Home — Essay Samples — Life — Career Goals — Why I Want to Become a Lawyer: My Future Career

Why I Want to Become a Lawyer: My Future Career
- Categories: Career Goals Lawyer
About this sample

Words: 502 |
Updated: 9 November, 2023
Words: 502 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
You may also be interested Turabian Citation Maker
Works Cited:
- Hobbes, T. (2018). Leviathan. Penguin UK.
- Rousseau, J.-J. (2019). A discourse on inequality. Oxford University Press.
- Avineri, S. (2018). The social and political thought of Karl Marx. Cambridge University Press.
- Baumeister, R. F. (1997). Evil: Inside human violence and cruelty. Holt Paperbacks.
- Brennan, G., & Pettit, P. (2019). The economy of esteem: An essay on civil and political society. Oxford University Press.
- Gauthier, D. (2016). Hobbes's social contract: An introduction. Cambridge University Press.
- Locke, J. (2019). Two Treatises of Government. Oxford University Press.
- Manent, P. (2018). Natural law and human rights: Toward a recovery of practical reason. University of Notre Dame Press.
- Sandel, M. J. (2012). Justice: What’s the right thing to do?. Macmillan.
- Skinner, Q. (2019). Hobbes and Republican Liberty. Cambridge University Press.
Video Version

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Life Law, Crime & Punishment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1038 words
1 pages / 483 words
5 pages / 2079 words
2 pages / 790 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Career Goals
My current professional role as a healthcare provider has well-positioned me to perform in the role of a dietetic intern with strong leadership skills and a responsive work ethic. I look to my resourcefulness, adaptability to [...]
Nurse practitioner is a master’s prepared registered nurse that has received additional training, education, and certification and is qualified to provide primary patient care. Many often wonder, "why I want to be a nurse [...]
American Nurses Association. (2021). Nursing: Scope and standards of practice. Silver Spring, MD: American Nurses Association.Potempa, K., & Forgit, J. J. (Eds.). (2019). Public health nursing: Practicing population-based care. [...]
While being an educator may not procure you the six-figure salary you have constantly longed for, it has different advantages a long way past that of a weighty check. The essential reward of being an instructor is having the [...]
Social work stands as a vocation that garners significant interest among students, primarily because it offers the promise of job satisfaction and the opportunity to contribute profoundly to the lives of others (Humprey, 2011). [...]
Mahatma Gandhi has said that “The future depends on what you do today.” and I personally believe that, “From thousands of species, Humankind is only the species on the earth that thinks about its future”. We are created to do [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Username or email *
Password *
Forgotten password?
[email protected]
+44 (0)20 8834 4579
How to Write a First-Class Law Essay
Studying law at university entails lots of essay writing. This article takes you through the key steps to writing a top law essay.
Writing a law essay can be a challenging task. As a law student, you’ll be expected to analyse complex legal issues and apply legal principles to real-world scenarios. At the same time, you’ll need to be able to communicate your ideas clearly and persuasively. In this article, we’ll cover some top tips to guide you through the process of planning, researching, structuring and writing a first-class law essay with confidence.
1. Start In Advance
Give yourself plenty of time to plan, research and write your law essay. Always aim to start your law essay as soon as you have the question. Leaving it until the last minute does not only create unnecessary stress, but it also leaves you insufficient time to write, reference and perfect your work.
2. Understand The Question
Do not begin until you fully comprehend the question. Take the time to read the question carefully and make sure that you understand what it’s asking you to do. Highlight key terms and annotate the question with definitions of key concepts and any questions that you have have. Think about how the question links back to what you’ve learned during your lectures or through your readings.
3. Conduct Thorough Research
Conducting thorough research around your topic is one of the most fundamental parts of the essay writing process. You should aim to use a range of relevant sources, such as cases, academic articles, books and any other legal materials. Ensure that the information you collect is taken from relevant, reliable and up to date sources. Use primary over secondary material as much as possible.
Avoid using outdated laws and obscure blog posts as sources of information. Always aim to choose authoritative sources from experts within the field, such as academics, politicians, lawyers and judges. Using high-quality and authoritative sources and demonstrating profound and critical insight into your topic are what will earn you top marks.
4. Write A Detailed Plan
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to plan your essay. When writing your plan, you’ll need to create an outline that clearly identifies the main points that you wish to make throughout your article. Try to write down what you wish to achieve in each paragraph, what concepts you want to discuss and arguments you want to make.
Your outline should be organised in a clear, coherent and logical manner to ensure that the person grading your essay can follow your line of thought and arguments easily. You may also wish to include headings and subheadings to structure your essay effectively This makes it easier when it comes to writing the essay as starting without a plan can get messy. The essay must answer the question and nothing but the question so ensure all of your points relate to it.
Start Writing Like A Lawyer
Read our legal writing tips now
5. Write A Compelling Introduction
A great introduction should, firstly, outline the research topic. The introduction is one of the most crucial parts of the law essay as it sets the tone for the rest of the paper. It should capture the readers attention and provide the background context on the topic. Most importantly, it should state the thesis of your essay.
When writing your introduction, avoid simply repeating the given question. Secondly, create a road map for the reader, letting them know how the essay will approach the question. Your introduction must be concise. The main body of the essay is where you will go into detail.
6. Include A Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis should clearly set out the argument you are going to be making throughout your essay and should normally go in the introduction. Your thesis should adopt a clear stance rather than being overly general or wishy-washy. To obtain the best grades, you’ll need to show a unique perspective based upon a critical analysis of the topic rather than adopting the most obvious point of view.
Once you’ve conducted your research and had a chance to reflect on your topic, ask yourself whether you can prove your argument within the given word count or whether you would need to adopt a more modest position for your paper. Always have a clear idea of what your thesis statement is before you begin writing the content of your essay.
7. Present the Counter-argument
To demonstrate your deeper understanding of the topic, it’s important to show your ability to consider the counter-arguments and address them in a careful and reasoned manner. When presenting your counterarguments, aim to depict them in the best possible light, aiming to be fair and reasonable before moving on to your rebuttal. To ensure that your essay is convincing, you will need to have a strong rebuttal that explains why your argument is stronger and more persuasive. This will demonstrate your capacity for critical analysis, showing the reader that you have carefully considered differing perspectives before coming to a well-supported conclusion.
8. End With A Strong Conclusion
Your conclusion is your opportunity to summarise the key points made throughout your essay and to restate the thesis statement in a clear and concise manner. Avoid simply repeating what has already been mentioned in the body of the essay. For top grades, you should use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide critical reflection and analysis on the topic. You may also wish to share any further insights or recommendations into alternative avenues to consider or implications for further research that could add value to the topic.
9. Review The Content Of Your Essay
Make sure you factor in time to edit the content of your essay. Once you’ve finished your first draft, come back to it the next day. Re-read your essay with a critical perspective. Do your arguments make sense? Do your paragraphs flow in a logical manner? You may also consider asking someone to read your paper and give you critical feedback. They may be able to add another perspective you haven’t considered or suggest another research paper that could add value to your essay.
10. Proofread For Grammatical Mistakes
Once you’re happy with the content of your essay, the last step is to thoroughly proofread your essay for any grammatical errors. Ensure that you take time to ensure that there are no grammar, spelling or punctuation errors as these can be one of the easiest ways to lose marks. You can ask anyone to proofread your paper, as they would not necessarily need to have a legal background – just strong grammar and spelling skills!
11. Check Submission Guidelines
Before submitting, ensure that your paper conforms with the style, referencing and presentation guidelines set out by your university. This includes the correct font, font size and line spacing as well as elements such as page numbers, table of content etc. Referencing is also incredibly important as you’ll need to make sure that you are following the correct referencing system chosen by your university. Check your university’s guidelines about what the word count is and whether you need to include your student identification number in your essay as well. Be thorough and don’t lose marks for minor reasons!
12. Use Legal Terms Accurately
Always make sure that you are using legal terms accurately throughout your essay. Check an authoritative resource if you are unsure of any definitions. While being sophisticated is great, legal jargon if not used correctly or appropriately can weaken your essay. Aim to be concise and to stick to the point. Don’t use ten words when only two will do.
12. Create a Vocabulary Bank
One recurring piece of advice from seasoned law students is to take note of phrases from books and articles, key definitions or concepts and even quotes from your professors. When it comes to writing your law essay, you will have a whole range of ideas and vocabulary that will help you to develop your understanding and thoughts on a given topic. This will make writing your law essay even easier!
13. Finally, Take Care of Yourself
Last but certainly not least, looking after your health can improve your attitude towards writing your law essay your coursework in general. Sleep, eat, drink and exercise appropriately. Take regular breaks and try not to stress. Do not forget to enjoy writing the essay!
Words by Karen Fulton
Free Guides
Our free guides cover everything from deciding on law to studying and practising law abroad. Search through our vast directory.
Upcoming Events
Explore our events for aspiring lawyers. Sponsored by top institutions, they offer fantastic insights into the legal profession.
Join Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list for weekly updates and advice on how to get into law.
Law Quizzes
Try our selection of quizzes for aspiring lawyers for a fun way to gain insight into the legal profession!
PREVIOUS ARTICLE
Legal Writing: Start Writing Like a Lawyer!
NEXT ARTICLE
LLM Jobs for Graduates
Loading More Content
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
College Application Essay Tips for Aspiring Lawyers
This article was written based on the information and opinions presented by Alexander Oddo in a CollegeVine livestream. You can watch the full livestream for more info.
What’s Covered:
Describe your reasons why, career goals, the personal statement.
Your aspirations are an important component of what makes you who you are, and if you aspire to become a lawyer, you should share this information with any college or university that you apply to. In the college application process, essays are the best opportunity for you to discuss your passion for the law and your interest in becoming a lawyer. You may incorporate your legal aspirations into your personal statement or they may form the backbone of your supplemental essays where you respond to questions about why you are interested in a particular school, program, or major.
Generally speaking, a smart way to approach your essays is to introduce your interests and connect them to specific personal stories and goals. As a person who aspires to be a lawyer, you want to introduce your interests that relate to the law and describe what attracts you to the legal field. What is it about studying the law and becoming a lawyer that you find most compelling? Why does this path feel meaningful and necessary to you? Draw on specific experiences in your life and lessons you have learned to formulate your rationale for pursuing this career path.
When you explain why you aspire to be a lawyer, be as specific as possible. “ Lawyers help people. The legal profession is lucrative.” These reasons are too simplistic and generic to provide any useful insight for an admissions officer to understand who you are. If you want to become a lawyer, you should explain your motivation to pursue this career path in terms of:
- Why you want to help others and who you want to help, such as immigrants or victims of domestic violence
- What areas of the law interest you, such as tax law, family law, or corporate law
- What it is about studying and practicing law that appeals to you intellectually, such as that you have an analytical mind and enjoy solving complex problems
- What disciplinary perspectives you find interesting in relation to the law, such as history, philosophy, political science, public policy, or criminology
- What experiences you have had and people you have met that have inspired you to pursue a legal career. Any experiences you cite should extend beyond your favorite episode of “Law and Order” or “How to Get Away with Murder.” Maybe a movie or TV show about the law initially sparked your interest, but then you developed this interest into an enduring passion by volunteering at your local courthouse, joining your high school’s mock trial team, or becoming certified as a paralegal.
After you have thoroughly explained why you are interested in becoming a lawyer, you should look to the future and discuss your career goals. Identify a specific area of the law that you want to practice, and ground this in the various reasons why you want to become a lawyer. It is completely fine if you are not entirely sure what area of law you want to practice. Regardless, the winning strategy is to pick a specific area of law that you want to pursue and cite this consistently throughout your college applications. It will allow you to construct an application that is specific, developed, and memorable rather than overly general, unfocused, and potentially forgettable.
Ultimately, colleges and admissions officers will not hold you accountable for matching the goals and plans you outline in your essays. You are free to start college and decide that you don’t want to pursue a legal career at all. You should know before you apply to and attend law school whether you want to practice law, but undergraduate institutions recognize that you are young and still trying to explore your interests and define your goals. If you do pivot, admissions officers will rest assured because they know you have been through the process of creating a goal and that you can go through this process in any field you choose.
If you are applying to a school that does not have any supplemental essays as part of its application, then you should discuss your legal aspirations in your Common Application personal statement. Your personal statement is the place in your application where you share your personal story, and you should tell this story in such a way that you weave your past, present, and future together. When you discuss your future, include some information about your interest in becoming a lawyer, drawing connections between this goal and your past experiences and present endeavors that inform and relate to your aspirations.
For more information, review this comprehensive guide on How to Write the Common Application Essays for the 2022-2023 application cycle.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

How to Write a 'Why This Law School' Essay
Here's how to respond when a law school asks about your specific interest in them.
Writing a 'Why This Law School' Essay

Getty Images
Law schools value applicants who show they have done their research about where they are applying, because the investment of time and energy shows genuine interest and because research is a core legal skill.
Strong law applicants tend to have carefully considered why they are applying to law school , and they understand that their application essays need to express their interest in a legal career.
However, many are stumped when law school applications ask them a narrower question: Why are you applying to this law school?
Most commonly, law schools may ask this question through a supplemental application essay , sometimes called a “Why X School” or “Why This School” essay.
For example, the University of Notre Dame Law School offers applicants an optional statement of no more than two double-spaced pages “to express a specific interest in Notre Dame Law School.” The School of Law at the University of California—Irvine has a mandatory essay of up to 750 words about why you are interested in their school.
Other schools may ask applicants to address this question within their personal statement with a short-answer prompt. It is also a common interview question.
By asking applicants about their specific interest in a school, admissions officers turn the table on applicants. After all, applicants take pains to distinguish themselves by showing that their grades and test scores don’t reveal other factors that set them apart. With a “Why This School” question, law schools say: We’re unique, too. Why are you choosing us?
Ironically, many applicants have given little thought to what separates one law school from another! As you can imagine, admissions offices are not thrilled about this. They certainly don’t see themselves as gatekeepers to a generic, interchangeable institution.
Answering a “Why This School” essay can be frustrating. How do you articulate your interest without resorting to boilerplate flattery about a school’s prestigious faculty and beautiful campus?
Learn About a Law School Through an Event, Interview or Visit
Since many applicants apply to a wide range of law schools, they may not know much about each one.
One of the best ways to learn about a law school is at a law school forum or information session. Many schools host online events, which can be convenient for applicants unable to visit the law school in person.
Look for these things
If you have a chance to speak with an admissions officer, you can ask good questions to learn more about how the school sets itself apart from others.
You may also learn about a law school by talking to current or former students about their experience on campus.
Research What a Law School Offers
Use search engines like Google News or LexisNexis to find any mentions of the school in the press. Did the law school recently open a new building or center, or announce a new policy that might affect your interest?
Most importantly, carefully review the law school’s website . Law school websites are one of the best ways to learn about a school: how it sees itself, what it offers and what’s going on. While law school websites might look unremarkable at first, close reading can reveal valuable details.
Compare multiple law school websites and notice the differences between them in style and content. Often, the words and images they use are meticulously crafted to present and promote a distinct identity. Without copying their phrasing word for word, reference these ideas in your essays to reflect an understanding of a school’s unique character while avoiding cliches and generalities.
Find Areas of Overlap
Law schools differ in their size, geography , culture, curricula, special programs, campus activities and many other ways. These distinctions provide perspectives on how each law school stands out.
Based on your research, make a list of strengths for each of your target schools that are relevant to your interests as a candidate. For example, if your personal statement is about your dream of becoming a prosecutor, look for clinics, research centers, programs, professors or distinguished alumni in the criminal law field.
Focus on a Few Specific Points
When elaborating on the reason you are interested in a school, don’t try to “flood the zone.” Broad compliments may sound insincere.
In a “Why This School” essay or interview response, center your answer on a few concrete reasons.
Try to keep the reasons varied. For example, rather than mention three clinics you find interesting, think about other potential points of intersection, like a personal connection or a geographic interest.
Think realistically about your plans for law school and beyond . It would be more effective to thoughtfully explain why a professor’s research interests align with your own than to rattle off every relevant course in the catalog.
Ultimately, “why” questions are about connecting a law school to yourself. Answer with confidence by researching and identifying a few specific ways in which a school’s unique offerings match with what sets you apart.
Tips to Boost a Law School Application

Tags: law school , graduate schools , education , students
About Law Admissions Lowdown
Law Admissions Lowdown provides advice to prospective students about the law school application process, LSAT prep and potential career paths. Previously authored by contributors from Stratus Admissions Counseling, the blog is currently authored by Gabriel Kuris, founder of Top Law Coach , an admissions consultancy. Kuris is a graduate of Harvard Law School and has helped hundreds of applicants navigate the law school application process since 2003. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Popular Stories
Best Colleges

Top Business Schools

Best Graduate Schools

The Short List: Grad School

Paying for Graduate School

You May Also Like
Mba programs that lead to good jobs.
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024
B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024
Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024
Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024

