- Military Awareness
- Exam Notifications
- Military News
- SSB Stories
- Current Affairs
- AFCAT eBooks


Structure and Formations of Indian Army Explained (In Simple Words)
Bestseller Books For Your preparation

Structure and Formations of Indian Army Explained
This article is about the structure and formations of the Indian Army. This tells what section, platoon, company, brigade, division, corps, commands, and regiments are. This will also give a rough estimate of the number of troops each of them has and who heads them.
Formations of Indian Army
Smallest could be a buddy pair.
Buddy pair are two individual who works as a pair, do everything together and have so much trust in each other that In Para SF, training is on the concept of a buddy system. For deadly missions, one needs to have great combat skills and tremendous trust in buddy. For trust exercises, they have to pass a Confidence Firing Test in which real bullets are used.
SEE BUDDY PAIR VIDEO
Squad around 5-6 soldiers. This will include weapon experts, demolition experts, a medic, a communication expert, and based on missions like a sniper or a language expert.
Squad and buddy-pairs are not real divisions but made for the purpose of training or patrols/missions.
After Squad, there comes Section . A section consists of about 10-15 soldiers. It is lead by an NCO of rank Havaldar.
The platoon may consist of 2-3 Sections. A platoon is a lead by a Captain or Lieutenant, or even a JCO(in few cases). It has a total strength of about 30-40 soldiers.
Company: also written (“Coy.”) has about 3-6 platoons. It may be headed by a Captain or Major depending upon size.
Battalion : A Battalion is commanded by a Colonel and is the Infantry’s main fighting unit. It consists of more than 900-1000 combat personnel. 3 fighting companies a support company. Every infantry battalion also possesses one Ghatak Platoon .
Brigade – multiple battalions and support attachments led by a Brigadier. A Brigade generally consists of around 3,000 combat troops with supporting elements. An Infantry Brigade usually has 3 Infantry Battalions along with various Support Elements. In addition to the Brigades in various Army Divisions, the Indian Army also has 5 Independent Armoured Brigades, 15 Independent Artillery Brigades, 7 Independent Infantry Brigades, 1 Independent Parachute Brigade,3 Independent Air Defence Brigades, 2 Independent Air Defence Groups and 4 Independent Engineer Brigades. These Independent Brigades operate directly under the Corps Commander (GOC Corps)
Division – Multiple brigades and support units led by major general or higher rank. Each Division is headed by GOC in the rank of Major General . It usually consists of 3 to 4 Brigades. Currently , the Indian Army has 37 Divisions including 4 RAPIDs (Re-organised Army Plains Infantry Division), 18 Infantry Divisions, 10 Mountain Divisions, 3 Armoured Divisions and 2 Artillery Divisions.
Corps : A command generally consists of two or more corps. Indian Army has 13 Corps & each one is commanded by a General Officer Commanding (GOC) , known as Corps Commander, who holds the rank of Lieutenant General . Each corps is composed of 3–4 Divisions. There are three types of corps in the Indian Army: Strike, Holding and Mixed. The Corps HQ is the highest field formation in the army.
- I Corps – Mathura (Uttar Pradesh)
- II Corps – Ambala (Haryana)
- III Corps – Dimapur (Nagaland)
- IV Corps – Tezpur (Asom)
- IX Corps – Dharamsala (Himachal Pradesh)
- X Corps – Bhatinda (Punjab)
- XI Corps – Jalandhar (Punjab)
- XII Corps – Jodhpur (Rajasthan)
- XIV Corps – Leh (J & K)
- XV Corps – Srinagar (J & K)
- XVI Corps – Nagrota (J & K)
- XXI Corps – Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh)
- XXXIII Corps – Siliguri (West Bengal)
Command : Indian Army has 6 operational commands and 1 training command. Each one is headed by a General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) , known as Army Commander, who is among the senior-most Lieutenant General officers in the army. Each command is directly affiliated to the Army HQ in New Delhi. There is also the Army Training Commanded abbreviated as ARTRAC.
The Andaman and Nicobar Command is the first and only Tri-service theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The Commands of the Indian Army are:
1. Northern Command, HQ- Udhampur(J&K)
2. Western Command, HQ- Chandigarh
3. Central Command, HQ- Lucknow(UP)
4. Eastern Command, HQ- Kolkata(WB)
5. Southern Command, HQ- Pune(MH)
6. Western Southern Command, HQ- Jaipur(RAJ)
7. Training Command, HQ- Shimla
Southern Command Insignia
Lt. Gen Anil Chauhan, who has vast experience in counter-insurgency operations, on Tuesday took charge as the new Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) of the Indian Army. He succeeds Lt General A K Bhatt who will assume charge of the Srinagar-based 15 Corps.
WHERE DOES REGIMENT FIT IN?
The ORBAT (Order of Battle) is not organised on the lines of Regiments in the Indian Army. Instead the fighting formations are organised on an ascending order from Battalion > Brigade > Division > Corps > Command. In the Indian Army, the Regiment is a purely administrative entity. All Battalions of a particular recruiting area are clubbed together into a Regiment. For example, The Assam Regiment contains say 10 Battalions and the Punjab Regiment contains for eg. 12 Battalions. Now for the purpose of recruitment and feeding new troops to the Battalions (due to retirement, medical invalidment or casualty in armed operations) all battalions of one name depend on one Recruit Training Centre which is designated as the Regimental Centre. Therefore, the Assam Regimental Centre and the Punjab Regimental Centre or the Grenadiers Regimental Centre etc.
In addition to the Regiments, the term Corps also has administrative existence apart from the fighting formation designated as Corps above. Therefore the Indian Army also has the Armoured Corps and the Corps of Signals and the Corps of Electrical and Mechanical Engineers and so on. Broadly from a civilians point of view, it can be said that Infantry Battalions are administratively organized as Regiments and other Fighting Arms and Services are organized on the basis of Corps – So we have the Army Educational Corps; the Army Medical Corps; the Ordnance Corps etc. The Guards Infantry Units don’t describe themselves as a Regiment. They are known as the Brigade of the Guards. The reason for this is their history continuing from the British Indian Army which took its organizational structure from the British Royal Army .
Artillery and Armoured units are an exception where a unit of combat arms is organized as regiments. For example 4 Armoured Regiment, 76 Field Artillery Regiment etc.
In addition to this Artillery as a group is also described as the Regiment of Artillery. Reason: Tradition starting from old Cavalry regiments.
Now there are some administrative corps of Indian Army as follows-
- Army Aviation Corps
- Army Medical Corps
- Army Ordnance Corps
- Corps of Military Police
- Defence Security Corps
- Indian Army Service Corps
- Indian Medical Service
- Military Nursing Service
- Indian Army Corps of Signals
Source of this article are multiple. Any suggestion/improvements are welcome.
Read my other posts here:
The story behind badluram ka badan
10 facts about the Indian Air Force
Central Armed Police Force
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment

RELATED POSTS
Nda exam marks of recommended candidates (check here), 30 important science questions for upsc exams, nda 2 2023 merit list (men & women)..., ssc tech 63 cut off for b.e/b.tech graduates, 30 important questions for upsc exam 2024, 11 nda ranks & powers earned by nda..., ssb interview articles, how many ssb’s if i clear ima,..., 21 important questions about the indian army..., 10 dos & don’ts of group discussion..., ssb interview attempts – how many times..., answer to common doubts on ssb service..., tips for personal interview in ssb [questions,..., stay connected, download ssb ebooks.

Latest Articles
Nda 2 2023 merit list (men & women) for national defence academy, 11 nda ranks & powers earned by nda cadet, 25 important polity questions for cds 2024 exam, 25 important geography questions for nda 2024 exam, indian navy agniveers passing out parade ins chilka, meet inayat vats who carried forward her battle-decorated father’s legacy, inspirational journey of lady cadets at officers training academy, 220 cadets passed out from the officers training academy chennai.
Defence Direct Education. India's Most Loved Defence Educational Portal
Reach Us At: [email protected] +91 8050303287
© Copyright - Defence Direct Education
Privacy Refund Work With Us Payments Advertise
Made In India 🇮🇳 By Team DDE.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
The Indian Army
Last updated on January 31, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

Indian army is the land-based branch of Indian defence forces. It is the largest of the three armed forces of India (army, air force , and navy ).
The primary mission of the Indian army is to defend the nation from external aggression as well as internal threats. It ensures national security and maintains peace within the borders.
The Indian army also conducts rescue operations and humanitarian missions during natural disasters.
The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army. The professional head is the Chief of Army Staff, a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the five-star rank of Field Marshal to date.
The motto of the Indian Army is “Service before Self”.
The Army Day is celebrated on January 15 th every year commemorating the taking over of the position of Commander in Chief of the Indian Army by Field Marshal Kodandera M. Cariappa from General Francis Roy Bucher in 1949.
Table of Contents
Learn more from: ClearIAS Study Materials
Ministry of Defence

