
Chapter Four: Theory, Methodologies, Methods, and Evidence

Research Methods
You are viewing the first edition of this textbook. a second edition is available – please visit the latest edition for updated information..
This page discusses the following topics:
Research Goals
Research method types.
Before discussing research methods , we need to distinguish them from methodologies and research skills . Methodologies, linked to literary theories, are tools and lines of investigation: sets of practices and propositions about texts and the world. Researchers using Marxist literary criticism will adopt methodologies that look to material forces like labor, ownership, and technology to understand literature and its relationship to the world. They will also seek to understand authors not as inspired geniuses but as people whose lives and work are shaped by social forces.
Example: Critical Race Theory Methodologies
Critical Race Theory may use a variety of methodologies, including
- Interest convergence: investigating whether marginalized groups only achieve progress when dominant groups benefit as well
- Intersectional theory: investigating how multiple factors of advantage and disadvantage around race, gender, ethnicity, religion, etc. operate together in complex ways
- Radical critique of the law: investigating how the law has historically been used to marginalize particular groups, such as black people, while recognizing that legal efforts are important to achieve emancipation and civil rights
- Social constructivism: investigating how race is socially constructed (rather than biologically grounded)
- Standpoint epistemology: investigating how knowledge relates to social position
- Structural determinism: investigating how structures of thought and of organizations determine social outcomes
To identify appropriate methodologies, you will need to research your chosen theory and gather what methodologies are associated with it. For the most part, we can’t assume that there are “one size fits all” methodologies.
Research skills are about how you handle materials such as library search engines, citation management programs, special collections materials, and so on.
Research methods are about where and how you get answers to your research questions. Are you conducting interviews? Visiting archives? Doing close readings? Reviewing scholarship? You will need to choose which methods are most appropriate to use in your research and you need to gain some knowledge about how to use these methods. In other words, you need to do some research into research methods!
Your choice of research method depends on the kind of questions you are asking. For example, if you want to understand how an author progressed through several drafts to arrive at a final manuscript, you may need to do archival research. If you want to understand why a particular literary work became a bestseller, you may need to do audience research. If you want to know why a contemporary author wrote a particular work, you may need to do interviews. Usually literary research involves a combination of methods such as archival research , discourse analysis , and qualitative research methods.
Literary research methods tend to differ from research methods in the hard sciences (such as physics and chemistry). Science research must present results that are reproducible, while literary research rarely does (though it must still present evidence for its claims). Literary research often deals with questions of meaning, social conventions, representations of lived experience, and aesthetic effects; these are questions that reward dialogue and different perspectives rather than one great experiment that settles the issue. In literary research, we might get many valuable answers even though they are quite different from one another. Also in literary research, we usually have some room to speculate about answers, but our claims have to be plausible (believable) and our argument comprehensive (meaning we don’t overlook evidence that would alter our argument significantly if it were known).
A literary researcher might select the following:
Theory: Critical Race Theory
Methodology: Social Constructivism
Method: Scholarly
Skills: Search engines, citation management
Wendy Belcher, in Writing Your Journal Article in 12 Weeks , identifies two main approaches to understanding literary works: looking at a text by itself (associated with New Criticism ) and looking at texts as they connect to society (associated with Cultural Studies ). The goal of New Criticism is to bring the reader further into the text. The goal of Cultural Studies is to bring the reader into the network of discourses that surround and pass through the text. Other approaches, such as Ecocriticism, relate literary texts to the Sciences (as well as to the Humanities).
The New Critics, starting in the 1940s, focused on meaning within the text itself, using a method they called “ close reading .” The text itself becomes e vidence for a particular reading. Using this approach, you should summarize the literary work briefly and q uote particularly meaningful passages, being sure to introduce quotes and then interpret them (never let them stand alone). Make connections within the work; a sk “why” and “how” the various parts of the text relate to each other.
Cultural Studies critics see all texts as connected to society; the critic therefore has to connect a text to at least one political or social issue. How and why does the text reproduce particular knowledge systems (known as discourses) and how do these knowledge systems relate to issues of power within the society? Who speaks and when? Answering these questions helps your reader understand the text in context. Cultural contexts can include the treatment of gender (Feminist, Queer), class (Marxist), nationality, race, religion, or any other area of human society.
Other approaches, such as psychoanalytic literary criticism , look at literary texts to better understand human psychology. A psychoanalytic reading can focus on a character, the author, the reader, or on society in general. Ecocriticism look at human understandings of nature in literary texts.
We select our research methods based on the kinds of things we want to know. For example, we may be studying the relationship between literature and society, between author and text, or the status of a work in the literary canon. We may want to know about a work’s form, genre, or thematics. We may want to know about the audience’s reading and reception, or about methods for teaching literature in schools.
Below are a few research methods and their descriptions. You may need to consult with your instructor about which ones are most appropriate for your project. The first list covers methods most students use in their work. The second list covers methods more commonly used by advanced researchers. Even if you will not be using methods from this second list in your research project, you may read about these research methods in the scholarship you find.
Most commonly used undergraduate research methods:
- Scholarship Methods: Studies the body of scholarship written about a particular author, literary work, historical period, literary movement, genre, theme, theory, or method.
- Textual Analysis Methods: Used for close readings of literary texts, these methods also rely on literary theory and background information to support the reading.
- Biographical Methods: Used to study the life of the author to better understand their work and times, these methods involve reading biographies and autobiographies about the author, and may also include research into private papers, correspondence, and interviews.
- Discourse Analysis Methods: Studies language patterns to reveal ideology and social relations of power. This research involves the study of institutions, social groups, and social movements to understand how people in various settings use language to represent the world to themselves and others. Literary works may present complex mixtures of discourses which the characters (and readers) have to navigate.
- Creative Writing Methods: A literary re-working of another literary text, creative writing research is used to better understand a literary work by investigating its language, formal structures, composition methods, themes, and so on. For instance, a creative research project may retell a story from a minor character’s perspective to reveal an alternative reading of events. To qualify as research, a creative research project is usually combined with a piece of theoretical writing that explains and justifies the work.
Methods used more often by advanced researchers:
- Archival Methods: Usually involves trips to special collections where original papers are kept. In these archives are many unpublished materials such as diaries, letters, photographs, ledgers, and so on. These materials can offer us invaluable insight into the life of an author, the development of a literary work, or the society in which the author lived. There are at least three major archives of James Baldwin’s papers: The Smithsonian , Yale , and The New York Public Library . Descriptions of such materials are often available online, but the materials themselves are typically stored in boxes at the archive.
- Computational Methods: Used for statistical analysis of texts such as studies of the popularity and meaning of particular words in literature over time.
- Ethnographic Methods: Studies groups of people and their interactions with literary works, for instance in educational institutions, in reading groups (such as book clubs), and in fan networks. This approach may involve interviews and visits to places (including online communities) where people interact with literary works. Note: before you begin such work, you must have Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval “to protect the rights and welfare of human participants involved in research.”
- Visual Methods: Studies the visual qualities of literary works. Some literary works, such as illuminated manuscripts, children’s literature, and graphic novels, present a complex interplay of text and image. Even works without illustrations can be studied for their use of typography, layout, and other visual features.
Regardless of the method(s) you choose, you will need to learn how to apply them to your work and how to carry them out successfully. For example, you should know that many archives do not allow you to bring pens (you can use pencils) and you may not be allowed to bring bags into the archives. You will need to keep a record of which documents you consult and their location (box number, etc.) in the archives. If you are unsure how to use a particular method, please consult a book about it. [1] Also, ask for the advice of trained researchers such as your instructor or a research librarian.
- What research method(s) will you be using for your paper? Why did you make this method selection over other methods? If you haven’t made a selection yet, which methods are you considering?
- What specific methodological approaches are you most interested in exploring in relation to the chosen literary work?
- What is your plan for researching your method(s) and its major approaches?
- What was the most important lesson you learned from this page? What point was confusing or difficult to understand?
Write your answers in a webcourse discussion page.

- Introduction to Research Methods: A Practical Guide for Anyone Undertaking a Research Project by Catherine, Dr. Dawson
- Practical Research Methods: A User-Friendly Guide to Mastering Research Techniques and Projects by Catherine Dawson
- Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches by John W. Creswell Cheryl N. Poth
- Qualitative Research Evaluation Methods: Integrating Theory and Practice by Michael Quinn Patton
- Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches by John W. Creswell J. David Creswell
- Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners by Ranjit Kumar
- Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques by C.R. Kothari
Strategies for Conducting Literary Research Copyright © 2021 by Barry Mauer & John Venecek is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Encyclopedia of Evidence in Pharmaceutical Public Health and Health Services Research in Pharmacy pp 1–15 Cite as
Methodological Approaches to Literature Review
- Dennis Thomas 2 ,
- Elida Zairina 3 &
- Johnson George 4
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 09 May 2023
442 Accesses
The literature review can serve various functions in the contexts of education and research. It aids in identifying knowledge gaps, informing research methodology, and developing a theoretical framework during the planning stages of a research study or project, as well as reporting of review findings in the context of the existing literature. This chapter discusses the methodological approaches to conducting a literature review and offers an overview of different types of reviews. There are various types of reviews, including narrative reviews, scoping reviews, and systematic reviews with reporting strategies such as meta-analysis and meta-synthesis. Review authors should consider the scope of the literature review when selecting a type and method. Being focused is essential for a successful review; however, this must be balanced against the relevance of the review to a broad audience.
- Literature review
- Systematic review
- Meta-analysis
- Scoping review
- Research methodology
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Akobeng AK. Principles of evidence based medicine. Arch Dis Child. 2005;90(8):837–40.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alharbi A, Stevenson M. Refining Boolean queries to identify relevant studies for systematic review updates. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(11):1658–66.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Article Google Scholar
Aromataris E MZE. JBI manual for evidence synthesis. 2020.
Google Scholar
Aromataris E, Pearson A. The systematic review: an overview. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(3):53–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Aromataris E, Riitano D. Constructing a search strategy and searching for evidence. A guide to the literature search for a systematic review. Am J Nurs. 2014;114(5):49–56.
Babineau J. Product review: covidence (systematic review software). J Canad Health Libr Assoc Canada. 2014;35(2):68–71.
Baker JD. The purpose, process, and methods of writing a literature review. AORN J. 2016;103(3):265–9.
Bastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: how will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2010;7(9):e1000326.
Bramer WM, Rethlefsen ML, Kleijnen J, Franco OH. Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):1–12.
Brown D. A review of the PubMed PICO tool: using evidence-based practice in health education. Health Promot Pract. 2020;21(4):496–8.
Cargo M, Harris J, Pantoja T, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 4: methods for assessing evidence on intervention implementation. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:59–69.
Cook DJ, Mulrow CD, Haynes RB. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126(5):376–80.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Counsell C. Formulating questions and locating primary studies for inclusion in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(5):380–7.
Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB. Conceiving the research question and developing the study plan. In: Cummings SR, Browner WS, Hulley SB, editors. Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiological Approach. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): P Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p. 14–22.
Eriksen MB, Frandsen TF. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: a systematic review. JMLA. 2018;106(4):420.
Ferrari R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing. 2015;24(4):230–5.
Flemming K, Booth A, Hannes K, Cargo M, Noyes J. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 6: reporting guidelines for qualitative, implementation, and process evaluation evidence syntheses. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:79–85.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Green BN, Johnson CD, Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J Chiropr Med. 2006;5(3):101–17.
Gregory AT, Denniss AR. An introduction to writing narrative and systematic reviews; tasks, tips and traps for aspiring authors. Heart Lung Circ. 2018;27(7):893–8.
Harden A, Thomas J, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 5: methods for integrating qualitative and implementation evidence within intervention effectiveness reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:70–8.
Harris JL, Booth A, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 2: methods for question formulation, searching, and protocol development for qualitative evidence synthesis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;97:39–48.
Higgins J, Thomas J. In: Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3, updated February 2022). Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.: Cochrane; 2022.
International prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO). Available from https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ .
Khan KS, Kunz R, Kleijnen J, Antes G. Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J R Soc Med. 2003;96(3):118–21.
Landhuis E. Scientific literature: information overload. Nature. 2016;535(7612):457–8.
Lockwood C, Porritt K, Munn Z, Rittenmeyer L, Salmond S, Bjerrum M, Loveday H, Carrier J, Stannard D. Chapter 2: Systematic reviews of qualitative evidence. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . https://doi.org/10.46658/JBIMES-20-03 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Lorenzetti DL, Topfer L-A, Dennett L, Clement F. Value of databases other than medline for rapid health technology assessments. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2014;30(2):173–8.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, the PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for (SR) and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;6:264–9.
Mulrow CD. Systematic reviews: rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ. 1994;309(6954):597–9.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Munthe-Kaas HM, Glenton C, Booth A, Noyes J, Lewin S. Systematic mapping of existing tools to appraise methodological strengths and limitations of qualitative research: first stage in the development of the CAMELOT tool. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):1–13.
Murphy CM. Writing an effective review article. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(2):89–90.
NHMRC. Guidelines for guidelines: assessing risk of bias. Available at https://nhmrc.gov.au/guidelinesforguidelines/develop/assessing-risk-bias . Last published 29 August 2019. Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
Noyes J, Booth A, Cargo M, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 1: introduction. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018b;97:35–8.
Noyes J, Booth A, Flemming K, et al. Cochrane qualitative and implementation methods group guidance series – paper 3: methods for assessing methodological limitations, data extraction and synthesis, and confidence in synthesized qualitative findings. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018a;97:49–58.
Noyes J, Booth A, Moore G, Flemming K, Tunçalp Ö, Shakibazadeh E. Synthesising quantitative and qualitative evidence to inform guidelines on complex interventions: clarifying the purposes, designs and outlining some methods. BMJ Glob Health. 2019;4(Suppl 1):e000893.
Peters MD, Godfrey CM, Khalil H, McInerney P, Parker D, Soares CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Healthcare. 2015;13(3):141–6.
Polanin JR, Pigott TD, Espelage DL, Grotpeter JK. Best practice guidelines for abstract screening large-evidence systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(3):330–42.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7(1):1–7.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. Brit Med J. 2017;358
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Br Med J. 2016;355
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Tawfik GM, Dila KAS, Mohamed MYF, et al. A step by step guide for conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis with simulation data. Trop Med Health. 2019;47(1):1–9.
The Critical Appraisal Program. Critical appraisal skills program. Available at https://casp-uk.net/ . 2022. Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
The University of Melbourne. Writing a literature review in Research Techniques 2022. Available at https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/explore-our-resources/research-techniques/reviewing-the-literature . Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison. Learn how to write a literature review in The Writer’s Handbook – Academic Professional Writing. 2022. Available at https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/reviewofliterature/ . Accessed 29 Aug 2022.
Thompson SG, Sharp SJ. Explaining heterogeneity in meta-analysis: a comparison of methods. Stat Med. 1999;18(20):2693–708.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16(1):15.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Yoneoka D, Henmi M. Clinical heterogeneity in random-effect meta-analysis: between-study boundary estimate problem. Stat Med. 2019;38(21):4131–45.
Yuan Y, Hunt RH. Systematic reviews: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(5):1086–92.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre of Excellence in Treatable Traits, College of Health, Medicine and Wellbeing, University of Newcastle, Hunter Medical Research Institute Asthma and Breathing Programme, Newcastle, NSW, Australia
Dennis Thomas
Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Elida Zairina
Centre for Medicine Use and Safety, Monash Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Monash University, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Johnson George
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Johnson George .
Section Editor information
College of Pharmacy, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
Derek Charles Stewart
Department of Pharmacy, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, United Kingdom
Zaheer-Ud-Din Babar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Thomas, D., Zairina, E., George, J. (2023). Methodological Approaches to Literature Review. In: Encyclopedia of Evidence in Pharmaceutical Public Health and Health Services Research in Pharmacy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50247-8_57-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50247-8_57-1
Received : 22 February 2023
Accepted : 22 February 2023
Published : 09 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-50247-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-50247-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life Sciences Reference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

Research Methods: Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Persuasive Arguments
- Subject Specific Methodology
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal. A literature review helps the author learn about the history and nature of their topic, and identify research gaps and problems.
Steps & Elements
Problem formulation
- Determine your topic and its components by asking a question
- Research: locate literature related to your topic to identify the gap(s) that can be addressed
- Read: read the articles or other sources of information
- Analyze: assess the findings for relevancy
- Evaluating: determine how the article are relevant to your research and what are the key findings
- Synthesis: write about the key findings and how it is relevant to your research
Elements of a Literature Review
- Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review
- Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely)
- Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclude which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of an area of research
Writing a Literature Review Resources
- How to Write a Literature Review From the Wesleyan University Library
- Write a Literature Review From the University of California Santa Cruz Library. A Brief overview of a literature review, includes a list of stages for writing a lit review.
- Literature Reviews From the University of North Carolina Writing Center. Detailed information about writing a literature review.
- Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), p.38-43
Literature Review Tutorial
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 12:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.auraria.edu/researchmethods
1100 Lawrence Street Denver, CO 80204 303-315-7700 Ask Us Directions
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper , the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research and your dissertation topic .
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analyzed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- How you mitigated or avoided research biases
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ? How did you prevent bias from affecting your data?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalizable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalized your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion and exclusion criteria , as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on July 4–8, 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
- Information bias
- Omitted variable bias
- Regression to the mean
- Survivorship bias
- Undercoverage bias
- Sampling bias
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyze?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness store’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
- The Hawthorne effect
- Observer bias
- The placebo effect
- Response bias and Nonresponse bias
- The Pygmalion effect
- Recall bias
- Social desirability bias
- Self-selection bias
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analyzed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analyzing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorizing and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviors, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalized beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalizable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Thematic analysis
- Cohort study
- Peer review
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
In a scientific paper, the methodology always comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion . The same basic structure also applies to a thesis, dissertation , or research proposal .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research, you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 7, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE : If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE : If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 1:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples


Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Why is research methodology important?
Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.
Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and....
- Open access
- Published: 05 December 2023
A scoping review to identify and organize literature trends of bias research within medical student and resident education
- Brianne E. Lewis 1 &
- Akshata R. Naik 2
BMC Medical Education volume 23 , Article number: 919 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
814 Accesses
1 Citations
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Physician bias refers to the unconscious negative perceptions that physicians have of patients or their conditions. Medical schools and residency programs often incorporate training to reduce biases among their trainees. In order to assess trends and organize available literature, we conducted a scoping review with a goal to categorize different biases that are studied within medical student (MS), resident (Res) and mixed populations (MS and Res). We also characterized these studies based on their research goal as either documenting evidence of bias (EOB), bias intervention (BI) or both. These findings will provide data which can be used to identify gaps and inform future work across these criteria.
Online databases (PubMed, PsycINFO, WebofScience) were searched for articles published between 1980 and 2021. All references were imported into Covidence for independent screening against inclusion criteria. Conflicts were resolved by deliberation. Studies were sorted by goal: ‘evidence of bias’ and/or ‘bias intervention’, and by population (MS or Res or mixed) andinto descriptive categories of bias.
Of the initial 806 unique papers identified, a total of 139 articles fit the inclusion criteria for data extraction. The included studies were sorted into 11 categories of bias and showed that bias against race/ethnicity, specific diseases/conditions, and weight were the most researched topics. Of the studies included, there was a higher ratio of EOB:BI studies at the MS level. While at the Res level, a lower ratio of EOB:BI was found.
Conclusions
This study will be of interest to institutions, program directors and medical educators who wish to specifically address a category of bias and identify where there is a dearth of research. This study also underscores the need to introduce bias interventions at the MS level.
Peer Review reports
Physician bias ultimately impacts patient care by eroding the physician–patient relationship [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. To overcome this issue, certain states require physicians to report a varying number of hours of implicit bias training as part of their recurring licensing requirement [ 5 , 6 ]. Research efforts on the influence of implicit bias on clinical decision-making gained traction after the “Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care” report published in 2003 [ 7 ]. This report sparked a conversation about the impact of bias against women, people of color, and other marginalized groups within healthcare. Bias from a healthcare provider has been shown to affect provider-patient communication and may also influence treatment decisions [ 8 , 9 ]. Nevertheless, opportunities within medical education curriculum are created to evaluate biases at an earlier stage of physician-training and provide instruction to intervene them [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. We aimed to identify trends and organize literature on bias training provided during medical school and residency programs since the meaning of ‘bias’ is broad and encompasses several types of attitudes and predispositions [ 13 ].
Several reviews, narrative or systematic in nature, have been published in the field of bias research in medicine and healthcare [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Many of these reviews have a broad focus on implicit bias and they often fail to define the patient’s specific attributes- such as age, weight, disease, or condition against which physicians hold their biases. However, two recently published reviews categorized implicit biases into various descriptive characteristics albeit with research goals different than this study [ 17 , 18 ]. The study by Fitzgerald et al. reviewed literature focused on bias among physicians and nurses to highlight its role in healthcare disparities [ 17 ]. While the study by Gonzalez et al. focused on bias curricular interventions across professions related to social determinants of health such as education, law, medicine and social work [ 18 ]. Our research goal was to identify the various bias characteristics that are studied within medical student and/or resident populations and categorize them. Further, we were interested in whether biases were merely identified or if they were intervened. To address these deficits in the field and provide clarity, we utilized a scoping review approach to categorize the literature based on a) the bias addressed and b) the study goal within medical students (MS), residents (Res) and a mixed population (MS and Res).
To date no literature review has organized bias research by specific categories held solely by medical trainees (medical students and/or residents) and quantified intervention studies. We did not perform a quality assessment or outcome evaluation of the bias intervention strategies, as it was not the goal of this work and is standard with a scoping review methodology [ 19 , 20 ]. By generating a comprehensive list of bias categories researched among medical trainee population, we highlight areas of opportunity for future implicit bias research specifically within the undergraduate and graduate medical education curriculum. We anticipate that the results from this scoping review will be useful for educators, administrators, and stakeholders seeking to implement active programs or workshops that intervene specific biases in pre-clinical medical education and prepare physicians-in-training for patient encounters. Additionally, behavioral scientists who seek to support clinicians, and develop debiasing theories [ 21 ] and models may also find our results informative.
We conducted an exhaustive and focused scoping review and followed the methodological framework for scoping reviews as previously described in the literature [ 20 , 22 ]. This study aligned with the four goals of a scoping review [ 20 ]. We followed the first five out of the six steps outlined by Arksey and O’Malley’s to ensure our review’s validity 1) identifying the research question 2) identifying relevant studies 3) selecting the studies 4) charting the data and 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [ 22 ]. We did not follow the optional sixth step of undertaking consultation with key stakeholders as it was not needed to address our research question it [ 23 ]. Furthermore, we used Covidence systematic review software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia) that aided in managing steps 2–5 presented above.
Research question, search strategy and inclusion criteria
The purpose of this study was to identify trends in bias research at the medical school and residency level. Prior to conducting our literature search we developed our research question and detailed the inclusion criteria, and generated the search syntax with the assistance from a medical librarian. Search syntax was adjusted to the requirements of the database. We searched PubMed, Web of Science, and PsycINFO using MeSH terms shown below.
