Home Collections Medical Science Research Research Objectives Presentation

Free - Research Objectives PPT Presentation And Google Slides

Research Objectives Presentation Slides
Features of the templates:.
- 100% customizable slides and easy to download
- The slides contained 16:9 and 4:3 formats.
- Easy to change the slide colors quickly.
- Planets animation inserted template.
- Ready-made nodes are given to you.
- science research
- Objectives Operations Research
- Research Objectives
- Research Questions
- Key Objectivies
- Project Objectives
- Research Proposal
- Business Objectives
- Google Slides

667+ Templates
-594.webp)
124+ Templates

Science & Research
182+ Templates

Telemedicine
40+ Templates

322+ Templates

86+ Templates

115+ Templates

44+ Templates

191+ Templates
You May Also Like These PowerPoint Templates


Research Planning
What do you think of this template.

Product details
You have probably often come across the fact that after coming home from the supermarket, you find that you forgot to buy some groceries. So that the next time the situation does not repeat itself, you make a detailed shopping list. When preparing to research an important topic, be it in the field of marketing or scientific research, it is important to draw up a research plan. It is very important to plan research. You can’t undertake effective research without planning the process and setting yourself clear objectives. The research process has nine stages – Write a Research Brief, Define The Issue, Set Research Objectives, Research Proposal and Plan of Work, Collection of Data, Analysis and Evaluation of Data, Presentation Of Findings, Evaluation of Research, Conclusion. In the first step, you inform what you will research. Then you need to identify the problems that prompted you to do this research. The next stage of the research will be the setting of specific goals and objectives of the research. Next, you present your work plan and indicate the preliminary time frame for each stage. Collecting data and defining methods for collecting data will be your next step. After collecting data, you can analyse it and deduce patterns or dependencies. In the final stages, you will present the data in the form of tables, graphs or charts so that your audience can easily understand your presentation. When developing a research plan, you must also consider the possibility of using various innovative technologies that will help you analyse the data and eliminate the possibility of error due to human error.
The Research Planning template contains four professional slides in a cool colour scheme. All slides in this template have the necessary tools to build a professional presentation. You can present the objectives of your research and give a brief description. The first slide of this template gives you the opportunity to present up to eight steps of your research plan. This slide can also be used by engineers when describing sequential actions in the operation of equipment. The slides of this template can be useful for researchers when preparing studies in various fields of science. Marketers and salespeople can use the slides from this template when preparing market research and competitor plan. Also, this template can be used by students in the preparation of term papers and theses. The slides of this template will also be useful for research institutes and laboratory workers. Medical professionals can use this template when preparing research on various diseases or developing new treatments. Also, this template can be used when preparing a sample research paper plan for obtaining a grant. If necessary, you can independently edit the Research Planning template according to your needs. This template will be a worthy addition to your presentation collection.
Related Products
Project Kickoff
Ruler Timeline
Stakeholder Engagement Plan

5 Year Plan

Strategic Account Planning

Pay Per Click

PowerPoint Stopwatch
Product Plan

Journey Road Maps
You dont have access, please change your membership plan., great you're all signed up..., verify your account.
PowerSlides.com will email you template files that you've chosen to dowload.
Please make sure you've provided a valid email address! Sometimes, our emails can end up in your Promotions/Spam folder.
Simply, verify your account by clicking on the link in your email.

