
Presentation Structures: Everything You Need to Organize Your Talk
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking , Speech Writing

A presentation structure includes an introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and scope for questions. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, this format can change. The article discusses various considerations for each section of a presentation structure.
For presentations to be understood and create a good impression, they can’t be haphazard. It has to have some sort of pre-planned presentation structure that is both logical and simple enough. Depending on the type of presentation you’re doing, there are likely some basic frameworks available that people tend to follow. Before we delve into the format, let’s consider key points to consider when planning a presentation.
How do you structure and plan a presentation?
We plan a presentation by considering the type of presentation, who our audience is, ideating the purpose, and formulating subtopics through research.
Consider the type of presentation
This leads to understanding the ideal flow to convey your content best. For instance, for persuasive presentations, you could use creative ways to convey what is best about a product, such as starting with a story about how it has helped many people achieve something.
On the other hand, for a progress presentation at your workplace, you might have conventions about what is expected, which must be followed precisely.
A few other types of presentations include:
- Informative presentations
- Instructive presentations
- Motivational presentations
- Analytical presentations
You might also want to consider if you want audience interaction and put that into the structure accordingly. While some allow questions mid-presentation for smaller audiences, it is typically left towards the end.
Consider your audience’s knowledge level and interests
This will determine if you can assume a particular knowledge base and not include it in your presentation structure or if you have to start off with basics and build up on that.
For instance, if you’re teaching 1st-year students about something, you might start with basics. But for graduates, a similar format would be unnecessary as they might have already learned about it.
Similarly, if your purpose is to deliver something entertaining, knowing about the interests and values of your audience helps a ton.
The most simple way is demographics. It’s typically quite easy to find out the expected age group, gender, etc of the audience. This information can help you have a basic idea of the sort of experiences they go through, which helps formulate an understanding.
Consider the purpose of your presentation
While this may seem obvious, many of us lose track of the main purpose and spend too much time on remotely related content. This diverts attention from the topic and might even cause boredom.
For example, if you’re advocating for some social action, it would be beneficial to stay on the topic itself, like the pros, cons, what can be done practically, etc. Instead, if the presenters spend more time criticizing others, the presentation will fall short of its purpose.
Few other examples of different purposes your presentation could have:
- Entertainment
- Providing information
- Telling your story
- Proposing ideas
- Discussing future plans for the company
Research your topic and start noting down the subtopics
Skip this if you already know exactly what needs to be a part of your presentation, and plan to include just that. While looking up your topic, you’ll discover the various sub-topics within that field. After you start noting them down, you can organize later what comes under which to build a structure.
Here is a guide on short presentations that you might be interested in.
So with these three considerations and subtopics in mind, we’re good to go over to decide our final structure.

What is the best presentation form?
The best presentation format is one that includes the introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Here, we will discuss a template or structure for a typical presentation.
Introduction
- Greet the audience and introduce yourself, e.g., what you do and why you’re here
- The purpose of your presentation
- The flow or outline gives a sense of what they can expect
- Depending on the topic and audience, you might have to provide more or less context about your topic
- This could include a brief history, terminologies, the current market status, the current status of the field, etc.
- Includes the full depth of the primary purpose of the presentation
- All major chunks of data, including examples, evidence like research studies, etc, are included here
- Care needs to be taken at times to ensure that your introduction and context are not taking up so much time that the main body isn’t receiving enough attention. Ever wonder if a presentation can be too short? Check out this article .
- Bring emphasis to the main takeaways
- Thank your audience if they have been a good one
- Take questions and encourage healthy discussion
- End with sharing ways they can address their questions later
To make sure that the structure works out, it is important that you practice your presentation. This will also tell you if you’re falling within the time constraints. Here is a guide on how you can go about practicing your presentation.
5 Ways to Structure Your Presentation
The five ways include ordered, problem-solution, comparative, storytelling, and demonstrating structures.
1. Ordered Structure
The presentation follows a logical sequence starting with an introduction, main points, and then conclusions. This is what this article has focused on, as it’s the most straightforward method and tends to be very clear for the audience. However, for presentations that do not follow a clear progression, this may not be useful.
2. Problem-Solution Structure
This is useful when persuading the audience. You explain the problem (+ its importance and impact) and then provide a solution that motivates the audience to take it. This could be in the form of a product, a particular method of communication, some technical thing, etc. There should be a decent amount of time spent on the benefits of the solution as well as the exact “How?” to implement it to make the audience convinced. It helps to address any questions or barriers you expect them to have during the speech itself.
3. Comparative Method
This is useful when you want to highlight the benefits of something over alternatives . It is ideal to first fully address the alternatives by talking about their benefits and limitations. Then you lastly talk about the solution that you possess that effectively addresses the other limitations or is in some way a better choice than others, based on your arguments.
Alternatively, if you do not want to highlight the benefits of something particular and just form a comparison that demonstrates the pros and cons of different subjects in an unbiased manner, this technique is still used. For instance, how the main benefit of a product is practically useful for the consumer in comparison to the main benefit of another product can be discussed.
4. Storytelling Structure
This is useful when your goal is just to tell a story. This could be to explain the context or history of a company. It could also serve to talk about yourself and how you got there. A story will typically have an introduction, a complicating factor that introduces some challenges, and then an ending that highlights the importance of some action or belief.
You may also go in a timewise order when explaining a story. This might take away from the thrill but is useful nonetheless when it is required for the audience to properly understand what is being conveyed. Storytelling can be done in various ways, so feel free to find your own structure.
5. Demonstration Structure
This is useful when demonstrating products or services . The benefits of the product/service are highlighted and it is demonstrated showing those capabilities. The goal should be on persuading the audience that it is useful to them for their needs.
How to structure a scientific presentation?
Structuring a scientific presentation typically includes an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
This typically follows the below format, but depending on the university/conference guidelines, you’ll have to adjust accordingly. The rest of the sub-topics revolves around these sections.
- Introduction/Background
- Literature review (if applicable)
- Acknowledgments (often optional)
After this, time is given to take questions.
How do you structure a presentation script?
The presentation never includes the full extent of the information. It’s just a concise version of what you’re speaking that adds as a visual aid at times while also highlighting major points.
The script is where the major content lies. The structure remains the same, but the content is greater in depth .
Sample Presentation Script
To make it easier for you to understand how you can structure your presentation script, here is a sample script for a presentation on the topic: Importance of Public Speaking.
This follows the same flow introduced earlier- introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and questions.
Title: Importance of Public Speaking
Slide 1: Why is Public Speaking Important?
Greetings, ladies, and gentlemen. Today, I will be exploring the importance of public speaking. My name is John, and I’m thrilled to discuss with you how improving our public speaking abilities may make a significant difference in our quality of life in the personal, social, and professional domains.
Slide 2: Introduction
Public speaking involves persuading an audience with a well-organized message. It is an essential part of our daily lives. We use it when we make conversation in social groups as well as when we address enormous crowds at social gatherings. It is a highly multifaceted and effective tool.
I will start off by giving some information about the context, moving on to its benefits, which is the main crux of our presentation, and then we will spend some time concluding.
Slide 3: Context
Effective communication is essential in our globally interconnected society. Speaking in front of an audience enables us to express our views and thoughts clearly and firmly. It facilitates the development of solid bonds and influences others, and acts as a catalyst for constructive change. Public speaking may open doors of opportunity and propel achievement for anyone, whether they are a student, professional, or member of the community.
Slide 4: Personal Development
Public speaking increases self-esteem and confidence, which are quite rudimentary to our self-efficacy. Effective communication skills help us to be more assertive and feel more in control of our lives. Research suggests that having an internal locus of control (i.e., feeling in control) leads to better outcomes in our personal lives as well as greater mental health. As we organize our ideas and arguments through public speaking, it improves critical thinking and organizational abilities. Furthermore, as we interact with others during talks and Q&A sessions, public speaking also enhances our listening abilities.
Slide 5: Professional Advancement
The ability to speak in front of an audience effectively is highly essential in most workplaces.
You ask Why? Well, it is because we are better able to communicate our qualifications and worth to potential employers, which enhances our performance in job interviews. Secondly, our influence within organizations grows when we can make a strong case for our points in meetings and conferences.
Next, for leadership positions, where success depends on inspiring and motivating others, public speaking is critical. And in general, you’ll need public speaking in any meeting or any talk you would typically deliver in front of a bunch of people.
Slide 6: Conclusion
Public speaking is a sought-after, multifaceted, and handy skill across many settings. It gives us the ability to inspire others, tell our stories, and make a lasting impression. Strong public speaking abilities help us communicate clearly and lead with influence in many facets of our lives.
Slide 7: Questions
I appreciate everyone here for being a great audience and cooperating wonderfully throughout the presentation. Now I will be taking any questions you all have. Feel free to discuss this now or reach out to me after the session is over.
Slide 8: Thank you
I want to thank you all for being here today.
I hope that the presentation did well to emphasize the importance of public speaking and perhaps motivated at least some of you to work on improving your abilities. We will end here.
[End of presentation]
Here are some tips for delivering an effective presentation.
We considered a few key points for presentation structure and the typical format that can be followed. We also covered five ways you can structure your presentation and the format for a scientific presentation. Lastly, we covered a sample script for presentations.
Public speaking coaching is a great way to increase your skills and get better at presentations as well.
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

10 Hand Gestures That Will Make You More Confident and Efficient

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.
Crafting an Effective Presentation Structure: From Introduction to Conclusion

