Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.

General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument . Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Words to Use in an Essay: 300 Essay Words

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
Words to use in the essay introduction, words to use in the body of the essay, words to use in your essay conclusion, how to improve your essay writing vocabulary.
It’s not easy to write an academic essay .
Many students struggle to word their arguments in a logical and concise way.
To make matters worse, academic essays need to adhere to a certain level of formality, so we can’t always use the same word choices in essay writing that we would use in daily life.
If you’re struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don’t worry—you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay.
The introduction is one of the hardest parts of an essay to write.
You have only one chance to make a first impression, and you want to hook your reader. If the introduction isn’t effective, the reader might not even bother to read the rest of the essay.
That’s why it’s important to be thoughtful and deliberate with the words you choose at the beginning of your essay.
Many students use a quote in the introductory paragraph to establish credibility and set the tone for the rest of the essay.
When you’re referencing another author or speaker, try using some of these phrases:
To use the words of X
According to X
As X states
Example: To use the words of Hillary Clinton, “You cannot have maternal health without reproductive health.”
Near the end of the introduction, you should state the thesis to explain the central point of your paper.
If you’re not sure how to introduce your thesis, try using some of these phrases:
In this essay, I will…
The purpose of this essay…
This essay discusses…
In this paper, I put forward the claim that…
There are three main arguments for…

Example: In this essay, I will explain why dress codes in public schools are detrimental to students.
After you’ve stated your thesis, it’s time to start presenting the arguments you’ll use to back up that central idea.
When you’re introducing the first of a series of arguments, you can use the following words:
First and foremost
First of all
To begin with
Example: First , consider the effects that this new social security policy would have on low-income taxpayers.
All these words and phrases will help you create a more successful introduction and convince your audience to read on.
The body of your essay is where you’ll explain your core arguments and present your evidence.
It’s important to choose words and phrases for the body of your essay that will help the reader understand your position and convince them you’ve done your research.
Let’s look at some different types of words and phrases that you can use in the body of your essay, as well as some examples of what these words look like in a sentence.
Transition Words and Phrases
Transitioning from one argument to another is crucial for a good essay.
It’s important to guide your reader from one idea to the next so they don’t get lost or feel like you’re jumping around at random.
Transition phrases and linking words show your reader you’re about to move from one argument to the next, smoothing out their reading experience. They also make your writing look more professional.
The simplest transition involves moving from one idea to a separate one that supports the same overall argument. Try using these phrases when you want to introduce a second correlating idea:
Additionally
In addition
Furthermore
Another key thing to remember
In the same way
Correspondingly
Example: Additionally , public parks increase property value because home buyers prefer houses that are located close to green, open spaces.
Another type of transition involves restating. It’s often useful to restate complex ideas in simpler terms to help the reader digest them. When you’re restating an idea, you can use the following words:
In other words
To put it another way
That is to say
To put it more simply
Example: “The research showed that 53% of students surveyed expressed a mild or strong preference for more on-campus housing. In other words , over half the students wanted more dormitory options.”
Often, you’ll need to provide examples to illustrate your point more clearly for the reader. When you’re about to give an example of something you just said, you can use the following words:
For instance
To give an illustration of
To exemplify
To demonstrate
As evidence
Example: Humans have long tried to exert control over our natural environment. For instance , engineers reversed the Chicago River in 1900, causing it to permanently flow backward.
Sometimes, you’ll need to explain the impact or consequence of something you’ve just said.
When you’re drawing a conclusion from evidence you’ve presented, try using the following words:
As a result
Accordingly
As you can see
This suggests that
It follows that
It can be seen that
For this reason
For all of those reasons
Consequently
Example: “There wasn’t enough government funding to support the rest of the physics experiment. Thus , the team was forced to shut down their experiment in 1996.”

When introducing an idea that bolsters one you’ve already stated, or adds another important aspect to that same argument, you can use the following words:
What’s more
Not only…but also
Not to mention
To say nothing of
Another key point
Example: The volcanic eruption disrupted hundreds of thousands of people. Moreover , it impacted the local flora and fauna as well, causing nearly a hundred species to go extinct.
Often, you'll want to present two sides of the same argument. When you need to compare and contrast ideas, you can use the following words:
On the one hand / on the other hand
Alternatively
In contrast to
On the contrary
By contrast
In comparison
Example: On the one hand , the Black Death was undoubtedly a tragedy because it killed millions of Europeans. On the other hand , it created better living conditions for the peasants who survived.
Finally, when you’re introducing a new angle that contradicts your previous idea, you can use the following phrases:
Having said that
Differing from
In spite of
With this in mind
Provided that
Nevertheless
Nonetheless
Notwithstanding
Example: Shakespearean plays are classic works of literature that have stood the test of time. Having said that , I would argue that Shakespeare isn’t the most accessible form of literature to teach students in the twenty-first century.
Good essays include multiple types of logic. You can use a combination of the transitions above to create a strong, clear structure throughout the body of your essay.
Strong Verbs for Academic Writing
Verbs are especially important for writing clear essays. Often, you can convey a nuanced meaning simply by choosing the right verb.
You should use strong verbs that are precise and dynamic. Whenever possible, you should use an unambiguous verb, rather than a generic verb.
For example, alter and fluctuate are stronger verbs than change , because they give the reader more descriptive detail.
Here are some useful verbs that will help make your essay shine.
Verbs that show change:
Accommodate
Verbs that relate to causing or impacting something:
Verbs that show increase:
Verbs that show decrease:
Deteriorate
Verbs that relate to parts of a whole:
Comprises of
Is composed of
Constitutes
Encompasses
Incorporates
Verbs that show a negative stance:
Misconstrue

Verbs that show a positive stance:
Substantiate
Verbs that relate to drawing conclusions from evidence:
Corroborate
Demonstrate
Verbs that relate to thinking and analysis:
Contemplate
Hypothesize
Investigate
Verbs that relate to showing information in a visual format:
Useful Adjectives and Adverbs for Academic Essays
You should use adjectives and adverbs more sparingly than verbs when writing essays, since they sometimes add unnecessary fluff to sentences.
However, choosing the right adjectives and adverbs can help add detail and sophistication to your essay.
Sometimes you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is useful and should be taken seriously. Here are some adjectives that create positive emphasis:
Significant
Other times, you'll need to use an adjective to show that a finding or argument is harmful or ineffective. Here are some adjectives that create a negative emphasis:
Controversial
Insignificant
Questionable
Unnecessary
Unrealistic
Finally, you might need to use an adverb to lend nuance to a sentence, or to express a specific degree of certainty. Here are some examples of adverbs that are often used in essays:
Comprehensively
Exhaustively
Extensively
Respectively
Surprisingly
Using these words will help you successfully convey the key points you want to express. Once you’ve nailed the body of your essay, it’s time to move on to the conclusion.
The conclusion of your paper is important for synthesizing the arguments you’ve laid out and restating your thesis.
In your concluding paragraph, try using some of these essay words:
In conclusion
To summarize
In a nutshell
Given the above
As described
All things considered
Example: In conclusion , it’s imperative that we take action to address climate change before we lose our coral reefs forever.
In addition to simply summarizing the key points from the body of your essay, you should also add some final takeaways. Give the reader your final opinion and a bit of a food for thought.
To place emphasis on a certain point or a key fact, use these essay words:
Unquestionably
Undoubtedly
Particularly
Importantly
Conclusively
It should be noted
On the whole
Example: Ada Lovelace is unquestionably a powerful role model for young girls around the world, and more of our public school curricula should include her as a historical figure.
These concluding phrases will help you finish writing your essay in a strong, confident way.
There are many useful essay words out there that we didn't include in this article, because they are specific to certain topics.
If you're writing about biology, for example, you will need to use different terminology than if you're writing about literature.
So how do you improve your vocabulary skills?
The vocabulary you use in your academic writing is a toolkit you can build up over time, as long as you take the time to learn new words.
One way to increase your vocabulary is by looking up words you don’t know when you’re reading.
Try reading more books and academic articles in the field you’re writing about and jotting down all the new words you find. You can use these words to bolster your own essays.
You can also consult a dictionary or a thesaurus. When you’re using a word you’re not confident about, researching its meaning and common synonyms can help you make sure it belongs in your essay.
Don't be afraid of using simpler words. Good essay writing boils down to choosing the best word to convey what you need to say, not the fanciest word possible.
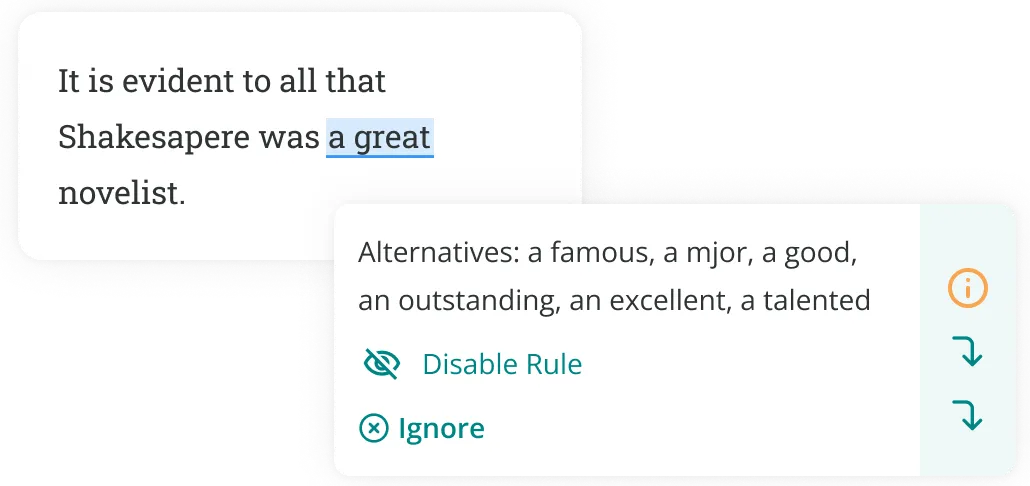
Finally, you can use ProWritingAid’s synonym tool or essay checker to find more precise and sophisticated vocabulary. Click on weak words in your essay to find stronger alternatives.
There you have it: our compilation of the best words and phrases to use in your next essay . Good luck!

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Hannah Yang is a speculative fiction writer who writes about all things strange and surreal. Her work has appeared in Analog Science Fiction, Apex Magazine, The Dark, and elsewhere, and two of her stories have been finalists for the Locus Award. Her favorite hobbies include watercolor painting, playing guitar, and rock climbing. You can follow her work on hannahyang.com, or subscribe to her newsletter for publication updates.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

100+ Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
By: Author Sophia
Posted on Last updated: October 25, 2023
Sharing is caring!
How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let’s take a look!
The secret to a successful essay doesn’t just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
Overview of an essay.

