
- Research Service
- Consumer Trend Report
- Poplite by Populix
- Partnership @Poplite
- Blog & Articles
- Join Telegram Channel
- Join Telegram Group

- Blog & Articles

Penelitian Lapangan: Definisi, Jenis, Metode, Contoh

Mungkin Anda pernah mendengar tentang penelitian lapangan, tetapi apakah itu? Penelitian lapangan adalah bentuk proses pengumpulan data atau informasi tentang interaksi manusia dengan subjek di lingkungan alaminya.
Melansir laman Indeed , melakukan penelitian lapangan dapat memberikan informasi yang diperlukan para profesional untuk membuat dan membuktikan teori-teori baru melalui berbagai metode pengumpulan data .
Oleh karena itu, yuk kenali lebih detail lagi tentang penelitian lapangan.
Apa Itu Penelitian Lapangan?

Field research atau penelitian lapangan adalah proses atau metode pengumpulan data kualitatif tentang interaksi orang atau kelompok di lingkungan alaminya.
Mengutip situs QuestionPro , salah satu contoh penelitian lapangan adalah para pelestari alam mengamati perilaku hewan di lingkungan alaminya dan cara mereka bereaksi terhadap skenario tertentu.
Dengan cara yang sama, ilmuwan sosial yang melakukan penelitian lapangan dapat melakukan wawancara atau mengamati orang-orang dari jarak jauh untuk memahami bagaimana mereka berperilaku dalam lingkungan sosial, serta bagaimana mereka bereaksi terhadap situasi di sekitar mereka.
Para peneliti menggunakan metode penelitian lapangan ini untuk mengumpulkan informasi dan mengembangkan teori baru tentang sosiologi, sifat manusia, dan interaksi antarpribadi.
Adapun tujuan penelitian lapangan adalah untuk membangun dan membuktikan hubungan sebab-akibat di berbagai lingkungan alam dan komunitas.
Baca juga: Consumer Insight: Pengertian, Contoh & Cara Mengoptimalkannya
Jenis Penelitian Lapangan
Ada berbagai jenis penelitian lapangan yang perlu diketahui. Setiap komponen prosesnya berkontribusi terhadap pengembangan teori dan kesimpulan secara keseluruhan.
1. Laporan Tertulis
Membuat laporan tertulis tentang penelitian lapangan mencakup pembuatan ringkasan metode, hipotesis, temuan, dan kesimpulan keseluruhan.
Laporan tertulis sering kali mengikuti struktur makalah atau jurnal formal. Memberikan laporan tertulis tentang penelitian lapangan memungkinkan Anda merefleksikan temuan dan berbagi informasi dengan peneliti lain.
2. Analisi Data
Tujuan utama melakukan penelitian lapangan mencakup kemampuan menganalisis temuan Anda dan mengembangkan teori yang sesuai dengan data yang diberikan.
Analisis data dalam penelitian lapangan adalah hal yang mencakup penggunaan data kualitatif dan kuantitatif untuk mengidentifikasi pola atau korelasi antara perilaku, faktor lingkungan, demografi, dan sistem kepercayaan.
Evaluasi hasil penelitian lapangan memungkinkan ilmuwan sosial untuk menetapkan makna dan parameter terhadap tindakan atau respons tertentu.
3. Catatan Observasi
Metode penelitian lapangan sangat bergantung pada penggunaan observasi untuk mengidentifikasi pola, penyebab, dan perilaku dalam sekelompok subjek.
Menyimpan catatan pengamatan yang terperinci memungkinkan Anda mengingat peristiwa, data, dan faktor-faktor yang dapat memengaruhi hasil dan kesimpulan secara keseluruhan.
Catatan observasi mencakup catatan lapangan informal, entri jurnal, dan rekaman dari proses penelitian lapangan.
Baca juga: Riset Konsumen: Definisi, Cara Melakukan, Manfaat bagi Bisnis
Metode Penelitian Lapangan
Penelitian lapangan biasanya dilakukan dengan 5 metode berbeda, di antaranya yaitu:
1. Wawancara Kualitatif
Biasanya langsung mengajukan pertanyaan tertutup kepada subjek penelitian. Wawancara kualitatif dapat bersifat informal dan percakapan, semi-terstruktur, terstandardisasi dan terbuka, atau gabungan dari ketiga hal di atas.
Metode ini memberikan banyak sekali data kepada peneliti yang dapat mereka pilah. Ini juga membantu mengumpulkan data relasional.
Metode penelitian lapangan ini dapat menggunakan campuran wawancara satu lawan satu, kelompok fokus, dan analisis teks.
2. Observasi Langsung
Dalam metode ini, data dikumpulkan melalui metode observasi atau subjek pada lingkungan alam. Dalam metode ini, perilaku atau hasil suatu situasi tidak diintervensi dengan cara apa pun oleh peneliti.
Keuntungan observasi langsung adalah menawarkan data kontekstual tentang pengelolaan manusia, situasi, interaksi, dan lingkungan sekitar.
Metode penelitian lapangan ini banyak digunakan di lingkungan publik, tetapi tidak di lingkungan privat karena menimbulkan dilema etika.
3. Observasi Peserta
Dalam metode penelitian lapangan ini, peneliti terlibat secara mendalam dalam proses penelitian, tidak sekedar sebagai pengamat, tetapi juga sebagai partisipan.
Metode ini juga dilakukan dalam lingkungan alami, tetapi satu-satunya perbedaan adalah peneliti terlibat dalam diskusi dan dapat menentukan arah diskusi.
Dalam metode ini, peneliti hidup dalam lingkungan yang nyaman dengan partisipan desain penelitian, sehingga membuat mereka nyaman dan terbuka untuk berdiskusi secara mendalam.
4. Studi Kasus
Penelitian studi kasus adalah analisis mendalam terhadap seseorang, situasi, atau peristiwa. Metode ini mungkin terlihat sulit untuk dioperasikan, tetapi ini adalah salah satu cara paling sederhana dalam melakukan penelitian karena melibatkan pemahaman yang mendalam dan menyeluruh tentang metode pengumpulan data dan menyimpulkan data.
5. Etnografi
Etnografi adalah pengamatan yang diperluas terhadap penelitian sosial dan perspektif sosial serta nilai-nilai budaya dari keseluruhan lingkungan sosial.
Dalam etnografi, seluruh komunitas diamati secara objektif. Misalnya, jika seorang peneliti ingin memahami bagaimana suku Baduy menjalani kehidupannya, dia dapat memilih untuk mengamati mereka atau tinggal di antara mereka dan secara diam-diam mengamati perilaku mereka sehari-hari.
Kelebihan dan Kekurangan Penelitian Lapangan

