your points fit together smoothly?
- Finally, polish up the details: is your grammar on point, your punctuation perfect, and your meaning crystal clear?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: look at the essay as a whole, step 2: dive into each paragraph, step 3: polish the language, other interesting articles.
There’s no sense in perfecting a sentence if the whole paragraph will later be cut, and there’s no sense in focusing on a paragraph if the whole section needs to be reworked.
For these reasons, work from general to specific: start by looking at the overall purpose and organization of your text, and don’t worry about the details for now.
Double-check your assignment sheet and any feedback you’ve been given to make sure you’ve addressed each point of instruction. In other words, confirm that the essay completes every task it needs to complete.
Then go back to your thesis statement . Does every paragraph in the essay have a clear purpose that advances your argument? If there are any sections that are irrelevant or whose connection to the thesis is uncertain, consider cutting them or revising to make your points clearer.
Organization
Next, check for logical organization . Consider the ordering of paragraphs and sections, and think about what type of information you give in them. Ask yourself :
- Do you define terms, theories and concepts before you use them?
- Do you give all the necessary background information before you go into details?
- Does the argument build up logically from one point to the next?
- Is each paragraph clearly related to what comes before it?
Ensure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence that sums up its point. Then, try copying and pasting these topic sentences into a new document in the order that they appear in the paper.
This allows you to see the ordering of the sections and paragraphs of your paper in a glance, giving you a sense of your entire paper all at once. You can also play with the ordering of these topic sentences to try alternative organizations.
If some topic sentences seem too similar, consider whether one of the paragraphs is redundant , or if its specific contribution needs to be clarified. If the connection between paragraphs is unclear, use transition sentences to strengthen your structure.
Finally, use your intuition. If a paragraph or section feels out of place to you, even if you can’t decide why, it probably is. Think about it for a while and try to get a second opinion. Work out the organizational issues as best you can before moving on to more specific writing issues.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Next, you want to make sure the content of each paragraph is as strong as it can be, ensuring that every sentence is relevant and necessary:
- Make sure each sentence helps support the topic sentence .
- Check for redundancies – if a sentence repeats something you’ve already said, cut it.
- Check for inconsistencies in content. Do any of your assertions seem to contradict one another? If so, resolve the disagreement and cut as necessary.
Once you’re happy with the overall shape and content of your essay, it’s time to focus on polishing it at a sentence level, making sure that you’ve expressed yourself clearly and fluently.
You’re now less concerned with what you say than with how you say it. Aim to simplify, condense, and clarify each sentence, making it as easy as possible for your reader to understand what you want to say.
- Try to avoid complex sentence construction – be as direct and straightforward as possible.
- If you have a lot of very long sentences, split some of them into shorter ones.
- If you have a lot of very short sentences that sound choppy, combine some of them using conjunctions or semicolons .
- Make sure you’ve used appropriate transition words to show the connections between different points.
- Cut every unnecessary word.
- Avoid any complex word where a simpler one will do.
- Look out for typos and grammatical mistakes.
If you lack confidence in your grammar, our essay editing service provides an extra pair of eyes.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, December 08). How to Revise an Essay in 3 Simple Steps. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/revising/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Unit 4: Fundamentals of Academic Essay Writing
20 Exploring the Essay
Parts of an essay.
An essay typically has three basic parts, the introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
Student Model for Essay 1
The essay below is an authentic student essay. This essay was chosen as a model because it effectively demonstrates the characteristics of academic writing and has an important message for the reader.
Student name ESL 117 Essay #1, Draft #3
The Value of Peer Review in Improving Students’ Writing
The process of writing academic papers involves many steps: exploring a topic through reading and writing, narrowing a topic, organizing the ideas, writing multiple drafts, getting feedback and making revisions. Over multiple drafts, the writer refines his/her ideas in part by getting feedback from readers. In a classroom, the teacher and the classmates, or peers, can serve as easily accessible readers. Peer feedback, also called peer review or peer response, is widely used in writing classes for both native speakers and English as a Second Language (ESL) students. Peer review benefits both the writer and the reviewer, and it can be just as useful as teacher feedback.
Peer review is used in ESL classes to improve student’s English writing or get better grades on writing assignments. Many ESL programs involve international students in peer review to improve their writing skills, and many studies support the idea that peer review is essential to improve students’ writing skills. Bijami, Kashef and Nejad (2013) state that critical and specific peer comments can be utilized to enhance students’ writing skills and help students become competent writers (p.93). Peer comments can address specific aspects of writing. For example, peer comments help students improve their writing ability in terms of organization and content (Zeqiri, 2012, p. 50). Moreover, helping the writer identify the strengths and weaknesses in their writing helps the writer develop self-awareness. According to Tsui and Ng (2000), it is often difficult for students to see their own weaknesses, but peers can point out these problems (p. 166). These examples illustrate how ESL students’ writing skills can be enhanced through peer review because it helps them improve awareness of their papers’ strengths and weaknesses.
Not only does peer review benefit the writer, identifying strengths and weaknesses in another student’s writing plays an important role in improving the reviewer’s own writing ability. An important writing skill is to be able to recognize good writing by critically evaluating writing. By reading their classmates’ papers critically, students learn more about what makes writing successful and effective (Bijami et al., 2013, p. 94). In this way, reading other’s papers and being given criteria to look for allows students have a chance to develop these skills.
Furthermore, peer review seems to have some unexpected benefits for the reviewer. There are some studies that show that students who review peers’ papers are more likely to improve their writing ability than students who receive peers’ comments. Lundstrom and Baker (2009) conducted a study which compared the improvements in writing between givers and receivers of peer feedback and found that of the two groups, the giver group made more progress in writing than the receiver group (p. 32). This finding shows the givers (or reviewers) learned to judge their own work self-critically by evaluating their peers’ writing and transferring this knowledge to their own writing, resulting in significant improvements on their own papers. Thus, responding to a peer’s paper is an important way for a student to improve his/her own writing.
There are additional advantages of peer review for both the writer and the reviewer in terms of language skills, classroom environment, and confidence. Peer review not only helps students improve their writing skills but also helps them develop language skills. Language skills are developed through interaction and communication. Lundstrom and Baker (2009) write that peer review enhances not only students’ writing skills but also students’ speaking and listening skills (p. 31). Such research suggests that peer review can improve ESL students’ oral skills because they are involved in meaningful discussion and negotiations. Furthermore, peer review creates a student-centered classroom environment where students work together. Peer review encourages collaborative learning, in which students learn from and support each other (Tsui & Ng, 2000, p. 167). This collaborative group work helps to form a community of learners. In addition, peer review can increase a student’s interest and confidence in writing. Rather than relying on the teacher, the student is actively involved in the writing process (Bijami et al., 2013, p. 94). Such emphasis on learning independently further demonstrates the claim that as students take more responsibility for their writing, from developing their topic to writing drafts, they become more confident and inspired.
Although many students tend to prefer teacher feedback to peer feedback, there is evidence that peer review can be as helpful and meaningful as teacher feedback. In fact, recent studies reveal that there is no significant difference between teacher feedback and peer feedback in terms of improvement in students’ writing skills. In their study, Ruegg (2015) found that even though students who received teacher comments showed better performance on grammar than students who received peer comments, there was little difference between teacher comments and peer comments with regard to students’ improvements in areas such as organization, content, vocabulary, academic style and final grades (pp. 79-80). That is, peer feedback can be as effective as teacher feedback in revising students’ compositions and covers a wide range of writing skills. Based on their research which compared students who received peer comments to students who received teacher comments, Eksi’s findings (2012) also support Ruegg’s point that peer feedback enabled students to make significant writing improvements (p. 43). In sum, both teacher feedback and peer feedback helped students improve the quality of their writing.
In addition, teacher feedback and peer feedback can complement each other. To demonstrate this, Tsui and Ng (2000) cite a study in which 90% of the ESL students gave peer feedback that was judged to be valid by the teacher, and 60% of the students gave appropriate advice on aspects that had not been pointed out by the teacher (p. 149). These results mean that the vast majority of the student feedback was useful and accurate, and the students got additional feedback from peers that they would not have had if only the teacher had read the paper. Thus, peer feedback can expand the amount of useful feedback that the writer receives.
Many studies have shown the advantages of peer review such as improving students’ writing ability and language skills, developing students’ critical thinking skills and creating a student-centered classroom environment. That peer review is a time-consuming activity for both writing teachers and students is an undeniable fact, and students who are inexperienced in peer review will need training and guidance. Nevertheless, this investment in time and training gives students a powerful way to improve not only their writing skills, but also their abilities as thinkers and problem-solvers.
Bijami, M., Kashef, S., & Nejad, M. (2013). Peer feedback in learning English writing: Advantages and disadvantages. Journal of Studies in Education 3 (4), 91-7. doi: 10.5296/jse.v3i4.4314
Eksi, G. (2012). Peer review versus teacher feedback in process writing: How effective? International Journal of Applied Educational Studies 13 (1), 33-48.
Lundstrom, K., & Baker, W. (2009). To give is better than to receive: The benefits of peer review to the reviewer’s own writing. Journal of Second Language Writing 18 (1), 30-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jslw.2008.06.002
Ruegg, R. (2015). The relative effects of peer and teacher feedback on improvement in EFL students’ writing ability. Linguistics and Education 29 , 73-82 . doi: 10.1016/j.linged.2014.12.001
Tsui, A., & Ng, M. (2000). Do secondary L2 writers benefit from peer comments? Journal of Second Language Writing 9 (2), 147-170. doi: 10.1016/S1060-3743(00)00022-9
Zeqiri, L. (2012). The role of peer feedback in developing better writing skills. SEEU Review 8 (1), 43-62. doi: 10.2478/v10306-012-0003-8
Academic Writing I Copyright © by UW-Madison ESL Program is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
Awesome Tips and Ideas on How to Write a Review Essay
How to Write a Fresh Essays Review?
The purpose of article reviews is to offer a critical perspective on a text, usually one that you have read. This can be done by discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the text, as well as offering your own interpretation. In order to write a fresh essays review, you will need to have a good understanding of what the text is about and what its main arguments are. You will also need to be able to express your thoughts clearly and concisely. So now let's answer the question: What is a review essay? Our online essay writing service review writers have prepared detailed instructions for you.
What is a Review Essay?
There are good chances you have heard of review essays before. But what is a review essay exactly? Well, it is a paper that critically analyzes another piece of writing. It can be used to examine a book, article, or other work of art. Review essays are typically shorter than other types of essays that explore and evaluate the work in question.
When writing a review essay, it is important to remember that you are not simply summarizing the work. Instead, you are critically analyzing it and offering your own words interpretations. This means that you will need to take a close look at the structure, argument, and style of the piece you are examining. You will also need to consider how well the work achieves its purpose. In order to write a successful review essay, you will need to provide your readers with a clear and concise evaluation of the assignment. If this sounds too much, don't worry. You will find useful tips on how to write an essay review at the end of this article. By the way you can read the best essay writing service reviews on our website NoCramming, just check it out.
Research article vs Review Article
A research paper is a primary source that provides the methodology and results of the authors' original study. A review article, on the other hand, is a secondary source that is published on previous articles and does not present original research.
In research papers, authors develop a research question, gather data, and carry out an initial report, while in review articles, authors choose a particular subject and then synthesize previous research on that subject.
Research papers report each study step in detail, including an abstract, the premise, underlying research, methods, results, and a conclusion. If there are inconsistencies, the authors make an effort to explain why the results could be in dispute. A review article will also address how the research contributes to the body of knowledge, the consequences of the findings, and ideas for future research. Here, the journal article review analyzes the material that is currently available from published work from a neutral point of view and indicates any issues or research gaps.
Review Essay Format and Structure
As a college student, you will likely be asked to write a review essay at some point. It will be assigned in order to assess your ability to analyze a text, object, or event and express your opinion on it. In order to write a good review essay, you will need first to understand the review essay format.
The outline of your review essay should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
The Introduction
In the introduction of your review essay, you should provide some background information on the text, object, or event that you are reviewing. This background information should help set up the main idea or theme of your essay. Then, after introducing the topic of your essay, you should state your thesis statement. The clear thesis statement is the most important part of your introduction, as it will express your opinion on the main idea or theme of the text, object, or event that you are reviewing.
The Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of your review essay should focus on a different aspect of the text, object, or event that you are reviewing. You should discuss one point that supports your thesis statement in each body paragraph. For example, if you are writing a review of a film, you may want to focus one body paragraph on the film’s cinematography, the other one on its acting, and another one on its plot. Whatever your review essay topics are, the review essay format and structure would be the same. The body paragraphs are a good opportunity to prove your writing skills. Here is a paragraph checklist that you can use to make sure your body paragraphs are well-organized:
- Does each paragraph have a topic sentence?
