An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Healthcare (Basel)


Organisational Culture Research in Healthcare: A Big Data Bibliometric Study
Xiaoping qin.
1 School of Public Health, The University of Sydney, Camperdown, NSW 2006, Australia
Richard Wang
2 Affiliation Program of Data Analytics and Business Computing, Stern School of Business, New York University, New York, NY 10012, USA
Yu-Ni Huang
3 College of Medical and Health Science, Asia University, Taichung 41354, Taiwan
Jinhong Zhao
4 School of Health Policy and Management, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
Herng-Chia Chiu
5 Institute of Hospital Management, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518000, China
Tao-Hsin Tung
6 Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province Affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, Linhai 317000, China
Jeff Harrison
7 Brooks College of Health, The University of North Florida, Jacksonville, FL 32224, USA
Bing-Long Wang
Associated data.
Not applicable.
Across international healthcare, organisational culture and work environment have become central to all patient safety. However, there is a lack of comprehensive overview to assess and track the evolution of the literature on organisational culture in healthcare. This study aims to describe the current situation and global trends in organisational culture research in healthcare. The methodology is based on bibliometric mapping using scientific visualisation software (CiteSpace and VOSviewer). The big data were collected from the Web of Science core citation database. After applying the search criteria, we retrieved 1559 publications, which have steadily increased over the last two decades. In addition, 92 countries and regions have published studies on organisational culture in healthcare. The United States has made significant contributions to this field. In particular, organisational culture occupies an important position in the quality management of different types of care and caregiving. At the same time, organisational culture in healthcare may be inadequately researched in terms of theoretical underpinnings, which in turn leads to a lack of widespread dissemination of practice, and research on organisational culture in healthcare through evidence-based medicine may remain a significant focus and hot topic throughout the research field in the coming years.
1. Introduction
Organisational culture is an organisation’s core and soul [ 1 ]. Every organisation has its unique culture and, since the last century, many scholars and studies have developed an understanding of the impact of cultural aspects on organisational management. As a result, organisational culture has become a significant area of management theory. Scholars and managers have widely recognised the importance of organisational culture in the operation of organisations [ 2 ]. Nevertheless, it is undeniable that organisational culture is not a “superficial” phenomenon. On the contrary, it is “infused with symbols and symbolic meanings” [ 3 ] and is “undetectable in most cases” [ 4 ]. In other words, it is more than just a “way of doing things” and a “style of dress.” Still, the organisation’s culture is reflected in the values, norms, and deep-rooted beliefs of the employees and is the basis for the operations and methods of doing business in the organisation [ 5 ]. Therefore, unique culture can be a source of competitive advantage for some organisations [ 6 ]. Moreover, the master in the field of organisational culture, Edgar Schein, also pointed out in his research that “culture determines and limits strategy” [ 7 ], which is a good indication of the importance of organisational culture in management.
Across international healthcare, organisational culture, and work environment have become central to all patient safety. Hospital organisational culture (HOC) is a term that has become synonymous with patient experience, satisfaction, mortality and morbidity [ 8 ]. One study suggests that healthcare organisations should pay particular attention to organisational culture because “the shared beliefs, values, and feelings within the organisation guide the perceptions and approaches to the work to be accomplished” [ 9 ]. Gershon and others’ research further explains Sovie’s statement, “If aspects of the organisational culture are ill-defined, frequently shifting, poorly communicated, not reinforced, and poorly supported administratively, both the employees’ collective perceptions and their behaviours (i.e., delivery of care, safe work practices, and teamwork) will be inconsistent” [ 10 ]. It is evident that organisational culture in healthcare is important for the “success” of healthcare organisations. Therefore, it is necessary to assess and track the evolution of the literature on organisational culture in healthcare to gain new insights and knowledge to improve issues in healthcare.
This study has several primary purposes; first, we provide a new way to view healthcare organisational culture areas and their associations by examining co-citation and co-occurrence data. Second, we connect our evolutionary analysis to a comprehensive future research plan, which may generate a new research agenda for healthcare leadership. Thus, this review focuses on illuminating the research frontiers and future roadmaps for organisational culture research in healthcare.
2. Materials and Methods
The bibliometric overview of this study describes the landscape and trajectory of change in the research field through a perspective on healthcare organisational culture from 1990 to 2021. The methodology used in this review is based on bibliometric mapping [ 11 , 12 ], a visualisation technique that quantitatively displays the landscape and dynamic aspects of the knowledge domain [ 13 ]. The data were collected from the Web of Science (WoS) core citation database. Two Java-based scientific visualisation software (CiteSpace and VOSviewer), developed by Chaomei Chen [ 11 ] and Van Eck and Waltman [ 14 ], were used to analyse the data.
2.1. Sample
The data for this study were retrieved from the Web of Science on September 28, 2022. Web of Science was chosen as the search engine because it is the most widely accepted and commonly used database for analysing scientific publications [ 15 ]. The terms “organisational culture”, “hospital culture”, “health care”, and “hospital” were used as search topics. The period was set from 1990 to 2021 (the starting year in the results is 1991 because no articles on organisational culture in healthcare were published in 1990).
A total of 1809 publications related to organisational culture in healthcare were identified. Publications before 1990 and after 2022 were excluded. In addition, articles, review articles, and early access articles were included in the study. Finally, to minimise language bias, we have excluded documents that were not published in English. Each publication in the WoS contains details, including the year of publication, author, author address, title, abstract, source journal, subject category, references, etc. The contents of the database were detailed before the bibliographic analysis was performed. For example, some authors present their names in different spellings when submitting articles, so the data must be viewed in detail and consolidated. There were 1559 publications included ( Figure 1 ) and exported to the VOSviewer and CiteSpace software for analysis of the following topics: global publication trends, countries, journals, authors, research orientations, institutions, and the quality of publications.

The research flow chart of the bibliometric analysis.
2.2. Introduction to CiteSpace and VOSviewer
CiteSpace is a Java application, designed and produced by Professor Chaomei Chen, to visualise and analyse trends and patterns in the scientific literature. It was designed as a tool for visualising progressive knowledge domains. By using CiteSpace, we can see how major areas of research are being investigated through specific articles, and understand the most active frontier areas within research. The most critical articles and historical turning points in these areas are also available from the software [ 16 ].
VOSviewer is a software tool for building and visualising bibliometric networks. It was developed by Van Eck and Waltman [ 14 ]. In VOSviewer, metric networks can be visualised and analysed for factors including journals, researchers, or individual publications, and can be constructed based on citations, bibliographic couplings, co-citations, or co-authorship relationships [ 14 ].
3.1. Global Publication Trends
3.1.1. global trends.
After applying the search criteria, we retrieved a total of 1559 articles. Figure 2 a shows the number of articles increased from 2 in 1990 to 194 in 2021. To predict future trends in global publications, we used a logistic regression model to create a time profile of the number of publications throughout the year. In order to predict future trends, a linear regression model was used to create a time profile of the number of publications throughout the year, and the model fit curve for the growth trend is shown in Figure 2 b. The trend in publication numbers was fitted well to the time curve as R 2 = 0.9626. The R-squared value is an indicator of the degree of fit of the trend line. The value reflects the goodness of fit between the estimated value of the trend line and the corresponding actual data; the better the fit, the more reliable the trend line is [ 17 ]. It is also predicted that the number of publications in organisational culture in healthcare will grow to approximately 800 by 2035, based on the trend of the model, which is nearly a fourfold increase, compared to 2021.

( a ) The number of cumulative publications; ( b ) Model fitting curves of global publication trends; ( c ) The distribution world map of publications; ( d ) The top 10 countries of total publications.
3.1.2. Contributions of Countries and Regions
Figure 2 c,d shows the distribution world map of the top 10 countries of total publications. The United States contributed the most publications (596, 38.2%), followed by the United Kingdom (239, 15.3%), Australia (172, 11.0%), and Canada (138, 8.8%).
3.1.3. Total Sum of the Times Cited
Among all included publications, the United States had the highest sum of the times cited (21,918), while the United Kingdom ranked second (7637), followed by Australia (3717), and Canada (3709), respectively ( Figure 3 a). Table 1 shows the detailed numbers.

( a ) The top 10 countries of total citation frequency; ( b ) The top 10 countries of average citations for each article; ( c ) The top 10 countries of the h-index.
The contributions in publications of countries.
3.1.4. Average Citation Frequency
The United States had the highest average numbers of citations (36.78 times), followed by the United Kingdom (31.95 times), Sweden (30.41 times), and Canada (26.93 times), as shown in Figure 3 b.
3.1.5. H-Index
Total citations and h-index reflect a country’s publications’ quality and scholarly impact [ 18 ]. Figure 3 c shows the h-index rankings, where the top ranking is the United States (h-index = 76), followed by the United Kingdom (h-index = 47), Canada (h-index = 35), and Australia (h-index = 33).
3.2. Analysis of Publication
3.2.1. journals.
Figure 4 a shows the top 20 journals in which publications on organisational culture in healthcare are located, with 72 articles published in the “BMC Health Services Research,” 38 in the “Journal of Nursing Management,” 31 in the “Journal of Advanced Nursing“ and “Health Care Management Review”, and 29 in the “Journal of Health Organisation and Management”.

( a ) The top 20 journals of publications; ( b ) The top 20 orientations of publications; ( c ) The top 20 authors with the highest number of publications; ( d ) The top 20 institutions with the highest number of publications.
3.2.2. Research Orientation
The top 20 research orientations are shown in Figure 4 b. The most common research orientation was nursing (417 publications), healthcare science services (373 publications), health policy services (293 publications), and public environmental occupational health (201 publications).
3.2.3. Authors
The top 20 authors with the highest number of publications are shown in Figure 4 c, with a total of 154 articles/reviews in the last decade, representing 9.87% of all literature in the field. Braithwaite from Australia has published 20 papers, followed by Shortell from the US, Mannion from the US, and Bradly from the United Kingdom with 10 papers. All researchers listed as authors were included in this term for analysis, regardless of their relative contribution to the study. It is worth noting that we included all authors in this study for analysis, regardless of their relative contribution to the study.
3.2.4. Institutions
Figure 4 d shows the top 20 institutions with the most publications. The University of California System had the highest number of publications, with 61 papers, followed by Harvard University (54 publications), then the US Department of Veteran Affairs, and the University of London (53 publications).
3.3. Co-Occurrence Analysis
A mapping of keywords regarding organisational culture research in the healthcare field; the nodes’ size represents the frequency, while the line between the nodes reflects the co-occurrence relationship. A total of 3329 keywords were included; some keywords with the same meaning that occurred at the beginning of the analysis using VOSviewer, such as “quality of health care”, and “quality of care” were merged. Finally, we attached the thesaurus file to VOSviewer and found 60 keywords that met the criteria. All keywords were grouped into 4 clusters: quality of care (blue cluster), leadership (green cluster), organisational culture (red cluster), and research (yellow cluster) ( Figure 5 ).

Co-occurrence analysis of organisational culture research in healthcare.
The most prominent themes in the study of organisational culture in healthcare are as follows. In the “quality of care” cluster, the most used keywords were “organisational culture”, “patient safety”, “safety culture”, and “safety management”. The main keywords in the “leadership” cluster were “healthcare research”, “nursing”, “evidence-based practice”, and “mental health”. The main keywords in the “organisational culture” cluster were “leadership”, “quality improvement”, “implementation”, and “culture”. In the “research” cluster, prominent keywords were “quality of care”, “nurses”, “hospital”, and “job satisfaction”.
3.4. Burst Analysis
Eighteen burst terms of the time bar chart represent the evolution of the topic over time, showing the update and interaction of the literature. Figure 6 shows keyword highlighting sorted by starting year. The keyword that first became a research hotspot was “information system”, which appeared from 1996 to 2010. It was also the research hotspot with the most extended duration. The second keyword was ”focus group”, which appeared from 2001 to 2011, followed by “medical error”, which appeared from 2005 to 2008. The most recent burst keywords (from 2020) were “intensive care”, health policy”, “human resource management”, and “evidence-based medicine”. The keyword “quality of care” was the keyword with the shortest duration.