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
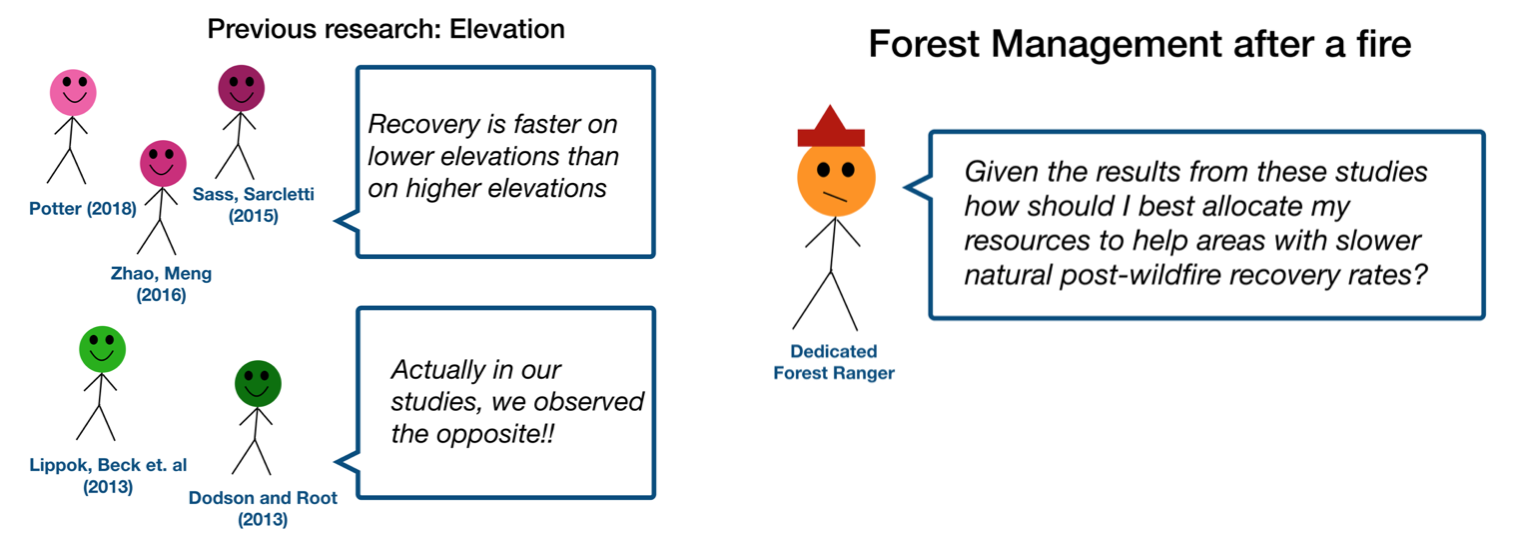
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr


Overview of the Research Process
Apr 07, 2019
230 likes | 631 Views
Overview of the Research Process. Krannert Memorial Library. Library and Information Literacy Tutorials. Module 1. The Research Process can be simple or complex, quick or lengthy, depending on the complexity of your information needs. Module 1: Overview of the Research Process.
Share Presentation
- specific questions
- research process go
- research guides
- best resources step
- information literacy tutorials module

