Networking | Cloud | DevOps | IaC

IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server is an important element to networking in the real world. User location cannot be predicted as they may be at and out of a desk and up and about should they need to do so. Tying them to a local VLAN may only be helpful if they are bound to desks in those locations, although the most ideal outcome, it is not the most practical.
It is only wise to incorporate IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server in areas where you expect different teams to come to. Meeting rooms could for a moment have the accounting group or the development group meeting there and based on the intelligent and dynamic vlan assignmnet with 802.1x authentication, users port-access are defined their appropriate vlans for their respective access to resources on the network.
How to Provision 802.1 X Authentication Step By Step With Dynamic VLAN Assignment With Windows Radius Server For 802.1x Clients.
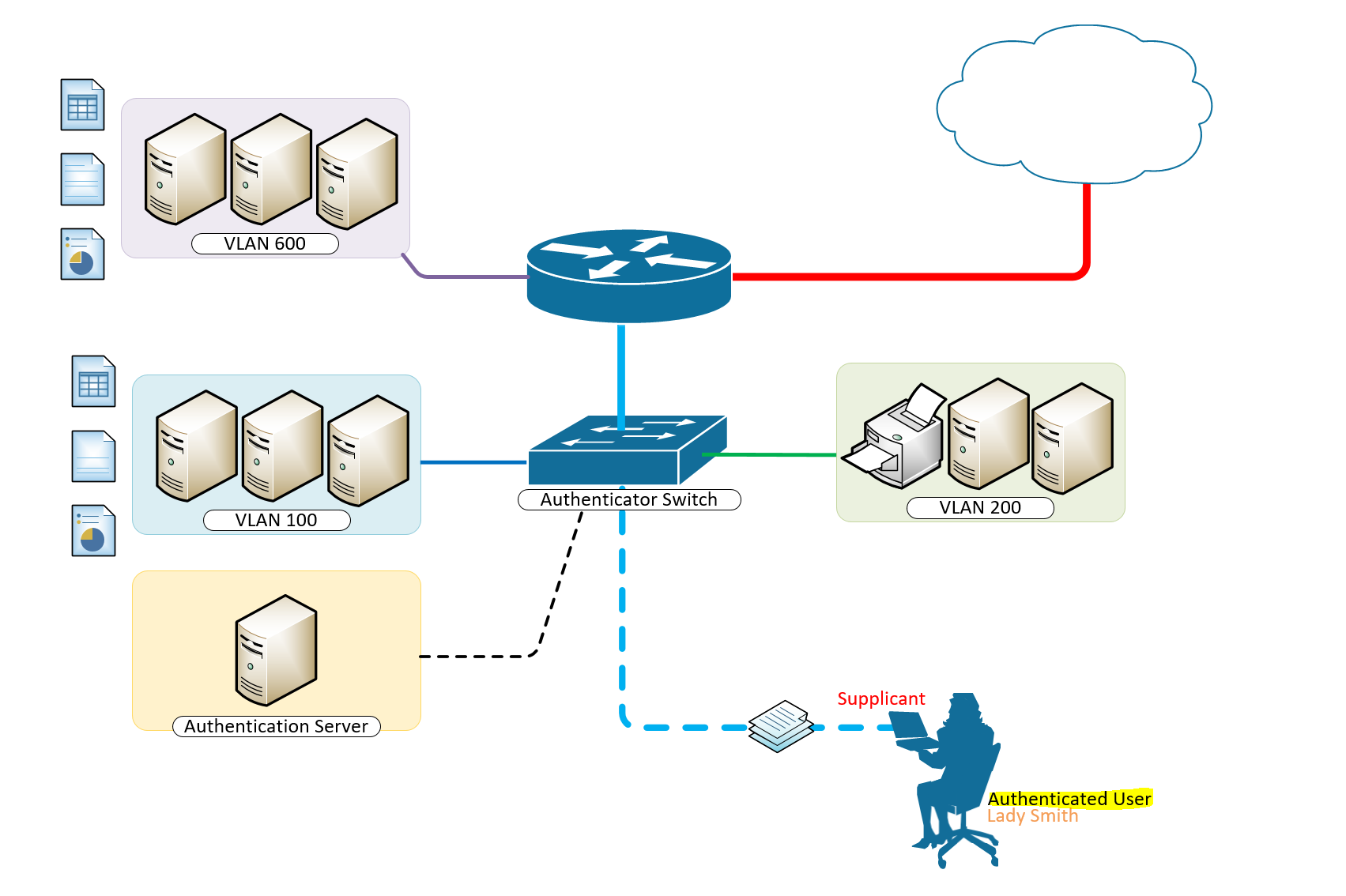
A typical configuration for a system under IEEE 802.1x Authentication control is shown in the following figure.
In this scenario, “Lady Smith” wishes to use services offered by servers on the LAN behind the switch. There are multiple VLANs with resources available based on user vlan membership. Her laptop computer is connected to a port on the Aruba 2920 Edge Switch that has 802.1x port authentication control enabled.
The laptop computer must therefore act in a supplicant role. Message exchanges take place between the supplicant and the authenticator which is the Aruba 2920 Switch, and the authenticator passes the supplicant’s credentials which is her (Windows Active Directory User Account Credentials) to the authentication server for verification. The NPS Server which is the authentication server then informs the authenticator whether or not the authentication attempt succeeded, at which point “Lady Smith” is either granted or denied access to the LAN behind the switch.
Setup Structure for IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
- Supplicant: Laptop running Microsoft Windows 10 or Windows 7
- Authenticator: HP Aruba 2920 Edge Switch
- Authentication Server: Microsoft NPS (Network Policy Server) running on Windows Server 2012 R2.
- User Database : Active Directory
For Windows Infrastructure
Create NPS Server – Add Role on Windows Server 2012 R2
- Create DHCP Scopes for VLANS
Create RADIUS Client on NAC using Network Policy Server
- Create Network Policies
- Configure a Network Policy for VLANs
- Start Wired Auto-Config Service
- Enable Network Authentication
Create the DHCP Scopes for VLAN100 and VLAN200 Groups
- Development Group Scope – VLAN 100
SVI: ip address 172.16.80.254 255.255.255.0 Scope Subnet: 172.16.80.1/24
- Accounting Group Scope – VLAN 200
SVI:ip address 172.16.70.254 255.255.255.0 Scope Subnet: 172.16.70.0/24
Secret Key: secret12
Add Edge Switch Management IP as the RADIUS Client
The Shared Secret Key: secret12 will be used in the Switch Configuration.
Create Network Policy Settings for Accounting Group for VLAN 200
Configuration Example
Here’s an example of how you might consider when configuring Microsoft NPS Server to assign users to a VLAN based on their user group, using NPS for the authentication and authorization of users. This configuration has worked flawlessly on the HP Aruba 2920 Switch. The key to getting this to work is the use of a RADIUS element called: ‘Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID’. This is a RADIUS attribute that may be passed back to the authenticator (i.e. the Aruba 2920 Switch) by the authentication server (i.e. Microsoft NPS Server) when a successful authentication has been achieved. There are a few other elements which need to accompany it, but this is the key element, as it specifies the VLAN number that the user should be assigned to.
The other elements that need to be returned by the NPS Server are as follows:
- Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID: 200
- Service-Type: Framed
- Tunnel-Type: VLAN
- Tunnel-Medium-Type: 802
For Client Infrastructure
On the Supplicant, Windows 7 or 10 configure the following steps on the Ethernet Adapter to enable IEEE 802.1X Authentication
For Network Infrastructure
Connect Server Infrastructure to VLAN 400
Create VLAN for Accounting Group
Create VLAN for Development Group
Create AAA Configuration on Switch for Radius Authentication
Download the Switch Configuration:
Test the IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
Verify Port-Access with the following user groups – VLAN 100 and VLAN 200
Think of what other clever things you can do from the information below;
Breakdown of Commands for RADIUS Authentication
Verification Commands
Thanks for reading. Please share your thoughts in the comment box below;
Published in Configuring , Design , Installing and Configuring , Networking , Security and Switching
- 802.1 x authentication step by step aruba
- 802.1 x authentication step by step cisco
- 802.1 x wireless authentication step by step
- 802.1x authentication process
- 802.1x authentication windows 10
- 802.1x authentication windows server 2012
- 802.1x certificate authentication
- assignment wlc
- cisco dot1x
- cisco ise dynamic vlan
- cisco ise dynamic vlan assignment wlc
- cisco wireless radius attributes
- configuration example
- dynamic vlan assignment cisco 2960 dynamic vlan configuration in packet tracer
- dynamic vlan assignment with windows radius server
- dynamic vlan cisco
- dynamic vlan ruckus
- meraki dynamic vlan assignment
- nps mac authentication wired
- nps policy for mac-based authentication
- radius multiple vlans
- vlan radius server
- vlan steering
- vmps server

- PORTNOX CLOUD Unified Access Control Any Device. Any Data. Anywhere.
Zero Trust Network Access Control
- Cloud-native RADIUS Stand up Portnox’s cloud-native RADIUS is minutes.
- Passwordless authentication Leverage certificates for passwordless network authentication.
- Risk posture assessment Monitor the potential risk of every connected device.
- Compliance enforcement Automate device remediation & stay compliant 24/7.
- Explore Pricing
Zero Trust Conditional Access
- How does it work? Discover how to better secure your apps with Portnox.
- Passwordless authentication Bolster application access by going passwordless.
- 24/7 risk monitoring Ensure only trusted devices gain access to your apps.
- Automated remediation Automate device-based compliance enforcement.

