

Samsung Electronics—A Detailed Case Study

Devashish Shrivastava
Samsung is a South Korean electronic gadget manufacturer in Samsung Town, Seoul. Samsung Electronics was established by Lee Byung-Chul in 1938 as an exchanging organization.
We all know this information about Samsung. Don't we? But what we don't know? Do you know how much Samsung has grown in these years? What are the Future Plans of Samsung? How much Samsung invested in its R&D? What difficulties did the company face coming all this way? What is the history behind this multinational conglomerate?
Don't worry we got you covered. We have penned down a detailed Case Study on Samsung Electronics. Let's find out in this thoroughly studied Samsung case study.
Let's start the detailed case study from here.
Samsung entered the electronics industry in the late 1960s and the development and shipbuilding ventures in the mid-1970. Following Lee's demise in 1987, Samsung was divided into five business groups - Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, Hansol Group and Joongang Group.
Some of the notable Samsung industrial subsidiaries include Samsung Electronics, Samsung Heavy Industries Samsung Engineering, and Samsung C&T (separately the world's 13th and 36th biggest development companies). Other notable subsidiaries include Samsung Life Insurance, Samsung Everland, and Cheil Worldwide.
Samsung has a powerful influence on South Korea's monetary advancement, legislative issues, media, and culture. Samsung has played a significant role behind the "Miracle on the Han River". Its subsidiary organizations produce around a fifth of South Korea's complete exports. Samsung's revenue was equivalent to 17% of South Korea's $1,082 billion GDP.
History of Samsung Electronics Samsung's Business Strategy Samsung Rides High In India Business Growth in India Future Plans of Samsung FAQ's
History of Samsung Electronics

1938 (Inception of Samsung)-
- In 1938, Lee Byung-Chul (1910–1987) of a huge landowning family in the Uiryeong region moved to nearby city Daegu and established Samsung Sanghoe.
- Samsung began as a little exchanging organization with forty representatives situated in Su-dong. It managed dried fish, privately developed staple goods and noodles. The organization succeeded and Lee moved its head office to Seoul in 1947.
- When the Korean War broke out, Lee had to leave Seoul. He began a sugar processing plant in Busan named Cheil Jedang. In 1954, Lee founded Cheil Mojik. It was the biggest woollen factory in the country.
- Samsung broadened into a wide range of territories. Lee wanted to build Samsung as a pioneer in a wide scope of enterprises.
- In 1947, Cho Hong-Jai, the Hyosung gathering's organizer, put resources into another organization called Samsung Mulsan Gongsa or the Samsung Trading Corporation with Samsung's founder Lee Byung-Chul. The exchanging firm developed into the present-day Samsung C&T Corporation .
- After few years in business, Cho and Lee got separated due to the differences in the management style. In 1980, Samsung acquired the Gumi-based Hanguk Jeonja Tongsin and entered the telecommunications market . During the initial days, it sold switchboards.
1987 (Demise of Lee Byung-Chul)-
- After Lee's demise in 1987, the Samsung Group was divided into four business gatherings—Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, and the Hansol Group.
- One Hansol Group agent stated, "Just individuals uninformed of the laws overseeing the business world could think something so ridiculous," while also adding, "When Hansol got separated from the Samsung Group in 1991, it cut off all installment assurances and offer holding ties with Samsung subsidiaries."
- One Hansol Group source attested, "Hansol, Shinsegae, and CJ have been under autonomous administration since their particular divisions from the Samsung Group."
- One Shinsegae retail chain official executive stated, "Shinsegae has no installment certifications related to the Samsung Group." In 1982, it constructed a TV get-together plant in Portugal, a plant in New York in 1984, a plant in Tokyo in 1985 and an office in England in 1996.
2000 (Samsung in 20th Century)
- In 2000, Samsung opened a development center in Warsaw, Poland. It started with set-top-box technology before moving to TV and cell phones. The cell phone stage was created with accomplices and formally propelled with the first Samsung Solstice line of gadgets and different subordinates in 2008. It later emerged into the Samsung Galaxy line of gadgets that is Notes, Edge, and other models.
- In 2010, Samsung declared a ten-year development system based on five businesses. One of these organizations was to be centered around bio-pharmaceuticals in which ₩2,100 billion was invested.
- In the first quarter of 2012, Samsung Electronics turned into the world's biggest cell phone creator by unit deals, surpassing Nokia which had been the market chief since 1998.
- In 2015, Samsung was granted U.S. patents as compared to other organizations like IBM , Google , Sony, Microsoft , and Apple. Samsung got 7,679 utility licenses before 11 December 2015.
- On 2 August 2016, Samsung Electronics revealed the Galaxy Note7 smartphone, which went on sale on 19 August 2016. At the beginning of September 2016, it halted its selling of smartphones due to some problems with the smartphones. Samsung suspended the selling of the smartphones and recalled its units for inspection.
- This happened after certain units of the telephones had batteries with a deformity that made them produce extreme warmth, prompting flames and blasts. Samsung replaced the reviewed units of the telephones with a new version. It was later found that the new version of the Galaxy Note 7 also had the same battery deformity.
- Samsung recalled all Galaxy Note7 cell phones worldwide on 10 October 2016 and permanently ended its production on the same day.
Samsung's Business Strategy
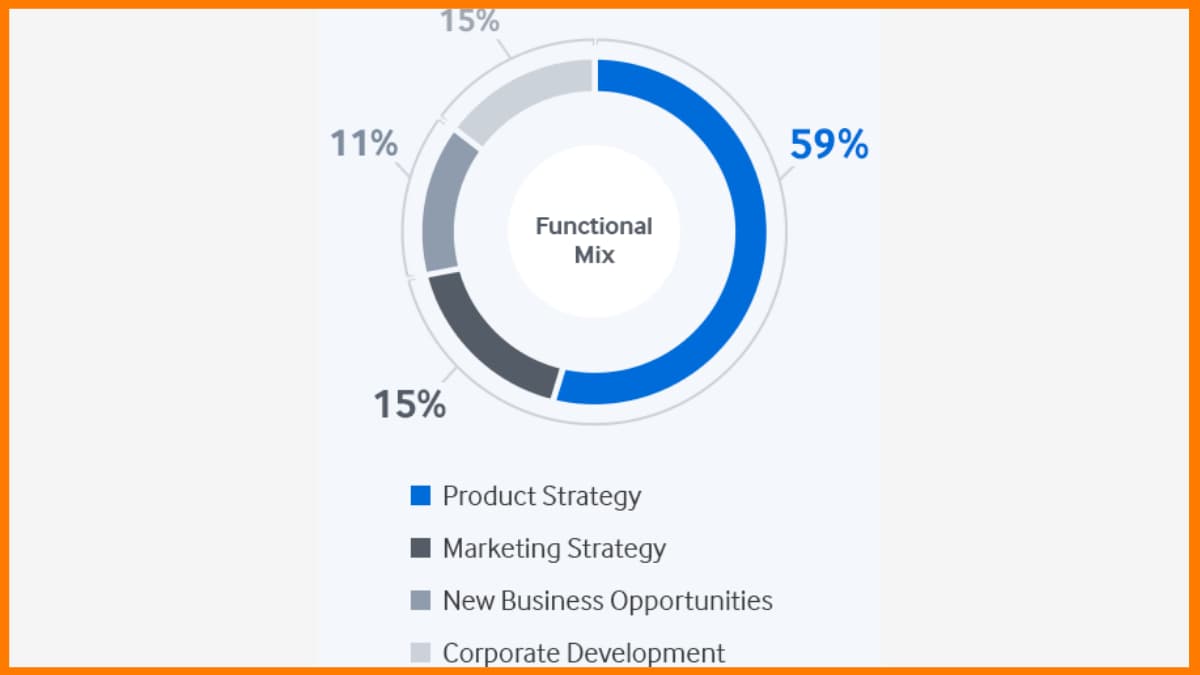
Great business strategies have been applied by Samsung over the years. Not very far back, Samsung wasn't as famous as now. Samsung has now advanced so much that it is the principal contender of Apple Inc. Samsung is the biggest tech business by income and the seventh most significant brand today. The showcasing procedure it applied encouraged Samsung electronics to turn into an industry driving innovation organization.
The Samsung marketing strategy was one of the best systems at any point because it helped a cost-driven organization to change its structure and become a power producer. Due to the consistently changing tastes of purchasers in the innovation business, organizations needed to pursue the pace and offer dynamic and advancing devices to their clients. In this way, Samsung additionally needed to change to pick up the high ground available, and the new Samsung showcasing methodology was the way to advancement.
Some of the business strategies of Samsung Electronics are listed below:
Promotional Mix Of Samsung
Samsung has arrived at fantastic statures with its cell phones which helped the brand to turn into an image of value and unwavering quality for its purchasers.
Samsung Marketing Mix Pricing Strategy and Samsung Advertising Methodology are the two estimating techniques used by the organization. Other than its items, Samsung is celebrated for its customer support . However, item variety is the most dominant part of the promoting blend of Samsung.
- Skimming Price
Like Apple , Samsung uses skimming costs to pick up the high ground over its rivals. For example, Galaxy S6 and S6 Edge are the brand's new results of Samsung conveying the trademark "Next is Now" and guaranteeing that they are the best smartphone maker at any point made.
What will happen when different contenders will dispatch a cell phone with indistinguishable highlights? Straightforward. Samsung will bring down the cost and effectively steal the customers from its competitors.
- Focused Pricing
Samsung experiences issues in increasing an edge over its rivals with different items. Doubtlessly, Samsung is a credible brand. However, regarding home appliances, it can't be in any way, shape, or form outperform LG In the cameras segment and other home appliance units. Also, Samsung cannot compete with Canon and Nikon.
For Samsung to withstand this savage challenge, it's crucial to utilize aggressive valuing of its products. Moreover, Samsung is neither a newbie underway nor non-inventive. For the most part, it is often the first company to be innovative with its products and present a change among its competitors.
- Putting in Samsung Marketing Strategy
Samsung uses divert advertising strategies. Retailers who present the innovation chain will undoubtedly incorporate Samsung in their rundown on account of the firm being a world-celebrated brand. Samsung can likewise fill in as an option for the purchasers. The circulation is a convincing piece of the Samsung promoting methodology.
In specific urban communities, Samsung has an agreement with a solitary dissemination organization that circulates the items all through the city. For example, Mumbai is an incredible case where Samsung conveys its products through a solitary organization.
Samsung Rides High In India

The greatest leader by far in the smartphone business is Samsung Electronics, the world's greatest cell phone and TV producer.
Samsung is India's greatest, versatile brand. It is the developer of Reliance Jio's 4G LTE system — the greatest and busiest information system on the planet.
Discernments, advertise wars, openings, rivalry — now and then from conventional remote adversaries, from nearby upstarts, and emerging Chinese brands trouble Samsung.
Be that as it may, every time Samsung has had the option to fight off the dangers and hold its ground. It has been leading the market in the TV fragment for more than 12 years and in the versatile business for a long time after it toppled Nokia in 2012.
Riding The Smartphone Wave
As indicated by some statistical surveying firms following cell phone shipments, Chinese firm Xiaomi is creeping nearer — or has even surpassed Samsung after December 2017 quarter.
While for the entire year 2017, Samsung was No. 1 in the cell phone space, IDC information indicated Xiaomi drove the last quarter with 26.8% piece of the overall industry. Samsung was at 24.2%. Different players, for example, Vivo, Lenovo, and Oppo stayed at 6.5, 5.6, and 4.9%, separately.
Warsi, who has been working with Samsung for as far back as 12 years and has as of late been advanced as Global Vice President, is unflinching, "These difficulties offer us the chance to work more earnestly for our customers and with our accomplices.
Furthermore, shoppers love marks that emphasis on them," he says. "Samsung is India's No. 1 cell phone organization crosswise over sections — premium, mid and reasonable. That is what makes a difference."
Statistical surveying firm GfK tracks disconnected offers of handsets — which make up around 70% of the market — in which Xiaomi is attempting to make advances.
Samsung had a 42% worth piece of the overall industry in the general cell phone showcase in the nation in 2019 and 55% in the superior fragment as indicated by GfK. An industry official who would not like to be named says that India must be Samsung's greatest market by large volumes.
The thought currently is to become the cell phone business which gets more worth. As indicated by reports, Samsung India's incomes from cell phone deals in 2018-19 remained at an astounding INR 34,300 crore. That is over $5.5 billion and development of 27%. Samsung's nearest adversaries are talking about incomes of $1 billion in India, going up to $2 billion.
Samsung is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronics by revenue. As of 2019, Samsung Electronics is the world's second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$301.65 billion, the 18th largest in the world.
Shopper Is At The Center

Samsung is a worldwide advancement powerhouse that leads the patterns. It profoundly put resources in India — 22 years of connections in the exchange, and tremendous interests in neighborhood R&D . It has around 10,000 architects working in research offices in India and is perhaps the greatest scout from the IITs.
"Samsung has a solid brand picture in India, as it has been available in various customer electronic portions with quality items for quite a while now. The brand is trusted because of its long history in the nation, dish India nearness, and a vigorous after deals support for buyers," says Shobhit Srivastava, explore expert at Counterpoint Research.
Indeed, even an item fizzle of the size of the Galaxy Note7 in September 2016 couldn't affect Samsung. While the organization was fast enough to get back to every one of the units that had been sold and cease the gadget totally, Samsung's activities and ensuing effective dispatches of leads like Galaxy S8, Note8, the Galaxy S9 and S9+, which were propelled in February, rescued the harm and raised the profile of the brand as a dependable organization. "They rushed to concede their error and that helped them interface with the perceiving clients of today far superior," says Koshy.
Make For India
Samsung's system 'Make for India', which resounds with the administration's ' Make in India ' activity, was conceived in the late spring of 2015. Samsung India's new President and CEO, H.C. Hong, had recently moved in from Latin America and was looked with the prompt tough assignment of fighting a firm challenge from two nearby versatile organizations that is Micromax and Intex.
Samsung's customer hardware business containing TVs, fridges, and other advanced machines were additionally confronting challenges from Sony and LG.
Around a similar time, the legislature of India propelled its 'Make in India' activity. "In this way, Mr. Hong revealed to us we have been doing Make in India effectively for two decades. What we should concentrate on widely to remain on top of things is Make for India (MFI)," says Dipesh Shah, Managing Director of Samsung R&D Institute in Bengaluru, the greatest R&D community for Samsung outside Korea.
Truth be told, the R&D focuses in India contribute intensely to the improvement of worldwide items, for example, Samsung's lead cell phones (Galaxy S9 and S9+). While different organizations focused on propelling their worldwide items in India, Samsung went about rethinking items for the nation at its R&D focuses.
India is significant for Samsung, thinking of the nation as the second biggest cell phone showcase on the planet today, and it is possibly the greatest undiscovered market for some advanced apparatuses. The entrance of iceboxes, clothes washers, microwaves, and forced air systems are appallingly low because of components like the accessibility of continuous power, social conduct, way of life, and earnings.
Business Growth in India

Samsung India crossed the INR 50,000 crore deals achievement in 2017 according to the simply distributed organization filings with the Registrar of Companies (RoC), uniting its situation as the nation's biggest unadulterated play purchaser products MNC. The Korean mammoth's all-out salary, including turnover and other pay, developed by 15.5% to INR 55,511.9 crore in FY 2017 from INR 48,053 crore in the earlier year regardless of Chinese organizations making genuine advances into the Indian cell phone advertise.
Samsung's cell phone business developed deals at 26.7% to INR 34,261 crore, while the home apparatus business developed by 12% to INR 6,395.6 crore. The organization's TV business stayed dormant at INR 4,481.2 crore even though Samsung held the market initiative.
The organization's net benefit developed at a quicker pace of 38% to INR 4,156.2 crore which industry examiners credited to more concentrate on premium models crosswise over cell phones and customer hardware having higher edges.
Samsung, in its filings, said the 'Make for India' activity, through which a large portion of the items was planned and created given the Indian customer's needs, has been an enormous achievement and a major factor behind the development.
All the units at Samsung India improved their gross productivity with the TV business dramatically increasing it and the home machine business nearly trebling it. The cell phone business was the biggest supporter of gross benefit having developed by 44% in FY17 at INR 5,005.9 crore.
Future Plans of Samsung