U.S. News Ranks Best Graduate Schools

MBA Scholarships
Sammy Allen April 4, 2024

Special Master's Programs and Med School
Renee Marinelli, M.D. April 2, 2024

15 Famous Fulbright Scholars
Cole Claybourn April 1, 2024

When to Expect Law School Decisions
Gabriel Kuris April 1, 2024

- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Uncategorized
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Law Essay: 8 Steps
December 28, 2023
1. Choosing an Essay Topic
When it comes to writing a law essay, choosing an appropriate topic is crucial. A well-chosen topic will make your research and writing process smoother and more enjoyable, while a poorly chosen topic can lead to frustration and a lackluster essay.
Firstly, consider what has piqued your interest in your law studies so far. Perhaps there was a case or topic that you found particularly intriguing, or an aspect of law that you feel needs further exploration. Alternatively, you could focus on a current legal issue that you feel strongly about and want to delve deeper into.
It’s also important to make sure your topic isn’t too broad or too narrow. Too broad of a topic can result in a lack of focus, while a topic that is too narrow won’t give you enough research material to work with.
Ultimately, choosing a law essay topic is about finding a balance between your personal interests and the practical aspects of your assignment. Take the time to carefully consider your options, and don’t be afraid to ask for input or guidance from your professor or classmates.
Possible Law Essay Topics
- The impact of social media on defamation laws.
- Analyzing the constitutionality of mandatory minimum sentencing.
- The effectiveness of restorative justice in reducing recidivism rates.
- Legal implications of artificial intelligence in the workplace.
- Exploring the rights of privacy versus national security in the digital age.
- Examining the legal and ethical issues surrounding euthanasia.
- Assessing the role of international law in combating climate change.
- Analyzing the legal framework for cyberbullying and online harassment.
- The legalization and regulation of recreational marijuana: a critical analysis.
- Exploring the intersection of intellectual property rights and emerging technologies.
Remember to choose a topic that aligns with your interests and research availability, while ensuring that it is adequately focused for a detailed analysis within the scope of your essay.
2. Researching the Topic
Before diving into writing a law essay, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on the chosen topic. This step is critical to ensure that the essay is factually correct, well-supported, and logically structured. Here are some tips on how to research effectively for a law essay:
- Begin by gathering basic information. Use specialized textbooks, journals, and databases to gain a foundational understanding of the topic.
- Use secondary sources to gain a broader perspective on the topic. Utilize reputable news sources, government publications, and online legal databases to broaden your search.
- Access case law. To support your arguments, cite legal cases that illustrate your argument. Access online case law databases that have accessible search functions.
- Use primary sources. Primary sources include statutes, regulation, and the constitution. It’s important to have a good grasp of the primary sources since they are the basis of much of legal research.
- Take notes. Keep track of all relevant information, including sources and citations. Use an organized format that will make outlining and writing the essay a simpler process.
- Evaluate and analyze. Through the research process, it’s important to analyze the information found. Determine what is and is not relevant, and how it factors into your argument.
By conducting thorough research, you will be able to support your argument with a well-evidenced and structured essay. Remember to keep track of all sources and citations as they will be necessary in the writing process.
3. Developing Strong Thesis Statement
Developing a strong thesis statement is essential when writing a law essay. This powerful statement sets the tone for the entire article and guides the reader’s understanding of your argument. To create an effective thesis statement, you must first fully understand the topic and question at hand. Take your time to research and gather relevant information to support your viewpoint. As you delve deeper into the subject, analyze different perspectives and identify the key arguments surrounding the topic. Once you have a clear understanding of the various viewpoints, narrow down your focus and craft a concise and persuasive thesis statement that clearly states your position. Remember, a strong thesis statement should be debatable, specific, and assertive. Spend time honing your thesis to ensure it effectively conveys your argument and engages the reader’s interest.
Example thesis statement:
“The death penalty should be abolished in the United States because it violates the Eighth Amendment, fails to act as an effective deterrent, and disproportionately affects marginalized communities.”
4. Structuring the Law Essay
Structuring your law essay is crucial to ensure clarity, coherence, and a logical flow of ideas. Here’s a breakdown of how to structure your law essay:
Introduction:
- Provide a brief overview of the topic and its significance.
- Present the thesis statement, clearly stating your argument.
Background and Context:
- Provide necessary background information to help the reader understand the topic.
- Explain relevant legal concepts, principles, or statutes related to your argument.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Present your arguments and support them with evidence, case law, or legal authorities.
- Use clear and concise language to explain your points and provide analysis.
Counter-Argument:
- Acknowledge and present the counter-argument(s) objectively and logically.
- Refute the counter-argument(s) with reasoned explanations and supportive evidence.
Conclusion:
- Summarize your main arguments and their supporting evidence.
- Restate your thesis statement and highlight its significance.
- Offer some final thoughts or suggestions for further research or action.
Remember to use appropriate headings and subheadings to structure your essay effectively. Use transition words and phrases to ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs. Additionally, ensure proper citations and referencing throughout the essay to maintain academic integrity.
5. Writing the Introduction
Writing the introduction is your opportunity to grab the reader’s attention and set the tone for your entire law essay. Here’s how you can effectively structure your introduction:
Start with a hook:
- Use a compelling statement, anecdote, or a relevant quote to engage the reader and create interest in your topic.
Provide background information:
- Give a brief overview of the legal issue or topic you will be discussing.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the topic to the field of law or society at large.
State the purpose and scope of your essay:
- Clearly state your thesis statement, which should encapsulate your main argument.
- Mention the key points you will address and the legal principles, cases, or statutes you will analyze.
Outline the essay structure:
- Provide a brief outline of how your essay will be structured.
- Mention the main sections or arguments you will present.
Establish the context:
- Explain any necessary legal concepts, terms, or background information that the reader needs to understand.
Remember to keep your introduction concise and focused. It should provide enough information to orient the reader and generate interest in your essay. However, save the detailed arguments and evidence for the main body of your essay. Aim to make your introduction clear, engaging, and persuasive, setting the stage for the rest of your law essay.
6. Developing the Body Paragraphs
Developing the body paragraphs is the core of your law essay, where you present and support your arguments with evidence and analysis. Here’s how to effectively structure and develop your body paragraphs:
Start with a topic sentence:
- Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- The topic sentence sets the tone and direction for the paragraph.
Present your argument:
- Clearly state your argument or point of view in the opening sentences of each paragraph.
- Provide supporting evidence, such as case law, statutory provisions, or legal principles, to back up your argument.
Analyze and interpret the evidence:
- Explain the significance of the evidence in relation to your argument.
- Analyze how the evidence supports and strengthens your position.
Use legal authorities and sources:
- Cite relevant cases, statutes, or legal commentary to support your arguments.
- Refer to authoritative legal sources, such as court decisions or academic articles, to provide credibility.
Use clear and concise language:
- Clearly articulate your ideas using logical transitions and precise language.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex language that may confuse the reader.
Remember to properly structure your paragraphs, provide sufficient evidence and analysis, and link your arguments back to your main thesis statement. Each paragraph should contribute to the overall coherence and flow of your essay, ensuring a convincing and well-supported argument.
7. Present the Counter-argument
Presenting the counter-argument is an essential component of writing a persuasive law essay. Failing to acknowledge opposing viewpoints weakens your argument and makes it appear biased. Therefore, it is crucial to identify different perspectives surrounding the topic and analyze these perspectives objectively. Once you have identified the counter-argument, you can present it in your essay, offering evidence and explanations to support it. Addressing counter-arguments in your essay strengthens your credibility as a writer and demonstrates your ability to look at a topic from multiple perspectives. Additionally, this approach makes your essay more convincing by acknowledging and addressing potential criticism of your argument. Keep in mind that effectively presenting the counter-argument requires thorough research, logical reasoning, and evidence-based arguments. Therefore, take your time to critically analyze opposing views to ensure your argument is backed up by relevant and reliable supporting evidence. By doing so, you can construct a well-reasoned and thoughtful essay that can withstand any counter-argument.
8. Crafting the Conclusion
Crafting a strong conclusion is essential to leave a lasting impression on the reader and effectively summarize your arguments in a law essay. Here are some key steps to consider when writing your conclusion:
Summarize your main points:
- Recapitulate the main arguments you presented in the body paragraphs.
- Provide a brief overview of the evidence you presented to support each argument.
Reinforce your thesis statement:
- Restate your thesis statement in a concise manner to remind the reader of your main argument.
- Emphasize the significance and relevance of your thesis in the context of the larger legal issue.
Offer a broader perspective:
- Connect your arguments to the wider legal or societal implications of the topic.
- Discuss the potential consequences or impact of your findings on the field of law or legal practice.
Suggest areas for further research:
- Highlight any unanswered questions or areas of debate that may require future exploration.
- Propose avenues for future research or policy development related to your topic.
Conclude with a compelling closing statement:
- Leave the reader with a thought-provoking final remark that leaves a lasting impression.
- Use a concise and powerful statement to tie together your essay and reinforce your main message.
Ensure that your conclusion is concise, focused, and aligned with your overall argument. It should serve as a strong ending to your law essay, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your position and the importance of the topic discussed.
Use Legal Terms Accurately
In the realm of writing law essays, the accurate and precise use of legal terms is paramount. This subheading focuses on the importance of correctly employing legal terminology in order to craft an exceptional law essay.
Mastering legal terminology is essential for two reasons. Firstly, it demonstrates an understanding and grasp of the subject matter, showcasing your expertise to both professors and potential employers. Secondly, using legal terms accurately enhances the clarity and coherence of your arguments, making your essay more persuasive and compelling. However, it is crucial to strike a balance – overusing legal jargon may alienate readers who are not well-versed in the law.
To ensure accuracy, it is imperative to consult reliable legal sources such as authoritative textbooks, journals, or statutes. Moreover, reading and analyzing sample essays or exemplary legal writing can provide guidance on how to effectively incorporate legal terms into your own work. By diligently honing your legal language skills, you will significantly elevate the quality and impact of your law essays.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Navigating the complexities of a Document-Based Question (DBQ) essay can be daunting, especially given its unique blend of historical analysis...
An introduction speech stands as your first opportunity to connect with an audience, setting the tone for the message you...
Embarking on the journey to write a rough draft for an essay is not just a task but a pivotal...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Law
Essay Samples on Lawyer
Why did you choose law as a career.
The decision to pursue a career in law is one that often carries profound motivations and aspirations. In this essay, I share my personal journey and delve into the factors that led me to choose law as a career path. By exploring the intricacies of...
Why I Want to Become a Lawyer: Advocating for Justice
Becoming a lawyer is a journey that resonates deeply with my passion for upholding justice, defending the rights of individuals, and navigating the complex web of legal intricacies. The prospect of making a difference in people's lives, advocating for those who need a voice, and...
- Career Goals
Thurgood Marshall and Spiral of Science in Marshall
The movie “Marshall” focusses on how a young black lawyer for The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), Thurgood Marshall, goes through one of his toughest trials in Bridgeport, Connecticut, where he defends Joseph Spell, a coloured man charged of rape against...
- Civil Rights
- Thurgood Marshall
Analysis of Thurgood Marshall, American Revolutionary
In Thurgood Marshall- American Revolutionary, William Juan takes a critical exploration of the life of Marshall; who is regarded as a seminal personality in America’s history during the 20th century. This groundbreaking work of fiction undertakes a journey into the definitive biography of the celebrated...
Lawyers' Interesting World of Employment Law
Anna and her boss, David, got into a big argument. Anna got paid less than her co-worker John for the same job position, causing them to argue. Their gender causes their only difference. The clients utilize an employment lawyer to attempt to resolve this issue....
- Employment Law
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Jurisprudence and Different Legal System Throughout Legal History
Common law and civil law conventions share comparable social goals (independence, ideology and individual rights) and that they have really been joined in one single family, the Western law family, since of this handy likeness. a serious distinction between the civil law and customary law...
The Path and Requirements to Becoming a Lawyer
Robert Kennedy makes a point in his novel, “Lawyers have their duties as citizens, but they also have special duties as lawyers. Their obligations go far deeper than earning a living as specialists incorporation or tax law. They have a continuing responsibility to uphold the...
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Lawyer Career
Ever since the time of the Greek and the Romans, lawyers have been an important part of society. They were the help needed in any legal case. The need for them is very high but there are also ways to become one. It is a...
Prestige of the Lawyer Profession: Pay Wage and the Ranking
A lawyer is a person who is licensed by the state that practises the law and guides their clients with their cases and legal matters. Lawyers have clients who need to settle a problem with the court or for any reason and the lawyer is...
How Personal Injury Lawyers Save The Day
No matter how much a person takes care of everything they do, there will always be something that will throw them off their game. One such unwanted events include accidents. These misfortunes can happen at any given moment – whether you are at work, whilst...
The Things You Should Know About The Profession Of A Lawyer
A lawyer is someone who practices or studies law. A lawyer could be an attorney or a counselor. A lawyer is sometimes paid to defend people in court. It can be a very difficult job at time but in the end you can make a...
- Professionalism
My Future Lawyer Career – My Risk
“A ship in harbor is safe, but that is not what ships are built for.” Life is based off a series of risk. Risk start off as our intuition, all we know. We learn to crawl regardless of the callus on our fingers and bruises...
Best topics on Lawyer
1. Why Did You Choose Law as a Career
2. Why I Want to Become a Lawyer: Advocating for Justice
3. Thurgood Marshall and Spiral of Science in Marshall
4. Analysis of Thurgood Marshall, American Revolutionary
5. Lawyers’ Interesting World of Employment Law
6. Jurisprudence and Different Legal System Throughout Legal History
7. The Path and Requirements to Becoming a Lawyer
8. Advantages and Disadvantages of the Lawyer Career
9. Prestige of the Lawyer Profession: Pay Wage and the Ranking
10. How Personal Injury Lawyers Save The Day
11. The Things You Should Know About The Profession Of A Lawyer
12. My Future Lawyer Career – My Risk
- First Amendment
- Criminal Law
- Legal cases
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
How To Write Law Essay?
23 October, 2020
8 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
If you are a law student, you have probably already faced the question of how to write an essay on this discipline. This is not an easy task because the requirements for a law essay often differ. In addition, you need to state your position and back it up with arguments clearly for others to understand. And to help you facilitate this process, we offer some preparation tips and tricks so that you could craft a decent work.

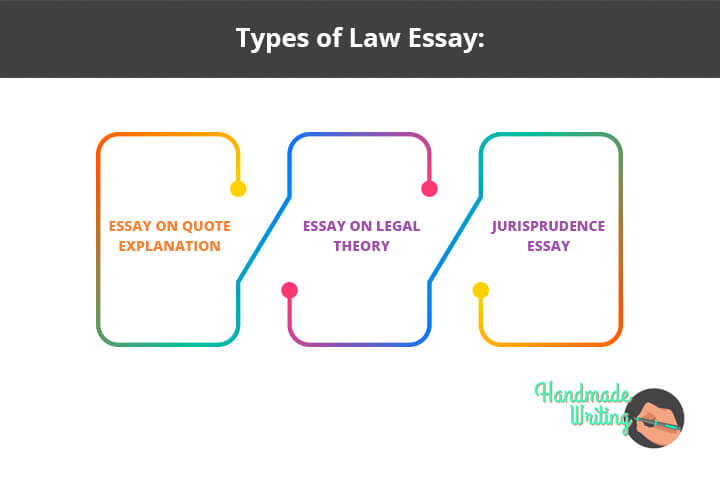
First things first, let’s discuss the legal essay scheme. It is rightly similar to the social science essay scheme. In both papers, it is necessary to explain a position on a particular issue or comment on a statement. For university law essay, especially in cases of specialties, it’s more complicated. There are several legal essay types :
- essay on quote explanation . Like in a school essay, the task here is to reveal the meaning of the expression and give a reasoned agreement or disagreement with it.
- essay on legal theory. The essence of this task is to describe one of the theories of law or any jurisprudence. This can be anything – for example, the theory that touches the Fifth Amendment.
- jurisprudence essay. In this assignment, you should review a specific case study or analyze the given document. Here, it’s important to adhere to special structure: first read the case, comprehend it, and only then give a critical account of this or that piece.
Law Essay Outline
The outline is one of the essential parts of law essay writing. At the point of creating it, you should jot down the structure of the main argument for each and every statement you deem appropriate for a text. This way, it’ll be much easier for you to organize the legal paper and facilitate its readability .
For example, if you need to comment on the quotation, it’s better to start an essay with brief information about the author. Then, consider the meaning of the citation in the context of his time and compare it to current conditions, as well as note whether you agree with the statement or not. Remember – the main task is to have a solid opinion in which you’re 100% confident. If not, switch the quote.
In the essay on legal theory, state the history of the issue, highlight the advantages and disadvantages of the case you are analyzing. Try to draw a parallel with the present, to indicate how relevant it is now for contemporary law students.
While reviewing a specific legal case or document, you should not be distracted by elements irrelevant or unrelated to the subject and give descriptions of similar situations. Consistently assess the actions of subjects or conduct an in-depth analysis of the provided regulation.
Write all of the crucial points in a short plan and shorten the above information into a couple of sentences. Afterward, you’ll be ready to use the crafted outline and write a law essay according to its key points .
Law Essay Structure
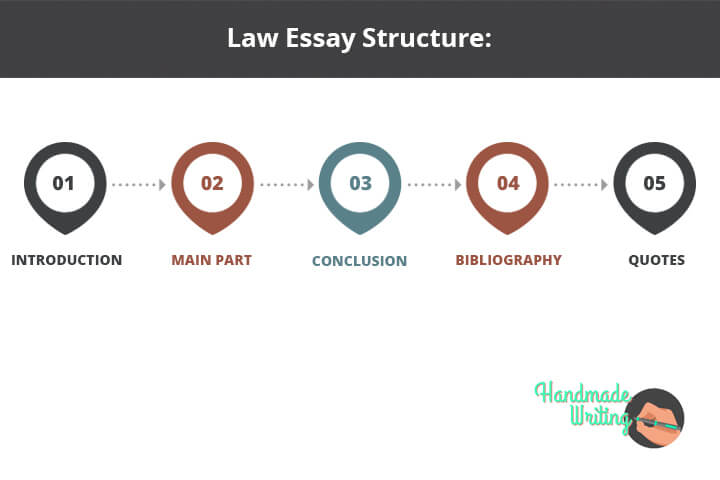
1. Introduction
Like any other type of writing, law essays start with introduction. A successful lead in is the one that captures attention instantly and forces readers to become interested in the law topic. In the beginning, you’ll need to clearly and precisely formulate a thesis statement of the entire piece, which you will then reveal in the following text. A great way to elaborate mediocre introduction with engaging filling is to state a concrete problem, controversy or issue that needs to be resolved.
2. Main part
This is the main element of the whole legal essay. It should contain an analysis of the quotation, legal theory, specific case, or document. Plus, your opinions about this or that aspect should be argued: for example, by references to other papers or practices. Another beneficial way to develop the main body of your essay is to use specific examples from law classes, including activities and important discussions , if applicable. Also, don’t forget that your law essay should always follow the thesis and develop it throughout the legal paper. This is a critical point to consider, as any departure from the established scheme will distort your work’s content.
3. Conclusion
Your finishing remarks should formulate the outcome of what was written above. A reasonable conclusion should be brief and powerful , as well as connected to the introduction. Besides, a good ending should contain a thesis of the whole law essay. However, don’t try to repeat your thesis word by word. Consider rephrasing it instead of mentioning the same statements so that the information is more easily digested for readers. Plus, you’ll need to provide a critical analysis of your work. For this, explain why your main argument backed up by primary and secondary sources is the highest point of conviction. Hence, your readers will see explicit reasoning and be more inclined to believe the truth you outlined in the paper.
4. Bibliography
A bibliography is a mandatory part of the work, and also the last one. At the end of your essay, you should list the documents (laws and other regulations) and books that were used in preparation for the article. Works cited page will help you validate the credibility of work and show readers that all statements and opinions are proven with relevant evidence. However, it doesn’t mean that your bibliography ought to be inserted just after you’ve written the entire text. To have a better vision of what source to pick for citing, include the list of used materials before writing the final version of your law essay. Accordingly, you’ll see sources in their entirety and easily cite them whenever needed.
The sayings of influential and famous people imbue any work with an air of authority . This is especially true for essays on law: professors appreciate it when students reinforce their considerations with the opinion of leaders and experts in their field.
Quotes for an essay on law are quite easy to find on the Internet or specialized digests.