Crafting an Effective Presentation Structure, from introduction to conclusion, is daunting and brings about a great deal of work. A great presentation leaves the audience feeling either inspired or informed on a specific topic. It generally is not because the speaker was knowledgeable or motivating.
Instead, they are aware of how to structure presentations logically and simply, allowing the audience to keep up with them and take away the key aspects of the presentation. A good structure helps the speaker deliver a presentation calmly, stay on topic and avoid any awkward silence between the presentations. This is precisely why individuals should look to enhance and develop effective presentation skills .
Factors that Determine the Presentation Structure
Before choosing and designing a presentation structure, the speaker should address a variety of factors, including:
- Who is the audience, and how knowledgeable are they already?
- Time duration of the presentation.
- The kind of setting in which the presentation is being delivered.
- Aim of the Presentation.
- What are the key points the audience should take away from the presentation?
Typical Presentation Structure
In general, the contents of a presentation include an introduction, body, and conclusion. At times, it may include visual aids. This is the usual flow for crafting an effective presentation structure: from introduction to conclusion, which covers all the necessary sections and allows the audience to follow along easily.
When designing a presentation,
- Create a solid, organized structure for the entire presentation.
- Keep the slides simple and clear to follow.
- Remember to be concise and do not confuse the audience.
- Make sure to add style and visual elements consistently in the presentation.
The Introduction – Greeting the audience & introducing the speaker
Be sure to create a positive environment by welcoming the audience with a friendly greeting. This allows the audience to arrive, settle down, and prepare for the presentation to start. The introduction is essential to establish a relationship between the speaker and the audience and gather their attention .
The introduction should help the audience comprehend and understand the subject and objective of the presentation as well as gain their attention and confidence . It should narrow down from a broad topic to the specifics of the talk.
- Stating the general topic.
- Narrowing to the area of interest/ subject of the presentation.
- Stating the problems/ challenges in the area being discussed.
- Stating the objective and purpose of the presentation.
- Providing a statement of the outcome of the presentation.
- Showing a preview of the content of the presentation.
This is a great time also to explain the length of the talk, indicate if the speaker wants an audience interaction, and inform the audience if they need to jot down the important points from the presentation. With effective presentation skills, people can keep the audience engaged and interested throughout the entire tenure of the presentation.
The Body
The body of the presentation should meet the objective and the information indicated in the introduction. This is an integral part of crafting an Effective Presentation Structure: From the Introduction to the Conclusion should make up about 75% of the total duration of the presentation.
- The topics should be segmented considering the nature of the presentation and then working through them individually for the audience to understand fully.
- The main points should be concise with relevant supportive evidence, statistics, and examples.
- Critical points should be indicated with reasons. Each important idea could be presented several times in different ways to help the audience fully absorb the meaning.
- State clear links between the ideas and internal summaries and always signal when moving on to the next point.
- Allow the audience to make relevant notes. Always remember to summarize the talk’s body and remind the audience of the topic.
After the main part of the presentation, the audience should understand the information and arguments clearly.
The Conclusion
The conclusion is frequently underdeveloped, and a poorly executed closing can completely undermine a successful presentation. However, the best section is to reflect more power onto the messages and create a lasting impression in the audience’s minds. The conclusion determines whether the speaker has achieved the presentation goal.
While crafting an Effective Presentation Structure: From Introduction to Conclusion, keep in mind that the conclusion should make up about 1/3 of the entire presentation and should contain the following elements:
- Summarize the key points: Keeping in mind the goal of the presentation, remember to summarise the main points and their implications. This is a good way to ensure the audience walks away with the precise information the speaker intended to convey.
- Repeating the core message: Repeating the core theme or message of the presentation can create a powerful conclusion. This will signal the end of the talk and will provide an overview of the argument, findings, and overall purpose of the talk.
- Offering a thought-provoking takeaway: Use a powerful and effective quote or saying that relates to the presentation’s theme and resonates with the audience.
- Visuals: Visuals can leave a lasting impression on the audience while the closing remarks are emphasized.
Final Steps – Thanking the audience and inviting questions
Conclude the talk by acknowledging and thanking the people present in the audience. Show them appreciation for their interest and the time that they have invested in the presentation. After this, the audience may be invited to ask any questions. It is best to focus on initially delivering the presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.
After finishing the entire presentation, the speaker should have built a relationship with their audience such that:
- The audience follows through on the presentation.
- It acts in the direction of the presentation’s goal.
- The audience remembers the presentation.
Collaborate with the expert Orator Academy team to gain more knowledge about this concept and enhance presentation skills. Check the official website of Orator Academy to develop your public speaking skills .

Vineeta Khanna
Vineeta Khanna is one of the most well known and successful public speaking coaches In New York and New Jersey. As the founder of Orator Academy, she has helped hundreds of young students and working professionals to become confident speakers.
Vineeta has worked with hundreds of students of all ages: elementary school students, college students, interns, job seekers, Wall Street professionals, home makers, IT professionals, teachers and more.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
You May Also Like