Bias* [ti] OR prejudice*[ti] OR racism[ti] OR homophobia[ti] OR mistreatment[ti] OR sexism[ti] OR ageism[ti]) AND (prejudice [mh] OR "Bias"[Mesh:NoExp]) AND (Education, Medical [mh] OR Schools, Medical [mh] OR students, medical [mh] OR Internship and Residency [mh] OR “undergraduate medical education” OR “graduate medical education” OR “medical resident” OR “medical residents” OR “medical residency” OR “medical residencies” OR “medical schools” OR “medical school” OR “medical students” OR “medical student”) AND (curriculum [mh] OR program evaluation [mh] OR program development [mh] OR language* OR teaching OR material* OR instruction* OR train* OR program* OR curricul* OR workshop*
Our inclusion criteria incorporated studies which were either original research articles, or review articles that synthesized new data. We excluded publications that were not peer-reviewed or supported with data such as narrative reviews, opinion pieces, editorials, perspectives and commentaries. We included studies outside of the U.S. since the purpose of this work was to generate a comprehensive list of biases. Physicians, regardless of their country of origin, can hold biases against specific patient attributes [ 17 ]. Furthermore, physicians may practice in a different country than where they trained [ 24 ]. Manuscripts were included if they were published in the English language for which full-texts were available. Since the goal of this scoping review was to assess trends, we accepted studies published from 1980–2021.
Our inclusion criteria also considered the goal and the population of the study. We defined the study goal as either that documented evidence of bias or a program directed bias intervention. Evidence of bias (EOB) had to originate from the medical trainee regarding a patient attribute. Bias intervention (BI) studies involved strategies to counter biases such as activities, workshops, seminars or curricular innovations. The population studied had to include medical students (MS) or residents (Res) or mixed. We defined the study population as ‘mixed’ when it consisted of both MS and Res. Studies conducted on other healthcare professionals were included if MS or Res were also studied. Our search criteria excluded studies that documented bias against medical professionals (students, residents and clinicians) either by patients, medical schools, healthcare administrators or others, and was focused on studies where the biases were solely held by medical trainees (MS and Res).
Data extraction and analysis
Following the initial database search, references were downloaded and bulk uploaded into Covidence and duplicates were removed. After the initial screening of title and abstracts, full-texts were reviewed. Authors independently completed title and abstract screening, and full text reviews. Any conflicts at the stage of abstract screening were moved to full-text screening. Conflicts during full-text screening were resolved by deliberation and referring to the inclusion and exclusion criteria detailed in the research protocol. The level of agreement between the two authors for full text reviews as measured by inter-rater reliability was 0.72 (Cohen’s Kappa).
A data extraction template was created in Covidence to extract data from included full texts. Data extraction template included the following variables; country in which the study was conducted, year of publication, goal of the study (EOB, BI or both), population of the study (MS, Res or mixed) and the type of bias studied. Final data was exported to Microsoft Excel for quantification. For charting our data and categorizing the included studies, we followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews(PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 25 ]. Results from this scoping review study are meant to provide a visual synthesis of existing bias research and identify gaps in knowledge.
Study selection
Our search strategy yielded a total of 892 unique abstracts which were imported into ‘Covidence’ for screening. A total of 86 duplicate references were removed. Then, 806 titles and abstracts were screened for relevance independently by the authors and 519 studies were excluded at this stage. Any conflicts among the reviewers at this stage were resolved by discussion and referring to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Then a full text review of the remaining 287 papers was completed by the authors against the inclusion criteria for eligibility. Full text review was also conducted independently by the authors and any conflicts were resolved upon discussion. Finally, we included 139 studies which were used for data extraction (Fig. 1 ).
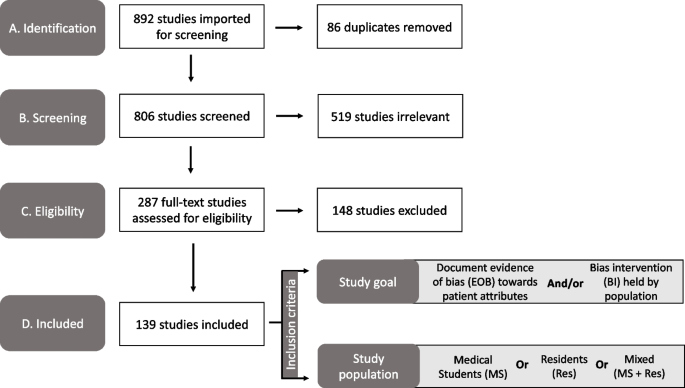
PRISMA diagram of the study selection process used in our scoping review to identify the bias categories that have been reported within medical education literature. Study took place from 2021–2022. Abbreviation: PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Publication trends in bias research
First, we charted the studies to demonstrate the timeline of research focused on bias within the study population of our interest (MS or Res or mixed). Our analysis revealed an increase in publications with respect to time (Fig. 2 ). Of the 139 included studies, fewer studies were published prior to 2001, with a total of only eight papers being published from the years 1985–2000. A substantial increase in publications occurred after 2004, with 2019 being the peak year where most of the studies pertaining to bias were published (Fig. 2 ).
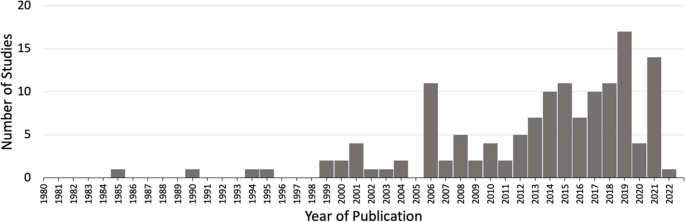
Studies matching inclusion criteria mapped by year of publication. Search criteria included studies addressing bias from 1980–2021 within medical students (MS) or residents (Res) or mixed (MS + Res) populations. * Publication in 2022 was published online ahead of print
Overview of included studies
We present a descriptive analysis of the 139 included studies in Table 1 based on the following parameters: study location, goal of the study, population of the study and the category of bias studied. All of the above parameters except the category of bias included a denominator of 139 studies. Several studies addressed more than one bias characteristic; therefore, we documented 163 biases sorted in 11 categories over the 139 papers. The bias categories that we generated and their respective occurrences are listed in Table 1 . Of the 139 studies that were included, most studies originated in the United States ( n = 89/139, 64%) and Europe ( n = 20/139, 20%).
Sorting of included research by bias category
We grouped the 139 included studies depending on the patient attribute or the descriptive characteristic against which the bias was studied (Table 1 ). By sorting the studies into different bias categories, we aimed to not only quantitate the amount of research addressing a particular topic of bias, but also reveal the biases that are understudied.
Through our analysis, we generated 11 descriptive categories against which bias was studied: Age, physical disability, education level, biological sex, disease or condition, LGBTQ + , non-specified, race/ethnicity, rural/urban, socio-economic status, and weight (Table 1 ). “Age” and “weight” categories included papers that studied bias against older population and higher weight individuals, respectively. The categories “education level” and “socio-economic status” included papers that studied bias against individuals with low education level and individuals belonging to low socioeconomic status, respectively. Within the bias category named ‘biological sex’, we included papers that studied bias against individuals perceived as women/females. Papers that studied bias against gender-identity or sexual orientation were included in its own category named, ‘LGBTQ + ’. The bias category, ‘disease or condition’ was broad and included research on bias against any patient with a specific disease, condition or lifestyle. Studies included in this category researched bias against any physical illnesses, mental illnesses, or sexually transmitted infections. It also included studies that addressed bias against a treatment such as transplant or pain management. It was not significant to report these as individual categories but rather as a whole with a common underlying theme. Rural/urban bias referred to bias that was held against a person based on their place of residence. Studies grouped together in the ‘non-specified bias’ category explored bias without specifying any descriptive characteristic in their methods. These studies did not address any specific bias characteristic in particular but consisted of a study population of our interest (MS or Res or mixed). Based on our analysis, the top five most studied bias categories in our included population within medical education literature were: racial or ethnic bias ( n = 39/163, 24%), disease or condition bias ( n = 29/163, 18%), weight bias ( n = 22/163, 13%), LGBTQ + bias ( n = 21/163, 13%), and age bias ( n = 16/163, 10%) which are presented in Table 1 .
Sorting of included research by population
In order to understand the distribution of bias research based on their populations examined, we sorted the included studies in one of the following: medical students (MS), residents (Res) or mixed (Table 1 ). The following distributions were observed: medical students only ( n = 105/139, 76%), residents only ( n = 19/139, 14%) or mixed which consisted of both medical students and residents ( n = 15/139, 11%). In combination, these results demonstrate that medical educators have focused bias research efforts primarily on medical student populations.
Sorting of included research by goal
A critical component of this scoping review was to quantify the research goal of the included studies within each of the bias categories. We defined the research goal as either to document evidence of bias (EOB) or to evaluate a bias intervention (BI) (see Fig. 1 for inclusion criteria). Some of the included studies focused on both, documenting evidence in addition to intervening biases and those studies were grouped separately. The analysis revealed that 69/139 (50%) of the included studies focused exclusively on documenting evidence of bias (EOB). There were fewer studies ( n = 51/139, 37%) which solely focused on bias interventions such as programs, seminars or curricular innovations. A small minority of the included studies were more comprehensive in that they documented EOB followed by an intervention strategy ( n = 19/139, 11%). These results demonstrate that most bias research is dedicated to documenting evidence of bias among these groups rather than evaluating a bias intervention strategy.
Research goal distribution
Our next objective was to calculate the distribution of studies with respect to the study goal (EOB, BI or both), within the 163 biases studied across the 139 papers as calculated in Table 1 . In general, the goal of the studies favors documenting evidence of bias with the exception of race/ethnic bias which is more focused on bias intervention (Fig. 3 ). Fewer studies were aimed at both, documenting evidence then providing an intervention, across all bias categories.
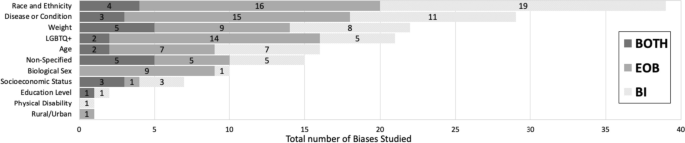
Sorting of total biases ( n = 163) within medical students or residents or a mixed population based on the bias category . Dark grey indicates studies with a dual goal, to document evidence of bias and to intervene bias. Medium grey bars indicate studies which focused on documenting evidence of bias. Light grey bars indicate studies focused on bias intervention within these populations. Numbers inside the bars indicate the total number of biases for the respective study goal. * Non-specified bias includes studies which focused on implicit bias but did not mention the type of bias investigated
Furthermore, we also calculated the ratio of EOB, BI and both (EOB + BI) within each of our population of interest (MS; n = 122, Res; n = 26 and mixed; n = 15) for the 163 biases observed in our included studies. Over half ( n = 64/122, 52%) of the total bias occurrences in MS were focused on documenting EOB (Fig. 4 ). Contrastingly, a shift was observed within resident populations where most biases addressed were aimed at intervention ( n = 12/26, 41%) rather than EOB ( n = 4/26, 14%) (Fig. 4 ). Studies which included both MS and Res (mixed) were primarily focused on documenting EOB ( n = 9/15, 60%), with 33% ( n = 5/15) aimed at bias intervention and 7% ( n = 1/15) which did both (Fig. 4 ). Although far fewer studies were documented in the Res population it is important to highlight that most of these studies were focused on bias intervention when compared to MS population where we documented a majority of studies focused on evidence of bias.
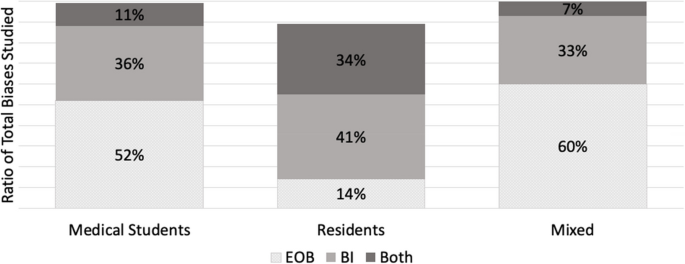
A ratio of the study goal for the total biases ( n = 163) mapped within each of the study population (MS, Res and Mixed). A study goal with a) documenting evidence of bias (EOB) is depicted in dotted grey, b) bias intervention (BI) in medium grey, and c) a dual focus (EOB + BI) is depicted in dark grey. * N = 122 for medical student studies. b N = 26 for residents. c N = 15 for mixed
Addressing biases at an earlier stage of medical career is critical for future physicians engaging with diverse patients, since it is established that bias negatively influences provider-patient interactions [ 171 ], clinical decision-making [ 172 ] and reduces favorable treatment outcomes [ 2 ]. We set out with an intention to explore how bias is addressed within the medical curriculum. Our research question was: how has the trend in bias research changed over time, more specifically a) what is the timeline of papers published? b) what bias characteristics have been studied in the physician-trainee population and c) how are these biases addressed? With the introduction of ‘standards of diversity’ by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, along with the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) and the American Medical Association (AMA) [ 173 , 174 ], we certainly expected and observed a sustained uptick in research pertaining to bias. As shown here, research addressing bias in the target population (MS and Res) is on the rise, however only 139 papers fit our inclusion criteria. Of these studies, nearly 90% have been published since 2005 after the “Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care” report was published in 2003 [ 7 ]. However, given the well documented effects of physician held bias, we anticipated significantly more number of studies focused on bias at the medical student or resident level.
A key component from this study was that we generated descriptive categories of biases. Sorting the biases into descriptive categories helps to identify a more targeted approach for a specific bias intervention, rather than to broadly intervene bias as a whole. In fact, our analysis found a number of publications (labeled “non-specified bias” in Table 1 ) which studied implicit bias without specifying the patient attribute or the characteristic that the bias was against. In total, we generated 11 descriptive categories of bias from our scoping review which are shown in Table 1 and Fig. 3 . Furthermore, our bias descriptors grouped similar kinds of biases within a single category. For example, the category, “disease or condition” included papers that studied bias against any type of disease (Mental illness, HIV stigma, diabetes), condition (Pain management), or lifestyle. We neither performed a qualitative assessment of the studies nor did we test the efficacy of the bias intervention studies and consider it a future direction of this work.
Evidence suggests that medical educators and healthcare professionals are struggling to find the appropriate approach to intervene biases [ 175 , 176 , 177 ] So far, bias reduction, bias reflection and bias management approaches have been proposed [ 26 , 27 , 178 ]. Previous implicit bias intervention strategies have been shown to be ineffective when biased attitudes of participants were assessed after a lag [ 179 ]. Understanding the descriptive categories of bias and previous existing research efforts, as we present here is only a fraction of the challenge. The theory of “cognitive bias” [ 180 ] and related branches of research [ 13 , 181 , 182 , 183 , 184 ] have been studied in the field of psychology for over three decades. It is only recently that cognitive bias theory has been applied to the field of medical education medicine, to explain its negative influence on clinical decision-making pertaining only to racial minorities [ 1 , 2 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 185 ]. In order to elicit meaningful changes with respect to targeted bias intervention, it is necessary to understand the psychological underpinnings (attitudes) leading to a certain descriptive category of bias (behaviors). The questions which medical educators need to ask are: a) Can these descriptive biases be identified under certain type/s of cognitive errors that elicits the bias and vice versa b) Are we working towards an attitude change which can elicit a sustained positive behavior change among healthcare professionals? And most importantly, c) are we creating a culture where participants voluntarily enroll themselves in bias interventions as opposed to being mandated to participate? Cognitive psychologists and behavioral scientists are well-positioned to help us find answers to these questions as they understand human behavior. Therefore, an interdisciplinary approach, a marriage between cognitive psychologists and medical educators, is key in targeting biases held by medical students, residents, and ultimately future physicians. This review may also be of interest to behavioral psychologists, keen on providing targeted intervening strategies to clinicians depending on the characteristics (age, weight, sex or race) the portrayed bias is against. Further, instead of an individualized approach, we need to strive for systemic changes and evidence-based strategies to intervene biases.
The next element in change is directing intervention strategies at the right stage in clinical education. Our study demonstrated that most of the research collected at the medical student level was focused on documenting evidence of bias. Although the overall number of studies at the resident level were fewer than at the medical student level, the ratio of research in favor of bias intervention was higher at the resident level (see Fig. 3 ). However, it could be helpful to focus on bias intervention earlier in learning, rather than at a later stage [ 186 ]. Additionally, educational resources such as textbooks, preparatory materials, and educators themselves are potential sources of propagating biases and therefore need constant evaluation against best practices [ 187 , 188 ].
This study has limitations. First, the list of the descriptive bias categories that we generated was not grounded in any particular theory so assigning a category was subjective. Additionally, there were studies that were categorized as “nonspecified” bias as the studies themselves did not mention the specific type of bias that they were addressing. Moreover, we had to exclude numerous publications solely because they were not evidence-based and were either perspectives, commentaries or opinion pieces. Finally, there were overall fewer studies focused on the resident population, so the calculated ratio of MS:Res studies did not compare similar sample sizes.
Future directions of our study include working with behavioral scientists to categorize these bias characteristics (Table 1 ) into cognitive error types [ 189 ]. Additionally, we aim to assess the effectiveness of the intervention strategies and categorize the approach of the intervention strategies.
The primary goal of our review was to organize, compare and quantify literature pertaining to bias within medical school curricula and residency programs. We neither performed a qualitative assessment of the studies nor did we test the efficacy of studies that were sorted into “bias intervention” as is typical of scoping reviews [ 22 ]. In summary, our research identified 11 descriptive categories of biases studied within medical students and resident populations with “race and ethnicity”, “disease or condition”, “weight”, “LGBTQ + ” and “age” being the top five most studied biases. Additionally, we found a greater number of studies conducted in medical students (105/139) when compared to residents (19/139). However, most of the studies in the resident population focused on bias intervention. The results from our review highlight the following gaps: a) bias categories where more research is needed, b) biases that are studied within medical school versus in residency programs and c) study focus in terms of demonstrating the presence of bias or working towards bias intervention.
This review provides a visual analysis of the known categories of bias addressed within the medical school curriculum and in residency programs in addition to providing a comparison of studies with respect to the study goal within medical education literature. The results from our review should be of interest to community organizations, institutions, program directors and medical educators interested in knowing and understanding the types of bias existing within healthcare populations. It might be of special interest to researchers who wish to explore other types of biases that have been understudied within medical school and resident populations, thus filling the gaps existing in bias research.
Despite the number of studies designed to provide bias intervention for MS and Res populations, and an overall cultural shift to be aware of one’s own biases, biases held by both medical students and residents still persist. Further, psychologists have recently demonstrated the ineffectiveness of some bias intervention efforts [ 179 , 190 ]. Therefore, it is perhaps unrealistic to expect these biases to be eliminated altogether. However, effective intervention strategies grounded in cognitive psychology should be implemented earlier on in medical training. Our focus should be on providing evidence-based approaches and safe spaces for an attitude and culture change, so as to induce actionable behavioral changes.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Medical student
Evidence of bias
- Bias intervention
Hagiwara N, Mezuk B, Elston Lafata J, Vrana SR, Fetters MD. Study protocol for investigating physician communication behaviours that link physician implicit racial bias and patient outcomes in Black patients with type 2 diabetes using an exploratory sequential mixed methods design. BMJ Open. 2018;8(10):e022623.
Article Google Scholar
Haider AH, Schneider EB, Sriram N, Dossick DS, Scott VK, Swoboda SM, Losonczy L, Haut ER, Efron DT, Pronovost PJ, et al. Unconscious race and social class bias among acute care surgical clinicians and clinical treatment decisions. JAMA Surg. 2015;150(5):457–64.
Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, Albrecht TL, Chapman R, Foster T, Harper FW, Hagiwara N, Hamel LM, Shields AF, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874–80.
Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Yeazel MW, Hellerstedt WL, Griffin JM, van Ryn M. Impact of weight bias and stigma on quality of care and outcomes for patients with obesity. Obes Rev. 2015;16(4):319–26.
Garrett SB, Jones L, Montague A, Fa-Yusuf H, Harris-Taylor J, Powell B, Chan E, Zamarripa S, Hooper S, Chambers Butcher BD. Challenges and opportunities for clinician implicit bias training: insights from perinatal care stakeholders. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):506–19.
Shah HS, Bohlen J. Implicit bias. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
Google Scholar
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Understanding and Eliminating Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. In: Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2003. PMID: 25032386.
Dehon E, Weiss N, Jones J, Faulconer W, Hinton E, Sterling S. A systematic review of the impact of physician implicit racial bias on clinical decision making. Acad Emerg Med. 2017;24(8):895–904.
Oliver MN, Wells KM, Joy-Gaba JA, Hawkins CB, Nosek BA. Do physicians’ implicit views of African Americans affect clinical decision making? J Am Board Fam Med. 2014;27(2):177–88.
Rincon-Subtirelu M. Education as a tool to modify anti-obesity bias among pediatric residents. Int J Med Educ. 2017;8:77–8.
Gustafsson Sendén M, Renström EA. Gender bias in assessment of future work ability among pain patients - an experimental vignette study of medical students’ assessment. Scand J Pain. 2019;19(2):407–14.
Hardeman RR, Burgess D, Phelan S, Yeazel M, Nelson D, van Ryn M. Medical student socio-demographic characteristics and attitudes toward patient centered care: do race, socioeconomic status and gender matter? A report from the medical student CHANGES study. Patient Educ Couns. 2015;98(3):350–5.
Greenwald AG, Banaji MR. Implicit social cognition: attitudes, self-esteem, and stereotypes. Psychol Rev. 1995;102(1):4–27.
Kruse JA, Collins JL, Vugrin M. Educational strategies used to improve the knowledge, skills, and attitudes of health care students and providers regarding implicit bias: an integrative review of the literature. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2022;4:100073.
Zestcott CA, Blair IV, Stone J. Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Process Intergroup Relat. 2016;19(4):528–42.
Hall WJ, Chapman MV, Lee KM, Merino YM, Thomas TW, Payne BK, Eng E, Day SH, Coyne-Beasley T. Implicit racial/ethnic bias among health care professionals and its influence on health care outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(12):E60–76.
FitzGerald C, Hurst S. Implicit bias in healthcare professionals: a systematic review. BMC Med Ethics. 2017;18(1):19.
Gonzalez CM, Onumah CM, Walker SA, Karp E, Schwartz R, Lypson ML. Implicit bias instruction across disciplines related to the social determinants of health: a scoping review. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2023;28(2):541–87.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:69.
Pat C, Geeta S, Sílvia M. Cognitive debiasing 1: origins of bias and theory of debiasing. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22(Suppl 2):ii58.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Thomas A, Lubarsky S, Durning SJ, Young ME. Knowledge syntheses in medical education: demystifying scoping reviews. Acad Med. 2017;92(2):161–6.
