Writing the Literature Review: Common Mistakes and Best Practices
- First Online: 21 November 2023

Cite this chapter

- Kelly Heider 3
Part of the book series: Springer Texts in Education ((SPTE))
409 Accesses
1 Altmetric
The literature review is an essential component of academic research writing, providing a comprehensive overview of existing research and informing the development of new studies. However, writing an effective literature review can be a challenging task for many authors, particularly those new to academic writing. This chapter aims to guide authors through the process of writing a literature review by highlighting common mistakes and best practices. The chapter begins with three short narratives that describe difficulties both novice and prolific authors encounter when writing the literature review. A chapter activity follows with steps that guide authors through the process of developing a research question to frame the literature review. Authors are then prompted to complete a self-assessment activity which includes a series of questions designed to build their skills as academic research writers. The body of the chapter recommends strategies and techniques to help authors locate and evaluate sources that will serve as the building blocks for a literature review that is thorough, current, and well-written. The chapter concludes with a discussion of the threats and benefits of artificial intelligence-based text production in relationship to academic research writing. Overall, this chapter provides practical guidance for authors looking to improve their literature review writing skills and enhance the quality of their research output.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Anson, C. M. (2022). AI-based text generation and the social construction of “fraudulent authorship”: A revisitation. Composition Studies, 50 (1), 37–46.
Google Scholar
Aylward, K., Sbaffi, L., & Weist, A. (2020). Peer-led information literacy training: A qualitative study of students’ experiences of the NICE evidence search student champion scheme. Health Information and Libraries Journal, 37 (3), 216–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12301
Article Google Scholar
Bohannon, J. (2013, October 4). Who’s afraid of peer review? Science, 342 (6154), 60–65. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.342.6154.60
Bouchrika, I. (2023, March 17). Top 10 qualities of good academic research . Research. https://research.com/research/top-10-qualities-of-good-academic-research
Bowler, M., & Street, K. (2008). Investigating the efficacy of embedment: Experiments in information literacy integration. Reference Services Review, 36 , 438–449. https://doi.org/10.1108/00907320810920397
De La Torre, M. (2018, August 29). Academic racism: The repression of marginalized voices in academia . The Activist History Review. https://activisthistory.com/2018/08/29/academic-racism-the-repression-of-marginalized-voices-in-academia/
Drewes, K., & Hoffman, N. (2010). Academic embedded librarianship: An introduction. Public Services Quarterly, 6 (2–3), 75–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228959.2010.498773
Elsevier Author Services. (n.d.a). Journal acceptance rates: Everything you need to know . Publication process. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/publication-process/journal-acceptance-rates/#:~:text=your%20paper%20to%3F-,What%20Our%20Research%20Shows,over%201%25%20to%2093.2%25 .
Elsevier Author Services. (n.d.b). What is a good H-index? Publication recognition. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/publication-recognition/what-good-h-index/
Emerald Publishing. (2023). How to…conduct empirical research . https://www.emeraldgrouppublishing.com/how-to/research-methods/conduct-empirical-research
Enago Academy. (2022, May 3). How much research is enough for a good literature review? https://www.enago.com/academy/research-for-a-good-literature-review/
Fitzgibbons, M. (2021). Literature review synthesis matrix . Concordia University Library. [Adapted from original table by the WI+RE Team at UCLA Library.] https://www.concordia.ca/content/dam/library/docs/research-guides/gradproskills/Lit-review-synthesis-matrix-Word.docx
Garrett, W. (n.d.) Marginalized populations . Minnesota Psychological Association. https://www.mnpsych.org/index.php?option=com_dailyplanetblog&view=entry&category=division%20news&id=71:marginalized-populations
George Mason University Libraries. (2021, August 20). Find authors . Finding diverse voices in academic research. https://infoguides.gmu.edu/c.php?g=1080259&p=7871669
Gyles, C. (2014, February). Can we trust peer-reviewed science? The Canadian Veterinary Journal, 55 (2), 109–111. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3894865/#b2-cvj_02_109
Hern, A. (2022, December 4). AI bot ChatGPT stuns academics with essay-writing skills and usability . The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2022/dec/04/ai-bot-chatgpt-stuns-academics-with-essay-writing-skills-and-usability
Hoffman, N., Beatty, S., Feng, P., & Lee, J. (2017). Teaching research skills through embedded librarianship. Reference Services Review, 45 , 211–226. https://doi.org/10.1108/RSR-07-2016-0045
Indeed Editorial Team. (2022, June 28). Create a theoretical framework for your research in 4 steps . Indeed. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/theoretical-framework
Jansen, D. (2021, June). How to choose your research methodology . GradCoach. https://gradcoach.com/choose-research-methodology/
Jansen, D., & Warren, K. (2020, June). What (exactly) is a literature review? GradCoach. https://gradcoach.com/what-is-a-literature-review/
Jin, Y. Y., Noh, H., Shin, H., & Lee, S. M. (2015). A typology of burnout among Korean teachers. Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 24 (2), 309–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-014-0181-6
Koufogiannakis, D., Buckingham, J., Alibhai, A., & Rayner, D. (2005). Impact of librarians in first-year medical and dental student problem-based learning (PBL) groups: A controlled study. Health Information and Libraries Journal, 22 , 189–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2005.00559.x
Larsen, C. M., Terkelsen, A. S., Carlsen, A. F., & Kristensen, H. K. (2019). Methods for teaching evidence-based practice: A scoping review. BMC Medical Education, 19 , 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1681-0
Liberties EU. (2021, October 5). What is marginalization? Definition and coping strategies . https://www.liberties.eu/en/stories/marginalization-and-being-marginalized/43767
Lucey, B., & Dowling, M. (2023). ChatGPT: Our study shows AI can produce academic papers good enough for journals—just as some ban it . The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/chatgpt-our-study-shows-ai-can-produce-academic-papers-good-enough-for-journals-just-as-some-ban-it-197762
Maior, E., Dobrean, A., & Păsărelu, C. (2020). Teacher rationality, social-emotional competencies, and basic needs satisfaction: Direct and indirect effects on teacher burnout. Journal of Evidence—Based Psychotherapies, 20 (1), 135–152. https://doi.org/10.24193/jebp.2020.1.8
Mertens, D. M. (2019). Research and evaluation in education and psychology: Integrating diversity with quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
Monash University. (2023). Structuring a literature review . Learn HQ. https://www.monash.edu/learnhq/excel-at-writing/how-to-write.../literature-review/structuring-a-literature-review
Nova, A. (2017, December 21). Learn how to write a literature review in simple steps . MyPerfectWords. https://myperfectwords.com/blog/research-paper-guide/how-to-write-a-literature-review
O’Byrne, I. (2018, February 9). Eight steps to write a literature review . https://wiobyrne.com/literature-review/
Online Campus Writing Center. (2023). Synthesis . The Chicago School of Professional Psychology. https://community.thechicagoschool.edu/writingresources/online/Pages/Synthesis.aspx
Phair, D. (2021, June). Writing a literature review: 7 common (and costly) mistakes to avoid . GradCoach. https://gradcoach.com/literature-review-mistakes/
Robinson, K. A., Akinyede, O., Dutta, T., Sawin, V. I., Li, T., Spencer, M. R., Turkelson, C. M., & Weston, C. (2013, February). Framework for determining research gaps during systematic review: Evaluation . Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (U.S.). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK126702/
Rommelspacher, A. (2020, November). How to structure your literature review: Three options to help structure your chapter . GradCoach. https://gradcoach.com/literature-review-structure/
Royal Literary Fund. (2023). The structure of a literature review . https://www.rlf.org.uk/resources/the-structure-of-a-literature-review/
Rudestam, K. E., & Newton, R. R. (1992). Surviving your dissertation: A comprehensive guide to content and process . SAGE Publications.
Scimago Lab. (2022a). About us . Scimago Journal and Country Rank. https://www.scimagojr.com/aboutus.php
Scimago Lab. (2022b). Journal rankings . Scimago Journal and Country Rank. https://www.scimagojr.com/journalrank.php
Shumaker, D. (2009). Who let the librarians out? Embedded librarianship and the library manager. Reference & User Services Quarterly, 48 (3), 239–257.
Statistics Solutions. (2023). Tips for the literature review: Synthesis and analysis . Complete dissertation. https://www.statisticssolutions.com/tips-for-the-literature-review-synthesis-and-analysis/
TechTarget. (2023). What is OpenAI? Open AI. https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/definition/OpenAI
Texas A&M University Writing Center. (2023). Self-assessment . https://writingcenter.tamu.edu/Faculty-Advisors/Resources-for-Teaching/Feedback/Self-Assessment
University of Colorado at Colorado Springs. (2022, May 13). Evaluate sources. Public administration research. https://libguides.uccs.edu/c.php?g=617840&p=4299162
University of Maryland Global Campus. (n.d.). Discipline-specific research methods . https://coursecontent.umgc.edu/umgc/shareable-content/toolkits/BEHS000/1402/ResearchMethods/Discipline-SpecificResearchMethods.html
University of Melbourne. (2017, September 21). Academic writing: Writing the literature review [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=70n2-gAp7J0
Walker, R., & Solvason, C. (2014). Methodology: Choosing your research approach . SAGE Publications.
Wardle, E., & Downs, D. (2019). Writing about writing (4th ed.). Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Wiggers, K. (2023, January 31). OpenAI releases tool to detect AI-generated text, including from ChatGPT . TechCrunch. https://techcrunch.com/2023/01/31/openai-releases-tool-to-detect-ai-generated-text-including-from-chatgpt/
Yilmaz, K., Altinkurt, Y., Guner, M., & Sen, B. (2015). The relationship between teachers’ emotional labor and burnout level. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 59 , 75–90.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Acting Assistant Vice Provost for University Libraries, Indiana University of PA, Indiana, PA, USA
Kelly Heider
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kelly Heider .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Indiana University of Pennsylvania, Emerita, Indiana, PA, USA
Mary Renck Jalongo
Teaching & Learning, Policy & Leadership, University of Maryland, College Park, College Park, MD, USA
Olivia N. Saracho
Issue: AI-Based Text Production in Academic Research Writing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a relatively new technological development that can be used to support academic research writing, particularly reviews of research. Although it holds promise as a research tool, there are also concerns that AI-based scholarly writing could threaten not only the integrity but also the creativity of academic research writing. ChatGPT, an advanced chatbot developed by OpenAI (a nonprofit research company founded by Elon Musk and Sam Altman in 2015) has been at the center of much controversy as of late because of its ability to produce academic papers using artificial intelligence-based text production that have fooled academics and academic journal publishers (Hern, 2022 ; Lucey & Dowling, 2023 ; TechTarget, 2023 ). To demonstrate ChatGPT’s capabilities, consider its response to the question, “What is artificial intelligence-based text production?”.
Artificial Intelligence-Based Text Production is a process where machine learning algorithms are used to generate written content such as articles, product descriptions, social media posts, and more. It involves training machine learning models with vast amounts of data to learn how to generate human-like text automatically. The process can involve different techniques such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), deep learning, and neural networks to analyze and understand language patterns, grammar, context, and semantics. The resulting AI-generated text can be used for a wide range of applications, including content marketing, chatbots, language translation, and more. One of the main benefits of AI-based text production is that it can help businesses and organizations automate their content creation process, saving time and resources while producing high-quality content. However, it is important to note that AI-generated text may not always be perfect and may require human editing and review to ensure accuracy and coherence.
This response was produced by ChatGPT in about ten seconds. According to Anson ( 2022 ), “cutting and pasting all or part of this auto-generated text into a new text box can continue to prompt further content. The material is not plagiarized from existing sources but freshly composed. For this reason, it usually evades plagiarism-detection programs like Turnitin” (p. 40).
How Might AI-Based Text Production Threaten Academic Research Writing?
Obviously, computer-generated text that evades plagiarism-detection programs threatens the integrity of academic research writing. Some academic publishers have already banned or limited the use of AI-generated text in papers submitted to their journals (Lucey & Dowling, 2023 ). However, that is easier said than done. OpenAI recently developed a tool that attempts to distinguish between human-written and AI-generated text to prevent chatbots like ChatGPT from being abused, but it is only 26% effective (Wiggers, 2023 ).
Lucey and Dowling ( 2023 ) tested the credibility of ChatGPT by having expert reviewers examine papers produced by the chatbot. First, they asked ChatGPT to generate four parts of a research study: (1) research idea, (2) literature review, (3) dataset, and (4) suggestions for testing and examination. They chose a broad subject and instructed the chatbot to create a paper that could be published in “a good finance journal” (para. 6). Second, they pasted 200 relevant abstracts into the ChatGPT search box and asked the chatbot to consider the abstracts when generating the four-part research study. Finally, they asked academic researchers to read both versions of the AI-generated text and make suggestions for improvement. A panel of thirty-two reviewers read all versions of the four-part research study and rated them. In all cases, the papers were considered acceptable by the reviewers, although the chatbot-created papers that also included input from academic researchers were rated higher. However, “a chatbot was deemed capable of generating quality academic research ideas. This raises fundamental questions around the meaning of creativity and ownership of creative ideas—questions to which nobody yet has solid answers” (Lucey & Dowling, 2023 , para. 10).
How Might AI-Based Text Production Benefit Academic Research Writing?
Despite several publishers deciding to ban the inclusion of AI-based text production in submissions, some researchers have already listed ChatGPT as a co-author on their papers (Lucey & Dowling, 2023 ). There are many who believe there is no difference between the way ChatGPT produces text and the way authors synthesize studies in their literature reviews. In fact, the chatbot’s review is much more exhaustive because it can analyze “billions of existing, human-produced texts and, through a process akin to the creation of neural networks, generate new text based on highly complex predictive machine analysis” (Anson, 2022 , p. 39).
There are other advantages to using AI-based text production. It has the potential to aid groups of researchers who lack funding to hire human research assistants such as emerging economy researchers, graduate students, and early career researchers. According to Lucey and Dowling ( 2023 ), AI-based text production “could help democratize the research process” (para. 18). Anson ( 2022 ) also sees the potential in AI-based text production to “spark some new human-generated ideas” (p. 42), extract keywords, and create abstracts. The development of AI-based text production might also force instructors to change the way they teach academic writing. Instead of trying to detect or prevent the use of chatbots like ChatGPT, “a more sensible approach could involve embracing the technology, showing students what it can and can’t do, and asking them to experiment with it” (Anson, 2022 , p. 44). In other words, students could be asked to write about writing which leads to a deeper understanding of the writing process and the ability to transfer that understanding to any writing project (Wardle & Downs, 2019 ).
The Responsible Use of AI-Based Text Production in Academic Research Writing
The responsible use of AI-based text production in academic research writing involves understanding the technology's capabilities and limitations, as well as considering its potential impact on the research process. Researchers must carefully evaluate the intended purpose and context of using AI-generated text and make certain they are not compromising the authenticity and integrity of their research work. To ensure responsible use, it is essential to balance the benefits of increased efficiency and new insights with the need for originality and critical thinking in academic research writing. Researchers must also be transparent in disclosing the use of AI-generated text when submitting their work for publication. By adopting a responsible and thoughtful approach to the use of AI-based text production, researchers can maximize the benefits of the technology while maintaining the quality and authenticity of their research.
Applications of Technology
How to Write a Paper in a Weekend : https://youtu.be/UY7sVKJPTMA
Note : University of Minnesota Chemistry Professor, Peter Carr is not advocating for procrastination. This video outlines a strategy for generating a first draft after you have all your reading and notes assembled.
Research Gap 101: What Is a Research Gap & How to Find One : https://youtu.be/Kabj0u8YQ4Y
Using Google Scholar for Academic Research : https://youtu.be/t8_CW6FV8Ac .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Heider, K. (2023). Writing the Literature Review: Common Mistakes and Best Practices. In: Renck Jalongo, M., Saracho, O.N. (eds) Scholarly Writing. Springer Texts in Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-39516-1_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-39516-1_3
Published : 21 November 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-39515-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-39516-1
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 16 April 2024
Structure peer review to make it more robust

- Mario Malički 0
Mario Malički is associate director of the Stanford Program on Research Rigor and Reproducibility (SPORR) and co-editor-in-chief of the Research Integrity and Peer Review journal.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have full access to this article via your institution.
In February, I received two peer-review reports for a manuscript I’d submitted to a journal. One report contained 3 comments, the other 11. Apart from one point, all the feedback was different. It focused on expanding the discussion and some methodological details — there were no remarks about the study’s objectives, analyses or limitations.
My co-authors and I duly replied, working under two assumptions that are common in scholarly publishing: first, that anything the reviewers didn’t comment on they had found acceptable for publication; second, that they had the expertise to assess all aspects of our manuscript. But, as history has shown, those assumptions are not always accurate (see Lancet 396 , 1056; 2020 ). And through the cracks, inaccurate, sloppy and falsified research can slip.
As co-editor-in-chief of the journal Research Integrity and Peer Review (an open-access journal published by BMC, which is part of Springer Nature), I’m invested in ensuring that the scholarly peer-review system is as trustworthy as possible. And I think that to be robust, peer review needs to be more structured. By that, I mean that journals should provide reviewers with a transparent set of questions to answer that focus on methodological, analytical and interpretative aspects of a paper.