How to keep Your Child’s Attention While Giving a Speech

Overcoming Stage Fright: Effective Strategies for Performers
Inquiry form.
" * " indicates required fields
View E-Book
To View E-Book Please Fill the Form.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
How to Structure a Presentation
Choosing the best format for your audience.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Have you ever sat through a rambling, disorganized presentation? If so, you probably found it hard to follow what the speaker was saying.
When presentations don't flow well, it's easy for audiences to get lost. This is why it's important to think carefully about the structure and organization of your presentation.
In this article, we'll explore some common structures that you can use next time you speak in front of other people.
The Importance of Structure
Without a defined structure, your audience may not be able to follow your presentation. When this happens, your opportunity is lost, the communication fails, and your reputation takes a hit. For example, if your aim is to persuade people, you'll want to use a different approach from the one you'd use if you wanted to demonstrate how a product works.
Many factors can influence your choice of structure, but the most important consideration is your presentation's purpose or goal. You need to identify what you want to achieve – do you want to inspire, motivate, inform, persuade, or entertain people?
Your audience's needs also affect the structure you choose. For example, those who are new to your topic need more background information than people with more expertise and experience. So, in this case, you'd want to choose an approach that gives you ample time to explain the context of your subject, as well as to reinforce your main points.
Structures to Consider
Below, we outline several structures that you can use to organize your presentation.
1. Open – Body – Conclusion
The Open – Body – Conclusion approach is one of the most practical structures you can use for presentations. (Click here to download a worksheet that helps you use it.)
People often call it the "tell 'em" approach, because you:
- Tell audience members what you're going to tell them (introduction).
- Tell them (body).
- Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
This structure is simple, effective and easy to remember. Its repetitive nature allows you to reinforce your points, which helps others remember them. It is also flexible: you can adjust the introduction and body to persuade, motivate, educate, or entertain them.
One downside, however, is that repetition can quickly bore people. The approach is also "old hat" to many, which can cause them to lose interest. If you choose to use it, balance repetition with plenty of interesting facts, images, anecdotes, or stories to hold your audience's interest.
Let's look at each stage of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure in detail and discuss the elements that you need to include in each. We'll start with the body, rather than the introduction, because the rest of your presentation will be based on that.
The body of your presentation needs to contain your key points. You should present these in a logical order, so that your audience can follow them easily.
Keep in mind that the body should comprise a limited number of ideas: the more you try to include, the fewer people will remember. A good guide is to cover three to five main points, but no more.
When organizing your ideas, use the chunking principle to put the information into specific units. This will make the concepts easier to grasp, and help people remember what you have told them.
Make sure that you back up your main points with facts. Use good information-gathering strategies in your research, and consider citing the sources that you use. To add credibility to your presentation, consider using the following information to support your ideas:
- Data, facts or statistics.
- Images or diagrams.
- Stories and examples.
- Quotes or testimonials from experts or industry leaders.
Reliable sources will strengthen your credibility , and build trust with your audience.
Your opening, or introduction, has two main purposes: to grab your audience's attention, and to cover the key points that you intend to talk about.
Instead of telling people what you plan to say, you can use a different approach and explain why they are there. What will they learn from your presentation, and how will the content benefit them?
It's also important to get their attention right from the beginning. You can do this in several ways:
- Tell a story.
- Ask a rhetorical question.
- Play a short video.
- Make a strong or unexpected statement.
- Challenge your audience.
- Use a quotation or example.
- Appeal to people's self-interest.
- Request a specific action.
- Use suspense.
If you plan to answer questions at the end of your presentation, it's a good idea to mention this in the introduction, so people don't interrupt you mid-flow.
Many presenters overlook the importance of a conclusion – but the statements you finish with are what many audience members will remember best.
With the "tell 'em" approach, your conclusion summarizes the main points in the body of your presentation. If you want people to take action, be specific about what you want them to do.
Think carefully about how you want them to feel once you've finished; your conclusion is a great opportunity to reinforce this. Why not inspire them with a great story, a quote or a compelling call to action?
2. The Sandwich Approach
The Sandwich Approach is a variation of the Open – Body – Conclusion structure. This three-part structure covers:
- Advantages and/or benefits of your message or idea.
- Risks and concerns.
- How the benefits manage or eliminate those risks.
This approach is effective when you want to persuade audience members, or change their minds.
Having evidence to support your position is critical. However, factual data and reams of spreadsheets and charts are not highly persuasive. What people respond to is "vivid" evidence that brings your concept or argument to life.
To brush up on your persuasion skills, look at The Rhetorical Triangle . This tool asks you to consider your communication from three perspectives: those of the writer, the audience and the context. It's a method that builds credibility, and helps you ensure that your arguments are logical.
3. Monroe's Motivated Sequence
Monroe's Motivated Sequence is another good structure to use when you need to motivate or persuade. This sequence consists of five key steps:
- Getting your audience's attention – Use an interesting "hook" or opening point, such as a shocking statistic. Be provocative and stimulating, not boring and unemotional.
- Creating a need – Convince the audience there's a problem, explain how it affects them. Persuade them that things need to change.
- Defining your solution – Explain what you think needs to be done.
- Describing a detailed picture of success (or failure) – Give people a vision; something they can see, hear, taste, and touch.
- Asking the audience to do something straight away – Get them involved right from the start. If you do this, it's then much easier to keep them engaged and active in your cause.
4. Demonstration Structure
Use a simple demonstration structure when you are unveiling a new product or service.
Start by explaining why the product or service is so good. What makes it special? What problem will it solve for people?
Next, demonstrate what it does. How you do this will depend on your product but, whatever you do, make sure it works! Bring any important points to the audience's attention and provide helpful tips, where appropriate. Show them the results, and finish by giving them useful information, a good understanding of your topic, and something to remember.
Don't get too wrapped up in the detail; remember to keep it simple. Your presentation will be more powerful and your audience will remember more if you highlight just a few of the most important features. This will whet their appetite, and leave them wanting to know more.
5. Opportunity, Benefits, Numbers Structure
The Opportunity, Benefits, Number (OBN) structure is useful when you face busy people who want to hear what you have to say in the shortest time possible.
To use this structure, give audience members a quick summary of the opportunity that they need to consider, and outline the benefits that they can expect. Then, show them the numbers that back up your claims. [1]
For example, imagine you are explaining why your company should implement a new performance management system. First, you might give some background on the proposal – for example, you want to drive a high-performance culture. Then, you could explain the benefits, such as improving organizational performance and profits. Finally, you could compare the cost of bringing the system in with the predicted return on investment, based on a similar system at another organization.
Presentations that lack a clear flow are confusing and ineffective. This is why it's important to pay careful attention when choosing the most appropriate structure.
Different structures fulfill different purposes. Before you begin, think about why you are giving your presentation. Do you want to inform, persuade, inspire, or entertain your audience?
The most common structure for presentations is Open – Body – Conclusion. This is often effective because it gives you the opportunity to repeat your key points a number of times. However, other structures can be more appropriate, depending on the circumstances, such as when you're trying to persuade an audience, demonstrate a product, or provide information in the most time-efficient way.
Download Worksheet
[1] Martinuzzi, B. (2013). '11 Ways to Structure a Knockout Presentation,' from American Express OPEN Forum [online]. Available here . [Accessed 7 August 2014.]
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Book Insights
People Follow You: The Real Secret to What Matters Most in Leadership
The benefits and pitfalls of mergers and acquisitions.
The Rocky Road to Organizational Growth
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Top tips for engaging an audience.
Putting the prep in when public speaking
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
Home Blog Business Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
Presentation Structure Guidelines for Effective Communication
In the business world, a presentation is so much more than just a bunch of slides or points—it’s a golden opportunity. It can sway decisions, propel change, or bring people together. How you structure your presentation is absolutely critical in getting your ideas across clearly and compellingly.
When you’ve got a structured presentation just right, it’s like you’re taking your audience by the hand and guiding them through your thoughts, making sure they pick up all the important bits along the way. Moreover, it speaks of your degree of professionalism and how much knowledge you bear on the topic in question.
Therefore, nailing your presentation structure isn’t just helpful; it’s downright necessary to get the results you’re after. Whether you’re pitching a new concept to the investors, sharing the latest findings with your team, or taking the stage at a conference, how you lay out your content becomes the language you use to interact with your audience. Get to know all that’s required to create a powerful presentation structure that will guarantee success in business meetings, academic dissertations, or motivational talks .
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Structure
Introduction, techniques to structure your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when designing a presentation structure, final words.
Let’s compare a presentation structure to a business plan . Just as a business plan is essential for guiding a company’s strategy and ensuring all aspects of the business are aligned toward common goals, a presentation structure is crucial for organizing the content and delivery of your talk.
The presentation structure lays out a clear and logical sequence of information, akin to the sections of a business plan that outline the company’s mission , market analysis , and financial projections. This clear sequence ensures that your audience can easily follow and understand your message, maximizing the impact your speech can deliver and influencing your target audience.
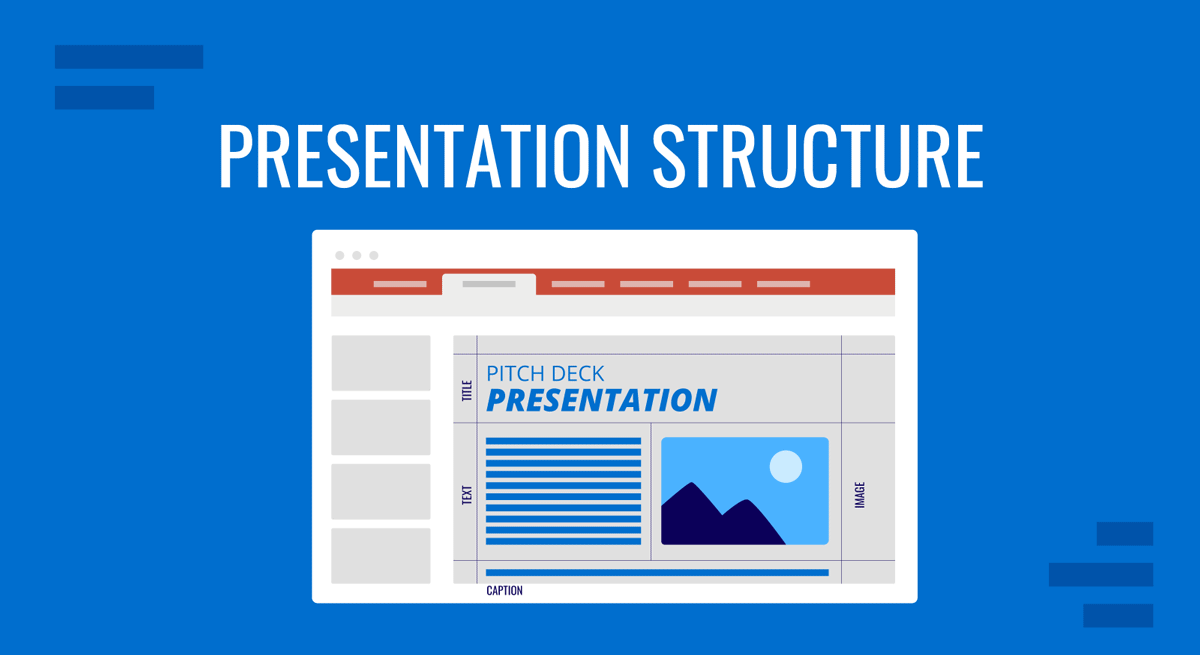
Key Elements of a Presentation Structure
The easiest way to study a presentation structure is to subdivide it into sections. Basically, every presentation has a structure that follows this formula: Introduction > Body > Conclusion.
The introduction is the first section of the presentation and sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. It should be attention-grabbing and make the audience want to listen to the rest of the presentation.
When defining how to start a presentation , these are the best tips we recommend you implement.
Start with a Hook
Kick off your introduction with a strong hook that grabs your audience’s attention. This could be an intriguing fact, a thought-provoking question, or a compelling story related to your topic. A captivating opening will make your audience want to listen and engage with your presentation.
Clearly State Your Topic
Be clear and concise when stating your topic. Your audience should immediately understand what your presentation is about and what they can expect to learn. A clear statement of your topic sets the stage and provides a roadmap for the rest of your presentation.
Establish Credibility
Take a moment to establish your credibility by briefly sharing your qualifications or experience related to the topic. This helps to build trust and rapport with your audience, and it shows that you are knowledgeable and well-prepared.
Engage Your Audience
Make your audience part of the presentation by engaging them from the start. Ask a question, encourage participation, or invite them to think about how the topic relates to their own experiences. Engagement helps to create a connection between you and your audience. Using a surprise factor is an alternative if you feel the topic you’re about to present may not fully resonate with the target audience.
Preview Main Points
End your introduction by briefly previewing the main points you will cover in your presentation. This provides a clear structure for your audience to follow and helps them understand what to expect in the body of your presentation. An agenda slide is the perfect tool for this purpose.
The body is the main part of the presentation and provides the content and information that the audience came to hear. It should feature the main points and details supporting your presentation’s objective. Depending on your topic, this could include data, arguments, case studies, examples, or demonstrations. Each main point should be clear and distinct, with evidence or examples substantiating it. The content should be tailored to your audience’s level of knowledge and interest.
Different presentations call for various structures. For example, a Product Presentation ’s structure should start by dividing the content into clear sections or headings. For instance, if presenting a new software tool, sections could include its features, benefits, and user feedback.

On the other hand, a Persuasive Presentation begins with stating the current situation or problem, followed by proposed solutions, evidence supporting those solutions, and the benefits of adopting your proposition.
Workshop or Training Presentations begin with an overview of what will be taught, followed by step-by-step instructions, examples, demonstrations, and summaries or quizzes after each major section.
One essential aspect is to plan the multimedia elements to include in your presentation, including audio, images, and video, depending on the presentation style you aim to deliver. Through our expertise, we want to share some tips on how to plan this kind of content:
- Using relevant content: Each image should be related to its accompanying content. Avoid using images just for decoration. If using videos, dedicate an entire slide to them rather than sticking them to a corner of your slide. Plan a powerful hook to connect your thoughts with these visual aids.
- Quality: Ensure all images are of high resolution and can be clearly viewed, even from a distance. Avoid pixelated or distorted images.
- Simplicity: Infographics and diagrams should be easy to understand. If presenting data, use simple charts or graphs instead of complex tables. Limit the amount of text on each slide to ensure clarity. This rule of simplicity also applies to written content and the structure of your speech. Use the Feynman Technique as a time-saver approach to simplify content to reach any knowledgeable audience.
- Consistency: A common cause of presentation failures is to distract the audience with an unprofessional look. Maintain a consistent style and color scheme for all images to give your presentation a polished and professional feel.
Along the path of creating these media elements, you can rethink your strategy for disclosing content. In general lines, you should present your points in a logical order, often from the most to least important or in a chronological sequence. This helps the audience follow along and build understanding step by step. Well-known practices like the storytelling technique follow this approach to maximize audience engagement.
Transition smoothly between points. Phrases like “moving on,” “in addition,” or “on the other hand” can guide your audience through your narrative. Break up long sections of spoken content with anecdotes, questions, or short videos. Such an approach adds variety and keeps the audience engaged.
A well-structured conclusion is the linchpin that holds your presentation together, reinforcing your main points and leaving a lasting impression on your audience. It is your final opportunity to communicate your message and encourage audience engagement. So, before you consider how to end a presentation , here are some powerful tips to ensure you conclude your presentation with impact.
End with a Strong Statement or Quote
This technique is commonly used in motivational presentations, where the speaker leaves the audience with a slide containing a quote related to the topic of the presentation, something that evokes inner reflection about the topic discussed.

Conclude your presentation with a strong, memorable statement or a powerful quote that ties back to your main message. This adds weight to your argument and leaves a lasting impression on your audience. If you aim to surprise your audience, silence can also be a strong statement if your presentation has to raise awareness about a problem.
Incorporate a Call-to-Action
Clearly communicate to your audience what you want them to do next. Whether it’s to adopt a new perspective, take specific action, or continue the conversation outside of the presentation, a clear call to action drives engagement and encourages your audience to act upon your message.
Ask Thought-Provoking Questions
Pose thought-provoking questions that stimulate reflection and discussion. This opens the door for audience participation and engagement and allows you to interact with the audience in a Q&A session, or reach after your presentation concluded to network.