Hagopian A, Thompson MJ, Fordyce M, Johnson KE, Hart LG. The migration of physicians from sub-Saharan Africa to the United States of America: measures of the African brain drain. Hum Resour Health. 2004;2(1):17.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Teal CR, Shada RE, Gill AC, Thompson BM, Frugé E, Villarreal GB, Haidet P. When best intentions aren’t enough: Helping medical students develop strategies for managing bias about patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(Suppl 2):S115–8.
Gonzalez CM, Walker SA, Rodriguez N, Noah YS, Marantz PR. Implicit bias recognition and management in interpersonal encounters and the learning environment: a skills-based curriculum for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2021;17:11168.
Hoffman KM, Trawalter S, Axt JR, Oliver MN. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(16):4296–301.
Mayfield JJ, Ball EM, Tillery KA, Crandall C, Dexter J, Winer JM, Bosshardt ZM, Welch JH, Dolan E, Fancovic ER, et al. Beyond men, women, or both: a comprehensive, LGBTQ-inclusive, implicit-bias-aware, standardized-patient-based sexual history taking curriculum. MedEdPORTAL. 2017;13:10634.
Morris M, Cooper RL, Ramesh A, Tabatabai M, Arcury TA, Shinn M, Im W, Juarez P, Matthews-Juarez P. Training to reduce LGBTQ-related bias among medical, nursing, and dental students and providers: a systematic review. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):325.
Perdomo J, Tolliver D, Hsu H, He Y, Nash KA, Donatelli S, Mateo C, Akagbosu C, Alizadeh F, Power-Hays A, et al. Health equity rounds: an interdisciplinary case conference to address implicit bias and structural racism for faculty and trainees. MedEdPORTAL. 2019;15:10858.
Sherman MD, Ricco J, Nelson SC, Nezhad SJ, Prasad S. Implicit bias training in a residency program: aiming for enduring effects. Fam Med. 2019;51(8):677–81.
van Ryn M, Hardeman R, Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Dovidio JF, Herrin J, Burke SE, Nelson DB, Perry S, Yeazel M, et al. Medical school experiences associated with change in implicit racial bias among 3547 students: a medical student CHANGES study report. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(12):1748–56.
Chary AN, Molina MF, Dadabhoy FZ, Manchanda EC. Addressing racism in medicine through a resident-led health equity retreat. West J Emerg Med. 2020;22(1):41–4.
DallaPiazza M, Padilla-Register M, Dwarakanath M, Obamedo E, Hill J, Soto-Greene ML. Exploring racism and health: an intensive interactive session for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10783.
Dennis SN, Gold RS, Wen FK. Learner reactions to activities exploring racism as a social determinant of health. Fam Med. 2019;51(1):41–7.
Gonzalez CM, Walker SA, Rodriguez N, Karp E, Marantz PR. It can be done! a skills-based elective in implicit bias recognition and management for preclinical medical students. Acad Med. 2020;95(12S Addressing Harmful Bias and Eliminating Discrimination in Health Professions Learning Environments):S150–5.
Motzkus C, Wells RJ, Wang X, Chimienti S, Plummer D, Sabin J, Allison J, Cashman S. Pre-clinical medical student reflections on implicit bias: Implications for learning and teaching. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(11):e0225058.
Phelan SM, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Perry SP, Hardeman RR, Dovidio JF, Herrin J, Dyrbye LN, White RO, Yeazel MW, et al. The effects of racism in medical education on students’ decisions to practice in underserved or minority communities. Acad Med. 2019;94(8):1178–89.
Zeidan A, Tiballi A, Woodward M, Di Bartolo IM. Targeting implicit bias in medicine: lessons from art and archaeology. West J Emerg Med. 2019;21(1):1–3.
Baker TK, Smith GS, Jacobs NN, Houmanfar R, Tolles R, Kuhls D, Piasecki M. A deeper look at implicit weight bias in medical students. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2017;22(4):889–900.
Eymard AS, Douglas DH. Ageism among health care providers and interventions to improve their attitudes toward older adults: an integrative review. J Gerontol Nurs. 2012;38(5):26–35.
Garrison CB, McKinney-Whitson V, Johnston B, Munroe A. Race matters: addressing racism as a health issue. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2018;53(5–6):436–44.
Geller G, Watkins PA. Addressing medical students’ negative bias toward patients with obesity through ethics education. AMA J Ethics. 2018;20(10):E948-959.
Onyeador IN, Wittlin NM, Burke SE, Dovidio JF, Perry SP, Hardeman RR, Dyrbye LN, Herrin J, Phelan SM, van Ryn M. The value of interracial contact for reducing anti-black bias among non-black physicians: a Cognitive Habits and Growth Evaluation (CHANGE) study report. Psychol Sci. 2020;31(1):18–30.
Poustchi Y, Saks NS, Piasecki AK, Hahn KA, Ferrante JM. Brief intervention effective in reducing weight bias in medical students. Fam Med. 2013;45(5):345–8.
Ruiz JG, Andrade AD, Anam R, Taldone S, Karanam C, Hogue C, Mintzer MJ. Group-based differences in anti-aging bias among medical students. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2015;36(1):58–78.
Simpson T, Evans J, Goepfert A, Elopre L. Implementing a graduate medical education anti-racism workshop at an academic university in the Southern USA. Med Educ Online. 2022;27(1):1981803.
Wittlin NM, Dovidio JF, Burke SE, Przedworski JM, Herrin J, Dyrbye L, Onyeador IN, Phelan SM, van Ryn M. Contact and role modeling predict bias against lesbian and gay individuals among early-career physicians: a longitudinal study. Soc Sci Med. 2019;238:112422.
Miller DP Jr, Spangler JG, Vitolins MZ, Davis SW, Ip EH, Marion GS, Crandall SJ. Are medical students aware of their anti-obesity bias? Acad Med. 2013;88(7):978–82.
Gonzalez CM, Deno ML, Kintzer E, Marantz PR, Lypson ML, McKee MD. A qualitative study of New York medical student views on implicit bias instruction: implications for curriculum development. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(5):692–8.
Gonzalez CM, Kim MY, Marantz PR. Implicit bias and its relation to health disparities: a teaching program and survey of medical students. Teach Learn Med. 2014;26(1):64–71.
Gonzalez CM, Nava S, List J, Liguori A, Marantz PR. How assumptions and preferences can affect patient care: an introduction to implicit bias for first-year medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2021;17:11162.
Hernandez RA, Haidet P, Gill AC, Teal CR. Fostering students’ reflection about bias in healthcare: cognitive dissonance and the role of personal and normative standards. Med Teach. 2013;35(4):e1082-1089.
Kushner RF, Zeiss DM, Feinglass JM, Yelen M. An obesity educational intervention for medical students addressing weight bias and communication skills using standardized patients. BMC Med Educ. 2014;14:53.
Nazione S, Silk KJ. Patient race and perceived illness responsibility: effects on provider helping and bias. Med Educ. 2013;47(8):780–9.
Ogunyemi D. Defeating unconscious bias: the role of a structured, reflective, and interactive workshop. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13(2):189–94.
Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, White RO, Przedworski J, Dovidio JF, Perry SP, Plankey M, A Cunningham B, Finstad D, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32(11):1193–201.
Phelan SM, Puhl RM, Burke SE, Hardeman R, Dovidio JF, Nelson DB, Przedworski J, Burgess DJ, Perry S, Yeazel MW, et al. The mixed impact of medical school on medical students’ implicit and explicit weight bias. Med Educ. 2015;49(10):983–92.
Barber Doucet H, Ward VL, Johnson TJ, Lee LK. Implicit bias and caring for diverse populations: pediatric trainee attitudes and gaps in training. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2021;60(9–10):408–17.
Burke SE, Dovidio JF, Przedworski JM, Hardeman RR, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Nelson DB, Burgess DJ, Yeazel MW, van Ryn M. Do contact and empathy mitigate bias against gay and lesbian people among heterosexual first-year medical students? A report from the medical student CHANGE study. Acad Med. 2015;90(5):645–51.
Johnston B, McKinney-Whitson V, Garrison V. Race matters: addressing racism as a health issue. WMJ. 2021;120(S1):S74–7.
Kost A, Akande T, Jones R, Gabert R, Isaac M, Dettmar NS. Use of patient identifiers at the University of Washington School of Medicine: building institutional consensus to reduce bias and stigma. Fam Med. 2021;53(5):366–71.
Madan AK, Aliabadi-Wahle S, Beech DJ. Ageism in medical students’ treatment recommendations: the example of breast-conserving procedures. Acad Med. 2001;76(3):282–4.
Marbin J, Lewis L, Kuo AK, Schudel C, Gutierrez JR. The power of place: travel to explore structural racism and health disparities. Acad Med. 2021;96(11):1569–73.
Phelan SM, Dovidio JF, Puhl RM, Burgess DJ, Nelson DB, Yeazel MW, Hardeman R, Perry S, van Ryn M. Implicit and explicit weight bias in a national sample of 4,732 medical students: the medical student CHANGES study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22(4):1201–8.
Van J, Aloman C, Reau N. Potential bias and misconceptions in liver transplantation for alcohol- and obesity-related liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(10):2089–97.
White-Means S, Zhiyong D, Hufstader M, Brown LT. Cultural competency, race, and skin tone bias among pharmacy, nursing, and medical students: implications for addressing health disparities. Med Care Res Rev. 2009;66(4):436–55.
Williams RL, Vasquez CE, Getrich CM, Kano M, Boursaw B, Krabbenhoft C, Sussman AL. Racial/gender biases in student clinical decision-making: a mixed-method study of medical school attributes associated with lower incidence of biases. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33(12):2056–64.
Cohen RW, Persky S. Influence of weight etiology information and trainee characteristics on physician-trainees’ clinical and interpersonal communication. Patient Educ Couns. 2019;102(9):1644–9.
Haider AH, Sexton J, Sriram N, Cooper LA, Efron DT, Swoboda S, Villegas CV, Haut ER, Bonds M, Pronovost PJ, et al. Association of unconscious race and social class bias with vignette-based clinical assessments by medical students. JAMA. 2011;306(9):942–51.
Lewis R, Lamdan RM, Wald D, Curtis M. Gender bias in the diagnosis of a geriatric standardized patient: a potential confounding variable. Acad Psychiatry. 2006;30(5):392–6.
Matharu K, Shapiro JF, Hammer RR, Kravitz RL, Wilson MD, Fitzgerald FT. Reducing obesity prejudice in medical education. Educ Health. 2014;27(3):231–7.
McLean ME, McLean LE, McLean-Holden AC, Campbell LF, Horner AM, Kulkarni ML, Melville LD, Fernandez EA. Interphysician weight bias: a cross-sectional observational survey study to guide implicit bias training in the medical workplace. Acad Emerg Med. 2021;28(9):1024–34.
Meadows A, Higgs S, Burke SE, Dovidio JF, van Ryn M, Phelan SM. Social dominance orientation, dispositional empathy, and need for cognitive closure moderate the impact of empathy-skills training, but not patient contact, on medical students’ negative attitudes toward higher-weight patients. Front Psychol. 2017;8:15.
Stone J, Moskowitz GB, Zestcott CA, Wolsiefer KJ. Testing active learning workshops for reducing implicit stereotyping of Hispanics by majority and minority group medical students. Stigma Health. 2020;5(1):94–103.
Symons AB, Morley CP, McGuigan D, Akl EA. A curriculum on care for people with disabilities: effects on medical student self-reported attitudes and comfort level. Disabil Health J. 2014;7(1):88–95.
Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Hasley P, Jeong K, Rubio D, Spagnoletti C. Comprehensive internal medicine residency curriculum on primary care of patients who identify as LGBT. LGBT Health. 2018;5(6):375–80.
Aultman JM, Borges NJ. A clinical and ethical investigation of pre-medical and medical students’ attitudes, knowledge, and understanding of HIV. Med Educ Online. 2006;11:1–12.
Bates T, Cohan M, Bragg DS, Bedinghaus J. The Medical College of Wisconsin senior mentor program: experience of a lifetime. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):93–103.
Chiaramonte GR, Friend R. Medical students’ and residents’ gender bias in the diagnosis, treatment, and interpretation of coronary heart disease symptoms. Health Psychol. 2006;25(3):255–66.
Friedberg F, Sohl SJ, Halperin PJ. Teaching medical students about medically unexplained illnesses: a preliminary study. Med Teach. 2008;30(6):618–21.
Gonzales E, Morrow-Howell N, Gilbert P. Changing medical students’ attitudes toward older adults. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2010;31(3):220–34.
Hinners CK, Potter JF. A partnership between the University of Nebraska College of Medicine and the community: fostering positive attitudes towards the aged. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):83–91.
Lee M, Coulehan JL. Medical students’ perceptions of racial diversity and gender equality. Med Educ. 2006;40(7):691–6.
Schmetzer AD, Lafuze JE. Overcoming stigma: involving families in medical student and psychiatric residency education. Acad Psychiatry. 2008;32(2):127–31.
Willen SS, Bullon A, Good MJD. Opening up a huge can of worms: reflections on a “cultural sensitivity” course for psychiatry residents. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2010;18(4):247–53.
Dogra N, Karnik N. First-year medical students’ attitudes toward diversity and its teaching: an investigation at one U.S. medical school. Acad Med. 2003;78(11):1191–200.
Fitzpatrick C, Musser A, Mosqueda L, Boker J, Prislin M. Student senior partnership program: University of California Irvine School of Medicine. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):25–35.
Hoffman KG, Gray P, Hosokawa MC, Zweig SC. Evaluating the effectiveness of a senior mentor program: the University of Missouri-Columbia School of Medicine. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):37–47.
Kantor BS, Myers MR. From aging…to saging-the Ohio State Senior Partners Program: longitudinal and experiential geriatrics education. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):69–74.
Klamen DL, Grossman LS, Kopacz DR. Medical student homophobia. J Homosex. 1999;37(1):53–63.
Kopacz DR, Grossman LS, Klamen DL. Medical students and AIDS: knowledge, attitudes and implications for education. Health Educ Res. 1999;14(1):1–6.
Leiblum SR. An established medical school human sexuality curriculum: description and evaluation. Sex Relatsh Ther. 2001;16(1):59–70.
Rastegar DA, Fingerhood MI, Jasinski DR. A resident clerkship that combines inpatient and outpatient training in substance abuse and HIV care. Subst Abuse. 2004;25(4):11–5.
Roberts E, Richeson NA, Thornhill JTIV, Corwin SJ, Eleazer GP. The senior mentor program at the University of South Carolina School of Medicine: an innovative geriatric longitudinal curriculum. Gerontol Geriatr Educ. 2006;27(2):11–23.
Burgess DJ, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Dovidio JF, Hardeman RR, Hou YF, Nelson DB, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Yeazel MW, et al. Medical students’ learning orientation regarding interracial interactions affects preparedness to care for minority patients: a report from medical student CHANGES. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:254.
Burgess DJ, Hardeman RR, Burke SE, Cunningham BA, Dovidio JF, Nelson DB, Perry SP, Phelan SM, Yeazel MW, Herrin J, et al. Incoming medical students’ political orientation affects outcomes related to care of marginalized groups: results from the medical student CHANGES study. J Health Pol Policy Law. 2019;44(1):113–46.
Kurtz ME, Johnson SM, Tomlinson T, Fiel NJ. Teaching medical students the effects of values and stereotyping on the doctor/patient relationship. Soc Sci Med. 1985;21(9):1043–7.
Matharu K, Kravitz RL, McMahon GT, Wilson MD, Fitzgerald FT. Medical students’ attitudes toward gay men. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:71.
Pearl RL, Argueso D, Wadden TA. Effects of medical trainees’ weight-loss history on perceptions of patients with obesity. Med Educ. 2017;51(8):802–11.
Perry SP, Dovidio JF, Murphy MC, van Ryn M. The joint effect of bias awareness and self-reported prejudice on intergroup anxiety and intentions for intergroup contact. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2015;21(1):89–96.
Phelan SM, Burgess DJ, Burke SE, Przedworski JM, Dovidio JF, Hardeman R, Morris M, van Ryn M. Beliefs about the causes of obesity in a national sample of 4th year medical students. Patient Educ Couns. 2015;98(11):1446–9.
Phelan SM, Puhl RM, Burgess DJ, Natt N, Mundi M, Miller NE, Saha S, Fischer K, van Ryn M. The role of weight bias and role-modeling in medical students’ patient-centered communication with higher weight standardized patients. Patient Educ Couns. 2021;104(8):1962–9.
Polan HJ, Auerbach MI, Viederman M. AIDS as a paradigm of human behavior in disease: impact and implications of a course. Acad Psychiatry. 1990;14(4):197–203.
Reuben DB, Fullerton JT, Tschann JM, Croughan-Minihane M. Attitudes of beginning medical students toward older persons: a five-campus study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1995;43(12):1430–6.
Tsai J. Building structural empathy to marshal critical education into compassionate practice: evaluation of a medical school critical race theory course. J Law Med Ethics. 2021;49(2):211–21.
Weyant RJ, Bennett ME, Simon M, Palaisa J. Desire to treat HIV-infected patients: similarities and differences across health-care professions. AIDS. 1994;8(1):117–21.
Ross PT, Lypson ML. Using artistic-narrative to stimulate reflection on physician bias. Teach Learn Med. 2014;26(4):344–9.
Calabrese SK, Earnshaw VA, Krakower DS, Underhill K, Vincent W, Magnus M, Hansen NB, Kershaw TS, Mayer KH, Betancourt JR, et al. A closer look at racism and heterosexism in medical students’ clinical decision-making related to HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): implications for PrEP education. AIDS Behav. 2018;22(4):1122–38.
Fitterman-Harris HF, Vander Wal JS. Weight bias reduction among first-year medical students: a quasi-randomized, controlled trial. Clin Obes. 2021;11(6):e12479.
Madan AK, Cooper L, Gratzer A, Beech DJ. Ageism in breast cancer surgical options by medical students. Tenn Med. 2006;99(5):37–8, 41.
Bikmukhametov DA, Anokhin VA, Vinogradova AN, Triner WR, McNutt LA. Bias in medicine: a survey of medical student attitudes towards HIV-positive and marginalized patients in Russia, 2010. J Int AIDS Soc. 2012;15(2):17372.
Dijkstra AF, Verdonk P, Lagro-Janssen AL. Gender bias in medical textbooks: examples from coronary heart disease, depression, alcohol abuse and pharmacology. Med Educ. 2008;42(10):1021–8.
Dobrowolska B, Jędrzejkiewicz B, Pilewska-Kozak A, Zarzycka D, Ślusarska B, Deluga A, Kościołek A, Palese A. Age discrimination in healthcare institutions perceived by seniors and students. Nurs Ethics. 2019;26(2):443–59.
Hamberg K, Risberg G, Johansson EE, Westman G. Gender bias in physicians’ management of neck pain: a study of the answers in a Swedish national examination. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2002;11(7):653–66.
Magliano L, Read J, Sagliocchi A, Oliviero N, D’Ambrosio A, Campitiello F, Zaccaro A, Guizzaro L, Patalano M. “Social dangerousness and incurability in schizophrenia”: results of an educational intervention for medical and psychology students. Psychiatry Res. 2014;219(3):457–63.
Reis SP, Wald HS. Contemplating medicine during the Third Reich: scaffolding professional identity formation for medical students. Acad Med. 2015;90(6):770–3.
Schroyen S, Adam S, Marquet M, Jerusalem G, Thiel S, Giraudet AL, Missotten P. Communication of healthcare professionals: Is there ageism? Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2018;27(1):e12780.
Swift JA, Hanlon S, El-Redy L, Puhl RM, Glazebrook C. Weight bias among UK trainee dietitians, doctors, nurses and nutritionists. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2013;26(4):395–402.
Swift JA, Tischler V, Markham S, Gunning I, Glazebrook C, Beer C, Puhl R. Are anti-stigma films a useful strategy for reducing weight bias among trainee healthcare professionals? Results of a pilot randomized control trial. Obes Facts. 2013;6(1):91–102.
Yertutanol FDK, Candansayar S, Seydaoğlu G. Homophobia in health professionals in Ankara, Turkey: developing a scale. Transcult Psychiatry. 2019;56(6):1191–217.
Arnold O, Voracek M, Musalek M, Springer-Kremser M. Austrian medical students’ attitudes towards male and female homosexuality: a comparative survey. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2004;116(21–22):730–6.
Arvaniti A, Samakouri M, Kalamara E, Bochtsou V, Bikos C, Livaditis M. Health service staff’s attitudes towards patients with mental illness. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2009;44(8):658–65.
Lopes L, Gato J, Esteves M. Portuguese medical students’ knowledge and attitudes towards homosexuality. Acta Med Port. 2016;29(11):684–93.
Papadaki V, Plotnikof K, Gioumidou M, Zisimou V, Papadaki E. A comparison of attitudes toward lesbians and gay men among students of helping professions in Crete, Greece: the cases of social work, psychology, medicine, and nursing. J Homosex. 2015;62(6):735–62.
Papaharitou S, Nakopoulou E, Moraitou M, Tsimtsiou Z, Konstantinidou E, Hatzichristou D. Exploring sexual attitudes of students in health professions. J Sex Med. 2008;5(6):1308–16.
Roberts JH, Sanders T, Mann K, Wass V. Institutional marginalisation and student resistance: barriers to learning about culture, race and ethnicity. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2010;15(4):559–71.
Wilhelmi L, Ingendae F, Steinhaeuser J. What leads to the subjective perception of a ‘rural area’? A qualitative study with undergraduate students and postgraduate trainees in Germany to tailor strategies against physician’s shortage. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18(4):4694.
Herrmann-Werner A, Loda T, Wiesner LM, Erschens RS, Junne F, Zipfel S. Is an obesity simulation suit in an undergraduate medical communication class a valuable teaching tool? A cross-sectional proof of concept study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e029738.
Ahadinezhad B, Khosravizadeh O, Maleki A, Hashtroodi A. Implicit racial bias among medical graduates and students by an IAT measure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ir J Med Sci. 2022;191(4):1941–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-021-02756-3 .
Hsieh JG, Hsu M, Wang YW. An anthropological approach to teach and evaluate cultural competence in medical students - the application of mini-ethnography in medical history taking. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:32561.
Poreddi V, Thimmaiah R, Math SB. Attitudes toward people with mental illness among medical students. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015;6(3):349–54.
Mino Y, Yasuda N, Tsuda T, Shimodera S. Effects of a one-hour educational program on medical students’ attitudes to mental illness. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;55(5):501–7.
Omori A, Tateno A, Ideno T, Takahashi H, Kawashima Y, Takemura K, Okubo Y. Influence of contact with schizophrenia on implicit attitudes towards schizophrenia patients held by clinical residents. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:8.
