While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.

Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
3 Steps to Writing an Awesome Thesis Statement

Krystal N. Craiker

One of the most important parts of any essay is the thesis statement. Unfortunately, this is also one of the biggest struggles for many students. But writing a great thesis statement doesn’t have to be scary. You can craft amazing statements with just a few easy steps.
What is a thesis statement, and why do I need one?
It starts with a question, step one: answer the question, step two: so what, step three: be specific, other tips for strong thesis statements, want to improve your essay writing skills.
A thesis statement is one or two sentences near the beginning of your essay. It quickly sums up what the essay is about and why it matters.
You might think you only need this because your teacher requires it. But the thesis statement is what helps keep your essay on track ! Think of it as a roadmap for your reader. If you write a good thesis statement, they'll know what they can expect, what your position is, and why they should care.
Every good essay starts with a question. It guides your entire essay. A thesis statement is just a one to two sentence answer to that question. Your instructor might provide the question for you or provide a prompt that you can reword into question format. But if the topic is up to you, you will create your research question, too.
How do you determine what question you are answering in your paper? Well, first you figure out your topic and what point you are trying to make. Let’s look at a few examples.
Topic : Compulsory voting Question: Should voting be compulsory in Canada?
Topic: Progressive Era Legislation Question: Which piece of legislation passed between 1890 and 1920 had the greatest impact on America?
Topic: Selective breeding of plants and animals Question: How has selective breeding been used by humans throughout history?
Now, let’s look at the steps for writing our thesis statements based on our research questions.

Remember, a thesis is just a short answer to your research question. So, the first thing you need to do is answer your question. Here are the most basic answers to our previous example.
Question: Should voting be compulsory in Canada? Answer: No, voting should not be compulsory in Canada.
Question: Which piece of legislation passed between 1890 and 1920 had the greatest impact on America? Answer: The Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 had the greatest impact on America.
Question: How has selective breeding been used by humans throughout history? Answer: Humans have used selective breeding of plants and animals for at least 10,000 years.
Technically, those sentences could be thesis statements, but they aren’t very good. A thesis statement needs to also answer the question, “So what?” In other words, why is this topic important? Let’s add that to our sentences.
Question: Should voting be compulsory in Canada? Answer: No, voting should not be compulsory in Canada because people might not be informed or care about who they vote for.
Question: Which piece of legislation passed between 1890 and 1920 had the greatest impact on America? Answer: The Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 had the greatest impact on America because it ensured food and medicines were manufactured safely and labeled properly.
Question: How has selective breeding been used by humans throughout history? Answer: Humans have used selective breeding of plants and animals for at least 10,000 years to improve their food supply.
Your thesis statement should be specific to what you are going to talk about. All of the above sentences answer the research question and tell why your audience should care. But they are vague. A great thesis statement is specific and relates to what the rest of your essay will include.
An easy way to do this is to list your main points. This is usually used in essays with only two or three main points. Here’s an example:
- Voting should not be compulsory in Canada because people who do not care about politics will make uninformed votes, candidates may bribe citizens for their votes, and campaigns will become more inflammatory and corrupt.
This is a perfectly acceptable way to write a thesis. But if you have more than three points, it will become very wordy. It’s also not the strongest way to write a thesis. Let’s reword it to make it stronger.
- Because compulsory voting does not ensure that citizens cast informed votes, it sets the stage for more corrupt campaigns as candidates vie for votes, and is therefore detrimental to Canadian democracy.
It’s specific without reading like a laundry list. Now we’ll take a look at our next two thesis statements.
- The Food and Drug Act of 1906 allowed the federal government to regulate food and medication labeling, which demonstrated a prioritization of human life over profit and paved the way for later food safety laws that are still in effect today.
- From the ancient Sumerians to modern scientists in sterile labs, selective breeding is a powerful tool that humans have used to create hardier and more productive food supplies, as well as animals bred to improve human quality of life.
- Take a stand, don’t just state facts
- A good thesis statement should have a dependent (subordinate) clause
- Two sentences is the absolute maximum
- Place your thesis statement at either the beginning or end of your introduction , not buried in the middle
What’s the hardest part of writing an essay for you? Let us know in the comment section. You can find more great resources for essay writing on our blog .
Use ProWritingAid!
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you're losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much.
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Krystal N. Craiker is the Writing Pirate, an indie romance author and blog manager at ProWritingAid. She sails the seven internet seas, breaking tropes and bending genres. She has a background in anthropology and education, which brings fresh perspectives to her romance novels. When she’s not daydreaming about her next book or article, you can find her cooking gourmet gluten-free cuisine, laughing at memes, and playing board games. Krystal lives in Dallas, Texas with her husband, child, and basset hound.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels
An Overview of the Writing Process
How to write a thesis statement.
Whether you are writing a short essay or a doctoral dissertation, your thesis statement will arguably be the most difficult sentence to formulate. An effective thesis statement states the purpose of the paper and, therefore, functions to control, assert and structure your entire argument . Without a sound thesis, your argument may sound weak, lacking in direction, and uninteresting to the reader.
Start with a question — then make the answer your thesis
Regardless of how complicated the subject is, almost any thesis can be constructed by answering a question.

- Thesis: “Computers allow fourth graders an early advantage in technological and scientific education.”
- Thesis: “The river comes to symbolize both division and progress, as it separates our characters and country while still providing the best chance for Huck and Jim to get to know one another.”
- Thesis: “Through careful sociological study, we’ve found that people naturally assume that “morally righteous” people look down on them as “inferior,” causing anger and conflict where there generally is none.”
Tailor your thesis to the type of paper you’re writing
N ot all essays persuade, and not all essays teach. The goals of your paper will help you find the best thesis.
- Ex. “This dynamic between different generations sparks much of the play’s tension, as age becomes a motive for the violence and unrest that rocks King Lear.”
- Ex. “The explosion of 1800’s philosophies like Positivism, Marxism, and Darwinism undermined and refuted Christianity to instead focus on the real, tangible world.”
- Ex. “Without the steady hand and specific decisions of Barack Obama, America would never have recovered from the hole it entered in the early 2000’s.”
Ensure your thesis is provable

Good Theses Examples:
- “By owning up to the impossible contradictions, embracing them and questioning them, Blake forges his own faith, and is stronger for it. Ultimately, the only way for his poems to have faith is to temporarily lose it.”
- “According to its well-documented beliefs and philosophies, an existential society with no notion of either past or future cannot help but become stagnant.”
- “By reading “Ode to a Nightingale” through a modern deconstructionist lens, we can see how Keats viewed poetry as shifting and subjective, not some rigid form.”
Bad Theses Examples:
- “The wrong people won the American Revolution.” While striking and unique, who is “right” and who is “wrong” is exceptionally hard to prove, and very subjective.
- “The theory of genetic inheritance is the binding theory of every human interaction.” Too complicated and overzealous. The scope of “every human interaction” is just too big
- “Paul Harding’s novel Tinkers is ultimately a cry for help from a clearly depressed author.” Unless you interviewed Harding extensively, or had a lot of real-life sources, you have no way of proving what is fact and what is fiction.”
Get the sound right

Example thesis statements with good statement language include:
- “Because of William the Conqueror’s campaign into England, that nation developed the strength and culture it would need to eventually build the British Empire.”
- “Hemingway significantly changed literature by normalizing simplistic writing and frank tone.”
Know where to place a thesis statement
Because of the role thesis statements play, they appear at the beginning of the paper, usually at the end of the first paragraph or somewhere in the introduction. Although most people look for the thesis at the end of the first paragraph, its location can depend on a number of factors such as how lengthy of an introduction you need before you can introduce your thesis or the length of your paper.
Limit a thesis statement to one or two sentences in length
Thesis statements are clear and to the point, which helps the reader identify the topic and direction of the paper, as well as your position towards the subject.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of question mark. Authored by : VirtualEyeSee. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/aiEhXH . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sunflowers. Authored by : marco magrini. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/24JYSq . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Image of megaphone. Authored by : MPCA Photos. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/ebE7WU . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Thesis Statement. Provided by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Thesis-Statement . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Research Paper Writing Guides
Research Paper Thesis
Last updated on: Mar 27, 2024
How to Write a Research Paper Thesis: A Detailed Guide
By: Donna C.
20 min read
Reviewed By: Jared P.
Published on: Jan 6, 2024

Have you ever had trouble making a thesis for your research paper? It's a common challenge, often leaving writers uncertain about where to begin and how to structure their thoughts.
A thesis statement is what your research paper revolves around. The argument, evidence, and facts stated in the thesis are carried out throughout the research paper .
Having said that, the importance of creating a thesis statement that stands out, cannot be denied. But, not everyone is competent enough to craft effective thesis statements.
Fear not!
We've streamlined the process for you, breaking it down into manageable steps. From brainstorming your topic to crafting a clear thesis, we’ll help you write the optimal thesis.
Let’s get going!