For example, editors might ask peer reviewers to consider whether the methods are described in sufficient detail to allow another researcher to reproduce the work, whether extra statistical analyses are needed, and whether the authors’ interpretation of the results is supported by the data and the study methods. Should a reviewer find anything unsatisfactory, they should provide constructive criticism to the authors. And if reviewers lack the expertise to assess any part of the manuscript, they should be asked to declare this.

Anonymizing peer review makes the process more just
Other aspects of a study, such as novelty, potential impact, language and formatting, should be handled by editors, journal staff or even machines, reducing the workload for reviewers.
The list of questions reviewers will be asked should be published on the journal’s website, allowing authors to prepare their manuscripts with this process in mind. And, as others have argued before, review reports should be published in full. This would allow readers to judge for themselves how a paper was assessed, and would enable researchers to study peer-review practices.
To see how this works in practice, since 2022 I’ve been working with the publisher Elsevier on a pilot study of structured peer review in 23 of its journals, covering the health, life, physical and social sciences. The preliminary results indicate that, when guided by the same questions, reviewers made the same initial recommendation about whether to accept, revise or reject a paper 41% of the time, compared with 31% before these journals implemented structured peer review. Moreover, reviewers’ comments were in agreement about specific parts of a manuscript up to 72% of the time ( M. Malički and B. Mehmani Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/mrdv; 2024 ). In my opinion, reaching such agreement is important for science, which proceeds mainly through consensus.

Stop the peer-review treadmill. I want to get off
I invite editors and publishers to follow in our footsteps and experiment with structured peer reviews. Anyone can trial our template questions (see go.nature.com/4ab2ppc ), or tailor them to suit specific fields or study types. For instance, mathematics journals might also ask whether referees agree with the logic or completeness of a proof. Some journals might ask reviewers if they have checked the raw data or the study code. Publications that employ editors who are less embedded in the research they handle than are academics might need to include questions about a paper’s novelty or impact.
Scientists can also use these questions, either as a checklist when writing papers or when they are reviewing for journals that don’t apply structured peer review.
Some journals — including Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , the PLOS family of journals, F1000 journals and some Springer Nature journals — already have their own sets of structured questions for peer reviewers. But, in general, these journals do not disclose the questions they ask, and do not make their questions consistent. This means that core peer-review checks are still not standardized, and reviewers are tasked with different questions when working for different journals.
Some might argue that, because different journals have different thresholds for publication, they should adhere to different standards of quality control. I disagree. Not every study is groundbreaking, but scientists should view quality control of the scientific literature in the same way as quality control in other sectors: as a way to ensure that a product is safe for use by the public. People should be able to see what types of check were done, and when, before an aeroplane was approved as safe for flying. We should apply the same rigour to scientific research.
Ultimately, I hope for a future in which all journals use the same core set of questions for specific study types and make all of their review reports public. I fear that a lack of standard practice in this area is delaying the progress of science.
Nature 628 , 476 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01101-9
Reprints and permissions
Competing Interests
M.M. is co-editor-in-chief of the Research Integrity and Peer Review journal that publishes signed peer review reports alongside published articles. He is also the chair of the European Association of Science Editors Peer Review Committee.
Related Articles

- Scientific community
- Peer review
Chemistry lab destroyed by Taiwan earthquake has physical and mental impacts
Correspondence 23 APR 24

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists
Career Feature 23 APR 24
India’s 50-year-old Chipko movement is a model for environmental activism

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing
Career Column 08 APR 24

Is AI ready to mass-produce lay summaries of research articles?
Nature Index 20 MAR 24
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Description Applications are invited for a postdoctoral fellow position at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Sinai Health, to participate...
Toronto (City), Ontario (CA)
Sinai Health
Postdoctoral Research Associate - Surgery
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Open Rank Faculty Position in Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics
The Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics (www.virginia.edu/bmg) and the University of Virginia Cancer Center
Charlottesville, Virginia
Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
Postdoctoral Position - Synthetic Cell/Living Cell Spheroids for Interactive Biomaterials
Co-assembly of artificial cells and living cells to make co-spheroid structures and study their interactive behavior for biomaterials applications.
Mainz, Rheinland-Pfalz (DE)
University of Mainz
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Peer Reviewed Literature
What is peer review, terminology, peer review what does that mean, what types of articles are peer-reviewed, what information is not peer-reviewed, what about google scholar.
- How do I find peer-reviewed articles?
- Scholarly vs. Popular Sources
Research Librarian
For more help on this topic, please contact our Research Help Desk: [email protected] or 781-768-7303. Stay up-to-date on our current hours . Note: all hours are EST.

This Guide was created by Carolyn Swidrak (retired).
Research findings are communicated in many ways. One of the most important ways is through publication in scholarly, peer-reviewed journals.
Research published in scholarly journals is held to a high standard. It must make a credible and significant contribution to the discipline. To ensure a very high level of quality, articles that are submitted to scholarly journals undergo a process called peer-review.
Once an article has been submitted for publication, it is reviewed by other independent, academic experts (at least two) in the same field as the authors. These are the peers. The peers evaluate the research and decide if it is good enough and important enough to publish. Usually there is a back-and-forth exchange between the reviewers and the authors, including requests for revisions, before an article is published.
Peer review is a rigorous process but the intensity varies by journal. Some journals are very prestigious and receive many submissions for publication. They publish only the very best, most highly regarded research.
The terms scholarly, academic, peer-reviewed and refereed are sometimes used interchangeably, although there are slight differences.
Scholarly and academic may refer to peer-reviewed articles, but not all scholarly and academic journals are peer-reviewed (although most are.) For example, the Harvard Business Review is an academic journal but it is editorially reviewed, not peer-reviewed.
Peer-reviewed and refereed are identical terms.
From Peer Review in 3 Minutes [Video], by the North Carolina State University Library, 2014, YouTube (https://youtu.be/rOCQZ7QnoN0).
Peer reviewed articles can include:
- Original research (empirical studies)
- Review articles
- Systematic reviews
- Meta-analyses
There is much excellent, credible information in existence that is NOT peer-reviewed. Peer-review is simply ONE MEASURE of quality.
Much of this information is referred to as "gray literature."
Government Agencies
Government websites such as the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) publish high level, trustworthy information. However, most of it is not peer-reviewed. (Some of their publications are peer-reviewed, however. The journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, published by the CDC is one example.)
Conference Proceedings
Papers from conference proceedings are not usually peer-reviewed. They may go on to become published articles in a peer-reviewed journal.
Dissertations
Dissertations are written by doctoral candidates, and while they are academic they are not peer-reviewed.
Many students like Google Scholar because it is easy to use. While the results from Google Scholar are generally academic they are not necessarily peer-reviewed. Typically, you will find:
- Peer reviewed journal articles (although they are not identified as peer-reviewed)
- Unpublished scholarly articles (not peer-reviewed)
- Masters theses, doctoral dissertations and other degree publications (not peer-reviewed)
- Book citations and links to some books (not necessarily peer-reviewed)
- Next: How do I find peer-reviewed articles? >>
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 9:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.regiscollege.edu/peer_review
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- Reading Journal Articles
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
How to Read and Comprehend Scientific Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
Peer-reviewed or scholarly journal articles are written in a very specific organized and formal way. If you haven't spent much time with this type of literature, this video provides some tips for reading journal articles.
- << Previous: Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Next: Does it Describe a Literature Review? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
- Open access
- Published: 13 December 2023
Arts and creativity interventions for improving health and wellbeing in older adults: a systematic literature review of economic evaluation studies
- Grainne Crealey 1 ,
- Laura McQuade 2 ,
- Roger O’Sullivan 2 &
- Ciaran O’Neill 3
BMC Public Health volume 23 , Article number: 2496 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1173 Accesses
22 Altmetric
Metrics details
As the population ages, older people account for a larger proportion of the health and social care budget. A significant body of evidence suggests that arts and creativity interventions can improve the physical, mental and social wellbeing of older adults, however the value and/or cost-effectiveness of such interventions remains unclear.
We systematically reviewed the economic evidence relating to such interventions, reporting our findings according to PRISMA guidelines. We searched bibliographic databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, Econlit and Web of Science and NHSEED), trial registries and grey literature. No language or temporal restrictions were applied. Two screening rounds were conducted independently by health economists experienced in systematic literature review. Methodological quality was assessed, and key information extracted and tabulated to provide an overview of the published literature. A narrative synthesis without meta-analysis was conducted.
Only six studies were identified which provided evidence relating to the value or cost-effectiveness of arts and creativity interventions to improve health and wellbeing in older adults. The evidence which was identified was encouraging, with five out of the six studies reporting an acceptable probability of cost-effectiveness or positive return on investment (ranging from £1.20 to over £8 for every £1 of expenditure). However, considerable heterogeneity was observed with respect to study participants, design, and outcomes assessed. Of particular concern were potential biases inherent in social value analyses.
Conclusions
Despite many studies reporting positive health and wellbeing benefits of arts and creativity interventions in this population, we found meagre evidence on their value or cost-effectiveness. Such evidence is costly and time-consuming to generate, but essential if innovative non-pharmacological interventions are to be introduced to minimise the burden of illness in this population and ensure efficient use of public funds. The findings from this review suggests that capturing data on the value and/or cost-effectiveness of such interventions should be prioritised; furthermore, research effort should be directed to developing evaluative methods which move beyond the confines of current health technology assessment frameworks, to capture a broader picture of ‘value’ more applicable to arts and creativity interventions and public health interventions more generally.
PROSPERO registration
CRD42021267944 (14/07/2021).
Peer Review reports
The number and proportion of older adults in the population has increased in virtually every country in the world over past decades [ 1 ]. In 2015, there were around 901 million people aged 60 years and over worldwide, by 2030, this will have increased to 1.4 billion [ 2 ]. An ageing population is one of the greatest successes of public health but it has implications for economies in numerous ways: slower labour force growth; working-age people will have to make greater provisions in welfare payments for older people who are no longer economically active; provisions for increased long-term care; and, society must adjust to the changing needs, expectations and capabilities of an expanding group of its citizens.
The Covid-19 pandemic shone an uncompromising light on the health and social care sector, highlighting the seriousness of gaps in policies, systems and services. It also focused attention on the physical and mental health consequences of loneliness and social isolation. To foster healthy ageing and improve the lives of older people, their families and communities, sustained and equitable investment in health and wellbeing is required [ 3 ]. The prevailing model of health and social care which is based ostensibly on formal care provision is unlikely to be sustainable over the longer term. New models, which promote healthy ageing and recognise the need for increasing reliance on self-care are required, as will be evidence of their effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and scalability.
Arts and creativity interventions (ACIs) can have positive effects on health and well-being, as several reviews have shown [ 4 , 5 ]. For older people, ACI’s can enhance wellbeing [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ], quality of life [ 10 , 11 ] and cognitive function [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. They can also foster social cohesion [ 17 , 18 , 19 ] and reduce social disparities and injustices [ 20 ]; promote healthy behaviour; prevent ill health (including enhancing well-being and mental health) [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ], reducing cognitive decline [ 26 , 27 ], frailty [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ] and premature mortality [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ]); support people with stroke [ 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 ]; degenerative neurological disorders and dementias and support end of life care [ 43 , 44 ]. Moreover, ACIs can benefit not only individuals, but also others, such as supporting the well-being of formal and informal carers, enriching our knowledge of health, and improving clinical skills [ 4 , 5 ].
The benefits of ACIs have also been acknowledged at a governmental level by those responsible for delivering health and care services: The UK All-Party Parliamentary Special Interest group on Arts, Health and Wellbeing produced a comprehensive review of creative intervention for health and wellbeing [ 45 ]. This report contained three key messages: that the arts can keep us well, aid recovery and support longer better lived lives; they can help meet major challenges facing health and social care; and that the arts can save money for the health service and social care.
Despite robust scientific evidence and governmental support, no systematic literature review has collated the evidence with respect to the value, cost or cost-effectiveness of such interventions. Our objective was to assess the economic impact of ACIs aimed at improving the health and wellbeing of older adults; to determine the range and quality of available studies; identify gaps in the evidence-base; and guide future research, practice and policy.
A protocol for this review was registered at PROSPERO, an international prospective register of systematic reviews (Registration ID CRD42021267944). We used pre-determined criteria for considering studies to include in the review, in terms of types of studies, participant and intervention characteristics.
The review followed the five-step approach on how to prepare a Systematic Review of Economic Evaluations (SR-EE) for informing evidence-based healthcare decisions [ 46 , 47 , 48 ]. Subsequent to developing and registering the protocol, the International Society for Pharmacoeconomic Outcomes and Research (ISPOR) published a good practice task force report for the critical appraisal of systematic reviews with costs and cost-effectiveness outcomes (SR-CCEOs) [ 49 ]. This was also used to inform the conduct of this review.
Eligibility criteria
Full economic evaluations are regarded as the optimal type of evidence for inclusion in a SR-EE [ 46 ], hence cost-minimisation analyses (CMA), cost-effectiveness analyses (CEA), cost-utility analyses (CUA) and cost–benefit analyses (CBA) were included. Social value analyses were also included as they are frequently used to inform decision-making and commissioning of services within local government. Additionally, they represent an important intermediate stage in our understanding of the costs and consequences of public health interventions, where significant challenges exist with regard to performing full evaluations [ 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ].
Development of search strategies
The population (P), intervention (I), comparator (C) and outcomes (O) (PICO) tool provided a framework for development of the search strategy. Studies were included if participants were aged 50 years or older (or if the average age of the study population was 50 years or over). Interventions could relate to performance art (dance, singing, theatre, drama etc.), creative and visual arts (painting, sculpture, art making and design), or creative writing (writing narratives, poetry, storytelling). The intervention had to be active (for example, creating art as opposed to viewing art; playing an instrument as opposed to listening to music). The objective of the intervention had to be to improve health and wellbeing; it had to be delivered under the guidance of a professional; delivered in a group setting and delivered on more than one occasion. No restrictions were placed on the type of comparator(s) or the type of outcomes captured in the study. We deliberately limited the study to professionally led activities to provide a sharper distinction between social events where arts and creativity may occur and arts and creativity interventions per se. We set no language restriction nor a restriction on the date from which studies were reported.
Search methods
PRESS (peer-review electronic search strategies) guidelines informed the design our search strategy [ 54 , 55 ] and an information specialist adapted the search terms (outlined in Table S 1 ) for the following electronic bibliographic databases: MEDLINE, PubMed, EMBASE, Econlit and Web of Science and NHSEED. We also inspected references of all relevant studies; and searched trials registers (ClinicalTrials.gov). Search terms used included cost, return on investment, economic, arts, music, storytelling, dancing, writing and older adult as well as social return on investment (SROI). The last search was performed on 09/11/2022. As many economic evaluations of ACIs (especially SROIs) are commissioned by government bodies or charitable organisations, a search of the grey literature was undertaken.
Handling searches
A PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow chart was used to document study selection, illustrating the numbers of records retrieved and selection flow through the screening rounds [ 56 , 57 , 58 ]; all excluded records (with rationale for exclusion) were documented.
Selection of studies
Two screening rounds were conducted independently by two health economists experienced in undertaking reviews (GC, CO’N). The first round screened the title and abstract of articles based on the eligibility criteria; those selected at this stage entered a second round of full text screening with eligibility based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any disagreements were discussed among the two reviewers, with access to a third reviewer available to resolve disagreements, though this proved unnecessary.
Data extraction and management
Two reviewers extracted relevant information independently using an proforma developed specifically for the purposes of this study, which included all 35 items suggested by Wijnen et al. (2016) [ 48 ]. Information was extracted in relation to the following factors: (1) general information including study title, author, year, funding source, country, setting and study design; (2) recruitment details, sample size, demographic characteristics (age, gender) and baseline health data (diagnosis, comorbidities); (3) interventions, effectiveness and cost data; (4) type of economic evaluation, perspective, payer, beneficiary, time horizon, measure of benefit and scale of intervention; (5) quality assessment, strength of evidence, any other important information; (6) results; (7) analysis of uncertainty and (8) conclusions. The quality assessment/risk of bias checklists were included in the data extraction proforma, and picklists were used to enhance uniformity of responses. The data extraction form was piloted by two reviewers (GC and CON) on one paper and discussion used to ensure consistent application thereafter.
Assessment of study quality
Two reviewers (GC & CON) independently assessed study quality, with recourse to a third reviewer for resolution of differences though this proved unnecessary. Quality assessment was based on the type of economic evaluation undertaken. Full and partial trial-based economic evaluations were assessed using the CHEC-extended checklist [ 59 ]. SROI analyses were assessed using a SROI-specific quality framework developed for the purpose of systematic review [ 60 ].
Data analysis methods
Due to the small number of evaluations detected, possible sources of heterogeneity and a lack of consensus on appropriate methods for pooling cost-effectiveness estimates [ 61 ] a narrative synthesis analysis was undertaken.