Presentation Transcript
Overview of the Research Process Krannert Memorial Library Library and Information Literacy Tutorials Module 1
The Research Process can be simple or complex, quick or lengthy, depending on the complexity of your information needs. Module 1: Overview of the Research Process • But in general, the process goes like this:
Step 1Identify and refine your topic Step 2 Identify your best resources Step 3 Access and search the resources Step 4 Evaluate results and repeat Steps 1 – 3 as needed! Module 1: Overview of the Research Process
Having the “big picture” in mind is helpful … it can keep you from getting bogged down in all the details once you actually start your research. Module 1: Overview of the Research Process • In the rest of this module, we will very brieflydescribe the kinds of activities you will do in each of the four steps of the research process. Later modules will cover in depth the skills and tools you will be using.
Step 1Identify and refine your topic Brainstorm Talk to professor(s) Module 1: Overview of the Research Process Check encyclopedias, Internet, textbooks, etc. for general information on your topic Consult with Writing Lab tutors State your topic as a question you want to answer (or a set of questions) Use your questions to identify keywords and concepts
Step 2 Identify your best resources • Brainstorm: What kind of materials would have the kind of information I need to answer my questions … Books? Scholarly Journals? Information from government or non-profit organizations? Popular or Trade Journals? Newspapers? …? Consult Research Guideson the KML website Module 1: Overview of the Research Process Go to Databases – By Subjecton the KML website Consult with Reference Librarian Talk to your professor
Step 3 Access and search the resources Find books and audiovisual materials Search library catalog & WorldCat Module 1: Overview of the Research Process Find journal articles Search databases Use Internet search engines and directories Find Internet sites Construct search queries that are appropriate to each resource
Second Pass Detailed investigation of specific questions and issues First Pass Third Pass Exploring topic Following up Step 1 Step 1 Step 1 Step 2 Step 2 Step 2 Step 3 Step 3 Step 3 Step 4 Step 4 Step 4 Step 4 Evaluate results and repeat Steps 1 – 3 as needed! Module 1: Overview of the Research Process
Step 1 Identify and refine your topic Brainstorm Consult professors, encyclopedias, Writing Lab, etc. Formulate qustions Identify keywords and concepts Step 2 Identify your best resources Brainstorm Consult library Research Guides, Reference Librarians, professors, Databases – By Subject library web page Module 1: Overview of the Research Process Step 3 Access and search the resources Construct search queries that are appropriate to each resource Step 4 Evaluate results and repeat Steps 1 – 3 as needed! For example, in your first pass through the process, you may be exploring a topic – doing preliminary research. In the second pass, you would focus your search on specific issues you identified in your exploration phase. In the third pass, you may need to find additional information that you had not considered before doing more in-depth research.
This concludes Module 1, our overview of the research process. • The remaining modules describe and demonstrate the tools you will be using during this process. Module 1: Overview of the Research Process
- More by User

Overview of the Research Process in Economics
Overview of the Research Process in Economics. Researchers in Economics, as a social science, use a version of the scientific method . The scientific method is a set of procedures for drawing valid, reliable, and objective conclusions. The scientific Method.
275 views • 5 slides

Overview of the RIA Process
Overview of the RIA Process. - Bryan Hubbell. Goals of an RIA. Provide national estimates of costs and benefits of fully attaining current and proposed NAAQS Analyze proposed standard(s) and at least one more and one less stringent standard
319 views • 7 slides

The Marketing Research Process: An Overview
The Marketing Research Process: An Overview. Chapter 3. Types of Marketing Research. Exploratory Descriptive Causal Concomitant variation. The Research Process. Defining the Problem Planning a Research Design Sampling Gathering the Data Processing and Analyzing the Data
415 views • 10 slides

Overview of the Compliance Process
Overview of the Compliance Process. Bureau of Waste Management. August 14, 2019. Overview of the Compliance Process. Regulatory Background. EPA promulgated and implemented regulations under RCRA to protect human health and the environment.
147 views • 7 slides

Overview of the Budget Process
Overview of the Budget Process. PLESD Budget Committee November 5, 2009. The “Normal” State Process. January 15 th - Governor’s Proposal May 15 th - Governor’s May Revise June 15 th the Legislature must submit a budget to the Governor. The State has met this 1 time since 1989.
202 views • 10 slides

Overview of the Disability Process
Overview of the Disability Process. Definition of Disability.
234 views • 13 slides

Overview of the action research process
Overview of the action research process. Chapter 2. Craig A. Mertler SAGE Publications, 2014. Action Research: Improving Schools and Empowering Educators (4/e). The Action Research Process. Four stages: The planning stage The acting stage
542 views • 9 slides

Overview of the Labeling Process
Overview of the Labeling Process. Labels. Proper and accurate labeling is one of the most important aspects of the study. Each woman, child, and man selected for the survey will have their own individual set of labels.
317 views • 19 slides

Overview of the VR Process
Overview of the VR Process. An Overview. The VR Process consists of:. 1. Outreach 2. Screening the Contact 3. Application 4. Initial Intake Interview 5. Eligibility Determination 6. Plan Development 7. VR Services provision 8. Closure/Employment Outcome 9. Post Employment Services.
286 views • 18 slides

