Terrorism Essay for Students and Teacher
500+ words essay on terrorism essay.
Terrorism is an act, which aims to create fear among ordinary people by illegal means. It is a threat to humanity. It includes person or group spreading violence, riots, burglaries, rapes, kidnappings, fighting, bombings, etc. Terrorism is an act of cowardice. Also, terrorism has nothing to do with religion. A terrorist is only a terrorist, not a Hindu or a Muslim.


Types of Terrorism
Terrorism is of two kinds, one is political terrorism which creates panic on a large scale and another one is criminal terrorism which deals in kidnapping to take ransom money. Political terrorism is much more crucial than criminal terrorism because it is done by well-trained persons. It thus becomes difficult for law enforcing agencies to arrest them in time.
Terrorism spread at the national level as well as at international level. Regional terrorism is the most violent among all. Because the terrorists think that dying as a terrorist is sacred and holy, and thus they are willing to do anything. All these terrorist groups are made with different purposes.
Causes of Terrorism
There are some main causes of terrorism development or production of large quantities of machine guns, atomic bombs, hydrogen bombs, nuclear weapons, missiles, etc. rapid population growth, Politics, Social, Economic problems, dissatisfaction of people with the country’s system, lack of education, corruption, racism, economic inequality, linguistic differences, all these are the major elements of terrorism, and terrorism flourishes after them. People use terrorism as a weapon to prove and justify their point of view. The riots among Hindus and Muslims are the most famous but there is a difference between caste and terrorism.
The Effects Of Terrorism
Terrorism spreads fear in people, people living in the country feel insecure because of terrorism. Due to terrorist attacks, millions of goods are destroyed, the lives of thousands of innocent people are lost, animals are also killed. Disbelief in humanity raises after seeing a terrorist activity, this gives birth to another terrorist. There exist different types of terrorism in different parts of the country and abroad.
Today, terrorism is not only the problem of India, but in our neighboring country also, and governments across the world are making a lot of effort to deal with it. Attack on world trade center on September 11, 2001, is considered the largest terrorist attack in the world. Osama bin Laden attacked the tallest building in the world’s most powerful country, causing millions of casualties and death of thousands of people.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Terrorist Attacks in India
India has suffered several terrorist attacks which created fear among the public and caused huge destruction. Here are some of the major terrorist attacks that hit India in the last few years: 1991 – Punjab Killings, 1993 – Bombay Bomb Blasts, RSS Bombing in Chennai, 2000 – Church Bombing, Red Fort Terrorist Attack,2001- Indian Parliament Attack, 2002 – Mumbai Bus Bombing, Attack on Akshardham Temple, 2003 – Mumbai Bombing, 2004 – Dhemaji School Bombing in Assam,2005 – Delhi Bombings, Indian Institute of Science Shooting, 2006 – Varanasi Bombings, Mumbai Train Bombings, Malegaon Bombings, 2007 – Samjhauta Express Bombings, Mecca Masjid Bombing, Hyderabad Bombing, Ajmer Dargah Bombing, 2008 – Jaipur Bombings, Bangalore Serial Blasts, Ahmedabad Bombings, Delhi Bombings, Mumbai Attacks, 2010 – Pune Bombing, Varanasi Bombing.
The recent ones include 2011 – Mumbai Bombing, Delhi Bombing, 2012 – Pune Bombing, 2013 – Hyderabad Blasts, Srinagar Attack, Bodh Gaya Bombings, Patna Bombings, 2014 – Chhattisgarh Attack, Jharkhand Blast, Chennai Train Bombing, Assam Violence, Church Street Bomb Blast, Bangalore, 2015 – Jammu Attack, Gurdaspur Attack, Pathankot Attack, 2016 – Uri Attack, Baramulla Attack, 2017 – Bhopal Ujjain Passenger Train Bombing, Amarnath Yatra Attack, 2018 Sukma Attack, 2019- Pulwama attack.
Agencies fighting Terrorism in India
Many police, intelligence and military organizations in India have formed special agencies to fight terrorism in the country. Major agencies which fight against terrorism in India are Anti-Terrorism Squad (ATS), Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), National Investigation Agency (NIA).
Terrorism has become a global threat which needs to be controlled from the initial level. Terrorism cannot be controlled by the law enforcing agencies alone. The people in the world will also have to unite in order to face this growing threat of terrorism.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Anti Terrorism
Students are often asked to write an essay on Anti Terrorism in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Anti Terrorism
Understanding terrorism.
Terrorism is a violent act done by people or groups to create fear. They use violence to achieve political, religious, or ideological goals. It is a major global concern because it threatens peace and security.
What is Anti-Terrorism?
Anti-terrorism involves actions taken to prevent terrorism. It includes laws, policies, and actions that governments and organizations use to stop terrorist activities. Anti-terrorism aims to keep people safe and maintain peace in society.
Importance of Anti-Terrorism
Anti-terrorism is important to ensure safety and peace. It helps protect people from harm and fear. Without anti-terrorism measures, terrorists might cause more damage and fear. This could disrupt our lives and society.
Role of Individuals in Anti-Terrorism
Everyone can help fight terrorism. We can report suspicious activities to the authorities. We can also promote peace and understanding among different cultures and religions. By doing these things, we can help prevent terrorism.
In conclusion, anti-terrorism is crucial for peace and security. Everyone has a role to play in preventing terrorism. Let’s work together to create a safer and more peaceful world.
250 Words Essay on Anti Terrorism
Terrorism is a scary word. It means acts of violence that aim to create fear and harm innocent people. These acts are often done for political, religious, or ideological reasons.
Anti-terrorism means actions taken to prevent and stop terrorism. It includes laws, policies, and actions that aim to keep people safe from terrorist acts.
Anti-terrorism is important because it helps to keep us safe. It stops harmful acts before they can happen. It also helps to catch those who plan to do harm and bring them to justice.
How Anti-Terrorism Works
Anti-terrorism works in many ways. Intelligence agencies gather information about potential threats. They use this information to stop plans for terrorist acts. Police and security forces also play a big role. They enforce laws and provide security to keep people safe.
The Role of Everyone
We all have a role in anti-terrorism. We can stay alert and report anything suspicious. We can also support laws and policies that aim to prevent terrorism.
In conclusion, anti-terrorism is a vital part of keeping our world safe. It involves everyone, from intelligence agencies to everyday people. By understanding and supporting anti-terrorism, we can all help to create a safer world.
500 Words Essay on Anti Terrorism
Terrorism is a big problem in our world today. It is when a person or group tries to scare others by using violence. They often want to change something in their country or the world. Many times, they hurt innocent people.
Anti-terrorism is the opposite of terrorism. It is all the things we do to stop terrorism. Governments, police, and even ordinary people can all work against terrorism. This can include making laws against terrorism, catching people who plan to do terrorist acts, and teaching people about the dangers of terrorism.
Anti-terrorism is very important. It helps to keep people safe. Without it, terrorists might feel free to do whatever they want. This could lead to more violence and fear. Anti-terrorism also helps to protect our rights and freedoms. If terrorists can change our way of life through fear, then we lose our freedom.
Ways to Counter Terrorism
There are many ways to fight against terrorism. One is through laws. Governments can make laws that make it harder for terrorists to plan and carry out attacks. They can also make punishments for terrorism very severe to discourage people from becoming terrorists.
Another way is through security. This can include things like police and soldiers, but also things like cameras and locks. Security can make it harder for terrorists to attack and easier for us to catch them.
Education is also a powerful tool against terrorism. By teaching people about the dangers of terrorism and the value of peace, we can discourage them from becoming terrorists. We can also teach them to recognize signs of terrorism and report them to the authorities.
Every person can play a part in anti-terrorism. We can all be aware of our surroundings and report anything suspicious. We can also support laws and policies that fight against terrorism. And, perhaps most importantly, we can refuse to be afraid. Terrorists want to make us live in fear. By choosing to live our lives normally, we deny them their victory.
Anti-terrorism is a vital part of keeping our world safe and free. Through laws, security, and education, we can all fight against terrorism. It may seem like a big, scary problem, but remember, every person can make a difference. By standing together, we can defeat terrorism and protect our way of life.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Apiculture
- Essay on Anxiety And Depression
- Essay on Home Sweet Home
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Does Counter-Terrorism Work? by Richard English review – a thoughtful and authoritative analysis
The Belfast academic offers vitally important lessons about government strategies, from Northern Ireland to the Middle East, warning that few campaigns are a complete success
I n January 2002, during his State of the Union address, President George W Bush said that in “four short months” the US had “rallied a great coalition, captured, arrested and rid the world of thousands of terrorists … and terrorist leaders who urged followers to sacrifice their lives are running for their own”.
The term “war on terror” had been coined a few days after al-Qaida’s attacks of 9/11 to describe the most extensive and ambitious counter-terrorism operation the world had seen. As Bush spoke, it all seemed to be going rather well.
Two decades later, with more than 300,000 people killed in Iraq, according to some estimates, and perhaps 240,000 deaths in Afghanistan, the violence of the “war on terror” can be seen to have created further chaos and carnage. Even excluding Iraq and Afghanistan, the numbers killed in terrorist attacks around the world rose from 109 a month in the years before 9/11, according to one study , to 158 a month during the six years that followed. Meanwhile, some of those whom Bush said were running for their lives are now in power in Kabul.
In Northern Ireland , on the other hand, the conflict came largely to an end – after 30 years – once British governments began to use the military and police to contain, rather than attempt to brutally extirpate, anti-state violence. Security forces patiently developed their intelligence-gathering capacities, while government ministers acknowledged the political causes of terrorism and, eventually, formed partnerships with those whom they had been fighting.
Richard English, the author of Does Counter-Terrorism Work? , is a professor of political history at Queen’s University Belfast, and has dedicated decades to the analysis of terrorism and to governments’ efforts to overcome it. Given that the choices made in counter-terrorism policy impact directly upon each of us every day, it is a vitally important area of study.
His previous work includes a 2016 volume, Does Terrorism Work? , and a highly regarded history of the IRA . Here, he offers a thoughtful and authoritative dissection of the counter-terrorism efforts of the “war on terror”, Northern Ireland’s Troubles and the Israel-Palestinian conflict, and the lessons that each can offer.
English believes that post-9/11 counter-terrorism was far too short-termist, that the histories of Afghanistan and Iraq were “substantially ignored in a disgraceful fashion” and that the US became overly impressed with its own early military successes in both countries.
In Iraq, the claim that the removal of Saddam Hussein from power was a necessary part of a global counter-terrorist campaign was, of course, founded on the false claim that Saddam was supporting al-Qaida and the mistaken belief that he possessed weapons of mass destruction. Moreover, English writes, the assumption that the Middle East could be recast “through naive invasion” took no account of the region’s past, its complex allegiances, or the possibility of something simply going wrong.
He cautions that very few counter-terrorism campaigns will ever achieve complete strategic success. Unconvinced by those who claim bullishly that the Provisional IRA was “defeated”, he argues persuasively that the republican movement’s sustainable campaign of violence was suspended only because its pragmatic leaders decided that they might more likely achieve their objective – a united Ireland – by peaceful means. Equally, he is sceptical of those among his fellow academics who argue that counter-terrorism operations will inevitably promote terrorism.