Additional Resources and Contact Info
Offer resources such as articles, websites, or books for those interested in exploring your topic further. This not only adds value to your presentation but also encourages the audience to engage with the content beyond the presentation itself.
Consider the way you leave a communication channel open with your audience. This can be in the format of a deliverable, writing down your contact data in the “Thank You” slide , or simply via speech to inform where they can know more about you and your work.
We already discussed the basic Introduction-Body-Conclusion framework for a presentation, but there are alternative approaches that can help you structure your talk.
Problem-Solution Framework
The Problem-Solution Framework is a compelling method to structure presentations, particularly when aiming to persuade or inform an audience about addressing specific challenges. The framework operates on a simple yet impactful premise: initially, highlight a problem or challenge that needs addressing and subsequently propose a viable solution or set of solutions.
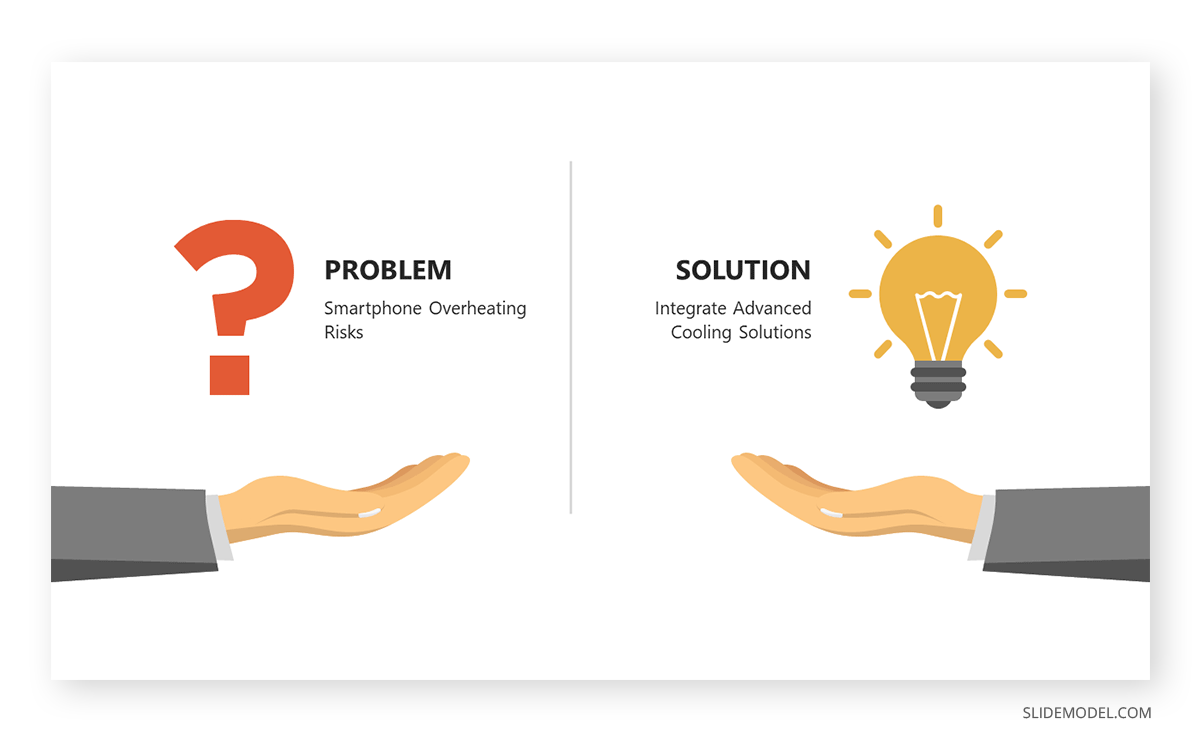
Starting with the problem establishes a context, engages the audience by highlighting pain points or challenges they may recognize, and creates a desire for resolution. It sets the stage for the solution to be perceived as necessary and valuable.
The solution phase offers that much-needed resolution. By presenting a clear, actionable solution or set of recommendations, the presenter provides a pathway to overcome the identified challenge. This structure is not only logical but also highly persuasive, as it appeals to the audience’s desire for resolution and improvement. In essence, the Problem-Solution Framework is both a guide for content organization and a psychological tool for persuasion.
Chronological Structure
The Chronological Structure is an intuitive and organized approach to presenting information based on a sequence of events or a progression in time. Whether recounting historical events, outlining the stages of a project, or narrating a personal story, this structure follows a clear beginning, middle, and end sequence. By presenting details in the order they occurred, the audience can easily follow the narrative, making connections between events and understanding causality.
This structure is especially effective when the timeline of events is crucial to the narrative or when showcasing developments, evolutions, or growth over time. It provides clarity and eliminates confusion that might arise from a non-linear presentation. Moreover, by anchoring information on a timeline, the Chronological Structure aids memory retention, as the audience can mentally “map out” the journey of events. In sum, this method offers clarity and a compelling narrative arc, ensuring audience engagement from start to finish.
Comparative Structure
The Comparative Structure is a strategic approach to presentations that hinges on juxtaposing two or more elements, ideas, or solutions side by side. By examining similarities and differences, this method illuminates unique qualities, advantages, or drawbacks inherent in each element. Often employed in business scenarios like product comparisons, market analysis, or debates, the comparative structure helps audiences critically analyze options and make informed decisions.
Presenters utilizing this structure typically start by introducing the elements for comparison. They then delve into detailed analysis, often using criteria or metrics to maintain objective evaluations. Visual aids like Venn diagrams or comparison charts can enhance clarity and visual appeal.
The strength of the Comparative Structure lies in its ability to foster critical thinking. By directly contrasting items, audiences are engaged, encouraged to weigh pros and cons, and ultimately arrive at a deeper understanding or more nuanced perspective on the subject matter.
Matrix Structure
The Matrix Structure offers an approach to organizing presentations by segmenting information into distinct categories or sections, akin to a grid or matrix. Instead of a linear flow, topics are grouped by themes, criteria, or any relevant classification, allowing for simultaneous exploration of multiple facets of a subject. Think of it as viewing a topic through various lenses concurrently.
For instance, in a business setting, a product might be examined in terms of design, functionality, market positioning, and customer feedback. Each of these constitutes a segment in the matrix.
Visually, the matrix can be represented using tables, grids, or quadrant charts, making the content easily digestible and engaging. A key advantage of this structure is its flexibility; presenters can delve deep into one segment or provide a broader overview of all areas, depending on the audience’s needs. Ultimately, the Matrix Structure ensures a comprehensive and multifaceted examination of a topic, providing depth and breadth in analysis.
Modular Structure
The final model we will study is the Modular Structure. It takes content and packs it into modules, which can be arranged at any other the presenter requires them to be. Each module addresses a specific topic or idea and is designed to be self-contained, ensuring clarity even if presented independently or in a different order. This adaptability makes the modular approach especially valuable in dynamic settings, such as workshops or conferences, where audience feedback or time constraints might necessitate adjustments on the fly.
For example, in a corporate training session, different modules could cover distinct skills or topics. Based on the attendees’ prior knowledge or the session’s time limit, the presenter can prioritize, omit, or rearrange modules without compromising the integrity of each segment.
By adopting the Modular Structure, presenters gain flexibility without sacrificing depth. This approach fosters a responsive presentation style, allowing speakers to tailor content in real-time, ensuring maximum relevance and engagement for their audience.
Even well-seasoned presenters can fall prey to these common mistakes in terms of presentation structure. Let’s learn how to prevent them.
Overloading with Information
It’s tempting to include every bit of knowledge you have on a topic. Still, information overload can quickly disengage an audience. Prioritize key points and leave out extraneous details. As famous architect, Mies van der Rohe famously coined, “Less is More.”
Weak Transitions
Jumping abruptly from one point to another can disrupt the flow and confuse listeners. Ensure smooth transitions between sections, signaling shifts in topics or ideas to keep the narrative cohesive.
Dull Design
While content is king, visual appeal matters. Relying solely on walls of text or bland slides can lose your audience’s interest. Incorporate engaging visuals, charts, and multimedia elements to enhance your message and retain attention.
Ignoring the Call to Action
Concluding your presentation without guiding the audience on the next steps or what’s expected of them can be a missed opportunity. Whether it’s seeking feedback, prompting a discussion, or encouraging an action, always have a clear call to action.
Good communication is all about making your point clear, especially in presentations. We’ve talked about how the right structure can keep your audience hooked. But there’s more to it. Think about your presentation. Is it telling your story the way you want? Is it reaching your audience? Take a step back and really look at how you’re laying it out. Don’t just go with the flow – choose your format wisely. Remember, every presentation tells a story, and how you set it up matters a lot.

Like this article? Please share
Design, Presentation Approaches Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 23rd, 2024
How to Align Objects in Google Slides
Optimize your layouts by learning how to align objects in Google Slides presentations. Step-by-step guide with screenshots.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024

How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.
Leave a Reply
You’re using an older browser version. Update to the latest version of Google Chrome , Safari , Mozilla Firefox , or Microsoft Edge for the best site experience.
- eLearning Blog
- eLearning Basics
- Instructional Design
- Corporate Training
- Course Selling
- Manufacturing
- Products iSpring Suite iSpring Learn
- Use Cases Onboarding Compliance Training Induction Training Product Training Channel Partner Training Sales Training Microlearning Mobile Learning
- Company About Us Case Studies Customers Partnership Course Development Contact Us
- Knowledge Hub Academy Blog Webinars Guides Experts on iSpring
- Language EN English Français Deutsch Español Italiano Nederlands Português Polski 中文 日本語 العربية Indonesia
- Shopping Cart
Free Online eLearning Conference | May 2nd–3rd
iSPRING DAYS 2024
Seize the human-centric future of learning
How to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation

Table of Contents

This is the main part of your presentation, which should keep the promises you made in the introduction. This is where you explain your topic and present all your information.
Depending on the nature of your presentation, divide it into segments/points. Arrange your points in a logical order and then provide information to support each of them. There are many different ways to organize your key points, for example:
- Number your points according to their priority (1, 2, 3, …)
- Place the points in a time frame (past, present, future)
- Use narration (tell a story from beginning to end)
- Present the points with a problem-solution dynamic (state a problem, describe its impact, offer ways to solve the issue)
A good conclusion summarizes the key points you made or highlights what the audience should have learned. It clarifies the general purpose of your presentation and reinforces the reason for viewing it. Here are the slides you may want to include:
- Summary. List what goals your audience have achieved, what knowledge they got, and how this information can help them in the future.
- Conclusion. Here you can thank your audience for viewing the presentation.
Tips for Structuring a Presentation in PowerPoint
Now that you know which parts a typical presentation should consist of, let’s see how to structure it in PowerPoint.
1. Combine slides into sections
When working with a large PowerPoint presentation (PPT), you can create sections that can be collapsed and expanded. This will help you keep presentation slides organized and facilitate navigation in editing mode. To do that, follow these steps:

- To shift a section, right-click on its name and use the Move Section Up and Move Section Down options.
- To collapse or expand a certain section, click on the collapse icon to the left of the section name. You can also minimize and maximize all sections at once by right-clicking on the section name and choosing Collapse All or Expand All .
As well, you can access these settings by choosing Slide Sorter under the VIEW tab.