Useful Phrases for Proficiency Essays
Developing the argument
- The first aspect to point out is that…
- Let us start by considering the facts.
- The novel portrays, deals with, revolves around…
- Central to the novel is…
- The character of xxx embodies/ epitomizes…
The other side of the argument
- It would also be interesting to see…
- One should, nevertheless, consider the problem from another angle.
- Equally relevant to the issue are the questions of…
- The arguments we have presented… suggest that…/ prove that…/ would indicate that…
- From these arguments one must…/ could…/ might… conclude that…
- All of this points to the conclusion that…
- To conclude…
Ordering elements
- Firstly,…/ Secondly,…/ Finally,… (note the comma after all these introductory words.)
- As a final point…
- On the one hand, …. on the other hand…
- If on the one hand it can be said that… the same is not true for…
- The first argument suggests that… whilst the second suggests that…
- There are at least xxx points to highlight.
Adding elements
- Furthermore, one should not forget that…
- In addition to…
- Moreover…
- It is important to add that…
Accepting other points of view
- Nevertheless, one should accept that…
- However, we also agree that…
Personal opinion
- We/I personally believe that…
- Our/My own point of view is that…
- It is my contention that…
- I am convinced that…
- My own opinion is…
Others’ opinions
- According to some critics… Critics:
- believe that
- suggest that
- are convinced that
- point out that
- emphasize that
- contend that
- go as far as to say that
- argue for this
Introducing examples
- For example…
- For instance…
- To illustrate this point…
Introducing facts
- It is… true that…/ clear that…/ noticeable that…
- One should note here that…
Saying what you think is true
- This leads us to believe that…
- It is very possible that…
- In view of these facts, it is quite likely that…
- Doubtless,…
- One cannot deny that…
- It is (very) clear from these observations that…
- All the same, it is possible that…
- It is difficult to believe that…
Accepting other points to a certain degree
- One can agree up to a certain point with…
- Certainly,… However,…
- It cannot be denied that…
Emphasizing particular points
- The last example highlights the fact that…
- Not only… but also…
- We would even go so far as to say that…
Moderating, agreeing, disagreeing
- By and large…
- Perhaps we should also point out the fact that…
- It would be unfair not to mention the fact that…
- One must admit that…
- We cannot ignore the fact that…
- One cannot possibly accept the fact that…
Consequences
- From these facts, one may conclude that…
- That is why, in our opinion, …
- Which seems to confirm the idea that…
- Thus,…/ Therefore,…
- Some critics suggest…, whereas others…
- Compared to…
- On the one hand, there is the firm belief that… On the other hand, many people are convinced that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 1

How to Write a Great Essay | Image 2
Phrases For Balanced Arguments
Introduction
- It is often said that…
- It is undeniable that…
- It is a well-known fact that…
- One of the most striking features of this text is…
- The first thing that needs to be said is…
- First of all, let us try to analyze…
- One argument in support of…
- We must distinguish carefully between…
- The second reason for…
- An important aspect of the text is…
- It is worth stating at this point that…
- On the other hand, we can observe that…
- The other side of the coin is, however, that…
- Another way of looking at this question is to…
- What conclusions can be drawn from all this?
- The most satisfactory conclusion that we can come to is…
- To sum up… we are convinced that…/ …we believe that…/ …we have to accept that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 3

