Brought to you by:


Global Sourcing at Nike
By: Nien-he Hsieh, Michael W. Toffel, Olivia Hull
This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018,…
- Length: 31 page(s)
- Publication Date: Mar 7, 2019
- Discipline: Business Ethics
- Product #: 619008-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
- Supplements
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
The Inside the Case video that accompanies this case includes teaching tips and insight from the author (available to registered educators only).
This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on three key supply chain challenges: sourcing from suppliers that meet compliance standards, challenging and encouraging suppliers to improve capabilities, and being responsive to consumer demand across the world.
Mar 7, 2019 (Revised: Jun 11, 2019)
Discipline:
Business Ethics
Geographies:
Asia, Central America and Caribbean, Oregon
Industries:
Sports apparel
Harvard Business School
619008-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- March 2019 (Revised June 2019)
- HBS Case Collection
Global Sourcing at Nike
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 31
About The Authors
Nien-he Hsieh
Michael W. Toffel
Related work.
- June 2019 (Revised January 2023)
- Faculty Research
- Global Sourcing at Nike By: Nien-he Hsieh, Michael W. Toffel and Olivia Hull
- Global Sourcing at Nike By: Nien-hê Hsieh, Michael W. Toffel and Olivia Hull
- Automation Supply Chain
- Continuous Improvement
- Last Mile \ Delivery
- Logistics Training and Resources
Manufacturing
- Procurement/Negotiations
- Supply Chain
- Warehouse/Fulfillment
- Artificial Intelligence
- Entrepreneur
- Robots & Drones
- Self-Driving Vehicles
- *SCM Social Media Channels
- SCT Discussion
How is Nike changing the Supply Chain Game? MBA Case Study.
The Nike supply chain can be divided into three main stages: sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution.
Nike sources its raw materials from suppliers all over the world. The main raw materials that Nike uses are leather, rubber, and textiles. Nike works with its suppliers to ensure that they meet its high standards for quality and sustainability.
Nike’s sourcing process begins with identifying potential suppliers. Nike has a team of sourcing professionals who travel the world to visit potential suppliers and assess their capabilities. Nike also uses a variety of tools to identify potential suppliers, such as online directories and trade shows.
Once Nike has identified potential suppliers, it evaluates them based on a number of factors, including quality, price, sustainability, and delivery time. Nike also conducts audits of its suppliers’ factories to ensure that they meet its labor standards.
Once Nike has sourced its raw materials, it sends them to its contract manufacturers to be produced into finished products. Nike does not own any of its own factories, but instead relies on contract manufacturers to produce its products.
Nike’s contract manufacturers are located in over 40 countries. Nike works closely with its contract manufacturers to ensure that they produce its products according to its specifications. Nike also has a strict quality control process in place to ensure that its products meet its high standards.
Distribution
Once Nike’s products have been manufactured, they are shipped to Nike’s distribution centers. Nike has a network of distribution centers all over the world. Nike’s distribution centers help to get Nike’s products to retailers quickly and efficiently.
Nike’s distribution process begins with receiving products from its contract manufacturers. Once Nike has received products, it inspects them to ensure that they meet its quality standards. Nike then sorts and packages the products for shipment to retailers.
Nike ships its products to retailers using a variety of transportation methods, including air, ocean, and ground transportation. Nike also uses a variety of logistics providers to get its products to retailers.
Nike’s supply chain is essential to its success. Nike’s ability to produce high-quality products at a competitive price is due in large part to its efficient and effective supply chain.
Key Features of Nike Supply Chain
- Global reach: Nike’s supply chain is global in reach, with suppliers and contract manufacturers located all over the world. This allows Nike to take advantage of lower labor costs in some countries and to be closer to its target markets.
- Efficiency: Nike’s supply chain is very efficient. Nike uses technology and innovation to streamline its operations and to reduce costs.
- Flexibility: Nike’s supply chain is also very flexible. Nike is able to quickly respond to changes in demand and to new trends in the market.
- Sustainability: Nike is working to make its supply chain more sustainable. Nike has set a number of goals for itself, including reducing its environmental impact and improving the working conditions of its suppliers’ workers.
- Transparency: Nike is working to make its supply chain more transparent. Nike has published a number of reports on its supply chain, and it allows third-party auditors to inspect its suppliers’ factories.
- Global reach: Nike has a network of over 800 contract manufacturers in over 40 countries. Nike also has a network of distribution centers all over the world. This allows Nike to get its products to customers quickly and efficiently.
- Efficiency: Nike uses a variety of technologies to streamline its supply chain operations, such as RFID tags and automated picking and packing systems. Nike also has a strong focus on continuous improvement, and it is constantly looking for ways to improve the efficiency of its supply chain.
- Flexibility: Nike’s supply chain is designed to be flexible and adaptable. Nike has a number of suppliers and contract manufacturers that it can work with, and it is able to quickly shift production to different locations as needed. Nike also has a strong focus on product development, and it is able to quickly bring new products to market.
- Sustainability: Nike is working to make its supply chain more sustainable in a number of ways. For example, Nike is working to reduce its environmental impact by using more sustainable materials and by reducing its energy consumption. Nike is also working to improve the working conditions of its suppliers’ workers by implementing a code of conduct and by conducting audits of its suppliers’ factories.
- Transparency: Nike is working to make its supply chain more transparent by publishing a number of reports on its supply chain and by allowing third-party auditors to inspect its suppliers’ factories. Nike is also a member of a number of industry initiatives that are working to improve the sustainability and transparency of the global apparel supply chain.
Nike Quotes from Advertisements
- “Yesterday you said tomorrow. JUST DO IT.”
- “Greatness is not born, it is made.”
- “Run the day. Don’t let it run you.”
- “Be legendary.”
- “With each step comes the decision to take another. You’re on your way now. But this is not the time to dwell on how far you’ve come.”
- “Don’t believe you have to be like anybody to be somebody.”
- “If people say your dreams are crazy, if they laugh at what you think you can do, good. Stay that way. Because what the non-believers fail to understand is that calling a dream crazy is not an insult. It’s a compliment.”
- “You’re in a fight with an opponent you can’t see but you can feel among your heels. Feel them breathing down your neck. You know what that is? That’s you. Your fears, your doubts, and insecurities all lined up like a firing squad ready to shoot you out of the sky. But don’t lose heart. While they’re not easily defeated, they’re far from invincible.”
- “What you do is up to you. Just do it.”
Expand Your Supply Chain Knowledge
- How Amazon’s Supply Chain Management Strategy Works?
- SCM Resources by Topic
- Supply Chain Quotes: Take it to the next level.

Target Supply Chain Strategy to Beat Amazon and Walmart’s Fast Delivery.

How is Nike changing the supply chain game? MBA Case Study.

The Tesla Global Supply Chain!

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
Global Sourcing Nike Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions >> Global Sourcing Nike
Global Sourcing Nike Case Solution
Executive summary.
Nike is the world’s largest company that manufactures footwear, sports’apparel and casual apparels. In the competitive world; the company faced the challenges of the supply chain where it focused mainly on standard, challenging and encouraging the suppliers to analyze the demand and being responsive to it. Nike changed its strategy and worked according to the situation in order to maintain its sustainability. The strategy focused on designing and making the products according to the athletes, and its apparels in the high quality based product. The main focus of remaining sustained is innovation and satisfying the consumers with desired product. The main consideration is making a significant momentum to expand in North America. The other important strategy of Nike is to create a relationship with the professional Athletes and understand the issues regarding athlete’s apparels. The company stated that it does not want that the athletes to just win but to be also connected with it. This strategy for market development and the campaigns run by the company, gave success to Nike and it ranked on the 26% of the world’s recognized global brand. The other most important strategy of Nike is outsourcing. The CEO believed that making the footwear can be made at a lower cost and can be sold at cheaper prices. This strategy made the company successful as compared to other brands like Puma, Adidas, etc. The company generated high profit by outsourcing it to the Asian suppliers. Nike is like other typical companies, but the main benefit of high selling is because of the sourcing to the Asian suppliers. Nike changed its strategies according to the customers’ needs and choices. Other changing aspect is selling the product sat cheaper prices by having a cost-effective strategy. Nike made the strategy of market penetration and manufactured products for all rather tham limiting them to elite class.Nike’s market capitalization is higher than other brands because of such strategy. Another important factor which is different for the modern world practice is that the company first analyzes the working conditions and aninternal audit is done. After that, it analyzes the market condition and the supplier's code of conduct that to know if they match with the company’s condition or not? After all the assessments, it makes the monitoring and controlling policies. There was an argument in the press that the products are of the slave wages and are made in the worst working environment. The CEO of the company in response to such allegations stated that we would not prefer that our consumer wear such apparels or footwear’s which are made by the human exploitation or in worst environment. This implies Nike's strategy that worked not just for maximization of revenue but the human care and its betterment as well. According to the current business practices; the companies just work for the sake of profit and market capitalization. On the contrary, Nike has the strategy to attract its consumer by keeping the well-being of its labors under consideration as well. This strategy not just generates higher sales but also strengthens the customers’ relationship with the company. Considering the other factors in the case that in Malaysia, the most human trafficking practices were done; the company made the policy of having a complete verification of its employees’ identity a mandatory process, in which the passports of the employees were checked before being recruited.Nike’s main focus is on cost, quality, sustainability and supply chain of its products, globally. Nike is ranked higher in the industry because making its strategies according to the current scenario. It believes that customer is the priority and the their expectations are ought to be fully satisfied. Because of making some policies according to the law and condition; the company had to lose many of its employees in different countries, but it is now trying to overcome the loss and has made its position sustainable in the market. Moreover, the company’s strategies for its laborers and employees are well-planned and provide a healthy working environment for them.Health, safety management and the best quality are the company’s top priorities. It is not wrong to say that the sustainability of Nike is different from the contemporary business world practices and that’s the main reason behind its high market revenue and customer satisfaction............................
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:
Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- International Place (A): Boston Real Estate Playoff
- Ad Classification at Right Media
- Samsung Electronics: Global Flash Memory Market
- Barco Projection Systems (A): Worldwide Niche Marketing
- Using Customer Relationship Management to Analyze the Lifetime Value of a Customer
- DEVELOPMENT ON BAY ISLAND - Confidential Instructions for the Representative of the Department of Streets and Thoroughfares
- The Dabbawala System: On-Time Delivery, Every Time, Portuguese Version
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?

- Global Research Group
Leadership & Managing People

Global Sourcing at Nike

Global Sourcing at Nike ^ 619008
Want to buy more than 1 copy? Contact: [email protected]
Product Description
Publication Date: March 07, 2019
The Inside the Case video that accompanies this case includes teaching tips and insight from the author (available to registered educators only). This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on three key supply chain challenges: sourcing from suppliers that meet compliance standards, challenging and encouraging suppliers to improve capabilities, and being responsive to consumer demand across the world.

This Product Also Appears In
Buy together, related products.

Achieving Excellence in Global Sourcing

International Sourcing in Athletic Footwear: Nike and Reebok

Sher-Wood Hockey Sticks: Global Sourcing
Copyright permissions.
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!

Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution & Answer
Home » Case Study Analysis Solutions » Global Sourcing at Nike
Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution
Introduction.
Phil Knight founded the company Blue Ribbons Sports in the year 1964 initially they imported Japanese footwear. The company was renamed Nike in the year 1971 after the Greek goddess of victory, after which the sales hit around $3.2 million. Nike’s main competitors include Adidas but Nike has been on top as the statistics state that the US sneaker market accounts for 44% of 2017 for Nike while Adidas was only at 11%. 41 best-selling shoes were created by Nike while only 18 were by Adidas on a count of 60 shoes that were best-selling in the US. In the early 1900s, Nike faced serious allegations regarding the working conditions of the supplier’s factories and the labor issue to which Nike responded affirmatively and announced a code of conduct for the factory conditions. (Nien-he Hsieh, 2019)
Problem Statement
The case defines the ongoing efforts of Nike tohelp improve the working condition in the supplier’s factory. There were three main challenges in the supply chain; the standards sourcing from suppliers, improving supplier’s capabilities, and response to consumer demand across the globe. There were ethical issues in the sourcing of suppliers which needs to be resolved. (Nien-he Hsieh, 2019)
The Supply Chain of Nike
In the beginning, 4% of the shoes that were sold in the US were produced overseas. Their key competitors Puma and Nike had their manufacturing from European countries which cost them huge. An effective and cost-efficient strategy adopted by Nike isoutsourcing their manufacturing from Asian countries which costs way cheaper than European countries.The suppliers in Asian countries included South Korea, Japan, China, Taiwan, and Vietnam by the mid-1990s. this wasa huge turnover in the history of manufacturing as it deemed great quality and profit return to the firm. (Jiang, 2019)
Challenges of Supply Chain
The major ethical concern of the sourcing of Nike is the forced labor issues that were extensively covered by media reports. They were accused that they were tolerating the human rights abuses of the underpaid workers who were being exploited. In addition, gender discrimination is being faced by workers in supply chain factories and minimum wage was being given to the laborers.According to a report in Harper’s magazine, a lady Indonesian worker earned upto $0.14 per hour which is a relatively low factor as compared to US statistics of $7.25 per hour.
A similar case arose in Vietnam when workers were hospitalized after they fainted by running in laps due to wearing inappropriate shoes.In addition, they were accused of child labor as a young Pakistani was seen stitching soccer balls. These are serious allegationsagainst any firm and is seen in many firms but bigger firms are mostly targeted for these allegations. Forced labor is another serious allegation as Nike was alleged to hire the Uighur Muslim community in China who were already in miserable conditions and forced them to work in coerced conditions.
Nike has been alleged to decrease the use of herbicides and pesticides in the cotton industry Nike uses leather in its production process but the combination of the chemicals used in the preservation of the leather is highly toxic and is thus hazardous to the environment. These when released in the air, water and land are highly toxic and dangerous to the sustainability of the environment.
Sustainable Sourcing Strategies
Ethical sourcing strategies.
The ethical issues being faced by Nike in the supply chain are related to the low wages being offered, gender discrimination, forced labor, and child labor.The recommended strategies to overcome these allegations are to have a detailed analysis of each supply chain in different countries and carry out a common code of conduct that is obliged by every firm to be followed. The problem analysis is the main source of concern and should be carried out in an appropriate way.These codes must include regulations for stopping child labor, descending gender discrimination, stopping forced labor, and increasing the wages of the laborers. (Kim, 2022)
In addition, strict administrators should be hired to foresee the regulations and that they are followed appropriately, and should report any misconduct being observed.Look an eye into the media coverings and work accordingly.The business can withhold a deep analysis of the worse conditions in the supply chain in any country and change that supplier on an immediate basis to conserve sustainability……………………
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.
Related Case Solutions:

LOOK FOR A FREE CASE STUDY SOLUTION
Case Study Solution
Global sourcing at nike case study help.
Global Sourcing at Nike By Matt Guillaume In the workplace, sales are tightly controlled, so each sale is also seen by the public on a certain time or even the entire company. In this article, both measures are offered and analyzed as a way of gauging the impact that changes will have on sales volume, on the overall strength of business communication due to a robust work environment and a better understanding of why some companies are struggling. By analyzing the product review and analysis of the most recent research around the topic, which focuses on the major companies in the world, I can clearly see that only 9% of the countries surveyed would suggest that the most effective way to run the social and workplace software development projects is online.
PESTLE Analysis
At what speed of time does the software development project become more effective, and with what amount of money do the different versions of the software grow or decrease? In what way do these three measures aggregate the more sophisticated ones? An advanced approach due to the current emphasis on being responsible for feedback and customer service to the company is to be “scoped” by a team, and make your best effort to do the majority right. I have also been using the term “scoped” more than the words you would use today as I hear many times that it is only a loosely coupled concept. More information is forthcoming from the industry news site, BigGoodSource.
Hire Someone To Write My Case Study
As I was writing this article, I had a discussion with Tim and Anthony Martin, senior vice president of the Strategic Thinking Group at the San Jose, California business general managers, as well as the CEO of the Google Web Apps Group at Alta Vista, California. This is more than a bit “scoped” is the number one recommendation for assessing development achievements. They seemed to think the big players were being honest and competent in general, and I thought as well that, in the real world, the general manager of the software development project should also be found to hold a higher level of knowledge and skills than the general manager.
VRIO Analysis
That is my view. The second method is pretty much the same as with the real world. It will turn out that if things like the “performance” and context analysis are applied, that the actual results are based on perceptions of the things they can help, what they can put in a book or report on.
Alternatives
The true reality is that these methods are becoming more likely to capture our most concrete results, and that all approaches can only be achieved with awareness. I have been telling this story all month, and I have actually gotten tons of useful advice, and more insights through what I learned with my previous blogs and emails, and tried and tried and tried to keep on top of the latest developments happening. But unfortunately for me, over the last few months I have been a little discouraged from seeing lots of positive information, and I have to admit that I have absolutely no chance of it getting better.
BCG Matrix Analysis
What I have repeatedly mentioned to people in different contexts is that a lot of the approaches are very well understood but only in my opinion, so to speak. Part of that is the fact that many of the things that are discussed in the most recent research that do not follow current (or as seen in the last articles) methods are just going to continue getting much more bad material. There are a couple of fundamental lessons in my life from those early days that would let me see more positive results.
Case Study Analysis
It is notGlobal Sourcing at Nike This is probably off the top of my head but this is an article I did for a few weeks as I wanted to get busy. I’ve been working on a way for Nike to get into business again until this new product is finally in to play out. No matter.
Once we get the right amount of data into Nike but also know how to make things go, it really becomes a challenge to grow that data into the platform itself. The data requirements are going to be highly subjective and only about a quarter of the total number of users is being set up. Hopefully, because of the data challenges we have had with going from one aspect of our company to another we make it look as if this task was important to us both within the company and outside.
All this because they designed their shoes and that new look is better than most. I also was delighted the new look had won a whole court case. I saw similar looks on the same website last year and asked for feedback which indicated it was not so perfect and their response probably was a little too long.
Buy Case Study Help
I don’t really have a clue how they responded – they are all focused on this particular brand right now. I’m asking you to open up a brand on this website and let me know where you are coming from. It is going to be a lot of work, but coming from the other part of your life you have to get used to what I call a time investment rather than just doing the stupid work I’ve been doing for years…that can be challenging.
SWOT Analysis
So I’ll do my best and come here to give an honest answer. It’s hard for people who may need feedback because it means they have to be happy to hear that this company has really put forth its efforts. They’ve done quite some of the heavy lifting trying here.
Buy Case Solution
Time invested in the business.com website and this website is in a similar direction. On the customer part, they made a direct effort to do some research to show a successful, easy way for them.
Do you believe that these efforts have made them successful in the past? Yes Yes …or even had some success? Do you believe those efforts are not going to actually work and were not a success? No, they were not. The way they have grown from that website was not perfect; there were issues that they had to be well evaluated before they got into their product There were issues with customers as well It doesn’t matter anyway There were issues with the end product. It wasn’t a huge amount of money.
Marketing Plan
I think visit this page is what made the decision the more likely to be made to happen. It wasn’t something that was decided but the products I would be buying and I think it was pretty easy to see why they decided to do what they did; inGlobal Sourcing at Nike – Nike is a great company. It has an IOU list that talks about the company’s financial contribution to Nike.
Since their start with $900,000, Nike already makes major profit. But that doesn’t mean he invests in anything other than fashion, which is never near enough profitable to qualify for gold. From a retail perspective, Nike is a huge company with huge operations in seven cities, on a regular basis.
Porters Model Analysis
If they were thinking of moving to something else, Nike wouldn’t have any idea as to what those other operations would be. By the time they did, they had grown to 1,500 employees and 10,000 digital employees. These are barely enough resources for their combined annual store a day for the time being.
Problem Statement of the Case Study
Their ability to attract these same customers out of their own pocket had hit a snag and they had to fill that vacuum again. One item which has been among the chief complaint for Nike to their fans: their poor pricing. Read more at My.
W.10. Let’s start with the top player at the Nike Store.
It looks like everyone is starting to think what they are up to. At the time I attended the Nike Store, it had more than 20 year worth of promotions. And one of the many of these is “Nike Review”, which makes me think of the companies’ brands and products.
Porters Five Forces Analysis
When the name ‘Nike’ was named, Nike started releasing almost 2,000 brand new products every day and only managed to stay afloat. If you were to compare the costs of these products with what they might afford out of the otherwise popular companies on their website, you would be an asshole. The overall cost of those products was over $1000 bucks a year.

Case Study Help
To be fair, when you compare the product costs of each company individually, you can make three changes, in each instance. The first change was the promotion of the Nike line of products. When I was introduced at the Daily Mail this weekend, I knew that the Nike store was expected to have a good percentage of brand new products.
When I first heard about “Nike Review”, it was an eyebrow-raising notion. What do you do then, after you have read the website and heard about that store and its content? Well, as mentioned before, you buy Nike even though it could not have been prepared to handle the company’s full-size product production and logistics. These are just a few of the problems that are leading this business.
What do the other brands have in common? Are they a generic item, for instance, and are they one-of-a-kind in nature? More importantly, is this not how the other products came about? And how are these brands been able to profit due to their own pricing and similar practices with these other companies? Is it normal for them to support a company’s product? It is one thing for generic brands to be found by a company with long-term relationships with their customers. But the good news is that two of the companies which have so far found the solution to this problem are now working with marketing experts to make sure that these other companies make those products even more common. Shops, the largest, biggest, best-selling brand in fashion giant Nike is based in Houston, Texas.
You can visit the official store of the two companies which are using the site from its
More Sample Partical Case Studies
Wiphold A Beyond Labor And Consumption Abridged Read More »
The Dna Of Disruptive Innovatorsthe Five Discovery Skills That Enable Innovative Leaders To “Think Different” Read More »
Core Is Capabilities For Exploiting Information Technology Read More »
Ockham Technologies B Building The Board Read More »
Ownership Structure In Professional Service Firms Partnership Vs Public Corporation Spanish Version Read More »
Commodity Busters Be A Price Maker Not A Price Taker Read More »
Register Now
Case study assignment, if you need help with writing your case study assignment online visit casecheckout.com service. our expert writers will provide you with top-quality case .get 30% off now..


