We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business

How to Write Business Proposal (Examples + Free Templates)
By Aditya Sheth , Jan 25, 2024

The great Mark Cuban once said, “Sales cure all.” If a business doesn’t sell, it doesn’t make money and by extension the business fails. That’s why you need to write business proposals .
A well-written business proposal can often mean the difference between winning or losing a prospective client.
In this in-depth guide to creating business proposals, we show you how to close more deals, make more sales and crush your business goals — all by using easy-to-edit professional business proposal templates .
Here’s what this guide will cover (click to jump ahead):
What is a business proposal, what are the components of a business proposal.
- How to write a business proposal step by step
What should you include in a business proposal?
What are the types of business proposals, more business proposal examples + writing and design tips.
- FAQs about business proposals
Looking for a shortcut? Watch this quick video for an overview of everything to include in your business proposal:
A business proposal is a document designed to outline a business plan to convince potential client, investor or partner to engage in a business agreement with you or your company. It’s basically a sales pitch in writing to persuade potential clients to show them benefits of working with you or your company for their business success.
A business proposal outlines what your business does and what you can do for your client . It can be general like this business proposal example:

Or it can be more specific, like this business proposal template which focuses on proposing a project for the Newton Center Rail:

Or this business proposal sample, which presents a plan for a social media strategy and campaign:

To design a business proposal that holds the client’s attention, identify their pain points . Then provide your buyer with the right solution to alleviate those frustrations.
Working on a new project? These project proposal examples might come in handy for you.
The components of a business proposal can change depending on the field, company size and client needs. While details may differ, strong proposals typically introduce your company, explain the problem, offer a solution and its benefits, highlight your team’s skills, and outline timeline, cost and next steps.
How to write a business proposal step by step
Before you start creating your business proposal template, you need to understand the business proposal format. At a high level, your effective business proposal should include the following:
- Create a compelling business proposal title
- Build a table of contents
- Craft the executive summary
- Write a detailed problem statement
- Propose your solutions
- Showcase your team’s expertise
- Create a realistic timeline
- Present your payment structure
- Specify the terms and conditions
- Receiving the decision
Below, you can see business proposal examples that demonstrate how to include these 10 sections.
1. Create a compelling business proposal title
A compelling title could mean the difference between someone reading your proposal or ignoring it in favor of a competitor’s .
What makes a good title page? Here are the essential elements to include:
- Your name along with your company’s name
- The name of the prospect (or their business)
- The date you’re submitting the proposal

The gray business consulting proposal template above contains all the details a prospect would want to know. The title also offers a strong tangible benefit to the prospective buyer. Honestly, “Who doesn’t want to grow their business?”
2. Build a table of contents
The table of contents is a fundamental part of every winning business proposal template. It makes your proposal scannable and easy to read.
The people you will be pitching to are usually C-level executives. These are busy people who don’t have time to read your entire proposal in one go.
That’s why most of the business proposal examples in this list include a table of contents.
Adding a table of contents to your document makes it easy for them to go through it at their own pace. They can also skim through parts of the proposal that they deem more important. You can see how this abstract business proposal template uses the table of contents:

You can also make your business proposal template easier to navigate by adding hyperlinks to the document, particularly in the table of contents. This way your clients can jump to specific sections without having to scroll through the entire document.
It’s easy to add hyperlinks in the Venngage editor. Select the text you’d like to turn into a link, then click the link icon in the top bar. From there, select the page you want to link to! Then download your completed design as an Interactive PDF .

3. Craft the executive summary
The executive summary is a staple in all kinds of annual reports , leadership development plan , project plans and even marketing plans . It is a concise summary of the entire contents of your document. In other words, write a business proposal outline that is easy to glance over and that highlights your value proposition.
The goals of your executive summary are:
- Introduce your company to your buyer
- Provide an overview of your company goals
- Showcase your company’s milestones, overall vision and future plans
- Include any other relevant details
This gray business proposal example has a detailed yet short executive summary including some social proof in the form of clients they’ve worked with:

Take note of how precise this business proposal example is. You want to keep your executive summary concise and clear from the get-go. This sets the right tone for the rest of your proposal. It also gives your buyer a reason to continue reading your proposal.
Crafting an executive summary and keeping it concise and compelling can be challenging. but you can use an AI summarizer online to generate an executive summary. Such tools are trained on relevant AI models that can extract core points from a given text. You can get such a point either in bullet form or in abstract summary form.
Pro Tip: Try to write an executive summary such that, even if your prospective client doesn’t read the entire proposal (with a good executive summary, they most likely will), they should have a clear idea about what your company does and how you can help them.
4. Write a detailed problem statement
The point of writing a business proposal is to solve a buyer’s problem. Your goal is to outline the problem statement as clearly as possible. This develops a sense of urgency in your prospect. They will want to find a solution to the problem. And you have that solution.
A well-defined problem statement does two things:
- It shows the prospect you have done your homework instead of sending a generic pitch
- It creates an opportunity for you to point out a problem your prospect might not be aware they had in the first place.

This bold business proposal template above clearly outlines the problem at hand and also offers a ray of hope i.e. how you can solve your prospect’s problem. This brings me to…
5. P ropose your solutions
The good stuff. In the proposed solution section, you show how you can alleviate your prospective buyer’s pain points. This can fit onto the problem statement section but if you have a comprehensive solution or prefer to elaborate on the details, a separate section is a good idea.
Spare no details regarding the solution you will provide. When you write a business proposal, explain how you plan to deliver the solution. Include an estimated timeline of when they can expect your solution and other relevant details.
For inspiration, look at how this business proposal template quickly and succinctly outlines the project plan, deliverables and metrics :

6. Showcase your team’s expertise
At this point, the prospect you’re pitching your solution to likes what they’re reading. But they may not trust you to deliver on your promises. Why is this?
It’s because they don’t know you. Your job is to convince them that you can fix their problem. This section is important because it acts as social proof. You can highlight what your company does best and how qualified your team is when you write a business proposal for a potential client.

This free business proposal template showcases the company’s accolades, client testimonials, relevant case studies, and industry awards. You can also include other forms of social proof to establish yourself as a credible business. This makes it that much more likely that they will say yes!
Pro Tip: Attaching in-depth case studies of your work is a great way to build trust with a potential client by showcasing how you’ve solved similar problems for other clients in the past. Our case study examples post can show you how to do just that.
7. Create a realistic timeline
To further demonstrate just how prepared you are, it’s important to outline the next steps you will take should your buyer decide to work with you.
Provide a timeline of how and when you will complete all your deliverables. You can do this by designing a flow chart . Or add a roadmap with deadlines. Pitching a long-term project? A timeline infographic would be a better fit.
If you look at this abstract business proposal template below, even something as simple as a table can do the trick.

The timeline is not always set in stone, rather it’s an estimation. The goal is to clarify any questions your potential client might have about how you will deliver for the underlying B2B sales process.
8. Present your payment and terms
On this page, you can outline your fees, payment schedule, invoice payment terms , as well as legal aspects involved in this deal. You can even use the Excel Invoice Template to create professional-looking invoices (including brand logo and other elements) and add them to this page.
The key to good pricing is to provide your buyer with options. A pricing comparison table can help with this. You want to give your client some room to work with. Make sure you’re not scaring off your client with a high price, nor undervaluing yourself.
Breaking up your pricing in stages is another great way to make sure your potential client knows what he’s paying for. Look at how this simple business proposal template does this:

The legal aspects can slot right into the terms and conditions section. Alternatively, you can add them to the signature section of the proposal to keep things simple.
9. Specify the terms and conditions
Summarize everything you have promised to deliver so far. Include what you expect from your prospective buyer in return. Add the overall project timeline from start to end, as well as payment methods and payment schedule, incorporating these details into an online digital project management tool. This way, both of you will be clear on what is being agreed on.
This step is very important as it outlines all the legal aspects of the deal. That is why the terms and conditions section of your proposal needs to be as clear as possible.

I recommend consulting a lawyer or your legal team when working on this section of the business proposal. If you’re a business veteran and understand the legalities of your business, you can use the same terms and conditions across all your proposals.
10. Receiving the decision
The final step of this whole process. Your client has read your business proposal and they want to buy what you have to offer.
Add a small section at the end of your proposal to get the necessary signatures. This way, you and your client can sign the proposal and the partnership becomes official.
Be sure to also include your contact information in your business proposal template. It acts as a gentle prompt to your client to contact you in case they have any questions. A professional way of doig that would be to include an e-business card with your contact details, email i.d and any other social links you want to share. You can go through this article for the best digital business cards .

A business proposal usually aims to answer the following questions:
- Who you are and what your company does
- The problem your buyer is facing
- The solution your company offers to alleviate the problem
- How your company will implement this solution effectively
- An estimate of resources (time, money, etc) required to implement the solution
You can see how this sample business proposal template covers the above points.

Notice how this proposal template addresses the same project like in one of the previous templates, but uses a completely different design style (more retro, while the previous business proposal template is more modern and minimalistic).
Generally, there are three types of business proposals:
1. Formally solicited
A formally solicited business proposal is made when you respond to an official request to write a business proposal.
In this scenario, you know all the requirements and have more (if not all) information about a prospective buyer. You simply need to write the business proposal for your buyer to evaluate so you can begin the sales process .
2. Informally solicited
Informally solicited business proposals are written when there isn’t an official request for a proposal. A prospective buyer is interested in your services and asks for a proposal so they can evaluate it.
An informally solicited proposal requires a lot more research from your end. These types of proposals are usually created out of informal conversations. They are not based on official requests which often contain more detail.
3. Unsolicited
Think of this as a marketing brochure or a cold email . Unsolicited business proposals will often take a generic, one-size-fits-all approach to business proposals. Unsolicited proposals lack any understanding of the buyer or their requirements.
But with additional market research , personalization and identifying customer pain points , you can propose a customized solution based on your buyer’s needs. This can be a very persuasive approach, such as in this business proposal example:

Now that you know how to write a business proposal, let’s look at how you can optimize your proposal to deliver results!
Below you’ll find some winning business proposal templates and examples to get you started. I’ve also included some design tips to keep in mind when you’re creating your next business proposal:
1. Know your audience
If you have some clarity on who your ideal buyer is — their pain points, their budget, deadlines, among other things — you’ve already won half the battle.
If you are a business that helps clients with everything from running giveaways or helping grow their blog , identify which customers to pitch. This is a sure-shot way to close the deal.
Mapping user personas for your ideal buyer can help bring some clarity. It will also help you position your business proposal correctly. This improves the chance of your buyer moving your business proposal to the “Yes!” pile.
2. Put your brand front and center
If your company follows certain brand guidelines, incorporate them in your business proposal templates. Consider how business proposal examples like the one below highlight brand identity :

From the color palettes to the company logos , everything follows their brand guidelines. The result: a business proposal that’s consistent across the board.
Pro Tip: Switching this template to match your brand assets is actually pretty easy. Venngage’s My Brand Kit feature allows you to import your color palettes, logos as well as font choices. Any Venngage template can now be your template.
You can also consider this sample business proposal template:

App design companies sure do know their design. They did a phenomenal job keeping their brand colors consistent while opting for a black design. This unique color scheme also makes their white logo prominent throughout the proposal.
3. Try less text, more visuals
Have you ever read a proposal and thought to yourself, “Wow, this is all text and has no images, I love it!”? Yeah, me neither.
The free business proposal template below is a perfect example of the “less is more” principle. It does a phenomenal job of communicating what it needs to. By substituting some of the text with icons and visuals, you get a clean business proposal that’s much more scannable.

Want to keep things strictly professional? Instead of icons, you can always add your team’s headshots. This shows your buyer exactly who they’ll be working with.
Check out this formal business proposal format for some inspiration:

4. Switch up your business proposal designs
It doesn’t hurt to go above and beyond once in a while. Jazz up your business proposal template with some extra colors. This helps make your business proposal more engaging. It also helps your buyers retain information faster.

The business proposal example alternates between black, white and grey backgrounds. It still manages to maintain consistency in its branding . Just switching up your backgrounds once in a while can also bring in some variety to an otherwise standard business proposal.
This SEO business proposal sample proves that it’s possible to switch up the colors in every other page. But it still maintains the same color scheme across the entire proposal just like a professionally designed website :

Pro Tip: Not a color expert? Our guide on picking colors can help you pick the right color scheme for your proposals.
FAQ about business proposals
What is the purpose of a business proposal.
A business proposal aims to streamline the B2B sales process (which is often complex ) between you as a seller and a buyer.
It does this by serving the dual purpose of acting as a source of information. The proposal also acts as a sales pitch aimed at convincing your buyer why they should buy what you have to offer.
What are the best practices for business proposal design?
- Do a thorough spell-check. The goal of your business proposal is to convince your buyer why you’re the perfect person for the job. A proposal with typos or grammatical errors communicates the opposite. A thorough spell-check before you send your proposal is a must.
- Keep things clear and readable: Clarity is an important aspect that you have to ensure in your business proposal. If you want your proposal to hit home and make an impact on the buyer, you have to write it in an understandable way. To keep things clear and readable, there are a couple of things that you can do. You can, for one, take care to use easy wording and segmented sentences from the get-go. You can also try paraphrasing the hard parts of your proposal once you are done writing it.
- Let your brand shine. As discussed before, writing a business proposal is all about knowing your ideal buyer and focusing on their pain points. But that doesn’t mean your business proposal template has to be boring. Demonstrate how different you are compared to other companies. You can do this through your brand guidelines , by using more visuals, switching up your proposal design or showing off your personality in your writing .
- Create a business proposal PDF. Downloading your business proposal in PDF format allows you to attach other collaterals with your business proposal. These can include a company explainer video or case studies showcasing the work done with past clients. Also, who doesn’t love saving paper?
How long should your business proposal be?
The length depends on the scope of the work as well as the complexity of the project. Here is a one-page business proposal template:

Can your business proposal template really be one page? Yes, as long as you understand who your buyer is and their pain points. You should also have the ability to communicate everything your ideal buyer needs to know about your business in a succinct manner.
Or if you’re feeling adventurous how about just two pages? Often, clients prefer if you go straight to the point and avoid all the fluff.
For example, this green modern marketing proposal template wastes no time in getting down to brass tacks:

Need more inspiration? Check out this blog on the 5 marketing proposal examples that’ll help elevate your business.
There is no one size fits all approach when it comes to deciding how many pages you should include in your business proposal template. And at the end of the day, “the only rules are the ones you set for yourself”.
At the end of the day, writing winning business proposals that sell is all about you understanding your buyer, their potential pain points and positioning yourself as someone who can alleviate those pain points.
Now that you know how to write compelling business proposals, what are you waiting for?
Take action and start creating your own business proposals to close more deals and grow your business today!
More business communications templates + writing tips you might be interested in…
- 31 Consulting Proposal Templates to Close Deals
- 20+ Professional Business Letterhead Templates + Branding Tips
- How to Write a White Paper [Tips & Templates]
How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: November 30, 2023
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a struggle. Before you can even begin to expect to earn their business, you need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on what your product or service promises.

Sure, you could say that you're great at X or that you're way ahead of the competition when it comes to Y. But at the end of the day, what you really need to win new business is cold, hard proof.
One of the best ways to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. In fact, HubSpot’s 2020 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so compelling that they are the fifth most commonly used type of content used by marketers.

Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what you need to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic. To jump to different areas of this post, click on the links below to automatically scroll.
Case Study Definition
Case study templates, how to write a case study.
- How to Format a Case Study
Business Case Study Examples
A case study is a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it's common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client. Perhaps the success you're highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers and help you attract new clients.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why write a case study?
I know, you’re thinking “ Okay, but why do I need to write one of these? ” The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples. Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain Complex Topics or Concepts
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies and show how they can be applied in a practical way. You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that shows how your product solved their issue and how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar successful results.
2. Show Expertise
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build Trust and Credibility
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework. They can have confidence in the solutions you’ve presented because they’ve read through as you’ve explained the problem and outlined step-by-step what it took to solve it. All of these elements working together enable you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create Social Proof
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof . People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — putting your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes work together to help you gain more clients. Plus you can even use quotes from customers featured in these studies and repurpose them in other marketing content. Now that you know more about the benefits of producing a case study, let’s check out how long these documents should be.
How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved. This may be easier said than done, but it's important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader's interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers. We’ve also seen brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience.
Ultimately, the length of your case study should be determined by the amount of information necessary to convey the story and its impact without becoming too long. Next, let’s look at some templates to take the guesswork out of creating one.
To help you arm your prospects with information they can trust, we've put together a step-by-step guide on how to create effective case studies for your business with free case study templates for creating your own.
Tell us a little about yourself below to gain access today:
And to give you more options, we’ll highlight some useful templates that serve different needs. But remember, there are endless possibilities when it comes to demonstrating the work your business has done.
1. General Case Study Template

Do you have a specific product or service that you’re trying to sell, but not enough reviews or success stories? This Product Specific case study template will help.
This template relies less on metrics, and more on highlighting the customer’s experience and satisfaction. As you follow the template instructions, you’ll be prompted to speak more about the benefits of the specific product, rather than your team’s process for working with the customer.
4. Bold Social Media Business Case Study Template

You can find templates that represent different niches, industries, or strategies that your business has found success in — like a bold social media business case study template.
In this template, you can tell the story of how your social media marketing strategy has helped you or your client through collaboration or sale of your service. Customize it to reflect the different marketing channels used in your business and show off how well your business has been able to boost traffic, engagement, follows, and more.
5. Lead Generation Business Case Study Template