Banwari G, Mistry K, Soni A, Parikh N, Gandhi H. Medical students and interns’ knowledge about and attitude towards homosexuality. J Postgrad Med. 2015;61(2):95–100.
Lee SY. Obesity education in medical school curricula in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2018;27(1):35–8.
Aruna G, Mittal S, Yadiyal MB, Acharya C, Acharya S, Uppulari C. Perception, knowledge, and attitude toward mental disorders and psychiatry among medical undergraduates in Karnataka: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Psychiatry. 2016;58(1):70–6.
Wong YL. Review paper: gender competencies in the medical curriculum: addressing gender bias in medicine. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2009;21(4):359–76.
Earnshaw VA, Jin H, Wickersham JA, Kamarulzaman A, John J, Lim SH, Altice FL. Stigma toward men who have sex with men among future healthcare providers in Malaysia: would more interpersonal contact reduce prejudice? AIDS Behav. 2016;20(1):98–106.
Larson B, Herx L, Williamson T, Crowshoe L. Beyond the barriers: family medicine residents’ attitudes towards providing Aboriginal health care. Med Educ. 2011;45(4):400–6.
Wagner AC, Girard T, McShane KE, Margolese S, Hart TA. HIV-related stigma and overlapping stigmas towards people living with HIV among health care trainees in Canada. AIDS Educ Prev. 2017;29(4):364–76.
Tellier P-P, Bélanger E, Rodríguez C, Ware MA, Posel N. Improving undergraduate medical education about pain assessment and management: a qualitative descriptive study of stakeholders’ perceptions. Pain Res Manage. 2013;18(5):259–65.
Loignon C, Boudreault-Fournier A, Truchon K, Labrousse Y, Fortin B. Medical residents reflect on their prejudices toward poverty: a photovoice training project. BMC Med Educ. 2014;14:1050.
Phillips SP, Clarke M. More than an education: the hidden curriculum, professional attitudes and career choice. Med Educ. 2012;46(9):887–93.
Jaworsky D, Gardner S, Thorne JG, Sharma M, McNaughton N, Paddock S, Chew D, Lees R, Makuwaza T, Wagner A, et al. The role of people living with HIV as patient instructors—Reducing stigma and improving interest around HIV care among medical students. AIDS Care. 2017;29(4):524–31.
Sukhera J, Wodzinski M, Teunissen PW, Lingard L, Watling C. Striving while accepting: exploring the relationship between identity and implicit bias recognition and management. Acad Med. 2018;93(11S Association of American Medical Colleges Learn Serve Lead: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Research in Medical Education Sessions):S82-s88.
Harris R, Cormack D, Curtis E, Jones R, Stanley J, Lacey C. Development and testing of study tools and methods to examine ethnic bias and clinical decision-making among medical students in New Zealand: the Bias and Decision-Making in Medicine (BDMM) study. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:173.
Cormack D, Harris R, Stanley J, Lacey C, Jones R, Curtis E. Ethnic bias amongst medical students in Aotearoa/New Zealand: findings from the Bias and Decision Making in Medicine (BDMM) study. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(8):e0201168.
Harris R, Cormack D, Stanley J, Curtis E, Jones R, Lacey C. Ethnic bias and clinical decision-making among New Zealand medical students: an observational study. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):18.
Robinson EL, Ball LE, Leveritt MD. Obesity bias among health and non-health students attending an Australian university and their perceived obesity education. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2014;46(5):390–5.
Sopoaga F, Zaharic T, Kokaua J, Covello S. Training a medical workforce to meet the needs of diverse minority communities. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17:19.
Parker R, Larkin T, Cockburn J. A visual analysis of gender bias in contemporary anatomy textbooks. Soc Sci Med. 2017;180:106–13.
Gomes MdM. Doctors’ perspectives and practices regarding epilepsy. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2000;58(2):221–6.
Caixeta J, Fernandes PT, Bell GS, Sander JW, Li LM. Epilepsy perception amongst university students - A survey. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;65:43–8.
Tedrus GMAS, Fonseca LC, da Câmara Vieira AL. Knowledge and attitudes toward epilepsy amongst students in the health area: intervention aimed at enlightenment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;65(4-B):1181–5.
Gomez-Moreno C, Verduzco-Aguirre H, Contreras-Garduño S, Perez-de-Acha A, Alcalde-Castro J, Chavarri-Guerra Y, García-Lara JMA, Navarrete-Reyes AP, Avila-Funes JA, Soto-Perez-de-Celis E. Perceptions of aging and ageism among Mexican physicians-in-training. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019;21(12):1730–5.
Campbell MH, Gromer J, Emmanuel MK, Harvey A. Attitudes Toward Transgender People Among Future Caribbean Doctors. Arch Sex Behav. 2022;51(4):1903-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-021-02205-3 .
Hatala R, Case SM. Examining the influence of gender on medical students’ decision making. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2000;9(6):617–23.
Deb T, Lempp H, Bakolis I, et al. Responding to experienced and anticipated discrimination (READ): anti -stigma training for medical students towards patients with mental illness – study protocol for an international multisite non-randomised controlled study. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1472-7 .
Morgan S, Plaisant O, Lignier B, Moxham BJ. Sexism and anatomy, as discerned in textbooks and as perceived by medical students at Cardiff University and University of Paris Descartes. J Anat. 2014;224(3):352–65.
Alford CL, Miles T, Palmer R, Espino D. An introduction to geriatrics for first-year medical students. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49(6):782–7.
Stone J, Moskowitz GB. Non-conscious bias in medical decision making: what can be done to reduce it? Med Educ. 2011;45(8):768–76.
Nazione S. Slimming down medical provider weight bias in an obese nation. Med Educ. 2015;49(10):954–5.
Dogra N, Connin S, Gill P, Spencer J, Turner M. Teaching of cultural diversity in medical schools in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland: cross sectional questionnaire survey. BMJ. 2005;330(7488):403–4.
Aultman JM, Borges NJ. A clinical and ethical investigation of pre-medical and medical students’ attitudes, knowledge, and understanding of HIV. Med Educ Online. 2006;11(1):4596.
Deb T, Lempp H, Bakolis I, Vince T, Waugh W, Henderson C, Thornicroft G, Ando S, Yamaguchi S, Matsunaga A, et al. Responding to experienced and anticipated discrimination (READ): anti -stigma training for medical students towards patients with mental illness – study protocol for an international multisite non-randomised controlled study. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):41.
Gonzalez CM, Grochowalski JH, Garba RJ, Bonner S, Marantz PR. Validity evidence for a novel instrument assessing medical student attitudes toward instruction in implicit bias recognition and management. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):205.
Ogunyemi D. A practical approach to implicit bias training. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13(4):583–4.
Dennis GC. Racism in medicine: planning for the future. J Natl Med Assoc. 2001;93(3 Suppl):1S-5S.
Maina IW, Belton TD, Ginzberg S, Singh A, Johnson TJ. A decade of studying implicit racial/ethnic bias in healthcare providers using the implicit association test. Soc Sci Med. 2018;199:219–29.
Blair IV, Steiner JF, Hanratty R, Price DW, Fairclough DL, Daugherty SL, Bronsert M, Magid DJ, Havranek EP. An investigation of associations between clinicians’ ethnic or racial bias and hypertension treatment, medication adherence and blood pressure control. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(7):987–95.
Stanford FC. The importance of diversity and inclusion in the healthcare workforce. J Natl Med Assoc. 2020;112(3):247–9.
Education LCoM. Standards on diversity. 2009. https://health.usf.edu/~/media/Files/Medicine/MD%20Program/Diversity/LCMEStandardsonDiversity1.ashx?la=en .
Onyeador IN, Hudson STJ, Lewis NA. Moving beyond implicit bias training: policy insights for increasing organizational diversity. Policy Insights Behav Brain Sci. 2021;8(1):19–26.
Forscher PS, Mitamura C, Dix EL, Cox WTL, Devine PG. Breaking the prejudice habit: mechanisms, timecourse, and longevity. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2017;72:133–46.
Lai CK, Skinner AL, Cooley E, Murrar S, Brauer M, Devos T, Calanchini J, Xiao YJ, Pedram C, Marshburn CK, et al. Reducing implicit racial preferences: II. Intervention effectiveness across time. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016;145(8):1001–16.
Sukhera J, Watling CJ, Gonzalez CM. Implicit bias in health professions: from recognition to transformation. Acad Med. 2020;95(5):717–23.
Vuletich HA, Payne BK. Stability and change in implicit bias. Psychol Sci. 2019;30(6):854–62.
Tversky A, Kahneman D. Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science. 1974;185(4157):1124–31.
Miller DT, Ross M. Self-serving biases in the attribution of causality: fact or fiction? Psychol Bull. 1975;82(2):213–25.
Nickerson RS. Confirmation bias: a ubiquitous phenomenon in many guises. Rev Gen Psychol. 1998;2(2):175–220.
Suveren Y. Unconscious bias: definition and significance. Psikiyatride Guncel Yaklasimlar. 2022;14(3):414–26.
Dietrich D, Olson M. A demonstration of hindsight bias using the Thomas confirmation vote. Psychol Rep. 1993;72(2):377–8.
Green AR, Carney DR, Pallin DJ, Ngo LH, Raymond KL, Iezzoni LI, Banaji MR. Implicit bias among physicians and its prediction of thrombolysis decisions for black and white patients. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(9):1231–8.
Rushmer R, Davies HT. Unlearning in health care. Qual Saf Health Care. 2004;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii10-15.
Vu MT, Pham TTT. Gender, critical pedagogy, and textbooks: Understanding teachers’ (lack of) mediation of the hidden curriculum in the EFL classroom. Lang Teach Res. 2022;0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688221136937 .
Kalantari A, Alvarez A, Battaglioli N, Chung A, Cooney R, Boehmer SJ, Nwabueze A, Gottlieb M. Sex and race visual representation in emergency medicine textbooks and the hidden curriculum. AEM Educ Train. 2022;6(3):e10743.
Satya-Murti S, Lockhart J. Recognizing and reducing cognitive bias in clinical and forensic neurology. Neurol Clin Pract. 2015;5(5):389–96.
Chang EH, Milkman KL, Gromet DM, Rebele RW, Massey C, Duckworth AL, Grant AM. The mixed effects of online diversity training. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(16):7778–83.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Misa Mi, Professor and Medical Librarian at the Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine (OWUB) for her assistance with selection of databases and construction of literature search strategies for the scoping review. The authors also wish to thank Dr. Changiz Mohiyeddini, Professor in Behavioral Medicine and Psychopathology at Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine (OUWB) for his expertise and constructive feedback on our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Foundational Sciences, Central Michigan University College of Medicine, Mt. Pleasant, MI, 48859, USA
Brianne E. Lewis
Department of Foundational Medical Studies, Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, 586 Pioneer Dr, Rochester, MI, 48309, USA
Akshata R. Naik
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.R.N and B.E.L were equally involved in study conception, design, collecting data and analyzing the data. B.E.L and A.R.N both contributed towards writing the manuscript. A.R.N and B.E.L are both senior authors on this paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Akshata R. Naik .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lewis, B.E., Naik, A.R. A scoping review to identify and organize literature trends of bias research within medical student and resident education. BMC Med Educ 23 , 919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04829-6
Download citation
Received : 14 March 2023
Accepted : 01 November 2023
Published : 05 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-023-04829-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Preclinical curriculum
- Evidence of bis
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 10 January 2024
A scoping review of theories, models and frameworks used or proposed to evaluate knowledge mobilization strategies
- Saliha Ziam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8892-9572 1 ,
- Sèverine Lanoue 2 ,
- Esther McSween-Cadieux 2 ,
- Mathieu-Joël Gervais 3 ,
- Julie Lane 2 , 4 ,
- Dina Gaid 5 ,
- Laura Justine Chouinard 1 ,
- Christian Dagenais 6 ,
- Valéry Ridde 7 , 8 ,
- Emmanuelle Jean 9 ,
- France Charles Fleury 10 ,
- Quan Nha Hong 5 &
- Ollivier Prigent 2
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 8 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2338 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
Evaluating knowledge mobilization strategies (KMb) presents challenges for organizations seeking to understand their impact to improve KMb effectiveness. Moreover, the large number of theories, models, and frameworks (TMFs) available can be confusing for users. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to identify and describe the characteristics of TMFs that have been used or proposed in the literature to evaluate KMb strategies.
A scoping review methodology was used. Articles were identified through searches in electronic databases, previous reviews and reference lists of included articles. Titles, abstracts and full texts were screened in duplicate. Data were charted using a piloted data charting form. Data extracted included study characteristics, KMb characteristics, and TMFs used or proposed for KMb evaluation. An adapted version of Nilsen (Implement Sci 10:53, 2015) taxonomy and the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) taxonomy (Powell et al. in Implement Sci 10:21, 2015) guided data synthesis.
Of the 4763 search results, 505 were retrieved, and 88 articles were eligible for review. These consisted of 40 theoretical articles (45.5%), 44 empirical studies (50.0%) and four protocols (4.5%). The majority were published after 2010 ( n = 70, 79.5%) and were health related ( n = 71, 80.7%). Half of the studied KMb strategies were implemented in only four countries: Canada, Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom ( n = 42, 47.7%). One-third used existing TMFs ( n = 28, 31.8%). According to the adapted Nilsen taxonomy, process models ( n = 34, 38.6%) and evaluation frameworks ( n = 28, 31.8%) were the two most frequent types of TMFs used or proposed to evaluate KMb. According to the ERIC taxonomy, activities to “train and educate stakeholders” ( n = 46, 52.3%) were the most common, followed by activities to “develop stakeholder interrelationships” ( n = 23, 26.1%). Analysis of the TMFs identified revealed relevant factors of interest for the evaluation of KMb strategies, classified into four dimensions: context, process, effects and impacts.
Conclusions
This scoping review provides an overview of the many KMb TMFs used or proposed. The results provide insight into potential dimensions and components to be considered when assessing KMb strategies.
Peer Review reports
Contribution to the literature
The evaluation of KMb strategies is a critical dimension of the KMb process that is still poorly documented and warrants researchers’ attention.
Our review identified the most common theories, models and frameworks (TMFs) proposed or used to assess KMb strategies and the main components to consider when evaluating a KMb strategy.
By developing an integrative reference framework, this work contributes to improving organizations’ capacity to evaluate their KMb initiatives.
It is widely recognized that research evidence has the potential to inform, guide, and improve practices, decisions, and policies [ 1 ]. Unfortunately, for diverse reasons, the best available evidence is still too seldom taken into account and used [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The field of research on knowledge mobilization (KMb) has been growing rapidly since the early 2000s [ 2 , 3 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Its purpose is to better understand how to effectively promote and support evidence use.
Knowledge mobilization is one of many terms and concepts developed over recent decades to describe processes, strategies, and actions to bridge the gap between research and practice. Other common terms often paired interchangeably with the term “knowledge” are “translation”, “transfer”, “exchange”, “sharing” and “dissemination”, among others. [ 12 , 13 ]. Some are more closely linked than others to specific fields or jurisdictions. For this study, we adopted the term knowledge mobilization (KMb) because it conveys the notions of complexity and multidirectional exchanges that characterize research-to-action processes. We used it as an umbrella concept that encompasses the efforts made to translate knowledge into concrete actions and beneficial impacts on populations [ 1 ]. Moreover, the term KMb is also used by research funding agencies in Canada to emphasize the medium- and long-term effects that research knowledge or research results can have on potential users [ 1 , 14 ].
KMb represents all processes from knowledge creation to action and includes all strategies implemented to facilitate these processes [ 14 ]. A KMb strategy is understood as a coordinated set of activities to support evidence use, such as dissemination activities to reach target audiences (for example, educational materials, practical guides, decision support tools) or activities to facilitate knowledge application in a specific context and support professional behaviour change (for example, community of practice, educational meetings, audits and feedback, reminders, deliberative dialogues) [ 15 ]. A KMb process may vary in intensity, complexity or actor engagement depending on the nature of the research knowledge and the needs and preferences of evidence users [ 7 ].
KMb is considered a complex process, in that numerous factors can facilitate or hinder its implementation and subsequent evidence use. The past two decades have seen the emergence of a deeper understanding of these factors [ 2 , 3 , 16 ]. These may be related to the knowledge mobilized (for example, relevance, reliability, clarity, costs), the individuals involved in the KMb process (for example, openness to change, values, time available, resources), the KMB strategies (for example, fit with stakeholder needs and preferences, regular interactions, trust relationships, timing), and organizational and political contexts (for example, culture of evidence use, leadership, resources) [ 2 , 6 , 17 , 18 ]. However, more studies are needed to understand which factors are more important in which contexts, and to evaluate the effects of KMb strategies.
On this last point, while essential, it is often very complex to study KMb impacts empirically to demonstrate the effectiveness of KMb strategies [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. Partly for this reason, high-quality studies that evaluate process, mechanisms and effects of KMb strategies are still relatively rare [ 2 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. As a result, knowledge about the effectiveness of different KMb strategies remains limited [ 10 , 17 , 19 , 23 , 26 , 27 , 28 ] and their development cannot be totally evidence informed [ 3 , 19 , 20 , 23 , 29 , 30 ], which may seem incompatible with the core values and principles of KMb.
The growing interest in KMb has led to an impressive proliferation of conceptual propositions, such as theories, models and frameworks (TMF) [ 2 , 3 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 31 , 32 ]. Many deplore the fact that these are poorly used [ 11 , 30 , 33 ] and insist on the need to test, refine and integrate existing ones [ 3 , 31 , 34 ]. Indeed, the conceptual and theoretical development of the field has outpaced its empirical development. This proliferation appears to have created confusion among certain users, such as organizations that need to evaluate their KMb strategies. Besides implementing and funding KMb strategies, knowledge organizations such as granting agencies, governments and public organizations, universities and health authorities are often required to demonstrate the impact of their strategies [ 21 , 35 , 36 ]. Yet this can be a significant challenge [ 20 , 23 , 29 ]. They may have difficulty knowing which TMFs to choose, in what context and how to use them effectively in their evaluation process [ 12 , 37 ].
Indeed, the evaluation of KMb strategies is still relatively poorly documented, with respect to the phases of their development and implementation. Our aim in this scoping review is to clarify, conceptually and methodologically, this crucial dimension of the KMb process. This would help organizations gain access to evidence-based, operational and easy-to-use evaluation toolkits for assessing the impacts of their KMb strategies.
To survey the available knowledge on evaluation practices for KMb strategies, we conducted a scoping review. According to Munn et al. [ 38 ], a scoping review is indicated to identify the types of available evidence and knowledge gaps, to clarify concepts in the literature and to identify key characteristics or factors related to a concept. This review methodology also allows for the inclusion of a diversity of publications, regardless of their nature or research design, to produce the most comprehensive evidence mapping possible [ 39 ]. The objective of the scoping review was to identify and describe the characteristics of theories, models and frameworks (TMFs) used or proposed to evaluate KMb strategies. The specific research questions were:
What TMFs to evaluate KMb strategies exist in the literature?
What KMb strategies do they evaluate (that is types of KMb objectives, activities, target audiences)?
What dimensions and components are included in these TMFs?
This scoping review was conducted based on the five steps outlined by Arksey and O’Malley [ 39 ]: (1) formulating the research questions; (2) identifying relevant studies; (3) selecting relevant studies; (4) extracting and charting data; and (5) analysing, collating, summarizing and presenting the data. Throughout the process, researchers and knowledge users (KMb practitioners) were involved in decisions regarding the research question, search strategy, selection criteria for studies and categories for data charting. We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 40 ]. No protocol was registered for this review.
Search strategy and information sources
The search strategy was developed, piloted and refined in consultation with our team’s librarian. Search terms included controlled vocabulary and keywords related to three main concepts: (1) knowledge mobilization (for example [knowledge or evidence or research] and transfer, translation, diffusion, dissemination, mobilization, implementation science, exchange, sharing, use, uptake, evidence-based practice, research-based evidence), (2) evaluation (for example, evaluat*, measur*, impact, outcome, assess, apprais*, indicator) and (3) TMF (for example, framework*, model*, method*, guide*, theor*). See Additional file 1 for the search terms and strategies used in the electronic searches.
The following databases were searched from January 2000 to August 2023: MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycInfo (Ovid), ERIC (ProQuest), Sociological Abstracts (ProQuest), Dissertations & Theses (Proquest), Érudit and Cairn. These databases were chosen to identify relevant references in the health, education and social fields. Several search strategies were tested by the librarian to optimize the retrieval of citations known to the investigators and to increase the likelihood that all relevant studies would be retrieved. We also searched reference lists of included articles and previous systematic reviews [ 11 , 12 , 15 , 41 ].
Eligibility criteria
A publication was considered eligible if it (1) presented or used a theory, model, or framework (TMF), (2) described dimensions or specific components to consider in the evaluation of KMb strategies, (3) presented or discussed KMb strategies or activities (any initiatives to improve evidence use), and (4) proposed outcomes that might result directly or indirectly from the KMb strategies. Studies were excluded from analysis if they (1) presented a TMF to assess the impact of research without mentioning KMb strategies or an intervention not related to KMb and (2) presented evaluation dimensions or components that could not be generalized. We considered publications in English or French. All types of articles and study designs were eligible, including study protocols.
Study selection
The results of the literature search were imported into Covidence, which the review team used for screening. After duplicate articles were removed, the titles and abstracts were screened independently by two of the three reviewers (EMC, MJG, GL). Publications identified as potentially relevant were retrieved in full text and screened independently by three reviewers (EMC, MJG, GL). Discrepancies regarding the inclusion of any publication were resolved through discussion and consensus among reviewers. The principal investigator (SZ) validated the final selection of articles.
Data synthesis
A data charting form was developed in Microsoft Excel and piloted by the research team. Data extracted included study characteristics (authors, authors’ country of affiliation, year, journal, discipline, article type, study setting, study aim), KMb strategies of interest, KMb objectives, KMb target audiences and TMFs used or proposed for KMb evaluation (existing or new TMF, specific dimensions or components of TMF and so on). Data were extracted by a single reviewer (SL, JC or OP) and validated by a second reviewer (SZ). Disagreements were discussed between reviewers and resolved by consensus. No quality appraisal of included studies was conducted, as this is optional in scoping reviews and the purpose was only to describe the content of identified TMFs [ 42 ].
Data analysis and presentation of results
Data were summarized according to study characteristics, KMb strategy characteristics (activities, objectives, target audiences), types of TMFs, and dimensions or components to consider for KMb evaluation. Disagreements during the process were discussed and resolved through consensus (SL, DG, SZ). A KMb strategy might have one or more objectives and include one or more activities. Thus, the objectives and activities of the KMb strategies extracted from the selected studies were summarized based on existing categorizations. The categorization of KMb objectives was inspired by Gervais et al. [ 15 ] and Farkas et al. [ 43 ] (Table 1 ).