Samsung has arranged a new venture of around INR 2,500 crore to transform its India tasks into a center for parts business, two senior industry administrators said. The ventures could be increased further, they included. The Korean organization has set up two new parts fabricating substances in India—Samsung Display Co and Samsung SDI India—for the generation of cell phones and batteries.
Independently, Samsung's funding arm—Samsung Venture Investment Corp—has set up activities in India to support new companies in gadgets equipment and programming organizations. The segment organizations will supply items to both Samsung India and other cell phone merchants who as of now source parts from Samsung's abroad tasks.
Samsung sees a big opportunity for segment business considering the administration's push on 'Make in India' where expense on imported cell phone segments and purchaser hardware is going up, the administrators said.
Samsung is likewise pitching to the administration for fare impetuses so it can even fare segments from India. Samsung Display has just marked an update of comprehension with the Uttar Pradesh government for an INR 1,500 crore plant for assembling telephone show to be operational by one year from now April. The plant will come up in Noida, the administrators said.
Samsung SDI India has plans to set up an assembling unit in India for lithium-particle batteries after the organization was drifted a month ago, according to its administrative filings with the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
As per the administrators, Samsung SDI has plans to contribute another INR 900-1,000 crore and will settle the plans after counseling with the Center post general races. These speculations come after it introduced the world's biggest cell phone fabricating unit in India a year ago at an all-out cost of INR 4,915 crore. It is expected to be completed in 2020.
That's all for now. Share your learnings and findings. What did you learn from this article? Which information surprised or amused you the most? Feel free to reach us and share your feedback. We would love to hear from you. Do comment us in the comments section below. Happy Reading.
Who is the owner of Samsung Electronics?
Samsung Group is the owner of Samsung Electronics.
Who is the Founder of Samsung?
Samsung Electronics was established by Lee Byung-Chul (1910–1987) in 1938 as an exchanging organization.
Who is the current CEO of Samsung?
Kim, Ki Nam, Kim, Hyun Suk and Koh, Dong Jin are the current CEO of multinational conglomerate Samsung.
What does Samsung Electronics make?
Samsung Electronics produces smartphones, TV sets, laptops, solid-state drives, digital cinemas screens, etc.
Is Samsung a Chinese company?
Samsung is a South Korean electronic gadget manufacturer in Samsung Town, Seoul.
What is Samsung's strategy?
- Promotional Mix of Samsung
How large is Samsung Electronics?
Samsung is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronics by revenue. Samsung Electronics is the world's second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$ 301.65 billion, the 18th largest in the world.
What are the future plans of Samsung Company?
Samsung has arranged a new venture of around INR 2,500 crore to transform its India tasks into a center for parts business, two senior industry administrators said.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Payment Gateway- Razorpay
- Spy on your Competitors- Adspyder
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Global Firms Advancing Electric Car Technology to Lead the Race
Automobile manufacturers have been stepping up their technological game to become industry leaders in electric vehicles ever since the notion was first presented globally. As a result of Tesla's success, worldwide corporations are racing to be the first to cash in on this industry's promising future. The electric vehicle market
Reliance Industries Carving the Business Landscape of India
For a long time now, Reliance Industries has been one of the major Indian conglomerates that has caused a stir. This ideal corporate realm, founded by Dhirajlal Hirachand Ambani, also known as Dhirubhai, a global business titan and visionary, has gone a long way since its beginnings. The narratives of
List of All the Brands Under Aditya Birla Fashion
Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail Limited (ABFRL) is a prominent player in the Indian fashion industry and is part of the prestigious Aditya Birla Group. With a rich bouquet of leading fashion brands and retail formats, ABFRL is India's first billion-dollar pure-play fashion powerhouse. The company has an impressive portfolio
Trell - Unleashing varied voices across sectors
Product reviews are the output of peoples' comments/feedback on an item they have purchased. A product review aids other customers in acquiring a thorough understanding of the product before making the purchase. Other people may read the comments and decide for themselves whether or not the product is worth
Remarkable Recovery: Samsung Crisis Management Case Study
Have you ever wondered how a global tech giant like Samsung managed to navigate a major crisis and bounce back stronger?
In the world of corporate governance, effective crisis management can be the difference between irreparable damage to a company’s reputation and a successful recovery.
In this blog post, we delve into a Samsung crisis management case study to learn about exploding batteries to the intricate strategies employed to restore trust.
Samsung’s journey offers valuable insights into the intricacies of crisis management in the digital age.
Join us as we explore the key lessons learned and best practices from this high-stakes situation, shedding light on the remarkable recovery efforts that propelled Samsung forward.
Let’s learn about sailing through tough times through Samsung crisis management case study
Background of Samsung History and growth of Samsung as a global conglomerate
Samsung, founded in 1938 by Lee Byung-chul, started as a small trading company in South Korea. Over the years, it steadily expanded into various industries, such as textiles, insurance, and retail.
In the 1960s, Samsung ventured into electronics, marking the beginning of its transformation into a global conglomerate.
With a focus on technological innovation and a commitment to quality, Samsung rapidly gained recognition for its consumer electronics products, including televisions and appliances.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Samsung significantly diversified its business portfolio, entering the semiconductor, telecommunications, and shipbuilding industries.
This diversification strategy helped Samsung become a key player in multiple sectors, solidifying its position as a global leader. Notably, Samsung’s semiconductor division became one of the largest chip manufacturers in the world, supplying components to various electronic devices worldwide.
Samsung’s ascent continued in the 2000s, driven by its successful expansion into the mobile phone market. The introduction of the Galaxy series, powered by the Android operating system, catapulted Samsung to the forefront of the smartphone industry.
The company’s innovative designs, cutting-edge features, and aggressive marketing campaigns contributed to its rise as a major competitor to Apple’s iPhone.
With its global reach, Samsung has consistently ranked among the world’s largest technology companies, epitomizing South Korea’s economic prowess and technological advancements.
Samsung has also been considered one the best companies that successfully managed and implemented change initiatives.
Overview of Samsung’s position in the technology industry
In the consumer electronics segment, Samsung has established itself as a dominant force. Its diverse product lineup encompasses televisions, smartphones, tablets, wearables, home appliances, and audio devices.
The Galaxy series of smartphones, in particular, has enjoyed immense popularity and has emerged as a fierce competitor to other industry giants. Samsung’s televisions are also highly regarded for their cutting-edge display technologies, such as QLED and MicroLED.
The company’s advancements in semiconductor technology have contributed to faster computing speeds, increased storage capacities, and improved energy efficiency.
Samsung’s influence extends beyond consumer electronics and semiconductors. The company is actively involved in telecommunications infrastructure, including the development of 5G networks and the production of network equipment.
Samsung has also made notable strides in the realm of software solutions, including its own mobile operating system, Tizen, and various software platforms for smart devices.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Crisis
The Note 7 battery issue marked a significant crisis for Samsung, leading to a widespread recall of the flagship smartphone and causing considerable damage to the company’s reputation.
The crisis began in September 2016 when reports emerged of Note 7 devices catching fire or exploding due to faulty batteries. These incidents raised concerns about consumer safety and triggered a wave of negative publicity for Samsung.
Upon receiving initial reports of battery-related incidents, Samsung initially responded by issuing a voluntary recall of the Note 7 in September 2016. The company acknowledged the problem and expressed its commitment to addressing the issue promptly and effectively.
Samsung attributed the battery malfunctions to a manufacturing defect, specifically a flaw in the design that caused a short circuit.
To ensure customer safety, Samsung advised Note 7 owners to power down their devices and refrain from using them. The company swiftly implemented measures to exchange the affected devices, offering customers the option to either replace their Note 7 with a new unit or receive a refund.
Samsung also collaborated with mobile network operators and retail partners to facilitate the recall process.
In its initial response, Samsung took steps to communicate with customers and the public about the issue. The company published official statements expressing regret for the inconvenience caused and assuring customers of its commitment to resolving the problem. Samsung emphasized its dedication to quality and safety, promising to conduct thorough investigations and implement necessary improvements to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Media coverage and public perception during the crisis
During the Note 7 crisis, media coverage played a significant role in shaping public perception and amplifying the negative impact on Samsung’s brand.
The crisis received extensive coverage from both traditional media outlets and online platforms, leading to widespread awareness and public scrutiny. Here’s an overview of media coverage and its influence on public perception:
- News Outlets: Major news organizations across the globe reported on the Note 7 battery issue, highlighting incidents, the recall, and subsequent developments. Television news segments, newspapers, and online news articles extensively covered the crisis , emphasizing the potential safety risks and consumer concerns. The constant media attention contributed to the widespread dissemination of information and increased public awareness of the issue.
- Online Platforms and Social Media: Social media platforms played a pivotal role in the crisis, enabling the rapid spread of information and user-generated content. Users took to platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube to share their experiences, express concerns, and criticize Samsung’s handling of the situation. Viral videos, photos, and personal accounts of Note 7 incidents gained traction, further fueling negative sentiment and influencing public perception.
- Expert Analysis and Opinions: Alongside news coverage, experts and industry analysts provided their insights and opinions on the crisis. Their assessments of Samsung’s response, the potential causes of the battery issue, and the implications for the company’s brand reputation contributed to the overall narrative. Expert opinions had the power to sway public perception and shape the understanding of the crisis.
- Consumer Forums and Discussion Platforms: Online forums and discussion boards dedicated to technology and consumer experiences became hubs for discussions surrounding the Note 7 crisis. Consumers shared their frustrations, exchanged information, and warned others about potential risks. These platforms served as gathering places for individuals affected by the crisis and amplified the negative sentiment surrounding Samsung’s brand.
Financial implications and losses incurred by Samsung
The Note 7 crisis had significant financial implications for Samsung, resulting in substantial losses for the company. Here are some of the key financial impacts experienced by Samsung as a result of the crisis:
- Recall and Replacement Costs: The recall and replacement process incurred significant costs for Samsung. The expenses involved in collecting and replacing over 2 million of Note 7 devices, including logistics, shipping, and refurbishment, were substantial. The costs also encompassed the testing and certification of replacement devices to ensure their safety. The total recall cost was estimated at $5.3 billion.
- Decline in Sales and Market Share: The crisis had a detrimental impact on Samsung’s sales and market share in the smartphone industry. As consumer confidence in the Note 7 and Samsung’s brand reputation declined, potential buyers shifted their preferences to alternative smartphone options. The decline in sales of the Note 7, coupled with the negative impact on the perception of other Samsung products, led to a loss of market share for the company.
- Stock Price Decline: The Note 7 crisis had an immediate impact on Samsung’s stock price. News of the battery issue, recalls, and subsequent negative media coverage led to a decline in Samsung’s stock value. Samsung shares fell approximately to 7 percent right after 2 months of the crisis.
Crisis Management Strategy Employed by Samsung
Following are the key aspects of Samsung Galaxy Note 7 crisis management strategy:
Immediate actions taken by Samsung to address the crisis
In the face of the Note 7 crisis, Samsung swiftly implemented a range of immediate actions to address the situation and mitigate the impact on consumers and the company’s brand reputation. Here are some of the key actions taken by Samsung:
- Voluntary Recall: As soon as reports of battery issues emerged, Samsung initiated a voluntary recall of the Note 7. This proactive step demonstrated the company’s commitment to consumer safety and willingness to take responsibility for the problem.
- Temporary Production Halt: To address the root cause of the battery issue, Samsung temporarily halted production of the Note 7. This decision aimed to prevent further distribution of potentially defective devices and allow for thorough investigations and corrective measures.
- Transparent Communication: Samsung made efforts to communicate openly and transparently about the crisis. The company issued official statements and press releases acknowledging the problem, expressing regret for the inconvenience caused, and reassuring customers of its commitment to resolving the issue. Transparent communication was crucial in maintaining trust and providing timely updates to affected consumers.
- Collaboration with Authorities: Samsung collaborated closely with regulatory authorities and industry experts to investigate the battery issue comprehensively. By engaging external expertise, the company aimed to identify the root cause and develop effective solutions. This collaboration demonstrated Samsung’s commitment to finding the best possible resolution.
- Customer Support and Safety Guidelines: Samsung provided clear instructions to consumers regarding the use of Note 7 devices, emphasizing the importance of safety. The company advised customers to power down their devices, participate in the recall, and utilize alternative devices in the interim. This approach prioritized customer safety and aimed to prevent further incidents.
- Increased Battery Testing and Safety Measures: Samsung implemented enhanced battery testing procedures and stringent safety measures to prevent similar incidents in the future. The company adopted more rigorous quality control processes, including additional safety certifications and testing standards, to ensure the highest levels of product safety.
Communication strategies employed by Samsung
Samsung employed various communication strategies to address the Note 7 crisis and manage the impact on its brand reputation. Effective communication was crucial in maintaining transparency, addressing consumer concerns, and rebuilding trust. Here are some of the communication strategies employed by Samsung:
- Official Statements and Press Releases: Samsung issued official statements and press releases to provide updates on the progress of the recall, investigations, and corrective actions. These statements expressed remorse for the inconvenience caused and reiterated the company’s commitment to customer safety. Clear and concise communication helped keep customers informed and reassured them that Samsung was actively working to resolve the issue.
- Direct Customer Communication: Samsung directly communicated with customers to provide instructions and updates on the recall process. The company utilized various channels such as email, SMS messages, and notifications through its official website and smartphone apps. This direct communication ensured that customers received important information and guidance regarding the recall and replacement program.
- Social Media Engagement: Samsung actively engaged with customers and the public on social media platforms, including Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. The company responded to customer queries, addressed concerns, and provided updates on the progress of the recall. By engaging in two-way communication, Samsung demonstrated its willingness to listen, respond, and provide assistance to affected customers.
- Collaboration with Industry Experts: Samsung collaborated with industry experts, battery manufacturers, and regulatory authorities to investigate the root cause of the battery issue. This collaboration was communicated to the public, showcasing Samsung’s commitment to finding solutions and ensuring that the necessary expertise was involved in resolving the crisis.
- Advertisements and Marketing Campaigns: Samsung launched advertising and marketing campaigns focused on rebuilding trust and emphasizing its commitment to quality and safety. These campaigns highlighted Samsung’s dedication to addressing the issue and regaining consumer confidence. Advertisements often emphasized the company’s rigorous testing procedures and quality control measures to assure customers of the safety of its products.
- CEO Apology: Samsung’s CEO issued a public apology, taking personal responsibility for the crisis and expressing regret for the inconvenience and concern caused to customers. The CEO’s apology aimed to convey sincerity, empathy, and a commitment to rectifying the situation, while also reinforcing the company’s accountability and determination to regain trust. The apology was published on a full page in 03 major US newspapers – the Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post and The New York Times.
Collaborations with regulatory authorities and industry experts
Samsung worked closely with government agencies and regulatory bodies in various countries where incidents related to the Note 7 were reported. The company shared information, conducted investigations, and cooperated with authorities to ensure compliance with safety regulations and guidelines. Collaboration with government agencies helped align efforts to address the crisis and establish industry-wide safety standards.
In the United States, Samsung collaborated with the CPSC, an independent federal agency responsible for ensuring the safety of consumer products. Samsung worked together with the CPSC to investigate the battery issue and coordinate the recall process. This collaboration ensured that the recall efforts followed established safety protocols and provided consumers with accurate information.
Samsung collaborated with battery manufacturers to investigate the specific manufacturing defects that caused the battery issue. The company worked closely with these partners to analyze the battery designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. By involving battery manufacturers in the investigation, Samsung aimed to identify the root cause and implement corrective actions to prevent similar issues in the future.
Samsung engaged independent testing labs to conduct thorough assessments of the Note 7 batteries and verify the effectiveness of corrective measures. These labs specialized in battery testing and certification, providing expertise and unbiased evaluation of the battery performance and safety. Collaboration with independent testing labs helped validate Samsung’s efforts to address the battery issue and instill confidence in the effectiveness of the solutions.
Post-Crisis Recovery and Rebuilding
Samsung implemented more stringent quality control measures across its product development and manufacturing processes. This included enhanced battery testing protocols, increased inspections, and stricter quality assurance standards. By demonstrating a commitment to producing reliable and safe products, Samsung aimed to rebuild customer trust.
Extended Warranty and Customer Support: Samsung extended warranty periods for existing and new devices, including the Note 7, to provide customers with added assurance. The company also enhanced its customer support services, ensuring that customers could easily access assistance, product information, and technical support. These initiatives aimed to demonstrate Samsung’s commitment to customer satisfaction and support.
Launch of subsequent product lines and their impact on brand perception
Following the Note 7 crisis, Samsung launched subsequent product lines, including flagship smartphones like the Galaxy S8 and subsequent iterations. These launches played a crucial role in shaping brand perception and rebuilding trust. Key factors that influenced brand perception and the recovery process include:
- Emphasis on Safety and Quality: Samsung placed a strong emphasis on safety and quality in its subsequent product launches. The company implemented rigorous testing procedures and introduced new safety features to ensure the reliability and safety of its devices. By highlighting these improvements, Samsung aimed to regain customer trust and reassure them of its commitment to producing high-quality products.
- Positive User Experience: Samsung focused on delivering positive user experiences with its new product lines. This included improvements in design, performance, and functionality to enhance customer satisfaction. By providing users with exceptional products, Samsung aimed to rebuild its reputation and generate positive word-of-mouth, contributing to brand recovery.
- Brand Messaging and Marketing: Samsung’s marketing efforts during subsequent product launches were carefully crafted to reinforce positive brand associations and regain customer trust. The company emphasized innovation, customer-centricity, and the commitment to quality and safety. Marketing campaigns highlighted features, benefits, and technological advancements to create a positive brand image and overcome the negative perceptions associated with the Note 7 crisis.
Final Words
Samsung’s handling of the Note 7 crisis serves as a case study in crisis management. Despite the significant financial and reputational setbacks, the company took proactive steps to address the crisis, regain customer trust, and prevent similar incidents in the future.
The Samsung crisis management case study highlights the importance of swift and transparent communication, customer-centric actions, and continuous improvement in product safety and quality. By effectively addressing the crisis, Samsung was able to navigate the challenging situation and rebuild its brand, reaffirming its position as a leading global technology company.
Overall, the Samsung crisis management case study provides valuable insights into how a company can recover from a major setback, restore customer trust, and strengthen its position in the market through strategic actions and a relentless commitment to customer satisfaction and product excellence.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

04 Key Concepts of Hyper Learning for Organizational Change

Exploring the Types of Crisis Communication
Kaizen Change Model – Phases, Advantages and Disadvantages
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Business Analysis » Case Study: Samsung’s Innovation Strategy
Case Study: Samsung’s Innovation Strategy
The success of Samsung has been widely acknowledged in the last decade. Samsung, the world’s largest television producer and second largest mobile phone manufacturer, is also the largest firm of flash memory maker. Furthermore, Samsung was ranked by Fast Company Magazine to be third most innovative company in the consumer electronics. The company grew from a local industrial leader into a worldwide consumer electronics brand, with up to 261,000 employees, 14 public listed companies, 470 offices and facilities in 67 countries. Samsung was ranked as 11th world’s most innovative companies. It is one of the two Korean companies in the Top 20 companies. While Sony, the Japan’s biggest consumer electronics, was ranked as 10th, only one position above Samsung. This has brought questions among management gurus how this growing company could drive innovation to create success within a short time and remain innovative despite the difficulties of internationalization . In addition, it could overcome many well-built rivals from Japan and Europe.