- Recent Posts
- Plural of Process in the English Grammar - October 3, 2023
- Best Kahoot Names: Get Creative with These Fun Ideas! - October 2, 2023
- List of Homophones for English Learners - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- How to Write a Formal Letter | Useful Phrases with ESL Image
- 50+ Questions to Start a Conversation with Anyone in English
- Useful English Greetings and Expressions for English Learners
- Asking for Help, Asking for Opinions and Asking for Approval
Nur Syuhadah Zainuddin
Friday 19th of August 2022
thank u so much its really usefull
12thSeahorse
Wednesday 3rd of August 2022
He or she who masters the English language rules the world!
Friday 25th of March 2022
Thank you so so much, this helped me in my essays with A+
Theophilus Muzvidziwa
Friday 11th of March 2022
Monday 21st of February 2022
How to Begin an Essay: 13 Engaging Strategies
ThoughtCo / Hugo Lin
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
An effective introductory paragraph both informs and motivates. It lets readers know what your essay is about and it encourages them to keep reading.
There are countless ways to begin an essay effectively. As a start, here are 13 introductory strategies accompanied by examples from a wide range of professional writers.
State Your Thesis Briefly and Directly
But avoid making your thesis a bald announcement, such as "This essay is about...".
"It is time, at last, to speak the truth about Thanksgiving, and the truth is this. Thanksgiving is really not such a terrific holiday...." (Michael J. Arlen, "Ode to Thanksgiving." The Camera Age: Essays on Television . Penguin, 1982)
Pose a Question Related to Your Subject
Follow up the question with an answer, or an invitation for your readers to answer the question.
"What is the charm of necklaces? Why would anyone put something extra around their neck and then invest it with special significance? A necklace doesn't afford warmth in cold weather, like a scarf, or protection in combat, like chain mail; it only decorates. We might say, it borrows meaning from what it surrounds and sets off, the head with its supremely important material contents, and the face, that register of the soul. When photographers discuss the way in which a photograph reduces the reality it represents, they mention not only the passage from three dimensions to two, but also the selection of a point de vue that favors the top of the body rather than the bottom, and the front rather than the back. The face is the jewel in the crown of the body, and so we give it a setting." (Emily R. Grosholz, "On Necklaces." Prairie Schooner , Summer 2007)
State an Interesting Fact About Your Subject
" The peregrine falcon was brought back from the brink of extinction by a ban on DDT, but also by a peregrine falcon mating hat invented by an ornithologist at Cornell University. If you cannot buy this, Google it. Female falcons had grown dangerously scarce. A few wistful males nevertheless maintained a sort of sexual loitering ground. The hat was imagined, constructed, and then forthrightly worn by the ornithologist as he patrolled this loitering ground, singing, Chee-up! Chee-up! and bowing like an overpolite Japanese Buddhist trying to tell somebody goodbye...." (David James Duncan, "Cherish This Ecstasy." The Sun , July 2008)
Present Your Thesis as a Recent Discovery or Revelation
"I've finally figured out the difference between neat people and sloppy people. The distinction is, as always, moral. Neat people are lazier and meaner than sloppy people." (Suzanne Britt Jordan, "Neat People vs. Sloppy People." Show and Tell . Morning Owl Press, 1983)
Briefly Describe the Primary Setting of Your Essay
"It was in Burma, a sodden morning of the rains. A sickly light, like yellow tinfoil, was slanting over the high walls into the jail yard. We were waiting outside the condemned cells, a row of sheds fronted with double bars, like small animal cages. Each cell measured about ten feet by ten and was quite bare within except for a plank bed and a pot of drinking water. In some of them brown silent men were squatting at the inner bars, with their blankets draped round them. These were the condemned men, due to be hanged within the next week or two." (George Orwell, "A Hanging," 1931)
Recount an Incident That Dramatizes Your Subject
"One October afternoon three years ago while I was visiting my parents, my mother made a request I dreaded and longed to fulfill. She had just poured me a cup of Earl Grey from her Japanese iron teapot, shaped like a little pumpkin; outside, two cardinals splashed in the birdbath in the weak Connecticut sunlight. Her white hair was gathered at the nape of her neck, and her voice was low. “Please help me get Jeff’s pacemaker turned off,” she said, using my father’s first name. I nodded, and my heart knocked." (Katy Butler, "What Broke My Father's Heart." The New York Times Magazine , June 18, 2010)
Use the Narrative Strategy of Delay
The narrative strategy of delay allows you to put off identifying your subject just long enough to pique your readers' interest without frustrating them.
"They woof. Though I have photographed them before, I have never heard them speak, for they are mostly silent birds. Lacking a syrinx, the avian equivalent of the human larynx, they are incapable of song. According to field guides the only sounds they make are grunts and hisses, though the Hawk Conservancy in the United Kingdom reports that adults may utter a croaking coo and that young black vultures, when annoyed, emit a kind of immature snarl...." (Lee Zacharias, "Buzzards." Southern Humanities Review , 2007)
Use the Historical Present Tense
An effective method of beginning an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now.
"Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother’s station wagon. We face glowing white headlights of cars following us, our sneakers pressed against the back hatch door. This is our joy—his and mine—to sit turned away from our moms and dads in this place that feels like a secret, as though they are not even in the car with us. They have just taken us out to dinner, and now we are driving home. Years from this evening, I won’t actually be sure that this boy sitting beside me is named Ben. But that doesn’t matter tonight. What I know for certain right now is that I love him, and I need to tell him this fact before we return to our separate houses, next door to each other. We are both five." (Ryan Van Meter, "First." The Gettysburg Review , Winter 2008)
Briefly Describe a Process That Leads Into Your Subject
"I like to take my time when I pronounce someone dead. The bare-minimum requirement is one minute with a stethoscope pressed to someone’s chest, listening for a sound that is not there; with my fingers bearing down on the side of someone’s neck, feeling for an absent pulse; with a flashlight beamed into someone’s fixed and dilated pupils, waiting for the constriction that will not come. If I’m in a hurry, I can do all of these in sixty seconds, but when I have the time, I like to take a minute with each task." (Jane Churchon, "The Dead Book." The Sun , February 2009)
Reveal a Secret or Make a Candid Observation
"I spy on my patients. Ought not a doctor to observe his patients by any means and from any stance, that he might the more fully assemble evidence? So I stand in doorways of hospital rooms and gaze. Oh, it is not all that furtive an act. Those in bed need only look up to discover me. But they never do." ( Richard Selzer , "The Discus Thrower." Confessions of a Knife . Simon & Schuster, 1979)
Open with a Riddle, Joke, or Humorous Quotation
You can use a riddle , joke, or humorous quotation to reveal something about your subject.
" Q: What did Eve say to Adam on being expelled from the Garden of Eden? A: 'I think we're in a time of transition.' The irony of this joke is not lost as we begin a new century and anxieties about social change seem rife. The implication of this message, covering the first of many periods of transition, is that change is normal; there is, in fact, no era or society in which change is not a permanent feature of the social landscape...." (Betty G. Farrell, Family: The Making of an Idea, an Institution, and a Controversy in American Culture . Westview Press, 1999)
Offer a Contrast Between Past and Present
"As a child, I was made to look out the window of a moving car and appreciate the beautiful scenery, with the result that now I don't care much for nature. I prefer parks, ones with radios going chuckawaka chuckawaka and the delicious whiff of bratwurst and cigarette smoke." (Garrison Keillor, "Walking Down The Canyon." Time , July 31, 2000)
Offer a Contrast Between Image and Reality
A compelling essay can begin with a contrast between a common misconception and the opposing truth.
"They aren’t what most people think they are. Human eyes, touted as ethereal objects by poets and novelists throughout history, are nothing more than white spheres, somewhat larger than your average marble, covered by a leather-like tissue known as sclera and filled with nature’s facsimile of Jell-O. Your beloved’s eyes may pierce your heart, but in all likelihood they closely resemble the eyes of every other person on the planet. At least I hope they do, for otherwise he or she suffers from severe myopia (near-sightedness), hyperopia (far-sightedness), or worse...." (John Gamel, "The Elegant Eye." Alaska Quarterly Review , 2009)
- 'Whack at Your Reader at Once': Eight Great Opening Lines
- What Is a Compelling Introduction?
- How to Structure an Essay
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Hookers vs. Chasers: How Not to Begin an Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Great Essay for the TOEFL or TOEIC
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How to Develop and Organize a Classification Essay
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- A Guide to Using Quotations in Essays
- What Is Expository Writing?
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
Essay Writing Guide
How To Start An Essay
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
20 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Starting an essay can be quite a challenge. It's a hurdle many writers stumble over, yet it's a crucial one.
Crafting an introduction that's not only attention-grabbing but also compelling is the cornerstone of successful essay writing .
In this blog, we will explain everything about starting an essay. We will discuss how to begin different types of essays and what are some common ways to start an essay. Additionally, we'll highlight some common mistakes to avoid in your essay's introduction.
So let's get started!
- 1. How to Start an Essay Introduction?
- 2. How to Start an Essay With a Quote?
- 3. How to Start an Essay With a Question?
- 4. How to Start an Essay With a Fact?
- 5. How to Start an Essay With an Anecdote?
- 6. Words To Start An Essay Introduction
- 7. Sentences To Start An Essay
- 8. How to Start an Essay - Examples
- 9. Other Common Ways of Starting an Essay
- 10. Mistakes to Avoid When Starting an Essay
How to Start an Essay Introduction?
In academic writing, the only chance to make readers stick to your paper is to start off with an interesting and engaging introductory paragraph.
The introduction typically starts by setting the stage and presenting vital background information about your specific topic.
Make your introduction catchy and interesting to both inform and motivate your readers. In this way, you can make your opening of the essay as compelling as possible.
Here are the steps that you need to follow to create an engaging essay introduction:
- Start With an Interesting Hook
- Provide Background Information
- Write Your Thesis Statement
- Map the Structure of Your Essay
- Edit and Revise at the End
Let’s explain these steps in detail below.
Step 1: Start With an Interesting Hook
An essay hook is an opening statement that strives to grab people’s interest and attention. Always start an essay introduction with a hook to make your essay appealing. Here are different types of hooks that can be used in your introduction paragraph:
- Rhetorical Questions
- Or a random funny statement
The kind of hook that should be used in the essay depends on the topic and type of your essay. If addressing a serious and sad issue, do not use a casual or funny statement. It would be better to use quotations or anecdotes for such essays.
Likewise, if your topic is casual and humorous, try to open your essay lightly and casually. You can ask a funny question or start with a random funny statement.
You can also go through an interesting hook example and learn how to start a paragraph with interesting hooks.
Step 2: Provide Background Information
After starting the introduction with a compelling hook, you need to provide background information about your topic.
The background information is provided to familiarize your audience with the topic and the main argument.
Providing background knowledge in the introduction is not as easy as it seems. You have to stop yourself from sharing excess information in the introductory paragraph. This will bore your audience, and they will stop reading for sure. Just slightly give an idea about your topic and move on. You should not spoil the surprise coming for readers in the body paragraphs.
Step 3: Write Your Thesis Statement
The last component of an introduction is the thesis statement. It is a 1-2 line sentence statement that sums up the main concept and the argument of your essay. A thesis statement is considered a road map for your essay and provides your reader with an idea about the essay. It sets the tone of the essay, and the reader gets a slight hint about what they are going to read further.
The rest of the paragraphs that come before the conclusion are the body of your essay. They contain all the reasons and shreds of evidence that support and back your thesis statement.
Quick Tip: Always firmly present your argument in the thesis statement. Do not fill it with excessive information. The thesis statement is meant to convey your stance!
Step 4: Map the Structure of Your Essay
This is especially helpful for longer essays as it informs the readers about what is to come in each section of the essay. Keep this part concise and to the point, and give your readers a clear direction of your essay.
If your essay is short or discusses fewer ideas, this step may not be necessary. But, in the case of a longer essay, the mapping will inform the readers about the things being further discussed in the essay.
Step 5: Edit and Revise at the End
Once done with the writing, edit and revise the introduction. Make sure that you have added a compelling hook, adequate background information, and a thesis statement.
Furthermore, keep in mind that your introduction should be according to the type of essay that you are writing.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Start an Essay With a Quote?
Here is how to start your essay with a quote:
- Begin with a relevant quote that ties directly to your essay's topic.
- Provide context for the quote to help readers understand its significance.
- Properly cite the author, source, and publication date of the quote.
- Transition smoothly from the quote to your thesis statement.
- Analyze the quote's meaning and how it supports your argument.
- Ensure the content of your essay's body aligns with the quote and analysis.
Here are some expert tips for putting a quote at the start of an essay:
- Avoid adding frequently used quotes that are familiar to everyone.
- Explain how the quote relates to your main point.
- Select a quote that your target audience can easily understand and relate to.
How to Start an Essay With a Question?
The easiest way to start an introduction is to ask a question to your readers to engage them immediately. Asking questions gives an image of a one-on-one conversation, which is super effective. Seeing a question first will make your audience look for the answer in the content.
A rhetorical question is a good kickstart to your essay, as such a type of beginning is attractive to readers.
If you start with an intriguing question, the answer of which is not clear, then you should provide the answer within the text. Keep in mind that the rhetorical question does not require any specific reply.
How to Start an Essay With a Fact?
Including interesting facts or statistics in your introduction helps you to take hold of your readers. Facts and stats are good attention grabbers for any piece of writing. Everyone gets entertained by the interesting and fun facts as they provide the context and background information of the topic.
For serious issues that are global, you can present shocking statistics or news to instantly grab your reader’s attention.
Choose facts and figures from credible and trustworthy sources. Your facts should support or prove your point of view or argument being presented later on in the essay.
Starting an essay with a shocking fact from a credible source is an effective way to start an essay, followed by explanations to convince the readers.
How to Start an Essay With an Anecdote?
Another interesting way to start an essay is with a brief anecdote. It is about setting a short story at the start to show how it reveals the important features of your theme.
This hook is appropriate to use if you are writing descriptive or narrative essays. The anecdote should be short, simple, and to the point. Make sure it relates to the central idea of your essay.
Words To Start An Essay Introduction
Here are some effective words and phrases to begin an essay introduction:
- Intriguingly: Intriguingly, the concept of...
- Unquestionably: Unquestionably, the most critical issue is...
- Surprisingly: Surprisingly, the data reveals...
- Notably: Notably, this phenomenon has far-reaching implications.
- Evidently: Evidently, the evidence suggests...
- Arguably: Arguably, one of the most contentious topics is...
- It is imperative to: It is imperative to address the issue of...
- Historically: Historically, this problem has persisted for centuries.
- In today's context: In today's context the relevance of this cannot be overstated.
- To illustrate: To illustrate, consider the following example….
- In contemporary society: In contemporary society, the issue of...
- Remarkably: Remarkably, few have explored the implications of...
- Undoubtedly: Undoubtedly, this problem warrants immediate attention.
- Consequently: Consequently, this leads us to question...
- In light of this: In light of this, it becomes evident that...
- Fundamentally: Fundamentally, the core issue revolves around...
- In recent years: In recent years, there has been a growing interest in...
- In an ever-changing world: In an ever-changing world, it is crucial to consider...
- To shed light on: To shed light on this matter, we will delve into...
- As a result: As a result, we are compelled to explore the implications of…
Sentences To Start An Essay
Here are some interesting sentences to start an essay:
- Have you ever wondered about the impact of climate change on our planet?
- In a remote village nestled among the mountains, a young girl's journey began.
- "The only thing we have to fear is fear itself," said Franklin D. Roosevelt.
- Shockingly, 70% of marine life is threatened by plastic pollution.
- While some embrace technology, others yearn for a simpler, analog life.
- Democracy, the cornerstone of modern societies, is often misunderstood.
- A tranquil dawn, with the sun's first rays painting the sky in hues of gold.
- Did you know that octopuses have three hearts and blue blood?
- As a child, I often marveled at the stars, wondering about the cosmos.
- Society teeters on the brink of a digital revolution that will redefine human existence.
How to Start an Essay - Examples
Examining various essay introduction examples provides valuable insights into captivating your reader's interest right from the start.
Check out these examples for guidance on crafting powerful opening lines.
How to Start an Informative Essay?
How to Start an Analysis Essay?
How to Start an Application Essay?
How to Start an Expository Essay?
How to Start an Analytical Essay?
How to Start an Essay About a Book?
How to start an Opinion Essay?
How to Start an Autobiography Essay?
How to Start an Essay on Climate Change?
How to Start an Essay on Covid-19?
How to Start an Essay About Women’s Rights?
How to Start a Paragraph in an Essay?
The best way to start a paragraph in an essay is to write the topic sentence. The topic sentence tells the reader what the paragraph is going to be about. After the topic sentence, the supporting details are further provided.
Read this example to know how to start a paragraph.
How to Start a Conclusion in an Essay?
To start a conclusion in an essay, you should write a rephrased thesis statement first. As it is the crux of your whole essay. Further on, the points discussed in the essay can be summarized one by one in the concluding paragraph.
Here is an example of how to write a conclusion to help you understand this better.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Other Common Ways of Starting an Essay
Besides the ones given above, here are some common ways of beginning your essay on a strong and engaging footing.
Stating the Thesis Statement Briefly
Instead of adding your thesis statement plainly, make the tone engaging and keep it brief.
Beginning with an Interesting Discovery
Discoveries and little-known details always interest the readers. They are curious and they want to know more. This makes this kind of essay very interesting and irresistible for your readers.
Describe the Setting of Your Essay
Presenting the setting of your essay to set the mood of your audience. This helps them know where your essay is heading.
Recount an Event
Recount an event to add drama to your essay. This also helps the readers to connect with you on a deeper level.
Use the Narrative Delay Technique
This technique works best in piquing your audience’s interest and keeping them on the edge of their seats. However, do not linger on it too much and use this technique carefully.
Present a Historical Event in the Present Tense
Use historical present tense to add weightage to your narrative. It makes the readers feel as if the event is taking place at the present moment.
Describe a Process Briefly
Describe a process briefly that leads to your main essay topic.
Reveal a Secret
“How to start an essay about yourself for college?”
People are always interested in knowing secrets. This is what makes this technique so good. Use it to reveal some secrets about yourself, if you are writing an essay about yourself.
Present a Comparison between the Past and Present
It is a very effective technique as it helps the readers see the comparison between past and present situations.
Give a Contrast between Virtual & Actual Reality
There are many things that we believe to be true, a.k.a. Virtual reality. This technique helps you in presenting what a myth is and what reality is. Breaking the myths is an effective technique to grab someone’s attention.
Mistakes to Avoid When Starting an Essay
Here are a few mistakes that should be avoided for writing a great essay introduction.
- Starting Without a Plan: Launching into your essay without a clear outline is a recipe for confusion.
- Weak, Generic Hooks: Using clichés or dull openings that fail to grab your reader's attention.
- Excessive Formality: Overloading your intro with formal language can bore your audience.
- Info Overload: Bombarding readers with too much background information can overwhelm them.
- Unclear Thesis: Failing to state your essay's purpose upfront leaves readers puzzled.
- Irrelevant Quotes: Using quotes that don't connect directly to your topic is a misstep.
- Ignoring Your Audience: Neglecting your audience's interests can lead to disengagement.
- Procrastinating Intro: Leaving the intro for last often results in rushed, ineffective beginnings.
- Repetitive Content: Repeating what's in the body of your essay makes the intro redundant.
- Skipping Proofreading: Overlooking errors in grammar and punctuation undermines your intro's credibility.
Still confused about how to begin your essay? Seek professional help from MyPerfectWords.com. We are a professional online essay writing service that provides quality and 100% custom help.
Professional assistance is all you need for your writing worries. Our online essay writer is available 24/7 to provide you with custom essays so you can score perfect grades.
Place your order now to get an amazing essay written in no time to impress the teachers!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction sentence for an essay.
A good instruction sentence for an essay is one that captures the reader's attention with an interesting hook. After writing the hook, give them some context by providing background information that will help set up what is to come in later paragraphs or sections of the paper/essay.
Finally, conclude your introduction with a thesis statement that states both concisely and specifically what main point(s) are being made about this topic along with why it matters.