It’s important to note that not every case study has to be the product of a sale or customer story, sometimes they can be informative lessons that your own business has experienced. A great example of this is the Lead Generation Business case study template.
If you’re looking to share operational successes regarding how your team has improved processes or content, you should include the stories of different team members involved, how the solution was found, and how it has made a difference in the work your business does.
Now that we’ve discussed different templates and ideas for how to use them, let’s break down how to create your own case study with one.
- Get started with case study templates.
- Determine the case study's objective.
- Establish a case study medium.
- Find the right case study candidate.
- Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
- Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
- Download a case study email template.
- Define the process you want to follow with the client.
- Ensure you're asking the right questions.
- Layout your case study format.
- Publish and promote your case study.
1. Get started with case study templates.
Telling your customer's story is a delicate process — you need to highlight their success while naturally incorporating your business into their story.
If you're just getting started with case studies, we recommend you download HubSpot's Case Study Templates we mentioned before to kickstart the process.
2. Determine the case study's objective.
All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives.
Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring. In other words, what will the client have succeeded in doing by the end of the piece?
The client objective you focus on will depend on what you want to prove to your future customers as a result of publishing this case study.
Your case study can focus on one of the following client objectives:
- Complying with government regulation
- Lowering business costs
- Becoming profitable
- Generating more leads
- Closing on more customers
- Generating more revenue
- Expanding into a new market
- Becoming more sustainable or energy-efficient
3. Establish a case study medium.
Next, you'll determine the medium in which you'll create the case study. In other words, how will you tell this story?
Case studies don't have to be simple, written one-pagers. Using different media in your case study can allow you to promote your final piece on different channels. For example, while a written case study might just live on your website and get featured in a Facebook post, you can post an infographic case study on Pinterest and a video case study on your YouTube channel.
Here are some different case study mediums to consider:
Written Case Study
Consider writing this case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form for readers to fill out before downloading the piece, allowing this case study to generate leads for your business.
Video Case Study
Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers.
Infographic Case Study
Use the long, vertical format of an infographic to tell your success story from top to bottom. As you progress down the infographic, emphasize major KPIs using bigger text and charts that show the successes your client has had since working with you.
Podcast Case Study
Podcasts are a platform for you to have a candid conversation with your client. This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success.
4. Find the right case study candidate.
Writing about your previous projects requires more than picking a client and telling a story. You need permission, quotes, and a plan. To start, here are a few things to look for in potential candidates.
Product Knowledge
It helps to select a customer who's well-versed in the logistics of your product or service. That way, he or she can better speak to the value of what you offer in a way that makes sense for future customers.
Remarkable Results
Clients that have seen the best results are going to make the strongest case studies. If their own businesses have seen an exemplary ROI from your product or service, they're more likely to convey the enthusiasm that you want prospects to feel, too.
One part of this step is to choose clients who have experienced unexpected success from your product or service. When you've provided non-traditional customers — in industries that you don't usually work with, for example — with positive results, it can help to remove doubts from prospects.
Recognizable Names
While small companies can have powerful stories, bigger or more notable brands tend to lend credibility to your own. In fact, 89% of consumers say they'll buy from a brand they already recognize over a competitor, especially if they already follow them on social media.
Customers that came to you after working with a competitor help highlight your competitive advantage and might even sway decisions in your favor.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
Most importantly at this point, however, is getting your subject's approval. When first reaching out to your case study candidate, provide them with the case study's objective and format — both of which you will have come up with in the first two steps above.
To get this initial permission from your subject, put yourself in their shoes — what would they want out of this case study? Although you're writing this for your own company's benefit, your subject is far more interested in the benefit it has for them.
Benefits to Offer Your Case Study Candidate
Here are four potential benefits you can promise your case study candidate to gain their approval.
Brand Exposure
Explain to your subject to whom this case study will be exposed, and how this exposure can help increase their brand awareness both in and beyond their own industry. In the B2B sector, brand awareness can be hard to collect outside one's own market, making case studies particularly useful to a client looking to expand their name's reach.
Employee Exposure
Allow your subject to provide quotes with credits back to specific employees. When this is an option for them, their brand isn't the only thing expanding its reach — their employees can get their name out there, too. This presents your subject with networking and career development opportunities they might not have otherwise.
Product Discount
This is a more tangible incentive you can offer your case study candidate, especially if they're a current customer of yours. If they agree to be your subject, offer them a product discount — or a free trial of another product — as a thank-you for their help creating your case study.
Backlinks and Website Traffic
Here's a benefit that is sure to resonate with your subject's marketing team: If you publish your case study on your website, and your study links back to your subject's website — known as a "backlink" — this small gesture can give them website traffic from visitors who click through to your subject's website.
Additionally, a backlink from you increases your subject's page authority in the eyes of Google. This helps them rank more highly in search engine results and collect traffic from readers who are already looking for information about their industry.
6. Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
So you know what you’re going to offer your candidate, it’s time that you prepare the resources needed for if and when they agree to participate, like a case study release form and success story letter.
Let's break those two down.
Case Study Release Form
This document can vary, depending on factors like the size of your business, the nature of your work, and what you intend to do with the case studies once they are completed. That said, you should typically aim to include the following in the Case Study Release Form:
- A clear explanation of why you are creating this case study and how it will be used.
- A statement defining the information and potentially trademarked information you expect to include about the company — things like names, logos, job titles, and pictures.
- An explanation of what you expect from the participant, beyond the completion of the case study. For example, is this customer willing to act as a reference or share feedback, and do you have permission to pass contact information along for these purposes?
- A note about compensation.
Success Story Letter
As noted in the sample email, this document serves as an outline for the entire case study process. Other than a brief explanation of how the customer will benefit from case study participation, you'll want to be sure to define the following steps in the Success Story Letter.
7. Download a case study email template.
While you gathered your resources, your candidate has gotten time to read over the proposal. When your candidate approves of your case study, it's time to send them a release form.
A case study release form tells you what you'll need from your chosen subject, like permission to use any brand names and share the project information publicly. Kick-off this process with an email that runs through exactly what they can expect from you, as well as what you need from them. To give you an idea of what that might look like, check out this sample email:
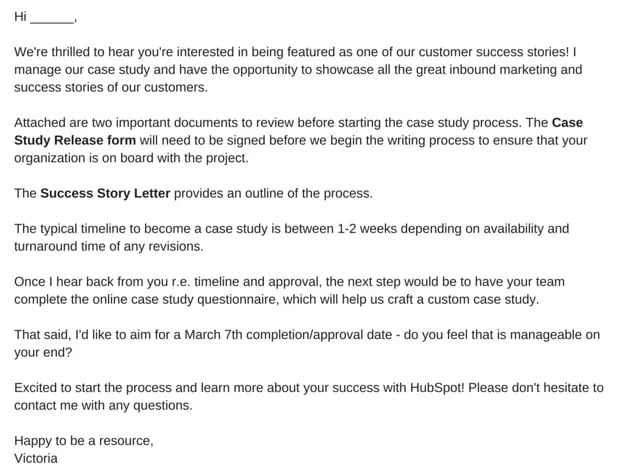
8. Define the process you want to follow with the client.
Before you can begin the case study, you have to have a clear outline of the case study process with your client. An example of an effective outline would include the following information.
The Acceptance
First, you'll need to receive internal approval from the company's marketing team. Once approved, the Release Form should be signed and returned to you. It's also a good time to determine a timeline that meets the needs and capabilities of both teams.
The Questionnaire
To ensure that you have a productive interview — which is one of the best ways to collect information for the case study — you'll want to ask the participant to complete a questionnaire before this conversation. That will provide your team with the necessary foundation to organize the interview, and get the most out of it.
The Interview
Once the questionnaire is completed, someone on your team should reach out to the participant to schedule a 30- to 60-minute interview, which should include a series of custom questions related to the customer's experience with your product or service.
The Draft Review
After the case study is composed, you'll want to send a draft to the customer, allowing an opportunity to give you feedback and edits.
The Final Approval
Once any necessary edits are completed, send a revised copy of the case study to the customer for final approval.
Once the case study goes live — on your website or elsewhere — it's best to contact the customer with a link to the page where the case study lives. Don't be afraid to ask your participants to share these links with their own networks, as it not only demonstrates your ability to deliver positive results and impressive growth, as well.
9. Ensure you're asking the right questions.
Before you execute the questionnaire and actual interview, make sure you're setting yourself up for success. A strong case study results from being prepared to ask the right questions. What do those look like? Here are a few examples to get you started:
- What are your goals?
- What challenges were you experiencing before purchasing our product or service?
- What made our product or service stand out against our competitors?
- What did your decision-making process look like?
- How have you benefited from using our product or service? (Where applicable, always ask for data.)
Keep in mind that the questionnaire is designed to help you gain insights into what sort of strong, success-focused questions to ask during the actual interview. And once you get to that stage, we recommend that you follow the "Golden Rule of Interviewing." Sounds fancy, right? It's actually quite simple — ask open-ended questions.
If you're looking to craft a compelling story, "yes" or "no" answers won't provide the details you need. Focus on questions that invite elaboration, such as, "Can you describe ...?" or, "Tell me about ..."
In terms of the interview structure, we recommend categorizing the questions and flowing them into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, and how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context. That helps match the customer's need with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes. Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you've collected and actually turn it into something, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. Where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
To help you get a handle on this step, it's important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study. They can be very visual, which you'll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated mostly through video or photos, with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections we suggest, which we'll cover in more detail down below:
- Title: Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle: Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary : A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject: An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives: A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped: A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results: A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes: Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans: Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call to Action (CTA): Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible. Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you've completed your case study, it's time to publish and promote it. Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas:
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier in this article, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF. To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client's success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they'd like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people here from your homepage with a "Case Studies" or "Testimonials" button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
Format for a Case Study
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

Image Source
The title is one of the most important parts of your case study. It should draw readers in while succinctly describing the potential benefits of working with your company. To that end, your title should:
- State the name of your custome r. Right away, the reader must learn which company used your products and services. This is especially important if your customer has a recognizable brand. If you work with individuals and not companies, you may omit the name and go with professional titles: “A Marketer…”, “A CFO…”, and so forth.
- State which product your customer used . Even if you only offer one product or service, or if your company name is the same as your product name, you should still include the name of your solution. That way, readers who are not familiar with your business can become aware of what you sell.
- Allude to the results achieved . You don’t necessarily need to provide hard numbers, but the title needs to represent the benefits, quickly. That way, if a reader doesn’t stay to read, they can walk away with the most essential information: Your product works.
The example above, “Crunch Fitness Increases Leads and Signups With HubSpot,” achieves all three — without being wordy. Keeping your title short and sweet is also essential.
2. Subtitle

Your subtitle is another essential part of your case study — don’t skip it, even if you think you’ve done the work with the title. In this section, include a brief summary of the challenges your customer was facing before they began to use your products and services. Then, drive the point home by reiterating the benefits your customer experienced by working with you.
The above example reads:
“Crunch Fitness was franchising rapidly when COVID-19 forced fitness clubs around the world to close their doors. But the company stayed agile by using HubSpot to increase leads and free trial signups.”
We like that the case study team expressed the urgency of the problem — opening more locations in the midst of a pandemic — and placed the focus on the customer’s ability to stay agile.
3. Executive Summary

The executive summary should provide a snapshot of your customer, their challenges, and the benefits they enjoyed from working with you. Think it’s too much? Think again — the purpose of the case study is to emphasize, again and again, how well your product works.
The good news is that depending on your design, the executive summary can be mixed with the subtitle or with the “About the Company” section. Many times, this section doesn’t need an explicit “Executive Summary” subheading. You do need, however, to provide a convenient snapshot for readers to scan.
In the above example, ADP included information about its customer in a scannable bullet-point format, then provided two sections: “Business Challenge” and “How ADP Helped.” We love how simple and easy the format is to follow for those who are unfamiliar with ADP or its typical customer.
4. About the Company

Readers need to know and understand who your customer is. This is important for several reasons: It helps your reader potentially relate to your customer, it defines your ideal client profile (which is essential to deter poor-fit prospects who might have reached out without knowing they were a poor fit), and it gives your customer an indirect boon by subtly promoting their products and services.
Feel free to keep this section as simple as possible. You can simply copy and paste information from the company’s LinkedIn, use a quote directly from your customer, or take a more creative storytelling approach.
In the above example, HubSpot included one paragraph of description for Crunch Fitness and a few bullet points. Below, ADP tells the story of its customer using an engaging, personable technique that effectively draws readers in.

5. Challenges and Objectives

The challenges and objectives section of your case study is the place to lay out, in detail, the difficulties your customer faced prior to working with you — and what they hoped to achieve when they enlisted your help.
In this section, you can be as brief or as descriptive as you’d like, but remember: Stress the urgency of the situation. Don’t understate how much your customer needed your solution (but don’t exaggerate and lie, either). Provide contextual information as necessary. For instance, the pandemic and societal factors may have contributed to the urgency of the need.
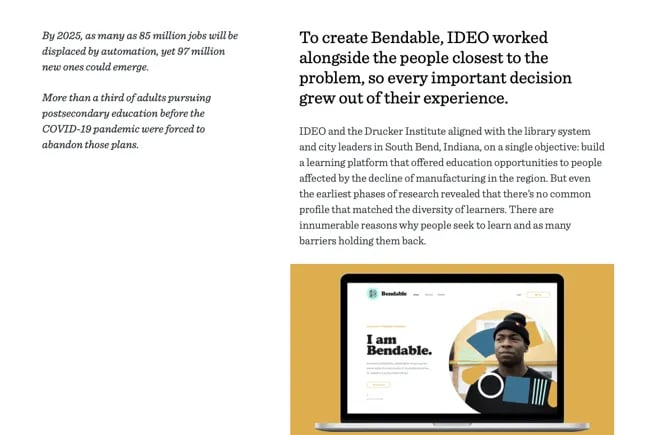
Take the above example from design consultancy IDEO:
“Educational opportunities for adults have become difficult to access in the United States, just when they’re needed most. To counter this trend, IDEO helped the city of South Bend and the Drucker Institute launch Bendable, a community-powered platform that connects people with opportunities to learn with and from each other.”
We love how IDEO mentions the difficulties the United States faces at large, the efforts its customer is taking to address these issues, and the steps IDEO took to help.
6. How Product/Service Helped
This is where you get your product or service to shine. Cover the specific benefits that your customer enjoyed and the features they gleaned the most use out of. You can also go into detail about how you worked with and for your customer. Maybe you met several times before choosing the right solution, or you consulted with external agencies to create the best package for them.
Whatever the case may be, try to illustrate how easy and pain-free it is to work with the representatives at your company. After all, potential customers aren’t looking to just purchase a product. They’re looking for a dependable provider that will strive to exceed their expectations.
In the above example, IDEO describes how it partnered with research institutes and spoke with learners to create Bendable, a free educational platform. We love how it shows its proactivity and thoroughness. It makes potential customers feel that IDEO might do something similar for them.

The results are essential, and the best part is that you don’t need to write the entirety of the case study before sharing them. Like HubSpot, IDEO, and ADP, you can include the results right below the subtitle or executive summary. Use data and numbers to substantiate the success of your efforts, but if you don’t have numbers, you can provide quotes from your customers.
We can’t overstate the importance of the results. In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and result.
8. Supporting Visuals or Quotes

Let your customer speak for themselves by including quotes from the representatives who directly interfaced with your company.
Visuals can also help, even if they’re stock images. On one side, they can help you convey your customer’s industry, and on the other, they can indirectly convey your successes. For instance, a picture of a happy professional — even if they’re not your customer — will communicate that your product can lead to a happy client.
In this example from IDEO, we see a man standing in a boat. IDEO’s customer is neither the man pictured nor the manufacturer of the boat, but rather Conservation International, an environmental organization. This imagery provides a visually pleasing pattern interrupt to the page, while still conveying what the case study is about.
9. Future Plans
This is optional, but including future plans can help you close on a more positive, personable note than if you were to simply include a quote or the results. In this space, you can show that your product will remain in your customer’s tech stack for years to come, or that your services will continue to be instrumental to your customer’s success.
Alternatively, if you work only on time-bound projects, you can allude to the positive impact your customer will continue to see, even after years of the end of the contract.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Not every case study needs a CTA, but we’d still encourage it. Putting one at the end of your case study will encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
It will also make it easier for them to reach out, if they’re ready to start immediately. You don’t want to lose business just because they have to scroll all the way back up to reach out to your team.
To help you visualize this case study outline, check out the case study template below, which can also be downloaded here .
You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down your findings into a compelling story. And after all of that, you're left with a little piece of sales enabling gold — a case study.
To show you what a well-executed final product looks like, have a look at some of these marketing case study examples.
1. "Shopify Uses HubSpot CRM to Transform High Volume Sales Organization," by HubSpot
What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. This reflects a major HubSpot value, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why Shopify uses HubSpot and is accompanied by a short video and some basic statistics on the company.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the additional text on the page. So, while case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
2. "New England Journal of Medicine," by Corey McPherson Nash
When branding and design studio Corey McPherson Nash showcases its work, it makes sense for it to be visual — after all, that's what they do. So in building the case study for the studio's work on the New England Journal of Medicine's integrated advertising campaign — a project that included the goal of promoting the client's digital presence — Corey McPherson Nash showed its audience what it did, rather than purely telling it.
Notice that the case study does include some light written copy — which includes the major points we've suggested — but lets the visuals do the talking, allowing users to really absorb the studio's services.
3. "Designing the Future of Urban Farming," by IDEO
Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, he or she is greeted with a big, bold photo, and two very simple columns of text — "The Challenge" and "The Outcome."
Immediately, IDEO has communicated two of the case study's major pillars. And while that's great — the company created a solution for vertical farming startup INFARM's challenge — it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, those pillars are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and additional visuals.
4. "Secure Wi-Fi Wins Big for Tournament," by WatchGuard
Then, there are the cases when visuals can tell almost the entire story — when executed correctly. Network security provider WatchGuard can do that through this video, which tells the story of how its services enhanced the attendee and vendor experience at the Windmill Ultimate Frisbee tournament.
5. Rock and Roll Hall of Fame Boosts Social Media Engagement and Brand Awareness with HubSpot
In the case study above , HubSpot uses photos, videos, screenshots, and helpful stats to tell the story of how the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame used the bot, CRM, and social media tools to gain brand awareness.
6. Small Desk Plant Business Ups Sales by 30% With Trello
This case study from Trello is straightforward and easy to understand. It begins by explaining the background of the company that decided to use it, what its goals were, and how it planned to use Trello to help them.
It then goes on to discuss how the software was implemented and what tasks and teams benefited from it. Towards the end, it explains the sales results that came from implementing the software and includes quotes from decision-makers at the company that implemented it.
7. Facebook's Mercedes Benz Success Story
Facebook's Success Stories page hosts a number of well-designed and easy-to-understand case studies that visually and editorially get to the bottom line quickly.
Each study begins with key stats that draw the reader in. Then it's organized by highlighting a problem or goal in the introduction, the process the company took to reach its goals, and the results. Then, in the end, Facebook notes the tools used in the case study.
Showcasing Your Work
You work hard at what you do. Now, it's time to show it to the world — and, perhaps more important, to potential customers. Before you show off the projects that make you the proudest, we hope you follow these important steps that will help you effectively communicate that work and leave all parties feeling good about it.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally published in February 2017 but was updated for comprehensiveness and freshness in July 2021.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![business proposal case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![business proposal case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![business proposal case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- eSignatures
- Product updates
- Document templates
How to write a business proposal (The modern way)
Yauhen Zaremba Director of Demand Generation at PandaDoc
Reviewed by:
Jenny Pak Director of Program Management at PandaDoc
- Copy Link Link copied
Streamline your document workflow & close deals faster
Get personalized 1:1 demo with our product specialist.
- Tailored to your needs
- Answers all your questions
- No commitment to buy
Schedule your free live demo
By submitting this form, I agree that the Terms of Service and Privacy Notice will govern the use of services I receive and personal data I provide respectively.
Nothing speaks to a customer’s direct needs like a well-written business proposal.
It’s the key to unlocking new opportunities, securing lucrative deals, and watching your ideas flourish.
But how do you make sure that your proposal is engaging to every potential client and business owner?
As it turns out, our customers might have some ideas.
More than 7 million documents were sent via PandaDoc in 2023, and the vast majority of those documents were proposals .
This article (originally released in 2021) has been updated with insights from our analysis into those documents.
Here’s a closer look at how to write a business proposal that actually works.
Key takeaways
- A business proposal outlines a product, service, or project that a company offers potential clients or partners to convince them the business can meet their needs.
- A well-crafted business proposal is essential and should include information about your company, demonstrated knowledge of the problem, and pricing and methodology.
- Modern business proposals are sent electronically. Platforms like PandaDoc have tools to help you create a collaborative environment for negotiation, feedback, and electronic signature.
- 65% of business proposals containing a signature block close within 24 hours. Don’t forget to follow up and ask your potential client if they have any questions.

