- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor

Harvard College Resumes & Cover Letter Guide
- Share This: Share Harvard College Resumes & Cover Letter Guide on Facebook Share Harvard College Resumes & Cover Letter Guide on LinkedIn Share Harvard College Resumes & Cover Letter Guide on X
A resume is a concise, informative summary of your abilities, education, and experience. It should highlight your strongest assets and skills, and differentiate you from other candidates seeking similar positions.

How to Write a Resume for College – A CollegeAdvisor Guide
How to Write a Resume for College – Introduction
Standing out as a stellar applicant in the college admissions process is tough. One way to separate yourself from the crowd is by crafting a strong resume for college. Your college resume can highlight information about your background, activities, and achievements. Some of these might not be indicated elsewhere in your college application or recommendation letters .
In this article, we will teach you how to write a college resume. We’ll highlight 5 simple steps to building your college application resume. We will also discuss what a college resume is and why you may need a resume for college. Additionally, we will provide examples on how to write a resume for college by reviewing college resume examples. Finally, we’ll walk you through some college resume templates in our example college resumes.
So, let’s look at how to write a college resume and explain what makes a good college resume, why you should include a resume for college in your applications, and more!
What is a college resume?
A high school resume is typically a one-page document that complements your college application . Your high school resume (or college resume) can help you showcase your achievements and extracurriculars for college. It does this by sharing information that is not elsewhere within your college applications. The goal of a college resume is to show the college admissions officers who you are and how you spend your time outside of the classroom .
Before we jump into how to write a college resume, let’s examine some things that make up a good college resume.
A good college resume should include:
- Clear structure
- Concise language (bullet points over essay-style)
- Relevant details
- Strong formatting
As we discuss how to write a resume for college, you might wonder what purpose a college resume serves. In short, a college resume is a summary of experiences that you can use to add depth to your college applications. You can also think of a college resume as your high school resume, or a resume for college. Your college resume will include a brief description of each of your experiences and extracurriculars for college.
While we examine how to write a resume for college, you should first note that your college resume should include key details like your educational details, GPA , extracurricular activities/jobs, and honors/awards. As we’ll discuss, your college resume will have other key features. We’ll go through each of these as we learn how to write a resume for college.
Many colleges list a college resume within their college application requirements. But, even if a college resume is not listed in the college application requirements, we recommend creating one anyway.
We will look at a sample college resume later in this article, along with a 5-step guide to creating a resume for college that you can use as you begin writing your college resume.

Do I need a resume for my college applications?
No, you do not necessarily need to include a college resume with your college applications. However, a high school resume or resume for college can be a helpful tool in the college admissions process.
So, how could including a resume for college application be beneficial? First, including a college resume in your college applications can help highlight your skills, experiences, and qualifications to the admissions office of your dream school.
Having a college resume can help you showcase your extracurricular activities in your college applications. You can highlight leadership positions, accomplishments, interests, and activities on your college resume that might not appear elsewhere in your college applications.
Creating a resume for college application can also demonstrate your accomplishments and experiences to college admissions officers. Even if a high school resume is optional in the list of college application requirements, including one in your college applications can help you stand out. Standing out is incredibly important in the admissions process, especially if your ideal college is high on the list of college rankings .
It is a good idea to start putting together your college resume as you near the end of high school.
You may forget the names of clubs, supervisors, mentors, teachers, etc. as you get ready to apply to college. So, the earlier you can gather all the information for your high school resume, the better! That way, all of your experiences are fresh in your mind, and you can create the strongest resume for college possible.
When should I prepare my college resume?
As you begin the process of applying to college, you might be wondering when to prepare your college resume. The ideal timeline for creating your high school resume can start as early as 9 th grade.
In general, you won’t want to include anything on your high school resume before 9 th grade. Like other college application requirements, college admissions officers are only interested in the activities you have participated in during high school.
Keep a list starting in 9th grade
As early as 9 th grade, you can start keeping a list of your accomplishments and activities. Even though you won’t need to format this list into a college resume yet, it will be the basis for your future college application resume.
As you begin the college admissions process, you can use the list you created and turn it into a college resume. As you apply to college and prepare your college resume, research which college resume format works best for you. Reviewing a sample college resume or college resume template can help you find the perfect college resume format.
As you look through college resume examples, think about which aspects of the college resume template you like the best. Then, adapt things from those college resume examples to fit your college resume. Once you have decided on a college resume format, list your accomplishments, jobs, and activities within that college resume format.
Summer before senior year
The best time to create your high school resume is during the summer before your senior year. This gives you plenty of time to perfect your college application resume.
We’ll examine the necessary components of a successful college resume in the next section of this article. So, read on!
What should a high school student put on a resume?
As you begin the college admissions process, you may be asking yourself what to include on your high school resume. You can start the college application resume writing process by brainstorming how you spend your time outside of your courses.
Think about everything you have done or achieved since you started high school and write it down. Your high school resume should highlight your activities, interests, and skills. Pay particular attention to these factors as you consider what to include on your high school resume.
Your high school resume will be organized categorically. Some of the most common categories for a resume for college application include personal information, work experience, extracurricular activities, volunteer experience/community service, education, and skills. In addition to the categories listed above, below is a list of some other things that high school students should list on their resume for college.
Top ten things to list on your college resume:
- School name and address
- Contact Info
- GPA or Class rank, if applicable
- Internships & volunteer roles
- Awards and honors
- Extracurricular activities
- Leadership positions
- Language competencies
As we mentioned earlier, you may not have information or experiences for every category listed above. That’s perfectly fine! Focus on what applies to you and what you can include on your high school resume as you learn how to write a college resume.
What does not belong on my high school resume?
Now that we have examined what to include on your high school resume, let’s discuss what does not belong on your college application resume.
Keep it current
In general, you should avoid including any activity or achievement from before 9 th grade on your resume for college. However, it’s okay to include something that is particularly impressive and/or attached to a current activity.
For example, if you have 12 years of experience in playing the violin, you will want to include that on your high school resume. However, if you joined your middle school band for a semester, you should likely leave that out of your college resume. Your resume for college should reflect activities that matter to you now.
Avoid listing daily duties
There is no need to include informal everyday activities on your college resume, such as cooking for your family or cleaning around the house. When you are crafting your resume for college, it’s best to stick to things that are relevant to admissions committees or future employers.
Note that this is one area where your college resume differs from your activities list. For instance, if you spend considerable time caretaking your three siblings, you may choose to include that on your activities list within the Common App. However, the same responsibilities likely shouldn’t appear on your resume for college.
Keep it clear
As you examine college resume templates and college resume examples, take note of the language and structure in a sample college resume. It’s important to use concise language and clear structure throughout your resume for college.
Additionally, do not include excessive text or overly detailed explanations on your college application resume. You want your resume for college to be simple and clear. In general, you should limit your high school resume to one page, or two at the absolute maximum. Most people who review your college resume will spend about 30 seconds with it. So, your resume for college should be easily scanned, above all.
When you use concise language throughout your college resume, it will make it easier for your reader to understand your accomplishments. Because most people will skim your high school resume, having a clear structure throughout will make it easy to read. Keep it simple and keep it consistent.

Steer clear of images and graphics
While you might come across this in your college resume format research, it’s best to avoid including images or graphics in your college application resume. Although this is a new trend and can be seen on multiple college resume examples and college resume templates, it can be distracting and take up valuable space on your high school resume.
For instance, if you volunteered at twelve different soup kitchens, there is no need to list each one separately. That will become tedious and take up too much space on your essential resume for college application.
Finally, you should never misrepresent your qualifications on your high school resume. Be honest about your involvements, however many you have. It’s not worth potentially getting caught in a lie or an exaggeration during a college interview.
Where do I submit my college application resume?
While you apply to college, you might be wondering what to do with your resume for college applications. Many college application portals will include a section for your college resume, especially if a resume for college is listed as one of the college application requirements.
Most college application portals list the high school resume section as optional. While you are applying to college, you might notice that most colleges require that you fill out an activities section as part of the application process. The activities section will ask you to list your extracurriculars for college. Often, your activities section will serve the same purpose as your college resume.
If you choose to include a high school resume with your college application, it should reflect your accomplishments in more detail than your activities section. Additionally, if you choose to include a resume for college with your application, make sure it adds something new to your activities list.