- Dilakukan di dunia nyata dan lingkungan alami sehingga tidak ada variabel yang diubah dan lingkungan tidak direkayasa.
- Penelitian dilakukan dalam lingkungan yang nyaman, data dapat dikumpulkan bahkan mengenai topik tambahan.
- Peneliti memperoleh pemahaman yang mendalam tentang subjek penelitian karena kedekatannya dengan mereka, oleh karena itu penelitiannya ekstensif, menyeluruh, dan akurat.
- Studi ini mahal dan memakan waktu, bahkan bisa bertahun-tahun untuk menyelesaikannya.
- Sangat sulit bagi peneliti untuk menjauhkan diri dari bias dalam penelitiannya.
- Catatan harus benar-benar sesuai dengan apa yang peneliti katakan, tetapi nomenklaturnya sangat sulit untuk diikuti.
- Metode ini bersifat interpretatif dan bersifat subjektif dan sepenuhnya bergantung pada kemampuan peneliti.
- Dalam metode ini, tidak mungkin mengendalikan variabel eksternal dan hal ini terus-menerus mengubah sifat penelitian.
Baca juga: Variabel Dikotomi Adalah: Definisi, Jenis, Tujuan, Contoh
Contoh Penelitian Lapangan
Salah satu contohnya yaitu mempelajari hubungan ras di suatu wilayah tertentu. Ya, untuk memahami interaksi dan sikap antara individu-individu dari ras yang berbeda di suatu wilayah tertentu memerlukan penggunaan penelitian lapangan.
Pengamatan langsung memungkinkan Anda mengamati subjek yang berinteraksi dalam konteks lingkungan alaminya dan tanpa gangguan.
Melakukan wawancara kualitatif juga memberikan data mengenai sikap dan cara pandang subjek dari berbagai ras serta hubungan di antara mereka.
Demikianlah penjelasan tentang penelitian lapangan, mulai dari pengertian, jenis, metode, kelebihan dan kekurangan, hingga contohnya. Jika Anda berminat untuk melakukan penelitian untuk kebutuhan apa pun, termasuk untuk kebutuhan bisnis maupun akademis, Anda bisa manfaatkan layanan survei dan riset Populix .