→DOWNLOAD NOW: FREE BUSINESS PROPOSAL TEMPLATE
Our data: the breakdown
Like we mentioned at the top, the insights in this article are compiled from our analysis of nearly 7 million documents that were sent through the PandaDoc platform in 2023.
Here’s a quick list of the most popular proposal and document types that were sent through our systems last year:
- NDA Template .
- Social media marketing proposal .
- Digital marketing proposal .
- Software development proposal .
- Business proposal (generic).
- Marketing proposal (generic) .
- Grant proposal .
- Sponsorship proposal .
Similar proposals of various types were also sent in smaller numbers, along with a wide array of other sales documents.
Because PandaDoc is more than a proposal platform, the lion’s share of documents flowing through our platform are invoices, quotes templates, contracts, and similar business collateral.
Proposals represent a small but essential segment of business documentation.
Other insights
While we were analyzing proposals and business documents, a few other statistics stood out to us.
- The average creation time for proposals dropped significantly when using automation tools like templates and the content library.
- The addition of an e-signature block made no significant difference in proposal creation time.

Business proposals are essential sales collateral in the business world. You’ll need one if you’re selling complete and/or complicated solutions.
Business proposals: the basics
This section covers basic information about business proposals, including an in-depth look at what they are and why you might need them.
While the technical specifications required for a proposal vary between industries, the basics regarding how a proposal is intended to function are largely the same.
We’ll cover the parts of a business proposal in the next section so, if you’re already familiar with the basics, feel free to skip ahead.
What are business proposals & why are they important?
A business proposal is a document that outlines a specific product, service, or project that a company offers to potential clients or partners, with the aim of persuading them that the business can meet their needs.
As proposals often present the benefits, features, and terms of a certain idea , these documents are important in many industries for sales, marketing, project management, and other business endeavors.
Typically, a business deal follows after a proposal has been accepted.
However, not all proposals are the same.
Depending on the needs of the client and the industry that you occupy, the content included in the business proposal format may fluctuate.
For example, while a digital marketing proposal and a proposal for building construction may have some broad similarities (introduction, pricing section, FAQs, etc.), both documents will vary wildly in terms of composition and overall goals.
It’s fair to say that the proposal required for building construction is probably longer, takes more time to create, and is likely to include a broader variety of business proposal topics than that of a sales representative trying to close a marketing deal.
The basic format of a business proposal
At a high level, most business proposals follow a similar structure and/or include similar information.
Based on our research into proposals created on the PandaDoc platform, most business proposals following this standard format are around nine pages in length .
However, keep in mind that lengths will vary depending on your industry and scope of work.
Particularly in industries like construction or home repair, where physical components and labor play a role, proposals become more complicated due to the parts and expertise involved.
As several of our own account executives and sales team members were quick to point out, longer doesn’t always mean better.
“ Short and sweet has a high conversion rate , fewer pages and less fluff is better. Ideally, a proposal should be fewer than 10 pages for transactional proposals below $10,000, and never more than 50 pages.” Josh Gillespie, Upmarket Sales
Artyom Voronetskiy, Account Executive with PandaDoc, agrees:
“ Keep it short, on-point, and eye-catching . Do not write more than six to ten pages unless your product is extremely complicated.”
While you’ll need to include all relevant information that prospective clients will need in order to make a decision, take care to avoid overcrowding them with irrelevant details.
To get a closer look at how to get started and bring your business proposal ideas to life using these steps, check out the next major section of this article.
Types of business proposals
Aside from the subject matter of your proposal — which is usually determined by the type of product/service your business provides — proposals fall into a handful of categories centered around how and why the proposal was initially created.
This information is particularly important, because proposals that originate from a request for proposal (RFP) document may be required to follow specific requirements and guidelines set forth by the requesting organization.
Here’s a breakdown of the types of proposals commonly used today.
Solicited business proposals
Solicited business proposals are proposals that a company has asked you to provide for their consideration.
The potential customer has reached out to your business and requested a proposal. These proposals fall into one of two categories:
Formally solicited proposals are typically competitive and follow a standardized (formal) process.
The prospective client sends out an RFP detailing the scope of work and requests that your business formally submit a bid to complete that work.
Informally solicited proposals are typically created based on conversations between a prospective client and a vendor that they want to work with.
There might not be any formal documentation, and there may be no competitive process.
This work can often lead to a sole-source, non-competitive contract.
Unsolicited business proposals
Unsolicited business proposals are proposals that your company sends to a prospective client who hasn’t asked for one.
They are not submitted in response to an RFP or an information request.
Such proposals are typically created based on a market opportunity — often one that the client is either unaware of or hasn’t yet acted upon.
How to write a business proposal
Writing a business proposal is like building a house.
While certain elements are always necessary — like the foundation — some components vary based on location and the architect or homeowner’s preferences.
In the same way, the components of a business proposal can vary based on industry, company size, and many other factors.
Just like writing anything else, a well-written proposal begins by gathering information and assessing the problems that your potential client is trying to solve.
When writing a business proposal, the following items are what readers are looking to understand. Think of these as the roof, walls, and foundation of your document:
- Information about your company. Your background, your qualifications, and why you’re a better fit than the rest of your competitors.
- Demonstrated knowledge of the problem. Proof that you’ve listened and done your research. You know what the client needs and you have a viable solution.
- Pricing and methodology. How you plan to solve the client’s problem, information about your proposed solution, and how much it’s going to cost.
In this section, we’ll take you through how to write a business proposal using a modified version of social media proposal template as an example.

Social Media Marketing Proposal Template
Used 13721 times
4.3 rating (24 reviews)
Legally reviewed by Yauhen Zaremba
If you’re not a social media company, don’t worry.
While the business proposal template we’re using is an example of a simple project proposal, the basic structure applies to nearly every business proposal — no matter how complex they might be.
You can download this business proposal example or other business proposal templates on our website.
Here are the main elements of a business proposal.
How to write an outline for a business proposal
A standard proposal outline typically includes most or all of the following elements:
- Title page.
- Cover letter.
- Table of contents.
- Executive summary.
- Proposal & solutions pages.
- Testimonials & social proof.
- Agreement & CTA.
However, this won’t always be the case. Shorter projects and abbreviated formats may not call for every single section.
When creating your business proposal, you should include everything you believe you need in order to sell your product or service to your prospective customer.
This usually includes the sections above, as well as any supplemental documentation to justify your costs and reinforce your proposed approach to solving the client’s problem.
If you’re sending your proposal electronically, you should also consider including an electronic signature block so that decision makers can quickly and easily seal the deal when they’re ready to proceed.
In addition to basic information about your product/service, you may want to include the following:
- Contact information.
- Value statements.
- Pricing tables.
- Client testimonials.
- Examples of past work (case studies).
- Images, graphics, and related multimedia.
To save time, gather this information before you start the proposal process.
Having this information on hand while building your proposal will make the process much easier.
Once you’ve got all the essential details and sales collateral you need, you’re ready to start creating your proposal document.

Many templates in the PandaDoc library feature fun, editable cover pages. We’re also integrated with Canva, if you want to take a hands-on approach to your layouts.
1. Create a cover page
This section of a business proposal includes basic information that your readers will need to understand the document and its content.
Consider including each of the following elements:
- Proposal title.
- Date of submission.
- Company information (company logo, company name, etc).
- Your name, title, and contact information.
- Client’s name, title, and contact information.
A cover page is the very first thing that your prospective client will see when they open your business proposal.
Give them all the details they need to identify the document at a glance, and take the time to make it look good.
Everyone knows how important that first impression can be.
Studies have shown that you have as little as 50 milliseconds to make a good first impression when designing visual content like websites.
The same holds true for the cover page of your business proposal.
This page is a place where you can freely place graphics and visual content to set the tone before the reader dives into the meat of your presentation.
Variables make it easy to modify proposal items that will change each time you send your content and allow you to reuse the same document by swapping the variable values.
PandaDoc supports variables by default, but you can also create them manually and replace the text using the find/replace tool in your word processor.
However, you won’t need to go overboard with complicated graphics and logos.
Users love simple and familiar designs , especially at a first glance.
Spending time on this page is also a great way to give your proposal a unique look and feel.
Based on what we’ve seen, some businesses skip cover pages entirely.
However, we don’t recommend it.
Take advantage of this missed opportunity from your competitors and use it to make your proposal stand out.

A simple cover letter is a great introduction to your proposal document. Using template tools and variables, each letter can be customized in moments.
2. Introduce yourself with a cover letter
You wouldn’t walk up to your potential client and dive into project specifics without taking the time to introduce yourself, would you?
A cover letter is that introduction. Consider including each of the following:
- A short blurb about your company.
- A quick summary of your proposal.
- A reason that your approach is best.
- A signoff with your contact information.
This section is essential because it helps anyone reading the document understand your relationship to their organization and how the proposal came about.
With your business proposal introduction, keep the tone light and friendly and encourage your reader to reach out with any questions.
Sign off by including your contact details so that the client can get in touch directly if they need to follow up or would like to move forward.
Cover letters don’t need to run to the point of exhaustion. They can be simple, short, and sweet.
This page can take on many forms, and you can use that flexibility to make your cover letter easier to parse.
This example rephrases the text in the image above by using bullets to make the formatting more legible:
Dear [Client.FirstName]
Thank you for considering [Sender.Company] for your social media marketing needs.
Enclosed, you’ll find a proposal based on our understanding of your social media expectations. Briefly, we propose:
An expanded social media strategy across currently unused platforms and channels.
A comprehensive distribution strategy designed to generate original and unique content.
Improved post automation for increased audience engagement during peak times.
Our methods and procedures are based on extensive analysis, an intense study of social media trends, and the application of specifics unique to [Client.Company].
We are confident in delivering effective results within your social media channels.
Thanks again for considering us, and please don’t hesitate to get in touch with questions.
My contact information is below.
Lastly, in our initial example, you’ll also notice that we’ve used an image to keep things fresh and interesting.
This is critical throughout your proposal. In our research, we found that a business proposal with media like photos and videos included is 34% more likely to close.

Including graphics and multimedia create visually appealing content that prompts engagement.
That’s huge!
As you’re making your proposal, don’t be afraid to add graphics and images to keep readers engaged.
A winning business proposal is more than just black text on a white page.

In a digital proposal, a clickable table of contents can make navigation easy. If you think the proposal will be printed, include page numbers for faster manual navigation.
3. Table of contents
A table of contents is an important, but often overlooked, part of any longer document because it helps the reader know what they can expect to find in the proposal.
Unless your business proposal is very brief, include a table of contents that outlines the basic structure of your document.
This element isn’t always necessary, but it can make a business proposal much easier to parse as your document is passed around to all appropriate parties.
How you want to approach this may vary, depending on the nature of the proposal and the client business.
Electronic documents
Electronic documents can benefit from a clickable table of contents .
Word processors typically generate these using the headings in your document .
Readers can click on them to jump to relevant sections without the need to navigate through multiple pages.
Physical documents
Physical documents will benefit from having page numbers associated with the table of contents since a business proposal PDF (hard copy) isn’t clickable.
Most word processors have an option to include page numbers in your table of contents , but make sure that you update the element when your document is complete in case the page numbers have changed.
Keep in mind that proposal documents may not be read chronologically.
Different decision makers will care about different things and will check your business proposal to see how it addresses their unique pain points.
Don’t lose a deal just because stakeholders couldn’t find what they were looking for!

The executive summary provides a high-level overview of your proposed solution and can be broken down with headings into multiple components.
4. Set the stage with an executive summary
The goal of an executive summary is to provide a holistic, high-level overview of your proposal, how it addresses the client’s problem, and its expected outcomes.
If you provided a few of these points in your cover letter, this is your opportunity to go into greater detail and summarize your overall strategy.
However, because this section needs to give a full overview, it’s difficult to write if you haven’t created the rest of your proposal.
For this reason, experienced proposal writers often write this section last.
Don’t get lost describing deliverable logistics or strategic plans.
Focus on the client’s needs and the outcomes they specifically wanted to address in their RFP.
Let your executive summary present a high-level overview and leave the other pages of the document to explain the details.
This will prevent your summary from getting overcrowded or bogged down with specifics best handled elsewhere.
Using the example in our social media proposal template , let’s pretend that our potential clients are primarily realtors in the greater Chicago area looking to reach new clients through social media marketing.
With that in mind, we could modify the executive summary in the existing template to something like this:
This proposal outlines a coordinated plan crafted with the intent of building [Client.Company]’s social media presence, primarily including Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, TikTok, and X (Twitter).
By engaging an audience through social media channels, our team will demonstrate the ability to generate awareness, widen your company’s potential reach within your target market, and contribute to driving more website traffic, which will ultimately result in top-line growth.
We help teams identify, target, and communicate with their ideal clients through each of the following:
1. Creating engaging social content.
2. Posting company-related updates.
3. Promotions and social campaigns.
4. Integrating social activity into marketing initiatives.
5. Sustained monitoring.
6. Analytics & reviews.
While our competitors work to serve multiple industries and target audiences, we specialize in the [Client.Industry] industry. Founder Mike Smith also has a background in both social media and [Client.Industry], giving him a unique perspective on the needs of the market.
Your own executive summary and the tone you use to address problems may shift depending on the duties you’re performing for your client, and what kind of industry they’re in.
For example, if you’re targeting a young travel startup run by new college graduates, you might use a more casual tone peppered with industry jargon and humor.
By contrast, a group of C-level executives might prefer a more formal summary styled with specific metrics and numbers.
Keep your audience in mind as you write this section and demonstrate that you understand what they’re trying to achieve.
Remember: The executive summary previews the rest of the document. If your summary fails to address reader concerns, your proposal may be discarded without a full review.

Make sure your approach is clear. Tables and other visual aids are useful when summarizing your solution.
5. Proposal and solutions pages
The proposal section is the heart of your entire document.
In this section, you’ll need to fully present the solution your company has devised for a potential client.
This section should do each of the following:
- Provide a comprehensive breakdown of the solution your company has devised to solve a client’s problem.
- Tell readers exactly what deliverables they can expect and when they should expect them.
- Answer obvious questions that reviewers may have about your approach and/or methodology.
While you can write this section out in full paragraphs, visual aids can be extremely helpful in conveying critical information in a digestible way.
A timetable that pairs deliverables with their expected date can make your document more visually appealing, and your information much easier to parse.
You might also break down your main objectives even further by describing how you plan to execute a given strategy.
In our executive summary example (above), we touched on six key goals. Let’s expand on those here.
1. Creating engaging social content
Beginning with quick and thorough planning/preparation, our team will plan out a dynamic, ongoing social content calendar to guide you to your goals.
We will grow an increasing social audience and follower base using each of the following techniques:
- Hashtag campaigns.
- Strong use of keywords.
- Sharing/retweeting relevant news.
- “Liking” posts.
- Staying updated within the industry.
- Contributing our own unique content to broaden reach.
2. Posting company-related updates
Our plan is to engage your social media audience by sharing company news, press releases, events, employee spotlights, and more.
We will also pay attention to industry trends and share them.
This will help to gain exposure to your target market.
3. Promotions and social campaigns
We will utilize social channels to connect with your follower base and engage them with promotions to get them excited about both current events and the brand itself.
These campaigns may be as short as a day or run up to six months.
We’ll analyze the results from each campaign, and then we will provide a report of its success.
Results of campaigns can be compared so the most effective promotions, offers, or contests can be replicated.
4. Integrating social media activity into other marketing plans
With clear communication and monthly brainstorm meetings, we’ll be able to consolidate the marketing initiatives to fit your goals and promotional material.
Campaigns via social media are more important than just sharing about giveaways, sales, contests, and/or promotions.
We will agree on a schedule for a series of posts to keep up the exciting momentum for all prospective customers.
5. Monitoring
For maximum growth, it’s important to regularly engage with users on social platforms.
We will continually monitor each social channel and will respond to any questions, comments, and posts within a two-hour time period (during business hours).
A small delay will allow us to confirm that the information we relay to customers is accurate.
6. Analytics
We will provide you with each of the following:
- Daily and weekly analytics. Follower growth, reach, demographics, comments, “likes”, shares, retweets, and additional metrics as provided by each platform and our own internal tracking data.
- Reporting. Summarizing various results and activities over each quarter.
We will also set up a monthly meeting to go over the results and then tweak our approach accordingly.
Your own content may look different than this depending on your business proposal writing skills and services, but you can still use the example as a framework. Add in more details as needed.
For example, a cybersecurity company would need to include information on penetration testing and how often it would be done to look for possible intrusions and hacks.
Breaking up this section
While writing business proposal content, keep in mind that this section is both the most important and the most flexible section of all.
Your entire proposal doesn’t need to be bundled into a single, long section. It can easily be broken down into smaller sections such as:
- Strategic Assessment.
- Implementation.
- Goals & Outlook.
There are other combinations you can try, depending on your business proposal and how your solution should be explained.
If you’re offering a complex solution to a client problem, breaking your proposal into bite-sized chunks is a great way to ensure that readers understand your solution.
The importance of good data
Leveraging good data is critical when creating an effective business proposal.
Use details surrounding impact and ROI around your products and services to prove your worth and add value to your proposal.
Consider these two phrases:
- “Our customers love us!”
- “To date, our products and methodologies have helped more than 700 companies increase their sales by 35%!”
Which sounds better? Which is more compelling?
Numbers and figures catch the eye and help readers build trust.
By demonstrating a proven record of success, with numbers and data, you’re adding tangible details that help to justify your costs.
This is especially useful when competing with other solicited proposals, especially if you can include these data points as visual representations (charts, graphs, etc.) of your success within your proposal document.