You will receive access to your college’s application portal once you have completed the process of applying to college but before you receive a college acceptance letter and officially enroll . When it’s time to upload your high school resume, be sure to upload it as a PDF rather than a Word document. That way, you can ensure that your formatting of your college resume stays consistent on every application.
We’ll provide more details about the college resume format later in this article, when we examine college resume examples and college resume templates.
How often should I update my college resume?
It may be helpful to update your resume (or other records) every six months to a year in order to avoid missing any important details. You can use your college resume for more than just your college application requirements. In fact, there may be internships or other opportunities you seek out in high school that will ask you to submit a high school resume. Updating your college resume often will help you keep track of your experiences and accomplishments.
In general, you should update your high school resume as often as it works for you. However, when you are almost done applying to college , you will want to make sure that your college resume is up-to-date and accurate before including it with your application.
No matter how often you update your resume for college applications, we encourage you to keep copies of any old college resume examples you might have. Having old copies of your college resume can help you in the future as you begin to tailor your college resume for potential reviewers.
How to write a resume for college
Now that we have a better understanding of what makes up a college resume, let’s focus on how to write a resume for college. You can begin writing your college resume by creating a list of your key details . Your key details will be the starting point for your college resume.
First, you will include information about where you go to school, as well as your current GPA and any Honors statuses. You will also want to list your academic interests on your high school resume, including what you hope to study or pursue beyond high school.
You will also include your extracurricular activities and the years you engaged in them on your resume for college. Additionally, you will want to add any jobs or internships you have had and the dates you held them. You can also list any leadership positions and the years you held them on your college resume.
Finally, you will want to include any special skills you have on your resume for college. This can include certifications as well.
Once you have a list of your key details, you will want to organize these details into sections on your high school resume. For some, these sections might include Objective, Education, Leadership Positions, Work and Internship History, and Special Skills.
College Resume Walkthrough
Linked about is our college resume walkthrough. Let’s do another walkthrough of these sections here to see what kind of information to include in each one.
Your objective is the reason why you are writing your college resume. This section will vary depending on where you send your resume.
If you are creating a resume for college applications, you should include information about your intended major or future career in this section. However, if you are sending your high school resume to a potential employer, your objective section will include information about why you are uniquely skilled for the job.
Education
The education section of your college resume should include all high schools you have attended, along with your GPA and anticipated date of graduation.
If your high school provides you with a class rank, you can also include that piece of information within this section of your resume for college.
Additionally, you can include your SAT or ACT score within this section, especially if you are submitting your resume for college applications.
Leadership Positions
Be sure to highlight any leadership positions you have held in your college resume. This includes any appointed positions you have received and even informal leadership positions.
For example, if you were voted Class President of your Student Council, you can include that information here. Or maybe you are a peer mentor on your soccer team—you can include those details within this section of your college resume.
Work and Internship History
This section of your high school resume will list your whole work history, including internships , summer jobs , or part-time jobs.
You will want to include the job title, company, dates of employment, and a brief outline of your duties for each of the work or internship experiences in this section of your resume for college.
Special Skills
Finally, this section of your college resume will outline any technical or soft skills you might have. Soft skills include things like teamwork, communication skills, and conflict resolution.
In this section of your resume for college, you can also include any languages you speak or certifications you have.

After you have organized your high school resume into sections, you will want to include a bulleted list detailing your responsibilities within each of your engagements/leadership roles. Be sure to include only relevant details in your descriptions, as it’s important to be concise on your college resume.
Remember to include the years for every role/activity on your college resume. You will want to list them with the most recent positions/activities at the top of your resume for college.
College resume format
Your college resume format is one of the most important features to consider as you apply to college. As you construct your college resume format, make sure that it’s readable.
Most people won’t look at your college resume for more than 30 seconds. So, any reader should be able to skim your high school resume and come away with a relatively clear idea of your qualifications and background.
The ideal college resume format will have the name of the student clearly listed at the top of the college resume. Another aspect of a strong college resume format will have clear sections with strong headlines. Additionally, the best college resume format will include bulleted lists where appropriate.
We will look at the college resume format in action as we review some college resume examples and college resume templates.
College resume examples
As we review our sample college resume, we will explain how to use it to craft your own college resume when you apply to college. Use this sample college resume as a reference point for your resume for college. Then, adapt it to fit your own unique needs.
We will discuss the sample college resume in the next two sections of this article. As we review the sample college resume, pay particular attention to what makes this college resume clear and effective. You can use this sample college resume as a college resume builder while you apply to college.

At first glance, you can see that this college resume is organized. This resume for college has clear sections and a concise structure. What makes this college resume clear and effective is its formatting, language, and length. Be sure to incorporate these same elements into your own high school resume as you apply to college.
Remember, this sample college resume is just one of many college resume examples available. Figure out what you like best about this sample college resume and use it to craft your own college resume.
Sample college resume – What works?
The key features of this sample college resume are its formatting, language, and length. Focusing on these in your own college resume will ensure that your resume for college stands out.
Clear delineated sections
The formatting in this college resume works so well because it includes clearly delineated sections and organized by year. Keeping your information and experiences organized by year is an effective format for a resume for college applications.
Simple and straightforward language
Another feature of this college resume that works well is the language. There is clear language and details throughout this resume for college that provide context for each role and accomplishment. For example, each of the work experiences in this high school resume feature a brief description of the student’s role and duties/responsibilities.

Concise structure
Additionally, this resume for college application features a concise structure that helps the reader clearly understand the purpose of each section. The descriptions within this college resume are brief but comprehensive. Having a concise structure and clear language throughout your college resume is key.
The final key feature that works well in this college resume is the length. This resume for college is just one page in length. Ideally, you want your college resume to fit on one page, but that is not a hard and fast rule. If you have a wealth of experiences and extracurriculars for college, your college resume can go over the typical one-page length.
Even though this high school resume is a little over one page, it does not have any irrelevant details or extraneous information on it. As you begin writing your college resume, be sure to only include relevant details on it.
As you learn how to write a college resume, keep track of what features work well and incorporate them into your own college resume. If you are unsure if the sample college resume will work for your college resume, don’t worry. There are plenty of college resume examples and college resume templates to choose from as you are applying to college.
College resume template
There are multiple college resume examples that you can review as you start your college resume or college application letter . Looking at a college resume template can help you decide on the formatting, language, and length that works best for you.

Hunter College has a web page with college resume examples and college resume templates. Use it as a resource as you build your high school resume.
If possible, you should avoid using form templates as you construct your college resume. Instead, think of the college resume template as a guide. You should aim to format your resume for college in the way that works best for you.
It’s best to be a bit unique as you create your high school resume. Looking at a college resume template can help you find your own distinct style. You can also incorporate different aspects from a college resume template into your own college resume.
However, be sure to avoid any hard-to-read fonts or unnecessary details in your formatting as you learn how to write a college resume. While your resume shouldn’t look like it was made using a stock college resume template, it also should not be overly crowded.
College resume builder
There are also college resume builder resources, like this one from Wheaton College , that will help students build their college resumes. You can use a college resume builder to format your own resume for college.
At CollegeAdvisor.com, we host webinars on topics that help you apply to college. We have a webinar on how to write a resume for college, with plenty of college resume examples. We also have a webinar with advice from former Admissions Officers on how to build your college resume.
Once again, you should generally avoid a pre-formatted college resume builder or college resume template. Instead, use these college resume examples as a jumping off point as you begin the college admissions process.
Formatting your high school resume yourself makes it easier to make any quick edits or fix any formatting quirks. If you were to use a college resume builder or college resume template, these adjustments may be a challenge.

Build your College Resume in 5 Simple Steps
Having examined some college resume examples, let’s review 5 simple steps for how to write a resume for college.
Five Steps to Build your College Resume
Make an accurate list of your experiences, awards, education, and qualifications. You will use this list as the outline for your resume for college.
Choose the best college resume format for the job. Before you finalize your choice of college resume format , review a college resume template or college resume examples for guidance. Then, create a resume header for your college resume.
Add your accurate information by section on your resume for college. Reference the college resume examples you reviewed previously to choose the sections you will use on your high school resume. Organize each list by year, placing the most recent item at the top of your resume for college. Be sure to separate your extracurricular experiences from your awards/honors, creating two lists (or more if necessary).
Format your lists to be clear and readable , and add your name and contact information as the header of your college resume.
Ask a friend, family member, or mentor to copy edit your resume for college! Having another set of eyes on your high school resume will help you create the strongest resume for college possible.
How to write a college resume – Final Thoughts
In this article, we reviewed how to write a college resume. As we discussed the purpose of a college application resume, we examined college resume examples and described key features that work in a college resume. We hope the college resume examples we featured in our article on how to write a resume for college help you craft your high school resume as you apply to college.
Need help crafting the perfect college application resume? CollegeAdvisor.com can teach you how to write a resume for college. Register for a free CollegeAdvisor.com account and receive access to hundreds of articles and webinars. These resources will help you craft your college resume as you begin applying to college.

This article was written by Claire Babbs . If you want to get help with your college applications from Claire or other CollegeAdvisor.com Admissions Experts , click here to schedule a free meeting with one of our Admissions Specialists. During your meeting, our team will discuss your profile and help you find targeted ways to increase your admissions odds at top schools. We’ll also answer any questions and discuss how CollegeAdvisor.com can support you in the college application process.
Personalized and effective college advising for high school students.
- Advisor Application
- Popular Colleges
- Privacy Policy and Cookie Notice
- Student Login
- California Privacy Notice
- Terms and Conditions
- Your Privacy Choices
By using the College Advisor site and/or working with College Advisor, you agree to our updated Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy , including an arbitration clause that covers any disputes relating to our policies and your use of our products and services.
College Application Resume for 2024 [With Examples, Tips & Template]