After independence, the Ministry of Defence was created under the charge of a Cabinet Minister, and each Service was placed under its own Commander-in-Chief.
1955: The Commanders-in-Chief were renamed the Chief of the Army Staff, the Chief of the Naval Staff, and the Air Staff.
1962 : The Department of Defence Production was set up to deal with research, development, and production of defence equipment.
1965 : The Department of Defence Supplies was created for the planning and execution of schemes for import substitution of defence requirements. These two Departments were later merged to form the Department of Defence Production and Supplies.
1980: The Department of Defence Research and Development was created.
2004: The name of the Department of Defence Production and Supplies was changed to the Department of Defence Production. The Department of Ex-Servicemen Welfare was also created.
Also read: Inter Services Organisations Bill
History of the Indian Army
The Indian Army was a British-commanded force until independence. It comprised locally recruited forces and expatriate British officers.
British Indian Army
The British Indian army has fought in numerous wars like the Anglo Burmese; the Anglo-Sikh wars; the Anglo-Afghan wars; the Opium Wars, and the Boxer Rebellion in China; and in Abyssinia, hence helping maintain British supremacy.
1776: A military department was created within the East India Company at Kolkatta.
1895: The Bengal, Bombay, and Madras Presidency Armies were merged into a single force called the Indian Army. It was divided into four commands- Punjab (Northwest Frontier), Bengal, Madras (with Burma), and Bombay (with Sindh, Quetta, and Aden).
1912: The Prince of Wales Royal Indian Military College was established at Dehradun to provide education to the wards of aristocratic and well-to-do Indian families and to prepare selected Indian boys for admission into the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. Cadets were given a King’s commission, after passing out, and were posted to one of the eight units selected for Indianisation.
1914-18: World War I saw 1.3 million Indian soldiers participate, out of which 74,187 were killed or missing in action. They contributed to European, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and African war theatres.
1939-45: During World War II , the Indian soldiers fought with the Allies. India had been pulled into war without the consent of the Indians. This has led to demands for complete independence in return.
Many Indian soldiers deflected during the war to support the independence movement from outside. This led to many joining the Free India Legion in Germany. The Indian POWs joined the Indian National Army in Singapore which was led by Subhash Chandra Bose .
Indian army after independence
After the independence and partition in 1947, four of the ten Gurkha regiments were transferred to the British Army. The rest of the British Indian army was divided between the newly created nations of India and Pakistan.
1947: Indo-Pak war of 1947 or the First Kashmir War saw the Indian army playing a crucial role. An intense war was waged across the state borders. Pakistan suffered significant losses and was stopped on the line formed which is now called the Line of Control (LOC).
1948: After partition, the Nizam of Hyderabad chose to remain independent and maybe join Pakistan later on. The Indian Army troops were ordered by then Deputy Prime Minister Saradar Vllabhai Patel to secure Hyderabad state after the talks between Nizam and the government of India reached a stalemate. The Indian army was backed by the Indian Air Force.
1950: The Indian Army sent its 60 th Parachute Field Ambulance unit to aid UN troops during the Korean War (1950-53).
1961: The Army participated in Operation Vijay launched to secure Goa Daman and Diu from the Portuguese.
1962: The Sino- Indian war broke out in the Aksai Chin region (now under Chinese control) and Arunachal Pradesh. The Chinese and Indian troops made incursions beyond the disputed McMahon Line increasing the tensions. However India lost footing in the war because of poor coordination among various divisions of the Indian Army, and the late decision to mobilize the Indian Air Force gave China a crucial tactical and strategic advantage over India. The Line of Actual Control (LAC) came into being after this.
The LAC is generally divided into three sectors:
- The western sector between Ladakh on the Indian side and the Tibet and Xinjiang autonomous regions on the Chinese side.
- The middle, mostly undisputed sector between Uttrakhand and Himachal Pradesh on the Indian side and the Tibet autonomous region on the Chinese side.
- The eastern sector is between Arunachal Pradesh on the Indian side and the Tibet autonomous region on the Chinese side. This sector generally follows the McMahon line.
1965: The Indo-Pak War of 1965 saw the Indian army in all its glory as they launched major and successful offensives. The infamous tank battle, the battle of Asal Uttar, and the largest tank battle, the battle of Chawinda after World War II saw the Indian Army’s victory.
1967: The Cho La incident or the Sino-Indian skirmish was a military conflict between the Indian army and the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in Sikkim. Indian army convincingly ousted the PLA from Sikkim.
1971: The president’s rule of 1971 saw the launch of counter-insurgency Operation Steeplechase by the Indian army and police against Naxalites in the Red Corridor.
The Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971 had heavy involvement of the Indian Armed forces. The Indian army battalions were engaged in clashes on both the eastern and western front, with air support from the Indian Air Force. Many famous battles like the Battle of Longewala were fought.
1984: The Indian army participated in Operation Meghdoot to secure the Siachen glacier from Pakistani incursions. An entire battalion of the Kumaon Regiment was airlifted to the glacier. The Indian Army continues to control all of the Siachen Glacier and its tributary glaciers, which is one of the harshest and inhospitable conditions for the troops to be posted in.
Indian army has played important roles in many counter-insurgency operations over the years, such as Operation Blue Star and Woodrose against Sikh insurgents in the 1980s and Operation golden bird in 1995 in the northeast.
1999: The Pakistani army had captured major vantage points in Kashmir. Once the scale of the Pakistani incursion was realized, the Indian Army quickly mobilized about 200,000 troops, and Op Vijay was launched. However, since the heights were under Pakistani control, India was at a clear strategic disadvantage. But by the end of the Kargil War, all the enemy-occupied areas were back under Indian army control. This war gave rise to many brave and gallant stories of bravery and sacrifice by the Indian army.
2016: The Indian Army carried out surgical strikes in PoK in the terrorist launch pads in response to the terrorist attack on Indian army soldiers in Uri. The final ceasefire was reached in 2018 between both countries.
2017: The Doklam crisis was a border stand-off between the Indian Army and the Chinese PLA over the Chinese construction of a road in Doklam, a trijunction between India, China, and Bhutan. Indian army has launched op juniper to stop the Chinese.
Major exercises of the Indian Army
Op. Brasstacks (1986): It was launched by the Indian Army to simulate a full-scale war on India’s western border. The exercise was the largest ever conducted in India. It included nine infantry, three mechanized, three armored divisions, and one air assault division, as well as three independent armored brigades.
Ex. Nomadic Elephant: The army has been conducting training exercises with the Mongolian army since 2004.
Ex. Yudh Abhyas: The Yudh Abhyas exercise is an ongoing series, since 2005. It is a joint exercise between the Indian and United States armies, agreed upon under the New Framework of the India-US Defence Relationship.
Ex. Shakti: The Shakti exercise is an ongoing series, since 2011, of joint exercises between the Indian and French armies. The exercise is conducted to practice and validate anti-terrorist operations in snowbound and mountainous areas.
Structure of the Indian Army
The Army is operationally and geographically divided into seven commands, with the basic field formation being a division. Below the division level are permanent regiments that are responsible for their recruiting and training.
Future of the army
The theme of the year 2022 is “In stride with the Future”, which signifies the army’s commitment to empowering the force through re-structuring and induction of modern weapon systems for future conflicts.
Emerging technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, Cyber Warfare, Robotics, and Aerospace, which have the potential for Military application and a disruptive impact on modern-day warfare are being explored and inducted.
To confront multifarious security challenges, the Indian Army is “In Stride with the Future” , fully committed to modernization with an impetus to indigenous solutions.
F-INSAS (Future Infantry Soldier As a System) is the Indian Army’s principal infantry modernization program, which aims to modernize the army’s 465 infantry and paramilitary battalions by 2020.
India is also reorganizing the mechanized forces to achieve strategic mobility by progressively deploying more Arjun main battle tanks (MBT). It also aims to develop and deploy the Arjun MK-II variant, as well as 1,657 Russian-made T-90 S MBTs.
Many weapons programs are going on such as:
- Arjun MK-IA, the main battle tank (MBT)
- Futuristic Battle Tank (FMBT), FMBT will be a lighter tank of 50 tons.
- Abhay IFV, the Future Infantry Combat Vehicle
- TATA Kestrel is a modern armored personnel carrier (APC) developed by Tata Motors and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Light Utility helicopters (LUH) to replace chetak and cheetah helicopters.
- HAL LUH for the army and air force
- HAL Light combat helicopters for the army.

Take a Test: Analyse Your Progress
Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Indian Army in 500+ Words
- Updated on
- Dec 28, 2023

Essay on Indian Army: The Indian army is the bravest and second largest army in the world with a total of 1.23 million soldiers. The Ministry of Defence of the Government of India is the governing body for the Indian Armed Forces. Commanded by the President of India as the supreme commander and commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), the Indian Army fulfils the aim of safeguarding the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the country.
General K.M. Cariappa, the first Indian commander-in-chief of the Indian Army, replaced British Commanding General Sir Francis Butcher and formed the Territorial Army in 1949, transforming the British Army into a national one.
From the date of replacement, the Indian Army didn’t look back. Whether in signing any pact with a country across the border or safeguarding the nation from internal or external threats, the Indian Army always marked success. It successfully maintained peace and security within the country’s frame.
Also Read: How to Join Indian Army?
Essay on Indian Army in 500+ words in English
The Indian Army is a forward-pushing force, embodied with the spirit of courage, discipline, and selfless service. With a rich history and a firm commitment to protecting the nation, the Indian Army holds a revered place in the hearts of citizens.
The soldiers in the Indian Army come from different parts of our diverse nation, representing its unity. They wear uniforms with pride, displaying not just their commitment but also the diverse weave of our country.
The Indian Army’s significance extends beyond borders and our everyday lives. Whether protecting us from external threats or assisting during natural disasters, the Indian Army is always there. Their bravery and selflessness inspire us and instil a sense of security.
Historical Significance
The roots of the Indian Army can be traced back to the British Indian Army, which played an essential role in various conflicts, including World War 1 and World War 2 .
The post-independence era marked the establishment of the Indian Army as the backbone of the country’s defence, safeguarding its borders and preserving its sovereignty.
Remarkable chapters in its history include the 1971 Indo-Pak War , which led to the creation of Bangladesh, and the Kargil War in 1999 , where the Army displayed exceptional courage in the face of adversity.
Organisational Structure
There are a total of 27 Regiments in the Indian Army. Popular regiments of the Indian Army are Rajputana Rifles, Dogra, Jat, Sikh and Bihar Regiment, Maratha Light Infantry and Gorkha Rifles. All these regiments are special in their respective fields.
From the infantry units stationed at the borders to the artillery units providing firepower, the harmonious collaboration of these components ensures the nation’s security. The hierarchical structure and extensive training programs reflect the dedication to maintaining the highest standards of professionalism.
Modern Challenges and Adaptations
In the modern scenario, the Indian Army faces various challenges, ranging from traditional threats along the borders to unconventional warfare and counter-terrorism operations.
Embracing the need for modernization, the Army actively incorporates advanced technology, weaponry, and communication systems. Collaborations with international defence partners contribute to staying abreast of evolving military capabilities. Moreover, the Indian Army’s active participation in United Nations peacekeeping missions showcases its commitment to global security and stability.
Values and Sacrifices
At the heart of the Indian Army lie values that go beyond the battlefield. Discipline, integrity, and selfless service are ingrained in the importance of every soldier. The life of a soldier demands immeasurable sacrifices, often involving extended periods away from families in challenging terrains.
The seriousness of a soldier’s duty oath is illustrated in their ultimate sacrifice. These sacrifices can easily resonate nationwide, reminding us of the dedication and courage that define the Indian Army.
Humanitarian Contributions
While the primary role of the Indian Army is defence, its impact extends beyond borders. Actively engaged in disaster relief operations, the Army emerges as a lifeline during natural calamities. Whether rescuing people from flooded areas or providing medical assistance in remote regions, the humanitarian endeavours of the Army underscore its role as the nation’s protector, both in times of war and peace.
In conclusion, the Indian Army is not merely a military force; it represents national pride, resilience, and sacrifice. From the battlefields to peacekeeping missions and humanitarian efforts, the Army’s influence is profound and multifaceted.
As citizens, we must honour and respect the commitment of the brave men and women who serve in the Indian Army, ensuring that their legacy of valour and patriotism endures for generations to come.
Also Read: How to Become a Para Commando Officer?
The Indian Army is like a protective shield for our country. Brave soldiers in uniform work together to keep us safe. They come from different parts of India, showing our unity. The army helps during wars, and natural disasters, and maintains peace within our borders. Our soldiers are strong and dedicated, always ready to face challenges. Families of soldiers also play an important role, supporting them with love and courage. The Indian Army has a rich history of bravery and sacrifice. They use advanced technology to stay prepared for any situation. The army not only defends but also contributes to nation-building. We salute the Indian Army for their selfless service and commitment to our nation.
The Indian Army is important for ensuring national security, maintaining peace within the country, contributing to disaster relief, representing unity in diversity, and symbolising discipline and sacrifice.
The father of the Indian Army is Field Marshal Sam Manekshaw. He was a great leader who played a key role in shaping the army.
The Indian Army is really big, with more than a million active soldiers. It’s one of the largest armies globally, showing our strong commitment to keeping our nation secure.
The motto of the Indian Army is “Service Before Self.” This means soldiers put the nation and its people first, showing their dedication and willingness to sacrifice for us.
Related Reads:
For more information on such informative articles for your school, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Deepika Joshi
Deepika Joshi is an experienced content writer with expertise in creating educational and informative content. She has a year of experience writing content for speeches, essays, NCERT, study abroad and EdTech SaaS. Her strengths lie in conducting thorough research and ananlysis to provide accurate and up-to-date information to readers. She enjoys staying updated on new skills and knowledge, particulary in education domain. In her free time, she loves to read articles, and blogs with related to her field to further expand her expertise. In personal life, she loves creative writing and aspire to connect with innovative people who have fresh ideas to offer.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Indian Army Day 2024 Essay