Zero Trust Infrastructure Administration
- How does it work? Explore cloud-native TACACS+ from Portnox.
- Admin authentication Get started with simple, secure admin authentication.
- Access policy enforcement Make sure not just anyone can tinker with your infrastructure.
- Granular accounting Keep auditors at bay with cloud-native TACACS+.

Unified Zero Trust Security
- How does it work? Learn the ins and outs of the Portnox Cloud.
- Cloud-native RADIUS authentication Spin up our cloud-native RADIUS server in minutes.
- Passwordless application security Bolster application access by going passwordless.
- Zero trust network access control See and control access for every device across your network.
- Network device administration Keep auditors at bay with cloud-native TACACS+.

- Authentication
- Access Control
- Risk Monitoring
- Remediation
- IoT Security
- Guest Access
Applications
Infrastructure.
- Authorization
Integrations
- Case Studies
- Infographics
- Product Briefs
- White Papers
- Cloud Documentation
Compliance Center
Regulations, cybersecurity center.
- What is 802.1X? What are the benefits of NAC? How does zero trust work? Why go passwordless? What is IoT profiling? Explore All »
- Reseller Program
- Managed Services
- Become a Partner
- Register a Deal
- Get Started
Network Access Control , Network Security
Segmenting your network with dynamic vlan.

What is Dynamic VLAN?
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) enable segmentation of the main organizational network. In practice, VLANs allow network administrators to keep devices and network resources separated despite being connected to the same physical network.
Dynamic VLAN assignment separates and isolates devices into different network segments based on the device or user authorization and their characteristics. The flow of traffic between those VLANs is governed by a firewall or another routing device which can then enforce specific network access rules.
Why Use Dynamic VLANs?
Segmenting the network is a security best practice, and in some cases is even a regulatory requirement – such as with PCI. Network segmentation is a measure that improves the effectiveness of all the current investments in other security tools, and can by itself help to prevent significant damage to critical organizational data across the network after a company has been breached.
Automating VLAN assignments and eliminating the need for manual intervention has historically been a challenge for network security teams. Today, automatic VLAN assignment is best implemented by the use of a RADIUS service, which functions as follows:
- A device connects to one of several the network access layers: wired ethernet switch or WiFi SSID
- The network access layer sends a request to the RADIUS server with the user’s credentials or certificates (using 802.1X)
- The RADIUS server sends a reply which contains attributes that provide the switch or access point with information on the device VLAN, result in properly VLAN assignment
Common Dynamic VLAN Assignment Use Cases
Network and security administrator most commonly encounter these use cases for dynamic VLAN assignment:
- The Sales & Marketing department does not need access to R&D resources, while R&D should not have access to the Finance Department resources. Using dynamic VLANs, each department will be placed in the correct VLAN with the required access.
- Devices that fail to authenticate due to wrong credentials or incorrect/expired certificate will be placed in a quarantine VLAN with internet access only.
- IP Phones using a dedicated voice VLAN and should be placed on that VLAN upon successful authentication.
- MAC bypass for devices that do not support 802.1X should be placed in their own dedicated VLAN.
- Devices that fail posture assessment (such as those without updated AntiVirus) should be placed in a quarantine VLAN with limited access.
- Employees connecting to one single WiFi SSID and get different access (VLANs) based on their authentication repository LDAP groups.
Dynamic VLAN Assignment with Portnox CLEAR
As mentioned earlier, the implementation of dynamic VLAN assignment has often been challenging for organizations since additional servers were needed on-site at the datacenter. This forced network teams to manage redundancies, complex configurations, and on-going maintenance.
To paint a clearer picture of this headache, consider this:
Take the case of connecting a new department, branch, or merely onboarding a lot of new employees at once…this can cause a surge in demand, which will in turn cause the whole network to “shutdown,” thus not accepting anyone who tries to connect.
Portnox CLEAR is a network access control solution, deployed as a cloud service, that provides all the mentioned use cases and more. CLEAR simplifies the implementation process of dynamic VLAN assignment. CLEAR allows you to easily set-up a cloud RADIUS server in a single click, and integrate with various authentication repositories like on-premise Active Directory, Azure AD, GSuite, OKTA. Plus, you can enforce your own unique access control policy to dynamically assign users to their respective VLANs.
In addition to VLAN assignment based on credentials authorization, CLEAR also allows you to implement dynamic VLAN assignment based on risk violation. This means that even devices that have authenticated successfully to the wired or wireless network can be dynamically moved to a dedicated VLAN if they fall out of compliance.
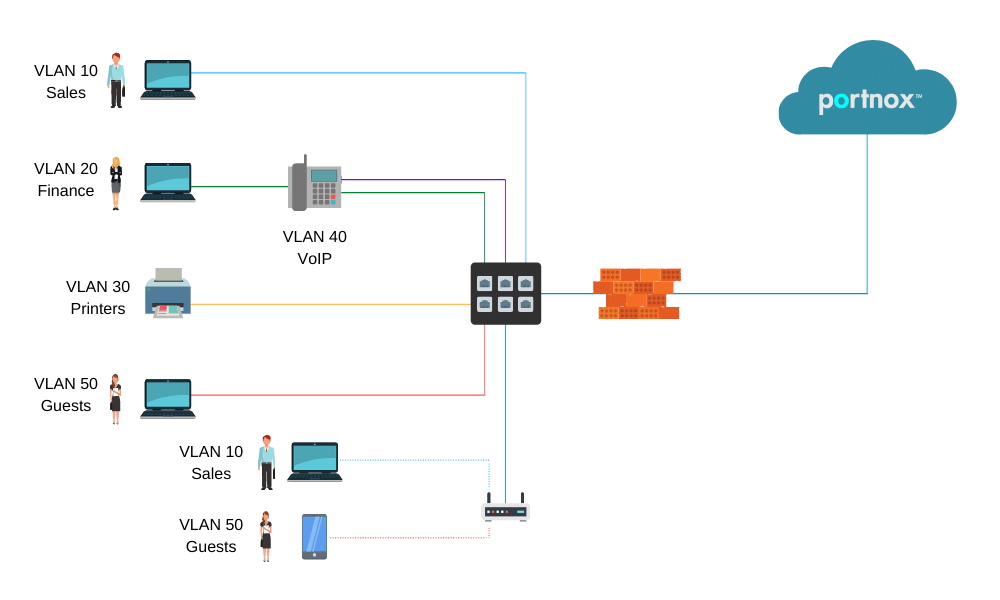
In the diagram above:
- PCs are dynamically assigned to the VLAN based on their credentials/certificate.
- IP Phones are assigned to the VOIP VLAN.
- Printers are assigned to the printers VLAN.
- Guests devices assigned to the internet-only access/quarantine VLAN.
How it Works – Setting up Dynamic VLAN Assignment in Portnox CLEAR:
1. enable cloud radius.
In the CLEAR portal, create your one-click cloud RADIUS server: Go to Settings > Services > CLEAR RADIUS Service , and add your RADIUS service instance:
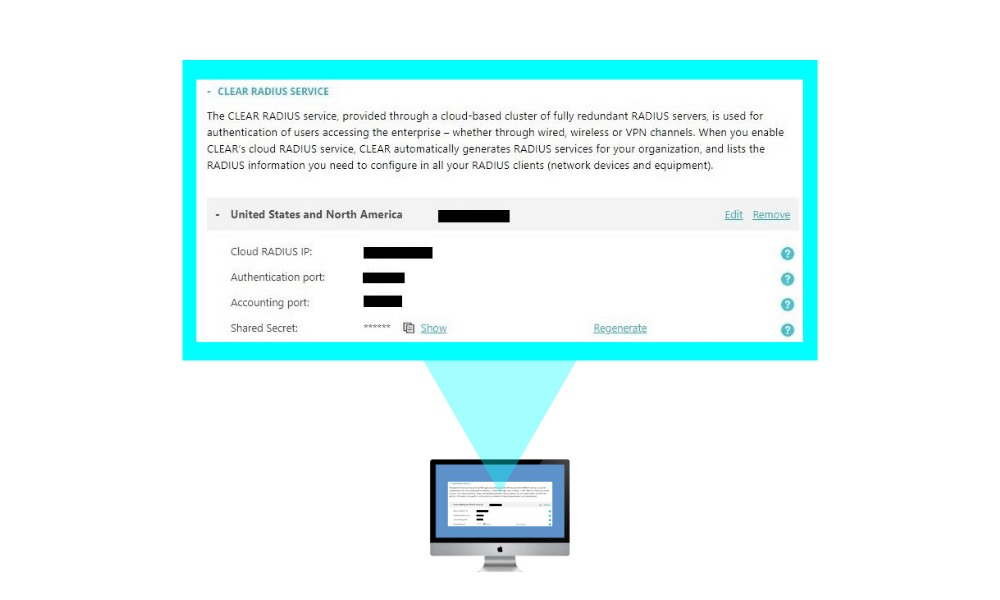
And point your network equipment: wired switches and/or wireless controllers to work with these CLEAR Radius service details.
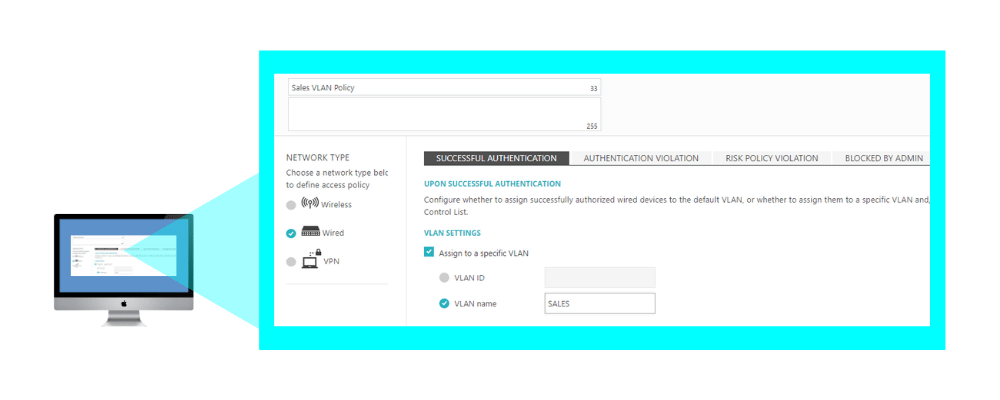
2. Creating an Access Control Policy – Dynamic VLAN Assignment:
In Policies > Access Control Policies , add or edit your existing access control policy, select the required access layer and add the correct VLAN ID or VLAN name for each event you want to create dynamic VLAN assignment for: successful authentication, authentication violation, risk assessment, blocked by admin. Then, map the access control policy to the relevant groups and users.
Related Reading