This kind of segmentation is a great way to overview the logical flow of your slides all at once and see if there are any changes required. For example, you may decide to break one slide into two or three, or the other way around.
2. Use the Outline View
One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View . You can choose it from the VIEW tab.

This view doesn’t display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents. Here you can go through the entire text and edit it instantly. You can also work with text (on the left) and slides (on the right) simultaneously, as the latter is shown on the right side of your screen.
Note that, to be displayed in an outline, text needs to be typed in a text placeholder, not a text box . A text placeholder is a box with the words “Click to add text” or “Click to add title”, and it appears when you choose a standard layout.
You can also use Outline View to promote bullet text to titles and the other way around. To do that, right-click on a relevant title or text and select the Promote or Demote options.

Be attentive about demoting a title, as this will delete the original slide and move its title and text to the adjacent slide.
PowerPoint only allows users to promote and demote text, not entire slides. Therefore, there’s no possibility to change the hierarchical order of slides.
3. Create a table of contents
All the aforementioned tips help you organize a presentation when formatting it. However, it’s crucial that your viewers can easily navigate through entire presentation too. One sure way to provide them with this opportunity is to create an interactive and structured table of contents.
Though there’s no native automatic outline in PowerPoint, it can be created manually:

- Press Ctrl+A to select all the names, and Ctrl+C to copy them.
- Then Press Ctrl+V to paste the copied titles on the desired slide. In case there are too many titles and they don’t fit onto a single page, you can divide the table of contents into two columns or place it on two slides.

You’ll need to repeat this procedure to link all the chapters to corresponding slides. For more information, read this step-by-step guide on how to add a hyperlink in PowerPoint .
Now all the chapters can be accessed from a single table of contents, which is very convenient. However, you will also need to link them back to that unifying page. You can do this by inserting an Action Button on every slide of your presentation in Slide Master mode:

Now there is a single page from which all the other pages can be easily accessed. As well, it’s possible to go back to the table of contents at any time with the intuitive Home button.
Depending on the size of your presentation, the time it takes to create an interactive outline may vary, as you will need to add hyperlinks to every chapter manually. Be aware that if you rename a slide or simply delete it, these changes will not be automatically registered in the table of contents. For example, if you delete a slide, its title will still be displayed in the table of contents, but clicking on it won’t lead the viewer to another point in the presentation.
This is what our sample presentation looks like:

A Better Way to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation
Creating a table of contents manually might be fine for a small presentation, but if you have 122 slides, it would require too much time and energy to do so. That’s why, instead of manually creating a table of contents, we took advantage of iSpring Suite and simply enabled the automatic outline.
iSpring Suite
Fully-stocked eLearning authoring toolkit for PowerPoint. No training required to start!

Note: iSpring Suite turns slides into HTML5 format, so your audience can view them online, right in their browsers.

As you can see, the new presentation has a pop-up outline and a navigation panel, which make it possible to move to any slide at any time without leaving the slide show mode.
How to set up navigation
To create navigation in your presentation, follow these simple steps:
- Get a free trial of iSpring Suite.

- When you’ve configured the Slide Properties settings, click on Save & Close in the upper-left corner.
How to configure an outline
Whereas PowerPoint requires the outline to be designed manually, iSpring Suite has already prepared it for you. At the same time, you don’t have to stick with the standard outline template, as you can easily customize the player’s final look and feel:

We recommend leaving Enable Search marked, as this will allow viewers to search for any content at any time, including the texts on the slides. This is especially useful for large presentations with a lot of text.
If you have previously arranged slides into multiple levels in the Slide Properties, then leave Multilevel outline marked. That way, the outline will display the nesting structure of the presentation, facilitating navigation. You can learn more about the other outline options here .

- When you have finished configuring the player, click on Apply & Close in the upper-left corner.
- Now you can publish your enhanced presentation either to HTML5, to make it easily accessible via browser on any device, or MP4 video format. If you’re going to upload your presentation to an LMS, you can publish it to any eLearning format: SCORM, AICC, Tin Can, or cmi5.
While a standard PowerPoint slideshow is straightforward and limited, iSpring Suite saves viewers from having to follow a strict slide order. An interactive and searchable outline allows non-linear navigation, where any information can be accessed at any time at a glance.
Also read : → How to Convert PowerPoint to MP4 Video
Also read : → How To Record Presentations With Audio
Another perk
iSpring Suite comes with Content Library , which provides a great collection of presentation templates and allows you to create professional-looking presentations in a matter of minutes. Each template includes basic course elements: a title slide, a table of contents, chapters, a timeline, and info slides. Organize them in the order you prefer, populate them with your texts and images, and your presentation is ready to go.

We hope this article will help you develop an ideal structure for your PowerPoint presentation and do this quickly and easily. Captivate your audience with a powerful and persuasive presentation!
Do you have any other insights on how to simplify PowerPoint slides design? Please share them in the comment section. We’d like to hear from you.
Fast course authoring toolkit
Create online courses and assessments in record time.

Content creator:
Helen Colman
She enjoys combining in-depth research with expert knowledge of the industry. If you have eLearning insights that you’d like to share, please get in touch .
You might also like this

Subscribe to our blog
Stay tuned to get our latest eLearning tips and tricks!
By clicking “Subscribe”, you agree to our Privacy Policy . All emails include an unsubscribe link, so that you can opt-out at any time.
We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website and also for analytics and marketing purposes. You can enable or disable optional cookies as desired. See our Cookie Policy for more details.
Manage your cookies
Essential cookies are always on. You can turn off other cookies if you wish.
Essential cookies
Analytics cookies
Social media cookies
This website is sponsored by the Leonhard Center for the Enhancement of Engineering Education at Penn State.
The Presentation
Most presentations are divided into 3 main parts (+ questions):
As a general rule in communication, repetition is valuable. In presentations, there is a golden rule about repetition:
- Say what you are going to say...
- then say what you have just said.
In other words, use the three parts of your presentation to reinforce your message. In the introduction, you tell your audience what your message is going to be. In the body, you tell your audience your real message. In the conclusion, you summarize what your message was.
We will now consider each of these parts in more detail.
Introduction
The introduction is a very important - perhaps the most important - part of your presentation. This is the first impression that your audience have of you. You should concentrate on getting your introduction right. You should use the introduction to:
- welcome your audience
- introduce your subject
- outline the structure of your presentation
- give instructions about questions
The following table shows examples of language for each of these functions. You may need to modify the language as appropriate.
The body is the 'real' presentation. If the introduction was well prepared and delivered, you will now be 'in control'. You will be relaxed and confident.
The body should be well structured, divided up logically, with plenty of carefully spaced visuals.
Remember these key points while delivering the body of your presentation:
- do not hurry
- be enthusiastic
- give time on visuals
- maintain eye contact
- modulate your voice
- look friendly
- keep to your structure
- use your notes
- signpost throughout
- remain polite when dealing with difficult questions
Use the conclusion to:
- (Give recommendations if appropriate)
- Thank your audience
- Invite questions
Questions are a good opportunity for you to interact with your audience. It may be helpful for you to try to predict what questions will be asked so that you can prepare your response in advance. You may wish to accept questions at any time during your presentation, or to keep a time for questions after your presentation. Normally, it's your decision, and you should make it clear during the introduction. Be polite with all questioners, even if they ask difficult questions. They are showing interest in what you have to say and they deserve attention. Sometimes you can reformulate a question. Or answer the question with another question. Or even ask for comment from the rest of the audience.
- Documentation

The Go-To Guide on How to Structure a PowerPoint Presentation
- Clarity for Your Audience
- Better Retention
- Confidence as a Presenter
- Introduction
- Create Slide Sections
- Use the Outline View
- Create a Table of Contents
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Craft An Impactful PowerPoint Presentation
Think about a fancy building that looks incredible from the outside but lacks a strong foundation. It won’t last long or work well. Similarly, having beautiful slides is not enough in PowerPoint presentations if you don’t organize them properly.
In this article, we’ll talk about how to set up a PowerPoint presentation correctly. We’ll explain what important parts it should have and give you practical tips on arranging your slides to make them effective. These practical ideas will help you organize your slides better and make it easier to create them.
Let’s dive in and understand why a good PowerPoint structure is so important.
Why Structuring PowerPoint Presentations is Important?

1. Clarity for Your Audience
Imagine telling a story with all the words mixed up. It would not be very clear. That’s how it feels for your audience when your slides are not structured. When your presentation has a clear beginning, middle, and end, people can follow along much better. They know where you’re starting, what’s coming next, and what you’ve concluded.
2. Better Retention
Research tells us that structured information is 40% more likely to be remembered than information everywhere. So, if you want your audience to remember your key points, structuring your slides is essential. It’s like putting important items in labeled boxes – easier to find and remember.
3. Confidence as a Presenter
A structure also benefits you as the presenter. It’s like having a map that guides you through the presentation. You know what’s coming next, which helps reduce nervousness and keeps you from getting lost in your talk.
4. Engagement
A well-structured presentation is more engaging. People are more likely to pay attention and stay interested when they can follow a clear flow of information. It’s like a good movie – it keeps you hooked because it makes sense.
Therefore, structuring your PowerPoint presentation is like giving your audience a clear roadmap. It helps them understand your message, remember it, and keep you on track as the presenter. So, if you want your presentation to succeed, take the important step of structuring it properly.
Typical PowerPoint Presentation Structure