On this Page

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
What is a Research Paper Thesis?
To understand the question, “What is a thesis for a research paper?” we’ll look at the standard definition :
“A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.”
Think of it as the roadmap for your readers that guides them throughout the entire research paper.
Usually, thesis statements consist of one or, at most, two sentences . A good thesis isn't just about summarizing; it's about making a clear point and an arguable claim.
The thesis takes place in the research paper introduction. It is a good practice to include the thesis at the end of the introduction paragraph.
For example, If you're exploring how technology affects learning, a strong thesis statement could be:
Now that you know what a research paper thesis is, let’s discuss some characteristics of a good thesis statement in the context of research.
Elements of a Good Research Paper Thesis
A solid research paper thesis is like a well-built foundation for your research work. Here are the key elements that make it strong:
A good thesis is crystal clear, leaving no room for confusion. It conveys the main point clearly and makes sure that the readers grasp the essence of the argument.
Specificity
It goes beyond generalities, providing specific aspects about the focus of the paper. Specificity adds depth and helps in guiding the research process.
Arguability
A strong thesis statement takes a stance on an issue and presents an arguable claim. It sparks curiosity and encourages discussion rather than stating an obvious fact.
Conciseness
Keeping it short and to the point is key. A good thesis doesn’t go off-track—it gets straight to the heart of your message in a sentence or two.
Alignment with Paper Content
A good thesis aligns seamlessly with the content, reflecting the direction and purpose of the research.
Incorporation of Main Ideas
It serves as a preview of the main ideas in the research. A good thesis introduces the key concepts that will be explored and substantiated throughout the research.
A relevant thesis statement connects directly to the research and questions that the author aims to answer. It avoids unnecessary information that might divert from the main focus.
Guidance for Research
An effective thesis summarizes the point and provides a roadmap for your research. It outlines the direction of the research and sets expectations for the reader.
Adaptability
A good thesis remains flexible. As the research progresses, it can be refined to accommodate new insights or changes in the direction of the paper.
Now, let’s see what are the different types of research paper theses.
Different Research Paper Thesis Types
Depending on different types of research papers, the thesis can take any of the following forms:
Argumentative Thesis
An argumentative thesis takes a firm stance on a controversial issue and aims to persuade the reader to adopt the same position on the topic. Your goal is not just to present information but to convince others that your perspective is valid.
Including supporting evidence and well-structured arguments play an important role in an argumentative thesis.
Analytical Thesis
An analytical thesis approaches a complex topic by breaking it down into its fundamental components. It aims to understand how these parts interact and contribute to the overall understanding of the subject.
Explanatory Thesis
An explanatory thesis aims to clarify a concept, process, or phenomenon by offering detailed information. It helps explain a topic without picking sides or breaking it into pieces.
These are the most common types of research paper theses. Although there are some other types as well.
- Comparative Thesis: Examines similarities and differences between two or more subjects, presenting an analysis of their relationships.
- Cause and Effect Thesis: Identifies a relationship between events, asserting that one event leads to another and explaining the consequences.
- Descriptive Thesis: Paints a vivid picture of a subject, providing detailed information to create a clear and rich understanding.
- Problem-Solution Thesis: Highlights an issue and proposes specific solutions to address the identified problem.
- Exploratory Thesis: Explores a subject with an open mind, aiming to understand different aspects and perspectives without necessarily forming a definite conclusion.
Now that you have a better understanding of what a research paper thesis is, we’ll get straight to the writing steps.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Write a Thesis for a Research Paper?
Follow these steps, and you’ll be writing compelling research thesis statements in no time.
Step 1. Brainstorm Your Topic
If you haven’t yet decided on the research paper topic , the first step is to brainstorm ideas.
- Start with identifying your key research areas and interests.
- Once you pick a general idea, dig deeper.
- Think about what makes you curious about the topic.
For example, if you’ve chosen climate change, your brainstorming might lead you to questions like:
- How does climate change affect wildlife in specific regions?
- What are the human activities contributing to climate change?
Topic brainstorming helps you create a roadmap and aids you in pinpointing areas within the broader topic that you’re most interested in.
Step 2. Conduct Preliminary Research
After brainstorming, the next step is to conduct research and explore what others have discovered about your topic.
You can read books, articles, and reliable sources. Gather information to understand the current state of knowledge on your topic.
Doing preliminary research helps build the foundation of your research thesis. You’ll have a better insight and understanding of your topic if you know it’s background.
Step 3. Choose a Clear Research Question
Now, it's time to narrow down your focus to a specific and well-defined research problem .
Make sure your question is relevant and it aligns with your interests and the assignment.
Here’s how you should narrow down your research questions:
- Get Specific
After looking at the overall topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect.
For example, Instead of saying “climate change,” think about something like “How does cutting down trees (deforestation) add to climate change?” It's like getting focused on one part of the bigger picture.
- Make it Matter
Your question should be important. Ask yourself why it's a big deal to you and why it matters for your assignment.
For example, instead of just wondering about technology and people, ask, “How do smartphones affect our work every day?” This makes your question relevant and calculated.
Be clear about your question and try not to make it confusing. Craft a question that's easy to understand. If your assignment doesn't come with a set question, make one up.
Ask yourself, “What do I want to find out about my topic?” Your self-made question becomes your guide for exploring.
Step 4. Answer the Research Question
After you’ve crafted your research question, comes the time to compose your answer. What you need to do is to think about why this is your response and how you will convince readers.
- First Answer, or Working Thesis:
This is your starting answer, kind of like a rough draft.
For example, If your question is “How does cutting down trees affect climate change?” your first answer could be something like:
- Get Your Direction:
Think of this answer as a compass. It helps you know where you're going in your research project. It's the beginning of your thesis statement, which is the big idea that leads your whole research paper.
Remember, it's okay if this answer changes later as you learn more. It's like starting with a map and adjusting your path as you find new stuff. The point is to start with a thoughtful and informed beginning for your research project.
Step 5. Include Evidence and Reasoning
After making your first educated guess (working thesis), it's time to collect evidence that supports your idea. This is like finding puzzle pieces that fit with your initial thoughts.
If your working thesis is “ Cutting down trees lets out carbon, adding to the warming of the Earth ,” find data that shows how deforestation releases carbon. This data is like your evidence that makes your thesis more convincing.
Use real-life examples and expert opinions to strengthen your thesis.
For instance, if case studies show the environmental impact of deforestation or if reputable scientists have published articles supporting your point, include them.
- Include data showing the correlation between deforestation rates and increased carbon emissions.
- Provide examples of regions where deforestation has led to changes in climate patterns.
- Reference scholarly articles written by environmental experts that discuss the impact of deforestation on global warming.
This step elevates your working thesis to a solid thesis statement by grounding it in concrete evidence and expert perspectives. It transforms your idea into a well-supported argument that has the potential to engage readers from the get-go.
Step 6. Refine Your Answer
Now that you've presented your initial answer backed by evidence and reasoning, it's time to fine-tune it.
- Take a step back and look at your initial answer or working thesis . Does it still hold up in light of the evidence you've gathered? Consider if any adjustments or clarifications are needed.
- Also, try to look at your answer from different angles and perspectives . Acknowledge alternative perspectives and see if there are valid counterarguments. This step adds depth and meaning to your thesis.
- Refine your answer to capture the complexity of your topic. Your thesis should not oversimplify; it should reflect the richness of your research project.
- Make sure that your thesis remains well-supported by the evidence you've gathered.
For example, if your working thesis is “Cutting down trees lets out carbon, adding to the warming of the Earth,” after evaluating, you might refine it to:
Step 7. Finalize Your Thesis Statement
Now comes the final step of the thesis writing process. In the last stage, summarize your refined answer into a powerful single sentence or, if required, two sentences.
It should capture the main point of your research project and set the tone for your entire paper.
The final version of the refined answer we discussed would look something like this in the form of a final thesis statement .
One thing to note here is that you shouldn’t exceed the number of sentences used to more than 2.
Comparing a Strong and a Weak Thesis Statement
Some thesis statements are strong, precise, and accurately address the scope of the research study. On the other hand, some statements lack these aspects in one way or the other.
It could be beneficial for you to look at some examples of strong and weak thesis statements for an even better understanding. Take a look at the comparison table below:
By now, you should have a clear idea about what elements are required to craft a strong and adequate thesis statement.
Research Paper Thesis - Examples
Here are some great research paper thesis statement examples for you. Go through them, and you’ll have a practical understanding of what makes a perfect research paper thesis.
Research Paper Thesis Example
See this effective research paper thesis example that brilliantly addresses the argument and the research direction.
Research Paper Thesis Template
Here is a good research paper thesis template that you can follow:
Thesis Statement Outline PDF
How to Write Thesis for a Research Paper APA Format - Example
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write a thesis statement for a research paper in APA format:
Middle School Research Paper Thesis
Research report thesis , history research paper thesis, thesis statement for a psychology research paper, thesis paragraph for a research paper.
Having read these examples, you should be able to give your research paper an edge with compelling thesis statements.
Thesis Statement vs. Research Question vs. Hypothesis
It is vital to understand the difference between your thesis, research question, and the hypothesis of the research paper . Look at the table below to know the key differences between them.
Things to Avoid in a Research Paper Thesis
There are some things that you avoid performing at all costs for a great thesis.
So, for an effective research paper thesis, you should avoid
- vague or overly broad statements.
- making statements without proper evidence
- ambiguous and complex language that might confuse your readers.
- using a personal bias to overshadow your thesis
- overly simplistic statements
- stating the obvious without adding any fresh perspective
To sum it up,
Learning how to create a thesis for a research paper can take some time. But, after a bit of research and getting help from experts, you can engage readers will well-written statements.
With our comprehensive and step-by-step guide, we aim to help you understand everything about creating a thesis statement. From the initial topic brainstorming to the final statement, we’ve covered every writing step in detail.However, if you’re still stuck somewhere, and you’re unsure how to move forward, don’t worry; we have a solution for that as well.
Our paper writing service online has a pool of experienced writing specialists who can take your research paper worries away in a breeze. Experts at our service are up for any challenge you throw at them.
Just visit our website, let us know what you require, and we’ll solve your writing-related woes at the best and most affordable rates!

Donna writes on a broad range of topics, but she is mostly passionate about social issues, current events, and human-interest stories. She has received high praise for her writing from both colleagues and readers alike. Donna is known in her field for creating content that is not only professional but also captivating.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Learning How to Write a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide

- Best 300+ Ideas For Research Paper Topics in 2024

- A Complete Guide to Help You Write a Research Proposal

- The Definitive Guide on How to Start a Research Paper
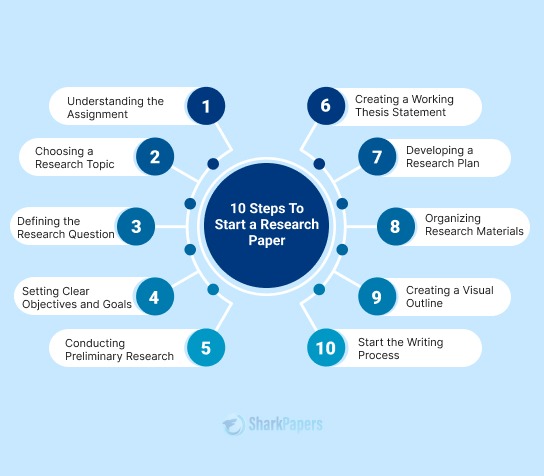
- How To Write An Introduction For A Research Paper - A Complete Guide
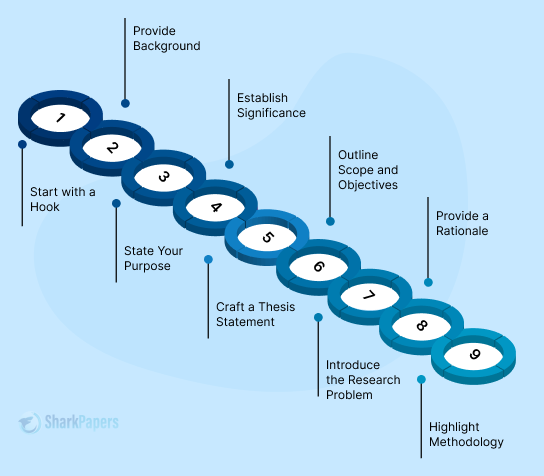
- Learn How To Write An Abstract For A Research Paper with Examples and Tips

- How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | A Complete Guide

- How To Write The Methods Section of A Research Paper

- How to Write a Research Paper Title That Stands Out

- A Detailed Guide on How To Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

- How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Tips

- How to Problem Statement for a Research Paper: An Easy Guide

- How to Find Credible Sources for a Research Paper

- A Detailed Guide: How to Write a Discussion for a Research Paper
)
- How To Write A Hypothesis In A Research Paper - A Simple Guide

- Learn How To Cite A Research Paper in Different Formats: The Basics

- The Ultimate List of Ethical Research Paper Topics in 2024
- 150+ Controversial Research Paper Topics to Get You Started

- How to Edit Research Papers With Precision: A Detailed Guide

- A Comprehensive List of Argumentative Research Paper Topics
- A Detailed List of Amazing Art Research Paper Topics