Decoding Unified Access Control: A Comprehensive Guide

Tackling Device Access with Custom TACACS+

Securing Your Network: Combat Insider Threats with Network Access Control
Try portnox cloud for free today.
Gain access to all of Portnox's powerful zero trust access control free capabilities for 30 days!
Privacy Overview
Portnox debuts passwordless zero trust conditional access for applications

Microsoft NPS as a RADIUS Server for WiFi Networks: Dynamic VLAN Assignment
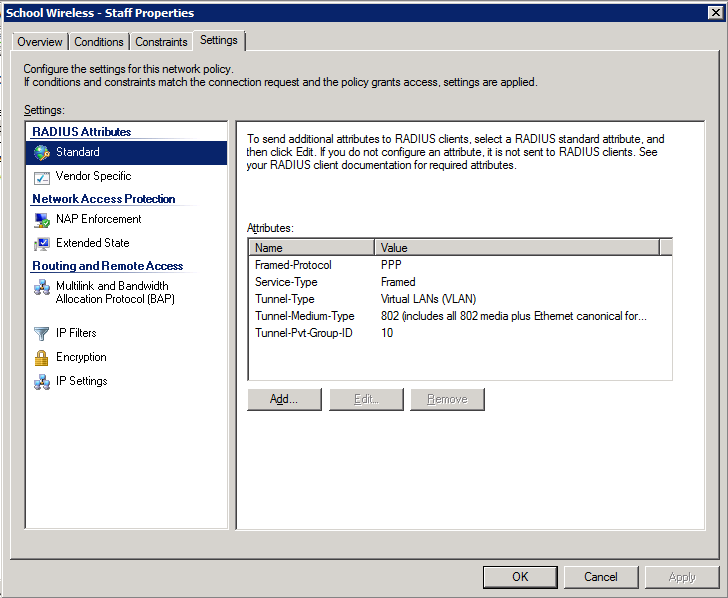
Configuration Example Here’s an example of how to configure NPS to assign users to a VLAN based on their user group, using NPS for the authentication and authorization of users. The key to getting this to work is the use of a RADIUS element called: ‘Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID’. This is a RADIUS attribute that may be passed back to the authenticator (i.e. the WLC or AP) by the authentication server (i.e.NPS) when a successful authentication has been achieved. There are a few other elements which need to accompany it, but this is the key element, as it specifies the VLAN number that the user should be assigned to. The other elements that need to be returned by NPS are:
- Service-Type: Framed
- Tunnel-Type: VLAN
- Tunnel-Medium-Type: 802
- Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID: <VLAN Number>
We’ll have a look at how we specify each of these attributes in an NPS policy. For our example, we’ll assign all ‘staff’ users to VLAN 10 and all ‘student’ users to VLAN 20. Here is an overview of what the network might look like (this is obviously very simplified, but gives an overview of the type of thing that might be achieved):
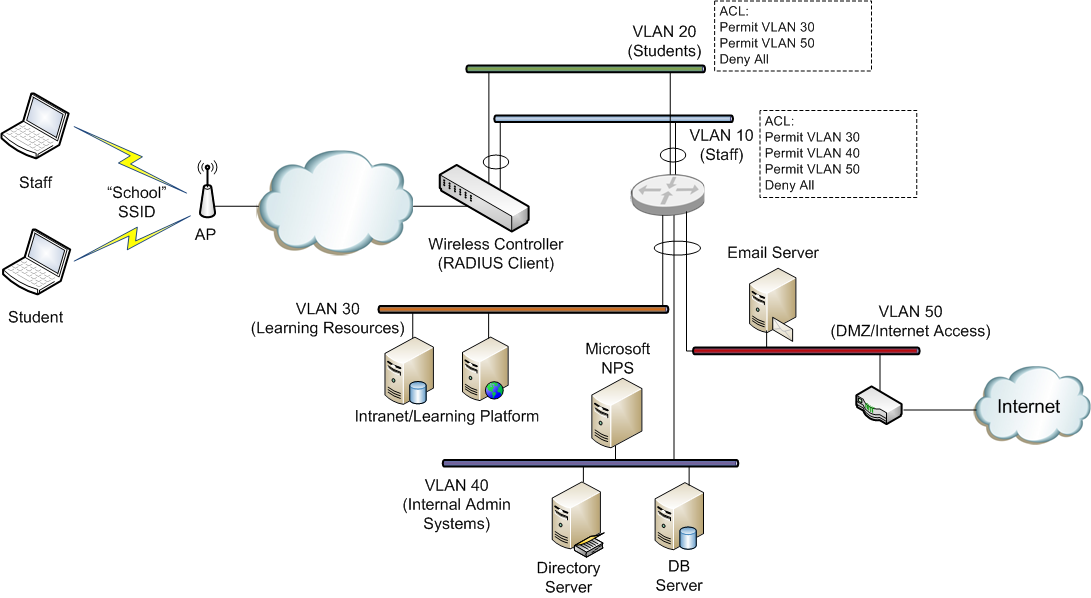
VLAN 10 has an ACL (access control list) that allows users on this VLAN to access all systems across the school network. The ACL would generally be configured on the layer 3 switch or router that interconnects the school VLANs) VLAN 20 has an ACL which only allow access to the learning system VLAN and the Internet related services. By studying the example above, you can see that if we can control a users VLAN assignment, based on their AD group membership, we can ensure that they only receive the network access to which they are entitled (purely via their AD group membership). Also, note that this is all being done on a single SSID (“School” in this case). Now we’ll take a look at how we achieve this using NPS. NPS Configuration To configure NPS to provide the VLAN assignments outlined above, we will create 2 policies within NPS:
- School Wireless – Staff (to assigned members of the staff AD group to VLAN 10)