Database searches returned 11,619 records; from this, 402 duplicates were removed leaving 11,214 reports. From these 113 reports were assessment against the inclusion and exclusion criteria resulting in 4 studies for inclusion in the review. Over 40 websites were searched for relevant content returning 2 further studies for inclusion. The PRISMA 2020 diagram is presented in Fig. 1 . A high sensitivity search strategy was adopted to ensure all relevant studies were identified, resulting in a large number of studies being excluded at the first stage of screening.
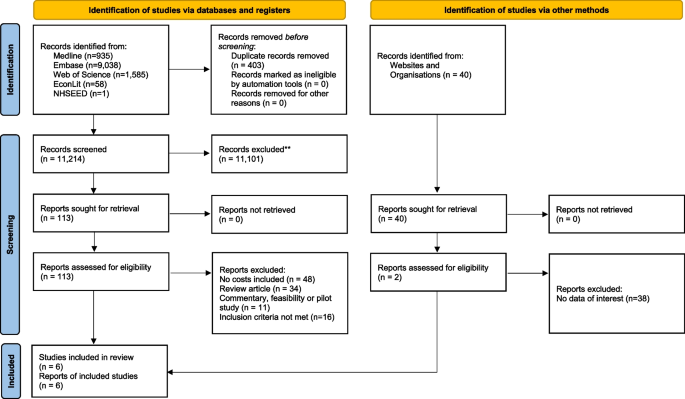
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews which include searches of databases, registers and other sources
A total of six studies were identified; key characteristics are presented in Table 1 . Identified studies were published between 2011 and 2020. Two studies used a health technology assessment (HTA) framework alongside clinical trials [ 62 , 63 ] to assess the cost-effectiveness of community singing interventions. Both evaluations scored highly on the CHEC-extended checklist (Table 2 ), with findings reported in line with the CHEERS (Consolidated Health Economic Estimation Reporting Standards) checklist 2022 [ 64 ].
Four further studies employed an SROI framework to assess art and/or craft interventions: two studies were published in the peer-reviewed literature [ 65 , 66 ] and a further two in the grey literature [ 67 , 68 ]. All four adhered closely to the suggested steps for performing an SROI and consequently secured high scores (Table 3 ). No quality differential was discerned between those studies published in the academic literature when compared with those from the grey literature.
Five of the studies were undertaken in the UK [ 63 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 ] and one in the US [ 63 ]. Four of the studies were designed for older adults with no cognitive impairment [ 62 , 63 , 67 , 68 ]; one was designed for participants with or without dementia [ 65 ], and another was specifically for older adults with dementia and their caregivers [ 66 ]. Three of the studies were delivered in a community setting [ 62 , 63 , 67 ], two in care homes [ 65 , 68 ] and one across a range of settings (hospital, community and residential) [ 66 ]. The length and duration of the ACIs varied; some lasted 1–2 h (with multiple classes available to participants) [ 65 ], whereas others were structured programmes with sessions lasting 90 min over a 14-week period [ 62 ]. The number of participants included in studies varied; the largest study contained data from 390 participants [ 63 ], whereas other studies measured engagement using numbers of care homes or housing associations included [ 67 , 68 ].
Costs were captured from a narrower perspective (i.e., the payer—health service) for those economic evaluations which followed a health technology assessment (HTA) framework [ 62 , 63 ]. Costs associated with providing the programme and health and social care utilisation costs were captured using cost diaries. Valuation of resource usage was in line with the reference case specified for each jurisdiction.
Social value analyses included in the review [ 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ] captured a broader picture of cost; programme provision costs included were similar in nature to those identified using an HTA framework, however, the benefits captured went beyond the individual to capture costs to a wide range of stakeholders such as family members, activity co-ordinations and care home personnel. Costs were apportioned using financial proxies from a range of sources including HACT Social Value Bank [ 69 ] and market-based valuation methods.
The range of outcomes captured and valued across HTAs and SROIs was extensive: including, but not limited to, wellbeing, quality of life, physical health, cognitive functioning, communication, control over daily life choices, engagement and empowerment, social isolation, mobility, community inclusion, depressive symptoms, sadness, anxiety, loneliness, positive affect and interest in daily life. In the programmes assessed using an HTA framework, outcomes were captured using standardised and validated instruments, for both control and intervention groups across multiple time points. Statistical methods were used to assess changes in outcomes over time. Programmes assessed using SROI relied primarily on qualitative methods (such as reflective diaries and in-depth interviews) combined with routinely collected administrative data.
The evidence from the singing interventions was encouraging but not conclusive. The ‘Silver Song Club’ programme [ 62 ] reported a 64% probability of being cost-effective at a willingness-to-pay threshold of £30,000. This study was also included in the Public Health England (PHE) decision tool to support local commissioners in designing and implementing services to support older people’s healthy ageing, reporting a positive societal return on investment [ 70 ]. Evidence from the ‘Community of Voices’ trial [ 63 ] suggested that although intervention group members experienced statistically significant improvements in loneliness and interest in life compared to control participants, no significant group differences were observed for cognitive or physical outcomes or for healthcare costs.
A positive return on investment was reported by all social value analyses undertaken. The ‘Imagine Arts’ programme, reported a positive SROI of £1.20 for every £1 of expenditure [ 65 ]. A higher yield of between £3.20-£6.62 for each £1 invested was reported in the ‘Dementia and Imagination’ programme [ 66 ]. The ‘Craft Café’ programme, reported an SROI of £8.27 per £1 invested [ 68 ], and the ‘Creative Caring’ programme predicted a SROI of between £3 to £4 for every £1 spent [ 67 ]. The time period over which return on investment was calculated differed for each evaluation from less than one year to 4 years.
The primary finding from our review concerns the paucity of evidence relating to the value, cost and/or cost-effectiveness of ACIs aimed at improving health and wellbeing in this population. Despite few restrictions being applied to our search, only six studies were found which met our inclusion criteria. This is not indicative of research into ACIs in this population, as evidenced by the identification of ninety-three studies where arts and creativity interventions were found to support better health and wellbeing outcomes in another recent review [ 5 ]. An alternative explanation is that funders do not see the added value of undertaking such evaluations in this area. That is, for funders, the cost of evaluating an ACIs is likely to be deemed unjustified given the relatively small welfare loss a misallocation of resources to them might produce. While at first glance this may seem reasonable, it disadvantages ACIs in competing with other interventions for funding and arguably exposes an implicit prejudice in the treatment of interventions from which it may be difficult to extract profit in general. That is, the paucity of evidence, may reflect inherent biases within our political economy that favour the generation of marketable solutions to health issues from which value can be appropriated as profit. Pharmaceuticals are an obvious example of such solutions, where the literature is replete with examples of evaluations sponsored by pharmaceutical companies or where public funds are used to test the claims made by pharmaceutical companies in respect of the value of their products. If the potential of ACIs to improve health and well-being is to be robustly established, ACIs must effectively compete for funding with other interventions including those from pharma. This requires a larger, more robust evidence base than is currently available and investment in the creation of such an evidence base. As there is currently no ‘for-profit’ industry to generate such an evidence base, public funding of evaluations will be central to its creation.
Our second finding concerns the values reported in the meagre evidence we did find. In five of the six studies we identified, evidence indicated that ACIs targeted at older people offered value for money [ 62 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ]. One study provided mixed evidence [ 63 ], however, in this study a ‘payer’ perspective was adopted when applying an HTA framework which, by virtue of the perspective adopted, excluded a range of benefits attributable to ACIs and public health interventions more generally. Among the four studies that adopted a SROI approach, estimated returns per £1 invested ranged from £1.20 to £8.27. Given the evident heterogeneity among studies in terms of context and methods, care is warranted in comparing estimates with each other or with other SROIs. Care is also required in accepting at face value the estimates reported given methodological issues that pertain to the current state of the art with respect to SROI. With these caveats in mind noted, the values reported for ACIs using the SROI approach are comparable with those from other SROI studies in other contexts including those as diverse as a first aid intervention [ 71 ], investment in urban greenways [ 72 ] and the provision of refuge services to those experiencing domestic violence [ 73 ] (a return on investment of £3.50-£4, £2.88-£5.81 and £4.94 respectively). Similarly, with respect to the study that adopted a cost-effectiveness approach, Coulton and colleagues (2015) reported a 64% probability of the intervention being cost-effective at a threshold of £30,000 [ 62 ]. Again, it is difficult to compare studies directly, but this is similar to that reported for interventions as diverse as a falls prevention initiative [ 74 ] and the treatment of depression using a collaborative approach [ 75 ] both in the UK. That the evidence base is meagre notwithstanding, there is, in other words, a prima facie case that ACIs are capable of offering value for money when targeted at older persons.
Our third finding relates to the state of the art with respect to SROIs in this area. Over the past 40 years, considerable time, effort and resources have been expended in the development of cost-effectiveness techniques in health and social care. While considerable heterogeneity can exist around their conduct, national guidance exists in many jurisdictions on the conduct of cost-effectiveness analyses (CEA) – such as the NICE reference case in the UK [ 76 ]– as well as in the reporting of these as set out in the CHEERS 2022 guidance [ 64 ]. This has helped raise the quality of published evaluations and the consistency with which they are reported. Despite the existence of a step-by-step guidance document on how to perform SROIs [ 77 ] which outlines how displacement effects, double counting, effect attribution and drop-off should be addressed, a significant body of work still remains to ensure that the methodology addresses a range of known biases in a robust manner. Where there is no comparator to the intervention being evaluated (as was the case in the SROIs reported here) it may be difficult to convince funders that the implicit incremental costs and benefits reported are indeed incremental and attributable to the intervention. Equally, where a comparator is present, greater consensus and standardisation is required regarding the identification, generation and application of, for example, financial proxies. Currently, SROI ratios combine value across a wide range of stakeholders, which is understandable if the objective is to capture all aspects of social benefit generated. This ratio, however, may not reflect the priorities and statutory responsibilities of healthcare funders. Whist all of the aforementioned issues can be addressed, investment is required to develop the SROI methodology further to more closely meet the needs of commissioning bodies.
Notwithstanding these challenges, social value analyses play a pivotal role within the procurement processes employed by government, local authorities and other non-departmental public bodies and should not be dismissed simply because the ‘burden of proof’ falls short of that required to secure remuneration within the health sector. As most SROIs are published in the grey literature, this means they often avoid peer scrutiny prior to publication and the potential quality assurance this can offer. It is noteworthy however that two of the SROIs included in this review [ 65 , 66 ] were published in the academic literature, suggesting that the academic community are engaging with this method which is to be applauded.
Moving forward, it is unlikely we will be able to meet all of the health and wellbeing needs of our ageing population solely in a primary or secondary care setting. New models of care are required, as are new models of funding to support interventions which can be delivered in non-healthcare settings. New hybrid models of evaluation will be required to provide robust economic evidence to assist in the allocation of scarce resources across health and non-healthcare settings; such evaluative frameworks must have robust theoretical underpinnings and be capable of delivering evidence from a non-clinical setting in a timely and cost-effective manner.
In the absence of a definitive evaluation framework for ACIs being currently available, we have a number of recommendations. First, and most importantly, all impact assessments should have a control group or credible counterfactual. This is currently not required when performing an SROI making it difficult to determine if all of the benefits ascribed to an intervention are in fact attributable. This recommendation is in line with the conclusion of a report by the London School of Economics [ 78 ] for the National Audit Office (NAO) which concluded that ‘any impact evaluation (and subsequent value for money calculation) requires construction of a counterfactual’. Second, a detailed technical appendix should accompany all impact assessments to allow independent review by a subject specialist. While this would assist peer review, it would allow providing greater transparency where peer review was not undertaken prior to publication. Furthermore, it would enable recalculation of SROI ratios to exclude ‘value’ attributable to stakeholders which are not relevant to a particular funder. Third, equity considerations should be addressed explicitly in all evaluations (this is currently not required in HTAs). Fourth, both costs and outcomes should be captured from a ‘broad’ perspective (adopting a ‘narrow’ healthcare perspective may underestimate the full economic impact), with non-healthcare sector costs being detailed as part of the analysis. Finally, data should be collected post-implementation to ensure that resources continue to be allocated efficiently.
As with any review, there are limitations which should be noted. A search of the grey literature was included as evaluations of applied public health interventions are not always reported in the academic literature. Systematically identifying grey literature and grey data can be problematic [ 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 ] as it is not collected, organised or stored in a consistent manner. Hence it is possible that we have not identified all relevant studies. Furthermore, as applied public health interventions can be performed in a non-healthcare setting we included SROIs in our review of economic evaluations. Current guidance on the systematic review of economic evaluations has been developed primarily for review of HTA as opposed to public health interventions and hence SROIs would be excluded, or if included would score poorly due to the inherent biases arising from no comparator or counterfactual being included.
This systematic review found that participation in group-based arts and creativity programmes was generally cost-effective and/or produced a positive return on investment whilst having a positive impact on older people’s physical, psychological, and social health and wellbeing outcomes. Unfortunately, the small number of studies identified, coupled with differences in methods used to assess economic impact hinders our ability to conclusively determine which types of art and creativity-based activities are more cost-effective or represent best value for money.
As well as the need for a greater focus on prevention of poor health as we age, new hybrid models of healthcare delivery are necessary to meet the needs of our ageing population. These models will integrate traditional medical care with other services such as home health aides (some of which may include artificial intelligence), telemedicine and social support networks. Alongside these, ACIs have the potential to provide a low cost, scalable, easily implementable and cost-effective solution to reduce the burden of illness in this age group and support healthy ageing.
Evidence on the cost-effectiveness of a range of ACIs is of utmost importance for policy and decision makers as it can both inform the development of policies that support the provision of ACIs in the context of ageing, but also identify the most cost-effective approaches for delivering such interventions. The development of hybrid models of evaluation, capable of capturing cost-effectiveness and social value, is becoming increasingly necessary as healthcare delivery for this age group moves beyond the realms of primary and secondary care and into the community. The development and refinement of such models will ensure a more comprehensive assessment of the impact of a diverse range of interventions providing a more nuanced understanding of the impact of an intervention. This will help inform decision making and ensure interventions are implemented in a cost-effective and socially beneficial manner.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the published article and its supplementary information files.
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.241. 2015.
Office for National Statistics. Living longer: how our population is changing and why it matters. https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarriages/ageing/articles/livinglongerhowourpopulationischangingandwhyitmatters/2018-08-13#how-do-incomes-of-older-people-compare-with-younger-ages . 2018. Accessed 07/12/2022
Dyakova M, Hamelmann C, Bellis MA, Besnier E, Grey CNB, Ashton K, Schwappach A, Clar C. Investment for health and well-being: a review of the social return on investment from public health policies to support implementing the Sustainable Development Goals by building on Health 2020 [Internet]. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2017.
Google Scholar
Fancourt D, Finn S. What is the evidence on the role of the arts in improving health and well-being? A scoping review. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2019.
McQuade L, O’Sullivan R. Examining arts and creativity in later life and its impact on older people’s health and wellbeing: a systematic review of the evidence. Perspect Publ Health. 2023;0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/17579139231157533
Skingley A, De’Ath S, Napleton L. Evaluation of Edna: arts and dance for older people. Work Older People. 2016;20(1):46–56.
Article Google Scholar
Brustio PR, Liubicich ME, Chiabrero M, et al. Dancing in the golden age: a study on physical function, quality of life, and social engagement. Geriatr Nurs. 2018;39(6):635–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Beauchet O, Bastien T, Mittelman M, et al. Participatory art-based activity, community-dwelling older adults and changes in health condition: results from a pre-post intervention, single-arm, prospective and longitudinal study. Maturitas. 2020;134:8–14.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Roswiyani R, Hiew CH, Witteman CLM, et al. Art activities and qigong exercise for the well-being of older adults in nursing homes in Indonesia: a randomized controlled trial. Aging Ment Health. 2020;24(10):1569–78.
Shanahan J, Bhriain ON, Morris ME, et al. Irish set dancing classes for people with Parkinson’s disease: the needs of participants and dance teachers. Complement Ther Med. 2016;27:12–7.
Garcia Gouvêa JA, Antunes MD, Bortolozzi F, et al. Impact of senior dance on emotional and motor parameters and quality of life of the elderly. Rev Rene. 2017;18(1):51–8.
Sun J, Zhang N, Buys N, et al. The role of Tai Chi, cultural dancing, playing a musical instrument and singing in the prevention of chronic disease in Chinese older adults: a mind–body meditative approach. Int J Ment Health Pr. 2013;15:227–39.
Fu MC, Belza B, Nguyen H, et al. Impact of group-singing on older adult health in senior living communities: a pilot study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2018;76:138–46.
Feng L, Romero-Garcia R, Suckling J, et al. Effects of choral singing versus health education on cognitive decline and aging: a randomized controlled trial. Aging-us. 2020;12(24):24798–816.
Seinfeld S, Figueroa H, Ortiz-Gil J, et al. Effects of music learning and piano practice on cognitive function, mood and quality of life in older adults. Front Psychol. 2013;4:810.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
MacRitchie J, Breaden M, Milne AJ, et al. Cognitive, motor and social factors of music instrument training programs for older adults’ improved wellbeing. Front Psychol. 2020;10:2868.