However, he writes, there are times when “those who criticise counter-terrorists for worsening their state’s strategic position regarding terrorism, and those who celebrate tactical-operational successes against terrorist adversaries, might shout past each other while yet both being right”.
English judges that if any counter-terrorism campaign is to achieve even partial strategic victory, it must be conducted in a patient, well-resourced manner, with clear objectives. Given that terrorists often seek to provoke outrage and overreaction, the public should be encouraged to be realistic about the limits to what can be accomplished.
He also concludes that to avoid failure, counter-terrorist efforts must be integrated into broader political initiatives: “We should not mistake the terrorist symptom for the more profound issues that are at stake.”
Although this book was written before the Hamas attacks of 7 October and the war in Gaza, English was already convinced that Israeli counter-terrorism tactics, no matter how carefully conceived or brilliantly executed, will not resolve the conflict unless there is a strategic engagement with Palestinian grievances and desire for statehood.
Finally, he cautions that his three case studies present serious warnings about the self-harm that can be inflicted by state actions judged to lack morality. All three have involved the abuse of prisoners; that an overreliance on aggressive military methods can shatter public support; that technical surveillance should be lawful and proportionate; and, as a senior British police officer warned in a report published this month , that there are serious questions to be asked about the morality and legality of allowing informants within terrorist organisations to commit serious crimes.
“A successful counter-terrorism will be a just counter-terrorism,” English writes: legally bound, accountable and proportionate. To stray from this, he says, risks delegitimising the objectives of the state. Or as a mural in Northern Ireland used to say: “When those who make the law, break the law, in the name of the law, there is no law.”
Ian Cobain is the author of Anatomy of a Killing: Life and Death on a Divided Island (Granta)
Does Counter-Terrorism Work? by Richard English is published by Oxford University Press (£25). To support the Guardian and Observer order your copy at guardianbookshop.com . Delivery charges may apply
- Politics books
- The Observer
- UK security and counter-terrorism
- Counter-terrorism policy
- Northern Ireland
- Israel-Gaza war
- Afghanistan
Most viewed
Terrorism in the United States of America Essay
Introduction.
Terrorism is a serious problem affecting the United States of America that is likely to worsen in the coming years. The number of terrorist groups operating within the borders has increased over the past decade. Data provided by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) shows that white supremacists pose the greatest risk to the nation’s security. Moreover, anarchists and religious extremists have been cited as perpetrators of terrorist activities within the US. Common types of terrorism include right-wing terrorism (white supremacists and anti-government extremists), left-wing terrorism, and religious terrorism. Recent events following the death of George Floyd have revealed the new face of terrorism in the US. The spread of false information, conspiracy theories, and incitements to violence are some of the means that terrorist groups are using to advance their agenda. Aryan Nations and the Ku Klux Klan are terrorist organizations that continue to promote racial and religious violence as well as anti-Semitic ideas.
Domestic Terrorist Organizations
Aryan nations.
Aryan Nations (AN) is a white supremacist terrorist organization that is headquartered in Hayden, Idaho. It is a form of right-wing terrorism that is anti-Semitic and neo-Nazi, and that was founded by Richard Girnt Butler in 1977. Its main objective is to establish a white state that excludes other races by fighting against people that pose a threat to the white race, including the Jews and African Americans (Perliger, 2020). Constructivism theory can be used to explain the development and motivations of AN. Originally, it was a branch of the Christian Identity church that has two core teachings: whites are the true Israelites and Jews originated from a union between Satan and Eve. The group has been involved in several criminal activities, hence its classification by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) as a terrorist threat in 2001. Moreover, it is founded on a wide spectrum of racist and anti-Semitic ideas that promote racial intolerance (Perliger, 2020). The organization has been described by the RAND Corporation as a pioneer nationwide terrorist network in the US.
Aryan Nations has a single leader who makes all the group’s decisions. Unlike other terrorist organizations, it lacks a hierarchical structure and its activities are determined by the leader. It has been infiltrated by the FBI through an informant. Dave Hall, the group’s propaganda minister was an informant who exposed the organization’s illegal activities (Perliger, 2020). He reported directly to Special Agent Tym Burkey, a security officer who was helping Dayton’s organized Jewish community fight the group’s hate campaign. AN is linked to other terrorist groups, including the Ku Klux Klan (KKK), National Alliance, and The Silent Brotherhood (Perliger, 2020). The group is funded privately by individuals who support its ideologies and through its involvement in criminal activities. It lacks a strong organization and communication strategy, and it relies on the internet to conduct recruitments and spread its ideologies.
In recent years, wrangles have developed within the organization since the death of its founder, and splinter groups have emerged. It weakened in 2001 after losing its Northern Idaho compound where it was headquartered (Perliger, 2020). The group might disintegrate in the future because of its dwindling number of followers, leadership wrangles, and a lack of finances to fund its activities. Law enforcement agencies have heightened surveillance on groups and individuals deemed to promote terrorism in the US. Therefore, people might be afraid of donating to their initiatives and joining them as members for fear of victimization and prosecution.
Ku Klux Klan
The KKK refers to a domestic left-wing terrorist group that uses fear to advance its white supremacist ideologies. The original group was disbanded in the 1870s, and it was revived in 1915 as a new outfit. The organization had more than 4 million members in the 1920s, and it was financed from member contributions and the sale of publications and costumes. Its objectives include the suppression of African Americans, Catholics, Jews, immigrants, leftists, and members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) community (Jones et al., 2020). Its motivations and ideologies can be explained using the constructivism theory because terrorism is a social construct. The group operates primarily in the Southern United States. They are active in several states, including Mississippi, Alabama, Kentucky, Georgia, Texas, Arkansas, Tennessee, Virginia, Florida, Illinois, Missouri, and North Carolina among others. Affiliate groups include Noble Klans of America, United Klans of America, the White Knights of Texas, and the Rebel Brigade Knights True Invisible Empire among others.
The group’s organization involves a hierarchical structure that includes a titular head, leaders for each congressional district, and county heads. The overall leader is referred to as the Grand Dragon while the head of a congressional district is referred to as the Grand Titan. The counties are overseen by a head known as the Grand Giant, who is responsible for organizing militia members and supplying them with weapons. The Grand Dragon makes the group’s most critical decisions and receives frequent reports from district heads regarding the organization’s activities. The KKK is funded primarily by individuals who support the group’s ideologies. Counterintelligence program (COINTELPRO) refers to a series of activities conducted by the FBI between 1956 and 1979 to disrupt political organizations that destabilized the US (Perliger, 2020). COINTELPRO-White Hate program involved the infiltration of the KKK by FBI agents through overt techniques that included paying informers, bribing Klansmen, and the use of wiretaps and bugs.
The KKK has experienced a steady decline in membership in the past decade. However, the organization continues to promote its ideologies and recruit more people. Its new techniques include creating new websites, opening accounts for donations, and creating content that spreads its ideologies (Jones et al., 2020). In the future, the organization is likely to plateau because of poor leadership, wrangles within the group, and the inability to create and maintain alliances. Moreover, the group has numerous affiliate hate groups. Therefore, the lack of a stable leadership system is a risk to the group’s stability. Moreover, increased surveillance and monitoring by security agencies hamper their activities around the country.
Terrorism is a serious threat to the security of the United States of America. For many decades, security agencies in the country have implemented several measures to curb the rise in terrorism within the country’s borders. Right-wing, left-wing, and religious forms of terrorism are common in the US. Aryan Nations (AN) and the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) are terrorist groups that have operated in the US for decades. They are funded mainly by individuals who subscribe to their ideologies. Their involvement in racial and anti-Semitic criminal activities renders them, terrorist groups, as classified by the FBI. The groups might disintegrate in the future because of leadership wrangles and the lack of funding. Moreover, increased surveillance by security agencies has hampered their recruitment and fundraising activities.
Jones, S. G., Doxsee, C., & Harrington, N. (2020). The escalating terrorism problem in the United States . Center for strategic and International Studies. Web.
Perliger, A. (2020). American zealots: Inside right-wing domestic terrorism . Columbia University Press.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, June 8). Terrorism in the United States of America. https://ivypanda.com/essays/terrorism-in-the-united-states-of-america/
"Terrorism in the United States of America." IvyPanda , 8 June 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/terrorism-in-the-united-states-of-america/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Terrorism in the United States of America'. 8 June.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Terrorism in the United States of America." June 8, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/terrorism-in-the-united-states-of-america/.
1. IvyPanda . "Terrorism in the United States of America." June 8, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/terrorism-in-the-united-states-of-america/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Terrorism in the United States of America." June 8, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/terrorism-in-the-united-states-of-america/.
- The Ku Klux Klan in the US: Historical and Cultural Information
- The Ku Klux Klan
- Ku Klux Klan Organization in the 1860-1960s
- Ku Klux Klan, Its Creation History and Activities
- Social Issues: Police Protection of the Ku Klux Klan
- Domestic Terrorism in the United States of America
- Ku Klux Klan and Fear-Fueled Hatred
- The Ku Klux Klan Role in Southern Politics
- The History of Ku Klux Klan: A Terrorist Organization Founded in the Southern States After the American Civil War
- Adolf Hitler's Anti-Semitic "Final Solution"
- The Use of Intelligence Collection Systems
- Counterterrorism and Intelligence
- Task Force and the Fusion Center: Terrorism Prevention
- Fusion Centers: The Role in Terrorism Prevention
- Australian Anti-Terrorism Laws
Your Article Library
Essay on anti-terrorism movements.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Terrorism and anti-terrorism movements have gained momentum over the past few years, particularly since the 9/11 attacks on the twin towers of the World Trade Center in 2001. Let us look at the dynamics of terrorism, and the factors that have led to the re-emergence of terrorism in the twenty first century.
Terrorism as a form of violence is as old as recorded history. Over centuries, it has been used to intimidate governments and strike fear into societies all over the world. Throughout the twentieth century, terrorist organizations have used acts of violence to focus attention on their causes.
These tactics have also been used to pressurize governments to give into their demands. On the other hand, various governments themselves have used terrorism to maintain their power. To a certain extent, terrorist organizations and incidents have shaped our world.
Terrorism is a special form of political violence. It is not a philosophy or a political movement. Terrorism is a weapon or method, which has been used throughout history by both states and sub-state organizations for a whole variety of political causes or purposes.
This special form of political violence has five major characteristics:
1. It is premeditated and aims at creating a climate of extreme fear or terror.
2. It is directed at a wider audience or target than the immediate victims of the violence.
3. It involves attacks on random and symbolic targets, including civilians.
4. The acts of violence committed are seen by the society in which they occur as extra-normal, in the literal sense that they breach the social norms, thus causing a sense of outrage.
5. Terrorism is generally used to try to influence political behavior in some way: for example, to force opponents into conceding some or all of the perpetrators demands, to provoke an over-reaction, to serve as a catalyst for a more general conflict or to publicize a political or religious cause, to inspire followers to emulate violent attacks, to give vent to deep hatred .and the thirst for revenge, and to help undermine governments and institutions designated as enemies by the terrorists.
Terrorism is a broad concept. It has been classified on the criterion of the extent and intensity of its operations. War crimes and mass terror have been, and continue to be committed by regimes. This poses a severe problem for humanity, much more severe than the containment and reduction of factional terror by tiny groups. Once regimes come to assume that their ends justify the means, they tend to get locked into a spiral of terror and counter-terror against their adversaries.
A distinction has to be made between international terrorism, involving the citizens of two or more states, and domestic or internal terrorism which confines its activities within the borders of a specific state or province.
A further complication is that almost all prolonged domestic terrorist campaigns have an international dimension. In most cases, their leaders expend considerable effort seeking external sources of political support, cash, weapons, safe haven, and other useful assets, from friendly governments and political movements as well as from their own diaspora.
No broad categorization can do full justice to the variety and complexity of the modern phenomenon of terrorism. However, there is abundant evidence of active groups currently involved in terrorist activity motivated by one or more of the following: nationalism, separatism, racism, ultra-left ideology, and religious fundamentalism.
Although the ending of the Cold War and the collapse of the former Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact communist regimes dramatically reduced the number of states involved in the routine use of regime terror and state sponsorship of terrorism for both domestic and foreign policy purposes, it by no means eradicated these forms of terrorism. And with regard to terrorism, this is still a low probability threat even if potentially of high consequence.
The phenomenon of terrorism is not a novel apparition but a time-honored tool of forceful political, religious, and social agitation. The face of terrorism began to change after 1968. The terrorist groups of that age, which were derived from the New Left and inspired by the socialist rhetoric of Marxism, in the 1960s and 1970s, were essentially ideological in nature and spirit in line with other contemporary political developments, ethnic, separatist, as well as religious motives have for the most part, driven recent manifestations of terrorism.
Ethnic and separatist political violence is an ancient but highly volatile phenomenon. For example, it might be argued that organizations such as the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and the Euzkadi Ta Askatasuna/Basque Fatherland and Liberty (ETA) were formed long before the more recent wave of terrorist groups surfaced. Such a position would be correct if one discounted the truth of the aforementioned groups’ operational intermittency.
Quite significantly, both the IRA and ETA intensified their respective campaigns against the British and Spanish governments after lying in the doldrums for years, whereas the several Red armies, (the Brigate Rosse, or Red Brigades, in Italy; the Rote Armee Fraktion [the Baader-Meinhof gang] in Germany; Action Direct In France; and Cellules Communistes Cpmbatantes in Belgium) have suffered decline and eventual extinction.
In the meantime, the Kosovo Liberation Army, the Chechen resistance, and several other political violence movements prepared to use terrorism in furtherance of their goals. These groups were conspicuous because of their prolonged existence. Their resilience can be explained by the fact that they made use of a greater reservoir of support than their ideological brethren.
The problem of the resurgence of religiously motivated terrorism also needs to be looked into. When focusing on religious terrorism, it is necessary to consider that its variety for religious terrorism is definitely not the exclusive preserve of a single religion or denomination.
Related Articles:
- Origin and Development of Terrorism in India
- Terrorism in Other Countries
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in A - General Economics and Teaching