What are 3 ways of starting your essay?
The three most recommended ways to start off an essay are:
- Quotation: By a famous person that fits the context of your essay.
- Question: That engages the reader to find the answer in your essay.
- Facts or Statistics: That is startling so that the reader’s attention can be grabbed.
What words can you use to start an essay?
Some words that can be used to start an essay are once, next, then, in fact, similarly, or a time word like first, second, third. You can also use sequential transitions to merge your hook to the rest of the introduction paragraph. These transition words include, for example, consequently, for this reason, or another addition transition.
What is a good paragraph starter?
A good paragraph starter is a brief yet complete topic sentence. The topic sentence should adequately give the reader an idea about what is going to be discussed in the rest of the paragraph. The topic sentence should also prove your thesis statement.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- ALL ARTICLES
- How To Study Effectively
- Motivation & Stress
- Smarter Study Habits
- Memorise Faster
- Ace The Exam
- Write Better Essays
- Easiest AP Classes Ranked
- Outsmart Your Exams
- Outsmart Your Studies
- Recommended Reads
- For Your Students: Revision Workshops
- For Your Teaching Staff: Memory Science CPD
- Our Research: The Revision Census
- All Courses & Resources
- For School Students and Their Parents
- For University Students
- For Professionals Taking Exams
- Study Smarter Network
- Testimonials

How To Start A Paragraph: 200+ Important Words And Phrases
by Kerri-Anne Edinburgh | Aug 3, 2022
There’s a lot to get right when you’re writing an essay. And a particularly important skill is knowing how to start a paragraph effectively. That first sentence counts!
Luckily for you, we’ve compiled HEAPS of advice, example phrases and top connective words to help you transition between paragraphs and guide your reader with ease.
So read on for a pick ’n’ mix of how to start a paragraph examples!
Paragraphs: the lowdown
So why exactly are paragraphs such an important tool for writing effectively ? Well:
- They’re an important part of keeping your reader captivated
- They help your reader to follow your argument or narrative
- And they keep your writing in easily digestible chunks of information!
And an important part of all that is nailing the start of your paragraphs . Honestly!
Start off strong and your reader will know exactly what you’re going to do next and how your information interrelates. Top marks here you come – and for the low, low cost of some clever vocab!
Start your paragraphs off weakly however, without setting up effective signposting and transitions , and they’ll get lost and ( horror !) might have to re-read your essay to make sense of it. Ugh.

What should your paragraphs contain?
If you’re writing an academic essay, there are a lot of popular conventions and guides about what a paragraph should include.
Academic writing guides favour well-developed paragraphs that are unified, coherent, contain a topic sentence, and provide adequate development of your idea. They should be long enough to fully discuss and analyse your idea and evidence.
And remember – you should ALWAYS start a new paragraph for each new idea or point .
You can read more about paragraph break guidelines in our helpful what is a paragraph article! If you’re wondering how long your paragraphs should be , check out our guideline article.
Paragraph structure (the PEEL method)
Academic paragraphs often follow a common structure , designed to guide your reader through your argument – although not all the time ! It goes like this:
- Start with a “topic sentence”
- Give 1-2 sentences of supporting evidence for (or against) your argument
- Next, write a sentence analysing this evidence with respect to your argument or topic sentence
- Finally, conclude by explaining the significance of this stance, or providing a transition to the next paragraph
(A quick definition: A “topic sentence” introduces the idea your paragraph will focus upon and makes summarising easy. It can occur anywhere but placing it at the start increases readability for your audience. )
One popular acronym for creating well-developed academic paragraphs is PEEL . This stands for Point, Evidence, Explanation, Link . Using this method makes it easy to remember what your paragraph should include.
- I.e. your point (the topic sentence), some evidence and analysis of how it supports your point, and a transitional link back to your essay question or forwards to your next paragraph.
NOTE : You shouldn’t start all your paragraphs the same way OR start every sentence in your paragraph with the same word – it’s distracting and won’t earn you good marks from your reader.
Free: Exam Success Cheat Sheet
My Top 6 Strategies To Study Smarter and Ace Your Exams
Privacy protected because life’s too short for spam. Unsubcribe anytime.
How to create clarity for your readers
Paragraphs are awesome tools for increasing clarity and readability in your writing. They provide visual markers for our eyes and box written content into easily digestible chunks.
But you still need to start them off strongly . Do this job well, and you can seamlessly guide your readers through the narrative or argument of your writing.
The first sentence of your paragraph is an important tool for creating that clarity . You can create links with the surrounding paragraphs and signal the purpose of this paragraph for your reader.
- Transitions show the links and relationships between the ideas you’re presenting: addition, contrast, sequential, conclusion, emphasis, example/citation
- Connective words help you to join together multiple paragraphs in a sequence
- Note: there is quite a lot of overlap in vocabulary! Some transitions are also great signposts etc.
Tip : Don’t overuse them! These techniques can make your writing sounds more professional and less like spoken language by smoothing over jarring jumps between topics. But using too many will make your writing stilted.
A common term that encompasses these three tools is “ sentence starter ”. They are typically set apart from the body of your sentence by a comma.
You can learn more about these key skills in our two helpful articles linked above – or explore a range of other writing skills advice, such as how to start an essay , structure an essay , and proofread an essay effectively!
Picking the right tone
It is important that the paragraph-starting phrases and connective words you choose complement the style of your writing and the conventions of the subject you are writing for .
For example, scientific papers usually have much clearer and expected structure and signposting conventions than arts and humanities papers.
If you’re unsure, it’s best to check some of the sources you’ve researched for your essay, explore the relevant academic style guide, or get help from a teacher – ask them for some examples!
Getting your grammar right
Grammatical conventions can be a minefield, but they’re worth remembering if you want to get top marks!
If you’re looking to increase the clarity of your writing and paragraphs, make sure you pick the right spot for your commas and colons .
For example, when you’re starting a new paragraph, many of the common signposting words and phrases require a comma. These include: however, therefore, moreover, what’s more, firstly, secondly, finally, likewise, for example, in general … (and more!).
These phrases should always be followed by a comma if it’s at the start of a sentence, or separated with a comma before and after like this if placed mid-sentence:
However, we cannot say for sure what happened here. We know, for example, that X claims to have lost the icon.
A word about “ this ” (a tip for really great writing)
As you start writing your paragraphs (and even sentences), you might be tempted to kick off with the word “ this” – as in the classic “ this shows that … ”.
But that’s not a great idea.
Why ? Academic essays aim should aim for maximum clarity, and “ this ” is just vague !
What’s important is that the connections that are clear to you , the writer (who is – hopefully – intimately familiar with your argument), are ALSO clear to your reader , who has probably never read your essay before.
Just imagine, your reader might be muttering “this what??” as they read, and then having to re-read the paragraph and the paragraph before to check … which is not ideal for getting good marks.
In complex documents (especially essays and theses) where a lot of information is presented at once, the points you’re referencing might be spread across several paragraphs of evidence and argument-building. So, unless your sentence/paragraph-starting “this” follows on immediately from the point it references, it’s best to try a different phrase.
And all it really takes is a little signposting and clarification to avoid the vagueness of “ this shows that ”. Ask yourself “ this WHAT shows that? ” And just point out what you’re referencing – and be obvious !
Here’s some examples:

You can also do a similar exercise with “ they ” and other demonstrative pronouns (that, these, those).
Specifying what your pronouns refer to will great help to increase the clarity of your (topic) sentences . And as an added bonus, your writing will also sound more sophisticated!
What type of paragraph are you starting?
When it comes to essay writing, there’s usually an expected structure: introduction, body (evidence and analysis) and conclusion .
With other genres of writing your paragraphs might not conform to such
Consider the structure of your paragraph. What do you want it to do? What is the topic? Do you want to open with your topic sentence?
How to start an introductory paragraph
Nailing the introduction of your essay is simultaneously one of the most important and hardest sections to write . A great introduction should set up your topic and explain why it’s significant.
One of the primary goals of an effective introduction is to clearly state your “ thesis statement ” (what your essay is about, and what you are setting out to achieve with your argument).
A popular (and easy) technique to start an introduction is to begin your first paragraph by immediately stating your thesis statement .
Here’s some examples of how to start a paragraph with your thesis statement:
- This paper discusses …
- In this paper, you will find …
- This essay argues that …
- This thesis will evaluate …
- This article will explore the complex socio-political factors that contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire between the reign of Constantine (312-337AD) and the fall of Rome in 476AD .
However, starting your introductory paragraph effectively is not all about immediately stating your thesis!
So head over to our great article on how to start an essay , for lots of more advice and examples on how to kick off your introductions and capture your reader’s attention with style!

How to start a body paragraph
Unless you’re writing an introduction or conclusion, you’ll be writing a “body paragraph”. Body paragraphs make up the majority of your essay, and should include all of your main points, data, evidence, analysis, deductions and arguments.
Each paragraph should have a particular purpose and be centred around one idea . Your body paragraphs might be analytical, evidential, persuasive, descriptive etc.
To help your reader make sense of the body of your essay, it’s important to guide them with signposts and transitions. These usually occur at the start of your paragraphs to demonstrate their relationship to preceding information.
However, that means there are LOTS of different techniques for starting your body paragraphs! So for 200+ words and phrases for effectively starting a body paragraph, simply keep reading!
How to start a concluding paragraph
Concluding paragraphs are a little different to other paragraphs because they shouldn’t be presenting new evidence or arguments . Instead, you’re aiming to draw your arguments together neatly, and tie up loose ends.
You might find them as part of a smaller sub-section within a longer academic dissertation or thesis. Or as part of the conclusion of your essay.
When starting your conclusion it’s always a great idea to let your reader know they’ve arrived by signposting its purpose . This is especially true if your essay doesn’t contain any headers!
Here are some examples of how to kick off your concluding paragraph:
- In conclusion, this paper has shown that …
- In summary, we have found that …
- A review of these analyses indicates that …
- To conclude, this essay has demonstrated that we must act immediately if we want to halt the drastic dwindling of our global bee population.
How to start a paragraph: 200+ top words and phrases for a winning first sentence
Choosing the best start for your paragraph is all about understanding the purpose of this paragraph within the wider context of the preceding (and following) paragraphs and your essay as a whole.
Where does it fit into the structure of your essay? Is it:
- Opening a new topic or theme?
- Providing explanations or descriptions?
- Continuing a list or sequence?
- Providing evidence?
- Presenting a different opinion or counter-argument?
- Beginning an analysis?
- Highlighting consequences?
- Drawing a conclusion?
It’s important to be direct in how you start each paragraph – especially if you’re struggling to get your point across!
The best way to craft a killer first sentence is to be clear on what you want it to do . We’ve covered 12 options below, packed with vocab and examples to get you started …
And don’t forget to consider when you should start a new paragraph , and how long you want your paragraphs to be . Where you place your paragraph breaks will have a big effect on the kind of starting sentence you need !
Finally – remember that the best time to craft effective opening sentences is after you’ve written your first draft and decided on your paragraph breaks! You should already have all your ideas arranged into a logical order.
Showing structure and presenting concepts
This first type of paragraphs are commonly found throughout your essay, whether you’re introducing your ideas, providing evidence and data, or presenting results.
There a lots of useful types of connective words and phrases to help you kick off your paragraphs with clarity:

Most notable are the sequential signposting words , which you can use throughout your essay to guide your reader through the steps of your argument, or a list of related evidence, for example.
If you’re looking for something a little more specific, read on for four sets of example academic phrases to use to start a paragraph!
1. Starting or continuing a sequence
One of the most important types of transitional phrases to help you start a paragraph is a sequential transition . These signposting transitions are great for academic arguments because they help you to present your points in order, without the reader getting lost along the way.
Sequential connectives and transitions create order within your narrative by highlighting the temporal relationship between your paragraphs. Think lists of events or evidence , or setting out the steps in your narrative .
You’ll often find them in combination with other paragraph-starting phrases ( have a look at the examples below to spot them !)
Why not try out some of these examples to help guide the readers of your essay?
- Before considering X, it is important to note that …
- Following on from Y, we should also consider …
- The first notion to discuss is …
- The next point to consider is …
- Thirdly, we know that Y is also an important feature of …
- As outlined in the previous paragraph, the next steps are to …
- Having considered X, it is also necessary to explore Y …
2. Providing evidence, examples or citations
Once you’ve made your claims or set out your ideas, it’s important to properly back them up. You’ll probably need to give evidence, quote experts and provide references throughout your essay .
If you’ve got more than one piece of evidence, it’s best to separate them out into individual paragraphs . Sequential signposting can be a helpful tool to help you and your reader keep track of your examples.
If your paragraph is all about giving evidence for a preceding statement, why not start with one of these phrases:
- For example, X often …
- This stance is clearly illustrated by …
- Consider the example of Y, which …
- This concept is well supported by …
If you want to quote or paraphrase a source or expert, a great way to start your paragraph is by introducing their views. You can also use phrases like these to help you clearly show their role in your essay:
- [Author], in particular, has argued that …
- According to [source], Y is heavily influenced by …
- [Source] for example, demonstrates the validity of this assertion by …
- This [counter-] argument is supported by evidence from X, which shows that …
Always remember to provide references for your sources in the manner most appropriate for your field ( i.e. footnotes, and author-date methods ).
3. Giving emphasis to your point
Not all points and paragraphs in an essay are made equal. It’s natural you’ll want to highlight ideas and evidence for your reader to make sure they’re persuaded by your argument !
So, if you want to give emphasis to what you’re about to discuss, be obvious ! In fact, you may need to be more direct than you think:
- This detail is significant because …
- Undoubtedly, this experience was …
- Certainly, there are ramifications for …
- The last chapters, in particular, are revealing of X …
4. Acknowledging uncertainty
In academia it’s common to find a little uncertainty in your evidence or results, or within the knowledge of your field . That’s true whether you’re a historian exploring artefacts from Ancient Greece, or a social scientist whose questionnaire results haven’t produced a clear answer.
Don’t hide from this uncertainty – it’s a great way to point ahead to future research that needs to be done. In fact, you might be doing it in your essay!
Why not try one of these examples to highlight the gaps in your academic field or experiment?
- Whether X is actually the case remains a matter of debate, as current explorations cannot …
- Although not proven, it is commonly understood that X …
- Whilst the likelihood of X is debateable …
- Given the age of the artifacts, it is impossible to say with accuracy whether Y …
- Although we cannot know for sure, the findings above suggest that …
- Untangling the causes of X is a complex matter and it is impossible to say for sure whether …
Showing the relationships between your points
As your essay progresses you will need to guide your reader through a succession of points, ideas and arguments by creating a narrative for them to follow. And important part of this task is the use of signposting to demonstrate the relationship between your paragraphs . Do they support each other? Do they present opposite sides of a debate?
Luckily there are lots of agreement , opposition and contextual connectives to help you increase your clarity:

Read on for four more sets of example academic phrases to help you present your ideas!
5. Making a new point
If there’s no connection between your new paragraph and the preceding material, you’re probably starting a new topic, point or idea.
That means it’s less likely ( although not impossible ) that you’ll need transitional phrases . However, it’s still important to signpost the purpose and position of this new paragraph clearly for your reader.
- We know that X …
- This section of the essay discusses …
- We should now turn to an exploration of Y …
- We should begin with an overview of the situation for X …
- Before exploring the two sides of the debate, it is important to consider …
You can find some great ideas and examples for starting a new topic in our how to start an essay article. Whilst they’re definitely applicable to introductions, these strategies can also work well for kicking off any new idea!
6. Presenting accepted concepts
If you’re aiming to take a new stance or question an accepted understanding with your essay, a great way to start a paragraph is by clearly setting out the concepts you want to challenge .
These phrases are also an effective way to establish the context of your essay within your field:
- It is commonly believed that …
- The accepted interpretation of X is …
- Until recently, it was thought that …
- Historically, X has been treated as a case of …
- Over the past two decades, scholars have approached X as an example of …
- The most common interpretation of Y is …
7. Adding similar points
Agreement connectives are an important tool in your arsenal for clearly indicating the continuation or positive relationship between similar ideas or evidence you’re presenting.
If you’re looking to continue your essay with a similar point, why not try one of these examples:
- Another aspect of X is …
- Another important point is …
- By the same token, Y should be explored with equal retrospection for …
- Moreover, an equally significant factor of X is …
- We should also consider …
- Proponents of Y frequently also suggested that …
8. Demonstrating contrast
In contrast, if you’re looking to present a counter-argument, opposite side of a debate, or critique of the ideas, evidence or results in your preceding paragraph(s), you’ll need to turn to contradiction and opposition connectives.
These phrases will help you to clearly link your paragraphs whilst setting them in contrast within your narrative:
- A contrary explanation is that …
- On the other side of this debate, X suggests that …
- Given this understanding of X, it is surprising that Y …
- On the other hand, critics of X point to …
- Despite these criticisms, proponents of X continue to …
- Whilst the discussion in the previous paragraph suggests X to be true, it fails to take into consideration Y …
Note : some paragraph-opening sentences can be modified using connective words to show either agreement or contrast! Here are some examples:
- It could also be said that X does [not] …
- It is [also] important to note that X … OR It is important, however, to note that X …
- There is [also/however], a further point to be considered …
Presenting analyses, arguments and results
An important stage of any essay is the analysis – that’s when you bring your own arguments to the table, based on your data and results.
Signalling this clearly, therefore, is pretty important! Happily, there are plenty of connective words and phrases that can help you out:

Read on for four sets of example academic phrases to use to start your analysis, results and summary paragraphs!
9. Conducting an analysis and constructing your argument
Once you’ve set out your evidence or data, it’s time to point out the connections within them. Or to analyse how they support the argument you want to make.
With humanities essays it is common to analyse the impact of your evidence as you present it. In contrast, sciences essays often contain a dedicated analysis section after the data has been presented.
You’ll probably need several analytical paragraphs to address each of your points. So, a great way to get started is to dive straight in by signposting the connections you want to make in each one:
- Each of these arguments make an important contribution to X because …
- In order to fully understand Y, we need to analyse the findings from …
- Each model of X and Y changed throughout the experiment because …
- Exploring this dataset reveals that, in fact, X is not as common as hypothesised …
- Notwithstanding such limitations, this data still shows that …
- Of central concern to Y, therefore, is the evidence that …
- This interpretation of X is …
- This critique implies that …
- This approach is similar to that of Y, who, as we have seen above, argues that …
- The resulting graphs suggest that …
- Whilst conducting the survey, it was discovered that …
10. Presenting results
Having completed your analyses of any evidence (and hopefully persuaded your reader of your argument), you may need to present your results. This is especially relevant for essays that examine a specific dataset after a survey or experiment .
If you want to signpost this section of your essay clearly, start your paragraph with a phrase like these:
- The arguments presented above show that …
- In this last analysis, we can see that X has shown …
- As we have seen, the data gathered demonstrates that …
- As demonstrated above, our understanding of X primarily stems from …
11. Demonstrating cause and effect
When writing an academic essay you may often need to demonstrate the cause and effect relationship between your evidence or data, and your theories or results . Choosing the right connective phrases can be important for showing this relationship clearly to your reader.
Try one of these phrases to start your paragraph to clearly explain the consequences:
- As a consequence, X cannot be said to …
- Therefore, we can posit that …
- Provided that X is indeed true, it has been shown that Y …
- As such, it is necessary to note that …
- For this reason, the decision was made to …
- The evidence show that the primary cause of X was …
- As a result of Y, it was found that …
12. Summarising a topic or analysis
In general, summary paragraphs should not present any new evidence or arguments. Instead, they act as a reminder of the path your essay has taken so far.
Of course, these concluding paragraphs commonly occur at the end of an essay as part of your conclusion. However, they are also used to draw one point or stage of your argument to a close before the next begins .
Within a larger essay or dissertation, these interludes can be useful reminders for your reader as you transition between providing context, giving evidence, suggesting new approaches etc.
It’s worth noting that concluding your topic or analysis isn’t always the same as presenting results, although there can be some similarities in vocabulary.
Connect your arguments into summaries with clear linking phrases such as:
- Altogether, these arguments demonstrate that …
- Each of these arguments make an important contribution to our understanding of X …
- From this overview of X and Y, we can conclude that …
- We can therefore see that …
- It was hypothesised that X, however, as we have seen …
- Therefore, we can [clearly] see that …
Time to get writing your paragraphs!
And that’s it! You should now have a much-improved understanding of how to start a paragraph.
Whether you we’re worried about how to start your introductions or conclusions, or were wondering about specific types of body paragraphs, hopefully you’ve found what you need in the examples above .
If you need more writing advice to help you nail top marks for your essay, we’ve got a whole series of articles designed to improve your writing skills – perfect ! Have a read for top tips to for capturing easy marks 😊
You can learn:
- how to create effective paragraphs
- about the ideal length(s) for your paragraphs
- how to start an essay AND how to structure an essay
- the 70+ top connective words and phrases to improve your writing
- how to signpost your essay for top marks
- about improving clarity with easy proofreading tricks
Good luck completing your essay!
The Science Of Studying Smart
Download my free exam success cheat sheet: all my #1 must-know strategies to supercharge your learning today.
Your privacy protected. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
- Latest Posts
- [2024] Are AP US Government & Politics and AP Comparative Government and Politics Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
- [2024] Is AP Human Geography Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
- [2024] Is AP Microeconomics Hard or Easy? Difficulty Rated ‘Quite Easy’ (Real Student Reviews + Pass Data) - 5 Jan 2024
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Read My Test-Taking Technique Book For More Marks In Exams

Top Picks: Recommended Reading From The Blog
How To Study Effectively : Ultimate Guide [READER FAVOURITE]
Exam Memorization Secrets
Inspirational Exam Quotes
Finding The Perfect Study Routine
Pomodoro Method : 9-Step Guide
Best Books About Studying
Listen To The Podcast

Awesome Guide on How to Write an Essay Introduction

'I'd like to recall the day I nearly burned myself in flames in my automobile while going 250 mph and escaping the police'. – Thankfully, we don't have a story like that to relate to, but we bet we piqued your interest.
That's what we refer to as an efficient hook. Fundamentally, it's an attention-grabbing first sentence that piques an audience's interest and encourages them to keep reading. While writing an essay, a strong hook in essay introductions is essential.
Delve into the article if you're wondering how to start an essay with a strong introduction. This is the ultimate guide for writing the parts of a introduction paragraph from our custom dissertation writing service to engage your readers.
Introduction Definition
The introduction paragraph, to put it simply, is the first section of an essay. Thus, when reading your essay, the reader will notice it right away. What is the goal of an opening paragraph? There are two things that an excellent introduction achieves. It initially informs the reader on the subject of your work; in other words, it should describe the essay's topic and provide some background information for its main point. It must also spark readers' interest and persuade them to read the remainder of your article.
To provide you with essay writing services , we only need your paper requirements to create a plagiarism-free paper on time.
How Long Should an Introduction Be
Typically, there are no strict restrictions on how long an opening paragraph should be. Professional essay writers often shape the size of it with the paper's total length in mind. For instance, if you wonder how to make introduction in essay with five paragraphs, keep your introductory sentence brief and fit it inside a single section. But, if you're writing a longer paper, let's say one that's 40 pages, your introduction could need many paragraphs or even be pages long.
Although there are no specific requirements, seasoned writers advise that your introduction paragraph should account for 8% to 9% of your essay's overall word length.
And, if you place an order on our coursework writing services , we will certainly comply with your introduction length requirements.
What Makes a Good Introduction
All of the following criteria should be fulfilled by a strong opening sentence:
- Start your introduction on an essay with a catchy sentence that draws the reader in.
- It needs to include baseline information about your subject.
- This should give readers a sense of the main argument(s) that your essay will address.
- It must include all necessary information on the setting, locations, and chronological events.
- By the end of your introduction, make a precise remark that serves as your essay's thesis.
What Are the 3 Parts of an Introduction Paragraph
So, what should be in a introduction paragraph? The introduction format essay has three sections: a hook, connections, and a thesis statement. Let's examine each component in more depth.