Providing totals as an itemized list or a package option are effective approaches to pricing.
The pricing section explains how much it will cost the client for you to solve their problem.
In this section, you’ll need to do each of the following:
- Break down your proposed solution by cost.
- Indicate any product quantities as line items.
- Give package options (if applicable).
Regardless of your pricing structure, clarity and specifics are critical in this section.
To eliminate confusion, consider creating a pricing table that clearly identifies each product or service, and pair it with the most accurate pricing information you can provide.
With a dedicated table, all you’ll need to do is set the price for the item and the quantity of distribution.
If you were sending an hourly contract, the quantity is the estimated number of hours invested at a predetermined rate.
For recurring payment schedules, you’ll need to structure the document in a way that accurately reflects your monthly workflow.
Transparency is critical in this section.
Potential customers need to know how you’re charging them, what they’re being charged for, and what to expect in return.
Be sure to include these details in a clear and accurate way.

A biographical section can speak to years of experience, awards and accolades, and more.
7. About us
While you already said hello with the cover letter, this section is where you get to explain what makes your company unique.
If you’re a small business or a new company, get personal and give your potential client a chance to get to know you and your team members.
Consider including the following items:
- A brief summary of your business and its operations.
- Bios and photos of the individuals they’ll be working with.
- Relevant qualifications, certifications, or experience.
If your company has a unique backstory, a mission, or a cause that your company stands for, share that with readers. For example:
Too often in social media, good things come at a price. At Jump, paying for followers or favorable reviews of products is tantamount to criminal activity.
Authenticity is important in today’s online world, and Jump Social Media Marketing makes this our No. 1 priority in your social media space.
The information on this page doesn’t have to be a stodgy company boilerplate or a cleverly designed sales pitch.
Don’t be afraid to let your team’s personality shine through.

Glowing reviews and positive feedback can help prospective clients better understand how your organization delivers on your initiatives.
8. Testimonials and social proof
No sales proposal is complete without information about your past successes, awards, and jobs well done.
In a business proposal, this comes in the form of a social proof section, which might include:
- Past client testimonials.
- Case studies.
- Reviews and/or ratings.
- Industry awards.
Regardless of what you choose to include, don’t skip this section. Social proof matters!
According to data, over half of customers are more likely to trust earned media, like recommendations from friends and family, above all other forms of advertising.
By including recommendations from satisfied customers and industry awards that prove your expertise, you can earn additional trust from prospective clients.
Here’s a good example of how Jump Social Media Marketing might leverage the accolades they’ve received:
Jump Social Media Marketing has received major public recognition for our work.
We’ve been named as Chicago’s Best Social Media Agency for Small Businesses by the Chicago Tribune for the past three years and have been recognized as a recommended partner by the National Association of Realtors.
We also grew the Chicago Real Estate Solutions Facebook page from 0 to 5,000 in six months , secured 250 new leads in that time frame, with 25% converting to sales .
You can also provide testimonials from past clients who can speak to your approach and how it worked for them.
However, keep your industry in mind when compiling testimonials and do your best to find user feedback that fits the mood.
If your industry has serious clients, a humorous approach may not be appropriate.
If you’re working with a manufacturing company focused on B2B industries, the messaging and tone they take with their own clients — and what they expect from the businesses they work with — may follow different expectations.
Be sure to plan accordingly.

With onboard e-signing in your document, the call to action is often the signoff itself. If you choose not to include an e-signature, provide your contact information and instructions on next steps.
9. Agreement and CTA
Depending on your business proposal, you may include an agreement, a call to action, and terms and conditions at the end of your document.
Your signature below indicates acceptance of this social media marketing proposal and entrance into a contractual agreement with Jump Social Media Marketing beginning on the signature date below.
Depending on your goals and your sales process, you need to be very careful in this section.
In many jurisdictions, proposals are considered legally binding agreements if they meet the criteria for a contract.
By adding legal language and/or an electronic signature request at the bottom of your document, you might be entering into a contract earlier than expected.
This may not be ideal if your proposal is only intended to provide a rough estimate of costs or bring the client into further negotiations.
If you don’t intend to create a legally binding contract from your proposal, be sure to note that in your document and prompt the reader to contact you when they’re ready to move forward.
On the other hand, well-built proposals can double as complete contracts with all the terms and conditions necessary to start work immediately.
If you’re confident in the scope of work and you’re ready to move forward, let the client know by prompting them for a signature and using a payment gateway to capture their first payment or deposit.
How should a business proposal look?
First things first: We’re well past the turn of the century.
Nobody likes getting thick envelopes in the mail.
Modern business proposals are sent electronically, and this is more convenient for both you and your potential customers.
While it’s possible to email a proposal created with a word processor like Microsoft Word, platforms like PandaDoc are a better fit.
Our tools help you create a collaborative environment for negotiation, feedback, and electronic signature .
Regardless of how you choose to send a business proposal, be sure to pay close attention to the look and feel of your document.
Especially because your proposal may be your first impression with several key stakeholders, it’s essential that you follow expected formats and make a good impression.

Having the right design and layout tools can transform your proposal from a black-on-white Word document to a standout document that readers want to engage with.
If you search for business proposal examples online or take a look at our template library , you’ll find that most proposals rely on the structure described above to emphasize their value propositions.
Taking care to create a visually appealing business proposal will help you communicate your ideas more easily.
It’s also something that your competitors are doing and something that many clients are beginning to expect.
In our research, we found that roughly 80% of proposals included an image and 20% included a video.
We also saw higher close rates when these multimedia tools were used compared to when they weren’t.
Exactly how a business proposal is designed still has some flexibility, depending on your brand and what you’re trying to achieve, but keep in mind that it can have a big impact on success.
Business proposals with pages of blocky text are much harder to navigate than proposals with charts, graphs, images, and bullet points.
Rather than writing a 1000-word About Us section, consider including team member headshots and a brief bio.
Rather than adding highly technical language about operational processes and leaving stakeholders to figure it out, provide visual aids that summarize the information in a clear and easy fashion.

Generating personalized content quickly improves relevance and helps your team clearly define a scope of work. Onboard formatting and AI tools inside the PandaDoc platform can help.
Clearly defining your milestones isn’t the only reason to pay careful attention to how your business proposal is written.
While there can be legal ramifications to poorly written proposal content, perhaps the most important consideration is the impression that your proposal leaves behind.
Your proposal introduces your client to the quality of work they can expect from your business.
If it’s full of typos, spelling, and grammatical errors, or just seems sloppy, you’re unlikely to close the deal.
Read and re-read. Be sure to proofread every passage for errors before you send it to prospective clients or save it as a template.
You can also offset some of this tedium, especially on smaller deals, by focusing on creating a concise offering rather than a long-winded document.
A word about costs
When you’re creating proposals, it’s easy for costs to add up.
Costs for customized professional business proposals can take hours of research, consultation, and preparation — all with no guarantee of success.
That’s why savvy companies do everything they can to lower the cost of proposal preparation.
Typically this is done by generating a template for business proposals — an outline or skeleton that someone can fill out quickly to save time and expedite internal company processes.
It’s an effective way to keep overhead low.
Based on our research, an average of 20 documents are generated from each template you create.
That’s a huge time saver for any business.
If these aren’t assets that you have on your staff, consider hiring that skillset onto your team or hiring a freelancer to assist with proofreading and correction.
While many clients will overlook a stray typo or a misplaced comma, too many errors will land your proposal in the discard pile.
After you hit ‘Send’ on your business proposal
Once you’ve sent your proposal, your next step will depend on the process.
Based on our information, about 65% of business proposals containing a signature block close within 24 hours.

Even for proposals that take a little longer to close, having an e-signature block and collaboration options inside an interactive document means that review, redlining, and signoff happen in one place.
However, your mileage may vary. RFPs tend to be competitive processes, so you may have to wait until the submission window closes before you hear a response.
Don’t forget to follow up and ask your potential client if they have any questions.
Based on the business proposals we looked at, you are 30% more likely to close a deal if you send a series of reminders to keep your proposal top of mind.

Roughly one out of every three proposals you send will close faster if you send reminders. It’s a big deal.
PandaDoc and other proposal software tools can help you monitor your proposal using document analytics so that you know exactly when to reach out.
These tools let you know when your potential client viewed your proposal, how many times they opened it, and which sections they spent the most time on.
With these insights, you can anticipate their questions or objections and have your responses ready to go.

A great proposal is a blend of text and modern design. Personalization is as much about how your document looks as about what it says.
5 ideas to make your business proposal stand out
Just because you may have a perfect business proposal all ready to go, it doesn’t mean it will stand out from the crowd.
Many startups fail due to larger competitors, so a unique proposal idea can make your readers sit up and take notice.
Pizazz isn’t what matters here, rather any idea that adds value to your proposal and communicates quality.
Here are a few ideas to put the spotlight on your business proposal.
Personalize your proposal for each client
Ensure that your business proposal meets the exact challenges and interests of each recipient, as this will show you understand their specific needs.

Send a digital proposal
While you may need to send a business proposal as a PDF, include a link to a digital copy of the proposal where potential clients can review content, ask questions, and collaborate with your team.
A tool like this will give your recipient access to additional resources and make your proposal interactive.
Add a video introduction
As part of the personalization process, create a memorable experience by recording a brief video introduction.
Small touches like this can help your proposal stand out by demonstrating that you’re willing to do a little more to grab their attention.
Provide effective visual aids
Charts, graphs, and other visual aids are game-changers when it comes to creating effective documents.
Whether you need to present a specific data set or pricing breakdown, take the time to use visuals when the opportunity presents itself.
Readers will thank you for it.
Hide a few Easter eggs
A hidden message, cute animation, or a secret section are all little surprises that add a touch of fun and intrigue to your business proposal.
Easter eggs can encourage exploration and will encourage your readers to spend more time on your proposal.
It won’t be one they’ll forget in a hurry!

Jumpstart your proposal creation process with one of 1000+ documents in the PandaDoc template library.
Start with a free business proposal template
Need to know how to write a business proposal but don’t know where to begin? PandaDoc can help with some great templates.
In the data we reviewed, proposals created using our business proposal templates regularly generated high-performing results for customers with minimal editing time.
Take a look at some of the metrics around the top professional business proposal templates currently in our template library .
With PandaDoc, it’s possible to modify our existing templates and then save them as new, private templates in your content library for faster reuse.
In doing so, you can slim the entire business proposal design process down from hours to minutes or spend more time refining your proposal for maximum appeal.
To see the true power of the PandaDoc editor, be sure to check out our community gallery for expertly designed templates from real PandaDoc customers.
If you’re a PandaDoc user, you can even grab these business proposals and load them directly into your PandaDoc editor with a single click.
It’s just that easy.

PandaDoc can dramatically increase your proposal output, allowing you to send custom proposals to more customers in less time.
Use specialized tools to streamline your workflow
Ultimately, your proposal should be focused on your client’s problems and how your business plans to fix them.
But that doesn’t mean you have to do it alone.
Personalizing documents and tailoring them to a client’s needs is a time-consuming process.
For most businesses, striking a balance between personalization and efficiency is essential.
PandaDoc can help.
Our document creation process streamlines your end-to-end document workflow so that you can generate beautiful, customized documents in less time.
Send better proposals. Close deals faster.
It’s possible with PandaDoc.
Sign up for a demo to see it for yourself, or jump into the driver’s seat with a free 14-day trial and change the way you handle proposals forever.
PandDoc is not a law firm, or a substitute for an attorney or law firm. This page is not intended to and does not provide legal advice. Should you have legal questions on the validity of e-signatures or digital signatures and the enforceability thereof, please consult with an attorney or law firm. Use of PandaDocs services are governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Originally was published in October 2016 and has been updated for comprehensiveness in April 2024
Related articles

Proposals 14 min

Proposals 12 min

Document templates 15 min
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- The beginner’s guide to writing an effe ...
The beginner’s guide to writing an effective business case

Nearly every project needs to be approved—whether that means getting the simple go-ahead from your team or gaining the support of an executive stakeholder. You may be familiar with using a project plan or project charter to propose a new initiative and get the green light for a project. But if your proposed project represents a significant business investment, you may need to build a business case.
If you’ve never written a business case, we’re here to help. With a few resources and a little planning, you can write a business case that will help you get the resources and support you need to manage a successful project.
What is a business case?
A business case is a document that explains the value or benefits your company will gain if you pursue a significant business investment or initiative. This initiative can be anything from the messaging for a new product or feature launch, a proposal to increase spend on a current initiative, or a significant investment with a new agency or contractor—to name a few. A compelling business case will outline the expected benefits of this significant investment decision. Key stakeholders will use the business case you provide to determine whether or not to move forward with an initiative.
If you’ve never created a business case, it may sound similar to other early project planning documentation. Here’s how it stacks up:
The difference between a business case and business plan
A business case is a proposal for a new strategy or large initiative. It should outline the business needs and benefits your company will receive from pursuing this opportunity.
A business plan , on the other hand, is an outline for a totally new business. Typically, you’d draft a business plan to map out your business strategy, your mission and vision statements, and how you’re planning on getting there. There may be a case where you create a business plan for an already-existing business, but you’d only do so if you’re trying to take your business in a significantly new direction.
Business case vs. executive summary
Business case vs. project charter.
If you need to create an elevator pitch for your project but you don’t quite need the full business case treatment, you might need a project charter. Much like a business case, a project charter outlines key details of an initiative. Specifically, a project charter will cover three main elements of your project: project objectives, project scope, and key project stakeholders. Your management team will then use the project charter to approve further project development.
Do you need a business case?
Not every project needs a business case—or even a project charter. Plan to build a business case only for initiatives or investments that will require significant business resources. If you’re working on a smaller initiative, consider creating a project charter to pitch your project idea to relevant stakeholders.
Even if you don’t need to pitch your project to any stakeholders, you should be ready to answer basic questions about your proposed project, like:
What is this project’s purpose?
Why are we working on this project?
How does this project connect to organizational goals and objectives?
Which metrics will we use to measure the success of the project ?
Who is working on this project?
When is this project going to be completed?
5 steps for creating and pitching a business case
Your business case shouldn’t just include key facts and figures—it should also tell a story of why pursuing a particular investment or initiative is a good idea for your business. When in doubt, avoid jargon and be brief—but always focus on communicating the value of the project. If this is your first time creating a business case, don’t worry. Follow these five steps to create a solid one.
1. Gather input
You don’t have to write a business case on your own. Instead, make sure appropriate team members and stakeholders are contributing to the relevant sections. For example, the IT team should be involved in any tooling and timeline decisions, while the finance team should review any budget and risk management sections. If you’re creating a business case to propose a new initiative, product line, or customer persona, make sure you also consult subject matter experts.
2. Plan to write your business case out of order
Some of the first things that appear in your business case—like your executive summary—should actually be drafted last, when you have all of the resources and information to make an informed suggestion. Your executive summary will present all of your findings and make a recommendation for the business based on a variety of factors. By gathering all of those details first—like project purpose, financial information, and project risk—you can ensure your executive summary has all of the relevant information.
3. Build your business case incrementally
A business case describes a significant investment for your company. Similarly, simply writing a business case is a significant investment of your time. Not every initiative is right for your business—so make sure you’re checking your work with stakeholders as you go. You don’t want to sink hours and weeks into this document only for it to be rejected by executive stakeholders right off the bat.
Consider doing a “soft launch” with an outline of your business case to your project sponsor or an executive stakeholder you have a good relationship with to confirm this initiative is something you should pursue. Then, as you build the different sections of your business case, check back in with your key stakeholders to confirm there are no deal-breakers.
4. Refine the document
As you create sections of your business case, you may need to go back and refine other sections. For example, once you’ve finished doing a cost-benefit analysis with your financial team, make sure you update any budget-related project risks.
Before presenting your business case, do a final read through with key stakeholders to look for any sections that can be further refined. At this stage, you’ll also want to write the executive summary that goes at the top of the document. Depending on the length of your business case, your executive summary should be one to two pages long.
5. Present the business case
The final step is to actually present your business case. Start with a quick elevator pitch that answers the what, why, and how of your proposal. Think of this presentation as your chance to explain the current business need, how your proposal addresses the need, and what the business benefits are. Make sure to address any risks or concerns you think your audience would have.
Don’t go through your business case page by page. Instead, share the document with stakeholders before the presentation so they have a chance to read through it ahead of time. Then, after your presentation, share the document again so stakeholders can dig into details.
A business case checklist
Start with the why.
The first section of the business case is your chance to make a compelling argument about the new project. Make sure you draft an argument that appeals to your audience’s interests and needs. Despite being the first section in your business case, this should be the last section you write. In addition to including the traditional elements of an executive summary , make sure you answer:
What business problem is your project solving? This is your chance to explain why your project is important and why executive stakeholders should consider pursuing this opportunity.
What is your business objective ? What happens at the end of a successful project? How will you measure success—and what does a successful project mean for your business?
How does this business case fit into your overall company business strategy plan? Make sure your proposed business case is connected to important company goals . The initiative proposed in your business case should move the needle towards your company's vision statement .
Outline financials and the return on investment
At this point in your business case, you should outline the project finance fundamentals. Don’t expect to create this section on your own—you should draft this in partnership with your company’s finance team. In particular, this section should answer:
How much will this project cost? Even if the initiative is completely new to your company, do some research to estimate the project costs.
What does each individual component of the project cost? In addition to estimating the total overall cost, break down the different project costs. For example, you might have project costs for new tools and resources, competitive intelligence resourcing, agency costs, etc.
What is the expected return on investment (ROI)? You’ve talked about the costs—now talk about how your company will benefit from this initiative. Make sure to explain how you calculated the ROI, too.
How will this project impact cash flow? Cash flow is the amount of money being transferred into and out of your business. Significant investments are going to cost a lot of money, so they’ll negatively impact cash flow—but you should also expect a high ROI, which will positively impact cash flow.
What is the sensitivity analysis? Sensitivity analysis is a summary of how uncertain your numbers are. There will be a variety of variables that impact your business case. Make sure to explain what those variables are, and how that could impact your projections.
Preview project details
Your business case is proposing a new initiative. In addition to the financial risks, take some time to preview project details. For example, your business case should include:
Your project objectives and key project deliverables . What will happen at the end of the project? What are you expecting to create or deliver once the project is over?
Your project plan . A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your team needs to accomplish in order to successfully achieve your project goals.
The project scope . What are the boundaries of your project? What exact goals, deliverables, and deadlines will you be working towards?
A list of relevant project stakeholders . Who are the important project stakeholders and key decision makers for this work? This can include the members of the project team that would be working on this initiative, executive stakeholders who would sponsor the project, and any external stakeholders who might be involved.
A general project roadmap in a Gantt-chart like view. At this stage in the process, you don’t need to provide a detailed project timeline, but you should outline a general sense of when each project stage will happen in relation to the others. To do this, create a project roadmap in Gantt-chart like software . Make sure to include any important project milestones in your roadmap as well.
Any important project dependencies. Is there anything that would get in the way of this project getting started? Does this work rely on any other work that’s currently in flight?
Discuss project risks
Once you’ve outlined the financial impact and important project details, make sure you include any potential project risks. If you haven’t already, create a project risk management plan for your business case. Project risk management isn’t the process of eliminating risk—instead, it’s about identifying, analyzing, and proactively responding to any potential project risks. Clearly defining each project risk and how that risk might impact your project can best equip you and the project team to manage and avoid those risks.
In the risk section of your business case, include:
A risk analysis of any potential project risks. What is the risk? How likely is it to happen? What is the priority level of this risk?
What, if any, assumptions you are making. In project risk management, assumptions are anything you think will be true about the project, without those details being guaranteed facts. Basing project decisions around an assumption can open your project up to risk. Make sure you ratify every project assumption to avoid jeopardizing project success.
Any comparable alternatives in the market. If you’re writing a business case to pitch a new product or angle in the market, evaluate anything that already exists. Could the alternative impact your financial assessment or project success?
Develop an action plan
In the final section of your business case, outline how you will turn this business case into an actionable project. This section should answer questions like:
How will decisions be made? Who is responsible for the project? Who is the project sponsor? If you haven’t already, consider creating a RACI chart to outline project responsibilities.
How will progress be measured and reported? Not every project stakeholder needs to be notified of every project change. Outline key parts of your project communication plan , as well as how you’ll communicate project status updates .
What is the next course of action? If the management team ratifies this business case, what next steps will you take to put this into action?
Bring your business case to life
You’ve built a solid business case and it’s been ratified—congratulations! The next step is to bring your business case to life. It can be intimidating to initiate large-scale change , and implementing your business case is no exception.
If you haven’t already, make sure you have a project management tool in place to manage and organize your new initiative. With a central source of truth to track who’s doing what by when, share status updates, and keep project stakeholders in the loop, you can turn a great business case into a successful project.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production
9 Tips to Win More Proposals with Case Studies
If you’re not including case studies in your proposals, you’re missing out on a huge opportunity. When it comes to winning new work, sales case studies are more than the icing on the cake, they’re the proof that’s in the pudding.