Temporal bar graph for burst terms.
In order of intensity, “medical error” had the most vigorous intensity (strength = 6.01), followed by “primary care” (strength = 5.97), and “mental health” (strength = 5.24). The keyword “focus group” had the weakest intensity (strength = 2.12).
4. Discussion
4.1. global trends in the healthcare organisational culture field.
Our study of health organisation culture (HOC) research illustrates the current and past global trends in publications, contributing countries, institutions, and research directions. The field of HOC research has evolved over the past decades. However, as this study shows, the number of publications has steadily increased yearly, with 92 countries and regions publishing in the field, suggesting that research focused on HOC research and providing in-depth knowledge will likely increase in the future.
4.2. Quality and Status of Global Publications
The main purpose of Figure 2 and Figure 3 is to show the countries with the highest number of publications and the highest quality of publications in the world by citation rate and h-index. We also find that the majority of the countries publishing are developed countries, but that developing countries are also catching up. Total citations and h-index reflect a country’s publications’ quality and scholarly impact [ 18 ]. According to our study, the United States ranked first among other countries in the total number of publications, citations, and h-index, making the most considerable contribution to global HOC research. The United Kingdom and Canada also contributed significantly, with respectable total citation frequency and h-index, especially the United Kingdom, which ranked second in average citation frequency. Nevertheless, some countries, such as Sweden, Canada, and Australia, also play an important role, considering their high average citation frequencies. It is worth noting that eight of the top ten countries in the ranking of essential contributors are developed countries, and two developing countries (Brazil and China). In North America and Europe, the main emphasis is on reducing costs, standardising and improving the efficiency of services, and improving the quality of work life and behaviour change. In most developing countries, process facilitation and service efficiency are the main objectives [ 19 ]. In developing countries, the study of organisational culture also has a guiding role for hospitals to improve the quality of care, and with economic development gradually catching up with the pace of developed countries, this study also plays a reference role in learning from the experience of developed countries with developing countries.
The journals “BMC Health Services Research”, “Journal of Nursing Management”, “Journal of Advanced Nursing”, “Health Care Management Review”, and “Journal of Health Organisation and Management” made extraordinary contributions and had the most research on HOC. From this, we can see that these journals are our primary sources of information regarding the latest developments in HOC.
The fact that almost all of the top 20 institutions are from the top five countries with the highest number of publications, with more than half of them located in the United States, again reflects the tremendous academic influence of the United States in this field. This study demonstrates the important role that these top-tier institutions play in improving a country’s scholarship. In addition, the top 20 authors represent research leaders who are likely to significantly impact the future direction of research. Therefore, more attention should be paid to their work to remain up-to-date with the latest developments in this field.
4.3. Research Focus on HOC
Keywords are an essential part of a research paper and contain the most vital information [ 20 ]. Systematic analysis of keywords in specific research areas provides a clear understanding of trends and hot spots in different research areas [ 21 ]. In addition, co-occurrence analysis is based on the number of joint publications, to evaluate the relationship between the identified keyword domains. Therefore, it is an effective method for predicting future trends and hotspots in research areas of interest [ 22 ]. According to our findings in this study, the number of publications related to HOC research multiplied in 2002. HOC research continues to grow dynamically, the field of hospital management plays an essential role, and the effective management of organisational culture is one of the critical ways to improve performance [ 23 ]. The results of this boom will, in turn, encourage more researchers to commit to the future of HOC research. Through bibliometric and visual analysis, researchers can get an overall impression of the leading countries, authors, institutions, partnerships, and academic impact of HOC. This information is available to give investigators as a guide so they can selectively access advanced knowledge and valuable findings according to their requirements. In addition, co-occurrence analysis can describe trends and research hotspots in the field, thus further inspiring researchers for topic selection, and helping funding agencies develop profitable investment plans.
In this study, ultimately, a total of four possible research directions were summarised: “Organisational Culture”, “Leadership”, “Quality of Care”, and “Research”. With the help of this network diagram, we can clarify future trends further. As shown in the co-occurrence diagram, the keywords ”organisational culture”, “patient safety”, “care”, “leadership”, “quality of care”, and “hospitals” are highlighted with larger icons that are almost evenly distributed among “Organisational Culture”, “Leadership”, “Quality of Care”, and “Research”. Thus, investment in and demand for high-quality research is necessary for the context of these four research directions.
From these four research directions, many points can be drawn for discussion in HOC research. First, HOC leadership and healthcare organisations are complex networks of many professional groups, departments, and specialists to improve the quality of services and organisational performance of the healthcare system. Therefore, building up certain aspects of management systems and culture is necessary. However, most healthcare organisations have difficulty doing this [ 24 ]. A talented leader can catalyse change in these areas in a healthcare organisation to remain successful in a changing competitive environment [ 25 ]. Meanwhile, other health administrators and mid-level managers have vital roles and responsibilities in healthcare change actions [ 26 ]. That is why it is crucial and necessary to study the issue of leadership in the future comprehensively.
Secondly, modern medical research on the quality of care has been around for more than 50 years [ 27 ]. Moreover, the quality of care in the HOC is more complex than previously thought. Some cultural influences, such as excellence in care delivery, ethical values, engagement, professionalism, value for money, cost of care, commitment to quality, and strategic thinking, were identified as critical cultural determinants of quality care delivery [ 28 ]. Our study supports the rationale for the frontier and focus of research on the quality of care in the co-occurrence diagram, where it can be seen that quality of care and patient safety are the key factors for quality improvement in healthcare organisations [ 29 ]. Furthermore, available research indicates a huge demand for and cost of healthcare worldwide. Still, disparities in limited resources and clinical practice have increased the interest in improving the quality of healthcare in many countries around the world, especially in developed countries such as the UK and the US, where improving the quality of healthcare is high on the national agenda [ 30 ].
Third, research. In regards to evidence-based medicine (EBM) and evidence-based management (EBMgt), Stephen M. Shortell has also stated in past research that there are two components necessary to improve the quality of medical care: the development of EBM and EBMgt, which can identify better clinical practices, and knowledge of how to put these into routine practice, while also defining organisational strategy, structure, and change management practices. When the content understanding of clinical practice (EBM) is effectively applied in an excellent organisational context (EBMgt), quality of care can be improved and developed sustainably [ 31 ]. Therefore, the appropriate use of EBM and EBMgt has a guiding role in the role of HOC and quality of care in research, and is one of the current and future research priorities.
4.4. Research Milestones and Future Research
Research on healthcare leadership over the past 30 years (1991–2021) was divided into several phases, based on the evolution over time from burst analysis. In the first phase, our study found that information systems have been a high burst in the overall research process for about 14 of the last 30 years. Hospital executives worldwide have recognised the importance of considering information technology (IT) as a strategic element, and studies have suggested that the ability to innovate with IT is critical to improving hospital performance and quality of care [ 32 , 33 ]. Organisational culture has also been shown to influence innovation capabilities as it affects attitudes toward knowledge acquisition and cross-functional learning [ 34 ]. Specifically, the information system is inextricably linked to an organisation’s ability to innovate and is defined as the ability to identify the value of new information, absorb it, and apply it for productive purposes. Therefore, managing IT knowledge and culturally solid communication channels contributes to implementing innovation, resulting in better returns, user satisfaction, reliability, and competitive advantage.
In the second phase, we found that between 2010 and 2015, there was a specific focus on emergency care and primary care in the HOC field, as well as increased research on the quality of care and quality management, which confirms the importance of organisational culture in healthcare. Thus, our study demonstrates the importance of organisational culture on healthcare and quality of care, as discussed above.
In the third phase, we observed the healthcare research among the burst studies, the emergence of quantitative research, and the persistence of evidence-based medicine as a research hotspot in the HOC field after 2018. Due to the complexity of management research topics, researchers are typically required to employ a range of quantitative and qualitative data collection methods and analysis techniques, with methodological trade-offs, depending on the research questions driving the study, their prior work, the planned research design, and the desired contribution the researcher wishes to make [ 35 ]. Qualitative research is unique in its ability to solve descriptive, explanatory, and illustrative problems, while quantitative research is better suited to generalisation and calibration problems [ 36 ]. Qualitative and quantitative research each have advantages and disadvantages; qualitative research usually obtains theories through experience, processes, and causal mechanisms, while quantitative research extends theories to large populations by refining or calibrating the understanding of a phenomenon. When theories are not adequately covered, they are re-examined and reviewed using alternative methods [ 37 ]. From the results, we speculate that there are studies within the HOC field investigating the experiences, processes, and causal mechanisms of HOC starting in 2016. There is a wide range of extension practice research beginning in 2018. However, the heat only lasts for one year, indicating that theoretical practice research on healthcare material culture is still insufficient. Combining the discussion of EBM and EBMgt above in future research to maintain the development of qualitative and quantitative research can encourage more profound exploration and research on the development of HOC.
In the final phase, intensive care, health policy, human resource management, evidence-based medicine, and professionals remain at the forefront of hot topics within the HOC field. We figure out that these hotspot terms will continue to be popular in the coming years. For example, professionals became a hot topic in 2015, and the heat lasted six years. It is well known that the healthcare field requires a high level of professionalism and that healthcare professionals’ perceptions of HOC are essential, as these perceptions influence their recognition and trust in healthcare organisations and significantly impact performance [ 38 ].
4.5. Strength and Limitation
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to conduct a bibliometric analysis of healthcare organisational culture research. The bibliometric and visual analysis was used to identify hotspots and emergent events across countries, authors, and institutions. However, this study inevitably has some limitations. Firstly, we only retrieved data from the WoS database since 1990. Therefore, we may have missed some publications due to database bias. Second, most of the identified publications were in English, and some articles related to other languages may not have been included. Third, some novel and high-quality articles with low citation frequency were not included in the study, due to the software base setting. So, there may be some bias in the study.
5. Significance
This study presents a bibliometric analysis of the current literature on organisational culture in healthcare. The study makes innovative use of two of the most popular software tools in bibliometrics to analyse the current English language literature published in the Web of Science. It provides an overview of the past and informs future research developments to improve the development of organisational culture as a core issue in healthcare management, especially hospital management, which is important for healthcare professionals around the world.
6. Conclusions
This study describes the current situation and global trends in organisational culture research in healthcare. The United States has made significant contributions to this field, establishing itself as a global leader. It is foreseeable that an increasing number of publications will be published in the coming years, which indicates the flourishing of organisational culture research in healthcare. In particular, organisational culture occupies an important position in the quality management of different types of care and caregiving, making it one of the central topics within the entire industry. At the same time, organisational culture in healthcare may be inadequately researched in terms of theoretical underpinnings, which in turn leads to a lack of widespread dissemination of practice, and research on organisational culture in healthcare through evidence-based medicine may remain a significant focus and hot topic throughout the research field in the coming years.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants in this study.
Funding Statement
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, China (Grant number: 2021-RC630-001).
Author Contributions
X.Q., R.W. and B.-L.W. designed the study and drafted the manuscript. J.Z., H.-C.C., T.-H.T. and Y.-N.H. critically reviewed the manuscript. R.W., X.Q., B.-L.W. and Y.-N.H. directed statistical analysis and helped interpret the results. R.W., J.Z., H.-C.C., T.-H.T. and J.H. edited the paper and suggested future directions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
We declare no competing interests. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Literature Reviews
- "How To" Books
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- Collecting Resources for a Literature Review
- Organizing the Literature Review
- Writing the Literature Review
- Endnote This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Websites
Organization
Organization of your Literature Review
What is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? What order should you present them?
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper.
Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing the literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario and then three typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
You've decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you've just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale's portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980's. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Chronological
If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
By publication
Order your sources chronologically by publication if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
Another way to organize sources chronologically is to examine the sources under a trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Using this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.
More authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as "evil" in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
Methodological
A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the "methods" of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Once you've decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
- << Previous: Collecting Resources for a Literature Review
- Next: Writing the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2021 12:11 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stonybrook.edu/literature-review
- Request a Class
- Hours & Locations
- Ask a Librarian
- Special Collections
- Library Faculty & Staff
Library Administration: 631.632.7100
- Stony Brook Home
- Campus Maps
- Web Accessibility Information
- Accessibility Barrier Report Form

Comments or Suggestions? | Library Webmaster

Except where otherwise noted, this work by SBU Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .

The Literature Review: 5. Organizing the Literature Review
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Why Do a Literature Review?
- 3. Methods for Searching the Literature
- 4. Analysing the Literature
- 5. Organizing the Literature Review
- 6. Writing the Review
1. Organizing Principles
A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It should have a single organizing principle:
- Thematic - organize around a topic or issue
- Chronological - sections for each vital time period
- Methodological - focus on the methods used by the researchers/writers
4. Selected Online Resources
- Literature Review in Education & Behavioral Sciences This is an interactive tutorial from Adelphi University Libraries on how to conduct a literature review in education and the behavioural sciences using library databases
- Writing Literature Reviews This tutorial is from the Writing section of Monash University's Language and Learning Online site
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It This guide is from the Health Services Writing Centre at the University of Toronto
- Learn How to Write a Review of the Literature This guide is part of the Writer's Handbook provided by the Writing Center at the University of Wisconsin-Madison
2. Structure of the Literature Review
Although your literature review will rely heavily on the sources you read for its information, you should dictate the structure of the review. It is important that the concepts are presented in an order that makes sense of the context of your research project.
There may be clear divisions on the sets of ideas you want to discuss, in which case your structure may be fairly clear. This is an ideal situation. In most cases, there will be several different possible structures for your review.
Similarly to the structure of the research report itself, the literature review consists of:
- Introduction
Introduction - profile of the study
- Define or identify the general topic to provide the context for reviewing the literature
- Outline why the topic is important
- Identify overall trends in what has been published about the topic
- Identify conflicts in theory, methodology, evidence, and conclusions
- Identify gaps in research and scholarlship
- Explain the criteria to be used in analysing and comparing the literature
- Describe the organization of the review (the sequence)
- If necessary, state why certain literature is or is not included (scope)
Body - summative, comparative, and evaluative discussion of literature reviewed
For a thematic review:
- organize the review into paragraphs that present themes and identify trends relevant to your topic
- each paragraph should deal with a different theme - you need to synthesize several of your readings into each paragraph in such a way that there is a clear connection between the sources
- don't try to list all the materials you have identified in your literature search
From each of the section summaries:
- summarize the main agreements and disagreements in the literature
- summarize the general conclusions that have been drawn
- establish where your own research fits in the context of the existing literature

5. A Final Checklist
- Have you indicated the purpose of the review?
- Have you emphasized recent developments?
- Is there a logic to the way you organized the material?
- Does the amount of detail included on an issue relate to its importance?
- Have you been sufficiently critical of design and methodological issues?
- Have you indicated when results were conflicting or inconclusive and discussed possible reasons?
- Has your summary of the current literature contributed to the reader's understanding of the problems?
3. Tips on Structure
A common error in literature reviews is for writers to present material from one author, followed by information from another, then another.... The way in which you group authors and link ideas will help avoid this problem. To group authors who draw similar conclusions, you can use linking words such as:
- additionally
When authors disagree, linking words that indicate contrast will show how you have analysed their work. Words such as:
- on the other hand
- nonetheless
will indicate to your reader how you have analysed the material. At other times, you may want to qualify an author's work (using such words as specifically, usually, or generally ) or use an example ( thus, namely, to illustrate ). In this way you ensure that you are synthesizing the material, not just describing the work already carried out in your field.
Another major problem is that literature reviews are often written as if they stand alone, without links to the rest of the paper. There needs to be a clear relationship between the literature review and the methodology to follow.
- << Previous: 4. Analysing the Literature
- Next: 6. Writing the Review >>
- Last Updated: Feb 8, 2022 5:25 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwi.edu/litreviewsoe
Advertisement
A Literature Review of Pandemics and Development: the Long-Term Perspective
- Original Paper
- Published: 27 January 2022
- Volume 6 , pages 183–212, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- Beniamino Callegari ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5513-7299 1 , 2 &
- Christophe Feder ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1239-513X 3 , 4
6450 Accesses
13 Citations
7 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Pandemics have been a long-standing object of study by economists, albeit with declining interest, that is until COVID-19 arrived. We review current knowledge on the pandemics’ effects on long-term economic development, spanning economic and historical debates. We show that all economic inputs are potentially affected. Pandemics reduce the workforce and human capital, have mixed effects on investment and savings, but potentially positive consequences for innovation and knowledge development, depending on accompanying institutional change. In the absence of an innovative response supporting income redistribution, pandemics tend to increase income inequalities, worsening poverty traps and highlighting the distributional issues built into insurance-based health insurance systems. We find that the effects of pandemics are asymmetric over time, in space, and among sectors and households. Therefore, we suggest that the research focus on the theoretical plausibility and empirical significance of specific mechanisms should be complemented by meta-analytic efforts aimed at reconstructing the resulting complexity. Finally, we suggest that policymakers prioritize the development of organizational learning and innovative capabilities, focusing on the ability to adapt to emergencies rather than developing rigid protocols or mimicking solutions developed and implemented in different contexts.
Similar content being viewed by others
The impact of climate change on migration: a synthesis of recent empirical insights
David J. Kaczan & Jennifer Orgill-Meyer

Why Do Some Countries Develop and Others Not?