Baca juga: Variabel Pengganggu Adalah: Definisi dan Dampak pada Riset

Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest updates & amazing offers deliverd directly to your email
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
What is Field Research: Definition, Methods, Examples and Advantages
What is Field Research?
Field research is defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims to observe, interact and understand people while they are in a natural environment. For example, nature conservationists observe behavior of animals in their natural surroundings and the way they react to certain scenarios. In the same way, social scientists conducting field research may conduct interviews or observe people from a distance to understand how they behave in a social environment and how they react to situations around them.
Learn more about: Market Research
Field research encompasses a diverse range of social research methods including direct observation, limited participation, analysis of documents and other information, informal interviews, surveys etc. Although field research is generally characterized as qualitative research, it often involves multiple aspects of quantitative research in it.
Field research typically begins in a specific setting although the end objective of the study is to observe and analyze the specific behavior of a subject in that setting. The cause and effect of a certain behavior, though, is tough to analyze due to presence of multiple variables in a natural environment. Most of the data collection is based not entirely on cause and effect but mostly on correlation. While field research looks for correlation, the small sample size makes it difficult to establish a causal relationship between two or more variables.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
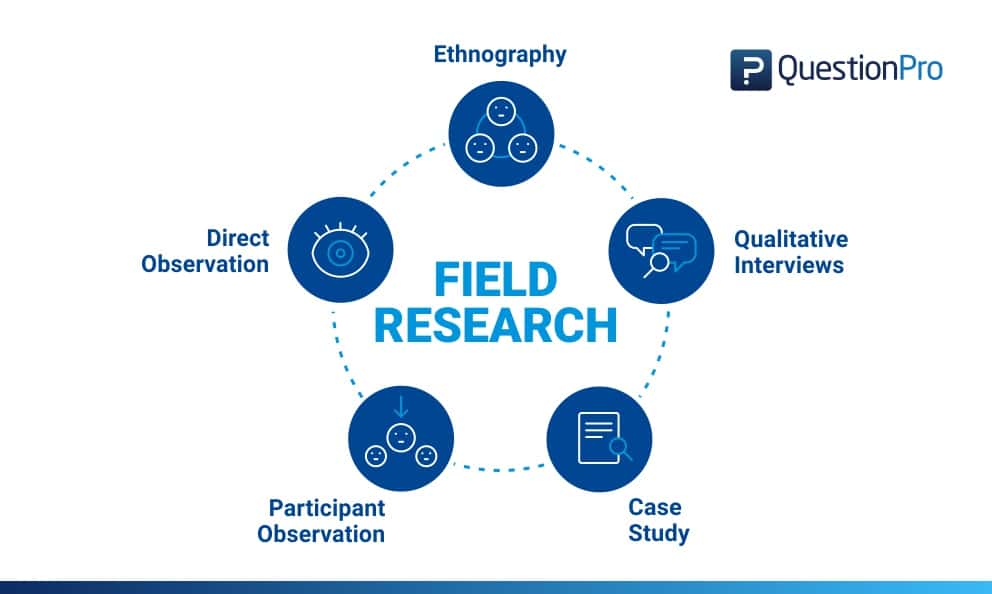
Methods of Field Research
Field research is typically conducted in 5 distinctive methods. They are:
- Direct Observation
In this method, the data is collected via an observational method or subjects in a natural environment. In this method, the behavior or outcome of situation is not interfered in any way by the researcher. The advantage of direct observation is that it offers contextual data on people management , situations, interactions and the surroundings. This method of field research is widely used in a public setting or environment but not in a private environment as it raises an ethical dilemma.
- Participant Observation
In this method of field research, the researcher is deeply involved in the research process, not just purely as an observer, but also as a participant. This method too is conducted in a natural environment but the only difference is the researcher gets involved in the discussions and can mould the direction of the discussions. In this method, researchers live in a comfortable environment with the participants of the research design , to make them comfortable and open up to in-depth discussions.
- Ethnography
Ethnography is an expanded observation of social research and social perspective and the cultural values of an entire social setting. In ethnography, entire communities are observed objectively. For example, if a researcher would like to understand how an Amazon tribe lives their life and operates, he/she may chose to observe them or live amongst them and silently observe their day-to-day behavior.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
- Qualitative Interviews
Qualitative interviews are close-ended questions that are asked directly to the research subjects. The qualitative interviews could be either informal and conversational, semi-structured, standardized and open-ended or a mix of all the above three. This provides a wealth of data to the researcher that they can sort through. This also helps collect relational data. This method of field research can use a mix of one-on-one interviews, focus groups and text analysis .
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
A case study research is an in-depth analysis of a person, situation or event. This method may look difficult to operate, however, it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding the data collection methods and inferring the data.
Steps in Conducting Field Research
Due to the nature of field research, the magnitude of timelines and costs involved, field research can be very tough to plan, implement and measure. Some basic steps in the management of field research are:
- Build the Right Team: To be able to conduct field research, having the right team is important. The role of the researcher and any ancillary team members is very important and defining the tasks they have to carry out with defined relevant milestones is important. It is important that the upper management too is vested in the field research for its success.
- Recruiting People for the Study: The success of the field research depends on the people that the study is being conducted on. Using sampling methods , it is important to derive the people that will be a part of the study.
- Data Collection Methodology: As spoken in length about above, data collection methods for field research are varied. They could be a mix of surveys, interviews, case studies and observation. All these methods have to be chalked out and the milestones for each method too have to be chalked out at the outset. For example, in the case of a survey, the survey design is important that it is created and tested even before the research begins.
- Site Visit: A site visit is important to the success of the field research and it is always conducted outside of traditional locations and in the actual natural environment of the respondent/s. Hence, planning a site visit alongwith the methods of data collection is important.
- Data Analysis: Analysis of the data that is collected is important to validate the premise of the field research and decide the outcome of the field research.
- Communicating Results: Once the data is analyzed, it is important to communicate the results to the stakeholders of the research so that it could be actioned upon.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Field Research Notes
Keeping an ethnographic record is very important in conducting field research. Field notes make up one of the most important aspects of the ethnographic record. The process of field notes begins as the researcher is involved in the observational research process that is to be written down later.
Types of Field Research Notes
The four different kinds of field notes are:
- Job Notes: This method of taking notes is while the researcher is in the study. This could be in close proximity and in open sight with the subject in study. The notes here are short, concise and in condensed form that can be built on by the researcher later. Most researchers do not prefer this method though due to the fear of feeling that the respondent may not take them seriously.
- Field Notes Proper: These notes are to be expanded on immediately after the completion of events. The notes have to be detailed and the words have to be as close to possible as the subject being studied.
- Methodological Notes: These notes contain methods on the research methods used by the researcher, any new proposed research methods and the way to monitor their progress. Methodological notes can be kept with field notes or filed separately but they find their way to the end report of a study.
- Journals and Diaries: This method of field notes is an insight into the life of the researcher. This tracks all aspects of the researchers life and helps eliminate the Halo effect or any research bias that may have cropped up during the field research.
LEARN ABOUT: Causal Research
Reasons to Conduct Field Research
Field research has been commonly used in the 20th century in the social sciences. But in general, it takes a lot of time to conduct and complete, is expensive and in a lot of cases invasive. So why then is this commonly used and is preferred by researchers to validate data? We look at 4 major reasons:
- Overcoming lack of data: Field research resolves the major issue of gaps in data. Very often, there is limited to no data about a topic in study, especially in a specific environment analysis . The research problem might be known or suspected but there is no way to validate this without primary research and data. Conducting field research helps not only plug-in gaps in data but collect supporting material and hence is a preferred research method of researchers.
- Understanding context of the study: In many cases, the data collected is adequate but field research is still conducted. This helps gain insight into the existing data. For example, if the data states that horses from a stable farm generally win races because the horses are pedigreed and the stable owner hires the best jockeys. But conducting field research can throw light into other factors that influence the success like quality of fodder and care provided and conducive weather conditions.
- Increasing the quality of data: Since this research method uses more than one tool to collect data, the data is of higher quality. Inferences can be made from the data collected and can be statistically analyzed via the triangulation of data.
- Collecting ancillary data: Field research puts the researchers in a position of localized thinking which opens them new lines of thinking. This can help collect data that the study didn’t account to collect.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
Examples of Field Research
Some examples of field research are:
- Decipher social metrics in a slum Purely by using observational methods and in-depth interviews, researchers can be part of a community to understand the social metrics and social hierarchy of a slum. This study can also understand the financial independence and day-to-day operational nuances of a slum. The analysis of this data can provide an insight into how different a slum is from structured societies.
- U nderstand the impact of sports on a child’s development This method of field research takes multiple years to conduct and the sample size can be very large. The data analysis of this research provides insights into how the kids of different geographical locations and backgrounds respond to sports and the impact of sports on their all round development.
- Study animal migration patterns Field research is used extensively to study flora and fauna. A major use case is scientists monitoring and studying animal migration patterns with the change of seasons. Field research helps collect data across years and that helps draw conclusions about how to safely expedite the safe passage of animals.
LEARN ABOUT: Social Communication Questionnaire
Advantages of Field Research
The advantages of field research are:
- It is conducted in a real-world and natural environment where there is no tampering of variables and the environment is not doctored.
- Due to the study being conducted in a comfortable environment, data can be collected even about ancillary topics.
- The researcher gains a deep understanding into the research subjects due to the proximity to them and hence the research is extensive, thorough and accurate.
Disadvantages of Field Research
The disadvantages of field research are:
- The studies are expensive and time-consuming and can take years to complete.
- It is very difficult for the researcher to distance themselves from a bias in the research study.
- The notes have to be exactly what the researcher says but the nomenclature is very tough to follow.
- It is an interpretive method and this is subjective and entirely dependent on the ability of the researcher.
- In this method, it is impossible to control external variables and this constantly alters the nature of the research.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer Communication Tool: Types, Methods, Uses, & Tools
Apr 23, 2024