If you choose to close the paper with a quote, it’ll be a great hook which will keep readers impressed by the essay long after they digest it. But feel free to add meaningful sayings also in the introduction or in the middle of a paper. Either way, quotes are a tool that helps make your reading highly impactful and appreciated.

These were the top advice on how to create a distinct law paper. We hope our advice will help you prepare an interesting and informative essay for college or university studies that’ll be graded with the highest mark. Once you manage to operate on the subtle art of legal essay writing, you’ll adjust to the complexities of its realization without difficulties. If you’re in doubt questioning your writing abilities, use custom essay writer service – we will create the best law essay tailored specifically for you.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
- Contributors
Lawyers as Professionals and Citizens: Key Roles and Responsibilities in the 21st Century
Ben W. Heineman, Jr. is a former GE senior vice president for law and public affairs and a senior fellow at Harvard University’s schools of law and government. This post is based on an essay by Mr. Heineman, William F. Lee , and David B. Wilkins ; the complete publication is available here .
We have written a detailed essay presenting practical vision of the responsibilities of lawyers as both professionals and as citizens at the beginning of the 21 st century. Specifically, we seek to define and give content to four ethical responsibilities that we believe are of signal importance to lawyers in their fundamental roles as expert technicians, wise counselors, and effective leaders: responsibilities to their clients and stakeholders; responsibilities to the legal system; responsibilities to their institutions; and responsibilities to society at large. Our fundamental point is that the ethical dimensions of lawyering for this era must be given equal attention to—and must be highlighted and integrated with—the significant economic, political, and cultural changes affecting major legal institutions and the people and institutions lawyers serve.
We have chosen to write this essay as a joint statement from a former general counsel of a global corporation, a former managing partner of an international law firm, and a professor of the legal profession at a major law school. We therefore focus our discussion on the four ethical duties in the institutions we know best—corporate legal departments, large law firms, and leading law schools—and on the important connections among them. But we also hope that both the ethical framework we propose and our commitment to a shared responsibility for giving it practical effect will have resonance in the many other important settings in which lawyers work. The four duties are, we believe, central to what it means to be a lawyer, even as the practical expression of these responsibilities will undoubtedly vary by context and will require new and greater collaboration that reaches across many of the profession’s traditional divides.
In presenting our views, we are mindful of the dramatic changes in both the legal profession and in society that make the realization of our—or any other—ethical vision of lawyering especially difficult today. There is widespread agreement that the legal profession is in a period of stress and transition; its economic models are under duress; the concepts of its professional uniqueness are narrow and outdated; and, as a result, its ethical imperatives are weakened and their sources ill-defined. We are also mindful that some will resist the invitation to review and address the broad array of ethical issues we raise in a time in which so many of the profession’s traditional economic assumptions are in question. Nevertheless, we reject the idea that there is an inherent and irresolvable conflict between “business” and “service.” To the contrary, we believe that, while tradeoffs about resource allocation will certainly be required, the proper recognition of each of the four ethical duties we explore is ultimately essential to the sustainability of “business”—whether that is the “business” of companies, law firms, or law schools, or more broadly, the health of our economic and political system as a whole. We therefore hope that this essay will stimulate an integrated discussion among the broad range of actors with a stake in the future of the legal profession not just about the pressing economic issues in major legal institutions but also about the equally pressing concerns relating to ethical responsibilities.
The essay has six parts.
We first set out our basic framework. It explicates lawyers’ three fundamental roles as expert technicians, wise counselors, and effective leaders. It describes the sources and broad definitions of lawyers’ four responsibilities: duties to clients and stakeholders; duties to the legal system; duties to one’s own institution; and duties to the broader society. To effectively discharge these responsibilities, it argues that lawyers must not only have “core” legal competencies but also “complementary” competencies involving broad vision, knowledge, and organizational skills that, while not unique to lawyers, are essential to the counseling and leadership roles. This Part thus describes how our framework goes beyond the limits of the bar’s formal ethical rules and challenges lawyers as both professionals and as citizens.
Second, we describe the context for our analysis. While recognizing the profound importance of other entities, we explain that we have chosen leading companies, law firms, and law schools as the focus of our analysis because of their influence in setting norms for lawyers, their role in providing counselors and leaders across society, and their standing in public perception of the law. It outlines our assumptions about the large-scale forces transforming the economics of these institutions. These include accelerating competition, costs, technology development and transparency—and, in the case of companies and firms, undue focus on short-term profit maximization and profits per partner. All these factors gain greater force from globalization. A final contextual dimension is the cost and paradox of regulation of the legal profession: increasing the cost of becoming a lawyer while reducing the competition from other more effective and efficient providers of legal or legally related services. And, while noting that efforts to discharge the four responsibilities will entail allocation of resources and trade-offs, we maintain that forging a new, contemporary partnership between “service” and “business” is essential to the success, sustainability, and durability of these institutions.
Third, we discuss corporate law departments. Due to major trends in recent decades—the General Counsel becoming the senior counselor to boards and CEOs and the shift of power over money and matters from outside law firms to inside law departments—the General Counsel and inside lawyers have a special obligation to give practical meaning to the four responsibilities in leading corporations. The overarching theme of this Part is that the purpose of corporations, especially transnational ones, is the fusion of high performance with high integrity. Integrity is defined as ensuring robust adherence to formal rules, establishing binding ethical standards, advocating balanced public policy and fair political processes, and instilling the values of honesty, candor, fairness, reliability, and trustworthiness in employees. The General Counsel should also have a broad scope beyond law to include ethics, reputation, and geopolitical risk and should function as expert, counselor, and leader to assist the board and the business leaders in establishing an integrity culture in the institution. The General Counsel and all inside lawyers should aspire to be “lawyer-statespersons” who ask first “is it legal” but ask last “is it right,” and who can resolve the central tension of being both a partner to the business leader and the ultimate guardian of the corporation’s integrity. Inside lawyers have a special calling to surface, analyze, and recommend actions relating both to the corporation’s employees and to other stakeholders that go beyond what the formal legal and accounting rules require and that address the many ethical issues facing global business in challenging environments. Finally, inside lawyers must recognize that they have a shared responsibility—and the obligation to share costs—with firms to provide challenging experiences and training for young lawyers. They must also use their influence (through, for example, new supplier guidelines) to encourage law firms to join with companies in addressing vital issues like provision of pro bono services, diversity, and needed reforms in the legal system both at home and abroad by making these issues important considerations in firm retention.
Fourth, we address law firms and the imbalance between “service” and “business” that has resulted from a myopic focus on short-term economics. To be sure, there have been benefits to the profession from increased transparency concerning operation of firms and the resulting increased competition among firms. But the relentless focus on short-term economic success has adversely affected the culture and institutional integrity of firms; the training, mentoring, and development of young lawyers; the ability of firms and their lawyers to service the poor and underprivileged; and the ability of firms and their lawyers to devote time to the profession and the broader needs of society. We urge a rebalancing of the sometimes competing goals of “economic” and “professional” success. This rebalancing will require leadership and vision which will (1) affirm the priority of excellence and quality over mere hours generation; (2) articulate a vision for and create a culture which revives and restores the institutional fabric of firms; (3) affirm the commitment to meaningful mentoring and development of young lawyers; (4) affirm the commitment to the profession, including pro bono services and the “Rule of Law”; and (5) affirm the role of lawyers as the architects of a well-functioning constitutional democracy. This rebalancing will not be easy and will require commitment to long-term goals and values, even at the expense of short-term economics.
Fifth, we turn our attention to the implications of our framework for “leading” law schools. We begin from the premise that law schools play a critical—but not exclusive—role both in teaching students to become expert technicians, wise counselors, and astute leaders, and in generating knowledge about law and legal institutions (including about the legal profession itself), and about the relationship between these institutions and the health and welfare of the broader society. To achieve these twin goals—and to find a proper balance between the two—law schools should reexamine how they are preparing students for the challenges that they will face throughout their increasingly diverse careers, and how faculty members understand their obligations to the legal framework and society, and to the law school as an institution. With respect to educating students, we urge law schools to create courses that focus directly on teaching lawyering roles and responsibilities in specific contexts and that explore key complementary competencies. We also advocate breaking down the artificial barriers that currently exist between “theory” and “practice,” and between “law” and other disciplines, by developing new teaching materials (for example “business school” style case studies), new faculty (for example, Professors of Practice with significant experience outside of the academy, and team teaching with faculty from other disciplines), and a new integration between the placement function and the core educational objectives of the school. To achieve these goals, we put forward a number of specific reforms designed to restructure and refocus the third year of law school, while rejecting calls to eliminate it altogether. Finally, we underscore the critical need for deans and faculty to rededicate themselves to articulating a broad but nevertheless common understanding of the purposes of legal education and legal scholarship that gives appropriate recognition to the role that law schools—and law professors—play as part of the legal profession in addition to their role as an important part of the academy. Faculty and administrators should then use this purpose to guide the difficult tradeoffs around hiring, promotion, curricula, research, funding, and the allocation of other scarce resources that will inevitably be required to begin to achieve these common goals.
Finally, we briefly discuss ways in which leading corporate law departments, law firms, and law schools can collaborate jointly to address the needs of young lawyers, to act on the needs of the legal system and society, to bridge the divide between the profession and the professoriate, and to develop better information on lawyers and the legal profession both here and abroad. It sets out next steps which include seeking short, written comments from leading thinkers which will be published early next year and holding a conference to discuss the issues raised both in this essay and in the comments at Harvard Law School in the first half of 2015.
The complete publication is available here .
Supported By:
Subscribe or Follow
Program on corporate governance advisory board.
- William Ackman
- Peter Atkins
- Kerry E. Berchem
- Richard Brand
- Daniel Burch
- Arthur B. Crozier
- Renata J. Ferrari
- John Finley
- Carolyn Frantz
- Andrew Freedman
- Byron Georgiou
- Joseph Hall
- Jason M. Halper
- David Millstone
- Theodore Mirvis
- Maria Moats
- Erika Moore
- Morton Pierce
- Philip Richter
- Marc Trevino
- Steven J. Williams
- Daniel Wolf
HLS Faculty & Senior Fellows
- Lucian Bebchuk
- Robert Clark
- John Coates
- Stephen M. Davis
- Allen Ferrell
- Jesse Fried
- Oliver Hart
- Howell Jackson
- Kobi Kastiel
- Reinier Kraakman
- Mark Ramseyer
- Robert Sitkoff
- Holger Spamann
- Leo E. Strine, Jr.
- Guhan Subramanian
- Roberto Tallarita

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What I Wish I Had Known Before Becoming a Lawyer
- Dustin S. McCrary