- School Wireless – Students (to assign members of the students AD group to VLAN 20)
The screen-shots below outline the configuration required. Here is the policy summary screen within NPS. Note that when configuring multiple policies, the order of the policies is important. Policies are assessed top-down, so make sure the policies that need to be hit are enabled and above any disabled polices.
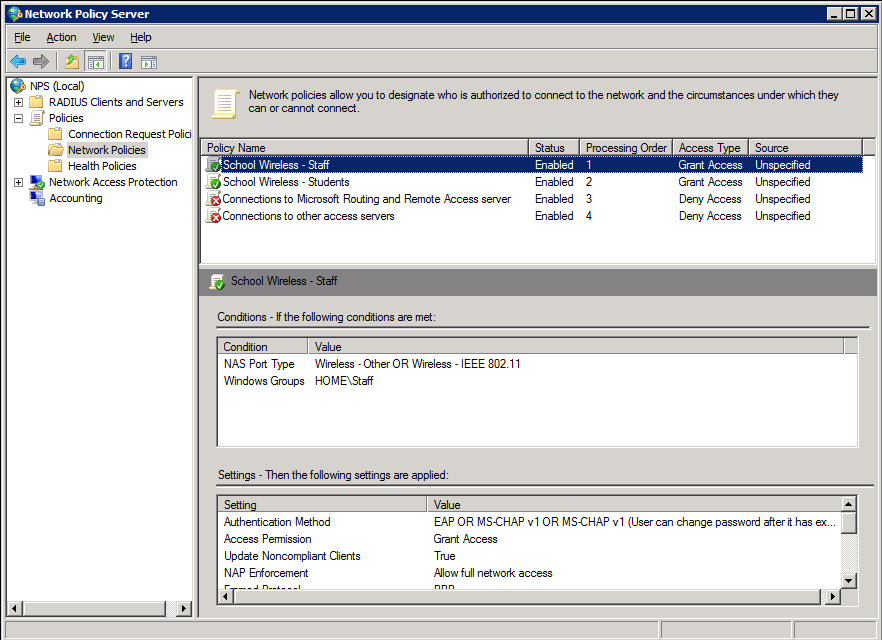
Staff Policy 1. Create the policy and enable it:
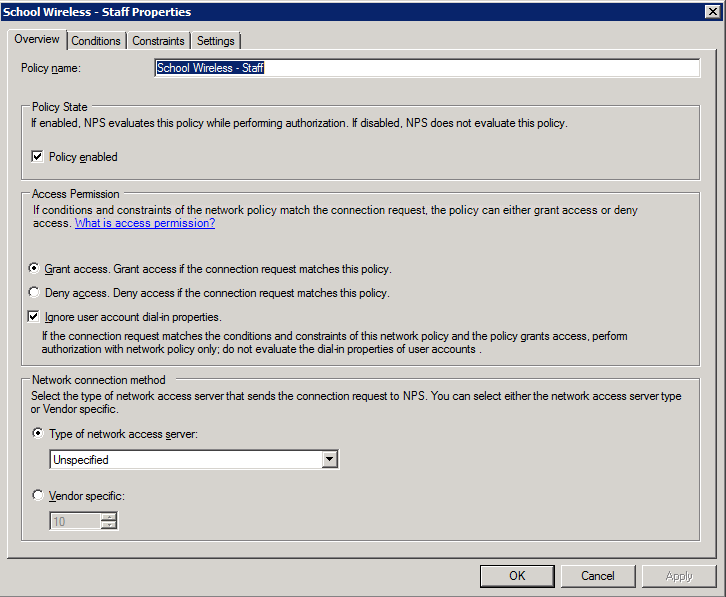
2. Add the NAS type and AD group membership conditions (must be members of the staff group):
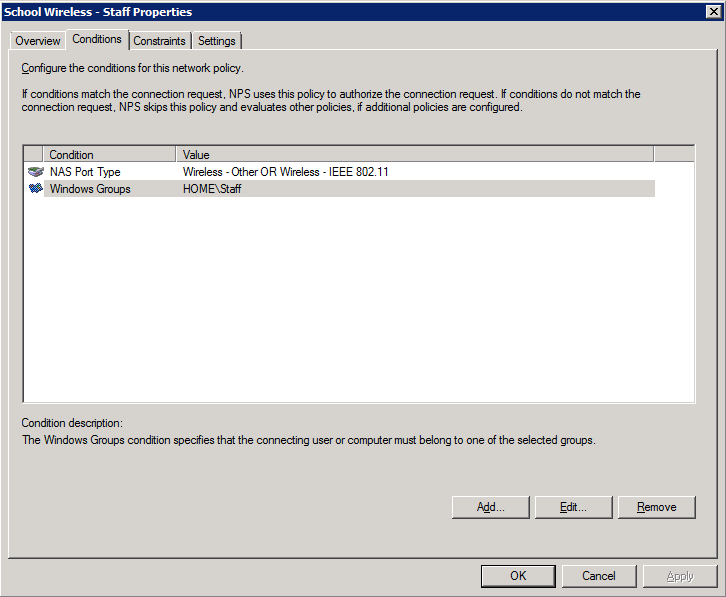
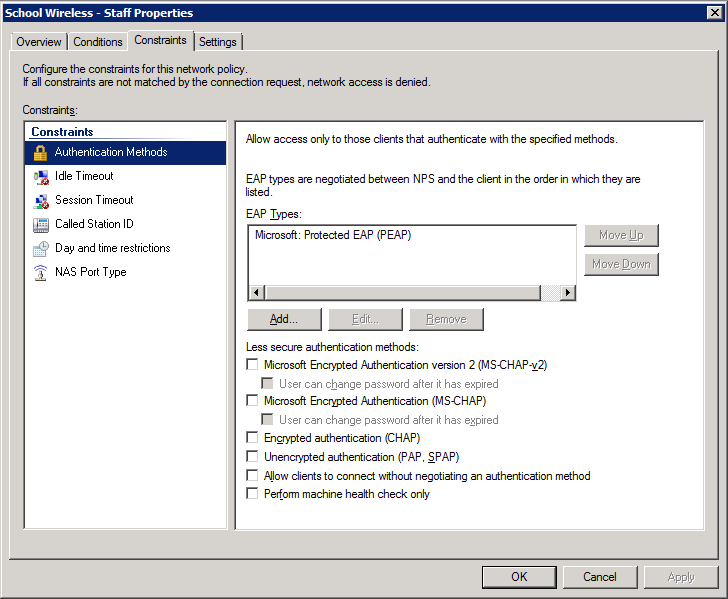
3. Select and configure an EAP type (note this may be PEAP or EAP-TLS – we’ve shown PEAP just as an example)
4. Configure the settings for this policy to assign any users which match this policy to VLAN 10:
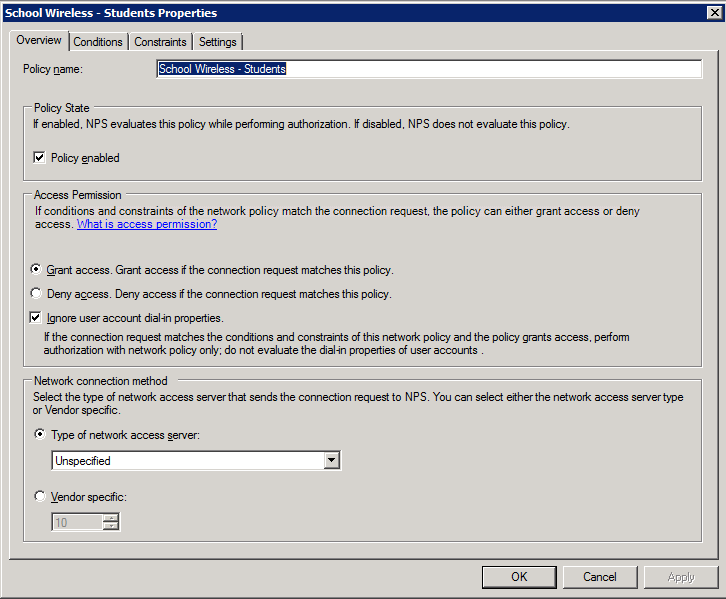
Students Policy 1. Create the policy and enable it:
2. Add the NAS type and AD group membership conditions: (must be members of the students group to match this policy)
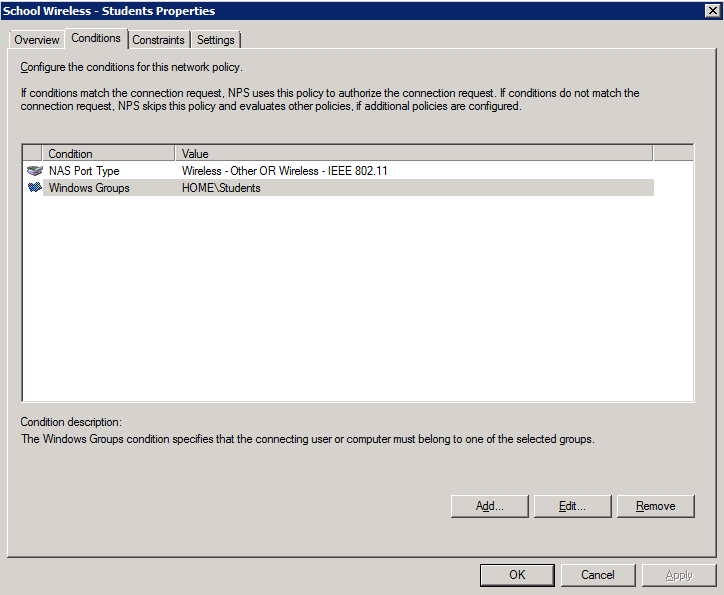
4. Configure the settings for this policy to assign any users which match this policy to VLAN 20:
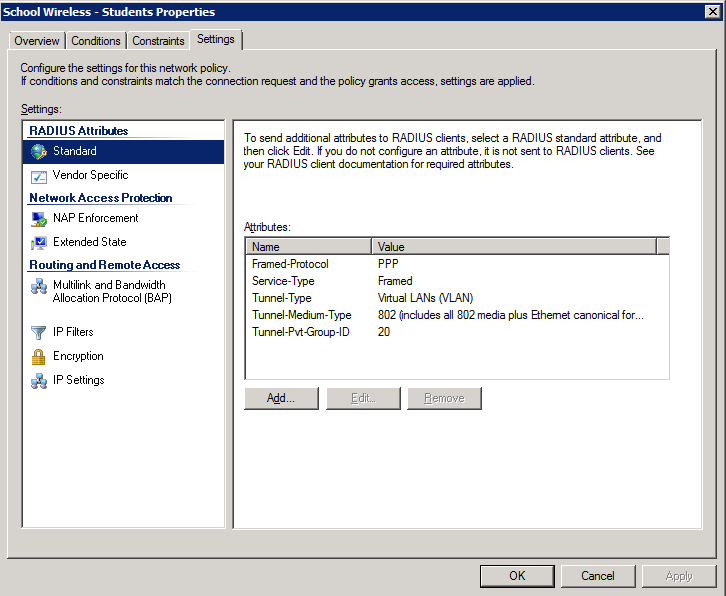
Once NPS has been configured with policies similar to those shown above, users can be dynamically assigned to an appropriate VLAN based on their AD group membership. As we’ve already discussed, this provides great benefits in reducing additional overheads associated with multiple SSIDs on a WiFi network. In addition, it simplifies user wireless management by allowing all users to be configured with a single wireless client profile, with their access being configured via Microsoft AD. One caveat to note when trying to use this technique is that all users must be using the same security mechanisms to join the SSID. For instance, all users must be using 802.1x (EAP) – you can’t have a mix of PSK & 802.1x authenticated devices on the same SSID. Generally, they should also be using the same WPA version (i.e. WPA or WPA2).
Related Articles
How to use openpath mobile pass (avigilon alta), integrate your existing network policy server (nps) infrastructure with azure ad multi-factor authentication, how to find out who the user profile disk belongs to terminal server rds, how to sign up and use chatgpt, sage 50 payroll – change database path, generate a report of all passwords for all cameras on your milestone xprotect vms., leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Power by IT Capture