- Does each paragraph contain evidence to support the topic sentence?
- Does each paragraph flow smoothly from one idea to the next?
- Are all of the body paragraphs relevant to the thesis statement?
The Conclusion
The conclusion of your essay writing should restate your thesis statement and summarize the main points of your essay. You may also want to include a final thought or opinion on the text, object, or event that you are reviewing.
Step by Step Guide on How to Write a Review Essay
.webp)
If you have been asked to write a review essay, there are a few things that you will need to keep in mind. In this guide, we will take you through the steps of writing review essays, and alternatively, you can check these best dissertation writing services to produce a well-written and successful essay.
1) Invent a Title for Fresh Essays Review
The first step is to come up with an interesting and catchy title for your fresh essays review. This will be the first thing that your reader sees, so make sure it is attention-grabbing and relevant to the rest of your essay.
2) Write a Summary of the Works You Make a Review On
After choosing your title, you will need to write a brief summary of the works you are reviewing. This is an important part of the review essay format and should include the main points and arguments of each piece, as well as your overall opinion of them.
3) Identify the Articles You Base Your Review On
Next, you will need to identify the articles you base your review on. Article identification is important so that your reader knows which work you are talking about and can follow along with your argument. We suggest checking some review essays examples to see how this is done.
4) Make a Paragraph Checklist
Why is it important to review an essay outline or make a paragraph checklist? Well, it will help you organize your thoughts and arguments in a logical and coherent manner. Plus, it will ensure that you don’t forget to include any key points.
Tips on How to Write a Review Essay
When you are writing a review essay, there are a few things that you will want to keep in mind.
The first step in writing a review essay is to read the text, object, or event that you are being asked to review. This may seem like an obvious first step, but it is important to read the text or view the event with a critical eye. As you read, take note of any initial thoughts or reactions that you have. These can be positive or negative, but they should be your own honest reaction to what you are reading or viewing.
Once you have completed your first reading, you should take some time to reflect on what you have seen or read. This is an important step in the review essay process, as it will allow you to put your thoughts and reactions into perspective. After reflecting on the text, object, or event, you should be able to identify the main idea or theme. This will be the focus of your review essay.
Don’t forget to develop a thesis statement. This should express your opinion on the main idea or theme of the text, object, or event that you are reviewing. Once you have developed a thesis statement, you can begin to outline your essay.
An Objective Approach
The second thing to keep in mind is that a review essay is not necessarily a positive or negative review. It is simply an evaluation of something. This means that you should try to be as objective as possible when you are writing. While reviewing, you may find some aspects that you like or don’t like, but it is important to remember that your job is not to take sides but to simply evaluate.
Finally, when writing a review essay, it is important to make sure your paper flows well. This means that you should have a clear and coherent introduction, body, and conclusion. If your essay feels choppy or disjointed, it will probably be difficult for your reader to follow along.
If you keep these things in mind, you should be able to write a review essay that is both informative and well-written. Make sure that you stick to the review essay format discussed above. With a bit of practice, you will find that writing fresh essays review is not as difficult as it may initially seem.
What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing an Article Review Essay?
One common mistake made when writing a review essay is to simply summarize the content of the article being reviewed. While it is important to provide a brief overview of the work, your essay should go beyond a summary page to offer a deep and insightful analysis.
Another mistake is to simply state whether you agree or disagree with the argument being made in the article. It is important to back up your assessment with concrete evidence from the text itself.
Finally, avoid making personal attacks on the author or their work; instead, focus on offering a well-reasoned and objective evaluation.
Review Essay Topics 2022
If you're looking for some fresh ideas, here are review essay topics for 2022:
- The shifting landscape of online education
- The increasing prevalence of "fake news" and its impact on society
- The rise of populism around the world
- The role of technology in society and its impact on human interaction
- The changing nature of work and its impact on the workforce
- The ongoing debate about climate change and its implications for the future
- The increasing income inequality around the world
- The refugee crisis and its impact on global politics
- The role of social media in our lives and its impact on our relationships
- The rise of artificial intelligence and its implications for the future
- The increasing number of natural disasters around the world and their impact on populations
- The declining state of the environment and its impact on human health
- The consequences of irresponsible human conduct on the environment
- The growing problem of obesity in developed countries
- The declining birth rates in developed countries
- Why is cultural heritage preservation important?
- Gender equality and women's rights in contemporary society
- Is peace education receiving enough attention from society?
- The role of the media in our lives and its impact on our perceptions of reality
Whatever you choose, make sure to pick something that you're passionate about and that you feel would be interesting to explore in depth. If you’d rather have a professional writer craft a perfect essay for you, check out essay service reviews and DoMyEssay review (where you can find the answer to the question " Is essay pro a scam ?") to see which one’s the best fit for your needs. Meanwhile, good luck with your fresh essays review!
All in all, always pay attention to how well the essay flows:
- introduces the subject of the review
- provides an overview of the main points of the review
- discusses the merits of the review
- provides a balanced assessment of the review
- concludes by summarizing the main points of the review
Keep these points in mind as you write your own paper. Remember, your goal is to provide a fair and objective assessment of the work under review.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of an article review, what is the key difference between a review essay and a summary, how should i structure a review essay, what are common mistakes to avoid when writing a review essay, still have no idea how to choose the best dissertation writing service.
There is no sure way to pick the best dissertation writing service and never risk disappointment or multiple revisions. Yet, this list of PhD dissertation writing services may be an aid for you in the moment of doubt. So, choose wisely but do not overthink.
.webp)
You Might Also Be Interested In

How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.

Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
How to write a review? | B2 First (FCE)
You always have to do two things describe and discuss something, for example, a film , a book , a restaurant , an experience or whatever the task might require you to talk about. Also, you have to make a recommendation at the end of your text.
Unlike an essay a review should be written in an informal or neutral register, this means:
- you CAN use phrasal verbs ,
- you CAN use idioms
- you CAN use contractions
- you CAN be creative!
Check our Writing Guide below – to see how to write an FCE review in detail.
B2 First (FCE) Review: Structure
Fce, cae, cpe, practice, write & improve, b2 first (fce) review: writing guide.
We will use the example FCE review topic below:
You see this announcement in your college English-language magazine.
Book reviews wanted Have you read a book in which the main character behaved in a surprising way?
Write us a review of the book, explaining what the main character did and why it was surprising. Tell us whether or not you would recommend this book to other people.
The best reviews will be published in the magazine.
Write your review (140-190 words)
Step 1: Briefly analyse the given topic…
The first thing you need to do is to underline a description part -in other words, just find what needs to be described.
Secondly, find a discussion part – in other words, try to find the specific points you need to comment on in your text.
Finally, find the target reader so you know exactly who you are writing for and who is going to read your review.
You see this announcement in your college English-language magazine. (our readers)
Book reviews wanted Have you read a book in which the main character behaved in a surprising way? (to describe)
Write us a review of the book, explaining what the main character did and why it was surprising. ( to comment)
Now we have all three elements we need to write a great review:
You need to describe: Book in which the main character behaved in a surprising way
You need to answer/discuss:
- What did the main character do?
- Why it was surprising?
Who is the target reader: college English-language magazine.
We know now that the target readers are students, teachers and probably parents so the writing style should be neutral or informal.
We don’t need to be too formal because after all some of the readers are students, but we also don’t want to be too informal as some of the readers are teachers and parents.
Now we can start building our structure and writing a review.
Step 2: Title
The review should start with the title, and there are few simple ways to write it:
- imagine you’re reviewing a book you can write: [Title] by [Author]
- if you were reviewing a restaurant you could write: [name of the restaurant] – a review
Title (book): Dark Souls by Stephen King (by) Title (restaurant): Taco Bell in London – a review (a review)
We will use this title in our guide : TITLE : Time Machine by Adam Smith
Tip : Nothing prevents you from writing something more unique but it has to point to what you are going to review.
Step 3: Introduction
The other function of your introduction is to engage the reader . You can do it by asking a question.
Make your introduction at least 2 sentences long.
INTRODUCTION: What would you do if you could travel back in time? Most people would probably meet their great-great-grandparents or watch how the amazing pyramids in Giza were built, but Tom Lee, the main character of the novel Time Machine by Adam Smith finds himself in a completely unexpected situation and he has to make a very difficult decision that will change history as we know it.
– question
– details about the book and main character
Step 4: The body paragraphs (main content)
The body paragraphs are the main parts of your review so they should be the longest and carry most of the information. Also, here you describe the points you’ve found in (Step 1)
You can use idioms , and phrasal verbs – neutral/informal language is appropriate for your target reader – students and teachers.
See the example below, in which we dedicated one paragraph to one point.
[Who is the main character and what did he do? – describe]
Tom, a teacher in a little town in Rotherham, finds a mysterious time portal in the back of a ragged diner which takes him back to the year 1935. He soon realises that every time he goes through the portal he gets to the exact same point in the past. Eventually, he makes the unexpected decision to stop Michael James Newton from brutally killing President John F. Kennedy on 22.11.1963.
[Why it was surprising? – comment]
It seems to me that Tom could choose many other and more personal things to do, but he decides to try and change history to a degree that he cannot predict . In my opinion , that came definitely unexpected an d if I were in his position I probably wouldn’t even consider a task this far-reaching.
– own opinion
– descriptive/interesting vocabulary
– relevant details about the main character and book
Step 5: Conclusion / Recommendations
Finally, we need to make a recommendation because after all, that’s the only reason why anyone would read a review they want to know what the reviewer thinks about the book , film or restaurant .
A good final paragraph of a review does exactly two things
- it includes a recommendation
- and a final sentence to round off the review
CONCLUSION: I definitely recommend “Time Machine” to everyone who has already read some of Adam Smith’s novels as well as to those who like stories with twists and turns around every corner plus you get some modern history on top of that. For me, it was absolutely worth reading and I’m sure you won’t be disappointed.
See full review…
Full review.
Time Machine by Adam Smith
What would you do if you could travel back in time? Most people would probably meet their great-great-grandparents or watch how the amazing pyramids in Giza were built, but Tom Lee, the main character of the novel Time Machine by Adam Smith finds himself in a completely unexpected situation and he has to make a very difficult decision that will change history as we know it.
Tom, a teacher in a little town in Rotherham, finds a mysterious time portal in the back of a ragged diner which takes him back to the year 1935. He soon realises that every time he goes through the portal he gets to the exact same point in the past. Eventually, he makes the unexpected decision to stop Michael James Newton from brutally killing President John F. Kennedy on 22.11.1963.
It seems to me that Tom could choose many other and more personal things to do, but he decides to try and change history to a degree that he cannot predict. In my opinion, that came definitely unexpected and if I were in his position I probably wouldn’t even consider a task this far-reaching.
I definitely recommend “Time Machine” to everyone who has already read some of Adam Smith’s novels as well as to those who like stories with twists and turns around every corner plus you get some modern history on top of that. For me, it was absolutely worth reading and I’m sure you won’t be disappointed.
Check your (FCE) Review
B2 first (fce) review: model answers, model answer 1.
You have seen this notice in your school library:
REVIEWS NEEDED We want to buy some new books for the library. Have you read a good book in English recently? Write us a review of a book you enjoyed, explaining why you liked it and why you think it would be a good choice for the school library.
We will use your reviews to help us decide which books to buy
Model answer
THE THIEVES OF OSTIA
„The thieves of Ostia‟ by Caroline Lawrence is the first in a series of books entitled„The Roman Mysteries‟ and I think it‟s an absolute must for the school library.
The book is set in the Roman port of Ostia nearly two thousand years ago. It tells the story of Flavia and her three friends, and their attempts to discover who has been killing the dogs of Ostia and why. It‟s full of mystery and excitement, and the plot has many twists and turns, which make you want to keep reading.
The book is aimed at ten – to twelve – year – old native English speakers, but it is very popular with older children and would be ideal for teenagers studying English. What‟s more, it gives a fascinating insight into life in Roman times, so readers learn about history as well as improve their language skills.
After finishing „The Thieves of Ostia‟, students will want to borrow further books from the series. By buying it, then, the library would be doing a lot to encourage students to read more in English
Model Answer 2
You have found the following advertisement online:
RESTAURANT REVIEWS WANTED!
Have you been to a great restaurant lately? If so, send us an honest review of the restaurant explaining what you liked and disliked of the place as well as its location, staff and how it looks on the inside.
We will publish the first 20 decent reviews we get!
Foster’s Hollywood
Being a huge fan of traditional American fast food and restaurant styles, it’s no wonder that my favourite restaurant in Granada is Foster’s Hollywood.