- Diverse Biology Research Paper Topics for Students: A Comprehensive List

- 230 Interesting and Unique History Research Paper Topics
- 190 Best Business Research Paper Topics
- 200+ Engaging and Novel Literature Research Paper Topics
- A Guide on How to Write a Social Science Research
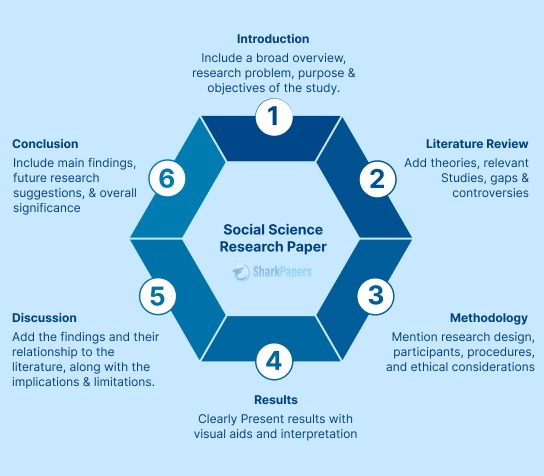
- Sociology Research Papers: Format, Outline, and Topics
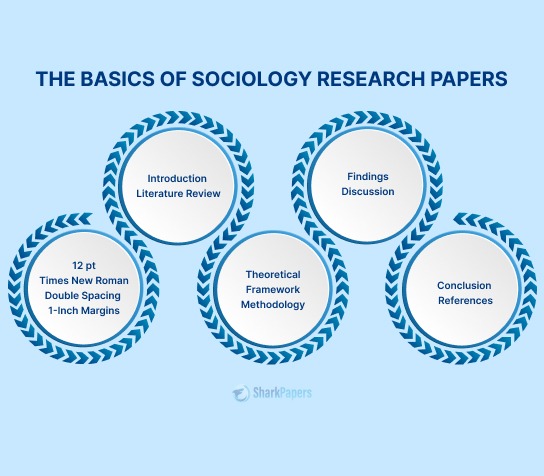
- Understanding the Basics of Biology Research Papers
- How to Write a Psychology Research Paper: Guide with Easy Steps
- Exploring the Different Types of Research Papers: A Guide

People Also Read
- thematic statement
- how to write a summary
- how to write an autobiography
- opinion essay
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
© 2024 - All rights reserved
2000+ SATISFIED STUDENTS
95% Satisfaction RATE
30 Days Money Back GUARANTEE
95% Success RATE
Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Contact Us
© 2021 SharkPapers.com(Powered By sharkpapers.com). All rights reserved.
© 2022 Sharkpapers.com. All rights reserved.
LOGIN TO YOUR ACCOUNT
SIGN UP TO YOUR ACCOUNT
- Your phone no.
- Confirm Password
- I have read Privacy Policy and agree to the Terms and Conditions .
FORGOT PASSWORD
- SEND PASSWORD
25 Thesis Statement Examples
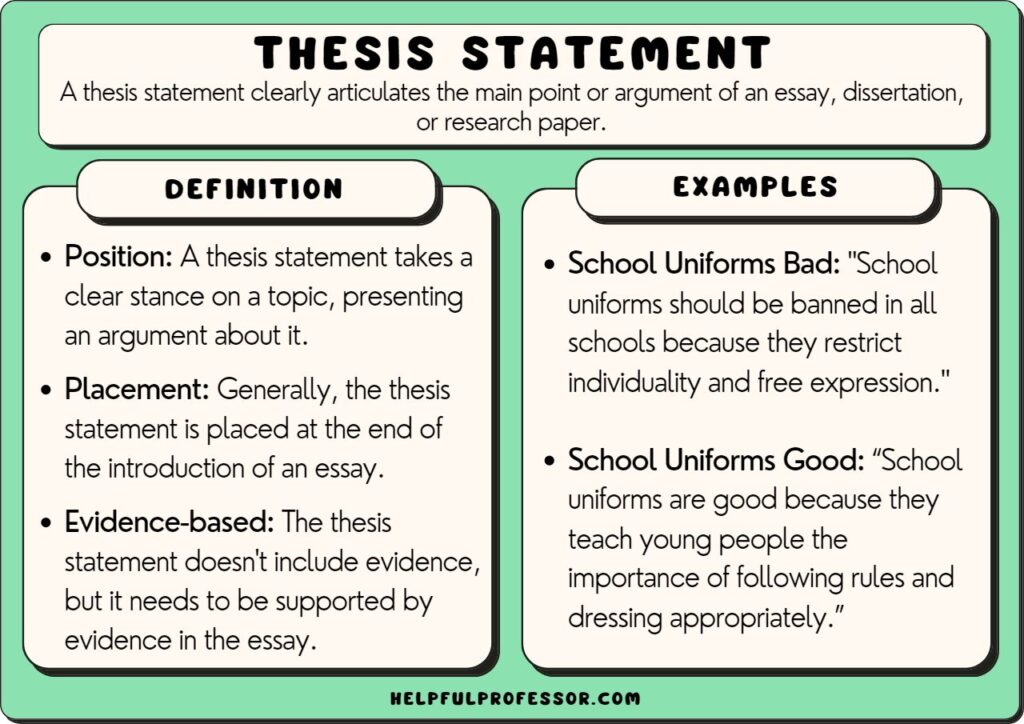
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
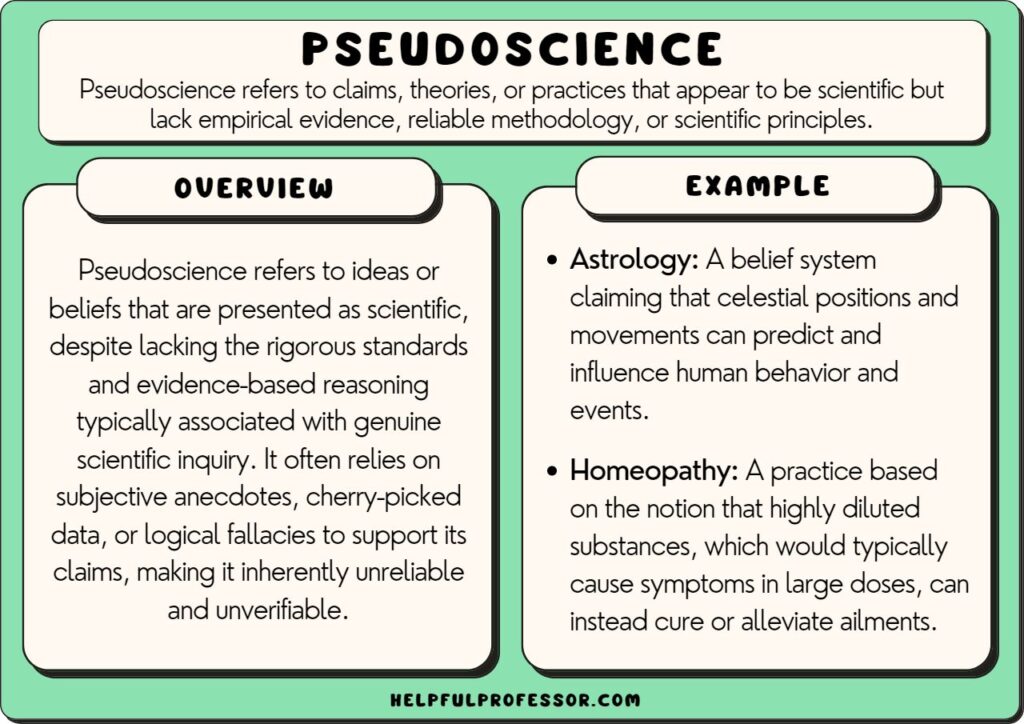
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples


23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Tips for writing a convincing thesis
To write a successful thesis, follow these simple steps on how to make it readable, interesting and convincing.

Clinton Golding
My advice for anyone writing a thesis is to identify what the examiners are looking for, and then give them what they want. While this is good guidance, to be really helpful it needs to be elaborated on, so I did some research. First, I carried out a systematic review of the literature on thesis examinations to confirm what examiners look for as they consider a thesis. Then, I studied different literature and identified advice for writing a thesis . Here is a summary of what I found.
Make your thesis a good read for your field
First, identify the field that you are contributing to. Are you writing for biochemists in general or for a subfield? Are you writing for art historians, even though you draw on theories in psychology? To find out what is expected, read well-written articles and theses in your field, and use these as a model for your own writing.
If your thesis is unusual (perhaps your research is cross-disciplinary or using a unique method or approach), you can improve it by justifying why you have deviated from the typical pattern.
Re-write to make your thesis reader-friendly
First, write down what you want to say. This may not be clear, so after you have done this, attempt a re-write to make sure that it is reader-friendly. It helps to ask for feedback. Find out where a reader is confused or engaged, interested or struggling and use this knowledge to improve your work.
Before you submit your thesis, you should also revise the writing that your examiners will see first – probably the abstract, introduction, literature review and the conclusion. You most likely wrote your literature review early in your candidature, when your writing was at its worst, so re-write it once your writing has improved. Always do a thorough proofread to remove any errors in grammar, spelling, formatting and references.
Make the thesis easy to follow
Examiners need to follow your ideas, so you need a clear flow both within and between chapters. Remember that your examiners will likely read your thesis in chunks over several weeks and may have forgotten what you said in the first chapter by the time they get to the sixth, so they could do with some help to follow your train of thought.
Some useful tools for this are:
- Summaries and reviews at the start or end of a section or chapter (In this chapter I will first…then…);
- Referring backwards and forwards in your thesis (I will expand on this point in chapter six…; As I said in chapter two…);
- Paragraphs with clear topic sentences that state the main point that you want to make;
- Repeating terms from one paragraph to the next to demonstrate the linking of ideas (if one paragraph was about “energy”, then the next should mention “energy” to show the connection);
- Linking phrases to show the reader how one paragraph is related to others (start one paragraph with “A first method is…” and the next paragraph with “A second method is…”).
To check whether your thesis is coherent, ask someone if they can follow what you have written. If they get lost and you have to explain what you mean, then add your explanation to your writing.
Make your thesis convincing
Above all, your thesis should convince the examiners. Make important claims and conclusions in each chapter and provide convincing evidence and citations to back up such claims. For example, it is not enough to conclude that: “Increasing C0 2 threatens human nutrition”. You also have to supply data, citations and reasons why the reader should agree. If in doubt, ask someone to read your claims and check whether they are convinced.
8 habits to help you get through your PhD
Engage with the literature in a convincing manner
You have to justify that your research is original and necessary, and you can demonstrate this by offering evidence from the literature about what has already been achieved and about the controversies, ambiguities and gaps.
Convince your examiners that your research will contribute to your field by providing evidence from the literature about what has already been done and what still needs to be done. In your literature review, present your conclusions about the main ideas, themes and claims and use the literature to back up each of your conclusions. Don’t merely list who said what. Instead, state the main conclusion that the reader needs to know and then use the references to back it up: “The crops that produce our needed source of zinc and iron have lower concentrations of these essential elements when grown under conditions of higher C0 2 (Thomas, 2012; Ying, 2013; Adelhardt 2016)”.
Choose the right approach
You must also show that you have an appropriate method for tackling your topic. Use the literature to justify your approach – is it based on an established approach that works well for your research topic, or does your topic demand a new approach?
Convince your examiners that your thesis is publishable
State your findings, but also explicitly discuss their implications for the literature in your field. Show how you have confirmed or complicated, elaborated or rejected, vindicated or discredited what has already been said (“I found x , which is consistent with the previous research, but I also found y, which gives a new perspective on the long-term effects”). Be explicit about how and where you have made a contribution and convince the examiner that this is a worthy addition.
The advice outlined here applies what we know about theses examiners to offer reassurance and guidance. Although some of this advice is not new, my aim was to frame it in a useful way.
Read more: looking for PhD tips? Why not check Twitter
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} What is a PhD? Advice for PhD students

PhD diary: Where do I begin?
Charlie Pullen

PhD diary: Having a bad day

Why study a PhD in English literature?
John Francis Davies
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.