They say college is the most exciting time in a student’s life and we couldn’t agree more!
The only thing standing between you and your dream university, though, is a college application resume.
You open the resume document, get ready to start writing…
And nothing comes out! After all, how can you even make a resume when you haven’t worked a day in your life?
Worry not - you don’t need any work experience to write a compelling college application resume. In this article, we’re going to teach you just how you can do that!
What Should a Resume for College Application Contain?
- 5+ College Application Resume Formatting Tips
- How to Write a Resume for College Applications?
- 3+ College Application Resume Tips
College Application Resume Template
So let’s dive in!
Before we get into the knits and grits of writing a resume for college application, let’s first do a quick review of what your resume should contain:
- Contact information , including your full name, address, phone number, and professional email.
- A resume objective , where you state the goal of your college application resume.
- Education section , where you list the history of your grades and exam scores.
- Relevant activities , including any work experience you might have.
- Skills relevant to a resume for a college application, e.g. soft skills such as active listening, interpersonal skills, communication skills, or hard skills such as public speaking, MS Office, or computer skills.
- Additional sections , such as awards and honors.
6 College Application Resume Formatting Tips
Before we dive into the nits and grits of CV making, let’s talk about formatting. Here are our top tips on how to format your college application resume:
- Choose the functional/skills-based resume format. This format is perfect for those who lack work experience , as it focuses more on your skill-set. If you DO have some work experience, though, then you can opt for the chronological format.
- Keep your college application resume one page long . As a rule of thumb, this is the optimal length for a resume—professionals with 10 years worth of work experience stick to the 1-page limit, so there’s no excuse for someone with little to no work experience to go overboard.
- Add plenty of white space , especially around your resume’s margins. It will make your resume look less cluttered and more reader-friendly.
- Include clear section headings and use the same heading for each section.
- Use an easy-to-read font. Some resume fonts (such as Ubuntu or Overpass) are resume friendly—professional-looking, easy-to-read, and yet modern. Others, like Comic Sans, are just one big NO.
- Save your college resume as a PDF. You might be used to Microsoft Word, or even think it’s the safest alternative, but MS Word has a good choice of messing up your resume format if opened in different computers or operating systems. PDF files, on the other hand, remain the same no matter what computer opens them.
How to Write a Resume for College Applications? (With Examples)
Once you’ve got the formatting done right, it’s time to get to writing your college application resume.
In this section, we’ll walk you through that process, starting with:
#1. Order Your Contact Information the Right Way
As we already mentioned, your college application resume should start with your contact information.
These are your contact information section must-haves :
- Full name and address
- Functional phone number where you can be reached.
- Professional email address, preferably consisting of your first and last name.
And here’s what this looks like in practice:
Sharon White
123 Main Street
New York, NY
Phone Number: 553-123-1234
Email: [email protected]
#2. Write an Attention-Grabbing College Resume Objective
A resume objective is a 2-3 sentence long paragraph that should communicate your motivation for getting into college or for studying a specific major.
As such, a well-crafted resume objective can instantly attract admission officers to read the rest of your college application resume.
There is, however, a right and wrong way to write a resume objective.
A convincing resume objective is:
- Tailored to the university/major you’re applying to, instead of looking like a one-fits-all kind of statement that you can use to apply to several colleges.
- Highlights the achievements that give you an edge over the competition.
The following example does that right:
Aspiring journalist with a knack for creative writing looking to deepen their knowledge through NYU’s renowned Journalism track. Founder of my high school’s first online newspaper, the ‘Daily Prophet,’ which now has over 2,000 subscribers. Hardworking, with a grade A average in social sciences and commitment to improving.
Now compare it to the following resume objective, which although articulated looks like a one-fits-all kind of statement that you can just insert into several college applications.
Very committed high-schooler with a calling for social sciences. With an SAT score of 1400, a passion for psychology, and experience as a peer counselor, I am confident that my hard work and motivation will shine through as a college student.
See, the resume objective is your chance to show exactly why you want to attend that college, right from the start.
So, even if you don’t have many achievements to highlight, make sure to personalize your statement by expressing a genuine interest in your application.

#3. Put Weight on Your Education
Taking into consideration that, as a student, you most likely lack significant work experience, your education is the first thing admission officers will look at.
As such, you should give your education its due importance in your college application resume.
For starters, make sure to include this must-have information:
- Your high school’s name and location
- The date of your graduation
In addition, though, combine that with some relevant achievements that can make your education pop out.
Let’s take a look at two examples. The second student has simply listed out the essential education information, whereas the first has taken their education section to the next level.
Dunnellon High School FL
2017 - 2021
- 3rd place at the International Mathematical Olympiad
- Vice-President of the Science Club
- SAT Scores: 1350 (650 Verbal, 700 Math)
- SAT Scores: 1400
#4. Showcase Relevant Activities
Extracurricular activities have a great number of benefits when it comes to your college application resume. Most importantly, they:
- Demonstrate you who are outside of the classroom
- Provide an opportunity to showcase your skills
Any activity and/or interest related to the college you’re applying to has a place on your college application resume, but you don’t have to necessarily stop there.
Any kind of interest, field, or activity where you’re good at can be of benefit to your application.
That’s because it can prove that your interests are not focused solely on your favorite subject or desired career path and that you are engaged and well-rounded .
So, don’t just list your college resume activities dryly (e.g. “reading” or “swimming”). Instead, be specific and creative about your interests, and rest assured that you will get extra points for diversity and commitment.
Don’t believe us? Compare for yourself how the activities sections of two different students look like: the first has put minimal effort into it, whereas the second has put his A-game into writing it.
- Passionate about science
- Co-founder of the Astrophysics Club
Activities
- Two-times winner of my high school’s Science Fair
- Co-founder of the Astrophysics Club, finalists of the MIT-founded THINK challenge
- Swimmer from an early age and member of my high school’s swim team during junior and senior year
- Traveling; I have so far visited 10 countries and 15 states in the USA.
- Photography, with a focus on architectural photography.
#5. Highlight Your Work Experience
Now, if you’ve spent your summer holidays working any type of job for teens , that means that you also have some work experience under your belt.
Although work experience is not necessary when you’re applying for college (meaning that you won’t get left out of college if you don’t have any), it does help to include it if you have it.
Here’s how to list work experience in your college application resume:
- Start with the company name (e.g. if you worked at Starbucks), your job title, and the period you worked there.
- Put your job title first if you worked, say, as a high-school tutor or camp counselor.
- Include 1-2 of your main responsibilities in bullets. If you have achievements to show for, however, make sure to put them first.
Let’s see how that works in a practical example.
Starbucks Coffee
- Awarded employee of the month for 3 months straight
- Fielding customer complaints and questions
- Maintaining good customer service and speedy delivery
Even if the above position isn’t related to the student’s desired field of study, the work experience still highlights some of their skills such as commitment, time management, effective communication, and motivation.
#6. Include Your Skills
Skills—we all got them, but not everyone knows how to demonstrate them effectively in a college application resume.
There are two things to consider when you include skills in your college resume:
- Know the kind of skills that are relevant to your major/field.
- Prove your skills, instead of just listing them
Let’s show you how that works through practical examples:
- Time management
- Critical thinking
Are these great skills for a college applicant? Sure!
But anyone can claim to have those skills (and frankly, most people do).
Rather than just listing these skills, you want to also back them up with achievements and experiences like so:
- Attention to deadline: managed to update the high school’s online newspaper daily
- Leadership: successfully led a team of 6 reporters.
- Creativity: won the 2021 Young Writers competition
- Self-motivation: founded the high school’s first online newspaper
Now, this is a skills section on a college application resume that proves you deserve a spot in your favorite university.
College application resume skills
Wondering which skills to include in your college application resume? Here’s a list to draw some inspiration:
Soft Skills
- Good judgment
- Open-mindedness
- Communication
- Self-motivation
- Interpersonal skills
- Active listening
- Problem-solving
Hard Skills
- Computer Skills
- Programming
- Public Speaking
#7. Use These Additional Sections
If you’ve followed all our tips till now, congrats - you’re around 90% into creating a top-notch college application resume.
Now, let’s talk about how you can take that to 100%!
In addition to the conventional resume sections we’ve covered till now, you can include the following to help you stand out in a sea of other applicants:
- Awards. Here, you can list any awards won in competitions (spelling, art, storytelling, math, etc).
- Volunteer experience . Did you clean up your town, or maybe you volunteered at an animal rescue center as a high school student? Any kind of volunteering can help your college application resume because it shows you’re a responsible community member. If it’s somehow related to your field or future major, that’s a big plus.
- Projects. Be them individual (e.g. you built a website from scratch, or started an informational podcast), or school-related (e.g. an art portfolio for a class, or a history documentary), projects can show that you’re passionate and creative.
- Sports. Poet Juvenal said “ a healthy mind in a healthy body. ” This means that physical exercise is an important part of mental and psychological well-being (which is why sports in a college application resume make all applicants look good). Do you excel at specific sports? Include them in your resume!.
- Languages. Being fluent (or even just a beginner) in a foreign language is another plus for a prospective college student. Make sure to show it in your college application resume.
5 College Application Resume Tips
Finally, here are some of our college application tips that didn’t fit anywhere else in the article:
- Be direct and to the point. Your college application resume is not the right place to show how many SAT-level words you know. Keep your language simple, direct, and to the point. Let your achievements and results speak for themselves.
- Don't lie about your academic background or accomplishments. Lying about the awards you’ve won or your achievements won’t get you into college. More often than not, admission officers will see through your lies by asking behavioral interview questions .
- Proofread your college application resume. Spelling and grammar mistakes can make you appear like a less serious applicant. Imagine telling recruiters that you have great SAT scores and GPA but having spelling mistakes in your resume. Kind of contradictory, isn’t it? To avoid these kinds of mistakes, use spelling and grammar apps such as Grammarly and Heminway .
- Have one or more people look at your resume before you send it out. There are kinds of mistakes that Grammarly or Hemingway cannot catch. To avoid such mistakes, have one or more people that know you give your college application resume a look.
- Emphasize specific achievements over general responsibilities. As mentioned before, emphasizing your achievements over your responsibilities is the best way to set yourself apart from other candidates. The reason is that your achievements effectively show how well you handle responsibilities and they are uniquely yours.
Making a resume from scratch can take what feels like ages—especially if it’s your first time doing it.
You’ve got to tweak the formatting.
You make a change at MS Word and the layout falls apart in front of your eyes. Or you end up using a bland and outdated template.
Well, you don’t have to worry about any of these things with Nóvóresume’s free resume templates .
With 8 free templates to choose from - college application resume included - you don’t have to worry about anything other than inputting your information.
Let our resume builder do the rest!