11 min. read
During the preparation of the countless number of proposals I worked on during my years in the agency trenches (and sadly we had no Proposify back in those dark ages), inevitably someone would raise the question, “Do you think we should include case studies?”.
As if it were a choice.
My strong belief is that you should ALWAYS include sales case studies with your proposals, especially when going after new leads who don’t know your experience, ability, or successes.
The exception to this rule might be when you’re doing up a quick proposal as a formality for a new project with an existing client. But be careful. It can be easy to assume existing clients already know everything you do and have done, but often they only know you in the context of the work you’ve done for them already.
Proposals outline what you’re going to do for a client. Case studies prove that you can do it.
Proposals outline what you’re going to do for a client. Case studies prove that you can actually do it.
No matter how many times you claim to have “extensive experience”, without a case study to back it up, those words can be meaningless, and risky, to a new prospect.
Businesses are often resistant to including proposal case studies because it’s more work to create them on top of everything else, especially when you’re in the time-sensitive throes of preparing a proposal.
The key is to stop seeing case studies as optional and instead view them as an essential selling tool; the tool that just might be the tipping point between you and competition.
Here at Proposify, we've seen a really good return from featuring case studies on our site:

Proposal case studies don’t have to be complicated; they just have to be convincing.
Here’s a simple guide to creating compelling case studies that close deals. You can expand on these to make your particular case studies more elaborate if you like, but as long as you have the basics, it should do the trick.
1. Develop sales case studies before you need them
I admit I have groaned at the thought of doing up case studies when we’re T-minus zero trying to get a proposal out the door. But the trick is to have them ready to go BEFORE you need them in a crisis.
Assign case study writing to your team as a proper internal project and start developing them between proposals.
It will be a lot easier if you’re regularly doing debriefs with clients after each project to see how things went and then following up a few months down the road to track results. This way you’ll already have source material to work with plus compelling stats that make your case studies stand out.
You can customize them to fit the particular need of each proposal once the time comes, but at least you won’t be running around trying to decide which projects to do, getting permission from clients, writing the copy, getting approval, hunting down images, and designing them all at the last minute.

2. Make them representative and recent
When deciding on which projects to turn into case studies, make sure they represent the range of your services. That way you have case studies ready to go that reflect all the types of projects you might be bidding on in a proposal.
Ideally, you have a couple of case studies for each service and main industry but if you can focus on having at least one good, results-driven case study for each area of your business offering then you’re covered.
Also, make sure each case study is fairly recent. Technology, markets, and industries change quickly, so you want to be sure you’re demonstrating that you’re relevant, leading edge, and in demand.
Depending on the industry and service two years, three tops is a good life cycle for a case study.
3. Get client permission
Once you have your list of projects you want to feature as case studies, the first thing you should do before actually going to work on them is to get permission from the client to feature their company.
Some clients don’t want their business challenges or practices talked about publicly for a variety of reasons. Issues related to liability, privacy, and competition can make clients a little shy of the spotlight.
Government clients can be hesitant about case studies, but sometimes they’ll work with you to omit sensitive details so you still get a solid case study that makes everyone happy.
For other clients, case studies can be a great way to promote their business. You can let them know the case studies will be featured on your website and blog in addition to being included in proposals.
Since you’re only going to feature projects that had a positive outcome, clients will be happy to be seen as “successes”. It makes them look smart for choosing the right solution, and they get to show off their good results.
4. Get a client testimonial
You can say all you want about how great your work was for Client X but a direct quote from Client X, about how awesome it was to work with your company or how their business improved as a result of your solution is GOLD.
Ask your client for a quote on the project you’re highlighting and make it as simple as possible for them respond. It’s helpful if you give them some direction, but you want to be careful that they don’t feel you’re putting words in their mouth. Sometimes a client will prefer to have you to write it for them, and then they tweak and approve it. You can offer that as an option to make it easier for them.
If you can, get a couple of quotes related to different aspects of the project that way you can mix and match depending on what you need for the proposal. You can make this easier by giving the client some framework for their testimonials by asking them questions like:
- What was it like working with the team at our agency? Did you find the process simple? Did you find people knowledgeable? Easy to work with? Flexible?
- What kind of benefits have you seen in your business since we did X project for your company?
- Would you work with us again? Why?
Here at Proposify, we book calls with our customers to get their feedback and we use this information as the basis for our proposal case studies.
We like the direct contact with our customers and it’s sometimes an easier way to get information from them compared to waiting for a response to an email when they’re super busy. Plus it allows us to get quotes that sound like they’re from real humans as we use their owns words.
We usually asks these five questions:
- What made you try Proposify?
- What was your ‘a-ha!’ moment to sign up for a paid account?
- Has Proposify improved your sales?
- Does using Proposify influence your close rate?
- Was there a situation where Proposify saved the day? Or helped you out?
We record the call so the content team can listen to it later and transform the conversation into a case study that we'll feature on our website and promote through social media. Check out some of our business case study examples on our site.
Obviously, you’ve picked this client because you already know these types of questions are going to prompt positives answers. Depending on how complete the answers are you may need to edit the testimonials a bit and if you do, be sure to send them back to the client for their approval.
5. Tell a story
When it comes to writing a case study, lead your reader on the journey of the project and keep it focused on the client. Don’t just say, “We built a new website for Bob’s Burgers because the other one was really out of date and not responsive.”
Tell a story that includes the following elements:
Background: Briefly introduce the company, what they do, their industry. It gives some context for the reader.
The Challenge: Why did the client come to you? What problem were they looking to solve? What issues were they facing in their industry that made them reach out? Why did they choose your company to help them? Be careful that you don’t paint your client or their business in too negatively when describing their challenges.
The Approach : What did your team do to address the problem? What was the process you went through to come up with that solution? Why did you decide that solution was the right one?
The Result: Explain the results your solution delivered to the client, whether anecdotally or even better with hard numbers if you have them. How it made life better for them, how it helped them achieve their goals, solved their challenge, and how they are now positioned for a successful future. RESULTS ARE CRITICAL. If you can’t demonstrate positive results, don’t include the case study. Results are everything.
In fact, we put results front and centre by including them in our case study headlines.

I find breaking a case study down into these chunks makes it less daunting to prepare, giving you a clear framework to follow.
6. Keep the format simple
There are lots of different formats for case studies. I like my case studies to be concise (one page TOPS, including images), easy to skim, and easy to determine the result of the project.
You don’t have to literally use the subheads of background, challenge, approach and results but like blog post subheads, it makes the whole thing easier to read and they get right to the point.
Just like your proposal, the client is likely skimming everything but the pricing page so make it easy for them to get the important juicy bits you want to drive home.
7. Use beautiful images or video
Include images of your work in your case study and for the love of PNG, make sure they are high res and LOOK GOOD.
If the project is non-visual like strategy, design a sharp-looking infographic that demonstrates some aspect of the project, like the results or something related to the client’s business.
Where appropriate show before and after shots but again tread carefully in this area. While it can illustrate how far the company has come and the awesome work you did for them, you want to be sure the company is not made to look bad.
To make your testimonial even more powerful, include a video clip in your proposal of the client talking about the project. Online proposal software like, oh, I don’t know...Proposify?...lets you seamlessly add videos to your proposal. But just like images, make sure the video quality is good, the sound is clear, and the whole thing is professionally shot and edited.

8. Customize case studies to your proposal
The question often falls to “how many case studies should we include?”. I think three is plenty and you can always direct the reader to the portfolio/work/customers section of your website for more (you do have a portfolio section on your site, right?).
The case studies you include should correspond to the needs of your prospect for the particular proposal. Maybe it’s a client who had a similar challenge or who experienced benefits from a similar solution that you’re proposing.
Take the time to review each case study before including it in a proposal to find ways to tailor it to help demonstrate to your sales lead that you have experience solving their particular challenge and you know how to deliver.
For example, if your prospect is looking for a new website that’s responsive with an e-commerce solution and requires copywriting, don’t just send them a case study about how you built a kick-ass website. Make sure it demonstrates all those services.
9. Practice plain language
As with anything you write, be sure to follow the rules of plain language writing. Don’t use jargon, be concise, be straightforward, be positive, avoid the passive voice, and if you need to use technical terms or acronyms, include explanations. Don’t assume your client knows what CSS is.
Case studies are the best way to put the walk in the talk of your proposals. They can help build trust with a prospect with whom you don’t yet have a relationship.
They don’t have to be long, complicated, or with earth-shattering results for the biggest brands in the land. They just need to demonstrate that you can do what you say you do and when it comes right down to it, that’s all a client really wants to know.

How To Write an Executive Summary
May 20, 2021

Discover the Always-Be-Closing tool that gives your sales team the competitive edge.
Proposify streamlines your proposal process from creation to close and every deal-making moment in between.
How to Write a Business Proposal (Examples & Templates)
A complete guide to writing business proposals that land deals. Easy-to-follow steps, actionable examples, and insider tips from sales pros.

John McTale
11 minute read

Not a fan of writing business proposals? Few people are. After all, it puts you in quite a vulnerable position. You need to convince prospects to pick you and make them understand why you’re the perfect fit for their needs.
This guide will show you a simple step-by-step process you can follow to ace every business proposal you create. Plus, for every section of your proposal, you’ll get sample content you can take as a point of reference and use to score more deals.
First, see a business proposal example created with Storydoc:

Interactive
Static, plain-text proposals are a relic of the past. With Storydoc, you’ll get engaging, interactive proposals looking better than anything you’ve ever created. Rise above your competitors and give your customers a proposal they will be proud to show their boss.
What is a business proposal ?
A business proposal is a formal document devised by a company and delivered to a prospect with the purpose of securing a contractual agreement between the two parties. A good business proposal shows to your potential clients why your offer is the most beneficial to them. Before we dig deeper, if you just need a quick checklist, here it is. To learn more about a specific section just click on a desired item in the interactive table of contents and we’ll take you right there.
Here's how to write a business proposal:
Now, let’s go through each step and see some examples.
1. Create a title page
Starting with the basics. The title page of your business proposal needs to feel professional and inviting. Most importantly, though, make it feel as personal as possible. Include:
- The name of your business
- The subject matter of your proposal
- Your prospect’s name and job title
- Your prospect’s company logo
- Submission date
Business proposal title page example:
Jane Atkins ABC Company Inbound Marketing Proposal for Acme Corp