The introduction is like the opening act of a performance, and it’s super important because it tells your audience what they’ll learn from your presentation. Here are the different slides you need to include in the beginning:
- The Title: Start your presentation with a clear and captivating title. It sets the stage for what your audience can expect. You can add a brief description under the title.
- A Table of Contents / Main Menu: A table of contents or main menu slide is like the map of your presentation. It provides your audience with an overview of what topics you’ll cover. It is especially helpful for longer presentations. You can easily make your presentation more engaging by using hyperlinks. This means your viewers can pick which part they want to see next by clicking on it, just like choosing a chapter in a book.
- Objectives: Clearly state what you aim to achieve with your presentation. It’s like telling your audience what to expect and why it matters. For example, if you’re giving a presentation about a new project, your objective could be to gain approval and support from your team.
- Definitions (Optional): Consider including a definitions slide if your presentation involves specific terms or concepts your audience may not know.
Main Content : The body of your presentation is where the real meat of your topic resides. Here’s how you can structure it effectively:
- Introduction to Topics : Start by introducing the main topics or sections you’ll cover. Think of this as the roadmap within your presentation. For instance, if you’re discussing the benefits of a new product, you might have sections like “Product Features,” “Market Opportunities,” and “Customer Feedback.”
- Content Slides : Each main topic or section should have its series of content slides. These slides delve into the details, providing information, examples, and visuals.
- Numbering: You should number your points according to priority. (1,2,3..)
- Narration: Narrate each slide like a story from beginning to end.
- Time Frame: You should place the slides in the time frame (Past, Present, Future)
- Problem-Solving : Explain a problem, talk about how it affects things, and then offer solutions to fix it.
- Transitions : Use transitional slides to guide your audience smoothly between sections or topics.
- Visuals : Incorporate visuals like images, diagrams, and charts to enhance understanding and engagement.
A strong conclusion wraps up your presentation nicely. It recaps the important things you discussed and reminds your audience what they should take away. Here are some slides you might consider including:
- Summary and Takeaways: The conclusion is where you tie everything together. Summarize the key points you’ve discussed in the body of your presentation. Reinforce your main message and objectives.
- Call to Action (Optional) : Depending on the nature of your presentation, you should include a call to action slide. It could be an invitation for questions, a request for feedback, or a specific action you want your audience to take after the presentation.
- Closing Remarks: End your presentation with some closing remarks. Thank your audience for their attention and participation. It helps create a sense of closure and leaves a positive impression.
Remember, while this structure is typical, it can be adapted to suit your specific presentation and audience. Flexibility is key. Ensure your slides are visually appealing, easy to read, and not overcrowded with text. Keep your audience’s attention by using a clear structure, engaging visuals, and a well-planned delivery.
By following this structure and considering your audience’s needs, you’ll be well on your way to creating a successful PowerPoint presentation.
Technical Tips for Structuring in PowerPoint

1. Create Slide Sections
When dealing with a big PowerPoint presentation, organizing it into sections that you can easily collapse or expand is helpful. This makes it neater and easier to work on. Here’s how you can do it in simple steps:
Create a Section :
- Find the slide in your list where you want to start a new section.
- Right-click on that slide.
- From the menu that appears, choose “Add Section.” It will create a new section.
- You’ll see it’s named “Untitled Section.” To give it a proper name, right-click on it and select “Rename Section.” Then, type in the name you want.
- If you need more sections, you can repeat this process to create and name them.
Move Sections :
- Sometimes, you might want to change the order of your sections.
- To do this, right-click on the section name you want to move.
- You’ll see options to “Move Section Up” or “Move Section Down.” Choose the one that suits your needs to shift the section.
Collapse or Expand Section
- If you have a lot of sections and want to focus on one, you can collapse the others.
- To collapse a section, click on the little collapse icon (usually a small triangle or arrow) to the left of the section name.
- You can collapse or expand all the sections by right-clicking on any section name and selecting “Collapse All” or “Expand All.”
- You can access these settings by going to the “VIEW” tab and choosing “Slide Sorter.” It’s like putting different presentation parts into folders to keep things tidy and organized.
2. Use the Outline View
Another way to organize your PowerPoint presentation while editing it is by using “Outline View.” Here’s how you can use it in simple terms:
- You can find Outline View in the “VIEW” tab of PowerPoint.
- When you switch to Outline View, you won’t see the sections, but you will see each slide’s titles and main text. It gives you a quick look at what’s on each slide. You have the text on the left, and on the right, you see how your slides look.
- You can edit your presentation directly in this view. If you want to change the text, you can do it here without going to each slide.
- The text must be in a “text placeholder” to appear in the outline. A text placeholder is a box with text like “Click to add text” or “Click to add title.” These show up when you use a standard layout for your slides.
- You can also change the order of your text. For example, if you have a bullet point that you want to turn into a slide title or vice versa, you can do it. Just right-click on the title or text to see options like “Promote” and “Demote.” Promote moves text up, and Demote moves it down.
- One thing to be careful about is demoting a title. If you do this, it will delete the original slide and move the title and text to the slide next to it. So, make sure you want to do that.
- Unfortunately, you can’t change the order of your slides in Outline View. You can only promote or demote text within slides, not entire slides.
Think of Outline View as a way to quickly see and edit the text in your presentation without getting lost in all the slides. It’s like having a summary of your content that you can work with easily.
3. Create a Table of Contents
Creating a table of contents in a PowerPoint presentation can make it easy for your viewers to navigate through it. While PowerPoint doesn’t offer an automatic table of contents feature, you can create one manually with these steps:
- Insert a Table of Contents Slide : Start by inserting a table of contents slide on the title or a blank slide. Add a new slide by pressing “New Slide” on the ribbon. Once you’ve added the slide, select all its objects and delete them.
- Right-click anywhere in the outline pane.
- Choose “Collapse” and then “Collapse All.” It will show only the slide titles.
- Click Ctrl+A to select all the slide titles, then press Ctrl+C to copy them.
- Paste the Titles : Go to your table of contents slide and press Ctrl+V to paste the copied slide titles. If you have too many titles that don’t fit on one page, you can divide the table of contents into two columns or spread it across two slides.
- · Select the title of the first chapter on your table of contents slide.
- · Right-click and choose ” the link.”
- · Press “Place in This Document” on the left-hand menu in the open window.
- · Then, choose the slide corresponding to the first chapter and click “OK.”
- · You must repeat this procedure to link all the chapters to their respective slides.
Creating a manual table of contents ensures viewers can jump to different parts of your presentation by clicking on the linked titles. It’s a helpful way to enhance navigation in your PowerPoint presentation.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them

- Overloading Slides with Text : One big mistake is cramming too much text onto slides. Use concise bullet points, visuals, and speaker notes for additional details to avoid this.
- Ignoring Visual Design : Neglecting visual appeal can make your presentation dull. Use consistent fonts, colors, and graphics to make your slides visually engaging but not overwhelming.
- Complex Charts and Graphs : Overly complex charts must be clarified for the audience. Simplify visuals and use clear labels. Consider breaking complex data into multiple slides if needed.
- Too Many Animations : Excessive animations can distract from your message. Use animations sparingly and purposefully to emphasize key points.
- Lack of Rehearsal : Not rehearsing leads to stumbling during the actual presentation. Practice your delivery multiple times to ensure a smooth flow.
- Ignoring Your Audience : Failing to consider your audience’s needs and knowledge level can result in a presentation that doesn’t resonate. Tailor your content to your audience’s background and interests.
- Skipping a Clear Structure : Your presentation can feel disjointed without a logical structure. Follow the introduction, body, and conclusion structure, and use transitions to connect ideas.
- Technical Glitches : Technical issues like malfunctioning equipment or unreadable fonts can disrupt your presentation. Always have a backup plan and test your setup beforehand.
- Reading Slides Aloud : Reading slides word-for-word is boring. Use slides as visual aids, and speak naturally to engage your audience.
- Neglecting Q&A Preparation : Not preparing for questions can leave you confused. Anticipate possible questions and rehearse answers.
In conclusion, structuring a PowerPoint presentation is as vital as its content. A well-organized presentation helps your audience understand and retain information while keeping you, the presenter, on track.
Remember to create sections, utilize Outline View for efficient editing, and add a table of contents for easy navigation.
Avoid common pitfalls like information overload, design neglect, and technical glitches. Instead, focus on engaging visuals, practice, and audience-centered content.
By implementing these strategies and maintaining a clear structure, you can create compelling presentations that captivate your audience and effectively convey your message. Your next PowerPoint presentation can be a powerful tool that informs, persuades, and leaves a lasting impact.

Our blogs will land in your inbox & keep you updated about the latest tech developments in Education, Healthcare, and Recruitment.

Sign up to download
Recent blogs.

Being a teenager is exciting. But let’s be real. It often comes with the desire for some financial independence. You may be saving for a dream gadget, a car, or want to treat yourself. Earning your own money can be empowering. However, with limited experience and age restrictions, finding high paying jobs for teens can… Read More » Top 20 High Paying Jobs For Teens

In today’s competitive job market, navigating your dream job can feel overwhelming. But fear not! With the right strategy and determination, you can stand out from the crowd and impress valuable employers. This comprehensive guide provides 30 powerful job-hunting tips designed to empower you at every stage. We’ll cover everything from crafting a compelling resume… Read More » 30 Job Hunting Tips To Secure Your Dream Job

Landing your dream job is like bringing in a catch that will earn a reward– it takes patience, skill, and a strategic tug at the right moment. You’ve crafted your resume, nailed the interview, hopefully, and submitted your job application. But the silence stretches on, leaving you wondering, “Did they even receive my resume? Are… Read More » How To Follow Up On A Job Application To Get Placed?

Technology Blogs

Did you know around 50% of the world’s digital media and marketing software market is currently controlled by Adobe? However, there has been a significant change due to Adobe Flash Player’s discontinuation, leading to an increase in alternative multimedia solutions. This in-depth tutorial will review the dynamic options that have swept the web. Learn about… Read More » 14 Handy Flash Alternatives To Play Media Files In 2024

In case you were unaware, 90% of the brain’s information is visual. It can be challenging to make captivating video presentations, especially if you need to familiarize yourself with the necessary tools and methods. You run the danger of losing your audience’s interest and needing help to communicate your idea properly. To help you out,… Read More » Creating a Video Presentation in PowerPoint – A Complete Guide

Want to know about screen recording software but don’t know where to start? In this guide we’ll delve into the vast world of free and premium screen recording tools, uncovering their distinct features, benefits, and restrictions. We aim to give you the knowledge to make informed decisions and discover the best screen recording software for… Read More » 19 Best Screen Recording Software For Windows PC Users