Located smack in the middle of the city, this fast-food chain serves a wide variety of mouthwatering, American dishes at a reasonable price. These range from typical Tex-Mex nachos or French fries to more elaborate meals like traditional, homemade Bourbon steak. And if you’re hungry, it’s the perfect place to go, as their servings are absolutely huge!
Another cool thing about this place is its magnificent decor. If you’re a film buff, you will quickly fall in love with this place, since all the walls are covered in famous movie posters! Apart from that, it’s got a spacious dining hall, super friendly staff and an outdoor terrace which is absolutely fantastic on summer nights!
The only negative thing I can say is that it is right next to a gym, which sometimes makes me feel guilty for eating so much!
Nevertheless, Foster’s Hollywood offers delicious meals in an unbeatable atmosphere, so you should definitely give it a try. I promise you won’t regret it!
B2 First (FCE) Review: Example Topics
Example topic 1.
Your teacher has asked you to write a review for a book you have read recently. The best reviews will go in the school magazine. Review the book giving your opinion and say whether or not you would recommend it.
Example Topic 2
Your teacher has asked you to write a review for a film you have seen recently on DVD or at the cinema.The best reviews will go in the school magazine. Review the book giving your opinion and saying whether ornot you would recommend it.
Example Topic 3
At school, you are building a tourist website in English. Your teacher has asked you to write a review of arestaurant you have eaten at in your town. Review the restaurant giving your opinion and saying whetheror not you would recommend it.
B2 First (FCE) Review: Writing Checklist
After writing your text, you can check it yourself using the writing checklist below.
How to do that? Simply check your text/email by answering the questions one by one:
- Have I covered all the key information required by the task?
- Have I written only information which is relevant to the task?
- Have I developed the basic points in the task with my own ideas?
Communicative Achievement
- Have I achieved the main purpose(s) of the text (for example, explaining, persuading, suggesting, apologising, comparing, etc.)?
- Have I communicated a balance of straightforward and more complex ideas?
- Have I used a suitable style and register (formal or informal) for the task?
Organisation
- Have I used paragraphs appropriately to organise my ideas?
- Have I used other organisational features appropriately for the genre of the text (for example, titles, headings, openings, closings, etc.)?
- Is the connection between my ideas clear and easy for the reader to follow? (For example, have I used appropriate linking words, pronouns, etc. to refer to different things within the text?)
- Are the ideas balanced appropriately, with suitable attention and space given to each one?
- Have I used a wide range of vocabulary?
- Have I avoided repeating the same words and phrases?
- Have I used a range of simple and more complex grammatical structures?
- Have I correctly used any common phrases which are relevant to the specific task or topic?
- Is my use of grammar accurate?
- Is my spelling accurate?
More than Practice Tests
B2 first (fce) review: tips.
- Make sure you have at least 4 paragraphs.
- Choose an appropriate title.
- The introduction will talk about what’s being reviewed.
- Use a relaxed , friendly , chatty style.
- You can use contractions such as I’m, I’ve etc..
- Use a new paragraph for each point you want to make.
- In the concluding paragraph give your opinion.
B2 First (FCE) Review: Grammar & Vocabulary
The grammar and vocabulary that you need unfortunately depend heavily on the type of question you get.
One thing you can do though is to make sure your grammar and vocabulary are related to the tasks . So for example, if you are writing a review about a film make sure your vocabulary is related to films.
So include words like “s cripts, director, cast, plot, setting, special effects, and stunts”
If you want to mention who directed the film or who played the part of a certain character then make sure you use the passive “The film was directed by Y”. “The the protagonist was played by X”.
If you are talking about an experience and you need to describe the experience then make sure you use narrative tenses because obviously this experience happened in the past.
This means you need to use the past simple, the past continuous and the past perfect. For example “I checked into the hotel at 10 am. I had been travelling all night and was feeling exhausted. The hotel staff were very welcoming and made me feel at home”.
B2 First (FCE) Review: Useful Phrases & Expressions
We will finish it with some useful vocabulary mostly used to organize information. Although it is taking a shortcut, if you learn several expressions for each paragraph in each type of text that could be on your exam, you will certainly be able to create a very consistent and well-organized text.
Giving background
This show stars… The play is directed by… The film is about… It‟s set in………. The story is based on (a book…) It‟s about….. There are many memorable characters including …. The main theme of the film is…..
Expressions that introduce a contrast
On the plus side,… On the down side,… On the one hand,… On the other hand,…
Recommending
Overall, I‟d recommend… All in all, the film was… I wouldn‟t hesitate to recommend… I wouldn‟t encourage anyone to … I would recommend this film to anyone. Although I enjoyed it, I would not recommend it for…. It‟s one of the best (shows) I’ve ever seen. Although I am not normally keen on (musicals),I am glad that I decided to go. The (film) lifts you out of your everyday life
B2 First (FCE) Review: Frequently Asked Questions
Who will read the review.
Your review will be read by readers of a magazine.
What is the purpose of the review?
The review is intended to give information to the reader which will help them decide whether to attend the event themselves.
What style should I use?
Use a style similar to an article that is likely to interest the reader.
What information should I include?
Give essential information about the story, cast, band members, etc. Say what you like and didn‟t like about the performances. Make a recommendation to the reader about whether or not they should go.
Comprar medicamentos genéricos baratos en línea Med Farmacia . Farmacia canadiense. ¡Grandes descuentos! Los mejores precios. Soporte en línea 24 horas. Farmacia canadiense en línea – Farmacia de Canadá – Medicamentos recetados con descuento. Proporcionamos una gama de tratamientos y servicio de médico en línea. Obtenga pastillas gratis (viagra – cialis – levitra).
What is your level of English?
Make your essay memorable to admissions

Submit an essay
Choose who you want an essay review from.
Peer review
Peer review community, expert review.
Alexandra Johnson
Daniel Berkowitz
Robert Carlson
Chinaza Ruth Okonkwo
Craig Aimar
Denise Karp
Robbie Herbst
Christopher Kilner
Elias Miller
Veronica Prout
Sophie Alina
Adrian Russian
Subha Subramanian
Jacquada Gray
Lori Zomback
Jake Patin-Sauls
Joseph Recupero
Priya Desai
Emily Kramer
Olga Ivleva
Kevin Dupont
Ethan Glasserman
Denise Haile
Stephanie Vitanzo
Samara Watkins
Emily Brother
Gabe Henry Woody
Pascale Bradley
Abby Purfeerst
Shane Niesen
Jonathan Sung
Review options, specialties, what students are saying, peer review, college essay guy, how it works, differentiating yourself is more important than ever, review a peer essay.


- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Essay Types
Review Essays
Most importantly, remember that a review essay paper is not only a summary or retelling of what the book or an article contains. The general writing pattern to follow is an introduction, a brief reminder about the contents, information about the author, critical discussion, and a conclusion that talks about your opinion. See our essay samples to see the share of each essay portion and the correct structure in practice. In most cases, about 60% of your writing must belong to the critical discussion part. Take your time to examine our essay examples that include references to the original article to see what parts have been taken for analysis and how exactly it has been implemented in every paragraph.
I assume the speaker is extremely convincing because he starts by providing some facts about himself before beginning to make his points. For eg, he says that he is an instructor who teaches his students to tackle multiple processes of multitasking designs (Conger, 2016). This tends to make the listener trust...
Dr Walter Paler has been labelled monster after he used to be found to have shot Cecil, the Lion in Zimbabwe. The result was that the detects had to flee from his domestic and protect himself from the guards as he tried to save himself from the embarrassment that he...
House of Mirrors: Edgar Allan Poe's 'The Fall of the House of Usher.'.""Short Story Criticism Poe’s work, The Fall of the House Usher, explores the mysteries and Gothic factors of the House of Usher and takes the reader on how those elements arouse a new understanding of divinity and...
Obesity and the Rise of the Fast-Food Industry Obesity has become an increasing issue in the United States of America in recent years, particularly with the rise of the fast-food industry. Obesity has become such a serious health problem that one out of every four residents in some counties, such as...
The film A Beautiful Mind The film A Beautiful Mind remains one of those sensitive and moving films telling the story of an outstanding mathematician known as John Forbes Nash, who is battling paranoid schizophrenia. Based on the true story of a scholarly genius, the film was played by Russel Crowe...
One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest, by Ken Kesey Explains activities at a psychiatric institution where the struggles between a new student, McMurphy, and Nurse Ratched continue and eventually involve all patients. McMurphy appears at the hospital from jail for evaluation, which leads him to feel that he might be innocent,...
Words: 1214
Suffer from writer’s block?
Your unique essay is just a few clicks away!
Clint Eastwood's "American Sniper," a record of the Iraq War as seen from the gun sights of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle, whose four voyages through obligation solidified his remaining as the deadliest marksman in U.S. military history, begins as a competent, straightforward combat image and gradually transforms into something more...
Words: 2240
Tonto in Disney's "The Lone Ranger" Tonto is the deuteragonist of the Disney's 2013 movie entitled, The Lone Ranger. He rides alone while looking for two men who were accountable for the ruin of his village. The film has acquired a series of critics ranging from its display of a noble...
Learning Objective: By the give up of the lesson, students will be able to identify and listing the various examples of geographical features on the land. Students will also be in a position to explain the existence of every named element and make quite a few sketches. They should also...
"Groundhog Day" film tells the story of Phil Connors, a reporter who finds himself trapped to relive the same day over and over again. In the beginning, the main character is a cruel, selfish, self-centered human, unhappy to all, while in the end, after being revived hundreds of times the...
Carlson, Jane. Annual Red Carpet Green Dress Contest Starts Again. 11 October 2013. Electronic print. 9 December 2015. A renowned stylist reporter currently working as a Hollywood reporter, Jane Carlson also writes articles related to fashion and beauty. She studied in the University of Nevada and obtained a degree in journalism:...
The Death of a Salesman embodies the quest for the impossible American Dream. The play not only identifies and discusses problems within a particular family but also delves into wider concerns surrounding basic American ideals. Arthur Miller investigates the blind hope that most Americans have about the American dream. Death...
Words: 1558
Trending Review Essays Topics
Related topics.

Join Discovery, the new community for book lovers
Trust book recommendations from real people, not robots 🤓
Blog – Posted on Friday, Mar 29
17 book review examples to help you write the perfect review.

It’s an exciting time to be a book reviewer. Once confined to print newspapers and journals, reviews now dot many corridors of the Internet — forever helping others discover their next great read. That said, every book reviewer will face a familiar panic: how can you do justice to a great book in just a thousand words?
As you know, the best way to learn how to do something is by immersing yourself in it. Luckily, the Internet (i.e. Goodreads and other review sites , in particular) has made book reviews more accessible than ever — which means that there are a lot of book reviews examples out there for you to view!
In this post, we compiled 17 prototypical book review examples in multiple genres to help you figure out how to write the perfect review . If you want to jump straight to the examples, you can skip the next section. Otherwise, let’s first check out what makes up a good review.
Are you interested in becoming a book reviewer? We recommend you check out Reedsy Discovery , where you can earn money for writing reviews — and are guaranteed people will read your reviews! To register as a book reviewer, sign up here.
Pro-tip : But wait! How are you sure if you should become a book reviewer in the first place? If you're on the fence, or curious about your match with a book reviewing career, take our quick quiz:
Should you become a book reviewer?
Find out the answer. Takes 30 seconds!
What must a book review contain?
Like all works of art, no two book reviews will be identical. But fear not: there are a few guidelines for any aspiring book reviewer to follow. Most book reviews, for instance, are less than 1,500 words long, with the sweet spot hitting somewhere around the 1,000-word mark. (However, this may vary depending on the platform on which you’re writing, as we’ll see later.)
In addition, all reviews share some universal elements, as shown in our book review templates . These include:
- A review will offer a concise plot summary of the book.
- A book review will offer an evaluation of the work.
- A book review will offer a recommendation for the audience.
If these are the basic ingredients that make up a book review, it’s the tone and style with which the book reviewer writes that brings the extra panache. This will differ from platform to platform, of course. A book review on Goodreads, for instance, will be much more informal and personal than a book review on Kirkus Reviews, as it is catering to a different audience. However, at the end of the day, the goal of all book reviews is to give the audience the tools to determine whether or not they’d like to read the book themselves.
Keeping that in mind, let’s proceed to some book review examples to put all of this in action.
How much of a book nerd are you, really?
Find out here, once and for all. Takes 30 seconds!
Book review examples for fiction books
Since story is king in the world of fiction, it probably won’t come as any surprise to learn that a book review for a novel will concentrate on how well the story was told .
That said, book reviews in all genres follow the same basic formula that we discussed earlier. In these examples, you’ll be able to see how book reviewers on different platforms expertly intertwine the plot summary and their personal opinions of the book to produce a clear, informative, and concise review.