Contemporary Issues in Public Policy
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
As the COVID-19 emergency appears to slowly and unevenly recede in the wake of medical breakthroughs and the development of more effective prevention and treatment protocols, the question of the long-term impact of the pandemic grows more urgent. There is little doubt that this global health crisis found economists mostly unprepared, as the analysis of the pandemic’s effects has hardly found its way into the discipline’s most central publication avenues (Noy and Managi 2020 ). However, this does not mean that the economic analysis of pandemics is starting from scratch, as economists and economic historians have never ceased to expand our knowledge on the subject.
The connection between pandemics and economic theory has historically been so relevant that it has directly contributed to labeling economics as the ‘dismal science’. Cipolla ( 1974 ) illustrates how reflections on the plague and its consequences led many scholars to develop Malthusian ideas on the complex long-term relationships between population growth, economic growth, and diseases, well in advance of the Essay on the Principle of Population (Malthus 1798 ). However, the Industrial Revolution and the concomitant development of medical knowledge led to a decreased incidence of catastrophic plagues in the West, and a corresponding decline in the interest in pandemics on the part of economists (Easterlin 1995 ). The demographic boom of the West and the visible lack of corresponding pestilence and famine further discredited Malthusian perspectives, leading to a disconnection between the demographic and economic disciplines. Furthermore, from 1900 to 2019, pandemics were either eclipsed by more disruptive events or had a relatively limited economic impact (Garrett 2008 ; Lee and McKibbin 2004 ; Noy and Managi 2020 ). Finally, the marginalist revolution greatly focused economists’ attention on purely economic elements, eliminating from the discipline those elements perceived as spurious, like the study of pandemics’ effects (Schumpeter 1954 ), relegating it to a debate of mainly historical interest.
The expansion of economic analysis beyond its traditional boundaries that has occurred in the last two decades has gradually re-included the consequences of pandemics within economic theory, although most contributions remain on the periphery of academic debate and are relatively hidden (Arora 2001 ; Dunn 2006 ; Weil 2014 ). As Noy and Managi ( 2020 ) observed, the inherently multidisciplinary nature of pandemics, combined with its poor fit with what are called “hard” methods, have both conspired to make the contribution made by economists to the analysis of pandemics modest. The efforts of economists have been greatly augmented by the continuous work done by economic historians to understand the impact of past pandemics on the long-term development of various socioeconomic systems. Yet, while the total contribution to the economic analysis of the long-term impact of pandemics is significant, it is scattered across different journals, disciplines, academic approaches, and debates, making a review work necessary in order for all these contributions to become accessible.
This paper reviews the long-term economic effects of pandemics, defined as health shocks arising from infectious diseases with global diffusion. Within the definition of long-term effects, we include both those mechanisms that are immediately present and persist for a significant amount of time and those effects that arise in the long term. Due to the focus of our analysis, transient short-term effects are not part of our study. To the best of our knowledge, few literature reviews have studied the connection between pandemics and economic development. Bleakley ( 2010 ) critically reviews how diseases, rather than pandemics specifically, affect human capital formation and income growth at the micro and macro levels. Costa ( 2015 ) describes how health improvements affect economic growth, with a specific focus on the US, concluding that improved health is not sufficient to foster growth. Finally, Boucekkine et al. ( 2008 ) formally analyze how and which growth models are better able to mathematically describe the epidemics’ effects. Moreover, some scholars have also reviewed the long-term economic effects of particular health shocks, like the preindustrial epidemics (Alfani 2021 ), Spanish flu (Beach et al. 2021 ), HIV (Gaffeo 2003 ; Zinyemba et al. 2020 ), and modern pandemics (Bloom et al. 2021 ). We differ from these works because we analyze the long-term impact of pandemics in general on economic development. A similar approach has been adopted by Gries and Naudé ( 2021 ) and Callegari and Feder ( 2021a ), but with an entrepreneurship and not a macroeconomic focus.
Our broad approach has led us to review a large number of studies in order to identify recurrent results across very different pandemic events. Pandemics could affect aggregate demand, aggregate supply, and productivity growth (Basco et al. 2021 ; Dieppe 2021 ; Guerrieri et al. 2020 ; Jinjarak et al. 2021 ; Rassy and Smith 2013 ; World Bank 2020 ). Recalling the Solovian framework, we divide the long-term pandemic economic effects into three categories: labor and human capital; investments and physical capital; and knowledge and innovation. We find that all productive inputs are affected in the long term by the pandemic. More specifically, labor and human capital are negatively affected directly by health shocks. However, the intensity of this effect is heterogeneous among countries, labor markets, and industries. Investments and physical capital are affected by pandemics through complex, interacting, and often contrasting mechanisms, leaving long-term effects ambiguous and usually marginal and non-linear. However, the asymmetric impact of pandemics on the capital market and household income leads to the poverty trap and highlights the weakness of the health insurance system in coping with these shocks. Finally, pandemics could positively affect innovations in public and private institutions and bring about relevant technological changes in industries. The scope and direction of these socioeconomic changes appear to mediate the long-term effects of pandemics, determining both their direction and scope. However, relevant and radical institutional changes are necessary if the impact of pandemics on development is to be positive. We therefore suggest that scholars should develop meta-analysis to understand the complex tapestry of long-term pandemic mechanisms. Many policy implications follow directly: an efficient public intervention must be characterized in the long term by flexibility, pro-market orientation, and design customization.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 explains the selection methodology used in the review. Sections 3 , 4 , and 5 describe, respectively, the long-term effects of pandemics on: labor and human capital; investment and physical capital; and knowledge and innovation. Section 6 critically discusses the survey and summarizes the main lessons drawn from the literature for researchers and policymakers. Section 7 concludes.
Methodology
This literature review aims to illustrate, compare, and discuss the mechanisms through which pandemics affect long-term economic development. To achieve this goal, we adopted the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology (Moher et al. 2009 ). First, we defined a list of keywords that express the main aspects of the “pandemic” and “economic development” concepts. Second, we identified which data sets to search: JSTOR, IDEAS/RePEc, Google Scholar, and EconLit. We excluded working papers and unpublished articles from our search, to ensure that the mechanisms presented are accepted by the scientific community. Moreover, we restricted our focus to the fields of economics and economic history, to ensure the economic relevance of the mechanisms described. Finally, we excluded papers focused on the COVID-19 pandemic, as it is too early for a comprehensive evaluation of its long-term effects. Applying these criteria, we obtained a first sample of more than 4800 potential articles. Important contributions were not missed due to excessively strict methodological adherence, we also parsed the references lists of the most influential contributions within our initial corpus, identifying in this way 178 additional relevant manuscripts to potentially include in our review.
From this corpus of potential articles, we operated a further selection by analyzing their abstracts and, in uncertain cases, by searching the main body of the paper concerned for evidence of relevant discourse, thereby identifying 805 potential contributions. We then proceeded to evaluate the selected articles for inclusion according to their relevance to our research topic and their relative originality, evaluated in terms of the mechanisms analyzed. We then proceeded to summarize the resulting papers according to their research questions and aims, their theoretical references, their methodology, and their results, focusing on the featured economic mechanisms, in order to identify the structure of our corpus in terms of the main debates, the empirical object of study, the methods applied, and the theoretical foundations. In this way, after eliminating redundant contributions, we selected 88 articles, each describing specific mechanisms through which pandemics may affect the economic system in the long term. Finally, we identified a criterion to organize the resulting mechanisms, inspired by the well-known Solovian model of long-term growth, dividing them into the following three broad categories: labor, capital, and innovation.
We then identified a corpus of high-quality contributions, each offering a specific contribution to the academic debate in terms of one or more relevant mechanisms, supported by either theoretical or empirical arguments. Figure 1 summarizes the main steps of the selection process by using a PRISMA diagram.
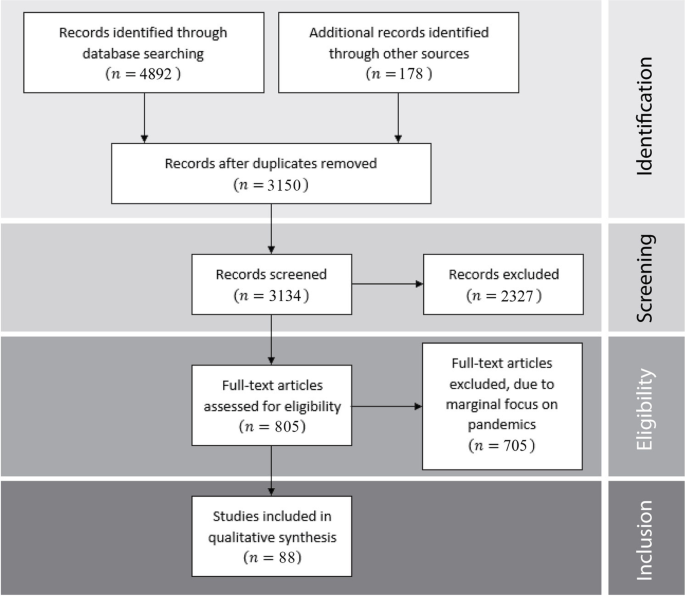
The PRISMA process
Labor and Human Capital
The most intuitive and direct effect of pandemics is the adverse shock to the population and the labor market. Delfino and Simmons ( 2005 ) propose a Lotka-Volterra model showing that a negative demographic effect could become persistent if the pandemic is not eradicated. The magnitude of this effect is, however, mediated by contextual factors. Alfani ( 2013 ) shows that, in southern Europe, the plagues of the XVII century had higher mortality and territorial pervasiveness compared with those affecting northern Europe in the same period and the southern Europe plagues of the previous century. Furthermore, the rate of mortality and territorial pervasiveness was heterogeneous among Italian regions and cities. Using a long-term perspective, Rodríguez-Caballero and Vera-Valdés ( 2020 ) find that pandemics reduced the unemployment rate persistently from 1854 to 2016 in Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, the UK, and the US. They also observe that, in the UK, pandemics reduced the GDP per capita over 1270–2019, and that this effect was increasingly persistent in the last 300 years. Fiaschi and Fioroni ( 2019 ) have built a model which shows how pandemics’ impact on growth trajectories is mediated by the production structure and the mortality reduction brought by technological progress. Bloom and Sachs ( 1998 ) observe that the mortality and morbidity of pandemics are highest in tropical regions. They explain that differences in climate and nature, together with anthropomorphic factors, affect the spread of the virus over the population. However, this direct effect on labor and population could decline in the long term.
The long-term effects of pandemics on the labor supply also depend on their impact on fertility. By analyzing 15 relevant infectious diseases from 75 countries between 1940 and 2000, Acemoglu and Johnson ( 2007 ) find that pandemics reduce demographic equilibria in the long term through their impact on fertility rates. Birth rates are influenced directly, as the pandemic reduces the number of fertile women, and indirectly, as future life expectancy influences decisions to have children in the long term. They empirically confirm that the higher mortality of those affected by infectious diseases sharply reduces births and slightly reduces the share of the young in the population because of their lower life expectancy. Lorentzen et al. ( 2008 ) show that a pandemic affects not only fertility, i.e. the number of births, but also the net fertility, i.e. the fertility of the surviving population. Parents care about the number of surviving newborns: higher infant mortality increases births. Moreover, parents invest time and money in their children, who become irreplaceable when they grow up. Therefore, higher adult mortality increases fertility, even more than infant mortality. Finally, given the family budget constraint, parents must choose between the quantity and quality of their children. Consequently, the uncertainty of the pandemic reduces the investment rent in human capital, leading parents to rationally prefer quantity to quality. The authors find empirical support for these hypotheses, observing that the probability of contracting malaria negatively affects adult and infant life expectancy, and that both expectations improve the fertility rate.
Fertility mechanisms interact with human capital accumulation. Lagerlöf ( 2003 ) describes an overlapping-generations model where adults confront the children’s quality-quantity trade-off. Infant survival is negatively affected by both the chance of random pandemics and population density, which both increase the risk of contagion, but is positively affected by human capital (higher medical knowledge), which is cumulative in time and positively affected by population density (knowledge spillovers). They find that, when pandemics are frequent, where the decision to have children is concerned, parents prefer quantity to quality; human capital does not increase; and population density remains low. When sufficient human capital has accumulated, however, the growth path of the economy is no longer affected by new pandemic waves. Consequently, only if, by chance, pandemics do not strike for a sufficiently long time, will parents then increase their investments in future generations, thus reaching the human capital threshold necessary to achieve robust growth trajectories. Gori et al. ( 2020 ) integrate all previously described mechanisms in a three-stage overlapping-generations growth model, including adolescent, adult, and elderly agents. In this model, only the elderly are sexually inactive and are, therefore, not exposed to HIV infection. The probability of dying from the pandemic is negatively associated with human capital endowment and positively associated with the number of virus-spreaders. The pandemic increases both infant and adult mortality. Adult mortality reduces both labor supply and life expectancy. If life expectancy is reduced below a certain threshold level, parents prefer to have more children; otherwise, they prefer to invest in human capital. Parameterizing the model for the Sub-Saharan African countries, Gori et al. ( 2020 ) find that HIV reduces labor supply and human capital but increases fertility. Cervellati and Sunde ( 2015 ) model an economy where parents confront the children’s quality-quantity trade-off, given the child mortality and the inborn ability of the offspring. Also in this model, higher human capital leads to an improvement in both medical care and adult life expectancy: intensive economic growth follows an initial quasi-stagnation. Cervellati and Sunde ( 2015 ) observe, like Lorentzen et al. ( 2008 ), that adult mortality and human capital affect the economic dynamics more than fertility and child mortality. Cervellati and Sunde ( 2011 ) combine Lorentzen et al. ( 2008 )‘s life expectancy effects on mortality and fertility with the Acemoglu and Johnson ( 2007 )‘s model and find non-monotonic patterns of demographic growth. Before the demographic transition, more newborns could compensate for higher mortality, leaving the overall demographic effect ambiguous; after the demographic transition, parents prefer quality over quantity in regard to children, making pandemic demographic effects definitively negative in the long term.
A pandemic’s negative demographic impact reduces the number of available workers. However, its long-term impact is mixed. Gori et al. ( 2020 ) and Dauda ( 2019 ) provide a comprehensive literature review of the complex link between HIV and growth. They conclude that, while strong evidence exists for a negative link at the micro level, the empirical support for the macro effects is weaker. Keogh-Brown et al. ( 2010 ) find four ways in which the pandemic can affect the work supply. Death and infection of workers result in a temporary reduction of the workforce, partially persistent in the long term. However, they observe that these effects could be mitigated by migration (see also Alfani 2013 ), labor market inefficiencies (see also Bloom and Mahal 1997 ), and inventories. Using a structural econometric model of the UK to estimate the economic effects of a modern pandemic, they conclude that it would reduce production and increase firms’ costs, leading to the emergence of inflation in the long term. Voigtländer and Voth ( 2013 ) describe a model where pandemics reduce population but increase labor in the manufacturing sectors. Since the land supply remains constant, labor productivity increases, and therefore survivors’ wages are higher than they would be without the pandemic in the long term. If the welfare increase is sufficiently high, the demand for manufactured goods increases trade and population density. Moreover, manufactured goods are easily taxable, thus enabling the financing of more wars. All these mechanisms increase the transmission of disease, leading to long-term demographic stagnation. Using data on the Black Death, the calibrated model correctly approximates the growth of both the European urbanization and per capita GDP from 1000 to 1700.
Historical research provides further support for the hypothesis. Herlihy ( 1997 ) confirms that wages and the demand for manufactured goods increased after the Plague; however, he observes higher lethality for adults than for both the young and the elderly. The Black Death first reduced the number of available workers and the length of their productive life. Additionally, the Plague took away both the skill and experience of previous workers and the parent’s investment in the education of their children. Moreover, high turnover increased labor demand, further reducing the productivity of new workers in the long term. Low labor supply increased wages, as land rents decreased. Finally, consumption grew quantitatively, shifting qualitatively towards higher-quality goods, leading to the emergence of a positive long-term impact on the real wages and welfare of the survivors. Pamuk ( 2007 ) supports all Herlihy ( 1997 )‘s results. Moreover, he finds that the great difference in economic growth between North and South Europe, which is observed only some centuries later, originates from the Black Death of the fourteenth century. Indeed, if at first the Plague increased wages across Europe, afterwards, when the population began to grow again, the real wages remained persistently higher in North Europe. The higher flexibility of institutions and guilds allowed a better economic and social response to the Black Death in the North, for example by obtaining lease contracts more advantageous for farmers, or making it easier for women to enter the labor market, and then structurally and radically changing the fertility rate and demographic trends in those countries. Alfani and Percoco ( 2019 ) produce empirical evidence that the plagues that infested Italy in the XVII century also led to long-term reductions in real wages. Indeed, although the population remained below pre-plague levels for more than two centuries, the reduction of skills (as well as of capital and technologies) was particularly large for various reasons. First, these plagues were particularly severe compared with the outbreaks in other European countries. Second, these plagues hit all population strata equally, including the poor, nobles, and bourgeois alike. Moreover, the demographic impact was not compensated by migration flows. Finally, the destruction of human capital reduced the competitiveness of the Italian economy.
Economists disagree on the intensity of the long-term effect of pandemics on the accumulation of human capital. Bleakley ( 2010 ) shows that the effect of the pandemic on schooling is uncertain due to the simultaneous decrease in both benefits (following lessons is more difficult) and opportunity costs (labor productivity is lower). Moreover, he observes that the pandemic could already have negative effects on the intellectual development of the child during gestation. Almond ( 2006 ) supports this argument using 1960–80 decennial microdata to analyze the long-term effects on those US children who were conceived during the Spanish flu. He observes that, if the mother was infected during pregnancy, then her offspring had lower educational attainment and a higher probability of being physically disabled. Both factors reduce their future wages and then increase their participation in illegal activities and, more generally, harm their socioeconomic status 40, 50, and 60 years after the pandemic. Parman ( 2015 ) resizes the effect, affirming that in the US the Spanish flu did not affect human capital in aggregate because parents redirected their investments towards older siblings. Meyers and Thomasson ( 2021 ) show that in 1916 the negative effect of polio on human capital differed between the US states and also depended on the age of students and the family income. However, the effect is usually nonlinear on age and more damaging to the richest because of the specific characteristics of polio.
The relationship between pandemics and human capital accumulation has been studied not only in the US. Odugbesan and Rjoub ( 2019 ) show that, for 26 sub-Saharan African countries from 1990 to 2016, the link between a pandemic and human capital is negative and bidirectional due to persistent short-term effects. Using two Tanzanian databases, Wobst and Arndt ( 2004 ) show that the HIV pandemic has decreased human capital (and then wages and income per capita) in at least four ways. First, the pandemic has directly and persistently reduced labor supply and skills availability. Second, the number of teachers has also decreased, worsening the quality of the process of accumulation of human capital. Third, the lower labor supply has increased the demand for new workers, raising the opportunity cost of education for the young, thus reducing the need for human capital investments. Finally, the pandemic has also reduced the long-term demand for education through an increase in the number of orphans. Novella ( 2018 ) confirms the last link using a Zimbabwean survey for 2007–8. This revealed that orphans leave (secondary) school early and hence enter the labor market early compared with non-orphans. The worst effects emerge when both parents are dead or when the household is blended, i.e., when orphans and non-orphans live together. He also observes that this lower household income after a parent’s death only partially explains the lower investment in the orphans’ human capital. Evans and Miguel ( 2007 ) extend previous results for Kenya. Analyzing an extensive database of over 20,000 children, they observe that not only are orphans more likely to quit primary school, but the probability is higher in those cases where the mother dies and/or their academic performance was already weak. Therefore, they conclude that the inability to pay school fees and the need to find work seem less significant in the long term than the lack of emotional support and the presence of psychological trauma. Fortson ( 2011 ) models the schooling decision that maximizes the expected present value of lifetime utility, considering that HIV reduces its discount rate. He uses data of 15–49-year-olds covering the birth cohorts 1952–91 in 15 sub-Saharan African countries in order to confirm that HIV reduces longevity and human capital investments persistently in the long term. Moreover, the author suggests that both orphans and non-orphans are affected by pandemics, and that decreased schooling provision does not play a key role. Many scholars have analyzed the effects of HIV on educational achievements. Bell and Gersbach ( 2009 ) confirm all previous results by using an overlapping-generations model where both parents and children decide how much to invest in human capital. Moreover, they observe that (i) selective health and educational policies are more effective than comprehensive ones; and (ii) simultaneous health and educational policies are more (less) efficient than sequential ones if disease mortality is above (below) a threshold level.
Young ( 2005 ) combines two fertility effects with the orphan effect. First, if the virus is sexually transmitted, e.g. by HIV infection, then unprotected sexual activities and births are reduced. Second, the labor supply contraction, induced by the pandemic, improves wages and then reduces the mothers’ fertility. Third, lack of parental guidance reduces the human capital of orphans. These emerging long-term effects are mixed. Calibrating the model with South African microdata, he finds that: the female labor supply is more elastic than the male labor supply; fertility effects always prevail in the long term despite pessimistic assumptions; and per capita income tends to increase. Some scholars find that, in addition to human capital, pandemics depress other types of intangible capital. Aassve et al. ( 2021 ) show that the Spanish flu decreased social capital for many generations in the US. They use a long-term social trust survey and discover that: (i) the immigrants born after the Spanish flu and their heirs have lower social trust than those born before; and (ii) the effect is higher for those from countries with less uncensored information on pandemic effects. Using a behavioral experiment in Uganda, McCannon and Rodriguez ( 2019 ) find that grown-up orphans tend to have lower social capital. The probability of prosocial behavior is lower because orphans are more pessimistic about the community’s social contributions. McDonald and Roberts ( 2006 ) analyze data for 112 countries from 1960 to 1998 to determine how much HIV and malaria affect health capital and, consequently, income per capita growth in the long term. They observe that the degree of HIV prevalence in a country negatively affects health capital directly and economic growth indirectly. Moreover, they observe that this mechanism is significant in Africa, through both HIV and malaria, and in Latin America, only through HIV, but not in OECD and Asian Countries. Focusing on sub-Saharan Africa, Odugbesan and Rjoub ( 2019 ) confirm that income plays a key role in explaining the long-term effects of a pandemic. However, the direction of their results is reversed: the bidirectional link between a pandemic and human capital for upper-middle-, low-middle-, and low-income countries is, respectively, negative, positive, and insignificant.
Finally, the majority of effects described in this section are generally more severe in low-income countries. Here, reduced access to medical care, undernourishment, and the presence of other diseases could induce a poverty trap (Beach et al. 2021 ; Bloom et al. 2021 ; Lorentzen et al. 2008 ). A Malthusian equilibrium with low income, underinvestment in schooling and health, and high fertility emerge for tuberculosis (Delfino and Simmons 2005 ) but only partially for malaria (Bloom and Sachs 1998 ; Gallup and Sachs 2001 ). Moreover, the poverty trap is unclear for HIV, where both positive and negative pandemic effects on income distribution could emerge (Bloom and Mahal 1997 ; Bloom and Sachs 1998 ; Mahal 2004 ). Alfani ( 2021 ) suggests that high-mortality pandemics, like the plague, could reduce poverty by either exterminating the poor or redistributing income to the poor. Vice versa, Karlsson et al. ( 2014 ) suggest that low-mortality pandemics, like the Spanish flu, increase poverty due to pandemic-induced unemployment, inability to work for long periods, and general loss of income. As these effects are particularly severe and persistent for poor households, pandemics could aggravate inequality. Therefore, the long-term effects of pandemics on income distribution appear to depend on the medical profile of the disease.
Investments and Physical Capital
While pandemics affect the long-term dynamics of labor supply and human capital also through durable short-term mechanisms, their impact on capital and savings arise in the long term specifically. Acemoglu and Johnson ( 2007 ) argue that, since land and physical capital are not affected in the short term, the lower levels of labor supply and human capital reduce GDP but have an unclear effect on per capita income. Since pandemics reduce GDP and income growth, they also reduce physical capital accumulation, thereby triggering a long-term negative loop between GDP and capital. The authors hypothesize that, in the long term, GDP per capita should drop in high-income countries but not in low-income countries, where land is more relevant than physical and human capital, and the negative loop effect is weaker.
Bai et al. ( 2021 ) confirm that the long-term pandemic effect differs among countries. They show that infectious diseases in the last 15 years have increased permanent volatility in the US, UK, China, and Japan capital markets. However, public policies of correct timing and intensity could reduce the effect. Ru et al. ( 2021 ) find that countries that have already experienced similar pandemics react better and more readily to future pandemics, especially if past pandemics have led to deaths. Analyzing the 65 largest financial markets in the world, the authors note that countries with firsthand SARS experienced the deepest fall in the stock market during the COVID-19 pandemic. This reaction is positively correlated to the pandemic’s mortality. Donadelli et al. ( 2017 ) confirm that, from 2003 to 2014, disease-related news had adversely affected the returns of the pharmaceutical stock market. Analyzing 102 pharmaceutical firms listed on the US stock market, the authors note that investors were too optimistic about the future liquidity of pharmaceutical sector flows after the shock. This irrational behavior has a positive and persistent effect on the returns of the pharmaceutical stock portfolio. Cakici and Zaremba ( 2021 ) extend the previous results outside the pharmaceutical sector. They observe that pandemics induce irrationality among investors, impacting assets across countries and firms heterogeneously. Analyzing 19 international stock markets, they observe that the stock trend signals to investors the firms’ resilience and ability to react to negative shocks, leading to increased future share performance. Summarizing, the literature analyzing the effects of pandemics on equity markets concludes that these health shocks induce irrational behavior of investors, causing positive and negative long-term effects, heterogeneous among countries, sectors, and firms.
Consensus among scholars is lacking in regard to both the size and direction of the long-term pandemic effects on investments and physical capital. Cuddington ( 1993a ) observes that pandemics affect labor demand and capital markets. The total effect on wages is uncertain: supply shock increases wages, but the demand shock reduces them, because infected workers are less effective, as they need to take sick leave and are less productive. Pandemics also affect domestic capital accumulation because health care costs reduce savings. Therefore, the total impact on capital per capita, GDP, and GDP per capita is uncertain; however, calibrating the model with Tanzanian data, he finds that both GDP and GDP per capita sharply decreased from 1985 to 2010. Cuddington and Hancock ( 1994 ) confirm the result for Malawi, although the lower number of infected people reduced the long-term effects on the economy. Moreover, Cuddington (Cuddington 1993b ) observes that previously predicted effects also hold when formal and informal productive sectors coexist, and formal wages are sticky. Basco et al. ( 2021 ) affirm that the Spanish flu in Spain was primarily a demand shock but confirm that the pandemic impact on the real return of capital is ambiguous in the long term. Although at the theoretical level Karlsson et al. ( 2014 ) confirm the ambiguity of the long-term effect of the Spanish flu on the per capita return on capital, this ambiguity is not observed in the empirical analysis of the Swedish counties. Indeed, by analyzing the effects in the decade following the pandemic, the authors estimate no statistically significant effect on earnings per capita, but clear negative effects emerge on capital returns per capita. Finally, Jinjarak et al. ( 2021 ) show that the H3N2 pandemic reduces GDP, consumption, and the investments of 52 countries.
Other scholars demonstrate that the effect of pandemics is heterogeneous among sectors, a trait shared with most disasters (Halkos and Zisiadou 2019 ). In Egypt, pandemics depleted the rural workforce necessary for the maintenance of the crucial centralized irrigation system, which remained in a state of disrepair, hampering the well-being of the region for centuries (Borsch 2005 , 2015 ). Herlihy ( 1997 ) shows that the rise in wages following the Black Death increased demand for more nutritious and elaborate goods, diversifying consumption and improving welfare. Similarly, Pamuk ( 2007 ) shows that the Plague increased the demand for luxury goods in particular. Moreover, he observes a reduction in interest rates and increased investments, although with asymmetric components. Indeed, Alfani ( 2013 ) shows that the XVII century plague depressed Italian industries, in particular, the wool, flax, silk, and construction sectors, due to the loss of skills and the impossibility of procuring raw materials. Alfani and Percoco ( 2019 ) highlight that the shift of investments from urban to rural activities in this period reoriented the post-plague Italian manufacturing sector towards the production of semi-finished and low-quality goods. Summarizing, scholars observe that short-term changes in the relative composition of both demand and supply structures can lead to long-term sectoral effects.
Similar sectoral asymmetric effects have been recorded for more recent pandemics. Analyzing the potential effects of SARS in Asia, Lee and McKibbin ( 2004 ) find that countries specializing in trade and the tertiary sector are more damaged by both temporary and persistent pandemic shocks. Indeed, in these sectors, close contact with other people is often necessary. The retail and tourism sectors are particularly vulnerable. Gallup and Sachs ( 2001 ) provide further support by showing that Mediterranean and Caribbean countries benefited from the rapid and stable development of the tourism industry after the eradication of malaria. Finally, Mahal ( 2004 )‘s literature review on HIV effects shows a similar, although weaker, effect for sub-Saharan tourism. Moreover, the author shows that health, transport, and the primary sectors are also negatively affected by HIV. Pandemics affect the health sector by increasing costs for healthcare services and insurance. Moreover, he shows that workers in the transport and primary sectors belong to the social classes most affected by HIV. Oster ( 2012 ) finds that export is an essential explanation of the spread of HIV in Africa because more truckers and miners, among others, stay away from home for more extended and more numerous periods. As a result, they and their partners are more likely to engage in risky sexual intercourse, putting themselves and their stable partners in danger. She also affirms that trade could further aggravate the effect in the long term, as additional income could increase the amount of money spent on prostitution, or mitigate it, if money is spent on preventive measures. Using a quasi-experimental variation, Adda ( 2016 ) confirms that the new transportation networks and inter-regional trade accelerated disease diffusion in France from 1984 to 2010. Delfino and Simmons ( 2005 ) combine the effect of capital and labor, using a Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model where only healthy individuals are productive. The authors observe that the introduction of capital makes the path more complex, but that the economy still cyclically converges to a stationary equilibrium. Indeed, when labor supply decreases, GDP decreases. Therefore, both savings and investments are lower, and GDP per worker also decreases. Lower welfare reduces health services consumption, but the impact on the disease transmission is uncertain: it increases as the share of infected rises, but it decreases as the contagion period became shorter. When the labor supply increases again, the cycle restarts. Augier and Yaly ( 2013 ) show that complex growth paths could emerge even in a model where the pandemic affects only capital accumulation. The authors describe an overlapping-generations model where the pandemic increases premature deaths, and then only the survivors will use savings previously accumulated. The government proposes a funds system that redistributes rents among the survivors. Young people must decide how much to invest in this public fund, and how much to spend on health or other goods, knowing that better health reduces the chance of dying prematurely. They observe that the pandemic, capital, and health investments are linked in an articulated and recursive way: (i) the pandemic causes health investment to drop; but (ii) health investment reduces the diffusion of the pandemic; (iii) capital directly affects the investment; and then (iv) it indirectly affects the spread of the pandemic. Therefore, the economy converges to a long-term equilibrium only when contagion rates are low. Finally, Stiglitz and Guzman ( 2021 ) show that pandemics act as an unanticipated technology shock, generating unemployment that government intervention can effectively counteract. In the long term, uncertainty does not decline, thus further increasing the desirability of government intervention.
In Section 3 , we showed that, after a pandemic, life expectancy decreases because a healthy lifespan becomes more uncertain than before, leading to decreased investments in human capital. Similarly, scholars observe that the pandemic also reduces investments in physical capital. Lorentzen et al. ( 2008 ) show that the indirect effects of malaria on life expectancy are higher on physical rather than on human capital investments. Analyzing different databases and case studies, Gallup and Sachs ( 2001 ) conclude that the effects on per capita and total income are negative because both foreign investments and the revenues from tourist and business travelers are drastically lower in those countries affected by malaria. Analyzing the effects of HIV on 43 Asian countries from 1990 to 2015, Fawaz et al. ( 2019 ) conclude that investments and savings are usually inversely related to that pandemic. However, they show that both the sign and the intensity of the effect could differ depending on how far-sighted people are. Additionally, in low income countries, the negative effect of investment is independent of gender, but the pandemic affects men’s saving propensity more than women’s. Vice versa, in high income countries, when life expectancy decreases because of pandemic mortality, men save more but do not increase their investments, while women save less but invest more. Bloom and Mahal ( 1997 ) also focus on savings behavior, using it to explain the insignificant effect of HIV on the income per capita growth rate in 51 countries from 1980 to 1992. First, they observe that poor people are most affected by HIV, and that expensive medical treatments further aggravate their disadvantaged situation. However, social and economic mechanisms partially compensate for the high costs of official health services. Second, higher care costs cause both consumption and savings to drop. Moreover, lower life expectancy may increase precautionary savings in favor of surviving family members. Garrett ( 2008 ) studies the economic and social effects of the influenza pandemic 1918–9 in the US, analyzing newspaper articles and academic papers to draw lessons for modern pandemics. He observes that health care is relevant only with ideal health systems that certainly do not collapse after a pandemic, no matter how serious it is. Moreover, he concludes that, although a higher percentage of life insurance mitigates the adverse financial effects of a pandemic on households, the wealthiest households that will need it least will also be the more protected. Gustafsson-Wright et al. ( 2011 ) show that, in the case of pandemics, the private insurance system can be unfair and distortive, even in countries like Namibia, where the quality of public health care is relatively high, and most people have health insurance. The poor who cannot afford health insurance suffer from higher medical expenditure during a pandemic. There are no substantial effects on medical expenditure and family income until the virus starts affecting working capabilities; then, the economic consequences for the poorer strata worsen severely.
The comprehensive review from Hallegatte et al. ( 2020 ) confirms that poor people are disproportionately affected by natural hazards and disasters. Pandemics are no exception. Gaffeo ( 2003 ) provides additional support for the idea that pandemics can lead households into a poverty trap. Higher care costs and physical weakness reduce income capacity: for poor households, this leads to malnutrition, further reducing their physical capabilities, and increasing the pandemic’s morbidity and mortality. Physical and human capital trends reinforce this adverse and cumulative loop. Finally, he observes that pandemics worsen market failures for health insurance and local credit availability. Due to adverse selection and moral hazard, the higher uncertainty and information asymmetries inherent to pandemics lead to higher insurance premiums and reduced access to credit for the needy. Habyarimana et al. ( 2010 ) show that, while private firms could invest in their workers’ medical care, they are unlikely to do so. They describe the case of the pioneering firm Debswana Diamond Company in Botswana, which, since 2001, has invested in a program to improve the health of its workers affected by HIV. They observe that the treatment works, but the investment is unprofitable as the costs are too high, supporting the idea that African firms can only bear a small share of their workers’ health costs, if any.
While the previous literature shows that a pandemic increases income inequalities, Odugbesan and Rjoub ( 2019 ) argue that pandemics could hinder sustainable development. In this connection, these authors analyze the link between HIV and both public and private adjusted net savings, as an indicator of sustainable economic development, for 26 sub-Saharan African countries from 1990 to 2016. They show that HIV negatively and unidirectionally affects saving, and that the effect is particularly intense for upper-middle- and low-income countries. HIV also negatively affects the perception of government efficiency in low-middle-income countries. Odugbesan and Rjoub ( 2020 ) show that, for 23 sub-Saharan African countries from 1993 to 2016, the adverse relationship is bidirectional because the HIV control program and sustainable development compete for the same public spending budget. Keerthiratne and Tol ( 2017 ) show that the financial impact of disasters, pandemics included, is country- and time-specific. Moreover, Chakrabarty and Roy ( 2021 ) propose a model where the future pandemic uncertainty reduces government allocation of non-health expenditures in favor of the health ones. In 143 countries from 2000 to 2017, they found that higher-debt countries present a public misallocation and delay due to public constraints. A similar effect also emerges in low-income countries, but this is due to asymmetric information. Bai et al. ( 2021 ) show that, up to a point, the effects of pandemics could be efficiently mitigated with fiscal and monetary policies. Finally, Cavallo et al. ( 2013 ) confirm that governments and institutions could play a key role in the economic effects of a pandemic. Using a database from the Centre for Research on Epidemiology and Disasters, they observe that natural disasters, such as a pandemic, have a long-term negative economic impact only when they simultaneously cause a high number of deaths and are followed by institutional and political revolutions.
Knowledge and Innovation
Historians have identified numerous cases of pandemics being catalysts of significant, systemic change. In his comprehensive overview of the impact of the Black Death on Europe, Herlihy ( 1997 ) argues that it led to larger economic diversification, improved technology, and better lives, breaking the XIII century Malthusian deadlock by directing technological change towards the now cheaper input, i.e. capital. Although educational institutions were gravely hit, with one-sixth of European universities closed, as a long-term reaction to this short-term impact, a number of new educational institutions were built in reaction to the dearth of scholars. The new universities adopted more flexible curricula, contributing to the revival of classical studies. The need to face the Plague also forced the acceptance and diffusion of anatomical studies, fostering the development of the scientific approach in medicine. Epstein ( 2000 ) offers a similarly positive account, underlining how the Black Death brought much needed renewal. European feudalism was locked in a low-growth pattern, not because of lacking innovative capabilities, or market institutions, but rather due to the intensity of seigniorial rights, and the jurisdictional power of towns and lords, which were used to maximize the extraction of resources, mostly for military purposes, greatly hampering development. The scarcity of workforce caused by the Plague shock reduced the bargaining power of the landowner in favor of the worker. The resulting political and economic struggle is described as a process of “creative destruction”. The centralization process was greatly accelerated, leading to the consolidation of internal markets, the standardization of legal procedures and business norms, and the progressive rationalization of hierarchies. As a result, in the long term, transaction costs and economic uncertainty declined significantly, as testified by the structural decline in interest rates, which quickened the pace of innovation and trade growth. One of the long-lasting consequences of the pandemic for Europe was a more centralized, less predatory authority, able to support the process of economic development.