Key Takeaways
And that’s a wrap on college application resumes. We hope to have made the process of writing yours easier and even more enjoyable.
For good measure, let’s go over the main points we covered:
- Your college application resume should contain the following sections: contact information , personal profile , education section , relevant activities , your skills , and additional sections , such as awards and honors.
- In terms of formatting, the functional resume template fits your college application best. Additionally, make sure to keep your resume one page long and save it as a PDF.
- Write a resume objective that doesn’t surpass 3 sentences and that clearly communicates your motivation for getting into college and your most relevant skills.
- Make sure to give your education section its due importance by being thorough about your grades, SAT scores, and achievements.
- Don’t forget to list all your relevant activities and passions, as well as soft and hard skills.
- Instead of writing your college application resume from scratch, use one of Nóvóresume’s ready-made templates to save yourself time and effort!

To provide a safer experience, the best content and great communication, we use cookies. Learn how we use them for non-authenticated users.
Skip navigation

- Spring Updates
- For Employers
- In the Know
- Make An Appointment
- Internships
- Employer Connections
- CCE Programs
- Funding Programs
- Drop-in Hours
- Career Counseling Appointments
- Practice Interviews
- Programs & Services
- Design Your Next Steps
- Resumes & CVs
- Cover Letters
- Negotiating
- Career Advancement
- Graduate School
- Premium Resources
- Communications & Media
- Engineering & Technology
- Environment & Sustainability
- Financial Services
- International Affairs
- Non-Profits & Social Justice
- Psychology, Counseling & Social Work
- Ways to Gain Experience
- Career Assessments
- Connect With Alumni
- Student Experiences
- First-Generation/Low-Income Students
- International Students
- Students with Disabilities
- Veteran Students
- LGBTQ Students
- Visiting Students
- Students of Color
Writing a Resume: Getting Started

If you’re applying for an internship or job, attending a networking event, or seeking a volunteer opportunity, chances are you’ll need a resume. What is a resume, and how can you go about creating one? This resource will walk you through the basics of creating, formatting, and tailoring your resume to help you make your best impression to employers.
What is a resume?
A resume is:
- a concise and industry-specific summary of your education, skills, and experiences
- a tool that evolves as you gain professional and academic experience
- a marketing document used to secure an interview
- an honest reflection of your accomplishments (it is unethical to mislead employers)
Your resume is often the first impression you make on employers, so be sure to read through and edit it carefully!
Wondering about the difference between a resume and a CV ? In the U.S., the term “CV” is used to refer to a longer, more detailed document typically used for careers in academia. For guidance on resume and CV conventions in other countries, check out Going Global .

What should my resume look like?
A one-page resume is preferable for most fields. Two-page resumes are typically more appropriate for those with extensive work experience.
Your resume should be clearly organized and easy to scan.
Font size: 10–12 points, for legibility. You may vary the size to provide further emphasis.
Font style: Keep the style consistent throughout. Use bold, underlining, and italics for emphasis, but use them sparingly and consistently to avoid clutter.
Margins: 0.5–1 inch.
A resume can be structured in one of two general formats:
- Chronological resumes list experiences starting from most recent, going backward in time. This is the most common resume format. Use this format if your education and experience match your career objectives.
- Hybrid resumes split the experience section into functional categories based on experience.
Use this Resume Checklist to make sure you’re on the right track.
How do I get started?
Think about your experiences and accomplishments, both past and present. These may include
- work experience
- internships
- summer jobs
- volunteer work
- extracurricular activities
- student group leadership
- research experience
- academic and independent projects
- publications
identify your transferable skills and accomplishments
You’ve likely gained a variety of transferable skills through your experiences. Identify them by
- making a list of your characteristics and abilities
- taking a skills assessment
- meeting with a career counselor to explore your transferable skills
Examples of transferable skills include
- collecting and analyzing data
- solving problems
- persuading people
- navigating uncertainty
- paying close attention to details
- synthesizing information
- explaining complex concepts to a range of audiences
Identify the skills you developed and the accomplishments you had in each position.
Research will help you learn to show how your skills can be valuable to an employer. Do this by
- reading job descriptions to identify skills and qualifications essential to the position
- reviewing employer websites to learn about the company mission, workplace culture, and values
- conducting informational interviews in the industry to learn about desired skills and experience
This research will help you learn about key skills, industry-specific language, recruitment cycles, and developing trends relevant to the position.
Write and Revise
You may have more than one version of your resume if you are applying for different types of positions.
Tailor your resume by organizing this information into relevant sections . Each experience will include basic information about your job as well as bullet points that highlight your relevant skills and accomplishments .
Then, review your draft. Do your descriptions reflect what you have learned through your research? How can you rephrase to incorporate the language of your target jobs and industry?
Edit, edit, edit! Get feedback from a CCE counselor in Quick Questions or from a friend. Your resume should never contain typos.
Special Considerations
What if i don’t have enough experience.
You probably have more experience than you think! Remember that you can list both experiences that were paid and those that were not. Employers are interested in skills and experiences you may have gained from academic, community, and volunteer projects. A leadership position in a club or volunteer organization can build a number of skills relevant to a variety of careers, as can class projects or research papers/projects.
What if I have many years of experience?
For experienced-level hires, employers are looking for candidates who can come in and start producing. Therefore, they seek candidates who have a track record of accomplishments. Wherever possible on your resume, quantify results, describe changes you have implemented, highlight areas where you were given or took on increased responsibilities.
As you gain more and more experience, everything you have done will no longer fit on your resume. While it is important to account for your time, you do not need to give an in-depth description of every job you have had nor do you need to continue to include all of your experience during college. If it is related, include it with an explanation; if not, you can start to cut down or eliminate older experiences. Generally, your resume should be one page in length, but if you have over ten years of experience it is acceptable to have two pages as long as you keep the information to the most recent and/or relevant experiences to the position you are applying for.
What if I want to change careers?
As a career changer , one of your biggest challenges is convincing a potential employer to interview you based on your resume. Your research and ability to restate your background in new terms is critical. Pay particular attention to your transferable skills and be sure your resume reflects what you can do for the new industry. The more knowledge and applicability you can show in your resume, the more likely you are to be viewed as someone ready to handle the new challenge.
What file format should I use when submitting my resume?
In most cases, you’ll submit your resume electronically—either by email or through a web-based application form.
Make sure you submit your resume in the format requested by the employer and that your resume looks the same when it reaches its destination. If you’re emailing your resume, send it as a PDF unless another format is requested, such as .doc or plain text. If you’re uploading your resume to a database, double check its formatting before finalizing your application.
Employers sometimes use electronic scanning systems called Applicant Tracking Systems to review resumes. See our Applicant Tracking Systems tipsheet for guidance on ensuring that your resume is not eliminated by electronic screening software.
Related Resources
Your resume: what to put in, what to leave out.
Wondering how to organize the information on your resume? This resource overviews the sections to include on your resume, and what information to include in each of them.

200+ Action Verbs to Spice Up Your Resume
Use varied, strong action verbs to grab the reader’s attention and make your resume stand out to potential employers. This resource includes over 200 action verbs you can use as a starting point.

Resumes with Impact: Creating Strong Bullet Points
How can you make your resume stand out to an employer? This resource will help you learn how to use the STAR method to develop strong bullet points that highlight your skills and accomplishments relevant to a position.
Optimizing Your Resume for Applicant Tracking Systems
90% of Fortune 500 Companies use Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) to manage high volumes of job applications. 75% of candidates are “phased out of consideration” because they don’t pass a screening! Our tips will help your resume make it through ATS.