The KMb activities were categorized according to the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) taxonomy [ 44 ]. The activities were first classified according to the full taxonomy and then grouped into the nine categories proposed by Waltz et al. [ 45 ] (Table 2 ).
The TMFs were categorized according to the categories of theoretical approaches described by Nilsen [ 32 ]: process models, evaluation frameworks, determinant frameworks and classic theories (Table 3 ). The category “implementation theories” originally described by Nilsen [ 32 ] was not used because we did not identify any article that fit this category. We also added a category named “logic models” due to the nature of the identified TMFs. Logic models are often used in theory-driven evaluation approaches and are usually developed to show the links among inputs (resources), activities and outputs (outcomes and short-, medium- and long-term effects) [ 46 ].
Finally, the content extracted from the TMFs was analysed using mainly an inductive method. This method allows, among other things, to develop a reference framework or a model from the emerging categories that are evident in the text data [ 50 ].
The classification of concepts is the result of multiple readings and interpretations. The concepts associated with each dimension of the framework were classified according to their meaning. Similar concepts were grouped together to form components. These grouped components were then associated with the subdimensions and main dimensions of the framework.
Search results
The searches yielded 4763 articles. Of those, 4258 were excluded during the title and abstract screening. Of the 505 full-text articles, we retained 88 in our final sample. The results of the search and selection processes (PRISMA flowchart) are summarized in Fig. 1 .
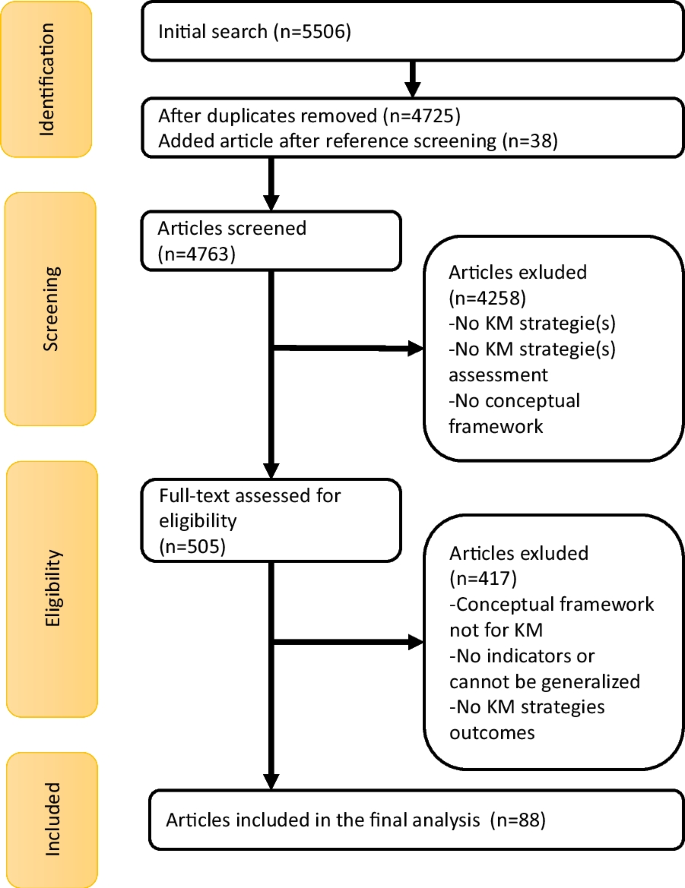
PRISMA flowchart summarizing search strategy and selection results [ 40 ]
Publication characteristics
Most articles were published after 2010 ( n = 70, 79.5%), with an average of 5 articles per year between 2010 and 2023 compared with an average of 2.1 articles per year between 2001 and 2009; there were no eligible articles from 2000. The search was conducted in August 2023, and only five articles were published in these 7 months of the year. Table 4 presents the main characteristics of the selected articles. A full list of the included articles with their main characteristics is presented in Additional file 2 .
The number of theoretical and empirical articles was relatively similar. Among the theoretical articles, 19 descriptive articles (21.6%) were aimed at describing a KMb strategy, a KMb infrastructure or a TMF related to a specific programme or context; 18 articles (20.5%) synthesized knowledge to propose a TMF (new or revised); and three articles conducted systematic reviews (3.4%).
The empirical articles category included studies with different methodological approaches (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods). We will not report the details of the methodologies used, as this would result in a long list with few occurrences. The empirical articles can be divided into three categories: (1) studies that evaluated a TMF related to KMb ( n = 16, 18.2%), (2) studies that evaluated a KMb strategy ( n = 21, 23.9%) and (3) studies that evaluated both a KMb strategy and a TMF ( n = 7, 8.0%).
Most articles were related to healthcare ( n = 71, 80.7%). This field of study was divided into three subdomains. The healthcare and social services articles usually described or assessed a KMb strategy targeting health professionals’ practices in a variety of fields (for example, occupational therapy, dentistry, mental health, pharmacology, gerontology, nursing and so on). The health policy and systems articles usually described or assessed KMb strategies targeting decision-making processes, decision-makers or public health interventions and policies. The continuing education articles assessed training programmes for health professionals aimed at increasing knowledge and skills in a specific field. The articles in the general field described or discussed TMFs and KMb strategies that could be applied to multiple disciplines or contexts. Finally, the articles in the education field described or assessed a KMb strategy targeting education professionals.
Almost half of the articles ( n = 42, 47.7%) studied KMB strategies implemented in only four countries: Canada, Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom. Countries in South America, the Caribbean, Africa, Asia, the Middle East, China and Europe were underrepresented ( n = 8, 9.1%). The remaining 34 articles (38.6%) did not specify an implementation context and were mostly theoretical articles. Regarding the authors’ countries of affiliation, Canada, the United States, Australia and the United Kingdom were again the most represented countries, featuring in 85% of the articles ( n = 75).
What theories, models or frameworks exist in the literature to evaluate KMb strategies?
Several articles proposed a new TMF ( n = 37, 42.0%), and some articles proposed a logic model specifically developed to evaluate their KMb strategy ( n = 17, 19.3%). One-third of the articles used existing TMFs ( n = 28, 31.8%). A few articles only referred to existing TMFs but did not use them to guide a KMb strategy evaluation ( n = 6, 8.5%).
The identified TMFs were then categorized according to their theoretical approaches (adapted from Nilsen, [ 32 ]) (Table 5 ). Five articles used or proposed more than one TMF, and three TMFs could be classified in two categories. Several articles proposed or used a process model ( n = 34, 38.6%) or an evaluation framework ( n = 28, 31.8%); these were the two most frequently identified types of TMFs. Fewer articles proposed or used a logic model ( n = 17, 19.3%), a determinant framework ( n = 12, 13.6%) or a classic theory ( n = 7, 8.0%). The TMFs most often identified in the articles were the RE-AIM framework ( n = 5, 5.7%), the Knowledge-to-Action framework [ 9 ] ( n = 4, 4.5%), the Theory of Planned Behavior [ 51 ] ( n = 3, 3.4%) and the Expanded Outcomes framework for planning and assessing continuing medical education [ 52 ] ( n = 3, 3.4%). In total, we identified 87 different TMFs in the 88 articles. Only nine TMFS were retrieved in more than one article.
What KMb strategies do the TMFs evaluate (activities, objectives, target audience)?
Thirty-eight articles reported using more than one activity in their KMb strategy. According to the ERIC compilation, “Train and educate stakeholders” activities were the most common, followed by “Develop stakeholder interrelationships” and “Use evaluative and iterative strategies”. Table 6 presents the various types of activities and the number of articles that referred to each.
Of the 88 articles analysed, 18 (20.4%) did not specify a KMb objective. The remaining articles proposed one or more KMb strategy objectives. Specifically, 39 (36.4%) articles had one objective, 15 (17.0%) had two, three (3.4%) had three, and 13 (14.8%) had four or five. Table 7 presents the different types of objectives and the number of times they were identified.
The target audiences for KMb strategies were clearly specified in half of the articles ( n = 44, 50.0%). Generally, these were empirical articles that targeted specific professionals ( n = 36, 40.9%) or decision-makers ( n = 8, 9.1%). Just under one-third of the articles identified a broad target audience (for example, professionals and managers in the health system, a health organization) ( n = 26, 29.5%). Finally, 18 articles (20.4%) did not specify a target audience for KMb; these were most often theoretical articles.
What are the dimensions and components included in TMFs for evaluating KMb strategies?
The analysis of the identified TMFs revealed many factors of interest relevant for the evaluation of KMb strategies. These specific components were inductively classified into four main dimensions: context, process, effects and impacts (Fig. 2 ). The context dimension refers to the assessment of the conditions in place when the KMb strategy is implemented. These include both the external (that is, sociopolitical, economic, environmental and cultural characteristics) and internal environments (that is, characteristics of organizations, individuals and stakeholder partnerships). These factors are understood to influence the selection and tailoring of a KMb strategy. The process dimension refers to the assessment of the planning, levels and mechanisms of implementation, as well as to the characteristics of the KMb strategy implemented. The effects dimension refers to the assessment of outcomes following the KMb strategy implementation. The potential effects vary depending on the strategy’s objectives and can be either the immediate results of the KMb strategy or short-, medium- and long-term outcomes. The conceptual gradation of effects was generally represented in a similar way in the TMFs analysed, but the temporality of effects could vary. A medium-term outcome in one study could be understood as a long-term outcome in another. However, the majority of authors group these effects into three categories (Gervais et al. 2016: p. 6): (1) short-term effects, measured by success of KMb strategy measured by success of KMb strategy (number of people reached, satisfaction, participation and so on); (2) medium-term effects linked to changes in individual attitude and the use of knowledge; and (3) the long-term effects that result from achieving the KMb objective (for example, improved practices and services, changed collective behaviour, sustainable use of knowledge).
The main evaluation dimensions that emerged from the TMFs analysed
Finally, the impacts dimension refers to the ultimate effects of KMb products or interventions on end users, as measured by the organization (Phipps et al. [ 36 ], p. 34). The evaluation of these ultimate effects can be measured by the integration of a promising practice into organizational routines, by the effects on service users or by the effects on the health and well-being of communities and society in general.
This gradation shows the importance of measuring effects at different points in time, to take account of the time they take to appear and their evolving nature (Gervais et al., 2016: p. 6).
Most of the articles presented the dimensions that should be evaluated, whereas the empirical articles presented the dimensions but also used them in practice to evaluate a KMb strategy. Only five articles (5.7%) did not mention specific dimensions that could be classified.
Table 8 presents both the number of articles that presented dimensions to be evaluated and the number of articles that evaluated them in practice. These results showed that the effects dimension was both the most often named and the most evaluated in practice. The other three dimensions (context, process, impacts), while quite often mentioned as relevant to assess, were less often evaluated in practice. For example, only five articles (5.7%) reported having assessed the impacts dimension.
As previously mentioned, the components relevant for the evaluation of KMb strategies were extracted from the identified TMFs. Table 9 presents these components, which represent the more specific factors of interest for assessing context, process, effects and impacts.
Although often overlooked, the evaluation of KMb strategies is an essential step in guiding organizations seeking to determine whether the expected outcomes of their initiatives are being realized. Evaluation not only allows organizations to make adjustments if the initiatives are not producing the expected results, but also helps them to justify their funding of such initiatives. Evaluation is also essential if the KMb science is to truly inform KMb practice, such that the strategies developed are based on empirical data [ 30 ]. To make KMb evaluation more feasible, evaluation must be promoted and practices improved.
This scoping review meets the first objective of our project, which was to provide an overview of reference frameworks used or proposed for evaluating KM strategies, and to propose a preliminary version of a reference framework for evaluating KM strategies. Several key findings emerged from this scoping review:
Proliferation of theories, models and frameworks, but few frequently used
We are seeing a proliferation of TMFs in KMb and closely related fields [ 132 , 133 ]. Thus, the results of this scoping review support the argument that the conceptual and theoretical development of the field is outpacing its empirical development. Most of the reviewed articles (42.0%) proposed a new TMF rather than using existing ones. Furthermore, we identified relatively few empirical studies (50.0%) that focused on the evaluation of KMb strategies. Consequently, the TMFs used were poorly consolidated, which does not provide a solid empirical foundation to guide the evaluation of KMb strategies. Also, not all the TMFs proposed in the articles were specifically developed for evaluation; some were focused on KMb implementation processes. These may still provide elements to consider for evaluation, although they were not designed to propose specific indicators.
A scoping review published in 2018 identified 596 studies using 159 different KMb TMFs, 95 of which had been used only once [ 11 ]. Many authors reported that these are rarely reused and validated [ 11 , 30 , 33 ] and that it is important to test, refine and integrate existing ones [ 3 , 31 , 34 , 133 ]. A clear, collective and consistent use of existing TMFs is recommended and necessary to advance KMb science and closely related fields [ 12 , 31 ]. The systematic review by Strifler et al. [ 11 ] highlights the diversity of available TMFs and the difficulty users may experience when choosing TMFs to guide their KMb initiatives or evaluation process. Future work should focus on the development of tools to better support users of TMFs, especially those working in organizations. By consolidating a large number of TMFs, the results of this scoping review contribute to these efforts.
The importance of improving evaluation practices for complex multifaceted KMb strategies
Another noteworthy finding was the emphasis on the evaluation of strategies focused on education and professional training for practice improvement (52.3%). Relatively few of the reviewed articles looked at, for example, the evaluation of KMb strategies aimed at informing or influencing decision-making (13.6%), or KMb strategies targeting decision-makers (9.1%). These results reaffirm the importance of conducting more large-scale evaluations of complex and multifaceted KMb strategies. These involve a greater degree of interaction and engagement, are composed of networks of multiple actors, mobilize diverse sources of knowledge and have simultaneous multilevel objectives [ 19 , 134 ].
The fact that some KMb strategies are complex interventions implemented in complex contexts [ 134 ] presents a significant and recurring challenge to their evaluation. Methodological designs, approaches and tools are often ill-suited to capture the short-, medium- and long-term outcomes of KMb strategies, as well as to identify the mechanisms by which these outcomes were produced in a specific context. It is also difficult to link concrete changes in practice and decision-making to tangible longer-term impacts at the population level. Moreover, these impacts can take years to be achieved [ 36 ] and can be influenced by several other factors in addition to KMb efforts [ 2 , 19 , 24 ]. Comprehensive, dynamic and flexible evaluation approaches [ 135 , 136 , 137 ] using mixed methods [ 20 ] appear necessary to understand why, for whom, how, when and in what context KMb strategies achieve their objectives [ 2 , 21 , 25 ]. For instance, realist evaluation, which belongs to theory-based evaluation, may be an approach that addresses issues of causality without sacrificing complexity [ 134 , 138 , 139 ]. This evaluation approach aims to identify the underlying generative mechanisms that can explain how the outcomes were generated and what characteristics of the context affected, or not, those mechanisms. This approach is used to test and refine theory about how interventions with a similar logic of action actually work [ 139 ].
Large heterogeneity of methodologies used in empirical studies
Despite the growth of the KMb field, a recurring issue is the relatively limited number of high-quality studies that evaluate KMb outcomes and impacts. This observation is shared by many of the authors of our scoping articles [ 2 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Only a limited number of empirical articles met the selection criteria ( n = 44/88) in this scoping review. Synthesizing these studies is challenging due to the diversity of research designs used and the large number of potential evaluation components identified. In addition, most of the identified studies used TMFs and measurement tools that were not validated [ 20 , 29 ] and that were specifically developed for their study [ 16 , 25 , 140 ]. Moreover, these studies did not describe the methods used to justify their choice of evaluation dimensions and components [ 25 ], which greatly hinders the ability to draw inferences and develop generalizable theories through replication in similar studies [ 110 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 ]. The lack of a widely used evaluation approach across the field is therefore an important issue [ 16 , 20 ] also highlighted by this scoping review.
Our aim in this review was not to identify specific indicators or measurement tools (for example, questionnaires) for assessing KMb strategies, but rather to describe dimensions and component of TMFs used for KMb evaluation. However, a recent scoping review [ 144 ] looked at measurement tools and revealed that only two general potential tools have been identified to assess KMb activities in any sector or organization: the Level of Knowledge Use Survey (LOKUS) [ 145 ] and the Knowledge Uptake and Utilization Tool (KUUT) [ 95 ]. The authors also assert the importance of developing standardized tools and evaluation processes to facilitate comparison of KMb activities’ outcomes across organizations [ 144 ].
Lack of description and reporting of KMb strategies and evaluation
Another important finding from this review was the sparsity of descriptions of KMb strategies in the published articles. In general, the authors provided little information on the operationalization of their KMb strategies (for example, objectives, target audiences, details of activities implemented, implementation context, expected effects). The KMb strategy objectives and the implemented activities should be carefully selected and empirically, theoretically or pragmatically justified before the evaluation components and specific indicators can be determined [ 146 ].
To improve consistency in the field and to contribute to the development of KMb science, many authors reported the need to better describe and report KMb strategies and their context [ 8 , 54 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 ]. KMb strategies are often inconsistently labelled across studies, poorly described and rarely justified theoretically [ 146 , 150 , 151 ]. It was not possible in this scoping review to associate the evaluation components to be used with the objectives and types of KMb strategies, as too much information was missing in the articles. Over the past 10 years, several guidelines have been proposed to improve the reporting of interventions such as KMb strategies: the “Workgroup for Intervention Development and Evaluation Research (WIDER) recommendations checklist” [ 147 ], the “Standards for Reporting Implementation Studies (StaRI)” [ 150 ] and the “Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDieR)” [ 152 ]. These guidelines should be used more often to enhance the reporting of KMb strategies and help advance the field [ 153 ].
Implications for future research
This scoping review provides an overview of potential factors of interest for assessing the context, process, effects and impacts of a KMb strategy. It also proposes a preliminary inventory of potential dimensions and components to consider when planning the evaluation of a KMb strategy. Given the broad spectrum of factors of interest identified across studies, not all of them can be assessed in every context. Rather, they should be targeted according to the objectives of the evaluation, the nature of the KMb strategy and the resources available to conduct the evaluation. Thus, this inventory should not be understood as a prescriptive, normative and exhaustive framework, but rather as a toolbox to identify the most relevant factors to include in the evaluation of a given KMB strategy, and to address a need often expressed by organizations wishing to evaluate their KMb efforts.
Additional work is needed to validate and operationalize these dimensions, to identify relevant measurement tools related to the different components and to see how this inventory could support KMb evaluation practices in organizations.
This scoping review is the first stage of a larger research project aimed at improving organizations’ capacity to evaluate their KMb initiatives by developing an integrative, interdisciplinary and easy-to-use reference framework. In the second phase of the project, the relevance and clarity of the evaluation dimensions identified in the scoping review will be validated through a Delphi study with KMb specialists and researchers. The enriched framework will then be pilot tested in two organizations carrying out and evaluating KMb strategies, to adapt the framework to their needs and to further clarify how the dimensions can be measured in practice. In this third phase, guidance will be provided to help organizations adopt the framework and its support kit. The aim of the project is to go beyond proposing a theoretical framework, and to help build organizations’ capacity to evaluate KT strategies by proposing tools adapted to their realities.
Review limitations
Some limitations of this scoping review should be acknowledged. First, given the numerous different terms used to describe and conceptualize the science of using evidence, it is possible that our search strategy did not capture all relevant publications. However, to limit this risk, we manually searched the reference lists of the selected articles. Second, the literature search was limited to articles published in English or French, and the articles were mostly from high-income countries (for example, North America); therefore, the application of the identified concepts in this scoping review to other contexts should be further explored.
In addition, the search strategy focused on scientific publications to assess progress made in the field of knowledge mobilization strategy evaluation. The grey literature was not examined. It should be considered in future research to complete the overview of evaluation needs in the field of knowledge mobilization.
Finally, the paucity of information in the articles sometimes made it difficult to classify the TMFs according to the taxonomies [ 32 , 44 ], which may have led to possible misinterpretation. However, to limit the risk of errors, the categorization was performed by two reviewers and validated by a third in cases of uncertainty.
Given the increasing demand from organizations for the evaluation of KMb strategies, along with the poorly consolidated KMb research field, a scoping review was needed to identify the range, nature and extent of the literature. This scoping review enabled us to synthesize the breadth of the literature, provide an overview of the many theories, models and frameworks used, and identify and categorize the potential dimensions and components to consider when evaluating KMb initiatives. This scoping review is part of a larger research project, in which the next steps will be to validate the integrative framework and develop a support kit to facilitate its use by organizations involved in KMb.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article and its additional files.
Abbreviations
- Knowledge mobilization
- Theories, models, and frameworks
Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council. Guidelines for Effective Knowledge Mobilization. 2019. https://www.sshrc-crsh.gc.ca/funding-financement/policies-politiques/knowledge_mobilisation-mobilisation_des_connaissances-eng.aspx Accessed 28 Dec 2022.
Boaz A, Davies H, Fraser A, Nutley S. What works now? evidence-informed policy and practice. Bristol: Policy press; 2019.
Book Google Scholar
Curran JA, Grimshaw JM, Hayden JA, Campbell B. Knowledge translation research: the science of moving research into policy and practice. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2011;31(3):174–80.
Article Google Scholar
Global Commission on Evidence. The Evidence Commission report: A wake-up call and path forward for decision-makers, evidence intermediaries, and impact-oriented evidence producers. McMaster University; 2022 p. 144. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/networks/evidence-commission/report/english
Morris ZS, Wooding S, Grant J. The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research. J R Soc Med. 2011;104(12):510–20.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Orton L, Lloyd-Williams F, Taylor-Robinson D, O’Flaherty M, Capewell S. The use of research evidence in public health decision making processes: systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(7): e21704.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Straus SE, Tetroe J, Graham ID, editors. Knowledge translation in health care: moving from evidence to practice. 2nd ed. Chichester, West Sussex ; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley/BMJ Books; 2013, 406
Barwick M, Dubrowski R, Petricca K. Knowledge translation: The rise of implementation. 2020; https://ktdrr.org/products/kt-implementation/KT-Implementation-508.pdf
Graham ID, Logan J, Harrison MB, Straus SE, Tetroe J, Caswell W, et al. Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map? J Continuing Educ Health Professions. 2006;26(1):13–24.
Grimshaw JM, Eccles MP, Lavis JN, Hill SJ, Squires JE. Knowledge translation of research findings. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):50.
Strifler L, Cardoso R, McGowan J, Cogo E, Nincic V, Khan PA, et al. Scoping review identifies significant number of knowledge translation theories, models, and frameworks with limited use. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;100:92–102.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Esmail R, Hanson HM, Holroyd-Leduc J, Brown S, Strifler L, Straus SE, et al. A scoping review of full-spectrum knowledge translation theories, models, and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):11.
McKibbon KA, Lokker C, Wilczynski NL, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Davis DA, et al. A cross-sectional study of the number and frequency of terms used to refer to knowledge translation in a body of health literature in 2006: a Tower of Babel? Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):16.