Top 12 Sentiment Analysis Tools for Understanding Emotions

QuestionPro BI: From Research Data to Actionable Dashboards
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Experience Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Home » Bahasa Indonesia » Penelitian Lapangan: Pengertian – Ciri dan Contohnya
Penelitian Lapangan: Pengertian – Ciri dan Contohnya
- Review Akademik by: Review Akademik by: Eva Yanuarti, S.Pd
- Post author Scientific Rev by: Redaksi Haloedukasi

Pengertian Penelitian Lapangan
Ciri-ciri penelitian lapangan, contoh penelitian lapangan, kelebihan dan kekurangan penelitian lapangan.
Setelah tadi membahas tentang Penelitian Dasar dan Penelitian Terapan , sekarang kami akan membahas tentang penelitian Lapangan.
Seperti namanya, yang berarti meneliti suatu onyek secara langsung. Penelitian Lapangan merupakan penelitian yang dilakukan dengan mengumpulkan data dan informasi yang diperoleh langsung dari responden.
Pengumpulan data dan informasi dilakukan dengan cara sebagai berikut:
- Metode Observasi Menurut Kriyantono (2008:106) mengatakan bahwa “Metode Observasi merupakan kegiatan mengamati secara langsung tanpa mediator sesuatu objek untuk melihat dengan dekat kegiatan yang dilakukan objek tertentu. Observasi merupakan metode pengumpulan data yang digunakan pada riset kualitatif.
- Metode Wawancara Menurut Berger dalam Kriyantono (2000:111) mengatakan bahwa Wawancara adalah percakapan antara periset seseorang yang berharap mendapatkan informasi, dan informan seseorang yang diasumsikan mempunyai informasi penting tentang sesuatu objek. Wawancara merupakan metode pengumpulan data yang digunakan untuk memperoleh informasi langsung dari sumbernya.
- Mengamati kejadian sehari-hari yang biasa/tidak biasa dalam setting kehidupan sehari-hari.
- Terlibat langsung apakah orang yang diteliti.
- Memperoleh sudut pandang orang yang diteliti sekaligus mempertahankan perspektif analitis orang luar.
- Menggunakan beragam teknik dan keterampilan sosial secara luwes.
- Menghimpun data berbentuk catatan rinci, bagan, peta, maupun gambar untuk keperluan deskripsi.
- Memandang gejala dalam konteks sosial.
- Mengembangkan empati dengan orang yang diteliti.
- Memperhatikan aspek-aspek kebudayaan.
Contoh penelitian menggunakan metode studi kasus ini adalah penelitian yang dilakukan oleh Jankowsiki di Amsterdam pertengahan dekade 1970-an yaitu analisis kontekstual mengenai perkembangan stasiun televisi lokal adapun topik lain yang dapat menggunakan metode ini yaitu perilaku memilih dikalangan perempuan perkotaan dalam hal ini kita dapat mengerucutkan dan memfokuskan pada satu kota tertentu, dalam hal ini peneliti bisa mengedintifikasikan berbagai kasus yang telah ada.
Kelebihan Penelitian Lapangan
Kelebihan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk subyek yang diselidiki observasi akan menghasilkan data dan jawaban yang lebih akurat.
Kekurangan Penelitian Lapangan
Kekurangan dari penelitian ini adalah akan memakan waktu yang lebih lama dan biaya yang lebih besar.
- Tags bahasa indonesia , Penelitian , Penelitian Lapangan
Related Posts
- Penelitian Eksploratif: Pengertian – Ciri dan Contohnya
- Nomina Majemuk: Pengertian – Ciri dan Jenisnya
- Makna Kontekstual: Pengertian dan Contohnya
- 8 Jenis Puisi Kontemporer Beserta Contohnya
- Kalimat Mayor: Pengertian – Ciri dan Contohnya
© 2024 HaloEdukasi.com
About | Quality Control | Term of Use | Privacy Policy | Contact
A guide to field studies
Last updated
18 April 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Field studies allow researchers to observe and collect data in real-world settings. Unlike laboratory-based or traditional research methods, field studies enable researchers to investigate complex phenomena within their environment, providing a deeper understanding of the research context.
Researchers can use field studies to investigate a wide range of subjects, from the behavior of animals to the practices of businesses or the experiences of individuals in a particular setting.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a field study?
A field study is a research method that involves conducting observations and collecting data in a natural setting. This method includes observing, interviewing, and interacting with participants in their environment, such as a workplace, community, or natural habitat.
Field studies can take many forms, from ethnographic studies involving extended periods of observation and using an anthropological lens to shorter-term studies focusing on specific behaviors or events. Regardless of its form, a successful field study requires careful planning, preparation, and execution to ensure the data collected is valid and reliable.
- How to plan a field study
Planning a field study is a critical first step in ensuring successful research. Here are some steps to follow when preparing your field study:
1. Define your research question
When developing a good research question , you should make it clear, concise, and specific. It should also be open-ended, allowing for various possible answers rather than a simple yes or no response. Your research question should also be relevant to the broader field of study and contribute new knowledge to the existing literature.
Once you have a defined research question, identify the key variables you need to study and the data you need to collect. It might involve developing a hypothesis or research framework outlining the relationships between different variables and how you’ll measure them in your study.
2. Identify your research site
A research site is a location where you’ll conduct your study and collect data. Here are the types of research sites to consider when planning a field study:
Natural habitats: For environmental or ecological research, you may need to conduct your study in a natural habitat, such as a forest, wetland, or coral reef.
Communities : If your research relates to social or cultural factors, you may need to study a particular community, such as a neighborhood, village, or city.
Organizations : For questions relating to organizational behavior or management, your location will be in a business environment, like a nonprofit or government agency.
Events : If your research question relates to a particular event, you may need to conduct your study at that event, such as, at a protest, festival, or natural disaster.
Ensure your research site represents the population you're studying. For example, if you're exploring cultural beliefs, ensure the community represents the larger population and you have access to a diverse group of participants.
3. Determine your data collection methods
Choosing a suitable method will depend on the research question, the type of data needed, and the characteristics of the participants. Here are some commonly used data collection methods in field studies:
Interviews : You can collect data on people's experiences, perspectives, and attitudes. In some instances, you can use phone or online interviews.