There is always going to be more work — we can’t say the same about our health.
In the past few years, we’ve learned how common burnout is. In this article, the author opens up about their experience of prioritizing their job as a lawyer over their own mental health, and shares some strategies young lawyers or new grads can use to avoid falling into this trap.
- Before taking a job, gauge the company culture. If you take a job in a work environment that doesn’t value you beyond your skills or take care of your psychological health, it’s going to be unsustainable in the long run.
- Don’t ignore your physical triggers. If you feel stressed during your workday, practice small things like staying hydrated, breathing deeply for a few seconds, or taking a short walk around your office to physically disconnect.
- The hard truth is that the legal profession is extremely draining. So, build a life outside work. This could look like taking regular time off such as vacation or personal days. Another option is to look for hobbies and activities outside work that energize you and give you joy.
- Finally, give yourself a little grace. At the end of the day, remind yourself that you’re doing the best you can.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
When I started law school, I loved it. The hypercompetitive classroom, the demanding coursework, and the adrenaline rush of solving complex cases drove me to pursue this career. Once I officially earned the job title “lawyer,” I was drawn even more to the fast-paced work culture. I wanted to stand out, make a difference, and find my own niche. My work was my passion and it empowered me.
- Dustin S. McCrary is the founder of the Law Office of Dustin S. McCrary, PLLC based in Statesville, N.C. He focuses his practice on the legal needs of divorce and separation serving his clients in all aspects of the process including separation, child custody, child support, alimony and spousal support, property distribution, and domestic violence. McCrary recently published a new book called “Helping Your Children Cope with Divorce.”
Partner Center
- Honour Code
- CSR Commitments
- Trademark Policy
- Authentication
- How to Cite
- Legal Executive
Case Summaries
- Jurisprudence
- Legal Writing
- Legal English
UOL Case Bank
- A-Level Law
- Exam Skills
- LLB Admissions
- PGDL / GDL Admissions
- MA Law Admissions
- MLaw Admissions
- LLM Admissions
- JD Admissions
- Law Schools
- Law Modules
- Study Skills
- Careers Advice
- Job Openings
- Internships
How to Plan and Outline Law Essays
Writing a law essay requires a structured approach to research, analysis, and argument construction. Whether you're tackling an assignment for a law school class, preparing for a law review submission, or composing essays for bar exam preparation, the process demands precision, clarity, and a deep understanding of the legal concepts at hand. Here is a comprehensive guide to help you plan and outline your law essays effectively.
1. Understand the Question
Before you start, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the essay question or topic. Law essays often come with specific prompts that require you to analyse a legal scenario, compare legal theories, or evaluate the application of law in certain cases. Break down the question to ensure you grasp what is being asked, identifying any specific legal issues or concepts that need to be addressed.
2. Conduct Thorough Research
The foundation of a strong law essay is comprehensive research. Start by gathering relevant statutes, case law, journal articles, and other legal texts that pertain to your topic. Use reputable legal databases and libraries to find authoritative sources. Keep track of your sources from the beginning to make citation easier later on.
3. Create a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly present the main argument or position you will be defending in your essay. It serves as a roadmap for your reader, indicating how you interpret the legal question and what your essay aims to demonstrate.
4. Plan Your Essay Structure
An effective law essay is well-organised and logically structured. Generally, your essay should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Introduction: Briefly introduce the topic, present your thesis statement, and outline the main points you will cover in your essay.
Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or argument that supports your thesis. Begin with a topic sentence that introduces the paragraph’s main point, followed by evidence from your research, including case law, statutes, and scholarly commentary. Analyse this evidence in the context of your argument, demonstrating how it supports your thesis.
Conclusion: Summarise the main arguments made in your essay, reinforcing how they support your thesis. Address any implications, suggest areas for further research, or provide a concluding thought on the essay topic.
5. Draft an Outline
An outline is a blueprint for your essay, helping you organise your thoughts and structure your arguments coherently. Start by listing the main points you plan to make in your essay, organising them in a logical sequence. Under each main point, include sub-points or evidence you will use to support your argument. This step will help you ensure a balanced and well-structured essay.
6. Write with Precision and Clarity
Law essays demand clear and precise language. Avoid unnecessary legal jargon or overly complex sentences. Your goal is to make your arguments as accessible as possible, even to those who might not have a legal background. Remember, clarity and conciseness are key.
7. Review and Revise
After completing your first draft, take time to review and revise your work. Check for any gaps in your argument, unnecessary repetition, or areas where further clarification is needed. Ensure your essay flows logically from one point to the next. Finally, proofread for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors.
8. Cite Your Sources
Proper citation is crucial in law essays to give credit to the original authors of your sources and to provide authority to your arguments. Familiarise yourself with the preferred citation style for your assignment, whether it is OSCOLA , APA, or another format, and apply it consistently throughout your essay.
Planning and outlining your law essays are critical steps that set the stage for writing a compelling and cogent paper. By understanding the question, conducting thorough research, creating a structured outline, and writing with precision, you can craft essays that not only meet the academic requirements but also demonstrate your deep understanding of the law. Remember, a well-planned essay is the foundation of effective legal writing.
Check out our Law Exam Guide for more exam tips.
Trusted by thousands of law students worldwide
All 30 law modules (best value), all 18 uol modules (uol international programme), sqe foundation package, pgdl / gdl law conversion, 12 qualifying llb modules (uol standard entry route), 9 qualifying llb modules (uol graduate entry route), first year llb modules (uol standard entry route), first year llb modules (uol graduate entry route), law exam guide, second year llb modules (uol standard entry route), second year llb modules (uol graduate entry route), third year llb modules (uol standard entry route), third year llb modules (uol graduate entry route), contract law, legal english and writing, legal executive package (level 6), certhe common law (uol international programme), graddip commercial law (uol international programme), graddip international law (uol international programme), where are our students from.
Yale University
Council of Europe
Baker Mckenzie
University of Chicago
Columbia University
New York University
University of Michigan
University College London (UCL)
London School of Economics (LSE)
King’s College London (KCL)
University of London
University of Manchester
University of Zurich
University of York
Brandeis University
University of Exeter
University of Sheffield
Boston University
University of Washington
University of Leeds
University of Law
Royal Holloway, University of London
Birkbeck, University of London
SOAS, University of London
University of Kent
University of Hull
Queen’s University Belfast
Toronto Metropolitan University
Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Your perfect companion for open-book and closed-book exams
Diagrams and charts.
Our carefully designed diagrams and charts will guide you through complex legal issues.
Clear and Succinct Definitions
Key concepts are concisely defined to help you understand legal topics quickly.
Statutory Provisions
Statutory provisions are provided side by side with legal concepts to help you swiftly locate the relevant legislation.
We have summarised important cases for you so that you don't need to read long and boring cases.
Rules and Exceptions
Rules and exceptions are clearly listed so that you know when a rule applies and when it doesn't.
Terminology
Legal terms and key concepts are explained at the beginning of each chapter to help you learn efficiently.
Case law is provided side by side with legal concepts so that you know how legal principles and precedents were established.
Law Essay Guide
You will learn essential law exam skills and essay writing techniques that are not taught in class.
Problem Question Guide
We will show you how to answer problem questions step by step to achieve first-class results.
Structured Explanations
Complex legal concepts are broken down into concise and digestible bullet point explanations.
Legal Research
You will learn legal research techniques with our study guide and become a proficient legal researcher.
Exam-focused
All essential concepts, principles, and case law are included so that you can answer exam questions quickly.
- American Express
By using this website, you agree to our use of cookies. We use cookies to provide necessary site functionality and provide you with a great experience.
Post A Comment
Flag comment.
Are you sure you'd like to flag this comment as inappropriate?
Thank you for commenting
Your comment is awaiting moderation, and will be published as soon as it has been approved
Delete Comment
You're logged in as the blog owner. Would you like to delete this comment?
Your message has been successfully sent
Your form has been submitted. Please check your email for a copy of your responses. If you're accepted, you'll receive an email with a link to checkout.
Could not add item to cart
- Admission Essay
- Statement of Purpose Editing
- Personal Statement Editing
- Recommendation Letter
- Motivation Letter
- Cover Letter
- Supplemental Essay
- Letter of Continued Interest
- Scholarship Essay
- Role Model Essay
- Our Editors
- College Admission Essay Examples
- College Cover Letter Examples
- College Personal Statement Examples
- Graduate Personal Statement Examples
- Graduate Statement of Purpose Examples
- MBA Essay Examples
- MBA Personal Statement Examples
- MBA Resume Examples
- MBA Recommendation Letter Examples
- Medical School Personal Statement Examples
- Medical School Recommendation Letter Examples
- Pricing Plans
- Public Health
- Dissertation
- Research Paper
- Thesis Editing
- Academic Editing
- Motivation letter
- Letter of Recommendation
- Personal Statement
- Statement of Purpose
Why I Want To Be a Lawyer Essay Sample For Law Student
EssayEdge > Blog > Why I Want To Be a Lawyer Essay Sample For Law Student
Note: This essay appears unedited for instructional purposes. Essays edited by experienced law editors are dramatically improved.
This applicant’s lively and unique approach to the “why I want to be a lawyer” essay captures the reader’s interest. Notice that the applicant discusses her religious beliefs sensitively, without proselytizing or preaching.
My interest in the law began with donuts. As a child, I developed early persuasive skills during family disagreements on how to divide boxes of the treats. My parents belonged to the “biggest people deserve the most donuts” school of thought; while as the youngest family member, I was a devout believer in the “one person, one donut” principle. The debates were often cutthroat, but when it came to donut distribution, I sought justice at any cost.
As my family grew older and more health-conscious we stopped eating donuts, and for many years I forgot our childhood debates. However, some recent life decisions have brought to mind those early explorations of justice. When I first arrived at the American International School of Rotterdam, I quickly learned that my colleagues were a diverse and talented group of people. Unsure of how to establish my own place among them, I tried phrases that had always worked to impress college friends. “When I work for the UN . . . ,” I told the second grade teacher, and she answered with an erudite discussion of the problems she faced as a consultant for that organization. “When I’m in law school . . . ,” I told the kindergarten teacher, only to hear about his own experiences in law school. By the time I discovered that even many grade-school students were better travelled than I, I learned to keep my mouth shut!
Need help? Check out EssayEdge editing services:
Living alone in a new country, removed from familiar personal and cultural clues to my identity and faced with these extraordinary co-workers, I started to feel meaningless. How, I wondered, could I possibly make a difference in a place as vast as our planet? To my own surprise, I found that answer at church. Although I was raised in the Bahá’í Faith, I have only recently understood the essential place that religion plays in my identity. Bahá’í social beliefs include the need to work against extreme poverty, nationalism, and prejudice; and I now realize that I cannot hold those beliefs without doing something about them. My identity rests on these convictions; I cannot see the need for help and just move on. I have to help; it’s who I am.
The lessons I’ve learned from my international colleagues have channeled my desire for service into the field of international development. I still wish to fight the “‘Biggest Get the Most’ Theory of Donut Distribution,” but now on an international scale.
There’s nothing easier than explaining what made you apply to law school, right? We don’t think so. Well, you can answer this question, but can this answer satisfy the admissions board? If you aren’t sure of your writing capability, don’t test your fate and get help from our law personal statement proofreading service.
Popular Posts
June 2, 2022 How To Start a Scholarship Essay: Catch Reader’s Attention Fast
May 16, 2022 My Role Model Essay: A Few Ways to Elaborate on The Subject
May 3, 2022 How To Start a Personal Statement? | Writing Tips and Samples
Related Posts
April 7, 2024 How to Write a Compelling College Essay Introduction? + [Examples]
May 27, 2022 How to Explain Low GMAT Scores in Your MBA Application
March 27, 2022 SAT Going Digital
©2024 Student Media LLC. All rights reserved.
EssayEdge: Essay Editing & Proofreading Service.
Our mission is to prepare you for academic and career success.
- Log In
- Sign Up
- Forgot password
Unable to log in? Please clear your browser's cache and then refresh this page and try again
Reset password Please enter your email address to request a password reset.
Check your email We’ve just sent a password reset link to your email.
This information is used to create your account

Sign up to our Newsletter
How to write the “why berkeley law” essay with examples.

Reviewed by:
David Merson
Former Head of Pre-Law Office, Northeastern University, & Admissions Officer, Brown University
Reviewed: 12/20/23
Getting ready to write your "Why Berkeley Law?" essay? In this blog, we'll offer tips and examples to help you write a standout essay.
When applying to Berkeley Law , one of the most crucial components of your application is the optional essay. This essay provides you with an opportunity to express your genuine interest in the school and explain why you are a perfect fit.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into strategies for crafting an effective "Why Berkeley Law?" essay, explore examples of successful essays, and address frequently asked questions.
Writing the "Why Berkeley Law?" Essay
If you’re applying to Berkeley’s Public Interest Scholars Program , you'll find an optional essay prompt that gives you up to 350 words to answer the following question:
“Tell us more about your interest in Berkeley Law. What makes our school a good fit for you in terms of academic interests, programmatic offerings, and learning environment?”
Let's explore how you can effectively respond to it.

Discover What Sets Berkeley Law Apart
Berkeley Law has a rich history and a lot to offer prospective students. When tackling this extra essay, be sure to explore the school's traditions, the variety of programs it offers, and the unique qualities that align with your academic goals.
Reflect on Academic Goals
Now, take a moment to think about your academic goals, including what you want to achieve in the short term and the long term. Think about the specific academic interests that have drawn you to Berkeley Law. Explore how the school's academic offerings can help you reach these goals.
Are there specific courses, areas of study, or research chances that align with your interests? Make sure to express these connections clearly in your essay to demonstrate how well your academic aspirations match with Berkeley Law.
Forge a Regional Connection
The Bay Area is a thriving legal hub, but breaking into it can be challenging without prior connections. If your goal is to practice law in California , don't hesitate to mention it in your essay. Take it a step further by aligning yourself with a specific Bay Area population or legal specialization, such as tech law.
Embrace Diversity and Activism
Berkeley prides itself on its diversity and rich tradition of activism, like the historic Free Speech Movement. Incorporate this culture into your essay to show your appreciation for a vibrant and inclusive campus if you want to stand out.
Though this isn’t necessarily a diversity essay , it is a good idea to highlight any personal experiences or values that demonstrate your commitment to diversity and social justice. Whether it's through your own background, extracurricular activities, or future aspirations, make it clear that you'll actively contribute to and benefit from Berkeley's diverse community.
Highlight Leadership and Initiative
Berkeley values students who take the lead and make a positive impact. Share examples of your leadership roles, whether in school, work, or community organizations. Highlight instances where you took the initiative to solve problems or create positive change. Demonstrating your potential to contribute actively to the Berkeley community will strengthen your essay.
Connect Your Past Experiences to Future Goals
Your essay should tell a story of your academic and personal journey, culminating in your desire to attend Berkeley. Explain how your past experiences have shaped your ambitions and why Berkeley is the ideal place to continue your growth. Discuss specific resources or opportunities that will help you achieve your long-term goals.
Be Authentic and Reflective
Lastly, be yourself in your essay. Berkeley is looking for authentic individuals who can contribute to their diverse and intellectually vibrant community.
Share your true passions, values, and aspirations. Reflect on your experiences and insights, and don't be afraid to acknowledge the challenges or setbacks you've faced. A genuine, thoughtful essay will make a lasting impression.
Structuring Your "Why Berkeley Law?" Essay
To effectively write the essay prompt, make sure to follow a structured approach:
Introduction (Approx. 50-75 words)
- Start by introducing yourself and your intention to join Berkeley Law.
- Mention your passion for public interest law and why you are excited to apply.
Academic Interests (Approx. 75-100 words)
- Talk about your academic interests and how they align with Berkeley Law's offerings.
- Highlight specific courses or professors that pique your interest.
Programmatic Offerings (Approx. 75-100 words)
- Explain why the Public Interest Scholars Program stands out to you.
- Discuss how the program's features, like mentorship or clinics, will benefit your career goals.
Learning Environment (Approx. 75-100 words)
- Describe what you admire about Berkeley Law's learning environment.
- Mention the diverse community and the emphasis on activism, and explain why these aspects resonate with you.
Conclusion (Approx. 25-50 words)
- Summarize your main points and reiterate your enthusiasm for Berkeley Law.
- Express your eagerness to contribute to the Berkeley Law community and make a difference in public interest law.
This approach will help you effectively convey your genuine interest in Berkeley Law's Public Interest Scholars Program within the 350-word limit.
Mistakes to Avoid in Your “Why Berkeley Law” Essay
As you work on your essay, it's crucial to steer clear of common mistakes that could hinder your application's impact.
- Generic Responses : Avoid generic statements that could apply to any law school. Your essay should be tailored to Berkeley Law specifically.
- Lack of Specifics : Provide concrete examples and specifics about Berkeley Law and how they relate to your goals.
- Negativity : Refrain from negative comments about other law schools or institutions.
- Ignoring the Word Limit : Stick to the specified word limit. Admissions committees appreciate applicants who can communicate concisely.
.jpg)
Examples of Successful “Why Berkeley Law” Essay
In this next part, let's dive into “Why Berkeley?” law essay examples that really hit the mark, demonstrating the applicants' genuine alignment with the school's ethos, academic programs, and dedication to public interest law.
Example Essay #1
“As an aspiring public interest attorney, Berkeley Law's commitment to social justice and its extensive programmatic offerings make it the ideal institution for me. From my research, it's clear that Berkeley Law's values align perfectly with my passion for advocating for marginalized communities. The Public Interest Scholars Program, in particular, stands out as an opportunity to further my commitment to public service.
Berkeley Law's wide array of clinics and centers, such as the Policy Advocacy Clinic and the International Human Rights Law Clinic, strongly resonates with my academic interests. These hands-on experiences will allow me to apply legal theory to real-world situations, honing my skills while making a meaningful impact on the lives of those in need. Additionally, the Pro Bono Program's emphasis on community service deeply aligns with my commitment to giving back.
The vibrant and inclusive learning environment at Berkeley Law is another compelling reason for my interest. The diverse student body and faculty create a dynamic atmosphere where I can learn from different perspectives and foster a global understanding of legal issues. The Berkeley Law community's dedication to activism and the Free Speech Movement is particularly appealing, as it mirrors my own desire to be a catalyst for change and contribute to a more just society.
In my pursuit of a legal career focused on public interest, Berkeley Law's dedication to fostering social justice and providing extensive resources for students aligns perfectly with my aspirations. I am eager to engage with the Berkeley Law community, contribute to its legacy of activism, and take full advantage of the opportunities it offers to develop into an effective public interest attorney.”
Why This Essay Was Successful
This essay succeeded because it showed that the applicant's goals match what Berkeley Law offers. They clearly expressed their passion for public interest law and mentioned specific programs and opportunities at the school that interested them.
They also talked about how Berkeley Law's diverse community and commitment to activism aligned with their values. Overall, the essay made a strong case for why the applicant would be a good fit for Berkeley Law.
Example Essay #2
“Berkeley Law is the epitome of my academic and professional aspirations as a future public interest attorney. Its exceptional academic offerings, programmatic diversity, and commitment to social justice have convinced me that this is where I belong.
My academic interests lie in environmental justice and sustainable development. Berkeley Law's esteemed Environmental Law Program, renowned for its interdisciplinary approach and impactful research, perfectly aligns with my goals. I am eager to engage with faculty members such as Professor [Faculty Name], whose work on environmental justice has been a constant source of inspiration for me.
Furthermore, the Public Interest Scholars Program is the embodiment of my career aspirations. It offers unparalleled resources and mentorship opportunities that will not only help me refine my legal skills but also empower me to make a meaningful difference in disadvantaged communities. The program's emphasis on experiential learning through clinics and community engagement resonates deeply with my commitment to public service.
The Berkeley Law community's dedication to diversity and activism is also a significant draw for me. Having been an advocate for social justice throughout my undergraduate years, I am excited about the prospect of contributing to Berkeley's legacy of activism and making a positive impact on pressing societal issues.
In conclusion, Berkeley Law's academic excellence, programmatic offerings, and unwavering commitment to social justice make it the perfect fit for my academic and career goals. I am enthusiastic about the prospect of joining the Berkeley Law community, where I can harness my passion for public interest law to effect change and promote justice for marginalized communities.”
This essay succeeds because it shows a strong match between the applicant's goals and Berkeley Law. They clearly express their interest in environmental justice and sustainable development and explain how Berkeley Law's programs align with these goals.
The essay also mentions a specific faculty member who inspires them, demonstrating their genuine interest in the school. Additionally, the writer emphasizes their commitment to hands-on learning and public service, which fits well with Berkeley Law's offerings.
Finally, they express their excitement about contributing to the school's diversity and activism, making a strong case for why they are a good fit for Berkeley Law.
Navigating the application process for Berkeley Law can be complex, but our FAQ section is here to provide you with clear and concise answers to your most pressing questions.
1. What Makes Berkeley Law School Unique?
Berkeley Law stands out for its commitment to academic excellence, social justice, and innovation. It offers a diverse range of courses, renowned faculty, and numerous clinics and centers focused on various legal fields.
2. What Is the Mission Statement of Berkeley Law?
Berkeley Law's mission is to educate leaders who will contribute to the development of law and society. They aim to promote diversity, inclusion, and equity while fostering a supportive and collaborative community.
3. What Is the Optional Essay for Berkeley Law?
Berkeley Law provides an optional essay prompt that allows applicants to address any aspects of their application they wish to clarify or expand upon. While it's not required, it can be a valuable opportunity to provide context if needed.
Writing the "Why Berkeley Law?" essay requires thoughtful reflection and a deep understanding of what makes Berkeley Law unique. By following the strategies outlined in this guide and studying successful examples, you can craft an essay that not only impresses the admissions committee but also conveys your genuine enthusiasm for joining the Berkeley Law community.
Remember to be specific, passionate, and authentic in your writing, and best of luck with your application!
Schedule A Free Consultation
You may also like.