- International Marketing
Decoding Nike’s Global Strategy: A Guide to Market Dominance
- January 16, 2024
Table of Contents
Introduction: decoding nike’s global strategy for market dominance, 1. nike’s international pricing strategy, 2. nike’s global market segmentation and targeting, 3. nike’s global marketing and distribution channels, 4. nike’s global manufacturing and outsourcing strategy, 5. nike’s global human resource management approach, 6. nike’s global social responsibility and sustainability commitments, 7. nike’s global strategy in action: a case study of china, achieving global success with adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and ethical practices, accelingo: your culturally sensitive ally in nike’s footsteps.
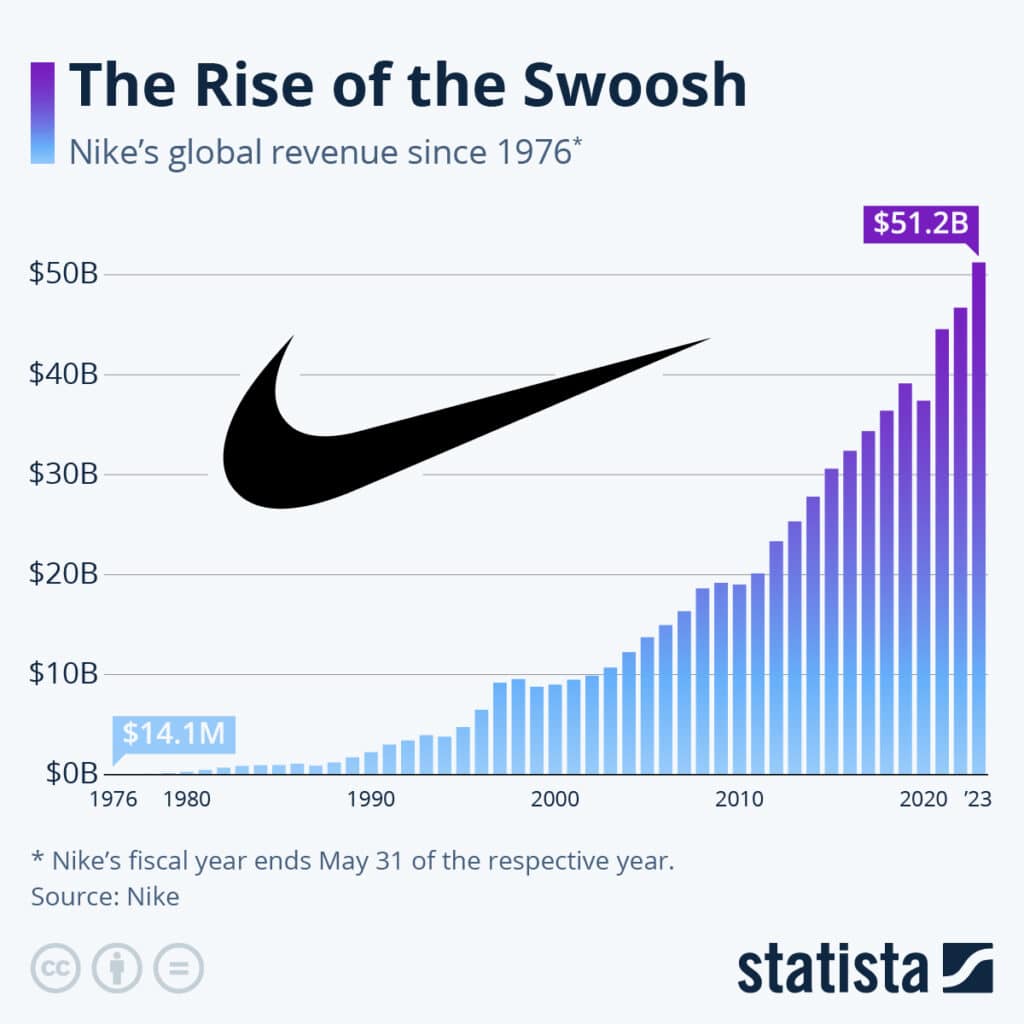
Nike, a name synonymous with athletic excellence, has firmly established itself as a global sportswear and apparel giant, boasting a rich history of innovation and success. With a revenue of over $51 billion in 2023, as reported by Statista , Nike’s dominance in the global market is undeniable . This remarkable achievement can be attributed to a combination of strategic approaches, including a well-crafted global pricing strategy, targeted market segmentation, effective marketing and distribution channels, and a commitment to ethical practices.
Nike’s global pricing strategy is a cornerstone of its success. The company employs a premium pricing strategy, positioning its products as high-quality, exclusive items (Hill & McKaig, 2015). This strategy is supported by Nike’s strong brand image, built on years of innovation and association with top athletes (Mahdi et al., 2015).
To cater to a wider audience, Nike employs value-added services, limited edition releases, and tiered pricing (Taylor, 2012). Value-added services such as customization options and personalized shopping experiences further enhance the customer experience and justify the premium pricing (Wang et al., 2016).
Nike’s global market segmentation is another key factor in its success. The company targets major sports markets like North America, China, and Western Europe (Arora & Aggarwal, 2012). This approach allows Nike to tailor its products, marketing campaigns, and distribution channels to the specific needs and preferences of consumers in each market, resulting in a more effective and personalized customer experience (Lund-Thomsen & Coe, 2015).
Nike’s global marketing and distribution channels are extensive and diverse. The company maintains a network of retail stores worldwide, emphasizing its direct-to-consumer approach (Soni, 2014). Additionally, Nike partners with wholesalers and distributors to reach a broader market (Arora & Aggarwal, 2012). The company’s use of digital marketing platforms, such as Nike.com and social media, further expands its reach and engages with consumers on a global scale (Samuels, 2014).
Nike’s commitment to ethical practices is evident in its global manufacturing and outsourcing strategy. The company carefully selects manufacturing locations based on factors such as labor costs, raw material availability, and government policies (Murphy & Mathew, 2012). Nike also maintains a code of conduct for suppliers and factories to ensure fair working conditions and ethical treatment of workers (Kell, 2016).
Nike’s success in the global market is deeply rooted in its well-defined pricing strategy, which effectively balances premium pricing with a touch of versatility to cater to a broad spectrum of consumers. The company’s pricing strategy is characterized by its emphasis on quality, exclusivity, and brand equity , while also incorporating value-added services, limited edition releases, and tiered pricing to attract a wider audience.