Observations : This method involves watching and recording behaviors and interactions in a specific setting.
Surveys : By using a survey , you can easily standardize and tailor the questions to provide answers for your research. Respondents can complete the survey in person, by mail, or online.
Document analysis : Organizational reports, letters, diaries, public records, policies, or social media posts can be analyzed to gain context.
When selecting data collection methods, consider factors such as the availability of participants, the ethical considerations involved, and the resources needed to carry out each method. For example, conducting interviews may require more time and resources than administering a survey.
4. Obtain necessary permissions
Depending on the research location and the nature of the study, you may require permission from local authorities, organizations, or individuals before conducting your research.
This process is vital when working with human or animal subjects and conducting research in sensitive or protected environments.
Here are some steps you can take to obtain the necessary permissions:
Identify the relevant authorities , including local governments, regulatory bodies, research institutions, or private organizations, to obtain permission for your research.
Reach out to the relevant authorities to explain the nature of your study. Be ready to hand out detailed information about your research.
If you're conducting research with human participants, you must have their consent . You'll also need to ensure the participants have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
Obtain necessary permits from regulatory bodies or local authorities. For example, if you're conducting research in a protected area, you may need a research permit from the relevant government agency.
The process of obtaining permissions can be time-consuming, and failure to obtain the necessary permits can lead to legal and ethical issues.
- Examples of field research
Researchers can apply field research to a wide range of disciplines and phenomena. Here are some examples of field research in different fields:
Anthropology : Anthropologists use field research methods to study different communities' social and cultural practices. For instance, an anthropologist might conduct participant observation in a remote community to understand their customs, beliefs, and practices.
Ecology : Ecologists use field research methods to learn the behavior of organisms and their interactions with the environment. For example, an ecologist might conduct field research on the behavior of birds in their natural habitat to understand their feeding habits, nesting patterns, and migration.
Sociology : Sociologists may use field research methods to study social behavior and interactions. For instance, a sociologist might conduct participant observation in a workplace to understand organizational culture and communication dynamics.
Geography : Geographers use field research methods to study different regions’ physical and human contexts. For example, a geographer might conduct field research on the impact of climate change on a particular ecosystem, such as a forest or wetland.
Psychology : Psychologists use field research methods to study human behavior in natural settings. For instance, a psychologist might conduct field research on the effects of stress on students in a school setting.
Education : Researchers studying education may use field research methods to study teaching and learning in real-world settings. For example, you could use field research to test the effectiveness of a new teaching method in a classroom setting.
By using field research methods, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of the natural world, human behavior, and social interaction theory and how they affect each other.
- Advantages of field research
Field research has several advantages over other research methods, including:
Authenticity : Field research conducted in natural settings allows researchers to observe and study real-life phenomena as it happens. This authenticity enhances the validity and accuracy of the data collected.
Flexibility : Field research methods are flexible and adaptable to different research contexts. Researchers can adjust their strategies to meet the specific needs of their research questions and participants and uncover new insights as the research unfolds.
Rich data : Field research provides rich and detailed data, often including contextual information that’s difficult to capture through other research methods. This depth of knowledge allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the research topic.
Novel insights : Field research can lead to discoveries that may not be possible with other research methods. Observing and studying phenomena in natural settings can provide unique perspectives and new understandings of complex issues.
Field research methods can enhance the quality and validity of research findings and lead to new insights and discoveries that may not be possible with other research methods.
- Disadvantages of field research
While field research has several advantages, there are also some disadvantages that researchers need to consider, including:
Time-consuming : Researchers need to spend time in the field, possibly weeks or months, which can be challenging, especially if the research site is remote or requires travel.
Cost : Conducting field research can be costly, especially if the research site is remote or requires specialized equipment or materials.
Reliance on participants : It may be challenging to recruit participants, and various factors, such as personal circumstances, attitudes, and beliefs, may influence their participation.
Ethical considerations : Field research may raise ethical concerns, mainly if the research involves vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
Causality: Researchers may have little control over the environmental or contextual variables they are studying. This can make it difficult to establish causality and then generalize their results with previous research.
Researchers must carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of field research and select the most appropriate research method based on their research question, participants, and context.
What is another name for field study?
Field study is also known as field research or fieldwork. These terms are often used interchangeably and refer to research methods that involve observing and collecting data in natural settings.
What is the difference between a field study and a case study?
Why is field study important.
Field study is critical because it allows researchers to study real-world phenomena in natural settings. This study can also lead to novel insights that may not be possible with other research methods.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Field Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2021
- pp 3108–3112
- Cite this reference work entry