Dynamic VLAN Assignment for Cloud RADIUS
The landscape of cybersecurity is always changing, but there are a few constants. One unchanging aspect is the use of VLANs as a primary method of segmenting users and network resources. Like the Local Area Network it emulates, a VLAN is a useful tool for isolating sensitive resources and sheltering it from risk created by unnecessary access.
Our networks are becoming increasingly virtual, as illustrated by the industry trend of moving to the cloud. That makes VLAN more important than ever and, fortunately, VLAN technology is keeping pace. In this article we will discuss the methods through which users are assigned to VLANs and how to automate the process for ease-of-use and increased security.
What is Dynamic VLAN Assignment?
Dynamic VLAN Assignment, also referred to as “ VLAN Steering ”, is exactly what it sounds like. The process of assigning users or groups of users to VLAN can be handled by a RADIUS at the time of authentication, though the infrastructure and expertise needed for dynamic VLAN assignment has historically been an obstacle for smaller organizations.
Why use Dynamic VLAN Assignment?
The default state of a wireless (or wired) network is sometimes described as “flat”. Every user in the organization is tossed into a shared network that also contains all of the resources that organization has (files, data, source code, applications, etc.). Everyone potentially has access to everything, even if there is another login portal between them and, say, the payroll system.
That’s an unnecessary risk. Developers need access to very sensitive resources like the source code for their app, but that doesn’t imply that they require access to everything that is less confidential. It’s a basic tenet of security, cyber or not, to restrict access to only people that require it.
Those are the guiding principles that lead us to implement VLANs, but the “dynamic assignment” portion of dynamic VLAN assignment is equally important. There needs to be an automated process by which users are automatically shunted to the appropriate VLAN. Relying on IT to manually assign VLANs is short-sighted – humans are fallible and it doesn’t scale past a couple dozen users.
RADIUS Attributes for Dynamic VLAN Assignment
That’s why we configure a RADIUS server to assign users for us. It already has the responsibility of authorizing and authenticating users for network access, so it’s a relatively simple task to configure it to send users to a switch that can further sort users to a specific access point and/or a specific VLAN.
How does a RADIUS decide where to send the user? By the attributes assigned to them. Attributes are often stored as part of the user profile in the directory or as a part of the device/client profile for MAC authentication. SecureW2’s Cloud PKI can even amend attributes to digital certificates for seamless certificate-based EAP-TLS authentication with dynamic VLAN assignment.
The majority of VLAN assignment is done by configuring these 3 attributes:
- Tunnel-Type
- Tunnel-Medium-Type
- Tunnel-Private-Group-ID
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS supports additional VLAN assignment attributes such as:
- Custom groups
These additional parameters allow you an even greater degree of control and flexibility in assigning users to VLANs so that you can efficiently maximize your network security.
Which RADIUS for Dynamic VLAN Assignment?
Most, though not all, RADIUS servers can be configured to support dynamic VLAN assignment. Keep in mind the other needs of your organization when choosing which to configure.
Microsoft’s NPS is a popular DIY RADIUS solution because many organizations are already using a Microsoft environment. The ubiquitous Active Directory remains one of the most popular identity providers even though it’s mostly incompatible with many cloud-based applications and services (including Microsoft’s own Azure AD). The lack of compatibility with cloud services more or less eliminates NPS as a choice.
FreeRADIUS is another DIY RADIUS which actually is able to interact with cloud directories and the like. Unfortunately, the lack of a GUI is a turn off for most enterprises that want deep customizability and reporting.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS is equipped with the latest in VLAN technology. Our Dynamic Policy Engine enables the RADIUS to make runtime-level policy decisions by directly referencing user attributes stored in any directory (including cloud directories like Google, Azure, and Okta). Not only does this reinforce the network segmentation of VLAN, but it also enables passwordless authentication for any cloud directory via the use of digital certificates.
If your organization already has an 802.1X network, SecureW2’s turnkey solutions can integrate into your network without any forklift upgrades. If you’re still considering the transition to a secure WPA2-Enterprise network, you’ll be interested in our managed Cloud PKI which has all the components necessary for top-of-the-line X.509 digital certificate security right out of the box.
We have affordable options for organizations of all sizes. See our pricing here.
Patrick Grubbs
Patrick is an experienced SEO specialist at SecureW2 who also enjoys running, hiking, and reading. With a degree in Biology from College of William & Mary, he got his start in digital content by writing about his ever-expanding collection of succulents and cacti.
Related Posts

How To Test RADIUS Response Time

Evil Twin Attacks Explained


Breaking Down the 802.1X Protocol

Configure EAP-TLS Authentication for Cloud Networks

Sync AD to Google for Cloud Authentication
How RADIUS/802.1X authentication affects VLAN operation
Static vlan requirement:.
RADIUS authentication for an 802.1X client on a given port can include a (static) VLAN requirement. (Refer to the documentation provided with your RADIUS application.) The static VLAN to which a RADIUS server assigns a client must already exist on the switch. If it does not exist or is a dynamic VLAN (created by GVRP), authentication fails. Also, for the session to proceed, the port must be an untagged member of the required VLAN. If it is not, the switch temporarily reassigns the port as described below.
If the port used by the client is not configured as an untagged member of the required static VLAN:
When a client is authenticated on port “N”, if port “N” is not already configured as an untagged member of the static VLAN specified by the RADIUS server, then the switch temporarily assigns port “N” as an untagged member of the required VLAN (for the duration of the 802.1X session). At the same time, if port “N” is already configured as an untagged member of another VLAN, port “N” loses access to that other VLAN for the duration of the session. (This is because a port can be an untagged member of only one VLAN at a time.)
Using a RADIUS server to authenticate clients, you can provide port-level security protection from unauthorized network access for the following authentication methods:
802.1X: Port-based or client-based access control to open a port for client access after authenticating valid user credentials.
MAC address: Authenticates a device’s MAC address to grant access to the network
WebAgent: Authenticates clients for network access using a web page for user login.
VLAN assignment on a port
Following client authentication, VLAN configurations on a port are managed as follows when you use 802.1X, MAC, or Web authentication:
The port resumes membership in any tagged VLANs for which it is already assigned in the switch configuration. Tagged VLAN membership allows a port to be a member of multiple VLANs simultaneously.
The port is temporarily assigned as a member of an untagged (static or dynamic) VLAN for use during the client session according to the following order of options.
The port joins the VLAN to which it has been assigned by a RADIUS server during client authentication.
If RADIUS authentication does not include assigning the port to a VLAN, then the switch assigns the port to the authorized-client VLAN configured for the authentication method.
If the port does not have an authorized-client VLAN configured, but is configured for membership in an untagged VLAN, the switch assigns the port to this untagged VLAN.
Operating notes
During client authentication, a port assigned to a VLAN by a RADIUS server or an authorized-client VLAN configuration is an untagged member of the VLAN for the duration of the authenticated session. This applies even if the port is also configured in the switch as a tagged member of the same VLAN. The following restrictions apply:
If the port is assigned as a member of an untagged static VLAN, the VLAN must already be configured on the switch. If the static VLAN configuration does not exist, the authentication fails. If the port is assigned as a member of an untagged dynamic VLAN that was learned through GVRP, the dynamic VLAN configuration must exist on the switch at the time of authentication and GVRP-learned dynamic VLANs for port-access authentication must be enabled.
If the dynamic VLAN does not exist or if you have not enabled the use of a dynamic VLAN for authentication sessions on the switch, the authentication fails.
To enable the use of a GVRP-learned (dynamic) VLAN as the untagged VLAN used in an authentication session, enter the aaa port-access gvrp-vlans command.
Enabling the use of dynamic VLANs in an authentication session offers the following benefits:
You avoid the need of having static VLANs pre-configured on the switch.
You can centralize the administration of user accounts (including user VLAN IDs) on a RADIUS server.
For information on how to enable the switch to dynamically create 802.1Q-compliant VLANs on links to other devices using the GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP), see “GVRP” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide .
For an authentication session to proceed, a port must be an untagged member of the (static or dynamic) VLAN assigned by the RADIUS server (or an authorized-client VLAN configuration). The port temporarily drops any current untagged VLAN membership.
If the port is not already a member of the RADIUS-assigned (static or dynamic) untagged VLAN, the switch temporarily reassigns the port as an untagged member of the required VLAN (for the duration of the session). At the same time, if the port is already configured as an untagged member of a different VLAN, the port loses access to the other VLAN for the duration of the session. (A port can be an untagged member of only one VLAN at a time.)
When the authentication session ends, the switch removes the temporary untagged VLAN assignment and re-activates the temporarily disabled, untagged VLAN assignment.
If GVRP is already enabled on the switch, the temporary untagged (static or dynamic) VLAN created on the port for the authentication session is advertised as an existing VLAN.
If this temporary VLAN assignment causes the switch to disable a different untagged static or dynamic VLAN configured on the port (as described in the preceding bullet and in Example of untagged VLAN assignment in a RADIUS-based authentication session , the disabled VLAN assignment is not advertised. When the authentication session ends, the switch:
Removes the temporary untagged VLAN assignment and stops advertising it.
Re-activates and resumes advertising the temporarily disabled, untagged VLAN assignment.
If you modify a VLAN ID configuration on a port during an 802.1X, MAC, or Web authentication session, the changes do not take effect until the session ends.
When a switch port is configured with RADIUS-based authentication to accept multiple 802.1X and/or MAC or Web authentication client sessions, all authenticated clients must use the same port-based, untagged VLAN membership assigned for the earliest, currently active client session.
Therefore, on a port where one or more authenticated client sessions are already running, all such clients are on the same untagged VLAN.
(See MAC-based VLANs ).
If a RADIUS server subsequently authenticates a new client, but attempts to re-assign the port to a different, untagged VLAN than the one already in use for the previously existing, authenticated client sessions, the connection for the new client will fail.
Example of untagged VLAN assignment in a RADIUS-based authentication session
The following example shows how an untagged static VLAN is temporarily assigned to a port for use during an 802.1X authentication session. In the example, an 802.1X-aware client on port A2 has been authenticated by a RADIUS server for access to VLAN 22. However, port A2 is not configured as a member of VLAN 22 but as a member of untagged VLAN 33 as shown in Active VLAN configuration .
For example, suppose that a RADIUS-authenticated, 802.1X-aware client on port A2 requires access to VLAN 22, but VLAN 22 is configured for no access on port A2, and VLAN 33 is configured as untagged on port A2:
Active VLAN configuration