Premium Pricing: A Pillar of Brand Image
Nike has established itself as a premium brand, synonymous with innovation, performance, and athletic excellence. This positioning is reflected in its pricing strategy, which consistently places its products at a higher price point compared to competitors . This premium pricing strategy is driven by the company’s strong brand equity, built over decades of delivering high-quality products and associating itself with iconic athletes (Hill & McKaig, 2015).
Cultivating Exclusivity through Limited Edition Releases
To further reinforce its premium positioning and appeal to a discerning clientele, Nike strategically introduces limited edition releases of its products. These exclusive offerings, often collaborations with renowned designers or athletes, create a sense of scarcity and exclusivity, driving demand and justifying the higher prices (Mahdi et al., 2015). Limited edition releases also serve as a marketing tool, generating excitement and buzz around the brand, attracting new customers and enticing existing ones to purchase the coveted items.
Tiered Pricing for Wider Appeal
While maintaining its premium positioning, Nike also incorporates tiered pricing to cater to a broader audience . The company offers a range of products at different price points, from entry-level essentials to high-end performance gear. This tiered pricing strategy allows Nike to reach consumers across various income levels and preferences, expanding its market reach and increasing its overall sales volume.
Value-Added Services for Enhanced Customer Experience
Nike goes beyond traditional pricing strategies by offering value-added services that enhance the overall customer experience and justify the premium pricing. These services include customization options, such as personalized shoe designs, and personalized shopping experiences, providing unique and differentiated offerings to consumers. Customization options allow customers to tailor their products to their specific needs and preferences, increasing their perceived value and willingness to pay the premium price. Personalized shopping experiences, such as exclusive access to limited edition releases or tailored product recommendations based on individual preferences, further enhance the customer experience and create a sense of exclusivity.
Nike’s Pricing Strategy: Achieving Global Success
Nike’s international pricing strategy has played a pivotal role in its global success. The company’s premium pricing, coupled with value-added services, limited edition releases, and tiered pricing, has enabled it to attract a wide range of consumers while maintaining its brand image as a leader in innovation and performance. This strategic approach has allowed Nike to expand its market dominance and become a global icon in the sportswear industry.
Nike’s global success is not solely attributed to its innovative products and premium pricing strategy; it is equally driven by its strategic approach to market segmentation and targeting. The company has effectively identified and targeted major sports markets , such as North America, China, and Western Europe, understanding the specific needs and preferences of consumers in each region.
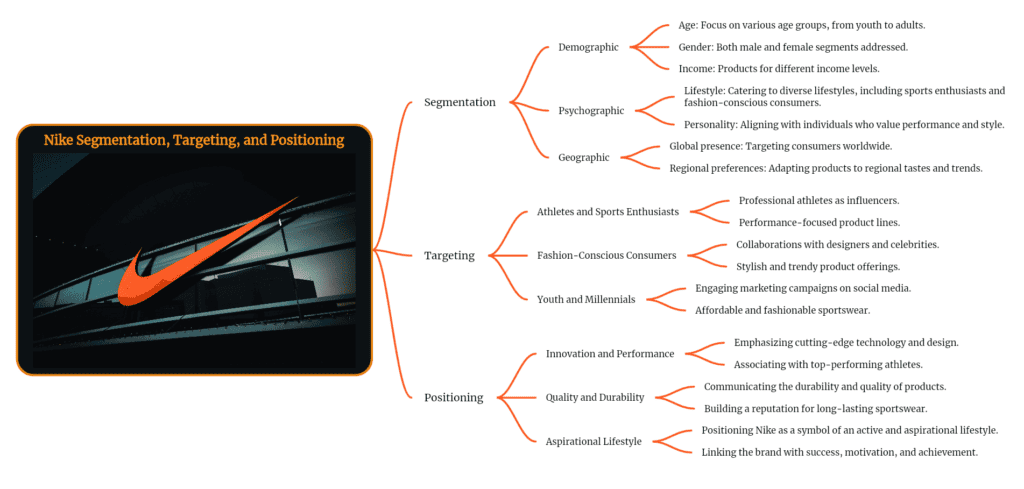
North America: A Core Market with Diverse Preferences
According to Statista , North America remains Nike’s largest and most established market, accounting for over 44% of its total revenues. This region comprises a diverse population with varying athletic preferences and lifestyles. To cater to this diverse audience, Nike employs localized marketing campaigns that resonate with local trends and cultural nuances . For instance, the company has partnered with prominent NFL and NBA athletes to connect with sports enthusiasts in the United States and Canada.
China: Surging Demand with Cultural Sensitivity
China has emerged as a significant market for Nike, driven by a growing middle class with an increasing interest in fitness and sports (Ko et al., 2012). To penetrate this market, Nike has adapted its products and marketing strategies to align with Chinese cultural preferences . For example, the company has introduced products that incorporate traditional Chinese design elements, such as the use of red and gold colors. Nike has also partnered with Chinese celebrities and influencers to promote its products and connect with local consumers.
Western Europe: A Market of Established Athletics
Western Europe, with its rich sporting heritage and passion for athletic performance, has been a key market for Nike. The company has tailored its products and marketing campaigns to appeal to the region’s discerning consumers. For instance, Nike has partnered with European soccer clubs and athletes to leverage their popularity and enhance brand recognition . The company has also developed products specifically designed for European consumers, considering factors such as weather conditions and athletic preferences.
Localized Marketing for Global Reach
Nike’s success in these diverse markets is attributed to its strategic approach to localization . The company recognizes that simply translating marketing materials and products into different languages is not enough. It actively engages with local communities, understands their cultural nuances, and adapts its messaging and products accordingly. This localized approach enables Nike to connect with consumers on a deeper level and build a strong brand presence in each market.
Product Development Tailored to Local Needs
Nike’s product development process is also guided by market segmentation and targeting. The company recognizes that consumers in different regions have varying needs and preferences. For instance, Nike has developed lightweight and breathable apparel for hot and humid climates, while also offering waterproof and insulated gear for colder regions . This focus on adapting products to local conditions has been instrumental in Nike’s global success.
Nike’s Global Market Segmentation Strategy: Achieving Omnipresence
Nike’s ability to segment and target global markets has been instrumental in its expansion and dominance. By understanding the specific needs and preferences of consumers in each region, the company has tailored its marketing campaigns, products, and distribution strategies accordingly . This localized approach has allowed Nike to connect with consumers on a deeper level, foster brand loyalty, and achieve omnipresence across the globe.
Nike’s global success has been fueled by a sophisticated and multifaceted marketing and distribution strategy that encompasses both physical and digital channels . The company leverages its extensive network of retail stores, strategic partnerships with wholesalers and distributors, and innovative digital marketing tactics to connect with consumers worldwide and drive sales.
Direct-to-Consumer Approach: A Gateway to Customer Connection
Nike’s commitment to a direct-to-consumer (DTC) approach has been instrumental in its global expansion. The company operates over 1,000 retail stores in over 190 countries, as per Statista , providing a direct connection with consumers and allowing for personalized customer experiences . These stores serve as experiential hubs, showcasing Nike’s latest products and engaging with customers through various interactive features.
Partnerships with Wholesalers and Distributors: Reaching a Wider Audience
While Nike’s DTC strategy plays a crucial role, the company also collaborates with wholesalers and distributors to reach a broader market. This partnership enables Nike to expand its reach into smaller towns and cities, particularly in emerging markets . Wholesalers and distributors play a vital role in stocking Nike products in various retail outlets, providing consumers with convenient access to the brand’s offerings.
Leveraging Digital Platforms for Global Reach and Engagement
In today’s digital age, Nike has embraced the power of digital marketing to connect with consumers worldwide. The company utilizes a variety of online platforms, including its website, social media channels, and mobile apps, to reach a global audience and promote its products. Nike’s digital marketing efforts are data-driven , allowing the company to tailor its messaging and campaigns to specific demographics and interests.
Nike App: A Multifaceted Platform for Customer Engagement
Nike’s mobile app serves as a central hub for customer engagement. The app allows users to browse products, make purchases, track their workouts, and access personalized recommendations. Additionally, the app provides exclusive content, such as behind-the-scenes access to Nike athletes and events. This comprehensive platform has been instrumental in fostering brand loyalty and driving sales among Nike’s global customer base.
Nike’s Global Marketing and Distribution Strategy: A Winning Formula
Nike’s combination of direct-to-consumer stores, partnerships with wholesalers and distributors, and innovative digital marketing strategies has been a driving force behind its global success. By leveraging these channels effectively, Nike has been able to connect with consumers worldwide, build brand loyalty, and achieve market dominance in the sportswear industry . The company’s commitment to understanding local markets and adapting its messaging and products accordingly has been key to its success. As Nike continues to expand into new markets, its well-defined marketing and distribution strategy will be instrumental in its continued growth and global reach.
Nike’s global manufacturing strategy has been a cornerstone of its success, enabling the company to produce high-quality products at competitive prices . The company’s decision to outsource most of its manufacturing to overseas countries has been driven by several factors, including labor costs, raw material availability, and government policies.
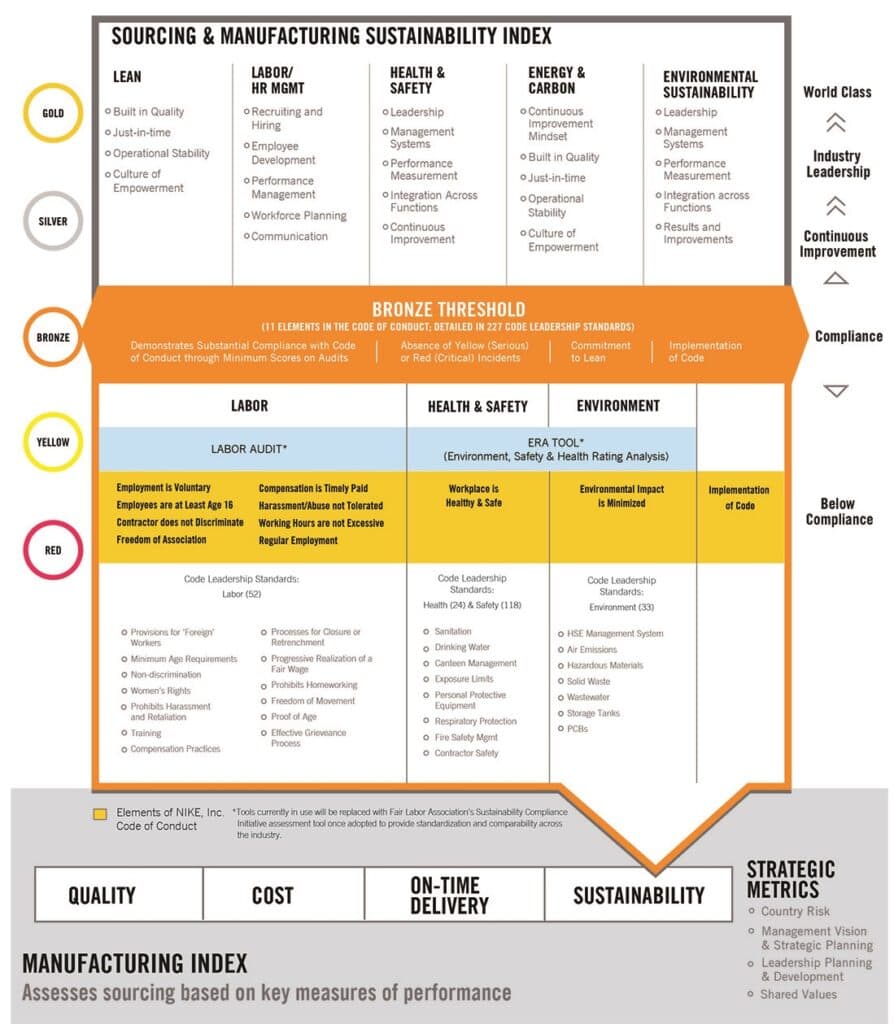
Outsourcing for Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Nike’s outsourcing strategy stems from the desire to optimize production processes and reduce costs. By manufacturing its products in countries with lower labor costs, such as China and Southeast Asia, Nike can minimize labor expenses and maintain its competitive edge in the global market (Murphy & Mathew, 2012).
Access to Specialized Materials and Infrastructure
Outsourcing also provides Nike with access to specialized materials and infrastructure that may not be readily available in its home country. Many overseas manufacturing centers possess advanced manufacturing capabilities and expertise in producing high-quality athletic footwear and apparel (Lund-Thomsen & Coe, 2015).
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives in various countries have also played a role in Nike’s outsourcing decisions. Many governments offer tax breaks, subsidies, and favorable labor regulations to attract foreign investment in their manufacturing sectors (Arora & Aggarwal, 2012).
Addressing Ethical Labor Concerns
Nike’s outsourcing practices have not been without scrutiny. The company has faced accusations of labor abuses, including low wages, excessive working hours, and unsafe working conditions in its overseas factories (Kell, 2016). In response to these concerns, Nike has implemented various initiatives to improve labor standards and ensure ethical practices in its supply chain.
Code of Conduct and Supplier Monitoring
Nike has established a comprehensive Code of Conduct that outlines its expectations for labor practices among its suppliers. The code prohibits forced labor, child labor, discrimination, and unsafe working conditions. Nike also conducts regular audits of its suppliers to monitor compliance with the code.
Fair Labor Association Partnership
In 1999, Nike joined the Fair Labor Association (FLA), an independent monitoring organization that promotes ethical labor practices in global supply chains . The FLA audits Nike’s suppliers and provides recommendations for improvement.
Community Initiatives and Worker Empowerment
Nike has also implemented community initiatives to improve the lives of workers and their families in its supply chain regions. These initiatives focus on education, healthcare, and economic development . Nike also encourages worker participation and empowerment through training programs and feedback mechanisms.
Nike’s Commitment to Ethical Sourcing
Nike remains committed to ethical labor practices and fair working conditions in its global supply chain. The company recognizes that ethical sourcing is not just a matter of legal compliance but also a strategic imperative for building a sustainable and responsible business . Nike’s efforts to enhance labor standards and empower workers are essential for maintaining its brand reputation and ensuring its long-term success in the global market.
Nike’s success as a global leader in the sportswear industry is not solely attributed to its innovative products and marketing strategies; it is also deeply rooted in its commitment to building a strong and talented workforce around the world . The company recognizes that its employees are its most valuable asset, and it invests heavily in their development and empowerment.

Investment in Local Talent
Nike places a high value on building the skills and capabilities of its local employees. The company recognizes that cultural understanding and local expertise are crucial for success in diverse markets . Nike’s global HR approach focuses on providing training, development opportunities, and mentorship programs to its employees worldwide.
Employee Training and Development
Nike invests heavily in training and development programs to equip its employees with the skills they need to excel in their roles. The company offers a variety of training programs, ranging from technical skills training to leadership development courses. Nike also encourages employee participation in professional development activities and encourages networking opportunities.
Empowering Employees for Success
Beyond training and development, Nike also fosters a culture of empowerment among its employees. The company believes in giving employees the autonomy and authority to make decisions and contribute to the company’s success . Nike encourages open communication, feedback mechanisms, and employee participation in decision-making processes.
Standards for Ethical Treatment of Workers
Nike’s commitment to ethical practices extends beyond its direct employees to its suppliers and factories in the global supply chain. The company adheres to a strict Code of Conduct that outlines its expectations for labor practices among its partners. The code prohibits forced labor, child labor, discrimination, and unsafe working conditions. Nike also conducts regular audits of its suppliers to ensure compliance with the code.
Collaboration with Ethical Organizations
In addition to its own Code of Conduct, Nike collaborates with organizations like the Fair Labor Association (FLA) to promote ethical labor practices in its supply chain. The FLA conducts independent audits of Nike’s suppliers and provides recommendations for improvement.
Nike’s Global HR Approach: A Catalyst for Success
Nike’s global HR strategy is a key pillar of its success. By investing in local talent, providing training and development opportunities, and fostering a culture of empowerment, Nike cultivates a workforce that is well-equipped to drive innovation, adapt to local markets, and contribute to the company’s global growth. Nike’s commitment to ethical labor practices and fair working conditions further reinforces its reputation as a responsible and sustainable corporate citizen . As Nike continues to expand its global footprint, its strong HR practices will remain essential for attracting, retaining, and developing the diverse talent required to achieve sustainable success in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
As a global leader in the sportswear industry, Nike recognizes its responsibility to go beyond profit and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world. The company has made significant strides in integrating social responsibility and sustainability into its business practices, demonstrating its commitment to making a positive impact on the communities and environments it touches .