Overview of the Aging Process
Overview of the Aging Process. Related Health Changes and Challenges. When Does Aging Begin?. Aging begins the day we are born No single measure of how “old” a person is Aging is highly individualized
553 views • 16 slides

Overview of the Design Process
Overview of the Design Process. User Centered Design. “Every designer wants to build a high-quality interactive system that is admired by colleagues, celebrated by users, circulated widely, and imitated frequently.” (Shneiderman, 1992, p.7) …and anything goes!…. Good Design (reminder!).
525 views • 31 slides

Overview of the Tender Process
Overview of the Tender Process. Danesh Sharma Category Manager Procurement & Commercial Function. Invitation to Tender. Competitive Open Tender Responses to set questions, with page length limits Evaluation criteria must be addressed Weighted scores, split between technical and commercial.
429 views • 4 slides

An Overview of the Process
An Overview of the Process. Potential Review need emerges. Risk Potential Assessment Form sent to SRO. PPM-CoE source and propose Review Team membership & key dates. PPM-CoE send Summary of Recs to SRO and AO. PPM-CoE arrange Assessment Meeting (ASM).
78 views • 1 slides

Nebraska ’ s Statewide Professional Development Institute. An Overview of the Process. What is the Learning Web Project?. Teams of teachers Year-long action plans for technology integration Meets national staff development standards Meets school improvement goals
253 views • 17 slides

Overview of the Surrogacy Process
The ray of hope is enough to make these unfortunate couples happy and undergo treatments for the same. Out of all the IVF or in vitro fertilization treatments available for the infertile couples, surrogacy is quite common. And if you are also confused as to why surrogacy is best or whether you must choose the surrogacy treatments or not Visit Progenesisivf Clinic today and get the detail information about Surrogacy. https://www.progenesisivf.com/blog/overview-of-the-surrogacy-process/
65 views • 5 slides

overview of The Research Process
overview of The Research Process. Islamic University College of Nursing. Introduction. The steps of the research process are systematic and orderly and relate to both nursing theory and nursing practice. The steps of the research process generally proceed in order (table 4-1).
474 views • 45 slides

Overview of the Research Process. These outlines of the research process were created using the book Schaum’s Quick Guide to Writing Great Research Papers by Laurie Rozakis, Ph.D. Overview of the Research Process. Choosing a Topic Selecting Sources Evaluating Sources Documenting Sources
123 views • 8 slides

327 views • 31 slides

Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process
Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process. Week 3/4. Critical Reading & Thinking. Critical reading is a technique for discovering information and ideas within a text.
202 views • 19 slides

Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process. Week 3. Critical Thinking. A rational examination of ideas, inferences, principles, conclusions Uses criteria for critiquing Clarifies Considers content appropriateness Questions own thinking Uses skepticism. Critical Reading.
598 views • 21 slides

RESEARCH PROCESS: AN OVERVIEW
RESEARCH PROCESS: AN OVERVIEW. INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS. Stages In The Research Process. Problem Formulation and Problem Definition Research Design*** Purpose of the Study Type of investigation Study setting : Population & Sampling Unit of analysis
185 views • 15 slides

Overview of the research process
Overview of the research process. Purpose of research. Research with us since early days (why?) Main reasons: Explain why things are the way they are (e.g. sun rises every morning?) Predict phenomena (e.g. human behaviour) Add value (improve things)
137 views • 12 slides
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips
Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips
Table of Contents