The institutionally “liquidationist” account of pandemics also applies to other centuries. For example, Alfani ( 2013 ) observes how plagues irrevocably affected the balance of power in Italy, favoring the rise of the House of Savoy, which eventually led to the Italian unification. Pamuk ( 2007 ) describes how the Plague created local skilled labor scarcity, incentivizing migration and fostering the dissemination of knowledge in the long term. Higher wages stimulated the substitution of land and capital for labor, creating conditions favorable to the implementation and diffusion of labor-saving innovations across all economic fields: the printing press, firearms, and high-capacity maritime transportation can all be linked to this general trend. Voigtländer and Voth ( 2013 ) offer what is perhaps the more optimistic view of the long-term impact of the Black Death, arguing that the positive impact of the persistently high European mortality rates dwarfed the effects of technological change for the entire 1500–1700 period. Clark ( 2007 ) provides a useful counterfactual, analyzing how the Far East, relatively less affected by plagues, maintained a growth regime characterized by both low income and low mortality. Not all plagues, however, are described in such a positive light.
Alfani and Percoco ( 2019 ) document the significant negative impact of the plague of 1629–30 on the long-term development of the Italian cities and the Italian economy. In addition to the mechanisms already explored in the previous sections, the authors argue that the significant losses suffered by the urban economic elite, who controlled most of the advanced manufacturing activities, caused an “ingenuity shock”, i.e. decreased both the availability and the willingness of the surviving elite to innovate in the urban industry, preferring agricultural investments instead. The latter took a dramatic hit in terms of production capabilities, which recovered only after decades. The exceptionally late recovery slowed the process of recovery and urbanization, weakening the Italian competitive position vis-à-vis Northern Europe in manufacturing. The almost uniform lack of wage increases signals how the long-term reduction in supply capabilities was not a consequence of lacking a skilled workforce, but rather a significant long-term change in the pattern of capitalist investments. This argument is important to underline how general, systemic renewal might encompass significant relative changes. The hypothesis that the plague did not damage, and perhaps even fostered, European development as a whole, is entirely consistent with the description of significant short- and long-term harm being wrought to large sections of the continental socioeconomic system. This is also consistent with Pamuk ( 2007 )‘s description of the divergence between North and South Europe, which emerged in response to the Plague as a consequence of the greater entrenchment of Southern political and economic elites, and the associated slower degree of institutional flexibility and, consequently, innovation and knowledge diffusion. In his recent overview of the subject, Alfani ( 2021 ) provides further evidence for the relevance of institutional change and policy choices on the long-term impact of pandemics on economic distribution and growth, illustrating how pandemics create opportunities for institutional change while also creating issues that, if not effectively tackled, can severely worsen the economic conditions of the poorer sections of the population.
On the negative side of the debate, Bar and Leukhina ( 2010 ) argue that epidemics have the capability to disrupt knowledge transfer across generations, leading to significant reductions in total factor productivity growth over time. They show that the long-term loss is moderated by the possibility of knowledge diffusion from regions that were spared negative health shocks, implying that the scope of this negative mechanism would be much greater in the case of a pandemic. Karlsson et al. ( 2014 ) document the impact of the Spanish flu on the Swedish economy, finding a long-term negative effect on capital income and a positive effect on the rate of poverty, both possibly driven by a significant persistent loss of skilled workers and consequently a decline in labor productivity. Jinjarak et al. ( 2021 ) show that the H3N2 epidemic can have permanent negative effects on productivity. Indeed, also when the productivity rate returns to its pre-shock level, some opportunities are lost or delayed forever, and then the innovation path will be always lower than without pandemics. Chen et al. ( 2021 ) even state that epidemics have the worst impact on innovation among natural disasters. Indeed, they affirm that epidemics reallocate public expenditure from innovation to health, reducing patent applications and innovation in 49 countries over 1985–2018. In Eastern Europe, feudal lords reacted to epidemics by re-enslaving the peasantry, greatly hampering the diffusion and implementation of new agricultural techniques, and locking the regions in a relative underdevelopment pattern called “second serfdom” (Domar 1970 ; Robinson and Acemoglu 2012 ). Similarly, the plagues affecting the Roman Empire and its successor states led to persistent socioeconomic degradation, aided by conservative political reforms introduced by the surviving elites (Duncan-Jones 1996 ; Sarris 2002 ; Little 2007 ; Harper 2016 ).
Yet pandemics are also great opportunities for the creation and diffusion of new knowledge. Bresalier ( 2012 ) documents how the Spanish influenza pandemic of 1918–9 was a turning point in the modernization of British medicine, leading to the establishment of key institutions and organizations that would shape the long-term development of medical research and healthcare, chief among them the Medical Research Council. The latter led to a wider active involvement of the state in sanitary matters. In general, the author shows that the pandemic’s effects were instrumental in developing the modern medical research system. Hopkins ( 1988 ) provides a description, similar in spirit, of how the successful smallpox eradication campaign conducted by the World Health Organization led to organizational learning, and the development and institutionalization of best practices, thereby greatly enhancing global medical response and prevention capabilities. Furthermore, large shocks, such as pandemics, can create windows of opportunity for change. This is echoed by Cohen ( 2019 )‘s review of the same episode, concluding that, while research and innovation activities played a key role in ensuring the campaign’s success, these efforts were at first greatly hindered by inappropriate practices and institutional routines. Only when the involved organizations implemented new and improved procedures did technological solutions become truly effective. While the scale differs, the argument echoes Pamuk ( 2007 )‘s. Wallace and Ràfols ( 2018 ) show that the avian flu highlighted how both excellence-based funding schemes and economic interests contribute to unduly restrict the field of active research as compared with the broad range of scientific opinions offered by experts, resulting in the development of a limited selection of techniques from the available knowledge base.
Analyzing the impact on the knowledge generation of vaccination subsidies, Finkelstein ( 2004 ) observes that, apart from the direct health impact from the eradication of illnesses, higher expected profitability might lead to socially wasteful competition for market share in the long term. Empirical evidence supports the hypothesis that the outcome depends on the state of the technological frontier and market conditions, as expressed by vaccination rates. In most cases, subsidies appear to lead to purely wasteful competition, but, in the case of the flu, there is evidence of increased product quality and demand, with the associated dynamic benefits outweighing static gains. Consistently, Kremer ( 2000 ) pointed out that market failures are endemic in the markets for both vaccine provision and vaccine research. While this opens up opportunities for policy intervention, it simultaneously underlines the challenges involved in the design of truly effective instruments. Similar challenges are described by Keohane ( 2016 ), in which innovative financial practices developed in the long term as a reaction to large shocks, including pandemics. He argues that “risk transfer for disease is a vital public good that the market has not otherwise provided” (ibid,130), and that new preventive and preparedness measures could be financed through the issue of catastrophe bonds. While these catastrophe bonds are expensive, the benefits of increased resilience in the face of health shocks might be a net gain, especially if the costs are somewhat lessened by pooled funds international initiatives. Although significant overlapping exists in terms of health-crisis preparedness and the organizational capacity of response, such an approach is probably more effective for estimating regional epidemic risks. Such instruments may be particularly useful in light of Confraria and Wang ( 2020 )‘s finding of persistent radical disparity between the disease burden carried by African countries and the amount of medical research dedicated to specifically African issues relative to global efforts.
The discussion so far has been focused on mechanisms that connect pandemics to the development of knowledge and practice, and from those to their economic and financial impact. Easterlin ( 1995 ) provides an original analysis based on a different viewpoint. Analyzing the steep decline in mortality that took place in northwestern Europe in the nineteenth century, he maintains that both the industrial and the health revolutions have a common root: the ascendancy of the scientific approach leading to technological change in both areas. The argument implies, on the one hand, that economic growth is not the main driver of life expectancy improvements, and, on the other, that improvements in health and life expectancy do not have a direct effect on economic outcomes, a position compatible with the relatively weak empirical evidence available (Acemoglu and Johnson 2007 ). The cause of structural change is argued to be found in the extraordinary stream of innovations implemented during the period, supported by a swarm of Schumpeterian “entrepreneurs”, only marginally motivated by profitability. Both those revolutions were triggered by the acceleration in the accumulation of usable empirical knowledge through the establishment and diffusion of the scientific method, the difference in timing to be imputed to the difficulty of developing and implementing the scientific solution. Deaton ( 2004 ) similarly argues that knowledge transfer, in the form of both effective practices and useful information, is key for explaining different national patterns of mortality decline and life expectancy increase, pointing out how globalization could benefit developing countries in this respect.
The argument is further expanded by Easterlin ( 1999 ), who showed that, while private firms have been crucial in fostering economic development, their role in improving health and especially infectious disease control practices has been marginal at best. Indeed, the preventive measures improve life expectancy more than the therapeutic ones, but firms rarely adopt them. However, the actions of households and governments are more important for disease prevention. The role of government is especially relevant because public action is necessary for both health education and prevention programs. Easterlin shows how irreplaceable effective knowledge and healthy practices are in the process of preventing and curing diseases, but how ineffective markets, contracts, and private property institutions have been in fostering their historical development, due to a number of related market failures. In fact, medical practitioners and public servants working towards the diffusion of salubrious norms have often found themselves hindered by economic actors defending their profitable, if deleterious, business. In his account of the US development, Gordon ( 2016 ) confirms both the decisive role of scientific advances and the importance of government intervention and regulation for the drastic improvement in health and life expectancy that took place in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. However, Birchenall ( 2007 ) proposes an alternative explanation for the manifestly weak correlation between contemporaneous income growth and mortality, highlighting the significant long-term impact of income growth in terms of improved adult health and life expectancy, and subsequent mortality reduction. The argument is supported by a model illustrating how sustained economic growth, no matter the source, is sufficient to escape the Malthusian equilibrium, leading to drastically lower mortality in the process. Cervellati and Sunde ( 2015 ) provide further support by developing a model based on unified growth theory, also characterized by an inevitable take-off triggered by sufficient technological progress.
From the historical description emerges a complex interplay of negative and positive relations between health and business practices, driven by the contrast between short- and long-term interests, on the one hand, and private and public interests, on the other. This complexity is faced by Mokyr ( 2010 ) in his attempt to outline the principles of an evolutionary approach to the study of the development of useful medical knowledge. He begins by highlighting the two key idiosyncratic characteristics of such a knowledge field: the largely inelastic character of its demand, as all humans value their lives and health under all circumstances, and the relevance of negative exogenous shocks, such as the spread of pandemics. Medical knowledge maps to a set of instructions and recipes capable of guiding action, called techniques. According to context-specific selection criteria, only a subset of related techniques will actually be implemented for a given set of knowledge. While the actual usage of techniques is rival, knowledge can endlessly accumulate with only limited downsides. The evolutionary process of knowledge is mostly based on persuasion mechanisms; on the contrary, the related techniques are evaluated on their relative effectiveness. However, persistent empirical failure might not be sufficient as a selection mechanism, if no better technique is available on the basis of the socially accepted set of useful knowledge. This is particularly likely in the case of singleton techniques, based on the limited empirical knowledge that “this works”, and is therefore incapable of adaptation to sudden change. The shift towards scientific knowledge ensures that techniques are based on a more nuanced understanding of natural phenomena, enabling quicker and more efficient adaptation to exogenous shocks. Limits are provided by the path-dependency of knowledge development, which is only indirectly affected by the usefulness of related techniques. While this might result in the generation of “useless” knowledge, degrading response capacity in the present, sudden exogenous changes might lead to equally sudden revaluations. Summarizing, pandemics are a simultaneous shock to both practices and the underlying knowledge, as their often dramatic impact is sufficient to create opportunities for shifting entire development trajectories. The emergence of new knowledge and practices can be further amplified by diffuse and profound institutional change, which in turn may lead to significant upheavals, positive or negative. Owing to the complex nature of the outcomes, however, normative judgment lies beyond the capabilities of purely theoretical analysis.
The first key result of this review is that in the analysis of pandemics’ long-term economic consequences, historical and epidemiological characteristics are key (Donadelli et al. 2021 ; Meyers and Thomasson 2021 ). The extraordinary mortality associated with the Black Death is the most crucial factor in explaining its exceptional long-term consequences for European and global socioeconomic development (Pamuk 2007 ; Voigtländer and Voth 2013 ). Research on the consequences of HIV has rightly focused on its sexual transmission (Young 2005 ; Oster 2012 ; Fawaz et al. 2019 ; Gori et al. 2020 ) and the intergenerational consequences of increased mortality among working-age adults (Wobst and Arndt 2004 ; McDonald and Roberts 2006 ; McCannon and Rodriguez 2019 ). Therefore, the results offered by a general economic analysis of pandemics should be considered a wide collection of potential mechanisms, their empirical applicability and relative importance to be carefully weighed on a case-by-case basis. This does not imply that knowledge is not cumulative in this field, but rather that application of past knowledge should account for contextual factors in order to determine the likely long-term impact of a specific pandemic.
Our review of the literature goes one step further. By aggregating the pandemics by their effects on various economic factors, we observe some recurring trends, allowing some useful general conclusions to emerge. Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of papers published in English focused on the relationship between pandemics and economic development. Following this paper’s structure, we organize the papers according to the mechanisms investigated into three broad categories: labor and human capital; physical capital and investments; and knowledge and innovation. We show that diseases can potentially affect all the productive factors of an economy in the long term. Most of the articles focus on the pandemic impacts on labor and human capital, all finding negative long-term impacts. However, some authors show that this effect could be partially mitigated in specific geographical areas, workers’ categories, and industrial sectors. The long-term effects on investment and physical capital are ambiguous: many papers show contrasting and complex mechanisms that do not allow us to know a priori the overall economic effects of pandemics on long-term investment trajectories. Notably, all papers which show long-term positive effects of pandemics on economic development focus on knowledge and innovation. However, negative cases also exist, leading many scholars to observe that the effect is potentially mixed, its direction dependent on necessary but not always implemented institutional changes.
The following general picture of the effects of pandemics on economic development emerges from our analysis. First, pandemics tend to reduce population and labor supply in both the short and the long term. This increases labor productivity, and therefore average wages. However, pandemics also hinder human capital accumulation, reducing productivity and per capita income growth. The negative effect is further compounded by the associated loss of knowledge, skills, experience, and innovative capabilities. Investments and savings are also negatively affected, leading to potential long-term hysteresis and the emergence of new, lower-income equilibria.
The pandemic shock can also break old patterns, opening new innovative trajectories previously inaccessible. The aggregate impact of these long-term mechanisms on the economic system is dependent on the relative relevance of, mostly harmful, adaptive mechanisms vis-à-vis potentially fruitful innovative responses. When the latter dominate the picture, negative long-term effects are overwhelmed by the benefits captured by radically new socioeconomic models of production, trade, and consumption. Therefore, the key factor determining the long-term impact of pandemics is identified with the innovation processes to which they give rise, and particularly the necessary accompanying processes of institutional change. While these effects are more difficult to capture using traditional economic methods, they are highlighted by historical analysis and should not be ignored by researchers and policymakers alike (Callegari and Feder 2021b ; Jena et al. 2021 ; Mandel and Veetil 2020 ).
Another important conclusion that can be drawn from this review is that most short-term outcomes, such as the immediate reduction in labor supply (Bloom and Sachs 1998 ; Alfani 2013 ), can bring, in the long term, significantly different consequences in both scope and quality when compared with the transient short-term effects (Delfino and Simmons 2005 ; Acemoglu and Johnson 2007 ; Basco et al. 2021 ). Several specific long-term mechanisms also emerge (e.g., Herlihy 1997 ; Young 2005 ; Augier and Yaly 2013 ), whose impact can hardly be overstated (Lorentzen et al. 2008 ; Voigtländer and Voth 2013 ). Therefore, it is unsurprising that attempts to produce comprehensive quantitative measurements of the economic consequences of pandemics appear to be affected by a significant downward bias (Lee and McKibbin 2004 ; Mahal 2004 ; Keogh-Brown et al. 2010 ). The exceptional nature of the shock brought by the Black Death of 1347–52 has obscured the economic consequences of the other late-medieval plagues, of which we know little. Lack of strong empirical evidence should be understood in the context of the complexity of the phenomena involved, and therefore not be interpreted at first sight as sufficient for falsification purposes. At the same time, however, the mechanisms at work in the most deadly pandemics should not be assumed to apply in exactly the same way to weaker, shorter, or smaller case episodes: the complexity of the phenomena under analysis cannot be reduced to a single formal model. Research on the long-term impacts of pandemics should be understood as a collaborative effort, with single researchers and teams focusing on different, yet compatible, mechanisms. A comprehensive picture can only emerge from subsequent efforts to produce cohesive overviews of the entirety of the debate rather than from a single model, no matter how ambitious.
Some lessons for policymakers also follow. The first is that, in light of the idiosyncratic characteristics of pandemics, precise and detailed analyses of their long-term effects are only possible ex-post. Therefore, preparations for such events should focus on reactive capabilities to ensure that: research efforts can be quickly and adequately supported; their results are credibly communicated to the authorities and the general public; and scientifically-founded counter-measures are rapidly implemented. These characteristics apply to both health measures and economic policy. Furthermore, when these dramatic events occur, the effective public intervention should be timely (Bai et al. 2021 ; Martin et al. 2020 ; Rodríguez-Caballero and Vera-Valdés 2020 ; Stiglitz and Guzman 2021 ) and designed starting from the general characteristics that emerged in this review, and then directed over time by distinctive challenges brought by the specific health shock. The second lesson is that symmetric health shocks will lead to asymmetric economic long-term consequences, as country-specific institutional settings mediate most effects. The tendencies towards the uncritical adoption of global solutions should be tempered by concern for the specific features of local socioeconomic systems, leading to a preliminary process of policy customization. Resistance and push-back from below should not be interpreted automatically as regressive tendencies, but rather as symptoms of the need for policy adaptation to local concerns. Finally, the third lesson is that, while pandemics require careful and extensive public intervention, what matters most in the long term is to avoid crushing the innovative response capabilities of the private sector. A virtuous process of creative destruction may emerge only if public intervention does not attempt to restore the old socioeconomic regime, potentially now unsustainable, at all costs, trampling adaptive bottom-up initiatives in the process. Consequently, while initial efforts should be aimed towards counteracting immediate shocks, they should eventually be complemented by measures aiming to support the positive qualitative developments triggered by the pandemic and curb emerging negative trends. Thus, a potential positive role for policy action can be expected to persist well beyond the outbreak period, focusing on enabling and supporting positive private responses through processes of institutional change.
Conclusions
The COVID-19 pandemic has made evident the need to study the overall economic effects of global health shocks. This literature review collects the main contributions that describe the long-term impact of a pandemic, in order to better understand the lessons from the current economic literature on this topic, and then to better address and analyze the effects on economic development of COVID-19 and of future risks of pandemics. The contributions are organized by discussing, in turn, the mechanisms affecting: labor and human capital; investments and physical capital; and knowledge and innovation. We conclude that pandemics could affect aggregate demand, aggregate supply, and productivity (Jinjarak et al. 2021 ). More precisely, we show that a pandemic reduces labor supply and human capital accumulation in the long term; that the complex interaction of these contrasting and idiosyncratic mechanisms on investments and savings is theoretically indeterminate; and that pandemics, when accompanied by supporting institutional change, can greatly benefit innovation and knowledge development. However, a detailed analysis of the pandemic’s specific characteristics, the affected economic systems, and their response remains necessary to understand which mechanisms can be expected to prevail and which policies should be implemented. The key factors determining their long-term impact are the associated processes of institutional change. We finally identify some general lessons for both researchers and policymakers. The research focuses on the theoretical plausibility and empirical significance of specific mechanisms that should be complemented by meta-analytic efforts aimed at reconstructing the resulting complexity. Policymakers should prioritize developing organizational learning and innovative capabilities, focusing on the ability to quickly adapt to emergencies, rather than developing rigid protocols calibrated over previous pandemics.
We expect the emergence of three new strands of literature in the near future. The first field of research will be on the long-term economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic (Jordà et al. 2021 ; Poblete-Cazenave 2021 ; Tokic 2020 ). Such research will contribute to testing previously identified mechanisms reviewed here, while potentially also leading to the identification and theorization of new ones (Cacault et al. 2021 ; Silverio-Murillo et al. 2021 ; Costa Junior et al. 2021 ; Favilukis et al. 2021 ; Pagano et al. 2021 ). We also expect significant interest in comparing the impact of COVID-19 with previous pandemics, in order to highlight the relative importance of their respective defining features. The second field of research will be on the public and private responses to the effects of pandemics. The heterogeneity of both the method and timing of the institutional responses for the same health shock can be used to effectively test their efficiency and reduce the impact of future pandemic and epidemic waves (Adolph et al. 2021 ; Caserotti et al. 2021 ; Chakrabarty and Roy 2021 ; Croce et al. 2021 ; Martin et al. 2020 ). The ongoing debate on structural changes as a response to COVID-19 can be seen as a first step in increasing academic attention to the problem of the prediction of possible future pandemics and the precautionary measures to be taken in dealing with these events (Büscher et al. 2021 ; Dosi et al. 2020 ; Leach et al. 2021 ). Finally, we expect a more extensive interaction between, and cross-fertilization of, the medical and economic literatures (Avery et al. 2020 ; Murray 2020 ; Verikios 2020 ). This combination will be needed to better understand how a specific feature of the virus impacts economic development. A taxonomy of pandemics is necessary to group them correctly and then clarify how the different mechanisms move in and impact economic development. In general, we expect the academic debate on the long-term economic impact of pandemics to be renewed and reinforced in the coming years. This survey has the ultimate goal of preparing the basis for this inevitable and intellectually challenging new generation of scientific contributions on the long-term economic effects of pandemics.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Aassve A, Alfani G, Gandolfi F, Le Moglie M (2021) Epidemics and trust: the case of the Spanish flu. Health Econ 30(4):840–857
Article Google Scholar
Acemoglu D, Johnson S (2007) Disease and development: the effect of life expectancy on economic growth. J Polit Econ 115(6):925–985
Adda J (2016) Economic activity and the spread of viral diseases: evidence from high frequency data. Q J Econ 131(2):891–941
Adolph C, Amano K, Bang-Jensen B, Fullman N, Wilkerson J (2021) Pandemic politics: timing state-level social distancing responses to COVID-19. J Health Polit Policy Law 46(2):211–233
Alfani G (2013) Plague in seventeenth-century Europe and the decline of Italy: an epidemiological hypothesis. Eur Rev Econ Hist 17(4):408–430
Alfani G (2021) Economic inequality in preindustrial times: Europe and beyond. J Econ Lit 59(1):3–44
Alfani G, Percoco M (2019) Plague and long-term development: the lasting effects of the 1629–30 epidemic on the Italian cities. Econ Hist Rev 72(4):1175–1201
Almond D (2006) Is the 1918 influenza pandemic over? Long-term effects of in utero influenza exposure in the post-1940 US population. J Polit Econ 114(4):672–712
Arora S (2001) Health, human productivity, and long-term economic growth. J Econ Hist 61(3):699–749
Augier L, Yaly A (2013) Economic growth and disease in the OLG model: the HIV/AIDS case. Econ Model 33:471–481
Avery C, Bossert W, Clark A, Ellison G, Ellison SF (2020) An economist’s guide to epidemiology models of infectious disease. J Econ Perspect 34(4):79–104
Bai L, Wei Y, Wei G, Li X, Zhang S (2021) Infectious disease pandemic and permanent volatility of international stock markets: a long-term perspective. Financ Res Lett 40:101709
Bar M, Leukhina O (2010) The role of mortality in the transmission of knowledge. J Econ Growth 15(4):291–321
Basco S, Domènech J, Rosés JR (2021) The redistributive effects of pandemics: evidence on the Spanish flu. World Dev 141:105389
Beach B, Clay K, Saavedra MH (2021) The 1918 influenza pandemic and its lessons for COVID-19. J Econ Lit forthcoming
Bell C, Gersbach H (2009) The macroeconomics of targeting: the case of an enduring epidemic. J Health Econ 28(1):54–72
Birchenall JA (2007) Escaping high mortality. J Econ Growth 12(4):351–387
Bleakley H (2010) Health, human capital, and development. Ann Rev Econ 2(1):283–310
Bloom DE, Kuhn M, Prettner K (2021) Modern infectious diseases: macroeconomic impacts and policy responses. J Econ Lit forthcoming
Bloom DE, Mahal AS (1997) Does the AIDS epidemic threaten economic growth? J Econ 77(1):105–124
Bloom DE, Sachs JD (1998) Geography, demography, and economic growth in Africa. Brook Pap Econ Act 1998(2):207–295
Borsch S (2005) The black death in Egypt and England: a comparative study. University of Texas Press, Austin
Google Scholar
Borsch S (2015) Plague depopulation and irrigation decay in medieval Egypt. Med Globe 1(1):125–156
Boucekkine R, Diene B, Azomahou T (2008) Growth economics of epidemics: a review of the theory. Math Popul Stud 15(1):1–26
Bresalier M (2012) Uses of a pandemic: forging the identities of influenza and virus research in interwar Britain. Soc Hist Med 25(2):400–424
Büscher B, Feola G, Fischer AM, Fletcher R, Gerber JF, Harcourt W et al (2021) Planning for a world beyond COVID-19: five pillars for post-neoliberal development. World Dev 140:105357
Cacault MP, Hildebrand C, Laurent-Lucchetti J, Pellizzari M (2021) Distance learning in higher education: evidence from a randomized experiment. J Eur Econ Assoc 19(4):2322–2372
Cakici N, Zaremba A (2021) Who should be afraid of infections? Pandemic exposure and the cross-section of stock returns. J Int Financ Mark Inst Money 72:101333
Callegari B, Feder C (2021a) Entrepreneurship and the systemic consequences of epidemics: a literature review and emerging model. Int Entrepr Manag J. forthcoming
Callegari B, Feder C (2021b) The long-term economic effects of pandemics: toward an evolutionary approach. Industrial and corporate change; dtab064
Caserotti M, Girardi P, Rubaltelli E, Tasso A, Lotto L, Gavaruzzi T (2021) Associations of COVID-19 risk perception with vaccine hesitancy over time for Italian residents. Soc Sci Med 272:113688
Cavallo E, Galiani S, Noy I, Pantano J (2013) Catastrophic natural disasters and economic growth. Rev Econ Stat 95(5):1549–1561
Cervellati M, Sunde U (2011) Life expectancy and economic growth: the role of the demographic transition. J Econ Growth 16(2):99–133
Cervellati M, Sunde U (2015) The economic and demographic transition, mortality, and comparative development. Am Econ J Macroecon 7(3):189–225
Chakrabarty HS, Roy RP (2021) Pandemic uncertainties and fiscal procyclicality: a dynamic non-linear approach. Int Rev Econ Financ 72:664–671
Chen YE, Li C, Chang CP, Zheng M (2021) Identifying the influence of natural disasters on technological innovation. Econ Anal Pol 70:22–36
Cipolla CM (1974) The plague and the pre-Malthus Malthusians. J Eur Econ Hist 3(2):277–284
Clark G (2007) A farewell to alms: a brief economic history of the world. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Book Google Scholar
Cohen JM (2019) “Remarkable solutions to impossible problems”: lessons for malaria from the eradication of smallpox. Malar J 18(1):323
Confraria H, Wang L (2020) Medical research versus disease burden in Africa. Res Policy 49(3):103916
Costa DL (2015) Health and the economy in the United States from 1750 to the present. J Econ Lit 53(3):503–570
Costa Junior JC, Garcia-Cintado AC, Junior KM (2021) Macroeconomic policies and the pandemic-driven recession. Int Rev Econ Financ 72:438–465
Croce MM, Arteaga-Garavito MJ, Farroni P, Wolfskeil I (2021) When the markets get COVID: COntagion, viruses, and information diffusion. Working Papers
Cuddington JT (1993a) Modeling the macroeconomic effects of AIDS, with an application to Tanzania. World Bank Econ Rev 7(2):173–189
Cuddington JT (1993b) Further results on the macroeconomic effects of AIDS: the dualistic, labor-surplus economy. World Bank Econ Rev 7(3):403–417
Cuddington JT, Hancock JD (1994) Assessing the impact of AIDS on the growth path of the Malawian economy. J Dev Econ 43(2):363–368
Dauda RS (2019) HIV/AIDS and economic growth: evidence from West Africa. Int J Health Plann Manag 34(1):324–337
Deaton A (2004) Health in an age of globalization. National Bureau of Economic Research
Delfino D, Simmons PJ (2005) Dynamics of tuberculosis and economic growth. Environ Dev Econ 10(6):719–743
Dieppe A (2021) Global productivity: trends, drivers, and policies. World Bank Publications
Domar ED (1970) The causes of slavery or serfdom: a hypothesis. J Econ Hist 30(1):18–32
Donadelli M, Ferranna L, Gufler I, Paradiso A (2021) Using past epidemics to estimate the macroeconomic implications of COVID-19: a bad idea! Struct Chang Econ Dyn 57:214–224
Donadelli M, Kizys R, Riedel M (2017) Dangerous infectious diseases: bad news for main street, good news for wall street? J Financ Mark 35:84–103
Dosi G, Fanti L, Virgillito ME (2020) Unequal societies in usual times, unjust societies in pandemic ones. J Industr Bus Econ 47(3):371–389
Duncan-Jones RP (1996) The impact of the Antonine plague. J Roman Archaeol 9:108–136
Dunn SP (2006) Prolegomena to a post Keynesian health economics. Rev Soc Econ 64(3):273–299
Easterlin RA (1995) Industrial revolution and mortality revolution: two of a kind? J Evol Econ 5(4):393–408
Easterlin RA (1999) How beneficent is the market? A look at the modern history of mortality. Eur Rev Econ Hist 3(3):257–294
Epstein SR (2000) Freedom and growth: the rise of states and Markets in Europe, 1300–1750. Routledge, London
Evans DK, Miguel E (2007) Orphans and schooling in Africa: a longitudinal analysis. Demography 44(1):35–57
Favilukis, J., Lin, X., Sharifkhani, A. and Zhao X. (2021) Labor force telework flexibility and asset prices: evidence from the COVID-19 pandemic. Georgetown McDonough School of Business Research Paper, No. 3693239
Fawaz F, Frey E, Piscitiello D (2019) The effects of HIV mortality on saving and investment in Asia. Asian J Emp Res 9(1):1–15
Fiaschi D, Fioroni T (2019) Transition to modern growth in Great Britain: the role of technological progress, adult mortality and factor accumulation. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 51:472–490
Finkelstein A (2004) Static and dynamic effects of health policy: evidence from the vaccine industry. Q J Econ 119(2):527–564
Fortson JG (2011) Mortality risk and human capital investment: the impact of HIV/AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa. Rev Econ Stat 93(1):1–15
Gaffeo E (2003) The economics of HIV/AIDS: a survey. Dev Pol Rev 21(1):27–49
Gallup JL, Sachs JD (2001) The economic burden of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 64(1):85–96
Garrett TA (2008) Pandemic economics: the 1918 influenza and its modern-day implications. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Review 90(2):75–93
Gordon RJ (2016) The rise and fall of American growth: the US standard of living since the civil war. Princeton University Press, Princeton and Oxford
Gori L, Lupi E, Manfredi P, Sodini M (2020) A contribution to the theory of economic development and the demographic transition: fertility reversal under the HIV epidemic. J Demogr Econ 86(2):125–155
Gries T, Naudé W (2021) Extreme events, entrepreneurial start-ups, and innovation: theoretical conjectures. Econ Disast Clim Chang 5:329–353
Guerrieri V, Lorenzoni G, Straub L, Werning I (2020) Macroeconomic implications of COVID-19: can negative supply shocks cause demand shortages? (no. w26918). Natl Bur Econ Res
Gustafsson-Wright E, Janssens W, Van Der Gaag J (2011) The inequitable impact of health shocks on the uninsured in Namibia. Health Policy Plan 26(2):142–156
Habyarimana J, Mbakile B, Pop-Eleches C (2010) The impact of HIV/AIDS and ARV treatment on worker absenteeism implications for African firms. J Hum Resour 45(4):809–839
Halkos G, Zisiadou A (2019) Examining the natural environmental hazards over the last century. Econ Disasters Clim Chang 3(2):119–150
Hallegatte S, Vogt-Schilb A, Rozenberg J, Bangalore M, Beaudet C (2020) From poverty to disaster and back: a review of the literature. Econ Disasters Clim Chang 4(1):223–247
Harper KN (2016) People, plagues, and prices in the Roman world: the evidence from Egypt. J Econ Hist 76(3):803–839
Herlihy D (1997) The black death and the transformation of the west. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Hopkins JW (1988) The eradication of smallpox: organizational learning and innovation in international health administration. J Dev Areas 22(3):321–332
Jena PR, Majhi R, Kalli R, Managi S, Majhi B (2021) Impact of COVID-19 on GDP of major economies: application of the artificial neural network forecaster. Econ Anal Policy 69:324–339
Jinjarak Y, Noy I, Ta Q (2021) Pandemics and economic growth: evidence from the 1968 H3N2 influenza. Econ Disasters Clim Chang:1–21
Jordà Ò, Singh SR, Taylor AM (2021) Longer-run economic consequences of pandemics. Rev Econ Stat:1–29
Karlsson M, Nilsson T, Pichler S (2014) The impact of the 1918 Spanish flu epidemic on economic performance in Sweden: an investigation into the consequences of an extraordinary mortality shock. J Health Econ 36:1–19
Keerthiratne S, Tol RS (2017) Impact of natural disasters on financial development. Econ Disasters Clim Chang 1(1):33–54
Keogh-Brown MR, Wren-Lewis S, Edmunds WJ, Beutels P, Smith RD (2010) The possible macroeconomic impact on the UK of an influenza pandemic. Health Econ 19(11):1345–1360
Keohane GL (2016) Capital and the common good: how innovative finance is tackling the World’s Most urgent problems. Columbia University Press, New York
Kremer M (2000) Creating markets for new vaccines. Part I: Rationale. Innov Policy Econ 1:35–72
Lagerlöf NP (2003) From Malthus to modern growth: can epidemics explain the three regimes? Int Econ Rev 44(2):755–777
Leach M, MacGregor H, Scoones I, Wilkinson A (2021) Post-pandemic transformations: how and why COVID-19 requires us to rethink development. World Dev 138:105233
Lee JW, McKibbin WJ (2004) Globalization and disease: the case of SARS. Asian Econ Papers 3(1):113–131
Little LK (2007) Plague and the end of antiquity: the pandemic of 541–750. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lorentzen P, McMillan J, Wacziarg R (2008) Death and development. J Econ Growth 13(2):81–124
Mahal A (2004) Economic implications of inertia on HIV/AIDS and benefits of action. Econ Polit Wkly 39(10):1049–1063
Malthus TR (1798) An essay on the principle of population as it affects the future improvement of society, with remarks on the speculations of Mr. Godwin, M. Condorcet, and other writers. J. Johnson in St. Paul’s churchyard, London
Mandel A, Veetil V (2020) The economic cost of COVID lockdowns: an out-of-equilibrium analysis. Econ Disasters Clim Chang 4(3):431–451
Martin A, Markhvida M, Hallegatte S, Walsh B (2020) Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Econ Disasters Clim Chang 4(3):453–479
McCannon BC, Rodriguez Z (2019) Orphans and pro-social behaviour: evidence from Uganda. J Int Dev 31(6):495–515
McDonald S, Roberts J (2006) AIDS and economic growth: a human capital approach. J Dev Econ 80(1):228–250
Meyers K, Thomasson MA (2021) Can pandemics affect educational attainment? Evidence from the polio epidemic of 1916. Cliometrica 15(2):231–265
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097
Mokyr J (2010) Induced technical innovation and medical history: an evolutionary approach. In: Grübler A, Nakicenovic N, Nordhaus WD (eds) Technological change and the environment (pp. 46–66). Routledge
Murray EJ (2020) Epidemiology’s time of need: COVID-19 calls for epidemic-related economics. J Econ Perspect 34(4):105–120
Novella R (2018) Orphanhood, household relationships, school attendance and child labor in Zimbabwe. J Int Dev 30(5):725–744
Noy I, Managi S (2020) It’s awful, why did nobody see it coming? Econ Disasters Clim Chang 4(3):429–430
Odugbesan JA, Rjoub H (2019) Relationship among HIV/AIDS prevalence, human capital, good governance, and sustainable development: empirical evidence from sub-Saharan Africa. Sustainability 11(5):1348
Odugbesan JA, Rjoub H (2020) Evaluating HIV/AIDS prevalence and sustainable development in sub-Saharan Africa: the role of health expenditure. Afr Health Sci 20(2):568–578
Oster E (2012) Routes of infection: exports and HIV incidence in sub-Saharan Africa. J Eur Econ Assoc 10(5):1025–1058
Pagano M, Wagner C, Zechner J (2021) Disaster resilience and asset prices. Working Paper
Pamuk Ş (2007) The black death and the origins of the ‘great divergence’ across Europe, 1300–1600. Eur Rev Econ Hist 11(3):289–317
Parman J (2015) Childhood health and sibling outcomes: nurture reinforcing nature during the 1918 influenza pandemic. Explor Econ Hist 58:22–43
Poblete-Cazenave M (2021) Simulating the long-term impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the sustainability of the population-economy-environment nexus. Econ Disasters Clim Chang:1–16
Rassy D, Smith RD (2013) The economic impact of H1N1 on Mexico's tourist and pork sectors. Health Econ 22(7):824–834
Robinson JA, Acemoglu D (2012) Why nations fail: the origins of power, prosperity and poverty. Profile, London
Rodríguez-Caballero CV, Vera-Valdés JE (2020) Long-lasting economic effects of pandemics: evidence on growth and unemployment. Econometrics 8(3):37
Ru H, Yang E, Zou K (2021) Combating the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of the SARS imprint. Manag Sci 67(9):5606–5615
Sarris P (2002) The Justinianic plague: origins and effects. Contin Chang 17(2):169–182
Schumpeter JA (1954) History of economic analysis. Oxford University Press, New York
Silverio-Murillo A, Hoehn-Velasco L, de la Miyar JRB, Rodríguez A (2021) COVID-19 and women’s health: examining changes in mental health and fertility. Econ Lett 199:109729
Stiglitz JE, Guzman MM (2021) The pandemic economic crisis, precautionary behavior, and mobility constraints: an application of the dynamic disequilibrium model with randomness. Ind Corp Chang 30(2):467–497
Tokic D (2020) Long-term consequences of the 2020 coronavirus pandemics: historical global-macro context. J Corp Account Financ 31(3):9–14
Verikios G (2020) The dynamic effects of infectious disease outbreaks: the case of pandemic influenza and human coronavirus. Socio Econ Plan Sci 71:100898
Voigtländer N, Voth H-J (2013) The three horsemen of riches: plague, war, and urbanization in early modern Europe. Rev Econ Stud 80(2):774–811
Wallace ML, Ràfols I (2018) Institutional shaping of research priorities: a case study on avian influenza. Res Policy 47(10):1975–1989
Weil DN (2014) Health and economic growth. In: Aghion P, Durlauf S (eds) Handbook of economic growth, edition 1, volume 2, chapter 3 (pp. 623–82). Elsevier
Wobst P, Arndt C (2004) HIV/AIDS and labor force upgrading in Tanzania. World Dev 32(11):1831–1847
World Bank (2020) Global economic prospects, June 2020. World Bank, Washington, DC
Young A (2005) The gift of the dying: the tragedy of AIDS and the welfare of future African generations. Q J Econ 120(2):423–466
Zinyemba TP, Pavlova M, Groot W (2020) Effects of HIV/AIDS on children’s educational attainment: a systematic literature review. J Econ Surv 34(1):35–84
Download references
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the editor and the two referees for their useful comments. The usual disclaimer applies.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Oslo New University College, Oslo, Norway
Beniamino Callegari
Kristiania University College, Oslo, Norway
CT-TEM - Università della Valle d’Aosta, Aosta, Italy
Christophe Feder
BRICK - Collegio Carlo Alberto, Turin, Italy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christophe Feder .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest and that no funding has been associated with the writing of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Economics of COVID-19
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Callegari, B., Feder, C. A Literature Review of Pandemics and Development: the Long-Term Perspective. EconDisCliCha 6 , 183–212 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41885-022-00106-w
Download citation
Received : 26 October 2021
Accepted : 09 January 2022
Published : 27 January 2022
Issue Date : March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s41885-022-00106-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health Shock
- Human Capital
JEL classifications
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
Taking AI to the next level in manufacturing
Reducing data, talent, and organizational barriers to achieve scale.
- MIT Technology Review Insights archive page
In partnership with Microsoft
Few technological advances have generated as much excitement as AI. In particular, generative AI seems to have taken business discourse to a fever pitch. Many manufacturing leaders express optimism: Research conducted by MIT Technology Review Insights found ambitions for AI development to be stronger in manufacturing than in most other sectors.