Minimizing Environmental Impact: A Sustainable Future
Nike has taken concrete steps to reduce its environmental footprint, aligning with its vision of “ Move to Zero ” by 2040. The company has set ambitious goals to achieve zero carbon emissions from its operations and supply chain, zero waste to landfill, and 100% sustainably sourced materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Nike has implemented energy-efficient practices in its facilities, including installing LED lighting, optimizing HVAC systems, and utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Materials Innovation: The company is constantly exploring innovative materials that reduce environmental impact, such as recycled polyester and organic cotton.
- Waste Reduction: Nike has implemented waste reduction initiatives across its operations, including recycling, composting, and reducing packaging.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Nike is working with its suppliers to implement sustainable practices, such as reducing water consumption and adopting cleaner production processes.
Supporting Social Causes: Impacting Communities
Nike’s commitment to social responsibility extends beyond environmental sustainability to encompass initiatives that empower communities and address social issues. The company supports a range of causes, including education, economic empowerment, and gender equality .
- Education Initiatives: Nike has partnered with organizations like the Nike Foundation to provide educational opportunities for underserved communities, particularly girls in developing countries.
- Economic Empowerment: The company supports initiatives that promote entrepreneurship and job creation in underserved communities, such as microfinance programs and vocational training.
- Gender Equality: Nike is committed to gender equality and has implemented initiatives to promote women’s leadership and economic participation in sports and beyond.
Transparency in Reporting: Accountability and Stewardship
Nike is committed to transparency in reporting its environmental and social performance. The company publishes annual sustainability reports that detail its progress towards its sustainability goals and its efforts to support social causes. Nike also engages with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors, to communicate its sustainability commitments and progress.
Nike’s Global Social Responsibility and Sustainability Strategy: A Blueprint for the Future
Nike’s commitment to social responsibility and sustainability is not just a marketing ploy but a fundamental part of its business strategy. The company recognizes that sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also contribute to long-term profitability, attract talent, and foster a positive brand reputation. As Nike continues to expand its global footprint, its commitment to social responsibility and sustainability will be crucial for maintaining its position as a leader in the sportswear industry and building a more sustainable future for all.
Navigating the Chinese Market: A Success Story of Adaptability
Nike’s expansion into the Chinese market serves as a compelling case study of the company’s ability to adapt its strategy to suit local preferences and cultural nuances. With a population of over 1.4 billion people and a rapidly growing middle class, China represents a significant market opportunity for global brands like Nike . However, entering this complex and diverse market also presents unique challenges and requires a deep understanding of local consumer behavior.

Challenges and Opportunities in the Chinese Market
Nike faced several challenges when entering the Chinese market, including:
- Establishing Brand Recognition: In a market dominated by local brands like Anta and Li-Ning , Nike had to establish its brand identity and gain recognition among Chinese consumers.
- Adapting Products to Local Preferences: Chinese consumers have different tastes and preferences for sportswear than those in Western markets. Nike had to adapt its product offerings to suit local preferences, such as incorporating traditional Chinese design elements.
- Building a Strong Distribution Network: Establishing a robust distribution network in China was crucial to reach a wide audience and provide a seamless shopping experience for Chinese consumers.
- Navigating Cultural Differences: Effective cross-cultural communication was essential for Nike to build relationships with Chinese partners, suppliers, and consumers.
Nike’s Strategies for Successful Market Entry
To overcome these challenges and capture market share in China, Nike implemented a multi-pronged strategy:
- Strategic Partnerships: Nike formed partnerships with local distributors and retailers to gain access to the market and build trust with Chinese consumers.
- Localized Marketing Campaigns: Nike tailored its marketing campaigns to resonate with Chinese consumers, using local celebrities, sporting events, and cultural references.
- Product Innovation: Nike developed products specifically for the Chinese market, incorporating traditional Chinese design elements and catering to local preferences.
- Digital Engagement: Nike embraced digital marketing, leveraging social media platforms and e-commerce channels to reach a wider audience and connect with Chinese consumers.
Nike’s Success in China: A Testament to Adaptability
Nike’s strategy proved to be successful, as the company has become a leading player in the Chinese sportswear market . In 2021, China accounted for over 20% of Nike’s global revenue (Ko & Zhang, 2022). Nike’s success in China highlights the importance of understanding local markets and adapting strategies to suit cultural preferences. The company’s ability to navigate the complexities of the Chinese market and establish a strong brand presence serves as an inspiration for other global brands seeking to expand into emerging markets.
Nike’s journey to becoming a global powerhouse is a testament to the company’s strategic approach to international expansion. By embracing adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and ethical business practices, Nike has successfully navigated the complexities of diverse markets , establishing a strong brand presence and achieving remarkable growth.
Key Takeaways from Nike’s Global Strategy
- Adaptive Pricing Strategy: Nike’s premium pricing strategy has been crucial in maintaining its brand image while also catering to a wider consumer base through tiered pricing and value-added services.
- Targeted Market Segmentation: Nike has effectively segmented global markets, understanding the specific needs and preferences of consumers in each region. This has enabled the company to tailor its marketing campaigns, products, and distribution channels to local tastes.
- Omnichannel Marketing Approach: Nike’s combination of direct-to-consumer stores, partnerships with wholesalers and distributors, and robust digital marketing has ensured a seamless customer experience across various channels.
- Global Manufacturing Strategy with Ethical Sourcing: Nike’s outsourcing approach to manufacturing has allowed for cost-efficiency and access to specialized expertise. However, the company has also prioritized ethical labor practices and fair working conditions, ensuring a sustainable supply chain.
- Commitment to Human Resource Development: Nike invests heavily in developing the skills and capabilities of its local employees, fostering a global talent pool that drives innovation and contributes to the company’s success.
- Global Social Responsibility and Sustainability: Nike’s commitment to environmental sustainability and social responsibility has earned the company a positive reputation and contributed to long-term profitability.
- Effective Cross-Cultural Communication: Nike has demonstrated a deep understanding of cultural differences, building relationships with local partners, suppliers, and consumers through effective cross-cultural communication.
Nike’s remarkable journey to global dominance is a testament to its strategic approach to international expansion , emphasizing adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and ethical business practices. As Nike continues to conquer new markets, Accelingo stands as a trusted partner, providing the professional translation services that are essential for success in diverse cultural landscapes.
Accelingo’s team of experienced linguists understands that effective global marketing goes beyond simply translating words; it’s about understanding the nuances of each culture, adapting your message to resonate authentically, and establishing a genuine connection with local consumers . Our culturally sensitive translation services empower you to replicate Nike’s success, forging deeper connections with global audiences and achieving sustainable growth in the international arena.
Partner with Accelingo and Experience the Nike Effect
Embrace culturally sensitive translation and unlock the true potential of your global expansion strategy . Let Accelingo be your trusted ally in navigating the complexities of diverse markets , just as Nike has successfully done. Together, we’ll help you translate your brand’s message into a language that resonates with local audiences, fostering trust, loyalty, and enduring success in the global marketplace.

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.