Law Schools in North Carolina: What You Need to Know

Fee Waivers for LSAC - Eligibility and How to Apply

Banking and Antitrust
This Essay seeks to recover the deeply rooted connection between U.S. banking law and antitrust. It reconceptualizes banking law as a sector-specific antimonopoly regime that imposes multiple structural constraints on publicly subsidized banks’ ability to abuse their power over the supply and alloca…
Policing the Polity
Interior immigration enforcement reaches well beyond deportation. In practice, it also offers a rationale for policing U.S. residents stereotyped as foreign. This Essay shows how a “deportation-centric” approach limits the ability of courts to recognize and redress unjustified surveillance, and it a…
The Moral Ambiguity of Public Prosecution
In a legal system where criminal prosecution is the institutional analog of moral blame, a state that acts as exclusive prosecutor exceeds its moral standing and incurs a debt to the victim. The nature of this debt and how we might discharge it are the primary subjects of this Essay.
The Voluntariness of Voluntary Consent: Consent Searches and the Psychology of Compliance
The Fourth Amendment allows police to perform warrantless searches of individuals if they give consent to be searched and that consent is voluntary. Based on original laboratory research, this Essay posits that fact-finders assessing voluntariness underappreciate the extent to which suspects feel pr…
Democratic Policing Before the Due Process Revolution
Prevailing narratives of the Warren Court’s Due Process Revolution emphasize how it constrained police behavior. This Essay questions this account. It returns to the legal culture before the Revolution, focusing on three lectures by the prominent scholar Jerome Hall. Due process, it concludes, as mu…
The Dilemma of Localism in an Era of Polarization
Localism discourse has long confronted a fundamental problem: how can we remain committed to decentralized decision-making while checking the excesses of local parochialism? This Essay proposes a new approach in our polarized era, emphasizing the joint role state individual rights and the often-igno…
Why Is It Wrong To Punish Thought?
It is an age-old maxim of criminal jurisprudence that the state must never punish people for their mere thoughts—for their beliefs, desires, and unexecuted intentions. Yet its justification is something of a mystery. This Essay argues that each of the prevailing justifications is deficient and propo…
Originalism Without Text
Originalism is not about the text. A society can be recognizably originalist without any words to interpret: without a written constitution, written statutes, or any writing at all. What originalism generally is about is our present constitutional law and its dependence on a crucial moment in the pa…
Police Reform and the Dismantling of Legal Estrangement
In police reform circles, many scholars and policymakers diagnose the frayed relationship between police forces and the communities they serve as a problem of illegitimacy, or the idea that people lack confidence in the police and thus are unlikely to comply or cooperate with t…
Cops and Pleas: Police Officers’ Influence on Plea Bargaining
abstract.Police officers play an important, though little-understood, role in plea bargaining. This Essay examines the many ways in which prosecutors and police officers consult, collaborate, and clash with each other over plea bargaining. Using original interviews with criminal justice of…
Agency Design and Political Control
Although historical debates about the separation of powers focus on Congress, the President, and the Judiciary, in modern times, the bureaucracy is the elephant in the room. In a world of seemingly inevitable widespread congressional delegation to administrative agencies, as we…
Fiduciary Political Theory: A Critique
“Fiduciary political theory” is a burgeoning intellectual project that uses fiduciary principles to analyze public law. This Essay provides a framework for assessing the usefulness and limitations of fiduciary political theory. Our thesis is that fiduciary principles can be…
The New Public
By exploring the intertwined histories of the automobile, policing, criminal procedure, and the administrative state in the twentieth-century United States, this Essay argues that the growth of the police’s discretionary authority had its roots in the governance of an automotiv…