- Improving Your Grades
- Article Use (a, an, the…)
- Apostrophes
- Run-On Sentences
- Parts of Speech
- Pronunciation
- Types of Writing
- Choosing the Right Words
- How Can I Make My Sentences Clearer?
- Varying Sentence Length
- Varying Sentence Structure
- Word Form: Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
- Use SEMICOLONS (;) For Emphasis
- Sentence Structure: For and Since
- Sentence Structure: Order of adjectives
- Preposition Problems: Prepositions of Time
- Sentence Structure: Tag Questions
- Word Choice: Personal Pronouns
- Using Evidence
- Research & Documentation
- Cover Letters
- The Secret to Eye Contact
- Three Keys for Better Slide Design
- Know your audience – presentation skills
- Lying With Charts
Select Page
Write a More ORIGINAL Thesis
Posted by 11trees | Argument
One of the largest challenges to moving from middle-school and early high school writing to more advanced work is the challenge to write something original . This doesn’t mean you have to invent some whole new theory of life, the universe, and everything. Rather, it means you have to make your reader think.
You can’t just regurgitate a bunch of facts you look up in a book or the internet. So how do you turn the general idea of “Holden Caulfield is alienated from his community” into something original? Something that hasn’t been written about hundreds of times already?
The first rule of writing is to consider audience, so consider the following suggestions and idea-generators. Your particular audience (i.e. your teacher) may not agree with some of the ideas here, so if you feel you’re getting into some truly weird/original/challenging territory perhaps check with them in advance. There’s nothing a teacher likes more than to receive an email from a student a week before a paper is due asking for some help kicking around ideas. This email (or phone call or appointment during office hours) should feature some good ideas from you, so that you aren’t just throwing yourself down and asking for help.
Defy the Conventional Wisdom
‘Conventional wisdom’ is a term often credited to John Kenneth Galbraith, a famous economist. The conventional wisdom is what most people (a simple majority) think about a particular issue. So if most people see Holden Caulfield (from The Catcher in the Rye ) as being alienated, then it will not be argumentative to point this out . So if you defy the conventional wisdom, but arguing that Holden is a total conformist, then you’ll be into more interesting territory. Other examples:
- Darth Vader is the hero of Star Wars .
- Suburban kids only like rap music because it makes them feel like their parents.
- Facebook is destroying young people’s ability to communicate.
Agree with the Conventional Wisdom, but for an Interesting/Controversial Reason
If you defy the conventional wisdom just for the heck of it, your reader will probably know. Unless you’re really good, which means you probably don’t need this help in the first place, and your enjoyment at playing with intellectual ideas will be obvious to your reader and they will love you for it.
So if you can’t come up with an oppositional argument, take the obvious view but have an original reason . So if you truly think Holden is alienated, think deeply about why he might be alienated. Acknowledge all the obvious reasons in your writing, and then hit your reader with a nuanced and thought provoking reason. For instance,
“Many see Holden Caulfield as alienated. He is a loner, he gets expelled from his school, and he is incapable of calling Jane Gallagher. But few understand his alienation’s origin: Holden considers himself a failure because he has not made any sports teams at this school. While this failure is not addressed directly, it runs through the book and we can see its caustic affect on the young man’s self esteem.”
This view might not be correct. In fact, we know we’re on to something because we aren’t sure whether it is correct or not. That’s why you would need to write a paper to explore the idea. In both of these approaches, it is enough to introduce some doubt – to shake the conventional wisdom enough that your reader says “huh!” as they read, and leaves your work not convinced beyond a reasonable doubt, perhaps, but intrigued and able to think more deeply about the subject matter. If you tell them what they already know, they’ll be bored to tears.
Introduce Unusual Research
If you are writing about a sports team, find some research from another field – like economics or music – to give your investigation a unique angle. Bringing two disparate subjects together like this will require analysis, clever transitions, and some deep thinking – exactly the kinds of skills you’re being asked to demonstrate.
Come Up With Something Truly Original
It’s possible! You might come across something someone has never said/written/thought about the subject matter. Then you’re really doing well, and you just have to write well enough to do the idea some justice.
Related Posts

ORGANIZE Your Argument
July 27, 2017

Include COMPETING Evidence into Your Argument
August 1, 2017

Analyzing Your Audience – the First Rule of Effective Writing

Stay Focused on YOUR thesis
- Verbs (ESL)
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Prepositions
- Sentence Structure
- Word Choice
- Coherence and Cohesion
- Information Literacy
- Adjusting Expectations
- Audience, Purpose, and Tone
- Writing Advice
- Slide Design
- Non-verbal Communication
- Writing Assignment Ideas

Choose a Great Thesis Topic in 4 Easy Steps!

No matter how much you enjoy the research process, choosing a great thesis topic is always a challenge.
What is a thesis topic anyway?
A thesis topic is just what it sounds like—it is the subject you aim to write your thesis about.
A thesis is a long, in-depth research paper that focuses on one specific subject. A thesis topic is just what it sounds like—it is the subject you aim to write your thesis about.
Theses are usually shorter for undergraduate students and book-length for Ph.D. students. However, one thing is always true. Regardless of whether you are an undergraduate or a graduate student, finding the right thesis topic isn’t easy!
Since you are reading this article, you are clearly wondering how you can choose a great thesis topic. We’ll walk you through some simple steps, give you insider tips to find the right thesis topic, and help you begin your research journey with confidence.
What makes a thesis topic great?
Your thesis topic will need to be clear and address a clearly defined research question. At the same time, the answer should contribute to a broader understanding of the research field.
The search for a good thesis statement begins with a good research question. Your thesis is the answer to that question. As the thesis is a relatively long research paper, a good research question should be sufficiently broad. In general, this will mean avoiding “yes/no” questions or reframing such questions.
For instance, instead of asking
“Does race influence standardized testing in high schools in the UK?”
Reframe your question as
“How does race influence standardized testing in high schools in the UK?”
This will allow you to explore different aspects, analyze interactions among variables, and write a longer, more substantive paper.
While your thesis topic should be broad enough, it should never be vague. Your thesis topic will need to be clear and address a clearly defined research question. At the same time, the answer should contribute to a broader understanding of the research field.
If you create a thesis based on research questions like “ How many kinds of fungi are there in the world? ” or “ What is love? ,” you are going to end up writing a long, frustrating paper. A good thesis topic will answer a much more specific question, like:
“ What kinds of fungi grow in the vicinity of drainage pipes? ” or
“ How do people in Myanmar express love during courtship rituals? ”
In other words, a great thesis topic is your answer to a:
- Somewhat broad
- Very precise and
- Somewhat open-ended question.
While yes/no questions can be acceptable on rare occasions, you should avoid them or rephrase them, especially in science fields.
Finally, a great thesis topic fills a niche in a research field where research on the topic already exists, but there is still more to be discovered or new aspects to be explored. Alternatively, thesis topics could offer a fresh take on an old topic or rebuttals to a well-known theory. You don’t need to necessarily perform groundbreaking research; however, a great thesis topic will always offer a unique element that could make your thesis stand out.
Step 1: Choosing a thesis topic - Getting started
Although thesis topics should ideally be chosen based on the relevance of the topic and its academic merit, requirements related to your assignment/program should also be taken into consideration before finalizing the topic. While this seems quite basic, it is in fact key to choosing your thesis topic. The requirements of your program or class will determine the scope of what you can research.
Every program differs in its requirements, which is why it is so important to check these details beforehand. Some programs might have a specific list of acceptable topics and a narrow range of allowable methodologies. Other programs might just have a minimum word count and a final deadline. This is why knowing the requirements is so important before you move on to the next step of brainstorming.
Step 2: Brainstorming thesis topic ideas
One of the first places to look for a thesis topic is your own past work, such as papers you have written or assignments you have completed.
Once you know the limitations and requirements for your thesis, it is time to begin brainstorming specific ideas. This is often the hardest part of choosing a thesis topic! Especially if your program or school doesn’t narrow down your topic choices, you may find yourself gazing out the window with a hazy mind. So where should you begin brainstorming?
One of the first places to look for a thesis topic is your own past work, such as papers you have written or assignments you have completed. What courses have you particularly enjoyed that are related to your major field of study? What topics have you written about already?
You must make a list of papers you have written as part of your program and rank them on a scale of most to least interesting. You can do this even if you are in a program that is not very writing intensive. Cross the boring half off your list and focus on the more interesting topics. Do any topics catch your eye? If you aren’t feeling excited about anything you’ve already researched, talk to your classmates or colleagues . What areas in your field are you interested in or passionate about? Do your friends, classmates, or peers have any ideas? You can also skim some articles from popular journals in your field to see the current trending research topics. The more you read, the better the chances of you stumbling on an interesting thesis topic.
Once you have come up with some potential thesis topics, it’s a good idea to rank them in order, so you at least have a list of your top three topics. You then need to do some preliminary research and consultations before you finally settle on one topic, and it’s always important to have backups in case your favorite choice isn’t viable.
Step 3: Preliminary research - Reviewing the literature
Any thesis based on a shorter paper will be longer and more involved than the original version.
Now that you have shortlisted your potential thesis topics, it is time to conduct some preliminary research on each topic by finding out what other research studies have been conducted so far. If you had chosen your potential thesis topics from papers you previously wrote, you might be familiar with the literature already. However, that doesn’t mean you can skip the literature review. Any thesis based on a shorter paper will be longer and more involved than the original version. The thesis is expected to cover new angles, which means you need to do some preliminary research .
Where can you find articles for your preliminary research?
Google Scholar is a great resource, and so is the academic library available at your institution. If you are a student, you may have access to a journal database like JSTOR through your university. Even if you don’t, more and more articles are freely available via open-access journals these days, so a quick Google Scholar search will help you find relevant information. If you find a particularly good article, check out the sources the author(s) have referenced for relevant articles to read.
It’s very possible that you will find yourself completely wanting to change your thesis topic once you start the literature review. That’s ok! If you come across something interesting or inspiring, you should read more about it to see if it would be a good thesis topic. However, you should set yourself some limits. If you take the freedom to simply read what interests you, it is possible you will never be able to decide on a thesis topic. Always remember to limit the time allowed to read about a potential new research interest.
Step 4: Finalizing your choice
Even the most interesting topics can become tortuous after spending enough time reading and writing about them.
Once you feel confident that you have narrowed down your potential thesis topics to a handful of options, it’s time to decide. This choice should not be made lightly—your thesis can take over your life . Even the most interesting topics can become tortuous after spending enough time reading and writing about them. With that in mind, you need to make sure your topic meets the following requirements:
- Is your proposed research feasible?
- Can you access all of the necessary research materials? Will you be able to obtain all of the necessary resources for conducting a research study? Will you be able to travel if it was required?
- Do you find the thesis topic interesting? Do you expect the interest to be sustained over the duration of the study?
- Is your topic meaningful and relevant in your field?
- Has anyone already published a paper on your thesis topic from the perspective research question?
- Do you have a suitable advisor willing to oversee the project?
You will need to extensively consult with your advisor, who will hopefully be able to give you the extra bit of guidance necessary to finalize your choice. If your advisor will be chosen depending on your thesis topic, see if you can consult with your potential advisors. Otherwise, talk to a trusted faculty member or mentor to get feedback on your proposed thesis topic. Your thesis topic will need to be approved by your advisor before it is finalized.
Selecting a thesis topic can be daunting, but once you have made your decision, you are ready for the real work to begin. No matter what topic you choose, you are about to embark on a great endeavor. Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services, and more about thesis editing and proofreading services.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Review Checklist
Below is a checklist for you to follow as you go through the process of choosing a thesis topic.
Check the requirements for selecting a thesis topic:
Make a note of the word count requirements and the final deadline before you begin
Check for any preliminary deadlines before the final deadline. For example, if there is a proposal deadline, or individual chapter deadlines.
Discuss with your professor to see if they have any specific requirements or limitations for your research.
Inquire about any requirements for your methodology; if a literature review is acceptable; or if you are required to do fieldwork.
Check to see if there is a minimum acceptable study size in case you are expected to do your own fieldwork.
Look out for any other requirements related to your fieldwork like specific required sources or any possible restrictions.
Review your past work and current trending research for potential topics
Talk to friends and professors about interests
Review relevant journals and publications for inspiration
Rank potential topics in the order of how interesting you find them
Review the literature on potential topics
Discuss the feasibility of your proposed topic with your advisor
Select your thesis topic
How do I begin my search for thesis topic ideas? +
- Start with your previous writing work.
- Shortlist topics you have an interest in or are passionate about
- Talk to your supervisors, peers and colleagues for suggestions
- Read popular journals for hot research topics
- Rank your top three thesis topic ideas in order of preference
- Finally, consult your advisor before seeking approval
How do I know if my thesis topic is promising and unique? +
- Begin with identifying a strong research question
- Always avoid yes/no type questions when finalizing a research question
- Make sure your thesis topic addresses all aspects of your clearly defined research question
- The topic should be broad never vague and precise
- It should contribute to a better understanding of the research field
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