- Browse content in A1 - General Economics
- A10 - General
- A12 - Relation of Economics to Other Disciplines
- A13 - Relation of Economics to Social Values
- A14 - Sociology of Economics
- Browse content in A2 - Economic Education and Teaching of Economics
- A29 - Other
- Browse content in B - History of Economic Thought, Methodology, and Heterodox Approaches
- B0 - General
- Browse content in B1 - History of Economic Thought through 1925
- B11 - Preclassical (Ancient, Medieval, Mercantilist, Physiocratic)
- B12 - Classical (includes Adam Smith)
- Browse content in B2 - History of Economic Thought since 1925
- B20 - General
- B21 - Microeconomics
- B22 - Macroeconomics
- B25 - Historical; Institutional; Evolutionary; Austrian
- B26 - Financial Economics
- Browse content in B3 - History of Economic Thought: Individuals
- B31 - Individuals
- Browse content in B4 - Economic Methodology
- B41 - Economic Methodology
- Browse content in B5 - Current Heterodox Approaches
- B55 - Social Economics
- Browse content in C - Mathematical and Quantitative Methods
- Browse content in C0 - General
- C00 - General
- C02 - Mathematical Methods
- Browse content in C1 - Econometric and Statistical Methods and Methodology: General
- C10 - General
- C11 - Bayesian Analysis: General
- C12 - Hypothesis Testing: General
- C13 - Estimation: General
- C14 - Semiparametric and Nonparametric Methods: General
- C15 - Statistical Simulation Methods: General
- C19 - Other
- Browse content in C2 - Single Equation Models; Single Variables
- C21 - Cross-Sectional Models; Spatial Models; Treatment Effect Models; Quantile Regressions
- C22 - Time-Series Models; Dynamic Quantile Regressions; Dynamic Treatment Effect Models; Diffusion Processes
- C23 - Panel Data Models; Spatio-temporal Models
- C24 - Truncated and Censored Models; Switching Regression Models; Threshold Regression Models
- C25 - Discrete Regression and Qualitative Choice Models; Discrete Regressors; Proportions; Probabilities
- C26 - Instrumental Variables (IV) Estimation
- Browse content in C3 - Multiple or Simultaneous Equation Models; Multiple Variables
- C31 - Cross-Sectional Models; Spatial Models; Treatment Effect Models; Quantile Regressions; Social Interaction Models
- C32 - Time-Series Models; Dynamic Quantile Regressions; Dynamic Treatment Effect Models; Diffusion Processes; State Space Models
- C33 - Panel Data Models; Spatio-temporal Models
- C34 - Truncated and Censored Models; Switching Regression Models
- C35 - Discrete Regression and Qualitative Choice Models; Discrete Regressors; Proportions
- C36 - Instrumental Variables (IV) Estimation
- Browse content in C4 - Econometric and Statistical Methods: Special Topics
- C41 - Duration Analysis; Optimal Timing Strategies
- C43 - Index Numbers and Aggregation
- Browse content in C5 - Econometric Modeling
- C51 - Model Construction and Estimation
- C52 - Model Evaluation, Validation, and Selection
- C53 - Forecasting and Prediction Methods; Simulation Methods
- C54 - Quantitative Policy Modeling
- Browse content in C6 - Mathematical Methods; Programming Models; Mathematical and Simulation Modeling
- C60 - General
- C61 - Optimization Techniques; Programming Models; Dynamic Analysis
- C62 - Existence and Stability Conditions of Equilibrium
- C63 - Computational Techniques; Simulation Modeling
- Browse content in C7 - Game Theory and Bargaining Theory
- C71 - Cooperative Games
- C72 - Noncooperative Games
- C73 - Stochastic and Dynamic Games; Evolutionary Games; Repeated Games
- C78 - Bargaining Theory; Matching Theory
- Browse content in C8 - Data Collection and Data Estimation Methodology; Computer Programs
- C81 - Methodology for Collecting, Estimating, and Organizing Microeconomic Data; Data Access
- C82 - Methodology for Collecting, Estimating, and Organizing Macroeconomic Data; Data Access
- C83 - Survey Methods; Sampling Methods
- Browse content in C9 - Design of Experiments
- C90 - General
- C91 - Laboratory, Individual Behavior
- C92 - Laboratory, Group Behavior
- C93 - Field Experiments
- Browse content in D - Microeconomics
- Browse content in D0 - General
- D00 - General
- D01 - Microeconomic Behavior: Underlying Principles
- D02 - Institutions: Design, Formation, Operations, and Impact
- D03 - Behavioral Microeconomics: Underlying Principles
- D04 - Microeconomic Policy: Formulation; Implementation, and Evaluation
- Browse content in D1 - Household Behavior and Family Economics
- D10 - General
- D11 - Consumer Economics: Theory
- D12 - Consumer Economics: Empirical Analysis
- D13 - Household Production and Intrahousehold Allocation
- D14 - Household Saving; Personal Finance
- D15 - Intertemporal Household Choice: Life Cycle Models and Saving
- D16 - Collaborative Consumption
- D18 - Consumer Protection
- D19 - Other
- Browse content in D2 - Production and Organizations
- D21 - Firm Behavior: Theory
- D22 - Firm Behavior: Empirical Analysis
- D23 - Organizational Behavior; Transaction Costs; Property Rights
- D24 - Production; Cost; Capital; Capital, Total Factor, and Multifactor Productivity; Capacity
- D29 - Other
- Browse content in D3 - Distribution
- D30 - General
- D31 - Personal Income, Wealth, and Their Distributions
- D33 - Factor Income Distribution
- Browse content in D4 - Market Structure, Pricing, and Design
- D40 - General
- D41 - Perfect Competition
- D43 - Oligopoly and Other Forms of Market Imperfection
- D44 - Auctions
- Browse content in D5 - General Equilibrium and Disequilibrium
- D50 - General
- D53 - Financial Markets
- D58 - Computable and Other Applied General Equilibrium Models
- Browse content in D6 - Welfare Economics
- D60 - General
- D61 - Allocative Efficiency; Cost-Benefit Analysis
- D62 - Externalities
- D63 - Equity, Justice, Inequality, and Other Normative Criteria and Measurement
- D64 - Altruism; Philanthropy
- D69 - Other
- Browse content in D7 - Analysis of Collective Decision-Making
- D70 - General
- D71 - Social Choice; Clubs; Committees; Associations
- D72 - Political Processes: Rent-seeking, Lobbying, Elections, Legislatures, and Voting Behavior
- D73 - Bureaucracy; Administrative Processes in Public Organizations; Corruption
- D74 - Conflict; Conflict Resolution; Alliances; Revolutions
- D78 - Positive Analysis of Policy Formulation and Implementation
- Browse content in D8 - Information, Knowledge, and Uncertainty
- D80 - General
- D81 - Criteria for Decision-Making under Risk and Uncertainty
- D82 - Asymmetric and Private Information; Mechanism Design
- D83 - Search; Learning; Information and Knowledge; Communication; Belief; Unawareness
- D84 - Expectations; Speculations
- D85 - Network Formation and Analysis: Theory
- D86 - Economics of Contract: Theory
- Browse content in D9 - Micro-Based Behavioral Economics
- D90 - General
- D91 - Role and Effects of Psychological, Emotional, Social, and Cognitive Factors on Decision Making
- D92 - Intertemporal Firm Choice, Investment, Capacity, and Financing
- Browse content in E - Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Browse content in E0 - General
- E00 - General
- E01 - Measurement and Data on National Income and Product Accounts and Wealth; Environmental Accounts
- E02 - Institutions and the Macroeconomy
- Browse content in E1 - General Aggregative Models
- E10 - General
- E11 - Marxian; Sraffian; Kaleckian
- E12 - Keynes; Keynesian; Post-Keynesian
- E13 - Neoclassical
- E19 - Other
- Browse content in E2 - Consumption, Saving, Production, Investment, Labor Markets, and Informal Economy
- E20 - General
- E21 - Consumption; Saving; Wealth
- E22 - Investment; Capital; Intangible Capital; Capacity
- E23 - Production
- E24 - Employment; Unemployment; Wages; Intergenerational Income Distribution; Aggregate Human Capital; Aggregate Labor Productivity
- E25 - Aggregate Factor Income Distribution
- E27 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E3 - Prices, Business Fluctuations, and Cycles
- E30 - General
- E31 - Price Level; Inflation; Deflation
- E32 - Business Fluctuations; Cycles
- E37 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E4 - Money and Interest Rates
- E40 - General
- E41 - Demand for Money
- E42 - Monetary Systems; Standards; Regimes; Government and the Monetary System; Payment Systems
- E43 - Interest Rates: Determination, Term Structure, and Effects
- E44 - Financial Markets and the Macroeconomy
- E47 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E5 - Monetary Policy, Central Banking, and the Supply of Money and Credit
- E50 - General
- E51 - Money Supply; Credit; Money Multipliers
- E52 - Monetary Policy
- E58 - Central Banks and Their Policies
- Browse content in E6 - Macroeconomic Policy, Macroeconomic Aspects of Public Finance, and General Outlook
- E60 - General
- E61 - Policy Objectives; Policy Designs and Consistency; Policy Coordination
- E62 - Fiscal Policy
- E63 - Comparative or Joint Analysis of Fiscal and Monetary Policy; Stabilization; Treasury Policy
- E65 - Studies of Particular Policy Episodes
- E69 - Other
- Browse content in E7 - Macro-Based Behavioral Economics
- E70 - General
- E71 - Role and Effects of Psychological, Emotional, Social, and Cognitive Factors on the Macro Economy
- Browse content in F - International Economics
- Browse content in F0 - General
- F02 - International Economic Order and Integration
- Browse content in F1 - Trade
- F10 - General
- F11 - Neoclassical Models of Trade
- F12 - Models of Trade with Imperfect Competition and Scale Economies; Fragmentation
- F13 - Trade Policy; International Trade Organizations
- F14 - Empirical Studies of Trade
- F15 - Economic Integration
- F16 - Trade and Labor Market Interactions
- F17 - Trade Forecasting and Simulation
- F18 - Trade and Environment
- Browse content in F2 - International Factor Movements and International Business
- F21 - International Investment; Long-Term Capital Movements
- F22 - International Migration
- F23 - Multinational Firms; International Business
- F24 - Remittances
- Browse content in F3 - International Finance
- F30 - General
- F31 - Foreign Exchange
- F32 - Current Account Adjustment; Short-Term Capital Movements
- F33 - International Monetary Arrangements and Institutions
- F34 - International Lending and Debt Problems
- F35 - Foreign Aid
- F36 - Financial Aspects of Economic Integration
- F37 - International Finance Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in F4 - Macroeconomic Aspects of International Trade and Finance
- F40 - General
- F41 - Open Economy Macroeconomics
- F42 - International Policy Coordination and Transmission
- F43 - Economic Growth of Open Economies
- F44 - International Business Cycles
- F45 - Macroeconomic Issues of Monetary Unions
- Browse content in F5 - International Relations, National Security, and International Political Economy
- F50 - General
- F51 - International Conflicts; Negotiations; Sanctions
- F52 - National Security; Economic Nationalism
- F53 - International Agreements and Observance; International Organizations
- F55 - International Institutional Arrangements
- F59 - Other
- Browse content in F6 - Economic Impacts of Globalization
- F62 - Macroeconomic Impacts
- F63 - Economic Development
- F64 - Environment
- Browse content in G - Financial Economics
- Browse content in G0 - General
- G01 - Financial Crises
- G02 - Behavioral Finance: Underlying Principles
- Browse content in G1 - General Financial Markets
- G10 - General
- G11 - Portfolio Choice; Investment Decisions
- G12 - Asset Pricing; Trading volume; Bond Interest Rates
- G14 - Information and Market Efficiency; Event Studies; Insider Trading
- G15 - International Financial Markets
- G18 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in G2 - Financial Institutions and Services
- G20 - General
- G21 - Banks; Depository Institutions; Micro Finance Institutions; Mortgages
- G22 - Insurance; Insurance Companies; Actuarial Studies
- G24 - Investment Banking; Venture Capital; Brokerage; Ratings and Ratings Agencies
- G28 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in G3 - Corporate Finance and Governance
- G32 - Financing Policy; Financial Risk and Risk Management; Capital and Ownership Structure; Value of Firms; Goodwill
- G33 - Bankruptcy; Liquidation
- G34 - Mergers; Acquisitions; Restructuring; Corporate Governance
- G35 - Payout Policy
- G38 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in H - Public Economics
- Browse content in H0 - General
- H00 - General
- Browse content in H1 - Structure and Scope of Government
- H10 - General
- H11 - Structure, Scope, and Performance of Government
- H12 - Crisis Management
- Browse content in H2 - Taxation, Subsidies, and Revenue
- H20 - General
- H21 - Efficiency; Optimal Taxation
- H22 - Incidence
- H23 - Externalities; Redistributive Effects; Environmental Taxes and Subsidies
- H24 - Personal Income and Other Nonbusiness Taxes and Subsidies; includes inheritance and gift taxes
- H25 - Business Taxes and Subsidies
- H26 - Tax Evasion and Avoidance
- Browse content in H3 - Fiscal Policies and Behavior of Economic Agents
- H30 - General
- H31 - Household
- Browse content in H4 - Publicly Provided Goods
- H40 - General
- H41 - Public Goods
- H42 - Publicly Provided Private Goods
- Browse content in H5 - National Government Expenditures and Related Policies
- H50 - General
- H51 - Government Expenditures and Health
- H52 - Government Expenditures and Education
- H53 - Government Expenditures and Welfare Programs
- H54 - Infrastructures; Other Public Investment and Capital Stock
- H55 - Social Security and Public Pensions
- H56 - National Security and War
- Browse content in H6 - National Budget, Deficit, and Debt
- H60 - General
- H61 - Budget; Budget Systems
- H62 - Deficit; Surplus
- H63 - Debt; Debt Management; Sovereign Debt
- Browse content in H7 - State and Local Government; Intergovernmental Relations
- H70 - General
- H71 - State and Local Taxation, Subsidies, and Revenue
- H72 - State and Local Budget and Expenditures
- H75 - State and Local Government: Health; Education; Welfare; Public Pensions
- H76 - State and Local Government: Other Expenditure Categories
- H77 - Intergovernmental Relations; Federalism; Secession
- Browse content in H8 - Miscellaneous Issues
- H83 - Public Administration; Public Sector Accounting and Audits
- H84 - Disaster Aid
- H87 - International Fiscal Issues; International Public Goods
- Browse content in I - Health, Education, and Welfare
- Browse content in I0 - General
- I00 - General
- Browse content in I1 - Health
- I10 - General
- I12 - Health Behavior
- I14 - Health and Inequality
- I15 - Health and Economic Development
- I18 - Government Policy; Regulation; Public Health
- I19 - Other
- Browse content in I2 - Education and Research Institutions
- I20 - General
- I21 - Analysis of Education
- I22 - Educational Finance; Financial Aid
- I23 - Higher Education; Research Institutions
- I24 - Education and Inequality
- I25 - Education and Economic Development
- I26 - Returns to Education
- I28 - Government Policy
- I29 - Other
- Browse content in I3 - Welfare, Well-Being, and Poverty
- I30 - General
- I31 - General Welfare
- I32 - Measurement and Analysis of Poverty
- I38 - Government Policy; Provision and Effects of Welfare Programs
- Browse content in J - Labor and Demographic Economics
- Browse content in J0 - General
- J00 - General
- J01 - Labor Economics: General
- J08 - Labor Economics Policies
- Browse content in J1 - Demographic Economics
- J10 - General
- J11 - Demographic Trends, Macroeconomic Effects, and Forecasts
- J12 - Marriage; Marital Dissolution; Family Structure; Domestic Abuse
- J13 - Fertility; Family Planning; Child Care; Children; Youth
- J14 - Economics of the Elderly; Economics of the Handicapped; Non-Labor Market Discrimination
- J15 - Economics of Minorities, Races, Indigenous Peoples, and Immigrants; Non-labor Discrimination
- J16 - Economics of Gender; Non-labor Discrimination
- J17 - Value of Life; Forgone Income
- J18 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J2 - Demand and Supply of Labor
- J20 - General
- J21 - Labor Force and Employment, Size, and Structure
- J22 - Time Allocation and Labor Supply
- J23 - Labor Demand
- J24 - Human Capital; Skills; Occupational Choice; Labor Productivity
- J26 - Retirement; Retirement Policies
- J28 - Safety; Job Satisfaction; Related Public Policy
- Browse content in J3 - Wages, Compensation, and Labor Costs
- J30 - General
- J31 - Wage Level and Structure; Wage Differentials
- J32 - Nonwage Labor Costs and Benefits; Retirement Plans; Private Pensions
- J33 - Compensation Packages; Payment Methods
- J38 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J4 - Particular Labor Markets
- J41 - Labor Contracts
- J42 - Monopsony; Segmented Labor Markets
- J45 - Public Sector Labor Markets
- J46 - Informal Labor Markets
- Browse content in J5 - Labor-Management Relations, Trade Unions, and Collective Bargaining
- J50 - General
- J51 - Trade Unions: Objectives, Structure, and Effects
- J52 - Dispute Resolution: Strikes, Arbitration, and Mediation; Collective Bargaining
- J53 - Labor-Management Relations; Industrial Jurisprudence
- J54 - Producer Cooperatives; Labor Managed Firms; Employee Ownership
- J58 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J6 - Mobility, Unemployment, Vacancies, and Immigrant Workers
- J60 - General
- J61 - Geographic Labor Mobility; Immigrant Workers
- J62 - Job, Occupational, and Intergenerational Mobility
- J63 - Turnover; Vacancies; Layoffs
- J64 - Unemployment: Models, Duration, Incidence, and Job Search
- J65 - Unemployment Insurance; Severance Pay; Plant Closings
- J68 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J7 - Labor Discrimination
- J71 - Discrimination
- Browse content in J8 - Labor Standards: National and International
- J81 - Working Conditions
- J88 - Public Policy
- Browse content in K - Law and Economics
- Browse content in K0 - General
- K00 - General
- Browse content in K1 - Basic Areas of Law
- K11 - Property Law
- K12 - Contract Law
- K13 - Tort Law and Product Liability; Forensic Economics
- K14 - Criminal Law
- K16 - Election Law
- Browse content in K3 - Other Substantive Areas of Law
- K31 - Labor Law
- K32 - Environmental, Health, and Safety Law
- K34 - Tax Law
- K37 - Immigration Law
- Browse content in K4 - Legal Procedure, the Legal System, and Illegal Behavior
- K41 - Litigation Process
- K42 - Illegal Behavior and the Enforcement of Law
- K49 - Other
- Browse content in L - Industrial Organization