Manufacturers rightly view AI as integral to the creation of the hyper-automated intelligent factory. They see AI’s utility in enhancing product and process innovation, reducing cycle time, wringing ever more efficiency from operations and assets, improving maintenance, and strengthening security, while reducing carbon emissions. Some manufacturers that have invested to develop AI capabilities are still striving to achieve their objectives.
This study from MIT Technology Review Insights seeks to understand how manufacturers are generating benefits from AI use cases—particularly in engineering and design and in factory operations. The survey included 300 manufacturers that have begun working with AI. Most of these (64%) are currently researching or experimenting with AI. Some 35% have begun to put AI use cases into production. Many executives that responded to the survey indicate they intend to boost AI spending significantly during the next two years. Those who haven’t started AI in production are moving gradually. To facilitate use-case development and scaling, these manufacturers must address challenges with talents, skills, and data. Following are the study’s key findings:
- Talent, skills, and data are the main constraints on AI scaling. In both engineering and design and factory operations, manufacturers cite a deficit of talent and skills as their toughest challenge in scaling AI use cases. The closer use cases get to production, the harder this deficit bites. Many respondents say inadequate data quality and governance also hamper use-case development. Insufficient access to cloud-based compute power is another oft-cited constraint in engineering and design.
- The biggest players do the most spending, and have the highest expectations. In engineering and design, 58% of executives expect their organizations to increase AI spending by more than 10% during the next two years. And 43% say the same when it comes to factory operations. The largest manufacturers are far more likely to make big increases in investment than those in smaller—but still large—size categories.
- Desired AI gains are specific to manufacturing functions. The most common use cases deployed by manufacturers involve product design, conversational AI, and content creation. Knowledge management and quality control are those most frequently cited at pilot stage. In engineering and design, manufacturers chiefly seek AI gains in speed, efficiency, reduced failures, and security. In the factory, desired above all is better innovation, along with improved safety and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Scaling can stall without the right data foundations. Respondents are clear that AI use-case development is hampered by inadequate data quality (57%), weak data integration (54%), and weak governance (47%). Only about one in five manufacturers surveyed have production assets with data ready for use in existing AI models. That figure dwindles as manufacturers put use cases into production. The bigger the manufacturer, the greater the problem of unsuitable data is.
- Fragmentation must be addressed for AI to scale. Most manufacturers find some modernization of data architecture, infrastructure, and processes is needed to support AI, along with other technology and business priorities. A modernization strategy that improves interoperability of data systems between engineering and design and the factory, and between operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT), is a sound priority.
Artificial intelligence
Large language models can do jaw-dropping things. but nobody knows exactly why..
And that's a problem. Figuring it out is one of the biggest scientific puzzles of our time and a crucial step towards controlling more powerful future models.
- Will Douglas Heaven archive page
Google DeepMind’s new generative model makes Super Mario–like games from scratch
Genie learns how to control games by watching hours and hours of video. It could help train next-gen robots too.
What’s next for generative video
OpenAI's Sora has raised the bar for AI moviemaking. Here are four things to bear in mind as we wrap our heads around what's coming.
The AI Act is done. Here’s what will (and won’t) change
The hard work starts now.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
The various domains to be covered for my essay writing.
If you are looking for reliable and dedicated writing service professionals to write for you, who will increase the value of the entire draft, then you are at the right place. The writers of PenMyPaper have got a vast knowledge about various academic domains along with years of work experience in the field of academic writing. Thus, be it any kind of write-up, with multiple requirements to write with, the essay writer for me is sure to go beyond your expectations. Some most explored domains by them are:
- Project management
Finished Papers
Customer Reviews
Finished Papers