Elite Editing
You write it. We right it.™

How to Write a Thesis Proposal
If you want to build a house, step one is not wandering over to the next vacant lot with a hammer, some nails, and a pile of boards. Your first step is probably finding an appealing place to build your house—an empty plot of land where the roads are good and where you can pretty easily connect the gas, electricity, and water. Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build.
If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint. It’s you figuring out how your thesis will fit into the space you’ve found, how you’ll build it, and whether it will stand up to the harsh winds of your thesis adviser’s opinions and the tremors of a difficult defense. A thesis proposal allows you to clearly define—and even more crucially, limit—the focus and scope of your research. Producing an excellent thesis blueprint means that you won’t accidentally find you’re trying to build a skyscraper when you should be aiming at a bungalow—and that you have all the supplies and equipment you need.
But how do you create a research proposal? How do you know what it should include? The style and length of your thesis proposal will vary a bit depending on your school’s requirements and the type of thesis you will eventually produce, but the fundamentals will always be the same, and those are what we’re going to cover here. So let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal.
Choosing a Topic
The first step (a step that you must take before figuring out how to write a thesis proposal or even a thesis proposal outline) is choosing a topic for your thesis. The point of embarking on this kind of project is that you’ll first find and then fill a gap in the established, preexisting research in your field. You’re looking for a manageable topic—something focused enough that you can cover it within your word limit but broad enough that you actually have something to write about.
Undergraduate theses are often less revolutionary and more about surveying or analyzing the existing research on a particular topic. This is appropriate because these projects are shorter in length—and you have much less time (typically months rather than years) to work on them. An undergraduate thesis can run anywhere from ten to thirty pages. A master’s thesis is typically forty to eighty pages and might present some original research, or it might be a significant reinterpretation of preexisting research.
A doctoral thesis is (naturally) the longest of these three, and the research it presents should be more groundbreaking and challenging to complete. That investment of time and mental energy is what’s going to earn you the right to demand that everyone call you “Doctor.”
Tips for Choosing a Thesis Topic
- Consider your interests. What makes you sit up and your brain feel fizzy? You’re about to spend a lot of time working on this topic. It had better be something that fascinates you.
- Explore open-ended questions. How or why questions offer you more scope and flexibility than what or who questions.
- Consider the time. How long will your project take to complete? Make sure you have enough time to get from here to there.
- Research any funding you’ll need. Will you need to travel or establish an experimental protocol? If so, can you get the funding for these projects? How do these affect your projected timeline? Save the long-view research for your later career, and find something you can finish.
- If it’s a controversial topic, choose wisely. Be realistic about whether you’re likely to encounter stiff resistance during your defense. Something that goes against all existing research will demand greater rigor and effort from you than something that challenges only a part of what is currently considered established knowledge.
- Make it publishable. Are all possible outcomes to your research interesting and academically publishable? Or is there a potential dead end that you can avoid by shifting your focus now?
- Think long term. How will the project affect (and improve) your marketability for the future? There is life after your thesis, after all. Where do you want to be, and how can your work now help get you there?
Structuring Your Thesis Proposal
A thesis proposal usually includes some or all of the following elements:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Literature review or annotated bibliography
- Approach/methods
- Preliminary results and discussion
- Work plan and schedule
- Research implications
The thesis proposal outline above shows one potential way to order the parts, but (and this is important) you won’t work on those elements in that order. For example, that table of contents? It’s probably the last thing you’ll work on. Similarly, you can’t write the abstract until you’ve written everything else.

Let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal in greater detail.
Title Page and Creating a Title
The title of your project is likely to be a brief statement of your research topic, approach, and intent. It will be far easier to write a title once you’ve written a thesis statement (see below) because it is likely to restate or incorporate your thesis statement.
Violence and Redemption in Modern Afghani Literature: A Marxist Analysis of Power Structures in The Kite Runner and The Wasted Vigil
Living the Fantasy: Addiction and Social Identity in World of Warcraft
Your title page will include this title, your name, your department and institution, your adviser, your adviser’s institution, and the date you’re submitting the proposal.
Writing an Abstract
An abstract is a short summary of your full proposal, usually about a page in length. It hits the highlights of the proposal as a whole, including your title, your thesis statement, a quick summary of your plan of research, and a statement about why this project matters.
Table of Contents
If you’re writing your table of contents, you’re minutes away from a celebratory “Woo-hoo!” because you’re almost finished. A table of contents will list all the headings and subheadings of your proposal with lovely indentations and the correct page numbers. If you’re using MS Word, and you’ve been formatting your headings in the appropriate styles, you can automatically generate a table of contents that will make everything look very pretty indeed.
Writing the Thesis Statement
It’s not a simple question: How do you write a good thesis statement? Your thesis statement may well be the hardest sentence (or two—three at the most) you ever have to write. Despairing tears or frustrated anger are not out of the question. However, once you formulate that thesis statement, you will be off and running because now you have a beautifully clear and specific goal to head for.
A thesis statement should clearly define the scope and intent of your project. It might be a hypothesis or a question, or it might be a firm statement. The hours of work that will become your thesis will then prove (or possibly disprove, though hopefully in a deeply productive way) your thesis statement, so it should be something provable—something that can in some way be measured.
Let’s look at some examples of how to write a good thesis statement.
Not so good:
Taking a year off between high school and college is a good idea.
A “good idea” is vague and indefensible. Good by whose standards? How can you prove that?
Students who take a year off between high school and college are more academically successful than their peers.
This is better because it limits the scope of the project to academics, but it’s still rather vague and unwieldy. It also doesn’t suggest what metrics will be used to judge “academically successful.”
Better still:
Students who take a year off between high school and college are significantly more likely than their peers to graduate within four years with a B average or better.
This thesis statement works because it is concrete and measurable. The data you collect will either clearly prove the statement or disprove it.
How does the internet affect social behavior?
Wow, that’s a huge question. Also, there is nothing to prove, measure, or evaluate. It’s a topic rather than a thesis. It might be what you’re generally interested in, but you have yet to find the aspect of this topic that you can effectively research.
The internet has changed how American teens approach gender.
At least this is a statement, but it’s still too vague. “Changed” how? And what does “approach” mean?
The social media profiles of American teens thirteen to eighteen years old reflect this demographic’s increasing comfort with fluid sexual and gender identities.
This thesis statement could probably still be improved, but it is getting toward something measurable and provable.
Writing a Thesis Proposal Introduction
Your introduction will do just that—introduce your readers to your topic and thesis. Don’t mistake this for an introductory paragraph, however. This is where you’ll summarize your project in the hopes of intriguing and engaging the committee that will either approve your thesis project or send you back to the drawing board. Your writing should be as clear, straightforward, and free from jargon as possible. You’ll contextualize your project within the broader scope of the topic, perhaps exploring the papers, research, or work that led to your formulation of your thesis. You’ll explain why your project excites you. You’ll illustrate your competence to embark on this project. Basically, you’ll sell your proposal.
Literature Review or Annotated Bibliography
You might be able to quickly cover the most relevant literature in your proposal introduction, but if there are many articles or books relevant to your research, your thesis proposal might include an annotated bibliography or a literature review (which is slightly more informal and conversational in approach). Here is where you’d not only list the most influential and crucial texts that underpin your research but also explain why they matter—that is, how they fit into your project. This is a way to show that gap in the research that you will be filling with your thesis project.
Explain Your Proposed Methods or Approach
Most thesis projects demand original research of some kind, and for degrees in the sciences (including the social sciences), that research may very well take the form of an experiment or raw data collection. Here is where you should describe your proposed methodology. What materials will you use? How will you collect your data? How will you analyze the data once it’s collected? Are you taking a qualitative or quantitative approach? Why? Will you need outside funding (for travel or other costs), and how do you propose to acquire that funding? Do you need space and equipment to conduct your research?
Provide Preliminary Results
It may be that you have already been testing the viability of your thesis project with some preliminary research (which is not a bad idea). If so, here is where you should provide the results of that research and your tentative interpretation of those results. Clearly show how this work fits into your larger project—and how it proves that you’re heading down a productive road of inquiry.
Design a Work Plan
Even if your particular program or professor doesn’t require you to include a work plan in your thesis proposal, you should still make one. There’s nothing more likely than a schedule—with deadlines!—to keep you on track and get your thesis done on time.
This section should
- lay out your plan,
- list the various stages of your project,
- set deadlines for the completion of each stage, and
- detail any work you’ve already completed.
In addition, your work plan should take into account any challenges (personal, practical, or institutional) that may affect the completion of the study.
Discuss Research Implications
Here, you are striving to answer this question: Why does this project matter in this place and at this time? It’s actually a wonderful exercise in focusing your own thoughts and evaluating the worth of your proposed project. Are you remedying a misunderstanding that might affect how to treat a particular medical condition? Are you exploring the dynamics of a culture that is (socially or politically) especially relevant at the moment? Are you providing new insight into a classic work of literature or music that will reinvigorate teachers and academics? Your research might have implications for the entire world or it might be of interest only to other specialists in your subject, but that really doesn’t matter. The point is to figure out and clearly state how your research will enhance the sum total of knowledge.
Notes and Bibliography
All statements in this thesis proposal need to be supported with data, whether that data is derived from your own research or gleaned from a third party. Using whatever citation style is most appropriate to your field, you should give credit to all your sources, primary or secondary. Note that this is separate from your literature review in that you’re only going to cite the sources you’ve used in your proposal.
Thesis Proposal Defense / Thesis Proposal Presentation
Your college or university may require you to appear in person at a thesis proposal defense or to make a thesis proposal presentation. In both cases, however, you’ll be presenting your proposal to your thesis committee (and possibly others) and then potentially answering their questions about your project. While this might seem alarming, this event is actually an excellent opportunity to pick your committee’s brain about possible obstacles or objections you will need to overcome while working on your project. Better to know right now that they’d rather you took a quantitative approach than do all the work and then discover their preference. It will also help focus you since knowing something is one level of understanding it—but explaining it to someone else can take your understanding to a much deeper level.
You should now have a much deeper understanding of how to write a thesis proposal. A clear, thorough, well-thought-out thesis proposal allows you to see the entire shape of your project before you invest huge amounts of time and energy into research that might end up leading nowhere. Your thesis proposal sets the stage for the success of your project as a whole, and it should reflect and predict the quality you intend to produce in your final thesis. That’s why your thesis proposal presentation also matters. In addition, remember that proofreading counts. It’s extremely important to carefully review your finished proposal for spelling, grammar, and structural errors.
With your thesis proposal completed and approved, you’re well on your way to embarking on what might be the most important project of your life to date. We wish you all the best with your studies, and if you decide you want an editor to cast an expert eye over any part—large or small—of your project, we here at Elite are happy to help!
Want more? Check out this post on credible online sources and how to find them.
Other Resources You Might Like

Crafting Timeless Content

Mastering the Art of Persuasive White Papers

Writing Effective Press Releases in a Digital Age
Get elite updates straight to your inbox..
- Content Writing
- Marketing and Sales Enablement
- Program Management
- AI Implementation
Who We Help
- Thought Leaders
- Cybersecurity
- Health Care
- Full-Time Careers
- Freelance Opportunities
- Press and Awards
- Success Stories
- About Elite
In the News
- Elite Creative Makes the Inc. 5000 for the Third Year in a Row

- Eating Like an Empress – Hungary's Gerbeaud Slices
- Music for Change, Resilience, and Hope in this Season of Spring

Search form
How to make a good thesis presentation.