Fonds de recherche du Québec. Stratégie de mobilisation des connaissances 2014–2017. 2014. https://frq.gouv.qc.ca/en/mobilization-of-knowledge/ . Accessed 28 Dec 2022.
Gervais MJ, Souffez K, Ziam S. Quel impact avons-nous ? Vers l’élaboration d’un cadre pour rendre visibles les retombées du transfert des connaissances. TUC Revue francophone de recherche sur le transfert et l’utilisation des connaissances. 2016;1(2):21.
Google Scholar
Williams NJ, Beidas RS. Annual research review: the state of implementation science in child psychology and psychiatry: a review and suggestions to advance the field. J Child Psychol Psychiatr. 2019;60(4):430–50.
Mitton C, Adair CE, Mckenzie E, Patten SB, Perry BW. Knowledge transfer and exchange: review and synthesis of the literature. Milbank Q. 2007;85(4):729–68.
Oliver K, Innvar S, Lorenc T, Woodman J, Thomas J. A systematic review of barriers to and facilitators of the use of evidence by policymakers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):2.
Fazey I, Bunse L, Msika J, Pinke M, Preedy K, Evely AC, et al. Evaluating knowledge exchange in interdisciplinary and multi-stakeholder research. Glob Environ Chang. 2014;25:204–20.
Gervais MJ, Marion C, Dagenais C, Chiocchio F, Houlfort N. Dealing with the complexity of evaluating knowledge transfer strategies: guiding principles for developing valid instruments. Res Eval. 2016;25(1):62–9.
Reed MS, Bryce R, Machen R. Pathways to policy impact: a new approach for planning and evidencing research impact. Evid policy. 2018;14(3):431–58.
Kim C, Wilcher R, Petruney T, Krueger K, Wynne L, Zan T. A research utilisation framework for informing global health and development policies and programmes. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16(1):9.
Langer L, Tripney J, Gough D University of London, Social Science Research Unit, Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre. The science of using science: researching the use of research evidence in decision-making. 2016.
Rajić A, Young I, McEwen SA. Improving the utilization of research knowledge in agri-food public health: a mixed-method review of knowledge translation and transfer. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013;10(5):397–412.
Scarlett J, Forsberg BC, Biermann O, Kuchenmüller T, El-Khatib Z. Indicators to evaluate organisational knowledge brokers: a scoping review. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020;18(1):93.
Bornbaum CC, Kornas K, Peirson L, Rosella LC. Exploring the function and effectiveness of knowledge brokers as facilitators of knowledge translation in health-related settings: a systematic review and thematic analysis. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):162.
Sarkies MN, Bowles KA, Skinner EH, Haas R, Lane H, Haines TP. The effectiveness of research implementation strategies for promoting evidence-informed policy and management decisions in healthcare: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):132.
Scott SD, Albrecht L, O’Leary K, Ball GD, Hartling L, Hofmeyer A, et al. Systematic review of knowledge translation strategies in the allied health professions. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):70.
Dagenais C, Malo M, Robert É, Ouimet M, Berthelette D, Ridde V. Knowledge transfer on complex social interventions in public health: a scoping study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12): e80233.
Davies HT, Powell AE, Nutley SM. Mobilising knowledge to improve UK health care: learning from other countries and other sectors – a multimethod mapping study. Health Serv Deliv Res. 2015;3(27):1–190.
Damschroder LJ. Clarity out of chaos: use of theory in implementation research. Psychiatry Res. 2020;283: 112461.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):53.
Ellen ME, Panisset U, Araujo de Carvalho I, Goodwin J, Beard J. A knowledge translation framework on ageing and health. Health Policy. 2017;121(3):282–91.
Wensing M, Bosch M, Grol R. Developing and selecting interventions for translating knowledge to action. CMAJ. 2010;182(2):E85–8.
Bennet A, Bennet D, Fafard K, Fonda M, Lomond T, Messier L, et al. Knowledge mobilization in the social sciences and humanities: moving from research to action. Frost: MQI Press; 2007.
Phipps D, Cummins J, Pepler D, Craig W, Cardinal S. The Co-produced Pathway to Impact Describes Knowledge Mobilization Processes. JCES. 2016;9(1). https://jces.ua.edu/articles/258 . Accessed 17 Nov 2022.
Birken SA, Rohweder CL, Powell BJ, Shea CM, Scott J, Leeman J, et al. T-CaST: an implementation theory comparison and selection tool. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):143.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Moullin JC, Sabater-Hernandez D, Fernandez-Llimos F, Benrimoj SI. A systematic review of implementation frameworks of innovations in healthcare and resulting generic implementation framework. Health Res Policy Syst. 2015;13(101170481):16.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synthesis Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85.
Farkas M, Jette AM, Tennstedt S, Haley SM, Quinn V. Knowledge dissemination and utilization in gerontology: an organizing framework. Gerontologist. 2003;43:47–56.
Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, et al. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):21.
Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Matthieu MM, Damschroder LJ, Chinman MJ, Smith JL, et al. Use of concept mapping to characterize relationships among implementation strategies and assess their feasibility and importance: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) study. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):109.
Smith JD, Li DH, Rafferty MR. The implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):84.
Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Public Health. 1999;89(9):1322–7.
Kitson A, Harvey G, McCormack B. Enabling the implementation of evidence based practice: a conceptual framework. Qual Health Care. 1998;7:149–58.
Sketris IS, Carter N, Traynor RL, Watts D, Kelly K, following contributing members of the CNODES Knowledge Translation Team: Pierre Ernst JG Brenda Hemmelgarn, Colleen Metge, Michael Paterson, Robert Platt W and Gary Teare. Building a framework for the evaluation of knowledge translation for the Canadian Network for Observational Drug Effect Studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020;29 Suppl 1(d0r, 9208369):8–25.
Thomas DR. A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data. Am J Eval. 2006;27(2):237–46.
Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1991;50(2):179–211.
Moore DE, Green JS, Gallis HA. Achieving desired results and improved outcomes: integrating planning and assessment throughout learning activities. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2009;29(1):1–15.
Tschida JE, Drahota A. Fidelity to the ACT SMART Toolkit: an instrumental case study of implementation strategy fidelity. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):52.
Colquhoun H, Leeman J, Michie S, Lokker C, Bragge P, Hempel S, et al. Towards a common terminology: a simplified framework of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into health practices, systems, and policies. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):781.
Bertone MP, Meessen B, Clarysse G, Hercot D, Kelley A, Kafando Y, et al. Assessing communities of practice in health policy: a conceptual framework as a first step towards empirical research. Health Res Policy Sys. 2013;11(1):39.
Gagliardi AR, Legare F, Brouwers MC, Webster F, Wiljer D, Badley E, et al. Protocol: developing a conceptual framework of patient mediated knowledge translation, systematic review using a realist approach. Implement Sci. 2011;6(101258411):25.
Sargeant J, Borduas F, Sales A, Klein D, Lynn B, Stenerson H. CPD and KT: models used and opportunities for synergy. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2011;31(3):167–73.
Stetler CB, Ritchie J, Rycroft-Malone J, Schultz A, Charns M. Improving quality of care through routine, successful implementation of evidence-based practice at the bedside: an organizational case study protocol using the Pettigrew and Whipp model of strategic change. Implement Sci. 2007;2(101258411):3.
Kok MO, Schuit AJ. Contribution mapping: a method for mapping the contribution of research to enhance its impact. Health Res Policy Syst. 2012;10(101170481):21.
Dadich A. From bench to bedside: methods that help clinicians use evidence-based practice. Aust Psychol. 2010;45(3):197–211.
Brown P, Bahri P. Engagement’ of patients and healthcare professionals in regulatory pharmacovigilance: establishing a conceptual and methodological framework. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;75(9):1181–92.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dobbins M, Ciliska D, Cockerill R, Barnsley J, DiCenso A. A framework for the dissemination and utilization of research for health-care policy and practice. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs Presents Arch Online J Knowl Synthesis Nurs. 2002;9(1):149–60.
Gagliardi AR, Brouwers MC, Bhattacharyya OK. The guideline implementability research and application network (GIRAnet): an international collaborative to support knowledge exchange: study protocol. Implement Sci. 2012;7(101258411):26.
Brooks SP, Zimmermann GL, Lang M, Scott SD, Thomson D, Wilkes G, et al. A framework to guide storytelling as a knowledge translation intervention for health-promoting behaviour change. Implement sci commun. 2022;3(1):35.
Cullen L, Hanrahan K, Edmonds SW, Reisinger HS, Wagner M. Iowa implementation for sustainability framework. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):1.
Labbé D, Mahmood A, Miller WC, Mortenson WB. Examining the impact of knowledge mobilization strategies to inform urban stakeholders on accessibility: a mixed-methods study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1561.
Straus SE, Tetroe J, Graham ID, Zwarenstein M, Bhattacharyya O, Shepperd S. Monitoring use of knowledge and evaluating outcomes. Can Med Assoc J. 2010;182(2):E94–8.
Bennett S, Whitehead M, Eames S, Fleming J, Low S, Caldwell E. Building capacity for knowledge translation in occupational therapy: learning through participatory action research. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16(1):257.
Brown C, Rogers S. Measuring the effectiveness of knowledge creation as a means of facilitating evidence-informed practice in early years settings in one London Borough. Lond Rev Educ. 2014;12(3):245–60.
Talbott E, De Los RA, Kearns DM, Mancilla-Martinez J, Wang M. Evidence-based assessment in special education research: advancing the use of evidence in assessment tools and empirical processes. Except Child. 2023;89(4):467–87.
Rosella LC, Bornbaum C, Kornas K, Lebenbaum M, Peirson L, Fransoo R, et al. Evaluating the process and outcomes of a knowledge translation approach to supporting use of the Diabetes Population Risk Tool (DPoRT) in public health practice. Canadian J Program Eval. 2018;33(1):21–48.
Couineau AL, Forbes D. Using predictive models of behavior change to promote evidence-based treatment for PTSD. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. 2011;3(3):266–75.
Dufault M. Testing a collaborative research utilization model to translate best practices in pain management. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2004;1:S26-32.
Beckett K, Farr M, Kothari A, Wye L, le May A. Embracing complexity and uncertainty to create impact: exploring the processes and transformative potential of co-produced research through development of a social impact model. Health Res Policy Syst. 2018;16(1):118.
Kramer DM, Wells RP, Carlan N, Aversa T, Bigelow PP, Dixon SM, et al. Did you have an impact? A theory-based method for planning and evaluating knowledge-transfer and exchange activities in occupational health and safety. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2013;19(1):41–62.
Duhamel F, Dupuis F, Turcotte A, Martinez AM, Goudreau J. Integrating the illness beliefs model in clinical practice: a family systems nursing knowledge utilization model. J FAM NURS. 2015;21(2):322–48.
Wimpenny P, Johnson N, Walter I, Wilkinson JE. Tracing and identifying the impact of evidence-use of a modified pipeline model. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2008;5(1):3–12.
Ward V, Smith S, House A, Hamer S. Exploring knowledge exchange: a useful framework for practice and policy. Soc Sci Med. 2012;74(3):297–304.
Grooten L, Vrijhoef HJM, Alhambra-Borras T, Whitehouse D, Devroey D. The transfer of knowledge on integrated care among five European regions: a qualitative multi-method study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):11.
Stetler CB. Updating the Stetler Model of research utilization to facilitate evidence-based practice. Nurs Outlook. 2001;49(6):272–9.
Ward V. Why, whose, what and how? A framework for knowledge mobilisers. Evid Policy J Res Debate Pract. 2017;13(3):477–97.
Levin RF, Fineout-Overholt E, Melnyk BM, Barnes M, Vetter MJ. Fostering evidence-based practice to improve nurse and cost outcomes in a community health setting: a pilot test of the advancing research and clinical practice through close collaboration model. Nurs Adm Q. 2011;35(1):21–33.
Currie M, King G, Rosenbaum P, Law M, Kertoy M, Specht J. A model of impacts of research partnerships in health and social services. Eval Program Plann. 2005;28(4):400–12.
Richard L, Chiocchio F, Essiembre H, Tremblay MC, Lamy G, Champagne F, et al. Communities of practice as a professional and organizational development strategy in local public health organizations in Quebec, Canada: an evaluation model. Healthc Policy. 2014;9(3):26–39.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rycroft-Malone J, Wilkinson J, Burton CR, Harvey G, McCormack B, Graham I, et al. Collaborative action around implementation in collaborations for leadership in applied health research and care: towards a programme theory. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2013;18(3 Suppl):13–26.
Gagliardi AR, Fraser N, Wright FC, Lemieux-Charles L, Davis D. Fostering knowledge exchange between researchers and decision-makers: exploring the effectiveness of a mixed-methods approach. Health Policy. 2008;86(1):53–63.
Paquette-Warren J, Harris SB, Naqshbandi Hayward M, Tompkins JW. Case study of evaluations that go beyond clinical outcomes to assess quality improvement diabetes programmes using the Diabetes Evaluation Framework for Innovative National Evaluations (DEFINE). J Eval Clin Pract. 2016;22(5):644–52.
Paquette-Warren J, Tyler M, Fournie M, Harris SB. The diabetes evaluation framework for innovative national evaluations (DEFINE): construct and content validation using a modified Delphi method. Can J diabetes. 2017;41(3):281–96.
Abbot ML, Lee KK, Rossiter MJ. Evaluating the effectiveness and functionality of professional learning communities in adult ESL Programs. TESL Canada J. 2018;35(2):1–25.
Ho K, Bloch R, Gondocz T, Laprise R, Perrier L, Ryan D, et al. Technology-enabled knowledge translation: frameworks to promote research and practice. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2004;24(2):90–9.
Yu X, Hu D, Li N, Xiao Y. Comprehensive evaluation on teachers’ knowledge sharing behavior based on the improved TOPSIS method. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022;2022(101279357):2563210.
Arora S, Kalishman SG, Thornton KA, Komaromy MS, Katzman JG, Struminger BB, et al. Project ECHO: a telementoring network model for continuing professional development. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2017;37(4):239–44.
Smidt A, Balandin S, Sigafoos J, Reed VA. The Kirkpatrick model: a useful tool for evaluating training outcomes. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2009;34(3):266–74.
Jeffs L, Sidani S, Rose D, Espin S, Smith O, Martin K, et al. Using theory and evidence to drive measurement of patient, nurse and organizational outcomes of professional nursing practice. Int J Nurs Pract. 2013;19(2):141–8.
Skinner K. Developing a tool to measure knowledge exchange outcomes. Can J Program Eval. 2007;22(1):49–75.
Lavis J, Ross S, McLeod C, Gildiner A. Measuring the impact of health research. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2003;8(3):165–70.
Boyko JA, Lavis JN, Abelson J, Dobbins M, Carter N. Deliberative dialogues as a mechanism for knowledge translation and exchange in health systems decision-making. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(11):1938–45.
Proctor E, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76.
Gainforth HL, Latimer-Cheung AE, Athanasopoulos P, Martin Ginis KA. Examining the feasibility and effectiveness of a community-based organization implementing an event-based knowledge mobilization initiative to promote physical activity guidelines for people with spinal cord injury among support personnel. Health Promot Pract. 2015;16(1):55–62.
Glasgow RE, Harden SM, Gaglio B, Rabin B, Smith ML, Porter GC, et al. RE-AIM planning and evaluation framework: adapting to new science and practice with a 20-year review. Front Public Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00064 .
Shelton RC, Chambers DA, Glasgow RE. An extension of RE-AIM to enhance sustainability: addressing dynamic context and promoting health equity over time. Front Public Health. 2020;8(101616579):134.
Bender BG, Simmons B, Konkoly N, Liu AH. The asthma toolkit bootcamp to improve rural primary care for pediatric asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(8):3091-3097.e1.
de la Garza Iga FJ, Mejia Alvarez M, Cockroft JD, Rabin J, Cordon A, Elias Rodas DM, et al. Using the project ECHO TM model to teach mental health topics in rural Guatemala: an implementation science-guided evaluation. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2023;69(8):2031–41.
Alkin M, Taut S. Unbundling evaluation use. Stud Educ Eval. 2003;29(1):1–12.
Varallyay NI, Langlois EV, Tran N, Elias V, Reveiz L. Health system decision-makers at the helm of implementation research: development of a framework to evaluate the processes and effectiveness of embedded approaches. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020;18(1):64.
McCabe KE, Wallace A, Crosland A. A model for collaborative working to facilitate knowledge mobilisation in public health. Evid Policy. 2015;11(4):559–76.
Gonzales R, Handley MA, Ackerman S, O’sullivan PS. A framework for training health professionals in implementation and dissemination science. Acad Med. 2012;87(3):271–8.
Edgar L, Herbert R, Lambert S, MacDonald JA, Dubois S, Latimer M. The joint venture model of knowledge utilization: a guide for change in nursing. Nurs Leadersh. 2006;9(2):41–55.
Stetler CB, Damschroder LJ, Helfrich CD, Hagedorn HJ. A Guide for applying a revised version of the PARIHS framework for implementation. Implement Sci. 2011;6(101258411):99.
Brennan SE, Cumpston M, Misso ML, McDonald S, Murphy MJ, Green SE. Design and formative evaluation of the policy liaison initiative: a long-term knowledge translation strategy to encourage and support the use of cochrane systematic reviews for informing. Evid Policy. 2016;12(1):25–52.
Hinchcliff R, Senserrick T, Travaglia J, Greenfield D, Ivers R. The enhanced knowledge translation and exchange framework for road safety: a brief report on its development and potential impacts. Inj Prev. 2017;23(2):114–7.
Ye J, Woods D, Bannon J, Bilaver L, Kricke G, McHugh M, et al. Identifying contextual factors and strategies for practice facilitation in primary care quality improvement using an informatics-driven model: framework development and mixed methods case study. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022;9(2): e32174.
Brangan J, Quinn S, Spirtos M. Impact of an evidence-based practice course on occupational therapist’s confidence levels and goals. Occup Ther Health Care. 2015;29(1):27–38.
Bonetti D, Johnston M, Pitts NB, Deery C, Ricketts I, Tilley C, et al. Knowledge may not be the best target for strategies to influence evidence-based practice: using psychological models to understand RCT effects. Int J Behav Med. 2009;16(3):287–93.
Buckley LL, Goering P, Parikh SV, Butterill D, Foo EKH. Applying a “stages of change” model to enhance a traditional evaluation of a research transfer course. J Eval Clin Pract. 2003;9(4):385–90.
Boyko JA, Lavis JN, Dobbins M, Souza NM. Reliability of a tool for measuring theory of planned behaviour constructs for use in evaluating research use in policymaking. Health Res Policy Syst. 2011;24(9):29.
Imani-Nasab MH, Yazdizadeh B, Salehi M, Seyedin H, Majdzadeh R. Validity and reliability of the Evidence Utilisation in Policymaking Measurement Tool (EUPMT). Health Res Policy Syst. 2017;15(1):66.
Dwan KM, McInnes P, Mazumdar S. Measuring the success of facilitated engagement between knowledge producers and users: a validated scale. Evid Policy. 2015;11(2):239–52.
Haynes A, Rowbotham S, Grunseit A, Bohn-Goldbaum E, Slaytor E, Wilson A, et al. Knowledge mobilisation in practice: an evaluation of the Australian Prevention Partnership Centre. Health Res Policy Sys. 2020;18(1):13.
Haines M, Brown B, Craig J, D’Este C, Elliott E, Klineberg E, et al. Determinants of successful clinical networks: the conceptual framework and study protocol. Implement Sci. 2012;7(101258411):16.
Ko LK, Jang SH, Friedman DB, Glanz K, Leeman J, Hannon PA, et al. An application of the science impact framework to the cancer prevention and control research network from 2014–2018. Prev Med. 2019;12: 105821.
Leeman J, Sommers J, Vu M, Jernigan J, Payne G, Thompson D, et al. An evaluation framework for obesity prevention policy interventions. Prev Chronic Dis. 2012;9(101205018):E120.
Pettman TL, Armstrong R, Waters E, Allender S, Love P, Gill T, et al. Evaluation of a knowledge translation and exchange platform to advance non-communicable disease prevention. Evid Policy. 2016;12(1):109–26.
Yearwood AC. Applying a logical theory of change for strengthening research uptake in policy: a case study of the Evidence Informed Decision Making Network of the Caribbean. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2018;42: e91.
Thomson D, Brooks S, Nuspl M, Hartling L. Programme theory development and formative evaluation of a provincial knowledge translation unit. Health Res Policy Syst. 2019;17(1):40.
Garad R, Kozica-Olenski S, Teede HJ. Evaluation of a center of research excellence in polycystic ovary syndrome as a large-scale collaborative research translation initiative, including evaluating translation of guideline impact. Semin Reprod Med. 2018;36(1):42–9.
Reddy S, Wakerman J, Westhorp G, Herring S. Evaluating impact of clinical guidelines using a realist evaluation framework. J Eval Clin Pract. 2015;21(6):1114–20.
Van Eerd D, Moser C, Saunders R. A research impact model for work and health. Am J Ind Med. 2021;64(1):3–12.
Yip O, Huber E, Stenz S, Zullig LL, Zeller A, De Geest SM, et al. A contextual analysis and logic model for integrated care for frail older adults living at home: The INSPIRE Project. Int J Integr Care. 2021;21(2):9.
Guo R, Bain BA, Willer J. Application of a logic model to an evidence-based practice training program for speech-language pathologists and audiologists. J Allied Health. 2011;40(1):e23–8.
PubMed Google Scholar
McDonald S, Turner T, Chamberlain C, Lumbiganon P, Thinkhamrop J, Festin MR, et al. Building capacity for evidence generation, synthesis and implementation to improve the care of mothers and babies in South East Asia: methods and design of the SEA-ORCHID Project using a logical framework approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10(100968545):61.
Tabak RG, Khoong EC, Chambers DA, Brownson RC. Bridging research and practice: models for dissemination and implementation research. Am J Prev Med. 2012;43(3):337–50.
Wensing M, Grol R. Knowledge translation in health: how implementation science could contribute more. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):88.
Kreindler SA. Advancing the evaluation of integrated knowledge translation. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16(1):104.
Best A, Holmes B. Systems thinking, knowledge and action: towards better models and methods. Evid Policy. 2010;6(2):145–59.
van Mil HGJ, Foegeding EA, Windhab EJ, Perrot N, van der Linden E. A complex system approach to address world challenges in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2014;40(1):20–32.
Wehrens R. Beyond two communities – from research utilization and knowledge translation to co-production? Public Health. 2014;128(6):545–51.
Ridde V, Pérez D, Robert E. Using implementation science theories and frameworks in global health. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(4): e002269.
Salter KL, Kothari A. Using realist evaluation to open the black box of knowledge translation: a state-of-the-art review. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):115.