- Browse content in L0 - General
- L00 - General
- Browse content in L1 - Market Structure, Firm Strategy, and Market Performance
- L10 - General
- L11 - Production, Pricing, and Market Structure; Size Distribution of Firms
- L12 - Monopoly; Monopolization Strategies
- L13 - Oligopoly and Other Imperfect Markets
- L14 - Transactional Relationships; Contracts and Reputation; Networks
- L16 - Industrial Organization and Macroeconomics: Industrial Structure and Structural Change; Industrial Price Indices
- Browse content in L2 - Firm Objectives, Organization, and Behavior
- L20 - General
- L21 - Business Objectives of the Firm
- L22 - Firm Organization and Market Structure
- L23 - Organization of Production
- L24 - Contracting Out; Joint Ventures; Technology Licensing
- L25 - Firm Performance: Size, Diversification, and Scope
- L26 - Entrepreneurship
- L29 - Other
- Browse content in L3 - Nonprofit Organizations and Public Enterprise
- L30 - General
- L31 - Nonprofit Institutions; NGOs; Social Entrepreneurship
- L32 - Public Enterprises; Public-Private Enterprises
- L33 - Comparison of Public and Private Enterprises and Nonprofit Institutions; Privatization; Contracting Out
- Browse content in L4 - Antitrust Issues and Policies
- L40 - General
- L41 - Monopolization; Horizontal Anticompetitive Practices
- L43 - Legal Monopolies and Regulation or Deregulation
- Browse content in L5 - Regulation and Industrial Policy
- L50 - General
- L51 - Economics of Regulation
- L52 - Industrial Policy; Sectoral Planning Methods
- L53 - Enterprise Policy
- Browse content in L6 - Industry Studies: Manufacturing
- L60 - General
- L66 - Food; Beverages; Cosmetics; Tobacco; Wine and Spirits
- Browse content in L7 - Industry Studies: Primary Products and Construction
- L71 - Mining, Extraction, and Refining: Hydrocarbon Fuels
- L78 - Government Policy
- Browse content in L8 - Industry Studies: Services
- L81 - Retail and Wholesale Trade; e-Commerce
- L83 - Sports; Gambling; Recreation; Tourism
- L86 - Information and Internet Services; Computer Software
- Browse content in L9 - Industry Studies: Transportation and Utilities
- L94 - Electric Utilities
- L98 - Government Policy
- Browse content in M - Business Administration and Business Economics; Marketing; Accounting; Personnel Economics
- Browse content in M1 - Business Administration
- M12 - Personnel Management; Executives; Executive Compensation
- M14 - Corporate Culture; Social Responsibility
- M16 - International Business Administration
- Browse content in M3 - Marketing and Advertising
- M31 - Marketing
- Browse content in M5 - Personnel Economics
- M50 - General
- M51 - Firm Employment Decisions; Promotions
- M52 - Compensation and Compensation Methods and Their Effects
- M53 - Training
- M54 - Labor Management
- M55 - Labor Contracting Devices
- Browse content in N - Economic History
- Browse content in N1 - Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics; Industrial Structure; Growth; Fluctuations
- N10 - General, International, or Comparative
- N11 - U.S.; Canada: Pre-1913
- N12 - U.S.; Canada: 1913-
- N13 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N15 - Asia including Middle East
- Browse content in N2 - Financial Markets and Institutions
- N20 - General, International, or Comparative
- N24 - Europe: 1913-
- N25 - Asia including Middle East
- Browse content in N3 - Labor and Consumers, Demography, Education, Health, Welfare, Income, Wealth, Religion, and Philanthropy
- N31 - U.S.; Canada: Pre-1913
- N33 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N34 - Europe: 1913-
- Browse content in N4 - Government, War, Law, International Relations, and Regulation
- N40 - General, International, or Comparative
- N45 - Asia including Middle East
- N47 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in N5 - Agriculture, Natural Resources, Environment, and Extractive Industries
- N50 - General, International, or Comparative
- N53 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N57 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in N7 - Transport, Trade, Energy, Technology, and Other Services
- N70 - General, International, or Comparative
- N72 - U.S.; Canada: 1913-
- Browse content in N9 - Regional and Urban History
- N97 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in O - Economic Development, Innovation, Technological Change, and Growth
- Browse content in O1 - Economic Development
- O10 - General
- O11 - Macroeconomic Analyses of Economic Development
- O12 - Microeconomic Analyses of Economic Development
- O13 - Agriculture; Natural Resources; Energy; Environment; Other Primary Products
- O14 - Industrialization; Manufacturing and Service Industries; Choice of Technology
- O15 - Human Resources; Human Development; Income Distribution; Migration
- O16 - Financial Markets; Saving and Capital Investment; Corporate Finance and Governance
- O17 - Formal and Informal Sectors; Shadow Economy; Institutional Arrangements
- O18 - Urban, Rural, Regional, and Transportation Analysis; Housing; Infrastructure
- O19 - International Linkages to Development; Role of International Organizations
- Browse content in O2 - Development Planning and Policy
- O22 - Project Analysis
- O23 - Fiscal and Monetary Policy in Development
- O24 - Trade Policy; Factor Movement Policy; Foreign Exchange Policy
- O25 - Industrial Policy
- Browse content in O3 - Innovation; Research and Development; Technological Change; Intellectual Property Rights
- O30 - General
- O31 - Innovation and Invention: Processes and Incentives
- O32 - Management of Technological Innovation and R&D
- O33 - Technological Change: Choices and Consequences; Diffusion Processes
- O34 - Intellectual Property and Intellectual Capital
- O38 - Government Policy
- O39 - Other
- Browse content in O4 - Economic Growth and Aggregate Productivity
- O40 - General
- O41 - One, Two, and Multisector Growth Models
- O42 - Monetary Growth Models
- O43 - Institutions and Growth
- O47 - Empirical Studies of Economic Growth; Aggregate Productivity; Cross-Country Output Convergence
- O49 - Other
- Browse content in O5 - Economywide Country Studies
- O50 - General
- O52 - Europe
- O53 - Asia including Middle East
- O55 - Africa
- O57 - Comparative Studies of Countries
- Browse content in P - Economic Systems
- Browse content in P1 - Capitalist Systems
- P10 - General
- P13 - Cooperative Enterprises
- P16 - Political Economy
- P17 - Performance and Prospects
- Browse content in P2 - Socialist Systems and Transitional Economies
- P20 - General
- P26 - Political Economy; Property Rights
- Browse content in P3 - Socialist Institutions and Their Transitions
- P31 - Socialist Enterprises and Their Transitions
- Browse content in P4 - Other Economic Systems
- P48 - Political Economy; Legal Institutions; Property Rights; Natural Resources; Energy; Environment; Regional Studies
- Browse content in P5 - Comparative Economic Systems
- P50 - General
- Browse content in Q - Agricultural and Natural Resource Economics; Environmental and Ecological Economics
- Browse content in Q0 - General
- Q02 - Commodity Markets
- Browse content in Q1 - Agriculture
- Q11 - Aggregate Supply and Demand Analysis; Prices
- Q13 - Agricultural Markets and Marketing; Cooperatives; Agribusiness
- Q15 - Land Ownership and Tenure; Land Reform; Land Use; Irrigation; Agriculture and Environment
- Q16 - R&D; Agricultural Technology; Biofuels; Agricultural Extension Services
- Q17 - Agriculture in International Trade
- Q18 - Agricultural Policy; Food Policy
- Browse content in Q2 - Renewable Resources and Conservation
- Q20 - General
- Q22 - Fishery; Aquaculture
- Q23 - Forestry
- Q25 - Water
- Q26 - Recreational Aspects of Natural Resources
- Q29 - Other
- Browse content in Q3 - Nonrenewable Resources and Conservation
- Q30 - General
- Q32 - Exhaustible Resources and Economic Development
- Q33 - Resource Booms
- Q34 - Natural Resources and Domestic and International Conflicts
- Q38 - Government Policy
- Browse content in Q4 - Energy
- Q40 - General
- Q41 - Demand and Supply; Prices
- Q42 - Alternative Energy Sources
- Q43 - Energy and the Macroeconomy
- Q48 - Government Policy
- Browse content in Q5 - Environmental Economics
- Q50 - General
- Q51 - Valuation of Environmental Effects
- Q52 - Pollution Control Adoption Costs; Distributional Effects; Employment Effects
- Q53 - Air Pollution; Water Pollution; Noise; Hazardous Waste; Solid Waste; Recycling
- Q54 - Climate; Natural Disasters; Global Warming
- Q56 - Environment and Development; Environment and Trade; Sustainability; Environmental Accounts and Accounting; Environmental Equity; Population Growth
- Q58 - Government Policy
- Browse content in R - Urban, Rural, Regional, Real Estate, and Transportation Economics
- Browse content in R1 - General Regional Economics
- R10 - General
- R11 - Regional Economic Activity: Growth, Development, Environmental Issues, and Changes
- R15 - Econometric and Input-Output Models; Other Models
- Browse content in R2 - Household Analysis
- R23 - Regional Migration; Regional Labor Markets; Population; Neighborhood Characteristics
- R29 - Other
- Browse content in R4 - Transportation Economics
- R40 - General
- R41 - Transportation: Demand, Supply, and Congestion; Travel Time; Safety and Accidents; Transportation Noise
- Browse content in R5 - Regional Government Analysis
- R58 - Regional Development Planning and Policy
- Browse content in Z - Other Special Topics
- Browse content in Z1 - Cultural Economics; Economic Sociology; Economic Anthropology
- Z10 - General
- Z11 - Economics of the Arts and Literature
- Z12 - Religion
- Z13 - Economic Sociology; Economic Anthropology; Social and Economic Stratification
- Z19 - Other
- Browse content in Z2 - Sports Economics
- Z21 - Industry Studies
- Z22 - Labor Issues
- Z29 - Other
- Browse content in Z3 - Tourism Economics
- Z30 - General
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About Oxford Economic Papers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
1. introduction, 2. on terrorism, 3. event data sets, 4. domestic and transnational terrorism: some data plots, 5. counterterrorism, 6. findings of the articles of the special issue, 7. concluding remarks, acknowledgements, terrorism and counterterrorism: an overview.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Todd Sandler, Terrorism and counterterrorism: an overview, Oxford Economic Papers , Volume 67, Issue 1, January 2015, Pages 1–20, https://doi.org/10.1093/oep/gpu039
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This introduction sets the stage for the articles collected in this special issue of Oxford Economic Papers . It begins by introducing essential concepts including domestic terrorism, transnational terrorism, defensive actions, proactive countermeasures, and guerrilla warfare. Three terrorist event databases, used by seven of the articles, are briefly introduced. These data sets are then used to display some stylized facts about domestic and transnational terrorism during the past four decades. Next, some essential strategic distinctions are drawn between defensive and proactive measures in the case of transnational terrorism when multiple countries are confronted by a common terrorist group. These strategic concerns vanish for domestic terrorism as a central government is able to internalize potential externalities. Finally, the key findings of the articles in the special issue are highlighted in two tables.
Terrorism is the premeditated use or threat to use violence by individuals or subnational groups to obtain a political or social objective through the intimidation of a large audience beyond that of the immediate noncombatant victims ( Enders and Sandler, 2012 , p.4). The two essential ingredients of terrorism are its violence and its political or social motive. Terrorists tend to employ shockingly violent acts, such as beheadings, downing of commercial airlines, bombings in public markets, and armed attacks in public places, to intimidate an audience. Their unpredictable and horrific attacks are meant to make everyone feel at risk even though the true likelihood of falling victim to a terrorist incident is rather minuscule, roughly equivalent to that of drowning in one's bathtub ( Mueller, 2006 ). Terrorists seek to circumvent normal channels for political change by traumatizing the public with brutal acts so that governments feel compelled to either address terrorist demands or divert public funds into hardening potential targets. Terrorist campaigns are more prevalent in liberal democracies, where the government's legitimacy hinges on its ability to protect the lives and property of its citizens ( Eubank and Weinberg, 1994 ).
The four airplane hijackings on 11 September 2001 (9/11) are terrorist acts since the perpetrators were members of al-Qaida, a subnational terrorist group, bent on pressuring the USA to remove its troops from Saudi Arabia, which was al-Qaida's primary political goal at the time. These skyjackings intimidated a global audience, caused huge temporary losses to the major stock exchanges ( Chen and Siems, 2004 ), and created $80–90 billion in direct and indirect damages ( Kunreuther et al ., 2003 ). Even though stock exchanges recovered lost values in just over a month, the death of almost 3,000 people caused rich industrial countries to allocate more resources to counterterrorism, shook insurance markets, and made an indelible impression on virtually the entire world. Heinous terrorist incidents continue to capture headlines with recent newsworthy incidents involving al-Shabaab's armed attack on the Westgate Mall in Nairobi, Kenya, on 21 September 2013; Chechen separatists’ suicide bombings of a train station and a trolley in Volgograd, Russia, on 29 and 30 December 2013, respectively; and Boko Haram's kidnapping of more than 200 female students in Chibok, Nigeria, on 14–15 April 2014. These and countless other incidents since 9/11 indicate that the government must allocate resources in an effective and measured manner to counterterrorism activities so that terrorists cannot circumvent legitimate political processes or cause significant economic losses. These losses may involve reduced foreign direct investment ( Enders and Sandler, 1996 ; Abadie and Gardeazabal, 2008 ), lower economic growth ( Abadie and Gardeazabal, 2003 ; Eckstein and Tsiddon, 2004 ; Gaibulloev and Sandler, 2008 , 2011 ), less trade ( Nitsch and Schumacher, 2004 ), reduced tourism ( Enders et al ., 1992 ; Drakos and Kutan, 2003 ), or lost values of stock and bond indexes ( Kollias et al ., 2013 ). Economic impacts of terrorism are greatest in small terrorism-plagued countries and developing countries ( Keefer and Loayza, 2008 ; Sandler and Enders, 2008 ). Modern industrial economies can insulate themselves through judicious fiscal and monetary policy, rapid counterterrorism responses, and the transference of economic activities ( Enders and Sandler, 2012 ). The latter involves economic activities moving from terrorism-prone sectors and regions to safer areas, which advanced, diversified economies allow. Thus, economic activity may switch from the tourism sector to other sectors when the former is targeted. In Spain, economic investment switched from the Basque Country to other Spanish provinces because of Euskadi ta Askatasuna attacks ( Abadie and Gardeazabal, 2003 ).
Modern-day econometric methods—time series, panel, and discrete-choice models—lend themselves to the quantification of these economic losses as shown in this special issue by Choi (2015) , Egger and Gassebner (2015) , and Younas (2015) . Additionally, game-theoretic models can display counterterrorism interactions among terrorists and governments as in the contributions in this issue by Carter (2015) and Kaplan (2015) . In fact, game theory is an excellent tool to study interactions among targeted governments, between rival terrorist groups, between a terrorist group and its sponsoring state, and among the media, the terrorist group, and the public. 1
The purpose of this article is to provide the requisite background to the studies in this special issue of Oxford Economic Papers . This task requires a fuller discussion of the notion of terrorism and its two primary subdivisions—domestic and transnational terrorism—in Section 2. The three event data sets employed in empirical studies, including seven of the eight articles in this issue, are briefly presented in Section 3. In Section 4, two of these data sets are used to display some recent trends and aspects of domestic and transnational terrorism during the last four decades. Essential concepts of counterterrorism are then presented in Section 5, where proactive measures are distinguished from defensive actions. Key findings of the four terrorism and four counterterrorism articles contained in this special issue are highlighted in two summarizing tables in Section 6. Concluding remarks follow in Section 7.
I now return to the definition of terrorism, given at the outset of this article. Any definition of terrorism involves much debate ( Hoffman, 2006 ; Enders and Sandler, 2012 ). The research community is converging to a consensus based on an operational definition on which to construct event data sets to test theoretical propositions. The article puts forward a definition that is consistent with that used by the main event data sets and relied on by researchers. Also, this definition possesses the main ingredients that are agreed on by economists, political scientists, and political economists.
The three stakeholders in this definition are the perpetrators, the victims, and the audience. By limiting terrorism to subnational agents including individuals or a ‘lone wolf’, my definition rules out state terror in which a government terrorizes its own people. The definition, however, does not rule out state-sponsored terrorism where a government clandestinely assists a terrorist group through various means, including supplying weapons, safe haven, intelligence, training, funding, or safe passage ( Mickolus, 1989 ; Bapat, 2006 ). There was a lot of state sponsorship of terrorism during the final decade of the Cold War with groups such as the Abu Nidal Organization serving as a terrorist group for hire ( Hoffman, 2006 ). 2 The most controversial element of my definition is the victim, since some definitions exclude combatants, so that attacks against an occupying army, such as US forces in Iraq or Afghanistan, are not viewed as terrorism. Generally, an attack against peacekeepers, such as the 23 October 1983 suicide bombing of the US Marines barracks at Beirut International Airport, is considered an act of terrorism. The barracks’ bombing had the political objective of removing peacekeepers from Lebanon, which happened in February 1984. Attacks against US soldiers and their dependents stationed in Germany constitute terrorist incidents, because these targeted individuals were noncombatants when attacked. ‘Audience’ refers to the collective that terrorists seek to intimidate through their wanton brutality. With sufficient and sustained intimidation, the audience will apply pressures on the besieged government to concede to the terrorist group's political demands or alternatively to take decisive action to annihilate the group. 3 In the latter case, the Italian authorities dismantled the Italian Red Brigades in the 1980s.