Reach out to us!
how to give the perfect presentation
How to organize your presentation, the key elements of a great presentation.
Your verbal message is the core of your presentation. Whether your presentation is long or short, it should still follow some basic rules, which have been passed down through the ages:
- Tell your audience what you’re going to say.
- Tell them what you have said.
Based on the above, all presentations can be divided into three parts: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Transition statements and transition words can be used to maintain flow.
Introduction
The way you begin determines how your audience will respond throughout your presentation. First impressions are important, so make sure you follow the guidelines below to make a strong start. Your introduction should consist of three parts; the grabber, the thesis, and the overview.
THE GRABBER consists of your introductory remarks, which set the tone for what is to follow. One purpose of the grabber is to gain audience attention and create positive expectations about the presentation. A second objective is to establish rapport with the audience and assist in overcoming barriers between the speaker and the audience. A third objective is to wake up the sleepy members of your audience, especially if your presentation is scheduled right after lunch!
THE THESIS is a statement of purpose for the presentation. This is where you present your position to the audience. You explain how the audience will benefit from the information, thereby providing the audience with a reason to listen.
THE OVERVIEW indicates the main points which you will discuss in developing your thesis.The purpose is to show the audience what to expect so they can prepare to listen. This is especially important for global learners in the audience, who need to have a clear idea of the big picture before listening to the step-by-step details.
The body is the core of the presentation, where you develop the thesis. This is where most of the information will be covered. The number of main points should be limited depending on the length of the presentation. Offering people too much information only makes them tune out. Provide sufficient information to support your thesis without repeating yourself or going into too much detail. Provide stories, case studies, and examples whenever applicable. They provide an energizing break and enable the listener to grasp abstract concepts more easily. Use short script-like phrases to write the points of your talk. They will be easier for your listeners to understand than long, complicated sentences. Use examples and stories from your own life, career, or industry to sound and feel more authentic. Remember to speak at the level of your audience in terms of subject knowledge as well as language fluency. Whenever possible, keep your audience involved by asking for a show of hands.
THE REVIEW reinforces and summarizes the message. This is the part of the presentation when you can choose what was most important and what you would like audience members to remember. Choose three main concepts, ideas, or principles at the most.
THE CALL TO ACTION is the impetus to use the information presented. This is where you tell the listeners what you would like them to do after attending your presentation. This section crystallizes the entire purpose of the presentation.
THE CONCLUDING GRABBER signals the end of the presentation. The purpose is to create a memorable impression before your audience disperses. This short message may be what attendees describe or report to others on their cellphones as soon as they have finished attending your presentation. It’s your last chance to leave a powerful impression. By connecting your concluding grabber to your original grabber, you are able to neatly frame your entire presentation.
It may be a “grabber” a special visual aid? Thank you in advance
About Presentation Prep

Being able to speak in public can change your life! Presentation Prep is your complete, free guide to delivering speeches, lectures, and presentations more successfully and confidently. Whether you're a native English-speaker who suffers from public speaking anxiety, or a non-native speaker who needs guidelines for presenting to international audiences, this site will give you everything you need. Presentation Prep is written by Rebecca Ezekiel, an experienced corporate trainer who specializes in the areas of communications, presentations, and cross-cultural skills. Her online English language training videos are watched by millions of students worldwide.
The 3 parts of a presentation: introduction, main part, closing part
The task of each part for the presentation structure.
A successful business presentation requires careful planning and structuring. In this article, we will look at presentation structure, focusing on the three parts: Introduction, main body, and conclusion of a presentation. We will explore what each part does and specific tips to help structure these parts of the presentation in the best possible way.
Part 1: The introduction of a presentation
Part 2: The main part of a presentation
Part 3: The conclusion of a presentation
A successful presentation needs a well-structured agenda. It helps your audience to keep track and follow the content of the presentation. The agenda ensures that all important aspects of a topic are covered in the presentation.
An attractively designed and worded agenda can also help to capture the audience’s attention right from the start and get them excited about the presentation. For example, the agenda can be designed using images, language, or terminology that is specific to the audience’s goals and interests. In this way, the presenter signals that they value the audience’s time and interest and are tailoring their presentation to meet their needs. Read more about the importance of the agenda in presentations and learn how to use action titles profitably as well.
Part 1: the introduction of a presentation
1. Greeting:
With a friendly greeting, you create a positive atmosphere right from the start. You give the audience the opportunity to arrive, get quiet and collect themselves and signal that it’s about to start. This phase is important to establish the audience’s concentration.
2. Introduction:
Briefly introduce yourself and your organization. Give an overview of who you are and what your role is in your organization. By doing this, you will give your audience direction and reinforce your expertise and credibility at the very beginning of the presentation.
3. Objective:
Briefly outline the topic of your presentation and explain what you hope to accomplish with the presentation. Make sure the goal of the presentation is clear and concise.
4. Context:
Explain the context in which the presentation will take place. Why is the topic important? Why is it relevant to the audience? Here you should also make sure that you connect with the audience and tailor your presentation to their needs and interests.

After the introduction, you should have achieved the following with your audience:
- The audience is focused
- They know who you are and that you bring expertise to the topic
- It knows what the presentation is about and why it is worth paying attention.

Part 2: the main part of a presentation
The main part is the most important part of your presentation from a content point of view. Here you present your information, argue for your position, try to convince the target audience or bring them to a decision. In short, the middle section is the heart of your presentation. It should be structured in a logical and comprehensible way and should be consistently oriented towards your presentation objective. The biggest challenge is to make the main part compact and not to ramble too much, but still not to make any jumps in content where you might lose your audience. Ideally, when building the main body, you follow the thought processes your audience might have and answer any questions that might pop into your target audience’s head. Of course, this requires a good knowledge of your target audience and also some experience. If you have given similar presentations before, you should take into account insights you can derive from audience reactions or questions, for example, when building your next presentation.
The main part should make up about 75% to 80% of the total duration of the presentation. These are our tips for the main body:
1. Precise headings:
Make sure the main body is clear and logical and use precise headings. They will ensure that your audience can follow your arguments. Headings that are to the point also help the speaker, for example, when you want to jump back and forth within the presentation.
2. Key messages:
Present your core messages and arguments in a logical order. Make sure to support your arguments with examples and facts to strengthen your position. Report from the field to show that you understand the needs of your target audience.
3. Visualization:
Make sure you make your information easy to grasp quickly. Whenever possible, you should make use of visualizations. Diagrams, icons, and images are quicker to grasp than columns of scrubs, and you’ll stick in their minds. Your audience is more likely to remember a good picture than the text on your slides.
After the main part, you should have achieved the following with your audience:
- The audience has understood your information and your arguments
- You have answered or anticipated your audience’s most important questions and objections
- The audience has recognized the relevance of the topic for their own needs and requirements
- The audience is ready to take the next step toward your goal.

The closing section is the last part of your presentation and gives you the opportunity to emphasize your message once again. It’s not just about leaving a strong impression. The conclusion of your presentation determines whether you have achieved your presentation goal. Were you able to find supporters for your topic? Were you able to bring about a decision? Were you able to win a new customer? In order to be able to measure the achievement of your objectives, it is important to be specific at the end of your presentation. Depending on the goal, you can give an outlook here, agree on next steps or deadlines, or already distribute tasks. Use all possibilities for a binding exit and a concrete connection. Make sure that your topic is thought about further, a project is pursued or a collaboration is started. Otherwise, unfortunately, your presentation will be forgotten very quickly or other topics will push in front of it.
The conclusion of your presentation should be about 10% to 15% of the total duration of the presentation and include the following elements:
Summarize the most important points of your presentation again in a short and concise way. This will remind the audience of the key messages and strengthen your overall impression.
2. Call-to-action
Conclude your presentation with a call-to-action that fits your presentation objective. Ask the audience to make a decision, buy a product, or schedule a follow-up appointment with you. This will create commitment and ensure that your presentation objective is achieved.
Give an outlook on future developments or projects. Show the next steps or point out follow-up topics. By doing so, you show that you know the processes and are also an expert for the next steps and implementation.
4. Thank you
Conclude your presentation by thanking the audience. Show your appreciation for the interest and time the audience invested in your presentation. You can also include your contact information and offer to answer questions or provide further information. The thank you note should come from you in person; you don’t need a slide for that. Also read our tips for PowerPoint closing slides .

- The audience follows your recommendation.
- It acts in the sense of your presentation goal.
- Your presentation is remembered and you are set with the audience as an expert on the presentation topic.
You can find many more very helpful tips on presentation structure in our blog articles on the golden thread of your presentation and presentation structure .
Share your new knowledge with others
- More QuickTools
- Master & Templates
- Creating presentations
- Presentation Trainings
- Agency Support
- Value Discovery
- Corporate Design
- Content Management
- Modular Sales Kit
- Training materials
- Data Visualization
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Masters and templates
- Agency support
- Modular sales kits
Unternehmen
- Weitere QuickTools
- Master und Templates
- Präsentationserstellung
- Präsentations-Trainings
- Agentur-Support
- Vertriebsbaukästen
- Schulungsunterlagen
- Datenvisualisierung
- Datenschutzerklärung
- Präsentationstraining