Submitted to: John Random, VP Growth Submitted on: May 5, 2023
Using your client’s logo is virtually a must. But you kick your title page up a notch by applying other elements of their branding, too: think colors, master visuals, and overall vibe. They will notice and appreciate it. These unique business name ideas will make you stand out from the crowd - your business name matters.
2. Include an interactive table of contents
One of the keys to success in business communication is setting up expectations and then meeting them. A table of contents achieves just that: you tell your readers exactly what they’ll find in your proposal. If you’re sending your proposal electronically, make the ToC clickable, with jump-to links to appropriate chapters of your proposal. It will make navigating through the document so much easier (much like we did with this piece, you're welcome!).
Speaking of electronic versions… Do your best to prevent your prospects from printing out your proposal. A 2020 study found that once someone prints your proposal, your chances of landing the deal shrink by 84%!
Sample table of contents:
Executive Summary
Assessment and Project Overview
Methodology - SEO Audit - Internal Linking Optimization - Digital PR Assets - Digital PR Outreach
Qualifications and Testimonials
Terms and Conditions
Agreement and Rollout Process
3. Write a compelling executive summary
As the name implies, an executive summary is a section that, well, summarizes the whole document. In business proposals, your executive summary should contain the essence of your value proposition: explain why you’re submitting the proposal, what makes your product or services relevant to the client’s specific needs, and how you’re going to tackle their problems. The key thing to remember? Don’t mistake an executive summary for an introduction. The summary is basically a shortened version of your whole proposal. Its purpose is to provide a busy reader ( who could be your prospect ’s boss, the titular executive) with an overview of your offer, clear enough for them to not have to read the proposal in full. If you want to learn more about writing executive summaries, specifically, see our dedicated guide: Executive Summary—Examples and Definition
Sample executive summary for a business proposal:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This proposal outlines a detailed plan of action aimed at maximizing the profits of Acme Corp by boosting the inbound organic traffic to your e-commerce store. As your company displays a very high on-site conversion rate and the online traffic you generate is highly monetizable, the best strategy for maximizing your revenue is boosting your SEO performance. Acme Corp is lagging behind its key competitors in most of the search performance metrics: domain rating, backlink quality , and, as a result, organic traffic. Applying basic SEO maintenance will result in a dramatic increase of relevant monthly visitors to your site, contributing to a substantial increase in revenue. In the second phase of the project, our team will enhance your online presence and earn high-quality backlinks through a data-driven digital PR campaign, further improving your domain rating and the consequent search engine rankings for the highest-converting keywords and phrases.
While executive summaries come at the beginning of business proposals, write this section last. Create the rest of your proposal beforehand, then “skim the cream:” compile the key bits into the summary.
4. Identify the problem and propose a solution
Here’s where the big guns come in. If you’ve managed to get them interested enough to reach this part, you’re halfway there. It doesn’t mean it gets easier at this point. Quite the contrary— This section, usually called “Assessment,” or “Project Overview,” is the meat and potatoes of your proposal. You need to make sure it tastes like Black Angus fillet mignon with gratin dauphinoise. Here are a few tips for making it powerful and convincing to your prospects:
- Focus on the grander scheme of things here. Paint a big picture, plant an idea: it’s not the time to get to the nitty-gritty yet.
- B2B buyers can smell generic from miles away. Do your best to customize this part to the exact needs of your customer, never use a copy-pastable template.
- Make it about them. Instead of “selling” your product or services, focus on the tangible business result they’ll get out of this. ROI is the most direct, hard-hitting metric after all.
- Don’t overuse jargon or highly technical terms. You’re communicating with a human, not an algorithm.
- It’s okay to use your sales deck as a point of reference. It’s what got them interested in the first place, so do rely on the same main message.
Sample project overview in a business proposal:
ASSESSMENT AND PROJECT OVERVIEW Acme Corp is currently looking for ways to bring more inbound traffic to the company website. As an e-commerce business with competitively priced, high-quality performance clothing, any traffic you generate is highly monetizable. Your current traffic sources mostly constitute direct (15%), AdWords (40%), and display ads (18%). Organic traffic acquisition has been heavily underperforming for your site. At the same time, both your key competitors, DoeSports and GreenWay, bring in twice as much organic traffic as you do through paid sources (via Ahrefs, and SimilarWeb analysis). This shows that SEO efforts can be highly profitable in your industry. Your e-commerce store suffers from a few easy-to-fix SEO issues that we will address immediately:
- Poor-quality backlinks from spam sites, low SEO health score, and irrelevant anchor text in internal links.
- Fixing these issues alone will boost your SERP positions by 5–10 places for highest-volume keywords, amounting to 5,000–8,000 more unique visitors per month.
- Considering your extremely high average conversion rate of 3% and an average conversion value of $75, those efforts will increase monthly revenue by at least $11,250.
Furthermore, in comparison to your competitors, AcmeCorp has a poor domain rating: 49, compared to 66 of DoeSports and 70 of GreenWay, indicating fewer relevant backlinks and weaker referring domains. Our team will acquire relevant, high-quality backlinks from key industry publications through digital PR and outreach campaigns based on unique data-driven studies. This will result in:
- A significant boost in your domain rating, directly contributing to all major search engines rankings.
- A projected boost in traffic to your website of further 12,000 visitors per month.
- Enhanced brand visibility.
Even at the stage of the deal where you send the proposal, don’t assume your customer understands what they’re buying and why they need it. You still need to get your sales message across: let your prospects understand the value attached to your price tag.
5. Explain your methodology
If the executive summary of a business proposal is the why , and the project overview, the what , here’s the part where you describe how . If you’ve nailed the previous sections, your prospect knows that your solutions are relevant to their problems and has a bird’s eye view of expected outcomes. It’s time to explain your methods for achieving what you promise to deliver. List all the deliverables they can expect from the project or service, together with a timetable and a list of dependencies detailing the deadlines or frequency of delivering specific items or milestones. How granular you are in this part largely depends on the duration of collaboration you’re discussing, and many other project-specific details.
Example #1:
If you’re writing an event video proposal, you’ll want to explain what the client can expect:
- Before the event (consulting your needs and ideal outcomes, auditing the venue, setting up lighting, and so on),
- During the event (how many videographers on site, exact timetable, total shooting time),
- After the event (post-production, sound and music, additional editing, total length of video material delivered).
Example #2:
If, on the other hand, your proposal refers to long-term marketing consulting contract, the description of your methodology will be more general:
- Month 1: identifying and fixing technical SEO issues (anchor text, internal linking, backlink quality).
- Month 2: auditing the site content and optimizing existing URLs for search engine performance using an SEO rank tracker tool .
- Month 3: automating the funnel, running A/B tests on form pages.
And so on… Let’s have a look at what it might look like in practice.
Business proposal sample—methodology:
METHODOLOGY
- Disavowing links from low-reputation websites
- Fixing critical issues on existing URLs
- Improving site speed
- Fixing errors in robots.txt
- Optimizing meta titles and meta descriptions
- Fixing errors in HTML tags
Internal Linking Optimization
- Identifying internal linking opportunities
- Creating SEO-friendly anchor text combinations
- Removing links to 404 URLs
Digital PR Assets
- Running unique surveys via OnePoll
- Creating data-driven content relevant to the audiences of industry online publications
- Creating shareable infographics depicting the findings of the study
Digital PR Outreach
- Identifying key leads in relevant industry websites
- Email outreach to our database of relevant contacts
- Passive link building via Google AdWords
6. Back up your proposal with proof of qualifications
Your business proposal might be visionary so far. Still, if it’s not credible, it will get you nowhere. The client might love your ideas. They might be beyond excited to see them come to life. But— They don’t know you. And remember the old saying: “Trust everybody, but always cut the cards.” (Yes, it’s a euphemism for “Trust no one, ever.”) How do you make them trust you? Show them you’ve done it before and you succeeded. Again, and again. List verifiable, measurable achievements you or your company can boast about and pepper those with social proof. See a few examples:
- Customer case studies,
- Testimonials,
- Certifications,
- Industry awards,
- Years of experience,
- Media mentions.
The ideal composition of those will depend on the type of project and the industry: If you’re a photographer, your client won’t care too much about the awards you might have gotten or what The New Yorker wrote about your solo show. They’ll want to review your portfolio to see if that’s the vibe they're into and hear from your past clients to check if you’re not a pain to work with. If, in turn, you’re writing a marketing business proposal, your best bet will be to emphasize examples of your past campaigns together with detailed key metrics you boosted for your clients. Writing a proposal in an informal tone? You can add a short “About Us” section. Introduce team members who would be working on the project and explain what makes them the best professionals available on the market for solving the particular problem in question.
7. Outline your pricing options
This is where things get rather technical. On the face of it, the pricing section seems fairly obvious. They might be in love with your solutions, but they don’t yet know if they can afford you. Pricing is a tricky part on your end, though. You don’t want to scare off your lead with a sky-high estimate; at the same time, you don’t want to undersell yourself. The best option is to go for an interactive pricing page where every type of service or activity has a separate price tag to it and your clients can easily select a package that suits their needs and meets their budget—ideally, the total price should get automatically calculated. Alternately, you can use an estimate generator , which is an effective tool for automatically calculating cost forecasts based on various criteria and input data. This tool is both affordable and consumes little computing resources, so you can get it along with the best laptop for the money in the $300-$500 range. If you don’t have such an option at hand, create a very specific pricing table that clearly identifies each item or service, as well as the billing period. Here’s a practical example.
Sample pricing for a business proposal:
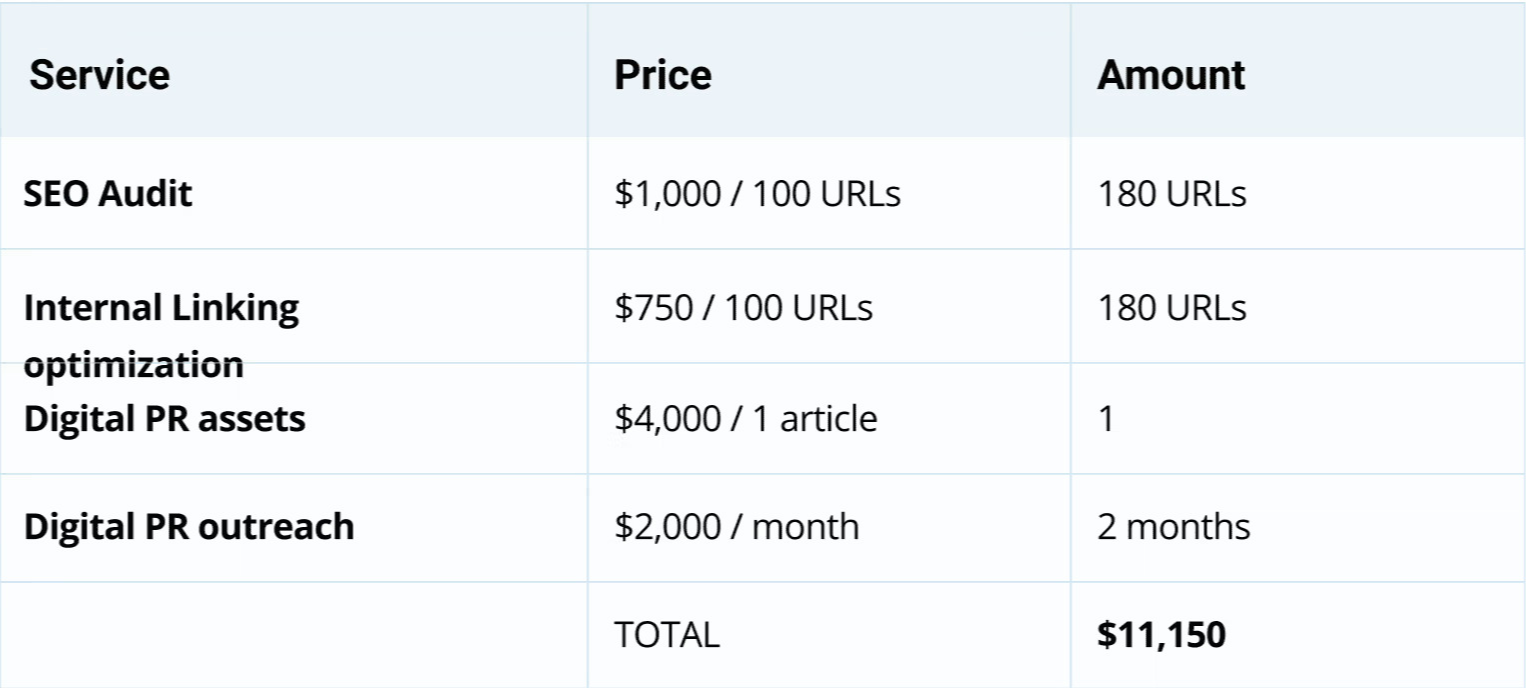
Remember, your goal is to make them comfortable with the pricing. Make them understand that your offer is not a cost but an investment worth every penny. A great way to achieve this is adding a live ROI calculator. It’s a perfect reminder of why they’re reading the proposal in the first place: to find a solution that will help them increase the revenue.
Below, you can see a sample ROI calculator created with our presentation maker tool :
Interactive ROI calculator example

8. Finish with terms and conditions + contractual agreement
Here’s a bad dream— The client loved your proposal, you’re midway through the project, and, all of a sudden, they’re refusing to make a second payment on your account. “We agreed on 30% upfront, and a full payment upon completion.” You know that’s not what you agreed on. Or do you? A proper business proposal comes with a detailed set of terms and conditions, together with contractual agreement at the bottom, helping both parties involved avoid any misunderstandings. In the terms and conditions, describe the timeline of the project, payment terms and schedule, cancellation policy (if applicable), and possible pre-agreement amendments to the proposal itself.
Sample terms and conditions for a business proposal:
TERMS AND CONDITIONS Timeline Start date: June 1, 2023 End date: July 31, 2023 Total payment due: $11,150 40% of the total payment is due upon signing. 100% of the total payment is due upon project completion. After the final payment, any elements of text, graphics, photos, or other creative work created by ABC Company for Acme Corp are owned by Acme Corp. ABC Company retains the right to showcase their creative work done for Acme Corp as examples in their portfolio. Prior to signing the contractual agreement, elements of this proposal might be amended in cooperation with Jane Atkins, ABC Company.
At the bottom of your document, include a legal agreement clause and a space for signatures. Make it easy for them to make a decision without additional documents. Adding a date and signature space in a business proposal will help you close the deal faster. For maximum convenience, you’ll want electronic signatures enabled.
Sample agreement clause for a business proposal:
If you agree to the terms of this inbound marketing proposal, please sign in the field below. Your signature indicates that you enter into a contractual agreement with ABC Company that commences on the date signed below. [ date ] [ signature ] John Random, Acme Corp
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
And that’s a wrap…
I hope this step-by-step overview of business proposal writing has straightened out any queries or doubts you might have had. For the final word, here are a few extra tips to keep in mind before you hit “send.”
Business proposal tips:
- Start with an outline.
- Never reuse old proposals.
- Use hard numbers whenever possible.
- Don’t shy away from your brand.
- Make next steps obvious.
- Re-read, proofread and edit.
Thanks for reading. Keeping my fingers crossed for your proposal!

Hi, I'm John, Editor-in-chief at Storydoc. As a content marketer and digital writer specializing in B2B SaaS, my main goal is to provide you with up-to-date tips for effective business storytelling and equip you with all the right tools to enable your sales efforts.
Make your best proposal to date
Try Storydoc for free for 14 days (keep anything you make for ever!)
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, how to write a business case, business case template, watch our business case training video, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project overweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
What is a Business Proposal? Definition, Types, and Examples
There's nothing better than getting a request for a business proposal . It means that your marketing and sales efforts have paid off.
If this step makes you worried, or if you haven't sent a business proposal in a while, it may seem like harrowing work.
But don’t panic. We've got you covered .
Let’s take a look at what makes a good business proposal, along with the most successful types used today.
What Is a Business Proposal?
A business proposal is a sales document that a supplier sends to a prospective client with the purpose of winning a specific project. It's an official document that outlines your proposed solution and value proposition.
Many service-based businesses and B2B Saas businesses depend on proposals to sell their services and bring in new business. The proposal can be either digital or printed . It explains the product or service features taking into consideration the potential client’s problem or needs.
In other words, an effective business proposal shows how a company can solve the prospect's problem and help you win a new client.
Types of Business Proposals
Business proposals can be solicited or unsolicited. A solicited business proposal is sent when a client specifically requests one. A client can ask for a proposal casually in conversation, during a meeting, or send a formal request for proposal (RFP) document.

Here’s how it works:
Formally Solicited Business Proposal
For example, a small boutique resort has been a regular client of your landscaping business . They have already hired you for a few one-time jobs and you know what they need. Now they want a regular service and need to double-check the terms before paying.
They ask you to send a business proposal that contains service names, prices, timelines, payment options, etc.
After receiving your offer, they are obliged to respond within an agreed period. In case the resort agrees to your terms, the proposal becomes a legally binding purchase agreement.
Informally Solicited Proposal
In this scenario, the boutique resort has discovered your landscaping business and is interested in your services.
In an informal conversation between the two reps, they ask for a document outlining more details about the quality of your services, previous clients’ reviews and testimonies, pricing, etc. The difference is that they are not obliged to respond to the offer.
Unsolicited Proposal
Your landscaping business is running a lead generation campaign and wants to inform the local boutique resorts about the services it offers. In this campaign, you'll create multiple unsolicited business proposals containing an introduction to your company, your expertise, etc.
Unsolicited proposals need to be especially convincing since you're sending them to a cold audience.
Business Proposal vs. Business Proposal Letter
A business proposal letter or cover letter is a document that businesses sometimes send to their prospects alongside a business proposal. A shorter proposal may even combine these two in a single document.
A cover letter helps provide context on why you’re sending the accompanying business proposal.
Keep your cover letter brief, no longer than one page . It definitely shouldn’t steal the show from the business proposal.
- Mention when the proposal was requested
- Credit people who helped prepare the proposal
- Offer an introduction (executive summary) of the proposal
- Thank the potential client
- Provide your contact information
You can mention the client’s RFP document or refer to a conversation where the potential client has expressed interest in seeing the business proposal.
Proposals vs. Estimates
Business proposals and estimates are both sales documents that businesses use in attempts to win projects.
However, a business proposal is much more detailed than an estimate and usually covers more complex projects and relevant details.
Proposals also tend to explain the value the company will provide to a potential client, together with listing its past projects and including client testimonials.
Some small businesses use estimates to detail the costs and tasks covered by the project. Then, they prove their value through other means, like during a call or a site visit. This way they avoid drawing a formal proposal altogether.
In some cases, the prospective client gets a referral from a trusted partner or they have read great online reviews. In both cases, the job is not overly complex and a project estimate will do.
However, in the majority of cases, the clients may need more proof to make sure your business is the right fit.
Then you need a proposal to prove that as a supplier or service provider, you are able to provide the right approach, design, timeline, etc. For example, if you are working with an executive coaching organization , they may require a long-form business proposal with plenty of client testimonials.
Key Parts of a Business Proposal
Let's take a look at how to create a well-written business proposal.
We recommend you start with a beautifully designed business proposal template. When using Better Proposals, you can rely on more than 100 business proposal templates that you can easily customize to your needs.

They make your entire proposal process easier and quicker. You won't have to write a business proposal outline, since the templates already come with all the essential business proposal elements.
The Cover Page of your Business Proposal
The cover page is the first thing your potential client sees, so make sure to make the right impression from the beginning. Ask any graphic designer and they’ll tell you that here less is more . Keep it simple and focus the client’s attention to:
- the project name
- the name of the person the proposal is addressed to
- your company name
- your contact information
- submission date
You also need to include your logo . Since this is the cover page, make sure you use a high-resolution version.

If you’re thinking about whether you need the cover page at all, let me assure you that you do. We did our own research that shows that if you include a cover in your proposal, you’re 4.6% more likely to land the account.
The Introduction or Executive summary section of a business proposal
Before they sign off on the project, the clients need to like you. And they can’t like you if they don’t know you.
Your intro needs to be tempting. After all:
- The introduction is the part of your business proposal on which people spend 38.2% of the total time reading your proposal.
This is the part where you tell them what your company is all about and how you can bring value to their business.

On the other hand, avoid the common misconception of making the intro all about you. Instead, you want to focus on the client’s pain point . This way, you’re holding their attention from the very start and raising your chances of sealing the deal.
Easier said than done, eh?
Here are a few pro tips.
Business Proposals should be short and sweet
The rule of thumb with introductions is to keep them short. For now, your goal is to hook your prospects and keep them reading.
Make it personal
Your business may be sending a lot of business proposals, but you don’t want to copy-paste the same generic content over and over again. Generic content always loses to customized pitches, so you’re ruining your chances of closing a deal.
Your potential client is likely entertaining other companies as well, so you need to stand out from the crowd. Use your executive summary to do just that.
This is fairly easy, especially if you’re using proposal software and AI writing tool .
Draw from meeting notes to build your business proposal
If you had a call with your potential client and asked the right questions , you should have a pretty good idea of your prospect's pain points. Now you only need to show why you're the right choice to tackle those problems.
You can mention the goals they shared with you, their current situation , and how you can help them achieve those goals.
Your Solution
When your prospect gets past the executive summary, they’ll be eager to know what’s in it for them. Here it’s important that you focus on the end result rather than the process that will get them there. Let’s say you’re selling landscaping services.
As a professional, you know how much work goes into each project. You need to do the on-site assessment, improve the soil, create the drainage slopes, select plants for each layer, etc. Not to mention the actual manual work.
Since you take pride in your expertise, you may be tempted to describe the entire process from start to finish. However, that’s not always the best idea.

The client is hiring you to get the results, not a crash course in gardening. At the end of the day, they are interested in the improved aesthetic appeal of the resort and the increase in traffic that goes along.
I admit that finding the right balance between describing your solution and results can be difficult. The trick is to focus on benefits while allowing just enough technical specs to resolve any potential disputes.
The Project Timeline

All clients want to know how long a project is going to take. Include a timeline to help your client get on board with the process and to set your own pace and milestones, suggests Ryan Zomorodi, co-founder of Real Estate Skills .
For example, a big project can have a six-month timeline, which may seem intimidating for the client. The best course is to break it up.
First, it helps the client distinguish between different phases. Second, it lets you set deadlines for yourself to keep you on track.
The Social Proof
There’s hardly a better way to win a client who’s on the fence than showing them that you’ve done similar projects before.
That’s why you absolutely must add a relevant case study to your business proposal.