Freeman WJI. A neurobiological role of music in social bonding. In: Wallin N, Merkur B, Brown S, editors. The origins of music. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2000. http://escholarship.org/uc/item/9025x8rt .
Huron D. Is music an evolutionary adaptation? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;930(1):43–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb05724.x .
Tarr B, Launay J, Dunbar RIM. Music and social bonding: “self–other” merging and neurohormonal mechanisms. Front Psychol. 2014;5:1096. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01096 .
Cain M, Lakhani A, Istvandity L. Short and long term outcomes for culturally and linguistically diverse (cald) and at-risk communities in participatory music programs: a systematic review. Arts Health. 2016;8(2):105–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/17533015.2015.1027934 .
Martin L, Oepen R, Bauer K, Nottensteiner A, Mergheim K, Gruber H, et al. Creative arts interventions for stress management and prevention – a systematic review. Behav Sci (Basel). 2018;8(2):pii:E28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8020028 .
Linnemann A, Wenzel M, Grammes J, Kubiak T, Nater UM. Music listening and stress in daily life: a matter of timing. Int J Behav Med. 2018;25(2):223–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-017-9697-5 .
Linnemann A, Strahler J, Nater UM. The stress-reducing effect of music listening varies depending on the social context. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;72:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.06.003 .
Panteleeva Y, Ceschi G, Glowinski D, Courvoisier DS, Grandjean DM. Music for anxiety? meta-analysis of anxiety reduction in non-clinical samples. Psychol Music. 2017;46(4):473–87. https://doi.org/10.1177/0305735617712424 .
Fancourt D, Tymoszuk U. Cultural engagement and incident depression in older adults: evidence from the English longitudinal study of ageing. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;214(4):225–9. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2018.267 .
Balbag MA, Pedersen NL, Gatz M. Playing a musical instrument as a protective factor against dementia and cognitive impairment: a population-based twin study. Int J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014;2014:836748. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/836748 .
Porat S, Goukasian N, Hwang KS, Zanto T, Do T, Pierce J, et al. Dance experience and associations with cortical gray matter thickness in the aging population. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2016;6(3):508–17. https://doi.org/10.1159/000449130 .
Federici A, Bellagamba S, Rocchi MBL. Does dance-based training improve balance in adult and young old subjects? a pilot randomized controlled trial. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2005;17(5):385–9 PMID: 16392413.
Alpert PT, Miller SK, Wallmann H, Havey R, Cross C, Chevalia T, et al. The effect of modified jazz dance on balance, cognition, and mood in older adults. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2009;21(2):108–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00392.x .
Jeon MY, Bark ES, Lee EG, Im JS, Jeong BS, Choe ES. The effects of a Korean traditional dance movement program in elderly women. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi. 2005;35(7):126876 (in Korean). PMID: 16418553.
Eyigor S, Karapolat H, Durmaz B, Ibisoglu U, Cakir S. A randomized controlled trial of Turkish folklore dance on the physical performance, balance, depression and quality of life in older women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009;48(1):84–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2007.10.008 .
Noopud P, Suputtitada A, Khongprasert S, Kanungsukkasem V. Effects of Thai traditional dance on balance performance in daily life among older women. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018;31(7):961–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-018-1040-8 .
Trombetti A, Hars M, Herrmann FR, Kressig RW, Ferrari S, Rizzoli R. Effect of musicbased multitask training on gait, balance, and fall risk in elderly people: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(6):525–33. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2010.446 .
Hyyppä MT, Mäki J, Impivaara O, Aromaa A. Individual-level measures of social capital as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: a population-based prospective study of men and women in Finland. Eur J Epidemiol. 2007;22(9):589–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-007-9153-y .
Hyyppä MT, Mäki J, Impivaara O, Aromaa A. Leisure participation predicts survival: a population-based study in Finland. Health Promot Int. 2006;21(1):5–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/dai027 .
Lennartsson C, Silverstein M. Does engagement with life enhance survival of elderly people in Sweden? the role of social and leisure activities. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2001;56(6):S335–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/56.6.s335 .
Sundquist K, Lindström M, Malmström M, Johansson SE, Sundquist J. Social participation and coronary heart disease: a follow-up study of 6900 women and men in Sweden. Soc Sci Med. 1982;58(3):615–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-9536(03)00229-6 .
Väänänen A, Murray M, Koskinen A, Vahtera J, Kouvonen A, Kivimäki M. Engagement in cultural activities and cause-specific mortality: prospective cohort study. Prev Med. 2009;49(2–3):142–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2009.06.026 .
Särkämö T, Soto D. Music listening after stroke: beneficial effects and potential neural mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1252(1):266–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06405.x .
Särkämö T, Pihko E, Laitinen S, Forsblom A, Soinila S, Mikkonen M, et al. Music and speech listening enhance the recovery of early sensory processing after stroke. J Cogn Neurosci. 2010;22(12):2716–27. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21376 .
Särkämö T, Ripollés P, Vepsäläinen H, Autti T, Silvenno HM, Salli E, et al. Structural changes induced by daily music listening in the recovering brain after middle cerebral artery stroke: a voxel-based morphometry study. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:245. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00245 .
Särkämö T, Tervaniemi M, Laitinen S, Forsblom A, Soinila S, Mikkonen M, et al. Music listening enhances cognitive recovery and mood after middle cerebral artery stroke. Brain. 2008;131(3):866–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn013 .
Fancourt D, Steptoe A, Cadar D. Cultural engagement and cognitive reserve: museum attendance and dementia incidence over a 10-year period. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;213(5):661–3. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2018.129 .
Fancourt D, Steptoe A, Cadar D. Cultural engagement predicts changes in cognitive function in older adults over a 10 year period: findings from the English longitudinal study of ageing. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10226. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2018.129 .
All Party Parliamentary group on arts, health and wellbeing. Creative health: the arts for health and wellbeing. 2017.
van Mastrigt GA, Hiligsmann M, Arts JJ, Broos PH, Kleijnen J, Evers SM, Majoie MH. How to prepare a systematic review of economic evaluations for informing evidence-based healthcare decisions: a five-step approach (part 1/3). Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2016;16(6):689–704. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2016.1246960 . Epub 2016 Nov 2 PMID: 27805469.
Thielen FW, Van Mastrigt G, Burgers LT, Bramer WM, Majoie H, Evers S, Kleijnen J. How to prepare a systematic review of economic evaluations for clinical practice guidelines: database selection and search strategy development (part 2/3). Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2016;16(6):705–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2016.1246962 . Epub 2016 Nov 2 PMID: 27805466.
Wijnen B, Van Mastrigt G, Redekop WK, Majoie H, De Kinderen R, Evers S. How to prepare a systematic review of economic evaluations for informing evidence-based healthcare decisions: data extraction, risk of bias, and transferability (part 3/3). Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2016;16(6):723–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737167.2016.1246961 . Epub 2016 Oct 21 PMID: 27762640.
Mandrik OL, Severens JLH, Bardach A, Ghabri S, Hamel C, Mathes T, Vale L, Wisløff T, Goldhaber-Fiebert JD. Critical appraisal of systematic reviews with costs and cost-effectiveness outcomes: an ISPOR good practices task force report. Value Health. 2021;24(4):463–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2021.01.002 . PMID: 33840423.
Kelly MP, McDaid D, Ludbrook A, Powell J: Economic appraisal of public health interventions. http://www.cawt.com/Site/11/Documents/Publications/Population%20Health/Economics%20of%20Health%20Improvement/Economic_appraisal_of_public_health_interventions.pdf
Weatherly H, Drummond M, Claxton K, Cookson R, Ferguson B, Godfrey C, Rice N, Sculpher M, Sowden A. Methods for assessing the cost-effectiveness of public health interventions: key challenges and recommendations. Health Policy. 2009;93(2–3):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2009.07.012 . Epub 2009 Aug 25 PMID: 19709773.
Payne K, McAllister M, Davies LM. Valuing the economic benefits of complex interventions: when maximising health is not sufficient. Health Econ. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/hec.2795 .
Edwards RT, Charles JM, Lloyd-Williams H. Public health economics: a systematic review of guidance for the economic evaluation of public health interventions and discussion of key methodological issues. BMC Public Health. 2013;24(13):1001. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-1001.PMID:24153037;PMCID:PMC4015185 .
Rethlefsen ML, Farrell AM, Osterhaus Trzasko LC, Brigham TJ. Librarian co-authors correlated with higher quality reported search strategies in general internal medicine systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68(6):617–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.11.025 . Epub 2015 Feb 7 PMID: 25766056.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.01.021 . Epub 2016 Mar 19 PMID: 27005575.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2008;6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 .
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;21(339):b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700.PMID:19622552;PMCID:PMC2714672 .
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097 Evers S, Goossens M, De Vet H, et al. Criteria list for assessment of methodological quality of economic evaluations: consensus on health economic criteria. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2005;21(02):240–245.
Evers S, Goossens M, de Vet H, van Tulder M, Ament A. Criteria list for assessment of methodological quality of economic evaluations: Consensus on Health Economic Criteria. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2005;21(2):240–5 PMID: 15921065.
Hutchinson CL, Berndt A, Gilbert-Hunt S, George S, Ratcliffe J. Valuing the impact of health and social care programmes using social return on investment analysis: how have academics advanced the methodology? A protocol for a systematic review of peer-reviewed literature. BMJ Open. 2018;8(12):e022534. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022534 . PMID:30530579;PMCID:PMC6303612.
Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1. 0. Chichester: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2013.
Coulton S, Clift S, Skingley A, Rodriguez J. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of community singing on mental health-related quality of life of older people: randomised controlled trial. Br J Psychiatry. 2015;207(3):250–5. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.113.129908 . Epub 2015 Jun 18 PMID: 26089304.
Johnson JK, Stewart AL, Acree M, Nápoles AM, Flatt JD, Max WB, Gregorich SE. A community choir intervention to promote well-being among diverse older adults: results from the community of voices trial. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2020;75(3):549–59. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gby132 . PMID:30412233;PMCID:PMC7328053.
Husereau D, Drummond M, Augustovski F, de Bekker-Grob E, Briggs AH, Carswell C, Caulley L, Chaiyakunapruk N, Greenberg D, Loder E, Mauskopf J, Mullins CD, Petrou S, Pwu RF, Staniszewska S, CHEERS 2022 ISPOR Good Research Practices Task Force. Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards 2022 (CHEERS 2022) statement: updated reporting guidance for health economic evaluations. Value Health. 2022;25(1):3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2021.11.1351 . PMID: 35031096.
Bosco A, Schneider J, Broome E. The social value of the arts for care home residents in England: a social return on investment (SROI) analysis of the imagine arts programme. Maturitas. 2019;124:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.02.005 . Epub 2019 Mar 13 PMID: 31097173.
Jones C, Windle G, Edwards RT. Dementia and imagination: a social return on investment analysis framework for art activities for people living with dementia. Gerontologist. 2020;60(1):112–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gny147 . PMID: 30476114.
Social Value Lab and Impact Arts Craft Café: creative solutions to isolation and loneliness; Social return on investment. 2011. http://www.socialvaluelab.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/CraftCafeSROI.pdf
MB associates. Make my day: the impact of Creative Caring in older people’s care homes. 2013. https://www.suffolkartlink.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/CreativeCarersSROIReport_Nov2013.pdf
HACT. n.d. UK Social Value Bank. Retrieved December 11, 2023. from https://hact.org.uk/tools-and-services/uk-social-value-bank/ .
The Older Adults’ NHS and social care return on investment tool. Project report. Public health England. December 2019. Last accessed 27/03/2023.
British Red Cross – Valuing First Aid Education. 2018. https://socialvalueuk.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Valuing-First-Aid-Education-Social-Return-on-Investment-Report-on-the-value-of-First-Aid-Education-Assured-Report.pdf . Accessed 17/02/2023
Hunter R, Dallat M, Tully M, O’Neill C, Heron L, Kee F. Social return on investment analysis of an urban greenway. Cities and Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1080/23748834.2020.1766783 .
NEF Consulting. Refuge: A social return on investment evaluation. 2016. https://socialvalueuk.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Refuge-SROI-2016.pdf Accessed 17/02/2022
Corbacho B, Cockayne S, Fairhurst C, Hewitt CE, Hicks K, Kenan AM, Lamb SE, MacIntosh C, Menz HB, Redmond AC, Rodgers S, Scantlebury A, Watson J, Torgerson DJ, on behalf of the REFORM study. Cost-Effectiveness of a Multifaceted Podiatry Intervention for the Prevention of Falls in Older People: The REducing Falls with Orthoses and a Multifaceted Podiatry Intervention Trial Findings. Gerontology. 2018;64(5):503–12. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489171 . Epub 2018 Jun 26 PMID: 29945150.
Green C, Richards DA, Hill JJ, Gask L, Lovell K, Chew-Graham C, Bower P, Cape J, Pilling S, Araya R, Kessler D, Bland JM, Gilbody S, Lewis G, Manning C, Hughes-Morley A, Barkham M. Cost-effectiveness of collaborative care for depression in UK primary care: economic evaluation of a randomised controlled trial (CADET). PLoS ONE. 2014;9(8):e104225. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104225.PMID:25121991;PMCID:PMC4133193 .
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). NICE health technology evaluations: the manual. 2022. Retrieved 27 March, 2023 from https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg36/chapter/introduction-to-health-technology-evaluation
NEF Consulting. SSE – Beatrice SROI framework – guidance document. https://www.sse.com/media/svnn5jpk/sroi-methodology-guidance-nef-consulting.pdf . Accessed 17/02/2022
Gibbons S, McNally S, Overman H. Review of Government Evaluations: A report for the NAO. London: National Audit Office; 2013.
Turner AM, Liddy ED, Bradley J, Wheatley JA. Modeling public health interventions for improved access to the gray literature. J Med Libr Assoc. 2005;93(4):487–94 PMID: 16239945; PMCID: PMC1250325.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Benzies KM, Premji S, Hayden KA, Serrett K. State-of-the-evidence reviews: advantages and challenges of including grey literature. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2006;3(2):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2006.00051.x . PMID: 17040510.
Franks H, Hardiker NR, McGrath M, McQuarrie C. Public health interventions and behaviour change: reviewing the grey literature. Public Health. 2012;126(1):12–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2011.09.023 . Epub 2011 Nov 29 PMID: 22130477.
Mahood Q, Van Eerd D, Irvin E. Searching for grey literature for systematic reviews: challenges and benefits. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(3):221–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1106 . Epub 2013 Dec 6 PMID: 26052848.
Godin K, Stapleton J, Kirkpatrick SI, Hanning RM, Leatherdale ST. Applying systematic review search methods to the grey literature: a case study examining guidelines for school-based breakfast programs in Canada. Syst Rev. 2015;22(4):138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-015-0125-0 . PMID:26494010;PMCID:PMC4619264.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms. Louise Bradley (Information Resource Officer, Institute of Public Health) for her assistance in refining search strategies and literature search.
This study was supported by the Institute of Public Health (IPH), 200 South Circular Road, Dublin 8, Ireland, D08 NH90. This study was a collaboration between two health economists (GC, CO’N) and two members of staff from the funding organisation (LM, RO’S). Input from IPH staff was fundamental in defining the scope of work and research question, refining search terms and review and editing of the manuscript. Staff from IPH were not involved in quality assurance or review of papers included in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Costing Solutions, Belfast, BT15 4EB, UK
Grainne Crealey
Institute of Public Health, 200 South Circular Road, Dublin 8, D08 NH90, Ireland
Laura McQuade & Roger O’Sullivan
Centre for Public Health, Institute of Clinical Sciences, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, BT12 6BA, UK
Ciaran O’Neill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LMcQ and ROS were involved in defining the scope of work, refining the research question, provision of subject specific (public health) context, review of search strategy, review & editing of manuscript. CON and GC were involved in refining the research question and search strategy, provision of health economics and systematic reviewing expertise, review of returned reports, original draft preparation, review, editing and submission of manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ciaran O’Neill .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.

Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1.
: Table S1. Search strategy for electronic databases and grey literature.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Crealey, G., McQuade, L., O’Sullivan, R. et al. Arts and creativity interventions for improving health and wellbeing in older adults: a systematic literature review of economic evaluation studies. BMC Public Health 23 , 2496 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-17369-x
Download citation
Received : 23 April 2023
Accepted : 28 November 2023
Published : 13 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-17369-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic evaluation
- Older adults
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 08 July 2023
Understanding geriatric models of care for older adults living with HIV: a scoping review and qualitative analysis
- Kristina Marie Kokorelias 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Anna Grosse 1 , 4 ,
- Alice Zhabokritsky 5 , 6 , 7 &
- Luxey Sirisegaram 1 , 4
BMC Geriatrics volume 23 , Article number: 417 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1419 Accesses
1 Citations
7 Altmetric
Metrics details
Advances in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) treatment have reduced mortality rates and consequently increased the number of individuals with HIV living into older age. Despite this, people aged 50 years and older have been left behind in recent HIV treatment and prevention campaigns, and a gold-standard model of care for this population has not yet been defined. Developing evidence-based geriatric HIV models of care can support an accessible, equitable, and sustainable HIV health care system that ensures older adults have access to care that meets their needs now and in the future.