- Emily Lescak 3
19 Accesses
Gathering information by observing individuals in their natural setting.
Introduction
Field research (“fieldwork”) refers to information gathered by observing individuals in their natural setting. Field research can be both qualitative and quantitative in nature. Qualitative research emphasizes the importance of observing variables and their interactions. Quantitative research attempts to objectively gather data to make associations, comparisons, and predictions among variables. Field studies that sought to associate behavior with inter-individual interactions and/or the environment formed the foundation for the field of behavioral ecology (Martin and Bateson 2007 ).
Field research involves observations of free-living wild animals in their natural habitats while minimizing perturbations or disturbances to their environment or behavior. Field excursions may require some or all of the following (Lagler 1956 ): funding for travel, salary, supplies, and...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Bart, J., Fligner, M., & Notz, W. (1998). Sampling and statistical methods for behavioral ecologists . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Cochran, W. (1977). Sampling techniques . Hoboken: Wiley.
Google Scholar
Crook, J. H. (1964). The evolution of social organisation and visual communication in the weaver birds ( Ploceinae ). Behaviour, 10 , 1–178.
Darwin, C. (1859). On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life . London: John Murray.
Dewsbury, D. A. (2003). The 1973 Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine: Recognition for behavioral science? American Psychology, 58 (9), 747–752.
Article Google Scholar
Goodall, J. (1990). Through a window: My thirty years with the chimpanzees of Gombe . New York: Soko Publications Limited.
Lack, D. (1947). Darwin’s finches . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Lagler, K. (1956). Freshwater fishery biology . Dubuque: Wm. C. Brown Company Publishers.
Lahti, D., & Lahti, A. (2002). How precise is egg discrimination in weaverbirds? Animal Behaviour, 63 , 1135–1142.
Lehner, P. (1996). Handbook of ethological methods . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Martin, P., & Bateson, P. (2007). Measuring behavior: An introductory guide . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Nice, M. M. (1937). Studies in the life history of the song sparrow. I. A population study of the song sparrow. Transactions of the Linnean Society of New York, 4 , 1–247.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Alaska Anchorage, Anchorage, AK, USA
Emily Lescak
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emily Lescak .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Oakland University, Rochester, MI, USA
Todd K Shackelford
Viviana A Weekes-Shackelford
Section Editor information
University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA
Russell Jackson
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Lescak, E. (2021). Field Research. In: Shackelford, T.K., Weekes-Shackelford, V.A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Psychological Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_2742
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19650-3_2742
Published : 22 April 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-19649-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-19650-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