Introduction
The Indian Army , the world's second-largest standing army, marks Indian Army Day 2024 theme as the Year of Technology Absorption, signifying a focused commitment to incorporating and harnessing technological advancements. when is Indian Army Day? The celebration of Indian Army Day occurs annually on the 15th of January. As we approach Indian Army Day 2024 , let's delve into the forces that safeguard our nation's security and why Indian Army Day is celebrated, exploring their evolving role in a rapidly changing world. The Indian Army's dedication to absorbing cutting-edge technology adds a dynamic dimension to their capabilities, reflecting a strategic vision for a modernized defense.In this context, we will explore the importance of celebrating Indian Army Day 2024 and examine the role of technology in shaping the future of our armed forces.
Essay on Indian Army Day 2024
The Indian Army is the land-based branch of the Indian Armed Forces. It is the world's second-largest standing army and the largest army. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two battalions of the Indian Army have been awarded the "Nations in conflict" peacekeeping medal.
The Indian Army has a regimental system but is operationally and geographically split into seven commands, with the basic field formation being a division. It is an all-volunteer force and comprises more than 81,000 active troops and a support element of close to 1,160,000 troops.
The primary objective of the Indian Army is to safeguard the nation's territorial integrity from external aggression and threats and maintain peace and security within its borders. It conducts humanitarian rescue operations during natural calamities and other restlessness, like Operation Surya Hope, and can also be requisitioned by the Government to assist in national emergencies. The Indian Army has been involved in four wars with neighbouring Pakistan and one with China. It has also conducted numerous peacekeeping operations across the world.
Indian Army consists of many regiments which are territorially based, and each regiment has its own cap badge, traditions and history. The units that make up the Indian Army are not all permanently based in one location. They are rotated between deployments in India and other countries as part of peacekeeping or training missions.
The Indian Army is a very disciplined force and follows a strict hierarchy. Officers must salute their seniors, regardless of rank, and must obey orders from their superiors without question. The soldiers are also expected to maintain a high degree of personal hygiene and be physically fit.
The Indian Army is one of the largest armies in the world. It has more than 1,160,000 troops who are available for deployment at short notice. These troops come from all over India and are drawn from all religions and regions. They are paid according to their rank and duration of service.
The Indian Army is the largest volunteer army in the world. It has more than 1,160,000 troops who are available for deployment at short notice.
India became independent from Britain in 1947. It was then ruled by the British Indian Empire. The independence day of Pakistan is on 14 august 1947. There was a lot of violence and bloodshed between the Hindus and Muslims in the partition of British India into India and Pakistan.
The British Indian Army was divided between the two countries. The British Indian Army in Pakistan became the Pakistani Army. The British Indian Army in India became the Indian Army.
A Long Indian Army Day 2024 Essay
The Happy Indian Army Day originated from armies of the East India Company's which at last became the British Indian Army, and the Princely States Army, which after its independence in 1947, merged into the National Army of India. The units of the Indian Army have fought many battles in the past where they gained honor for the country with their bravery. One will find out more facts about the Indian Army through this essay on the Indian Army in English.
The Indian Army has the sole objective of protecting the nation from any foreign aggression that arises, ensuring the nation's security. They also try to prevent the nation from internal threats. During natural calamities, the Indian Army conducts humanitarian rescue operations to save many people's lives. There are a total of 65 regiments in the Indian Army that are divided based on their skills. These are some facts that one can learn from the essay on the Indian Army.
There are various medals presented by the President of India to different Indian Army recruits for their bravery on the battlefield. The medals awarded for the valor shown on the battlefield in the face of the enemy are Param Vir Chakra, Maha Vir Chakra, and Vir Chakra, and the medals awarded for bravery and courage shown away from the battlefield are Ashoka Chakra, Kirti Chakra, and Shaurya Chakra.
The Indian Army, till now, has fought four battles, from which three were with Pakistan, and one was with China. Some other operations that are performed by the Indian Army are Operation Vijay, Operation Meghdoot, Operation Cactus, and Operation Brasstacks. One can also learn about some more missions conducted by the Army from this essay on the Indian Army, as they were also involved in many peacekeeping missions organized by the United States. Some of these peacekeeping missions were conducted in Lebanon, Angola, Cambodia, Vietnam, and many other countries.
The Government is now planning to increase the capabilities of the Indian Force by introducing some new policies. Recently, it has been planned that the Indian Army with the Indian Navy will set up a marine brigade.
The current formations that the Army follows are holding formations and combat formations. Holding formations are meant for holding and containing the enemies, and combat formation is meant for counter-attacking the enemies in order to neutralize them and stop them from attacking.
One can gain knowledge of the Army's uniform from this Indian Army essay. The Indian Army camouflage uniform includes a shirt, trousers, and a synthetic material cap. The Indian Army's camouflage dress has a jungle camouflage pattern that is designed to be used in woodland environments.
Regiments that are posted in the desert or dusty area have desert camouflage pattern uniforms. The modern recruited armies are required to wear distinctive parade uniforms, which are classified by variegated turbans and waist-sashes in regimental colors.
The Indian Army gives the perfect example of gender inequality by recruiting women in different regiments of the Army. The first women were appointed in the Indian Army when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in the year 1888. These women nurses have served the Army in both World War I and II.
With all the facts relating to the Indian Army covered in this essay, one can understand the importance of the Indian Army essay. The essay about the Indian Army gave an overview of the Army as a whole. The Indian Army is the third-largest on the globe, and has many features that one can see from this essay. It is also visible how the Government has planned to make the Army better every passing day so that they are ready to face any danger, be it internal or external.
A Short Note on Happy Indian Army Day 2024
Indian Army is the third-largest Army in the globe, is one of the most powerful and strongest among the armies of other countries. In the past, they have proved their superiority in different battles and missions that have been conducted. Through this short essay on Happy Indian Army Day in English, one will be able to see the power and strength that the Indian Army possesses.
The Indian Army has only one goal, which is to safeguard the nation's security and maintain unity in the country. All the recruits in the Army perform to achieve this one goal. The Indian Army consists of a total number of 65 regiments that are classified or divided based on their skills and capabilities. They are trained with two formations that are holding formation and combat formation. Holding formation is meant for defense, and combat formation is meant for an attack.
The Indian Army improves its skills by conducting training missions with different powerful countries such as The United States, Russia, and Israel.
Through this essay on the Indian Army Day 2024 in 100 words , it is clear that the Indian Army is well prepared for any unwanted situation in the future and has the capability to deal with it. The Indian Army epitomizes unwavering commitment and valor, safeguarding our nation's sovereignty with courage. Beyond borders, they contribute to disaster relief and peacekeeping, embodying humanity's spirit. Their sacrifices inspire national pride. Let us honor and support our armed forces, recognising their pivotal role in preserving our cherished freedom and unity. Jai Hind!

FAQs on Indian Army Day 2024 Essay
1. What is the Indian Army?
The Indian Army, which is one of the strongest armies in the world, and has all the features that make it an efficient army. The Indian Army has a total number of 65 regiments which are divided based on their skills and capabilities. These soldiers undergo training with two formations: holding formation and combat formation, which consists of the following: Holding Formation: This is meant for defense, Combat Formation: This formation is meant for attacking. For more information, read this Indian Army essay on Vedantu.
2. What are the different types of uniforms in the Indian Army?
The Indian Army has two types of uniforms: a camouflage uniform and a parade uniform. The camouflage uniform includes a shirt, trousers, and a synthetic material cap, while the parade uniform consists of a variegated turban and waist-sash in regimental colors. The color of the uniform differs according to the regiments. The Indian Army's uniform is a combination of different colors, which represents the culture and tradition of the country. Army uniform is a matter of pride for every soldier because it gives the mental satisfaction that on a special occasion, they are given a chance to wear their best uniform.
3. What is the role of the Indian Army in India?
The Indian Army has been playing many different roles from protecting its borders from any external danger; apart from this, they have also played a crucial role in the development of the country. Indian Army helps to build infrastructure, assists in natural calamities and provides medical assistance during any emergency. The Indian Army is one of the most powerful armies in the world. It has all the features that make it an efficient army. The Army consists of a total number of 65 regiments grouped and divided based on their skills and capabilities. These soldiers go through training with two formations holding formation and combat formation, which is described in the wiki. The Indian Army improves its skills by conducting training missions with different powerful countries such as the US, Russia and Israel.
4. What are the roles played by women in the Indian Army?
The first women were appointed in the Indian Army when the Indian Military Nursing Service was formed in 1888. These women nurses served the Army in both world war I and II. Women have also participated in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, the Sri Lankan Civil War and the Kargil War. Presently, women are recruited in the Army as doctors, engineers, lawyers, air warriors etc., and they are performing their duties efficiently. The Indian Army has only one goal, which is to safeguard the nation's security and maintain unity in the country. All recruits in the Army perform to achieve this one goal. The Indian Army has all it takes to face any challenges in the future if any arise. The Indian Army essay covers all these points.
5. What is the role of the Indian Army in development?
The Indian Army plays a crucial role in the development and progress of the country. The main aim of this research paper on the Indian Army is to make people aware of the Indian Army and its roles. India, which is considered one of the biggest democratic countries, has faced many internal conflicts throughout its history. It is the Indian Army that has protected the country from any external danger and guarded its borders. The Indian Army not only defends India's land but also gives medical assistance to people during emergencies such as floods, earthquakes etc.
6. How Many Regiments Are There in the Indian Army?
The Indian Army has a total number of 65 regiments in which army recruits are divided according to their skills. Some of the important regiments are Gurkha Regiment, Dogra Regiment, Kumaon Regiment, Ladakh Scouts Regiment, and many others.
7. Who Started the Army in India?
Mohan Singh established the first Indian National Army. He was an officer in the British Indian Army, and he was captured in the Malayan Campaign. The nationalist sympathies of Mohan Singh led him to find an ally in Fujiwara that helped him a lot.
- Skip to main
- My india my pride
- Indian armed forces
- Print this page
Indian Armed Forces