In Active VLAN configuration , if RADIUS authorizes an 802.1X client on port A2 with the requirement that the client use VLAN 22, then:
VLAN 22 becomes available as Untagged on port A2 for the duration of the session.
VLAN 33 becomes unavailable to port A2 for the duration of the session (because there can be only one untagged VLAN on any port).
To view the temporary VLAN assignment as a change in the active configuration, use the show vlan < vlan-id > command as shown in The active configuration for VLAN 22 temporarily changes for the 802.1X session where < vlan-id > is the (static or dynamic) VLAN used in the authenticated client session.
The active configuration for VLAN 22 temporarily changes for the 802.1X session

However, as shown in Active VLAN configuration , because VLAN 33 is configured as untagged on port A2 and because a port can be untagged on only one VLAN, port A2 loses access to VLAN 33 for the duration of the 802.1X session on VLAN 22.
You can verify the temporary loss of access to VLAN 33 by entering the show vlan 33 command as shown in The active configuration for VLAN 33 temporarily drops port 22 for the 802.1X session .
The active configuration for VLAN 33 temporarily drops port 22 for the 802.1X session

When the 802.1X client’s session on port A2 ends, the port removes the temporary untagged VLAN membership. The static VLAN (VLAN 33) that is “permanently” configured as untagged on the port becomes available again. Therefore, when the RADIUS-authenticated 802.1X session on port A2 ends, VLAN 22 access on port A2 also ends, and the untagged VLAN 33 access on port A2 is restored as shown in The active configuration for VLAN 33 restores port A2 after the 802.1X session ends .
The active configuration for VLAN 33 restores port A2 after the 802.1X session ends

Enabling the use of GVRP-learned dynamic VLANs in authentication sessions
aaa port-access gvrp-vlans Enables the use of dynamic VLANs (learned through GVRP) in the temporary untagged VLAN assigned by a RADIUS server on an authenticated port in an 802.1X, MAC, or Web authentication session. Enter the no form of this command to disable the use of GVRP-learned VLANs in an authentication session. For information on how to enable a switch to dynamically create 802.1Q-compliant VLANs, see “GVRP” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide . NOTE: If a port is assigned as a member of an untagged dynamic VLAN, the dynamic VLAN configuration must exist at the time of authentication and GVRP for port-access authentication must be enabled on the switch. If the dynamic VLAN does not exist or if you have not enabled the use of a dynamic VLAN for authentication sessions on the switch, the authentication fails. After you enable dynamic VLAN assignment in an authentication session, it is recommended that you use the interface unknown-vlans command on a per-port basis to prevent denial-of-service attacks. The interface unknown-vlans command allows you to: Disable the port from sending advertisements of existing GVRP-created VLANs on the switch. Drop all GVRP advertisements received on the port. See “GVRP” in the Advanced Traffic Management Guide . If you disable the use of dynamic VLANs in an authentication session using the no aaa port-access gvrp-vlans command, client sessions that were authenticated with a dynamic VLAN continue and are not deauthenticated. (This behavior differs from how static VLAN assignment is handled in an authentication session. If you remove the configuration of the static VLAN used to create a temporary client session, the 802.1X, MAC, or Web authenticated client is deauthenticated.) However, if a RADIUS-configured dynamic VLAN used for an authentication session is deleted from the switch through normal GVRP operation (for example, if no GVRP advertisements for the VLAN are received on any switch port), authenticated clients using this VLAN are deauthenticated.
Copyright © 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Your browser does not support JavaScript. Please turn it on for the best experience.
Configuration Guide on Dynamic VLAN with the VLAN Assignment function of RADIUS
OC200 , OC300 , Omada Software Controller , Omada Cloud-Based Controller
The "This Article Applies to" section is not updated in a timely manner, to determine if your model supports a specific feature, please refer to the Specifications page of the corresponding product on the TP-Link website.
With the VLAN Assignment feature of RADIUS, the Omada SDN solution can put clients authenticated by different accounts to the corresponding VLANs. In this way, clients will obtain IP addresses from different VLANs, and you don't have to create many SSIDs bound with different VLANs for wireless networks, or bind the PVIDs of the switch ports to specific VLANs for wired networks.
To achieve the above features, you will need the Omada SDN Controller, EAP for wireless assignment, JetStream Switch for wired assignment, and an external RADIUS server. In this article, we will share the configuration guide for below network topology.
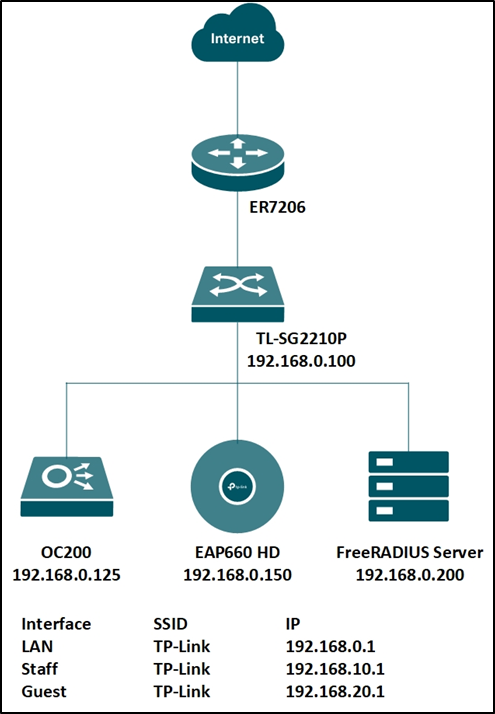
Step 1. Set up the RADIUS server.
Here we run a FreeRADIUS ® server on a Linux server. For more information on installation and configuration, please refer to the official website: https://freeradius.org/
First, edit the “ clients.conf ” file, set the client IP address as “192.168.0.0/24” and the password as “tplink”.

Next, edit the “ users ” file, create two accounts “test10” and “test20” in VLAN10 and VLAN20, respectively.