PENELITIAN LAPANGAN (FIELD RESEARCH) PADA METODE KUALITATIF
Studi Kasus, Fenomenologi, Etnometodologi, Interaksi Simbolik, Etnografi, Biografi, Grounded Research.
Related Papers
METODOLOGI PENELITIAN
Mohammad Natsir H Igirisa
TUGAS METODOLOGI PENELITIAN Oleh MOHAMMAD NATSIR HAMID IGIRISA INDRA HAMIM ELVIRA TAHABU YELITA OKONG NURJANA BATALIPU HIJRA APRILIA REKSI KAMARU ILHAM NAPU RISKI MUHARAM IAIN SULTAN AMAI GORONTALO
dewi nurlaily
Izhra Ichca
perbedaan tentang penelitian kuantitatif dengan penelitian kualitatif
Rifda Tanfiziyah
Jamora Gani Nasution
RaZtha Phyta
Qualitative method has been widely be adopted in research practices in Indonesian tradition of social sciences including sociology. However, it seems there is misunderstanding on the method that is seen as additional to the quantitative one. This literature study intend to discuss related issues to the strengths and weaknesses of qualitative method. We do conclude here, that the method has productive potential for fostering the develomment of social theories as well as methodology in the context of Indonesian world. Hence, it is possible to bring Indonesian social sciences especially sociology into equal position of future dialog with the counterparts from the Western communities. Keywords: qualitative method, method in practice, theorizing, contextualization, relevancy
Chris Puspita
Nadia Ahbab
RELATED PAPERS
May Sitohang
LIBER Quarterly
Matthijs van Otegem
Marcin Kiciński
Clio Femmes Genre Histoire
catherine marry
ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems
Hitesh Joshi
Tomoko Matsui
Arsen Duplančić
Dalet Solange
American Journal of Otolaryngology
Meltem Tulgar
Mobile Genetic Elements
Fernando de la Cruz
PEDAGOGIA Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan
Asep Saepudin
The European Physical Journal A
Katrien Vyvey
Annals of Surgery
Enrique Izaguirre
Revista da …
katya alexandrina matos barreto motta
FORMULARIO DEGLI ATTI PENALI, dir. Beltrani-Marandola, Giuffrè, Milano
Pietro Insolera
The Journal of Physical Chemistry A
Franck Rabilloud
Irina Polikanova
Malang Neurology Journal
Yoke Lian Lau
Acta Materialia
Nucleic Acids Research
African Study Monographs
Ethelbert Kari
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology
Materialwissenschaft Und Werkstofftechnik
Esther Akinlabi
Raul Maranhão
Physical Review B
Saurav Giri
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Privacy Policy
Aneka Ragam Makalah

Field Research (Penelitian Lapangan)

- Add Document
- BAB II METODE PENELITIAN. lapangan (Field Research) dengan pendekatan kualitatif. Menurut Bogdan
Recommend Documents

Report "BAB II METODE PENELITIAN. lapangan (Field Research) dengan pendekatan kualitatif. Menurut Bogdan"