The Government of India is responsible for ensuring the defence of India and every part thereof. The Supreme Command of the Indian Armed Forces vests in the President. The responsibility for national defence rests with the Cabinet. This is discharged through the Ministry of Defence, which provides the policy framework and wherewithal to the Armed Forces to discharge their responsibilities in the context of the defence of the country. The Indian Armed Forces comprise of three divisions – Indian Army, Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force. Check more important links .
Indian Army
The Indian subcontinent had witnessed the cohesive concentration of many Empires in the quest for control of military power, and governance of the State. As time rolled by, societal norms found an ethos in the workplace, the system of rights and privileges, and service under the flag.
The Indian Army, as we know it today became operational after the Country gained independence from British colonialism. The Indian Army's HQ is located in New Delhi and functions under the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is responsible for the command, control, and administration as a whole. The Army is divided into six operational commands (field armies) and one training command, each under the command of a Lieutenant General, who has an equal status to the Vice-Chief of Army Staff (VCOAS), working under the control of Army HQ in New Delhi. More about the Indian Army .
Indian Navy
The foundation of the modern Indian Navy was laid in the seventeenth century when the East India Company had established a maritime force, thereby graduating in time to the establishment of the Royal Indian Navy in 1934. The Headquarters of the Indian Navy is located in New Delhi, and is under the command of the Chief of the naval staff – an Admiral. The Indian navy is deployed under three area commands, each headed by a flag officer. The Western Naval Command is headquartered in Bombay on the Arabian Sea; the Southern Naval Command in Kochi (Cochin), in Kerala, also on the Arabian Sea; and the Eastern Naval Command in Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, on the Bay of Bengal. More about the Indian Navy .
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force was officially established on 8th October 1932, and on 1st April 1954, Air Marshal Subroto Mukherjee, one of the founding members of the Air Force took over as the first Indian Chief of Air Staff. With the passage of time, the Indian Air Force undertook massive upgrading of its aircraft and equipments, and as part of the process, it introduced more than twenty new types of aircrafts. The last decade of the twentieth century saw a phenomenal change in the structure of the Indian Air Force with induction of women into the Air Force for short service commissions. It was also a time when the Air Force undertook some of the most perilous operations ever undertaken. More about the Indian Air Force .
About India
India is one of the oldest civilizations in the world with a kaleidoscopic variety and rich cultural heritage. It has achieved all-round socio-economic progress since Independence. As the 7th largest country in the world, India stands apart from the rest of Asia, marked off as it is by mountains and the sea, which give the country a distinct geographical entity. Bounded by the Great Himalayas in the north, it stretches southwards and at the Tropic of Cancer, tapers off into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal on the east and the Arabian Sea on the west.

Formation and Structure of Indian Army
This article contains Formation and Structure of Indian Army. To know more about the Seven Command Structure, read the complete article.

Table of Contents
The Second Largest standing army in the world and the largest component of Indian Armed Forces. The Indian Army is Undoubtedly the pride of India. The Indian Army has 1.2 million active troops and 1 million reserve troops right now. In this article, we will discuss the structure and Formation of Indian Army.
The Headquarter of Indian Army is in New Delhi and and is under the overall command of COAS , Chief of Army Staff. Currently COAS of India is General Manoj Mukund Narvane.
Field Formations of Army
The Basic Field Formations of Army are Discussed below:
Command : Two or three corps together form a command , Indian Army has six operational commands and one training command. Each command is headed by a general officer commanding-in-chief (GOC-in-C), known as the army commander.
Corps: Three or Four Division together make a Corp, Indian Army has 14 Corps each one commanded by a general officer commanding (GOC), known as the corps commander, who holds the rank of Lieutenant General. In Indian Army there are three types of corps : Strike, Holding and Mixed .
The Corps HQ is the highest field formation in the army.
Division : A Division is made up of three or four Brigades, each division is headed by GOC (division commander) in the rank of major general. Currently, the Indian Army has 40 Divisions including four RAPIDs (Re-organised Army Plains Infantry Division), 18 Infantry Divisions, 12 Mountain Divisions, three Armoured Divisions and three Artillery Divisions.
Brigade: Around 3,000 combat troops with supporting elements make a Brigade. In addition to the Brigades in various Army Divisions, the Indian Army also has five Independent Armoured Brigades, 15 Independent Artillery Brigades, seven Independent Infantry Brigades, one Independent Parachute Brigade, three Independent Air Defence Brigades, two Independent Air Defence Groups and four Independent Engineer Brigades. These Independent Brigades operate directly under the Corps Commander (GOC Corps).
Battalion: Four rifle companies together make a Battalion. it is Commanded by a battalion commander who is a Colonel and is the Infantry’s main fighting unit. Every infantry battalion also possesses one Ghatak Platoon.
Company: A Company is Composed of three platoons. it is Commanded by a company commander who is a major or lieutenant-colonel.
Battery: A Battery Comprises of either 3 or 4 sections, in artillery and air defence units. Every battery has two officers, the senior of which is the Battery Commander.
Platoon: A Platoon is Composed of three sections. it is Commanded by a platoon commander who is a JCO.
Section: A Section is the Smallest military outfit, with a strength of 10 personnel. it is Commanded by a section commander of the rank of Havaldar.
Indian Army Command Structure
Indian Army has a total of 7 commands including one training command, Each command is headed by a general officer commanding-in-chief (GOC-in-C), known as the army commander. Each command directly reports to the army headquarter at New Delhi.
Here we will learn about all seven commands.
1. Central Command
Headquarter- Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
Sub-ordinate Unit- I Corps — Currently assigned to South Western Command
2. Eastern Command
Headquarter- Kolkata
Sub-ordinate Unit-
- 23rd Infantry Division headquartered at Ranchi
- III Corps, headquartered at Dimapur, Nagaland
- IV Corps, headquartered at Tezpur, Assam
- XXXIII Corps, headquartered at Siliguri, West Bengal
3. Northern Command
Headquarter- Udhampur
- XIV Corps, headquartered at Leh, Jammu and Kashmir
- XV Corps, headquartered at Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir
- XVI Corps, headquartered at Nagrota, Jammu and Kashmir
4. Southern Command
Headquarter- Pune
- 41st Artillery Division, headquartered at Pune, Maharashtra
- XII Corps, headquartered at Jodhpur, Rajasthan
- XXI Corps, headquartered at Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
5. South Western Command
Headquarter- Jaipur
- 42nd Artillery Division headquartered at Jaipur
- I Corps, headquartered at Mathura, Uttar Pradesh
- X Corps, headquartered at Bhatinda, Punjab
6. Western Command
Headquarter- Chandimandir
- 40th Artillery Division headquartered at Ambala
- II Corps, headquartered at Ambala, Haryana
- IX Corps, headquartered at Yol, Himachal Pradesh
- XI Corps, headquartered at Jalandhar, Punjab
7. Army Training Command
Headquarter- Shimla
Basic Organizational Structure
To understand the structure better, we need to know that Indian army is broadly divided into three Groups, that are
Combat Arms
- Combat support Arms
- Supporting arm
- The Armoured Corp
- The Mechanized Infantry
- The Regiment of Artillery
- Corps of Army Air Defence
- Army Aviation Corps
Combat Support Arms
- Corps of Engineers
- Corps of EME
- Corps of Signals
- Army Ordnance Corps
- Army Supply Corps
- Army Medical Corps
Supporting Arms
- Intelligence Corps
- Corps of Military Police
- Territorial Army
- Judge Advocate General’s Department
- Remount and Veterinary Corps
- Army Education Corps
- Army Dental Corps
- Military Nursing Service
- Army Postal Service Corps
- Pioneer Corps
- Defence Security Corps
- Military Farms Services
Queen of the Battle: Infantry
The most Pivotal role in a war is played by the Infantry. Infantry is the soul of whole army organization. The Indian Army’s Infantry consist of many regiments, each of which further comprises many battalions / units. The battalions are sequenced in a particular fashion, generally in order of when they were raised. Below we are providing names of all infantry Regiment with their regiment headquarters and all other related information.
We Tried Our best to equip you with all the important facts regarding Formation of Indian Army. Hope you find your Answers.


Structure of Indian Army: FAQs
Q1. How many soldiers are in a platoon?
Ans. Three or four squads make up a platoon, which has 20 to 50 soldiers.
Ans. General Manoj Mukund Naravane is the Chief of Indian Army.
Q3. What is the highest rank of Indian Army?
How many soldiers are in a platoon?
Three or four squads make up a platoon, which has 20 to 50 soldiers.
Who is the Army Chief of Indian Army?
General Manoj Mukund Naravane is the Chief of Indian Army.
What is the highest rank of Indian Army?
Field Marshal (or field marshal, abbreviated as FM) is a five–star general officer rank and the highest attainable rank in the Indian Army

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recent Posts
- CDS Full Form
- AFCAT Full Form
- NCC Full Form
- CRPF Full Form
- BSF Full Form
- CISF Full Form
- ITBP Full Form
- NSG Full Form
- SSB Full Form
- ISRO Full Form
- DRDO Full Form
- Dams and Reservoirs
- Scientific Names of Animals
- National Parks
- United Nation Agencies
- First Ranked States in Minerals
- Sports Cups and Trophies
- Rivers and their Tributaries
- Mountain Passes
- Famous Inventions and Inventors
- Mountain Passes of India
- IAF Command Training Institutes
- Gallantry Awards
- List of Military Operations
- List of India’s Missiles
- List of Presidents of France
- Largest Telescopes in The World
- List of UK Prime Ministers
- Chief Ministers of Tripura
- Father of Computer
- Largest State in India by Population
- Highest Waterfall in India
- Highest Peak in India
- Longest National Highway
- List of IPL Winners
- Prime Ministers of India
- Languages of India
- Famous Books and Authors
- List of RBI Governors
- Fathers of Various Fields
- Terminologies in Sports
- Folk Dances of India
- Bird Sanctuary in India
- How To Prepare For Psychology Test In SSB
- What After CDS Exam? CDS SSB Interview Process
- How To Clear NDA SSB Interview
- How To Maintain Physical Fitness For SSB Interview
- SSB Lecturette Tips For Freshers
- SSB Interview Questions, Download PDF
- SSB Day 1 Process, Get Complete Detail Of Day 1
- 25 PPDT Pictures for AFCAT AFSB Interview
IMPORTANT EXAMS
- AFCAT Notification
- AFCAT Admit Card
- AFCAT Eligibility
- AFCAT Syllabus
- AFCAT Salary
- CDS Notification
- CDS Admit Card
- CDS Syllabus
- CDS Eligibility
- NDA Notification
- NDA Syllabus
- NDA Eligibility
- NDA Admit Card
- ICG Notification
- ICG Eligibility
- ICG Selection Process
- ICG Syllabus
Agniveer 2024
- Army Agniveer Notification
- Army Agniveer Syllabus
- Army Agniveer Result
- Army Agniveer Cut Off
- Army Agniveer Eligibility
- Army Agniveer Selection Process
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Adda Malayalam
- Adda Punjab
- Current Affairs
- Defence Adda
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School