Note: Some of the book review examples run very long. If a book review is truncated in this post, we’ve indicated by including a […] at the end, but you can always read the entire review if you click on the link provided.
Examples of literary fiction book reviews
Kirkus Reviews reviews Ralph Ellison’s The Invisible Man :
An extremely powerful story of a young Southern Negro, from his late high school days through three years of college to his life in Harlem.
His early training prepared him for a life of humility before white men, but through injustices- large and small, he came to realize that he was an "invisible man". People saw in him only a reflection of their preconceived ideas of what he was, denied his individuality, and ultimately did not see him at all. This theme, which has implications far beyond the obvious racial parallel, is skillfully handled. The incidents of the story are wholly absorbing. The boy's dismissal from college because of an innocent mistake, his shocked reaction to the anonymity of the North and to Harlem, his nightmare experiences on a one-day job in a paint factory and in the hospital, his lightning success as the Harlem leader of a communistic organization known as the Brotherhood, his involvement in black versus white and black versus black clashes and his disillusion and understanding of his invisibility- all climax naturally in scenes of violence and riot, followed by a retreat which is both literal and figurative. Parts of this experience may have been told before, but never with such freshness, intensity and power.
This is Ellison's first novel, but he has complete control of his story and his style. Watch it.
Lyndsey reviews George Orwell’s 1984 on Goodreads:
YOU. ARE. THE. DEAD. Oh my God. I got the chills so many times toward the end of this book. It completely blew my mind. It managed to surpass my high expectations AND be nothing at all like I expected. Or in Newspeak "Double Plus Good." Let me preface this with an apology. If I sound stunningly inarticulate at times in this review, I can't help it. My mind is completely fried.
This book is like the dystopian Lord of the Rings, with its richly developed culture and economics, not to mention a fully developed language called Newspeak, or rather more of the anti-language, whose purpose is to limit speech and understanding instead of to enhance and expand it. The world-building is so fully fleshed out and spine-tinglingly terrifying that it's almost as if George travelled to such a place, escaped from it, and then just wrote it all down.
I read Fahrenheit 451 over ten years ago in my early teens. At the time, I remember really wanting to read 1984, although I never managed to get my hands on it. I'm almost glad I didn't. Though I would not have admitted it at the time, it would have gone over my head. Or at the very least, I wouldn't have been able to appreciate it fully. […]
The New York Times reviews Lisa Halliday’s Asymmetry :
Three-quarters of the way through Lisa Halliday’s debut novel, “Asymmetry,” a British foreign correspondent named Alistair is spending Christmas on a compound outside of Baghdad. His fellow revelers include cameramen, defense contractors, United Nations employees and aid workers. Someone’s mother has FedExed a HoneyBaked ham from Maine; people are smoking by the swimming pool. It is 2003, just days after Saddam Hussein’s capture, and though the mood is optimistic, Alistair is worrying aloud about the ethics of his chosen profession, wondering if reporting on violence doesn’t indirectly abet violence and questioning why he’d rather be in a combat zone than reading a picture book to his son. But every time he returns to London, he begins to “spin out.” He can’t go home. “You observe what people do with their freedom — what they don’t do — and it’s impossible not to judge them for it,” he says.
The line, embedded unceremoniously in the middle of a page-long paragraph, doubles, like so many others in “Asymmetry,” as literary criticism. Halliday’s novel is so strange and startlingly smart that its mere existence seems like commentary on the state of fiction. One finishes “Asymmetry” for the first or second (or like this reader, third) time and is left wondering what other writers are not doing with their freedom — and, like Alistair, judging them for it.
Despite its title, “Asymmetry” comprises two seemingly unrelated sections of equal length, appended by a slim and quietly shocking coda. Halliday’s prose is clean and lean, almost reportorial in the style of W. G. Sebald, and like the murmurings of a shy person at a cocktail party, often comic only in single clauses. It’s a first novel that reads like the work of an author who has published many books over many years. […]
Emily W. Thompson reviews Michael Doane's The Crossing on Reedsy Discovery :
In Doane’s debut novel, a young man embarks on a journey of self-discovery with surprising results.
An unnamed protagonist (The Narrator) is dealing with heartbreak. His love, determined to see the world, sets out for Portland, Oregon. But he’s a small-town boy who hasn’t traveled much. So, the Narrator mourns her loss and hides from life, throwing himself into rehabbing an old motorcycle. Until one day, he takes a leap; he packs his bike and a few belongings and heads out to find the Girl.
Following in the footsteps of Jack Kerouac and William Least Heat-Moon, Doane offers a coming of age story about a man finding himself on the backroads of America. Doane’s a gifted writer with fluid prose and insightful observations, using The Narrator’s personal interactions to illuminate the diversity of the United States.
The Narrator initially sticks to the highways, trying to make it to the West Coast as quickly as possible. But a hitchhiker named Duke convinces him to get off the beaten path and enjoy the ride. “There’s not a place that’s like any other,” [39] Dukes contends, and The Narrator realizes he’s right. Suddenly, the trip is about the journey, not just the destination. The Narrator ditches his truck and traverses the deserts and mountains on his bike. He destroys his phone, cutting off ties with his past and living only in the moment.
As he crosses the country, The Narrator connects with several unique personalities whose experiences and views deeply impact his own. Duke, the complicated cowboy and drifter, who opens The Narrator’s eyes to a larger world. Zooey, the waitress in Colorado who opens his heart and reminds him that love can be found in this big world. And Rosie, The Narrator’s sweet landlady in Portland, who helps piece him back together both physically and emotionally.
This supporting cast of characters is excellent. Duke, in particular, is wonderfully nuanced and complicated. He’s a throwback to another time, a man without a cell phone who reads Sartre and sleeps under the stars. Yet he’s also a grifter with a “love ‘em and leave ‘em” attitude that harms those around him. It’s fascinating to watch The Narrator wrestle with Duke’s behavior, trying to determine which to model and which to discard.
Doane creates a relatable protagonist in The Narrator, whose personal growth doesn’t erase his faults. His willingness to hit the road with few resources is admirable, and he’s prescient enough to recognize the jealousy of those who cannot or will not take the leap. His encounters with new foods, places, and people broaden his horizons. Yet his immaturity and selfishness persist. He tells Rosie she’s been a good mother to him but chooses to ignore the continuing concern from his own parents as he effectively disappears from his old life.
Despite his flaws, it’s a pleasure to accompany The Narrator on his physical and emotional journey. The unexpected ending is a fitting denouement to an epic and memorable road trip.
The Book Smugglers review Anissa Gray’s The Care and Feeding of Ravenously Hungry Girls :
I am still dipping my toes into the literally fiction pool, finding what works for me and what doesn’t. Books like The Care and Feeding of Ravenously Hungry Girls by Anissa Gray are definitely my cup of tea.
Althea and Proctor Cochran had been pillars of their economically disadvantaged community for years – with their local restaurant/small market and their charity drives. Until they are found guilty of fraud for stealing and keeping most of the money they raised and sent to jail. Now disgraced, their entire family is suffering the consequences, specially their twin teenage daughters Baby Vi and Kim. To complicate matters even more: Kim was actually the one to call the police on her parents after yet another fight with her mother. […]
Examples of children’s and YA fiction book reviews
The Book Hookup reviews Angie Thomas’ The Hate U Give :
♥ Quick Thoughts and Rating: 5 stars! I can’t imagine how challenging it would be to tackle the voice of a movement like Black Lives Matter, but I do know that Thomas did it with a finesse only a talented author like herself possibly could. With an unapologetically realistic delivery packed with emotion, The Hate U Give is a crucially important portrayal of the difficulties minorities face in our country every single day. I have no doubt that this book will be met with resistance by some (possibly many) and slapped with a “controversial” label, but if you’ve ever wondered what it was like to walk in a POC’s shoes, then I feel like this is an unflinchingly honest place to start.
In Angie Thomas’s debut novel, Starr Carter bursts on to the YA scene with both heart-wrecking and heartwarming sincerity. This author is definitely one to watch.
♥ Review: The hype around this book has been unquestionable and, admittedly, that made me both eager to get my hands on it and terrified to read it. I mean, what if I was to be the one person that didn’t love it as much as others? (That seems silly now because of how truly mesmerizing THUG was in the most heartbreakingly realistic way.) However, with the relevancy of its summary in regards to the unjust predicaments POC currently face in the US, I knew this one was a must-read, so I was ready to set my fears aside and dive in. That said, I had an altogether more personal, ulterior motive for wanting to read this book. […]
The New York Times reviews Melissa Albert’s The Hazel Wood :
Alice Crewe (a last name she’s chosen for herself) is a fairy tale legacy: the granddaughter of Althea Proserpine, author of a collection of dark-as-night fairy tales called “Tales From the Hinterland.” The book has a cult following, and though Alice has never met her grandmother, she’s learned a little about her through internet research. She hasn’t read the stories, because her mother, Ella Proserpine, forbids it.
Alice and Ella have moved from place to place in an attempt to avoid the “bad luck” that seems to follow them. Weird things have happened. As a child, Alice was kidnapped by a man who took her on a road trip to find her grandmother; he was stopped by the police before they did so. When at 17 she sees that man again, unchanged despite the years, Alice panics. Then Ella goes missing, and Alice turns to Ellery Finch, a schoolmate who’s an Althea Proserpine superfan, for help in tracking down her mother. Not only has Finch read every fairy tale in the collection, but handily, he remembers them, sharing them with Alice as they journey to the mysterious Hazel Wood, the estate of her now-dead grandmother, where they hope to find Ella.
“The Hazel Wood” starts out strange and gets stranger, in the best way possible. (The fairy stories Finch relays, which Albert includes as their own chapters, are as creepy and evocative as you’d hope.) Albert seamlessly combines contemporary realism with fantasy, blurring the edges in a way that highlights that place where stories and real life convene, where magic contains truth and the world as it appears is false, where just about anything can happen, particularly in the pages of a very good book. It’s a captivating debut. […]
James reviews Margaret Wise Brown’s Goodnight, Moon on Goodreads:
Goodnight Moon by Margaret Wise Brown is one of the books that followers of my blog voted as a must-read for our Children's Book August 2018 Readathon. Come check it out and join the next few weeks!
This picture book was such a delight. I hadn't remembered reading it when I was a child, but it might have been read to me... either way, it was like a whole new experience! It's always so difficult to convince a child to fall asleep at night. I don't have kids, but I do have a 5-month-old puppy who whines for 5 minutes every night when he goes in his cage/crate (hopefully he'll be fully housebroken soon so he can roam around when he wants). I can only imagine! I babysat a lot as a teenager and I have tons of younger cousins, nieces, and nephews, so I've been through it before, too. This was a believable experience, and it really helps show kids how to relax and just let go when it's time to sleep.
The bunny's are adorable. The rhymes are exquisite. I found it pretty fun, but possibly a little dated given many of those things aren't normal routines anymore. But the lessons to take from it are still powerful. Loved it! I want to sample some more books by this fine author and her illustrators.
Publishers Weekly reviews Elizabeth Lilly’s Geraldine :
This funny, thoroughly accomplished debut opens with two words: “I’m moving.” They’re spoken by the title character while she swoons across her family’s ottoman, and because Geraldine is a giraffe, her full-on melancholy mode is quite a spectacle. But while Geraldine may be a drama queen (even her mother says so), it won’t take readers long to warm up to her. The move takes Geraldine from Giraffe City, where everyone is like her, to a new school, where everyone else is human. Suddenly, the former extrovert becomes “That Giraffe Girl,” and all she wants to do is hide, which is pretty much impossible. “Even my voice tries to hide,” she says, in the book’s most poignant moment. “It’s gotten quiet and whispery.” Then she meets Cassie, who, though human, is also an outlier (“I’m that girl who wears glasses and likes MATH and always organizes her food”), and things begin to look up.
Lilly’s watercolor-and-ink drawings are as vividly comic and emotionally astute as her writing; just when readers think there are no more ways for Geraldine to contort her long neck, this highly promising talent comes up with something new.
Examples of genre fiction book reviews
Karlyn P reviews Nora Roberts’ Dark Witch , a paranormal romance novel , on Goodreads:
4 stars. Great world-building, weak romance, but still worth the read.
I hesitate to describe this book as a 'romance' novel simply because the book spent little time actually exploring the romance between Iona and Boyle. Sure, there IS a romance in this novel. Sprinkled throughout the book are a few scenes where Iona and Boyle meet, chat, wink at each, flirt some more, sleep together, have a misunderstanding, make up, and then profess their undying love. Very formulaic stuff, and all woven around the more important parts of this book.