How to Write a Resume Profile or Summary Statement
If you are in the process of changing careers, craft a powerful summary to highlight your accomplishments and relevant skills. Show an employer, at a glance, why you’re qualified for the job!
The Engineering Resume
We’ve shared some tips for crafting a competitive engineering resume.
Privacy Policy Accessibility Notice of Non-Discrimination Terms of Use
How to Write a Resume That Stands Out
You finally found it! The perfect job for you. Now, all you have to do to get the process started is to submit your resume. The problem is that hundreds of your peers are probably thinking exactly the same thing. How do you stand out?
You finally found it! The perfect job for you. Now, all you have to do to get the process started is to submit your resume. The problem is that hundreds or even thousands of your peers are probably thinking exactly the same thing about exactly the same job. So how do you create a one-page document that will make you and your accomplishments stand out from the crowd?
Your resume is a key part of the job application process: it is the first document that an employer reviews to determine whether they will interview and eventually employ you. Remember that employers often have very limited time to perform this duty. Crafting a strong resume really matters!
Resumes communicate who you are and what you have accomplished. They may be the only document an employer sees to evaluate your record before making a decision to move forward with your application, or they may be used in conjunction with resources like LinkedIn or professional networking profiles and/or a cover letter. A resume that “stands out” in a positive way is one that has been written thoughtfully, clearly and concisely, effectively communicating your abilities and strengths in a very brief space.
Six basic tips will help you build an outstanding professional resume. Note that resumes may vary by professional field (e.g. engineering vs. non-engineering), by location or by other factors such as professional degree. These tips are designed around some of the most common sections and most useful points for resumes across different types.
Tip 1: How to Write an Education Section that Stands Out
The education section demonstrates that you have the academic qualifications for the position. The key questions you should ask yourself while writing this section is, “Have I clearly communicated the strongest and most relevant aspects of my educational experience?” The next question is, “Is this section organized in a way that is easily readable by the employer?”
The education section is important for all applicants but may be weighted differently depending on how long it has been since you graduated from a degree program. For instance, an employer may have a different level of interest in the educational history of a college senior, compared to someone who has been professionally working for several years after college. Understanding this fact may influence where you choose to place this section on your resume.
In general, you should include all of the higher education that you may have had, including undergraduate, graduate, or professional schooling. You may also consider including online courses, certificates, and completed programs through companies like Coursera. Most people list their experiences in an order called reverse chronological, meaning that they list the most recent experience first, and work backwards down the page.
For each listed school, provide the full name of the school or online program, the years of your attendance, your major or majors, if applicable, as well as a minor if applicable. Include the type of degree received (e.g. a Bachelor of Arts or Master of Science) and the year of graduation. If you are graduating soon, include the month and year of graduation so employers know when you will be available to work. If you have studied abroad, include the institution, program of study, and any relevant coursework.
You may want to include which semesters you qualified for special academic recognition, if any. Other special awards, scholarships, or competitive grants can also be listed in this section. If you have non-academic awards, such as for sports or community service, you may choose to create a separate section of your resume for honors and awards.
Tip 2: How to Make the Experience Section Stand Out
Along with education, your experience is one of the most important ways to show that you are qualified for a position. Use this section to clearly convey your strongest professional experiences, whether paid or unpaid. Be sure to give detailed aspects of your roles and responsibilities for each listed position. Emphasize any relationships or similarities between your past experiences and the job you want. You should also include the start and end dates of your involvement with each organization, and any key accomplishments from the role. Don’t forget to include where the company is located, including city and state/province, or even country if different from your home country.
Ask yourself: while involved with the company, did I win any awards, get any special recognition, make new discoveries, start a new program? If so, what happened and what were the results? Quantify your experiences when you can! As the expression goes, “Show don’t tell.” In other words, you can more effectively convey a point by giving concrete examples, rather than through vague descriptions. Consider the following examples.
Instead of:
Improved worker productivity significantly, leading to recognition from upper management.
(A resume reader may ask: What does ‘improved’ mean? What does recognition mean? How much have you improved it by?)
Improved quarter returns by 25%, exceeding projections and leading to the Top Manager Award, given to only one manager in the company per year.
When it comes to language, be honest about your job functions while thinking of professional ways to present your experiences.
Sometimes people fall into a trap of thinking that their job or internship experience won’t sound impressive enough to list. The job may have felt like “sitting at a desk, answering the phone.” True, but you may have been performing other responsibilities or developing useful job-related skills without realizing that you were!
When you were at a desk, were you at the FRONT desk? Were you the only person or the main person in this position? Were you overseeing anything while you were sitting there? Were you the sole person responsible for any tasks? Did you have to learn how to deal calmly and confidently with any customer issues? Did people occasionally ask you to take on additional responsibilities, even for a short time?
It is fair to say that a person sitting at a front desk, may have been MANAGING the front desk, or even managing the desk when the person’s boss was away. Time during which an individual is placed in charge of a business or an office, even if for a limited time, can convey responsibility to a prospective employer.
Look at your accomplishment bullet and ask yourself:
- What did I do in the job?
- Using what?
- To what extent or impact?
Sometimes you may need to pare down your list in order to avoid making your resume too lengthy. Try to select the accomplishments based partly on how impressive they are and partly on how well they relate to the position you want. To describe your experience, always use more than one sentence or bullet. That said, word economy in your bulleted descriptions is also important. Try to keep each bulleted description or sentence to one or two lines at most. You can often rephrase a description, eliminating words while keeping the meaning. The more information you can present clearly and concisely within the short resume format, the more the employer will understand what you can do for them.
Remember that by providing relevant details in each statement of your experience, you will give the employer enough information to evaluate you and also provide them with ideas of what they might want to discuss with you in an interview.
Tip 3: How to Create a Leadership and Activities Section that Stands Out
For many people, especially students and recent graduates, a Leadership & Activities section can be a fantastic differentiator for your resume. If you have not been in the workforce for long, or if you have only worked summers and part-time, then you may not have much relevant content to add to your Experience section. A strong Leadership & Activities section can help you fill that gap while also telling an employer something about you as a person.
When creating the section, you should first consider what student organizations and activities you would want to include. Then, you should consider what you would want to write about each one. In general, this section is much like the Experience section, except that it is about what you have done in a personal, rather than professional, setting.
Of course, because student organizations and activities are personal, you should be careful about which ones you choose to list; they should be appropriate to a professional setting. For example, you should probably not choose to share that you were chosen “Top Drinker” of your college’s “Beer Keg of the Day” club. On the other hand, if you volunteered at a food bank, wrote for a school publication, or had a membership in an honor society, those accomplishments would be worth sharing.
Most importantly, you should include student organizations and activities where you have made significant contributions or held leadership positions. Just as you did in the Experience section, you should think about what you did in the organization, any responsibilities you had, any skills you used, and any knowledge you gained. If you made improvements to the student organization or activity, definitely include concrete examples. Make sure to consider if any of your experiences with student organizations and activities could be related to the position you are applying for. Could any of the skills you have learned be useful in the job?
Because student organizations and activities can offer students leadership opportunities and experiences that are often limited to experienced professionals in companies, this section is your chance to show not only that you are qualified for the position but that you have even greater potential. Make the most of this opportunity to show the employer what you can do!
Tip 4: How to Highlight Your Skills
Another important component of what defines an attractive candidate in the modern economy is their skill set. Because employers want people who can quickly start being productive, they care about what skills a job prospect has, particularly in certain technical fields. In most cases, skills are incorporated into the Experience section, if you acquired skills as part of your internship or job, and in the Education section, if you obtained the skills through coursework, research, or projects. Sometimes people with additional skills, such as technical skills, foreign language, or certifications obtained outside of university, will place them into a separate section at the end of the resume. Whichever format you choose, you still need to emphasize the skills you have, so that an employer can easily see how you can help them.
You should ask yourself a few important questions. What skills do I have? What skills are my target employers looking for? Are my skills hard skills (i.e. technical, like computer programming) or soft skills, such as the ability to listen?
Make a list! Separate the skills into hard skills and soft skills. What skills are most in demand (on both lists) for the position you are interested in (One good way to decide this is to look at job listings for many similar positions and note how often a particular skill is listed.)? How can you highlight your proficiency in these skills?
Lead with your strongest skills and/or the ones that seem the most marketable. Let’s say you know the programming language Python. How well do you know it? How many years have you used it? Do you have any specialized knowledge and ability that may set you apart from a competing applicant? Do you have demonstrations of your work anywhere for a prospective employer to see?
Here’s an example of a skills entry that might be included into the Experience section:
Programming: 8 years of experience with Python and similar scripting languages, wrote MyFirstPythonProject software available on GitHub
Useful tip: Artists may have portfolios for their artistic work. Examples of appropriate work, such as for coding, may not be a bad idea to have available in addition to a resume!
Even if your field is not technical, you may still have important hard skills. Do you have experience with popular office software, such as Excel, PowerPoint, or Access? Do you know any foreign languages, even at a basic level? Think about not only what might be required in the day-to-day performance of the job, but what other skills could potentially be useful to the employer.