Welcome to Defence Adda, your one-stop solution to prepare for all Defence Examinations!! Adda247 Defence portal has complete information about all Sarkari Jobs and Naukri Alerts related to defence and its latest recruitment notifications, from all state, grand rush and national level jobs and their updates.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Essay On Indian Army

Table of Contents
Short Essay On Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch of the Indian Armed Forces responsible for securing the country’s territorial integrity and national security. With over 1.3 million active personnel, it is one of the largest standing armies in the world. The Indian Army has a rich history, dating back to the colonial era and has been involved in various wars, peacekeeping missions, and humanitarian operations.
The primary objectives of the Indian Army are to defend the country against external aggression, to maintain internal security, and to support national development. The Army has played a crucial role in maintaining peace and stability in the region and has been actively involved in United Nations peacekeeping operations. The Army is also tasked with providing humanitarian aid and disaster relief during times of crisis.
The Indian Army is known for its bravery and valor, with many soldiers receiving recognition for their exceptional service and sacrifice. The Army also provides opportunities for education and professional growth to its personnel through its well-established training institutions, such as the Indian Military Academy and the National Defense Academy.
In conclusion, the Indian Army is a crucial component of the country’s national security apparatus and has played a vital role in safeguarding India’s territorial integrity and national interests. The sacrifices and dedication of the Indian soldiers serve as a testament to the strength of the nation and its commitment to peace and stability.
Long Essay On Indian Army
The Indian Army is one of the largest and most powerful armies in the world. It is also one of the oldest and most respected, with a long history of protecting India’s borders and fighting for its citizens. In this essay, we’ll explore the importance of the Indian Army, its structure, and its role in defending India from external threats. Then we’ll discuss how it has evolved over time to meet new challenges and remain prepared for any situation. Let’s start by looking at why it is so important to India.
Introduction to Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general.Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour.
The primary mission of the Indian Army is to ensure national security and national unity, defending the nation from external aggression and internal threats, and maintaining peace and security within its borders. It conducts humanitarian rescue operations during natural calamities and other disturbances, such as Operation Surya Hope, and can also be requisitioned by the government to cope with internal threats. It is a major component of national power alongside the Indian Navy and the Indian Air Force. The army has been involved in four wars with neighbouring Pakistan and one with China. Other major operations undertaken by the army include: Operation Vijay, Operation Meghdoot and Operation Cactus. Apart from conflicts, the army has conducted large peace time exercises like Operation Brasstacks and Exercise Shoorveer, it has also been an active participant in numerous United Nations peacekeeping missions including those in: Cyprus, Lebanon, Congo, Angola, Cambodia, Somalia & Bosnia.
History of the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general.
The history of the Indian Army can be traced back to the time of the East India Company, which was formed in 1600. The company’s army initially consisted of just a few hundred soldiers, but it rapidly expanded during the 18th century as the company took control of more and more territory in India. By 1757, the company’s army had grown to over 100,000 men.
During the 19th century, the Indian Army served in a number of campaigns against various indigenous groups as well as in support of British operations in other parts of the world such as Afghanistan, Burma, and China. In 1857, there was a major uprising by Indians against British rule known as the Sepoy Mutiny. This was followed by a period of intense modernization of the Army under British rule.
During World War I, Indian troops fought on behalf of Britain in a number of campaigns including in Mesopotamia and Palestine. Over one million Indian soldiers served during World War II, both in Europe and Asia. After Independence in 1947, the Indian Army continued to play an important role in defending India’s borders and also took part in various peacekeeping operations around the world. Today, it is one of the largest and most powerful armies in the world.
Role of Indian Army in Current Scenario
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army has been involved in a number of major military operations, including: Operation Vijay, Operation Meghdoot, Operation Cactus and Operation Prakaram. In addition to conflict resolution, the Indian Army has also been an active participant in UN peacekeeping missions.
The current scenario in India is one where there is a constant threat of cross-border terrorism from Pakistan and China. In such a scenario, the role of the Indian Army becomes even more important. The army has to be constantly on alert and be ready to take on any challenge that may come its way. Apart from guarding our borders, the army also has to play an important role in disaster management and relief operations. With climate change leading to more extreme weather events, the army has to be prepared to deal with floods, storms and other natural calamities.
Thus, we can see that the role of the Indian Army in our current scenario is very important. It is responsible for protecting our borders as well as our people from any internal or external threat.
Structure and Organization of the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is headed by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. An army officer serves a minimum of ten years in service before being eligible for retirement.
The Indian Army has its headquarters in New Delhi, and its units are spread across the country. It has seven commands, each under the control of a lieutenant general. The commands are: Northern Command (headquartered in Udhampur), Western Command (Chandimandir), Central Command (Lucknow), Eastern Command (Kolkata), Southern Command (Pune), South Western Command (Jaipur) and Northern Western Command (Shimla). Each command is responsible for a specific geographical area.
The Indian Army has a total strength of over 1.3 million active personnel and 960,000 reserve personnel. It is one of the largest standing armies in the world and is ranked as the fourth most powerful army in terms of military equipment by Jane’s Information Group.
Benefits of Serving in the Indian Army
Serving in the Indian Army comes with a number of benefits. For one, you get to serve your country and protect its citizens. This is an honorable profession that comes with a great sense of pride and satisfaction. Additionally, serving in the Indian Army also gives you the opportunity to travel and see different parts of the country. You will also meet new people and make new friends. Furthermore, you will gain valuable skills and experience that will benefit you in your future career.
Challenges Faced by the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the world’s second largest army, with over 1.3 million soldiers serving in its ranks. It is responsible for the security of India’s land borders, as well as for maintaining internal security and law and order. The army also has a vital role to play in disaster relief operations and in providing humanitarian assistance during times of crisis.
However, the Indian Army faces a number of challenges in fulfilling its mandate. Firstly, it is a large and bureaucratic organisation, which can make it difficult to respond quickly to changing situations. Secondly, it is often hamstrung by political interference, with politicians seeking to use the army for their own ends. Thirdly, the army has been accused of human rights abuses, particularly in relation to its handling of separatist movements in Kashmir and the Northeast. Finally, the army faces an ongoing challenge from Pakistan-based terrorist groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed, which have carried out a number of high-profile attacks on Indian soil in recent years.
How to Join the Indian Army
If you wish to join the Indian Army, there are a few things you must do. First, research which branch of the Army you wish to join. There are many different options available, each with their own requirements. Once you have decided which branch is right for you, meet with a recruiter to discuss your options and begin the enlistment process.
After completing the necessary paperwork and tests, you will be scheduled for basic training. This is where you will learn the basics of being a soldier and how to function as part of a team. Once you have completed basic training, you will be assigned to a unit and begin your career in the Indian Army.
The Indian Army is a well-oiled machine serving India and its citizens with dignity, honor, and pride. The Army has played an important role in protecting our nation from many internal as well as external threats. It has also been at the forefront of providing relief during natural calamities and helping to rebuild affected areas. Whenever we think of our nation’s safety, we must not forget to thank the brave soldiers who have sacrificed their lives for us. We owe a debt of gratitude to them that can never be repaid.
Manisha Dubey Jha is a skilled educational content writer with 5 years of experience. Specializing in essays and paragraphs, she’s dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that enriches learning experiences.
Related Posts
Essay on importance of yoga, essay on cow, climate change essay, essay on slaver, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay on Indian Army
Students are often asked to write an essay on Indian Army in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Indian Army
Introduction.
The Indian Army is one of the most powerful and respected institutions in India. It is the land-based branch of the Indian Armed Forces and is responsible for protecting the country’s sovereignty and maintaining peace.
Structure and Role
The Indian Army is divided into various regiments and battalions. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the country’s security, defending the nation from external aggression and internal threats.
Training and Discipline
Indian Army personnel undergo rigorous training to develop physical strength, mental resilience, and tactical skills. Discipline and teamwork are highly valued.
Service and Sacrifice
The Indian Army is known for its bravery and sacrifice. Many soldiers have laid down their lives to protect the nation, showing immense courage and dedication.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Indian Army
- Paragraph on Indian Army
- Speech on Indian Army
250 Words Essay on Indian Army
The Indian Army, a symbol of valor, discipline, and unity, is one of the most respected institutions in the country. It is a source of pride for the nation, safeguarding the territorial integrity and maintaining peace and security.
The Structure
The Indian Army is divided into several regiments, each with its unique history, traditions, and ethos. These regiments are further divided into battalions and companies. The President of India serves as the Supreme Commander, while the Chief of Army Staff, a four-star General, leads the operations.
The Role and Duties
The primary role of the Indian Army is to ensure national security and national unity, defend the nation from external aggression and internal threats, and maintain peace and security within its borders. It also conducts humanitarian rescue operations during natural calamities and other disturbances.
Training and Recruitment
The Indian Army has a rigorous recruitment and training process to ensure the soldiers are physically fit and mentally robust. The National Defence Academy, Indian Military Academy, and Officers Training Academy are among the prestigious institutions that mold the future leaders of the Army.
The Indian Army, with its unwavering commitment and indomitable spirit, continues to serve the nation with utmost dedication. It is a beacon of courage, exhibiting unparalleled bravery and sacrifice. The Indian Army is not just a profession, but a way of life, instilling values of patriotism, loyalty, and selflessness, inspiring millions across the nation.
500 Words Essay on Indian Army
The Indian Army, an integral part of India’s defense system, is the world’s second-largest standing army. It is a beacon of discipline, bravery, and service to the nation, working tirelessly to ensure the safety and security of the country’s borders and maintaining peace within its territory. The Indian Army not only plays a vital role in protecting the nation from external threats but also assists in disaster management, social upliftment, and nation-building activities.
Historical Background
The Indian Army’s origins can be traced back to the East India Company’s military department in the 18th century. However, the present structure was established after India achieved independence in 1947. Since then, the Indian Army has been involved in several significant wars and operations, including the Indo-Pakistani wars, the Sino-Indian war, and peacekeeping operations under the United Nations.
Structure and Composition
The Indian Army is divided into seven commands, each headed by a Lieutenant General. These include the Central, Eastern, Northern, Southern, Western, South Western, and the newly formed Cyber and Space commands. The President of India serves as the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army. The Army is further divided into various regiments, each with its unique history, customs, traditions, and insignia.
Role in National Security
The primary role of the Indian Army is to safeguard national security and sovereignty from external aggression and threats. It maintains a high state of combat readiness to effectively respond to any form of aggression. The Indian Army also plays a crucial role in counter-insurgency operations and maintaining internal security, particularly in regions affected by militancy and insurgency.
Contribution to Society
Beyond its military role, the Indian Army also contributes significantly to societal development. It provides aid during natural calamities like floods, earthquakes, and cyclones, conducting rescue operations and providing medical aid. The Army also plays a crucial role in community development, providing education, healthcare, and infrastructure in remote areas.
Challenges and the Way Forward
The Indian Army faces numerous challenges, including modernizing its equipment, maintaining troop morale, dealing with cross-border terrorism, and managing the diverse socio-political dynamics within the country. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, including technological advancements, robust diplomatic ties, and effective policy-making.
The Indian Army stands as a symbol of unity, integrity, and service to the nation. Its dedication towards the cause of the nation’s defense and societal development is commendable. As India continues to evolve, the role of the Indian Army will also transform. However, its core values of duty, honor, and sacrifice will remain steadfast. The Indian Army, with its ethos and courage, will continue to be a vital pillar of the nation.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on India Before Independence
- Essay on Historical Places in India
- Essay on Future of Sports in India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
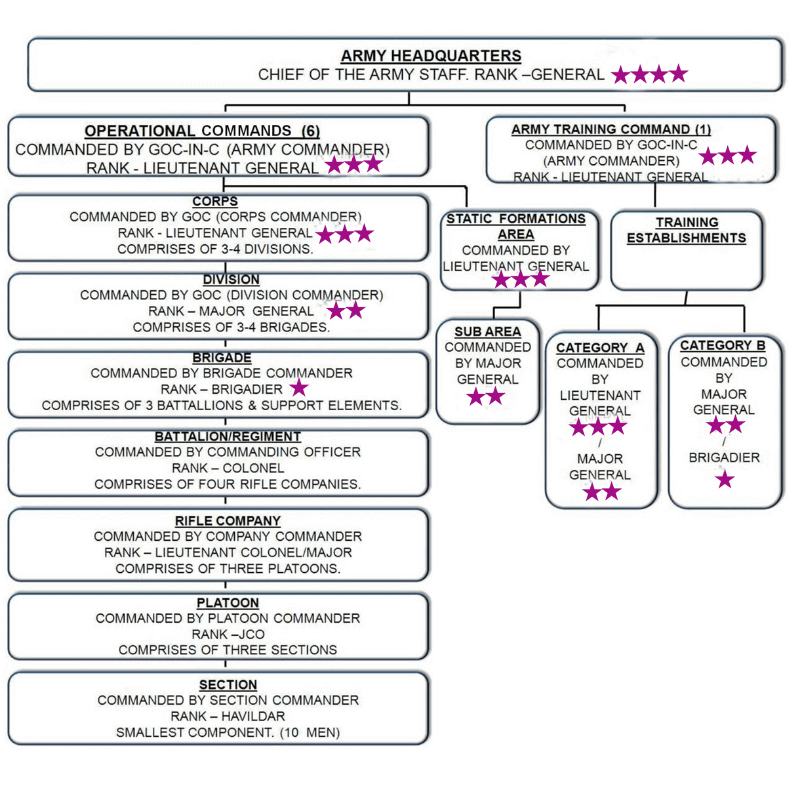
The Indian Army is the 2nd largest active-duty military force in the world in 2020 second only to China. With over 1.23 million personnel and counting, a sound structure for the army is essential. The Indian Army is divided into 40 divisions & 14 corps. The Indian Army Headquarters is in New Delhi.
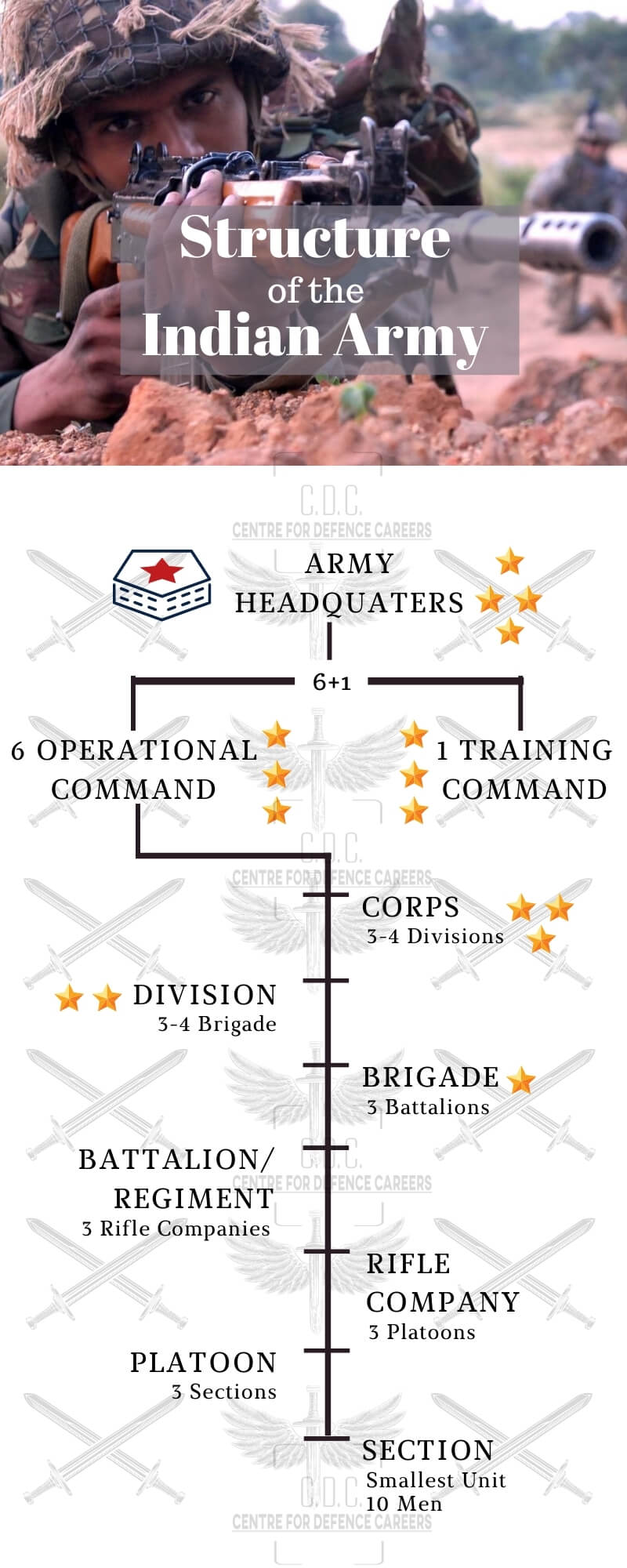
The Army operates six operational commands and one training command.
Each command is headed by a General Officer Commanding-in-Chief with the rank of Lieutenant-General. Each command directly reports to Army HQ.
Under the Operational Commands, we have Corps. The Corps comprises of 3-4 divisions and is commanded by an officer of the rank of Lieutenant General.
Every Division is made up of 3-4 Brigades and is commanded by an officer of the rank of Major General.
Then follows the Brigade which is under the command of an officer of Brigadier rank. Every Brigade has 3 battalions in them.
Each Battalion comprises of 4 Rifle Companies. A battalion is commanded by an officer of the rank of Colonel. Sometimes a Battalion is also known as a Regiment.
Then comes the Rifle Company which has 3 platoons under it. The Rifle Company is commanded by an officer of the rank of Lieutenant Colonel/Major.
Each platoon comprises 3 Sections a platoon is commanded by Platoon Commander of the rank JCO.
The Section forms the smallest component of the Indian Army. Each section has 10 men & is commanded by Section Commander of the rank Havildar.
Would you like to continue reading?
Would you like to continue reading , indian army: an insight into its structure, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Centre for Defence Careers
- NDA Training + Class 11, 12 Coaching (Science)
- NDA Regular Batch
- NDA Crash Course
- CDS/OTA Regular Batch
- Territorial Army (Age Till 42 years)
Non Commissioned
- Indian Army Agniveer Bharti - GD, SKT, Tech, etc.
- Indian Navy Agniveer - SSR/AA , MR
- Indian AirForce Agniveer Vayu - Group X,Y
- Indian Coast Guard - DB, Navik
- ParaMilitary - BSF, CRPF, CISF,etc.
- Police Bharti
- FREE GUIDANCE
- CDS/OTA - Physical/Medical Standards
- AFCAT - Physical/Medical Standards
- Best Way for Preparation
- 110, Ecstasy Business Park, JSD Marg, Mulund West
Whatsapp : 9320704957 , 9833958444
- 613, Pearl Plaza, Next to McDonald's, Andheri West
Phone: 9320704957 , 9833958444
© All rights reserved by Centre for Defence Careers.