Guided by Arksey & O’Malley (2005)’s methodological framework, a scoping review was conducted to determine the key components of, identify gaps in the literature about, and provide recommendations for future research into geriatric models of care for individuals with HIV. Five databases and the grey literature were systematically searched. The titles, abstracts and full texts of the search results were screened independently in duplicate. Data were analyzed using a qualitative case study and key component analysis approach to identify necessary model components.
5702 studies underwent title and abstract screening, with 154 entering full-text review. 13 peer-reviewed and 0 grey literature sources were included. Most articles were from North America. We identified three primary model of care components that may improve the successful delivery of geriatric care to people living with HIV: Collaboration and Integration; Organization of Geriatric Care; and Support for Holistic Care. Most articles included some aspects of all three components.
To provide effective geriatric care to older persons living with HIV, health services and systems are encouraged to use an evidence-based framework and should consider incorporating the distinct model of care characteristics that we have identified in the literature. However, there is limited data about models in developing countries and long-term care settings, and limited knowledge of the role of family, friends and peers in supporting the geriatric care of individuals living with HIV. Future evaluative research is encouraged to determine the impact of optimal components of geriatric models of care on patient outcomes.
Peer Review reports
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) continues to be characterized as one of the most prominent public health threats [ 1 ], although advances in antiretroviral therapy (ART) have reduced mortality rates and transformed HIV into a manageable, chronic disease [ 2 ]. The life expectancy for people living with HIV who have had early and sustained access to ART is now similar to that of HIV-negative populations [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Thus, there is now an increase in the number of individuals living with HIV into older age [ 6 ] and the number of older adults (aged ≥ 50 years [ 7 ]) living with HIV is expected to increase even further in the coming years [ 8 ]. The proportion of older adults living with HIV has nearly tripled since 2000 [ 9 ].
Older adults with HIV have an increased risk of dementia, diabetes, frailty, depression, osteoporosis, and some cancers, compared to those who are HIV negative [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Comorbidities commonly associated with ageing (e.g., diabetes) have been found to increase the risk of opportunistic infections (e.g., HIV-related concerns) in older adults with HIV [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Moreover, stigma is associated with higher rates of loneliness, social isolation and depression in the HIV population [ 17 ]. Despite their increased risk of poor health and social outcomes, older adults living with HIV face many challenges accessing appropriate health and social care, further exacerbating their poor health outcomes [ 18 ]. The stigma associated with HIV may result in a fear of disclosure that delays treatment [ 19 ], and individuals with HIV can feel discriminated against by healthcare providers, resulting in hesitation about or refusal to seek medical care [ 20 , 21 ]. Older adults also tend to not access social services designed for the HIV-infected population because of their own assumption that these programs are created only for younger individuals [ 22 ]. Consequently, HIV scholars have urged for a health and social care system where knowledge and communication about geriatric HIV care are encouraged amongst advocates who work directly with this population, such as geriatric healthcare workers [ 23 ].
Geriatric specialists have expertise in managing many comorbidities that share associations with both ageing and HIV, despite geriatricians being hesitant to take a prominent role in the care of HIV in older adults [ 24 ] due to a lack of experience and training [ 25 ]. While health policy reports a preference for general practice-based HIV care over specialist care [ 26 , 27 ], general practitioners may have a less nuanced understanding about the holistic care of an older adult with complex comorbidities, geriatric syndromes, and metabolic complications when compared with geriatricians [ 28 ]. The use of the Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA) has been explored, and may lead to improved health and social outcomes in the older adult-HIV population [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ], and may be used to measure outcomes in clinical trials that aim to improve the delivery of HIV care for the older adult-HIV population [ 36 ]. However, in the absence of specialized geriatric models of HIV care, many older adults with HIV fail to receive a CGA [ 37 , 38 ] and the recommendations from CGAs are rarely implemented due to a lack of feasibility following a geriatric consult for older adults with HIV [ 39 ].
Numerous models of care, defined as “the way health services are delivered” [ 40 ] (pg., 3), have been developed for older adults with HIV. Many involve geriatric specialists in HIV care, with geriatricians taking on various responsibilities ranging from consultation to leadership roles [ 36 , 41 ]. However, the gold-standard model of care for older adults living with HIV have not yet been defined [ 34 , 35 ], and geriatric care is often delivered by non-geriatric specialists [ 16 ]. Instead of examining models of care, recent literature reviews have tended to focus on the prevalence and experiences of older adults in HIV care [7, NaN], or the experiences of geriatricians [ 24 ]. As implementing geriatric models of HIV care into healthcare settings requires unique considerations [ 28 ], an improved understanding of existing models of care may inform best-practices. This approach has been done to inform the design and delivery of other models of healthcare [ 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ]. Therefore, we conducted a scoping review of the existing evidence about geriatric models of care for older adults within the context of HIV. To our knowledge, this is the first review to systematically identify the core operational components of existing models of care specific to older adults living with HIV.
A scoping review was selected to map the available literature on geriatric models of care for older adults within the context HIV [ 46 ]. The protocol for our scoping review followed the well-established framework outlined by Arksey and O’Malley [ 46 ] and later refined by Levac et al. [ 47 ] and Colquhoun et al. [ 48 ]. The framework was selected as it provides guidance to ensure a rigorous scoping review approach utilizing a comprehensive search strategy [ 46 ]. Our protocol has been published elsewhere (blinded for review #1) but is briefly described within this section of the manuscript. There were no deviations from our protocol. The framework includes five steps: 1) identifying the research questions; 2) identifying relevant literature; 3) study selection; 4) charting the data; 5) collating, summarizing and reporting the results [ 46 ]. The optional sixth step of consulting with key stakeholders was not followed due to financial resource constraints. We briefly summarize each step and report our findings in accordance with The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-Scr) [ 49 ] (see Supplemental Material A).
Step 1: Identifying the research questions
Our questions were developed to support a knowledge synthesis that could mobilize the current evidence into practice. Our study aimed to answer: What are the key components of the existing models of HIV care for older adults (aged ≥ 50 years [ 7 , 29 ])?
Step 2: Searching for relevant studies
To identify studies, we developed a comprehensive search strategy with an experienced medical information specialist (CDC) who first conducted the search in MEDLINE(R) ALL (in Ovid, including Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily) and then translated it into NLM’s PubMed OVID Embase + Embase Classic, EBSCO’s CINAHL Complete, Clarivate’s Web of Science Core Collection, and Elsevier’s Scopus from the earliest record to 2022 (see Supplemental Material B for the full strategies ) . The search strategy was peer-reviewed according to the peer-review of electronic search strategy guidelines (the PRESS strategy) [ 50 ]. MeSH terms were used. All searches were limited to English language. The final searches were completed on Friday, October 21, 2022. Duplicates were removed using the Bramer method in EndNote [ 51 ]. Covidence was used to manage the review process, including the deduplication of database results [ 52 ].
Gray literature and non-indexed articles were searched for using Google Scholar, Open Grey, open Google searches and relevant websites, including the World Health Organization, UK National Research Register, CADTH’s “Grey Matters”, New York Academy of Medicine's Grey Literature Report, the Canadian Medical Association InfoBase and the National Institute for Heath and Care Excellence – Guidance. Similar search terms used in the scientific search were used. We also consulted with stakeholders of our research (i.e. geriatricians, infectious disease specialists) for any gray literature missed.
Step 3: Selecting studies
Three reviewers (LS, KMK and AG) independently screened article titles and abstracts (level 1-screening) and then full articles (level 2-screening) were screened in duplicate to identify potentially relevant studies. In both levels of screening, any disagreements were resolved through team-based discussion. Articles were included if they described an implemented model or models of care to treat older adults living with HIV exclusively (i.e., not as part of the treatment for multi-morbidity including HIV) and included a registered healthcare provider that specialized in geriatric care (e.g., gerontology social worker, geriatric clinical nurse specialist, geriatrician). Perspective (viewpoint) papers that describe implemented models of HIV care were also included. Book sections, theses, film broadcasts, abstracts without adequate data, and literature reviews were excluded. Articles were also excluded if they: (1) did not propose an original model of HIV care specifically for older adults (i.e., models of care for all adults or models that may include older adults), (2) focused on ethical issues or the theoretical understandings of HIV care or geriatric care, (3) focused on training healthcare providers on how to deliver HIV and/or geriatric care; and (4) described social support, rather than care in a clinical, health-care context. Forward and backward searching were conducted on the final full-text articles to ensure a broad search using EndNote and Citationchaser [ 53 , 54 ].
Step 4: Charting the data
The same three reviewers independently extracted data from the included studies using a data abstraction form that was developed and pilot tested by two researchers (LS and KMK). The data form was tested on five articles for consistency in understanding and ensuring that all relevant data was captured. No changes were made after comparing the pilot test results. The fields for abstraction included author last name, year, study type, setting, geographic location (country), methodology, characteristics of intervention (model of care) and delivery method, participant and provider characteristics, patient inclusion and exclusion criteria, desired outcomes (primary and secondary), results and key conclusions.
Step 5: Collating, summarizing and reporting the results
Data were analyzed using a systematic qualitative case study analytic approach [ 55 ]. First, each author reviewed the abstracted data and independently noted the core operational components (i.e., model structure and process for delivery) described in the models of care. Then the authors came together to list all the identified model components across the included articles, by exploring the similar and different terms to describe the same model components. Each model component was given a label and a definition. These components became the basis of codes that were then appropriately applied by one author (KMK) to each article using NVivo 12 software [ 56 ]. Next the coded data was reviewed by all authors to determine how each model of care described in the articles adhered or did not adhere to each of the particular model components (codes). The authors met weekly to discuss the process of adherence. This discussion process was informed by adherence analyses [ 57 ]. During this process, authors were encouraged to identify any components that were potentially originally overlooked. No additional suggestions were made on key model components. The model components adhered to across the articles and models of care formed the basis of the results.
After a comprehensive list of the identified model components had been determined, two authors (KMK and AG) went through each article and identified them as either adhering or not adhering to each particular characteristic component, as determined by written evidence within the articles. This was done by having the two authors each providing their vote (i.e., adhering or not) and then comparing the two scoring. Any uncertainty in adherence assignment or discrepancies in voting was resolved through discussion amongst all the investigators as done in other reviews with similar methodologies [ 42 ].
Step 6: Consultation
To further contribute to our component adherence, we shared our model components with the senior investigators of our peer-reviewed articles for feedback. We also asked the investigators to assess their level of agreement with our interpretations of their study's component adherence. Lastly, we asked authors to send along any studies that they believed would be relevant to our review. This was done via email by the first (KMK) and senior author (LS) in December 2022. After two months, we only received five replies from 13 potential authors (n = 5/13, 38%) and all five authors agreed with the adherence we provided their article with, suggesting an accurate adherence analysis. No investigators provided us with additional materials or feedback on the model components, rather just commenting on their article specifically.
The databases search yielded a total of 5699 unique citations, from which 151 articles were selected for full text review. Of these 151 articles, 12 peer-reviewed articles were included. An additional peer-reviewed article was obtained from hand searching. No grey literature was included. Thirteen articles were included in the final analysis (see Fig. 1 PRISMA flow chart).
PRISMA flow chat diagram
Most ( n = 10/13, 77%) of the publication activity occurred in the United States (USA) [ 28 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 ]. The remaining three articles ( n = 3/13,23%) were from the United Kingdom (UK)[ 66 , 67 , 68 ]. Over half ( n = 9/13,69%) of the articles were published in the last 5 years (2018–2023) [ 28 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 ]. In published papers, the most common research methods were qualitative. The key description from these studies were abstracted and are summarized in Table 1 .
Patient population
Patients in the included models of care ranged from 48 [ 60 ]–87 years of age [ 67 ]. The number of patients served ranged from 76 [ 39 ] over 4 years to a maximum of 4000 at the time of data collection (period unspecified) [ 66 ]. Of those articles that reported sex ( n = 9/13,69%), the majority described primarily male samples [ 39 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 68 ]. Articles that reported race/ethnicity ( n = 7/13, 54%), described including participants who were mostly White [ 60 , 61 , 67 ] or African American [ 39 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 68 ]. These articles all included White individuals. Of the two ( n = 2/13, 15%) studies that reported the median time since HIV diagnosis [ 39 ], the average was 12.5 [ 63 ]- 21.5 [ 39 ] years. Medicaid was used as the patients’ primary health insurance in the USA [ 39 , 61 , 62 ].
Key operational components of geriatric models of HIV care
The qualitative analysis identified three distinct model of care components, each with one or more sub-components. These components are listed and described in Table 2 . Table 3 also lists the articles adherent to each component. These model components entail: Collaboration and Integration; Organization of Geriatric Care; and Support for Holistic Care. These three components are described and are illustrated in Fig. 2 .
Main Model Components
Model Component 1: Collaboration and integration
Eleven ( n = 11/13, 85%) [ 28 , 39 , 41 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ] articles described the importance of collaboration and integration for providers caring for older adults with HIV. Models of care frequently incorporated a team of multidisciplinary professionals from the health and social care sectors that were linked in with community supports to improve healthcare delivery for older adults with HIV.
i) Multidisciplinary care roles
Multidisciplinary teams supported the care of older adults living with HIV in all eleven articles that adhered to the Collaboration and Integration model component ( n = 11/13, 85%). These articles described several provider roles, including designated HIV specialists (infectious diseases or internal medicine physicians) [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ], geriatricians [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 67 , 68 ] and/or dual-trained HIV and geriatric physicians. Other physician roles included psychiatrists [ 39 ], endocrinologists [ 65 ], cardiologists [ 41 , 60 , 61 , 68 ] and medicine fellows [ 64 ]. Numerous nursing roles [ 41 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 ] were involved, such as HIV clinical nurse specialists [ 41 , 66 , 67 ] and nurse practioners [ 41 , 64 , 65 ]. Allied health professionals included dieticians [ 39 , 65 , 66 ]/ nutritionists[ 41 ], social workers[ 39 , 41 , 59 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 68 ], phsysiotherapists [ 41 , 59 , 66 ], occupational therapists [ 41 , 59 , 66 ], speech-language pathologists[ 59 ], counselors/therapists [ 59 ], homecare aides [ 59 ], clinical psychologists [ 65 , 66 ] and specialist pharmacists [ 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 ].
In addition to healthcare providers, several models of care also included research team members (i.e. research coordinators [ 39 ], research assistants [ 39 ], graduate students in gerontology and epidemiology [ 41 ]), medical directors and administrative staff [ 59 , 61 ] (e.g., program coordinator[ 60 ], a gerontologist [i.e., non-clinician] [ 41 ]), chaplains [ 59 ] and volunteers [ 59 ]. Peer navigator roles were also described [ 28 , 41 , 65 , 68 ].
The key responsibilities of these providers differed between models of care and many had overlapping functions. Physicians [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ] and nurses [ 41 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 ] were often responsible for overseeing and ensuring appropriate medical care, such as disease and symptom management. Other healthcare professional roles and designated navigation-specific roles [ 28 , 65 , 68 ], provided medication, rehabilitation [ 41 , 59 , 66 ], dietary [ 39 , 59 , 65 , 66 ], or emotional counseling to patients and caregivers [ 59 ]. Geriatricians, in particular, provided evidence-based, best-practice advice that was shared with patients’ primary care providers [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 67 , 68 ]. HIV specialists generally oversaw HIV-related treatments and community services [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ]. Pharmacists often provided medication instructions and explained care protocols [ 41 , 60 , 65 , 66 , 67 ]. All care providers were described as providing informational and tangible (i.e., hands-on care) support. Administrative and research staff were responsible for documenting relevant information accurately [ 39 , 41 , 59 , 61 ]. Only one article mentioned the role of non-professional caregivers (i.e., spouse, partner, or friend) as part of the care team [ 59 ], in which they were described as providing much of the personal care involved in the home management of HIV [ 59 ].