There are some crucial distinctions to draw between terrorism and related concepts. For instance, there is the distinction between terrorism and crime. A kidnapping for ransom is a criminal act of extortion when the kidnappers are not pursuing or financing a political agenda. If a political motive is tied to the kidnapping, then it is a terrorist incident even with ransom demands being made. The hijacking of a commercial airliner by a deranged person is a crime but not terrorism. In the absence of a political motive, an armed attack by a student on fellow students or teachers is a criminal action. Next consider an insurrection, which ‘is a politically based uprising intended to overthrow the established system of governance and to bring about a redistribution of income’ ( Sandler and Hartley, 1995 , p. 307). Leaders of insurrections recruit from the peasantry and general population in the hopes of challenging the government's hold on power ( Grossman, 1991 ). Successful rebel operations can generate new recruits and may ideally cause the government to impose draconian measures on its citizens, which subsequently create more support for the insurgency. If a tipping point is attained, then the government may be sufficiently challenged to lose its power to the rebels.
In distinction to insurrections, guerrilla warfare generally involves a band of rebel forces (e.g., the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia [FARC], Abu Sayyaf in the Philippines, or Shining Path in Peru) that controls a sector of the country, from which to dispatch its operatives to confront government forces. Some guerrilla wars take place in urban centers. In contrast to most terrorist groups, guerrilla groups are larger in number and organized like a military force. Some guerrilla groups engage in terrorist acts, such as the three just-mentioned groups, to raise funds to secure their operations and pursue their political aims. For example, FARC kidnaps government officials and others for ransoms. Unlike an insurrection, guerrilla groups are not bent on overthrowing the government or engaging in propaganda to gain popular support ( Hoffman, 2006 ). Shining Path and FARC apply threats and harsh measures to gain the compliance of the people in the territory that they control. Guerrilla groups rely on surprise and cover to harass numerically superior government forces. Terrorism is a tactic employed by both insurrections and guerrilla movements. As a consequence, many guerrilla groups are listed as terrorist groups despite their control of territory. Often, countries with jungle cover or mountainous terrain provide remote areas where guerrillas can conduct training and operations. In this special issue, Carter (2015) is interested in the interaction between a guerrilla group and the government, as the former chooses between terrorism and the control of territory and the latter chooses between defensive counterterrorism actions and proactive military responses to influence the group's decision.
2.1 Domestic versus transnational terrorism
Domestic terrorism is homegrown and home-directed, and represents the most common form of terrorism. For domestic acts of terrorism, the perpetrators, victims, and audience hail from the venue country, where the attack takes place. Domestic terrorist incidents include Timothy McVeigh's bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City on 19 April 1995 or Eric Rudolph's anti-abortionist bombing of Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, Georgia, on 27 July 1996. Civil wars often involve numerous domestic terrorist attacks before and during the conflict by the adversaries ( Findley and Young, 2012 ). 4 These terrorist acts are more apt to be domestic when an intervention by a third party from outside the country is not involved. Boko Haram's kidnapping of more than 200 female students is a domestic terrorist incident, which involves victims and perpetrators from the venue country of Nigeria. Boko Haram is an Islamic jihadist terrorist group that controls territory in the northeast portion of Nigeria. Given the country's limited military capabilities, its government sought some assistance from the USA in terms of military advisors and intelligence in addressing the significant threat that Boko Haram poses. At times, Boko Haram crosses into Chad. If one or more of the schoolgirls are moved into a neighboring country, then the kidnapping becomes a transnational terrorist incident. In general, poor countries may request foreign assistance if they cannot properly confront an indigenous terrorist group that may attack at home or abroad ( Azam and Thelen, 2010 ; Fleck and Kilby, 2010 ; Bandyopadhyay et al ., 2011 , 2014 ; Young and Findley, 2011 ).
Terrorism is transnational when an incident in the venue country concerns perpetrators or victims from another country. If a terrorist attack in the UK is perpetrated by terrorists from Yemen, then the incident is one of transnational terrorism. When a terrorist attack in France harms Dutch citizens, the attack is transnational. If one or more victims or perpetrators are not citizens of the venue country, then the terrorist attack is transnational. The kidnapping in January 2002 and subsequent murder of US reporter Daniel Pearl in Pakistan is classified as a transnational terrorist incident. The same is true of the near-simultaneous bombings of the US embassies in Kenya and Tanzania on 7 August 1998. Terrorist attacks against another country's embassy, even when perpetrated by citizens of the venue country, are transnational terrorist events because an embassy's grounds represent foreign soil. Similarly, terrorist attacks against international organizations’ personnel or property are considered to be transnational terrorist acts. An important transnational terrorist incident is the August 2006 plot to use liquid explosives to blow up 10 or more transatlantic flights departing the UK for the USA and Canada. A skyjacking originating in one country that is diverted to another country for political purposes is a transnational terrorist event. If a politically motivated hijacked plane has citizens from more than one country, the event is transnational terrorism even if the flight is domestic and ends in the country of origin. On 9/11, the four skyjackings are transnational terrorist acts since the victims were citizens from upward of 80 nations and the perpetrators were foreigners. The kidnapping of US journalist James Foley in Syria on 22 November 2012 and his beheading on 19 August 2014 is a transnational terrorist act. The victim was American, whereas the murderer is allegedly a British citizen from the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS), also known as Islamic State (IS).
Transnational terrorist incidents frequently imply transnational externalities—for example, perpetrators from one country impose uncompensated costs on the victims of another country. If a country provides safe haven to a transnational terrorist group that attacks other countries’ interests, then transnational externalities ensue. 5 The Taliban in Afghanistan had given safe haven to Osama bin Laden's al-Qaida, which planned and executed the events of 9/11. When the Taliban would not surrender bin Laden to the USA following 9/11, the USA led an invasion of Afghanistan on 7 October 2001 ( Enders and Sandler, 2012 ). In this extreme case, the transnational externality resulted in a military invasion with the intent to defeat the Taliban and al-Qaida. Transnational externalities also arise from counterterrorism policies of targeted countries, which result in inefficient levels of these policies ( Sandler and Lapan, 1988 ; Sandler and Siqueira, 2006 ; Bueno de Mesquita, 2007 ). Actions by one targeted country to secure its borders and ports of entry may merely transfer the attack abroad, where borders are more porous (see Section 5). Since 9/11, few transnational terrorist incidents occur on US soil but 35% to 40% of such incidents involve US people or property in other countries ( Enders and Sandler, 2006 , 2012 ).
2.2 Some historical considerations of transnational terrorism
Hoffman ( 2006 , pp.63–5) traces the modern era of transnational terrorism to the 22 July 1968 hijacking of an Israeli El Al flight en route from Rome to Athens by three armed members of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) terrorist group. This skyjacking was motivated by the intention of the PFLP terrorist to trade its hostages for Palestinian prisoners held by Israel. This event is noteworthy for a number of reasons. First, through its protracted 40-day negotiations, the Israelis were forced to negotiate with the Palestinian terrorists, which the Israelis had hitherto vowed they would never do ( Hoffman, 1998 , p.68). Second, the media coverage demonstrated to terrorists worldwide that such incidents could garner worldwide attention for their cause. Not surprisingly, transnational terrorist attacks increased greatly in numbers during the years following this incident (see the figures in Section 4). Third, there was evidence of state sponsorship after the diverted plane landed in Algiers as Algerian forces secured the hostages and held some Israeli hostages until 1 September 1968 when a deal was concluded ( Mickolus, 1980 , pp.93–4). Fourth, Israel eventually traded 16 Arab prisoners from the 1967 Arab-Israeli War for the remaining Israeli hostages. This trade showed terrorists that hostage taking could yield significant concessions.
Transnational terrorist groups were primarily nationalists/separatists or leftists (socialists) during the late 1960s until the late 1980s ( Rapoport, 2004 ). Even the Palestinian terrorists were secular until the end of the 1980s with the rise of Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, and other groups. After the mid-1990s, the religious fundamentalists came to dominate and increased the carnage ( Enders and Sandler, 2000 ; Gaibulloev and Sandler, 2014 ). The phenomenon of religious-based transnational terrorism is not novel and can be traced back to the Sicarii or Zealots, a Jewish sect that conducted a terror campaign against the Romans and their Jewish collaborators in Judea from CE 48 to 73 ( Rapoport, 1984 ; Bloom, 2005 ). Sicarii terrorists engaged in daytime assassinations in public places that typically resulted in the death of the assassin. As such, their dagger attacks were an early form of suicide terrorism, since the perpetrator had little chance of escape. 6 From 1090 to 1256, the Islamic Assassins opposed Sunni rule in Persia and Syria, with the intent to set up their own community and state of believers in the region ( Bloom, 2005 ). Although the Assassins’ terrorist campaign was on a much smaller scale, their goal was similar to that of ISIS. Like the Sicarii, the Assassins relied on politically motivated assassinations, performed with a dagger. Perpetrators usually sacrificed their own lives by making no efforts to escape after the deed.
In the beginning of the 1980s, the first terrorist event data set—International Terrorism: Attributes of Terrorist Events (ITERATE)—was made available to researchers. ITERATE only includes transnational terrorist attacks. Coverage starts in 1968, the beginning of the modern era of transnational terrorism, and runs until the end of 2012, with annual updates in August ( Mickolus et al ., 2013 ). ITERATE codes many variables—for example, incident date, country start location, country end location, attack type, target entity, terrorist group, perpetrators’ nationalities, number of deaths, number of injuries, victims’ nationalities, logistical outcome, US victims, state sponsorship, and scene of attack—in its Common File of over 40 variables. In addition, there is a Fate File indicating the fate of the terrorists—for example, the number of terrorists captured, the number of terrorists sentenced, and their length of incarceration. There is also a Hostage File, which has invaluable observations used by researchers to analyze logistical and negotiation success of hostage taking ( Santifort and Sandler, 2013 ). If an attack is completed as planned, then it is a logistical success. For hostage missions, securing one or more hostages is deemed a logistical success. The Hostage File of ITERATE is currently updated through 2010. Finally, there is a Skyjacking file with additional observations, and variables on skyjacking missions such as the duration of the incidents, airline involved, and negotiation strategies used. ITERATE, like the other event data sets, relies on the news media—print, broadcast, and digital—for the observations of its variables.
An initial focus of empirical studies was on transnational terrorism because ITERATE was the most extensive data set available throughout the 1980s and 1990s. Its lengthy series of daily data were ideal for time-series studies, which dominated the research landscape except for a few survival studies, the first being Atkinson et al .'s (1987) study of the duration of hostage-taking incidents. Today, panel studies are prevalent including those in this special issue— Berrebi and Ostwald (2015) , Choi (2015) , Egger and Gassebner (2015) , Gries et al . (2015) , and Younas (2015) .
Another competing event data set, modeled after ITERATE, is the RAND (2012) data set, which currently codes incidents for 1968–2009 and is not being updated. Gaibulloev (2015) uses the RAND event data in conjunction with Jones and Libicki's (2008) classification of terrorist groups’ ideologies in his study of groups’ location decisions. For 1968–97, RAND event data only include transnational terrorist attacks; after 1998, RAND data distinguish between transnational and domestic terrorist attacks in a manner consistent with my early definitions. Compared to ITERATE, RAND data code fewer variables and, for transnational terrorist incidents, have more limited coverage than ITERATE as demonstrated by Enders (2007) .
The third event data set, germane to this special issue, is that of the Global Terrorism Database (GTD), which records both domestic and transnational terrorist incidents ( La Free and Dugan, 2007 ; National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Response to Terrorism, 2013 ). Although GTD recorded both kinds of incidents, until 2013 it did not distinguish between the two kinds of incidents. Enders et al . (2011) devised a five-step procedure for distinguishing between domestic and transnational terrorist incidents in GTD for 1970–2007 and made their breakdown available to researchers. This division is now applied to 2008–2012 (see Enders et al ., 2014 ). A breakdown of terrorism into its two components is essential because the two types of terrorism may affect economic variables and counterterrorism differently—for example, economic growth or foreign direct investment is more influenced by transnational terrorism ( Gaibulloev and Sandler, 2008 ). Moreover, the influence of other variables on domestic and transnational terrorism may differ ( Sandler, 2014 ; Choi, 2015 ). The Enders et al . (2011) procedure does a much better job in distinguishing between the two types of events than recent GTD efforts, based on the authors’ method without attribution. GTD has tens of thousands of unclassified incidents compared to Enders et al . (2011) .
There are some things to note about GTD. First, it has changed its coding conventions a few times, most recently for the 2012 data. Coding was also changed after the National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism (2013) , based at the University of Maryland, took charge of the data around 2005. As shown by Enders et al . (2011) , there are periods of undercounting and overcounting of incidents, which can be addressed by these authors’ calibration methods. Second, GTD data for 1993 are very incomplete because in an office move by Pinkerton, which originated the database, the box containing 1993 fell off of the truck! Third, perpetrators’ nationalities are not identified. Fourth, GTD does not contain any hostage negotiation variables, making the study of hostage-taking incidents impossible with this database. Fifth, GTD coverage of some kinds of domestic incidents, such as kidnappings, is virtually nonexistent prior to the late 1990s ( Enders et al ., 2011 ).
Key aspects of the articles for the special issue
Notes: *denotes that Enders et al . (2011) breakdown of GTD into domestic and transnational terrorist incidents was used. ITERATE = International Terrorism: Attributes of Terrorist Events; GTD = Global Terrorism Database.
A variety of empirical techniques are applied by the six empirical articles. In his cross-sectional study of the location choice of terrorist groups, Gaibulloev (2015) relies on a conditional logit estimator. To account for the count nature of the dependent terrorism variable, Choi (2015) and Gries et al . (2015) apply a negative binomial panel estimator. Endogeneity between the dependent variable and one or more independent variables is addressed in various ways: the Berrebi and Ostwald (2015) article employs instrumental variables (IV), consisting of lagged domestic terrorist attacks in neighboring countries, whereas the Younas (2015) article uses system generalized method of moments (SGMM) to augment his feasible generalized least squares (FGLS) estimates. The Gries et al . (2015) article addresses endogeneity with lagged values of the independent variables and also SGMM estimates. The Choi (2015) article primarily uses lagged independent variables to partly handle the endogeneity concern.