Search form
Transformation of the indian armed forces: future challenges.
Early in his second term, Prime Minister Narendra Modi embarked on an ambitious vision for defense reforms. By creating the post of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), whose first incumbent was the late General Bipin Rawat, the government is currently undertaking arguably the greatest post-independence transformation of the Indian military. Central to this initiative is the debate surrounding integration of the armed forces. Integration refers to the process by which the army, air force, and the navy discard their single service approach and embrace a joint vision. Such integration has occurred in most large militaries, such as the United States and China. A process as complex as this is bound to have its share of challenges. However, perhaps the most critical one relates to the challenge of India transitioning from a single service approach to a joint entity.
Modi’s decision to create a CDS has created significant change and generated debates within the Indian military. One of the more consequential debates pertains to the precise role of the CDS. In a December 2019 note, the government clearly indicated that the CDS will not exercise military command “so as to provide impartial advice to the political leadership.” This implied that the CDS would not be a part of the command chain. This chain, in any military hierarchy, flows from a battalion or its equivalent in the army, a squadron in the air force, or a ship in the navy, to the top echelon of the organization. In India, this culminates at the level of the chiefs of the three services. However, with the creation of integrated headquarters (which have representatives from all three services), as has been envisaged and announced, no single chief will be in a position to exercise command over them. And the CDS who represents all three services will not exercise military command over them. Within this organizational arrangement, how will military commanders interact with political decision makers?
The Indian military has been a relative latecomer to creating integrated military structures. There have been misgivings regarding entrusting command of all three services to a single individual—in this case, the CDS. Over the decades, this played a major part in not going in for the appointment despite repeated recommendations in its favor. By appointing the CDS, this government successfully overcame these objections. However, the operational role of a CDS remains unclear, with two major options available to the government to ensure clarity in this regard.
The first option is for the CDS to remain in an advisory role without being a part of the chain of command. In this case, the highest joint structure that gets created (the proposed joint theatre command) will report to the defense minister. This is, in some ways, how the political leadership in the United States interacts with the military, wherein the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee (the CDS counterpart), only has a coordinating and advisory role.
The second option is to bring the CDS and the team of service chiefs within the chain of command to function as a collective command body, with the CDS as its head. This group, called the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC) in the Indian context, then becomes an intermediary between civilian leadership and subordinate military commanders. This will ensure the CDS has a clear mandate and is responsible for its execution. However, doing so runs contrary to the guidance issued by the government in December 2019 (which needs rectification).
A CDS-led empowered COSC would be better suited for India—at least in the immediate future—for two reasons. First, the ongoing process of integration would likely result in a period of dissonance prior to settling down, requiring greater oversight by a professional body than was the case in the past. Eventually, once the newly created integrated structures matured, one could consider granting a coordinating and advisory role to the CDS and COSC. Second, such a step-by-step approach would smoothen the transition, especially during a period when India faces serious challenges along the unresolved borders with Pakistan and China.
If a CDS-led COSC does take on command responsibilities, then it becomes even more important that the distinctiveness the services have maintained and zealously guarded over the years is better integrated. This operates at multiple levels, from the most fundamental at the level of the soldier to the operational domain. Differences among services commence with the educational levels of soldiers, sailors, and airmen being recruited. While soldiers in the army continue to be recruited after clearing Class 10 examination, sailors and airmen need to qualify Class 12, with mathematics and physics as their subjects. Such differences continue within the services as well. For instance, orders on ships are passed in English, including technical terms used to describe various actions. On the other hand, in the army, despite vast linguistic differences, Hindi is more commonly used when communicating with soldiers.
Additionally, over the years, each service has created its human resource parameters to suit their conditions. Air force fighter pilots retire at 54, naval officers at 56, and army officers at 54, with the provision for re-employment thereafter for four years. Naval officers who get promoted to the rank of captain (equivalent to colonel in the army) are automatically eligible for promotion to the next rank as commodores (equivalent to brigadiers in the army). However, this is not followed in the air force and the army. Annual confidential reports of all three services follow a different format and grading parameters. What is considered outstanding in one service may well lead to supersession in another, as the rating is likely to be viewed poorly.
While these and many more aspects can still be overcome through sustained effort, what really sets the services apart is their distinct service culture. While this is understandable and even desirable when related to specific responsibilities, it is most likely to become evident during military operations when cultural differences come to the forefront. A soldier who has operated in the grey zone of counterterrorism thinks and functions very differently from one who has followed the peacetime rule book, wherein, the black and white are clearly delineated. Over time, this becomes a character trait with officers as well, making officers from the three services look at operational, and by extension, routine peacetime situations very differently. This does not imply that structural integration, and more importantly, the meeting of hearts and minds is a lost cause. On the contrary, these challenges suggest that decision makers and especially the services need to take these aspects into account as they press on with the reforms.
With the creation of the CDS, India embarked upon a much-delayed process of integration of the armed forces and the defense establishment. The success of this initiative depends, to a large extent, on clarifying the mandate of the CDS and the ability of the military to set aside its service-specific perspectives and define a singular approach to its professional responsibilities. Politicians need to imagine the appointment of the CDS, and other associated reforms, as the first step toward military transformation, not an end. That, above all else, is perhaps the greatest takeaway from this process.
Colonel Vivek Chadha (Retd) is a Research Fellow at the Manohar Parrikar Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses and the author of CDS and Beyond: Integration of the Indian Armed Forces (Knowledge World Publishers, New Delhi, 2021) .
This article is the first in a two-part guest-edited IiT series. The articles in this series seek to make sense of the changing dynamics of India’s security and foreign policies. On August 15, 2019, soon after returning to power, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced his decision to create a Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) with an explicit mandate to carry out much needed defense reforms. This fulfilled a long-pending demand from military reformists and initiated the process for perhaps the most significant post-independence defense reforms. However, despite some progress, as highlighted by author Colonel Vivek Chadha, “the operational role of a CDS remains unclear.” For this initiative to succeed, he contends that “politicians need to imagine the appointment of a CDS, and other associated reforms, as the first step toward military transformation, and not an end.”
(guest editor: anit mukherjee , rsis, nanyang technological university).
India in Transition ( IiT ) is published by the Center for the Advanced Study of India (CASI) of the University of Pennsylvania. All viewpoints, positions, and conclusions expressed in IiT are solely those of the author(s) and not specifically those of CASI.
© 2022 Center for the Advanced Study of India and the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. All rights reserved.