Research Process
Definition:
Research Process is a systematic and structured approach that involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data or information to answer a specific research question or solve a particular problem.
Research Process Steps
Research Process Steps are as follows:
Identify the Research Question or Problem
This is the first step in the research process. It involves identifying a problem or question that needs to be addressed. The research question should be specific, relevant, and focused on a particular area of interest.
Conduct a Literature Review
Once the research question has been identified, the next step is to conduct a literature review. This involves reviewing existing research and literature on the topic to identify any gaps in knowledge or areas where further research is needed. A literature review helps to provide a theoretical framework for the research and also ensures that the research is not duplicating previous work.
Formulate a Hypothesis or Research Objectives
Based on the research question and literature review, the researcher can formulate a hypothesis or research objectives. A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested to determine its validity, while research objectives are specific goals that the researcher aims to achieve through the research.
Design a Research Plan and Methodology
This step involves designing a research plan and methodology that will enable the researcher to collect and analyze data to test the hypothesis or achieve the research objectives. The research plan should include details on the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used.
Collect and Analyze Data
This step involves collecting and analyzing data according to the research plan and methodology. Data can be collected through various methods, including surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. The data analysis process involves cleaning and organizing the data, applying statistical and analytical techniques to the data, and interpreting the results.
Interpret the Findings and Draw Conclusions
After analyzing the data, the researcher must interpret the findings and draw conclusions. This involves assessing the validity and reliability of the results and determining whether the hypothesis was supported or not. The researcher must also consider any limitations of the research and discuss the implications of the findings.
Communicate the Results
Finally, the researcher must communicate the results of the research through a research report, presentation, or publication. The research report should provide a detailed account of the research process, including the research question, literature review, research methodology, data analysis, findings, and conclusions. The report should also include recommendations for further research in the area.
Review and Revise
The research process is an iterative one, and it is important to review and revise the research plan and methodology as necessary. Researchers should assess the quality of their data and methods, reflect on their findings, and consider areas for improvement.
Ethical Considerations
Throughout the research process, ethical considerations must be taken into account. This includes ensuring that the research design protects the welfare of research participants, obtaining informed consent, maintaining confidentiality and privacy, and avoiding any potential harm to participants or their communities.
Dissemination and Application
The final step in the research process is to disseminate the findings and apply the research to real-world settings. Researchers can share their findings through academic publications, presentations at conferences, or media coverage. The research can be used to inform policy decisions, develop interventions, or improve practice in the relevant field.
Research Process Example
Following is a Research Process Example:
Research Question : What are the effects of a plant-based diet on athletic performance in high school athletes?
Step 1: Background Research Conduct a literature review to gain a better understanding of the existing research on the topic. Read academic articles and research studies related to plant-based diets, athletic performance, and high school athletes.
Step 2: Develop a Hypothesis Based on the literature review, develop a hypothesis that a plant-based diet positively affects athletic performance in high school athletes.
Step 3: Design the Study Design a study to test the hypothesis. Decide on the study population, sample size, and research methods. For this study, you could use a survey to collect data on dietary habits and athletic performance from a sample of high school athletes who follow a plant-based diet and a sample of high school athletes who do not follow a plant-based diet.
Step 4: Collect Data Distribute the survey to the selected sample and collect data on dietary habits and athletic performance.
Step 5: Analyze Data Use statistical analysis to compare the data from the two samples and determine if there is a significant difference in athletic performance between those who follow a plant-based diet and those who do not.
Step 6 : Interpret Results Interpret the results of the analysis in the context of the research question and hypothesis. Discuss any limitations or potential biases in the study design.