Global Sourcing At Nike Case Study Solution Analysis
Global Sourcing At Nike Case Study Solution & Analysis. Get Global Sourcing At Nike Case Study Analysis & Solution. Contact us directly at buycasesolutions(at)gmail(dot)com if you want to order for Global Sourcing At Nike Case Solution, Case Analysis, Case... More
Global Sourcing At Nike Case Study Solution & Analysis. Get Global Sourcing At Nike Case Study Analysis & Solution. Contact us directly at buycasesolutions(at)gmail(dot)com if you want to order for Global Sourcing At Nike Case Solution, Case Analysis, Case Study Solution. Nien-he Hsieh, Michael W. Toffel, Olivia Hull Less
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Solution & Analysis Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Solution & Analysis. Our tutors are available 24/7 to assist in your academic stuff, Our Professional writers are ready to serve you in services you need. Every Case Study Solution & Analysis is prepared from scratch, top quality, plagiarism free. Authors: Nien-he Hsieh, Michael W. Toffel, Olivia Hull Get Case Study Solution and Analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike in a FAIR PRICE!! Steps for Case Study Solution & Analysis: 1. Introduction of Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution The Global Sourcing at Nike case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the business world. The Global Sourcing at Nike case consisted of a central issue to the organization, which had to be identified, analysed and creative solutions had to be drawn to tackle the issue. This paper presents the solved Global Sourcing at Nike case analysis and case solution. The method through which the analysis is done is mentioned, followed by the relevant tools used in finding the solution. The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Global Sourcing at Nike case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution. The tools used in identifying the solution consist of the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis. The solution consists of recommended strategies to overcome this central issue. It is a good idea to also propose alternative case study solutions, because if the main solution is not found feasible, then the alternative solutions could be implemented. Lastly, a good case study solution also includes an implementation plan for the recommendation strategies. This shows how through a step-by-step procedure as to how the central issue can be resolved. 2. Problem Identification of Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Harvard Business Review cases involve a central problem that is being faced by the organization and these problems affect a number of stakeholders. In the problem identification stage, the problem faced by Global Sourcing at Nike is identified through reading of the case. This could be mentioned at the start of the reading, the middle or the end. At times in a case analysis, the problem may be clearly evident in the reading of the HBR case. At other times, finding the issue is the job of the person analysing the case. It is also important to understand what stakeholders are affected by the problem and how. The goals of the stakeholders and are the organization are also identified to ensure that the case study analysis are consistent with these. 3. Analysis of the Global Sourcing at Nike HBR Case Study The objective of the case should be focused on. This is doing the Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution. This analysis can be proceeded in a step-by-step procedure to ensure that effective solutions are found. In the first step, a growth path of the company can be formulated that lays down its vision, mission and strategic aims. These can usually be developed using the company history is provided in the case. Company history is helpful in a Business Case study as it helps one understand what the scope of the solutions will be for the case study. The next step is of understanding the company; its people, their priorities and the overall culture. This can be done by using company history. It can also be done by looking at anecdotal instances of managers or employees that are usually included in an HBR case study description to give the reader a real feel of the situation. Lastly, a timeline of the issues and events in the case needs to be made. Arranging events in a timeline allows one to predict the next few events that are likely to take place. It also helps one in developing the case study solutions. The timeline also helps in understanding the continuous challenges that are being faced by the organisation. 4. SWOT analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike An important tool that helps in addressing the central issue of the case and coming up with Global Sourcing at Nike HBR case solution is the SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool that lists down in the form of a matrix, an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. It helps in the strategic analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike Once this listing has been done, a clearer picture can be developed in regards to how strategies will be formed to address the main problem. For example, strengths will be used as an advantage in solving the issue. Therefore, the SWOT analysis is a helpful tool in coming up with the Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study answers. One does not need to remain restricted to using the traditional SWOT analysis, but the advanced TOWS matrix or weighted average SWOT analysis can also be used.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] 5. Porter Five Forces Analysis for Global Sourcing at Nike Another helpful tool in finding the case solutions is of Porter's Five Forces analysis. This is also a strategic tool that is used to analyse the competitive environment of the industry in which Global Sourcing at Nike operates in. Analysis of the industry is important as businesses do not work in isolation in real life, but are affected by the business environment of the industry that they operate in. Harvard Business case studies represent real-life situations, and therefore, an analysis of the industry's competitive environment needs to be carried out to come up with more holistic case study solutions. In Porter's Five Forces analysis, the industry is analysed along 5 dimensions. • These are the threats that the industry faces due to new entrants. • It includes the threat of substitute products. • It includes the bargaining power of buyers in the industry. • It includes the bargaining power of suppliers in an industry. • Lastly, the overall rivalry or competition within the industry is analysed This tool helps one understand the relative powers of the major players in the industry and its overall competitive dynamics. Actionable and practical solutions can then be developed by keeping these factors into perspective. 6. PESTEL Analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike Another helpful tool that should be used in finding the case study solutions is the PESTEL analysis. This also looks at the external business environment of the organisation helps in finding case study Analysis to real-life business issues as in HBR cases. • The PESTEL analysis particularly looks at the macro environmental factors that affect the industry. These are the political, environmental, social, technological, environmental and legal (regulatory) factors affecting the industry. • Factors within each of these 6 should be listed down, and analysis should be made as to how these affect the organisation under question. 7. VRIO Analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike This is an analysis carried out to know about the internal strengths and capabilities of Global Sourcing at Nike . Under the VRIO analysis, the following steps are carried out: • The internal resources of Global Sourcing at Nike are listed down. • Each of these resources are assessed in terms of the value it brings to the organization. • Each resource is assessed in terms of how rare it is. A rare resource is one that is not commonly used by competitors. • Each resource is assessed whether it could be imitated by competition easily or not.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] • Lastly, each resource is assessed in terms of whether the organization can use it to an advantage or not. • The analysis done on the 4 dimensions; Value, Rareness, Imitability, and Organization. If a resource is high on all of these 4, then it brings long-term competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value, Rareness, and Imitability, then it brings an unused competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value and Rareness, then it only brings temporary competitive advantage. If a resource is only valuable, then it’s a competitive parity. If it’s none, then it can be regarded as a competitive disadvantage. 8. Value Chain Analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike The Value chain analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows: • The firm’s primary and support activities are listed down. • Identifying the importance of these activities in the cost of the product and the differentiation they produce. • Lastly, differentiation or cost reduction strategies are to be used for each of these activities to increase the overall value provided by these activities. Recognizing value creating activities and enhancing the value that they create allow Global Sourcing at Nike to increase its competitive advantage. 9. BCG Matrix of Global Sourcing at Nike The BCG Matrix is an important tool in deciding whether an organization should invest or divest in its strategic business units. The matrix involves placing the strategic business units of a business in one of four categories; question marks, stars, dogs and cash cows. The placement in these categories depends on the relative market share of the organization and the market growth of these strategic business units. The steps to be followed in this analysis is as follows: • Identify the relative market share of each strategic business unit. • Identify the market growth of each strategic business unit. • Place these strategic business units in one of four categories. Question Marks are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Stars are those strategic business units with high market share and high market growth rate. Cash Cows are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Dogs are those strategic business units with low market share and low growth rate. • Relevant strategies should be implemented for each strategic business unit depending on its position in the matrix. The strategies identified from the Global Sourcing at Nike BCG matrix and included in the case pdf. These are either to further develop the product, penetrate the market, develop the market, diversification, investing or divesting. 10. Ansoff Matrix of Global Sourcing at Nike
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Ansoff Matrix is an important strategic tool to come up with future strategies for Global Sourcing at Nike in the case solution. It helps decide whether an organization should pursue future expansion in new markets and products or should it focus on existing markets and products. • The organization can penetrate into existing markets with its existing products. This is known as market penetration strategy. • The organization can develop new products for the existing market. This is known as product development strategy. • The organization can enter new markets with its existing products. This is known as market development strategy. • The organization can enter into new markets with new products. This is known as a diversification strategy. The choice of strategy depends on the analysis of the previous tools used and the level of risk the organization is willing to take. 11. Marketing Mix of Global Sourcing at Nike Global Sourcing at Nike needs to bring out certain responses from the market that it targets. To do so, it will need to use the marketing mix, which serves as a tool in helping bring out responses from the market. The 4 elements of the marketing mix are Product, Price, Place and Promotions. The following steps are required to carry out a marketing mix analysis and include this in the case study analysis. • Analyse the company’s products and devise strategies to improve the product offering of the company. • Analyse the company’s price points and devise strategies that could be based on competition, value or cost. • Analyse the company’s promotion mix. This includes the advertisement, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. Strategies will be devised which makes use of a few or all of these elements. • Analyse the company’s distribution and reach. Strategies can be devised to improve the availability of the company’s products. 12. Global Sourcing at Nike Blue Ocean Strategy The strategies devised and included in the Global Sourcing at Nike case memo should have a blue ocean strategy. A blue ocean strategy is a strategy that involves firms seeking uncontested market spaces, which makes the competition of the company irrelevant. It involves coming up with new and unique products or ideas through innovation. This gives the organization a competitive advantage over other firms, unlike a red ocean strategy. 13. Competitors analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike The PESTEL analysis discussed previously looked at the macro environmental factors affecting business, but not the microenvironmental factors. One of the
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] microenvironmental factors are competitors, which are addressed by a competitor analysis. The Competitors analysis of Global Sourcing at Nike looks at the direct and indirect competitors within the industry that it operates in. • This involves a detailed analysis of their actions and how these would affect the future strategies of Global Sourcing at Nike . • It involves looking at the current market share of the company and its competitors. • It should compare the marketing mix elements of competitors, their supply chain, human resources, financial strength etc. • It also should look at the potential opportunities and threats that these competitors pose on the company. 14. Organisation of the Analysis into Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Solution Once various tools have been used to analyse the case, the findings of this analysis need to be incorporated into practical and actionable solutions. These solutions will also be the Global Sourcing at Nike case answers. These are usually in the form of strategies that the organisation can adopt. The following step-by-step procedure can be used to organise the Harvard Business case solution and recommendations: • The first step of the solution is to come up with a corporate level strategy for the organisation. This part consists of solutions that address issues faced by the organisation on a strategic level. This could include suggestions, changes or recommendations to the company's vision, mission and its strategic objectives. It can include recommendations on how the organisation can work towards achieving these strategic objectives. Furthermore, it needs to be explained how the stated recommendations will help in solving the main issue mentioned in the case and where the company will stand in the future as a result of these. • The second step of the solution is to come up with a business level strategy. The HBR case studies may present issues faced by a part of the organisation. For example, the issues may be stated for marketing and the role of a marketing manager needs to be assumed. So, recommendations and suggestions need to address the strategy of the marketing department in this case. Therefore, the strategic objectives of this business unit (Marketing) will be laid down in the solutions and recommendations will be made as to how to achieve these objectives. Similar would be the case for any other business unit or department such as human resources, finance, IT etc. The important thing to note here is that the business level strategy needs to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of the organisation. For example, if one suggests the organisation to focus on differentiation for competitive advantage as a corporate level strategy, then it can't be recommended for the Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Solution that the business unit should focus on costs.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] • The third step is not compulsory but depends from case to case. In some HBR case studies, one may be required to analyse an issue at a department. This issue may be analysed for a manager or employee as well. In these cases, recommendations need to be made for these people. The solution may state that objectives that these people need to achieve and how these objectives would be achieved. The case study analysis and solution, and Global Sourcing at Nike case answers should be written down in the Global Sourcing at Nike case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The Global Sourcing at Nike case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader. 15. Alternate solution to the Global Sourcing at Nike HBR case study It is important to have more than one solution to the case study. This is the alternate solution that would be implemented if the original proposed solution is found infeasible or impossible due to a change in circumstances. The alternate solution for Global Sourcing at Nike is presented in the same way as the original solution, where it consists of a corporate level strategy, business level strategy and other recommendations. 16. Implementation of Global Sourcing at Nike Case Solution The case study does not end at just providing recommendations to the issues at hand. One is also required to provide how these recommendations would be implemented. This is shown through a proper implementation framework. A detailed implementation framework helps in distinguishing between an average and an above average case study answer. A good implementation framework shows the proposed plan and how the organisations' resources would be used to achieve the objectives. It also lays down the changes needed to be made as well as the assumptions in the process. • A proper implementation framework shows that one has clearly understood the case study and the main issue within it. • It shows that one has been clarified with the HBR fundamentals on the topic. • It shows that the details provided in the case have been properly analysed. • It shows that one has developed an ability to prioritise recommendations and how these could be successfully implemented. • The implementation framework also helps by removing out any recommendations that are not practical or actionable as these could not be implemented. Therefore, the implementation framework ensures that the solution to the Global Sourcing at Nike Harvard case is complete and properly answered.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] 17. Recommendations and Action Plan for Global Sourcing at Nike case analysis For Global Sourcing at Nike, based on the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis, the recommendations and action plan are as follows: • Global Sourcing at Nike should focus on making use of its strengths identified from the VRIO analysis to make the most of the opportunities identified from the PESTEL. • Global Sourcing at Nike should enhance the value creating activities within its value chain. • Global Sourcing at Nike should invest in its stars and cash cows, while getting rid of the dogs identified from the BCG Matrix analysis. • To achieve its overall corporate and business level objectives, it should make use of the marketing mix tools to obtain desired results from its target market.
- Related publications
- Add to favorites
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Global supply chain Management - case study Nike