- Spoken English
Verbal Ability
- NCERT Solutions
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse


Essay on Indian Army in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Essay on Indian Army: Indian army needs no introduction. We all have love, respect and admiration for our soldiers and the Indian army as a whole. As we all know, Indian army has a long and glorious history. Therefore, it is difficult to talk about everything in such a limited space. Still I have tried to touch all the main points and also have tried to speak my heart out. I hope you will be able to appreciate my efforts and the essays.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Also Check: Army Day
Long and Short Essay on Indian Army in English
Whenever I think of Indian army (I also wanted to become a solider), I become happy. I feel, we are lucky to have such an institution of which we can really feel proud.
A common person knows very little about Indian Army because maximum of the things are classified. Still there is sufficient information in public domain.
In the following Indian Army essay, I have tried to put all that information here and also have given my view point. I hope following essay on Indian Army will be appreciated and liked by you.
Short Essay on Indian Army in English 200 words
Indian armed forces are divided into three parts – Indian army, Indian Airforce and the Indian Navy. Indian army is the land-based unit, while Indian Airforce deals in air defence and Indian Navy is the naval unit. Our Indian army is the second largest in the world with about 1.23 million personnel on active rolls and another 9.6 lakhs in reserves.
Indian army is mainly responsible to protect the country against land based attacks. It also lends a helping hand to other agencies in dealing with terrorism, tackling emergency situations in the country and also rescuing people in case of natural calamities like flood, earthquake etc.
The current chief of army staff (COAS) is General Bipin Rawat (as of 2018). As Indian army is very huge, it is divided into regiments. Some important regiments are Punjab regiment, Madras regiment, Rajputana rifles, Sikh regiment etc. It also has its own intelligence unit, known as “Military Intelligence” or “MI” in short.
Indian army before independence (under British rule) had participated in World War I and II. After independence it has also fought many full-fledged wars like the Kargil war (1999), Bangladesh liberation war (1971), India -Pakistan war (1965), India-China war (1962) and first Kashmir war (1947). Besides these, Indian army has also handled some smaller conflicts like Siachen conflict (1984), Operation Polo (1948), India-China conflict (1967) etc.
There is no doubt that our Indian army is one of the best armies in the world.
Also Check: Essay on Life of Soldier

Essay on Indian Army in 300 words
Asking about the importance of Indian Army in India is like asking the importance of heart in a human body. It would not be wrong to say that there would be no India without Indian Army. It is the backbone of the country. It is also one of the few institutions left in the country which could be considered as completely neutral and reliable. If any thing goes really wrong in the country, we look at the army for solutions, be it riot control, counter insurgency, fighting terrorism, fighting Naxalites and even getting medals in international sporting events.
Importance of Indian Army
The main role of the Indian army is of course defending our country from external and internal threats. It has proven its mettle many times. After independence it has fought five major wars and has also handled many smaller conflicts successfully. It has fought wars and won even when enemies had superior weapons.
For example, in 1965 Pakistan had Patton tanks (gifted to them by America). They were considered invincible at that time. India did not have anything that could match those Patton tanks. Still Indian army was able to defeat Pakistani tanks in the battle of Asal Uttar.
Havildar Abdul Hamid single handily destroyed six Pakistani tanks with his jeep mounted recoilless rifle and died trying to destroy the seventh. For this he was awarded with India’s highest military honour – the Param Vir Chakra. It is believed that Americans came to India to know the method and equipment by which their invincible Patton tanks were destroyed. It is believed that India refused their request.
Indian army also had successfully handled many riots, for example Godhra riots, 1992 Mumbai riots, 1984 riots etc. It is currently also tackling terrorism in Jammu & Kashmir and in some north eastern states.
It’s also a very good employer. Currently it has about 1.23 million persons on active rolls while another 9.6 lakhs in reserves. It has also produced many notable sports persons who have brought laurels to our country. Some of them are Milkha Singh, Rajya Vardhan Rathore, Vijay Kumar, and Major Dhayan Chand etc.
Also Check: Essay on Republic day
Indian army is one of the best forces in the world. It has the ability to handle any external and internal threat. Overall, we can say that Indian Army is the soul of our country.
Essay on Indian Army Day in 400 words
If you pick a person, randomly and ask him birthdays of film stars, politicians, sports persons etc. There is a good chance that he/she will be able to tell quite a few but if you him/her that, “when and why is Indian army day celebrated”? There is a good chance he/she will have no answer.
The problem is that, we have taken so many things for granted. One among them is freedom/security. We have taken for granted that someone is always deployed to guard our borders while we sleep in our cosy homes or there will be someone to take the bullets of the enemies and terrorists for us.
Indian Army day
I think the occasions like Army day, Republic day etc are of course day’s celebration and jubilation but I think we must also introspect on these days. Why everyone wants to become a doctor, engineer, lawyer etc but very few of us wants to become soldiers.
As far as celebrations are concerned, Army day is celebrated formally in New Delhi at “Amar Jawan Jyoti”, India Gate every year on 15 th of January. The day was started celebrating from 1949 through various activities like Military Parade, cultural programs, etc. It is also celebrated at all army establishments. Some schools and social organisations also celebrate army day.
Also Check: Essay on Our Country
The day is celebrated to commemorate the appointment of our first army chief, Lieutenant general K.M. Cariappa. The story of his appointment is also very interesting. The story goes something like this – Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru was having a meeting with senior army personals and cabinet ministers. He suggested that the post of first army chief should be given to a British officer because Indian officers have no experience in handling such a post.
One of the army personnel present their, objected to this and said that, “as we also don’t have the experience of leading a nation, so we should appoint a British person as our first Prime Minister.” After hearing this, Nehru realised his mistake and asked the person that would he like to become the first army chief? On this he suggested the name of Lieutenant general K.M. Cariappa who was also present there and thus he became the first army chief.
It’s high time, we should mend our ways and start giving real respect to the soldiers otherwise a time may come when there will be no one to defend our motherland.
Essay on Army Life in 500 words
I wondered as a kid, as to how is the life of a soldier. I assumed that it must be a bed of roses as opposed to mine which was like hell because I had to go to school, finish homework, learn answers, appear in tests and exams and had no time to play. On the other hand, I felt that a soldier just has to move around here and there in his smart green uniform with his gun. The problem is that, even many grownups also feel the same, not realizing how wrong they are. Maximum people think that its like a regular 9 to 5 job but this is far from reality.
I used to tell my dad that I would also like to become an army officer like him (he served in the Territorial Army as a junior commissioned officer). When asked, “why I wanted to become an army officer”? My reply was, “I would get a gun and a strong stick and with that I would beat up the bad guys”. On this my dad used to laugh loudly.
Now I realize how wrong I was. The reality is that, it is one of the toughest working environments and definitely not a bed of roses. I got some idea of the work environment of the army from the media but I soon realized it was half-truth. The only way by which I could get the real information was by talking to the real “Faujis”. Luckily my dad and some of his friends (who also served in the army) were more than willing to share their stories.
He told me that their training days were quite tough because the new environment was quite different from the civilian environment which they were used to. In civilian life 6 o’clock reporting time means 6.15 or may be even 6.30 but in army 6.00am means exactly 6.00am. My dad and his colleagues got punished many times for coming late. The punishment was usually quite difficult. Normally it was running with full gear for miles or something like that.
After morning P.T, physical endurance training started and that continued for few hours. Instructors were normally considered villains by most of the trainees. Once my dad and his colleagues were denied water after a ten-mile run. Their reaction was as expected. They had jokingly wished to kill the instructor then.
There were theory classes after that. Evening time was play time. Cadets used to play all type of games including football, volleyball, basketball etc. Dinner was a formal affair. They made so many friends there. Time passed like that and the training of my dad finished.
He got posted at many places but there was one posting which according to him was the toughest. For that he even got a gallantry medal.
My dad says that if you want a routine life then army is not for you but if you want to be pushed to your limit and want your life to be little adventurous then you must join army.
Long Essay on Indian Army in 600 words
There are very few institutions left in the country for which it can be said that country will cease to exist if these institutions fail. Indian army is one of them. Many institutions in the country which were supposed to remain neutral and impartial (let’s not name them) got corrupted but in all these years somehow Indian army has managed to remain neutral and impartial.
Role of Indian Army towards Country
All institutions of the country contribute towards nation building. It’s like the various organs of a body which perform in synchronization. It would not be wrong to say that Indian army is like the heart of a body. If it stops, the whole body (nation) stops. There are many roles which the army plays. Some of them are discussed below.
- Indian Army – an Uniting Force
We all know that Indian army is our first line of defence. It has defended us from many foreign attacks (5 major wars and few other minor conflicts). It is also helping other agencies in dealing with terrorism, insurgency, law and order, riots etc. Its professionalism and secularity remains unquestioned.
This is why it’s a unifying force. When our country got victory in Kargil war, the whole country (I mean every one, irrespective of caste, religion creed, sex) celebrated. The only other thing which has this kind of effect is cricket, I suppose. Indian army has persons from all religions. It does not discriminate on the basis of caste, religion, sect etc. This is why it’s a unifying force.
- Indian army – our “Mr. Dependable”
The tag of “Mr. dependable” cannot go to any other agency according to me. This is because when every thing fails, Indian army does not. There are so many examples which can be quoted in support of this argument. Apart from its core duties, it is asked to perform many other duties for example riot control. When police and other agencies are unable to control the situation then Indian army is called and till date they have a 100% track record. Some important riots which the army controlled were, Sikh riots, Mumbai riots, Godhra riots etc.
In natural calamities like flood and earthquakes, Indian army is called because other agencies lack the coordination and training which Indian army has. Even in sports, we depend on Indian army to bring medals in international sporting events like commonwealth games, Asian games, Olympics etc. Some of the best sportspersons like Milkha Singh, Rajya Vardhan Rathore, Vijay Kumar, Dhyan Chand, Jitu Rai, Ram Singh Yadav are from army background.
- Indian Army – a Good and Large Employer
It is said that, lucky are those who get selected for Indian army. It is now-a-days considered a very good employer because of the salary and perks which it gives. It is one of the largest employment providers in the country.
- Indian Army – Producer of Honest and Dedicated Persons
My dad used to say this thing and I strongly agree with it. He said, “dear, what you learn in army training is definitely useful in army career and also remains very useful in civilian life”. There are so many persons in civilian life who are doing very good because they had served in the army or had military training at some point of time. What is taught in a military school is not taught anywhere else.
In the end I would like to say that we are lucky to have an institution like Indian army at our disposal, without which we could never have survived. Long live India and long live Indian army…Jai hind.