ITERATE transnational terrorist incidents and total casualties per year, 1968–2012

GTD terrorist incidents per year, 1970–2012

ITERATE attacks against US interests per year, 1968–2012

Annual number of casualties per attack
This special issue contains articles on terrorism and counterterrorism. Given my discussion of terrorism and its concepts, it is now instructive to introduce some basic concepts and concerns that are associated with the practice of counterterrorism.
Quite simply, counterterrorism corresponds to actions to ameliorate the threat and consequences of terrorism. These actions can be taken by governments, military alliances, international organizations (e.g., INTERPOL), private corporations, or private citizens. Counterterrorism comes in two basic varieties: defensive and proactive measures.
Defensive countermeasures protect potential targets by making attacks more costly for terrorists or reducing their likelihood of success. When, however, successful terrorist attacks ensue, defensive actions also serve to limit the resulting losses to the target. Defensive measures have generally been reactive, instituted after some successful or innovative terrorist attacks. In the USA, airline passengers are now required to remove their shoes when being screened, following the innovative, but fortunately unsuccessful, attempt by Richard Reid to bring down American Airlines flight 63 en route from Paris to Miami on 22 December 2001 with explosives hidden in his shoes. Before the installation of metal detectors to screen passengers at US airports on 5 January 1973, there were on average over 25 skyjackings each year in the USA ( Enders et al ., 1990 ). After their installation, attempted US skyjackings dropped to fewer than four a year. The success of these metal detectors in US airports led to their installation worldwide over the next six months. Following the downing of Pan Am flight 103 over Lockerbie, Scotland, on 21 December 1988 and the downing of UTA flight 772 over Niger on 19 September 1989, bomb-detecting devices were used to screen checked luggage. Defensive or protective counterterror actions may involve more than technological barriers. Other instances of defensive measures include target hardening, such as defensive perimeters around government buildings or embassies, or guards at key points of a country's infrastructure. Defensive measures can also take the form of issuing terrorism alerts, enacting stiffer penalties for terrorism offenses, enhancing first-responder capabilities, and stockpiling antibiotics and antidotes for biological and chemical terrorist attacks. This list of defensive actions is by no means exhaustive.
By contrast, proactive measures are offensive as a targeted government directly confronts the terrorist group or its supporters. Proactive measures may destroy terrorists’ resources (e.g., training camps), curb their finances, eliminate their safe havens, or kill and capture their members. In recent years, the Obama administration has relied on drone attacks to assassinate terrorist leaders and operatives. Proactive operations may assume myriad other forms, including a retaliatory raid against a state sponsor that provides resources, training, sanctuary, logistical support, or intelligence to a terrorist group. On 15 April 1986, the USA launched a retaliatory bombing raid on targets in Libya for its alleged support in the terrorist bombing of the La Belle discotheque in West Berlin on 4 April 1986, where 3 died and 231 were wounded, including 62 Americans ( Mickolus et al ., 1989 , vol. 2, pp.365–7). Another proactive measure takes the form of a preemptive attack against a terrorist group or a harboring country, such as the US-led invasion of Afghanistan four weeks after 9/11. A preemptive strike differs from a retaliatory raid because the former is more sustained and meant to severely compromise the capabilities of the terrorists to conduct future missions. Such strikes or raids concern transnational terrorism where a targeted country confronts the foreign threat. Other proactive measures include infiltrating terrorist groups, engaging in military action, conducting propaganda campaigns against the terrorists, and gathering intelligence to foil terror plots ( Kaplan, 2015 ). ‘Military action’ generally refers to operations by the host government against a resident terrorist group as in Carter (2015) . Actions that improve the economy, which in turn reduces grievances, can also be proactive ( Choi, 2015 ). Younas (2015) demonstrates empirically that increased globalization of a country's economy may also be proactive by limiting harmful and therefore grievance-causing effects of terrorism on economic growth. In this special issue, the four counterterrorism articles primary address aspects of proactive measures. Only Carter (2015) considers both defensive and proactive counterterrorism responses.
The game-theoretic literature on counterterrorism draws some fascinating strategic contrasts between defensive and proactive countermeasures. Suppose that two or more countries are confronted by the same Islamic jihadist terrorist group—for example, al-Qaida in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP). In this transnational terrorism scenario, each at-risk country is inclined to work at cross-purposes by engaging in a defensive race in the hopes of transferring the terrorist attacks to other targeted countries ( Sandler and Lapan, 1988 ; Arce and Sandler, 2005 ). In the process, the countries engage in too much defense since the negative transference externality is not internalized. The only check on this adverse ‘defense race’ stems from the countries having large interests abroad, which may be hit when attacks are transferred abroad—recall Fig. 3 and attacks against US interests ( Bandyopadhyay and Sandler, 2011 ; Bandyopadhyay et al ., 2011 ).
Next consider proactive measures in these multicountry scenarios. Any country's actions to confront the common terrorist threat confer purely public (nonrival and nonexcludable) benefits to all potential target countries. As a result, there is too little proactive response as each country tries to free ride on the actions of other countries. Thus, defensive measures are strategic complements as one country's actions encourage those of other countries (i.e., reaction paths are upward-sloping), whereas proactive measures are strategic substitutes as one country's actions inhibit those of other countries (i.e., reaction paths are downward-sloping) ( Eaton, 2004 ; Sandler and Siqueira, 2006 ). Moreover, leadership can be shown to curb the defensive race, whereas leadership exacerbates the free-riding underprovision of offensive measures ( Sandler and Siqueira, 2006 ). Thus, there is no simple fix for these concerns among sovereign targeted nations.
For domestic terrorism, countries possess the proper incentives to choose defensive and proactive measures judiciously, because all associated costs and benefits are internalized ( Enders and Sandler, 2012 ). Thus, Kaplan's (2015) finding that the USA staffs about the right number of intelligence analysts to intercept terror plots is consistent with past game-theoretic findings regarding domestic counterterrorism optimality. Carter's (2015) article is also geared to domestic terrorism, whereas Choi (2015) and Younas (2015) may involve economic-based countermeasures for either type of terrorism.
Key findings of terrorism studies
Key findings of counterterrorism studies
This special issue contains many noteworthy advances in the study of terrorism. Gaibulloev (2015) is the first article to address terrorist groups’ base location choice; currently, the study of terrorist group survival is an active area of research. Berrebi and Ostwald (2015) is the initial study to examine the impact of terrorism on fertility. Younas (2015) and Choi (2015) refine the relationship between terrorism and growth; Egger and Gassebner (2015) show that terrorism has less of an effect on trade than conventionally believed. Kaplan (2015) investigates the social efficiency of intelligence staffing in intercepting terror plots. Carter's (2015) analysis is novel because the terrorist group must decide between terrorist attacks and holding territory in reaction to the government's countermeasures. The interface between terrorism and other forms of political violence is seldom studied. Finally, the Gries et al . (2015) study extends knowledge of the determinants of anti-American terrorist attacks, which comprise 35–40% of all transnational terrorism.
Terrorism remains an active research area in economics, political economy, and political science. Given the microeconomic and macroeconomic consequences of terrorism, its study is a fitting topic for a general economics journal such as Oxford Economic Papers . Following 9/11, industrial countries engaged in a huge reallocation of resources toward counterterrorism, whose efficacy can be best studied and understood with the theoretical and empirical tools drawn from economics.
The rise of ISIS and the considerable threat that its Western fighters pose for their home countries means that terrorism will remain a policy concern. AQAP's war on the USA and its allies is yet another terrorist threat. Just as Africa appears to be achieving sustained economic growth in select countries, significant terrorist challenges arise from Boko Haram and al-Shabaab in Nigeria and Kenya, respectively. Failed states—for example, Afghanistan, Iraq, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen—supply safe havens for terrorist groups that threaten Western interests. It is my hope that this special issue on terrorism and counterterrorism will stimulate further research in these two topics.
The present collection arises from a set of papers presented at the sixth conference on Terrorism and Counterterrorism Policy at the University of Texas, Dallas. Held between 21 May and 24 May 2014, this conference invited many leading contributors to the study of terrorism and counterterrorism. Past conferences resulted in special issues published in Economics &Politics (November 2009), Journal of Conflict Resolution (April 2010), Journal of Peace Research (May 2011), Public Choice (December 2011), and Southern Economic Journal (April 2013). While assuming full responsibility for any remaining shortcomings, this article has profited from comments from Anindya Banerjee, who also advised me on the special issue. Khusrav Gaibulloev read and commented on an earlier version. Finally, I thank all of this special issue's reviewers, most of whom are major contributors to the study of terrorism. These reviewers provided rigorous reviews in a timely fashion. All articles went through a careful and demanding prescreening process, followed by two rounds of reviews by two to three anonymous referees. I appreciate the understanding of those authors whose papers did not make it into the special issue.
On the game-theoretic literature on terrorism, see Bandyopadhyay and Sandler (2011) , Bandyopadhyay et al . ( 2011 , 2014 ), Sandler and Arce (2003) , Bueno de Mesquita (2005) , and Sandler and Siqueira (2009) .
The Abu Nidal Organization was headed by Sabri Khali al-Banna. Its notorious attacks included the simultaneous armed attacks on the Rome and Vienna airports on 27 December 1985, the armed attack on the Neve Shalom Synagogue in Istanbul on 6 September 1986, and the attempted hijacking of Pan Am flight 73 in Karachi, Pakistan, on 5 September 1986 ( Enders and Sandler, 2012 ). This group is credited with the first simultaneous terrorist attacks.
On alternative ways that terrorist groups end, see Carter (2012) , Gailbulloev and Sandler (2014) , and Phillips (2014a) .
On the relationship between civil wars and terrorism, see Sambanis (2008) .
How terrorist groups choose their home base is discussed in this special issue by Gaibulloev (2015) . On the definition of terrorist groups, see Phillips (2014b) .
In this special issue, Choi (2015) investigates suicide terrorism, which may be domestic or transnational in nature. Suicide terrorist attacks grew in numbers after 1988 ( Santifort-Jordan and Sandler, 2014 ).
Abadie A. Gardeazabal J. ( 2003 ) The economic cost of conflict: a case study of the Basque Country , American Economic Review , 93 , 113 – 32 .
Google Scholar
Abadie A. Gardeazabal J. ( 2008 ) Terrorism and the world economy , European Economic Review , 52 , 1 – 27 .
Arce D.G. Sandler T. ( 2005 ) Counterterrorism: a game-theoretic analysis , Journal of Conflict Resolution , 49 , 183 – 200 .
Atkinson S.E. Sandler T. Tschirhart J. ( 1987 ) Terrorism in a bargaining framework , Journal of Law and Economics , 30 , 1 – 21 .
Azam J.-P. Thelen V. ( 2010 ) Foreign aid versus military intervention in the war on terror , Journal of Conflict Resolution , 54 , 237 – 61 .
Bandyopadhyay S. Sandler T. ( 2011 ) The interplay between preemptive and defensive counterterrorism measures: a two-stage game , Economica , 78 , 546 – 64 .
Bandyopadhyay S. Sandler T. Younas J. ( 2011 ) Foreign aid as counterterrorism policy , Oxford Economic Papers , 63 , 423 – 47 .
Bandyopadhyay S. Sandler T. Younas J. ( 2014 ) Foreign direct investment, aid, and terrorism , Oxford Economic Papers , 66 , 25 – 50 .
Bapat N. A. ( 2006 ) State bargaining with transnational terrorist groups , International Studies Quarterly , 50 , 213 – 29 .
Berrebi C. Ostwald J. ( 2015 ) Terrorism and fertility: evidence for a causal inference of terrorism on fertility , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 63 – 82 .
Bloom M. ( 2005 ) Dying to Kill: The Allure of Suicide Terror , Columbia University Press , New York .
Google Preview
Bueno de Mesquita E. ( 2005 ) The quality of terror , American Journal of Political Science , 49 , 515 – 30 .
Bueno de Mesquita E. ( 2007 ) Politics and the suboptimal provision of counterterror , International Organization , 61 , 9 – 36 .
Carter D.B. ( 2012 ) A blessing or curse? State support for terrorist groups , International Organization , 66 , 129 – 51 .
Carter D.B. ( 2015 ) When terrorism is evidence of state success: securing the state against territorial groups , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 116 – 32 .
Chen A.H. Siems T.F. ( 2004 ) The effects of terrorism on global capital markets , European Journal of Political Economy , 20 , 249 – 66 .
Choi S.-W. ( 2015 ) Economic growth and terrorism: domestic, international, and suicide , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 157 – 81 .
Drakos K. Kutan A.M. ( 2003 ) Regional effects of terrorism on tourism in three Mediterranean countries , Journal of Conflict Resolution , 47 , 621 – 41 .
Eaton B.C. ( 2004 ) The elementary economics of social dilemmas , Canadian Journal of Economics , 37 , 805 – 29 .
Eckstein Z. Tsiddon D. ( 2004 ) Macroeconomic consequences of terror: theory and the case of Israel , Journal of Monetary Economics , 51 , 971 – 1002 .
Egger P. Gassebner M. ( 2015 ) International terrorism as a trade impediment? Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 42 – 62 .
Enders W. ( 2007 ) Terrorism: an empirical analysis , in Sandler T. Hartley K. (eds) Handbook of Defense Economics: Defense in a Globalized World , North-Holland , Amsterdam .
Enders W. Hoover G.A. Sandler T. ( 2014 ) The changing nonlinear relationship between income and terrorism , Journal of Conflict Resolution , doi: 10.1177/0022002714535252 .
Enders W. Sandler T. ( 1996 ) Terrorism and foreign direct investment in Spain and Greece , Kyklos , 49 , 331 – 52 .
Enders W. Sandler T. ( 2000 ) Is transnational terrorism becoming more threatening? A time-series investigation , Journal of Conflict Resolution , 44 , 307 – 32 .
Enders W. Sandler T. ( 2006 ) Distribution of transnational terrorism among countries by income classes and geography after 9/11 , International Studies Quarterly , 50 , 367 – 93 .
Enders W. Sandler T. ( 2012 ) The Political Economy of Terrorism , 2nd edn., Cambridge University Press , New York .
Enders W. Sandler T. Cauley J. ( 1990 ) UN conventions, technology, and retaliation in the fight against terrorism: an econometric evaluation , Terrorism and Political Violence , 2 , 83 – 105 .
Enders W. Sandler T. Gaibulloev K. ( 2011 ) Domestic versus transnational terrorism: data, decomposition, and dynamics , Journal of Peace Research , 48 , 319 – 37 .
Enders W. Sandler T. Parise G.F. ( 1992 ) An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism , Kyklos , 45 , 531 – 54 .
Eubank W.L. Weinberg L.B. ( 1994 ) Does democracy encourage terrorism? , Terrorism and Political Violence , 6 , 417 – 35 .
Faria J.R. ( 2003 ) Terror cycles , Studies in Nonlinear Dynamics and Econometrics , 7 , 1 – 11 .
Findley M.G. Young J.K. ( 2012 ) Terrorism and civil war: a spatial and temporal approach to a conceptual problem , Perspectives on Politics , 10 , 285 – 305 .
Fleck R.K. Kilby C. ( 2010 ) Changing aid regimes? US foreign aid from the Cold War to the war on terror , Journal of Development Economics , 91 , 185 – 97 .
Gaibulloev K. ( 2015 ) Terrorist group location decision: an empirical investigation , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 21 – 41 .
Gaibulloev K. Sandler T. ( 2008 ) Growth consequences of terrorism in Western Europe , Kyklos , 61 , 411 – 24 .
Gaibulloev K. Sandler T. ( 2011 ) The adverse effect of transnational and domestic terrorism on growth in Africa , Journal of Peace Research , 48 , 355 – 71 .
Gaibulloev K. Sandler T. ( 2014 ) An empirical analysis of alternative ways that terrorist groups end , Public Choice , 160 , 25 – 44 .
Gries T. Meierrieks D. Redlin M. ( 2015 ) Oppressive governments, dependence on the United States and anti-American terrorism , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 83 – 103 .
Grossman H.I. ( 1991 ) A general equilibrium model of insurrections , American Economic Review , 81 , 912 – 21 .
Hoffman B. ( 1998 ) Inside Terrorism , Columbia University Press , New York .
Hoffman B. ( 2006 ) Inside Terrorism , rev. edn., Columbia University Press , New York .
Jones S.G. Libicki M.C. ( 2008 ) How Terrorist Groups End: Lessons for Countering al Qa'ida , Monograph MG-741-1, RAND, Santa Monica, CA .
Kaplan E.H. ( 2015 ) Socially efficient detection of terror plots , Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 104 – 15 .
Keefer P. Loayza N. (eds) ( 2008 ) Terrorism, Economic Development, and Political Openness , Cambridge University Press , New York .
Kollias C. Papadamou S. Arvanitis V. ( 2013 ) Does terrorism affect the stock-bond covariance? Evidence from European countries , Southern Economic Journal , 79 , 832 – 48 .
Kunreuther H. Michel-Kerjan E. Porter P. ( 2003 ) Assessing, managing and financing extreme events: dealing with terrorism , Working Paper 10179, National Bureau of Economic Research .
La Free G. Dugan L. ( 2007 ) Introducing the global terrorism database , Terrorism and Political Violence , 19 , 181 – 204 .
Mickolus E.F. ( 1980 ) Transnational Terrorism: A Chronology of Events 1968–1979 , Greenwood Press , Westport, CT .
Mickolus E.F. ( 1989 ) What constitutes state support to terrorism? , Terrorism and Political Violence , 1 , 287 – 93 .
Mickolus E.F. Sandler T. Murdock J.M. ( 1989 ) International Terrorism in the 1980s: A Chronology of Events , 2 vols. , Iowa State University Press , Ames .
Mickolus E.F. Sandler T. Murdock J.M. Flemming P. ( 2013 ) International Terrorism: Attributes of Terrorist Events, 1968–2013 (ITERATE) , Vinyard Software , Ponte Vedra, FL .
Mueller J. ( 2006 ) Overblown: How Politicians and the Terrorism Industry Inflate National Security Threats and Why We Believe Them , Free Press , New York .
National Consortium for the Study of Terrorism and Responses to Terrorism . ( 2013 ) Global Terrorism Database , available at http://www.start.umd.edu/gtd/ (accessed 25 August 2013) .
Nitsch V. Schumacher D. ( 2004 ) Terrorism and international trade: an empirical investigation , European Journal of Political Economy , 20 , 423 – 33 .
Phillips B.J. ( 2014a ) Terrorist group cooperation and longetivity , International Studies Quarterly , 58 , 336 – 47 .
Phillips B.J. ( 2014b ) What is a terrorist group? Conceptual issues and empirical implications , Terrorism and Political Violence , doi: 10.1080/09546553.2013.800048 .
RAND . ( 2012 ) RAND database of worldwide terrorism incidents , available at http://www.rand.org/nsrd/projects/terrorism-incidents.html (accessed 3 August 2012) .
Rapoport D.C. ( 1984 ) Fear and trembling: terrorism in three religious traditions , American Political Science Review , 78 , 658 – 77 .
Rapoport D.C. ( 2004 ) Modern terror: the four waves , in Cronin A.K. Ludes J.M. (eds) Attacking Terrorism: Elements of a Grand Strategy , Georgetown University Press , Washington, DC .
Sambanis N. ( 2008 ) Terrorism and civil war , in Keefer P. Loayza N. (eds) Terrorism, Economic Development and Political Openness , Cambridge University Press , New York .
Sandler T. ( 2014 ) The analytical study of terrorism: taking stock , Journal of Peace Research , 51 , 257 – 71 .
Sandler T. Arce D.G. ( 2003 ) Terrorism and game theory , Simulation &Gaming , 34 , 319 – 37 .
Sandler T. Enders W. ( 2008 ) Economic consequences of terrorism in developed and developing countries: an overview , in Keefer P. Loayza N. (eds) Terrorism, Economic Development and Political Openness , Cambridge University Press , New York .
Sandler T. Hartley K. ( 1995 ) The Economics of Defense , Cambridge University Press , Cambridge .
Sandler T. Lapan H.E. ( 1988 ) The calculus of dissent: an analysis of terrorists’ choice of targets , Synthese , 76 , 245 – 61 .
Sandler T. Siqueira K. ( 2006 ) Global terrorism: deterrence versus preemption , Canadian Journal of Economics , 50 , 1370 – 87 .
Sandler T. Siqueira K. ( 2009 ) Games and terrorism: recent developments , Simulation &Gaming , 40 , 164 – 92 .
Santifort C. Sandler T. ( 2013 ) Terrorist success in hostage-taking mission , Public Choice , 156 , 125 – 37 .
Santifort-Jordan C. Sandler T. ( 2014 ) An empirical study of suicide terrorism: a global analysis , Southern Economic Journal , 80 , 981 – 1001 .
Younas J. ( 2015 ) Does globalization mitigate the adverse effects of terrorism on growth? Oxford Economic Papers , 67 , 133 – 56 .
Young J.K. Findley M.G. ( 2011 ) Can peace be purchased? A sectoral-level analysis of aid's influence on transnational terrorism , Public Choice , 149 , 365 – 81 .
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1464-3812
- Print ISSN 0030-7653
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Essay on Terrorism
India has a lengthy history of terrorism. It is a cowardly act by terrorist organisations that want to sabotage the nation's tranquillity. It seeks to instil fear among the population. They seek to maintain a permanent climate of dread among the populace to prevent the nation from prospering. Here are a few sample essays on Terrorism .

100 Words Essay on Terrorism
Terrorism is the use of violence and intimidation in the pursuit of political and personal aims. It is a global phenomenon that has affected countries worldwide, causing harm to innocent civilians, damaging economies, and destabilizing governments. The causes of terrorism are complex and can include religious extremism, political oppression, and economic inequality.
Terrorist groups use a variety of tactics, including bombings, kidnappings, and hijackings, to achieve their goals. They often target symbols of government and military power, as well as civilians in crowded public spaces. The impact of terrorism on society is devastating, leading to loss of life, injury, and psychological trauma.
Combating terrorism requires a multifaceted approach, including intelligence gathering, law enforcement, and military action. Additionally, addressing underlying issues such as poverty and political marginalization is crucial in preventing the radicalization of individuals and the emergence of terrorist groups.
200 Words Essay on Terrorism
Terrorism is a complex and ever-evolving threat that affects countries and communities around the world. It involves the use of violence and intimidation to achieve political or ideological goals. The causes of terrorism can vary, but often include religious extremism, political oppression, and economic inequality.
To truly understand the impact of terrorism, it's important to consider not only the physical harm caused by terrorist attacks but also the emotional and psychological toll it takes on individuals and communities. The loss of life and injury caused to innocent civilians is devastating and can leave families and communities reeling for years to come. In addition, terrorism can cause physical damage to infrastructure and buildings, as well as economic disruption, leading to decreased tourism and investment.
To effectively combat terrorism, it's important to take a holistic approach that addresses not only the immediate threat of terrorist attacks but also the underlying issues that can lead to radicalization and the emergence of terrorist groups. This can include addressing poverty and economic inequality, promoting political and religious tolerance, and providing support and resources to individuals and communities at risk of radicalization.
It's also important to remember that the fight against terrorism is not just the responsibility of governments and law enforcement agencies, but also of individuals and communities. By promoting understanding and compassion, and by standing up against hate and extremism, we can all play a role in preventing terrorism and creating a more peaceful world.
500 Words Essay on Terrorism
According to a United Nations Security Council report from November 2004, terrorism is any act that is "intended to result in the death or serious bodily harm of civilians or non-combatants to intimidate the population or to compel the government or an international organisation to do or abstain from doing any act."
The Origins of Terrorism
The development or production of massive numbers of machine guns, atomic bombs, hydrogen bombs, nuclear weapons, missiles, and other weapons fuels terrorism. Rapid population growth, political, social, and economic problems, widespread discontent with the political system, a lack of education, racism, economic inequality, and linguistic discrepancies are all important contributors to the emergence of terrorism. Sometimes one uses terrorism to take a position and stick with it.
The Effects Of Terrorism
People become afraid of terrorism and feel unsafe in their nation. Terrorist attacks result in the destruction of millions of items, the death of thousands of innocent people, and the slaughter of animals. After seeing a terrorist incident, people become less inclined to believe in humanity, which breeds more terrorists.
Different forms of terrorism can be found both domestically and overseas. Today, governments worldwide are working hard to combat terrorism, which is an issue in India and our neighbouring nations. The 9/11 World Trade Centre attack is considered the worst terrorist act ever. Osama bin Laden attacked the tallest building in the world’s most powerful country, causing millions of casualties and the death of thousands of people.
The major incidents of the terrorist attack in India are—
12 March 1993 - A series of 13 bombs go off, killing 257
14 March 2003 - A bomb goes off in a train in Mulund, killing 10
29 October 2005 Delhi bombings
2005 Ram Janmabhoomi attack in Ayodhya
2006 Varanasi bombings
11 July 2006 - A series of seven bombs go off in trains, killing
26 November 2008 to 29 November 2008 - A series of coordinated attacks killed at least 170.
According to this data, India has experienced an upsurge in terrorist activity since 1980. India has fought four wars against terrorism , losing more than 6000 persons in total. Already, we have lost around 70000 citizens. Furthermore, we lost over 9000 security staff. In this country, about 6 lakh individuals have undergone.
Agencies In India Fighting Terrorism
There are numerous organisations working to rid our nation of terrorism. These organizations operate continuously, from the municipal to the national levels. To stop local terrorist activity, police forces have various divisions.
The police departments have a specialized intelligence and anti-terrorism division that is in charge of eliminating Naxalites and other terrorist organizations. The military is in charge of bombing terrorist targets outside of our country. These departments engage in counterinsurgency and other similar operations to dismantle various terrorist organisations.
There are numerous organisations that work to prevent terrorism. Anti-Terrorism Squad (ATS) , National Investigation Agency (NIA) , and Research and Analysis Wing are a few of the top organizations (RAW) . These are some of the main organizations working to rid India of terrorism.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Geotechnical engineer
The role of geotechnical engineer starts with reviewing the projects needed to define the required material properties. The work responsibilities are followed by a site investigation of rock, soil, fault distribution and bedrock properties on and below an area of interest. The investigation is aimed to improve the ground engineering design and determine their engineering properties that include how they will interact with, on or in a proposed construction.
The role of geotechnical engineer in mining includes designing and determining the type of foundations, earthworks, and or pavement subgrades required for the intended man-made structures to be made. Geotechnical engineering jobs are involved in earthen and concrete dam construction projects, working under a range of normal and extreme loading conditions.
Cartographer
How fascinating it is to represent the whole world on just a piece of paper or a sphere. With the help of maps, we are able to represent the real world on a much smaller scale. Individuals who opt for a career as a cartographer are those who make maps. But, cartography is not just limited to maps, it is about a mixture of art , science , and technology. As a cartographer, not only you will create maps but use various geodetic surveys and remote sensing systems to measure, analyse, and create different maps for political, cultural or educational purposes.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.