The meat of this book is far more focused on the story of the Dark witch and her magically-gifted descendants living in Ireland. Despite being weak on the romance, I really enjoyed it. I think the book is probably better for it, because the romance itself was pretty lackluster stuff.
I absolutely plan to stick with this series as I enjoyed the world building, loved the Ireland setting, and was intrigued by all of the secondary characters. However, If you read Nora Roberts strictly for the romance scenes, this one might disappoint. But if you enjoy a solid background story with some dark magic and prophesies, you might enjoy it as much as I did.
I listened to this one on audio, and felt the narration was excellent.
Emily May reviews R.F. Kuang’s The Poppy Wars , an epic fantasy novel , on Goodreads:
“But I warn you, little warrior. The price of power is pain.”
Holy hell, what did I just read??
➽ A fantasy military school
➽ A rich world based on modern Chinese history
➽ Shamans and gods
➽ Detailed characterization leading to unforgettable characters
➽ Adorable, opium-smoking mentors
That's a basic list, but this book is all of that and SO MUCH MORE. I know 100% that The Poppy War will be one of my best reads of 2018.
Isn't it just so great when you find one of those books that completely drags you in, makes you fall in love with the characters, and demands that you sit on the edge of your seat for every horrific, nail-biting moment of it? This is one of those books for me. And I must issue a serious content warning: this book explores some very dark themes. Proceed with caution (or not at all) if you are particularly sensitive to scenes of war, drug use and addiction, genocide, racism, sexism, ableism, self-harm, torture, and rape (off-page but extremely horrific).
Because, despite the fairly innocuous first 200 pages, the title speaks the truth: this is a book about war. All of its horrors and atrocities. It is not sugar-coated, and it is often graphic. The "poppy" aspect refers to opium, which is a big part of this book. It is a fantasy, but the book draws inspiration from the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Rape of Nanking.
Crime Fiction Lover reviews Jessica Barry’s Freefall , a crime novel:
In some crime novels, the wrongdoing hits you between the eyes from page one. With others it’s a more subtle process, and that’s OK too. So where does Freefall fit into the sliding scale?
In truth, it’s not clear. This is a novel with a thrilling concept at its core. A woman survives plane crash, then runs for her life. However, it is the subtleties at play that will draw you in like a spider beckoning to an unwitting fly.
Like the heroine in Sharon Bolton’s Dead Woman Walking, Allison is lucky to be alive. She was the only passenger in a private plane, belonging to her fiancé, Ben, who was piloting the expensive aircraft, when it came down in woodlands in the Colorado Rockies. Ally is also the only survivor, but rather than sitting back and waiting for rescue, she is soon pulling together items that may help her survive a little longer – first aid kit, energy bars, warm clothes, trainers – before fleeing the scene. If you’re hearing the faint sound of alarm bells ringing, get used to it. There’s much, much more to learn about Ally before this tale is over.
Kirkus Reviews reviews Ernest Cline’s Ready Player One , a science-fiction novel :
Video-game players embrace the quest of a lifetime in a virtual world; screenwriter Cline’s first novel is old wine in new bottles.
The real world, in 2045, is the usual dystopian horror story. So who can blame Wade, our narrator, if he spends most of his time in a virtual world? The 18-year-old, orphaned at 11, has no friends in his vertical trailer park in Oklahoma City, while the OASIS has captivating bells and whistles, and it’s free. Its creator, the legendary billionaire James Halliday, left a curious will. He had devised an elaborate online game, a hunt for a hidden Easter egg. The finder would inherit his estate. Old-fashioned riddles lead to three keys and three gates. Wade, or rather his avatar Parzival, is the first gunter (egg-hunter) to win the Copper Key, first of three.
Halliday was obsessed with the pop culture of the 1980s, primarily the arcade games, so the novel is as much retro as futurist. Parzival’s great strength is that he has absorbed all Halliday’s obsessions; he knows by heart three essential movies, crossing the line from geek to freak. His most formidable competitors are the Sixers, contract gunters working for the evil conglomerate IOI, whose goal is to acquire the OASIS. Cline’s narrative is straightforward but loaded with exposition. It takes a while to reach a scene that crackles with excitement: the meeting between Parzival (now world famous as the lead contender) and Sorrento, the head of IOI. The latter tries to recruit Parzival; when he fails, he issues and executes a death threat. Wade’s trailer is demolished, his relatives killed; luckily Wade was not at home. Too bad this is the dramatic high point. Parzival threads his way between more ’80s games and movies to gain the other keys; it’s clever but not exciting. Even a romance with another avatar and the ultimate “epic throwdown” fail to stir the blood.
Too much puzzle-solving, not enough suspense.
Book review examples for non-fiction books
Nonfiction books are generally written to inform readers about a certain topic. As such, the focus of a nonfiction book review will be on the clarity and effectiveness of this communication . In carrying this out, a book review may analyze the author’s source materials and assess the thesis in order to determine whether or not the book meets expectations.
Again, we’ve included abbreviated versions of long reviews here, so feel free to click on the link to read the entire piece!
The Washington Post reviews David Grann’s Killers of the Flower Moon :
The arc of David Grann’s career reminds one of a software whiz-kid or a latest-thing talk-show host — certainly not an investigative reporter, even if he is one of the best in the business. The newly released movie of his first book, “The Lost City of Z,” is generating all kinds of Oscar talk, and now comes the release of his second book, “Killers of the Flower Moon: The Osage Murders and the Birth of the FBI,” the film rights to which have already been sold for $5 million in what one industry journal called the “biggest and wildest book rights auction in memory.”
Grann deserves the attention. He’s canny about the stories he chases, he’s willing to go anywhere to chase them, and he’s a maestro in his ability to parcel out information at just the right clip: a hint here, a shading of meaning there, a smartly paced buildup of multiple possibilities followed by an inevitable reversal of readerly expectations or, in some cases, by a thrilling and dislocating pull of the entire narrative rug.
All of these strengths are on display in “Killers of the Flower Moon.” Around the turn of the 20th century, oil was discovered underneath Osage lands in the Oklahoma Territory, lands that were soon to become part of the state of Oklahoma. Through foresight and legal maneuvering, the Osage found a way to permanently attach that oil to themselves and shield it from the prying hands of white interlopers; this mechanism was known as “headrights,” which forbade the outright sale of oil rights and granted each full member of the tribe — and, supposedly, no one else — a share in the proceeds from any lease arrangement. For a while, the fail-safes did their job, and the Osage got rich — diamond-ring and chauffeured-car and imported-French-fashion rich — following which quite a large group of white men started to work like devils to separate the Osage from their money. And soon enough, and predictably enough, this work involved murder. Here in Jazz Age America’s most isolated of locales, dozens or even hundreds of Osage in possession of great fortunes — and of the potential for even greater fortunes in the future — were dispatched by poison, by gunshot and by dynamite. […]
Stacked Books reviews Malcolm Gladwell’s Outliers :
I’ve heard a lot of great things about Malcolm Gladwell’s writing. Friends and co-workers tell me that his subjects are interesting and his writing style is easy to follow without talking down to the reader. I wasn’t disappointed with Outliers. In it, Gladwell tackles the subject of success – how people obtain it and what contributes to extraordinary success as opposed to everyday success.
The thesis – that our success depends much more on circumstances out of our control than any effort we put forth – isn’t exactly revolutionary. Most of us know it to be true. However, I don’t think I’m lying when I say that most of us also believe that we if we just try that much harder and develop our talent that much further, it will be enough to become wildly successful, despite bad or just mediocre beginnings. Not so, says Gladwell.
Most of the evidence Gladwell gives us is anecdotal, which is my favorite kind to read. I can’t really speak to how scientifically valid it is, but it sure makes for engrossing listening. For example, did you know that successful hockey players are almost all born in January, February, or March? Kids born during these months are older than the others kids when they start playing in the youth leagues, which means they’re already better at the game (because they’re bigger). Thus, they get more play time, which means their skill increases at a faster rate, and it compounds as time goes by. Within a few years, they’re much, much better than the kids born just a few months later in the year. Basically, these kids’ birthdates are a huge factor in their success as adults – and it’s nothing they can do anything about. If anyone could make hockey interesting to a Texan who only grudgingly admits the sport even exists, it’s Gladwell. […]
Quill and Quire reviews Rick Prashaw’s Soar, Adam, Soar :
Ten years ago, I read a book called Almost Perfect. The young-adult novel by Brian Katcher won some awards and was held up as a powerful, nuanced portrayal of a young trans person. But the reality did not live up to the book’s billing. Instead, it turned out to be a one-dimensional and highly fetishized portrait of a trans person’s life, one that was nevertheless repeatedly dubbed “realistic” and “affecting” by non-transgender readers possessing only a vague, mass-market understanding of trans experiences.
In the intervening decade, trans narratives have emerged further into the literary spotlight, but those authored by trans people ourselves – and by trans men in particular – have seemed to fall under the shadow of cisgender sensationalized imaginings. Two current Canadian releases – Soar, Adam, Soar and This One Looks Like a Boy – provide a pointed object lesson into why trans-authored work about transgender experiences remains critical.
To be fair, Soar, Adam, Soar isn’t just a story about a trans man. It’s also a story about epilepsy, the medical establishment, and coming of age as seen through a grieving father’s eyes. Adam, Prashaw’s trans son, died unexpectedly at age 22. Woven through the elder Prashaw’s narrative are excerpts from Adam’s social media posts, giving us glimpses into the young man’s interior life as he traverses his late teens and early 20s. […]
Book Geeks reviews Elizabeth Gilbert’s Eat, Pray, Love :
WRITING STYLE: 3.5/5
SUBJECT: 4/5
CANDIDNESS: 4.5/5
RELEVANCE: 3.5/5
ENTERTAINMENT QUOTIENT: 3.5/5
“Eat Pray Love” is so popular that it is almost impossible to not read it. Having felt ashamed many times on my not having read this book, I quietly ordered the book (before I saw the movie) from amazon.in and sat down to read it. I don’t remember what I expected it to be – maybe more like a chick lit thing but it turned out quite different. The book is a real story and is a short journal from the time when its writer went travelling to three different countries in pursuit of three different things – Italy (Pleasure), India (Spirituality), Bali (Balance) and this is what corresponds to the book’s name – EAT (in Italy), PRAY (in India) and LOVE (in Bali, Indonesia). These are also the three Is – ITALY, INDIA, INDONESIA.
Though she had everything a middle-aged American woman can aspire for – MONEY, CAREER, FRIENDS, HUSBAND; Elizabeth was not happy in her life, she wasn’t happy in her marriage. Having suffered a terrible divorce and terrible breakup soon after, Elizabeth was shattered. She didn’t know where to go and what to do – all she knew was that she wanted to run away. So she set out on a weird adventure – she will go to three countries in a year and see if she can find out what she was looking for in life. This book is about that life changing journey that she takes for one whole year. […]
Emily May reviews Michelle Obama’s Becoming on Goodreads:
Look, I'm not a happy crier. I might cry at songs about leaving and missing someone; I might cry at books where things don't work out; I might cry at movies where someone dies. I've just never really understood why people get all choked up over happy, inspirational things. But Michelle Obama's kindness and empathy changed that. This book had me in tears for all the right reasons.
This is not really a book about politics, though political experiences obviously do come into it. It's a shame that some will dismiss this book because of a difference in political opinion, when it is really about a woman's life. About growing up poor and black on the South Side of Chicago; about getting married and struggling to maintain that marriage; about motherhood; about being thrown into an amazing and terrifying position.
I hate words like "inspirational" because they've become so overdone and cheesy, but I just have to say it-- Michelle Obama is an inspiration. I had the privilege of seeing her speak at The Forum in Inglewood, and she is one of the warmest, funniest, smartest, down-to-earth people I have ever seen in this world.
And yes, I know we present what we want the world to see, but I truly do think it's genuine. I think she is someone who really cares about people - especially kids - and wants to give them better lives and opportunities.
She's obviously intelligent, but she also doesn't gussy up her words. She talks straight, with an openness and honesty rarely seen. She's been one of the most powerful women in the world, she's been a graduate of Princeton and Harvard Law School, she's had her own successful career, and yet she has remained throughout that same girl - Michelle Robinson - from a working class family in Chicago.
I don't think there's anyone who wouldn't benefit from reading this book.
Hopefully, this post has given you a better idea of how to write a book review. You might be wondering how to put all of this knowledge into action now! Many book reviewers start out by setting up a book blog. If you don’t have time to research the intricacies of HTML, check out Reedsy Discovery — where you can read indie books for free and review them without going through the hassle of creating a blog. To register as a book reviewer , go here .
And if you’d like to see even more book review examples, simply go to this directory of book review blogs and click on any one of them to see a wealth of good book reviews. Beyond that, it's up to you to pick up a book and pen — and start reviewing!