Shared vision and top management commitment are the important component leading to create innovative atmosphere . In creating such organization, if leaders are not committed in their actions, innovation couldn’t be systematic in a company. Top executive’s role modelling is one of the main differences between innovative and non-innovative organizations. Moreover, employees should realize a company’s goals to align with their innovative effort. Samsung’s new management beliefs applied in the late 1990’s is “we will devote our human resources and technology to create superior products and services, thereby contributing to a better global society.” This shows the company’s strong willpower to contribute to the worldwide people’s prosperity in the 21st century. This message encourages every employee in the firm to innovate with the clear goal of being global superior producer.
Appropriate Structure
The innovative organization tends to have characteristics of organic structures with open and dynamics systems. At first, the reduction of organizational layer and downsizing are concerned as cost control . An increase in use of information technologies, such as email, internal blog, shared data repository, also leads to the need of eliminating middle management. The possible consequences for this are faster responsiveness to market, higher competitiveness, more flexibility, and reducing processes between divisions. This leads to flatter organisation that is not only the change of organisational structure but also the change of decision-making process . In order to avoid delays and support for rapid innovation, decisions should be delegated to the innovation team. The approval of top management is only needed at the checkpoints or gates of the innovation process. Furthermore, Innovation is not suitable with multi-level hierarchy as the new idea and radical innovation must pass through many approvals with high possibility of ideas being rejected. Moreover, this will discourage strong leaders, who try to overcome its cumbersome, but the slow-response organisation will eventually obstruct their abilities. For example, in 1989, Samsung had 3-7 steps for project approval. This took up 24 days for the proposal to go through 7 approvals to arrive final decision step from the president. On the contrary, proposal in 1995 needed maximum of 3 approvals decided on the same day. This change of the important process leads to speed of running business. Furthermore, the proposal form in 1995 is in English, this signified an attempt for globalization .
Key Individuals
With the goal of creating innovation in the company, Samsung needs the world-class human resources from both technical and business backgrounds. Its branding strategy is not only to create a brand that people trust and admire, but also to be a company that they desire to join. To foster this breakthrough R&D, Samsung set up worldwide objectives to catch the attention of the smartest people from around the world, and retain them. These people will be trained and implanted Korean and Samsung culture through one week of intensive Korean daily conversation class, one week of Orientation about company’s history, philosophy, and culture, and develop general management skills delivered by senior Samsung executives. The recruitment of world’s smartest innovators, inventors and designers are fundamental to the company’s success in creating the future technology.
Besides having the best people for the development of innovative capabilities, Samsung has a tool to identify the key players, such as Project leader, promoters, idea champions, or gatekeeper, in the organization. Experiential education programs that are enjoyable, innovative and effective have performed this identification task. For example in the Samsung Semiconductor unit, 90 managers were organised into groups and assigned to build up new equipment through the use of Lego blocks. The tool was just simple Lego blocks, but the equipment created in this experiment had to be functional. This activity, which required both creativity and teamwork, provided managers comprehension of the role each member played in team. Who is promoter, supporter, idea generator, and critical thinker are identified.
Effective Team-working
Currently, team-working increasingly reflects a deeper recognition that this method of working offers greater economic benefits. Cross-functional teams is an effective tool to bring in different knowledge sets needed for solving production problems, creating new businesses , or develop new strategies. Work as a team needs more participation, higher commitment, sharing knowledge and self-management . This is more organic and flexible approach that helps to initiate innovation implanting across organisational and national boundaries. For example, Automakers from USA and Japan collectively worked on the development of new car model. Committing to consumer trends, Samsung set up a group of about 30 businessmen called CNB (Create New Businesses) who had to discover long-term social and technological fashions and imagine new products, which fulfill promising demands. Samsung has harvested the fruits from its team-working and strong commitment to innovation , transforming low-quality producer to become a brand that create stylish mobile phone. In 2010, its sales of mobile phones were ranked as number one in the US market.
Long-term Commitment to Education
Invest in people is another key initiative needed to emphasize in the development of innovative organisation. Army without essential weapons cannot deliver its full potential. Those needed weapons are knowledge, which has to be developed by best practice training. Companies, such as Hewlett Packard, and Samsung, have committed in training and development programs to help spread innovation capability all over the organisation. Besides internal training programs, offering scholarship, postgraduate study opportunities and international work placement for its staff in 120 offices across 57 countries provide Samsung linkage with renowned universities, also bringing in knowledge and collaboration to the organisation. The by-product from doing so is incentives that help to attract and retain of the best and brightest inventor and businessperson from the global industry.
Extensive Communication
Communication is one of the factors causing failure in investing in ideas that go wrong since the beginning. These are those ideas that do not align with the company’s need. Communication within company about its strategy and customer demands is needed for the clear innovation pathways of researchers. Idea generated from either internal or external organisation must go through many steps of modification before adopting into a company. These steps become troubles for the huge companies. In the case of Samsung, idea management has been introduced to manage ideas from thinkers and distribute them all over the company. They will be evaluated by colleagues, supervisors, or assigned review staffs who add views, opinions and knowledge. In addition to internal communication, networking between firms is also key component in the creation of innovation . The network organisation is a group of several independent companies, which perform different tasks and contract one another. For example, one firm in the network focus on research and product design, another manufactures it, and a third does distribution. This approach gains a wide acceptance as it has strong rationale including rapid change of business environment , the cumbersome of large-size companies, importance of speed and flexibility. Moreover, partners’ collaboration helps to blend and complement different core competency in creating better innovation. Samsung has utilized this concept by building a team, called TechnoValley, undertaking only planning and marketing of product. Other partners in the network took care of technology, production, distribution, and promotion.
High Involvement in Innovation
Building a visionary company requires 1 percent vision and 99 percent alignment. In order to build a sustainable innovation culture, staffs have to practice innovation in everything they do. Practicing to tackle small challenge will make them ready for a bigger challenge. Samsung manager plays an important role in supporting this culture of practicing innovation by encouraging the innovation process and not pushing employees to short circuit the solution process.
External Forces
External forces shapes Samsung to become technology leaders. Previously, closed innovation was the model that Samsung Electronics followed. They invested in the best people and centralized their R&D unit. Today, Samsung cannot depend only on internal innovations, which may create the advanced operating system for mobile phone but not attractive one. Samsung open innovation center established to create striking design and user-friendly interface of Samsung mobile phone. It successfully engaged customers and suppliers in the innovation process at the early stage. Being based in Korea with large group of young technology-concerned consumers provides Samsung an innovative edge in consumer electronics including mobile phones. The replacement rate for mobile phones in Korea is estimated at 6-18 months, thanks to young Koreans who swiftly adapt new technology. Therefore, these trendy people have participated in testing and giving feedback, which provide significant information about customers’ desire. Korea, therefore, becomes an invaluable testing location for innovations prior to the companies unveil them on the world stage.
Creative Climate
Public reward for those who distinguish themselves as mains actor in innovation culture and who promote the value of innovation is the powerful tool to expand innovative thinking throughout the enterprise. There are many examples of escalating the visibility of innovation success, such as the company innovation award, inventor hall of fame. This illustrates the commitment a company have on its innovation and inspire employees by making them proud of their success. Idea management through the use of IT have increased the rate of product and process improvement, as contributions of ideas are traceable. It open up the communication all over the company and promote culture of sharing and creativity. Ideas are developed and talked widely not only in vertical but in horizontal fashion leading to innovative atmosphere. After the introduction of knowledge management solution in Samsung Electronics, there was a change in organizational climate. Employees have been become confident to be more suggestive, trustful, responsive to change, and eager to innovate. Forum and blog postings are the place for knowledge sharing where an automatic rewarding system is executed. The profitability of the products launched, have been chosen as the innovation performance indicators.
Learning Organization
Sharing knowledge and skill of employees brings about innovative performance. Samsung has identified two main challenges in the creation of learning organisation that are knowledge discovery and knowledge sharing. In the past, problems occurred due to lack of knowledge management, for example, lost of valuable knowledge from poor management, or repeating the same failures. To tackle such problems, organizational mechanisms and technological solutions to facilitate the innovation process in Samsung have been introduced. Firstly, Samsung Brainstorming Hours has been arranged to capture and spread ideas in any step of innovation process from idea generation to conversion and commercialization. This is not applied only in the new product development process, but also solving complex problems or business improvement. Two hours weekly meeting for cross-functional team in the room with tall windows, wireless connection, big-screen TV, snacks and drinks is designed to foster innovation process. This comfortable surroundings helps innovation workers to socialise with each other and share ideas. Secondly, company-wide simple but powerful blog has been introduced to encourage knowledge sharing and discovery. The blog helps employees understand and discuss ideas so as to extend previous knowledge continuously. Thirdly, knowledge warehouses have been built to have codifiable critical knowledge stored and accessible throughout Samsung Company. The “Lessons Learned System with Alert function” has been used to manage this knowledge and share it. For storing lesson learned, project managers has been trained about how and what knowledge to collect and given the project management manuals including many useful procedures such as how to write a closing report, how to create and store a project model, how to perform an After Action Review. In order to control overwhelming information, Alerts system notifies employees of newly stored knowledge that might be of interest and useful to their work.
Samsung has successfully transformed from local low quality manufacturer to a brand that produce admirable and stylish consumer electronics. Company performance has proven that Samsung has come to the right direction in last decade. The achievement of becoming innovative organisation started from the declaration to be the global leader in the industry in late 1990s. After the re-configuration and adopting team-working practice, Samsung organisation has been altered to be flexible and organic, leading to ability to develop innovative capability. In addition to the recruitment of the best people into the organization , Samsung has an experimental education tool to identify the key individuals, such as project leader, promoters, or gatekeeper, so as to blend different roles in creating innovation . These people are working under the well-designed knowledge management system and trustful and suggestive communication with the support of supervisors, fostering creative climate. Rewards system for innovative contributor, organisational mechanism and technological solutions has brought about the knowledge discovery and sharing throughout the company, creating learning organisation that sustains Samsung innovation competency.
Related Posts:
- Case Study: The Collaboration Between Sony and Ericsson
- Case Study: Failure of Vodafone in Japan
- Case Study of LG Electronics: Repositioning a Successful Brand
- Case Study on Ad Campaign for Bharti AirTel: "Express Yourself"
- Case Study of Dyson: Competitive Advantage through Innovation
- Case Study: "Intel Inside" Campaign by Intel
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of Samsung
- Case Study of Motorola: Brand Revitalization Through Design
- Competitive Analysis of DELL using Porter's Five Forces Model
- Case Study: The Daewoo Group and the Asian Financial Crisis
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy & Growth Strategies

Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies set business goals for technological innovation as a critical factor in developing competitive advantages. Headquartered in Korea, the conglomerate competes with technology-intensive firms, such as Apple , Google (Alphabet) , Microsoft , Sony , and Intel , which create strong competitive forces, as determined through a Five Forces analysis of Samsung. The industry environment imposes aggressive competitive behavior that typically involves rapid technological innovation for product differentiation, as seen in the evolution of smartphones available in the global market. To effectively compete, Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and growth strategies must involve investment in technological innovation. The resulting competitive advantages enable the company to keep its competitive position as one of the best performers in the semiconductors, consumer electronics, and home appliances industries. Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive strategies for growth are suited to the current business environment and the strategic positioning of the multinational organization’s operations.
The generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies of Samsung Group permeate its entire organization, influencing the strategic choices and implementations of its divisions and subsidiaries. The Group’s unitary leadership is responsible for the corporate strategic direction and competitive advantages of the conglomerate and its technology-focused subsidiaries. Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies are observable in product design, marketing strategies, and the business organizational development direction of subsidiaries.
Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy (Porter Model)
Samsung applies broad differentiation as its generic competitive strategy. Based on Michael E. Porter’s competitive strategy model, the strategic objective of broad differentiation is to maintain competitive advantage by providing unique (or differentiated) products targeting a wide market, which in this case is industry-wide, involving practically every person or group that buys smartphones, laptops, and other equipment. To achieve Samsung’s strategic plans for growth and expansion in the global market, this generic competitive strategy requires the application of product development as a main intensive growth strategy to compete with other technology firms.
Samsung’s investments in product development are a strategic implication of differentiation as its generic competitive strategy. For example, the company invests in technological innovation to support the competitive advantage of its products in the consumer electronics market. Another implication of this generic competitive strategy is Samsung’s marketing mix (4Ps) and related strategies that promote products as unique or different alternatives to the majority of competitors. This marketing approach and technological innovation sustain the corporation’s competitive advantages and value chain effectiveness in satisfying customers’ needs in consumer electronics, computing technology, and home appliances.
Other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership, differentiation focus, and cost focus, are also applied in Samsung’s operations, but to a limited extent. Cost focus leads to the company’s being the best-cost provider in some segments of the semiconductor and electronic components markets. The limited application of cost focus still comes with innovation standards that reflect Samsung’s main generic competitive strategy of broad differentiation. These generic strategies align with the company’s intensive growth strategies to succeed in sustaining the technology firm’s competitive advantages.
Samsung’s Intensive Growth Strategies (Ansoff Matrix)
Market Penetration (Primary) . Samsung’s revenue growth depends on market penetration as the primary intensive strategy. In Igor Ansoff’s matrix, the strategic objective of market penetration is to grow the technology business by increasing its revenues from the sale of current products in current markets, such as the European Union’s consumer electronics market, where the corporation already has operations. Competitive advantages and business strengths identified in the SWOT analysis of Samsung combat negative forces from competition in these markets. As an intensive growth strategy, market penetration depends on the effectiveness of the generic competitive strategy of broad differentiation, in terms of how the company creates technologically innovative products that are differentiated enough to attract target customers in current or existing markets.
Product Development (Secondary) . Considering the emphasis of product superiority in Samsung’s corporate mission and vision statements , product development is a major intensive growth strategy of the enterprise. A strategic objective of product development in this case is to grow the business through new products, such as new electronic gadgets. Also, this intensive strategy grows Samsung’s operations through iterative innovation, which leads to improved versions or variants of existing products. For example, the company regularly rolls out new smartphone models, similar to what competitors are doing in their product development strategy. The implementation of product development as an intensive growth strategy is based on Samsung’s generic competitive strategy of differentiation, which requires product development for uniqueness that differentiates the business from the competition. Economies of scope based on the conglomerate’s various subsidiaries support product development and competitive advantage by providing technological expertise and material inputs from the subsidiaries. Samsung’s organizational culture (work culture) affects human-resource support for operational effectiveness, value chain efficiencies, supply chain management, and other business activities that fulfill the strategic objectives of product development.
Market Development . The global scale of Samsung’s operations makes market development a minor intensive strategy for business growth. Market development’s strategic objective is to enter new markets using the company’s existing products, such as introducing new Galaxy tablets in Latin American markets after these products’ introduction in the United States. As an intensive growth strategy, market development’s success depends on product value and competitive advantage, which in this case comes with Samsung’s generic strategy of differentiation via technological innovation. For example, effective innovation for cutting-edge technological design makes the corporation’s products more competitive when rolled out in target markets. With this intensive growth strategy, introducing products to new markets may come with changes in the geographical units of Samsung’s organizational structure (company structure) .
Diversification . Samsung’s diversified business operations maintain multiple revenue channels and spread risk across industries and markets. This intensive growth strategy’s implementation is infrequent in the technology conglomerate, considering regulatory hurdles and other barriers. With the strategic objective of establishing new profitable businesses, the diversification strategy grows Samsung typically through acquisitions of smaller firms, such as Harman International Industries. The minor role designation of this intensive growth strategy limits the risks of establishing new business operations. In implementing diversification, the generic competitive strategy of differentiation is also applied for competitiveness and strategic alignment among Samsung subsidiaries’ business operations.
Some Considerations – Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy & Intensive Growth Strategies
Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies direct the organization’s growth and development. Differentiation plays a major role in building the company’s competitive advantage, although other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership and focus strategies, also support the technology enterprise and its competitiveness. Samsung’s operations management strategies and administration must align with the differentiation generic competitive strategy and the intensive growth strategies to support business growth while competing with aggressive multinational companies.
- López, D., & Oliver, M. (2023). Integrating innovation into business strategy: Perspectives from innovation managers. Sustainability, 15 (8), 6503.
- Samsung – Brand Identity .
- Samsung R&D Center .
- Samsung Catalyst Fund .
- Taherdoost, H. (2023). An overview of trends in information systems: Emerging technologies that transform the information technology industry. Cloud Computing and Data Science , 1-16.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
- SMB Technology
- Mobile Productivity
- Mobile Security
- Computing & Monitors
- Memory & Storage
- Digital Signage
- Trending Tech
- Hospitality
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Food & Beverage
- Live Events & Sports
- Spectaculars & DOOH
- Gaming & Esports
- White Papers
- Infographics
- Assessments & Calculators
Case Studies
- About Samsung Insights
- Our Experts
Subscribe to Insights
Get the latest insights from Samsung delivered right to your inbox.
See our Privacy Policy
Samsung Business Insights
All Case Studies

The Wall powers collaborative design at Lucid Motors
While reviewing new designs, the design team at Lucid Motors benefits from the high-definition image quality and color resolution on Samsung’s The Wall.

Hilton Waikiki Beach welcomes and wows guests with The Wall
Located above the main lobby bar, Samsung’s The Wall in the Hilton Waikiki enhances the experience for both guests and locals. Hospitality TVs in guest rooms and other Samsung displays throughout the property elevate the property.

Buona Beef selects Samsung Kiosk for its digital transformation
Buona Beef, a renowned Chicago brand, added Samsung Kiosks to their locations to increase sales and efficiency of service.

West Sayville Fire Department leads the way with interactive displays
Samsung digital signage throughout the West Sayville Fire Department improves operations, communications, and productivity for all its members.

Miami high school’s connected campus elevates education and engagement
College preparatory Christopher Columbus High School recently outfitted their campus with Samsung display technology to create a connected campus. Interactive whiteboards in the classroom promote effective, collaborative learning, while digital signage throughout the campus streamline communication for all.

The Wall brings digital excellence to Syracuse University
The S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications at Syracuse University installed Samsung's The Wall to provide a wow factor to current and prospective students.

Stevens Institute of Technology gets on board with interactive boards
Stevens Institute of Technology in Hoboken, NJ uses Samsung interactive whiteboards throughout classrooms and meeting rooms for hybrid classrooms and in-person collaboration.

The Wall brings design at the Hyundai America Technical Center to life
The Wall's MicroLED technology gives designers at Hyundai America Technical Center true to life renditions of their design.

Samsung’s The Wall hits the right notes in Clive Davis’ home theater
Five-time Grammy winner and legendary record producer Clive Davis upgraded his at-home theater with Samsung’s The Wall.