Product Manager
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Operations manager.
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Bank Probationary Officer (PO)
Investment director.
An investment director is a person who helps corporations and individuals manage their finances. They can help them develop a strategy to achieve their goals, including paying off debts and investing in the future. In addition, he or she can help individuals make informed decisions.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
An expert in plumbing is aware of building regulations and safety standards and works to make sure these standards are upheld. Testing pipes for leakage using air pressure and other gauges, and also the ability to construct new pipe systems by cutting, fitting, measuring and threading pipes are some of the other more involved aspects of plumbing. Individuals in the plumber career path are self-employed or work for a small business employing less than ten people, though some might find working for larger entities or the government more desirable.
Construction Manager
Individuals who opt for a career as construction managers have a senior-level management role offered in construction firms. Responsibilities in the construction management career path are assigning tasks to workers, inspecting their work, and coordinating with other professionals including architects, subcontractors, and building services engineers.
Urban Planner
Urban Planning careers revolve around the idea of developing a plan to use the land optimally, without affecting the environment. Urban planning jobs are offered to those candidates who are skilled in making the right use of land to distribute the growing population, to create various communities.
Urban planning careers come with the opportunity to make changes to the existing cities and towns. They identify various community needs and make short and long-term plans accordingly.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Naval Architect
A Naval Architect is a professional who designs, produces and repairs safe and sea-worthy surfaces or underwater structures. A Naval Architect stays involved in creating and designing ships, ferries, submarines and yachts with implementation of various principles such as gravity, ideal hull form, buoyancy and stability.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Veterinary Doctor
Pathologist.
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Speech Therapist
Gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
Hospital Administrator
The hospital Administrator is in charge of organising and supervising the daily operations of medical services and facilities. This organising includes managing of organisation’s staff and its members in service, budgets, service reports, departmental reporting and taking reminders of patient care and services.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Videographer
Multimedia specialist.
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Linguistic meaning is related to language or Linguistics which is the study of languages. A career as a linguistic meaning, a profession that is based on the scientific study of language, and it's a very broad field with many specialities. Famous linguists work in academia, researching and teaching different areas of language, such as phonetics (sounds), syntax (word order) and semantics (meaning).
Other researchers focus on specialities like computational linguistics, which seeks to better match human and computer language capacities, or applied linguistics, which is concerned with improving language education. Still, others work as language experts for the government, advertising companies, dictionary publishers and various other private enterprises. Some might work from home as freelance linguists. Philologist, phonologist, and dialectician are some of Linguist synonym. Linguists can study French , German , Italian .
Public Relation Executive
Travel journalist.
The career of a travel journalist is full of passion, excitement and responsibility. Journalism as a career could be challenging at times, but if you're someone who has been genuinely enthusiastic about all this, then it is the best decision for you. Travel journalism jobs are all about insightful, artfully written, informative narratives designed to cover the travel industry. Travel Journalist is someone who explores, gathers and presents information as a news article.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
Merchandiser.
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Metallurgical Engineer
A metallurgical engineer is a professional who studies and produces materials that bring power to our world. He or she extracts metals from ores and rocks and transforms them into alloys, high-purity metals and other materials used in developing infrastructure, transportation and healthcare equipment.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
ITSM Manager
Information security manager.
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
Business Intelligence Developer
Applications for admissions are open..

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN

NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score upto 100% marks
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Last updated on October 29, 2022 by ClearIAS Team

Defining terrorism is a tedious and confusing task as there is a lack of consensus at the international level. However several efforts have been made in this regard.
Table of Contents
Defining Terrorism
An agreed, comprehensive definition of terrorism has never been created by the international community. The United Nations’ attempts to define the term during the 1970s and 1980s failed mostly because of disagreements among its members over the use of violence in conflicts over self-determination and national liberation. Due to these differences, a conclusion cannot be reached.
According to the FBI: “Terrorism is the unlawful use of force or violence against persons or property to intimidate or coerce a government, the civilian population, or any segment thereof, in furtherance of political or social objectives.”
Causes of Terrorism
There are many causes for terrorism such as:
Political causes
Insurgency and guerrilla warfare, a type of organized conflict, were the contexts in which terrorism was first theorized. A non-state army or organization committing political violence. Because they dislike the current system, they pick terrorism. They oppose the current social structure and wish to change it.
Religious reasons
In the 1990s, experts started to claim that a brand-new sort of terrorism propelled by religious zeal was on the increase. They cited groups like Al Qaeda, the Japanese cult Aum Shinrikyo, and Christian identity movements. Religious concepts like martyrdom were viewed as especially hazardous.
Learn more from: ClearIAS Study Materials
Socio-Economic
According to socio-economic theories, persons who experience different types of deprivation are more likely to turn to terrorism or are more open to being recruited by groups that use terrorist tactics. Lack of political freedom, lack of access to education, and poverty are a few examples.
Types of Terrorism
The following are the various types of terrorism.
Ethno-Nationalist Terrorism
According to Daniel Byman, ethnic terrorism is the premeditated use of violence by a subnational ethnic group to further its cause. Such violence typically aims at either the establishment of a separate State or elevating one ethnic group above another.
Activities by Tamil nationalist groups in Srilanka are an example of Ethno-Nationalist terrorism.
Hoffman claims that those who engage in terrorism who are either wholly or partially driven by religious imperative view violence as a sacramental or heavenly responsibility. Religious terrorism is more destructive in nature because it adopts different justifications and modes of legitimization than other terrorist organizations.
Ideology oriented
Several ideologies have been used to legitimize terrorism. They include:
Left-Wing Extremism
The idea focuses on overthrowing the state through an armed struggle and establishing a communist state.
Right Wing Terrorism
Right-wing organizations typically aim to preserve the status quo or go back to a scenario from the past that they believe should have been preserved.
They might compel the government to seize a piece of land or to step in to defend the rights of a minority that is being “oppressed” in a neighboring nation.
State Sponsored Terrorism
State-sponsored terrorism and proxy war are as old as organized warfare itself. According to Walter Laqueur, these customs were in place in antiquity in the Eastern Empires, Rome and Byzantium, Asia, and Europe.
Impacts of Terrorism
It seriously jeopardizes global peace and security and undercuts the fundamental principles of growth, peace, and humanity. Terrorist activities not only have a catastrophic human cost in terms of lives lost or permanently changed, but they also endanger political stability and economic and social advancement.
Often, terrorist attacks disregard international boundaries.CBRNE (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives) materials are used in terrorist attacks that have devastating effects on infrastructure and communities.
Measures To Counter Terrorism
- The United Nations Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) is responsible for leading and coordinating the UN system’s efforts to prevent and combat terrorism and violent extremism worldwide.
- Under UNOCT, the UN Counter-Terrorism Centre (UNCCT) encourages global collaboration in the fight against terrorism and assists the Member States in putting the Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy into practice.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime’s (UNODC) Terrorism Prevention Branch (TPB) is a key player in global efforts.
- International standards are established by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) , a global organization that monitors money laundering and terrorist funding with the goal of preventing these illicit actions and the harm they do to society.
A combined effort at the international level is the need of the hour to tackle the perils of terrorism. Terrorism of any form is unacceptable in a civilized society.
Article written by: Vivek Rajasekharan

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
- Subscribe Now
[OPINION] Responding to the Anti-Terror Law from the United States
Already have Rappler+? Sign in to listen to groundbreaking journalism.
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.
![essay on anti terrorism [OPINION] Responding to the Anti-Terror Law from the United States](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2020/07/ispeak-responding-to-anti-terror-law.jpg)
RA 11479, or the Duterte regime’s Anti-Terror Law of 2020, took effect on midnight of July 18. Under this supposed national security law, Duterte will create an Anti-Terrorism council that can make warrantless arrests, freeze assets of suspects, and surveil suspects. Furthermore, as a result of the law’s vague definition of “terrorism,” the council would have the power to decide who is a terrorist. The long reach of the legislation also makes it potentially applicable to Filipinos abroad.
Through this law, Duterte fortifies his power by absorbing the functions granted to the judicial and legislative branches of the government. Sedition charges are now being filed against ordinary citizens critiquing the Duterte regime on social media. Duterte said that law-abiding citizens need not worry if they are not terrorists, but Duterte’s political machinery has expanded its energy from the vitriolic trolling of critics online, by broadening what the state perceives as “terror.”
The Commission on Human Rights reported on the difficulty in tracking down the sustained extrajudicial killings in the Philippines, especially within the militarized handling of the pandemic. Earlier this month, it was reported that there were 107 complaints on arrests and detention and 55 on extrajudicial killings. Authorities will also carry out house-to-house searches for people with or without COVID-19 symptoms, who will then be transferred to government-run isolation facilities. Government officers cited a Philippine law stating those refusing to cooperate may be fined or imprisoned. The house-to-house search that the state euphemistically calls “Oplan Kalinga,” kalinga meaning care, intimidates Filipinos seeking shelter from the pandemic in their own homes.
Intimidation occurs on a bigger scale, with the government striking at the media. Recently, the Manila Regional Trial Court found journalist Maria Ressa guilty of cyberlibel, in what critics believe was a politically motivated ruling. On July 10, 70 members of the Philippine Congress voted “no” on ABS-CBN’s appeal to renew their media franchise, affirming the spreading power of the Duterte regime. Our elders would remember the ABS-CBN shutdown during the Marcos dictatorship. This time, media censorship is even more staggering because of the display of complicity by state officials. The Philippines is already the 5 th most dangerous country in the world for journalists . The future is not looking bright in a situation that mixes impunity with complicity.
We have seen throughout Duterte’s presidency, and in particular in the last couple of months, a targeting of those that stand in the name of democratic freedoms and human rights. The recent arrests of activists such as those involved in a Global Pride March as well as Senator Bong Go’s deployment of the National Bureau of Investigation to look into social media criticisms of the senator are worrying signs that point to the potential abuses of the Anti-Terror Law. The Duterte government’s actions have shown that if you stand for a free press, if you oppose the government in any way, if you defend the human rights of others, you are treated as an enemy of the state. With such a record, it is no wonder why so many are worried that such a government would have the power to define who is a terrorist.
In this context, we ask two questions: What can we, in the diaspora, materially do? How are we to proceed, beyond the performative expressions of care, and beyond our nostalgic attachments to the islands?
We might start with continuing to challenge complicities happening at our dinner tables. Our scholarship and energy could be directed inwards, recruiting our own family members as audiences of our own work and pushing back against the anti-human rights discourse that is circulated in our own intimate circle and homes.
Another potential action is to contact our government representatives in the countries where we are and urge them to publicly oppose the Anti-Terror Law in the Philippines. In the US, over 50 representatives are currently publicly in opposition to the ATL, and it would certainly help to see more. Calls from US government leaders towards the Philippines are potentially irksome to the Duterte government, as we saw Presidential Spokesperson Harry Roque directly respond to the opposition of US reps just a few days ago.
We can also urge these representatives to support the Philippine Human Rights Act , a legislation that aims to tie US security aid to the Philippines to improvements in the human rights situation in the Philippines. Individuals and organizations can also sign on to support PHRA .
Lastly, we can find people that are doing the work of organizing and join them. There has been no lack of folks in the diaspora mobilizing on Philippine issues. Malaya Movement , for example, is made up of a wide range of people all brought together by the following points:
- Stop the killings
- No to fascist dictatorship
- Scrap Executive Order 70 , Memorandum Order 32 and all other de facto Martial Law policies
- End corruption and the practice of political dynasty in the Philippines
- Stand for genuine democracy
- Defend Philippine sovereignty against all foreign powers
We happen to think Malaya Movement and Respond and Break the Silence Against the Killings are among the organizations that are doing important work, but there are many more that we can work with.
In closing, to briefly speak directly to those of us that might hold citizenship outside of the Philippines – acts like these are targeting Filipinos and aiming to silence them into submission. If we are in a position to do so, this would be a key moment to be loud about our opposition to these attacks on democracy and human rights. Our vocal dissent can help amplify their struggles and support their efforts. We can do this by mobilizing in our localities and taking opportunities to speak up and educate ourselves and each other. – Rappler.com
This essay merges the presentations of the authors delivered at the Pino/a/x/y Powerpoint Party on July 18, 2020, organized by Michael Salgarolo and Noelle Malvar.
Dada Docot is an assistant professor in the Department of Anthropology at Purdue University. She is an anthropologist of her hometown in Bicol, and of the Filipino diaspora.
Mark John Sanchez is a lecturer in History & Literature at Harvard University. He is a historian of Philippine social movements and human rights.
Add a comment
Please abide by Rappler's commenting guidelines .
There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.
How does this make you feel?
Related Topics
Recommended stories, {{ item.sitename }}, {{ item.title }}, overseas filipinos, 3 filipinos hurt in powerful taiwan quake.

Globe, Smart offer free roaming services to Filipinos in Taiwan after earthquake

Marcos’ Mindanao trust rating drops | The wRap

Scientists’ group names Filipina in Germany as ‘Planet Earth’ awardee

Overstaying OFWs in Kuwait given until June to avail amnesty

Checking your Rappler+ subscription...
Upgrade to Rappler+ for exclusive content and unlimited access.
Why is it important to subscribe? Learn more
You are subscribed to Rappler+
Against Zionism—and Anti-Zionism Too
Jews in the united states and elsewhere are at war over these labels. but the distinctions are clearer on paper than they are in real life..
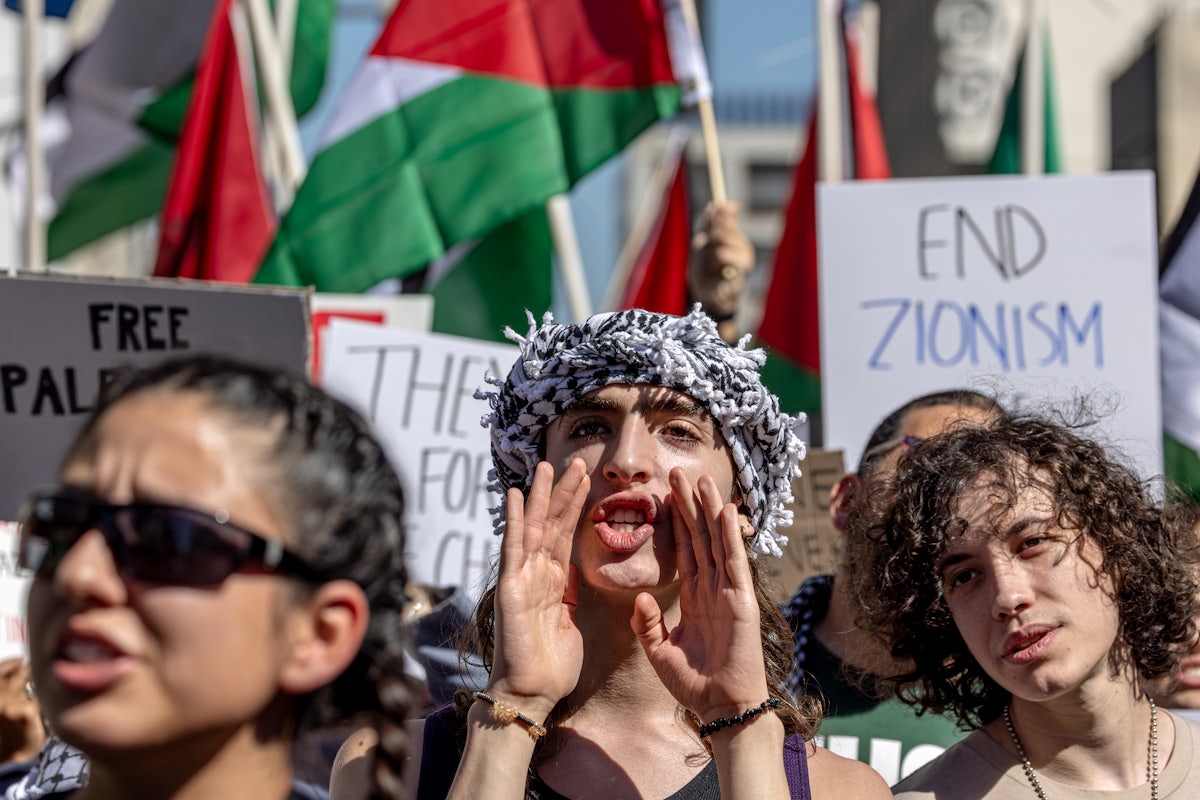