Continue reading
More posts from across the blog.
The 21 Best Places to Find Free Books Online
You'll never run out of something to read when you bookmark these 21 best places to find free books online.
The 12 Best Roman History Books (for the Caesar in You)
From gladiators to martyrs, lark-throated orators to fiddling despots, ancient Rome has given us enough colorful characters to populate an entire slate of HBO dramas. But the history of the Roman Empire, and the Republic it supplanted, is more than just a toga-cl...
The 53 Best Book Series of All Time
With new books being published every single day, figuring out your next read can be a daunting task. Lucky for you, we’ve created a list of the 53 best book series of all time — ranging from fantasy and science fiction to romance and thriller — to keep you occupied for days (o...
Heard about Reedsy Discovery?
Trust real people, not robots, to give you book recommendations.
Or sign up with an
Or sign up with your social account
- Submit your book
- Reviewer directory

Want to be a book reviewer?
Review new books and start building your portfolio.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- The Cass review: an...
The Cass review: an opportunity to unite behind evidence informed care in gender medicine
- Related content
- Peer review
- Kamran Abbasi , editor in chief
- kabbasi{at}bmj.com
- Follow Kamran on Twitter @KamranAbbasi
At the heart of Hilary Cass’s review of gender identity services in the NHS is a concern for the welfare of “children and young people” (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q820 ). 1 Her stated ambition is to ensure that those experiencing gender dysphoria receive a high standard of care. This will be disputed, of course, by people and lobbying groups angered by her recommendations, but it is a theme running through the review. Cass, a past president of the UK’s Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health, seeks to provide better care for children and adolescents on one of the defining issues of our age. Her conclusion is alarming for anybody who genuinely cares for child welfare: gender medicine is “built on shaky foundations” (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q814 ). 2
That verdict is supported by a series of review papers published in Archives of Disease in Childhood , a journal published by BMJ and the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health (doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2023-326669 doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2023-326670 doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2023-326499 doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2023-326500 ). 3 4 5 6 The evidence base for interventions in gender medicine is threadbare, whichever research question you wish to consider—from social transition to hormone treatment.
For example, of more than 100 studies examining the role of puberty blockers and hormone treatment for gender transition only two were of passable quality. To be clear, intervention studies—particularly of drug and surgical interventions—should include an appropriate control group, ideally be randomised, ensure concealment of treatment allocation (although open label studies are sometimes acceptable), and be designed to evaluate relevant outcomes with adequate follow-up.
One emerging criticism of the Cass review is that it set the methodological bar too high for research to be included in its analysis and discarded too many studies on the basis of quality. In fact, the reality is different: studies in gender medicine fall woefully short in terms of methodological rigour; the methodological bar for gender medicine studies was set too low, generating research findings that are therefore hard to interpret. The methodological quality of research matters because a drug efficacy study in humans with an inappropriate or no control group is a potential breach of research ethics. Offering treatments without an adequate understanding of benefits and harms is unethical. All of this matters even more when the treatments are not trivial; puberty blockers and hormone therapies are major, life altering interventions. Yet this inconclusive and unacceptable evidence base was used to inform influential clinical guidelines, such as those of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH), which themselves were cascaded into the development of subsequent guidelines internationally (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q794 ). 7
The Cass review attempted to work with the Gender Identity Development Service (GIDS) and the NHS adult gender services to “fill some of the gaps in follow-up data for the approximately 9000 young people who have been through GIDS to develop a stronger evidence base.” However, despite encouragement from NHS England, “the necessary cooperation was not forthcoming.” Professionals withholding data from a national inquiry seems hard to imagine, but it is what happened.
A spiralling interventionist approach, in the context of an evidence void, amounted to overmedicalising care for vulnerable young people. A too narrow focus on gender dysphoria, says Cass, neglected other presenting features and failed to provide a holistic model of care. Gender care became superspecialised when a more general, multidisciplinary approach was required. In a broader sense, this failure is indicative of a societal failure in child and adolescent health (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q802 doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-073448 ). 8 9 The review’s recommendations, which include confining prescription of puberty blockers and hormonal treatments to a research setting (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q660 ), now place the NHS firmly in line with emerging practice internationally, such as in Scandinavia (doi: 10.1136/bmj.p553 ). 10 11
Cass proposes a future model of regional multidisciplinary centres that provide better access and, importantly, standardised care for gender dysphoria, including a smoother transition between adolescent and adult services. Staff will need training. All children and young people embarking on a care pathway will be included in research to begin to rectify the problems with the evidence base, with long term outcomes being an important area of focus. An already stretched workforce will need to extend itself further (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q795 doi: 10.1136/bmj-2024-079474 ). 12 13 In the meantime, some children and young people will turn to the private sector or online providers to meet their needs. The dangers in this moment of service transition are apparent.
But it’s also a moment of opportunity. Families, carers, advocates, and clinicians—acting in the best interests of children and adolescents—face a clear choice whether to allow the Cass review to deepen division or use it as a driver of better care. The message from the evidence reviews in Archives of Disease in Childhood is as unequivocal as it could be. Cass’s review is independent and listened to people with lived experience. Without doubt, the advocacy and clinical practice for medical treatment of gender dysphoria had moved ahead of the evidence—a recipe for harm.
People who are gender non-conforming experience stigmatisation, marginalisation, and harassment in every society. They are vulnerable, particularly during childhood and adolescence. The best way to support them, however, is not with advocacy and activism based on substandard evidence. The Cass review is an opportunity to pause, recalibrate, and place evidence informed care at the heart of gender medicine. It is an opportunity not to be missed for the sake of the health of children and young people. It is an opportunity for unity.
- Mitchell A ,
- Langton T ,
- Heathcote C ,
- Hewitt CE ,
- Hardiman L ,
- Wilkinson E
- Dixon-Woods M ,
- Summers C ,
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Year in Review
- Published: 04 April 2024
Climate chronicles
Global carbon emissions in 2023
- Zhu Liu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8968-7050 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Zhu Deng ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6409-9578 1 , 2 , 4 ,
- Steven J. Davis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9338-0844 5 &
- Philippe Ciais ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8560-4943 6
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment volume 5 , pages 253–254 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
12k Accesses
217 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Climate change
- Climate-change mitigation
Global CO 2 emissions for 2023 increased by only 0.1% relative to 2022 (following increases of 5.4% and 1.9% in 2021 and 2022, respectively), reaching 35.8 Gt CO 2 . These 2023 emissions consumed 10–66.7% of the remaining carbon budget to limit warming to 1.5°C, suggesting permissible emissions could be depleted within 0.5–6 years (67% likelihood).
Data from the Carbon Monitor indicate 35.8 Gt CO 2 were emitted globally in 2023.
Although the trend is upwards, the pace of growth has been slowing, suggesting global emissions might have plateaued.
India overtook the EU as the third highest emitter globally.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Annual global CO 2 emissions dropped markedly in 2020 owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, decreasing by 5.8% relative to 2019 (ref. 1 ). There were hopes that green economic stimulus packages during the COVD crisis might mark the beginning of a longer-term decrease in global emissions toward net-zero emissions, but instead emissions rebounded and quickly exceeded pre-pandemic levels by 2021. However, year-on-year growth has slowed, with 5.4% increases in 2021 (ref. 2 ) (reaching 35.1 Gt CO 2 ) and 1.9% increases in 2022 (ref. 3 ) (reaching 35.7 Gt CO 2 ), rapidly using up the remaining carbon budget. Here, we outline global CO 2 emissions (encompassing fossil fuel combustion and cement production) from the Carbon Monitor project ( https://carbonmonitor.org ) for the year 2023.
Global CO 2 emissions in 2023
Overall, global CO 2 emissions in 2023 reached 35.8 ± 0.3 Gt CO 2 , an all-time high (Fig. 1 ). Total emissions were 35.3, 33.3, 35.1 and 35.7 in 2019–2022, meaning year-on-year changes of –5.8% from 2019 to 2020, 5.4% from 2020 to 2021, 1.9% from 2021 to 2022 and 0.1% from 2022 to 2023. This slight increase of 0.1% (–0.6 to + 1.1%) from 2022 to 2023 is less than the 1.1 ± 1.0% increase forecast by the Global Carbon Project (GCP) 4 . Although difficult to predict, the continued deceleration in growth rates might signal a plateauing or peaking of global CO 2 emissions in 2023, as has been suggested by the International Energy Agency (IEA) 5 . The trajectory of emissions in 2024 will offer further evidence.
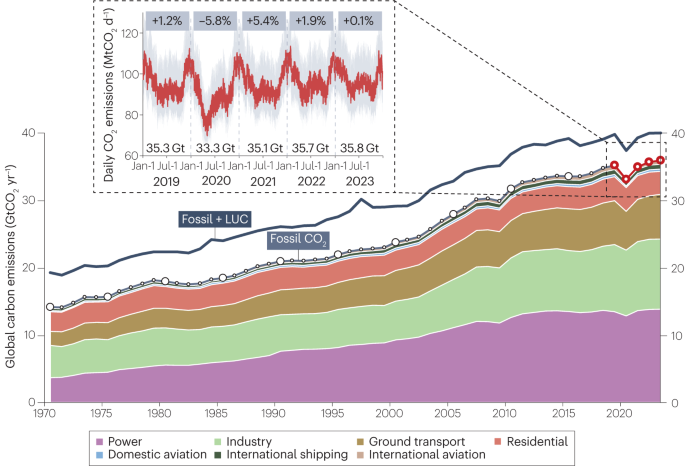
Historical CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion and the process of cement production (‘Fossil CO 2 ’) 8 coloured by industry sector, and those with land-use change (LUC) emissions 4 (‘Fossil + LUC’). International bunkers describe emissions from international aviation and international shipping. The inset displays daily near-real-time CO 2 emissions since 2019 from the Carbon Monitor 1 initiative and year-on-year percent changes. Note that total emissions and percent changes have been revised slightly from earlier estimates 2 , 3 owing to revised data and updated methodologies 9 , 10 . Global CO 2 emissions continued to grow after a brief decline in 2020, but the rate of that growth slowed in 2023; if these progressions continue, the remaining 1.5 °C carbon budget could be used within 0.5–6 years.
The sectoral contributions to these emissions are broadly similar to previous years. The power sector accounted for 38.4% of global CO 2 emissions, industry for 29.0%, ground transportation for 18.6%, residential for 9.4%, international bunkers (international aviation and shipping) for 3.5%, and domestic aviation for 1.0%. Moreover, the pattern of decelerating growth of 2023 global emissions is also evident at the sectoral level. For instance, year-on-year changes in power sector emissions went from + 0.9% in 2022 to –0.2% in 2023, industry emissions from + 1.6% to –0.8%, residential emissions from + 0.9% to –5.5%, and international bunkers from + 18.1% to + 8.9%. However, there were exceptions: ground transportation growth increased from + 2.5% in 2022 to + 3.1% in 2023, while domestic aviation rebounded from –1.0% in 2022 to + 14.0% in 2023. Nevertheless, both domestic and international aviation remain below pre-pandemic levels (2023 emissions were –1.9% and –9.6% less than 2019, respectively).
At the country level, combined emissions from the top five emitters remain similar to previous years. In descending order, China, the United States, India, the European Union (excluding the UK), and Russia collectively accounted for 64% of global emissions, or 23.0 Gt CO 2 . However, interannual fluctuations are apparent when comparing 2022 and 2023, making it difficult to predict long time trends toward zero emissions. For instance, emissions from China (the largest emitter) decreased by 1.9% to 11.0 Gt CO 2 in 2022 but rebounded + 2.9% to 11.3 Gt CO 2 in 2023. By contrast, other regions have maintained earlier increases. Emissions from India, for example, surged by 6.9% to 2.6 Gt CO 2 in 2022 and by another 4.4% to 2.8 Gt CO 2 in 2023; in doing so, India surpassed the EU to become the third highest emitter. Russia exhibited a similar increase, whereby emissions increased by 1.0% to 1.5 Gt CO 2 in 2022 and grew by 2.4% to 1.6 Gt CO 2 in 2023. Meanwhile, emissions began to decrease in other regions. In the United States, emissions increased by 3.0% to 5.0 Gt CO 2 in 2022 but decreased by 2.4% to 4.9 Gt CO 2 in 2023. Similarly, the European Union’s emissions increased by 0.3% to 2.8 Gt CO 2 in 2022 but decreased by 6.2% to 2.6 Gt CO 2 in 2023.