Interactive whiteboards promote learning, collaboration at Hogg New Tech Center
The James S. Hogg New Tech Center elementary school replaced its aging technology with versatile, interactive displays, enabling teachers to create more immersive learning experiences and students to collaborate more effectively and creatively.
- Open access
- Published: 21 October 2019
Planting and harvesting innovation - an analysis of Samsung Electronics
- Seung Hoon Jang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7984-7383 1 ,
- Sang M. Lee 2 ,
- Taewan Kim 3 &
- Donghyun Choi 4
International Journal of Quality Innovation volume 5 , Article number: 7 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
21k Accesses
1 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
This study explores how firms manage the entire life cycle of innovation projects based on the framework of harvesting and planting innovation. While harvesting innovation seeks new products in the expectation of financial performance in the short term, planting innovation pursues creating value over a long time period. Without proper management of the process of planting and harvesting innovation, firms with limited resources may not be successful in launching innovative new products to seize a momentum in high tech industries. To examine this issue, the case of Samsung Electronics (SE), now an electronics giant originated from a former developing country, is analyzed. SE has shown to effectively utilize co-innovation to maintain numerous planting and harvesting innovation projects. Both researchers and practitioners would be interested in learning about how SE shared risks of innovation investment with external partners at the early stage of innovation cycles.
Introduction
Globalization and advances in technologies have made the global market extremely dynamic and competitive. While companies like Apple have created new customer value by introducing such products as iMac computer and iPhone, many other firms have failed to adapt to the fast-changing environment. Kodak, the creator of the film camera, became history since it failed to adapt to the digital era in a timely fashion. To compete successfully in the dynamic global market, organizations must continuously innovate ways to create value [ 1 ]. Thus, innovation has been an important topic to both management researchers and practitioners [ 2 ]. Many studies have explored the relationship between innovative activities and organizational performance [ 3 , 4 ]. The firm’s ability of managing innovative projects has been considered as a key dynamic capability, resulting in new product development [ 5 ]. Innovative activities of the firm have generally shown to positively impact organizational outcome.
Although a number of studies in this research stream have introduced various types of innovation based on learning styles [ 6 , 7 ] or objects [ 3 ], few have paid attention to the timing of financial return from innovation. Given the importance of financial payoff from innovation for firm survival and sustained competitive advantage, research on how a real business should manage both innovation and cash flow is critical. Thus, in this study, we intend to answer the following two research questions.
RQ1: Which classification of innovation can best explain the heterogeneous timing of financial payoff realization?
To answer this question, we applied a classification scheme of planting and harvesting innovation [ 8 , 9 ]. Planting innovation involves pursuing potential sources of competitive advantage, including original technology, which may create value in a long term perspective. In contrast, harvesting innovation aims to develop new ways to monetize planted innovation, including new products for market launching, in the expectation of commercial success in a relatively short term. The aim of this research stream is to determine how to implement planting and harvesting innovation and measure the results of ensuing innovative activities. From this perspective, this study examines how a real global firm manages both types of innovation.
RQ2: How are planting and harvesting activities of innovation actually implemented in a successful global business firm?
To answer this question, we focus on Samsung Electronics (SE) which has become the world’s largest electronics firm through successful planting and harvesting of innovation. While SE has developed many innovative new commercial products, it has focused on fundamental breakthrough technologies as the source of future growth momentum. This case may provide valuable implications for firms from developing economies. To compete in high tech industries, these businesses need to invest a large amount of capital to risky innovation projects. Otherwise, they may remain low value added entities, like assemblers or fast followers. The case of SE, like many other success stories, exhibits a possibility that multinationals originated from developing countries can become leading global firms based on their efforts and vision for breakthrough innovations.
Given the current turbulent global business environment, as observed by trade disputes between the USA and China and the recently disrupted supply of critical input resources from Japan to Korea, it is imperative for firms to develop core competences based on innovation. In the digital age, businesses must rely on innovation to enhance their dynamic capabilities [ 10 ] to enhance agility, flexibility, and resilience for value creation [ 1 ]. Thus, this study which focuses on the effective management of planting and harvesting innovation is expected to make important contributions to the literature.
This study examines how firms can implement innovation projects for both short- and long-term perspectives. For this purpose, we first reviewed the literature for major research streams of innovation. Then, a case method is used to examine how planting and harvesting of innovation have helped SE became a dominant global electronics firm, around 2012. In addition to secondary data, executive interviews reported in media also describe how SE employees implemented planting and harvesting innovation. The results of qualitative analyses are presented and articulated. Finally, the implications and limitations of this research are presented. The framework of planting and harvesting innovation provides a theoretical background on how firms can strive for both short-term cash flow and a long-term momentum despite their limited resources. Furthermore, the study results provide insights to practitioners through the case study of SE which struggled initially to save the cost of innovation by collaborating with external partners for planting and harvesting innovation.
Innovation under resource constraints
Planting versus harvesting innovation.
Researchers in various fields, including economics, sociology, and technology management, have been interested in innovation [ 11 ]. The characteristics of innovative outcomes have been investigated as a major research agenda [ 12 , 13 ]. As Damanpour and colleagues [ 14 ] suggested, the introduction of novel ideas or technologies is the core of innovation. According to Van de Ven [ 15 ], innovation can be described as “the development and implementation of new ideas by people who over time engage in transactions with others within an institutional order ([ 15 ], p590).” Several definitions of innovation have focused on how to apply creativity to business operations and processes [ 15 , 16 ]. These studies imply that the main focus of innovation research has been on whether the firm creates new tangible or intangible values.
However, innovation has shown to lead to varied results. The meta-analysis by Rosenbusch et al. [ 17 ] reported that different contexts explain heterogeneous outcomes resulting from innovation. Even if firms implement similar innovation projects, the result can be different due to environmental factors. In addition, innovation sometimes improves the value of marketing skills rather than creating new technical capabilities [ 18 , 19 ]. What these results imply is that characteristics of innovative activities are complex. Since a single concept cannot explain the nature and outcome of innovation, researchers need to consider diverse classifications to explain the phenomena of innovation. Given the importance of cash flow in business, a greater focus is required on the influence of innovation on the survival and prosperity of the firm. Even when firms obtain breakthrough technologies, they may not survive when they fail to create new products/services and resulting cash flow as discussed by Jang [ 8 ] and Jang and Grandzol [ 9 ]. Furthermore, the large amount of investment needed for innovative activities requires firms to prioritize and manage their projects based on the commercial potential. Thus, there is a need to search for a new framework that can provide better explanations on innovation with respect to this issue. The most existing classifications of innovation are not based on the timing of financial outcomes of innovative activities.
One of the typologies regarding this topic is the categorization of radical and incremental innovation based on the sharpness of change in innovative practices [ 20 ]. A more drastic transformation can be expected from radical innovation projects while a relatively slight newness can be added to existing technologies during the incremental innovation process. Since radical innovation can pursue both drastic breakthrough and immediate commercialization, there exists the disparity between the distinction of radical and incremental innovation, the main focus of this paper. Space shuttle can be considered as an example of radical innovation as the realization of reusable spacecraft but it is generally considered as a product for immediate use rather than a long-term growth momentum. Such discrepancy leads researchers to develop a new categorization of innovation based on the expected timing of financial outcome.
The Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA) wireless technology is an interesting case for this point. The CDMA technology was developed by Qualcomm ( www.qualcomm.com ), but the commercial CDMA phones were first created and produced by Korean manufacturers, including SE and LG. While Qualcomm was interested in developing CDMA as planting innovation, SE and LG focused on commercializing the technology for harvesting that innovation. Qualcomm could benefit from licensing fees in the long term with the success of commercial products based on CDMA. In contrast, the short-term cash flow was derived by SE and LG as they sold more CDMA phones to individual consumers.
From this perspective, innovation can be categorized based on its relatedness to the firm’s performance in the short or long term [ 8 , 9 ]. While certain types of innovative activities may result in an increase of the firm resources engaged in the current competition, others can create value that has long-term potential. This approach modifies the definition of innovations by Gumusluoglu and Ilsev [ 21 ] as described in Jang [ 8 ] and Jang and Grandzol [ 9 ]. First, harvesting innovation can be described as the development of a new resource that can help launch new products/services in the short term. New products, such as Toyota Prius, would be a good example of this type of innovation. Planting innovation refers to the creation of potential firm resources that are based on the state-of-the-art innovation in the expectation of long-term financial benefits. For instance, the invention of hybrid engine technology “plants” potential for future value while the creation of a hybrid car like Prius “harvests” the results of the planting of that innovation.
There are several reasons why planting innovation may not result in new commercial products/services in the short term. First, there may be social constraints that would not allow the use of innovative technology, resulting in no market for new products/services. The commercial use of human stem cell research in the USA has been prohibited by the Food and Drug Administration [ 22 ]. Firms initiating planting innovation in this area cannot expect commercial success due to this regulation, except perhaps in other countries. Second, firms may need to wait for the advent of other complementing technologies for the commercialization process. Thus, firms face a high degree of uncertainty about the financial outcome of planting innovation in the long term, especially in the biotech industry. The development of a new technology usually has a high probability of failure. Therefore, planting innovation may not lead to financial gains in the short term even if firms succeed in developing a technology.
The characteristic of planting innovation makes it distinct from invention. Innovation requires entrepreneurial utilization of technological newness by definition, while invention includes scientific and/or technological breakthrough for discovery purposes [ 23 ]. Firms invest in planting innovation projects in the expectation of long-term profits. Although the result of planting innovation may directly create cash flows in the form of patent fee, firms usually wait until finding out how to apply the result of planting innovation. In contrast, harvesting innovation pursues short-term profits by launching new products or services. In the 1970s, the Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) at Xerox initiated the development of innovative technologies such as Ethernet (or LAN technology) and copper wire-based Ethernet communication [ 24 ]. Due to the lack of commercial intention of Xerox both short and long term, these developments can be classified as examples of invention rather than planting innovation.
Given the heterogeneous characteristics of planting and harvesting innovation, ambidexterity can be important in balancing such innovative activities. Studies on exploitative and explorative innovations have examined this issue [ 6 , 7 , 25 ]. Since pioneering efforts for new processes or technology involve much risk, firms need to optimize the return of their investment in both types of innovation. One possible approach is to utilize external capabilities through M&A, alliances, or industry-academia collaborations through open innovation. Such arrangements would allow firms to share the risk of innovation with other participants [ 1 ].
In addition, convergence has played a major role in explaining value added activities in modern firms [ 1 , 26 ]. Globalization has encouraged the convergence revolution which allows value creation from the synergy of diverse disciplines, industries including IT, biotechnology, and nanotechnology [ 26 ]. The co-innovation platform helps converge diverse types of innovations for value creation [ 1 ]. Multinationals participating in co-innovation are expected to collaborate with stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, partners, and outsiders. Therefore, outside stakeholders can be active partners who co-create shared goals.
Overall, the classification of innovation can contribute to research by providing clearer guidelines related to the timing of financial outcome of innovation. While planting innovation can result in potential resources for long-term value creation, harvesting innovation is intended to generate continuous cash flows to those engaged in the current market. Following the case of exploitative and explorative innovation, researchers in this field should also consider ambidexterity of the organization. By doing so, firms under resource constraints can be prepared for an optimal portfolio of innovation projects, resulting in better organizational performance in the long term.
- Case analysis
In this study, the case of Samsung Electronics (SE), now the largest electronic firm in the world from a former emerging economy, is examined to unveil the processes of harvesting and planting innovation and their results. Innovative activities have been the core strength of SE and are expected to continue creating value for SE. The Mission 2020 of Samsung ( http://www.samsung.com ) states that it will “inspire the world, create the world” through creative and innovative solutions. This implies that the firm intends to pursue innovation over time beyond the development of commercial products for short-term returns.
Several qualitative techniques are employed to investigate the SE case. First, we collected articles including executive interviews from 2000 to 2012. The articles were manually coded into planting and harvesting innovation frameworks after a careful review of contents. News reports were analyzed via local portal sites, including Lexis-Nexis ( http://www.lexisnexis.com ) and Naver ( www.naver.com ). Particularly, we searched Naver, the major Korean portal website, to collect news articles concerning SE research topics from 2002 to 2012. We chose this period, 2002 and 2012, to collect data for this study as this is when SE made the significant transformation to become a dominant global IT leader. The search keywords used were “Samsung Electronics” and “Innovation.” The search using the keywords assured the study to verify that all related articles are captured. After removing duplicates, we investigated the contents of 183 related news articles. Based on the analysis, all the key interviews of executives and managers at SE were collected and examined. In addition, the other secondary data sources like the websites of companies, universities, and local governments were examined.
Samsung Electronics
SE has been a major global player in electronics and related industries for over three decades. Hoovers ( www.hoovers.com ), a leading corporate information provider on large businesses, describes the overall state of this firm as the new “Electronics Samson.” In year 2015, it reported $171 billion revenue and $16 billion net profit. Its major products include digital electronics, semiconductors, and DVD players. Financial Times ranked Samsung Electronics as 19th in their 2015 FT Global 500 ( www.ft.com/ft500 ). It is beyond doubt that this firm has been successful in creating value for its customers.
The webpage of Samsung Electronics ( www.samsung.com ) and Samsung C&T ( www.samsungcnt.co.kr ) describes the history of Samsung Group and Electronics as follows. Samsung group was founded in 1938 as a small retail firm in Daegu, Korea. The founding chairman, Lee Byung-Chull, established Samsung-Sanyo Electronics to diversify the business in 1969. As the name implies, the firm collaborated with Japan’s electronics giant Sanyo. It began production of black-and-white TV sets for the first time in 1970, as an outsource manufacturer. After changing its name to Samsung Electronics, the firm began to produce color TV sets, video recorders, microwaves, and personal computers. It has rapidly developed as a global firm since it entered the semiconductor industry in the early 1980s. Since South Korea has recently been accepted as a developed economy [ 27 ], it can be said that SE began as an emerging market firm.
Given the fact that SE was founded only about five decades ago, the current performance and growth are astonishing. Despite the current status, the firm used to be considered as a fast follower [ 28 ]. SE had focused on producing existing products with better quality at lower prices than other global firms. It is an interesting research topic to examine how and why SE has evolved into a global giant in the electronics industry.
To provide an explanation on this issue, we investigated how SE has implemented innovation to achieve strategic objectives. In 2001, President of Booz Allen and Hamilton Korea stated that Korean firms need to pursue breakthrough innovations to adapt to new market environments [ 29 ]. In other words, SE as well as other major Korean manufacturers began to pursue innovation rather than continue to follow market leaders to survive in the dynamic global marketplace.
Harvesting innovation at Samsung Electronics
SE has engaged in various innovation activities to gain global competitive advantage. By doing so, the firm has been able to create value and benefit from new markets with expectations of stable cash inflows. For instance, SE developed new products like Rambus DRAM and Nand flash memory rather than increasing the accumulation rate of semiconductors [ 28 ]. Since these new products reflect the needs of customers, including PC or smartphone manufacturers, the innovation brought a large amount of profit in the short term. Given the astonishing results that SE has accomplished, its process of harvesting innovation has drawn much attention.
SE has continued implementing innovative activities steadily. The Value Innovation Program (VIP) Centre, setup in 1998, has played a key role in developing innovative new products at SE [ 28 , 30 , 31 ]. This Centre has shown to nurture creativity and broaden the ideas of R&D staff. As the chief researcher at SE stated, the introduction of value innovation methods has contributed to the creation of many new ideas [ 28 ]. Through this system, all participants were expected to overcome the trap of past success syndrome, leading to what is possible.
Blue Ocean Strategy (BOS) [ 32 ] has been the backbone of the harvesting innovation process at SE [ 30 ]. SE invited W. Kim, the main author of BOS, to train its executives. Senior executives have encouraged the dissemination of value innovation at SE based on the BOS approach [ 33 ]. SE strives to create value which its customers never even expected through value innovation for new products. SE’s value innovation includes value management and value creation [ 33 ]. While the former focuses on cost reduction and efficiency improvement, the latter aims to generate added value. Therefore, the firm searches for creative ideas rather than implementing traditional continuous improvement type programs.
SE has found practical tools to implement harvesting innovation based on BOS [ 31 ]. First, the VIP Centre has utilized the strategy canvas, a framework of implementing BOS [ 32 , 34 ]. In the Centre, managerial decisions on important projects have been made based on the value curve of each unit against competitors, resulting in new products like 40-inch LCD TV. In addition, the “7 Tools Method” practiced in Japan, which enables firms to empirically recognize value factors of their customers, was introduced [ 35 ]. For instance, a survey of 226 Japanese employees triggered the production of a laptop that works well even in a bad wireless environment. These types of techniques have helped SE create new products successfully by reflecting innate needs and requirements of individual and business customers.
It has been reported that all of the creative ideas from the VIP Centre have been reflected in the design and development of new products of SE [ 36 ]. As a result, innovativeness of the firm’s new products has been globally recognized as the numerous Innovation Awards of the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) attest (see Table 1 ). These achievements prove that the innovative results of SE have been widely recognized by professionals in the field as well as ordinary customers. SE has succeeded in developing new products through harvesting innovation activities.
Planting innovation at Samsung Electronics
SE has also focused on the creation of innovative ideas which may not realize any meaningful revenue in the short term. The major results of planting innovation are original technologies which can result in competitive advantage and lead to future business success. The CEO of SE stressed the importance of “technology preparation management,” pursuing core technologies in order to respond to the convergence across technologies and products [ 37 ]. This statement exhibits the strong will of top management of SE to implement the planting innovation strategy.
The Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT) has played a critical role in developing original technologies. The website ( www.site.samsung.com ) describes the research efforts currently in place. The Future IT and Convergence domain seeks technologies across real 3D processing, communication theory and network, multicore processing, data intelligence, and medical imaging. The New Materials and Nanotechnology domain aims at developing flexible electronics, solid state lighting, film ceramic crystal composite materials, micro-system integration, oxide materials and devices, spintronics, and nanostructure and materials research. The Energy and Environment domain focuses on energy storage, energy conversion, and environment fields. The Bio and Health domain explores gene analysis and point of care testing (POCT). Indeed, SE has encouraged researchers to create a broad range of intellectual capital for the purpose of leading future technologies.
Furthermore, it seems likely that SE seeks Chesbrough’s [ 2 , 38 ] open innovation to improve efficiency and effectiveness of planting innovation. By doing so, the firm can create innovative results with less burden in time and resources. The CEO mentioned that open innovation needs to be encouraged to shorten the technology life cycle and to enable convergence in the electronics industry [ 37 ]. Thus, SE senior managers have aggressively focused on the utilization of external ideas and capabilities [ 39 ].
M&A has been a major instrument to acquire external intellectual capital. SE has acquired several firms, including SanDisk, Amica (a Polish electronics firm) in 2009, and Transchip (a non-memory semiconductor manufacturer in Israel) in 2008 [ 40 ]. SE informed the board of directors of SanDisk about its intention of collaborative innovation orientation and human resource retention in SanDisk [ 41 ]. Such M&A activities have enabled SE to obtain proven and complimentary intellectual capital and dynamic capabilities, including R&D employees.
SE has also managed a broader range of intellectual capital without much investment by sharing their proprietary technologies with partners. For example, SE and IBM, two top US patent firms, established a cross-licensing agreement which allows the participants to utilize each other’s patents for innovation in 2011 [ 42 ]. These firms can share their patents without additional investment, resulting in a more stable basis for innovative activities. This type of contract enables SE to implement planting innovation with finite capabilities. Executives of SE and IBM also announced that the objective of cross-licensing lies in sharing intellectual capital in the expectation of continuous innovative outputs. In sum, SE has implemented planting innovation through SAIT internally and has utilized external capabilities through M&A and licensing for significant financial gains in the long run. SAIT has implemented several major research projects independently as well.
Ambidexterity and co-innovation
Since SE is implementing planting and harvesting innovation simultaneously, one major task is balancing both types of innovative activities. Otherwise, the firm may suffer from lack of financial cash flows or future leadership in the industry. Despite their brand image, major manufacturers of wristwatch had to overcome the loss of sales volume in the 1970s due to the revolutionary quarts movement technology [ 43 ]. Although US electronic giants initiated the transistor technology, Japanese manufacturers like Sony harvested the lion’s share of its benefits with their transistor radios [ 44 ].
The significance of inter-organizational cooperation in attaining competitive advantage cannot be ignored [ 45 ]. Thus, any organization, however large or global it may be, cannot be competitive for long without collaboration with other world-class partners. From this perspective, the success or failure of firms today lies in managing the relationships with other value chain partners and stakeholders [ 4 ].
Beyond the conventional exploration and open innovation focusing on the use of external resources, SE has been searching for the best way to simultaneously implement planting and harvesting innovation through co-innovation with stakeholders [ 1 ] (see Fig. 1 ). The main focus of the VIP Centre has been on how to encourage collaboration among internal departments. Resulting convergence across departments has enabled the firm to recognize the diverse viewpoints other than the opinions of core engineers. The VIP Centre director stated that those firms interested in value innovation need to adopt the cross-functional team (CFC) concept with a separate space to promote inter-departmental collaboration for value innovation [ 34 ]. This process is expected to encourage formal and informal sharing of ideas, opinions, and viewpoints since participants have more opportunities to communicate with many people. For instance, the CFC team consisting of marketers, designers, and engineers developed a new slim style laptop which caught the fancy of Japanese consumers [ 35 ]. Furthermore, the members of the Centre frequently collaborate with external partners [ 35 ].
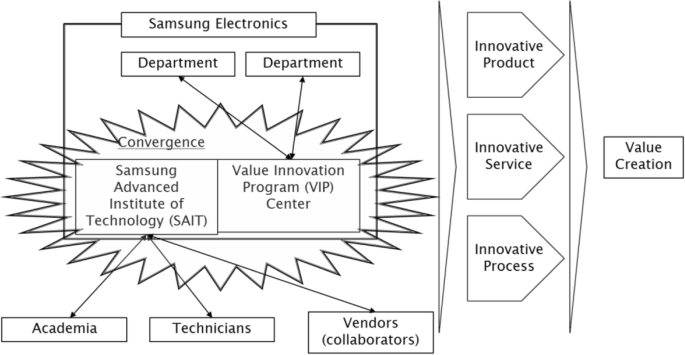
Co-innovation at Samsung Electronics. Based on the information from SAIT ( www.SAIT.samsung.com ) and Kim’s [ 35 ] study
SAIT has played a significant role in connecting SE with external entities ( http://www.sait.samsung.co.kr ), such as universities, through the Global Research Outreach (GRO) program and other collaborators via the Collaborative Open Research Expert (CORE) program. These efforts have allowed the firm to share the risks inherent in planting innovation. Thus, the firm has been able to reduce the uncertainty involved in innovative practices and maximize its value with finite organizational resources.
Another example of collaboration lies in its value-chain management beyond the use of external capabilities. An association of Samsung’s collaborating vendors, Hyup-Sung-Hoe, has played a key role in co-innovation processes [ 46 ]. SE and collaborating vendors have participated in innovation activities, including sectional committee meetings. It is evident that SE’s innovation activities cover not only its own value chain but also that of its partners. Given the fact that current business activities must include vendors, the improvement of innovation capabilities of the entire value chain is essential for gaining competitive advantage. SE also considers the creation of new ventures with excellent technologies as another outcome of its open innovation strategy [ 47 ]. The firm manages its entire value chain to compete successfully, as opposed to conducting business with partners for short-term monetary rewards. Figure 1 presents SE’s value chain convergence activities.
SE has participated in the various industry-academia collaboration projects. This partnership has enabled SE to interact with partners to utilize their tangible and intangible resources. Particularly, research universities can provide professional human resources, research expertise, and infrastructure. In 2012, SE established the Centre for Intelligent Computing (CIC) with Seoul National University [ 48 ]. While the former supports the facilities and programs, the latter provides research ideas and its faculty resource. Such projects allow SE to benefit from the results of collaborative innovation while sharing the burden of investment. Furthermore, individual participants would likely to share ideas and opinions due to their “relationships” even after the official project is completed, beyond organizational boundaries. SE has also established the Samsung Talent Program (STP) with 14 Korean universities [ 48 ]. This program is intended to nurture and develop R&D employees to fit its needs.
The use of a co-innovation mechanism has played a key role in managing planting and harvesting innovation with limited organizational resources. SE has established networks with the various innovation partners, including diverse internal departments, academia, technicians, customers, and suppliers to collaborate and co-create for shared goals. In addition to external resources, the closely interconnected relationships among participants are expected to nurture collective intelligence. Overall, co-innovation allows SE to manage both types of innovation, harvesting and planting, while coping with its fast expanding global presence.
Firm performance
The innovation investment of Samsung Electronics has shown tremendous financial return as can be seen in Fig. 2 . The financial information from Daum ( www.daum.net ), a major portal site in Korea, exhibits that SE’s sales volume has dramatically increased since the early 2000s. As SE has paid more attention to harvesting innovation, its sales volume surged from 2001 to 2004. This implies that the firm continued its growth by actively pursuing innovative activities which created much financial gain in the short term.
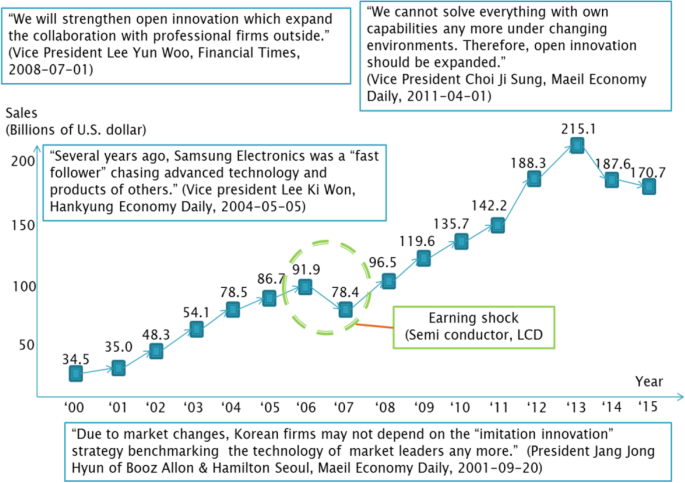
Annual revenue of Samsung Electronics. Based on the financial information from Daum ( www.daum.net ) and Hoovers ( www.hoovers.com ) and news articles from Naver ( www.naver.com )
The revenue of the firm diminished drastically in 2007 with the global financial crisis. This “earning shock” was due to the decrease of demands for LCDs and semiconductors [ 49 ]. The global economy was in recession for several years afterward. For example, in 2012, the Federal Reserve Bank announced that the net asset of median family in the USA decreased by 38.8% from December 2007 to June 2009 [ 50 ]. Given that the consumption of middle-class families in the USA has been the locomotive of global economy for decades, the effect of the macro-economic crisis would be challenging for many global firms.
SE executives began to search solutions for the creation of original technologies, while continuing its innovation harvesting efforts. Despite the global financial crisis, SE has continued its growth [ 50 ]. In 2017, the revenue was approximately $224 billion [ 51 ]. SE has steadily expanded its business after it introduced harvesting and planting innovation despite the hostile macro-economic environment and recent ownership succession.
Discussion and evaluation
This study investigated planting and harvesting innovation to answer the research question, “Which classification of innovation best explains the heterogeneous timing of revenue realization?” While harvesting innovation seeks commercial results in a relatively short term, planting innovation pursues the development of new ideas and technologies for a long term. For instance, a firm with the CDMA wireless technology may not succeed financially without the dispersion of CDMA phones. Given the finite amount of resources, firms need to efficiently balance planting and harvesting innovation. Otherwise, they would fail to develop both new products/services for market launching and original technologies for future market expansion while continuing their business activities.
A case analysis was employed to answer the second research question, “How are planting and harvesting activities of innovation implemented in a successful global business firm?” Samsung Electronics (SE) was chosen as a case study since it has become the largest electronics firm in the world but originated from a former emerging economy, South Korea. Despite its limitations, SE continued to grow by using innovation as a vehicle to move from an outsourcing firm to a global leader in innovation. It is a dramatic success story for a local firm in Korea which began its business in the 1970s. Since SE established innovation as the core of its business activities in its mission statement, it has implemented the dual strategy of planting and harvesting innovation.
SE has participated in various activities to develop innovative new technologies as well as products. The interviews reported were collected from news articles to analyze the stream of innovative activities of SE. Harvesting innovation has led to the initiation of a broad range of new products, allowing the firm to access global customers and also received world-renowned innovation awards. SE has also focused on planting innovation which can result in original technologies. Based on Blue Ocean Strategy, the Value Innovation Program (VIP) Centre has been primarily responsible for developing new products. The Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT) pursues original technologies which can continuously support technological leadership in the years to come.
Co-innovation [ 1 ] has enabled SE to focus both planting and harvesting innovation activities with limited resources. External collaborators have contributed to the application of SE’s tacit knowledge for convergence that is difficult to imitate by competitors. The VIP Centre and SAIT have played a critical role in encouraging collaboration among innovation value chain partners, including academic researchers, technicians, vendors, and customers to co-create value. It has enabled the firm to pursue innovative outcomes while managing financial stability. The financial performance of SE exhibits that its innovation activities have resulted in a remarkable success.
Conclusions
The digital age is characterized by the increased complexity and uncertainty of the business environment [ 1 ]. In the environment of increasing velocity of change, business firms must develop dynamic capabilities through innovation to adapt to change with agility, flexibility, and speed [ 4 ]. There have been various innovation approaches in the literature: exploitative vs. explorative [ 7 ], disruptive [ 52 ] vs. non-disruptive [ 53 ], ambidexterity [ 54 ], and convergence innovation [ 55 ]. However, the purpose of innovation remains the same, which is to create new or added value by applying ideas or technologies in a fundamentally different way [ 1 ]. What is not widely known is that innovation is not one integrated process. Instead, there are several steps and cycles in innovation. Planting innovation involves creating new ideas, scientific breakthroughs, or new technologies. Planting seeds does not guarantee a good harvest. Many nurturing steps such as careful planning, risk taking, and entrepreneurship are needed to have a successful harvest. Thus, studying the most spectacular success transformation case of SE through its innovation process provides meaningful theoretical and practical insights and a contribution to the literature of innovation.
This study is not free from limitations. Although SE can be considered as one of global leading innovators originated from Korea, a success story from one of the poorest countries in the world to an advanced economy, the generalizability of the single case study can be limited as Tversky and Kahneman [ 56 ] suggested. Future researchers should conduct relevant studies in various contexts to overcome such limitation. In addition, the qualitative analysis tool of Gibbert et al. [ 57 ] can be used to lessen the concern on generalizability.
There are many factors that have contributed to the success of SE. In this study, we used the revenue as the reference of SE’s efforts of harvesting innovation. There could be many other factors that contributed to the performance of SE. However, we believe these factors all contributed to the combined efforts of SE in harvesting innovation.
In addition, it is also expected that future studies may apply more refined research methods to examine the process and consequences of planting and harvesting innovation. While we believe in the merits of the research method applied in this study, it is also possible that executives might have exaggerated the process and outcomes of their projects. Future researchers are expected to cross-check the results of planting and harvesting innovation by utilizing multiple research methods.
Despite the limitations, this research provides several meaningful implications. It uses a distinction of planting and harvesting innovation [ 8 , 9 ] to examine how a firm grows into a global leader despite its finite managerial and financial resources. While planting innovation aims to implement technological advancement as a potential source of long-term profits, harvesting innovation focuses on the development of new products for market expansion in the short term. The framework of planting and harvesting innovation is expected to provide a tool for managers to distribute limited funds for various types of innovation projects. It shall enable them to clarify whether the current focus of innovation investment lies in launching new innovative products or seeking competitive advantage for future profits. The case of Samsung Electronics exhibited that its innovation has focused on both short-term profits and technological innovation for the future growth momentum. Firms are recommended to follow this notion to compete successfully in high tech industries with limited financial, technological, and managerial competencies.
Collaboration is also required for firms seeking both planting and harvesting innovation. Given their shortage of resources and competencies, firms need to share the risks and the burdens of innovation projects with external partners. Following the case of Samsung, they are expected to cooperate with various entities, including research institutions, suppliers, customers, or new ventures. It enables firms to afford the cost of breakthrough innovation despite their finite resources and experiences. Collaboration helps these firms create innovation results for advanced as well as emerging economies.
This study also provides implications from methodological perspectives (Table 2 ). The use of indirect interviews from news articles allowed us to observe the opinions of SE executives over time. In addition, it can collect the opinions of executives at the time of innovative activities rather than asking current employees’ perceptions about what happened in the past. It provides future researchers with an effective method for exploratory research. The use of this underused but promising methodology can contribute to overcoming the limitations of research in the management field despite its possible limitations.
Practitioners can obtain lessons from the results of this study. They could observe how SE, a former emerging market firm, dispersed investment risks by collaborating with the various stakeholders to implement planting innovation. The convergence of internal and external ideas, from suppliers, academia, other businesses, and customers, is essential for the implementation of both types of innovation with finite resources. Furthermore, they need to nurture innovative capabilities of entire internal and external stakeholders as co-innovators. This shall allow firms to achieve the network effect of innovation.
As suggested by Lee [ 4 ], the main focus of innovation projects has been on how to benefit business activities in new ways. Lee [ 58 ] and Schniederjans and Schniederjans [ 59 ] also examined how practical operational issues like quality practices can be improved by innovation.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Blue Ocean Strategy
Consumer Electronics Association
Cross-functional team
Centre for Intelligent Computing
Collaborative Open Research Expert
Global Research Outreach
Palo Alto Research Center
Point of care testing
Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology
Code-Division Multiple Access
Samsung Talent Program
Value Innovation Program
Lee SM, Lim SB (2018) Living innovation: from value creation to the greater good. Emerald Publishing, Bingley, U.K
Book Google Scholar
Chesbrough H (2003) Open innovation: the new imperative for creating and profiting from technology. Harvard Business School Publishing, Boston, MA
Google Scholar
Damanpour F, Walker RM, Avellaneda CN (2009) Combinative effects of innovation types and organizational performance: a longitudinal study of service organizations. J Manage Stud 46(4):650–675
Article Google Scholar
Lee SM (2018) Innovation: from small “i” to large “I”. Int J Quality Inno. 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-018-0022-4
Lawson B, Samson D (2001) Developing innovation capability in organizations: a dynamic capabilities approach. Int J Innov Manage 5(3):377–400
He Z-L, Wong P-K (2004) Exploration vs. exploitation: an empirical test of the ambidexterity hypothesis. Organ Sci 15(4):481–494
March J (1991) Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning. Organ Sci 2(1):71–87
Jang S H (2012) Ownership structure, absorptive capacity, and innovation: planting vs harvesting innovation (doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/businessdiss/29/
Jang SH, Grandzol C (2014) Value co-creation in emerging economies: planting and harvesting innovation perspectives. Int J Serv Sci 5(3/4):171–181
Teece DJ (2014) The foundation of enterprise performance: dynamic and ordinary capabilities in an (economic) theory of firms. Acad Manage Perspect 28(4):324–338
Gopalakrishnan S, Damanpour F (1997) A review of innovation research in economics, sociology, and technology management. Omega 25(1):15–28
Nohria N, Gulati R (1996) Is slack good or bad for innovation? Acad Manage J 39(5):1245–1264
Johannessen JA, Olsen B, Lumpkin GT (2001) Innovation as newness: what is new, how new, and new to whom? Eur J Innov Manage 4(1):20–31
Damanpour F, Szabat KA, Evan WM (1989) The relationship between types of innovation and organizational performance. J Manage Stud 26(6):587–602
Van de Ven AH (1986) Central problems in the management of innovation. Manage Sci 32(5):590–607
Rogers M (1998) The definition and measurement of innovation. Working Paper. Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, Melbourne, Australia
Rosenbusch N, Brinckmann J, Bausch A (2011) Is innovation always beneficial? A meta-analysis of the relationship between innovation and performance in SMEs. J Bus Venturing 26(4):441–457
Stieglitz N, Heine K (2007) Innovations and the role of complementarities in a strategic theory of the firm. Strateg Manage J 28(1):1–15
Teece D (1986) Profiting from technological innovation: implications for integration, collaboration, licensing and public policy. Res Policy 15(6):285–305
Dewar R, Dutton J (1986) The adoption of radical and incremental innovations: an empirical analysis. Manage Sci 32(11):1422–1433
Gumusluoglu L, Ilsev A (2009) Transformational leadership, creativity, and organizational innovation. J Bus Res 62(4):461–473
Halme DG, Kessler DA (2006) FDA regulation of stem-cell based therapies. New Engl J Med 355(16):1730–1735
Schmookler J (1966) Invention and economic growth. Harvard Business School Press, Cambridge, MA
Chesbrough H, Rosenbloom RS (2002) The role of business model in capturing value from innovation: wvidence from Xerox Corporation’s technology spin-off companies. Ind Corp Change 11(3):529–555
Simsek Z (2009) Organizational ambidexterity: towards a multilevel understanding. J Manage Stud 46(4):597–624
Lee SM, Olson DL, Trimi S (2010) The impact of convergence on organizational innovation. Organ Dyn 39(3):218–225
Park Y, Lee JY, Hong S (2011) Effects of international entry-order strategies on foreign subsidiary exit. Manage Decis 49(9):1471–1488
Song D (2004a) Open the era of value innovation: (3) the case of Samsung Electronics. Hankyung Business Daily (April 19) Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=015&aid=0000701971
Hwang I (2001) No future for Korean firms: (1) technology imitation. Maeil Business Newspaper, September, 20 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=009&aid=0000151003
Lee T (2005) [Searching blue ocean] Large firms: Samsung Electronics, be a consumer. Hankyung Business Daily, October 10 Retrieved from http://www.hankyung.com/news/app/newsview.php?aid=2005100701291
Lee T (2006) Korea innovation forum 2006: Samsung electronics VIP centre. Hankyung Business Daily, February 14 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=015&aid=0000872791
Kim W, Maugborne W (2005) Blue ocean strategy: how to create uncontested market space and make the competition irrelevant. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA
Song D (2004b) Open the era of value innovation: (5) VI from executives. Hankyung Business Daily, May 5 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=015&aid=0000706660
Song D (2005) Toward the blue ocean: an interview with Lee Dong Jin, a VIP centre Vice President at Samsung Electronics. Hankyung Business Daily, November 8 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=015&aid=0000848475
Kim M (2004) The era of value innovation: (4) VI embedded in Samsung. Hankyung Business Daily, May 4 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=015&aid=0000706224
Kim Y (2007) Samsung value innovation program (VIP) centre. Financial News, November 4 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=014&aid=0000355858
Yang H (2008) Samsung Electronics Vice President Lee Yun Woo: initiate future core technologies. Financial News, July 1 Retrieved from http://www.fnnews.com/news/200807011810110422?t=y
Chesbrough H (2012) Open innovation: where we’ve been and where we’re going. Res Techno Manage 55(4):20–27
Lee D (2011) Samsung Electronics Vice President Choi Jisung: respond early to even natural disasters. Daily Maekyung, April 1 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=009&aid=0002439029
Jin S (2009) Samsung takes over Polish Amica. Moneytoday December 22 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=008&aid=0002254573
Kim B (2008) Samsung Electronics announces proposal for combination with SanDisk in letter to board of directors. Moneytoday, September 17 Retrieved from https://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=008&aid=0002034388
Yonhap (2011) AsiaNet: Samsung Electronics and IBM announce patent cross-license agreement. February 9 Retrieved from https://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=104&oid=001&aid=0004904103
Barrett ME (2000) Time marches on: the worldwide watch industry. Thunderbird Int Bus Rev 42(3):349–372
Lynn LH (1998) The commercialization of the transistor radio in Japan: the functioning of an innovation community. IEEE T Eng Manage 45(3):220–229
Dyer JH, Singh H (1998) Relational view: cooperative strategy and sources of interorganizational competitive advantage. Acad Manage Rev 23(4):660–679
Kim C (2009a) Collaborating vendors benefit from Samsung Electronics. Maekyung Economy, August 23 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=024&aid=0000026894
Kim M (2009b) Samsung embraces ventures. Munhwailbo, November 4 Retrieved from https://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=021&aid=0002013900
Park Y (2012) Industry-academia collaboration, ‘upgrade.’ Economic Review. In: March 9 Retrieved from http://www.econovill.com/archives/39043
Park S (2007) The bad performance of Samsung Electronics in the first quarter, Why? Sekyeilbo, April 14 Retrieved from http://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=022&aid=0000220925
Bae B, Go S (2012) The middle class in Korea and U.S. was demolished as the result of the global financial crisis in 2008. Kukminilbo, June 12 Retrieved from https://news.naver.com/main/read.nhn?mode=LSD&mid=sec&sid1=101&oid=005&aid=0000514948
Hoover’s Company Records (2019) Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. In-depth Records, January 23 Retrieved from https://advance-lexis-com.proxy-bloomu.klnpa.org/api/document?collection=company-financial&id=urn:contentItem:5H1P-0GF1-JBPR-X276-00000-00&context=1516831
Christensen CM, Rayner M, McDonals R (2015) What is disruptive innovation? Harvard Bus Rev 93(12):44–53
Kim WC, Maubourgne R (2019) Nondisruptive creation: rethinking innovation and growth. MIT Sloan Manage Rev Spring:46–56
O’Reilly CA, Tushman ML (2013) Organizational ambidexterity: the past, present, and future. Acad Manage Perspect 27(4):324–338
Lee SM, Olson D (2010) Convergenomics: strategic innovation in the convergence era. Gower, Surrey, UK
Tversky A, Kahneman D (1986) Rational choice and the framing of decisions. J Bus 59(4):251–278
Gibbert M, Ruigrok W, Wicki B (2008) What passes as a rigorous case study? Strategic Manage J 29(13):1465–1474
Lee D (2015) The effect of operational innovation and QM practices on organizational performance in the healthcare sector. Int J Quality Inno 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-015-0008-4
Schniederjans D, Schniederjans M (2015) Quality management and innovation: new insights on a structural contingency framework. Int J Quality Inno 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-015-0004-8
Download references
There was no funding support for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Zeigler College of Business, Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania, Bloomsburg, USA
Seung Hoon Jang
Department of Management, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, USA
Sang M. Lee
Kania School of Management, University of Scranton, Scranton, USA
School of Air Transport and Logistics, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang, South Korea
Donghyun Choi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the developing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Seung Hoon Jang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jang, S.H., Lee, S.M., Kim, T. et al. Planting and harvesting innovation - an analysis of Samsung Electronics. Int J Qual Innov 5 , 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-019-0032-x
Download citation
Received : 25 April 2019
Accepted : 11 September 2019
Published : 21 October 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-019-0032-x

Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Planting innovation
- Harvesting innovation
- Co-innovation
- Multinationals
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Analysis of Strategic Management of Samsung Electronics Company through the Generic Value Chain Model

Related Papers
International Journal of Value Chain Management
yuanita handayati
Mike Morris
Lest anyone feel overwhelmed by the depth of detail in this Handbook, especially with respect to the sections on methodology, we would like to emphasise at the outset: this Handbook is not meant to be used or read as a comprehensive step by step process that has to be ...
Anthony Michail
Industrial Management & Data Systems
Rapee Kanchana
PurposeThe purpose of this paper is to describe key factors in sustaining effective business value chains for companies operating in the electronic industry and identify their potential future challenges.Design/methodology/approachThe research methodology includes the survey development, the hypothesis development, and the statistical analyses, especially the Pearson correlation. Altogether, a total of 129 firms participated in this study – 97 companies from Hong Kong/China and 32 firms from Thailand. Included in this methodology are a pre‐test of a survey, a development of the research hypotheses, and follow‐up discussions with participating executives on possible future challenges for their business value chains.FindingsAn effective business value chain essentially depends on a good internal operational system and constructive relationships with suppliers and customers. In other words, the collective efficacy depends on a manufacturer's internal operations (IO) and its supplie...
Togar Simatupang , Pairach (Champ) Piboonrungroj , Sharon Williams
The concept value chain has been promoted by Porter for more than three decades. A value chain represents a chain of activities that an organization performs to deliver a valuable product for the market. Porter’s value chain assumes that an organization is a system composed of inputs, transformation processes, and outputs. Each activity in the system involves the acquisition and consumption of resources. How the organization carries out value chain activities determines costs and profits. One enhances the competitiveness of a company by improving its value chain structure. However, little attention has been given to developing value chain thinking. This paper examines the emergence of value chain thinking and proposes new value chain thinking that involves a chain of activities linked to one another in order to sustain value. A conceptual model is presented which consists of four steps: value discovery, value design, value delivery, and value capture. A methodology is also proposed in which to operationalize the value chain thinking.
Antonie Rensburg
mahmoud nawaiseh
Abstract This study aims at identifying the extent of applying value chain analysis (VCA) to achieve and sustain competitive advantage in manufacturing companies in Jordan. To achieve the study’s objectives, a questionnaire was developed and pre -tested. The population of the study consists of the (93) company which are listed in the Amman Stock Exchange of Jordan in the end of the 2012, (65) companies of them accepted to fill the questionnaires. (81.5)% of the distributed questionnaires was received. Descriptive and analytical statistical techniques such as frequencies, percentages, standard deviation, means, one sample T test and one way ANOVA were applied to test the study’s hypotheses. The study revealed the following results: manufacturing companies in Jordan apply VCA, but don’t use it to achieve and sustain competitive advantage and there is no statistically significant effect of the respondents’ demographic characteristics on their perceiving the importance of applying VCA to achieve competitive advantage. The study recommends manufacturing companies in Jordan train their employees on strategic analysis of the company's internal and external environment, exercise the value chain analysis, calculate the unit cost of production and enter them in courses for achieving and sustaining competitive advantage through cost reduction and differentiation strategies.
Asian Journal of Innovation and Policy
Elvira Zamora
Supply Chain Forum: an International Journal
ravi shankar
International conference KNOWLEDGE-BASED ORGANIZATION
Lucian Grigorescu
Competitive advantage is a difference in relative prices or the relative costs and it results from differences in their work done. These differences may occur in two different ways, namely either the organization performs better the same types of activities, or it chooses different types of activities. To establish whether between an organization and other competitors in the same industry there are differences in terms of relative prices and relative costs, it is recommended to make use of Porter's value chain, the more so as these differences are determined by the activities of the organization. Value chain plays an important role in the diagnosis of an organization's competitive advantage because through it we can get an insight into the mode of action of costs and the influences they have on the strategy that the organization has taken. Also, through the value chain there can be identified the potential sources of differentiation of products or services offered by the org...
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Table of Contents
Digital presence of samsung, digital marketing campaigns of samsung , marketing mix of samsung, swot analysis, results of samsung marketing strategy, conclusion , how samsung marketing strategy solidifies its brand value.