A strong thesis defense is crucial for any doctorate or graduate student. Although researching and writing about your thesis topic can be a Herculean effort, the work doesn't end there. The thesis presentation is a crucial part of the dissertation defense in many academic programs.

Your impressive presentation will show the depth of research in your thesis clearly and compellingly. Your presentation gives your committee an excellent visual to validate the thesis. Impress your jury with impactful PowerPoint presentations.
What is a thesis presentation?
A thesis is an accumulation of all your research on paper. A thesis presentation can be a digital summary of your research, focusing on the core knowledge in your thesis. It's short and concise. Each slide should have a purpose, as this presentation provides a detailed insight into your thesis research and conclusions.
https://thesisgeek.com/ allows you to display the narrative progression of your thesis. The process begins by asking questions, researching the topic, creating the study, and evaluating it. By using this, you will be able to create the wow-worthy presentation.
You must pass your thesis presentation to be awarded your degree.
The Structure of Your Thesis Presentation
You can use this structure to help you align your slides to help you maintain consistency in your narrative by guiding the flow of design.
* Problem Statement * Literature Review * The Purpose of the Study * Research Questions * Instruments * Data collection * Research findings * Implications * Recommendations * You can also read about it here * Acknowledgements * Questions
Are you unsure of how to create a memorable and perfect thesis presentation? SlideModel provides unique thesis presentation templates that will impress your committee.
8 Tips for a stunning thesis presentation

1. Decluttered Slides
When the thesis presentation is structured smoothly, it will have the greatest impact. Overloaded slides will confuse both you and the panel. Each slide should be focused on a single topic, and contain minimal information.
Create a title slide that will grab the audience's attention. Keep your thesis presentation simple and concise to echo your topic.
2. Compelling Templates
Remember that the committee reviewing your thesis presentation is likely to have seen countless slideshows throughout their life. How can you impress them with something different?
Using eye-catching, customized templates adds a new dimension to the information you have collected. The fact that the templates are 100% editable allows you to save time and create a beautiful presentation in minutes. Templates also have a carefully chosen and attractive color scheme that will make your job easier.
3. Design Consistency
Each slide of your thesis presentation should be visually synchronized. Consistency in design creates a pleasing aesthetic. This consistency also makes your presentation look logical and smooth. Your committee might be distracted by sudden changes in style and lose the thread of your argument.
Choose a color scheme that corresponds to your topic, and then incorporate it into a thesis template. Stick to the color scheme and avoid changing themes drastically. Remember the primary and secondary colors of your slides. Dark-colored text should be placed on a lighter background, and light-colored text on a darker one. Keep in mind accessibility issues when choosing colors and backgrounds.
4. Engaging Visuals
Humans tend to remember more when presented with visually appealing information. Include multimedia that is relevant to your topic in your thesis defense presentation. This allows your audience to quickly glance at information.
Use HD images, audio clips, and videos to enhance your thesis presentation. Focusing on visual hierarchy is a tip you should keep in mind. You should place your content on your slides in the order you would like your audience to view it. This can be achieved by either highlighting text or increasing the slide content proportionally.
5. Data Visualizations
Data visualizations are the best way to present your research and analysis. Textual numbers and conclusions are not recommended. These slides are from a past era. Visualizations are always a great way to spice up your slide topics, whether it's about blended models or data on hybrid learning.
You can create top-notch data visualisations using a variety of templates, including charts, graphs, and trend lines. The combination of comprehensive analysis and data visualizations has a double effect of uniqueness and information digestability.
6. Attractive Infographics
Infographics can be used to draw your audience in and help you defend your thesis. Instantly, they make your information look more lively and attractive. You can create vibrant infographics using a variety of presentation templates (see above).
Use infographics to show the uniqueness of your thesis topic. You can also use it to show comparisons or improvements made in previous research on your thesis topic. These infographics are able to visualize nearly every topic, from research analysis and implications.
7. Typography
You will not get very far if you fill your slides with text. It is better to write one-liners and points instead of long paragraphs. We can assure you that your committee will not be interested in large paragraphs. Your visuals and verbal content will be the focus of their attention.
Save the rest of the information for your speech. Choose functional fonts for your slides to make the text legible. Fancy fonts can give your slides a amateur appearance and confuse your audience.
8. Include Storytelling
When presented as a story, any information or thesis becomes more engaging than a simple speech. Create a story that will help you move your presentation forward. Your audience will be captivated and want more.
Storytelling, when skillfully integrated into a thesis defense, offers several benefits. Firstly, it humanizes the research. Behind every dataset and analysis lies a researcher who embarked on a quest to unravel mysteries and contribute to knowledge. By sharing the personal journey and struggles encountered during the research, a narrative is created that resonates with the audience on a human level. This connection fosters empathy, making the defense not just a presentation of facts, but a shared experience.
Moreover, storytelling facilitates comprehension. Complex theories and intricate methodologies can be difficult for non-experts to grasp. Through storytelling, these concepts can be simplified and contextualized, making them accessible to a wider audience. Analogies, anecdotes, and relatable examples become tools to bridge the gap between specialized knowledge and general understanding.

The story you tell in your thesis presentation slide must be engaging and captivating from the beginning. Bestselling author Robin Sharma believes that starting strong can be beneficial. Finishing strong is more impressive.
To achieve this, you should design your title slide and final slides in a striking way. Practice before the final and practice the narration. Create a stunning slideshow to defend your thesis. Use the tips above...you'll be glad you did!
- Log in to post comments
Popular Tags
Wandering Educators
Music for Shifting Times

Through the Eyes of an Educator: A Compendium

Exploring Michigan's Coasts: A Compendium

Generation Study Abroad Commitment Partner

I'm a White House Travel Blogger

Wandering Educators Youth Travel Blogging Mentorship Program

Travel with Awe and Wonder: A Compendium

- Accommodations
- Books & Film
- Global Citizenship
- Intercultural Education
- Marketplace
- Opportunities
- Performing Arts
- Southeast Asia
- Special Interest
- Transportation
- Travel Planning
- Travel Tips
Recent posts
My top 3 inexpensive things....

Through the Eyes of an Educa...
Eternal sunshine of a spotle..., read this: keith taylor..., the one thing that’s even mo....
- Request new password