You will want to include all the relevant skills to demonstrate your qualifications, without including too much less-relevant information which could distract from your message. Think carefully about which skills you want to include, and which could be left out. Remember to choose your words economically to maximize content in a minimum of space. With a little effort, your skills details can transform your resume from a simple list of accomplishments to a document that gets an employer thinking about all the great ways you could contribute!
Tip 5: Formatting and Making the Resume Look Professional
Believe it or not, the appearance and organization of a resume can greatly affect the response. The first hurdle for any resume is to get the employer to read it. An attractively presented, concise resume is easy for a recruiter to pick up. On the other hand, if a resume is 5 pages, written in 6-point font, a prospective employer may not think that it is worth the time to find a magnifying glass and read it. In most cases, a resume should not exceed one page (sometimes two pages, mostly for more experienced candidates, or in scientific and technical fields where publication lists can be lengthy), which has a few key sections that are separated from one another or clearly delineated.
Here are some suggestions to make the format stand out positively:
- Use 10-12-point font or larger. (10 point may even sometimes be too small, and the choice can depend on the chosen font.) Your audience should easily be able to read the size of the writing. Often prospective employers may not have perfect vision, so readability may create problems if the text is too small.
- Use a clean, professional-looking font. Don’t use fonts that are overly artistic and hinder the ability for the reader to understand them. Some find fonts like Times New Roman most clearly readable; others find competing fonts better. The font is just an aspect of the writing; don’t let it overpower the words themselves.
- Use respectable margins. Don’t try to deviate too much from 0.5 margins at either side. Also, don’t make the margins too large, beyond 0.75 or 1 unit on either side. Around 1 unit on the top and bottom should be acceptable.
- Use adequate spacing.
- Abbreviate months of employment.
- Include proper contact information. Most people include full name, address, email address and at least one phone number at the top of the document.
Tip 6: Revision and Review
One of the most important steps to writing a good resume is having others you trust look it over. A small spelling or grammar error on a resume could cause problems by making it seem like you lack attention to detail.
You can start with standard spelling and grammar checking programs. However, while these programs are very helpful, they are not enough by themselves. For example, the programs may not flag errors with homophones (e.g. hair and hare). They also have difficulty with uncommon, technical, or foreign words that may not be in their dictionaries. In addition, they are not looking for formatting inconsistencies or at the overall appearance of the resume. While computer programs can help with many issues, there is still no substitute for the human eye.
Start by printing a copy of your resume and looking for errors and inconsistencies yourself. Then, present copies to others along with a description of the job or educational opportunity that you are applying for. When presenting your resume to others, consider at least two kinds of people: a peer, and an experienced professional or teacher. Each may identify different issues with the resume.
Ask the reviewers to provide two types of notes: technical revisions and feedback on the writing, organization and effectiveness of the resume.
Once you get feedback, discuss it with them for a few minutes. Remember, don’t take constructive criticism personally! They are trying to help you, and their points of view may be similar to that of the employer. Your goal is to create a resume that most people will appreciate.
Once you obtain proper feedback, you can work on improving your resume. Try to incorporate your reviewers’ suggestions. Their ideas may even make you think of other ways to improve your resume! Most importantly, always remember that once you have made your revisions, review your resume again before you send it out!
The stronger your resume, the better your chance of getting an interview and landing a meaningful job. Just by following these simple tips, you will be well on your way to resume success, creating a clear, detailed, and concise document designed to impress employers. So, get writing and get yourself noticed!
A good resume can help you land an interview, but even minor errors can take you out of the running. Schedule an appointment with a counselor to ensure it will be effective.
Quick Resume Tips:
- Use the position description to decide what to include.
- Pick a standard and consistent format.
- Describe your experiences with specificity and strong action verbs.
- Record accomplishments and contributions, not just responsibilities.
- Revise carefully!
- Don’t include personal information about your age, religion, health or marital status.
- Photos are generally not preferred for U.S. resumes.
- Typically, you will not be expected to share past salary information on a resume.
- Employers assume that “references will be available upon request,” so you don’t need to include them on your resume unless asked.
- Employers may use keyword scanning on resumes, so know what words are relevant to the industry and position and ensure they appear in your resume.
Home » Campus Life » Career Education » Career Studio » Job Search » Resume and Curriculum Vitae (CV) » How to Write a Resume
How to Write a Resume
An effective resume is more than a list of your skills and experience. It serves as your professional introduction and a way for you to market and differentiate yourself.
It is often the only information a potential employer will have when deciding whether or not to invite you for an interview. Moreover, most employers receive hundreds of resumes for any given opportunity and have very little time to evaluate each one. Your resume must therefore clearly convey your skills, strengths, relevant experience, and do so in an efficient and visually appealing manner.
The following guide will walk you through creation of a resume that will best represent you to the organizations, programs and opportunities you hope to pursue.
Step 1: Choose a Format
Select a simple and appealing format for your resume. If you are just beginning your career or working in a traditional industry, choose something simple. Avoid borders, colors, images or graphics, as these tend to be difficult for automated Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) to read. Our basic formatting suggestions are below.
- Center name at top of page and make it two font sizes larger than the rest of the text
- Use a professional-sounding e-mail address that you check often; remove the hyperlink
- Include a physical address . If you prefer, you can list just city, state and ZIP code with no street address. You may include your current and permanent addresses, or just one.
- Optional: Include your LinkedIn profile URL
- Font: Arial, Calibri, Tahoma, Times New Roman (same font throughout)
- Font size: 10-11 point
- Margins: .5 to 1 inch, all sides
- Page Numbers: Include if the document goes beyond one page (start numbering on page 2)
- Use consistent formatting for dates throughout (e.g., 2/18, Feb. 2018, February 2018)
- Consider aligning all dates on the right side of your document
- Use bullet points to give relevant details and explanation of your experiences
- Bullet point style and formatting should match throughout
- Bullet points in a resume typically do not use a period because they are usually not complete sentences
- Within each section, list information in reverse chronological order (most recent first)
- Consider using bold and all caps for HEADINGS in the body of your resume
- Consider using bold for Names of Degrees and Position Titles
- Consider using italics for Name of Organization, City, and State
Looking for visual examples? Check out these templates for reference:
- Resume Outline Option 1 (download)
- Resume Outline Option 2 (download)
- Resume Outline for First- or Second-Year Undergraduate Student (download)
- Resume Outline with Licensure and Certification (download)
Step 2: Collect and Fill in Information
Make a list of all your prior experience including but not limited to education, internships, co-ops, full-time work, part-time work, volunteering, service-learning, awards and scholarships, achievements, study abroad, training programs, student organizations, leadership roles, lab and computer skills, languages, and certifications. Use exact names for degrees , programs, organizations, and titles; you may have to look some of them up.
Then, use this information to populate the resume sections outlined below. Among the optional sections, choose those that help convey your unique strengths and skills. Remember that many sections are flexible can be combined to tell your unique story. There is no one “correct” way to compose a resume since it is just as unique as you are!
Summary (optional)
If you choose to use a Summary, it should be specific to the industry and position. A vague Summary can do more harm than good.
- Should be at the top of your resume if you are a recent graduate
- Degree (Bachelor of Arts, Bachelor of Science, etc.) and month/year of graduation or expected graduation
- Major(s), minor(s), and any concentration(s) within your major(s) or minor(s) if applicable
- University name, city, and state
- (Optional) A list of relevant courses specifically related to the position
- (Optional) Awards and/or honors that you earned for academics, athletics, or in a work environment (this may be included under Education or listed in a separate section at the end, according to your preference)
- (Optional) Other universities, if applicable, should be formatted the same as current university
- (Optional) For first- and second-year students, including high school is acceptable. Format the name consistently with the current university.
- Always include job title, dates of employment, name of organization, and location
- Address what you learned and the skills you developed in addition to the tasks or jobs you performed, using strong bullet points
- “Experience” can include clubs or project work in addition to jobs or employment
- If you have a significant amount of experience, you can consider subdividing your experience section. For example, “Relevant Experience,” “Other Experience, “Research Experience,” etc.
Leadership, Activities and Service (optional)
- Your resume may contain one or all of these sections
- You may combine some, such as “Activities and Service”
- Choose quality over quantity. Only include experiences where you’ve developed skills that are relevant to the position you’re applying for.
- This section typically includes computer skills, language skills, and science/laboratory skills, if applicable.
- It’s better to incorporate soft skills or transferable skills into the Experience section, where you should demonstrate how you used and developed those skills. This is more effective than simply listing them under Skills.
Step 3: Carefully Review Your Resume
Since resumes involve a lot of detail and careful formatting, it is easy to make mistakes. The last stage of crafting your resume should be a meticulous review of your formatting and content and a careful search for typographical errors. If possible, have a friend, family member, or career coach conduct a final check.
Resume Checklist
- Is first and last name at the top of the page and in bold?
- Are address, phone number, and email easy to read?
- Does Education follow directly after the contact information?
- Is formatting (e.g. bold, font, bullet sizes, heading styles) consistent throughout?
- Are the headings and statements evenly spaced?
- Are dates evenly aligned along the right margin of the page?
- Are verb tenses present tense for current experiences and past for previous experiences?
- Are there one to four bullet points under each entry in the Experience section?
- If included, does the Objective statement clearly state the desired industry, position and two to three skill sets?
- Does the resume include the applicable headings, such as Education, Experience, Activities/Leadership/Service and Skills?
- Does the Education section state official degree and graduation date? Is the cumulative GPA included if higher than 3.0? Is the GPA accurate and not rounded up?
- Do the bulleted descriptions demonstrate major accomplishments rather than routine tasks/duties? Are they quantified whenever possible?
- Do the bulleted descriptions start with action verbs and demonstrate the use of key skills?
- Is the resume free of personal pronouns (e.g. no references to “I,” “we,” “me,” “us,” or “my”)?
- Is the resume completely free from errors in spelling, punctuation, abbreviations and grammar?
Want a second opinion?
- Run your resume through the ResumeAI online resume review tool
- Come to walk-in hours to review your resume with a career coach