Step 7: Draw Conclusions Based on the results, draw conclusions about whether a plant-based diet has a significant effect on athletic performance in high school athletes. If the hypothesis is supported by the data, discuss potential implications and future research directions.
Step 8: Communicate Findings Communicate the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner. Use appropriate language, visuals, and formats to ensure that the findings are understood and valued.
Applications of Research Process
The research process has numerous applications across a wide range of fields and industries. Some examples of applications of the research process include:
- Scientific research: The research process is widely used in scientific research to investigate phenomena in the natural world and develop new theories or technologies. This includes fields such as biology, chemistry, physics, and environmental science.
- Social sciences : The research process is commonly used in social sciences to study human behavior, social structures, and institutions. This includes fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and economics.
- Education: The research process is used in education to study learning processes, curriculum design, and teaching methodologies. This includes research on student achievement, teacher effectiveness, and educational policy.
- Healthcare: The research process is used in healthcare to investigate medical conditions, develop new treatments, and evaluate healthcare interventions. This includes fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Business and industry : The research process is used in business and industry to study consumer behavior, market trends, and develop new products or services. This includes market research, product development, and customer satisfaction research.
- Government and policy : The research process is used in government and policy to evaluate the effectiveness of policies and programs, and to inform policy decisions. This includes research on social welfare, crime prevention, and environmental policy.
Purpose of Research Process
The purpose of the research process is to systematically and scientifically investigate a problem or question in order to generate new knowledge or solve a problem. The research process enables researchers to:
- Identify gaps in existing knowledge: By conducting a thorough literature review, researchers can identify gaps in existing knowledge and develop research questions that address these gaps.
- Collect and analyze data : The research process provides a structured approach to collecting and analyzing data. Researchers can use a variety of research methods, including surveys, experiments, and interviews, to collect data that is valid and reliable.
- Test hypotheses : The research process allows researchers to test hypotheses and make evidence-based conclusions. Through the systematic analysis of data, researchers can draw conclusions about the relationships between variables and develop new theories or models.
- Solve problems: The research process can be used to solve practical problems and improve real-world outcomes. For example, researchers can develop interventions to address health or social problems, evaluate the effectiveness of policies or programs, and improve organizational processes.
- Generate new knowledge : The research process is a key way to generate new knowledge and advance understanding in a given field. By conducting rigorous and well-designed research, researchers can make significant contributions to their field and help to shape future research.
Tips for Research Process
Here are some tips for the research process:
- Start with a clear research question : A well-defined research question is the foundation of a successful research project. It should be specific, relevant, and achievable within the given time frame and resources.
- Conduct a thorough literature review: A comprehensive literature review will help you to identify gaps in existing knowledge, build on previous research, and avoid duplication. It will also provide a theoretical framework for your research.
- Choose appropriate research methods: Select research methods that are appropriate for your research question, objectives, and sample size. Ensure that your methods are valid, reliable, and ethical.
- Be organized and systematic: Keep detailed notes throughout the research process, including your research plan, methodology, data collection, and analysis. This will help you to stay organized and ensure that you don’t miss any important details.
- Analyze data rigorously: Use appropriate statistical and analytical techniques to analyze your data. Ensure that your analysis is valid, reliable, and transparent.
- I nterpret results carefully : Interpret your results in the context of your research question and objectives. Consider any limitations or potential biases in your research design, and be cautious in drawing conclusions.
- Communicate effectively: Communicate your research findings clearly and effectively to your target audience. Use appropriate language, visuals, and formats to ensure that your findings are understood and valued.
- Collaborate and seek feedback : Collaborate with other researchers, experts, or stakeholders in your field. Seek feedback on your research design, methods, and findings to ensure that they are relevant, meaningful, and impactful.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