Van Eerd D, Cole D, Keown K, Irvin E, Kramer D, Gibson B, et al. Report on knowledge transfer and exchange practices: A systematic review of the quality and types of instruments used to assess KTE implementation and impact. Toronto: Institute for Work & Health; 2011 p. 130. https://www.iwh.on.ca/sites/iwh/files/iwh/reports/iwh_sys_review_kte_evaluation_tools_2011_rev.pdf
Dobbins M, Robeson P, Ciliska D, Hanna S, Cameron R, O’Mara L, et al. A description of a knowledge broker role implemented as part of a randomized controlled trial evaluating three knowledge translation strategies. Implement Sci. 2009;4(1):23.
Rychetnik L, Bauman A, Laws R, King L, Rissel C, Nutbeam D, et al. Translating research for evidence-based public health: key concepts and future directions. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2012;66(12):1187–92.
Weiner BJ, Lewis CC, Stanick C, Powell BJ, Dorsey CN, Clary AS, et al. Psychometric assessment of three newly developed implementation outcome measures. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):108.
Bhawra J, Skinner K. Examination of tools associated with the evaluation of knowledge uptake and utilization: a scoping review. Eval Program Plann. 2020;83: 101875.
Lane JP, Stone VI, Nobrega A, Tomita M. Level Of Knowledge Use Survey (LOKUS): a validated instrument for tracking knowledge uptake and use. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;217:106–10.
Proctor EK, Powell BJ, McMillen JC. Implementation strategies: recommendations for specifying and reporting. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):139.
Albrecht L, Archibald M, Arseneau D, Scott SD. Development of a checklist to assess the quality of reporting of knowledge translation interventions using the Workgroup for Intervention Development and Evaluation Research (WIDER) recommendations. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):52.
Bragge P, Grimshaw JM, Lokker C, Colquhoun H, Albrecht L, Baron J, et al. AIMD - a validated, simplified framework of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into health practices, systems, and policies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):38.
Kastner M, Makarski J, Hayden L, Lai Y, Chan J, Treister V, et al. Improving KT tools and products: development and evaluation of a framework for creating optimized, Knowledge-activated Tools (KaT). Implement Sci Commun. 2020;1(1):47.
Pinnock H, Barwick M, Carpenter CR, Eldridge S, Grandes G, Griffiths CJ, et al. Standards for Reporting Implementation Studies (StaRI) Statement. BMJ. 2017;6(356): i6795.
Lokker C, McKibbon KA, Colquhoun H, Hempel S. A scoping review of classification schemes of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into practice in healthcare. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):27.
Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D, et al. Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ. 2014;7(348): g1687.
Wilson PM, Sales A, Wensing M, Aarons GA, Flottorp S, Glidewell L, et al. Enhancing the reporting of implementation research. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):13.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Julie Desnoyers for designing and implementing the search strategy, Gabrielle Legendre for her contribution in the screening phase and Karine Souffez and Caroline Tessier for their input during the project.
This project was supported by an Insight Grant from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC) and by the Équipe RENARD (FRQ-SC). The funding bodies had no role in the conduct of this scoping review.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business Administration, Université TÉLUQ, Montreal, Canada
Saliha Ziam & Laura Justine Chouinard
Department of School and Social Adaptation Studies, Faculty of Education, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Canada
Sèverine Lanoue, Esther McSween-Cadieux, Julie Lane & Ollivier Prigent
Department of Psychology, Université du Québec à Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Mathieu-Joël Gervais
Centre RBC d’expertise Universitaire en Santé Mentale, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Canada
School of Rehabilitation, Faculty of Medicine, Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Dina Gaid & Quan Nha Hong
Department of Psychology, Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Christian Dagenais
Université Paris Cité, IRD (Institute for Research on Sustainable Development, CEPED, Paris, France
Valéry Ridde
Institute of Health and Development (ISED), Cheikh Anta Diop University, Dakar, Senegal
Public Health Intelligence and Knowledge Translation Division, Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, Canada
Emmanuelle Jean
Coordinator of the Interregional Consortium of Knowledge in Health and Social Services (InterS4), Rimouski, Canada
France Charles Fleury
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SZ, MJG, EMC, JL, CD, EJ, KS, VR and CT were involved in developing and designing the scoping review. EMC, MJG and GL (collaborator) screened articles in duplicate. SL, DG, LJC and OP extracted data from the included articles. SL and DG synthesized the data. SL, SZ and EMC drafted the manuscript. SZ led the project, supervised and assisted the research team at every stage, and secured the funding. All authors provided substantive feedback and approved the manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Saliha Ziam .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Keywords and search strategy.
Additional file 2.
Summary of included articles.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ziam, S., Lanoue, S., McSween-Cadieux, E. et al. A scoping review of theories, models and frameworks used or proposed to evaluate knowledge mobilization strategies. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01090-7
Download citation
Received : 16 June 2023
Accepted : 07 December 2023
Published : 10 January 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01090-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Knowledge translation
- Scoping review
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Search Menu
- Chemical Biology and Nucleic Acid Chemistry
- Computational Biology
- Critical Reviews and Perspectives
- Data Resources and Analyses
- Gene Regulation, Chromatin and Epigenetics
- Genome Integrity, Repair and Replication
- Methods Online
- Molecular Biology
- Nucleic Acid Enzymes
- RNA and RNA-protein complexes
- Structural Biology
- Synthetic Biology and Bioengineering
- Advance Articles
- Breakthrough Articles
- Special Collections
- Scope and Criteria for Consideration
- Author Guidelines
- Data Deposition Policy
- Database Issue Guidelines
- Web Server Issue Guidelines
- Submission Site
- About Nucleic Acids Research
- Editors & Editorial Board
- Information of Referees
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Introduction, system overview, materials and methods, data availability, supplementary data, pubtator 3.0: an ai-powered literature resource for unlocking biomedical knowledge.
The first two authors should be regarded as Joint First Authors.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Chih-Hsuan Wei, Alexis Allot, Po-Ting Lai, Robert Leaman, Shubo Tian, Ling Luo, Qiao Jin, Zhizheng Wang, Qingyu Chen, Zhiyong Lu, PubTator 3.0: an AI-powered literature resource for unlocking biomedical knowledge, Nucleic Acids Research , 2024;, gkae235, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae235
- Permissions Icon Permissions
PubTator 3.0 ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/ ) is a biomedical literature resource using state-of-the-art AI techniques to offer semantic and relation searches for key concepts like proteins, genetic variants, diseases and chemicals. It currently provides over one billion entity and relation annotations across approximately 36 million PubMed abstracts and 6 million full-text articles from the PMC open access subset, updated weekly. PubTator 3.0's online interface and API utilize these precomputed entity relations and synonyms to provide advanced search capabilities and enable large-scale analyses, streamlining many complex information needs. We showcase the retrieval quality of PubTator 3.0 using a series of entity pair queries, demonstrating that PubTator 3.0 retrieves a greater number of articles than either PubMed or Google Scholar, with higher precision in the top 20 results. We further show that integrating ChatGPT (GPT-4) with PubTator APIs dramatically improves the factuality and verifiability of its responses. In summary, PubTator 3.0 offers a comprehensive set of features and tools that allow researchers to navigate the ever-expanding wealth of biomedical literature, expediting research and unlocking valuable insights for scientific discovery.
The biomedical literature is a primary resource to address information needs across the biological and clinical sciences ( 1 ), however the requirements for literature search vary widely. Activities such as formulating a research hypothesis require an exploratory approach, whereas tasks like interpreting the clinical significance of genetic variants are more focused.
Traditional keyword-based search methods have long formed the foundation of biomedical literature search ( 2 ). While generally effective for basic search, these methods also have significant limitations, such as missing relevant articles due to differing terminology or including irrelevant articles because surface-level term matches cannot adequately represent the required association between query terms. These limitations cost time and risk information needs remaining unmet.
Natural language processing (NLP) methods provide substantial value for creating bioinformatics resources ( 3–5 ), and may improve literature search by enabling semantic and relation search ( 6 ). In semantic search, users indicate specific concepts of interest (entities) for which the system has precomputed matches regardless of the terminology used. Relation search increases precision by allowing users to specify the type of relationship desired between entities, such as whether a chemical enhances or reduces expression of a gene. In this regard, we present PubTator 3.0, a novel resource engineered to support semantic and relation search in the biomedical literature. Its search capabilities allow users to explore automated entity annotations for six key biomedical entities: genes, diseases, chemicals, genetic variants, species, and cell lines. PubTator 3.0 also identifies and makes searchable 12 common types of relations between entities, enhancing its utility for both targeted and exploratory searches. Focusing on relations and entity types of interest across the biomedical sciences allows PubTator 3.0 to retrieve information precisely while providing broad utility (see detailed comparisons with its predecessor in Supplementary Table S1 ).
The PubTator 3.0 online interface, illustrated in Figure 1 and Supplementary Figure S1 , is designed for interactive literature exploration, supporting semantic, relation, keyword, and Boolean queries. An auto-complete function provides semantic search suggestions to assist users with query formulation. For example, it automatically suggests replacing either ‘COVID-19″ or "SARS-CoV-2 infection’ with the semantic term ‘@DISEASE_COVID_19″. Relation queries – new to PubTator 3.0 – provide increased precision, allowing users to target articles which discuss specific relationships between entities.
PubTator 3.0 system overview and search results page: 1. Query auto-complete enhances search accuracy and synonym matching. 2. Natural language processing (NLP)-enhanced relevance: Search results are prioritized according to the strength of the relationship between the entities queried. 3. Users can further refine results with facet filters—section, journal and type. 4. Search results include highlighted entity snippets explaining relevance. 5. Histogram visualizes number of results by publication year. 6. Entity highlighting can be switched on or off according to user preference.
PubTator 3.0 offers unified search results, simultaneously searching approximately 36 million PubMed abstracts and over 6 million full-text articles from the PMC Open Access Subset (PMC-OA), improving access to the substantial amount of relevant information present in the article full text ( 7 ). Search results are prioritized based on the depth of the relationship between the query terms: articles containing identifiable relations between semantic terms receive the highest priority, while articles where semantic or keyword terms co-occur nearby (e.g. within the same sentence) receive secondary priority. Search results are also prioritized based on the article section where the match appears (e.g. matches within the title receive higher priority). Users can further refine results by employing filters, narrowing articles returned to specific publication types, journals, or article sections.
PubTator 3.0 is supported by an NLP pipeline, depicted in Figure 2A . This pipeline, run weekly, first identifies articles newly added to PubMed and PMC-OA. Articles are then processed through three major steps: (i) named entity recognition, provided by the recently developed deep-learning transformer model AIONER ( 8 ), (ii) identifier mapping and (iii) relation extraction, performed by BioREx ( 9 ) of 12 common types of relations (described in Supplementary Table S2 ).
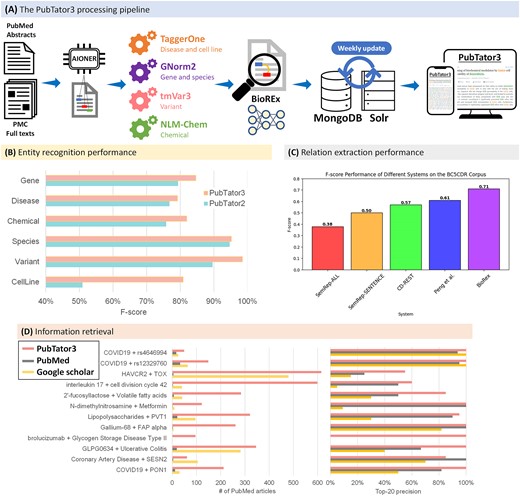
( A ) The PubTator 3.0 processing pipeline: AIONER ( 8 ) identifies six types of entities in PubMed abstracts and PMC-OA full-text articles. Entity annotations are associated with database identifiers by specialized mappers and BioREx ( 9 ) identifies relations between entities. Extracted data is stored in MongoDB and made searchable using Solr. ( B ) Entity recognition performance for each entity type compared with PubTator2 (also known as PubTatorCentral) ( 13 ) on the BioRED corpus ( 15 ). ( C ) Relation extraction performance compared with SemRep ( 11 ) and notable previous best systems ( 12 , 13 ) on the BioCreative V Chemical-Disease Relation ( 14 ) corpus. ( D ) Comparison of information retrieval for PubTator 3.0, PubMed, and Google Scholar for entity pair queries, with respect to total article count and top-20 article precision.
In total, PubTator 3.0 contains over 1.6 billion entity annotations (4.6 million unique identifiers) and 33 million relations (8.8 million unique pairs). It provides enhanced entity recognition and normalization performance over its previous version, PubTator 2 ( 10 ), also known as PubTator Central (Figure 2B and Supplementary Table S3 ). We show the relation extraction performance of PubTator 3.0 in Figure 2C and its comparison results to the previous state-of-the-art systems ( 11–13 ) on the BioCreative V Chemical-Disease Relation ( 14 ) corpus, finding that PubTator 3.0 provided substantially higher accuracy. Moreover, when evaluating a randomized sample of entity pair queries compared to PubMed and Google Scholar, PubTator 3.0 consistently returns a greater number of articles with higher precision in the top 20 results (Figure 2D and Supplementary Table S4 ).
Data sources and article processing
PubTator 3.0 downloads new articles weekly from the BioC PubMed API ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/bionlp/APIs/BioC-PubMed/ ) and the BioC PMC API ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/bionlp/APIs/BioC-PMC/ ) in BioC-XML format ( 16 ). Local abbreviations are identified using Ab3P ( 17 ). Article text and extracted data are stored internally using MongoDB and indexed for search with Solr, ensuring robust and scalable accessibility unconstrained by external dependencies such as the NCBI eUtils API.
Entity recognition and normalization/linking
PubTator 3.0 uses AIONER ( 8 ), a recently developed named entity recognition (NER) model, to recognize entities of six types: genes/proteins, chemicals, diseases, species, genetic variants, and cell lines. AIONER utilizes a flexible tagging scheme to integrate training data created separately into a single resource. These training datasets include NLM-Gene ( 18 ), NLM-Chem ( 19 ), NCBI-Disease ( 20 ), BC5CDR ( 14 ), tmVar3 ( 21 ), Species-800 ( 22 ), BioID ( 23 ) and BioRED ( 15 ). This consolidation creates a larger training set, improving the model's ability to generalize to unseen data. Furthermore, it enables recognizing multiple entity types simultaneously, enhancing efficiency and simplifying the challenge of distinguishing boundaries between entities that reference others, such as the disorder ‘Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency’ and the protein ‘Alpha-1 antitrypsin’. We previously evaluated the performance of AIONER on 14 benchmark datasets ( 8 ), including the test sets for the aforementioned training sets. This evaluation demonstrated that AIONER’s performance surpasses or matches previous state-of-the-art methods.
Entity mentions found by AIONER are normalized (linked) to a unique identifier in an appropriate entity database. Normalization is performed by a module designed for (or adapted to) each entity type, using the latest version. The recently-upgraded GNorm2 system ( 24 ) normalizes genes to NCBI Gene identifiers and species mentions to NCBI Taxonomy. tmVar3 ( 21 ), also recently upgraded, normalizes genetic variants; it uses dbSNP identifiers for variants listed in dbSNP and HGNV format otherwise. Chemicals are normalized by the NLM-Chem tagger ( 19 ) to MeSH identifiers ( 25 ). TaggerOne ( 26 ) normalizes diseases to MeSH and cell lines to Cellosaurus ( 27 ) using a new normalization-only mode. This mode only applies the normalization model, which converts both mentions and lexicon names into high-dimensional TF-IDF vectors and learns a mapping, as before. However, it now augments the training data by mapping each lexicon name to itself, resulting in a large performance improvement for names present in the lexicon but not in the annotated training data. These enhancements provide a significant overall improvement in entity normalization performance ( Supplementary Table S3 ).
Relation extraction
Relations for PubTator 3.0 are extracted by the unified relation extraction model BioREx ( 9 ), designed to simultaneously extract 12 types of relations across eight entity type pairs: chemical–chemical, chemical–disease, chemical–gene, chemical–variant, disease–gene, disease–variant, gene–gene and variant–variant. Detailed definitions of these relation types and their corresponding entity pairs are presented in Supplementary Table S2 . Deep-learning methods for relation extraction, such as BioREx, require ample training data. However, training data for relation extraction is fragmented into many datasets, often tailored to specific entity pairs. BioREx overcomes this limitation with a data-centric approach, reconciling discrepancies between disparate training datasets to construct a comprehensive, unified dataset.
We evaluated the relations extracted by BioREx using performance on manually annotated relation extraction datasets as well as a comparative analysis between BioREx and notable comparable systems. BioREx established a new performance benchmark on the BioRED corpus test set ( 15 ), elevating the performance from 74.4% ( F -score) to 79.6%, and demonstrating higher performance than alternative models such as transfer learning (TL), multi-task learning (MTL), and state-of-the-art models trained on isolated datasets ( 9 ). For PubTator 3.0, we replaced its deep learning module, PubMedBERT ( 28 ), with LinkBERT ( 29 ), further increasing the performance to 82.0%. Furthermore, we conducted a comparative analysis between BioREx and SemRep ( 11 ), a widely used rule-based method for extracting diverse relations, the CD-REST ( 13 ) system, and the previous state-of-the-art system ( 12 ), using the BioCreative V Chemical Disease Relation corpus test set ( 14 ). Our evaluation demonstrated that PubTator 3.0 provided substantially higher F -score than previous methods.
Programmatic access and data formats
PubTator 3.0 offers programmatic access through its API and bulk download. The API ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/ ) supports keyword, entity and relation search, and also supports exporting annotations in XML and JSON-based BioC ( 16 ) formats and tab-delimited free text. The PubTator 3.0 FTP site ( https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lu/PubTator3 ) provides bulk downloads of annotated articles and extraction summaries for entities and relations. Programmatic access supports more flexible query options; for example, the information need ‘what chemicals reduce expression of JAK1?’ can be answered directly via API (e.g. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3-api/relations?e1=@GENE_JAK1&type=negative_correlate&e2=Chemical ) or by filtering the bulk relations file. Additionally, the PubTator 3.0 API supports annotation of user-defined free text.
Case study I: entity relation queries
We analyzed the retrieval quality of PubTator 3.0 by preparing a series of 12 entity pairs to serve as case studies for comparison between PubTator 3.0, PubMed and Google Scholar. To provide an equal comparison, we filtered about 30% of the Google Scholar results for articles not present in PubMed. To ensure that the number of results would remain low enough to allow filtering Google Scholar results for articles not in PubMed, we identified entity pairs first discussed together in the literature in 2022 or later. We then randomly selected two entity pairs of each of the following types: disease/gene, chemical/disease, chemical/gene, chemical/chemical, gene/gene and disease/variant. None of the relation pairs selected appears in the training set. The comparison was performed with respect to a snapshot of the search results returned by all search engines on 19 May 2023. We manually evaluated the top 20 results for each system and each query; articles were judged to be relevant if they mentioned both entities in the query and supported a relationship between them. Two curators independently judged each article, and discrepancies were discussed until agreement. The curators were not blinded to the retrieval method but were required to record the text supporting the relationship, if relevant. This experiment evaluated the relevance of the top 20 results for each retrieval method, regardless of whether the article appeared in PubMed.
Our analysis is summarized in Figure 2D , and Supplementary Table S4 presents a detailed comparison of the quality of retrieved results between PubTator 3.0, PubMed and Google Scholar. Our results demonstrate that PubTator 3.0 retrieves a greater number of articles than the comparison systems and its precision is higher for the top 20 results. For instance, PubTator 3.0 returned 346 articles for the query ‘GLPG0634 + ulcerative colitis’, and manual review of the top 20 articles showed that all contained statements about an association between GLPG0634 and ulcerative colitis. In contrast, PubMed only returned a total of 18 articles, with only 12 mentioning an association. Moreover, when searching for ‘COVID19 + PON1’, PubTator 3.0 returns 212 articles in PubMed, surpassing the 43 articles obtained from Google Scholar, only 29 of which are sourced from PubMed. These disparities can be attributed to several factors: (i) PubTator 3.0's search includes full texts available in PMC-OA, resulting in significantly broader coverage of articles, (ii) entity normalization improves recall, for example, by matching ‘paraoxonase 1’ to ‘PON1’, (iii) PubTator 3.0 prioritizes articles containing relations between the query entities, (iv) Pubtator 3.0 prioritizes articles where the entities appear nearby, rather than distant paragraphs. Across the 12 information retrieval case studies, PubTator 3.0 demonstrated an overall precision of 90.0% for the top 20 articles (216 out of 240), which is significantly higher than PubMed's precision of 81.6% (84 out of 103) and Google Scholar's precision of 48.5% (98 out of 202).
Case study II: retrieval-augmented generation
In the era of large language models (LLMs), PubTator 3.0 can also enhance their factual accuracy via retrieval augmented generation. Despite their strong language ability, LLMs are prone to generating incorrect assertions, sometimes known as hallucinations ( 30 , 31 ). For example, when requested to cite sources for questions such as ‘which diseases can doxorubicin treat’, GPT-4 frequently provides seemingly plausible but nonexistent references. Augmenting GPT-4 with PubTator 3.0 APIs can anchor the model's response to verifiable references via the extracted relations, significantly reducing hallucinations.
We assessed the citation accuracy of responses from three GPT-4 variations: PubTator-augmented GPT-4, PubMed-augmented GPT-4 and standard GPT-4. We performed a qualitative evaluation based on eight questions selected as follows. We identified entities mentioned in the PubMed query logs and randomly selected from entities searched both frequently and rarely. We then identified the common queries for each entity that request relational information and adapted one into a natural language question. Each question is therefore grounded on common information needs of real PubMed users. For example, the questions ‘What can be caused by tocilizumab?’ and ‘What can be treated by doxorubicin?’ are adapted from the user queries ‘tocilizumab side effects’ and ‘doxorubicin treatment’ respectively. Such questions typically require extracting information from multiple articles and an understanding of biomedical entities and relationship descriptions. Supplementary Table S5 lists the questions chosen.
We augmented the GPT-4 large language model (LLM) with PubTator 3.0 via the function calling mechanism of the OpenAI ChatCompletion API. This integration involved prompting GPT-4 with descriptions of three PubTator APIs: (i) find entity ID, which retrieves PubTator entity identifiers; (ii) find related entities, which identifies related entities based on an input entity and specified relations and (iii) export relevant search results, which returns PubMed article identifiers containing textual evidence for specific entity relationships. Our instructions prompted GPT-4 to decompose user questions into sub-questions addressable by these APIs, execute the function calls, and synthesize the responses into a coherent final answer. Our prompt promoted a summarized response by instructing GPT-4 to start its message with ‘Summary:’ and requested the response include citations to the articles providing evidence. The PubMed augmentation experiments provided GPT-4 with access to PubMed database search via the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) E-utils APIs ( 32 ). We used Azure OpenAI Services (version 2023-07-01-preview) and GPT-4 (version 2023-06-13) and set the decoding temperature to zero to obtain deterministic outputs. The full prompts are provided in Supplementary Table S6 .