The global electronics powerhouse– Samsung began its journey as a low-tier manufacturing brand. A strong Samsung marketing strategy revolutionized its stance in the market, making it the No.1 smartphone producer worldwide. The tech giant ranks 4th in Forbes' list of the World's Largest Tech Companies. A perfect blend of digital marketing and innovation has established Samsung as a unique, high-quality brand worthy of customer loyalty.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
Samsung's adept use of social currency has contributed to its success in digital marketing. Expanding its social media presence, Samsung provides customers and brand loyalists several chances to share their experiences with those in their circle.

Samsung YouTube Channel
To connect with the various segments of the population their products target, Samsung has social profiles on all of the major social networks, including
- Facebook: 162M
- Twitter: 12.5M
- YouTube: 6.24M
- Instagram: 4.5M
Samsung Facebook Page with 162 Million Likes
Moreover, Samsung has several profiles on each platform. For instance, Instagram has Samsung, Samsung India, Samsung UK, Samsung UA, Samsung Mobile and more.
The company adheres to the best digital marketing practices like SEO and quality content creation that solves customer problems.
Being a community-oriented brand that impacts audiences worldwide, Samsung introduces various marketing campaigns. The promising Samsung marketing strategy focuses on leveraging the power of exceptional marketing campaigns to promote its products and appeal to the audience.
Social media ads, sponsorships, and online advertising strengthened the brand. Some exceptional Samsung marketing campaigns are as follows:
- #YouMake Campaigns: It brings up a global marketing platform for consumers to take the lead with device customization. It brings a better way of personalization via customized control enabled by SmartThings IoT solutions. The #YouMake campaign offers continuous services and virtual benefits, encouraging customer participation by utilizing the best metaverse platforms.
- Growing Up: Another commercial on YouTube that made people reconsider their options. The company directly targeted its main competitor–Apple, and the video took the internet by storm.
Product, Price, Place, and Promotion–the 4Ps of the marketing mix constitute an integrated marketing model. Samsung’s marketing mix plan gives insights into the company’s success secret.
1. Product Mix
Delivering excellent results in recent years, Samsung products are well-known for their services and quick support. Samsung’s marketing mix in its product line is one of its major strong points. The products fall into the following categories:
- Mobile phones
- Televisions – LEDs, Plasma TV, LCDs, SMART TV, HDTV
- Refrigerators
- Air Conditioners
- Washing Machine
- IT – Printers, laptops, and accessories
2. Price Mix
Price mix is one of the strongest points in the Samsung marketing strategy. It offers two pricing schemes to satisfy its clients. The corporation adopts a price skimming tactic whenever it releases a new smartphone with the latest technology. Moreover, it reduces the price of that product when the competitors launch identical products.
3. Promotion Mix
Samsung attracts customers via advertising while employing the best tactics to push products through sales promotions.
The company employs several marketing vehicles both during the festive season and outside of it. It grants numerous discounts and incentives to business partners, encouraging them to sell Samsung products above the competition.
4. Place Mix
Samsung service dealers are responsible for corporate sales. Its selling point is its distribution. They distribute their goods via a single distribution business. They then distribute them to other locations.
SWOT analysis is one of the best ways to dive deeper into the Samsung marketing technique. It provides insights into Samsung’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats concerning its marketing competitiveness.
Samsung’s Strengths
- It has held a strong position in the smartphone manufacturing industry for years. Climbing the ladder, Samsung ranks first on the world’s best smartphone manufacturers list.
- Significant investments in the innovative research and development sector have helped Samsung generate a diverse product offering compared to its competitors.
- Its transition to a customer-centric management system has brought about revolutionary changes.
- Its consistent efforts for sustainable development, such as the adoption of eco-packaging for TVs, give it the upper hand.
- Samsung leads the development of advanced technologies like AI, 5G, automotive and robotics.
- Lastly, it is rapidly expanding commercial marketing in India and China.
Samsung’s Weakness
- Despite expanding its operations in Asia, the company relies heavily on American markets.
- Samsung’s defective items, such as the Samsung Galaxy A20e and a malfunctioning foldable phone.
Samsung’s Opportunities
- Samsung can achieve tremendous development in the smartphone industry by setting the standard with innovative goods like foldable phones.
- As the world adopts 5G, Samsung has the know-how to capitalize on the opportunity.
- The company can hire exceptionally skilled professionals using its brand image.
Samsung’s Threats
- Samsung’s entanglement in controversies can jeopardize its business, such as the lawsuit filed by Apple for patent infringement.
- Xiaomi, Apple, and Huawei stand as major threats and technological competitors who can outsmart Samsung.
Samsung’s revamped marketing programs and competitive strategy implementation have significantly contributed to its huge success over the years.
Performing continuous market research, adding new features, serving customer pain points and employing special efforts to reduce costs, Samsung has paved the way for its success from the very beginning.
Its global value increased by more than 200% in a short span ranging from 2003 to 2008.
Samsung took over Sony–one of the most valuable consumer-electronics brands worldwide. Consequently, Samsung’s sales reached $119 billion by 2009. When the company introduced Samsung Galaxy and leveraged the power of digital platforms for promotions and marketing, its revenue grew to $218 billion in 2018.
Today, Samsung stands 5th on Interbrand’s list of Best Global Brands with a brand value of USD 74.6 billion. It has witnessed a 20% increase in comparison to the last year.
Sparking creativity worldwide, Samsung is the most profitable tech company. The robust Samsung marketing strategy has made it one of the most valuable brands today. Its smart digital marketing tactics set an excellent example of how to revamp your online business as a digital marketer.
Want to know more about Digital Marketing? Enroll on Simplilearn’s Digital Marketing Specialist Program and upskill yourself digitally.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
A Case Study on Netflix Marketing Strategy
12 Powerful Instagram Marketing Strategies To Follow in 2021
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
A Case Study on Apple Marketing Strategy
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

- Order Status
- Testimonials
- What Makes Us Different
Samsung Electronics Company Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Home >> Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions >> Samsung Electronics Company
Introduction
Samsung started its operations in the late 60’s. Over the period of time, Samsungdeveloped its stance in the television market by offering black and white TVs in the Korean market. After some time, the Vicepresidentforglobal marketing revealedthe overall brand strategy of Samsung in order to make itselfa global brand, leading to more sustainableoperations and long term brand building.
The company from itsinitiation focused on research and development techniques and invested heavily to capture the market opportunity. In addition, Samsung also invested in the different product categories, from TVs to mobile phones to recorder and thirdparty chip productions . All these strategies allowed Samsung to effectively pursue productdevelopment strategies that made it a strong and competitive player in the tech market.
However, in the current situation, withadvancement in technology and increasing market competition, Samsung has to devise a new strategy in order to sustain its position in the market and retain its market share along with the elevation of its market position as the top brand in the mind of customer. Therefore to deal with this, two alternatives have been proposed in order to enable Samsung elevate its position in theglobal marketand rank itself among the top ten global brands.
Problem statement
“ Samsung has elevated its position in the global market making itself a renowned brand, howeverreaching thetop10 rank in global market and sustaining it is a challenge for the company ”
Samsung Electronics Company Harvard Case Solution & Analysis
Justification
Since competition is increasing in the market, as Chinese brands are entering with strongerbrandstrategy along withcheaper immitigabletechnology, maintaining the valueproposition has become difficult for Samsung, making it a huge challenge for the company to elevate its position in the global market.
Qualitative Analysis
Swot analysis.
- The company has strong brand image and market recognition that allow the customer to quickly choose Samsung over other brands.
- The company has strong financial background. This allows the company to invest heavily in the research and development department and establish new and innovative product base in the market.
- The company has corporative culture based on merit.This allows the new talent to invest the energy and efforts to rise in position and on the other hand, allows the company to achieve its goals timely.
- The company has high brand equity and market yield as compared to other competitors.
- The company has well established brand strategy that allows it to pursue economies of scale.
- The company has weak global strategy to address the market changes and trends.
- The company overly depends on the DRAMs and since technology is imitable, it hinders the company’s stance in sustaining its competitive edge.
- The Chinese market players are emerging in the market, capturing the market of Samsung.
- The brand image of Samsung remains inferior to Ios, as it uses Google free platform of Android.
Opportunities
- The semi-conductor market is increasing on a high scale, allowing the company to pursue the market development and market penetration strategy.
- Since in the current scenario, DRAMs are at the peak level, there is no other alternative present for the technology, giving company exclusiveness in the market.
- The demand for DRAMS is ever rising in the market.................
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.
Related Case Solutions & Analyses:

Hire us for Originally Written Case Solution/ Analysis
Like us and get updates:.
Harvard Case Solutions
Search Case Solutions
- Accounting Case Solutions
- Auditing Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- Economics Case Solutions
- Finance Case Studies Analysis
- Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Human Resource Cases
- Ivey Case Solutions
- Management Case Studies
- Marketing HBS Case Solutions
- Operations Management Case Studies
- Supply Chain Management Cases
- Taxation Case Studies
More From Harvard Case Study Analysis Solutions
- Worldwide Orphans Foundation
- STATOIL ASA—GLOBAL ENERGY COMPANY
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD): Five Failures and Counting (B)
- Managing the Layoff Process: France
- Case: Airbus A380 – Turbulence Ahead
- VITAS: Innovative Hospice Care
- Charlie Eitel CEO Simmons - 2008 Video
Contact us:

Check Order Status

How Does it Work?
Why TheCaseSolutions.com?

- Predictive Analytics Workshops
- Corporate Strategy Workshops
- Advanced Excel for MBA
- Powerpoint Workshops
- Digital Transformation
- Competing on Business Analytics
- Aligning Analytics with Strategy
- Building & Sustaining Competitive Advantages
- Corporate Strategy
- Aligning Strategy & Sales
- Digital Marketing
- Hypothesis Testing
- Time Series Analysis
- Regression Analysis
- Machine Learning
- Marketing Strategy
- Branding & Advertising
- Risk Management
- Hedging Strategies
- Network Plotting
- Bar Charts & Time Series
- Technical Analysis of Stocks MACD
- NPV Worksheet
- ABC Analysis Worksheet
- WACC Worksheet
- Porter 5 Forces
- Porter Value Chain
- Amazing Charts
- Garnett Chart
- HBR Case Solution
- 4P Analysis
- 5C Analysis
- NPV Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- Cost Optimization
Samsung Electronics
- Strategy & Execution / MBA EMBA Resources
Next Case Study Solutions
- Intel Corp.--1968-2003 Case Study Solution
- Social Strategy at Cisco Systems Case Study Solution
- $19B 4 txt app WhatsApp...omg! Case Study Solution
- E Ink in 2005 Case Study Solution
- LinkedIn Corp., 2008 Case Study Solution
Previous Case Solutions
- Mobileye: The Future of Driverless Cars Case Study Solution
- Head Ski Co., Inc. Case Study Solution
- Undermining Staying Power: The Role of Unhelpful Management Theories Case Study Solution
- DreamCycles: Sustaining Growth Case Study Solution
- THEOTIS WILEY - Confidential Instructions for Erive's Vice-President of Business Development Case Study Solution

Predictive Analytics
March 23, 2024

Popular Tags
Case study solutions.

Case Study Solution | Assignment Help | Case Help
Samsung electronics description.
To maximize their effectiveness, color cases should be printed in color.When is it possible to create a dual advantage of being both low cost and differentiated? In this case, students assess whether Samsung Electronics has been able to achieve such a dual advantage, and if so, how this was possible. Moreover, Samsung Electronics' long-held competitive advantage is under renewed attack. Students also can assess how Samsung should respond to large-scale Chinese entry into its industry.
Case Description Samsung Electronics
Strategic managment tools used in case study analysis of samsung electronics, step 1. problem identification in samsung electronics case study, step 2. external environment analysis - pestel / pest / step analysis of samsung electronics case study, step 3. industry specific / porter five forces analysis of samsung electronics case study, step 4. evaluating alternatives / swot analysis of samsung electronics case study, step 5. porter value chain analysis / vrio / vrin analysis samsung electronics case study, step 6. recommendations samsung electronics case study, step 7. basis of recommendations for samsung electronics case study, quality & on time delivery.
100% money back guarantee if the quality doesn't match the promise
100% Plagiarism Free
If the work we produce contain plagiarism then we payback 1000 USD
Paypal Secure
All your payments are secure with Paypal security.
300 Words per Page
We provide 300 words per page unlike competitors' 250 or 275
Free Title Page, Citation Page, References, Exhibits, Revision, Charts
Case study solutions are career defining. Order your custom solution now.
Case Analysis of Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics is a Harvard Business (HBR) Case Study on Strategy & Execution , Texas Business School provides HBR case study assignment help for just $9. Texas Business School(TBS) case study solution is based on HBR Case Study Method framework, TBS expertise & global insights. Samsung Electronics is designed and drafted in a manner to allow the HBR case study reader to analyze a real-world problem by putting reader into the position of the decision maker. Samsung Electronics case study will help professionals, MBA, EMBA, and leaders to develop a broad and clear understanding of casecategory challenges. Samsung Electronics will also provide insight into areas such as – wordlist , strategy, leadership, sales and marketing, and negotiations.
Case Study Solutions Background Work
Samsung Electronics case study solution is focused on solving the strategic and operational challenges the protagonist of the case is facing. The challenges involve – evaluation of strategic options, key role of Strategy & Execution, leadership qualities of the protagonist, and dynamics of the external environment. The challenge in front of the protagonist, of Samsung Electronics, is to not only build a competitive position of the organization but also to sustain it over a period of time.
Strategic Management Tools Used in Case Study Solution
The Samsung Electronics case study solution requires the MBA, EMBA, executive, professional to have a deep understanding of various strategic management tools such as SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis.
Texas Business School Approach to Strategy & Execution Solutions
In the Texas Business School, Samsung Electronics case study solution – following strategic tools are used - SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis. We have additionally used the concept of supply chain management and leadership framework to build a comprehensive case study solution for the case – Samsung Electronics
Step 1 – Problem Identification of Samsung Electronics - Harvard Business School Case Study
The first step to solve HBR Samsung Electronics case study solution is to identify the problem present in the case. The problem statement of the case is provided in the beginning of the case where the protagonist is contemplating various options in the face of numerous challenges that Samsung Electronics is facing right now. Even though the problem statement is essentially – “Strategy & Execution” challenge but it has impacted by others factors such as communication in the organization, uncertainty in the external environment, leadership in Samsung Electronics, style of leadership and organization structure, marketing and sales, organizational behavior, strategy, internal politics, stakeholders priorities and more.
Step 2 – External Environment Analysis
Texas Business School approach of case study analysis – Conclusion, Reasons, Evidences - provides a framework to analyze every HBR case study. It requires conducting robust external environmental analysis to decipher evidences for the reasons presented in the Samsung Electronics. The external environment analysis of Samsung Electronics will ensure that we are keeping a tab on the macro-environment factors that are directly and indirectly impacting the business of the firm.
What is PESTEL Analysis? Briefly Explained
PESTEL stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors that impact the external environment of firm in Samsung Electronics case study. PESTEL analysis of " Samsung Electronics" can help us understand why the organization is performing badly, what are the factors in the external environment that are impacting the performance of the organization, and how the organization can either manage or mitigate the impact of these external factors.
How to do PESTEL / PEST / STEP Analysis? What are the components of PESTEL Analysis?
As mentioned above PESTEL Analysis has six elements – political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal. All the six elements are explained in context with Samsung Electronics macro-environment and how it impacts the businesses of the firm.
How to do PESTEL Analysis for Samsung Electronics
To do comprehensive PESTEL analysis of case study – Samsung Electronics , we have researched numerous components under the six factors of PESTEL analysis.
Political Factors that Impact Samsung Electronics
Political factors impact seven key decision making areas – economic environment, socio-cultural environment, rate of innovation & investment in research & development, environmental laws, legal requirements, and acceptance of new technologies.
Government policies have significant impact on the business environment of any country. The firm in “ Samsung Electronics ” needs to navigate these policy decisions to create either an edge for itself or reduce the negative impact of the policy as far as possible.
Data safety laws – The countries in which Samsung Electronics is operating, firms are required to store customer data within the premises of the country. Samsung Electronics needs to restructure its IT policies to accommodate these changes. In the EU countries, firms are required to make special provision for privacy issues and other laws.
Competition Regulations – Numerous countries have strong competition laws both regarding the monopoly conditions and day to day fair business practices. Samsung Electronics has numerous instances where the competition regulations aspects can be scrutinized.
Import restrictions on products – Before entering the new market, Samsung Electronics in case study Samsung Electronics" should look into the import restrictions that may be present in the prospective market.
Export restrictions on products – Apart from direct product export restrictions in field of technology and agriculture, a number of countries also have capital controls. Samsung Electronics in case study “ Samsung Electronics ” should look into these export restrictions policies.
Foreign Direct Investment Policies – Government policies favors local companies over international policies, Samsung Electronics in case study “ Samsung Electronics ” should understand in minute details regarding the Foreign Direct Investment policies of the prospective market.
Corporate Taxes – The rate of taxes is often used by governments to lure foreign direct investments or increase domestic investment in a certain sector. Corporate taxation can be divided into two categories – taxes on profits and taxes on operations. Taxes on profits number is important for companies that already have a sustainable business model, while taxes on operations is far more significant for companies that are looking to set up new plants or operations.
Tariffs – Chekout how much tariffs the firm needs to pay in the “ Samsung Electronics ” case study. The level of tariffs will determine the viability of the business model that the firm is contemplating. If the tariffs are high then it will be extremely difficult to compete with the local competitors. But if the tariffs are between 5-10% then Samsung Electronics can compete against other competitors.
Research and Development Subsidies and Policies – Governments often provide tax breaks and other incentives for companies to innovate in various sectors of priority. Managers at Samsung Electronics case study have to assess whether their business can benefit from such government assistance and subsidies.
Consumer protection – Different countries have different consumer protection laws. Managers need to clarify not only the consumer protection laws in advance but also legal implications if the firm fails to meet any of them.
Political System and Its Implications – Different political systems have different approach to free market and entrepreneurship. Managers need to assess these factors even before entering the market.
Freedom of Press is critical for fair trade and transparency. Countries where freedom of press is not prevalent there are high chances of both political and commercial corruption.
Corruption level – Samsung Electronics needs to assess the level of corruptions both at the official level and at the market level, even before entering a new market. To tackle the menace of corruption – a firm should have a clear SOP that provides managers at each level what to do when they encounter instances of either systematic corruption or bureaucrats looking to take bribes from the firm.
Independence of judiciary – It is critical for fair business practices. If a country doesn’t have independent judiciary then there is no point entry into such a country for business.
Government attitude towards trade unions – Different political systems and government have different attitude towards trade unions and collective bargaining. The firm needs to assess – its comfort dealing with the unions and regulations regarding unions in a given market or industry. If both are on the same page then it makes sense to enter, otherwise it doesn’t.
Economic Factors that Impact Samsung Electronics
Social factors that impact samsung electronics, technological factors that impact samsung electronics, environmental factors that impact samsung electronics, legal factors that impact samsung electronics, step 3 – industry specific analysis, what is porter five forces analysis, step 4 – swot analysis / internal environment analysis, step 5 – porter value chain / vrio / vrin analysis, step 6 – evaluating alternatives & recommendations, step 7 – basis for recommendations, references :: samsung electronics case study solution.
- sales & marketing ,
- leadership ,
- corporate governance ,
- Advertising & Branding ,
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) ,
Amanda Watson
Leave your thought here

© 2019 Texas Business School. All Rights Reserved
USEFUL LINKS
Follow us on.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive news on update.