My neighborhood, Manhattan’s Upper West Side, is currently engaged in a semiotic battle over Zionism. Go for walk on a nice spring day, and you will learn from storefront sheds, sidewalks, street barriers, park benches, even the handlebars of a Citi Bike I picked up recently, that “Zionism sucks” and is the equivalent of “racism,” “fascism,” and “genocide.” Of course, it’s not just in my own neighborhood that I see these signs. They follow me to work as well. At a rally outside the chancellor of CUNY’s office on East 42nd Street, one protester’s banner summed up nearly the entire linguistic case: “ Call It What It Is: Genocide, Occupation, Imperialism, White Supremacy, Ethnic Cleansing !”
I don’t know how many people are politically convinced by graffiti, but to be fair, such scribbling has long been the weapon of those without access to newspaper editorial pages, full-page advertisements, and other forms of Gramscian opinion management. Mainstream Jewish organizations, neoconservative pundits, funders of Ivy League universities, and the entire Republican Party have better options. And of course, everybody has social media.
But the anti-Zionist street scribes have one point in their favor. The history of the American debate over Zionism has always centered on its etymological underpinnings. During the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, most American Jews, originally from Germany and only lightly observant, were also outspoken, fervent anti-Zionists. They understood the idea of Jewish “peoplehood” to be contradictory to Jewish American “patriotism.” Judaism, to Reform Jews of the nineteenth century, was a religion and nothing more, just like Protestantism, and certainly offered no reason to question the commitment of these immigrants to their beloved new home country.
Eventually, during the slow-motion collapse of the sustainability of Jewish life in the Russian “Pale of Settlement”—the area in the czarist empire where the vast majority of Jews had settled following various expulsions and migrations—Eastern European immigration overwhelmed the small German American Jewish population and brought with it a “peoplehood”-dominated understanding of Jewish identity consistent with the concern Jews felt for their families. While not Zionists themselves—they had, after all emigrated to America, not to Palestine—they felt a deep connection to those Jews who had, as well as those seeking to get out of the Pale and go anywhere that might take them. Louis Brandeis, soon to be appointed to the Supreme Court and a German Jewish hero to East European Jews and almost certainly the most famous landsman in America at the time, helped enormously to bring these two groups together in a pro-Zionist consensus by developing a formula by which Zionism became a form of American patriotism (“Let no American imagine that Zionism is inconsistent with patriotism,” he proclaimed.) A safe homeland was something Jews who faced persecution elsewhere in the world might need, but not those lucky enough to live in the land of the free.
As the horrible news of the Holocaust began arriving in the last years of the World War II, surviving Jews seeking a “homeland”—not necessarily a state—in Palestine were fighting British “colonialism,” as the League of Nations had put that nation under a British mandate in 1920 in the wake of the collapse of Ottoman rule. They had the support of nearly all American Jews, as well as most American leftists and, not incidentally, the Soviet Union. And yes, some Jewish groups resorted to “terrorism” in this battle, but American Jews did not approve of these tactics, at least not in public. There were still anti-Zionists and, especially among the Germans, “non-Zionists,” but most lacked both the numbers and the inclination to put up much of a fight against the founding of the first Jewish commonwealth in 2,000 years “out of the ashes of the Holocaust,” in the parlance of the day.
After Israel’s sweeping 1967 victory over Egypt, Syria, and Jordan, together with its ensuing conquest of East Jerusalem, the West Bank, and Gaza, the linguistic battle reversed itself in many quarters. The new left condemned Zionism as an ideology of Western “imperialism” and a form of anti-Arab “racism.” Israel’s supporters insisted that virtually all Palestinian resistance to its violent occupation constituted “terrorism,” ignoring the fact that its own side had credibly claimed the same mantle when it was fighting for independence. Today both sides fight over who are the real “terrorists” and which side owns the rights to “liberation movement.” Meanwhile, the anti-Zionist side has succeeded, at least in leftist circles and college campuses, in attaching the words “settler colonialism,” “apartheid,” and (especially since October 7) “genocide” to discussions of Zionist ideology. Because of its explicit equation of anti-Zionism with antisemitism, the pro-Israel side insists that these terms, together with the oft-heard slogan “From the river to the sea” (and sometimes even the words “Free Palestine”), are out of bounds in responsible discourse and should result in firings, expulsions, and other forms of banishment in universities, media institutions, and just about anywhere else they can be found.
What we rarely if ever see, because it is simply assumed, are definitions of the most basic terms of the debate itself. Exactly, what is Zionism ?
The question is a lot more complicated than it sounds, and not only because Jews are famous for having more opinions than there are Jews. It’s complicated because there have always been, and remain today, countless species of groups calling themselves “Zionist.” There are religious, ultrareligious, and anti-religious Zionists, and evangelical Zionists (and significant subsets of each one). There is political Zionism of the sort that led to the creation of the state, and purely cultural Zionism that had no interest in statehood. There are Zionists who say they want to live in peace side by side with Palestinians in separate states; Zionists who want to share the land with Palestinians; and Zionists who want to expel all Palestinians, not only from the West Bank and Gaza but also from Israel proper. All of these distinctions tend to be lost in our increasingly furious debates owing to the fact that when debating the question of “Zionism” versus “anti-Zionism,” the instinct of either side is almost always to demonize one definition and defend the other.
Not long ago, 75 percent of the students at one Modern Orthodox middle school told questioners that they felt “a strong emotional attachment to Israel.” But when asked to define Zionism , fully 60 percent wrote, “ I don’t know what Zionism is.”
They had a point. Today, both Zionism and anti-Zionism are more feelings than ideas, much less coherent ideologies: A person is either cool with the idea of Israel or isn’t. It’s that simple.
According to the ADL website , “Zionists believe in and support the right of the democratic State of Israel to exist as a Jewish homeland. Israel is the only Jewish state in the world. Being a Zionist is distinct from supporting the policies of the government of Israel.” But according to the Jewish Voice for Peace website, the definition is rather different: “While it had many strains historically, the Zionism that took hold and stands today is a settler-colonial movement, establishing an apartheid state where Jews have more rights than others.”
And what of anti-Zionism ? ADL chief Jonathan Greenblatt insists that “anti-Zionism is antisemitism, full stop”; a view that appears to animate pretty much every mainstream U.S. Jewish organizational leader, countless political pundits, and some of the wealthiest donors to America’s most prestigious universities. Lately, some conservative writers, including the neocon Joshua Muravchik writing in The Wall Street Journal, have taken the view that “some say that anti-Zionism isn’t tantamount to antisemitism. If so, it’s worse.… The fulfillment of anti-Zionism means nothing less than a second Holocaust.” Pish-posh, says JVP: Anti-Zionism is merely “a loose term referring to criticism of the current policies of the Israeli state, and/or moral, ethical, or religious criticism of the idea of a Jewish nation-state.”
The distinctions sound pretty clear on paper but, IRL, perhaps not so much. Writing in The Forward, author Lux Alptraum describes a “war raging within my synagogue” between its self-proclaimed Zionists and anti-Zionists. What upsets Alptraum is that rarely are the two sides “actually in disagreement about their ultimate hopes for Israelis and Palestinians.… The arguments that have unfolded are rarely about substantive issues like a cease-fire, hostage return, or Palestinian human rights. More often than not, it feels far more like people are simply fighting over the use of the labels ‘Zionist’ and ‘anti-Zionist,’” which she sees as being “wielded as a way of closing off any dissent, packaged into simplistic catchphrases that only make sense if you already know what the speaker understands Zionism or anti-Zionism to mean.” Similarly, Rabbi Emily Cohen, who works at an Upper West Side Reconstruction synagogue, notes that she has “heard people who identify as Zionist and who identify as anti-Zionist say the same thing about what they think should happen in Israel and Palestine. I’ve heard people who are anti-Zionists identify with what I would describe as Zionist views, and I’ve heard people who are Zionists advocate for what I would describe as anti-Zionist positions.”
Brooklyn College professor Louis Fishman, who describes himself as a “post-Zionist,” worries that the “pro-Palestine bar of acceptance for Jews is not based on shared values of peace, equality, and human rights. It is based on one simple question : Are you willing to separate yourself not just from Israelis but from the Jewish people at large, who overwhelmingly sympathize with Zionism? ” Fishman laments that in his experience, it is necessary, for Jews to be welcomed in pro-Palestinian groups and organizations, to “declare vociferously that you’re anti-Zionist and renounce your support for any Jewish political presence in the territory of Israel-Palestine.” One can see the logic of what he describes in action in the writings of the Palestinian author Miriam Barghouti, who, speaking for the popular “intersectional” view among progressives, wrote , “Being a feminist and a Zionist is a contradiction in terms because the Zionist feminist is complicit in propagating supremacy and domination over a people on the one hand, while on the other hand calling for an end to patriarchy.”
Arguments over the nature of Zionism, anti-Zionism, and their relationship to progressive politics belong in seminar rooms and scholarly publications, not in our political arena. Israel has been around for 75 years and is not going anywhere. Yes, many people continue to dispute Israel’s “right to exist.” Lately, some leftist anti-Zionists have begun to deny the “right to exist” of the United States, as well. (They call it “Turtle Island” and demand its “liberation.”) But so what? None of these people have the power to do anything about it. As the Israeli philosopher and adviser to numerous governments Menachem Brinker explained in an essay published more than 25 years ago, “The task of Zionism is very nearly completed. That is to say, the problem that Zionism set out to address is just about solved. Soon we will be living in a post-Zionist era, and there will no longer be a good reason for a Zionist movement to exist alongside the State of Israel.”
Meanwhile, back IRL, the current political-military-humanitarian crisis between the Israelis and Palestinians is approaching unimaginable catastrophe. Having experienced a devastating day of terrorist mass murder together with a complete failure of both its political and military leadership on October 7, a traumatized Israel has embarked on a military campaign that is leading directly not merely to the mass murder of tens of thousands of civilians but also to mass starvation, disease, and generalized chaos such as the world has rarely ever witnessed. With nearly 33,000 people so far killed, and more than 75,000 injured, little if any remaining medical infrastructure, a daily crisis of food and water, it is this crisis that deserves all of our attention. (Though perhaps we can also take note of the fact that over in the West Bank and off the front pages, with the continuing theft of their land by lawless Israeli settlers/terrorists operating under the protection of Israel’s extremist leadership, the persecution of the Palestinians living on the occupied West Bank is also growing ever more untenable by the day.) To the degree that one can point to an actual, existing form of Zionism today, it is one described by the Israeli scholar and sometimes government adviser Daniel Levy: a “Zionist Jewish political spectrum [that] is essentially all nationalist—running from apartheidists with a smiling face, through to just racist apartheidists, right through to expulsionists and eradicationists.”
At the same time, the Palestinians, like the Israelis, are increasingly acting on the basis of an ideology of murderous nihilism. Most do not support Hamas , but 70 percent tell pollsters that the horrific attacks of October 7, in which over a thousand innocent people were murdered in cold blood, were somehow justified. (Just one party in Palestinian politics has the support of more than a third of its population, and that party is Hamas.)
The behavior of the leadership on both sides is morally indefensible and politically counterproductive. But however horrific and inhumane the Hamas attacks and hostage-taking on October 7 may have been, responsibility for this mass death and potential famine rests squarely with the Netanyahu government. The Israelis rule historic Palestine literally “from the river to the sea,” and every day, their leaders appear intent on making the lives of the Palestinians under their thumb more miserable, and the Palestinians can do little or nothing to stop them. Meanwhile, Hamas continues to hold, by Israel’s count, 130 of the hostages it took on October 7, and Israel jails more and more Palestinian activists every day.
Despite Israel’s undeniable dependence on U.S. financial, military, and diplomatic support, the Biden administration appears impotent to impose any meaningful limits on Israel’s actions, despite a constant stream of Susan Collins–style statements of “concern.” (Last Friday, in honor of Secretary of State Antony Blinken’s visit, the Israeli government announced its largest confiscation of Palestinian land since the Oslo Accords were put into effect in 1993 . )
Clearly, what is needed now more than ever is immediate measures to end the killing; prevent mass starvation; improve health, medical, and sanitation services in Gaza; to effect a return of the hostages; and to end the land seizures in the West Bank and begin some sort of plan for postwar reconstruction of Gaza, together with democratic elections in Gaza, the West Bank, and (as Senator Schumer correctly insisted) Israel. All of this is, I admit, difficult to imagine at the present moment, much less implement.
But none of it, I can promise you, will happen in the context of an argument over the meaning of the word Zionism. It’s fair to say that words themselves do not kill anyone. But as this argument has demonstrated time again, focusing on etymology at the expense of actual lives certainly does. Israel-Palestine is not, after all, ultimately a war of words. It’s a war of people. And right now, too many are dying, starving, and desperate for decent medical care to allow the decent among us to argue for even one more minute over whose ideology is the winning one in a fight in which there are only losers.
Eric Alterman is a CUNY distinguished professor of English at Brooklyn College and the author of We Are Not One: A History of America’s Fight Over Israel .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Terrorism Essay. Terrorism is an act, which aims to create fear among ordinary people by illegal means. It is a threat to humanity. It includes person or group spreading violence, riots, burglaries, rapes, kidnappings, fighting, bombings, etc. Terrorism is an act of cowardice. Also, terrorism has nothing to do with religion.
It should come as no surprise, twenty years after 9/11, that much needs to change for the future of counterterrorism. The 9/11 attacks killed 2,977 people and led to a "Global War on Terrorism" against the terrorists responsible—as well as wider conflicts involving South Asia, Europe, the United States, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
Anti-terrorism is very important. It helps to keep people safe. Without it, terrorists might feel free to do whatever they want. This could lead to more violence and fear. Anti-terrorism also helps to protect our rights and freedoms. If terrorists can change our way of life through fear, then we lose our freedom.
International Terrorism as a Global Challenge. International terrorism has become the greatest danger to world security, overtaking the threats of military confrontations from rival great powers. Stewart (2006) observes that the international security threat posed by military confrontations between rival great powers has reduced dramatically ...
Before briefly tracing the history of international responses to terrorism, this essay presents observations on the question of definition or nomenclature. The first ... The classic anti-terrorism conventions of the post-World War II era were more successful. These conventions were designed to promote cooperation between
The term "war on terror" had been coined a few days after al-Qaida's attacks of 9/11 to describe the most extensive and ambitious counter-terrorism operation the world had seen. As Bush ...
Researching of Morals of Terrorists. Terrorism attacks are a form of violence, and the moral implication is death in the form of revenge. Realism is a form of acceptance that everyone on the battlefield is a civilian with their families. The Structures, Motivations, and Qualities of Terrorist Groups.
Aryan Nations (AN) is a white supremacist terrorist organization that is headquartered in Hayden, Idaho. It is a form of right-wing terrorism that is anti-Semitic and neo-Nazi, and that was founded by Richard Girnt Butler in 1977. Its main objective is to establish a white state that excludes other races by fighting against people that pose a ...
Introduction. The prominence of far-right terrorism and extremism has grown considerably within terrorism studies in recent years as evidenced by special issues (such as this!) (also Ravndal and Bjørgo Citation 2018); published bibliographies (Axelsen Citation 2018; Tinnes Citation 2020); research networks, centres and projects; and even university degrees (Schooling Citation 2021).
Essay on Anti-Terrorism Movements. Terrorism and anti-terrorism movements have gained momentum over the past few years, particularly since the 9/11 attacks on the twin towers of the World Trade Center in 2001. Let us look at the dynamics of terrorism, and the factors that have led to the re-emergence of terrorism in the twenty first century.
The results presented in. Table 1. clearly show that al-Qaeda, jihadism more generally and Iraq were the most frequently researched topics overall in the 2007-2016 period. Several other topics, such as "United States", "Counterterrorism/War on Terror" and "Afghanistan" were also frequent top-5 contenders.
1. Introduction. Terrorism is the premeditated use or threat to use violence by individuals or subnational groups to obtain a political or social objective through the intimidation of a large audience beyond that of the immediate noncombatant victims (Enders and Sandler, 2012, p.4).The two essential ingredients of terrorism are its violence and its political or social motive.
Introduction. Terrorism has been the most prominent security issue since the start of the new millennium. Footnote 1 Since 2014, series of deadly attacks in France, Belgium, Germany, the United States, and Great Britain have fueled new anxieties about terrorist incidents, particularly in Western countries. That the terrorism label has remained ambiguous and contentious, with hundreds of ...
1 Review Summary. Since September 11 th, there have been massive increases in personal, commercial, and governmental expenditures on anti-terrorism strategies, as well as a proliferation of programs designed to fight terrorism.These increases in spending and program development have focused attention on the most significant and central policy question related to these interventions: Do these ...
Terrorism, the calculated use of violence to create a general climate of fear in a population and thereby to bring about a particular political objective. Definitions of terrorism are complex and controversial; because of the inherent ferocity of terrorism, the term in its popular usage has developed an intense stigma.
TWELVE ESSAYS ON TERRORISM A VIF Analysis Edited by Lt Gen Gautam Banerjee Foreword by Gen NC Vij, PVSM, UYSM, AVSM ... However, the 1980s saw a new turn of anti-nationalism manifesting in the form of rise of terr orism. It appear ed fist in P unjab and then in Kashmir , just as Maoist terrorism raised its head in Central India. Meanwhile, unable
100 Words Essay on Terrorism. Terrorism is the use of violence and intimidation in the pursuit of political and personal aims. It is a global phenomenon that has affected countries worldwide, causing harm to innocent civilians, damaging economies, and destabilizing governments. The causes of terrorism are complex and can include religious ...
Defining Terrorism. An agreed, comprehensive definition of terrorism has never been created by the international community. The United Nations' attempts to define the term during the 1970s and 1980s failed mostly because of disagreements among its members over the use of violence in conflicts over self-determination and national liberation.
Terrorism Essay in English: Short Essay on Terrorism in 500+ Words. Terrorism Essay: Terrorism is a cheap act of threatening people and promoting violence. It destroys communal harmony and evokes fear in the public. Terrorism can include violent acts that aim to spread unrest and fear among the local populations.
Just before day's end on July 3, President Duterte signed into law what is now the Anti-Terrorism Act of 2020, which repeals the 2007 Human Security Act. Republic Act No. 11479 is an abomination ...
Introduction. The academic study of terrorism is often described as beset by numerous and pervasive conceptual and methodological problems. Footnote 1 Critiques of the state of the art have appeared since the 1970s and their conclusions have been worryingly similar. Footnote 2 One of these is that the definitional debate on what exactly constitutes terrorism continues to exert a detrimental ...
What is India Doing to Combat the Threat of Terrorism? In the wake of the 26/11 terrorist attack. In January 2009, the National Investigation Agency was established to deal with terrorist crimes. In India, the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act is the primary anti-terrorism law.
Under this supposed national security law, Duterte will create an Anti-Terrorism council that can make warrantless arrests, freeze assets of suspects, and surveil suspects. Furthermore, as a ...
Pish-posh, says JVP: Anti-Zionism is merely "a loose term referring to criticism of the current policies of the Israeli state, and/or moral, ethical, or religious criticism of the idea of a ...