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Penelitian lapangan. Penelitian lapangan merupakan salah satu metode pengumpulan data dalam penelitian kualitatif yang tidak memerlukan pengetahuan mendalam akan literatur yang digunakan dan kemampuan tertentu dari pihak peneliti. [1] [2] Penelitian lapangan biasa dilakukan untuk memutuskan ke arah mana penelitiannya berdasarkan konteks. [1]
Apa Itu Penelitian Lapangan? Field research atau penelitian lapangan adalah proses atau metode pengumpulan data kualitatif tentang interaksi orang atau kelompok di lingkungan alaminya. Mengutip situs QuestionPro , salah satu contoh penelitian lapangan adalah para pelestari alam mengamati perilaku hewan di lingkungan alaminya dan cara mereka ...
93. BAB III METODE PENELITIAN. A. Jenis Penelitian dan Pendekatan. Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian lapangan (field research) yaitu penelitian yang data dan informasinya diperoleh dari kegiatan di wilayah kerja penelitian.1Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah metode kualitatif yaitu jenis penelitian yang temuan-temuannya tidak ...
Field research atau penelitian lapangan merupakan jenis penelitian yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini. Field research atau penelitian lapangan ini adalah penelitian yang data informasinyaa dikumpulkan langsung menggunakan media observasi, wawancara dan kuesioner. Penelitian ini menjadikan masyarakat sebagai sasaran, masayaraknya
Field research is defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims to observe, interact and understand people while they are in a natural environment. This article talks about the reasons to conduct field research and their methods and steps. This article also talks about examples of field research and the advantages and disadvantages of this research method.
Pengertian Penelitian Lapangan. Seperti namanya, yang berarti meneliti suatu onyek secara langsung. Penelitian Lapangan merupakan penelitian yang dilakukan dengan mengumpulkan data dan informasi yang diperoleh langsung dari responden. Pengumpulan data dan informasi dilakukan dengan cara sebagai berikut: Menurut Kriyantono (2008:106) mengatakan ...
Planning a field study is a critical first step in ensuring successful research. Here are some steps to follow when preparing your field study: 1. Define your research question. When developing a good research question, you should make it clear, concise, and specific.
Field research, field studies, or fieldwork is the collection of raw data outside a laboratory, library, or workplace setting. The approaches and methods used in field research vary across disciplines.For example, biologists who conduct field research may simply observe animals interacting with their environments, whereas social scientists conducting field research may interview or observe ...
Field research involves observations of free-living wild animals in their natural habitats while minimizing perturbations or disturbances to their environment or behavior. Field excursions may require some or all of the following (Lagler 1956): funding for travel, salary, supplies, and lodging; field assistants to help with data collection ...
Field research is research done in natural surroundings. It is used in biology to contrast with research done in the laboratory . Field research is defined as a qualitative method of data collection that aims to observe, interact and understand people while they are in a natural environment. For example, nature conservationists observe behavior ...
PENELITIAN LAPANGAN (FIELD RESEARCH) FADLUN MAROS - JULIAN ELITEAR ARDI TAMBUNAN - ERNAWATI KOTO KELAS KOMINFO ANGKATAN III MAGISTER ILMU KOMUNIKASI FAKULTAS ILMU SOSIAL DAN ILMU POLITIK UNIVERSITAS SUMATERA UTARA 2016 PENDAHULUAN Hakikat dari tujuan Ilmu pengetahuan adalah menemukan kebenaran, jalan untuk sampai pada tujuan ini berberbeda-beda tergantung waktu, sifat dan metodenya.
MAGISTER ILMU KOMUNIKASI FAKULTAS ILMU SOSIAL DAN ILMU POLITIK UNIVERSITAS SUMATERA UTARA 2016 Kelas Kominfo Angkatan III PENELITIAN LAPANGAN (FIELD RESEARCH) FADLUN MAROS - JULIAN ELITEAR ARDI TAMBUNAN - ERNAWATI KOTO PENGERTIAN Mengadakan pengamatan secara langsung untuk memperoleh informasi yang dibutuhkan Studi Kasus Fenomenologi Etnometodologi Interaksi Simbolik Etnografi Biografi ...
(Field Research) yang juga dianggap sebagai pendekatan luas dalam penelitian kualitatif. Ide penting dari jenis penelitian ini adalah bahwa peneliti berangkat ke lapangan untuk mengadakan pengamatan langsung tentang sesuatu fenomena yang terjadi. Dalam hal ini lokasi penelitian yang akan peneliti lakukan pengamatan
Disamping itu dengan menggunakan studi pustaka penulis dapat memperoleh informasi tentang teknik-teknik penelitian yang diharapkan, sehingga pekerjaan peneliti tidak merupakan duplikasi. 2. Studi Lapangan (Field Research) Yaitu peninjauan yang dilakukan langsung oleh penulis pada Polsek Majalaya yang menjadi objek penelitian dengan tujuan yakni ...
Selain itu karena masalah yang dicermati adalah suatu bentuk realita yang abstrak, dimana indikatornya hanya dapat diketahui melalui ucapan, sikap moralitas dan perilaku atau tindakan. Menurut Moleong (2012: 26), Penelitian lapangan (Field Research) dapat juga dianggap sebagai pendekatan luas dalam penelitian kualitatif atau sebagai
Kuantitatif, Mixed Methods, serta Research & Development, ed. oleh Rusmini (Jambi: Pusaka Jambi, 2017), 125. 3 Sony Vaisal Rinaldi dan Bagya Mujianto, Metodologi Penelitian dan Statistik (Badan Pengembangan dan Pemberdayaan Sumber Daya Manusia Kesehatan, 2017), 57.
Oleh sebab itu, salah satu aspek penting dalam field research adalah si peneliti sebaiknya memiliki apa yang oleh Neuman[6] diistilahkan sebagai sikap keasingan. Peneliti sebaiknya berasal dari kalangan yang sama sekali berbeda latar belakang dengan subjek penelitian sehingga memiliki kemampuan untuk menyerap informasi yang terasa asing dari ...
Penelitian ini pada dasarnya merupakan penelitian lapangan (field research) yaitu penelitian yang berusaha memahami fenomena apa yang dialami oleh subjek penelitian dengan suatu konteks khusus yang alamiyah.1 Penelitian ini difokuskan pada implementasi model pembelajaran cooperative dalam upaya peningkatan
ilmiah berbasis Uji Kompetensi Lapangan/Field Study secara individual. 4) Berpenampilan sopan (memunculkan wajah pada saat ikut media zoom, dsb.); 5) Ketua kelompok mahasiswa/yang mewakili memenuhi undangan monev secara virtual dan memberikan laporan secara lisan/tertulis (file/foto/ film) terkait dengan kegiatan UKL/Field Study.
Apa itu definisi dari metodologi penelitian, apa saja yang perlu dilakukan saat melakukan penelitian. ... Lecture Note Week 1 : Research Methodology. Research Methods. Research. Methodology ...
menggunakan lapangan (field research), dan studi pustaka (library research) yaitu penelitian yang dilakukan dengan cara terjun langsung kelapangan atau daerah objek penelitian guna memperoleh data yang ... kesimpulan bahwa sesuatu itu benar sesuai atau tidak dengan hukum Islam4, atau untuk mendapatkan landasan dan konsep dasar dalam agama,
A trusted reference in the field of psychology, offering more than 25,000 clear and authoritative entries. ... APA.org; APA Style; APA Services; Divisions; About APA; Events; Join APA; Help; Cart ; APA Dictionary of Psychology. Search Button. field research. Share button. Updated on 04/19/2018. Browse Dictionary.
36 BAB II METODE PENELITIAN A. Jenis Penelitian Dalam penelitian ini peneliti menggunakan metode penelitian lapangan (Field Research) dengan pendekatan kualitatif. Menurut Bogdan dan Taylor, dalam (Moleong, 2002:3), metode kualitatif sebagai penelitian yang menghasilkan data deskriptif berupa kata-kata tertulis atau dari orang-orang yang diamati sebagai objek penelitian.