Part 1: Essay Hook
A hook is among the most effective parts of a introduction paragraph to start an essay. A strong hook will always engage the reader in only one sentence. In other words, it is a selling point.
Let's now address the query, 'how to make an essay introduction hook interesting?'. Well, to create a powerful hook, you can employ a variety of techniques:
- A shocking fact
- An anecdote
- A short summary
And here is what to avoid when using a hook:
- Dictionary definitions
- Generalizations
- Sweeping statements that include words like 'everywhere,' 'always,' etc.
Once you've established a strong hook, you should give a general outline of your major point and some background information on the subject of your paper. If you're unsure how to write an introduction opening, the ideal approach is to describe your issue briefly before directing readers to particular areas. Simply put, you need to give some context before gradually getting more specific with your opinions.
The 5 Types of Hooks for Writing
Apart from the strategies mentioned above, there are even more types of hooks that can be used:
- A Common Misconception — a good trick, to begin with, to claim that something your readers believe in is false.
Example: 'Although many falsely believe that people working from home are less productive – employees who get such work-life benefits generally work harder.'
- Statistics — Statistical facts may provide a great hook for argumentative essays and serious subjects focusing on statistics.
Example: 'A recent study showed that people who are satisfied with their work-life balance work 21% harder and are 33% more likely to stay at the same company.'
- Personal Story — sometimes, personal stories can be an appropriate hook, but only if they fit into a few brief sentences (for example, in narrative essays).
Example: 'When I had my first work-from-home experience, I suddenly realized the importance of having a good work-life balance; I saw plenty of the benefits it can provide.'
- Scenes — this type of hook requires making the readers imagine the things you are writing about. It is most suitable when used in descriptive and narrative essays.
Example: 'Imagine you could have as much free time as you wish by working or studying from home—and spend more time with your loved ones.'
- Thesis Statement — when unsure how to do an essay introduction, some writers start directly with their thesis statement. The main trick here is that there is no trick.
Example: 'I strongly believe there is a direct correlation between a healthy work-life balance and productivity in school or at work.'
Part 2: Connections
Give readers a clearer sense of what you will discuss throughout your article once you have given a hook and relevant background information about your essay topic. Briefly mentioning your main points in the same sequence in which you will address them in your body paragraphs can help your readers progressively arrive at your thesis statement.
In this section of your introduction, you should primarily address the following questions:
You may make sure that you are giving your readers all the information they need to understand the subject of your essay by responding to each of these questions in two to three lines. Be careful to make these statements brief and to the point, though.
Your main goal is gradually moving from general to specific facts about your subject or thesis statement. Visualize your introduction as an upside-down triangle to simplify the essay writing process. The attention-grabbing element is at the top of this triangle, followed by a more detailed description of the subject and concluding with a highly precise claim. Here is some quick advice on how to use the 'upside-down triangle' structure to compose an essay introduction:
- Ensure that each subsequent line in your introduction is more focused and precise. This simple method will help you progressively introduce the main material of your piece to your audience.
- Consider that you are writing a paper on the value of maintaining a healthy work-life balance. In this situation, you may start with a query like, 'Have you ever considered how a healthy work-life balance can affect other areas of your life?' or a similar hook. Next, you could proceed by giving broad factual information. Finally, you could focus your topic on fitting your thesis statement.
Part 3: The Thesis Statement
If you're unsure of the ideal method to create an introduction, you should be particularly attentive to how you phrase your thesis statement.
The thesis of your work is, without a doubt, the most crucial section. Given that the thesis statement of your piece serves as the foundation for the entire essay, it must be presented in the introduction. A thesis statement provides readers with a brief summary of the article's key point. Your main assertion is what you'll be defending or disputing in the body of your essay. An effective thesis statement is often one sentence long, accurate, exact, unambiguous, and focused. Your thesis should often be provided at the end of your introduction.
Here is an example thesis statement for an essay about the value of a proper work-life balance to help you gain a better understanding of what a good thesis should be:
Thesis Statement Example: 'Creating flexible and pleasant work schedules for employees can help them have a better work-life balance while also increasing overall performance.'
Catchy Introductions for Different Essay Types
Although opening paragraphs typically have a fixed form, their language may vary. In terms of academic essays, students are often expected to produce four primary intro to essay examples. They include articles that are analytical, argumentative, personal, and narrative. It is assumed that different information should appear in these beginning paragraphs since the goals of each sort of essay change. A thorough overview of the various paper kinds is provided below, along with some good essay introduction samples from our argumentative essay writers:
Narrative Introduction
- The writer of a narrative essay must convey a story in this style of writing. Such essays communicate a story, which distinguishes them from other essay types in a big way.
- Such a paper's hook will often be an enticing glimpse into a specific scene that only loosely links to the thesis statement. Additionally, when writing such an essay, a writer should ensure that every claim included in the introduction relates to some important moments that have significantly impacted the story's outcome.
- The thesis in narrative writing is usually the theme or main lesson learned from the story.
Narrative introduction example: 'My phone rang, and my mother told me that Dad had suffered a heart attack. I suddenly experienced a sense of being lifted out from under me by this immaculately carpeted flooring. After making it through, Dad left me with a sizable collection of lessons. Here are three principles that I know dad would have wanted me to uphold...'
Still Can't Think of a Perfect Intro?
When assigned to write an essay, students end up with a ton of questions, including 'How to structure an essay?', 'How to choose a good topic?'. Here at EssayPro, we employ only the best essay writers who are committed to students’ success.
Analytical Introduction
- Analytical essay introduction format is another popular type. In contrast to a narrative paper, an analytical paper seeks to explore an idea and educate the reader about a topic.
- Three important facts that support the analytical premise should be included in the middle section of the introduction.
- A well-researched and well-thought-out claim will form a wonderful thesis because the main goal of this paper is to study the topic and educate readers. It's crucial to remember that this assertion shouldn't initially have any real weight. Although it will still be theoretical, it has to be articulated practically.
Analytical introduction example: “... Hence even though presidents, CEOs, and generals still have their daily schedules full of economic crises and military conflicts, on the cosmic scale of history humankind can lift its eyes up and start looking towards new horizons. If we bring famine, plague, and war under control, what will replace them at the top of the human agenda? Like firefighters in a world without fire, so humankind in the twenty-first century needs to ask itself an unprecedented question: what are we going to do with ourselves? What will demand our attention and ingenuity in a healthy, prosperous, and harmonious world? In a healthy, prosperous, and harmonious world, what will demand our attention and ingenuity? This question becomes doubly urgent given the immense new powers that biotechnology and information technology are providing us with. What will we do with all that power? ...” Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow, Yuval Noah Harari
Persuasive Introduction
- To persuade readers of anything is the sole goal of persuasive essay writing. This may be accomplished using persuasive strategies like ethos, pathos, and logos.
- A hook statement for this paper may be anything from a fascinating fact to even comedy. You can use whatever technique you choose. The most crucial advice is to ensure your hook is in line with your thesis and that it can bolster further justifications.
- Generally speaking, a persuasive essay must include three supporting facts. Hence, to gradually lead readers to the major topic of your paper, add a quick summary of your three arguments in your introduction.
- Last, the thesis statement should be the main claim you will be disputing in this paper. It should be a brief, carefully thought-out, and confident statement of your essay's major argument.
Persuasive introduction example: 'Recycling waste helps to protect the climate. Besides cleaning the environment, it uses waste materials to create valuable items. Recycling initiatives must be running all around the world. ...'
Personal Introduction
- The final sort of academic writing that students frequently encounter is a personal essay. In principle, this essay style is creative nonfiction and requires the author to reflect on personal experiences. The goals of such a paper may be to convey a story, discuss the lessons that certain incidents have taught you, etc. This type of writing is unique since it is the most personal.
- Whatever topic you choose can serve as the hook for such an essay. A pertinent remark, query, joke, or fact about the primary plot or anything else will be acceptable. The backdrop of your narrative should then be briefly explained after that. Lastly, a thesis statement can describe the impact of particular experiences on you and what you learned.
Personal introduction example: 'My parents always pushed me to excel in school and pursue new interests like playing the saxophone and other instruments. I felt obligated to lead my life in a way that met their standards. Success was always expected on the route they had set out for me. Yet eight years after my parents' separation, this course was diverted when my dad relocated to California...'
Tips for Writing a Winning Introduction Paragraph
You now understand how to do introduction and have specific intro example for essays to help you get going. Let's quickly examine what you should and shouldn't do during the writing process.
- Keep the assignment's purpose in mind when you write your introduction, and ensure it complies with your instructor's requirements.
- Use a compelling and relevant hook to grab the reader's attention immediately.
- Make sure your readers understand your perspective to make it apparent.
- If necessary, establish key terms related to your subject.
- Show off your expertise on the subject.
- Provide a symbolic road map to help readers understand what you discuss throughout the post.
- Be brief; it's recommended that your introduction make up no more than 8 to 9 percent of the entire text (for example, 200 words for a 2500 words essay).
- Construct a strong thesis statement.
- Create some intrigue.
- Make sure there is a clear and smooth transition from your introduction to the body of your piece.
- If you're looking for a custom writer , request assistance from the EssayPro team. We know how to write a term paper along with many other types of essays.
Don'ts
- Provide too much background information.
- Use sentences that are off-topic or unnecessary.
- Make your opening paragraph excessively long.
- Keep some information a secret and reveal it later in conclusion.
- Employ overused phrases or generalizations.
- Using quotation marks excessively
Now that you know what is in the introduction of an essay, we recommend reading the information on how to critique an article to gain more academic insight.
If you are still struggling with that, keep in mind that you can always send us your request to get professional assistance from our law essay writing service .
Get Help With Your ESSAY INTRO!
Address to our professional writers to get help with your homework.
How To Write An Essay Introduction?
What is the purpose of the introduction in an essay, how to start an essay introduction, related articles.
%20(1).webp)
105 Best Words To Start A Paragraph
The first words of a paragraph are crucial as they set the tone and inform the reader about the content that follows.
Known as the ‘topic’ sentence, the first sentence of the paragraph should clearly convey the paragraph’s main idea.
This article presents a comprehensive list of the best words to start a paragraph, be it the first, second, third, or concluding paragraph.
Words to Start an Introduction Paragraph
The words you choose for starting an essay should establish the context, importance, or conflict of your topic.
The purpose of an introduction is to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the topic, its significance, and the structure of the ensuing discussion or argument.
Students often struggle to think of ways to start introductions because they may feel overwhelmed by the need to effectively summarize and contextualize their topic, capture the reader’s interest, and provide a roadmap for the rest of the paper, all while trying to create a strong first impression.
Choose one of these example words to start an introduction to get yourself started:
- The debate surrounding [topic]…
- [Topic] has garnered attention due to…
- Exploring the complexities of [topic]…
- The significance of [topic] lies in…
- Over the past decade, [topic] has…
- The critical question of [topic]…
- As society grapples with [topic]…
- The rapidly evolving landscape of [topic]…
- A closer examination of [topic] reveals…
- The ongoing conversation around [topic]…
Don’t Miss my Article: 33 Words to Avoid in an Essay
Words to Start a Body Paragraph
The purpose of a body paragraph in an essay is to develop and support the main argument, presenting evidence, examples, and analysis that contribute to the overall thesis.
Students may struggle to think of ways to start body paragraphs because they need to find appropriate transition words or phrases that seamlessly connect the paragraphs, while also introducing a new idea or evidence that builds on the previous points.
This can be challenging, as students must carefully balance the need for continuity and logical flow with the introduction of fresh perspectives.
Try some of these paragraph starters if you’re stuck:
- Building upon previous research…
- As [source] suggests, [topic]…
- Analyzing [topic] through [theory]…
- Considering the impact of [policy]…
- Delving deeper into [topic]…
- Drawing from [author]’s findings…
- [Topic] intersects with [related topic]…
- Contrary to popular belief, [topic]…
- The historical context of [topic]…
- Addressing the challenges of [topic]…
Words to Start a Conclusion Paragraph
The conclusion paragraph wraps up your essay and leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
It should convincingly summarize your thesis and main points. For more tips on writing a compelling conclusion, consider the following examples of ways to say “in conclusion”:
- In summary, [topic] demonstrates…
- The evidence overwhelmingly suggests…
- Taking all factors into account…
- In light of the analysis, [topic]…
- Ultimately, [topic] plays a crucial role…
- In light of these findings…
- Weighing the pros and cons of [topic]…
- By synthesizing the key points…
- The interplay of factors in [topic]…
- [Topic] leaves us with important implications…
Complete List of Transition Words
Above, I’ve provided 30 different examples of phrases you can copy and paste to get started on your paragraphs.
Let’s finish strong with a comprehensive list of transition words you can mix and match to start any paragraph you want:
- Secondly, …
- In addition, …
- Furthermore, …
- Moreover, …
- On the other hand, …
- In contrast, …
- Conversely, …
- Despite this, …
- Nevertheless, …
- Although, …
- As a result, …
- Consequently, …
- Therefore, …
- Additionally, …
- Simultaneously, …
- Meanwhile, …
- In comparison, …
- Comparatively, …
- As previously mentioned, …
- For instance, …
- For example, …
- Specifically, …
- In particular, …
- Significantly, …
- Interestingly, …
- Surprisingly, …
- Importantly, …
- According to [source], …
- As [source] states, …
- As [source] suggests, …
- In the context of, …
- In light of, …
- Taking into consideration, …
- Given that, …
- Considering the fact that, …
- Bearing in mind, …
- To illustrate, …
- To demonstrate, …
- To clarify, …
- To put it simply, …
- In other words, …
- To reiterate, …
- As a matter of fact, …
- Undoubtedly, …
- Unquestionably, …
- Without a doubt, …
- It is worth noting that, …
- One could argue that, …
- It is essential to highlight, …
- It is important to emphasize, …
- It is crucial to mention, …
- When examining, …
- In terms of, …
- With regards to, …
- In relation to, …
- As a consequence, …
- As an illustration, …
- As evidence, …
- Based on [source], …
- Building upon, …
- By the same token, …
- In the same vein, …
- In support of this, …
- In line with, …
- To further support, …
- To substantiate, …
- To provide context, …
- To put this into perspective, …
Tip: Use Right-Branching Sentences to Start your Paragraphs
Sentences should have the key information front-loaded. This makes them easier to read. So, start your sentence with the key information!
To understand this, you need to understand two contrasting types of sentences:
- Left-branching sentences , also known as front-loaded sentences, begin with the main subject and verb, followed by modifiers, additional information, or clauses.
- Right-branching sentences , or back-loaded sentences, start with modifiers, introductory phrases, or clauses, leading to the main subject and verb later in the sentence.
In academic writing, left-branching or front-loaded sentences are generally considered easier to read and more authoritative.
This is because they present the core information—the subject and the verb—at the beginning, making it easier for readers to understand the main point of the sentence.
Front-loading also creates a clear and straightforward sentence structure, which is preferred in academic writing for its clarity and conciseness.
Right-branching or back-loaded sentences, with their more complex and sometimes convoluted structure, can be more challenging for readers to follow and may lead to confusion or misinterpretation.
Take these examples where I’ve highlighted the subject of the sentence in bold. Note that in the right-branching sentences, the topic is front-loaded.
- Right Branching: Researchers found a strong correlation between sleep and cognitive function after analyzing the data from various studies.
- Left-Branching: After analyzing the data from various studies, a strong correlation between sleep and cognitive function was found by researchers.
- The novel was filled with vivid imagery and thought-provoking themes , which captivated the audience from the very first chapter.
- Captivating the audience from the very first chapter, the novel was filled with vivid imagery and thought-provoking themes.
The words you choose to start a paragraph are crucial for setting the tone, establishing context, and ensuring a smooth flow throughout your essay.
By carefully selecting the best words for each type of paragraph, you can create a coherent, engaging, and persuasive piece of writing.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Start a College Essay – 12 Techniques and Tips
August 1, 2023