Administrative team members and researchers support the collection of client information to systematically standardize clinical and research operations [ 39 , 41 , 59 , 60 , 61 ].
ii) Team-Based care
Ten articles ( n = 10/13, 77%) described the team-based delivery of multidisciplinary care, which was facilitated by several different mechanisms. Informational continuity was identified as being vital in ensuring a consistent and coherent approach to the management of older adults’ evolving needs [ 67 ]. A shared electronic health record was found to enable team-based care, including the ability for multiple providers to chat in real-time [ 28 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 68 ]. Moreover, the multidisciplinary team would often meet to discuss each patient’s background, their outcome measures, current clinical problems, and anticipated needs [ 28 ]. Consequently, the team would facilitate the appropriate screenings through access to different providers, services, and resources [ 28 , 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 65 , 68 ]. Following a referral and initial clinical visit, the HIV-geriatric specialists would maintain communication with the primary care team [ 28 ], make recommendations based on the identified age-related needs for care [ 28 ], initiate referrals to other specialist care providers and communicate with community stakeholders to meet other needs [ 59 ]. Team-based care allowed for all members of the circle of care to have a comprehensive knowledge of patients’ health and social care needs (e.g., functional, cognitive) [ 28 ]. Results from retrospective medical and pharmacy chart reviews helped inform all team decisions [ 65 ]. When deemed necessary, the team would be able to create a new action plan [ 39 ] and determine follow-up [ 64 ]. Nurses who worked in case manager roles helped to facilitate this care by coordinating a comprehensive, holistic care plan in collaboration with the patient, caregiver(s), physician(s), and other members of the care team [ 59 ]. Team-based models of care were felt to improve the coordination of care [ 41 ].
iii) Community linkages
Nine articles ( n = 9/13, 69%) described how the management of HIV in older adults involved active, collaborative partnerships between multidisciplinary healthcare providers and the various community resources available to individuals living with HIV. Models of care were often delivered in linkage with community resources (e.g., social groups) [ 41 ] and through community partners (e.g., volunteer organizations) [ 41 ]. Social workers often helped to facilitate community linkages [ 59 ], and grant-funding helped to pay for community services [ 65 ]. By working with community partners [ 41 ], models of care were able to deliver both nonclinical care [ 39 ] (e.g., peer support to decrease isolation and depression [ 41 ]), as well as clinical care [ 28 ] (e.g., care facilitated by a community nurse [ 39 ]). Community outreach also helped to foster friendships amongst older adults living with HIV through social and community-building activities including dinners, speeches, dances, and trips [ 59 ]. Local partner agencies assisted with meeting the housing needs for patients with marginal housing [ 61 ], and with the provision of legal services [ 61 ]. Partnering medical HIV-geriatric services with community services was thought to result in improved access to services [ 28 ], reduced social isolation [ 60 ], improved home safety management [ 59 ] and the provision of spiritual care such as priests, rabbis, or pastoral personnel [ 59 ].
Model Component 2: Organization of geriatric care
The specific organizational structure of each model of care varied, particularly as it related to staffing models, processes for access and referrals, and the implementation of evidence-based, best-practice care and follow-up. All articles adhered and contributed to this model component. Models of care were often delivered through clinics that were predominantly hospital-based (i.e., operating within a hospital) [ 39 , 60 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 67 ]. Additionally, geriatric clinics were outpatient clinics housed within existing HIV clinics [ 41 ] or community-based services providing home care [ 59 ]. Some models of care were able to be delivered virtually, either solely via phone [ 62 ] or in addition to in-person delivery [ 65 , 66 ]. Some clinics ran weekly [ 66 ], bi-weekly [ 65 ] or monthly [ 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 ], whereas others were full-time [ 39 , 65 ].
i) Staffing models
Within the identified models of care, various staffing models were described. All articles contributed to this sub-component. The Geriatrician-Referral model included a geriatrician who consulted on patients [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 ] based on a referral from the primary care team (often an HIV provider [ 41 ]), according to the perceived need (e.g., cognitive concerns). Six articles ( n = 6/13, 46%) adhered to this. The Joint-Clinic model involved a geriatrician and HIV physician who were present in a single, combined clinic [ 41 , 66 , 67 , 68 ]. Four articles ( n = 4/13, 31%) adhered to this model. The HIV-Physician-led model involved staffing clinics with a HIV physician and clinical nurse specialist trained in geriatrics, without geriatrician involvement [ 65 , 66 ]. Two articles ( n = 2/13, 15%) adhered to this model. A further staffing model, the Dual-Trained Provider model, involved a dually-trained HIV and geriatrics provider, as either a physician [ 41 , 68 ] or psychotherapist [ 62 , 63 ]. Four articles ( n = 4/13, 31%) adhered to this model. The Nurse-led model, involved nurse-lead teams of allied health professionals [ 59 ]. Only one article ( n = 1/13, 8%) adhered to this model [ 59 ].
i) Access and referrals
All articles described processes to ensure appropriate access to care, and thus contributed to this sub-component. Referrals and on-call services [ 59 ] were used to facilitate access to care [ 59 ]. In some models of care, older adults were only able to access geriatric services via a referral from their HIV primary care team [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 67 ], while in other models, referrals were triggered by a combination of age (i.e., 50 years of age or older) and need (e.g., complexity) [ 28 , 66 , 67 , 68 ]. The process of receiving geriatric care often began with an assessment of patients’ needs and functional status (e.g., cognition) [ 39 ] and the collection of demographic information (e.g., age, sex, race/ethnicity, HIV risk factors, marital status, insurance status [ 39 ])[ 28 , 61 , 65 ]. Provider referrals were often documented through tracking scheduled appointments [ 60 , 61 , 68 ], however, limitations of this method included HIV providers not remembering to refer [ 41 ] and patient barriers such as confusion over the need for the referral which may result in skipping geriatric appointments [ 41 ]. One model of care implemented patient reminders to help ensure appointments were attended [ 64 ]. Two articles ( n = 2/13, 15%) relied on referrals through an AIDS service organization [ 62 , 63 ]Moreover, across the models, patients could choose to be referred to one service (e.g. cardiology clinic) or multiple (e.g., geriatrics clinic) [ 60 , 68 ]. Patients could choose to have follow up with the geriatrician[ 28 ] and/or be connected with a primary care provider [ 41 ]. Clinics have developed guidelines and policies to guide the operation of services [ 28 ].
ii) Implementation of evidence-based screening
All articles described the incorporation of gold-standard, evidence-based screening practices into their geriatric care. Mood symptoms were assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [ 60 , 62 , 63 , 67 ], the Geriatric Depression Scale [ 62 , 63 ], the Older Peoples’ Quality of Life Questionnaire [ 67 ] and/or the Patient Health Questionnaire [ 39 ], while cognition was assessed using tools such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment [ 60 ]. CGAs were followed up with direct actions such as counseling (e.g., about ageing) [ 28 , 39 , 60 ], assessments of comorbidities, age-appropriate preventative health screening[ 41 , 60 , 61 ], and pharmacist reviews targeting polypharmacy and drug safety [4, NaN]. In addition to the CGA, clinics offered British HIV Association (BHIVA)-recommended screening (i.e., guidelines for the management of HIV), an antiretroviral review, a functional review and full medication review [ 28 , 66 ]. Emotional support was monitored using the ‘Therapy Content Checklist’ [ 62 , 63 ]. The goal of using valid measurements was to promote best practice [ 59 ].
Model Component 3: Support for holistic care
As older persons are more likely to experience cumulative health challenges that affect their quality of life, models of care for people ageing with HIV have incorporated a comprehensive holistic management approach. All included articles adhered and contributed to this model component. Clinics provided care for patients with multimorbidity [ 60 , 61 , 66 , 67 ] and helped them to overcome socioeconomic challenges [ 41 ], substance use disorders [ 60 , 65 ] and social isolation [ 60 , 62 , 63 ] by understanding their backgrounds[ 41 ]. Physical health consultations considered cardiovascular disease, dental health, eye health and bone health[ 28 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 68 ] to address HIV and metabolic-related complications [ 41 ]. Care plans incorporated medication prescriptions [ 28 , 39 , 60 , 61 , 66 , 67 , 68 ], preventative screening [ 28 , 39 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ], age-related disease processes (e.g., cognitive-testing) [ 28 , 39 , 41 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ], psychosocial interventions to improve social networks and mental health [ 28 , 39 , 59 , 60 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 ], exercise and nutrition regimens [ 39 ] and behavioural health supports (e.g., smoking cessation, therapy) [ 28 , 39 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 67 ] to meet the holistic needs of each patient. Spiritual support delivered through religious leaders, mental health counselors/therapists, and emotional support volunteers was also offered [ 59 , 64 ].
i)Comprehensive geriatric assessment
Most models of care ( n = 8/13,61.5%) involved a CGA [ 28 , 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 66 , 68 ] or utilized geriatric screening tools [ 65 ] to guide holistic care plans. Most CGAs were delivered by geriatricians who would write full consultation notes [ 39 , 60 , 61 ], although non-geriatrician health care providers were often trained to administer geriatric screening tests [ 41 , 64 ]. The CGA provided an overview of physical and mental health, as well as social support systems [ 39 ], using validated scales [ 39 ].
ii)Supporting self-management
The models of care in six articles ( n = 6/13, 46%) aimed to support the self-management of older adults living with HIV. The goal of self-management was to enable patients to better manage their health outside of the clinic setting by involving older adults in medical decision-making [ 60 , 68 ] and managing their chronic illnesses [ 59 , 60 , 61 ]. Self-management involved education [ 39 , 59 , 60 , 65 ] and coaching [ 28 ] about health behaviours, guidance for choosing appropriate interventions [ 39 , 59 , 65 ] to improve a patient’s health status [ 28 , 65 ], and increased health care utilization to improve patient involvement in care [ 60 , 65 ]. Some models involved classes where older adults could learn about various health conditions [ 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ]. Where self-management was not possible due to cognitive or functional impairments, healthcare professionals provided education to individuals’ social support networks such as to encourage their inclusion in care [ 39 , 59 ]. To evaluate self-management, some studies included surveys about knowledge in the evaluations of the clinic models [ 60 , 61 ].
Our scoping review of the literature identified thirteen articles describing geriatric models of care for older adults living with HIV. The identified models came from two countries, the USA and the United Kingdom, and incorporated screening for geriatric syndromes [ 28 , 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 65 , 66 , 68 ]. From these articles, we identified three overarching key model components: Collaboration and Integration; Organization of Geriatric Care; and Support for Holistic Care. The models of care were largely delivered by a consulting geriatrician [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 ] via a referral from an HIV provider [ 41 ], from a joint clinic model involving a geriatrician and HIV physician[ 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 ], or through a dually-trained HIV-geriatrics provider [ 41 , 62 , 63 , 68 ]. However, some models did not involve a geriatrician [59, NaN]. Table 4 summarizes the future recommendations from the included articles.
Our review identified that most models of geriatric-HIV care are delivered by multidisciplinary teams that facilitate integrated health and social care. Multidisciplinary providers who work in team-based care models have been shown to improve clinical outcomes among HIV patients [ 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 ]. This study provided examples of collaborations in which practitioners worked together to meet the diverse needs of patients. Our data expand this finding by suggesting that multidisciplinary care providers help to facilitate referrals to even more providers, particularly those working in community settings, to ensure care continuity and care coordination to meet holistic needs for support. However, it is important for future research to further understand what staffing model of multidisciplinary team care contributes best to the quadruple aim of optimizing health system performance (i.e., improving the individual experience of care; improving the health of populations; reducing the per capita cost of healthcare and creating better provider experiences [ 74 ]) and the limitations of the existing approaches. Moreover, given the shortage of geriatricians [ 45 ] to meet patient needs, it is important to consider the transferability of models that involve a geriatrician [ 39 , 41 , 60 , 61 , 64 , 65 ][ 66 , 67 , 68 ], or dually-trained HIV-geriatrics provider [ 41 , 62 , 63 , 68 ].
The increasing proportion of older adults living with multimorbidity, including HIV, has evoked calls for tailored geriatric services that respond to their evolving needs. Our results suggest that care delivery should address multiple complex and multidimensional aspects of health and wellness, including psychosocial needs such as strategies to reduce social isolation. However, none of the articles discussed the provision of palliative or hospice care. Palliative care has been posited to augment HIV patients’ health and social care outcomes [ 75 ]. Implementation science may help researchers identify how to implement novel palliative care interventions into exiting practices and support uptake and sustainability by considering why, how and in what circumstances barriers and facilitators may be present [ 76 ]. In addition, older adults were described as being decision makers in their care such as being able to choose the follow up services they receive [ 60 , 68 ]. While some programs sought the input of older adults (e.g., through focus groups, none explicitly mentioned partnering with older adults to co-design their models of HIV care. Other HIV interventions have included individuals living with HIV on their steering committees and in development teams, such that care meaningfully reflects their wishes and preferences [ 77 , 78 , 79 ]. These interventions do not include older adults. Future models of care may wish to engage older adults in co-design to conceptualize and brainstorm program delivery [ 80 , 81 ].
Our review identified several areas of research with limited information. Most literature was published in the USA. Only one article mentioned the role of family caregivers in the care of HIV [ 59 ]. However, individuals living with HIV may receive support from non-kin family caregivers, such as friends [ 82 ]. Research is needed to better understand how broader conceptualizations of family can be embedded into the multidisciplinary care teams to help facilitate family-centered care [ 43 , 83 ]. Moreover, none of the articles mentioned care being delivered in the context of nursing or long-term care homes, nor did they mention offered referrals to long-term care facilities or services. Research is needed to determine the optimal approach for delivering geriatric services in long-term care settings to older adults living with HIV. Strategies are also needed to effectively embed HIV care into the already overburdened and under-resourced long-term care sector. While telehealth has proven to be an effective strategy for delivering HIV care [ 84 , 85 ], particularly in rural and remote communities where specialists may not be readily available [ 86 ], additional research is needed to identify the best practices and limitations for delivering geriatric-focused models of care virtually. Lastly, no studies have evaluated how to best incorporate culturally-sensitive geriatric care across racial and ethnic groups [ 87 , 88 ]. Thus, more data are needed to develop culturally-informed models of care to better engage and care for diverse populations of older adults living with HIV, particularly for adults with certain racial and ethnic backgrounds who may face pervasive stigma for accessing HIV care [ 89 , 90 ].
Limitations
As with any review, our findings must be considered within the context of the limitations. Despite our best efforts (i.e., multiple databases, peer-reviewed strategy, screening in duplicate, bibliographic searches, contacting authors of the reviewed articles), we may have inadvertently missed potentially relevant articles. Moreover, we may have missed papers of programs not yet described in the literature, such as those recently funded or piloted. Similarly, we limited the inclusion criteria to studies available in English due to resource constraints (i.e., lack of funding to support translation) and, consequently, may have biased our included studies to those published in English-speaking countries [ 91 ]. However, the intention of scoping reviews is to provide an overview or “map” of the breadth of existing literature, and thus, future exploration is warranted that builds upon our search strategy. Studies focused on individuals with HIV, but did not include description of older adults living with co-morbidities that impair healthcare decision-making, such as dementia, making it difficult to comment about models of care for individuals who require decision-making support. Lastly, stakeholders in implementing, delivering and receiving models of care (e.g., individuals with HIV, policy-makers, healthcare professionals) were not involved in the study design nor analysis.
Conclusions
Our review suggests that novel models of geriatric care for older adults living with HIV should include collaboration and integration, an organization of care that considers appropriate and timely referrals, communication of medical information and the implementation of evidence-based recommendations, as well as a holistic understanding of the dimensions of care, such that they support self-management. This proposed geriatric-based model can provide the framework to inform future implementation science and evaluative research to support further refining and developing this model. However, further research is needed to inform models of geriatric-HIV care in long-term care settings. Given the increasing number of older adults living with HIV, the development of best-practice models of integrated care can hopefully guide healthcare professionals to provide optimal care in the context of the complexities of care for older adults with HIV.
Availability of data and materials
The analysis files and data used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Organization WH. Consolidated guidelines on HIV prevention, testing, treatment, service delivery and monitoring: recommendations for a public health approach: World Health Organization 2021.
Gardner EM, McLees MP, Steiner JF, et al. The spectrum of engagement in HIV care and its relevance to test-and-treat strategies for prevention of HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(6):793–800.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Higgins JA, Hoffman S, Dworkin SL. Rethinking gender, heterosexual men, and women’s vulnerability to HIV/AIDS. Am J Public Health. 2010;100(3):435–45.
Marcus JL, Chao CR, Leyden WA, et al. Narrowing the gap in life expectancy between HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals with access to care. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 2016;73(1):39.
Nakagawa F, May M, Phillips A. Life expectancy living with HIV: recent estimates and future implications. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2013;26(1):17–25.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Guaraldi G, Milic J, Mussini C. Aging with HIV. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2019;16(6):475–81.
Sankar A, Nevedal A, Neufeld S, et al. What do we know about older adults and HIV? A review of social and behavioral literature. AIDS Care. 2011;23(10):1187–207.
Flaer PJ, Benjamin PL, Malow RM, et al. The growing cohort of seniors with HIV/AIDS: changing the scope of Medicare Part D. AIDS Care. 2010;22(7):903–8.
Autenrieth CS, Beck EJ, Stelzle D, et al. Global and regional trends of people living with HIV aged 50 and over: Estimates and projections for 2000–2020. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(11): e0207005.
Yendewa GA, Poveda E, Yendewa SA, et al. HIV/AIDS in Sierra Leone: Characterizing the hidden epidemic. AIDS Reviews 2018;20(2):104–13. doi: https://dx.doi.org/ https://doi.org/10.24875/AIDSRev.M18000022
Desmarais P, Gao AF, Lanctôt K, et al. White matter hyperintensities in autopsy-confirmed frontotemporal lobar degeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s research & therapy. 2021;13(1):129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-021-00869-6[publishedOnlineFirst:2021/07/15] .