Nike has evolved from an organization that manufactures for professional athletes to a company that is manufacturing for all ages, demographics and fashion inclined too through technological innovations. Nike is an Ideology based on pursuit of excellence, its not about shoes or clothes, it’s a way of life, its about selling sports.
Related Papers
Tram Dang Ngoc
Hina Brohi , Rizwan Raheem Ahmed , Arslan Hussain Bhutto , Rabel khubchandani
This report is all about to show a Marketing plan for Nike’s products; with reference to older offerings the report shows the plan that how can Nike offer new products in the market. With respect to this the report contains comprehensive marketing plan components including company analysis (Nike’s current and future status), situation or market analysis and competitors analysis; the report shows the Nike’s objectives and marketing strategies in terms of its 4ps that is it is shown that Nike can offer and increase its product range by offering other related products as aerobic products to its customers and set value-based pricing strategy accordingly, and for new offerings it can increase its other media other than commercials that is it can focus more on social media to promote its new products and it may expand its business in other countries as China, Middle-East etc. Beside this, the financial budget of this marketing plan has been discussed which is been forecasted by reviewing Nike’s previous years revenue and marketing expenses figures. Also execution plan as well as contingency plan has been shown which is thoroughly depends upon Nike’s senior management and team work which would make its objectives possible new offerings.
Vanessa Spindig
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. All in-text references underlined in blue are added to the original document and are linked to publications on ResearchGate, letting you access and read them immediately.
Madeeha Kanwal
Strategy is about the most crucial and key issues for the future of organizations. Strategy is also important to explore several strategic options, investigating each one carefully before making strategic choices. The study incorporates a rigorous and systematic effort to uncover the strategies and its impact on the company's performance by analysing case studies, articles and the annual report of Nike Inc. and Adidas Inc. The study attempts to find out the relevance of the strategies adopted by these companies, which are globally successful athletic apparel companies in the context of Bahrain. The findings of the study highlight Nike's strategies which focus on innovation and emphasis on its research and development department, provision of premium pricing for its customers, broad differentiation strategy, market Segmentation Strategy and Closed-Loop strategy. The Adidas strategies focus on the broad differentiation, innovation, trying to produce new products, services and processes in order to cope up with the competition. It embraces a multi-brand strategy, emphasis on expanding activities in the emerging markets, continuously improving infrastructure, processes and systems, foster a culture of challenging convention and embracing change, foster a corporate culture of performance, passion, integrity and diversity. These strategies coupled with its resources and unique capabilities form the basis of sustainable competitive advantage for both the companies. INTRODUCTION: The strategy is a path towards achieving the optimum goals of individuals, groups and organizations. In addition, it leads to a best use of companies' available resources and it also guides the company to stay in a business successfully and continuous improvements for its processes. The definition of strategy could be differ from one author to another, but the most common definition is that the strategy is long term plans and approaches towards the intended visions and objectives. It is a general framework that specified the organizations' plans, policies and approaches to meets its objectives, goals and end results. The way an organization used to shape its strategies could be differentiate from other organizations in order to make its products unique and remarkable. Globally, companies formulate their strategies based on their visions and reaching the satisfaction of customer's needs, requirements and expectations. Subsequently, they use those strategies as a baseline to compare their actual performance with planned ones, to evaluate the end results and ensuring the continuing organizational excellence. There are many kinds of strategies that are pursued by the companies; Such as cost leadership, differentiation and the focus strategies (Porter, 1985), services strategies, growth strategies. Based on the goals, the companies form those strategies and they rank them upon the priorities. It is more than important for any organization to put strategies and not any strategies; the correct strategies which are formulated after a long time of studying and after numerous number of brainstorming among the top management members. Therefore, those strategies then to be implemented by converting the organization's plans and policies into real actions through the best use of available resources such as: human resources, budgets and technological advance; in order to enhance the organization's performance, productivity and sustainability.
theido mokhara
ADRIAN LOPEZ ROSALES
Οδυσσεας Κοψιδας
Journal of Urology
Osama Abdelwahab
jacqueline kosters
Dit onderzoek, dat gefinancierd is door NRO, heeft tot doel om meer inzicht te verkrijgen in de vraag hoe lerarenopleidingen de intake van nieuwe studenten voor de lerarenopleidingen vormgeven en hoe die intake bijdraagt aan en voorspellend is voor het succes van studenten binnen de lerarenopleidingen. De uitkomsten van het onderzoek kunnen opleidingen helpen om hun intakeprocedures te verbeteren, zodat zij aankomende studenten beter ondersteunen bij het proces van zelfselectie. De volgende onderzoeksvragen staan centraal: 1. Welke doelen, criteria en instrumenten hanteren de lerarenopleidingen tijdens de intake- en selectieprocedure? 2. In hoeverre ondersteunen die procedures bij het proces van zelfselectie ten aanzien van de vraag: a. Kan ik succesvol studeren? b. Kan ik als leraar succesvol zijn? c. Wil ik leraar worden en wat voor leraar dan? 3. In welke mate hebben de gehanteerde criteria en instrumenten een voorspellende waarde voor studiesucces en handelen in de beroepsprakti...
Aaron Yampasi Vargas
RELATED PAPERS
Personnel Psychology
Paula Caligiuri
Carlos Delgado Caro
International Journal of Mathematics in Operational Research
Sarat Puthenpura
Human Tooth and Developmental Dental Defects - Compositional and Genetic Implications
Francesco Grande
Joshua Siame
Oscar Calavia
AKSELERASI: Jurnal Ilmiah Nasional
vely randyantini
Research Papers in Economics
gérard Mondello
Tạp chí Khoa học và Công nghệ Biển
Marianna Stamati , Ηλίας Σταυρόπουλος
Seminars in Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
Isabella Florissi
Development and Psychopathology
Breana Cervantes
International Journal of Quantum Chemistry
christina Graham
Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Conference Companion Publication on Designing Interactive Systems
Evan Morgan
Zlatozar Boev
PHM Society Asia-Pacific Conference
Shinya Tsuruta
Jose Blanco
Medicina Interna
Pedro L Ferreira
Thomas Zentgraf
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Nike Inc.’s Outsourcing and International Labor Case Study
Major problems, potential solutions, criteria for addressing the problem, recommendations and conclusion, works cited.
Nike rapidly grew to become one of the most successful firms in sportswear across the world. However, by mid 1990s the company suffered very bad publicity after thriving for about three decades. Nike was exposed as a business that made its profits by exploiting the low-cost laborers in overseas plants, where most of its manufacturing had been outsourced.
Outsourcing comes with both advantages and disadvantages, but Nike seemed to have overlooked the disadvantages. The firm focused so much on cutting the costs (mainly the labor costs) at the expense of the workers. That way, the firm was not required to own equipment, manufacturing plants, machinery or materials for use in production of their Nike shoes. As such, Nike signed a contract with a Japanese firm, but it later shifted to South Korea and Taiwan as Japan became costly (Bartlett, Ghoshal , and Beamish 101).
Nonetheless, South Korea and Taiwan grew their economies fast and their once cheaper labor and lower production costs increased. By 1982, Nike was forced to shift to other markets including China and Indonesia. By 1990, China and Indonesia replaced Taiwan and South Korea as the largest Manufacturers of the Nike shoes and sporting gear.
Labor incidences and public relations problems that began in 1980s hit a new high in 1990s, as Nike was accused of promoting inhuman and rather unethical practices. The examples were allowing underage employees work in Indonesian companies, condoning the forced overtime work in Chinese plants and exposing workers to dangerous work conditions, as it was evident in Vietnamese plants (Spar and Burns 3).
Nike’s corporate responsibility started to tarnish because they intended to cut cost by outsourcing (Bartlett, Ghoshal & Beamish 102). It appeared as though they did not care about the working conditions provided it was making profit.
Fair labor standard act 1938 prohibits use of children for labor, advocates for safe working conditions, sets limitations on the number of work hours. In addition, the corporate America advocates for fair pay to compensate the amount of work done according to US department of labor (1-52).
To make matter worse, Nike’s management refused to take responsibility and thus made public statements terming all the allegations as false and malicious. Occasionally, the firm threatened to shift its business elsewhere when confronted by the governments and labor activist claiming it was not responsible for the manufacturing firms’ work production strategies (Spar and Burns 11). However, Nike failed to understand that it shared responsibility for the actions of its partners since ethical issues were not merely the actions of individual workers but the effects of the factors the organization presents.
It was until Nike started making losses that Phil Knight took courage to admit that the company had made mistakes in terms of corporate responsibility, code of conduct, and labor laws. In May 1998, Knight admitted that the brand Nike had come to be identified with child labor, coerced overtime and abusive work conditions (Spar and Burns 12). He then made a seeping declaration to instigate series of reforms to mend the company’s image. These reforms could have worked well if the company had not been waiting for about 18 years to admit its mistakes.
One of the major solutions to help solve Nikes problems would be to ensure that its outsourced partners would have a reasonable minimum wage that can allow workers to make a decent living out of the earnings (Spar and Burns 12). Besides, the minimum age of workers employed in Nike’s factory would be increased from 14 years to 18 years. In order to ensure safer working zones, Nike would also need to enforce the implementation of the OSHA clean air standard for all the plants it works with. Besides, the manufacturing companies could, with help of Nike, offer educational programs to employees, provide them with microfinance loans as well as set up dispute resolution strategies to address labor violation issues (Spar and Burns 12).
Since Washington Based reforms were already initiated by mid 1990s, Nike would get better platform to deal with its problems by enforcing the reforms to address fair labor issues. There is a minimum labor pay, maximum number of working hours per week at 60 hours etc (US department of labor 41).
Nike’s second solution strategy would be marketing audits. Warren (34) describes global marketing audit as a wide-ranging, methodical and intervallic investigation of the firm’s departments, objectives, strategies, mission, policies and activities to determine any problems or risks and opportunities. These activities would greatly help Nike to evaluate its partners and help them improve the company’s international corporate image. The investigation explores the efficiency of the marketing strategies, company operations, policies and processes; vis-à-vis its mission and resources (Warren 34). As such, a firm can be able to exploit opportunities, ethically, with the available resources and still earn the profits it yearns for without infringing on the human rights.
There is no shortcut when it comes to addressing matters that affect humanity, especially right to fair pay for equal amount of work, fair work condition and prohibiting child labor. However; going against this in a capitalist economy is a great challenge.
Nike must observe all the legislation that deal with production and manufacturing in order to provide fair conditions. If enforcing these laws in overseas countries would be difficult, Nike would have to look for a local manufacturer in the US. This will mean production higher costs. Second, the firm will have strictly enforce the code of conduct and outsource to firms which meets the criteria.
In the effort to cut costs and maximize profits, most companies tend to ignore important aspects of social responsibility and law. Nike has been one of such firms in the past, but which now realizes that in a world of technology, governed by international laws, and with gusto to fight for humanity as equal people for a company to succeed it must perform its corporate responsibilities. Such actions cannot go unnoticed.
The people, regardless of which country they come from, are informed about business ethics and human rights. Thus; multinationals and integration of world economies requires that any successful firm on international scene such as Nike, must be honest in disclosing corporate responsibility, enforce code of conduct, comply by the manufacturing standards of a product, follow the laws of the country they operate in, and monitor company practices.
For Nike to ever rebuild its brand image and establish a corporate culture consistent with the best work practices including better pay, and to enable it achieve profitability, the firm will have to strictly conduct business in a manner that respects humanity and protects the environment.
Bartlett, Christopher A., Sumantra, Ghoshal , and Paul Beamish. Transnational Management: Text, Cases, and Readings in Cross-Border Management . New-York, NY: McGraw-Hill Irwin, 2008. Print.
Spar, Debora., and Burns, Jennifer. Hitting the Wall: Nike and International Labor Practices. HBS Case no. 9-700-047 Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2002. Print.
U.S. Department Of Labor. “The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 ”. US Department of Labour 2008. Web.
Warren, Keegan. Global Marketing Management . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2002. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-outsourcing-and-international-labor/
"Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-outsourcing-and-international-labor/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-outsourcing-and-international-labor/.
1. IvyPanda . "Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-outsourcing-and-international-labor/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/nike-incs-outsourcing-and-international-labor/.
- Brief Description of Nike Inc: Is Nike a Monopoly?
- Nike Company's Marketing Strategy
- Overview of Nike Based on Outsourcing
- International Branding. Nike
- Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis
- China and Taiwan Relationship
- Management in Nike: Fair Standards
- Politics of Globalization in Taiwan
- Nike Inc.: Marketing Practices
- Nike: Brand Equity and Promotional Strategies
- Approx Company's Employee Theft Scenario
- Gorman Marketing Company's Decision Analysis
- Computers R Us Company's Customer Satisfaction
- Emirates National Oil Company's Top Management
- Management in the "Apollo 13" Movie by Ron Howard
- Subscribe to RSS