Carbon budget countdown
Global CO 2 emissions are rapidly depleting reported carbon budgets — that is, the amount of carbon that can be released while limiting anthropogenic warming to 1.5 °C and 2 °C above pre-industrial temperatures, as outlined by the Paris Agreement. At 67% likelihood, the IPCC set this budget (starting from 2020 and assuming no overshoot) at 400 Gt CO 2 for 1.5 °C warming 6 . The years 2020, 2021 and 2022 depleted the budget by 9.4% (38 Gt CO 2 ), 9.9% (39 Gt CO 2 ) and 10.0% (40 Gt CO 2 ), respectively, with 2023 emissions using a further 10% (40 Gt CO 2 ). A total of 243 Gt CO 2 remain, which could be exhausted within 6.1 years unless emissions fall sharply. At 83% likelihood, the post-2020 budget to avoid 1.5 °C is only 300 Gt CO 2 . In this case, 2023 emissions depleted 13.3% of the budget, with the remaining 143 Gt CO 2 potentially exhausted within 3.6 years. The carbon budgets for 2 °C warming are larger. At 67% likelihood, the 2°C budget is 1,150 Gt CO 2 , 3.5% of which was used in 2023; the remaining 993 Gt CO 2 could be exhausted within 24.8 years unless growth rates fall. At 83% likelihood, the 2 °C budget is 900 Gt CO 2 , 4.4% of which was used in 2023; 743 Gt CO 2 remains that could be used within 18.6 years.
Other estimates of the remaining carbon budget imply much lower permissible emissions 7 . Under those tighter constraints, only 250 Gt CO 2 or 60 Gt CO 2 remain from January 2023 to achieve the 1.5 °C target at 50% and 66% likelihood, respectively. Accordingly, they convey a more dire timeline. Focusing on the 66% scenario to facilitate comparison with the IPCC likelihoods above, 2023 emissions used 66.7% of the budget, leaving only 20 GtCO 2 ; at the current pace, the entire 1.5 °C target could be depleted halfway through 2024. By comparison, 1,200 Gt CO 2 or 940 Gt CO 2 remains to constrain warming to 2 °C at 50% and 66% likelihood, respectively. For the 66% scenario, 2023 emissions used 4.2% of the budget, leaving 900 Gt CO 2 , which could be diminished within 22.6 years.
Detailed and near-real-time monitoring of CO 2 emissions since 2019 has enabled timely insights into changes in CO 2 emissions worldwide. In 2023, global annual emissions reached an all-time high of 35.8 Gt CO 2 , which reflects a very slight increase of 0.1% year-on-year. While these estimates indicate that post-pandemic emissions growth is slowing, there is not yet convincing evidence of a peak in global emissions — CO 2 emissions continue to rise, particularly in China, India and Russia. Given dwindling carbon budgets to constrain warming to 1.5 °C — the threshold above which climate impacts will become even more disastrous — the absence of a clear downward trend in emissions is troubling. The window of opportunity to meet the most ambitious international climate goals is rapidly closing. Meeting such goals would entail nations accelerating their decarbonization efforts and embracing the consensus from COP28 to “transition away from all fossil fuels in energy systems” as quickly as possible. This call to action is particularly pressing for countries with energy systems heavily reliant on coal, like China, India and Russia, where power generation accounts for approximately half of national carbon emissions. Transitioning these countries’ power sectors away from coal is critical for international climate mitigation efforts. Continued monitoring of global and national carbon emissions could be instrumental in evaluating the efficacy of these efforts.
Liu, Z. et al. Global patterns of daily CO2 emissions reductions in the first year of COVID-19. Nat. Geosci. 15 , 615–620 (2022).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Liu, Z., Deng, Z., Davis, S. J., Giron, C. & Ciais, P. Monitoring global carbon emissions in 2021. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 3 , 217–219 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Liu, Z., Deng, Z., Davis, S. & Ciais, P. Monitoring global carbon emissions in 2022. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 4 , 205–206 (2023).
Friedlingstein, P. et al. Global Carbon Budget 2023. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 15 , 5301–5369 (2023).
IEA. World Energy Outlook 2023 (IEA, 2023); https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2023 .
IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2021).
Lamboll, R. D. et al. Assessing the size and uncertainty of remaining carbon budgets. Nat. Clim. Change. 13 , 1360–1367 (2023).
Crippa, M. et al. Fossil CO 2 and GHG Emissions of All World Countries - 2020 report . (Publications Office of the European Union, 2020).
Zhu, B. et al. CarbonMonitor-Power near-real-time monitoring of global power generation on hourly to daily scales. Sci. Data 10 , 217 (2023).
Ke, P. et al. Carbon Monitor Europe near-real-time daily CO 2 emissions for 27 EU countries and the United Kingdom. Sci. Data 10 , 374 (2023).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute for Climate and Carbon Neutrality, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Zhu Liu & Zhu Deng
Department of Geography, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Department of Earth System Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Alibaba Cloud, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA
Steven J. Davis
Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement LSCE, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
Philippe Ciais
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zhu Liu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Liu, Z., Deng, Z., Davis, S.J. et al. Global carbon emissions in 2023. Nat Rev Earth Environ 5 , 253–254 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00532-2
Download citation
Published : 04 April 2024
Issue Date : April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00532-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Commercial Insights
- Philanthropic Solutions
- Wealth Insights
- Online Banking Login
- Regions Total Wealth
- Investment Account Access
- Open an Account
- En Español
Regions Riding Forward® Scholarship Contest

Their Story. Your Voice.
Your voice is your own. But it's also been impacted by others. Who, we wonder, has inspired you? Let us know by entering the Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest.
You could win an $8,000 college scholarship
For the opportunity to win an $8,000 scholarship, submit a video or written essay about an individual you know personally (who lives in your community) who has inspired you and helped you build the confidence you need to achieve your goals.

The details
The 2024 Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest consists of four (4) separate Quarterly Contests - one for each calendar quarter of 2024. Regions is awarding four $8,000 scholarships through each Quarterly Contest.
Each Quarterly Contest has its own separate entry period, as provided in the chart below.
The entry deadline for each Quarterly Contest is 11:59:59 PM Central Time on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date (set forth in the chart above).
No purchase or banking relationship required.
Regions believes in supporting the students whose passion and actions every day will continue to make stories worth sharing. That’s why we have awarded over $1 million in total scholarships to high school and college students.
How to enter, 1. complete an online quarterly contest application.
Enter the Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest by completing a Quarterly Contest application. The second Quarterly Contest runs from April 1, 2024 through June 30, 2024. Complete and save all requested information.
2. Prepare your Written Essay or Video Essay
For each Quarterly Contest, the topic of your Written Essay or Video Essay (your “Essay Topic”) must be an individual you know personally, who lives in your community. Your Written Essay or Video Essay must address how the individual you have selected as your Essay Topic has inspired you and helped you build the confidence you need to achieve your goals.
Written Essay and Video Essay submissions must meet all of the requirements described in the contest Official Rules. Your Written Essay or Video Essay must be (i) in English, (ii) your own original work, created solely by you (and without the use of any means of artificial intelligence (“AI”)), and (iii) the exclusive property of you alone.
Written Essays must be 500 words or less. You can write your Written Essay directly in the application, or you can copy and paste it into the appropriate area in the application form.
Video Essay submissions must be directly uploaded to the contest application site. Video Essays must be no more than 3 minutes in length and no larger than 1 GB. Only the following file formats are accepted: MP4, MPG, MOV, AVI, and WMV. Video Essays must not contain music of any kind nor display any illegal, explicit, or inappropriate material, and Video Essays must not be password protected or require a log-in/sign-in to view. You must upload your Video Essay to the application, and you may not submit your Video Essay in DVD or other physical form. (Video Essays submitted via mail will not be reviewed or returned.)
Tips to Record Quality Videos on a Smartphone:
- Don’t shoot vertical video. Computer monitors have landscape-oriented displays, so shoot your video horizontally.
- Use a tripod. Even small movements can make a big difference when editing.
- Don’t use zoom. If you need to get a close shot of the subject, move closer as zooming can cause pixilation.
- Use natural lighting. Smartphone lighting can wash out your video.
3. Review and submit your Quarterly Contest application
Review your information on your Quarterly Application (and check the spelling of a Written Essay) and submit your entry by 11:59:59 p.m. Central Time on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date. The second Quarterly Contest period end date is June 30, 2024.
4. Await notification
Winning entries are selected by an independent panel of judges who are not affiliated with Regions. If your entry is selected as a Quarterly Contest winner, you will need to respond to ISTS with the required information.
Eligibility
For purposes of this contest:
- The “Eligible States” are defined as the following states: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and Texas.
- An “accredited college” is defined as a nonprofit, two- or four-year college or university located within one of the fifty (50) United States or the District of Columbia.
To be eligible to enter this contest and to win an award in a Quarterly Contest, at the time of entry, you must:
- Be a legal U.S. resident of one of the Eligible States.
- Be age 16 or older.
- Have at least one (1) year (or at least 18 semester hours) remaining before college graduation.
- If you are not yet in college, begin your freshman year of college no later than the start of the 2025 – 2026 college academic school year.
- As of your most recent school enrollment period, have a cumulative grade point average of at least 2.0 in school (and if no GPA is provided at school, be in “good standing” or the equivalent thereof in school).
View Official Rules
NO PURCHASE OR BANKING RELATIONSHIP REQUIRED. PURCHASE OR BANKING RELATIONSHIP WILL NOT INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF WINNING. VOID WHERE PROHIBITED. The 2024 Regions Riding Forward Scholarship Contest (the “Contest”) consists of four (4) separate quarterly contests (each a “Quarterly Contest”): (1) the “Q-1 Contest;” (2) the “Q-2 Contest;” (3) the “Q-3 Contest;” and (4) the “Q-4 Contest.” The Q-1 Contest begins on 02/01/24 and ends on 03/31/24; the Q-2 Contest begins on 04/01/24 and ends on 06/30/24; the Q-3 Contest begins on 07/01/24 and ends on 09/30/24; and the Q-4 Contest begins on 10/01/24 and ends on 12/31/24. (For each Quarterly Contest, entries must be submitted and received by 11:59:59 PM CT on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date.) To enter and participate in a particular Quarterly Contest, at the time of entry, you must: (a) be a legal U.S. resident of one of the Eligible States; (b) be 16 years of age or older; (c) have at least one (1) year (or at least 18 semester hours) remaining before college graduation; (d) (if you are not yet in college) begin your freshman year of college no later than the start of the 2025 – 2026 college academic school year; and (e) as of your most recent school enrollment period, have a cumulative grade point average of at least 2.0 in school (and if no grade point average is provided at school, be in “good standing” or the equivalent thereof in school). (For purposes of Contest, the “Eligible States” are defined as the states of AL, AR, FL, GA, IA, IL, IN, KY, LA, MS, MO, NC, SC, TN and TX.) Visit regions.com/ridingforward for complete Contest details, including eligibility and Written Essay and Video Essay requirements and Official Rules. (Limit one (1) entry per person, per Quarterly Contest.) For each Quarterly Contest, eligible entries will be grouped according to form of entry (Written Essay or Video Essay) and judged by a panel of independent, qualified judges. A total of four (4) Quarterly Contest Prizes will be awarded in each Quarterly Contest, consisting of two (2) Quarterly Contest Prizes for the Written Essay Entry Group and two (2) Quarterly Contest Prizes for the Video Essay Entry Group. Each Quarterly Contest Prize consists of a check in the amount of $8,000 made out to winner’s designated accredited college. (Limit one (1) Quarterly Contest Prize per person; a contestant is permitted to win only one (1) Quarterly Contest Prize through the Contest.) Sponsor: Regions Bank, 1900 Fifth Ave. N., Birmingham, AL 35203.
© 2024 Regions Bank. All rights reserved. Member FDIC. Equal Housing Lender. Regions and the Regions logo are registered trademarks of Regions Bank. The LifeGreen color is a trademark of Regions Bank.
2023 Winners
High school:.