You may also edit the “ eap.conf ” to modify the EAP type for WPA-Enterprise. After configuration, run the RADIUS server to listen for access requests.
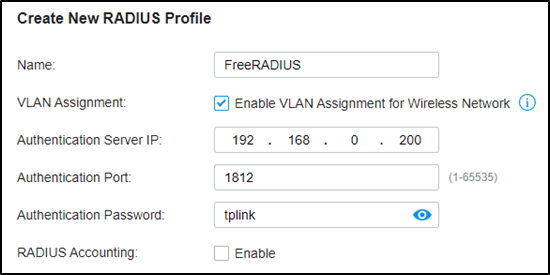
Step 2. Create the RADIUS profile.
Go to Authentication --- RADIUS Profile, create a new profile bound with the RADIUS server, and check “Enable VLAN Assignment for Wireless Network” to assign VLANs for wireless clients.
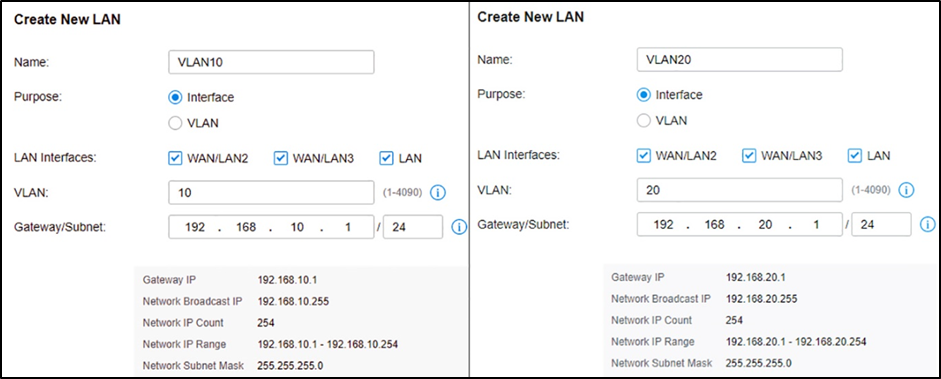
Step 3. Create more VLAN for VLAN assignments.
Assuming all Omada devices have been adopted by the controller, go to Settings --- Wired Networks --- LAN, and create two interfaces with VLAN10 and VLAN20.
Step 4. VLAN assignment for wireless networks.
Go to Settings – Wireless Networks, and create a new SSID with WPA-Enterprise as below. For differences between WPA-Personal and WPA-Enterprise, please refer to FAQ500 .
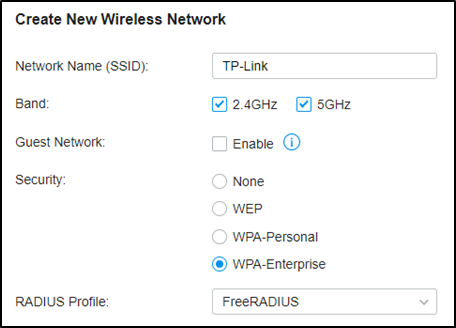
When connecting your client to the SSID, you will be asked to choose the authentication type of WPA-Enterprise, and enter the account username and password. After successfully authenticating with account “test10”, the client will obtain an IP address from VLAN10, while with account “test20”, it will get that from VLAN20.
Step 5. VLAN assignment for wired networks.
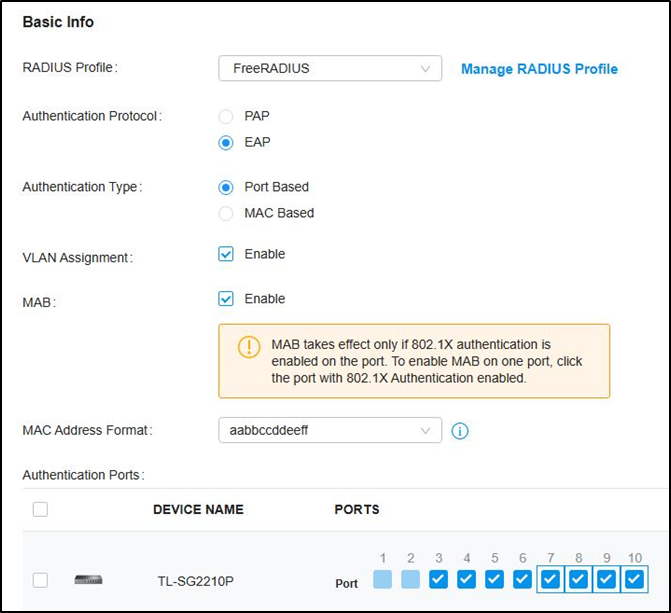
Go to Authentication --- 802.1X and enable the feature, select Authentication Type as “Port Based”, enable “VLAN Assignment” and check the Ports to be authenticated according to your requirements.
Not to click the ports twice to enable MAB for them.
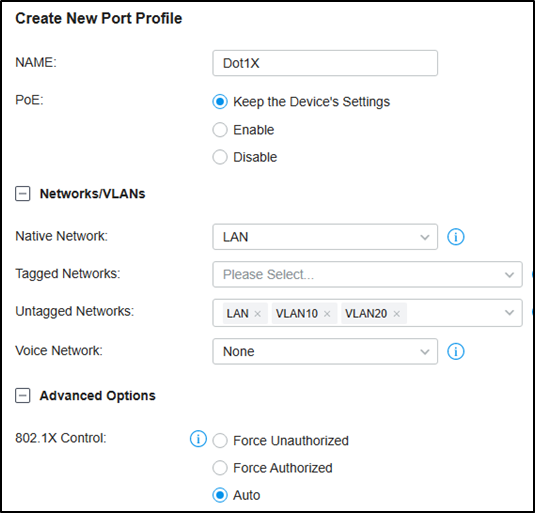
Then go to Wired Networks --- LAN --- Profile, create a new port profile, add VLAN10 and VLAN20 to untagged networks, and make sure the 802.1X Control mode is Auto.
Then Go to Devices, click your switch, go to Ports, check the authentication ports, and batch edit to change the port profile to the one created just now.
For 802.1X authentication, you may need to run TP-Link 802.1X Client Software (click here to download) for authentication. Please refer to FAQ787 and Step 3. For detailed guidance.
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
What’s your concern with this article?
- Dissatisfied with product
- Too Complicated
- Confusing Title
- Does not apply to me
We'd love to get your feedback, please let us know how we can improve this content.
We appreciate your feedback. Click here to contact TP-Link technical support.
Recommend Products
Omada Cloud-Based Controller
Omada Software Controller

Omada Hardware Controller
TP-Link Community
Still need help? Search for answers, ask questions, and get help from TP-Link experts and other users around the world.
Visit the Community >
We have updated our Policies. Read Privacy Policy and Terms of Use here. This website uses cookies to improve website navigation, analyze online activities and have the best possible user experience on our website. You can object to the use of cookies at any time. You can find more information in our privacy policy .
Basic Cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be deactivated in your systems.
accepted_local_switcher, tp_privacy_base, tp_privacy_marketing, tp_smb-select-product_scence, tp_smb-select-product_scenceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userChoice, tp_smb-select-product_userChoiceSimple, tp_smb-select-product_userInfo, tp_smb-select-product_userInfoSimple, tp_top-banner, tp_popup-bottom, tp_popup-center, tp_popup-right-middle, tp_popup-right-bottom, tp_productCategoryType
__livechat, __lc2_cid, __lc2_cst, __lc_cid, __lc_cst, CASID
id, VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE, LOGIN_INFO, SIDCC, SAPISID, APISID, SSID, SID, YSC, __Secure-1PSID, __Secure-1PAPISID, __Secure-1PSIDCC, __Secure-3PSID, __Secure-3PAPISID, __Secure-3PSIDCC, 1P_JAR, AEC, NID, OTZ
Analysis and Marketing Cookies
Analysis cookies enable us to analyze your activities on our website in order to improve and adapt the functionality of our website.
The marketing cookies can be set through our website by our advertising partners in order to create a profile of your interests and to show you relevant advertisements on other websites.
Google Analytics & Google Tag Manager
_gid, _ga_<container-id>, _ga, _gat_gtag_<container-id>
Google Ads & DoubleClick
test_cookie, _gcl_au
cebsp_, _ce.s, _ce.clock_data, _ce.clock_event, cebs
OptanonConsent, _sctr, _cs_s, _hjFirstSeen, _hjAbsoluteSessionInProgress, _hjSessionUser_14, _fbp, ajs_anonymous_id, _hjSessionUser_<hotjar-id>, _uetsid, _schn, _uetvid, NEXT_LOCALE, _hjSession_14, _hjid, _cs_c, _scid, _hjAbsoluteSessionInProgress, _cs_id, _gcl_au, _ga, _gid, _hjIncludedInPageviewSample, _hjSession_<hotjar-id>, _hjIncludedInSessionSample_<hotjar-id>
lidc, AnalyticsSyncHistory, UserMatchHistory, bcookie, li_sugr, ln_or
FAQ How to configure dynamic vlan assignment via radius
Issue description.
- Documentation
- Software Download
- Write an article
Thank you for taking the time to respond. The NETGEAR documentation team uses your feedback to improve our knowledge base content.
Rating Submitted
Do you have a suggestion for improving this article?
Characters Left : 500

MyNETGEAR® Account
Welcome back
Access your NETGEAR

NETGEAR Support
How do I enable dynamic VLAN assignment on my access point using a RADIUS server?
Was this article helpful? Yes No
First you must enable dynamic vlan assignment on your switch and download and instal FreeRADIUS for windows.
- Open a web browser.
The default IP address is 192.168.0.239 and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
You are prompted to enter your password.
The default password is password . Passwords are case-sensitive.
After the system authenticates you, the System Information screen displays.
- Select Switching > VLAN > Basic > VLAN Configuration .
- Enter 2 in the VLAN ID field.
- Enter VLAN2 in the VLAN Name field.
- Select Add .
- Select Security > Port Authentication > Advanced > Port Authentication .
- Check Port boxes 0/1 and 0/2.
- Set Control Mode to Force Authorized .
- Click Apply .
Last Updated:12/06/2022 | Article ID: 000061876
Was this article helpful?
This article applies to:, looking for more about your product.
Get information, documentation, videos and more for your specific product.
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Quick and easy solutions are available for you in the NETGEAR community.
Need to Contact NETGEAR Support?
With NETGEAR’s round-the-clock premium support, help is just a phone call away.
Complimentary Support
NETGEAR provides complimentary technical support for NETGEAR products for 90 days from the original date of purchase.
NETGEAR Premium Support
Gearhead support for home users.
GearHead Support is a technical support service for NETGEAR devices and all other connected devices in your home. Advanced remote support tools are used to fix issues on any of your devices. The service includes support for the following:
- Desktop and Notebook PCs, Wired and Wireless Routers, Modems, Printers, Scanners, Fax Machines, USB devices and Sound Cards
- Windows Operating Systems (2000, XP or Vista), MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook and Adobe Acrobat
- Anti-virus and Anti-Spyware: McAfee, Norton, AVG, eTrust and BitDefender
ProSUPPORT Services for Business Users
NETGEAR ProSUPPORT services are available to supplement your technical support and warranty entitlements. NETGEAR offers a variety of ProSUPPORT services that allow you to access NETGEAR's expertise in a way that best meets your needs:
- Product Installation
- Professional Wireless Site Survey
- Defective Drive Retention (DDR) Service
Where to Find Your Model Number
To find the model/version number, check the bottom or back panel of your NETGEAR device.
Select a product or category below for specific instructions.