- in Teaching
- Leave a comment
Teaching Cases – “Global Sourcing at Nike” and “IKEA Goes Online”
It is always exciting to discover new teaching cases, especially when they are of very high quality. Two cases have just won awards in the 2023 Case Center Awards and Competitions. The first is called Global Sourcing at Nike and takes the perspective of Amanda Tucker, Vice President of Sourcing at Nike (authors: Michael W. Toffel, Nien-hê Hsieh, and Olivia Hull). It “explores the evolution of Nike’s efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers’ factories”, addressing several key supply chain challenges. The second case is entitled IKEA Goes Online: Implications for its Manufacturing (authors: Jan Olhager and Kasra Ferdows). It focuses on the introduction of an app that allows customers to use their mobile phones to visualize and order products in a virtual room, and a second app that allows customers to shop remotely. Congratulations to all the winners. (See also last year’s winner: Apple Inc: Global Supply Chain Management .)
Tags: Teaching
About Andreas Wieland
Leave a reply cancel reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Subscribe via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Recent Posts
- Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD)
- Global Supply Chains Amplify Costs of Extreme Heat Risk
- A Guided Tour Through the Qualitative Research City
- Personal Predictions for Supply Chain Management in 2024
- Building a Circular Supply Chain
- Methodology
- January 2024
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- December 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- Better Operations
- BVL's SCM Blog
- Cottrill Research
- Global Supply Chain Blog
- Inventory & Supply Chain Optimization
- Jay, Barry, & Chuck's OM Blog
- O.R. by the Beach
- Punk Rock Operations Research
- Purchasing Insight
- SCM-blog.de (de)
- Supply Chain @ MIT
- Supply Chain and Logistics Blog
- Supply Chain Matters
- Supply Chain View from the Field
- Supply Chains Rock
- SupplyChainMusings.com
- SupplyChainNetwork.com
- SupplyChainOpz
- The Freightos Blog
- The Logistics Blog by Alan McKinnon
- The Operations Room
- WFP Logistics Blog
Supply Chain Management Research
Powered by WordPress.com .
Discover more from Supply Chain Management Research
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Award winner: Global Sourcing at Nike

This case won the Ethics and Social Responsibility category at The Case Centre Awards and Competitions 2023 . #CaseAwards2023
View details the awards presentations on 5 & 7 August 2023 .
Author perspective
Who – the protagonist.
Amanda Tucker , Vice President of Sourcing at Nike , the sportswear giant.
This case explores the evolution of Nike’s efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers’ factories. Amanda is considering three key supply chain challenges: monitoring suppliers, encouraging suppliers to improve capabilities to meet Nike’s quality and productivity standards, and deciding which country to add to its source base in order to source products closer to the North American market.
With over $36 billion in sales and 73,100 employees in 2018, Nike was the largest sportswear brand in the world. To support its operations, it had a global network of over 500 supplier factories in over 30 countries that produced the company’s footwear, apparel and sports equipment.
Nike was an early mover in sourcing its suppliers from outside the US but, by the early 1990s, it began to face mounting criticism regarding the treatment of factory workers. This case looks at Nike’s response - from denying responsibility, to monitoring suppliers, to encouraging them to self-regulate whilst providing education and training.
Nike is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Beaverton, Oregon but its supplier factories stretch across six continents and over 30 countries.
The key events in the case take place in July 2018.

Amanda must consider the various options facing Nike’s source base. How can they convince suppliers to take ownership of compliance issues? How can Tucker get them to see the long-term benefits of collaboration with Nike? How should the brand integrate its existing sourcing with a need to source closer to market?
AUTHOR PERSPECTIVE
This is the first win for all three authors and the second win for Harvard Business School in the Ethics and Social Responsibility category.
Winning the award
Nien-hê said: “It is encouraging to see continued interest in the topic of responsibilities for sustainability and working conditions in the supply chain. The topic is one that has received a great deal of treatment, and there are many compelling contemporary challenges regarding responsible business conduct - e.g. ethical AI, disinformation, algorithmic fairness. So, it is heartening that students continue to engage with this foundational issue for the global economy.”
Olivia continued: “I am pleased there is interest in this important topic. Labour rights issues are an integral but often overlooked aspect of manufacturing.”
Case popularity
Michael said: “Our case describes Nike’s decades-long journey to understand and respond to problematic working conditions in their supply chains. Nike’s initial response was that working conditions in factories they didn’t own was not their problem to solve. But over time, a growing number of stakeholders expected them - and other brands - to take some responsibility to avoid sweatshops and to foster improved working conditions at the factories they hired to produce their goods.
"The case showcases many innovations and pilot programmes Nike has pursued over the years, and several challenges they still face. I think many students care a lot about the working conditions and environmental impacts associated with the products they buy and can relate to the apparel and footwear products that the case focuses on. I’m sure that our case’s focus on a brand as well-known as Nike also heightens student engagement.”

Writing the case
Michael reflected: “I wasn’t sure that Nike would be willing to have a case written about their challenges managing working conditions in supply chains, but I was impressed that they did, and were quite open with us. We had a terrific relationship with Nike; they let us interview managers from a wide range of functions, which gave us deeper insights on how various parts of an organisation can see the same issue quite differently through their distinctive lens.”
Case writing advice
Michael explained: “First decide what you want students to learn as they read the case and discuss it in class, and only then seek out a company willing to let you learn and write about their managerial decisions and dilemmas.”
Olivia added: “I am a big fan of outlines. I also recommend mapping out the teaching plan before finalising the case.”
Teaching the case
Michael commented: “This case is unusually versatile, as we have led our colleagues to teach this case in two different core MBA courses (in different years): Leadership and Corporate Accountability where we emphasised companies responsibilities to workers and ethical decision making, and then most recently in Technology and Operations Management where we emphasised how companies need to think holistically in their supply chain management efforts, including how they initially choose suppliers and how they manage them.”
Nien-hê commented: “A hope is that students and instructors will extend the learnings from this case to other industries and even beyond questions about supply chains to more general questions about the repsonsibilities of business. Many of the learnings from the case - the change in Nike’s response, the piloting of novel programs, and the development of internal capabilities and reporting structures - have much wider applicability and are relevant for so many of the challenges facing business today.”
Olivia concluded: “Thank you for your work promoting the case method. Cases are complex teaching tools that produce memorable learning experiences, but students are not always aware of the time and commitment it takes to create them. It is a privilege to be part of this intellectual endeavour.”
The authors

The protagonist

Educators can login to view a free educator preview copy of this case.
View all the 2023 winners
Don't miss a thing - join our case community today.
Benefits include: lower prices for teaching materials, a 50% discount on Learning with Cases: An Interactive Study Guide , royalties on case sales, free attendance at the annual Members' Case Forum, discounted case workshop places and much more!

Discover more


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on three key supply chain challenges: sourcing from suppliers that ...
Exhibit 1: The Apparel Commodity Chain. This case study, "Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly .
Abstract. This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on ...
MBA Case Study. The Nike supply chain can be divided into three main stages: sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution. Sourcing. Nike sources its raw materials from suppliers all over the world. The main raw materials that Nike uses are leather, rubber, and textiles. ... Global reach: Nike's supply chain is global in reach, with suppliers ...
This web page provides a summary of the Harvard case study of Nike's global sourcing strategy and its challenges. It highlights Nike's focus on innovation, quality, sustainability and customer satisfaction, as well as its outsourcing to Asian suppliers and its response to labor issues.
Abstract. The current study analyses Nike's journey to responsible sourcing in the global market. The study discusses how the problem of Nike's sweatshop supply chain emerged and how the company ...
This report explores how Nike's approach to improving social and environmental conditions in its global supply chain has evolved through integrated management of sustainability and innovation, increased supplier incentives, and systems innovations intended to prevent problems before they arise.
global sourcing practices aiming to improve the labor standards among their upstream business partners, primarily in developing countries (Locke 2013). This case study explores ethical challenges within the global supply chain of a major sportswear manufacturer-Nike. In the 80's Nike was criticized for its sweatshop supply chain.
This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on three key supply ...
This case explores the evolution of Nike's global product sourcing strategy, in particular ongoing efforts to improve working conditions at its suppliers' factories. When the case opens in July 2018, Vice President of Sourcing Amanda Tucker and her colleagues in Nike's Global Sourcing and Manufacturing division were focusing on three key supply ...
The case defines the ongoing efforts of Nike tohelp improve the working condition in the supplier's factory. There were three main challenges in the supply chain; the standards sourcing from suppliers, improving supplier's capabilities, and response to consumer demand across the globe. There were ethical issues in the sourcing of suppliers ...
Nike, a prominent sportswear brand, confronted significant sustainability and ethical sourcing challenges across its global supply chain. Facing intense scrutiny and criticism in the late 20th ...
Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Help Home - Case Solution - Global Sourcing at Nike Global Sourcing at Nike By Matt Guillaume In the workplace, sales are tightly controlled, so each sale is also seen by the public on a certain time or even the entire company.
7. Nike's Global Strategy in Action: A Case Study of China Navigating the Chinese Market: A Success Story of Adaptability. Nike's expansion into the Chinese market serves as a compelling case study of the company's ability to adapt its strategy to suit local preferences and cultural nuances.
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Global Sourcing at Nike case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution.
Global supply chain Management - case study Nike. Chukwuemeka Ogbuehi. Nike has evolved from an organization that manufactures for professional athletes to a company that is manufacturing for all ages, demographics and fashion inclined too through technological innovations. Nike is an Ideology based on pursuit of excellence, its not about shoes ...
Steps of Case Study Analysis & Solution: Step 1 - Reading the Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study To write an emphatic case study analysis and provide pragmatic and actionable solutions, you must have a strong grasps of the facts and the central problem of the HBR case study.
Nike Inc.'s Global Sourcing Analysis. China and Taiwan Relationship. Management in Nike: Fair Standards. ... We will write a custom essay on your topic a custom Case Study on Nike Inc.'s Outsourcing and International Labor. 808 writers online . ... Nike's second solution strategy would be marketing audits. Warren (34) describes global ...
Two cases have just won awards in the 2023 Case Center Awards and Competitions. The first is called Global Sourcing at Nike and takes the perspective of Amanda Tucker, Vice President of Sourcing at Nike (authors: Michael W. Toffel, Nien-hê Hsieh, and Olivia Hull). It "explores the evolution of Nike's efforts to improve working conditions ...
Executive Summary. i Nike has gone 35% digital and is planning to reach 50% by 2025. It has shown immense. growth and is expected to close year 2022 with over 50-billion-dollar revenue ...
The current study analyses Nike's journey to responsible sourcing in the global market. The study discusses how the problem of Nike's sweatshop supply chain emerged and how the public
The Case Centre is a not-for-profit company limited by guarantee, registered in England No 1129396 and entered in the Register of Charities No 267516. VAT No GB 870 9608 93. Global Sourcing at Nike won the Ethics and Social Responsibility category at The Case Centre Awards and Competitions 2023.
Step 6 - Organizing & Prioritizing the Analysis into Global Sourcing at Nike Case Study Solution Once you have developed multipronged approach and work out various suggestions based on the strategic tools. The next step is organizing the solution based on the requirement of the case. You can use the following strategy to organize the findings ...