Depending on the project, you can choose an industry- or project-centred case study.
As you can see in our business proposal template, it can be in a short format. No need to include your entire portfolio.
Keep your prospective client in mind when creating your business proposal. The whole experience should be positive for them instead of feeling like doing homework.
The Pricing
You’ve shown that you understand your client’s needs and offered appropriate solutions. Now it's time to nail the pricing section.

Help them choose you by making small adjustments:
- Use “Investment” instead of “Pricing "
It sounds much better this way because it assures your client that they are investing in the future.
- Add a brief testimonial
After seeing the price, the client needs to see how your solution has helped someone else's business take off. It helps them realize the value you provide for the money.
- No optional services
You may be tempted to offer your clients upsells and package prices. However, our report shows that this can actually hurt your conversion rate. It’s much better not to give any choices. If you go with one price, you can ask for a 20.6% higher upfront fee and 33% higher monthly fees.
The Guarantee
Some businesses embrace the idea of a guarantee. Others are less enthusiastic about giving guarantees, fearing abuse.
Still, guarantees can be the last piece the client needs to convert. Instead of a typical money-back guarantee, consider guaranteeing a part of your service or a timescale.
For example, for smaller projects, you can offer a “curb appeal in a day” guarantee.
The Next Steps
At this point, you need to tell the client how they should proceed. Take some time to explain the steps they need to take to close the deal. You don’t have to go overboard here. Everything up to now should be clear.

As you can see in our business proposal template, this section should be pretty straightforward.
By signing, the client agrees to the terms of the proposal and agrees that their typed name can be used as a digital signature.

Terms and Conditions
Finally, it’s always better to include your terms and conditions in your proposal. That way, the new client only needs to sign one document. They know what to expect and you're legally covered.
All our business proposal templates come with proposed terms and conditions sections which you can adapt to your liking.
Once your proposal is done, read it and make sure that there are no grammatical errors.
Wrapping Up
A business proposal is a complex sales document that can be simplified if you're using the right proposal software.
Instead of starting with a blank page, you'll be able to write an amazing business proposal that converts in less than an hour.
When you choose your business proposal template, you won’t have to figure out how to structure your offer. Our templates are always being updated with the latest marketing trends, as we hone the features that regularly make the most conversions.
Sign up for our 14-day free trial and see for yourself why we're the best choice.

Feature Update: New Sidebar + Document Types
Thanks to our new sidebar and document types, your Better Proposals workflow is now more streamlined than ever before. Log in and see for yourself.
How to Price Your Services: 5 Ways to Charge for Your Work
Struggling to price your services? Uncover how to successfully navigate these hurdles and accurately price a service with our expert guide.
- See what's new - 2024 editions
- Shop Proposals & Contracts
- My Past Orders
- Shopping Cart
- New for 2024 - now includes automated quoting, schedules, and financials. No subscription fees.

Articles / How to Write a Case Study Document /

How to Write a Case Study Document
Did you know? Proposal Packs are designed for writing complex studies as well as proposals with pre-written templates, samples, graphic design options and automation software.

Do you need to describe in detail the effectiveness of a project, or document the situation or experiences of an individual or a group of people? This sort of detailed study is called a case study.
Case studies are used to test hypotheses, help plan for real-world problems, and generate a discussion of potential needs and solutions, among other things.
For example, a pharmaceutical company might do a case study to determine how a group of individuals has benefited from a drug therapy, or a school administrator might do a case study to show whether or not individual students have benefited from tutoring programs.
Case study reports are usually complete standalone documents. However, if you write business proposals or grant applications, you may find that including summaries of case studies within your proposal can show how your product or service has benefited groups or provided the solution to needs in the past. And if you write business proposals, you may already be aware of a product called Proposal Kit. But you might not realize that Proposal Kit includes everything you need to write all sorts of studies and reports, too.
Each case study report should include these sections within the body of the report:
- Goal(s) of the study. Do you want to determine whether a past process, product, or service has been successful in order to modify it for future use? Are you trying to determine if there's a need for a product or service among a certain group of people, or show the benefits of a project your organization has done in the past?
- A hypothesis or proposition you want to test. Depending on your organization, this might be demonstrating that a group has a specific need or that recipients of a product or service benefited in measurable ways.
- The specific questions you want to answer. These will be derived from the goals and hypothesis of the study.
- The methodology (how information was collected). This might include interviews, measurements, sampling, and so forth. Be sure to include all relevant details such as schedules, dates and times, locations, and personnel who performed the collection. You may want to summarize this information in the body of the report and include details in an appendix.
- Participants. How did you select participants or subjects for the study? What is each participant's background and history?
- The data that was or will be collected. Depending on what you are studying, this section could include videos, transcripts of interviews, collections of documents, descriptions of test results, recorded observations - all kinds of topics could go in this section. If your data is extensive, you may want to summarize it in the body of your report and provide the details in an appendix.
- Analysis of the data. This section is likely to include statistical summaries and patterns found in the data.
- Conclusions. Were your questions answered? Did the study meet the goals? Was the hypothesis supported or refuted? What are the implications for the future?
As with any report, you'll start off with a Title Page and a Table of Contents (Proposal Kit can produce one for you). You'll probably want to include a summary of the important summary points, too, for the high-level readers who will only skim your report. After the body of the report, you may need all sorts of appendices, too - lists of statistics, diagrams, charts, a bibliography or list of sources, and so forth. Proposal Kit will contain all of the individual topics used to flesh out the details of your study.
Remember to always keep your readers in mind. What do they know about you and the study? What do you need to tell them so they can judge the results? You may need to include background information about your organization, the resumes of personnel who participated, your training or education credentials, and so forth.
- Feasibility Study Sample
- Case Study Sample
It's important that your case study sounds professional, so be sure to proofread every page. If possible, get someone who is unfamiliar with the study to read and comment on your work. It's always a good idea to choose a reviewer with a similar background to your readers so that he or she can ask appropriate questions and provide useful comments to improve your report.
After you have all the information written for your proposal, work on making your document visually appealing. Add some color and graphics by incorporating your company logo, using colored borders, and selecting custom bullet points and fonts that match your business's style. Learn how to effectively select colors for a winning business proposal.
You also want your report to look professional, too. Proposal Kit can help with that because it allows you to choose from a variety of graphic designs.
There's no need to start each section of your case study report by staring at a blank page. Proposal Kit includes templates for all the topics mentioned in this article. Each template includes instructions and examples of information to include on that page to give you a jump start on writing. And Proposal Kit includes samples of all kinds of proposals and studies, too. You'll find yourself using the product for business documents and reports of all kinds.
How to Write a Case Study
This video demonstrates how to use Proposal Kit to create a customized case study document. While Proposal Kit is typically used to write proposals, quotes and business plans it can also create many types of business documents such as case studies.

Using our professional quality proposal and contract packages, wizards, and support documents to develop your proposals, business plans, and other business documents will give you a comprehensive final document that will present you and your organization as a highly professional alternative that instantly inspires trust.
It will provide you with the inside track.You can order and instantly download the Proposal Kit that best suits your needs.

- Proposal Templates

- Help Center & Site Map
© 1997 - 2024, Proposal Kit , Inc. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy .

- How It Works
- Integrations
How to Win New Clients by Using Case Studies in Your Business Proposals
One of the key pieces for creating an excellent business proposal is to incorporate engaging, well-written case studies. A well-written case study is a powerful, informative tool that can help you convert your proposal into a contract.
Often, case studies are an opportunity to showcase experience and expertise relative to the types of problems that the client’s firm has. They play a significant role in helping others see the benefits of using your products or services ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/johnrampton/2015/08/07/content-marketing-for-startups/#df0d9d33eac2 ).
People who use case studies in their proposals will develop partnerships more quickly with their prospects. This is because they can control the sales process more effectively. And that means they have a better chance of meeting their sales targets.
People who don’t use case studies often struggle to achieve their sales targets. This is because they don’t have the ability to develop the same partnerships with their prospects. And that means they won’t have effective control over the sales process ( https://www.storiesthatsellguide.com/store/tip-of-the-month/getting-short-listed/ ).
There are several other great reasons why case studies are one of the most valuable tools in your arsenal. Sure, they’ve been around since time immemorial, but they deserve a fresh look in today’s business environment.
A Guide to Writing Great Case Studies
Case studies are a lot like stories. A general format introduces your clients, describes the problems they had and then wraps it up with the solution you provided. Your clients are the highlights of these stories, and your services or products are the solutions to the problems faced ( https://www.inc.com/theupsstore/5-components-of-effective-case-studies.html )
With that said; a good case study must fulfil your business needs as well as being of interest to your prospect. As such, you should pick past clients who you believe are the right brand for your business, keen to share the results you’ve given them and eager to speak of your role in helping them solve a problem ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/markevans/2013/03/22/for-startups-case-studies-are-sexy/#24e2ac861463 ).
The art of writing convincing case studies is to stay away from the 'salesy’ path by going easy on your advertorial content. They don’t need to be complex or long. This isn’t an opportunity to loudly hoot your firm’s capabilities but to subtly show how your products or services can benefit the prospect.
Here is a simple structure outlining the fundamentals of a case study:
-A basic introduction of who the client is
-A description of the client’s situation, challenges, frustration relative to the issue they were facing
-A description of the services your firm offered to solve the problem- methodology, tools, approach and anything proprietary
-A description of the end results in quantifiable terms- show movement from situation X to situation Y.
-A customer testimonial
The secret is in the numbers. If you aren’t able to quantify your results and clearly show movement from problem to solution, then you don’t have a case study ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/markevans/2013/03/22/for-startups-case-studies-are-sexy/#24e2ac861463 ).
How to Get the Testimonial
Most people ask for testimonials and after a diligent follow-up, they get the testimonials. But without asking the right questions to probe the client, the testimonial might end up looking like this:
Sam did a fantastic job on this project. We’re very happy and plan to work with him again in future.
This isn’t a bad review but does it sell your products/services and tell a good story about you? Most clients don’t know how to provide good testimonials, so as an expert you need to direct them to write stories that will inspire your next prospect to hire you ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/markevans/2013/03/22/for-startups-case-studies-are-sexy/#24e2ac861463 ).
Here are the three most important questions to ask when looking for a powerful testimonial:
-What was your experience doing business with me?
-What did you like most about the solution we offered?
-Would you hire my company again? If so, why?
By asking these questions, you will be able to get a client testimonial that credibly sells your business and tells a vivid story. Here is a good example.
Sam was great to work with while building our site. He invested a lot of time learning about our brand personality, style and mission. He was completely transparent and easy to communicate with. We relied on Sam to turn everything we wanted into a success and the result was totally impressive. We are highly grateful to have had the opportunity to work with him, and we plan to work with him again. Highly recommended.
How to Package Your Case Study
One way to package your case studies is to use a PDF format. When you do this, it becomes very easy to add them to the end of a proposal using ClientPoint . Aim to keep all case studies at least one page regardless of how long the project is. The truth is, most clients generally skim through the case study part ( https://www.2020strategyinc.com/business-beat-blog/want-to-learn-to-write-good-five-tips-to-improve-your-writing-today ).
Don’t Underestimate the Power of Quality
When you submit your case studies to the prospect, they will assess the quality of the case study as well as the quality of the proposed solution within the proposal. It is, therefore, imperative to consider investing some money into having a professionally designed case study. It can make all the difference when converting your proposal into a contract ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/matzucker/2016/03/11/visual-content-a-case-for-beautiful/ ).
Use Images and Videos
It is always a good idea to include images and videos of your previous work in your case study as well as throughout your business proposal. If the project is non-visual, design a clever infographic highlighting the major aspects of the project. You don’t have to cram tens of shots in the case study, remember you need to keep it under one page and straight to the point. So make it easy for the prospect to get the important bits you intend to drive home ( https://www.forbes.com/sites/matzucker/2016/03/11/visual-content-a-case-for-beautiful/ ).
The Hidden Value of Case Studies
Case studies are more than just a tool to package and showcase your work to prospects. They represent the views of your clients, not your business. Webinars, blog posts and other types of content that come from your business are sometimes viewed as self-interested, meaning clients tend to be a little skeptical of them. Case studies come directly from the consumer, so they act as a powerful third party endorsement of your brand ( https://www.inc.com/theupsstore/5-components-of-effective-case-studies.html ).
Bottom Line
It is clear that case studies can yield good results, but at the end, those results are solely reliant on your efforts to create them. With the information in this blog post, there is no reason why you shouldn’t start creating case studies with the projects you’ve had success with.
___________________________________
Win more clients by creating impressive digital business proposals, quotes and contracts with ClientPoint Software
If you really want your business proposals, quotes and contracts to stand out and give you the best chance at winning new clients, use ClientPoint Software. It makes creating and formatting professional business proposals, quotes, and contracts fast and easy. Click here to schedule a free demo of ClientPoint Software or call us at 888-972-7375 .
Click here to read a case study of how ClientPoint Software helped a business double sales.
Related Readings
Case study: how clientpoint helped vortex aquatic structures international decrease the time they spent creating business proposals by 980%, the ultimate business proposal checklist, the top 20 reasons why b2b companies will reject your business proposal.

Headquarters
6790 Embarcadero Lane Suite 100 Carlsbad, CA 92011
Contact Info
- Privacy Policy
- Master Subscription Agreement
- ClientPoint Brand Style Guide
7 Favorite Business Case Studies to Teach—and Why
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Course Materials
FEATURED CASE STUDIES
The Army Crew Team . Emily Michelle David of CEIBS
ATH Technologies . Devin Shanthikumar of Paul Merage School of Business
Fabritek 1992 . Rob Austin of Ivey Business School
Lincoln Electric Co . Karin Schnarr of Wilfrid Laurier University
Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth . Gary Pisano of Harvard Business School
The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron . Francesca Gino of Harvard Business School
Warren E. Buffett, 2015 . Robert F. Bruner of Darden School of Business
To dig into what makes a compelling case study, we asked seven experienced educators who teach with—and many who write—business case studies: “What is your favorite case to teach and why?”
The resulting list of case study favorites ranges in topics from operations management and organizational structure to rebel leaders and whodunnit dramas.
1. The Army Crew Team
Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS)

“I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
I deliver the case to executives in a nearby state-of-the-art rowing facility that features rowing machines, professional coaches, and shiny red eight-person shells.
After going through the case, they hear testimonies from former members of Chinese national crew teams before carrying their own boat to the river for a test race.
The rich learning environment helps to vividly underscore one of the case’s core messages: competition can be a double-edged sword if not properly managed.

Executives in Emily Michelle David’s organizational behavior class participate in rowing activities at a nearby facility as part of her case delivery.
Despite working for an elite headhunting firm, the executives in my most recent class were surprised to realize how much they’ve allowed their own team-building responsibilities to lapse. In the MBA pre-course, this case often leads to a rich discussion about common traps that newcomers fall into (for example, trying to do too much, too soon), which helps to poise them to both stand out in the MBA as well as prepare them for the lateral team building they will soon engage in.
Finally, I love that the post-script always gets a good laugh and serves as an early lesson that organizational behavior courses will seldom give you foolproof solutions for specific problems but will, instead, arm you with the ability to think through issues more critically.”
2. ATH Technologies
Devin Shanthikumar, Associate Professor of Accounting, Paul Merage School of Business

“As a professor at UC Irvine’s Paul Merage School of Business, and before that at Harvard Business School, I have probably taught over 100 cases. I would like to say that my favorite case is my own, Compass Box Whisky Company . But as fun as that case is, one case beats it: ATH Technologies by Robert Simons and Jennifer Packard.
ATH presents a young entrepreneurial company that is bought by a much larger company. As part of the merger, ATH gets an ‘earn-out’ deal—common among high-tech industries. The company, and the class, must decide what to do to achieve the stretch earn-out goals.
ATH captures a scenario we all want to be in at some point in our careers—being part of a young, exciting, growing organization. And a scenario we all will likely face—having stretch goals that seem almost unreachable.
It forces us, as a class, to really struggle with what to do at each stage.
After we read and discuss the A case, we find out what happens next, and discuss the B case, then the C, then D, and even E. At every stage, we can:
see how our decisions play out,
figure out how to build on our successes, and
address our failures.
The case is exciting, the class discussion is dynamic and energetic, and in the end, we all go home with a memorable ‘ah-ha!’ moment.
I have taught many great cases over my career, but none are quite as fun, memorable, and effective as ATH .”
3. Fabritek 1992
Rob Austin, Professor of Information Systems, Ivey Business School

“This might seem like an odd choice, but my favorite case to teach is an old operations case called Fabritek 1992 .
The latest version of Fabritek 1992 is dated 2009, but it is my understanding that this is a rewrite of a case that is older (probably much older). There is a Fabritek 1969 in the HBP catalog—same basic case, older dates, and numbers. That 1969 version lists no authors, so I suspect the case goes even further back; the 1969 version is, I’m guessing, a rewrite of an even older version.
There are many things I appreciate about the case. Here are a few:
It operates as a learning opportunity at many levels. At first it looks like a not-very-glamorous production job scheduling case. By the end of the case discussion, though, we’re into (operations) strategy and more. It starts out technical, then explodes into much broader relevance. As I tell participants when I’m teaching HBP's Teaching with Cases seminars —where I often use Fabritek as an example—when people first encounter this case, they almost always underestimate it.
It has great characters—especially Arthur Moreno, who looks like a troublemaker, but who, discussion reveals, might just be the smartest guy in the factory. Alums of the Harvard MBA program have told me that they remember Arthur Moreno many years later.
Almost every word in the case is important. It’s only four and a half pages of text and three pages of exhibits. This economy of words and sparsity of style have always seemed like poetry to me. I should note that this super concise, every-word-matters approach is not the ideal we usually aspire to when we write cases. Often, we include extra or superfluous information because part of our teaching objective is to provide practice in separating what matters from what doesn’t in a case. Fabritek takes a different approach, though, which fits it well.
It has a dramatic structure. It unfolds like a detective story, a sort of whodunnit. Something is wrong. There is a quality problem, and we’re not sure who or what is responsible. One person, Arthur Moreno, looks very guilty (probably too obviously guilty), but as we dig into the situation, there are many more possibilities. We spend in-class time analyzing the data (there’s a bit of math, so it covers that base, too) to determine which hypotheses are best supported by the data. And, realistically, the data doesn’t support any of the hypotheses perfectly, just some of them more than others. Also, there’s a plot twist at the end (I won’t reveal it, but here’s a hint: Arthur Moreno isn’t nearly the biggest problem in the final analysis). I have had students tell me the surprising realization at the end of the discussion gives them ‘goosebumps.’
Finally, through the unexpected plot twist, it imparts what I call a ‘wisdom lesson’ to young managers: not to be too sure of themselves and to regard the experiences of others, especially experts out on the factory floor, with great seriousness.”
4. Lincoln Electric Co.
Karin Schnarr, Assistant Professor of Policy, Wilfrid Laurier University