Resume How-To Guide
How to: resumes — introduction.
How to: Format Your Resume
How to: Improve Your Resume's Content
Quick Resume Tips:
The Center provides many resources to help you create your resume. As you are writing it, we encourage you to check out the following helpful guides:
- Preparing Your Resume
- Samples of Work Experience
- Action Verbs
- Resume Checklist
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS)
Many companies use software known as an applicant tracking system (ATS) to identify applicants who either appear qualified or unqualified for the available position. Only those who appear qualified will be moved to the recruiter or hiring manager. The federal government also uses a similar process.
Luckily, there are several techniques you can put in place to try to move past these "resume bots" and get in the hands of the hiring manager.
Utilize Specific Keywords Found in the Job Description
When updating your resume to apply to an opportunity, read through the internship or job description with high attention to detail. Highlight the keywords and qualifications that you have prior experience with through part-time jobs, internships, major class projects, student organization involvement, military experience, and more. You should then incorporate this language into your resume.

Other Considerations to "Beat the Bots" - Applicant Tracking Systems
- Use both long-form and acronym versions of keywords (e.g. User Experience (UX) for maximum searchability
- Avoid tables or columns on your resume as they may cause major parsing errors
- Use traditional resume fonts like Helvetica or Georgia
- Avoid headers or footers as the information may get lost or cause a parsing error
- Use mostly standard resume section headings (i.e. Work Experience; Design Experience) instead of being cute or clever (i.e. Where I’ve Been)
- Save your file as a .docx if possible. PDF is relatively okay, too!
Other tips on how to get past ATS, check out this article through Firsthand: 4 Tips for Beating the Resume Bots
- Beginning/Early College Resumes
- Advanced/Later College Resumes
- Veteran/Adult Learner Resumes
- Graduate Student Resumes
- Undergraduate Curriculum Vitae (CV) sample
- If you are a Master’s student at the University of Maryland, click here for an example .
- If you are a doctoral student at the University of Maryland, please enroll in Doctoral Career Navigator within Open Catalog . Doctoral Career Navigator is a free self-paced online course in UMD’s ELMS-Canvas platform. It contains 13 modules of sample job application packets, career-related videos, worksheets, and links to relevant resources for all UMD doctoral students and postdocs.
- Behavioral & Social Sciences
- Engineering
- Finance & Economics
- Graphic Design/Digital Media , and Advertising/PR
- Journalism
- Performing Arts
- Sciences , Technical , and Health
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Sample Résumés

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This section of resources contains samples of skills, chronological, and functional résumés. The Interactive Résumé resource contains a sample résumé on which you can click each section to learn more about the different sections of the résumé and how to write each section of the résumé.
This section offers information on three common résumé styles: skills, chronological, and functional. Each section also contains a sample résumé of the particular style the section discusses.
The Interactive Résumé resource contains a sample résumé on which you can click each section to learn more about the different sections of the résumé and how to write each section of the résumé.
Sample Résumés:
Skills Résumé
Chronological Résumé
Functional Résumé
Interactive Résumé
CV for University Application example
Getting into university and getting a degree will give you a huge head-start in your career, but getting into university isn’t easy
This guide contains an example University Applicant CV and plenty of tips on how to create your own winning CV, so you can stand out amongst the other candidates and get into the university of your dreams.
Guide contents
CV for University Application example 1
Cv for university application example 2.
- Structuring and formatting your CV
- Writing your CV profile
- Detailing work experience
- Your education
CV templates

Unsure of what your University Applicant CV should look like?
Have a look at the CV example above to get familiar with the structure, layout and format of a professional CV.
As you can see, it provides plenty of relevant information about the applicant but is still very easy to read, and brief – which will please busy university recruiters.
University Applicant CV structure and format
The format and structure of your CV is important because it will determine how easy it is for recruiters and employers to read your CV.
If they can find the information they need quickly, they’ll be happy; but if they struggle, your application could be overlooked.
A simple and logical structure will always create a better reading experience than a complex structure, and with a few simple formatting tricks, you’ll be good to go.

Formatting Tips
- Length: Recruiters will be immediately put off by lengthy CVs – with hundreds of applications to read through, they simply don’t have the time! Grabbing their attention with a short, snappy and highly relevant CV is far more likely to lead to success. Aim for two sides of A4 or less.
- Readability : Make sure your CV is easy to read and looks professional by applying some simple formatting tricks. Bullet points are great for making large paragraphs more digestible, while formatting your headings with bold or coloured text will help the reader to find the information they need, with speed.
- Design: It’s generally best to stick to a simple CV design, as funky or elaborate designs rarely add any value to your application. A clear, modern font and a subtle colour scheme work perfectly and allow your skills, experience and achievements to speak for themselves.
- Avoid photos: Logos, profile photos or other images aren’t necessary and rarely add any value – save the space for written content, instead!

Structuring your CV
As you write your CV , work to the simple but effective structure below:
- Name and contact details – Pop them at the top of your CV, so it’s easy for recruiters to contact you.
- CV profile – Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.
- Core skills section – Add a short but snappy list of your relevant skills and knowledge.
- Work experience – A list of your relevant work experience, starting with your current role.
- Education – A summary of your relevant qualifications and professional/vocational training.
- Hobbies and interests – An optional sections, which you could use to write a short description of any relevant hobbies or interests.
Now I’ll guide you through exactly what you should include in each CV section.
CV Contact Details

Tuck your contact details into the corner of your CV, so that they don’t take up too much space. Stick to the basic details, such as:
- Mobile number
- Email address – It should sound professional, such as your full name.
- Location -Just write your rough location, rather than your full address.
- LinkedIn profile or portfolio URL – If you include these, ensure they’re sleek, professional and up-to-date.
University Applicant CV Profile
Recruiters read through countless applications every day.
If they don’t find what they’re looking for quickly, they’ll simply move onto the next one.
That’s what makes your CV profile (or personal statement , if you’re an entry-level/graduate candidate) so important.
This short and snappy summary sits at the top of your CV, and should give a high-level overview of why you’re a good match for the university.
This way, you can ensure that busy recruiters see your suitability from the outset, and so, feel your CV is worth their time.
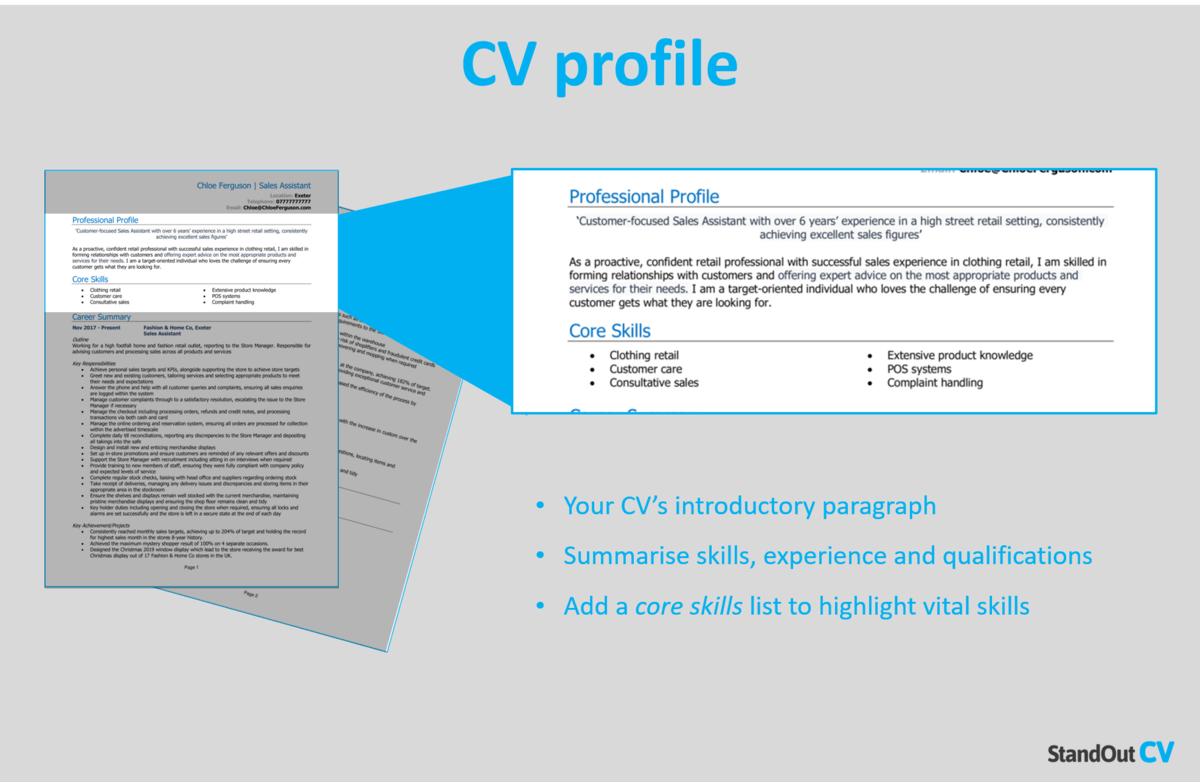
Tips for creating an impactful CV profile:
- Keep it brief: It might be tempting to submit a page-long CV profile, but recruiters won’t have the time to read it. To ensure every word gets read, it’s best to include high-level information only; sticking to a length of 3-5 lines.
- Tailor it: Before writing your CV, make sure to do some research. Figure out exactly what your desired employers are looking for and make sure that you are making those requirements prominent in your CV profile, and throughout.
- Don’t add an objective: Leave your career objectives or goals out of your profile. You only have limited space to work with, so they’re best suited to your cover letter .
- Avoid cliches: “Determined team player who always gives 110%” might seem like a good way to fill up your CV profile, but generic phrases like this won’t land you an interview. Recruiters hear them time and time again and have no real reason to believe them. Instead, pack your profile with your hard skills and tangible achievements.
What to include in your University Applicant CV profile?
- Summary of experience: Recruiters will want to know what type of companies you’ve worked for, industries you have knowledge of, and the type of work you’ve carried out in the past, so give them a summary of this in your profile.
- Relevant skills: Highlight your skills which are most relevant, to ensure that recruiters see your most in-demand skills as soon as they open your CV.
- Essential qualifications: Be sure to outline your relevant qualifications, so that anyone reading the CV can instantly see you are qualified for the universities you are applying to.
Quick tip: Your CV is your first impression on recruiters, so it’s vital to avoid spelling and grammar mistakes if you want to appear professional. Use our quick-and-easy CV Builder to add pre-written content that has been crafted by recruitment experts.
Core skills section
In addition to your CV profile, your core skills section provides an easily digestible snapshot of your skills – perfect for grabbing the attention of busy hiring managers.
As University places might receive a huge pile of applications, this is a great way to stand out and show off your suitability for the role.
It should be made up of 2-3 columns of bullet points and be made up of skills that are highly relevant to the universities you are targeting.