The Domestic Analogy Revisited: Hobbes on International Order
This Essay reexamines Thomas Hobbes’s understanding of international order. Hobbes defended the establishment of an all-powerful sovereign as the solution to interpersonal conflict, and he advanced an analogy between persons and states. Extending this “domestic analogy,” the…
Which Way To Nudge? Uncovering Preferences in the Behavioral Age
Behavioral Law and Economics has created a dilemma for policymakers. On the one hand, research from the field suggests a wide range of unconventional policy instruments (“nudges”) may be used to shape people’s voluntary choices in order to lead them to the option they most pref…
On Evidence: Proving Frye as a Matter of Law, Science, and History
This Essay is a cautionary tale about what the law does to history. It uses a landmark ruling about whether scientific evidence is admissible in court to illustrate how the law renders historical evidence invisible. Frye v. United States established o…
The End of Jurisprudence
For more than forty years, jurisprudence has been dominated by the Hart-Dworkin debate. The debate starts from the premise that our legal practices generate rights and obligations that are distinctively legal, and the question at issue is how the cont…
Bounded Institutions
This Essay examines two alternative designs for hierarchical institutions: “bounded” and “unbounded.” In a bounded structure, a principal decides on a bounded aggregate numerical allocation, and then an agent makes the allocation to an underly…
We the People : Each and Every One
In his book series, We the People, Bruce Ackerman offers a rich description of how constitutional law comes to be changed by social movements. He also makes some normative claims about “popular sovereignty,” “popular consent,” “higher law,” …
Reactionary Rhetoric and Liberal Legal Academia
As celebrations mark the fiftieth anniversary of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, it is essential to recover the arguments mainstream critics made in opposing what has become a sacrosanct piece of legislation. Prominent legal scholarship now appears to m…
Popular Sovereignty and the United States Constitution: Tensions in the Ackermanian Program
The very title of Bruce Ackerman’s now three-volume masterwork, We the People, signifies his commitment to popular sovereignty and, beyond that, to the embrace of democratic inclusion as the leitmotif of American constitutionalism. But “popular…
The Neo-Hamiltonian Temptation
The central force behind the development of constitutional law, according to Bruce Ackerman’s magisterial We the People: The Civil Rights Revolution, is not the courts but the People, acting through the elected officials who were responsible for th…
The Civil Rights Canon: Above and Below
This essay builds on the constitutional history of the civil rights movement from below to complement and complicate the canon identified in We the People: The Civil Rights Revolution. Like Professor Ackerman’s work, this essay embraces the concept o…
Changing the Wind: Notes Toward a Demosprudence of Law and Social Movements
This essay was influenced by a class on Law and Social Movements that Professors Guinier and Torres taught at the Yale Law School in 2011. This essay was also informed by numerous conversations with Bruce Ackerman regarding his book that is under review in this Symposium. …
Protecting Civil Rights in the Shadows
Beyond grand constitutional moments such as the New Deal and the civil rights era, the American people also remove other, less prominent issues from majoritarian politics. This process of petit popular constitutionalism resolves numerous important issues of government …
Universalism and Civil Rights (with Notes on Voting Rights After Shelby )
After the Supreme Court’s decision in Shelby County v. Holder, voting rights activists proposed a variety of legislative responses. Some proposals sought to move beyond measures that targeted voting discrimination based on race or ethnicity. They ins…
Separate Spheres
This essay is about the mixed legacy, or incomplete achievement, of the landmark legal changes of the Second Reconstruction. This mixed legacy is one of the central themes of The Civil Rights Revolution, the third volume of Bruce Ackerman’s We the…
Ackerman’s Civil Rights Revolution and Modern American Racial Politics
Bruce Ackerman’s The Civil Rights Revolution makes a signal contribution by documenting how the major civil rights statutes of the 1960s, especially the 1964 Civil Rights Act, the 1965 Voting Rights Act, and the 1968 Fair Housing Act, pragmatically …
Rethinking Rights After the Second Reconstruction
The Civil Rights Act was remarkably successful in fighting overt bigotry and discrimination, but much less so in combating the subtler, institutionalized disadvantages that are now the main sources of social injustice. The heroic idea of rights as protecti…
A Revolution at War with Itself? Preserving Employment Preferences from Weber to Ricci
Two aspects of the constitutional transformation Bruce Ackerman describes in The Civil Rights Revolution were on a collision course, one whose trajectory has implications for Ackerman’s account and for his broader theory of constitutional change. Ackerman makes a co…
Have We Moved Beyond the Civil Rights Revolution?
Bruce Ackerman’s account of the Civil Rights Revolution stresses the importance of popular sovereignty and the separation of powers as the basis of constitutional significance. In this view, key spokespersons, including Martin Luther King, Jr. and Ly…
Equal Protection in the Key of Respect
This essay challenges the three related claims embedded within Professor Ackerman’s assertion that the distinctive wisdom of Chief Justice Warren’s opinion in Brown v. Board of Education lies in its recognition of segregation as institutionalized humiliation. Ack…
Ackerman’s Brown
This essay contends that, despite its revisionist ethos, Professor Ackerman’s We the People: The Civil Rights Revolution is conventional in its assessment of Brown v. Board of Education. Ackerman praises Brown as “the greatest judicial opinion of the twentieth cen…
The Anti-Humiliation Principle and Same-Sex Marriage
Bruce Ackerman’s volume on the civil rights revolution argues that the Second Reconstruction was centrally concerned with the concept of institutionalized humiliation. Ackerman inveighs against the fact that we have turned away from this “anti-humiliat…
De-Schooling Constitutional Law
For more than two centuries, constitutional law has been created by a dialogue between generations. As newcomers displace their predecessors, they begin to challenge parts of the legacy they have inherited while cherishing other elements of their tradition. The…
Five to Four: Why Do Bare Majorities Rule on Courts?
Interrogating a commonsense assumption
Federalism as the New Nationalism: An Overview
Federalism has had a resurgence of late, with symposia organized,1 stories written,2 and new scholarly paths charted. Now is an appropriate moment to assess where the new “new federalism”3 is heading. This Feature thus brings together five scholars who have made unique contribution…
From Sovereignty and Process to Administration and Politics: The Afterlife of American Federalism
Announcing the death of dual federalism, Edward Corwin asked whether the states could be “saved as the vital cells that they have been heretofore of democratic sentiment, impulse, and action.” The federalism literature has largely answered in the affirmative. Unwilling to aband…
The Loyal Opposition
The term loyal opposition is not often used in American debates because (we think) we lack an institutional structure for allowing minorities to take part in governance. On this view, we’ve found our own way to build loyalty while licensing opposition, but it’s been a rights-…
Our [National] Federalism
“National Federalism” best describes the modern allocation of state and federal power, but it is a federalism without doctrine. Federalism today comes primarily from Congress—through its decisions to give states prominent roles in federal schemes and so to ensure the stat…
The Shadow Powers of Article I
This essay argues that the interpretive struggle over the meaning of American federalism has recently shifted from the Commerce Clause to two textually marginal but substantively important battlegrounds: the Necessary and Proper Clause and, to a lesser extent, the General Welfa…
Negotiating Conflict Through Federalism: Institutional and Popular Perspectives
The contours of our federal system are under constant negotiation, as governments construct the scope of one another’s interests and powers while pursuing their agendas. For our institutions to manage these dynamics productively, we must understand the value the system is capab…
The Moral Impact Theory of Law
I develop an alternative to the two main views of law that have dominated legal thought. My view offers a novel account of how the actions of legal institutions make the law what it is, and a correspondingly novel account of how to interpret legal texts. According to my view, legal obl…
Pretrial Detention and the Right to Be Monitored
Although detention for dangerousness has received far more attention in recent years, a significant number of non-dangerous but impecunious defendants are jailed to ensure their presence at trial due to continued, widespread reliance on a money bail system. This Essay develops two rel…
Reconsidering Citizens United as a Press Clause Case
The central flaw in the analysis of Citizens United by both the majority and the dissent was to treat it as a free speech case rather than a free press case. The right of a group to write and disseminate a documentary film criticizing a candidate for public office falls within the core…
Tops, Bottoms, and Versatiles: What Straight Views of Penetrative Preferences Could Mean for Sexuality Claims Under Price Waterhouse
This Essay reports the results of a survey experiment that we conducted on over eight hundred heterosexual respondents to compare associational attitudes toward gay men who engage in different types of sexual practices. Specifically, we randomly assigned respondents to hear one…
The Unbundled Union: Politics Without Collective Bargaining
Why civil gideon won’t fix family law.
This Essay explains why we should hesitate before throwing full support behind a civil Gideon initiative for family law, regardless of how wholeheartedly we embrace the proposition that parental rights are as important as physical liberty. The comparable importance of these interests does not necess…
Gideon Exceptionalism?
122 Yale L.J. 2126 (2013). There is no doubt that Gideon v. Wainwright is extraordinary, but in thinking about its uniqueness, we are reminded of “American exceptionalism” and the diametrically opposed meanings that advocates have ascribed to the phrase. Gideon too is exceptional, in both the laudato…
Fifty Years of Defiance and Resistance After Gideon v. Wainwright
122 Yale L.J. 2150 (2013). In its 1963 ruling Gideon v. Wainwright , the Supreme Court declared the right to a lawyer “fundamental and essential” to fairness in the criminal courts and held that lawyers must be provided for people who could not afford them so that every person “stands equal before the…
Poor People Lose: Gideon and the Critique of Rights
122 Yale L.J. 2176 (2013). A low income person is more likely to be prosecuted and imprisoned post- Gideon than pre- Gideon . Poor people lose in American criminal justice not because they have ineffective lawyers but because they are selectively targeted by police, prosecutors, and law makers. The crit…
Celebrating the “Null” Finding: Evidence-Based Strategies for Improving Access to Legal Services
122 Yale L.J. 2206 (2013). Recent empirical studies tested whether litigants with access to lawyers fared better than litigants with access only to advice or limited assistance. Two of the three studies produced null findings—the litigants with access to lawyers, the treatment group, fared no better …
Race and the Disappointing Right to Counsel
122 Yale L.J. 2236 (2013). Critics of the criminal justice system observe that the promise of Gideon v. Wainwright remains unfulfilled. They decry both the inadequate quality of representation available to indigent defendants and the racially disproportionate outcome of the criminal process. Some hop…
Participation, Equality, and the Civil Right to Counsel: Lessons from Domestic and International Law
122 Yale L.J. 2260 (2013). Domestic efforts to establish a right to civil counsel by drawing narrow analogies to Gideon v. Wainwright have met with limited success. In contrast, two principles drawn from international jurisprudence—the human right to “civic participation” and the concept of “equality…
Gideon’s Migration
122 Yale L.J. 2282 (2013). For the past fifty years, immigration law has resisted integration of Gideon v. Wainwright ’s legacy of appointed counsel for the poor. Today, however, this resistance has given way to Gideon ’s migration. At the level of everyday practice, criminal defense attorneys appointe…
Searching for Solutions to the Indigent Defense Crisis in the Broader Criminal Justice Reform Agenda
122 Yale L.J. 2316 (2013). As we mark the fiftieth anniversary of the Gideon v. Wainwright decision, the nearly universal assessment is that our indigent defense system remains too under-resourced and overwhelmed to fulfill the promise of the landmark decision, and needs to be reformed. At the same t…
Gideon’s Amici: Why Do Prosecutors So Rarely Defend the Rights of the Accused?
122 Yale L.J. 2336 (2013). In Gideon v. Wainwright , twenty-three state attorneys general, led by Walter F. Mondale and Edward McCormack, joined an amicus brief on the side of the criminal accused, urging the Supreme Court to recognize indigent defendants’ Sixth Amendment right to appointed counsel in…
Valuing Gideon’s Gold: How Much Justice Can We Afford?
122 Yale L.J. 2358 (2013). In this Essay, we explore Gideon ’s impact in our community, El Paso, Texas, which has the will to try to meet Gideon ’s challenge, but lacks the resources to deliver fully Gideon ’s promise. We look at the origins of our community’s indigent defense reform and examine our off…
Investigating Gideon’s Legacy in the U.S. Courts of Appeals
122 Yale L.J. 2376 (2013). This Essay investigates the legacy of Gideon by examining the de facto courts of last resort for convicted offenders: the federal courts of appeals. Part I focuses on the U.S. courts of appeals’ judges and caseloads, revealing that very few federal appellate judges have pri…
An Immigration Gideon for Lawful Permanent Residents
122 Yale L.J. 2394 (2013). In evaluating the legacy of Gideon v. Wainwright , it is critical to remember that the Supreme Court’s decision rested on the Sixth Amendment right to counsel for the accused in criminal cases. American law sharply demarcates between the many rights available to criminal def…
Gideon at Guantánamo
122 Yale L.J. 2416 (2013). The right to counsel maintains an uneasy relationship with the demands of trials for war crimes. Drawing on the author’s personal experiences from defending a Guantánamo detainee, the Author explains how Gideon set a baseline for the right to counsel at Guantánamo. Whether …
Enforcing Effective Assistance After Martinez
122 Yale L.J. 2428 (2013). This Essay argues that the Court’s effort to expand habeas review of ineffective assistance of counsel claims in Martinez v. Ryan will make little difference in either the enforcement of the right to the effective assistance of counsel or the provision of competent represen…
Gideon’s Law-Protective Function
122 Yale L.J. 2460 (2013). Gideon v. Wainwright dramatically affects the rights of indigent defendants by entitling them to representation. But Gideon has another systemic consequence as well. In addition to protecting the rights of individual defendants in particular trials, Gideon also protects the…
Gideon’s Shadow
122 Yale L.J. 2482 (2013). The right to counsel is regarded as a right without peer, even in a field of litigation saturated with constitutional protections. But from this elevated, elite-right status, the right to counsel casts a shadow over the other, less prominent criminal procedure rights. Elabo…
Gideon at Guantánamo: Democratic and Despotic Detention
122 Yale L.J. 2504 (2013). One measure of Gideon v. Wainwright is that it made the U.S. government’s efforts to isolate 9/11 detainees from all outsiders at Guantánamo Bay conceptually and legally unsustainable. Gideon , along with Miranda v. Arizona , is part of a democratic narrative shaped over dec…
Fear of Adversariness: Using Gideon To Restrict Defendants’ Invocation of Adversary Procedures
122 Yale L.J. 2550 (2013). Fifty years ago Gideon promised that an attorney would vindicate the constitutional rights of any accused too poor to afford an attorney. But Gideon also promised more. Writ small, Gideon promised to protect individual defendants; writ large, Gideon promised to protect our …
Federal Public Defense in an Age of Inquisition
122 Yale L.J. 2578 (2013). This Essay asks whether federal criminal defendants receive fairer process today than they did in 1963, when Gideon v. Wainwright was decided. It concludes that in many situations they do not; indeed, they often receive far worse. Although Gideon and the Criminal Justice Ac…
Effective Trial Counsel After Martinez v. Ryan: Focusing on the Adequacy of State Procedures
122 Yale L.J. 2604 (2013). Everyone knows that excessive caseloads, poor funding, and a lack of training plague indigent defense delivery systems throughout the states, such that the promise of Gideon v. Wainwright is largely unfulfilled. Commentators have disagreed about how best to breathe life int…
Implicit Racial Bias in Public Defender Triage
122 Yale L.J. 2626 (2013). Despite the promise of Gideon , providing “the guiding hand of counsel” to indigent defendants remains unmanageable, largely because the nation’s public defender offices are overworked and underfunded. Faced with overwhelming caseloads and inadequate resources, public defend…
Effective Plea Bargaining Counsel
122 Yale L.J. 2650 (2013). Fifty years ago, Clarence Earl Gideon needed an effective trial attorney. The Supreme Court agreed with Gideon that the Sixth Amendment guaranteed him the right to counsel at trial. Recently, Galin Frye and Anthony Cooper also needed effective representation. These two men,…
The Continuum of Excludability and the Limits of Patents
122 Yale L.J. 1900 (2013). In IP scholarship, patents are commonly understood as more efficient than other approaches to innovation policy. Their primary ostensible advantage is allocative: as a form of property rights, patents act as a conduit between market signals and potential innovators, ostensi…
Spite and Extortion: A Jurisdictional Principle of Abuse of Property Right
122 Yale L.J. 1444 (2013). This Essay puts forward the conceptual and normative underpinnings of a principle of abuse of property right. Owners abuse their right, I argue, when their decisions about a thing are designed just to produce harm. This is so whether that harm is an end in itself (spite) or…
Reconceptualizing the Burden of Proof
122 Yale L.J. 1254 (2013). The preponderance standard is conventionally described as an absolute probability threshold of 0.5. This Essay argues that this absolute characterization of the burden of proof is wrong. Rather than focusing on an absolute threshold, the Essay reconceptualizes the preponder…
Can the President Appoint Principal Executive Officers Without a Senate Confirmation Vote?
122 Yale L.J. 940 (2013). It is generally assumed that the Constitution requires the Senate to vote to confirm the President’s nominees to principal federal offices. This Essay argues, to the contrary, that when the President nominates an individual to a principal executive branch position, the Senat…
Asymmetries and Incentives in Plea Bargaining and Evidence Production
122 Yale L.J. 690 (2012). Legal rules severely restrict payments to fact witnesses, though the government can often offer plea bargains or other nonmonetary inducements to encourage testimony. This asymmetry is something of a puzzle, for most asymmetries in criminal law favor the defendant. The asymm…
Contra Nemo Iudex in Sua Causa: The Limits of Impartiality
122 Yale L.J. 384 (2012).
Regularly invoked by the Supreme Court in diverse contexts, the maxim nemo iudex in sua causa —no man should be judge in his own case—is widely thought to capture a bedrock principle of natural justice and constitutionalism. I will argue that the nemo iudex principle is a m…
Judicial Capacity and the Substance of Constitutional Law
122 Yale L.J. 422 (2012). Courts can decide only a small fraction of constitutional issues generated by the American government. This is widely acknowledged. But why do courts have such limited capacity? And how does this limitation affect the substance of constitutional law? This Essay advances a tw…
How Much Difference Does the Lawyer Make? The Effect of Defense Counsel on Murder Case Outcomes
122 Yale L.J. 154 (2012). One in five indigent murder defendants in Philadelphia is randomly assigned representation by public defenders while the remainder receive court-appointed private attorneys. We exploit this random assignment to measure how defense counsel affect murder case outcomes. Compare…
One in five indigent murder defendants in Philadelphia is randomly assigned representation by public defenders while the remainder receive court-appointed private attorneys. We exploit this random assignment to measure how defense counsel affect murder case outcomes. Comp…
The Antitrust/Consumer Protection Paradox: Two Policies at War with Each Other
121 Yale L.J. 2216 (2012) . The potential complementarities between antitrust and consumer protection law—collectively, “consumer law”—are well known. The rise of the newly established Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) portends a deep rift in the intellectual infrastructure of consumer law …
Due Process as Separation of Powers
121 Yale L.J. 1672 (2012) . From its conceptual origin in Magna Charta, due process of law has required that government can deprive persons of rights only pursuant to a coordinated effort of separate institutions that make, execute, and adjudicate claims under the law. Originalist debates about whether t…
Income Tax Discrimination: Still Stuck in the Labyrinth of Impossibility
121 Yale L.J. 1118 (2012).
In previous articles, we have argued that the European Court of Justice’s reliance on nondiscrimination as the basis for its decisions did not (and could not) satisfy commonly accepted tax policy norms, such as fairness, administrability, economic efficiency, production o…
Intrastatutory Federalism and Statutory Interpretation: State Implementation of Federal Law in Health Reform and Beyond
121 Yale L.J. 534 (2011).
State implementation of federal law is commonplace, but has been largely ignored by the interpretive doctrines of legislation and administrative law. We have no Chevron , federalism canon, or anything else for state implementation, nor any doctrines that ask how Congress’s…
The Principle of Misalignment: Duty, Damages, and the Nature of Tort Liability
121 Yale L.J. 142 (2011). When a tort rule is fully aligned, harms are valued equally across the elements. Because the valuation of harm within duty equals the valuation within the damages remedy, a fully aligned rule gives dutyholders the option to fully comply with the duty with respect to any harm by…
Justifications, Power, and Authority
117 Yale L.J. 1070 (2008).
Criminal law theory made a significant advance roughly thirty years ago when George Fletcher popularized the important conceptual distinction between justifications and excuses. In the intervening years, however, very little progress has been made in exploring the structu…
Irreparable Benefits
116 Yale L.J. 1284 (2007)
The conventional approach to preliminary relief focuses on irreparable harm but entirely neglects irreparable benefits. That is hard to understand. Errant irreversible harms are important because they distort incentives and have lasting distributional consequences. But the…
The Efficient Performance Hypothesis
116 Yale L.J. 568 (2006) Notable American jurists and scholars have advanced an approach to contract enforcement that would render breach legally and morally uncontestable, assuming compensation follows. Much of the justification for this endeavor has rested upon claims of judicial and economic effic…
Executive Branch Usurpation of Power: Corporations and Capital Markets
115 Yale L.J. 2416 (2006) Agencies in the executive branch are better situated than other political institutions to take advantage of opportunities to expand their power base by responding quickly and decisively to real or imagined crises. The executive has structural advantages over the other branch…
Beyond Marbury: The Executive's Power To Say What the Law Is
115 Yale L.J. 2580 (2006) Under Marbury v. Madison , it is "emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is." But in the last quarter-century, the Supreme Court has legitimated the executive's power of interpretation, above all in Chevron, U.S.A., Inc. v. Natural R…
Can Strong Mayors Empower Weak Cities? On the Power of Local Executives in a Federal System
This Essay considers the historic weakness of the American mayoralty and recent reform efforts designed to strengthen it. I argue that the strong mayoralty is a potential instrument for democratic self-government to the extent that it is able to amass power on behalf of the city.
Rational War and Constitutional Design
115 Yale L.J. 2512 (2006) Contemporary accounts of the allocation of war powers authority often focus on textual or historical debates as to whether the President or Congress holds the power to initiate military hostilities. In this Essay, we move beyond such debates and instead pursue a comparative …
Break Up the Presidency? Governors, State Attorneys General, and Lessons from the Divided Executive
115 Yale L.J. 2446 (2006) Proponents of the unitary executive have contended that its adoption by the framers "swept plural executive forms into the ash bin of history." Virtually every state government, however, has a divided executive in which executive power is apportioned among different executiv…
Gubernatorial Foreign Policy
115 Yale L.J. 2380 (2006) In a variety of circumstances, state governors exercise independent decision-making power over matters affecting the foreign policy of the United States. This Essay describes and defends this emerging system of gubernatorial foreign policy on both legal and functional ground…
Setting the World Right
115 Yale L.J. 2350 (2006) Five years after September 11, 2001, America's response to that traumatic day has effectively turned the world of American public law upside down. Claiming that a global war on terror calls for an entirely new legal paradigm, the Bush Administration and its supporters have p…
The President's Completion Power
115 Yale L.J. 2280 (2006) This Essay identifies and analyzes the President's completion power: the President's authority to prescribe incidental details needed to carry into execution a legislative scheme, even in the absence of congressional authorization to complete that scheme. The Essay shows tha…
Quasipublic Executives
115 Yale L.J. 2254 (2006) In this Essay, we first observe the rise of what we call "quasipublic executives": both "nominally private executives," that is, private executives in charge of public functions such as corrections, education, and national defense; and "nominally public executives," that is,…
Why (and When) Cities Have a Stake in Enforcing the Constitution
115 Yale L.J. 2218 (2006) This Essay examines independent constitutional interpretation from the bottom up. It focuses on San Francisco's recent challenge to the California ban against same-sex marriage and the judicial response it provoked in Lockyer v. City & County of San Francisco . The Essay argu…
Inherent Executive Power: A Comparative Perspective
115 Yale L.J. 2480 (2006) In light of recent debates regarding the scope and basis of inherent executive power, particularly with regard to foreign affairs and national security, this Essay examines different conceptions of executive power in five modern democracies. The Essay's study of British and …
Internal Separation of Powers: Checking Today's Most Dangerous Branch from Within
115 Yale L.J. 2314 (2006) The standard conception of separation of powers presumes three branches with equivalent ambitions of maximizing their powers. Today, however, legislative abdication is the reigning modus operandi. Instead of bemoaning this state of affairs, this Essay asks how separation of …
Absolute Priority, Valuation Uncertainty, and the Reorganization Bargain
115 Yale L.J. 1930 (2006) In a Chapter 11 reorganization, senior creditors can insist on being paid in full before anyone junior to them receives anything. In practice, however, departures from "absolute priority" treatment are commonplace. Explaining these deviations has been a central preoccupation…
Evolution and Chaos in Property Rights Systems: The Third World Tragedy of Contested Access
115 Yale L.J. 996 (2006) According to conventional law-and-economics theory, private property rights tend to evolve as resource values rise. This optimistic assessment fails to explain the development of open access in many Third World property systems. Indeed, while the evolution of property has bee…
Of Property and Federalism
115 Yale L.J. 72 (2005) This Essay proposes a mechanism for expanding competition in state property law, while sketching out the limitations necessary to protect third parties. The fact that property law is produced by the states creates a unique opportunity for experimentation with such property and…
Democratic Disobedience
114 Yale L.J. 1897 (2005) Traditional justifications for civil disobedience emphasize the limits of legitimate political authority and defend civil disobedience as a just response when governments overstep these limits. Such liberal justifications are well suited to certain classes of civil disobedie…
To Insure Prejudice: Racial Disparities in Taxicab Tipping
114 Yale L.J. 1613 (2005) Many studies have documented seller discrimination against consumers, but this Essay tests and finds that consumers discriminate based on the seller's race. The authors collected data on more than 1000 taxicab rides in New Haven, Connecticut in 2001. After controlling for a …
Copy This Essay: How Fair Use Doctrine Harms Free Speech and How Copying Serves It
114 Yale L.J. 535 (2004) Recent cases and scholarship have debated whether copyright law is consistent with the First Amendment. Much of the discussion has centered on copyright law's ability to suppress transformative, creative reuses of copyrighted works and on copyright's fair use doctrine as a m…
Sharing Nicely: On Shareable Goods and the Emergence of Sharing as a Modality of Economic Production
114 Yale L.J. 273 (2004) This Essay offers a framework to explain large-scale effective practices of sharing private, excludable goods. It starts with case studies of carpooling and distributed computing as motivating problems. It then suggests a definition for shareable goods as goods that are "lump…
Integrating Remorse and Apology into Criminal Procedure
114 Yale L.J. 85 (2004) Criminal procedure largely ignores remorse and apology or, at most, uses them as proxies for an individual defendant's badness. The field is preoccupied with procedural values such as efficiency, accuracy, and procedural fairness, to the exclusion of the criminal law's substan…
The Priority of Morality: The Emergency Constitution's Blind Spot
113 Yale L.J. 1753 (2004) INTRODUCTION In the wake of the terrorist attacks of September 11, Attorney General John Ashcroft announced a campaign of aggressive preventive detention. Invoking Robert Kennedy, the Attorney General announced that just as Kennedy would arrest a mobster for "spitting on the…
Editor's Note: The Constitution in Times of Emergency
113 Yale L.J. 1751 (2004) Earlier in this Volume of The Yale Law Journal, Professor Bruce Ackerman published his essay The Emergency Constitution, in which he advocated a new constitutional regime to confront the potential for recurring terrorist attacks among modern nations--and the United States in…
The Anti-Emergency Constitution
113 Yale L.J. 1801 (2004) INTRODUCTION The season for talk of leaving the Constitution behind, while we grit our teeth and do what must be done in times of grave peril--the season for talk of saving the Constitution from the distortions wrought by sheer necessity, while we save ourselves from the d…
Adverse Selection in Insurance Markets: An Exaggerated Threat
113 Yale L.J. 1223 (2004) The phrase "adverse selection" was originally coined by insurers to describe the process by which insureds utilize private knowledge of their own riskiness when deciding to buy or forgo insurance. If A knows he will die tomorrow (but his insurer does not), life insurance th…
The Emergency Constitution
113 Yale L.J. 1029 (2004) Terrorist attacks will be a recurring part of our future. The balance of technology has shifted, making it possible for a small band of zealots to wreak devastation where we least expect it--not on a plane next time, but with poison gas in the subway or a biotoxin in the wat…
Juries and Race in the Nineteenth Century
113 Yale L.J. 895 (2004) The Supreme Court's jurisprudence on criminal juries has overlooked an important piece of history. This is most notable in the context of its jury discrimination jurisprudence over the past twenty years. In Batson v. Kentucky, the Court held that the Equal Protection Clause p…
Bargaining in the Shadow of Takeover Defenses
113 Yale L.J. 621 (2003) For decades, practitioners and academic commentators who believe that target boards should have broad discretion to resist hostile takeover attempts have put forward the "bargaining power hypothesis" to support their view. This hypothesis states that a target with strong tak…
Insider Abstention
113 Yale L.J. 455 (2003) Scholars writing on insider trading have long believed that insiders can beat the market simply by using nonpublic information to decide when not to trade. Using a simple model, this Essay has shown that the conventional wisdom is wrong. Insiders prevented from trading while …
Minorities, Shareholder and Otherwise
113 Yale L.J. 119 (2003) "[M]en are described as I think they are," Adolf Berle writes of his work, "rather than as they think they are." He continues: "Some will be shocked. The businessman will find that he is a politician and a commissar--perhaps even a revolutionary one. The liberal finds himsel…
Digital Architecture as Crime Control
112 Yale L.J. 2261 (2003) The first generation of cyberlaw was about what regulates cyberspace. Led by Larry Lessig's path-breaking scholarship isolating architecture as a constraint on behavior online, a wide body of work has flourished. In a recent article, I took those insights and reverse-engine…
How Much Redistribution Should There Be?
112 Yale L.J. 2291 (2003) Egalitarianism ties people's fortunes together. It takes the good and bad things in people's lives--their blessings and their afflictions--and shares them out, or redistributes them, among their fellows. Where egalitarianism operates, each person's fortunes and misfortunes c…
Eldred and Lochner: Copyright Term Extensionand Intellectual Property as Constitutional Property
112 Yale L.J. 2331 (2003) As intellectual property has become increasingly important to the national economy, a consensus has emerged among academics that courts should scrutinize congressional legislation closely under the Constitution's Copyright Clause. This Essay has challenged the academic conse…
Common Law, Common Ground, and Jefferson's Principle
112 Yale L.J. 1717 (2003) Why do we care about the Framers of the Constitution? After all, they lived long ago, in a world that was different in countless ways from ours. Why does it matter what their views were, for any reasons other than purely historical ones? And if we don't care about the Framer…
The Secret History of Race in the United States
112 Yale L.J. 1473 (2003) In the beginning, there was a man named Looney. George Looney's world was Buchanan County, Virginia, a pocket of Appalachian hills and hollows that juts into Kentucky and West Virginia. In 1911, his place in this world was secure. Where lumber was the only industry in town, …
Economic Analysis of Contract Law After Three Decades: Success or Failure?
112 Yale L.J. 829 (2003) Modern economic analysis of contract law began about thirty years ago and, many scholars would agree, has become the dominant academic style of contract theory. Traditional doctrinal analysis exerts less influence than it did prior to 1970 and enjoys little prestige. Philosop…
Vigorous Race or Leisurely Walk: Reconsidering the Competition over Corporate Charters
112 Yale L.J. 553 (2002) Does American corporate law work effectively to enhance shareholder value? The recent corporate governance crisis makes this time as good as any for reexamining the basic structure of this body of law. This Essay provides such a reconsideration of a defining feature of U.S. c…
100 Million Unnecessary Returns: A Fresh Start for the U.S. Tax System
112 Yale L.J. 261 (2002) We are now in a quiet interlude awaiting the next serious political debate over the nation's tax system. No fundamental tax policy concerns were at stake in the 2002 disputes over economic stimulus or the political huffing and puffing about postponing or accelerating the inco…
Probability Neglect: Emotions, Worst Cases, and Law
112 Yale L.J. 61 (2002) In this Essay, my central claim has been that the probability of harm is often neglected when people's emotions are activated, especially if people are thinking about the worst-case scenario. If that scenario is vivid and easy to visualize, large-scale changes in thought and b…
Local Policing After the Terror
111 Yale L.J. 2137 (2002) Crime waves always carry with them calls for more law enforcement authority. What happened on September 11, 2001 was, among other things, a crime wave--because of that one day, the number of homicides in America in 2001 will be twenty percent higher than the year before. It…
Legislative Entrenchment: A Reappraisal
111 Yale L.J. 1665 (2002) There is a principle of constitutional law holding that "one legislature may not bind the legislative authority of its successors." The Supreme Court recently discussed that principle at length in United States v. Winstar, and although the case was decided on other grounds,…
Judicial Review, the Congressional Process, and the Federalism Cases: An Interdisciplinary Critique
111 Yale L.J. 1707 (2002) Following the lead of Alexander Bickel's The Least Dangerous Branch: The Supreme Court at the Bar of Politics, legal scholars have been obsessed with the countermajoritarian aspects of judicial review. Much of the literature is normative--how can the dilemma of judicial re…
Stopping Above-Cost Predatory Pricing
111 Yale L.J. 941 (2002) This Essay has refocused the predatory pricing debate on ex ante incentives--i.e., the incentives for entry and limit pricing before the predatory period--instead of the traditional focus of high prices after the predatory period. Ideally, a monopoly incumbent should price re…
Categorical Federalism: Jurisdiction, Gender, and the Globe
111 Yale L.J. 619 (2001) An absence of bounded categories may be unsettling but, in lieu of (false) comfort, multi-faceted federalism offers something else, hopefully more useful if less supportive. Under the rubric of multi-faceted federalism, the deployment of categories is accompanied by a sense t…
Veil of Ignorance Rules in Constitutional Law
111 Yale L.J. 399 (2001) A veil of ignorance rule (more briefly a "veil rule") is a rule that suppresses self-interested behavior on the part of decisionmakers; it does so by subjecting the decisionmakers to uncertainty about the distribution of benefits and burdens that will result from a decision. …
What Happened to Property in Law and Economics?
111 Yale L.J. 357 (2001) Property has fallen out of fashion. Although people are as concerned as ever with acquiring and defending their material possessions, in the academic world there is little interest in understanding property. To some extent, this indifference reflects a more general skepticism…
Drug Designs are Different
111 Yale L.J. 151 (2001) In an essay published in this Journal entitled Is There a Design Defect in the Restatement (Third) of Torts: Products Liability?, George Conk criticizes the American Law Institute and the Reporters of the new Restatement for immunizing prescription drug manufacturers from lia…
Bush v. Gore and the Boundary Between Law and Politics
110 Yale L.J. 1407 (2001) Shortly after the Supreme Court's 5-4 decision in Bush v. Gore, one member of the majority, Associate Justice Clarence Thomas, addressed a group of students in the Washington, D.C., area. He told them that he believed that the work of the Court was not in any way influenced…
Pennhurst, Chevron, and the Spending Power
110 Yale L.J. 1187 (2001) Narrowly construed, Pennhurst is a sensible (even if not necessary) process-based limitation on Congress's power to bind states to costly burdens. If read to mean that a state can never be bound by a grant condition when the statute itself does not unmistakably speak to a pa…
The Internet and the Dormant Commerce Clause
110 Yale L.J. 785 (2001)
Equal Protection by Law: Federal Antidiscrimination Legislation After Morrison and Kimel
110 Yale L.J. 441 (2000) Last Term, the Supreme Court sent ominous signals about the future of federal antidiscrimination law. The Court twice ruled that Congress lacked power under Section 5 of the Fourteenth Amendment to enact laws prohibiting discrimination. In Kimel v. Florida Board of Regents, …
Disaggregating Constitutional Torts
110 Yale L.J. 259 (2000) This Essay has attempted to clarify and reconceptualize constitutional tort law. Current doctrine severs remedies from rights and authorizes money damages on terms that apply indifferently to all constitutional violations. This remedial uniformity is faithful to the Monroe mo…
Deliberative Trouble? Why Groups Go to Extremes
110 Yale L.J. 71 (2000) In this Essay, I have discussed the phenomenon of group polarization and explored some of its implications for deliberation generally and deliberative democracy in particular. The central empirical finding is that group discussion is likely to shift judgments toward a more ext…
Announcing the Editors of Volume 134
Announcing the first-year editors of volume 133, announcing the seventh annual student essay competition, featured content, lock them™ up: holding transnational corporate human-rights abusers accountable, administrative law at a turning point, law and movements: clinical perspectives.