- Customer Favourites
Research Objective
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

- You're currently reading page 1

Stages // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsPerPage = parseInt(paginator); var itemsCount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemsCount ? ’Stages’ here means the number of divisions or graphic elements in the slide. For example, if you want a 4 piece puzzle slide, you can search for the word ‘puzzles’ and then select 4 ‘Stages’ here. We have categorized all our content according to the number of ‘Stages’ to make it easier for you to refine the results.
Category // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsperpage = parseint(paginator); var itemscount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemscount.
- Anatomy (2)
- Block Chain (1)
- Branding (1)
- Business Plan Word (56)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The document outlines the major and minor objectives of research. The major objectives are to gain new insights into phenomena, accurately portray characteristics of individuals or groups, determine the frequency of occurrences, discover truths and facts, and test hypotheses of relationships between variables. The minor objectives are to seek ...
257 likes • 478,527 views. MAHESWARI JAIKUMAR. Follow. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES. Health & Medicine. 1 of 37. Download now. Download to read offline. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
Research process. Oct 13, 2012 •. 939 likes • 870,055 views. aditi garg. Follow. 1 of 12. Download now. Download to read offline. Research process - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Use this PPT deck to showcase your research objectives, timeline, funding, methodology, and more. Grab it right here! GET IT HERE . Template 4: Research Proposal Template PowerPoint Presentation Slides . Create a convincing proposal to study your research objectives and keep relevant people in the loop at all times with this PPT Template Bundle.
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8. Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process; Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings; Key takeaways . Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
Template 2: Research Methodology Process Analysis Template. This is a content-ready PowerPoint template to maximize the effectiveness of your research. This professional and appealing template guides you step-by-step through the research process, from defining your research question to analyzing and interpreting data.
Shape your study's trajectory, articulate objectives with confidence, and captivate your audience with the strategic journey this template provides. Features of the templates: 100% customizable slides and easy to download. The slides contained 16:9 and 4:3 formats. Easy to change the slide colors quickly. Planets animation inserted template.
Presenting this set of slides with name market research project context and objectives for market assessment services ppt powerpoint presentation outline slides pdf. This is a two stage process. The stages in this process are project context, project objectives, further expand business, require detailed market assessment, strategies.
Presenting this set of slides with name writing research proposal outline market research context and objective ppt summary slide download pdf. This is a two stage process. The stages in this process are context, objective. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download.
The Research Planning template contains four professional slides in a cool colour scheme. All slides in this template have the necessary tools to build a professional presentation. You can present the objectives of your research and give a brief description. The first slide of this template gives you the opportunity to present up to eight steps ...
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor's standpoint.
13. Exploratory Research design is defined as the initial research into a hypothetical or theoretical idea. This is where a researcher has an idea of getting a solution of his problem. The main purpose of this study is to determine the general nature of the problem & the variables related to it & then discover new ideas.
The Research Process can be simple or complex, quick or lengthy, depending on the complexity of your information needs. Module 1: Overview of the Research Process • But in general, the process goes like this: Step 1Identify and refine your topic Step 2 Identify your best resources Step 3 Access and search the resources Step 4 Evaluate results ...
The research process has numerous applications across a wide range of fields and industries. Some examples of applications of the research process include: Scientific research: The research process is widely used in scientific research to investigate phenomena in the natural world and develop new theories or technologies. This includes fields ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
The stages in this process are Objectives, Approach, Research, Measure, Implement, Queue, Prioritize, Brainstorm. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download. Download now and impress your audience. Slide 1 of 2.
2. The research process involves identifying, locating, assessing, and analyzing the information you need to support your research question, and then developing and expressing your ideas. The research process can be broken down into seven steps, making it more manageable and easier to understand. • Step 1 : Define researchproblem • Step 2 : Review of literature • Step 3 ...
Steps Of Process Selecting a topic Data Collection Execution of project Defining the Resea r c h Problem Sample Design Data Analysis and Hypothesis testing Objective of Research Preparing Research Design Generalization and Interpretation c) Of Literature Working Hypothesis Report. Selecting a topic Following factors to be considered: Relevance ...
5. OBJECTIVES OF RESEARCH RESEARCH is an organised investigation of a problem where an investigator attempts to gain solution to a problem. In order to get the right solution a clearly defined objectives are very important. Without a clear objective researcher is aimless and directionless in conducting the study. Without focused objectives no replicable scientific findings can be expected ...
Research Objective found in: Research questions objectives examples ppt powerpoint presentation layouts mockup cpb, Machine learning traditional research data warehousing project management, Phases Of Syndicated Research For.. ... Stages in market research process example ppt example file. Animated . Slide 1 of 2 Research question hypothesis ...
1.0 OBJECTIVES . Research is a scientific way to find factual information. It is carried out in an . objective manner following certain specific steps. After reading this unit, you should be able to: • enlist various steps in conducting a social research • appraise the relevance and significance of each step of the research process
162 likes • 128,271 views. Shruti Jain. Follow. Education. 1 of 27. Download Now. Download to read offline. research process - Download as a PDF or view online for free.