- Amyrrean Acoff
- Leon Aldridge
- Kharis Andrews
- Colton Collier
- Indya Griffin
- Christopher Hak
- Aquil Hayes
- Jayden Haynes
- McKenna Jodoin
- Paris Kelly
- Liza Latimer
- Dylan Lodle
- Anna Mammarelli
- Karrington Manley
- Marcellus Odum
- Gautami Palthepu
- Melody Small
- Lauryn Tanner
- Joshua Wilson
- Mohamed Ali
- Kayla Bellamy
- Lauren Boxx
- Alexandria Brown
- Samuel Brown
- Thurston Brown
- Conner Daehler
- Tsehai de Souza
- Anjel Echols
- Samarion Flowers
- Trinity Griffin
- Kristina Hilton
- Ryan Jensen
- Miracle Jones
- Shaniece McGhee
- Chelby Melvin
- Lamiya Ousley
- Kiera Phillips
- Gabrielle Pippins
- Ethan Snead
- Sydney Springs
- Kirsten Tilford
- Tamira Weeks
- Justin Williams
2022 Winners
- Paul Aucremann
- William Booker
- Robyn Cunningham
- Kani'ya Davis
- Oluwatomi Dugbo
- Lillian Goins
- Parker Hall
- Collin Hatfield
- Gabrielle Izu
- Kylie Lauderdale
- Jacob Milan
- Jackson Mitchell
- Carmen Moore
- Madison Morgan
- Kaden Oquelí-White
- Kaylin Parks
- Brian Perryman
- De'Marco Riggins
- Brianna Roundtree
- Sydney Russell
- Carlie Spore
- Morgan Standifer
- Ionia Thomas
- Ramaya Thomas
- Jaylen Toran
- Amani Veals
- Taylor Williams
- Alana Wilson
- Taryn Wilson
- Aryaunna Armstrong
- Hannah Blackwell
- T'Aneka Bowers
- Naomi Bradley
- Arianna Cannon
- Taylor Cline
- Catherine Cummings
- Margaret Fitzgerald
- Chloe Franklin
- Camryn Gaines
- Thomas Greer
- Kayla Helleson
- Veronica Holmes
- Logan Kurtz
- Samuel Lambert
- Jaylon Muchison
- Teresa Odom
- Andrew Payne
- Carey Price
- Emily SantiAnna
- Curtis Smith
- Jered Smith
- Mariah Standifer
- Maura Taylor
- Anna Wilkes
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The New Movie ‘Civil War’ Matters for Reasons Different Than You Think

By Stephen Marche
Mr. Marche is the author of “The Next Civil War.”
“Not one man in America wanted the Civil War, or expected or intended it,” Henry Adams, grandson of John Quincy Adams, declared at the beginning of the 20th century. What may seem inevitable to us in hindsight — the horrifying consequences of a country in political turmoil, given to violence and rived by slavery — came as a shock to many of the people living through it. Even those who anticipated it hardly seemed prepared for its violent magnitude. In this respect at least, the current division that afflicts the United States seems different from the Civil War. If there ever is a second civil war, it won’t be for lack of imagining it.
The most prominent example arrives this week in the form of an action blockbuster titled “Civil War.” The film, written and directed by Alex Garland, presents a scenario in which the government is at war with breakaway states and the president has been, in the eyes of part of the country, delegitimized. Some critics have denounced the project, arguing that releasing the film in this particular election year is downright dangerous. They assume that even just talking about a future national conflict could make it a reality, and that the film risks becoming a self-fulfilling prophecy. This is wrong.
Not only does this criticism vastly overrate the power of the written word or the moving image, but it looks past the real forces sending the United States toward ever-deeper division: inequality; a hyperpartisan duopoly; and an antiquated and increasingly dysfunctional Constitution. Mere stories are not powerful enough to change those realities. But these stories can wake us up to the threats we are facing. The greatest political danger in America isn’t fascism, and it isn’t wokeness. It’s inertia. America needs a warning.
The reason for a surge in anxiety over a civil war is obvious. The Republican National Committee, now under the control of the presumptive nominee, has asked job candidates if they believe the 2020 election was stolen — an obvious litmus test. Extremism has migrated into mainstream politics, and certain fanciful fictions have migrated with it. In 1997, a group of Texas separatists were largely considered terrorist thugs and their movement, if it deserved that title, fizzled out after a weeklong standoff with the police. Just a few months ago, Texas took the federal government to court over control of the border. Armed militias have camped out along the border. That’s not a movie trailer. That’s happening.
But politicians, pundits and many voters seem not to be taking the risk of violence seriously enough. There is an ingrained assumption, resulting from the country’s recent history of global dominance coupled with a kind of organic national optimism, that in the United States everything ultimately works out. While right-wing journalists and fiction writers have been predicting a violent end to the Republic for generations — one of the foundational documents of neo-Nazism and white supremacy is “The Turner Diaries” from 1978, a novel that imagines an American revolution that leads to a race war — their writings seem more like wish fulfillment than like warnings.
When I attended prepper conventions as research for my book, I found their visions of a collapsed American Republic suspiciously attractive: It’s a world where everybody grows his own food, gathers with family by candlelight, defends his property against various unpredictable threats and relies on his wits. Their preferred scenario resembled, more than anything, a sort of postapocalyptic “Little House on the Prairie.”
We’ve seen more recent attempts to grapple with the possibility of domestic conflict in the form of sober-minded political analysis. Now the vision of a civil war has come to movie screens. We’re no longer just contemplating a political collapse, we’re seeing its consequences unfold in IMAX.
“Civil War” doesn’t dwell on the causes of the schism. Its central characters are journalists and the plot dramatizes the reality of the conflict they’re covering: the fear, violence and instability that a civil war would inflict on the lives of everyday Americans.
That’s a good thing. Early on when I was promoting my book, I remember an interviewer asking me whether a civil war wouldn’t be that terrible an option; whether it would help clear the air. The naïveté was shocking and, to me, sickening. America lost roughly 2 percent of its population in the Civil War. Contemplating the horrors of a civil war — whether as a thought experiment or in a theatrical blockbuster — helps counteract a reflexive sense of American exceptionalism. It can happen here. In fact, it already has.
One of the first people to predict the collapse of the Republic was none other than George Washington. “I have already intimated to you the danger of parties in the state, with particular reference to the founding of them on geographical discriminations,” he warned in his Farewell Address. “This spirit, unfortunately, is inseparable from our nature.” This founder of the country devoted much of one of his most important addresses, at the apex of his popularity, to warning about the exact situation the United States today finds itself in: a hyper-partisanship that puts party over country and risks political collapse. Washington knew what civil war looked like.
For those Americans of the 1850s who couldn’t imagine a protracted, bloody civil war, the reason is simple enough: They couldn’t bear to. They refused to see the future they were part of building. The future came anyway.
The Americans of 2024 can easily imagine a civil war. The populace faces a different question and a different crisis: Can we forestall the future we have foreseen? No matter the likelihood of that future, the first step in its prevention is imagining how it might come to pass, and agreeing that it would be a catastrophe.
Stephen Marche is the author of “The Next Civil War.”
Source photographs by Yasuhide Fumoto, Richard Nowitz and stilllifephotographer, via Getty Images.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To write a good critical review, you will have to engage in the mental processes of analyzing (taking apart) the work-deciding what its major components are and determining how these parts (i.e., paragraphs, sections, or chapters) contribute to the work as a whole. Analyzing the work will help you focus on how and why the author makes certain ...
Synthesize Information: Go beyond summarizing sources to draw new insights and perspectives. Write Clearly and Concisely: Ensure that your essay is well-structured, with clear transitions and a logical flow of ideas. Review and Refine: Revise your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammatical accuracy.
Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4.
Write your review based on reasonable expectations. Assume the best. You're often assessing someone's execution of their vision or product of their hard work, especially when it comes to art or food. You're also more than likely writing this review on the internet, where the creator could probably find and see it in just a few clicks.
these papers. More detailed review-writing instructions that walk a prospective author through each component of the paper (title, abstract, introduction, etc.) can be found in Mayer (2009). Steps for Writing a Review Paper. Before You Begin to Search or Write . 1. Clearly define the topic. Typically, a review writer works in the related field ...
Course Number Instructor's Name Your Name The titles of the readings under review. Part 1 (about 1-2 pages) • state a question you wish to answer or a theme you wish to address using the readings. • state your answer to the question or conclusion about the theme. • give a road-map for how you are going to make that argument. Part 2 ...
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow: Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. It offers a process and suggests some strategies for writing book reviews. What is a review? A review is a critical evaluation of a text, event, object, or phenomenon. Reviews can consider books, articles, entire genres or fields of ...
Evaluate a significant experience, achievement, risk you have taken, or ethical dilemma you have faced and its impact on you (500 word limit). A misplaced foot on the accelerator instead of the brakes made me the victim of someone's careless mistake. Rushing through the dark streets of my hometown in an ambulance, I attempted to hold back my ...
Guide to Writing a Review Essay 1. Select the books (ideally 3 to 4). They should be published in the last two to three years (i.e., if a person undertakes to write a review in 2016, the books published before 2013 should not be reviewed although they could be mentioned in the body of the review). 2.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Step 1: Look at the essay as a whole. There's no sense in perfecting a sentence if the whole paragraph will later be cut, and there's no sense in focusing on a paragraph if the whole section needs to be reworked.. For these reasons, work from general to specific: start by looking at the overall purpose and organization of your text, and don't worry about the details for now.
Step-By-Step Guide To Write A Book Review Essay For SPM. Step 1: Read the question carefully. The first thing to do is to read the essay question carefully so you are clear on what you must include in your SPM book review essay. Pay attention to any keywords in the question. For example, some questions may ask you to share a synopsis of the ...
ESL 117. Essay #1, Draft #3. The Value of Peer Review in Improving Students' Writing. The process of writing academic papers involves many steps: exploring a topic through reading and writing, narrowing a topic, organizing the ideas, writing multiple drafts, getting feedback and making revisions. Over multiple drafts, the writer refines his ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
1) Invent a Title for Fresh Essays Review. The first step is to come up with an interesting and catchy title for your fresh essays review. This will be the first thing that your reader sees, so make sure it is attention-grabbing and relevant to the rest of your essay. 2) Write a Summary of the Works You Make a Review On ...
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...
An essay is the first part of the writing and it is obligatory. You need to answer the question with between 140-190 words. In the text you need to analyse a question using different points of view. It is a semi-formal text and should be impartial until the conclusion. ... Write your review (140-190 words) Step 1: Briefly analyse the given ...
How it works. Expert review. Peer review. Select an expert and submit your essay. 📣 Pay now or send to your parent or guardian to complete payment. Track your essay review's progress. Get detailed feedback with inline edits and direction on your topic and flow.
Review Essays; Review Essays. Most importantly, remember that a review essay paper is not only a summary or retelling of what the book or an article contains. The general writing pattern to follow is an introduction, a brief reminder about the contents, information about the author, critical discussion, and a conclusion that talks about your ...
powell / review essay. that helps us become more self-reflexive about our own biases, binaries, and boundaries and more attentive to the increasingly blurred and shifting bound- aries between self and other, past and present, and local and global" (209). This attention to multiple and shifting mappings of self, terrain, and boundaries has ...
A review will offer a concise plot summary of the book. A book review will offer an evaluation of the work. A book review will offer a recommendation for the audience. If these are the basic ingredients that make up a book review, it's the tone and style with which the book reviewer writes that brings the extra panache. This will differ from ...
The Trail of Tears Essay; The Pilgrim Girl Who Dreaded the First Thanksgiving; Rainbow crow essay - The Crow, the Snow, and the Fire I was assigned to write my own story based ... Film Review Essay #1 History since 1877. Course: American History Since 1877 (HIST1152 ) 4 Documents. Students shared 4 documents in this course.
The Cass review: an opportunity to unite behind evidence informed care in gender medicine. At the heart of Hilary Cass's review of gender identity services in the NHS is a concern for the welfare of "children and young people" (doi: 10.1136/bmj.q820 ). 1 Her stated ambition is to ensure that those experiencing gender dysphoria receive a ...
A brief review of the ongoing debate on the subject, in a work that now is a classic attack on judicial review, is Westin, Introduction: Charles Beard and American Debate Over Judicial Review, ... Jump to essay-1 5 U.S. (1 Cr.) 137 (1803).
Global CO2 emissions for 2023 increased by only 0.1% relative to 2022 (following increases of 5.4% and 1.9% in 2021 and 2022, respectively), reaching 35.8 Gt CO2. These 2023 emissions consumed 10 ...
Capacity Development (CD), comprising technical assistance and training, fosters economic development by improving human capital and institutions in member countries. Every five years, the IMF reviews its CD Strategy to ensure that CD continues to be of high quality and well-focused on the needs of its members. This review calls for CD to become more flexible, integrated with the Fund's ...
3. Review and submit your Quarterly Contest application. Review your information on your Quarterly Application (and check the spelling of a Written Essay) and submit your entry by 11:59:59 p.m. Central Time on the applicable Quarterly Contest period end date. The second Quarterly Contest period end date is June 30, 2024. 4. Await notification
By Stephen Marche. Mr. Marche is the author of "The Next Civil War.". "Not one man in America wanted the Civil War, or expected or intended it," Henry Adams, grandson of John Quincy Adams ...
Killer Papers is the ONLY site with USA-based tutors and payment plans like Affirm, PayPal Pay Later and Venmo. 500 reviews on IG. 100 reviews on Google. DM the owner 24/7. Extra Essay?