Essay on Why I Want to Become a Lawyer
A lawyer is a person, in which, people deal with judicial actions and help others to get their rights. They can help people from any kind of social problem. There is a law in every country and one should definitely follow it and when someone disobeys or creates problems for others, then people need a lawyer to deal with them. Get here some essays on this topic; I am sure these will be helpful in your academic needs:
Short and Long Essays on why I want to become a Lawyer in English
Essay on Why I want to become a Lawyer for students of class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and class 12 in English in 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 500 words. Also find short Why I want to become a Lawyer essay 10 lines.
Why I want to become a Lawyer Essay 10 Lines (100 – 150 Words)
1) Since childhood, I loved the profession of a lawyer and want to become the same.
2) From a younger age, I like to fight for the rights of others.
3) I want to be a lawyer because I am a great supporter of truth.
4) By becoming a lawyer I want to aware people of their rights.
5) I want to become a lawyer because I want to fight for justice.
6) Every issue can be solved through law and order and I want to be that resolver.
7) I pose logical thinking and influence talks, thus I’m perfect for this profession.
8) I would love to be a lawyer because I can see a better career prospect in this profession.
9) I would love to fight for the poor whose rights are always neglected.
10) Finding evidence and punishing the culprit attracts me to this profession.
Essay 1 (250 Words) – Why I want to become a Lawyer?
Introduction
When we ask a child what he really wants to become, some of them want to be a doctor, whereas some of them want to be an engineer. Similarly, when I was young, I wanted to become a lawyer. I like this profession because it is all about getting our rights. I like to solve other’s problems and I found this profession perfect for me.
My Hidden Inspiration
When I was young, I use to watch TV a lot and also use to watch news channels. I liked news channels because they use to tell us various incidents all across the world. When I use to see something awkward, it uses to provoke me to find the thieves or criminals and punish them. But I had no rights and was also very young.
So, one day I ask my mother, as if how can I bring justice to the poor. Then she told me that I have to become a lawyer, to deal with such situations. From that day this profession started attracting me. I decided to become a lawyer and will definitely become someday.
Do whatever attracts you and this will definitely make you successful one day. When our profession becomes our passion then no one can stop us. Bring that spirit and see the change in yourself. I love to deal with the truth, justice, so I chose this profession. Your reason can be something else to choose yours.
Essay 2 (400 Words) – Law as a Profession
Different people like different colours similarly when we talk about professions, all of us have different opinions. Suppose all of us become a doctor and if one of them have to make his house. When society is full of doctors who will build his house? So, he needs an engineer too in the society. Similarly, different professions have their own different importance. We need police to maintain the peace, a lawyer to deal with judiciary problems, a sweeper to sweep your dust, etc. No profession is either small or big. A doctor’s clinic will not be clean if there are no cleaning professionals. All of us have different taste and we choose our profession accordingly.
Some Positive Aspects of Being a Lawyer
- Being a Lawyer is not only a profession but also helps us to know our potential. Sometimes we don’t even know how much we can do and what are the powers of a commoner. This profession helps us to know our own powers.
- They also know how to deal with a problem; actually our law has a solution for every problem. So, in my onion, it is one of the best professions.
- A lawyer should be smart and should have a very good logical power because this helps them to find evidence and also helps them to have a good verbal battle in the court.
- Believe me or not but people never like to mess-up with a lawyer because they know they themselves can become the victim. So, many people stay away from them and it is a good thing.
- People like me love this profession because I like to dig the truth at any cost. This profession teaches how professionally I can handle a case and help people.
Educational Qualification of a Lawyer
If you are willing to be a lawyer then you have to peruse the below;
- After completing senior secondary one should complete his graduation in Law stream. They can have LLB with some other bachelor courses like BA, BBA, B.Com, etc.
- One should complete his graduation in any stream and should also peruse LLB. There are many colleges which provide this course together and it takes near about 5 years to complete the entire course. Apart from this, there are many foreign colleges which also provide different courses for law students.
If you have good learning abilities and are also good at remembering things, then you should definitely go for it; because one should have to byheart a lot of Acts and Rules. One should have a sharp mind to understand all these. One more thing, I would like to say, if you are really passionate about your profession, no one can stop you.
Essay 3 (500 – 600 Words) – Why One should be a Lawyer?
A lawyer is a wonderful profession where a person should know all types of laws and should be well aware of judiciary actions. He should be capable to deal with any kind of law actions. Lawyers are also known as legal practitioners, attorneys, barristers, law agents, advocate, barrister, etc.
The First-Ever Lawyer
The description of this post was very first mentioned in the Bible and it was ‘Zenas’ the first-ever known Lawyer.
Apart from the Bible, the evidence of lawyers can also be seen in Ancient Greece, where the orators use to do the same job. So, they also get the credit of ancient lawyers in our history and we can say the evidence of lawyers can also be seen the ancient Rome.
When we had lawyers in the ancient period of Roam then they also furnished and progressed in this area first. Slowly it was 1848 when the United States bought this profession into existence.
There are different names proving the title of the first-ever lawyer in the world in the male category. Whereas there are some worldwide famous females’ in this profession like ‘Arabella Mansfield’ was the first female lawyer in the United States of America; whereas ‘Cornelia Sorabji’ was the first female who was from India and studied Law at Oxford University.
Why do I like this Profession?
There are many factors that attract me in this profession; I have listed them below;
- In my opinion, one should know his rights and should also know his powers. This is only possible if you have a deep knowledge of the law. Apart from our fundamental rights, there are also some rules and regulations that one should know. Like knowledge of your property and its successors, etc.
- Law helps us to deal with many problems. Sometimes many of us don’t even know what we can do in a particular case and we easily forget it. Actually, a person can even fight for his single penny but very few of us know about the right procedure and we leave it.
- If you are one of those who like to fight for the truth then you can stick to this profession. Sometimes we see one of our known sufferings and although they are correct, lack of evidence and some social powers they suffer. In such type of case this profession can really help and you can also work as a professional lawyer or can also work for charity.
- After winning some cases and gaining experience, one can also earn a lot and there are many lawyers who also earn even a crore for a single hearing. So, the money factor, which is one of the important things nowadays.
- If you want to do some charity and help the poor and helpless people who do not have money to hire a good lawyer, then you can help them by becoming a lawyer.
- Lawyers have a very good presence of mind and they are intelligent, challenging, brave, etc all these qualities can also make you a smart person.
I am one of those who love to figure out the truth and I find this profession suitable for me. This not only helps people but also helps us and in our daily life. Generally, lawyers charge a lot of money and there is a stage of life when all of us need them. So, it is better to choose this profession and if needed you can also earn, can also help people as social work. In my opinion, it is one of the best professions.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
I Hope to Repeal an Arcane Law That Could Be Misused to Ban Abortion Nationwide

By Tina Smith
Ms. Smith is a Democratic senator from Minnesota and a former Planned Parenthood executive.
A long discredited, arcane 150-year-old law is back in the news in 2024, and that should terrify anyone who supports reproductive freedom. Last week at the Supreme Court, the Comstock Act of 1873 was referenced on three separate occasions during oral arguments in a case dealing with access to mifepristone, one of two drugs typically used in medication abortions.
Anti-abortion activists like to bring up the Comstock Act because one of its clauses prohibits sending through the mail “every article, instrument, substance, drug, medicine or thing” that could possibly lead to an abortion. Even if the Supreme Court doesn’t take the bait, a newly re-elected President Trump could order his Department of Justice to start interpreting that line to mean that it is illegal to mail mifepristone — a safe, effective, Food and Drug Administration-approved drug — to doctors and pharmacies, as well as to patients directly. The same could go for medical supplies that are used in performing surgical abortions. That could effectively make abortion impossible to access even in places like Minnesota, which has affirmatively protected a woman’s right to choose by passing reproductive freedom laws.
In response, I’m prepared to fight back — including by introducing legislation to take away the Comstock Act as a tool to limit reproductive freedom.
Let me take a step back and explain how ridiculous it is that we’re even talking about this legislative relic today. The Comstock Act hasn’t been broadly enforced since the 1930s. The Biden administration considers it utterly irrelevant. Many legal experts consider it dead letter law. And once you know its back story, it becomes clear why no one has paid much attention to it in nearly a century.
Back in the 1860s, a former Civil War soldier from rural Connecticut named Anthony Comstock moved to New York City for work. He was shocked and appalled by what he found. Advertisements for contraception! Open discussions of sexual health! It all struck Comstock as terribly lewd and anti-Christian.
So he made it his mission to clean up society, creating the loftily named New York Society for the Suppression of Vice and gathering evidence for police raids on places that distributed material he thought was obscene or promoted indecent living. In the early 1870s he took his crusade to Washington, lobbying for federal legislation that would empower the post office to search for and seize anything in the mail that met Comstock’s criteria for being “obscene,” “lewd” or just plain “filthy.” Morality, as determined by Comstock, would be the law of the land, and Comstock himself would be its enforcer, appointed by Congress as a special agent of the post office.
In a fit of Victorian puritanism, Congress passed the Comstock Act into law. But it quickly became apparent that Comstock’s criteria were unworkably vague. In its broad wording, the law not only made it illegal to send pornography through the mail, it also outlawed the sending of medical textbooks for their depictions of the human body, personal love letters that hinted at physical as well as romantic relationships, and even news stories.
The whole thing was very silly and impracticable, and that’s why the Comstock Act was relegated to the dustbin of history.
But conservative activists recently revived it from obscurity as part of their playbook for a potential second Trump term: The 887-page plan nicknamed Project 2025 being promoted by groups like the Heritage Foundation explicitly calls for a newly elected second-term President Trump to use this zombie law to severely ratchet back abortion access in America without congressional action.
Legislation to repeal Comstock could take many forms, and we need to do it the right way. That’s why I’ve begun reaching out to my colleagues in the House of Representatives and the Senate to build support and see what legislation to repeal the Comstock Act might look like. Anti-abortion extremists will continue to exploit any avenue they can find to get the national ban they champion, and I want to make sure my bill shuts down every one of those avenues. Once the Supreme Court has had its say (and many legal analysts speculate that the mifepristone case heard last week should be thrown out on procedural grounds, and may well be), I’ll be ready to have mine.
Here’s the bottom line: We can’t let anyone — not the Supreme Court, not Donald Trump and certainly not a random busybody from the 19th century — take away Americans’ right to access medication abortion. We must protect the ability of doctors, pharmacies and patients to receive in the mail the supplies they need to exercise their right to reproductive care.
As the only former Planned Parenthood executive serving in the Senate, I feel I have a special responsibility to protect not just abortion rights but also abortion access.
Very few Republicans will admit to wanting to see a total, no-exceptions ban on abortion in all 50 states, but the Comstock Act could allow them to achieve that in effect, if not in so many words.
Americans deserve better. The Constitution demands better. And common sense dictates that we stop this outrageous backdoor ploy to eliminate abortion access in its tracks.
Tina Smith is a Democratic senator from Minnesota and a former Planned Parenthood executive.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

'Panama Papers' trial starts. 27 people charged in the worldwide money laundering case
P ANAMA CITY (AP) — The trial of 27 people charged in connection with the worldwide “Panama Papers” money laundering started Monday in a Panamanian criminal court.
Those on trial include the owners of the Mossack-Fonseca law firm that was at the heart of the 2016 massive document leak.
The Panama Papers include a collection of 11 million secret financial documents that illustrate how some of the world's richest people hide their money.
The repercussions of the leaks have been far-ranging, prompting the resignation of the prime minister of Iceland and bringing scrutiny to the leaders of Argentina and Ukraine, Chinese politicians and Russian President Vladimir Putin, among others.
The often-delayed trial opened Monday, with lawyers Juergen Mossack, Ramón Fonseca and other former representatives, lawyers or ex-employees of the firm facing money laundering charges.
Mossack was present in the courtroom, and said “I am not guilty of such acts.”
Lawyers for Fonseca said he was in a hospital in Panama.
The case centers on allegations the firm set up shell companies to acquire properties in Panama with money from a sprawling corruption scheme in Brazil known as the Car Wash , or Lava Jato in Portuguese.
Fonseca has said the firm, which closed in 2018, had no control over how its clients might use offshore vehicles created for them. Both Mossack and Fonseca have Panamanian citizenship, and Panama does not extradite its own citizens.
The two were acquitted on other charges in 2022.
The records were first leaked to the German daily Suddeutsche Zeitung, and were shared with the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, which began publishing collaborative reports with news organizations in 2016.
U.S. federal prosecutors have alleged that Mossack Fonseca conspired to circumvent American laws to maintain the wealth of its clients and conceal tax dollars owed to the IRS. They alleged the scheme dates to 2000 and involved sham foundations and shell companies in Panama, Hong Kong and the British Virgin Islands.
Follow AP’s coverage of Latin America and the Caribbean at https://apnews.com/hub/latin-america