Essay on Indian Army FAQs
What is indian army essay.
The Indian Army essay talks about the bravery, dedication, and service of the soldiers protecting the nation's borders and ensuring safety.
What is the Indian Army 10 lines?
The Indian Army in 10 lines highlights its role in defending the country, fostering unity, upholding peace, and serving with honor and sacrifice.
What is important in Indian Army?
The commitment to safeguarding the nation's sovereignty, maintaining peace, and offering selfless service defines the significance of the Indian Army.
What is the navy essay?
The Navy essay covers the maritime defense force that secures coastal borders, promotes trade, and contributes to national security through naval operations.
What is the importance of Indian Navy?
The Indian Navy's importance lies in protecting maritime interests, ensuring safe sea routes for trade, and safeguarding the nation's coastline and waters.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Indian Army has 13 Corps & each one is commanded by a General Officer Commanding (GOC), known as Corps Commander, who holds the rank of Lieutenant General. Each corps is composed of 3-4 Divisions. There are three types of corps in the Indian Army: Strike, Holding and Mixed. The Corps HQ is the highest field formation in the army.
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces.The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS). The Indian Army was established on 1 April 1895 alongside the long established presidency armies of the East India Company, which too were absorbed into it in 1903.
100 Words Essay On Indian Army. The Indian Army was formed in 1895 by The East India Company. It was earlier called the British India Army, and after independence, on January 26' 19501950, it was renamed as the Indian Army. The Supreme Commander of the Indian Army is the President of India, and a four-star general is appointed as the Chief of ...
Indian army is the land-based branch of Indian defence forces. It is the largest of the three armed forces of India (army, air force, and navy ). The primary mission of the Indian army is to defend the nation from external aggression as well as internal threats. It ensures national security and maintains peace within the borders.
This in turn demands a force structure built around large ground-holding formations to prevail in heavily contested battlespace—drawing away resources that could otherwise be spent on military modernization. 65 Large numbers of personnel have become a proxy measure of military capability in the Indian Army—as well as being a politically ...
Essay on Indian Army: The Indian army is the bravest and second largest army in the world with a total of 1.23 million soldiers. The Ministry of Defence of the Government of India is the governing body for the Indian Armed Forces. Commanded by the President of India as the supreme commander and commanded by the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), the Indian Army fulfils the aim of safeguarding the ...
The British Indian Army in India became the Indian Army. A Long Indian Army Day 2024 Essay. The Happy Indian Army Day originated from armies of the East India Company's which at last became the British Indian Army, and the Princely States Army, which after its independence in 1947, merged into the National Army of India. The units of the Indian ...
500 Words Essay on Indian Defence System Introduction to the Indian Defence System. The Indian Defence System is a robust and comprehensive structure that safeguards the nation's sovereignty and territorial integrity. It comprises the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, and the newly instituted Defence Space Agency and Cyber Agency.
The mission and responsibilities of the Indian Army extend far beyond the conventional notions of defense, encompassing a multifaceted role that reflects the dynamic challenges faced by the nation. 1. Defense Against External Aggression: The Indian Army's primary purpose is to maintain the country's territorial integrity from external threats.
The Indian Army is the third largest army in the world and is regarded as one of the strongest armies in the world. Indian Army has approximately 11 Lakh men and women in its ranks. The Army headquarters is located in New Delhi. You have studied about Senapathy who was the head of the King's army. Similarly modern armies have a senapathy.
The Indian Air Force was officially established on 8th October 1932, and on 1st April 1954, Air Marshal Subroto Mukherjee, one of the founding members of the Air Force took over as the first Indian Chief of Air Staff. With the passage of time, the Indian Air Force undertook massive upgrading of its aircraft and equipments, and as part of the ...
Women in Indian army have proved their steel time and again. According to a recent study released by Defence website Military Direct, after China, superpower USA and Russia, India has the 4 th strongest military power in the world. The Indian Army is well-equipped with powerful equipment and weapons. The Indian Army has 296 aircraft of its own.
The Basic Field Formations of Army are Discussed below: Command : Two or three corps together form a command , Indian Army has six operational commands and one training command. Each command is headed by a general officer commanding-in-chief (GOC-in-C), known as the army commander. Corps: Three or Four Division together make a Corp, Indian Army ...
Short Essay On Indian Army. The Indian Army is the land-based branch of the Indian Armed Forces responsible for securing the country's territorial integrity and national security. With over 1.3 million active personnel, it is one of the largest standing armies in the world. ... Structure and Organization of the Indian Army.
10 Lines on Essay on Indian Army 150 Words. Indian Army is the part of India that contributes itself to the safety and unity of India. It first originated under the name of the 'British Indian Army'. There are three uniformed parts of the Indian army - the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Airforce. Armies in India were first ...
100 Words Essay on Indian Army Introduction. The Indian Army is one of the most powerful and respected institutions in India. It is the land-based branch of the Indian Armed Forces and is responsible for protecting the country's sovereignty and maintaining peace. Structure and Role. The Indian Army is divided into various regiments and ...
As India is emerging a important strategic partner for the U.S. in the Asia-Pacific, Gurmeet Kanwal assesses the progress of India's military modernization and argues that in order to achieve interoperability with U.S. and other friendly armed forces, the Indian military needs to create force structures capable of undertaking network-centric warfare on land, at sea, and in the air.
Dharvi Vaid New Delhi. 01/05/2022. The changing geopolitical situation and security landscape has prompted the Indian government to accelerate military modernization, say experts. India is one of ...
The Indian Army is the 2nd largest active-duty military force in the world in 2020 second only to China. With over 1.23 million personnel and counting, a sound structure for the army is essential. The Indian Army is divided into 40 divisions & 14 corps. The Indian Army Headquarters is in New Delhi.
India in Transition (IiT), allows scholars from all over the world, the opportunity to exchange various analyses and innovative ideas about India's current status and growth. IiT presents brief, analytical perspectives on the ongoing transformations in contemporary India based on cutting-edge research in the areas of economy, environment, foreign policy and security, human capital, science and ...
Essay on Indian Army. We sleep comfortably in our homes because we know that even if we are not alert, there are some people who are always aware so that we can be safe. These people are part of the country's Army. Likewise, the Indian Army is known all over the world for its strength, which is dedicated to protecting Indians from dangers.
Short Essay on Indian Army in English 200 words. Indian armed forces are divided into three parts - Indian army, Indian Airforce and the Indian Navy. Indian army is the land-based unit, while Indian Airforce deals in air defence and Indian Navy is the naval unit.
This Indian army day is celebrated every year on the 15th of January. This day recognises the absolute transfer of power from the British administration to the Indian administration that happened 2 years after the independence. The military capabilities of the Indian army can be traced back to industrialization and not just some recent scenarios.