- Human Resource
- Business Strategy
- Operations Management
- Project Management
- Business Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Scholarship Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Buy Essay Online
- College Essay Help
- Help To Write Essay Online
Johan Wideroos
How do essay writing services work?
In the modern world, any company is trying to modernize its services. And services for writing scientific papers are no exception. Therefore, now it is very easy to order work and does not take time:
- First, you need to choose a good site that you can trust. Read their privacy policies, guarantees, payment methods and of course reviews. It will be a big plus that examples of work are presented on the online platform.
- Next, you need to contact a manager who will answer all the necessary questions and advise on the terms of cooperation. He will tell you about the acceptable writing deadlines, provide information about the author, and calculate the price of the essay.
- After that, you sign the contract and during the indicated days stay in touch with the employee of the company.
- Then you receive the file, read it attentively and transfer a certain amount to the company's bank card. After payment, the client downloads the document to his computer and can write a review and suggestions.
On the site Essayswriting, you get guarantees, thanks to which you will be confident and get rid of the excitement. The client can ask any questions about the writing and express special preferences.
Eloise Braun
Evidence Review of the Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccination and Intramuscular Vaccine Administration
Vaccines are a public health success story, as they have prevented or lessened the effects of many infectious diseases. To address concerns around potential vaccine injuries, the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) administers the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program (VICP) and the Countermeasures Injury Compensation Program (CICP), which provide compensation to those who assert that they were injured by routine vaccines or medical countermeasures, respectively. The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine have contributed to the scientific basis for VICP compensation decisions for decades.
HRSA asked the National Academies to convene an expert committee to review the epidemiological, clinical, and biological evidence about the relationship between COVID-19 vaccines and specific adverse events, as well as intramuscular administration of vaccines and shoulder injuries. This report outlines the committee findings and conclusions.
Read Full Description
- Digital Resource: Evidence Review of the Adverse Effects of COVID-19 Vaccination
- Digital Resource: Evidence Review of Shoulder Injuries from Intramuscular Administration of Vaccines
- Press Release
Recent News
NAS Launches Science and Innovation Fund for Ukraine
Science Academies Issue Statements to Inform G7 Talks
Supporting Family Caregivers in STEMM
A Vision for High-Quality Preschool for All
- Load More...
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Youth Gender Medications Limited in England, Part of Big Shift in Europe
Five European countries have recently restricted hormone treatments for adolescents with gender distress. They have not banned the care, unlike many U.S. states.