Work experience/Career history
Next up is your work experience section, which is normally the longest part of your CV.
Start with your current (or most recent) job and work your way backwards through your experience.
Can’t fit all your roles? Allow more space for your recent career history and shorten down descriptions for your older roles.

Structuring your roles
If you don’t pay attention to the structure of your career history section, it could quickly become bulky and overwhelming.
Get in recruiters’ good books by creating a pleasant reading experience, using the 3-step structure below:

Begin with a summary of your role, detailing what the purpose of your job was, who you reported to and what size of team you were part of (or led).
Key responsibilities
Next, write up a punchy list of your daily duties and responsibilities, using bullet points.
Wherever you can, point out how you put your hard skills and knowledge to use – especially skills which are applicable to your target role.
Key achievements
Finish off by showcasing 1-3 key achievements made within the role.
This could be anything that had a positive effect on your company, clients or customers, such as saving time or money, receiving exemplary feedback or receiving an award.
At the bottom of your CV is your full education section. You can list your formal academic qualifications, such as:
- GCSE’s
As well as any specific qualifications that are essential to the jobs you are applying for. Note down the name of the qualification, the organisation at which you studied, and the date of completion.
Interests and hobbies
This section is entirely optional, so you’ll have to use your own judgement to figure out if it’s worth including.
If your hobbies and interests could make you appear more suitable for your dream job, then they are definitely worth adding.
Interests which are related to the industry, or hobbies like sports teams or volunteering, which display valuable transferable skills might be worth including.
Writing your University Applicant CV
An interview-winning CV for a University Application needs to be both visually pleasing and packed with targeted content.
Whilst it needs to detail your experience, accomplishments and relevant skills, it also needs to be as clear and easy to read as possible.
Remember to research the role and review the university before applying, so you’re able to match yourself up to the requirements.
If you follow these guidelines and keep motivated in your university search, you should land an interview in no time.
Best of luck with your next application!
Schedule Appointments in CatCloud

- CALES Competencies
- Explore Interests & Opportunities
- Graduate & Professional School
- Resume / CV / Cover Letter / Personal Statement
- Skills Assessment
- The Search Process
- Business & Commerce
- Environment & Sustainability
- Agriculture, Food & Natural Resources
- Health Professions
- Helping Professions
- Science, Technology & Engineering
- Undecided/No Major Selected
- Recruit Talent
- Engage with Students
- CALES Career Talks
- Learn More About CALES
- Faculty & Staff
- Featured Internships
- Featured Jobs
- Federal Internships
- Labor Market Trends
- CALES Advisory Board
- Our Mission
Resume Tip Sheet
- Share This: Share Resume Tip Sheet on Facebook Share Resume Tip Sheet on LinkedIn Share Resume Tip Sheet on X

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Harvard College Resumes & Cover Letter Guide. A resume is a concise, informative summary of your abilities, education, and experience. It should highlight your strongest assets and skills, and differentiate you from other candidates seeking similar positions. View Resource.
Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the document. Choose a readable font, such as Times New Roman or Georgia, in a 10- or 12-point size. Bold your name and section headers so colleges can scan key parts of your resume quickly. Use bullet points to structure your resume in a readable format.
For example, if you're applying to an arts-focused school, try starting your resume with a resume section called "creative accomplishments" or "artistic talents.". 2. Include resume keywords for your college resume. Use appropriate resume keywords when writing your college resume.
How to write a university resume The structure of a university resume differs from most resumes, as your purpose is to impress recruiters with your potential, rather than your experience. Here are the key sections you should consider when writing your university resume: Related: Resume Writing 101: Tips for Creating a Resume (With Examples) 1.
To create an effective high-school student resume, follow these steps: Add your name, surname, and contact details at the top of the resume. Write a career objective or a resume summary that can catch the recruiter's attention. Mention any relevant work experience, such as part-time jobs, tutoring, babysitting, etc.
Here's how to list your education history on an undergrad resume: Start with your associate degree or bachelor's degree at the top. Add the major, school name, school location, and completion date. If you've taken any classes related to the job you're applying to, add them under a "relevant coursework" subsection.
Download Undergraduate Resume Template. To upload the template into Google Docs, go to File > Open > and select the correct downloaded file. Learn what an effective undergraduate resume looks like, complete with samples, then review how to build one and try writing your own using a template.
Step 3. Add your accurate information by section on your resume for college. Reference the college resume examples you reviewed previously to choose the sections you will use on your high school resume. Organize each list by year, placing the most recent item at the top of your resume for college.
resume is a work in progress. hile there are some basic rules (spellcheck is a must!) and standard practices to resume writing, it is largely a personal undertaking. We encourage you to take a holistic approach to creating your resume, considering your unique set of experiences in relation to the types of roles to which you aspire.
Order Your Contact Information the Right Way #2. Write an Attention-Grabbing College Resume Objective #3. Put Weight on Your Education #4. Showcase Relevant Activities #5. Highlight Your Work Experience #6. Include Your Skills College application resume skills #7.
Check our college student resume examples and follow the instructions to write a resume for a college student. Tools. Resume Builder Create a resume in 5 minutes. Get the job you want. ... Motivated college student with a Bachelor of Arts in Sociology from Montana State University, Bozeman seeking an internship opportunity with Synthex Inc., to ...
Writing a detailed education section is key to creating a successful college resume. Here are seven education-related details you'll need to include on your college resume: University or school name; Major and level of degree (i.e., Bachelor's or Master's) Location (city and state) Graduation date (month and year) Your GPA (3.5 or above)
Format. Your resume should be clearly organized and easy to scan. Font size: 10-12 points, for legibility. You may vary the size to provide further emphasis. Font style: Keep the style consistent throughout. Use bold, underlining, and italics for emphasis, but use them sparingly and consistently to avoid clutter.
Abbreviate months of employment. Include proper contact information. Most people include full name, address, email address and at least one phone number at the top of the document. Tip 6: Revision and Review . One of the most important steps to writing a good resume is having others you trust look it over.
Here are some helpful tips to help you write an impressive resume: Choose a professional font. To ensure your format is simple and attractive, use a font like Times New Roman or Georgia that is easy to read and avoids unnecessary flourishes. Size your font correctly. Font size is important for optimising the space.
How to write a resume for a university student. 1. Analyze the job posting. As each employment opportunity is likely to have different requirements, it's important to understand exactly what the employer is looking for in a candidate. You can do that by thoroughly analyzing the job posting for insight into the specific traits the hiring ...
Step 3: Carefully Review Your Resume. Since resumes involve a lot of detail and careful formatting, it is easy to make mistakes. The last stage of crafting your resume should be a meticulous review of your formatting and content and a careful search for typographical errors. If possible, have a friend, family member, or career coach conduct a ...
1. Write your contact information. The header of your resume contains your full name, followed by your contact details. Include your residential address, personal phone number and email address so that a recruiter can easily get in touch with you with their questions.
Use mostly standard resume section headings (i.e. Work Experience; Design Experience) instead of being cute or clever (i.e. Where I've Been) Save your file as a .docx if possible. PDF is relatively okay, too! Other tips on how to get past ATS, check out this article through Firsthand: 4 Tips for Beating the Resume Bots.
Create an Impressive Resume. A resume is like a movie trailer. It should give a brief but compelling preview of your skills and experience to pique the interest of the hiring manager and entice them to learn more about you. This guide will help you create a powerful resume that highlights your credentials to stand out from the crowd.
Sample Résumés. This section offers information on three common résumé styles: skills, chronological, and functional. Each section also contains a sample résumé of the particular style the section discusses. The Interactive Résumé resource contains a sample résumé on which you can click each section to learn more about the different ...
Structuring your CV. As you write your CV, work to the simple but effective structure below:. Name and contact details - Pop them at the top of your CV, so it's easy for recruiters to contact you.; CV profile - Write a snappy overview of what makes you a good fit for the role; discussing your key experience, skills and accomplishments.; Core skills section - Add a short but snappy list ...
Tailor your job mentions so that you impress your future employer with the most relevant work experiences for this specific job ad. This also keeps your resume short, clean, and concise. Expert tip. If you can name percentages, numbers or specific projects that prove your productivity in past jobs - do so.
10 Behavioral Interview Questions (With Sample Answers) How To Write a Curriculum Vitae (CV) Federal Resume Template. Resumes: Writing about your skills. Show more Instructions and 'How-to' Guides.
Here's a resume template you can use without work experience. Here's the resume filled out below. How to write a resume with no experience: 5 tips. When you have no work experience to add to your resume, highlight your education, include relevant non-work experience, list your skills, and include a summary. 1. Highlight your education.
How To Write a Basic Resume. Gather your experience, skills, and education information to create a basic resume. Make a list of your recent jobs and what you did at each. Think about the value you brought to those organizations, and brainstorm a list of skills you have relevant to the job you want. Then, use a resume template to present all ...
Next up on your medical coder resume should be your education. When highlighting your education, make sure you list the following details: Graduation date (or expected graduation date if still in school) Name of your academic degree or certificate. Name of the school. GPA (if it's above 3.5)
Write a convincing cover letter. While the resume may be a copy, the cover letter must be personal. Use the name and title of the person who can give you the interview. Prepare specifically for each interview. Know the company's history and competition. Try to grasp the problems of the job you're applying for.