Your college tours are scheduled, you’re knee-deep in SAT/ACT prep , application deadlines are quickly approaching, and then it happens: writer’s block hits you hard. You’re stumped, wondering how to start a college essay. It’s all too easy to overthink it when acceptances are on the line. But don’t fret! We’ve got you covered with 12 tips and techniques, plus answers to common questions like: Can I start my essay with a quote? Should I try to sound as smart as possible? Is it okay to use humor?
Keep reading for all you need to know about how to start a college essay:
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
How to Start a College Essay: The Content
How to start a college essay: the style.
- More Resources
How to Start a College Essay: Common Mistakes to Avoid
Since admissions readers are looking to be surprised and engaged right away, it’s safest to avoid these overused techniques.
1) Pulling out the dictionary
Chances are, your reader already knows the definition of the word you’re tempted to copy and paste from Merriam-Webster . Unless you’re starting with a word in a non-English language or a word that 98% of the population truly does not know, there’s no need to turn to the dictionary. Assume your reader is a smart person who is already in the know.
2) Choosing clichés
Clichés are boring in writing because they’re, well…cliché. Before you tell an admissions reader that all that glitters isn’t gold or there’s a silver lining to every cloud, remember that their job involves reading hundreds if not thousands of college essays. The way to impress them is to stand out as someone with unique insights, opinions, or creativity. Not sure if the phrase you’re using is trite or overused? Look it up online and see if there is an overabundance of results.
How to Start a College Essay (Continued)
3) beginning broadly.
Since the dawn of time, students have been starting essays too broadly. Your college admissions essays are about you, your experiences, your values, and your goals. So, starting with general statements like “Different cultures have different traditions and values” or “We have to be the change we want to see in the world” don’t center you as the topic of your essay. If you’re writing your essay about, say, your Polynesian identity and your love of Hula dance or the summer you spent making vats of soup for a food kitchen, jump right into sharing a vivid memory from those experiences instead.
4) Leading with a quote
“Can I start my college essay with a quote?” is one of the most common questions we get. The problem with starting with a quote is the same as starting too broadly: you don’t center yourself as the topic of your essay. Since college essays are short, the quote itself and the many sentences it will take to transition to the rest of your content will eat up precious word count. Unless it’s a deep-cut quote that’s highly particular to you and your niche interests, quotes anywhere in your essay can come across as cliché.
A stand-out college admissions essay will grab your reader’s attention and immediately give them a sense of who you are, what you value, and what’s unique about you. Trying to decide how to start a college essay? First, take a look at our guide to the Common App Prompts . Then, use one of these five techniques to brainstorm content:
1) Share a challenge you’ve overcome
Since college is all about growth and learning, one tried and true strategy is describing a challenge you’ve overcome that you’ve learned a lot from. Example:
For my first three months of middle school choir, I was nothing more than a ventriloquist’s dummy, mouthing words with no sound coming out. I was terrified to use my voice. Then, one fateful morning, Mrs. Garcia asked me to solo in front of the whole class.
A strong essay about a challenge you’ve overcome will explain who you were before, how you overcame the challenge, and who you are now. Taking this approach allows you to demonstrate that you’re able to rise to meet challenges, learn through difficulty, and apply yourself even when you’re uncomfortable. A word of warning though: avoid writing about very common challenges like pushing yourself to beat your cross-country time, studying for the SAT/ACT or other big tests, or transitioning from middle to high school. Since so many students share these experiences as common ground, these topics will make it hard to stand out from the crowd.
Want even more tips on writing about a challenge you’ve overcome? Check out our full guide to the Overcoming Challenges prompt.
2) Show your funny side
Yes, humor works well in college essays! Poking fun at one of your quirks or (inconsequential) shortcomings can be a great way to reveal your personality. Example:
Every day, I begged. At bedtime, at breakfast, for my birthday, for Christmas—I begged for a skateboard. Mom said it was too dangerous, Dad thought they were too noisy, but still I dreamed of cruising the neighborhood and learning to ollie in our driveway. My 14th birthday was the day my begging finally ended. It was also the day I learned I have absolutely no sense of balance.
Opening with a humorous story paints a vivid picture of you right away, but where you take it from there matters. You probably wouldn’t want to write a whole essay about breaking your tailbone and this isn’t the right forum for a stand-up routine. But you could take an opening like this in a variety of directions that reveal more meaningful truths about you. For example, after this opener, this writer could go on to:
- Talk about other new skills they tried that they were able to land better than an ollie.
- Describe how they learned about balance in other avenues of their life.
3) Clear up a misconception about you
Although college essays are brief, you’ll want to squeeze in as much depth and breadth as you can. Starting by addressing an assumption or stereotype you’ve faced can be an efficient and engaging way to move past the superficial. Example:
Blonde. Four foot eight. Size five feet. Strangers and well-meaning friends sometimes offer me a booster seat or ask if I need help carrying heavy things. Little do they know I can deadlift 135 pounds. My first teen powerlifting competition is coming up this spring.
Clearing up a misconception allows you to surprise your admissions reader and share something meaningful about yourself in one stroke. When using this strategy, think about all the different layers of your identity. What assumptions do others make of you and what might casual acquaintances or strangers be surprised to learn? A word of warning: steer clear of being too critical of others. Although stereotypes and assumptions are difficult to bear, for this essay, you’ll want to focus on you —your accomplishments, skills, and passions—instead of others.
4) Invite us in
Are Shabbat dinners with your whole extended family the highlight of your week? Do you feel most alive when you’re at your keyboard composing a new song or when you’re at a Robotics Club meeting, throwing out wild design ideas with your team? When you invite us in, you’re letting your reader in on the places you’re most at home, most excited, or most yourself. Example:
When I was seven years old, my grandma sat me down at her sewing table and taught me how to sew back on the button that had popped off my sweater. I can still feel her hands on mine, showing me where to place the needle. It was the first of what became weekly lessons on backstitching, basting, hemming pants, and embroidery. I didn’t know it then, but it was the first day of my journey into fashion design.
To brainstorm for this technique, list experiences that have helped shape your values, goals, and interests. Think of things you do every week but also once-in-a-lifetime events. You’ll want to begin this essay by choosing one meaningful experience to share in the beginning of your essay. Use vivid details that help a reader imagine the experience for themselves and then explain why this experience matters to you.
5) Nerd out about a problem you’ve solved
If you’ve hit the library stacks to find the answer to a burning question, stayed after class to ask your teacher for more homework, worked with a student club to improve a campus issue, or concocted your own science experiment, this might be the essay tactic for you. Example:
As a volunteer at my local pet rescue, I surprised myself by becoming a crusader for birds. Dogs and cats were adopted all the time, but the parrots, cockatiels, and parakeets sat in their cages for ages, chattering away and waiting for their forever homes. I realized it was an issue of awareness: no one knew our shelter rescued birds. Thirty YouTube tutorials and one online digital marketing class later, I had developed a ten-step social media strategy.
A great way to share your unique interests, this technique lets you showcase the curiosity and eagerness to learn you’ll be bringing with you to college. To brainstorm for this essay, think of times when you’ve worked solo or with a team to discover something new or solve a tricky problem. As you write about this experience, describe the initial problem, any difficulties you encountered, and the strategies you used to find a solution.
We’ve covered essay content, but you may still be wondering how to start a college essay that grabs your reader’s attention. Here are three key style tips that will help breathe life into your writing:
1) Share a story
As you can probably tell from the examples above, we recommend starting your essay off with an engaging story. Before you tell a reader that you’re an introvert who also loves performing in musical theater, you’ll want to tell the tale of the first time you braved the spotlight. Before you explain that you plan to major in political science, describe the town hall meeting you attended in the 7 th grade that started it all.
2) Use vivid descriptions
When we read, we’re most engaged when we feel like we can clearly imagine the scene. To draw a reader in, use the same storytelling strategies that fiction writers use: sensory descriptions, concrete details, and passing time.
- Sensory descriptions: Describe the smell of your mother’s biryani cooking on the stove, the temperature of the air at the start of your first half marathon. Sight, sound, smell, touch, taste. Engage as many of the five senses as you can.
- Concrete details: Concrete details are particular descriptions of places, people, and objects. If you’re describing a service trip to Honduras, describe the buildings, streets, and food you ate so your reader can imagine it.
- Passing time: Making time pass means ensuring you have a clear sense of the beginning, middle, and end of your story. To keep things clear, put your details in linear order and make sure to include temporal transitional phrases like “When I was six years old,” “Later, in high school,” and “Now, as I reflect back.”
3) Use your own voice
When you’re wondering how to start your college essay, it can be tempting to write in the same style you use for academic essays. But the college essay is a personal essay, not an essay for school. For this style of writing, you’ll want to be clear, thoughtful, and grammatically correct, but you’ll also want to be personable, engaging, and, most importantly, yourself. With that in mind, skip the SAT vocabulary words and opt for a more conversational tone instead.
How to Start a College Essay: More Resources
Looking to learn even more about how to start a college essay? If you’re ready to get started on your supplemental essays, check out our walk-through of the Why This College essay and explore our blog posts discussing the supplemental essay prompts for 50+ schools . You may also wish to read our piece on How to End a College Essay .
- College Essay