Article Google Scholar
Buchacz K, Baker RK, Palella FJ Jr, et al. Disparities in prevalence of key chronic diseases by gender and race/ethnicity among antiretroviral-treated HIV-infected adults in the US. Antivir Ther. 2013;18(1):65–75.
Mateen FJ, Mills EJ. Aging and HIV-Related Cognitive Loss. JAMA, J Am Med Assoc. 2012;308(4):349–50. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.8538 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kong AM, Pozen A, Anastos K, et al. Non-HIV Comorbid Conditions and Polypharmacy Among People Living with HIV Age 65 or Older Compared with HIV-Negative Individuals Age 65 or Older in the United States: A Retrospective Claims-Based Analysis. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2019;33(3):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.2018.0190 .
McMillan JM, Gill MJ, Power C, et al. Comorbidities in Older Persons with Controlled HIV Infection: Correlations with Frailty Index Subtypes. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2020;34(7):284–94. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.2020.0051 .
Erlandson KM, Karris MY. HIV and aging: reconsidering the approach to management of comorbidities. Infect Dis Clin. 2019;33(3):769–86.
Emlet CA, Brennan DJ, Brennenstuhl S, et al. The impact of HIV-related stigma on older and younger adults living with HIV disease: does age matter? AIDS Care. 2015;27(4):520–8.
Emlet CA. Social, economic, and health disparities among LGBT older adults. Generations. 2016;40(2):16–22.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alexandra Marshall S, Brewington KM, Kathryn Allison M, et al. Measuring HIV-related stigma among healthcare providers: a systematic review. AIDS Care. 2017;29(11):1337–45.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hibbert M, Wolton A, Crenna-Jennings W, et al. Experiences of stigma and discrimination in social and healthcare settings among trans people living with HIV in the UK. AIDS Care. 2018;30(7):836–43.
Emlet CA, Brennan DJ, Brennenstuhl S, et al. Protective and risk factors associated with stigma in a population of older adults living with HIV in Ontario. Canada AIDS care. 2013;25(10):1330–9.
Fritsch T. HIV/AIDS and the older adult: An exploratory study of the age-related differences in access to medical and social services. J Appl Gerontol. 2005;24(1):35–54.
Wallach IS, Brotman SH. Gaps in health and social care services to older adults living with HIV: a qualitative study on the perspectives of older adults and service providers. NursCare Open Access J. 2019;6(1):28–33.
Google Scholar
Jones HT, Barber TJ. How do geriatricians feel about managing older people living with HIV? A scoping review European geriatric medicine. 2022;13(4):987–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-022-00642-4 .
Chambers LA, Wilson MG, Rueda S, et al. Evidence Informing the Intersection of HIV, Aging and Health: A Scoping Review. AIDS Behav. 2014;18(4):661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-013-0627-5 .
Liddy C, Shoemaker ES, Crowe L, et al. How the delivery of HIV care in Canada aligns with the Chronic care model: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(7):e0220516-e220616. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220516 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mapp F, Hutchinson J, Estcourt C. A systematic review of contemporary models of shared HIV care and HIV in primary care in high-income settings. Int J STD AIDS. 2015;26(14):991–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956462415577496 .
Siegler EL, Burchett CO, Glesby MJ. Older people with HIV are an essential part of the continuum of HIV care. Journal of the International AIDS Society 2018;21(10):e25188-n/a. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jia2.25188
Sánchez-Conde M, Díaz-Alvarez J, Dronda F, et al. Why are people with HIV considered “older adults” in their fifties? European Geriatric Medicine. 2019;10(2):183–8.
Grov C, Golub SA, Parsons JT, et al. Loneliness and HIV-related stigma explain depression among older HIV-positive adults. AIDS Care. 2010;22(5):630–9.
Greene M, Shi Y, Boscardin J, Sudore R, Gandhi M, Covinsky K. Geriatric conditions and healthcare utilisation in older adults living with HIV. Age and Ageing. 2022 May;51(5):afac093.
Sangarlangkarn A, Appelbaum JS. Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment in Older Persons With HIV. Open forum infectious diseases 2020;7(11):ofaa485-ofaa85. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaa485
Yip KF, Wong TH, Alhamid SM, et al. Integrating advance care planning as part of comprehensive geriatric assessment for hospitalised frail elderly patients: findings of a cross-sectional study. Singapore Med J. 2020;61(5):254–9. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2019098 .
Guaraldi G. Rockwood K. Geriatric-HIV medicine is born: Oxford University Press US; 2017. p. 507–9.
Guaraldi G, Palella FJ Jr. Clinical implications of aging with HIV infection: perspectives and the future medical care agenda. AIDS (London, England). 2017;31:S129–35.
Brañas F, Ryan P, Troya J, et al. Geriatric-HIV Medicine: the geriatrician’s role. European geriatric medicine. 2019;10(2):259–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-018-0144-1 .
Sangarlangkarn A, Apornpong T, Justice AC, et al. Screening tools for targeted comprehensive geriatric assessment in HIV-infected patients 50 years and older. Int J STD AIDS. 2019;30(10):1009–17. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956462419841478 .
Morrow H, Horner M, Thomson-Glover R. 992 RESULTS OF A PILOT HIV/FRAILTY CLINIC - CAN COMPREHENSIVE GERIATRIC ASSESSMENT BENEFIT FRAIL PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV? Age and ageing 2022;51(Supplement_2) doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afac126.043
Bitas C, Jones S, Singh HK, et al. Adherence to Recommendations from Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment of Older Individuals with HIV. Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care. 2019;18:2325958218821656–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325958218821656 .
Innovation AfC. Understanding the Process to Develop a Model of Care: An ACI Framework: Agency for Clinical Innovation Chatswood NSW, 2013.
Davis AJ, Greene M, Siegler E, et al. Strengths and Challenges of Various Models of Geriatric Consultation for Older Adults Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;74(6):1101–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab682 .
Sinha SK, Bessman ES, Flomenbaum N, et al. A systematic review and qualitative analysis to inform the development of a new emergency department-based geriatric case management model. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(6):672–82.
Kokorelias KM, Gignac MA, Naglie G, et al. Towards a universal model of family centered care: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):1–11.
Korthuis PT, McCarty D, Weimer M, et al. Primary care–based models for the treatment of opioid use disorder: A scoping review. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(4):268–78.
Krause KE, Kokorelias KM, Sinha SK. A systematic review and qualitative analysis of geriatric models of care for rural and remote populations. Rural Remote Health. 2022;22(3):7486–586.
PubMed Google Scholar
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):1–9.
Colquhoun HL, Levac D, O’Brien KK, et al. Scoping reviews: time for clarity in definition, methods, and reporting. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(12):1291–4.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, et al. PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;75:40–6.
Bramer WM, Giustini D, de Jonge GB, et al. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA. 2016;104(3):240.
Babineau J. Product review: covidence (systematic review software). Journal of the Canadian Health Libraries Association/Journal de l’Association des bibliothèques de la santé du Canada. 2014;35(2):68–71.
Bramer WM, Milic J, Mast F. Reviewing retrieved references for inclusion in systematic reviews using EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA. 2017;105(1):84.
Haddaway NR, Grainger MJ, Gray CT. Citationchaser: A tool for transparent and efficient forward and backward citation chasing in systematic searching. Research Synthesis Methods 2022
Miles MB, Huberman AM, Saldaña J. Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook: Sage publications 2018.
Beekhuyzen J. Putting the pieces of the puzzle together: Using Nvivo for a literature review. Proceedings of QualIT2007: Qualitative Research, From the Margins to the Mainstream, Wellington, New Zealand, Victoria University of Wellington 2007:18–20.
Bissonnette JM. Adherence: a concept analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2008;63(6):634–43.
Bhatta M, Nandi S, Dutta N, et al. HIV care among elderly population: Systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS research and human retroviruses 2020;36(ja):475–89. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/AID.2019.0098
Garvey C. AIDS care for the elderly: A community-based approach. AIDS Patient Care. 1994;8(3):118–20. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.1994.8.118 .
Greene M, Myers J, Tan JY, et al. The Golden Compass Program: Overview of the Initial Implementation of a Comprehensive Program for Older Adults Living with HIV. Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care. 2020;19:2325958220935267–67. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325958220935267 .
Greene ML, Tan JY, Weiser SD, et al. Patient and provider perceptions of a comprehensive care program for HIV-positive adults over 50 years of age: The formation of the Golden Compass HIV and aging care program in San Francisco. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(12):e0208486-e208586. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208486 .
Heckman TG, Heckman BD, Anderson T, et al. Common Factors and Depressive Symptom Relief Trajectories in Group Teletherapy for Persons Ageing with HIV: Common Factors and Depression in HIV-infected Older Adults. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2017;24(1):139–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.1989 .
Heckman TG, Sikkema KJ, Hansen N, et al. A randomized clinical trial of a coping improvement group intervention for HIV-infected older adults. J Behav Med. 2010;34(2):102–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-010-9292-6 .
Ruiz M, Cefalu C, Ogbuokiri J. A Dedicated Screening Program for Geriatric HIV-Infected Patients Integrating HIV and Geriatric Care. Journal of the International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care (Chicago, Ill : 2002) 2010;9(3):157–61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1545109710367519
Schmalzle SA, Viviano NA, Mohanty K, et al. People aging with HIV - protecting a population vulnerable to effects of COVID-19 and its control measures. AIDS Care. 2022;34(11):1355–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2021.2020208 .
Cresswell FV, Levett T. Specialist care of older adults with HIV infection in the UK: a service evaluation. HIV Med. 2017;18(7):519–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/hiv.12481 .
Levett T, Alford K, Roberts J, et al. Evaluation of a combined hiv and geriatrics clinic for older people living with hiv: The silver clinic in brighton, uk. Geriatrics (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;5(4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics5040081 .
Tan JY, Greene M, Blat C, et al. Examining the Impact of the Golden Compass Clinical Care Program for Older People with HIV: A Qualitative Study. AIDS Behav. 2022;26(5):1562–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-021-03509-0 .
Siegler, E. L., Burchett, C. O., & Glesby, M. J. (2018). Older people with HIV are an essential part of the continuum of HIV care. Journal of the International AIDS Society , 21 (10).
Elgalib A, Al-Sawafi H, Kamble B, et al. Multidisciplinary care model for HIV improves treatment outcome: a single-centre experience from the Middle East. AIDS Care. 2018;30(9):1114–9.
Handford CD, Tynan A-M, Agha A, et al. Organization of care for persons with HIV-infection: a systematic review. AIDS Care. 2017;29(7):807–16.
Sherer R, Stieglitz K, Narra J, et al. HIV multidisciplinary teams work: support services improve access to and retention in HIV primary care. AIDS Care. 2002;14(sup1):31–44.
Soto TA, Bell J, Pillen M, et al. Literature on integrated HIV care: a review. AIDS Care. 2004;16(sup1):43–55.
Bodenheimer T, Sinsky C. From triple to quadruple aim: care of the patient requires care of the provider. The Annals of Family Medicine. 2014;12(6):573–6.
Simms V, Higginson IJ, Harding R. Integration of palliative care throughout HIV disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(7):571–5.
Demiris G, Parker Oliver D, Capurro D, et al. Implementation science: implications for intervention research in hospice and palliative care. Gerontologist. 2014;54(2):163–71.
Mackworth-Young C, Dringus S, Dauya E, et al. Putting youth at the centre: co-design of a community-based intervention to improve HIV outcomes among youth in Zimbabwe. Wellcome open research. 2022;7:53.
Marent B, Henwood F, Darking M, et al. Development of an mHealth platform for HIV care: gathering user perspectives through co-design workshops and interviews. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2018;6(10): e9856.
Lee MJ, Onyango D, Hamza H, et al. Surveying testing preferences in Black, Latin American, and other minorities for the co-design of digital vending machines for HIV self-testing. Int J STD AIDS. 2020;31(2):158–65.
Tong C, Kernoghan A, Lemmon K, et al. Lessons and Reflections From an Extended Co-design Process Developing an mHealth App With and for Older Adults: Multiphase, Mixed Methods Study. JMIR aging. 2022;5(4): e39189.
Long-term co-design guidelines: Empowering older adults as co-designers of social robots. 2021 30th IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN); 2021. IEEE.
Prachakul W, Grant JS. Informal caregivers of persons with HIV/AIDS: A review and analysis. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2003;14(3):55–71.
Nelson MK. Fictive kin, families we choose, and voluntary kin: What does the discourse tell us? J Fam Theory Rev. 2013;5(4):259–81.
Dandachi D, Dang BN, Lucari B, et al. Exploring the attitude of patients with HIV about using telehealth for HIV care. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2020;34(4):166–72.
Dandachi D, Lee C, Morgan RO, et al. Integration of telehealth services in the healthcare system: with emphasis on the experience of patients living with HIV. J Investig Med. 2019;67(5):815–20.
Ohl M, Dillon D, Moeckli J, et al. Mixed-methods evaluation of a telehealth collaborative care program for persons with HIV infection in a rural setting. J Gen Intern Med. 2013;28(9):1165–73.
Bucharski D, Reutter LI, Ogilvie LD. “You need to know where we’re coming from”: Canadian aboriginal women’s perspectives on culturally appropriate HIV counseling and testing. Health Care Women Int. 2006;27(8):723–47.
Sauceda JA, Brooks RA, Xavier J, et al. From theory to application: a description of transnationalism in culturally-appropriate HIV interventions of outreach, access, and retention among Latino/a populations. J Immigr Minor Health. 2019;21(2):332–45.
Chakrapani V, Gulfam FR, Arumugam V, et al. Intersectional stigma and gender non-affirmation hinder HIV care engagement among transgender women living with HIV in India. AIDS care 2022:1–9.
Ziersch A, Walsh M, Baak M, et al. “It is not an acceptable disease”: A qualitative study of HIV-related stigma and discrimination and impacts on health and wellbeing for people from ethnically diverse backgrounds in Australia. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1–15.
Neimann Rasmussen L, Montgomery P. The prevalence of and factors associated with inclusion of non-English language studies in Campbell systematic reviews: A survey and meta-epidemiological study. Syst Rev. 2018;7(1):129–229. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-018-0786-6 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank and acknowledge the contributions of Charmaine De Castro, Information Specialist at the Mount Sinai Hospital– Sinai Health System, for providing guidance on the search strategy development, and conducting the literature search. We would like to thank and acknowledge the contributions of the authors who replied to our emails for contributing to our analysis.
This work was supported by Sinai Health’s Healthy Ageing and Geriatrics Program Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Geriatric Medicine, Department of Medicine, Sinai Health System and University Health Network, Suite 475 - 600 University Avenue, Toronto, ON, M5G 1X5, Canada
Kristina Marie Kokorelias, Anna Grosse & Luxey Sirisegaram
Department of Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, 160 - 500 University Ave, Toronto, ON, M5G 1V7, Canada
Kristina Marie Kokorelias
Rehabilitation Sciences Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Division of Geriatric Medicine, Department of Medicine, Medical Sciences Building, University of Toronto, 1 King’s College Cir, Toronto, ON, M5S 1A8, Canada
Anna Grosse & Luxey Sirisegaram
Department of Medicine, Medical Sciences Building, The University of Toronto, King’s College Cir, Toronto, ON, M5S 1A8, Canada
Alice Zhabokritsky
Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University Health Network, 610 University Ave, Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5G 2M9, Canada
CIHR Canadian HIV Trails Network, 570-1081 Burrard Street, Vancouver, BC, V6Z 1Y6, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the project idea and initiated the project. KMK and LS conceptualized the study design. KMK wrote the first draft of this manuscript and revised the article during the review process. KMK and LS provided guidance to the Information Specialist with respect to the design of the search strategy. All authors finalized the literature search strategy. KMK piloted the search strategy. AG and LS were involved in editing and revising the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the protocol and are accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Luxey Sirisegaram .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not Required.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kokorelias, K.M., Grosse, A., Zhabokritsky, A. et al. Understanding geriatric models of care for older adults living with HIV: a scoping review and qualitative analysis. BMC Geriatr 23 , 417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04114-7
Download citation
Received : 18 January 2023
Accepted : 16 June 2023
Published : 08 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04114-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Models of care
- Older adults
- Qualitative
- Scoping review
BMC Geriatrics
ISSN: 1471-2318
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Reumatologia
- v.59(1); 2021

Peer review guidance: a primer for researchers
Olena zimba.
1 Department of Internal Medicine No. 2, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Armen Yuri Gasparyan
2 Departments of Rheumatology and Research and Development, Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust (Teaching Trust of the University of Birmingham, UK), Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, West Midlands, UK
The peer review process is essential for quality checks and validation of journal submissions. Although it has some limitations, including manipulations and biased and unfair evaluations, there is no other alternative to the system. Several peer review models are now practised, with public review being the most appropriate in view of the open science movement. Constructive reviewer comments are increasingly recognised as scholarly contributions which should meet certain ethics and reporting standards. The Publons platform, which is now part of the Web of Science Group (Clarivate Analytics), credits validated reviewer accomplishments and serves as an instrument for selecting and promoting the best reviewers. All authors with relevant profiles may act as reviewers. Adherence to research reporting standards and access to bibliographic databases are recommended to help reviewers draft evidence-based and detailed comments.