How to write a unique thesis acknowledgement (+ FAQs)
Crafting a thesis acknowledgement is typically one of the final steps in completing a thesis. This post aims to assist you in gaining insights and guidance by addressing common questions related to thesis acknowledgements. By doing so, it enables you to create a distinct and meaningful acknowledgment section that reflects your gratitude and appreciation.
What is a thesis acknowledgement?
Do i need a thesis acknowledgement, who should i thank in my thesis acknowledgment, how can i make my thesis acknowledgement uniquely personal, how formal should a thesis acknowledgement be, to what extent should i express personal sentiments in my thesis acknowledgement, how should i structure my thesis acknowledgement, how long should a thesis acknowledgement be, where is the thesis acknowledgement located, where can i find examples of thesis acknowledgements.
A thesis acknowledgement is a special section commonly included at the beginning of a thesis or dissertation. In this section, the author of the thesis expresses gratitude and appreciation to individuals or groups who have contributed to the successful completion of their academic work. It is a way for the author to acknowledge the support, guidance, and assistance they received during the research and writing process.
While a thesis acknowledgement is typically not a mandatory requirement, omitting it might not be seen positively. Writing a thesis almost always involves some form of assistance or support, whether from a supervisor, family, or friends.
Acknowledging these contributions is not only considerate but also showcases your gratitude and reflects well on your character. Including a thesis acknowledgement demonstrates your appreciation for the help you received throughout your academic journey, underscoring the collaborative nature of research and academic pursuits.
- Yes, it is strongly recommended to include a thesis acknowledgement.
The thesis acknowledgement offers flexibility, but thanking your thesis supervisor/s is an absolute must—non-negotiable. It would be highly unusual to omit their appreciation.
Additionally, it’s customary to thank those who contributed data, such as interviewees or survey participants. While listing every individual may be impractical, acknowledging their assistance shows respect and gratitude. If someone went above and beyond to help you establish contacts for your case study, it’s worth mentioning.
Apart from these essentials, you have the freedom to thank anyone you desire. Common mentions include parents, partners, friends, peers, and colleagues. Some may even extend gratitude to pets or coffee! Injecting humor is acceptable, but maintaining a certain level of formality is advised, as explained in the subsequent section.
- Acknowledging your thesis supervisor/s is a non-negotiable requirement.
- Show appreciation to those who contributed data or support, like interviewees or survey participants.
- Feel free to thank parents, partners, friends, and colleagues.
How to deal with a thesis supervisor with whom I had a challenging relationship in my thesis acknowledgement?
Regrettably, not everyone shares a positive relationship with their thesis supervisor. Nevertheless, it is important to acknowledge them in your thesis.
When doing so, maintain a concise approach while ensuring a respectful and diplomatic tone, refraining from any negative aspects or conflicts. Instead, emphasize the professional aspects of their contribution, such as supporting the development of the theoretical framework or providing valuable critical feedback that enhanced the quality of your work.
- Acknowledge your thesis supervisor, even if your relationship was challenging.
- Maintain a concise and respectful tone.
- Focus on the supervisor’s professional contributions.
Once you have decided whom to thank in your thesis acknowledgement, consider going beyond generic expressions of gratitude. Making your acknowledgements more personal and specific can make them truly special. Instead of simply thanking someone for their guidance and support, include examples that highlight the unique contributions of those individuals.
For instance, if you are thanking your fellow thesis writers, you can say something like: “Long study sessions at the library with John and Sabine made thesis writing a joyful experience.” This demonstrates the specific way they contributed to your journey.
Similarly, if you had engaging conversations during walks in the park with someone, you can mention: “Our thoughtful discussions while strolling through the park were a crucial aspect of getting excited about my thesis topic.”
By providing concrete examples, your acknowledgements become more heartfelt and memorable, showing the genuine impact of each person you thank.
- If possible, make thesis acknowledgements personal and specific.
- Include examples of how each person contributed uniquely.
- Highlight specific interactions or experiences that made a difference in your thesis journey.
While there are no strict rules for writing a thesis acknowledgement, it’s essential to consider its significance as one of the first things readers encounter in your thesis. Therefore, maintaining a certain level of formality is advised.
Avoid including details of personal experiences like drinking excesses with friends or lavish parties to cope with thesis stress. Such content could create a negative impression and should be avoided.
Remember that your thesis is an academic work, and the acknowledgement should not detract from its academic merit. Focus on expressing gratitude to those who contributed to your academic journey in a professional and appropriate manner.
- Keep a level of formality, as your acknowledgement section is one of the first things readers see.
People have different boundaries in terms of how open they are, and you should do what you feel comfortable with. But don’t forget that your thesis will likely be a document open to the public. So make sure that you will be comfortable with the information out there, also 2, 5 or ten years from now.
That said, the thesis acknowledgement is there to showcase your human side and your gratitude for your loved ones. So don’t hold back when you really want to thank someone deep from your heart.
And of course make sure that the information you reveal about the people you thank, they are also comfortable with it. You should not, for instance, describe your messy breakup with a person and even worse naming the person by name. Instead, you can write something more neutral in a way that people who know you well still know what you mean. For instance, you could thank your friends for always being there for you during challenging times, which you are grateful for.
- Remember that your thesis is public, so ensure you’ll be okay with the information long-term.
- Thank people genuinely but avoid sharing sensitive or personal details about others.
When writing a thesis acknowledgement, there are several acceptable ways to structure it, each serving its purpose. Three commonly used approaches stand out.
The first method is the chronological structure, typically employed in longer theses like PhD dissertations. In a chronological acknowledgement, you express gratitude to those who supported you throughout your entire thesis journey . For instance, you can start by thanking your supervisor for their guidance from the very beginning, then acknowledge the organizers of the PhD summer school you attended in year two, followed by appreciation for your friends who encouraged you during the challenging writing phase in year three, and so on.
The second approach involves structuring the acknowledgement based on the nature of relationships, ranging from formal to personal. Here, you begin by expressing thanks to your formal supervisors and professors who played a significant role in shaping your research, then move on to more informal yet professional mentors. Subsequently, you extend your gratitude to friends, family, and, if applicable, your partner or spouse.
The third common method is essentially the reverse of the second one, starting with personal relationships and ending with formal ones. In this arrangement, you begin by thanking your close friends and family members for their unwavering support, then move on to acknowledge professional mentors who contributed to your academic growth, and finally conclude the acknowledgement with appreciation for your thesis supervisor.
- Thesis acknowledgements can be structured chronologically.
- Thesis acknowledgements can be structured from formal to personal.
- Thesis acknowledgements can be structured from personal to formal.
The general guideline is that the length of the thesis acknowledgement can vary depending on the length of the thesis itself. However, this doesn’t imply that it must be excessively long.
For bachelor or master theses, the average length typically ranges from 100 to 250 words, equivalent to about half a page.
PhD thesis acknowledgements, on the other hand, tend to be longer, given the extended duration of PhD research. The average length for a PhD thesis acknowledgement ranges from 250 to 1000 words, or approximately half a page to 2 pages.
- Bachelor’s theses: usually 100-250 words
- Master’s theses: usually 100-350 words
- PhD theses: usually 250 – 1000 words
The thesis acknowledgement is typically positioned right at the beginning of the thesis, following the title page and preceding the table of contents. This placement ensures that it remains distinct from the academic content of the thesis.
When formatting your document, it’s advisable to insert blank pages to maintain a proper layout in the printed version, especially when double-paged printing is used. To achieve this layout, page 1 is reserved for the title page, page 2 is often left empty, and page 3 contains the thesis acknowledgement. Additionally, page four is frequently left blank as well. This arrangement enhances the reading experience of the printed version and provides a more polished appearance to the document.
- The thesis acknowledgement is typically placed at the beginning of the thesis, after the title page and before the table of contents.
- Leaving empty pages, such as page 2 and often page 4, helps in maintaining a visually pleasing layout, when double-sided printing is used.

Many universities maintain thesis repositories, providing students access to previous years’ theses. This serves a twofold purpose: firstly, it helps students gain clarity on the university’s expectations, preferred style, and required length for a thesis. Secondly, it offers a valuable opportunity to explore a diverse array of thesis acknowledgements, serving as a source of inspiration for crafting one’s own acknowledgment section.
In addition to utilizing the university’s repository, I have created five examples of PhD thesis acknowledgements that you can review for further guidance and ideas.
- Check your university’s thesis repository.
- Find five PhD thesis acknowledgement examples here .
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
How to thrive in academia as an extrovert
How to end a professional email in a university setting, related articles.

How to find a reputable academic dissertation editor

How to deal with procrastination productively during thesis writing

5 inspiring PhD thesis acknowledgement examples

How to prepare your viva opening speech
#Mission2.0 is here to disrupt the mundane. Are you? Join Now
- BIM Professional Course for Architects
- Master Computational Design Course
- BIM Professional Course For Civil Engineers
- Hire From Us

Request a callback

- Architecture & Construction
- Computational Design
- Company News
- Expert Talks
Writing an Architecture Thesis: A-Z Guide
ishika kapoor
14 min read
January 5, 2022

Table of Contents
How to Choose Your Architecture Thesis Topic
As with most things, taking the first step is often the hardest. Choosing a topic for your architecture thesis is not just daunting but also one that your faculty will not offer much help with. To aid this annual confusion among students of architecture, we've created this resource with tips, topics to choose from, case examples, and links to further reading!
[Read: 7 Tips on Choosing the Perfect Architecture Thesis Topic for you ]
1. What You Love
Might seem like a no-brainer, but in the flurry of taking up a feasible topic, students often neglect this crucial point. Taking up a topic you're passionate about will not just make for a unique thesis, but will also ensure your dedication during tough times.
Think about the things you're interested in apart from architecture. Is it music? Sports? History? Then, look for topics that can logically incorporate these interests into your thesis. For example, I have always been invested in women's rights, and therefore I chose to design rehabilitation shelters for battered women for my thesis. My vested interest in the topic kept me going through heavy submissions and nights of demotivation!
Watch Vipanchi's video above to get insights on how she incorporated her interest in Urban Farming to create a brilliant thesis proposal, which ended up being one of the most viewed theses on the internet in India!
2. What You're Good At
You might admire, say, tensile structures, but it’s not necessary that you’re also good at designing them. Take a good look at the skills you’ve gathered over the years in architecture school- whether it be landscapes, form creation, parametric modelling- and try to incorporate one or two of them into your thesis.
It is these skills that give you an edge and make the process slightly easier.
The other way to look at this is context-based , both personal and geographical. Ask yourself the following questions:
• Do you have a unique insight into a particular town by virtue of having spent some time there?
• Do you come from a certain background , like doctors, chefs, etc? That might give you access to information not commonly available.
• Do you have a stronghold over a particular built typology?
3. What the World Needs
By now, we’ve covered two aspects of picking your topic which focus solely on you. However, your thesis will be concerned with a lot more people than you! A worthy objective to factor in is to think about what the world needs which can combine with what you want to do.
For example, say Tara loves photography, and has unique knowledge of its processes. Rather than creating a museum for cameras, she may consider a school for filmmaking or even a film studio!
Another way to look at this is to think about socio-economically relevant topics, which demonstrate their own urgency. Think disaster housing, adaptive reuse of spaces for medical care, etcetera. Browse many such categories in our resource below!
[Read: 30 Architecture Thesis Topics You Can Choose From ]
4. What is Feasible
Time to get real! As your thesis is a project being conducted within the confines of an institution as well as a semester, there are certain constraints which we need to take care of:
• Site/Data Accessibility: Can you access your site? Is it possible to get your hands on site data and drawings in time?
• Size of Site and Built-up Area: Try for bigger than a residential plot, but much smaller than urban scale. The larger your site/built-up, the harder it will be to do justice to it.
• Popularity/Controversy of Topic: While there’s nothing wrong with going for a popular or controversial topic, you may find highly opinionated faculty/jury on that subject, which might hinder their ability to give unbiased feedback.
• Timeline! Only you know how productive you are, so go with a topic that suits the speed at which you work. This will help you avoid unnecessary stress during the semester.
How to Create an Area Program for your Architecture Thesis