Christina Wood
Christina Wood holds a BA in Literature & Writing from UC San Diego, an MFA in Creative Writing from Washington University in St. Louis, and is currently a Doctoral Candidate in English at the University of Georgia, where she teaches creative writing and first-year composition courses. Christina has published fiction and nonfiction in numerous publications, including The Paris Review , McSweeney’s , Granta , Virginia Quarterly Review , The Sewanee Review , Mississippi Review , and Puerto del Sol , among others. Her story “The Astronaut” won the 2018 Shirley Jackson Award for short fiction and received a “Distinguished Stories” mention in the 2019 Best American Short Stories anthology.
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight

“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
I am a... Student Student Parent Counselor Educator Other First Name Last Name Email Address Zip Code Area of Interest Business Computer Science Engineering Fine/Performing Arts Humanities Mathematics STEM Pre-Med Psychology Social Studies/Sciences Submit
33 Transition Words and Phrases
Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one.
Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that “this follows logically from the preceding” include accordingly, therefore, and consequently . Words that mean “in addition to” include moreover, besides, and further . Words that mean “contrary to what was just stated” include however, nevertheless , and nonetheless .
as a result : THEREFORE : CONSEQUENTLY
The executive’s flight was delayed and they accordingly arrived late.
in or by way of addition : FURTHERMORE
The mountain has many marked hiking trails; additionally, there are several unmarked trails that lead to the summit.
at a later or succeeding time : SUBSEQUENTLY, THEREAFTER
Afterward, she got a promotion.
even though : ALTHOUGH
She appeared as a guest star on the show, albeit briefly.
in spite of the fact that : even though —used when making a statement that differs from or contrasts with a statement you have just made
They are good friends, although they don't see each other very often.
in addition to what has been said : MOREOVER, FURTHERMORE
I can't go, and besides, I wouldn't go if I could.
as a result : in view of the foregoing : ACCORDINGLY
The words are often confused and are consequently misused.
in a contrasting or opposite way —used to introduce a statement that contrasts with a previous statement or presents a differing interpretation or possibility
Large objects appear to be closer. Conversely, small objects seem farther away.
used to introduce a statement that is somehow different from what has just been said
These problems are not as bad as they were. Even so, there is much more work to be done.
used as a stronger way to say "though" or "although"
I'm planning to go even though it may rain.
in addition : MOREOVER
I had some money to invest, and, further, I realized that the risk was small.
in addition to what precedes : BESIDES —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
These findings seem plausible. Furthermore, several studies have confirmed them.
because of a preceding fact or premise : for this reason : THEREFORE
He was a newcomer and hence had no close friends here.
from this point on : starting now
She announced that henceforth she would be running the company.
in spite of that : on the other hand —used when you are saying something that is different from or contrasts with a previous statement
I'd like to go; however, I'd better not.
as something more : BESIDES —used for adding information to a statement
The city has the largest population in the country and in addition is a major shipping port.
all things considered : as a matter of fact —used when making a statement that adds to or strengthens a previous statement
He likes to have things his own way; indeed, he can be very stubborn.
for fear that —often used after an expression denoting fear or apprehension
He was concerned lest anyone think that he was guilty.
in addition : ALSO —often used to introduce a statement that adds to and is related to a previous statement
She is an acclaimed painter who is likewise a sculptor.
at or during the same time : in the meantime
You can set the table. Meanwhile, I'll start making dinner.
BESIDES, FURTHER : in addition to what has been said —used to introduce a statement that supports or adds to a previous statement
It probably wouldn't work. Moreover, it would be very expensive to try it.
in spite of that : HOWEVER
It was a predictable, but nevertheless funny, story.
in spite of what has just been said : NEVERTHELESS
The hike was difficult, but fun nonetheless.
without being prevented by (something) : despite—used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
Notwithstanding their youth and inexperience, the team won the championship.
if not : or else
Finish your dinner. Otherwise, you won't get any dessert.
more correctly speaking —used to introduce a statement that corrects what you have just said
We can take the car, or rather, the van.
in spite of that —used to say that something happens or is true even though there is something that might prevent it from happening or being true
I tried again and still I failed.
by that : by that means
He signed the contract, thereby forfeiting his right to the property.
for that reason : because of that
This tablet is thin and light and therefore very convenient to carry around.
immediately after that
The committee reviewed the documents and thereupon decided to accept the proposal.
because of this or that : HENCE, CONSEQUENTLY
This detergent is highly concentrated and thus you will need to dilute it.
while on the contrary —used to make a statement that describes how two people, groups, etc., are different
Some of these species have flourished, whereas others have struggled.
NEVERTHELESS, HOWEVER —used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way
It was pouring rain out, yet his clothes didn’t seem very wet.
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 more grammar terms you used to know: special verb edition, point of view: it's personal, 31 useful rhetorical devices, grammar & usage, 7 pairs of commonly confused words, did we change the definition of 'literally', more commonly mispronounced words, the tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, 10 bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), eavesdrop, fiasco, and 8 more words with surprising origins, 'when pigs fly' and other barnyard idioms, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
If you're struggling to choose the right words for your essay, don't worry—you've come to the right place! In this article, we've compiled a list of over 300 words and phrases to use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essay. Contents: Words to Use in the Essay Introduction. Words to Use in the Body of the Essay.
A sentence starter is simply a word or a phrase that will help you to get your sentence going when you feel stuck, and it can be helpful in many different situations. A good sentence starter can help you better transition from one paragraph to another or connect two ideas. If not started correctly, your sentence will likely sound choppy, and ...
Sharing is caring! How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let's take a look! The secret to a successful essay doesn't just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Use the Historical Present Tense. An effective method of beginning an essay is to use historical present tense to relate an incident from the past as if it were happening now. "Ben and I are sitting side by side in the very back of his mother's station wagon.
Step 1: Start With an Interesting Hook. An essay hook is an opening statement that strives to grab people's interest and attention. Always start an essay introduction with a hook to make your essay appealing. Here are different types of hooks that can be used in your introduction paragraph: Quotation.
On average, the body comprises 60-80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8-10 pages. Paragraph structure. To give your essay a clear structure, it is important to organize it into paragraphs. Each paragraph should be centered ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Tips for Using Transition Words and Phrases. 1. Use a variety of transition words, not the same one. 2. Put a comma after the transition word. 3. Put the subject of the sentence after the comma.
A good sentence starter is one that easily indicates what the tone and layout of the paragraph is going to be. If the paragraph is going to be a compare and contrast style of content, then it ...
Start with a "topic sentence". Give 1-2 sentences of supporting evidence for (or against) your argument. Next, write a sentence analysing this evidence with respect to your argument or topic sentence. Finally, conclude by explaining the significance of this stance, or providing a transition to the next paragraph.
To do this, use any of the below words or phrases to help keep you on track. 1. Firstly, secondly, thirdly. Even though it sounds obvious, your argument will be clearer if you deliver the ideas in the right order. These words can help you to offer clarity and structure to the way you expose your ideas.
Be brief; it's recommended that your introduction make up no more than 8 to 9 percent of the entire text (for example, 200 words for a 2500 words essay). Construct a strong thesis statement. Create some intrigue. Make sure there is a clear and smooth transition from your introduction to the body of your piece.
It will allow you to create a piece of writing which is coherent, interesting and above all, diverse. It will depend greatly on the type of sentence that you are writing as to which sentence starter you use and using a good variety within your essay will make it much more engaging for the reader. Once you have finished writing, it is a good ...
Words to Start a Conclusion Paragraph. The conclusion paragraph wraps up your essay and leaves a lasting impression on the reader. It should convincingly summarize your thesis and main points. For more tips on writing a compelling conclusion, consider the following examples of ways to say "in conclusion": In summary, [topic] demonstrates…
While the words "also," "and," and "so" are used in academic writing, they are considered too informal when used at the start of a sentence. Also, a second round of testing was carried out. To fix this issue, we can either move the transition word to a different point in the sentence or use a more formal alternative.
3) Clear up a misconception about you. Although college essays are brief, you'll want to squeeze in as much depth and breadth as you can. Starting by addressing an assumption or stereotype you've faced can be an efficient and engaging way to move past the superficial. Example: Blonde.
33 Transition Words and Phrases. 'Besides,' 'furthermore,' 'although,' and other words to help you jump from one idea to the next. Transitional terms give writers the opportunity to prepare readers for a new idea, connecting the previous sentence to the next one. Many transitional words are nearly synonymous: words that broadly indicate that ...
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion. There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
To select everything below the cursor in a Word document, press the Ctrl + Shift + End shortcut keys. This shortcut key combination will swiftly select all words from the cursor's current ...