Introduction
The peer review process is essential for evaluating the quality of scholarly works, suggesting corrections, and learning from other authors’ mistakes. The principles of peer review are largely based on professionalism, eloquence, and collegiate attitude. As such, reviewing journal submissions is a privilege and responsibility for ‘elite’ research fellows who contribute to their professional societies and add value by voluntarily sharing their knowledge and experience.
Since the launch of the first academic periodicals back in 1665, the peer review has been mandatory for validating scientific facts, selecting influential works, and minimizing chances of publishing erroneous research reports [ 1 ]. Over the past centuries, peer review models have evolved from single-handed editorial evaluations to collegial discussions, with numerous strengths and inevitable limitations of each practised model [ 2 , 3 ]. With multiplication of periodicals and editorial management platforms, the reviewer pool has expanded and internationalized. Various sets of rules have been proposed to select skilled reviewers and employ globally acceptable tools and language styles [ 4 , 5 ].
In the era of digitization, the ethical dimension of the peer review has emerged, necessitating involvement of peers with full understanding of research and publication ethics to exclude unethical articles from the pool of evidence-based research and reviews [ 6 ]. In the time of the COVID-19 pandemic, some, if not most, journals face the unavailability of skilled reviewers, resulting in an unprecedented increase of articles without a history of peer review or those with surprisingly short evaluation timelines [ 7 ].
Editorial recommendations and the best reviewers
Guidance on peer review and selection of reviewers is currently available in the recommendations of global editorial associations which can be consulted by journal editors for updating their ethics statements and by research managers for crediting the evaluators. The International Committee on Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) qualifies peer review as a continuation of the scientific process that should involve experts who are able to timely respond to reviewer invitations, submitting unbiased and constructive comments, and keeping confidentiality [ 8 ].
The reviewer roles and responsibilities are listed in the updated recommendations of the Council of Science Editors (CSE) [ 9 ] where ethical conduct is viewed as a premise of the quality evaluations. The Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) further emphasizes editorial strategies that ensure transparent and unbiased reviewer evaluations by trained professionals [ 10 ]. Finally, the World Association of Medical Editors (WAME) prioritizes selecting the best reviewers with validated profiles to avoid substandard or fraudulent reviewer comments [ 11 ]. Accordingly, the Sarajevo Declaration on Integrity and Visibility of Scholarly Publications encourages reviewers to register with the Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCID) platform to validate and publicize their scholarly activities [ 12 ].
Although the best reviewer criteria are not listed in the editorial recommendations, it is apparent that the manuscript evaluators should be active researchers with extensive experience in the subject matter and an impressive list of relevant and recent publications [ 13 ]. All authors embarking on an academic career and publishing articles with active contact details can be involved in the evaluation of others’ scholarly works [ 14 ]. Ideally, the reviewers should be peers of the manuscript authors with equal scholarly ranks and credentials.
However, journal editors may employ schemes that engage junior research fellows as co-reviewers along with their mentors and senior fellows [ 15 ]. Such a scheme is successfully practised within the framework of the Emerging EULAR (European League Against Rheumatism) Network (EMEUNET) where seasoned authors (mentors) train ongoing researchers (mentees) how to evaluate submissions to the top rheumatology journals and select the best evaluators for regular contributors to these journals [ 16 ].
The awareness of the EQUATOR Network reporting standards may help the reviewers to evaluate methodology and suggest related revisions. Statistical skills help the reviewers to detect basic mistakes and suggest additional analyses. For example, scanning data presentation and revealing mistakes in the presentation of means and standard deviations often prompt re-analyses of distributions and replacement of parametric tests with non-parametric ones [ 17 , 18 ].
Constructive reviewer comments
The main goal of the peer review is to support authors in their attempt to publish ethically sound and professionally validated works that may attract readers’ attention and positively influence healthcare research and practice. As such, an optimal reviewer comment has to comprehensively examine all parts of the research and review work ( Table I ). The best reviewers are viewed as contributors who guide authors on how to correct mistakes, discuss study limitations, and highlight its strengths [ 19 ].
Structure of a reviewer comment to be forwarded to authors
Some of the currently practised review models are well positioned to help authors reveal and correct their mistakes at pre- or post-publication stages ( Table II ). The global move toward open science is particularly instrumental for increasing the quality and transparency of reviewer contributions.
Advantages and disadvantages of common manuscript evaluation models
Since there are no universally acceptable criteria for selecting reviewers and structuring their comments, instructions of all peer-reviewed journal should specify priorities, models, and expected review outcomes [ 20 ]. Monitoring and reporting average peer review timelines is also required to encourage timely evaluations and avoid delays. Depending on journal policies and article types, the first round of peer review may last from a few days to a few weeks. The fast-track review (up to 3 days) is practised by some top journals which process clinical trial reports and other priority items.
In exceptional cases, reviewer contributions may result in substantive changes, appreciated by authors in the official acknowledgments. In most cases, however, reviewers should avoid engaging in the authors’ research and writing. They should refrain from instructing the authors on additional tests and data collection as these may delay publication of original submissions with conclusive results.
Established publishers often employ advanced editorial management systems that support reviewers by providing instantaneous access to the review instructions, online structured forms, and some bibliographic databases. Such support enables drafting of evidence-based comments that examine the novelty, ethical soundness, and implications of the reviewed manuscripts [ 21 ].
Encouraging reviewers to submit their recommendations on manuscript acceptance/rejection and related editorial tasks is now a common practice. Skilled reviewers may prompt the editors to reject or transfer manuscripts which fall outside the journal scope, perform additional ethics checks, and minimize chances of publishing erroneous and unethical articles. They may also raise concerns over the editorial strategies in their comments to the editors.
Since reviewer and editor roles are distinct, reviewer recommendations are aimed at helping editors, but not at replacing their decision-making functions. The final decisions rest with handling editors. Handling editors weigh not only reviewer comments, but also priorities related to article types and geographic origins, space limitations in certain periods, and envisaged influence in terms of social media attention and citations. This is why rejections of even flawless manuscripts are likely at early rounds of internal and external evaluations across most peer-reviewed journals.
Reviewers are often requested to comment on language correctness and overall readability of the evaluated manuscripts. Given the wide availability of in-house and external editing services, reviewer comments on language mistakes and typos are categorized as minor. At the same time, non-Anglophone experts’ poor language skills often exclude them from contributing to the peer review in most influential journals [ 22 ]. Comments should be properly edited to convey messages in positive or neutral tones, express ideas of varying degrees of certainty, and present logical order of words, sentences, and paragraphs [ 23 , 24 ]. Consulting linguists on communication culture, passing advanced language courses, and honing commenting skills may increase the overall quality and appeal of the reviewer accomplishments [ 5 , 25 ].
Peer reviewer credits
Various crediting mechanisms have been proposed to motivate reviewers and maintain the integrity of science communication [ 26 ]. Annual reviewer acknowledgments are widely practised for naming manuscript evaluators and appreciating their scholarly contributions. Given the need to weigh reviewer contributions, some journal editors distinguish ‘elite’ reviewers with numerous evaluations and award those with timely and outstanding accomplishments [ 27 ]. Such targeted recognition ensures ethical soundness of the peer review and facilitates promotion of the best candidates for grant funding and academic job appointments [ 28 ].
Also, large publishers and learned societies issue certificates of excellence in reviewing which may include Continuing Professional Development (CPD) points [ 29 ]. Finally, an entirely new crediting mechanism is proposed to award bonus points to active reviewers who may collect, transfer, and use these points to discount gold open-access charges within the publisher consortia [ 30 ].
With the launch of Publons ( http://publons.com/ ) and its integration with Web of Science Group (Clarivate Analytics), reviewer recognition has become a matter of scientific prestige. Reviewers can now freely open their Publons accounts and record their contributions to online journals with Digital Object Identifiers (DOI). Journal editors, in turn, may generate official reviewer acknowledgments and encourage reviewers to forward them to Publons for building up individual reviewer and journal profiles. All published articles maintain e-links to their review records and post-publication promotion on social media, allowing the reviewers to continuously track expert evaluations and comments. A paid-up partnership is also available to journals and publishers for automatically transferring peer-review records to Publons upon mutually acceptable arrangements.
Listing reviewer accomplishments on an individual Publons profile showcases scholarly contributions of the account holder. The reviewer accomplishments placed next to the account holders’ own articles and editorial accomplishments point to the diversity of scholarly contributions. Researchers may establish links between their Publons and ORCID accounts to further benefit from complementary services of both platforms. Publons Academy ( https://publons.com/community/academy/ ) additionally offers an online training course to novice researchers who may improve their reviewing skills under the guidance of experienced mentors and journal editors. Finally, journal editors may conduct searches through the Publons platform to select the best reviewers across academic disciplines.
Peer review ethics
Prior to accepting reviewer invitations, scholars need to weigh a number of factors which may compromise their evaluations. First of all, they are required to accept the reviewer invitations if they are capable of timely submitting their comments. Peer review timelines depend on article type and vary widely across journals. The rules of transparent publishing necessitate recording manuscript submission and acceptance dates in article footnotes to inform readers of the evaluation speed and to help investigators in the event of multiple unethical submissions. Timely reviewer accomplishments often enable fast publication of valuable works with positive implications for healthcare. Unjustifiably long peer review, on the contrary, delays dissemination of influential reports and results in ethical misconduct, such as plagiarism of a manuscript under evaluation [ 31 ].
In the times of proliferation of open-access journals relying on article processing charges, unjustifiably short review may point to the absence of quality evaluation and apparently ‘predatory’ publishing practice [ 32 , 33 ]. Authors when choosing their target journals should take into account the peer review strategy and associated timelines to avoid substandard periodicals.
Reviewer primary interests (unbiased evaluation of manuscripts) may come into conflict with secondary interests (promotion of their own scholarly works), necessitating disclosures by filling in related parts in the online reviewer window or uploading the ICMJE conflict of interest forms. Biomedical reviewers, who are directly or indirectly supported by the pharmaceutical industry, may encounter conflicts while evaluating drug research. Such instances require explicit disclosures of conflicts and/or rejections of reviewer invitations.
Journal editors are obliged to employ mechanisms for disclosing reviewer financial and non-financial conflicts of interest to avoid processing of biased comments [ 34 ]. They should also cautiously process negative comments that oppose dissenting, but still valid, scientific ideas [ 35 ]. Reviewer conflicts that stem from academic activities in a competitive environment may introduce biases, resulting in unfair rejections of manuscripts with opposing concepts, results, and interpretations. The same academic conflicts may lead to coercive reviewer self-citations, forcing authors to incorporate suggested reviewer references or face negative feedback and an unjustified rejection [ 36 ]. Notably, several publisher investigations have demonstrated a global scale of such misconduct, involving some highly cited researchers and top scientific journals [ 37 ].
Fake peer review, an extreme example of conflict of interest, is another form of misconduct that has surfaced in the time of mass proliferation of gold open-access journals and publication of articles without quality checks [ 38 ]. Fake reviews are generated by manipulating authors and commercial editing agencies with full access to their own manuscripts and peer review evaluations in the journal editorial management systems. The sole aim of these reviews is to break the manuscript evaluation process and to pave the way for publication of pseudoscientific articles. Authors of these articles are often supported by funds intended for the growth of science in non-Anglophone countries [ 39 ]. Iranian and Chinese authors are often caught submitting fake reviews, resulting in mass retractions by large publishers [ 38 ]. Several suggestions have been made to overcome this issue, with assigning independent reviewers and requesting their ORCID IDs viewed as the most practical options [ 40 ].
Conclusions
The peer review process is regulated by publishers and editors, enforcing updated global editorial recommendations. Selecting the best reviewers and providing authors with constructive comments may improve the quality of published articles. Reviewers are selected in view of their professional backgrounds and skills in research reporting, statistics, ethics, and language. Quality reviewer comments attract superior submissions and add to the journal’s scientific prestige [ 41 ].
In the era of digitization and open science, various online tools and platforms are available to upgrade the peer review and credit experts for their scholarly contributions. With its links to the ORCID platform and social media channels, Publons now offers the optimal model for crediting and keeping track of the best and most active reviewers. Publons Academy additionally offers online training for novice researchers who may benefit from the experience of their mentoring editors. Overall, reviewer training in how to evaluate journal submissions and avoid related misconduct is an important process, which some indexed journals are experimenting with [ 42 ].
The timelines and rigour of the peer review may change during the current pandemic. However, journal editors should mobilize their resources to avoid publication of unchecked and misleading reports. Additional efforts are required to monitor published contents and encourage readers to post their comments on publishers’ online platforms (blogs) and other social media channels [ 43 , 44 ].
The authors declare no conflict of interest.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions. ... Advanced search. Find articles. with all of the words. with the exact phrase. with at least one of the words. without the words. where my words occur ...
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review - or a review article - is "a study that analyzes and synthesizes an existing body of literature by identifying, challenging, and advancing the building blocks of a theory through an examination of a body (or several bodies) of prior work (Post et al. 2020, p. 352).Literature reviews as standalone pieces of work may allow researchers to enhance their understanding of ...
The Literature Review Defined. In medical education, no organization has articulated a formal definition of a literature review for a research paper; thus, a literature review can take a number of forms. Depending on the type of article, target journal, and specific topic, these forms will vary in methodology, rigor, and depth.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
The bulk of the peer-reviewed journal articles included in a literature review should describe empirical research. According to Emerald Publishing ( 2023 ): Empirical research is research that is based on observation and measurement of phenomena, as directly experienced by the researcher.
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
This should ideally be peer-reviewed and published (journals such as Environmental ... and has been widely shown to be inappropriate as a main source of studies for literature review 34,35,36. ...
In February, I received two peer-review reports for a manuscript I'd submitted to a journal. One report contained 3 comments, the other 11. Apart from one point, all the feedback was different.
The most common types are: Single-blind review. Double-blind review. Triple-blind review. Collaborative review. Open review. Relatedly, peer assessment is a process where your peers provide you with feedback on something you've written, based on a set of criteria or benchmarks from an instructor.
The major advantage of a peer review process is that peer-reviewed articles provide a trusted form of scientific communication. Since scientific knowledge is cumulative and builds on itself, this trust is particularly important. Despite the positive impacts of peer review, critics argue that the peer review process stifles innovation in ...
The inclusion criteria include search boundary, time of publication, language, and search string. The search boundary was determined by focusing on academic journals in organization, management, and business. The search was limited to peer-reviewed articles published by English language in the past 9 years (from January 2014-December 2022).
Peer review - Why, when and how. Peer review has a key role in ensuring that information published in scientific journals is as truthful, valid and accurate as possible. It relies on the willingness of researchers to give of their valuable time to assess submitted papers, not just to validate the work but also to help authors improve its ...
This article investigates the prevalence dynamics of such terms in academic papers published in all fields of knowledge. The literature review uses the Semantic Scholar Open Research Corpus (SSORC) containing, as of 2020, over 175 million published scholarly articles and associated metadata. The author quantifies the prevalence of words denoting prejudice against ethnicity, gender, sexual ...
The terms scholarly, academic, peer-reviewed and refereed are sometimes used interchangeably, although there are slight differences.. Scholarly and academic may refer to peer-reviewed articles, but not all scholarly and academic journals are peer-reviewed (although most are.) For example, the Harvard Business Review is an academic journal but it is editorially reviewed, not peer-reviewed.
Review articles do not require Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval if the data reviewed are public (including private and government databases) and if the articles reviewed have received IRB approval previously. ... Literature reviews include peer-reviewed original research, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses, but also may include ...
How to Read and Comprehend Scientific Journal Articles Peer-reviewed or scholarly journal articles are written in a very specific organized and formal way. If you haven't spent much time with this type of literature, this video provides some tips for reading journal articles.
Two screening rounds were conducted independently by health economists experienced in systematic literature review. Methodological quality was assessed, and key information extracted and tabulated to provide an overview of the published literature. ... two studies were published in the peer-reviewed literature [65, 66] and a further two in the ...
The databases search yielded a total of 5699 unique citations, from which 151 articles were selected for full text review. Of these 151 articles, 12 peer-reviewed articles were included. An additional peer-reviewed article was obtained from hand searching. No grey literature was included.
The broader literature on peer review supports the focus of JAPNA editorials (Lu et al., 2022; Severin & Chataway, 2020).Peer review remains a vibrant part of scholarly publishing in all disciplines, marked by an increasing need for peer reviewers given the rise in scientific publication submissions (Lu et al., 2022).An ongoing theme in peer review discussions with pertinence to JAPNA involves ...
The peer review process is essential for evaluating the quality of scholarly works, suggesting corrections, and learning from other authors' mistakes. The principles of peer review are largely based on professionalism, eloquence, and collegiate attitude. As such, reviewing journal submissions is a privilege and responsibility for 'elite ...
Our peer-reviewed reports present the evidence-based consensus of committees of experts. Published proceedings record the presentations and discussions that take place at hundreds of conferences, workshops, symposia, forums, roundtables, and other gatherings every year. ... the committee conducted an in-depth review of literature on adverse ...