Special counsel urges Supreme Court to reject Trump’s immunity claim

Special counsel Jack Smith on Monday urged the Supreme Court to reject Donald Trump’s “novel and sweeping” claim that he is immune from criminal prosecution on charges of conspiring to overturn the results of the 2020 presidential election.
“The President’s constitutional duty to take care that the laws be faithfully executed does not entail a general right to violate them,” Smith said in his office’s main brief to the justices before the Supreme Court reviews the case on April 25 , the final day of the court’s oral argument calendar for this term.
Trump’s D.C. prosecution for allegedly trying to block Joe Biden’s victory is on hold while the justices consider his immunity claim, and the high court’s ruling will determine whether and how quickly Trump faces trial.
The justices’ decision to take up Trump’s claim — rather than let stand an appeals court decision that he can be prosecuted — has drawn criticism for delaying the trial, which initially was scheduled to begin in early March.
Subscribe to The Trump Trials, our weekly email newsletter on Donald Trump's four criminal cases
Trump, the presumptive 2024 Republican nominee for president, has tried to push the D.C. trial and the other legal challenges he faces until after the general election rematch with Biden. If Trump is again elected president, he could appoint an attorney general who would seek to have the federal cases dropped.
The justices can rule on the immunity issue at any time after the April 25 argument, and are expected to do so before the term ends in late June or early July. That would push any trial at least into the second half of the summer or the fall.
In addition, the Supreme Court next week will review the validity of a law that has been used to charge hundreds of people with obstruction in connection with the Jan. 6 , 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol — and that is also a key element of the D.C. charges that Trump is facing.
In the special counsel’s filing in the immunity case on Monday, the office pushed back on what Smith called Trump’s “radical suggestion” of immunity that he said would allow a former president to escape accountability even for crimes such as murder or bribery. The criminal justice system, Smith added, includes numerous safeguards to ensure the law is applied fairly, including to an ex-president.
“These layered safeguards provide assurance that prosecutions will be screened under rigorous standards and that no President need be chilled in fulfilling his responsibilities by the understanding that he is subject to prosecution if he commits federal crimes,” Smith wrote.
Trump faces four felony counts in connection with what prosecutors allege was a plan to block Biden’s 2020 presidential victory: conspiring to defraud the United States, conspiring to obstruct the formal certification in Congress of Biden’s victory, obstructing a congressional proceeding and conspiracy against rights — in this case, the right to vote.
He has asked the justices to reverse a unanimous appeals court ruling that said he may be prosecuted on those counts.
In their brief filed last month, Trump’s legal team said a president’s official acts, including the conduct alleged in the indictment, should be shielded from criminal prosecution. The threat of prosecution and imprisonment hanging over the head of any president, they wrote, would take away “the strength, authority, and decisiveness” of the person holding the office.
“The President cannot function, and the Presidency itself cannot retain its vital independence, if the President faces criminal prosecution for official acts once he leaves office,” the filing said.
The ruling on the matter from the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit took a starkly differently position, saying “any executive immunity that may have protected him while he served as President no longer protects him against this prosecution.”
The panel concluded that it could not “accept former President Trump’s claim that a president has unbounded authority to commit crimes that would neutralize the most fundamental check on executive power — the recognition and implementation of election results.”
When the Supreme Court agreed to take the immunity case in late February, the justices said the issue they would decide was: “whether and if so to what extent does a former president enjoy presidential immunity from criminal prosecution for conduct alleged to involve official acts during his tenure in office.”
The question appears to give the court an opening to distinguish between a president’s actions that are private and those that are official duties, which the lower appeals court ruling does not do.
If the Supreme Court then returns the case to the lower courts for additional litigation over whether Trump’s alleged activity was official, that could push the trial until after the election.
Trump’s lawyers noted in their brief that no court has addressed whether immunity applies to the actions alleged in the indictment and said the matter could be sent back for “further factfinding as to specifics of this case.”
Smith also addressed the possibility that the justices could find a former president entitled to some immunity for official acts. That protection would not apply to Trump’s efforts to subvert the election results, Smith wrote, in part because of Trump’s alleged use of official power to achieve a private aim — to remain in office after his election defeat.
More on the Trump Jan. 6 case
The latest: The Supreme Court will review Donald Trump’s unprecedented claim that he is shielded from prosecution for actions taken while in office. Supreme Court arguments are set for the week of April 22. Here’s what happens next .
The charges: Former president Donald Trump pleaded not guilty to charges that he plotted to overturn the 2020 election in the run-up to the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol. Here’s a breakdown of the charges against Trump and what they mean, and things that stand out from the Trump indictment . Read the full text of the 45-page indictment .
The trial: The March 4 trial date has been taken off the calendar and jury selection has been postponed indefinitely while Trump’s claim of presidential immunity from criminal prosecution remains on appeal .
The case: The special counsel’s office has been investigating whether Trump or those close to him violated the law by interfering with the lawful transfer of power after the 2020 presidential election or with Congress’s confirmation of the results on Jan. 6, 2021. It is one of several ongoing investigations involving Trump .
Can Trump still run for president? While it has never been attempted by a candidate from a major party before, Trump is allowed to run for president while under indictment in four separate cases — or even if he is convicted of a crime.
- Special counsel urges Supreme Court to reject Trump’s immunity claim April 8, 2024 Special counsel urges Supreme Court to reject Trump’s immunity claim April 8, 2024
- Supreme Court sets Trump immunity claim in D.C. trial for April 25 March 6, 2024 Supreme Court sets Trump immunity claim in D.C. trial for April 25 March 6, 2024
- What happens next after Supreme Court agrees to hear Trump immunity case February 28, 2024 What happens next after Supreme Court agrees to hear Trump immunity case February 28, 2024

Recommended
Trump’s lawyers subpoena wrong ‘jeremy rosenberg’ before hush money trial: ‘i don’t have any files for you’.
- View Author Archive
- Email the Author
- Follow on Twitter
- Get author RSS feed
Contact The Author
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Donald Trump’s lawyer in his “hush money” case served the wrong guy with court papers — demanding that a Brooklyn man with nothing to do with the upcoming trial turn over evidence, prosecutors said Tuesday.
The pre-trial flub came after Trump attorney Todd Blanche sent a subpoena to a man they believed to be former District Attorney Supervising Rackets Investigator Jeremy Rosenberg in March, seeking files related to Trump’s fixer-turned-enemy Michael Cohen, the Manhattan DA’s office said.

But the man was, in fact, a separate Jeremy Rosenberg — a Brooklyn resident who appears to have had a bit of fun with Trump’s attorneys.
“I don’t have any files for you,” Rosenberg wrote back to the Trump lawyers, according to a filing from Trump’s attorneys released Monday.
Rosenberg added that the “phone number you provided was disconnected” and that he’d be keeping the $15 Trump’s lawyers had sent him to help pay for sending the documents.
Blanche, a veteran ex-prosecutor, complained earlier this week that the man they believed was the ex-DA Rosenberg had displayed a “flippant and dismissive approach” to the request “despite ample experience with the criminal justice system that should have instilled in him respect for this process and a criminal defendant’s rights.”

But in fact, Trump’s lawyers had simply served court papers on the wrong man, prosecutor Matthew Colangelo wrote.
“The people believe the defendant has served the incorrect person,” Colangelo said in the filing.
“The people spoke with Mr. Rosenberg’s counsel, who informed the People that Mr. Rosenberg was not, in fact, served with the subpoena, that Mr. Rosenberg had not corresponded with defense counsel, and that Mr. Rosenberg does not have any connection to the Brooklyn address where the subpoena purportedly was served,” Colangelo added.

Blanche did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
The case, set for jury selection April 15, involves allegations that Trump covered up payments made before the 2016 election that kept porn star Stormy Daniels from telling the public about an alleged affair that she had with him.
Keep up with today's most important news
Stay up on the very latest with Evening Update.
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Never miss a story.
Trump, 77, has pleaded not guilty to 34 counts of falsifying business records in the case, which each carry a potential prison sentence of up to four years.
Trump’s lawyers plan to ask the Rosenberg they’re looking for — once they reach him that is — for all records of communications he had with Cohen from February 2021 until this May.
Rosenberg got into hot water last year over his contact with the one-time Trump lawyer, The Post exclusively reported last year.
He was suspended and had his gun removed as Bragg’s office investigated how Rosenberg shared communications about Cohen with the office, a law enforcement source said.
The interactions were “always professional and focused on Mr. Cohen’s personal security, which we appreciated,” Cohen’s lawyer Lanny J. Davis said at the time.
Share this article:

Advertisement
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Panama Papers: trial begins of 27 Mossack Fonseca employees
Law firm’s founders among those to face money laundering charges after leak of 11.5m files in 2016
A criminal trial of 27 employees working for the law firm at the heart of the Panama Papers on money laundering charges has commenced in a Panamanian court.
Eight years ago, leaked financial records from the law firm Mossack Fonseca sparked international outrage at the use of offshore companies by wealthy individuals to commit tax fraud and hide assets.
In 2016, files from Mossack Fonseca were leaked to reporters at the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung and shared with the US-based International Consortium of Investigative Journalists. Reporters from more than 100 media organisations, including the Guardian, collaborated to investigate the 11.5m files.
The firm’s founders, Jürgen Mossack and Ramón Fonseca Mora, are among those facing charges. They have previously denied any allegations against them, arguing that they had no control over the offshore companies that the firm set up for its clients. If convicted, they reportedly face up to 12 years in prison.
According to the Associated Press , Mossack attended the hearing to declare his innocence, telling reporters outside the courtroom that he was “very optimistic”. A representative for Fonseca told the court that his client was in hospital.
Battered by international criticism, Panama adopted new legislation modernising the country’s legal definition of money laundering in 2019. Aspects of the charges against the Mossack Fonseca employees concern activities predating the change in the law, which could complicate prosecutors’ attempts to convict them, according to the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists .
Panama’s supreme court previously ruled that creating shell companies used for tax fraud could not be considered a crime if the companies in question were created prior to 2019.
Mossack and Fonseca were both acquitted of separate charges two years ago after a judge directed that the firm did not handle or attempt to hide money stolen from Brazil as part of a major corruption scandal involving the state oil company codenamed Lava Jato or the Car Wash.
Offshore companies linked more than 100 politicians from around the world, including 12 national leaders, were discovered by journalists analysing the Panama Papers. They included $2bn in an offshore company belonging to the Russian cellist Sergei Roldugin, the friend of the President Vladimir Putin.
Nawaz Sharif , then prime minister of Pakistan, and Sigmundur Davíð Gunnlaugsson , prime minister of Iceland, were both forced from office amid public fury at hidden offshore wealth connected to their families.
after newsletter promotion
Sharif was disqualified from office and sentenced to 10 years’ imprisonment by the Pakistani supreme court after reporters discovered undeclared real estate secretly owned by his family through offshore companies. Gunnlaugsson was forced to resign after it was revealed that he had never declared his family’s ownership of an offshore company with a $1m claim against one of Iceland’s failed banks.
After publication of the Panama Papers investigation, countries around the world initiated proceedings to recover unpaid taxes that had been hidden using offshore companies. By 2021 more than $1.36bn in fines and penalties for unpaid taxes were said to have been recovered by exchequers around the world, including $253m recovered by HMRC in the UK.
- Panama Papers

Panama Papers whistleblower speaks out: ‘Politicians must act – now’

We were leaked the Panama Papers. Here’s how to bring down Putin’s cronies

EU states 'dragging their feet' over financial transparency, report finds

Panama Papers law firm Mossack Fonseca sues Netflix over The Laundromat

Meryl Streep on the Panama Papers: ‘People died to get the word out’

Fears UK law change could prevent scrutiny of money launderers

Deutsche Bank offices raided in connection with Panama Papers

Nevis: how the world’s most secretive offshore haven refuses to clean up

Money-laundering crackdown on public schools and law firms
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get original essay. I want to become a lawyer because I believe that it is a good way to help people in my society. I also believe that it will help me develop skills I can also use in life. Since I was young people have told me I should become a lawyer because of me being a talkative and inquisitive personality.
Restate key supporting arguments. The final stage of creating the plan of your law essay is to pick 2 to 3 key supporting arguments which you discussed in the main body of your paper and outline them again. This time, however, you will not be getting into a detailed discussion of how case law or statute sections justify your supporting arguments.
In this article, we'll cover some top tips to guide you through the process of planning, researching, structuring and writing a first-class law essay with confidence. 1. Start In Advance. Give yourself plenty of time to plan, research and write your law essay. Always aim to start your law essay as soon as you have the question.
Draw on specific experiences in your life and lessons you have learned to formulate your rationale for pursuing this career path. When you explain why you aspire to be a lawyer, be as specific as possible. " Lawyers help people. The legal profession is lucrative.". These reasons are too simplistic and generic to provide any useful insight ...
The School of Law at the University of California—Irvine has a mandatory essay of up to 750 words about why you are interested in their school. Other schools may ask applicants to address this ...
Here are some practical and practical tips for planning a one good law essay. Highlight specific words and phrases in the essay's title. Take a brain dump for the words that you have highlighted and note them down. Find a connection between these phrases and words. Develop a strategy to come up with your answer basedon these phrases.
How to Write a Law Essay: 8 Steps. 1. Choosing an Essay Topic. When it comes to writing a law essay, choosing an appropriate topic is crucial. A well-chosen topic will make your research and writing process smoother and more enjoyable, while a poorly chosen topic can lead to frustration and a lackluster essay.
This resource will focus on theoretical based law essays. There are a number of strategies that may help you in starting, structuring and presenting a law essay. 1. Starting your answer. The first step to a successful law essay is understanding the question. One of the most effective ways of breaking down the question is to identify the ...
The legal writing process is not "one size fits all" and "people need to find the one that fits them best, David Howard Spratt, professor of legal rhetoric at American University Washington College of Law, said in the recent "Landslide Webinar Series: Take Your Legal Writing from Good to Great—Drafting Tips from the Pros". The webinar was sponsored by the ABA Section of ...
Essay Samples on Lawyer. Essay Examples. Essay Topics. Why Did You Choose Law as a Career. The decision to pursue a career in law is one that often carries profound motivations and aspirations. In this essay, I share my personal journey and delve into the factors that led me to choose law as a career path. By exploring the intricacies of...
Lawyer Essay. Sort By: Page 1 of 50 - About 500 essays. Decent Essays. Lawyer. 1228 Words; 5 Pages; Lawyer. Lawyer The working field I want to link my future with is becoming a lawyer. Lawyer is a complicated profession that has a lot of responsibilities- to find evidence, to defend a person using them, to argue someones rights, to give advices ...
essay on legal theory. The essence of this task is to describe one of the theories of law or any jurisprudence. This can be anything - for example, the theory that touches the Fifth Amendment. jurisprudence essay. In this assignment, you should review a specific case study or analyze the given document. Here, it's important to adhere to ...
We have written a detailed essay presenting practical vision of the responsibilities of lawyers as both professionals and as citizens at the beginning of the 21 st century. Specifically, we seek to define and give content to four ethical responsibilities that we believe are of signal importance to lawyers in their fundamental roles as expert technicians, wise counselors, and effective leaders ...
When I started law school, I loved it. The hypercompetitive classroom, the demanding coursework, and the adrenaline rush of solving complex cases drove me to pursue this career. Once I officially ...
4. Plan Your Essay Structure. An effective law essay is well-organised and logically structured. Generally, your essay should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Introduction: Briefly introduce the topic, present your thesis statement, and outline the main points you will cover in your essay.
From a young age, I have been fascinated by the law and its ability to promote fairness, equality, and social change. My academic studies and practical experiences have equipped me with the legal knowledge, critical thinking skills, and advocacy capabilities necessary to become an effective lawyer. In this essay, I will explain why I want to ...
Essays edited by experienced law editors are dramatically improved. This applicant's lively and unique approach to the "why I want to be a lawyer" essay captures the reader's interest. Notice that the applicant discusses her religious beliefs sensitively, without proselytizing or preaching. My interest in the law began with donuts.
Example Essay #1. "As an aspiring public interest attorney, Berkeley Law's commitment to social justice and its extensive programmatic offerings make it the ideal institution for me. From my research, it's clear that Berkeley Law's values align perfectly with my passion for advocating for marginalized communities.
This Essay seeks to recover the deeply rooted connection between U.S. banking law and antitrust. It reconceptualizes banking law as a sector-specific antimonopoly regime that imposes multiple structural constraints on publicly subsidized banks' ability to abuse their power over the supply and alloca…
lawyers write in the same way: by laying out the issue to be discussed, the legal rule relevant to the issue, the analysis of the pertinent facts based on that rule, and the overall conclusion reached. Although this may sound daunting at first, it will quickly become second nature. Below is a primer on how to structure a legal argument using IRAC.
Introduction: A lawyer is a guide to social and bears great importance. The common masses may not understand the exact language of the law and the procedure of its proper implementation. It is the role of the lawyer who makes society aware of the rule of law and its bindings. The lawyers create a bridge between the legal system and the people.
Why I want to become a Lawyer Essay 10 Lines (100 - 150 Words) 1) Since childhood, I loved the profession of a lawyer and want to become the same. 2) From a younger age, I like to fight for the rights of others. 3) I want to be a lawyer because I am a great supporter of truth. 4) By becoming a lawyer I want to aware people of their rights.
Lawyers for NYC Mayor Eric Adams Reject Sexual Assault Allegations in New Court Papers. The mayor is represented in the matter by Corp. Counsel - as he was a city employee at the time of the ...
A long discredited, arcane 150-year-old law is back in the news in 2024, and that should terrify anyone who supports reproductive freedom. Last week at the Supreme Court, the Comstock Act of 1873 ...
Lawyers and court workers leave the Supreme Court during a recess for the trial of the "Panama Papers" money laundering case in Panama City, Monday, April 8, 2024. (AP Photo/Agustin Herrera ...
Special counsel Jack Smith on Monday urged the Supreme Court to reject Donald Trump's "novel and sweeping" claim that he is immune from criminal prosecution on charges of conspiring to ...
Donald Trump's lawyer in his "hush money" case served the wrong Jeremy Rosenberg with court papers — demanding that a Brooklyn man with nothing to do with the trial turn over evidence.
David Pegg. Tue 9 Apr 2024 10.18 EDT. A criminal trial of 27 employees working for the law firm at the heart of the Panama Papers on money laundering charges has commenced in a Panamanian court ...
April 9 (UPI) -- A Panamanian criminal court on Tuesday launched a trial for 27 people charged in the Panama papers money laundering scandal, eight years after a leak from a law firm in the tax ...