Watch SPA Delhi Thesis Gold-Medallist Nishita Mohta talk about how to create a good quality area program.
Often assumed to be a quantitative exercise, creating an area program is just as much a qualitative effort. As Nishita says, “An area program is of good quality when all user experiences are created with thought and intention to enhance the usage of the site and social fabric.”
Essentially, your area program needs to be human-centric, wherein each component is present for a very good reason. Rigorously question the existence of every component on your program for whether it satisfies an existing need, or creates immense value for users of your site.
To this end, you need to create three lists:
• A list of proposed spaces by referring to area programs of similar projects;
• A list of needs of your users which can be fulfilled by spatial intervention.
• A list of existing functions offered by your immediate context.
Once you put these lists side-by-side, you’ll see that you are able to match certain needs of users to some proposed spaces on your list, or to those in the immediate context.
However, there will be some proposed spaces which do not cater to any need, and needs that are not catered to by any of the spaces. There will also be certain proposed spaces which are redundant because the context already fulfils that need.
This when you remove redundant spaces to create ones for unmatched needs, and viola, you have a good quality area program!
Confused? Here’s an example from the above video. Nishita originally intended to provide a typical eatery on her site, which she later realised was redundant because several eateries already existed around it. In this manner, she was able to fulfil the actual needs of her users- one of which was to be able to rest without having to pay for anything- rather than creating a generic, unnecessary space.
How to Identify Key Stakeholders for Your Architecture Thesis
“A stakeholder? You mean investors in my thesis?”, you scoff.
You’re not wrong! Theoretically, there are several people invested in your thesis! A stakeholder in an architectural project is anyone who has interest and gets impacted by the process or outcome of the project.
At this point, you may question why it’s important to identify your stakeholders. The stakeholders in your thesis will comprise of your user groups, and without knowing your users, you can’t know their needs or design for them!
There are usually two broad categories of stakeholders you must investigate:
• Key Stakeholders: Client and the targeted users
• Invisible Stakeholders: Residents around the site, local businesses, etc.
Within these broad categories, start by naming the kind of stakeholder. Are they residents in your site? Visitors? Workers? Low-income neighbours? Once you’ve named all of them, go ahead and interview at least one person from each category!
The reason for this activity is that you are not the all-knowing Almighty. One can never assume to know what all your users and stakeholders need, and therefore, it’s essential to understand perspectives and break assumptions by talking directly to them. This is how you come up with the aforementioned 'List of Needs', and through it, an area program with a solid footing.
An added advantage of carrying out this interviewing process is that at the end of the day, nobody, not even the jury, can question you on the relevance of a function on your site!
Why Empathy Mapping is Crucial for Your Architecture Thesis
Okay, I interviewed my stakeholders, but I can’t really convert a long conversation into actionable inputs. What do I do?
This is where empathy mapping comes in. It basically allows you to synthesize your data and reduce it to the Pain Points and Gain Points of your stakeholders, which are the inferences of all your observations.
• Pain Points: Problems and challenges that your users face, which you should try to address through design.
• Gain Points: Aspirations of your users which can be catered to through design.
In the above video, Nishita guides you through using an empathy map, so I would highly recommend our readers to watch it. The inferences through empathy mapping are what will help you create a human-centric design that is valuable to the user, the city, and the social fabric.
Download your own copy of this Empathy Map by David Gray , and get working!
Beyond Case Studies: Component Research for your Architecture Thesis
Coming to the more important aspects, it’s essential to know whether learning a new skill will expand your employability prospects. Otherwise, might as well just spend the extra time sleeping. Apart from being a highly sought-after skill within each design field, Rhinoceros is a unique software application being used across the entire spectrum of design. This vastly multiples your chances of being hired and gives you powerful versatility as a freelancer or entrepreneur. The following are some heavyweights in the design world where Rhino 3D is used:
Case Studies are usually existing projects that broadly capture the intent of your thesis. But, it’s not necessary that all components on your site will get covered in depth during your case studies.', 'Instead, we recommend also doing individual Component (or Typology) Research, especially for functions with highly technical spatial requirements.
For example, say you have proposed a residence hall which has a dining area, and therefore, a kitchen- but you have never seen an industrial kitchen before. How would you go about designing it?', 'Not very well!', 'Or, you’re designing a research institute with a chemistry lab, but you don’t know what kind of equipment they use or how a chem lab is typically laid out.
But don’t freak out, it’s not necessary that all of this research needs to be in person! You can use a mixture of primary and secondary studies to your advantage. The point of this exercise is to deeply understand each component on your site such that you face lesser obstacles while designing.
[Read: Site Analysis Categories You Need to Cover For Your Architecture Thesis Project ]" ]
The Technique of Writing an Experiential Narrative for your Architecture Thesis
A narrative? You mean writing? What does that have to do with anything?
A hell of a lot, actually! While your area programs, case studies, site analysis, etc. deal with the tangible, the experience narrative is about the intangible. It is about creating a story for what your user would experience as they walk through the space, which is communicated best in the form of text. This is done for your clarity before you start designing, to be your constant reference as to what you aim to experientially achieve through design.
At the end of the day, all your user will consciously feel is the experience of using your space, so why not have a clear idea of what we want to achieve?
This can be as long or as short as you want, it’s completely up to you! To get an example of what an experience narrative looks like, download the ebook and take a look at what Nishita wrote for her thesis.
Overcoming Creative Blocks During Your Architecture Thesis
Ah, the old enemy of the artist, the Creative Block. Much has been said about creative blocks over time, but there’s not enough guidance on how to overcome them before they send your deadline straight to hell.
When you must put your work out into the world for judgement, there is an automatic fear of judgement and failure which gets activated. It is a defensive mechanism that the brain creates to avoid potential emotional harm.
So how do we override this self-destructive mechanism?
As Nishita says, just waiting for the block to dissolve until we magically feel okay again is not always an option. Therefore, we need to address the block there and then, and to systematically seek inspiration which would help us with a creative breakthrough.
This is where the concept of Divergent and Convergent Thinking comes in.
• Divergent Thinking: Say you browse through ideas on pinterest to get inspired. If you’re in a creative rut, do just that, but don’t worry about implementing any of those ideas. Freely and carelessly jot down everything that inspires you right now regardless of how unfeasible they may be. This is called Divergent Thinking! This process will help unclog your brain and free it from anxiety.
Divergent and convergent thinking.
• Convergent Thinking: Now, using the various constraints of your architecture thesis project, keep or eliminate those ideas based on how feasible they are for your thesis. This is called Convergent Thinking. You’ll either end up with some great concepts to pursue, or have become much more receptive to creative thinking!
Feel free to use Nishita’s Idea Dashboard (example in the video) to give an identity to the ideas you chose to go forward with. Who knows, maybe your creative block will end up being what propels you forward in your ideation process!
How to Prototype Form and Function During Your Architecture Thesis
Prototyping is one of the most crucial processes of your architecture thesis project. But what exactly does it mean?
“A preliminary version of your designed space which can be used to give an idea of various aspects of your space is known as a prototype.”
As Nishita explains in the video above, there can be endless kinds of prototypes that you can explore for your thesis, and all of them explain different parts of your designed space. However, the two aspects of your thesis most crucial to communicate through prototyping are Form and Function.
As we know, nothing beats physical or 3D models as prototypes of form. But how can you prototype function? Nishita gives the example of designing a School for the Blind , wherein you can rearrange your actual studio according to principles you’re using to design for blind people. And then, make your faculty and friends walk through the space with blindfolds on! Prototyping doesn’t get better than this.
In the absence of time or a physical space, you may also explore digital walkthroughs to achieve similar results. Whatever your method may be, eventually the aim of the prototype is to give a good idea of versions of your space to your faculty, friends, or jury, such that they can offer valuable feedback. The different prototypes you create during your thesis will all end up in formulating the best possible version towards the end.
Within the spectrum of prototypes, they also may vary between Narrative Prototypes and Experiential Prototypes. Watch the video above to know where your chosen methods lie on this scale and to get more examples of fascinating prototyping!
How to Convert Feedback (Crits) into Action During Your Architecture Thesis Project

Nishita talks about how to efficiently capture feedback and convert them into actionable points during your architecture thesis process.
If you’ve understood the worth of prototyping, you would also know by now that those prototypes are only valuable if you continuously seek feedback on them. However, the process of taking architectural ‘crits’ (critique) can often be a prolonged, meandering affair and one may come out of them feeling dazed, hopeless and confused. This is especially true for the dreaded architecture thesis crits!
To avoid that, Nishita suggests capturing feedback efficiently in a simple grid, noting remarks under the following four categories:
• Amplify: There will be certain aspects of your thesis that your faculty and friends would appreciate, or would point out as key features of your design that must be made more prominent. For example, you may have chosen to use a certain definitive kind of window in a space, which you could be advised to use more consistently across your design. This is the kind of feedback you would put under ‘Amplify’.
• Address: More often, you will receive feedback which says, ‘this is not working’ or ‘you’ve done nothing to address this problem’. In such cases, don’t get dejected or defensive, simply note the points under the ‘Address’ column. Whether you agree with the advice or not, you cannot ignore it completely!
• Explore: Sometimes, you get feedback that is totally out of the blue or is rather unclear in its intent. Don’t ponder too long over those points during your crit at the cost of other (probably more important) aspects. Rather, write down such feedback under the ‘Explore’ column, to investigate further independently.
• Consider: When someone looks at your work, their creative and problem-solving synapses start firing as well, and they are likely to come up with ideas of their own which you may not have considered. You may or may not want to take them up, but it is a worthy effort to put them down under the ‘Consider’ column to ruminate over later!
Following this system, you would come out of the feedback session with action points already in hand! Feel free to now go get a coffee, knowing that you have everything you need to continue developing your architecture thesis project.
How to Structure Your Architecture Thesis Presentation for a Brilliant Jury
And so, together, we have reached the last stage of your architecture thesis project: The Jury. Here, I will refrain from telling you that this is the most important part of the semester, as I believe that the process of learning is a lot more valuable than the outcome. However, one cannot deny the satisfaction of a good jury at the end of a gruelling semester!
Related Topics
- design careers
- Architecture and Construction
- future tech
Subscribe to Novatr
Always stay up to date with what’s new in AEC!
Get articles like these delivered to your inbox every two weeks.
Related articles
.png)
Everything You Need to Know About Rhino 3D
September 6, 2022
15 min read

Rhino 3D v/s Fusion 360: Which Software Should You Learn in 2024?
Saumya Verma
October 15, 2022
10 min read

10 Best 3D Modelling Software for Civil Engineers in 2024

Pragya Sharma
November 19, 2023
10 Fields Using Computational Design Besides Architecture
January 18, 2023

Ready to skyrocket your career?
Your next chapter in AEC begins with Novatr!
As you would have gathered, we are here to help you take the industry by storm with advanced, tech-first skills.

Dare to Disrupt.
Join thousands of people who organise work and life with Novatr.
Join our newsletter
We’ll send you a nice letter once per week. No spam.
- Become a Mentor
- Careers at Novatr
- Events & Webinars
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
©2023 Novatr Network Pvt. Ltd.
All Rights Reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
Include an opposing viewpoint to your main idea, if applicable. A good thesis statement acknowledges that there is always another side to the argument. So, include an opposing viewpoint (a counterargument) to your opinion. Basically, write down what a person who disagrees with your position might say about your topic.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Step Three: Be Specific. Your thesis statement should be specific to what you are going to talk about. All of the above sentences answer the research question and tell why your audience should care. But they are vague. A great thesis statement is specific and relates to what the rest of your essay will include.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point. 3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Get the sound right. You want your thesis statement to be identifiable as a thesis statement. You do this by taking a very particular tone and using specific kinds of phrasing and words. Use words like "because" and language which is firm and definitive. Example thesis statements with good statement language include:
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Steps for Writing a Thesis. While crafting a complete thesis can often seem overwhelming at first, by breaking it down into manageable steps, the process is much easier to manage. Here are six steps to help you: Step 1: Choose a topic that you find interesting and relevant to your field of study.
Step 7. Finalize Your Thesis Statement. Now comes the final step of the thesis writing process. In the last stage, summarize your refined answer into a powerful single sentence or, if required, two sentences. It should capture the main point of your research project and set the tone for your entire paper.
1 Identify your research gap. The first step to writing a thesis that shows your unique contribution is to identify a research gap in the existing literature. A research gap is a problem, question ...
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Re-write to make your thesis reader-friendly. First, write down what you want to say. This may not be clear, so after you have done this, attempt a re-write to make sure that it is reader-friendly. It helps to ask for feedback. Find out where a reader is confused or engaged, interested or struggling and use this knowledge to improve your work.
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right. Example of a thesis that is too broad:
Write a More ORIGINAL Thesis. One of the largest challenges to moving from middle-school and early high school writing to more advanced work is the challenge to write something original. This doesn't mean you have to invent some whole new theory of life, the universe, and everything. Rather, it means you have to make your reader think.
By doing this you will always keep clear in your mind what you are doing, why you are doing it and how. Key questions are almost always "why", and "how". 5. Increase your vocabulary ...
Step 2: Brainstorming thesis topic ideas. One of the first places to look for a thesis topic is your own past work, such as papers you have written or assignments you have completed. Once you know the limitations and requirements for your thesis, it is time to begin brainstorming specific ideas. This is often the hardest part of choosing a ...
Your first step is probably finding an appealing place to build your house—an empty plot of land where the roads are good and where you can pretty easily connect the gas, electricity, and water. Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build. If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint.
Create a title slide that will grab the audience's attention. Keep your thesis presentation simple and concise to echo your topic. 2. Compelling Templates. Remember that the committee reviewing your thesis presentation is likely to have seen countless slideshows throughout their life.
The thesis acknowledgement is typically placed at the beginning of the thesis, after the title page and before the table of contents. Leaving empty pages, such as page 2 and often page 4, helps in maintaining a visually pleasing layout, when double-sided printing is used. Where to position the acknowledgement when double-sided printing is used.
1. What You Love. Might seem like a no-brainer, but in the flurry of taking up a feasible topic, students often neglect this crucial point. Taking up a topic you're passionate about will not just make for a unique thesis, but will also ensure your dedication during tough times.