Nighthawk Routers

Powerline and Wall Plug Extenders

Cable and DSL Modem Routers

ReadyNAS Network Storage

Wireless Access Points

Other Business Products

Mobile Broadband
Dynamic VLANs with RADIUS
Written by Ryan Squires on January 17, 2019
Share This Article
Creating dynamic VLANs with RADIUS represents a powerful security concept, but one that’s difficult to implement. There are a lot of variables that go into its set up. Components such as wireless access points (WAPs), RADIUS servers, and identity providers (IdPs) each contribute to its complexity. The good news is that there is a next generation cloud identity management platform that is making VLAN steering easier to execute than ever before.
What is Dynamic VLAN Assignment?
Dynamic VLAN assignment is a great way for IT organizations to step up their network security efforts. The idea at play here is that users, or groups of users, can be placed into different VLANs, or segmented chunks of the same network, to increase security. For example, the sales team doesn’t need to be on the same VLAN with developers and vice versa. That means that if a bad actor were to gain access to either the sales or engineering VLAN, they still could not access other segments of that network, like the development VLAN. Effectively, this provides IT admins the ability to limit the the attack surface on a given network. Less attack surface, less potential for problems.
VLAN and RADIUS Implementation

So, while the benefits of dynamic VLANs with RADIUS are hard to overstate, the implementation process can present quite the challenge to IT admins. Segmenting a network can be done through WiFi infrastructure or through the network switches and routers. Users and groups of users are assigned VLANs and those assignments are placed into the RADIUS server , which is backended by an identity provider which validates credentials. All of these different components, network gear, RADIUS servers, directory services, and even endpoints need to be tied together to make the process of dynamic VLAN assignments work effectively. Of course, that can be a tall order for many IT organizations which is why the adoption of network segmentation hasn’t been nearly as high as it should be.
A Cloud-based Security Booster

Thankfully, a new generation of identity and access management solution is taking the heavy lifting out of implementing dynamic VLAN assignment with RADIUS. With an on-board RADIUS server and directory service, this cloud IAM platform has the majority of the the identity and networking components ready to use. Assuming IT admins are in possession of WAPs with VLAN capability, IT admins simply point their compatible WAPs to the cloud RADIUS solution and load their users into the cloud directory. The Directory-as-a-Service platform takes care of the rest. This ability is just one facet of JumpCloud’s security offering. With the ability to automate SSH key management , execute remote Policy and command deployment, and enable True Single Sign-On™ , your users will stay safe and your organization secure.
Learn More About JumpCloud

If you’re ready to enjoy the benefits of dynamic VLANs with RADIUS without all the heavy lifting, sign up for a free JumpCloud account today. With a free JumpCloud account, you’ll be able to test all the functionality of JumpCloud while managing up to 10 users for free. Be sure to check out our Knowledge Base and YouTube channel for more information.
- Remote Work
- User Access

Reduce IT costs and complexity
Ryan Squires is a content writer at JumpCloud, a company dedicated to connecting users to the IT resources they need securely and efficiently. He has a degree in Journalism and Media Communication from Colorado State University.
Continue Learning with Related Posts
Continue learning with our newsletter.
Meraki Community
- Community Platform Help
- Contact Community Team
- Meraki Documentation
- Technical Forums
802.1X /w Dynamic VLAN Assignment
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Report Inappropriate Content
- All forum topics
- Previous Topic

- New April 1: And we're live! New community look & feel is here!
- March 27: [LAUNCH POSTPONED] Planned downtime for the launch of the new Community look & feel
- March 26: New community look & feel, coming soon!
- Interfaces 215
- Layer 2 230
- Layer 3 162
- Community guidelines
- Cisco privacy
- Khoros privacy
- Terms of service

COMMENTS
Dynamic VLAN Assignment with RADIUS Server. In most WLAN systems, each WLAN has a static policy that applies to all clients associated with a Service Set Identifier (SSID), or WLAN in the controller terminology. Although powerful, this method has limitations because it requires clients to associate with different SSIDs in order to inherit ...
Setup Structure for IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server. Supplicant: Laptop running Microsoft Windows 10 or Windows 7; Authenticator: HP Aruba 2920 Edge Switch; Authentication Server: Microsoft NPS (Network Policy Server) running on Windows Server 2012 R2. User Database : Active Directory; For Windows ...
Dynamic VLAN Assignment with RADIUS Server. In most Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) systems, each WLAN has a static policy that applies to all clients associated with a Service Set Identifier (SSID). Although powerful, this method has limitations because it requires clients to associate with different SSIDs to inherit different QoS and ...
Learn how to assign VLANs dynamically with RADIUS to Unleashed access points.For more information on this topic and many others, check out the Ruckus Support...
The network access layer sends a request to the RADIUS server with the user's credentials or certificates (using 802.1X) The RADIUS server sends a reply which contains attributes that provide the switch or access point with information on the device VLAN, result in properly VLAN assignment . Common Dynamic VLAN Assignment Use Cases
Administrators therefore create VLANs and configure the corresponding VLAN number to each switch port with access mode. Conversely, administrator only needs to set switch port as trunk and fixed port and a few policies on RADIUS server for Dynamic VLAN Assignment. It mitigates considerable actions/jobs for network administrator.
Dynamic VLAN Assignment using RADIUS Version 1.0 RADIUS Server Configuration Download and install FreeRADIUS for Windows. Once installed, the icon will appear in the system tray. Right click on the FreeRADIUS icon and choose Edit Radius Clients.conf - in this file we need to add an entry for our RADIUS client, the GSM7224v2.
2. Add the NAS type and AD group membership conditions: (must be members of the students group to match this policy) 3. Select and configure an EAP type (note this may be PEAP or EAP-TLS - we've shown PEAP just as an example) 4. Configure the settings for this policy to assign any users which match this policy to VLAN 20: Once NPS has been ...
Refer to Configuring the RADIUS server to support dynamic VLAN assignment for flexible authentication for a list of the attributes that must be set on the RADIUS server. If one of the attributes in the Access-Accept message specifies a VLAN identifier, and the VLAN is available on the Brocade device, the port becomes a MAC VLAN member of the ...
RADIUS Attributes for Dynamic VLAN Assignment. That's why we configure a RADIUS server to assign users for us. It already has the responsibility of authorizing and authenticating users for network access, so it's a relatively simple task to configure it to send users to a switch that can further sort users to a specific access point and/or ...
Syntax: Enables the use of dynamic VLANs (learned through GVRP) in the temporary untagged VLAN assigned by a RADIUS server on an authenticated port in an 802.1X, MAC, or Web authentication session. Enter the no form of this command to disable the use of GVRP-learned VLANs in an authentication session.
After configuration, run the RADIUS server to listen for access requests. Step 2. Create the RADIUS profile. Go to Authentication --- RADIUS Profile, create a new profile bound with the RADIUS server, and check "Enable VLAN Assignment for Wireless Network" to assign VLANs for wireless clients. Step 3.
Dynamic VLAN assignments from the RADIUS server can be enabled in multiple formats. VLAN assignments can be tagged, untagged, single, multiple, and a combination of tagged and untagged VLANs for different use cases; for example, client devices such as computers, IP phones, wireless access points, servers running hypervisors with mulitple Virtual Machines (VMs), and so on.
How Configure NPS and Active Directory For Dynamic Radius based Vlan assignment ===== This document is to describe the steps to configure NPS(network policy servicer)server with below use case. Vlans need to be assigned based on different Radius group i.e Sales group to Vlan 10; Account group to Vlan 20. Steps:-Open Active directory Users and ...
Go to the user1's Edit page. From the User Edit page, scroll down to the Cisco Airespace RADIUS Attributes section. Check the check box next to the Aire−Interface−Name attribute and specify the name of the dynamic interface to be assigned upon successful user authentication. This example assigns the user to admin VLAN.
Add to Favorites. This case will reveal how to configure dynamic vlan assignment via radius. In some situation you would like to bind a mac-address to a specific VLAN and allow a host to get access the network only to a specific VLAN. You can use any Radius server, Huawei recommended solution is Agile Controller.
This document describes how to dynamically assign your access point to VLANs using a RADIUS server. This is useful is you have multiple clients using the same physical network and need to assign them to different VLANs depending on their login credentials. This process removes the need to manually assign ports into VLANs.
A Cloud-based Security Booster. Thankfully, a new generation of identity and access management solution is taking the heavy lifting out of implementing dynamic VLAN assignment with RADIUS. With an on-board RADIUS server and directory service, this cloud IAM platform has the majority of the the identity and networking components ready to use.
As @PhilipDAth states the switch assigns the VLAN based on the information received back from the RADIUS (NPS) server. These are the attributes that need to be returned: Dynamic VLAN Assignment In lieu of CoA, MS switches can still dynamically assign a VLAN to a device by assigned the VLAN passed in the Tunnel-Pvt-Group-ID attribute. It may be necessary to perform dynamic VLAN assignment on a ...
• Dynamic ARP - 24,576 dynamic entries • Proxy ARP • DHCP Server: - Max 8K IP Pools - Max 1,000 Manual Binding Entries • DHCP Relay: - Relayed Interface - Relayed VLAN L2 Features • Link Aggregation - Static link aggregation - 802.3ad LACP - Up to 8 ports per group - Up to 120 LAG Groups • Spanning Tree Protocol - 802.1d STP - 802 ...