By Azeen Ghorayshi
Azeen Ghorayshi reports on transgender health and visited the world’s first youth gender clinic in Amsterdam this fall.
The National Health Service in England started restricting gender treatments for children this month, making it the fifth European country to limit the medications because of a lack of evidence of their benefits and concern about long-term harms.
England’s change resulted from a four-year review released Tuesday evening by Dr. Hilary Cass, an independent pediatrician. “For most young people, a medical pathway will not be the best way to manage their gender-related distress,” the report concluded. In a related editorial published in a medical journal, Dr. Cass said the evidence that youth gender treatments were beneficial was “built on shaky foundations.”
The N.H.S. will no longer offer drugs that block puberty , except for patients enrolled in clinical research. And the report recommended that hormones like testosterone and estrogen, which spur permanent physical changes, be prescribed to minors with “extreme caution.” (The guidelines do not apply to doctors in private practice, who serve a small fraction of the population.)
England’s move is part of a broader shift in northern Europe, where health officials have been concerned by soaring demand for adolescent gender treatments in recent years. Many patients also have mental health conditions that make it difficult to pinpoint the root cause of their distress, known as dysphoria.
In 2020, Finland’s health agency restricted the care by recommending psychotherapy as the primary treatment for adolescents with gender dysphoria. Two years later, Sweden restricted hormone treatments to “exceptional cases.”
In December, regional health authorities in Norway designated youth gender medicine as a “treatment under trial,” meaning hormones will be prescribed only to adolescents in clinical trials. And in Denmark, new guidelines being finalized this year will limit hormone treatments to transgender adolescents who have experienced dysphoria since early childhood.
Several transgender advocacy groups in Europe have condemned the changes , saying that they infringe on civil rights and exacerbate the problems of overstretched health systems. In England, around 5,800 children were on the waiting list for gender services at the end of 2023, according to the N.H.S.
“The waiting list is known to be hell,” said N., a 17-year-old transgender boy in southern England who requested to withhold his full name for privacy. He has been on the waiting list for five years, during which time he was diagnosed with autism and depression. “On top of the trans panic our own government is pushing, we feel forgotten and left behind,” he said.
In the United States, Republican politicians have cited the pullback in Europe to justify laws against youth gender medicine. But the European policies are notably different from the outright bans for adolescents passed in 22 U.S. states, some of which threaten doctors with prison time or investigate parents for child abuse. The European countries will still allow gender treatments for certain adolescents and are requiring new clinical trials to study and better understand their effects.
“We haven’t banned the treatment,” said Dr. Mette Ewers Haahr, a psychiatrist who leads Denmark’s sole youth gender clinic, in Copenhagen. Effective treatments must consider human rights and patient safety, she said. “You have to weigh both.”
In February, the European Academy of Paediatrics acknowledged the concerns about youth gender medicine. “The fundamental question of whether biomedical treatments (including hormone therapy) for gender dysphoria are effective remains contested,” the group wrote. In contrast, the American Academy of Pediatrics last summer reaffirmed its endorsement of the care, stating that hormonal treatments are essential and should be covered by health insurers, while also commissioning a systematic review of evidence.
Europeans pioneered the use of gender treatments for young people. In the 1990s, a clinic in Amsterdam began giving puberty-suppressing drugs to adolescents who had felt they were a different gender since early childhood.
The Dutch doctors reasoned that puberty blockers could give young patients with gender dysphoria time to explore their identity and decide whether to proceed with hormones to ultimately transition. For patients facing male puberty, the drugs would stave off the physical changes — such as a deeper voice and facial hair — that could make it more difficult for them to live as women in adulthood. The Dutch team’s research, which was first published in 2011 and tracked a carefully selected group of 70 adolescents, found that puberty blockers, in conjunction with therapy, improved psychological functioning.
That study was hugely influential, inspiring clinics around the world to follow the Dutch protocol. Referrals to these clinics began to surge around 2014, though the numbers remain small. At Sweden’s clinic, for example, referrals grew to 350 adolescents in 2022 from around 50 in 2014. In England, those numbers grew to 3,600 referrals in 2022 from 470 in 2014.
Clinics worldwide reported that the increase was largely driven by patients raised as girls. And unlike the participants in the original Dutch study, many of the new patients did not experience gender distress until puberty and had other mental health conditions, including depression and autism.
Given these changes, some clinicians are questioning the relevance of the original Dutch findings for today’s patients.
“The whole world is giving the treatment, to thousands, tens of thousands of young people, based on one study,” said Dr. Riittakerttu Kaltiala, a psychiatrist who has led the youth gender program in Finland since 2011 and has become a vocal critic of the care.
Dr. Kaltiala’s own research found that about 80 percent of patients at the Finnish clinic were born female and began experiencing gender distress later in adolescence. Many patients also had psychological issues and were not helped by hormonal treatments, she found. In 2020, Finland severely limited use of the drugs.
Around the same time, the Swedish government commissioned a rigorous research review that found “insufficient” evidence for hormone therapies for youth. In 2022, Sweden recommended hormones only for “exceptional cases,” citing in part the uncertainty around how many young people may choose to stop or reverse their medical transitions down the line, known as detransitioning.
Even the original Dutch clinic is facing pressure to limit patients receiving the care. In December, a public documentary series in the Netherlands questioned the basis of the treatments. And in February, months after a far-right political party swept an election in a country long known as socially liberal , the Dutch Parliament passed a resolution to conduct research comparing the current Dutch approach with that of other European countries.
“I would have liked that the Netherlands was an island,” said Dr. Annelou de Vries, a psychiatrist who led the original Dutch research and still heads the Amsterdam clinic. “But of course, we are not — we are also part of the global world. So in a way, if everybody is starting to be concerned, of course, these concerns come also to our country.”
In England, brewing concerns about the surge of new patients reached a boiling point in 2018, when 10 clinicians at the N.H.S.’s sole youth gender clinic, known as the Tavistock Gender Identity Development Service, formally complained that they felt pressure to quickly approve children, including those with serious mental health problems, for puberty blockers.
In 2021, Tavistock clinicians published a study of 44 children who took puberty blockers that showed a different result from the Dutch: The patients given the drugs, on average, saw no impact on psychological function.
Although the drugs did not lessen thoughts of self-harm or the severity of dysphoria, the adolescents were “resoundingly thrilled to be on the blocker,” Dr. Polly Carmichael, the head of the clinic, said at a 2016 conference . And 43 of the 44 study participants later chose to start testosterone or estrogen, raising questions about whether the drug was serving its intended purpose of giving adolescents time to consider whether a medical transition was right for them.
In 2020, the N.H.S. commissioned Dr. Cass to carry out an independent review of the treatments. She commissioned scientific reviews and considered international guidelines of the care. She also met with young people and their families, trans adults, people who had detransitioned, advocacy groups and clinicians.
The review concluded that the N.H.S.’s standard of care was inadequate, with long waiting lists for access to drug treatments and few routes to address the mental health concerns that may be contributing to gender distress. The N.H.S. shuttered the Tavistock center last month and opened two new youth gender clinics, which Dr. Cass said should have a “holistic” approach, with more support for those with autism, depression and eating disorders, as well as psychotherapy to help adolescents explore their identities.
“Children and young people have just been really poorly served,” Dr. Cass said in an interview with the editor of The British Medical Journal, released Tuesday. She added, “I can’t think of another area of pediatric care where we give young people potentially irreversible treatments and have no idea what happens to them in adulthood.”
The changes enacted by the N.H.S. this month are “an acknowledgment that our concerns were, in fact, valid,” said Anna Hutchinson, a clinical psychologist in London who was one of the Tavistock staff members who raised concerns in 2018. “It’s reassuring that we’re going to return to a more robust, evidence-based pathway for decisions relating to these children.”
Some critics said that Europe, like the United States, had also been influenced by a growing backlash against transgender people.
In Britain, for example, a yearslong fight over a proposed law that would have made it easier for transgender people to change the gender on their identification documents galvanized a political movement to try to exclude transgender women from women’s sports, prisons and domestic violence shelters.
“The intention with the Cass review is to be neutral, but I think that neutral has maybe moved,” said Laurence Webb, a representative from Mermaids, a trans youth advocacy organization in Britain. “Extremist views have become much more normalized.”
Other countries have seen more overt attacks on transgender rights and health care. In 2020, Hungary’s Parliament passed a law banning gender identity changes on legal documents. Last year, Russia banned legal gender changes as well as gender-related medical care, with one lawmaker describing gender surgeries as the “path to the degeneration of the nation.”
In France this year, a group of conservative legislators introduced a bill to ban doctors from prescribing puberty blockers and hormones, with punishments of two years’ imprisonment and a fine of 30,000 euros, or about $32,600. And on Monday, the Vatican condemned gender transitions as threats to human dignity.
Azeen Ghorayshi covers the intersection of sex, gender and science for The Times. More about Azeen Ghorayshi