“As a strategy professor, my favorite case to teach is the classic 1975 Harvard case Lincoln Electric Co. by Norman Berg.
I use it to demonstrate to students the theory linkage between strategy and organizational structure, management processes, and leadership behavior.
This case may be an odd choice for a favorite. It occurs decades before my students were born. It is pages longer than we are told students are now willing to read. It is about manufacturing arc welding equipment in Cleveland, Ohio—a hard sell for a Canadian business classroom.
Yet, I have never come across a case that so perfectly illustrates what I want students to learn about how a company can be designed from an organizational perspective to successfully implement its strategy.
And in a time where so much focus continues to be on how to maximize shareholder value, it is refreshing to be able to discuss a publicly-traded company that is successfully pursuing a strategy that provides a fair value to shareholders while distributing value to employees through a large bonus pool, as well as value to customers by continually lowering prices.
However, to make the case resonate with today’s students, I work to make it relevant to the contemporary business environment. I link the case to multimedia clips about Lincoln Electric’s current manufacturing practices, processes, and leadership practices. My students can then see that a model that has been in place for generations is still viable and highly successful, even in our very different competitive situation.”
5. Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth
Gary Pisano, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach these days is Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth .
I love teaching this case for three reasons:
1. It demonstrates how a company in a super-tough, highly competitive business can do very well by focusing on creating unique operating capabilities. In theory, Pal’s should have no chance against behemoths like McDonalds or Wendy’s—but it thrives because it has built a unique operating system. It’s a great example of a strategic approach to operations in action.
2. The case shows how a strategic approach to human resource and talent development at all levels really matters. This company competes in an industry not known for engaging its front-line workers. The case shows how engaging these workers can really pay off.
3. Finally, Pal’s is really unusual in its approach to growth. Most companies set growth goals (usually arbitrary ones) and then try to figure out how to ‘backfill’ the human resource and talent management gaps. They trust you can always find someone to do the job. Pal’s tackles the growth problem completely the other way around. They rigorously select and train their future managers. Only when they have a manager ready to take on their own store do they open a new one. They pace their growth off their capacity to develop talent. I find this really fascinating and so do the students I teach this case to.”
6. The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron
Francesca Gino, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach is The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron .
The case surprises students because it is about a leader, known in the unit by the nickname Chaos , who inspired his squadron to be innovative and to change in a culture that is all about not rocking the boat, and where there is a deep sense that rules should simply be followed.
For years, I studied ‘rebels,’ people who do not accept the status quo; rather, they approach work with curiosity and produce positive change in their organizations. Chaos is a rebel leader who got the level of cultural change right. Many of the leaders I’ve met over the years complain about the ‘corporate culture,’ or at least point to clear weaknesses of it; but then they throw their hands up in the air and forget about changing what they can.
Chaos is different—he didn’t go after the ‘Air Force’ culture. That would be like boiling the ocean.
Instead, he focused on his unit of control and command: The 99th squadron. He focused on enabling that group to do what it needed to do within the confines of the bigger Air Force culture. In the process, he inspired everyone on his team to be the best they can be at work.
The case leaves the classroom buzzing and inspired to take action.”
7. Warren E. Buffett, 2015
Robert F. Bruner, Professor of Business Administration, Darden School of Business

“I love teaching Warren E. Buffett, 2015 because it energizes, exercises, and surprises students.
Buffett looms large in the business firmament and therefore attracts anyone who is eager to learn his secrets for successful investing. This generates the kind of energy that helps to break the ice among students and instructors early in a course and to lay the groundwork for good case discussion practices.
Studying Buffett’s approach to investing helps to introduce and exercise important themes that will resonate throughout a course. The case challenges students to define for themselves what it means to create value. The case discussion can easily be tailored for novices or for more advanced students.
Either way, this is not hero worship: The case affords a critical examination of the financial performance of Buffett’s firm, Berkshire Hathaway, and reveals both triumphs and stumbles. Most importantly, students can critique the purported benefits of Buffett’s conglomeration strategy and the sustainability of his investment record as the size of the firm grows very large.
By the end of the class session, students seem surprised with what they have discovered. They buzz over the paradoxes in Buffett’s philosophy and performance record. And they come away with sober respect for Buffett’s acumen and for the challenges of creating value for investors.
Surely, such sobriety is a meta-message for any mastery of finance.”
More Educator Favorites

Emily Michelle David is an assistant professor of management at China Europe International Business School (CEIBS). Her current research focuses on discovering how to make workplaces more welcoming for people of all backgrounds and personality profiles to maximize performance and avoid employee burnout. David’s work has been published in a number of scholarly journals, and she has worked as an in-house researcher at both NASA and the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.

Devin Shanthikumar is an associate professor and the accounting area coordinator at UCI Paul Merage School of Business. She teaches undergraduate, MBA, and executive-level courses in managerial accounting. Shanthikumar previously served on the faculty at Harvard Business School, where she taught both financial accounting and managerial accounting for MBAs, and wrote cases that are used in accounting courses across the country.

Robert D. Austin is a professor of information systems at Ivey Business School and an affiliated faculty member at Harvard Medical School. He has published widely, authoring nine books, more than 50 cases and notes, three Harvard online products, and two popular massive open online courses (MOOCs) running on the Coursera platform.

Karin Schnarr is an assistant professor of policy and the director of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program at the Lazaridis School of Business & Economics at Wilfrid Laurier University in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada where she teaches strategic management at the undergraduate, graduate, and executive levels. Schnarr has published several award-winning and best-selling cases and regularly presents at international conferences on case writing and scholarship.

Gary P. Pisano is the Harry E. Figgie, Jr. Professor of Business Administration and senior associate dean of faculty development at Harvard Business School, where he has been on the faculty since 1988. Pisano is an expert in the fields of technology and operations strategy, the management of innovation, and competitive strategy. His research and consulting experience span a range of industries including aerospace, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, health care, nutrition, computers, software, telecommunications, and semiconductors.

Francesca Gino studies how people can have more productive, creative, and fulfilling lives. She is a professor at Harvard Business School and the author, most recently, of Rebel Talent: Why It Pays to Break the Rules at Work and in Life . Gino regularly gives keynote speeches, delivers corporate training programs, and serves in advisory roles for firms and not-for-profit organizations across the globe.

Robert F. Bruner is a university professor at the University of Virginia, distinguished professor of business administration, and dean emeritus of the Darden School of Business. He has also held visiting appointments at Harvard and Columbia universities in the United States, at INSEAD in France, and at IESE in Spain. He is the author, co-author, or editor of more than 20 books on finance, management, and teaching. Currently, he teaches and writes in finance and management.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
A Case Study: Real-Life Business Planning A planning meeting should set the foundation for real strategy, not set forth the strategy itself. Find out how one company made the most of its two-day session.
By Tim Berry • Feb 3, 2009
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
I'm writing this the day after a two-day planning meeting for Palo Alto Software. It was the start of the company's annual planning cycle, plus a refresher for changed assumptions in a changed economy. Reflecting on the meeting now provides me with a great opportunity to explore a real-world, real-business example of how a planning cycle works.
I'm not trying to suggest that there's one right way to do this, or that this way is the right way. But with so much material out there on business planning written by consultants who don't actually run companies with more than a few employees, this seems like an opportunity to share what really happened, at least with this company, last month.
For the record, although I'm founder of Palo Alto Software, I no longer run it. Sabrina Parsons has been CEO for two years now. I'm still a full-time employee, but my new jobs as president are blogging, writing, speaking and teaching. I wasn't in charge of this meeting--I didn't set it up and I didn't run it. The company started in 1988 but really started growing in the mid-1990s; it now has 40-plus employees and multi-million dollar sales. And of course I'm not going to include details about the discussions or anything else that might be inappropriate because of confidentiality. Here's what happened:
The Setup The meeting was scheduled about a month in advance. It was held in a meeting room a few blocks away from the Palo Alto Software offices, in Eugene, Ore. They served coffee in the morning and lunch. The cost was $100 per day plus food for a nice meeting room on the top floor with a big conference table--very comfortable for the 10 key managers in attendance. One of them was charged with setting up the agenda and facilitating the discussion. We met from 9:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., each day for two days.
The Ground Rules This became very important, and was a big surprise. Ground rules: no cell phones, no laptops, no tablet computers, no BlackBerrys, no iPhones, no "devices." Gulp. I had no idea how much difference that makes these days. I've become an addict. At least seven of our 10 attendees suffered similar addictions. It was so hard to go from break to break without checking e-mail, Twitter, blog comments or Yahoo! Messenger. I suffered severe withdrawal symptoms.
More important, we were all focused on the meeting. I'd forgotten how for so many years meetings have been given off-and-on attention, at least for me, as I use my computer, making the arrogant assumption that I can actually focus on two things at once. I can't. My colleagues can't. Locking out all our devices made an enormous difference in improving this meeting.
Discussions Following a planned agenda, we did a lot of SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analyses: not just for the company, but also for each of our main product lines ( Business Plan Pro , Marketing Plan Pro , Email Center Pro ). From there we went into good, lengthy discussions about changed assumptions--the economic downturn, results of new releases, results of some recent projects and programs and long-term development maps. Eventually, we went over some specific action points and next steps.
Results I think it's important to point out that the output of the two days isn't strategy. Strategy isn't really done in two days, and it isn't done by vote of consensus by the top management team, either. What you get is a really strong first step toward strategy; a refresher and review of past strategy, reminders of results and a team working together to formulate strategy.
In the end, strategy has to be developed by the leadership of the company. Good leaders listen, but they also lead. They watch for the problems of "group think," and they also watch that functional experts--product developers or web producers for example--have leadership roles related to strategy for their areas. Ideally, this two-day meeting sets the foundations of strategy; and when that strategy is fully developed and articulated, everybody on the team recognizes where it came from. This was a really good first step. Make sure your business is taking good first steps, too.
Entrepreneur, Business Planner and Angel Investor
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This 103-Year-Old Doctor Opened Her Medical Practice Before Women Could Have Bank Accounts — Here Are Her 6 Secrets to a Healthy, Successful Life
- Lock 5 Ways You Might Be Cheating on Your Taxes — And Why You Will Get Caught
- I've Had a Secret Side Hustle for Decades. It Keeps Tens of Thousands of Dollars in My Pocket — and Gets Me Into Places I Wouldn't Go Otherwise .
- Lock Here's How Steve Jobs Dealt With Negative Press and Avoided Brand Disasters
- One Factor Is Helping This Entrepreneur Tackle Business Ownership Later in Life. Now, She's Jumping Into a $20 Billion Industry .
- Lock Narcissism Can Help You Be Successful — Here's How to Harness It Without Going Too Far, According to an Ivy League-Trained Psychotherapist
Most Popular Red Arrow
This dad started a side hustle to save for his daughter's college fund — then it earned $1 million and caught apple's attention.
In 2015, Greg Kerr, now owner of Alchemy Merch, was working as musician when he noticed a lucrative opportunity.
I Designed My Dream Home For Free With an AI Architect — Here's How It Works
The AI architect, Vitruvius, created three designs in minutes, complete with floor plans and pictures of the inside and outside of the house.
Skip the Business Equipment, Get Faxing and Scanning for Life for Just $60
Why spend money on equipment that will take up unnecessary space, when the same things can be done with your mobile devices?
Here's How Business Leaders Can Cultivate Happiness in the Workplace
Learn some of the progressive tactics business owners use to promote a more joyful and productive work environment.
Adobe's Firefly Image Generator Was Reportedly Partially Trained on AI Images From Midjourney, Other Rivals
Adobe gave bonus payments to people who contributed to the Adobe Stock database to train its AI, even those who submitted AI-generated images.
6 Things That Will Tell You If You Are Destined for Leadership
These qualities are inherent in natural-born leaders.
Successfully copied link
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Case Study: How Aggressively Should a Bank Pursue AI?
- Thomas H. Davenport
- George Westerman

A Malaysia-based CEO weighs the risks and potential benefits of turning a traditional bank into an AI-first institution.
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-based NVF Bank, faces a pivotal decision. Her head of AI innovation, a recent recruit from Google, has a bold plan. It requires a substantial investment but aims to transform the traditional bank into an AI-first institution, substantially reducing head count and the number of branches. The bank’s CFO worries they are chasing the next hype cycle and cautions against valuing efficiency above all else. Siti must weigh the bank’s mixed history with AI, the resistance to losing the human touch in banking services, and the risks of falling behind in technology against the need for a prudent, incremental approach to innovation.
Two experts offer advice: Noemie Ellezam-Danielo, the chief digital and AI strategy at Société Générale, and Sastry Durvasula, the chief information and client services officer at TIAA.
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-headquartered NVF Bank, hurried through the corridors of the university’s computer engineering department. She had directed her driver to the wrong building—thinking of her usual talent-recruitment appearances in the finance department—and now she was running late. As she approached the room, she could hear her head of AI innovation, Michael Lim, who had joined NVF from Google 18 months earlier, breaking the ice with the students. “You know, NVF used to stand for Never Very Fast,” he said to a few giggles. “But the bank is crawling into the 21st century.”
- Thomas H. Davenport is the President’s Distinguished Professor of Information Technology and Management at Babson College, a visiting scholar at the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy, and a senior adviser to Deloitte’s AI practice. He is a coauthor of All-in on AI: How Smart Companies Win Big with Artificial Intelligence (Harvard Business Review Press, 2023).
- George Westerman is a senior lecturer at MIT Sloan School of Management and a coauthor of Leading Digital (HBR Press, 2014).
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's how to write a business proposal to close more deals, make more sales and crush your business goals (includes examples and templates). ... This free business proposal template showcases the company's accolades, client testimonials, relevant case studies, and industry awards. You can also include other forms of social proof to establish ...
Share a brief explanation of your company and the products or services you provide. 7. Call-to-action (CTA) Add a call to action with the appropriate contact information (or a contact button, if this is a web-based case study) so that users can get in touch for additional information after reading the case study.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them. To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
A case study proposal, on the other hand, is an agreement between the vendor and its clients to make the case study. What is the format for conducting a case study? A business case study usually follows the following format: introduction of the problem, search for a solution, intervention of a product to solve the problem, and the outcomes of ...
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Proposal title. Date of submission. Company information (company logo, company name, etc). Your name, title, and contact information. Client's name, title, and contact information. A cover page is the very first thing that your prospective client will see when they open your business proposal.
6 QUALITIES OF GREAT CASE WRITERS. Curiosity. Comfort with ambiguity, since cases may have more than one "right" answer. Command of the topic or subject at hand. Ability to relate to the case protagonists. Enthusiasm for the case teaching method. Capacity for finding the drama in a business situation and making it feel personal to students.
The difference between a business case and business plan. A business case is a proposal for a new strategy or large initiative. It should outline the business needs and benefits your company will receive from pursuing this opportunity. A business plan, on the other hand, is an outline for a totally new business. Typically, you'd draft a ...
Pain Points. One of the most important steps in writing a case study for business proposal template is to explain the problem. Before directly jumping to the issue, explain their backstory before your involvement, and then slowly get the reader's attention to the actual problem and specify why they asked for your services.
1. Cover page. The cover page, also called a title page, should be kept simple. It prominently features a photograph or graphic design that is on-brand, you can use graphic design templates as a starting point. It also usually includes the project name, or the client name, as well as your company name.
Depending on how complete the answers are you may need to edit the testimonials a bit and if you do, be sure to send them back to the client for their approval. 5. Tell a story. When it comes to writing a case study, lead your reader on the journey of the project and keep it focused on the client.
Here's how to write a business proposal: 1. Create a title page 2. Include an interactive table of contents 3. Write a compelling executive summary 4. Identify the problem and propose a solution 5. Explain your methodology 6. Back up your proposal with proof of qualifications 7. Outline your pricing options 8.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects. ProjectManager's free business case template.
The business plan admits the entrepreneur to the investment process. Without a plan furnished in advance, many investor groups won't even grant an interview. ... Global Business Case Study. Paul ...
That's why you absolutely must add a relevant case study to your business proposal. Depending on the project, you can choose an industry- or project-centred case study. As you can see in our business proposal template, it can be in a short format. No need to include your entire portfolio.
1 Title Page. Your name, your business name, the name of the potential client's company, and the date you sent the proposal. 2 Table of contents. An enumerated list of what's inside your proposal. 3 Executive summary. A brief two to three paragraphs introducing your business and your proposed solution.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Case study reports are usually complete standalone documents. However, if you write business proposals or grant applications, you may find that including summaries of case studies within your proposal can show how your product or service has benefited groups or provided the solution to needs in the past.
If you really want your business proposals, quotes and contracts to stand out and give you the best chance at winning new clients, use ClientPoint Software. It makes creating and formatting professional business proposals, quotes, and contracts fast and easy. Click here to schedule a free demo of ClientPoint Software or call us at 888-972-7375.
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction In recent years, a great increase in the number of students working on their final dissertation across business and management disciplines has been noticed ( Lee & Saunders, 2017 ).
1. The Army Crew Team. Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS) EMILY MICHELLE DAVID Assistant Professor, CEIBS. "I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
A Case Study: Real-Life Business Planning A planning meeting should set the foundation for real strategy, not set forth the strategy itself. Find out how one company made the most of its two-day ...
Siti Rahman, the CEO of Malaysia-based NVF Bank, faces a pivotal decision. Her head of AI innovation, a recent recruit from Google, has a bold plan. It requires a substantial investment but aims ...