Dark Brown Leather Watch
$200.00 $180.00

Dining Chair
$300.00 $220.00

Creative Wooden Stand
$100.00 $80.00
2 x $180.00
2 x $220.00
Subtotal: $200.00
Free Shipping on All Orders Over $100!

Wooden round table
$360.00 $300.00
Hurley Dry-Fit Chino Short. Men's chino short. Outseam Length: 19 Dri-FIT Technology helps keep you dry and comfortable. Made with sweat-wicking fabric. Fitted waist with belt loops. Button waist with zip fly provides a classic look and feel .
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, samsung electronics: analyzing qualitative complaint data.
Publication date: 20 January 2017
Teaching notes
“Samsung Electronics had experienced a series of quality-related problems, including the recall of one of its LCD TV models. Unfortunately for quality director Kevin Sarni, there was no single root cause behind these problems: Samsung's supply chain management, product design, and testing/quality assurance functions all played a role.
Sarni regularly worked with quantitative data from Samsung's customer complaint database, but recently he had been shown comments about Samsung products posted on the website ConsumerAffairs.com . The number and emotional tone of the website postings concerned him; he worried these kinds of complaints might touch off a social media—fueled public relations firestorm that would make his job more difficult.
He wanted to analyze this feedback, but had no experience with qualitative data. An internal Six Sigma Black Belt consultant suggested he start by creating an affinity diagram and use that to create a Pareto chart to determine which issues to address first. Once Sarni completed the unfamiliar diagrams he had still another task ahead of him: examining the results to see if they justified taking short—term action to address the quality problems raised in the complaints.”
Organize and analyze qualitative data using affinity diagrams
Identify priorities using Pareto charts
The case reinforces the importance of approaching problem solving in a methodical and data-driven manner and demonstrates the power of visual (vs. table-driven) tools.
- Business Process Improvement
- Crisis Management
- Customer Relationship Management
- Customer Service
- Manufacturing
- Operations Management
- Organizational Effectiveness
- Total Quality
- Customer Satisfaction
Boepple, J. (2017), "Samsung Electronics: Analyzing Qualitative Complaint Data", . https://doi.org/10.1108/case.kellogg.2016.000291
Kellogg School of Management
Copyright © 2013, The Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University
You do not currently have access to these teaching notes. Teaching notes are available for teaching faculty at subscribing institutions. Teaching notes accompany case studies with suggested learning objectives, classroom methods and potential assignment questions. They support dynamic classroom discussion to help develop student's analytical skills.
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study
Introduction, conclusions.
In August 2016, several Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Smartphones were reported to explode. The manufacturer called upon its engineers hurriedly to diagnose the source of the problem. The initial report pointed to a fault in batteries procured from one of the suppliers. This led to a recall of these smartphones and continued shipping of the same mobile device with batteries from a different supplier [1]. However, the issue surfaced again with reports of the new replacements also exploding, prompting the company to halt the entire Samsung Galaxy Note 7 production. The failure, subsequent recall, and the complete halt of the Galaxy Note 7 production have had social and legal ramifications.
This Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure case study aims to analyze the issue, its history, and the aftermath, including the crisis management and the discovered reasons behind the battery explosion.
Smartphones have very advanced computing capabilities, such as high-definition cameras, media players, sensors, GPS navigation units, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, among other features. For most Smartphones, an Android operating system is used. The features need to be supported by stable memory, batteries with the correct power output, an efficient power system, and a good shell to operate efficiently. The risk of failure of Smartphones is mainly in the memory access violation and mobile phone hardware such as the batteries and the shell [2]. Overall, studies on the failure of Smartphones have pointed to two major types of failures, i.e., accidental or malfunction of the software or Android. For this report, the focus is on the hardware or software malfunction.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure
The explosion of the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 resulted in the recall of the phones [1]. The phones that were overheating were analyzed to establish the causes of the explosion. The techniques employed for the analysis were Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA). This entails a critical analysis of the entire lifecycle of a product. It analyzes the specifications of the design, operation, and maintenance by establishing the system functions, identification of the failure modes in the system, and functions which then determine the effects and possible causes [3]. The analysis covers both the software and hardware functionalities.
The FMEA is used by engineers in the design stages of a product or post-analysis in the case of issues arising. The initial FMEA conducted after the failure was hardware FMEA. This is a straightforward analysis guided by the understanding that mechanical, electronic, and electrical failures happen due to some issues, such as unanticipated stress, overload, and faulty wiring. The analysis by the engineers concluded that lithium-ion batteries from one of the suppliers had a fault. Part of the battery’s inside was coiled incorrectly, causing stress to the battery.
By performing critical risk analysis, the possible malfunction of software or hardware can be established before the product is launched into the market. The critical failure modes can be ascertained by calculating the Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) through brainstorming [2]. This helps to establish the potential areas of failure and the possible degree of damage. As a result, mitigation measures are taken before the product is released to ensure that the risk is contained.
It is thus paramount that Samsung should have carried out a thorough risk analysis for all the hardware and software from the suppliers before launching the product. Also, after the recall, the analysis was hurriedly carried out; hence, the conclusion that the failure was from a battery procured from a particular manufacturer was theorized rather than being scientifically proven with quantifiable data.
Discussion on Samsung Note 7 Failure
The failure of Samsung’s Galaxy Note 7 has had enormous financial implications. It is estimated that it may lead to a revenue loss of over $ 5 billion. Even though the company could easily deal with the loss of income, the failure has great social and legal ramifications. For instance, the failure has already attracted class-action lawsuits against the company, which touch on how the recall and replacement were carried out.
Also, there is a high likelihood of lawsuits that relate to the damages and injuries caused by the explosions. These lawsuits will affect the consumer perception of Samsung’s Smartphones. For example, the Google search for ‘Samsung Explosion’ spiked in August and September despite the recall being only for Galaxy Note 7. The failure has also had social implications for Samsung phone users. Some airlines in the U.S. do not allow passengers to use any Samsung phone onboard their planes.
The failure of any product leads to unintended consequences for the manufacturer and the consumers. Even though investigations are still ongoing to establish the exact cause of the Samsung Note 7 explosions, Samsung’s engineers need to give more care to the materials used to develop the software and hardware of its Smartphones. Also, there should be a critical risk analysis in which an RPN for each possible failure mode is calculated before a product is released to the market. This will ensure that parameters with high-risk factors are properly investigated, and risk reduction measures are taken in advance.
- B. Chen and C. Sang-Hun, “Why Samsung Abandoned Its Galaxy Note 7 Flagship Phone”, The New YorK Times, 2016.
- K. Krishnakanth and P. Kavipriya, “Android application development for environment monitoring using Smartphones”, International journal of Mobile Network Communications & Telematics, vol . 3, no. 3, pp. 41-45, 2013.
- S. Malek, R. Roshandel, D. Kilgore and I. Elhag, “Improving the reliability of mobile software systems through continuous analysis and proactive reconfiguration,” Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering-Companion Volume. ICSE-Companion 2009. Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp. 275-278, 2009.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 29). Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/
"Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." IvyPanda , 29 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study'. 29 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
1. IvyPanda . "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 29, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
- Failure Modes and Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)
- The FMEA-Quality Risk Register Analysis
- Novel Framework to Assist the Novice
- Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Smartphone's Security Issue
- The Samsung Galaxy Tab
- Application of FMEA in the Successful Implementation of ERPs
- Samsung Galaxy SIII Product Features
- Benchmarking Description on Apple iphone 4s vs. BlackBerry, Android and Samsung Galaxy
- Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Product Recall and Influence
- Short Message Service (Center) Technologies
- Outcomes of the Phone Usage While Driving
- Steering Wheel and Smartphone: A Deadly Combination
- International Students and Mobile Services in Australia
- Wireless Communication and the Trends in This Industry

- Free Case Studies
- Business Essays
Write My Case Study
Buy Case Study
Case Study Help
- Case Study For Sale
- Case Study Service
- Hire Writer
Samsung Case Analysis
Issues As South Korea’s largest conglomerate, Samsung includes Samsung Electronics, Samsung Heavy Industries, and Samsung Engineering ; Construction.
Started in 1938 as a company that produced agricultural products, the company began to focus on shipbuilding, chemicals, and textiles in 1970. Since after Samsung Electronics Company (SEC) was founded in 1969, Samsung acquired a semiconductor business and supplied global markets with massive quantities of commodity products. With the transformation that was led by the leadership of SEC Chairman Kun Hee Lee, Samsung rebuilt its image as a global business leader.
We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically For You For Only $13.90/page!
Following the chairman’s new management initiative, Samsung is now in a stage of investing in innovative and premium products to increase their brand value. Despite Samsung’s rapidly increasing global market share, the Samsung brand was not widely known outside of Korea until Samsung decided to recruit a Korea-born general manager, Eric Kim. With his effort to build the corporate brand image across the markets of 200 countries, Samsung was able to generate tremendous brand visibility worldwide with its DigitAll campaign.
While Samsung has experienced great success in marketing, some important issues remain to be addressed to increase their market share and brand power: ? ? ? ? Market share should be expanded by penetrating weaker markets; Marketing communications need to move more consumers into the “delights me” and “perfect fit” relationship categories; Less emphasis should be placed on youth and creativity, as that might be inappropriate; and A more complex customer segmentation should be marketed in its marketing planning.
Related posts:
- Marketing Strategy of Samsung Mobile
- Case Study on Samsung Electronics
- Samsung product development Case study
- Global Marketing case study-Samsung
- Samsung – Competitive Analysis
- Samsung Case
- Samsung Case Study
Quick Links
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Testimonials
Our Services
Case Study Writing Service
Case Studies For Sale
Our Company
Welcome to the world of case studies that can bring you high grades! Here, at ACaseStudy.com, we deliver professionally written papers, and the best grades for you from your professors are guaranteed!
[email protected] 804-506-0782 350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118, USA
Acasestudy.com © 2007-2019 All rights reserved.

Hi! I'm Anna
Would you like to get a custom case study? How about receiving a customized one?
Haven't Found The Case Study You Want?
For Only $13.90/page
- Privacy Policy
Samsung Case Study Analysis
The advancing technology has narrowed the knowledge boundary amongst the organizations, necessitating innovative approaches that would provide their goods and services with differentiating elements to give them cutting edge leverage. Analysis and identification of the changing trends of the customer requirements are essential ingredients to gain leverage against their rivals (Grant, 2007). In such a scenario, the five forces analysis of producer business becomes critical factors of a competitive advantage, which are: industry rivalry, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers; competition from substitute; and the threat of entry.
The industry rivalry amongst the producer businesses is an essential criterion for introducing cutting edge differentiating elements in the products to gain leverage. This is one of the primary motivating factors for Samsung Inc to be highly innovative in its products and development processes.

The quality and creative input within the product gives a huge advantage to the suppliers and puts him in a bargaining position. Samsung producing high-quality memory chips at relatively low cost has been able to bargain with its customers.
The bargaining power of buyers is reduced when there is a short supply of quality goods that have a high demand. In the case of Samsung, the buyers increasingly prefer them because of their quality products and their credibility of supplying goods timely.
Technological advancements have brought forth an explosion of information that is easily accessible to the public through the internet and other media like television, radio, mobile phones, etc. The competition from substitute become highly likely, and the company needs to adopt an innovative approach to its marketing . Samsung has successfully met this aspect by evolving flexible strategies like an innovative product like and introducing elements of surprise within the products as well within the marketing of the products and services.
Last but not least is the threat from new entrants of the business. Globalization has provided facilitating grounds for new entrants. Therefore, the existing firms must ensure that speed and flexibility become an intrinsic part of their strategy as they become essential ingredients for the products so that the organizations can timely and efficiently meet the fast-changing preferences of the customers.
Under the dynamic leadership of Kun Hee Lee, the company enjoyed a competitive advantage over its rivals in the world market, primarily because of the sharp business foresight and risk-taking capability. The Chairman’s long-term vision and ability to harness the potential of the customers’ shifting tastes have given them leverage in the highly competitive sector of semiconductor and electronic gadgets. The company became known for their revolutionary product lines of fairly low-cost quality. It was able to give stiff competition to electronic majors like Sony, Nokia, Phillips, etc. by the continuous development of new features in all its products.
Many factors contributed to the company’s continued leadership position in the world market. The foremost was its business model focusing on creative goods focused on speed. The business has concentrated on its research and development skills strategy to develop and improvise innovatively on Sony’s electrical and digital products, Phillips, Matsushita, and Nokia. Samsung’s ability to launch its products with added features with high speed was a huge success with the target population. Samsung had set up his professional teams to keep a close eye on the pulse of the people and was thus able to predict their demands and used to come up with new products and features that were envied by its rivals.
Samsung’s business strategy was its focused approach towards R&D and utilizing his human resource as capital investment. His team was able to develop a vast range within the same product because they were able to customize new products around their core design. He also introduced the concept of competing for product development teams, which were located at diverse locations, thus promoting competition with the group for innovation. Within the party, the merit-based promotion ensured that the best earned their dues. High potential employees were encouraged to MBA and Ph.D. in a foreign country on the company’s expenses so that the expert team could be indigenously developed and fostered for improved business performance.
Samsung has a great future because, in the changing paradigms of the business environment, it continuously strives to identify factors and issues that would help meet the challenges with efficiency and unmatched proficiency. There are two major areas where Samsung is able to stay ahead of the Chinese companies. The first one is its state of the art R&D, which significantly facilitates the development of new products through specialized product development teams. The latest products ensure that the constantly changing preferences of the customers are met timely, thus making sure that they maintain their leadership position. One can, therefore, conclude that one of the main factors that have facilitated the company to keep abreast with the changes and maintain a competitive edge over their rivals, in its market plan, it’s been able to check new strategies.
Samsung was a market leader in the semiconductor, electronics, and telecommunications accessories business in 2005. With 337 international operations spread in 58 countries and 212,000 safe workforces, overall revenue of the company reached $135 billion in 2004. The major cost drivers for Samsung have been its policy of innovation and state of the art R&D programs. The second most crucial factor has been the intrinsic belief of its CEO on the capabilities of its workforce and merit-based promotions that motivate the employees of all ages.
The fact that the Chief operating officer intrinsically believed in the potential of its rivals and through continuous vigil on its rivals’ business strategy and product line, he was able to anticipate their future course. Porter argues that a ‘company can outperform rivals only if it can establish a difference that it can preserve. It must deliver greater value to customers or create comparable value at a lower cost, or do both’ (Porter, 1980). This was the main reason that the CEO of Samsung was able to keep ahead of the Chinese firms and maintain its competitive edge in the area of semiconductors, microchips, and electronic goods.
Yes, because Samsung has understood that it needs to look at the various options of competitive advantage to respond appropriately so that it could maintain its leadership position within the semiconductor market. The sustainability of the product shelf life has lost relevance because the brands ensure the sustainability of their products through creative changes in the product that brings them at par with the latest technology and caters to the universal appeal for the product, making it perennially popular. Backed by a capable R&D team, the company has the requisite infrastructure and capabilities to design and produce innovative products. The Chinese firms have yet to acquire expert knowledge about core semiconductor units design and manufacturing technology. This gives a massive advantage to Samsung to go in for new products and create a niche market for them in the emerging modern economies like India, China, Brazil, etc. It is assumed that despite huge government concessions to Chinese firms in China, lack of adequate intellectual property laws would be a significant deterrent for other big companies to transfer technology. Samsung, therefore, would be right to continue innovative products and add-ons for existing as well as for new markets.
References;
- Grant, Robert M. (2007). Contemporary Strategic Analysis. (6th edition). Blackwell.
- Porter, Michael, E.(June 1, 1980). Competitive Strategy: Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors. NY: Free Press 1998
- Siegel, Jordon, and Chang, James Jinho. (2009). Samsung Electronics. Harvard Business School .
Related Posts
A case study on sustainable building, suspicious behaviors of malware in android, how epa links with the superfund in new..., nokia case study analysis, importance of public spaces in a neighbourhood of..., community based tourism in uganda and tanzania, mount st. helens hazardous simulations, the contradiction of homosexuality, walmart cross-cultural issues case study analysis, case study on leadership and management, leave a comment cancel reply.
Please enter an answer in digits: eight − three =

Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Analysis
by HBR Fifty Three
Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Analysis. Get Samsung Electronics Case Study Analysis Solution. Contact us directly at buycasesolutions(at)gmail(dot)com if you want to order for Samsung Electronics Case Solution, Case Analysis, Case Study Solution.... More
Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Analysis. Get Samsung Electronics Case Study Analysis Solution. Contact us directly at buycasesolutions(at)gmail(dot)com if you want to order for Samsung Electronics Case Solution, Case Analysis, Case Study Solution. Jordan Siegel, James Jinho Chang Less
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Analysis Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Analysis. Our tutors are available 24/7 to assist in your academic stuff, Our Professional writers are ready to serve you in services you need. Every Case Study Solution & Analysis is prepared from scratch, top quality, plagiarism free. Authors: Jordan Siegel, James Jinho Chang Get Case Study Solution and Analysis of Samsung Electronics in a FAIR PRICE!! Steps for Case Study Solution Analysis: 1. Introduction of Samsung Electronics Case Solution The Samsung Electronics case study is a Harvard Business Review case study, which presents a simulated practical experience to the reader allowing them to learn about real life problems in the business world. The Samsung Electronics case consisted of a central issue to the organization, which had to be identified, analysed and creative solutions had to be drawn to tackle the issue. This paper presents the solved Samsung Electronics case analysis and case solution. The method through which the analysis is done is mentioned, followed by the relevant tools used in finding the solution. The case solution first identifies the central issue to the Samsung Electronics case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution. The tools used in identifying the solution consist of the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis. The solution consists of recommended strategies to overcome this central issue. It is a good idea to also propose alternative case study solutions, because if the main solution is not found feasible, then the alternative solutions could be implemented. Lastly, a good case study solution also includes an implementation plan for the recommendation strategies. This shows how through a step-by-step procedure as to how the central issue can be resolved. Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] 2. Problem Identification of Samsung Electronics Case Solution Harvard Business Review cases involve a central problem that is being faced by the organization and these problems affect a number of stakeholders. In the problem identification stage, the problem faced by Samsung Electronics is identified through reading of the case. This could be mentioned at the start of the reading, the middle or the end. At times in a case analysis, the problem may be clearly evident in the reading of the HBR case. At other times, finding the issue is the job of the person analysing the case. It is also important to understand what stakeholders are affected by the problem and how. The goals of the stakeholders and are the organization are also identified to ensure that the case study analysis are consistent with these. 3. Analysis of the Samsung Electronics HBR Case Study The objective of the case should be focused on. This is doing the Samsung Electronics Case Solution. This analysis can be proceeded in a step-by-step procedure to ensure that effective solutions are found. In the first step, a growth path of the company can be formulated that lays down its vision, mission and strategic aims. These can usually be developed using the company history is provided in the case. Company history is helpful in a Business Case study as it helps one understand what the scope of the solutions will be for the case study. The next step is of understanding the company; its people, their priorities and the overall culture. This can be done by using company history. It can also be done by looking at anecdotal instances of managers or employees that are usually included in an HBR case study description to give the reader a real feel of the situation. Lastly, a timeline of the issues and events in the case needs to be made. Arranging events in a timeline allows one to predict the next few events that are likely to take place. It also helps one in developing the case study solutions. The timeline also helps in understanding the continuous challenges that are being faced by the organisation. 4. SWOT analysis of Samsung Electronics An important tool that helps in addressing the central issue of the case and coming up with Samsung Electronics HBR case solution is the SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool that lists down in the form of a matrix, an organisation's internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. It helps in the strategic analysis of Samsung Electronics Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Once this listing has been done, a clearer picture can be developed in regards to how strategies will be formed to address the main problem. For example, strengths will be used as an advantage in solving the issue. Therefore, the SWOT analysis is a helpful tool in coming up with the Samsung Electronics Case Study answers. One does not need to remain restricted to using the traditional SWOT analysis, but the advanced TOWS matrix or weighted average SWOT analysis can also be used. 5. Porter Five Forces Analysis for Samsung Electronics Another helpful tool in finding the case solutions is of Porter's Five Forces analysis. This is also a strategic tool that is used to analyse the competitive environment of the industry in which Samsung Electronics operates in. Analysis of the industry is important as businesses do not work in isolation in real life, but are affected by the business environment of the industry that they operate in. Harvard Business case studies represent real-life situations, and therefore, an analysis of the industry's competitive environment needs to be carried out to come up with more holistic case study solutions. In Porter's Five Forces analysis, the industry is analysed along 5 dimensions. • These are the threats that the industry faces due to new entrants. • It includes the threat of substitute products. • It includes the bargaining power of buyers in the industry. • It includes the bargaining power of suppliers in an industry. • Lastly, the overall rivalry or competition within the industry is analysed This tool helps one understand the relative powers of the major players in the industry and its overall competitive dynamics. Actionable and practical solutions can then be developed by keeping these factors into perspective. 6. PESTEL Analysis of Samsung Electronics Another helpful tool that should be used in finding the case study solutions is the PESTEL analysis. This also looks at the external business environment of the organisation helps in finding case study Analysis to real-life business issues as in HBR cases. • The PESTEL analysis particularly looks at the macro environmental factors that affect the industry. These are the political, environmental, social, technological, environmental and legal (regulatory) factors affecting the industry. • Factors within each of these 6 should be listed down, and analysis should be made as to how these affect the organisation under question. Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] 7. VRIO Analysis of Samsung Electronics This is an analysis carried out to know about the internal strengths and capabilities of Samsung Electronics . Under the VRIO analysis, the following steps are carried out: • The internal resources of Samsung Electronics are listed down. • Each of these resources are assessed in terms of the value it brings to the organization. • Each resource is assessed in terms of how rare it is. A rare resource is one that is not commonly used by competitors. • Each resource is assessed whether it could be imitated by competition easily or not. • Lastly, each resource is assessed in terms of whether the organization can use it to an advantage or not. • The analysis done on the 4 dimensions; Value, Rareness, Imitability, and Organization. If a resource is high on all of these 4, then it brings long-term competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value, Rareness, and Imitability, then it brings an unused competitive advantage. If a resource is high on Value and Rareness, then it only brings temporary competitive advantage. If a resource is only valuable, then it’s a competitive parity. If it’s none, then it can be regarded as a competitive disadvantage. 8. Value Chain Analysis of Samsung Electronics The Value chain analysis of Samsung Electronics helps in identifying the activities of an organization, and how these add value in terms of cost reduction and differentiation. This tool is used in the case study analysis as follows: • The firm’s primary and support activities are listed down. • Identifying the importance of these activities in the cost of the product and the differentiation they produce. • Lastly, differentiation or cost reduction strategies are to be used for each of these activities to increase the overall value provided by these activities. Recognizing value creating activities and enhancing the value that they create allow Samsung Electronics to increase its competitive advantage. 9. BCG Matrix of Samsung Electronics The BCG Matrix is an important tool in deciding whether an organization should invest or divest in its strategic business units. The matrix involves placing the strategic business units of a business in one of four categories; question marks, stars, dogs and cash cows. The placement in these categories depends on the Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] relative market share of the organization and the market growth of these strategic business units. The steps to be followed in this analysis is as follows: • Identify the relative market share of each strategic business unit. • Identify the market growth of each strategic business unit. • Place these strategic business units in one of four categories. Question Marks are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Stars are those strategic business units with high market share and high market growth rate. Cash Cows are those strategic business units with high market share and low market growth rate. Dogs are those strategic business units with low market share and low growth rate. • Relevant strategies should be implemented for each strategic business unit depending on its position in the matrix. The strategies identified from the Samsung Electronics BCG matrix and included in the case pdf. These are either to further develop the product, penetrate the market, develop the market, diversification, investing or divesting. 10. Ansoff Matrix of Samsung Electronics Ansoff Matrix is an important strategic tool to come up with future strategies for Samsung Electronics in the case solution. It helps decide whether an organization should pursue future expansion in new markets and products or should it focus on existing markets and products. • The organization can penetrate into existing markets with its existing products. This is known as market penetration strategy. • The organization can develop new products for the existing market. This is known as product development strategy. • The organization can enter new markets with its existing products. This is known as market development strategy. • The organization can enter into new markets with new products. This is known as a diversification strategy. The choice of strategy depends on the analysis of the previous tools used and the level of risk the organization is willing to take. 11. Marketing Mix of Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics needs to bring out certain responses from the market that it targets. To do so, it will need to use the marketing mix, which serves as a tool in helping bring out responses from the market. The 4 elements of the marketing mix are Product, Price, Place and Promotions. The following steps are required to carry out a marketing mix analysis and include this in the case study analysis. • Analyse the company’s products and devise strategies to improve the product offering of the company. Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] • Analyse the company’s price points and devise strategies that could be based on competition, value or cost. • Analyse the company’s promotion mix. This includes the advertisement, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and direct marketing. Strategies will be devised which makes use of a few or all of these elements. • Analyse the company’s distribution and reach. Strategies can be devised to improve the availability of the company’s products. 12. Samsung Electronics Strategy The strategies devised and included in the Samsung Electronics case memo should have a strategy. A strategy is a strategy that involves firms seeking uncontested market spaces, which makes the competition of the company irrelevant. It involves coming up with new and unique products or ideas through innovation. This gives the organization a competitive advantage over other firms, unlike a red ocean strategy. 13. Competitors analysis of Samsung Electronics The PESTEL analysis discussed previously looked at the macro environmental factors affecting business, but not the microenvironmental factors. One of the microenvironmental factors are competitors, which are addressed by a competitor analysis. The Competitors analysis of Samsung Electronics looks at the direct and indirect competitors within the industry that it operates in. • This involves a detailed analysis of their actions and how these would affect the future strategies of Samsung Electronics . • It involves looking at the current market share of the company and its competitors. • It should compare the marketing mix elements of competitors, their supply chain, human resources, financial strength etc. • It also should look at the potential opportunities and threats that these competitors pose on the company. 14. Organisation of the Analysis into Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution Once various tools have been used to analyse the case, the findings of this analysis need to be incorporated into practical and actionable solutions. These solutions will also be the Samsung Electronics case answers. These are usually in the form of strategies that the organisation can adopt. The following step-by-step procedure can be used to organise the Harvard Business case solution and recommendations: Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] • The first step of the solution is to come up with a corporate level strategy for the organisation. This part consists of solutions that address issues faced by the organisation on a strategic level. This could include suggestions, changes or recommendations to the company's vision, mission and its strategic objectives. It can include recommendations on how the organisation can work towards achieving these strategic objectives. Furthermore, it needs to be explained how the stated recommendations will help in solving the main issue mentioned in the case and where the company will stand in the future as a result of these. • The second step of the solution is to come up with a business level strategy. The HBR case studies may present issues faced by a part of the organisation. For example, the issues may be stated for marketing and the role of a marketing manager needs to be assumed. So, recommendations and suggestions need to address the strategy of the marketing department in this case. Therefore, the strategic objectives of this business unit (Marketing) will be laid down in the solutions and recommendations will be made as to how to achieve these objectives. Similar would be the case for any other business unit or department such as human resources, finance, IT etc. The important thing to note here is that the business level strategy needs to be aligned with the overall corporate strategy of the organisation. For example, if one suggests the organisation to focus on differentiation for competitive advantage as a corporate level strategy, then it can't be recommended for the Samsung Electronics Case Study Solution that the business unit should focus on costs. • The third step is not compulsory but depends from case to case. In some HBR case studies, one may be required to analyse an issue at a department. This issue may be analysed for a manager or employee as well. In these cases, recommendations need to be made for these people. The solution may state that objectives that these people need to achieve and how these objectives would be achieved. The case study analysis and solution, and Samsung Electronics case answers should be written down in the Samsung Electronics case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The Samsung Electronics case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader. 15. Alternate solution to the Samsung Electronics HBR case study It is important to have more than one solution to the case study. This is the alternate solution that would be implemented if the original proposed solution is found infeasible or impossible due to a change in circumstances. The alternate solution for Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Samsung Electronics is presented in the same way as the original solution, where it consists of a corporate level strategy, business level strategy and other recommendations. 16. Implementation of Samsung Electronics Case Solution The case study does not end at just providing recommendations to the issues at hand. One is also required to provide how these recommendations would be implemented. This is shown through a proper implementation framework. A detailed implementation framework helps in distinguishing between an average and an above average case study answer. A good implementation framework shows the proposed plan and how the organisations' resources would be used to achieve the objectives. It also lays down the changes needed to be made as well as the assumptions in the process. • A proper implementation framework shows that one has clearly understood the case study and the main issue within it. • It shows that one has been clarified with the HBR fundamentals on the topic. • It shows that the details provided in the case have been properly analysed. • It shows that one has developed an ability to prioritise recommendations and how these could be successfully implemented. • The implementation framework also helps by removing out any recommendations that are not practical or actionable as these could not be implemented. Therefore, the implementation framework ensures that the solution to the Samsung Electronics Harvard case is complete and properly answered. 17. Recommendations and Action Plan for Samsung Electronics case analysis For Samsung Electronics, based on the SWOT Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, PESTEL Analysis, VRIO analysis, Value Chain Analysis, BCG Matrix analysis, Ansoff Matrix analysis, and the Marketing Mix analysis, the recommendations and action plan are as follows: • Samsung Electronics should focus on making use of its strengths identified from the VRIO analysis to make the most of the opportunities identified from the PESTEL. • Samsung Electronics should enhance the value creating activities within its value chain. • Samsung Electronics should invest in its stars and cash cows, while getting rid of the dogs identified from the BCG Matrix analysis. Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] • To achieve its overall corporate and business level objectives, it should make use of the marketing mix tools to obtain desired results from its target market. Email us for Any Case Solution at: [email protected] Note: This article is just a sample and not an actual case solution. If you want original case solution, please place your order on the Email. Please do check Junk/Spam folder of your E-mail for our reply, if not in Inbox.
- Related publications
- Add to favorites
Parrots love playing tablet games. That’s helping researchers understand them.
- Search Search

New research from Rébecca Kleinberger’s lab at Northeastern University delves deep into the data on how parrots use touchscreen devices, with the help of a bespoke gaming app.

- Copy Link Link Copied!
Touchscreens have long been integral to our everyday life — humans use them to work, play, talk with loved ones and snag Lightning Deals on Prime Day. In recent years, they’ve shown potential for the animal kingdom as well, leading to a growing body of academic research and a proliferation of consumer products promising to leverage technology to enhance our relationships with our pets.
Northeastern assistant professor Rébecca Kleinberger and her collaborators have been at the forefront of that exploration, using computer interaction to enrich and understand the lives of dogs, orcas and parrots. Their latest research begs the next logical question: If animals are going to use touchscreens, how should we design for them?
Parrots are helping them find the answer — by playing tablet games.
In a new study released Wednesday, Kleinberger; Megan McMahon, an undergraduate studying behavioral neuroscience; and collaborators Ilyena Hirskyj-Douglas at the University of Glasgow and Jennifer Cunha in Florida used a bare-bones, Balloon Pop -style tablet game to collect data on a group of 20 pet birds’ tactile interactions with their touchscreens.
In doing so, they hoped to establish a framework to build tech intentionally designed for parrot use.
Northeastern Global News, in your inbox.
Sign up for NGN’s daily newsletter for news, discovery and analysis from around the world.
“Cognitive enrichment is a crucial component for parrot health and well-being, and tablet games are one method of providing this enrichment,” McMahon says. “Designing apps specifically made for birds and their unique touchscreen tendencies makes this form of enrichment more accessible.”
The parrot participants ranged from small species, like a green-cheeked parakeet, to a hyacinth macaw, the world’s largest. All had prior experience using touchscreens and completed the study in their homes. With the help of their caregivers, they learned to use a basic app game on Samsung Galaxy tablets. Adapted by McMahon, the game challenged the birds to tap multi-colored target circles of different sizes on varying locations around their screens with their beaks and tongues.
The birds engaged in short sessions (no longer than 30 minutes) each day, playing the game over the course of three months. Seventeen completed the study; three dropped out after showing slight signs of aggression or a lack of interest during the training period. The game collected information on the birds’ accuracy, tap locations and frequency, as well as tactile elements like touch pressure and drag rate.
The team’s data evaluated how well existing, human-based touchscreen design principles translated to parrots. Specifically, they honed in on Fitts’ Law , a formula that predicts human pointing movement toward targets.
Some of the paper’s findings are intuitive enough: Parrots primarily use their tongues to work tablets, for example, which means their eyes are much closer to the screen than a human’s. As a result, they are quantifiably less accurate, and they fare better hitting larger targets. There was also a lot of variability in performance based on the birds’ size — smaller birds tended to have more trouble.
But the data-based assessment revealed much about the parrots themselves, as well. Kleinberger was surprised “just how fast some parrot species can control their tongue,” she says. “Some parrots could touch the tablet up to 41 times in a row, resulting in a touch every few milliseconds.”
That led to a real-time ergonomic adjustment: the team added a “multi-tap threshold” to the app’s interface during the study, making it less frustrating for the birds to use. “This …is a good example of how studying animals’ bodies can inform the design of new interfaces to empower animals,” Kleinberger says.
The findings, to be presented at the CHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in May, signal a next step for Kleinberger and her collaborators. Their past research has shown that parrots — with their prodigious intelligence, high sociability and singular physical capabilities — are uniquely poised to benefit from touchscreen technology.
Last year, the team showed a group of parrots how to video call one another, finding that the birds both overwhelmingly enjoyed the activity and could make the calls themselves, when given the option.
The latest research further bolsters the case that touchscreens can enrich parrots’ lives. In surveys after the study was completed, human handlers said the experience was positive for their birds, and that participating in the study together was a great bonding experience. Kleinberger says that is by design. She stresses that the systems her lab is developing are meant for humans and animals to use together, and as an enhancement to their interactions rather than as a replacement.
As with humans and touchscreens, there are potential drawbacks — some familiar (“Participants in our study often emphasized the risk of their birds’ overuse, likening their screen time needs to those of children,” the paper reads); others uniquely avian (“When asked what risks tablet applications could pose to parrots, the most common answer was ‘potential damage to the tablet.’”)
In the longer term, the researchers hope the findings will serve as a starting point in adapting screen technologies for parrots and, eventually, other species. Kleinberger thinks it can bring some academic rigor to the booming “pet tech” market, “with new products promising to improve animal welfare with often very little data and research to back up the claims,” she says.
“My goal is for these insights not only to benefit the pet tech industry but also to offer valuable guidance to the wider research community, technology developers, [and] pet owners,” Kleinberger says.
Science & Technology

Recent Stories


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's start the detailed case study from here. Samsung entered the electronics industry in the late 1960s and the development and shipbuilding ventures in the mid-1970. Following Lee's demise in 1987, Samsung was divided into five business groups - Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, Hansol Group and Joongang Group.
PDF | On Apr 19, 2020, Ahmed Gadalla published SAMSUNG MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
In this blog post, we delve into a Samsung crisis management case study to learn about exploding batteries to the intricate strategies employed to restore trust. Samsung's journey offers valuable insights into the intricacies of crisis management in the digital age. Join us as we explore the key lessons learned and best practices from this ...
Case Study: Samsung's Innovation Strategy. The success of Samsung has been widely acknowledged in the last decade. Samsung, the world's largest television producer and second largest mobile phone manufacturer, is also the largest firm of flash memory maker. Furthermore, Samsung was ranked by Fast Company Magazine to be third most innovative ...
Business Analysis Case Study Introduction. Samsung is one of the well-known companies in South Korea and is the abbreviation of Samsung Group, Korea's largest enterprise group. The Samsung Group is Korea's largest multinational conglomerate and can be regarded as one of the 'World's Most Admired Companies. The Samsung Group includes a number of ...
Other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership, differentiation focus, and cost focus, are also applied in Samsung's operations, but to a limited extent. Cost focus leads to the company's being the best-cost provider in some segments of the semiconductor and electronic components markets. The limited application of cost focus ...
Case Studies Interactive Displays Interactive whiteboards promote learning, collaboration at Hogg New Tech Center The James S. Hogg New Tech Center elementary school replaced its aging technology with versatile, interactive displays, enabling teachers to create more immersive learning experiences and students to collaborate more effectively and ...
In this study, the case of Samsung Electronics (SE), now the largest electronic firm in the world from a former emerging economy, is examined to unveil the processes of harvesting and planting innovation and their results. Innovative activities have been the core strength of SE and are expected to continue creating value for SE.
The Analysis of Strategic Management of Samsung Electronics Company through the Generic Value Chain Model ... The case study is the methodology when the focus is on a contemporary phenomenon within a real-business context. Findings - The findings reveal that Samsung electronic uses a number of the generic value chain model in creating a shared ...
When the company introduced Samsung Galaxy and leveraged the power of digital platforms for promotions and marketing, its revenue grew to $218 billion in 2018. Today, Samsung stands 5th on Interbrand's list of Best Global Brands with a brand value of USD 74.6 billion. It has witnessed a 20% increase in comparison to the last year.
Samsung Electronics Company Case Solution,Samsung Electronics Company Case Analysis, Samsung Electronics Company Case Study Solution, Introduction Samsung started its operations in the late 60's. Over the period of time, Samsungdeveloped its stance in the television market by offering
STEP 1. Problem Identification in Samsung Electronics case study. STEP 2. External Environment Analysis - PESTEL / PEST / STEP Analysis of Samsung Electronics case study. STEP 3. Industry Specific / Porter Five Forces Analysis of Samsung Electronics case study. STEP 4. Evaluating Alternatives / SWOT Analysis of Samsung Electronics case study.
Samsung's Mobile team does so at least twice a year. With mounting pressure from lower-quality competitors and a rapidly changing global marketplace, it's critical to understand the complex galaxy of variables that can impact success. ... Read this case study to learn how Samsung is able to successfully address critical business decisions ...
Samsung Case Study: Samsung is one of the most successful corporations which offer a wide choice of products and services, mostly based on electronics, finance, building and industry. ... Analysis of Samsung's business strategy and competitive advantage Porter's 5 forces model in Exhibit 1 is […] Samsung - Competitive Analysis.
Table 1. Samsung's risk assessment. According to the risk events highlighted in Table 1 above, two risk categories affect Samsung's operations - COVID-19 and trade wars. The above risks have been ranked according to the risk profile matrix highlighted in figure 2 below and trade wars is the most impactful. Figure 2.
After analyzing the case, students should be able to: Organize and analyze qualitative data using affinity diagrams. Identify priorities using Pareto charts. The case reinforces the importance of approaching problem solving in a methodical and data-driven manner and demonstrates the power of visual (vs. table-driven) tools.
So, let's understand how to write a Samsung case study SWOT analysis. Understanding SWOT Analysis. Samsung was founded in 1938 in South Korea. It has various affiliated businesses that have ...
The key focus of this article is on the external environmental drivers. The STEEPLE analysis will focus on the following 7 factors: Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical. The initials for these make up the acronym STEEPLE. S for Social. As I mentioned already, Samsung is a South Korean Chaebol.
Discussion on Samsung Note 7 Failure. The failure of Samsung's Galaxy Note 7 has had enormous financial implications. It is estimated that it may lead to a revenue loss of over $ 5 billion. Even though the company could easily deal with the loss of income, the failure has great social and legal ramifications.
With the transformation that was led by the leadership of SEC Chairman Kun Hee Lee, Samsung rebuilt its image as a global business leader. We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically. For You For Only $13.90/page! order now. Following the chairman's new management initiative, Samsung is now in a stage of investing in innovative and premium ...
The quality and creative input within the product gives a huge advantage to the suppliers and puts him in a bargaining position. Samsung producing high-quality memory chips at relatively low cost has been able to bargain with its customers. Samsung Case Study Analysis discusses about five forces analysis, R & D of company, business strategy and ...
The case study analysis and solution, and Samsung Electronics case answers should be written down in the Samsung Electronics case memo, clearly identifying which part shows what. The Samsung Electronics case should be in a professional format, presenting points clearly that are well understood by the reader. 15.
The parrot participants ranged from small species, like a green-cheeked parakeet, to a hyacinth macaw, the world's largest. All had prior experience using touchscreens and completed the study in their homes. With the help of their caregivers, they learned to use a basic app game on Samsung Galaxy tablets.