PubTator-augmented GPT-4 generally processed the questions in three steps: (i) finding the standard entity identifiers, (ii) finding its related entity identifiers and (iii) searching PubMed articles. For example, to answer ‘What drugs can treat breast cancer?’, GPT-4 first found the PubTator entity identifier for breast cancer (@DISEASE_Breast_Cancer) using the Find Entity ID API. It then used the Find Related Entities API to identify entities related to @DISEASE_Breast_Cancer through a ‘treat’ relation. For demonstration purposes, we limited the maximum number of output entities to five. Finally, GPT-4 called the Export Relevant Search Results API for the PubMed article identifiers containing evidence for these relationships. The raw responses to each prompt for each method are provided in Supplementary Table S6 .
We manually evaluated the accuracy of the citations in the responses by reviewing each PubMed article and verifying whether each PubMed article cited supported the stated relationship (e.g. Tamoxifen treating breast cancer). Supplementary Table S5 reports the proportion of the cited articles with valid supporting evidence for each method. GPT-4 frequently generated fabricated citations, widely known as the hallucination issue. While PubMed-augmented GPT-4 showed a higher proportion of accurate citations, some articles cited did not support the relation claims. This is likely because PubMed is based on keyword and Boolean search and does not support queries for specific relationships. Responses generated by PubTator-augmented GPT-4 demonstrated the highest level of citation accuracy, underscoring the potential of PubTator 3.0 as a high-quality knowledge source for addressing biomedical information needs through retrieval-augmented generation with LLMs such as GPT-4. In our experiment, using Azure for ChatGPT, the cost was approximately $1 for two questions with GPT-4-Turbo, or 40 questions when downgraded to GPT-3.5-Turbo, including the cost of input/output tokens.
Previous versions of PubTator have fulfilled over one billion API requests since 2015, supporting a wide range of research applications. Numerous studies have harnessed PubTator annotations for disease-specific gene research, including efforts to prioritize candidate genes ( 33 ), determine gene–phenotype associations ( 34 ), and identify the genetic underpinnings of disease comorbidities ( 35 ). Several projects have used PubTator to create gene and genetic variant resources ( 36 , 37 ) or to enrich disease knowledge graphs ( 38 , 39 ). Moreover, PubTator has supported biocuration efforts ( 40 , 41 ) and the creation of NLP benchmarks ( 42 ). With enhanced accuracy, PubTator 3.0 will better support these use cases.
Introducing relation annotations to PubTator 3.0 opens novel avenues for expanded use scenarios. With relations precomputed from the literature, complex research questions can often be answered directly. Drug repurposing, for example, can be formulated as identifying chemicals which target specific genes. Conversely, determining the genetic targets of a chemical can be achieved by querying the same chemical/gene relations. Clinicians evaluating genetic variants, e.g. for rare diseases or personalized medicine, may explore the relationships between specific genetic variants and disease. Biologists, on the other hand, may utilize interactions between multiple genes to assemble complex molecular pathways.
There are several notable limitations for PubTator 3.0. Although it is capable of extracting relations from full-text articles, this feature is currently restricted to abstracts due to computational constraints. However, the system has been designed to support full-text relation extraction in a future enhancement. The current system only extracts 12 relation types, though these represent common uses. Finally, entity annotation and relation extraction are automated; though these systems exhibit high performance, their accuracy remains imperfect.
PubTator 3.0 offers a comprehensive set of features and tools that allow researchers to navigate the ever-expanding wealth of biomedical literature, expediting research and unlocking valuable insights for scientific discovery. The PubTator 3.0 interface, API, and bulk file downloads are available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/ .
Data is available through the online interface at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/ , through the API at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/pubtator3/api or bulk FTP download at https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lu/PubTator3/ .
The source code for each component of PubTator 3.0 is openly accessible. The AIONER named entity recognizer is available at https://github.com/ncbi/AIONER . GNorm2, for gene name normalization, is available at https://github.com/ncbi/GNorm2 . The tmVar3 variant name normalizer is available at https://github.com/ncbi/tmVar3 . The NLM-Chem Tagger, for chemical name normalization, is available at https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lu/NLMChem . The TaggerOne system, for disease and cell line normalization, is available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/research/bionlp/Tools/taggerone . The BioREx relation extraction system is available at https://github.com/ncbi/BioREx . The code for customizing ChatGPT with the PubTator 3.0 API is available at https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/pubtator-gpt . The details of the applications, performance, evaluation data, and citations for each tool are shown in Supplementary Table S7 . All source code is also available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10839630 .
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
Intramural Research Program of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health; ODSS Support of the Exploration of Cloud in NIH Intramural Research. Funding for open access charge: Intramural Research Program of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Conflict of interest statement . None declared.
Present address: Alexis Allot, The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital), McGill University, Montreal, Quebec H3A 2B4, Canada.
Present address: Ling Luo, School of Computer Science and Technology, Dalian University of Technology, 116024 Dalian, China.
Present address: Qingyu Chen, Biomedical Informatics and Data Science, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT 06510, USA.
Lindberg D.A. , Humphreys B.L. Rising expectations: access to biomedical information . Yearb Med. Inform. 2008 ; 3 : 165 – 172 .
Google Scholar
Jin Q. , Leaman R. , Lu Z. PubMed and beyond: biomedical literature search in the age of artificial intelligence . EBioMedicine . 2024 ; 100 : 104988 .
Rzhetsky A. , Seringhaus M. , Gerstein M. Seeking a new biology through text mining . Cell . 2008 ; 134 : 9 – 13 .
Mayers M. , Li T.S. , Queralt-Rosinach N. , Su A.I. Time-resolved evaluation of compound repositioning predictions on a text-mined knowledge network . BMC Bioinf. 2019 ; 20 : 653 .
Zhao S. , Su C. , Lu Z. , Wang F. Recent advances in biomedical literature mining . Brief Bioinform . 2021 ; 22 : bbaa057 .
Li P.-H. , Chen T.-F. , Yu J.-Y. , Shih S.-H. , Su C.-H. , Lin Y.-H. , Tsai H.-K. , Juan H.-F. , Chen C.-Y. , Huang J.-H. pubmedKB: an interactive web server for exploring biomedical entity relations in the biomedical literature . NucleicAcids Res. 2022 ; 50 : W616 – W622 .
Westergaard D. , Staerfeldt H.H. , Tonsberg C. , Jensen L.J. , Brunak S. A comprehensive and quantitative comparison of text-mining in 15 million full-text articles versus their corresponding abstracts . PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018 ; 14 : e1005962 .
Luo L. , Wei C.-H. , Lai P.-T. , Leaman R. , Chen Q. , Lu Z. AIONER: all-in-one scheme-based biomedical named entity recognition using deep learning . Bioinformatics . 2023 ; 39 : btad310 .
Lai P.T. , Wei C.H. , Luo L. , Chen Q. , Lu Z. BioREx: improving biomedical relation extraction by leveraging heterogeneous datasets . J. Biomed. Inform. 2023 ; 146 : 104487 .
Wei C.-H. , Allot A. , Leaman R. , Lu Z. PubTator central: automated concept annotation for biomedical full text articles . NucleicAcids Res. 2019 ; 47 : W587 – W593 .
Kilicoglu H. , Rosemblat G. , Fiszman M. , Shin D Broad-coverage biomedical relation extraction with SemRep . BMC Bioinf. 2020 ; 21 : 188 .
Peng Y. , Wei C.-H. , Lu Z. Improving chemical disease relation extraction with rich features and weakly labeled data . J. Cheminformatics . 2016 ; 8 : 53 .
Xu J. , Wu Y. , Zhang Y. , Wang J. , Lee H.J. , Xu H. CD-REST: a system for extracting chemical-induced disease relation in literature . Database . 2016 ; 2016 : baw036 .
Li J. , Sun Y. , Johnson R.J. , Sciaky D. , Wei C.-H. , Leaman R. , Davis A.P. , Mattingly C.J. , Wiegers T.C. , Lu Z. BioCreative V CDR task corpus: a resource for chemical disease relation extraction . Database . 2016 ; 2016 : baw068 .
Luo L. , Lai P.-T. , Wei C.-H. , Arighi C.N. , Lu Z. BioRED: a Rich Biomedical Relation Extraction Dataset . Brief. Bioinf. 2022 ; 23 : bbac282 .
Comeau D.C. , Islamaj Doğan R. , Ciccarese P. , Cohen K.B. , Krallinger M. , Leitner F. , Lu Z. , Peng Y. , Rinaldi F. , Torii M.J.D. BioC: a minimalist approach to interoperability for biomedical text processing . Database . 2013 ; 2013 : bat064 .
Sohn S. , Comeau D.C. , Kim W. , Wilbur W.J. Abbreviation definition identification based on automatic precision estimates . BMC Bioinf. 2008 ; 9 : 402 .
Islamaj R. , Wei C.-H. , Cissel D. , Miliaras N. , Printseva O. , Rodionov O. , Sekiya K. , Ward J. , Lu Z. NLM-Gene, a richly annotated gold standard dataset for gene entities that addresses ambiguity and multi-species gene recognition . Sci. Data . 2021 ; 118 : 103779 .
Islamaj R. , Leaman R. , Kim S. , Kwon D. , Wei C.-H. , Comeau D.C. , Peng Y. , Cissel D. , Coss C. , Fisher C. NLM-Chem, a new resource for chemical entity recognition in PubMed full text literature . Sci. Data . 2021 ; 8 : 91 .
Doğan R.I. , Leaman R. , Lu Z. NCBI disease corpus: a resource for disease name recognition and concept normalization . J. Biomed. Inform. 2014 ; 47 : 1 – 10 .
Wei C.-H. , Allot A. , Riehle K. , Milosavljevic A. , Lu Z. tmVar 3.0: an improved variant concept recognition and normalization tool . Bioinformatics . 2022 ; 38 : 4449 – 4451 .
Pafilis E. , Frankild S.P. , Fanini L. , Faulwetter S. , Pavloudi C. , Vasileiadou A. , Arvanitidis C. , Jensen L.J. The SPECIES and ORGANISMS resources for fast and accurate identification of taxonomic names in text . PLoS One . 2013 ; 8 : e65390 .
Arighi C. , Hirschman L. , Lemberger T. , Bayer S. , Liechti R. , Comeau D. , Wu C. Bio-ID track overview . BioCreative VI Challenge Evaluation Workshop . 2017 ; 14 – 19 .
Google Preview
Wei C.H. , Luo L. , Islamaj R. , Lai P.T. , Lu Z. GNorm2: an improved gene name recognition and normalization system . Bioinformatics . 2023 ; 39 : btad599 .
Lipscomb C.E. Medical subject headings (MeSH) . Bull. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2000 ; 88 : 265 .
Leaman R. , Lu Z. TaggerOne: joint named entity recognition and normalization with semi-Markov Models . Bioinformatics . 2016 ; 32 : 2839 – 2846 .
Bairoch A. The Cellosaurus, a cell-line knowledge resource . J. Biomol. Tech. 2018 ; 29 : 25 – 38 .
Gu Y. , Tinn R. , Cheng H. , Lucas M. , Usuyama N. , Liu X. , Naumann T. , Gao J. , Poon H. Domain-specific language model pretraining for biomedical natural language processing . ACM Trans. Comput. Healthcare . 2021 ; 3 : 1 – 23 .
Yasunaga M. , Leskovec J. , Liang P. LinkBERT: Pretraining Language Models with Document Links . Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) . 2022 ; 8003 – 8016 .
Jin Q. , Leaman R. , Lu Z. Retrieve, summarize, and verify: how will ChatGPT affect information seeking from the medical literature? . J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023 ; 34 : 1302 – 1304 .
Tian S. , Jin Q. , Yeganova L. , Lai P.T. , Zhu Q. , Chen X. , Yang Y. , Chen Q. , Kim W. , Comeau D.C. et al. . Opportunities and challenges for ChatGPT and large language models in biomedicine and health . Brief Bioinform . 2023 ; 25 : bbad493 .
Sayers E. Entrez Programming Utilities Help . 2010 ; Bethesda, MD National Center for Biotechnology Information (US) .
Lieberwirth J.K. , Buttner B. , Klockner C. , Platzer K. , Popp B. , Abou Jamra R. AutoCaSc: prioritizing candidate genes for neurodevelopmental disorders . Hum. Mutat. 2022 ; 43 : 1795 – 1807 .
Buch A.M. , Vertes P.E. , Seidlitz J. , Kim S.H. , Grosenick L. , Liston C. Molecular and network-level mechanisms explaining individual differences in autism spectrum disorder . Nat. Neurosci. 2023 ; 26 : 650 – 663 .
Pinto B.G.G. , Oliveira A.E.R. , Singh Y. , Jimenez L. , Goncalves A.N.A. , Ogava R.L.T. , Creighton R. , Schatzmann Peron J.P. , Nakaya H.I. ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19 . J. Infect. Dis. 2020 ; 222 : 556 – 563 .
Mitsuhashi N. , Toyo-Oka L. , Katayama T. , Kawashima M. , Kawashima S. , Miyazaki K. , Takagi T. TogoVar: a comprehensive Japanese genetic variation database . Hum. Genome Var . 2022 ; 9 : 44 .
Jiang J. , Yuan J. , Hu Z. , Zhang Y. , Zhang T. , Xu M. , Long M. , Fan Y. , Tanyi J.L. , Montone K.T. et al. . Systematic illumination of druggable genes in cancer genomes . Cell Rep. 2022 ; 38 : 110400 .
Pu Y. , Beck D. , Verspoor K. Graph embedding-based link prediction for literature-based discovery in Alzheimer's disease . J. Biomed. Inform. 2023 ; 145 : 104464 .
Chen C. , Ross K.E. , Gavali S. , Cowart J.E. , Wu C.H. COVID-19 Knowledge Graph from semantic integration of biomedical literature and databases . Bioinformatics . 2021 ; 37 : 4597 – 4598 .
Lou P. , Jimeno Yepes A. , Zhang Z. , Zheng Q. , Zhang X. , Li C. BioNorm: deep learning-based event normalization for the curation of reaction databases . Bioinformatics . 2020 ; 36 : 611 – 620 .
Percha B. , Altman R.B. A global network of biomedical relationships derived from text . Bioinformatics . 2018 ; 34 : 2614 – 2624 .
Legrand J. , Gogdemir R. , Bousquet C. , Dalleau K. , Devignes M.-D. , Digan W. , Lee C.-J. , Ndiaye N.-C. , Petitpain N. , Ringot P. PGxCorpus, a manually annotated corpus for pharmacogenomics . Sci. Data . 2020 ; 7 : 3 .
Author notes
Email alerts, citing articles via.
- Editorial Board
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1362-4962
- Print ISSN 0305-1048
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

The use and impact of surveillance-based technology initiatives in inpatient and acute mental health settings: A systematic review
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Jessica L. Griffiths
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- ORCID record for Katherine R. K. Saunders
- ORCID record for Una Foye
- ORCID record for Anna Greenburgh
- ORCID record for Antonio Rojas-Garcia
- ORCID record for Brynmor Lloyd-Evans
- ORCID record for Sonia Johnson
- ORCID record for Alan Simpson
- Info/History
- Supplementary material
- Preview PDF
Background: The use of surveillance technologies is becoming increasingly common in inpatient mental health settings, commonly justified as efforts to improve safety and cost-effectiveness. However, the use of these technologies has been questioned in light of limited research conducted and the sensitivities, ethical concerns and potential harms of surveillance. This systematic review aims to: 1) map how surveillance technologies have been employed in inpatient mental health settings, 2) identify any best practice guidance, 3) explore how they are experienced by patients, staff and carers, and 4) examine evidence regarding their impact. Methods: We searched five academic databases (Embase, MEDLINE, PsycInfo, PubMed and Scopus), one grey literature database (HMIC) and two pre-print servers (medRxiv and PsyArXiv) to identify relevant papers published up to 18/09/2023. We also conducted backwards and forwards citation tracking and contacted experts to identify relevant literature. Quality was assessed using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool. Data were synthesised using a narrative approach. Results: A total of 27 studies were identified as meeting the inclusion criteria. Included studies reported on CCTV/video monitoring (n = 13), Vision-Based Patient Monitoring and Management (VBPMM) (n = 6), Body Worn Cameras (BWCs) (n = 4), GPS electronic monitoring (n = 2) and wearable sensors (n = 2). Twelve papers (44.4%) were rated as low quality, five (18.5%) medium quality, and ten (37.0%) high quality. Five studies (18.5%) declared a conflict of interest. We identified minimal best practice guidance. Qualitative findings indicate that patient, staff and carer perceptions and experiences of surveillance technologies are mixed and complex. Quantitative findings regarding the impact of surveillance on outcomes such as self-harm, violence, aggression, care quality and cost-effectiveness were inconsistent or weak. Discussion: There is currently insufficient evidence to suggest that surveillance technologies in inpatient mental health settings are achieving the outcomes they are employed to achieve, such as improving safety and reducing costs. The studies were generally of low methodological quality, lacked lived experience involvement, and a substantial proportion (18.5%) declared conflicts of interest. Further independent coproduced research is needed to more comprehensively evaluate the impact of surveillance technologies in inpatient settings, including harms and benefits. If surveillance technologies are to be implemented, it will be important to engage all key stakeholders in the development of policies, procedures and best practice guidance to regulate their use, with a particular emphasis on prioritising the perspectives of patients.
Competing Interest Statement
AS and UF have undertaken and published research on BWCs. We have received no financial support from BWC or any other surveillance technology companies. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Clinical Protocols
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=463993
Funding Statement
This study is funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Policy Research Programme (grant no. PR-PRU-0916-22003). The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. ARG was supported by the Ramon y Cajal programme (RYC2022-038556-I), funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities.
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
The template data extraction form is available in Supplementary 1. MMAT quality appraisal ratings for each included study are available in Supplementary 2. All data used is publicly available in the published papers included in this review.
View the discussion thread.
Supplementary Material
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (316)
- Allergy and Immunology (618)
- Anesthesia (160)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2277)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (279)
- Dermatology (201)
- Emergency Medicine (370)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (798)
- Epidemiology (11579)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (678)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3582)
- Geriatric Medicine (337)
- Health Economics (617)
- Health Informatics (2305)
- Health Policy (913)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (864)
- Hematology (335)
- HIV/AIDS (753)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13155)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (757)
- Medical Education (359)
- Medical Ethics (100)
- Nephrology (389)
- Neurology (3351)
- Nursing (191)
- Nutrition (507)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (651)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (646)
- Oncology (1758)
- Ophthalmology (525)
- Orthopedics (209)
- Otolaryngology (284)
- Pain Medicine (223)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (438)
- Pediatrics (1004)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (422)
- Primary Care Research (406)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3062)
- Public and Global Health (5992)
- Radiology and Imaging (1223)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (715)
- Respiratory Medicine (811)
- Rheumatology (367)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (353)
- Sports Medicine (316)
- Surgery (386)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (170)
- Urology (142)

COMMENTS
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
When you write a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to: Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context; Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
Most commonly used undergraduate research methods: Scholarship Methods: Studies the body of scholarship written about a particular author, literary work, historical period, literary movement, genre, theme, theory, or method. Textual Analysis Methods: Used for close readings of literary texts, these methods also rely on literary theory and ...
The literature review can serve various functions in the contexts of education and research. It aids in identifying knowledge gaps, informing research methodology, and developing a theoretical framework during the planning stages of a research study or project, as well as reporting of review findings in the context of the existing literature.
In the field of research, the term method represents the specific approaches and procedures that the researcher systematically utilizes that are manifested in the research design, sampling design, data collec-tion, data analysis, data interpretation, and so forth. The literature review represents a method because the literature reviewer chooses ...
This article is organized as follows: The next section presents the methodology adopted by this research, followed by a section that discusses the typology of literature reviews and provides empirical examples; the subsequent section summarizes the process of literature review; and the last section concludes the paper with suggestions on how to improve the quality and rigor of literature ...
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works. Also, we can define a literature review as the ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
The conventional focus of rigorous literature reviews (i.e., review types for which systematic methods have been codified, including the various approaches to quantitative systematic reviews [2-4], and the numerous forms of qualitative and mixed methods literature synthesis [5-10]) is to synthesize empirical research findings from multiple ...
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal.
Literature search. Fink has defined research literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners."[]Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the ...
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about methodology.
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences: ... Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method ...
Method details Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12].An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a ...
Keywords: literary research methods or methodologies, literary theories, research skills, oral history, archival, discourse analysis, textual analysis, interviewing, ICT Discover the world's ...
Qualitative Research Methodology. This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Keywords: A literature review, Research Methodology, Methods of Review . Process. 1. Introduction. In all studies, the literature r eview is a significant consideration as well as it is an.
How to choose a research methodology? Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8 Research objectives, aims, and questions—these would help structure the research design.; Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.; Check the statistical requirements—if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the ...
evaluations of the literature regarding problematic methods topics, which have the potential to promote clearer, shared understandings, and accelerate advances in research methods. Further work is warranted to develop more definitive guidance. Keywords: Systematic review, Literature selection, Research methods, Research methodology, Overview of
Zhenguo Yuan points out that "literature research methodology" include non-structured qualitative analysis and structured quantitative analysis. They access to and process information contained in literatures from different perspectives. Generally speaking, literatures are descriptions of the nature, functions and characteristics of objects.
We conducted an exhaustive and focused scoping review and followed the methodological framework for scoping reviews as previously described in the literature [20, 22].This study aligned with the four goals of a scoping review [].We followed the first five out of the six steps outlined by Arksey and O'Malley's to ensure our review's validity 1) identifying the research question 2 ...
To survey the available knowledge on evaluation practices for KMb strategies, we conducted a scoping review. According to Munn et al. [], a scoping review is indicated to identify the types of available evidence and knowledge gaps, to clarify concepts in the literature and to identify key characteristics or factors related to a concept.This review methodology also allows for the inclusion of a ...
Activities such as formulating a research hypothesis require an exploratory approach, whereas tasks like interpreting the clinical significance of genetic variants are more focused. Traditional keyword-based search methods have long formed the foundation of biomedical literature search . While generally effective for basic search, these methods ...
As a result, the use of quantitative methods is essential in built environment evaluation research. In the current literature, despite the growing number of empirical studies to quantify the relationship between human perception and the built environment, there are few articles that provide a systematic review of the existing literature, so ...
Of the two research priorities, recruitment continues to attract substantially more research, but the retention literature may be more robust, with a higher percentage of randomised evaluations of retention strategies. ... (TMRP) and Health Research Board-Trials Methodology Research Network (HRB-TMRN).
Background: The use of surveillance technologies is becoming increasingly common in inpatient mental health settings, commonly justified as efforts to improve safety and cost-effectiveness. However, the use of these technologies has been questioned in light of limited research conducted and the sensitivities, ethical concerns and potential harms of surveillance. This systematic review aims to ...