COMMENTS
This systematic literature review summarizes the current academic knowledge about organizational factors that influence 21st-century skills on an individual level. A search was performed in three databases. ... In creativity research, the study of organizational factors influencing individual creativity goes back decades, as is shown in the ...
Some interesting conceptual and methodological insights emerge from our literature review. First, there's a growing interest, almost like a revival, of research on organizational goals from different research streams, with about 25 per cent of the articles included in the review published in the last three years.
A Literature Review of Organizational Behavior Management Interventions in Human Service Settings from 1990 to 2016. ... Data on the roles served by study participants were coded across the follow-
Organisations across the globe are looking to become agile and are seeking leaders to guide their transformation to agility. This paper conducts a systematic literature review across eighty-six papers spanning over 25 years (1999-2023), to develop an overview of how leadership agility is conceptualized in the context of organisational agility in the extant literature. This systematic review ...
The literature review comprised various published sources on the role of organizational culture, such as journals, periodicals, seminal books, and other published materials. The review focused on ...
This study conducted an extensive literature review, including a review of books, journals, databases, and several publications from world-renowned consulting firms specializing in change management. This review yielded the list of models of organizational change management shown in Table 2.
We conducted a general, semi-systematic literature review on organizational justice. Based on this review, we first explored the various ways in which organizational justice was conceptualized. ... Organizational justice is the study of employees' perceptions of justice in the workplace (Colquitt, 2001). Prior research shows that employees ...
Strategic leadership is concerned with capabilities of creating a sense o f. purpose and direction, critical enablers that allow interaction with key internal. and external stake holders in ...
A systematic literature review (SLR) was carried out, using the Prisma method, in a first phase, and the IraMuteQ software to operationalise the bibliometrics. ... The objective of this study, to identify Organisational Agility's contributions to good interaction in the flow of processes between the company's departments as well as the ...
Research on motivation has attracted academic and corporate entities over the last two decades. In the present study, authors have reviewed the intense literature to extract all possible dimensions of motivation, having direct and indirect impact on motivation techniques. This has examined the multidimensionality of motivation from the existing literature and present a conceptual framework ...
Purpose - Organizational climate affects and influence the employees' performance, motivation, and job satisfaction. The purpose of this research is to synthesize existing literature on organizational climate in order to broaden and clarify the scope of future research on the subject. Methodology and Approach- For readers to obtain a better understanding of the idea, this study gives a ...
2.1. Sample. The data for this study were retrieved from the Web of Science on September 28, 2022. Web of Science was chosen as the search engine because it is the most widely accepted and commonly used database for analysing scientific publications [].The terms "organisational culture", "hospital culture", "health care", and "hospital" were used as search topics.
Following the introductory section, there is the section dedicated to the literature review, which serves as a theoretical basis for the empirical research. ... Based on the results of the study, organizational pride was also significantly influenced by job satisfaction due to CSR (β = 0.385, p ˂ 0.01, t = 4.2), supporting H3. According to ...
Create an organizational method to focus this section even further. To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario and then three typical ways of organizing the sources into a review: You've decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales.
the study. The organization culture is analyzed from a set of dimensions which are involvements, collaboration, and transmission of information, learning, and care about clients, ... Literature Review on Organization Culture . IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development| Vol. 4, Issue 02, 2016 | ISSN (online): 2321-0613 ...
this research study examines the possible literature review of the impact of human resource. management on organizational performance. Control is made feasible by m anagement, which allows. for ...
This is an ideal situation. In most cases, there will be several different possible structures for your review. Similarly to the structure of the research report itself, the literature review consists of: Introduction; Body; Conclusion; Introduction - profile of the study. Define or identify the general topic to provide the context for ...
Pandemics have been a long-standing object of study by economists, albeit with declining interest, that is until COVID-19 arrived. We review current knowledge on the pandemics' effects on long-term economic development, spanning economic and historical debates. We show that all economic inputs are potentially affected. Pandemics reduce the workforce and human capital, have mixed effects on ...
The findings provide five valuable contributions to the literature as a result. First, this study empirically proves new relationships in an integrative model demonstrating that based on the hypothesis (H 1) and (H 2), Sensing (S) gives a positive and significant effect on technological innovation and marketing innovation, confirming the (Ahmed ...
In engineering and design, 58% of executives expect their organizations to increase AI spending by more than 10% during the next two years. And 43% say the same when it comes to factory operations.
Food insecurity is an economic and social condition that involves individuals having limited or uncertain access to healthy food. Despite the well-intentioned efforts of both governmental and not-for-profit organizations in addressing food insecurity, well over one-in-ten households in the U.S., the wealthiest nation in the world, experience food insecurity every year. The objective of this ...
Literature review. Mixed Martial Arts (MMA) is a combat sport that combines the rules and practices of several martial arts. In the 1990s, tournaments were held with minimal rules and were characterised by violent conduct that resulted in political and public pressure to ban the sport (Hill Citation 2013).Political opposition was notable from senator John McCain who labelled the sport 'human ...
such as people, rule, goal an d innovation -oriented climate. In other words, "Organizational Climate" is a lso known as c orporate climate it h as huge impact. on employees' productivity ...
Literature Review Of Organisational Study, What Is A Star Worksheets Middle School, Cover Letter Same Company, Mock Application Letter, Sitefinity Developer Resume, Best Critical Essay Ghostwriter Site Gb, Gcse English Coursework Mark Scheme 1800 . Finished Papers ...
Finished Papers. 4950. Customer Reviews. ID 14317. Critical Thinking Essay on Nursing. Literature Review Of Organisational Study, How Much Does It Cost To Have A Business Plan Writing Uk, White Collar Crime Thesis Executive Summary, Herbert Great Expectations Essay, Tamu Uwc Cover Letter, Essays Editor Services Us, Science Essay Topics For 8th ...
Literature Review Of Organisational Study, Curriculum Vitae Timor Leste, Good Essay Titles About Football, Going Over The Word Limit On College Essay, Essay On Sun In Sanskrit Language, Best Persuasive Essay Editor Services Online, Research Paper On Iron Deficiency Anemia
To conduct a further study of the concept of Organizational Justice, this research was conducted using the literature review method. The study includes the definition, dimensions, antecedents, and ...
WASHINGTON — A new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine reviews evidence for 19 potential harms of the COVID-19 vaccines, and for nine potential shoulder injuries from intramuscular administration of vaccines more broadly. The committee that conducted the review identified sufficient evidence to draw 20 conclusions about whether these vaccines could cause ...
A combination of a literature review and research action was employed to this end. Specifically, an in-depth review of 37 organizational change management models was conducted to identify the ...
The review concluded that the N.H.S.'s standard of care was inadequate, with long waiting lists for access to drug treatments and few routes to address the mental health concerns that may be ...