30 Examples: How to Conclude a Presentation (Effective Closing Techniques)
By Status.net Editorial Team on March 4, 2024 — 9 minutes to read
Ending a presentation on a high note is a skill that can set you apart from the rest. It’s the final chance to leave an impact on your audience, ensuring they walk away with the key messages embedded in their minds. This moment is about driving your points home and making sure they resonate. Crafting a memorable closing isn’t just about summarizing key points, though that’s part of it, but also about providing value that sticks with your listeners long after they’ve left the room.
Crafting Your Core Message
To leave a lasting impression, your presentation’s conclusion should clearly reflect your core message. This is your chance to reinforce the takeaways and leave the audience thinking about your presentation long after it ends.
Identifying Key Points
Start by recognizing what you want your audience to remember. Think about the main ideas that shaped your talk. Make a list like this:
- The problem your presentation addresses.
- The evidence that supports your argument.
- The solution you propose or the action you want the audience to take.
These key points become the pillars of your core message.
Contextualizing the Presentation
Provide context by briefly relating back to the content of the whole presentation. For example:
- Reference a statistic you shared in the opening, and how it ties into the conclusion.
- Mention a case study that underlines the importance of your message.
Connecting these elements gives your message cohesion and makes your conclusion resonate with the framework of your presentation.
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation
- 1. “In summary, let’s revisit the key takeaways from today’s presentation.”
- 2. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s move forward together.”
- 3. “That brings us to the end. I’m open to any questions you may have.”
- 4. “I’ll leave you with this final thought to ponder as we conclude.”
- 5. “Let’s recap the main points before we wrap up.”
- 6. “I appreciate your engagement. Now, let’s turn these ideas into action.”
- 7. “We’ve covered a lot today. To conclude, remember these crucial points.”
- 8. “As we reach the end, I’d like to emphasize our call to action.”
- 9. “Before we close, let’s quickly review what we’ve learned.”
- 10. “Thank you for joining me on this journey. I look forward to our next steps.”
- 11. “In closing, I’d like to thank everyone for their participation.”
- 12. “Let’s conclude with a reminder of the impact we can make together.”
- 13. “To wrap up our session, here’s a brief summary of our discussion.”
- 14. “I’m grateful for the opportunity to present to you. Any final thoughts?”
- 15. “And that’s a wrap. I welcome any final questions or comments.”
- 16. “As we conclude, let’s remember the objectives we’ve set today.”
- 17. “Thank you for your time. Let’s apply these insights to achieve success.”
- 18. “In conclusion, your feedback is valuable, and I’m here to listen.”
- 19. “Before we part, let’s take a moment to reflect on our key messages.”
- 20. “I’ll end with an invitation for all of us to take the next step.”
- 21. “As we close, let’s commit to the goals we’ve outlined today.”
- 22. “Thank you for your attention. Let’s keep the conversation going.”
- 23. “In conclusion, let’s make a difference, starting now.”
- 24. “I’ll leave you with these final words to consider as we end our time together.”
- 25. “Before we conclude, remember that change starts with our actions today.”
- 26. “Thank you for the lively discussion. Let’s continue to build on these ideas.”
- 27. “As we wrap up, I encourage you to reach out with any further questions.”
- 28. “In closing, I’d like to express my gratitude for your valuable input.”
- 29. “Let’s conclude on a high note and take these learnings forward.”
- 30. “Thank you for your time today. Let’s end with a commitment to progress.”
Summarizing the Main Points
When you reach the end of your presentation, summarizing the main points helps your audience retain the important information you’ve shared. Crafting a memorable summary enables your listeners to walk away with a clear understanding of your message.
Effective Methods of Summarization
To effectively summarize your presentation, you need to distill complex information into concise, digestible pieces. Start by revisiting the overarching theme of your talk and then narrow down to the core messages. Use plain language and imagery to make the enduring ideas stick. Here are some examples of how to do this:
- Use analogies that relate to common experiences to recap complex concepts.
- Incorporate visuals or gestures that reinforce your main arguments.
The Rule of Three
The Rule of Three is a classic writing and communication principle. It means presenting ideas in a trio, which is a pattern that’s easy for people to understand and remember. For instance, you might say, “Our plan will save time, cut costs, and improve quality.” This structure has a pleasing rhythm and makes the content more memorable. Some examples include:
- “This software is fast, user-friendly, and secure.”
- Pointing out a product’s “durability, affordability, and eco-friendliness.”
Reiterating the Main Points
Finally, you want to circle back to the key takeaways of your presentation. Rephrase your main points without introducing new information. This reinforcement supports your audience’s memory and understanding of the material. You might summarize key takeaways like this:
- Mention the problem you addressed, the solution you propose, and the benefits of this solution.
- Highlighting the outcomes of adopting your strategy: higher efficiency, greater satisfaction, and increased revenue.
Creating a Strong Conclusion
The final moments of your presentation are your chance to leave your audience with a powerful lasting impression. A strong conclusion is more than just summarizing—it’s your opportunity to invoke thought, inspire action, and make your message memorable.
Incorporating a Call to Action
A call to action is your parting request to your audience. You want to inspire them to take a specific action or think differently as a result of what they’ve heard. To do this effectively:
- Be clear about what you’re asking.
- Explain why their action is needed.
- Make it as simple as possible for them to take the next steps.
Example Phrases:
- “Start making a difference today by…”
- “Join us in this effort by…”
- “Take the leap and commit to…”
Leaving a Lasting Impression
End your presentation with something memorable. This can be a powerful quote, an inspirational statement, or a compelling story that underscores your main points. The goal here is to resonate with your audience on an emotional level so that your message sticks with them long after they leave.
- “In the words of [Influential Person], ‘…'”
- “Imagine a world where…”
- “This is more than just [Topic]; it’s about…”
Enhancing Audience Engagement
To hold your audience’s attention and ensure they leave with a lasting impression of your presentation, fostering interaction is key.
Q&A Sessions
It’s important to integrate a Q&A session because it allows for direct communication between you and your audience. This interactive segment helps clarify any uncertainties and encourages active participation. Plan for this by designating a time slot towards the end of your presentation and invite questions that promote discussion.
- “I’d love to hear your thoughts; what questions do you have?”
- “Let’s dive into any questions you might have. Who would like to start?”
- “Feel free to ask any questions, whether they’re clarifications or deeper inquiries about the topic.”
Encouraging Audience Participation
Getting your audience involved can transform a good presentation into a great one. Use open-ended questions that provoke thought and allow audience members to reflect on how your content relates to them. Additionally, inviting volunteers to participate in a demonstration or share their experiences keeps everyone engaged and adds a personal touch to your talk.
- “Could someone give me an example of how you’ve encountered this in your work?”
- “I’d appreciate a volunteer to help demonstrate this concept. Who’s interested?”
- “How do you see this information impacting your daily tasks? Let’s discuss!”
Delivering a Persuasive Ending
At the end of your presentation, you have the power to leave a lasting impact on your audience. A persuasive ending can drive home your key message and encourage action.
Sales and Persuasion Tactics
When you’re concluding a presentation with the goal of selling a product or idea, employ carefully chosen sales and persuasion tactics. One method is to summarize the key benefits of your offering, reminding your audience why it’s important to act. For example, if you’ve just presented a new software tool, recap how it will save time and increase productivity. Another tactic is the ‘call to action’, which should be clear and direct, such as “Start your free trial today to experience the benefits first-hand!” Furthermore, using a touch of urgency, like “Offer expires soon!”, can nudge your audience to act promptly.
Final Impressions and Professionalism
Your closing statement is a chance to solidify your professional image and leave a positive impression. It’s important to display confidence and poise. Consider thanking your audience for their time and offering to answer any questions. Make sure to end on a high note by summarizing your message in a concise and memorable way. If your topic was on renewable energy, you might conclude by saying, “Let’s take a leap towards a greener future by adopting these solutions today.” This reinforces your main points and encourages your listeners to think or act differently when they leave.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some creative strategies for ending a presentation memorably.
To end your presentation in a memorable way, consider incorporating a call to action that engages your audience to take the next step. Another strategy is to finish with a thought-provoking question or a surprising fact that resonates with your listeners.
Can you suggest some powerful quotes suitable for concluding a presentation?
Yes, using a quote can be very effective. For example, Maya Angelou’s “People will forget what you said, people will forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel,” can reinforce the emotional impact of your presentation.
What is an effective way to write a conclusion that summarizes a presentation?
An effective conclusion should recap the main points succinctly, highlighting what you want your audience to remember. A good way to conclude is by restating your thesis and then briefly summarizing the supporting points you made.
As a student, how can I leave a strong impression with my presentation’s closing remarks?
To leave a strong impression, consider sharing a personal anecdote related to your topic that demonstrates passion and conviction. This helps humanize your content and makes the message more relatable to your audience.
How can I appropriately thank my audience at the close of my presentation?
A simple and sincere expression of gratitude is always appropriate. You might say, “Thank you for your attention and engagement today,” to convey appreciation while also acknowledging their participation.
What are some examples of a compelling closing sentence in a presentation?
A compelling closing sentence could be something like, “Together, let’s take the leap towards a greener future,” if you’re presenting on sustainability. This sentence is impactful, calls for united action, and leaves your audience with a clear message.
- How to Build Rapport: Effective Techniques
- Active Listening (Techniques, Examples, Tips)
- Effective Nonverbal Communication in the Workplace (Examples)
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
- 2 Examples of an Effective and Warm Letter of Welcome
- 8 Examples of Effective Interview Confirmation Emails
- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas
Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Transdisciplinary Learning
- Postgraduate Research Degree
Structure of a presentation

Supporting Study
Your go-to for support options, study resources, fun stuff and general help with being a student at UTS.
Get uni sorted now
A presentation:
- has an introduction, body and conclusion
- may include visual aids
- is usually followed by questions and discussions
- may also have a handout for the audience to take away.
Introduction
- The introduction should orient the audience to your subject and purpose. To capture interest and set up rapport, it should tell the audience what to expect.
- Be sure to carefully define the central point (or thesis) that is the basis of your talk and ensure that your supporting argument or information relates closely to it.
- If you are not proceeding from an already written assignment, it might help to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped, with the content coming out of the funnel. See the diagram below:
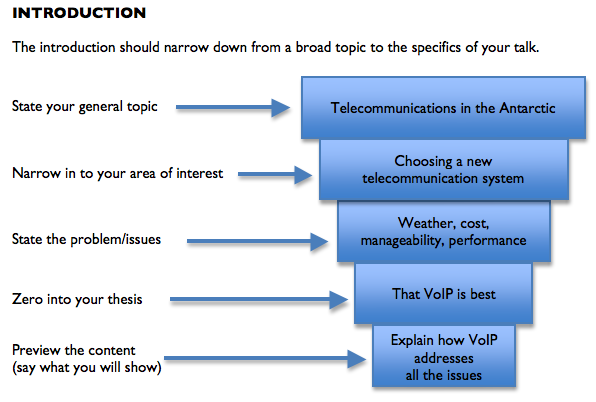
Useful language for presentations
Staging the introduction.
The body of the presentation should meet the promises of purpose and information made in the introduction.
The structure of the presentation is crucial.
Whether you organise:
- chronologically,
- by priority,
the body of your talk must proceed logically. The main points should be brought out one by one, with concise and relevant supportive evidence, statistics or examples and verbal ‘signposting’ of your progress through your argument or report.
You could present each important idea or point several times in different ways, because a listening audience needs several opportunities to fully absorb meaning.
You need to state clearly the links between your ideas and always signal when the next point is coming. If you think something is particularly important, say so and why.
If you don’t have a written assignment, it will help to think of your main points as paragraph topic sentences, each of which needs to be followed by supporting sentences and a conclusion.
Staging the body of your talk
Group presentations.
It may be that you are making a presentation as part of a group. Essentially the same information applies to group presentations as individual ones. It is important that they are logical and well structured as well as professional and meaningful. It is also doubly important that the group rehearse and practise together several times to ensure the presentation runs smoothly on the day.
Handing over to a co-presenter
Your talk may involve several speakers in your group presentation. You need to manage the handover smoothly and professionally, for example:
“I would like to conclude my discussion/report at this point and hand over to my partner/colleague XYZ who will examine/discuss/report the area/topic/perspective of…”
Similar to a written assignment, the conclusion again states your main points and what has been learned or shown but you also may raise implications inherent in the findings and offer creative recommendations.
Staging the conclusion
Back to top
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.

Informative Presentations
Instructional presentation overview, oral presentation.
The format for the Instructional Oral Presentation is Introduction, Body and Conclusion.
In the introduction , you must
- tell the audience how the presentation is meaningful to them,
- show openness
- tell how the presentation relates to past experiences of the audience
- tell your expertise regarding the topic/issue.
The presentation of these steps is referred to as the MORE (+E) principle: M eaningful to audience, O penness of speaker, R elates to past experiences, E xpertise of the speaker on the subject, and the speaker E valuated the audience (knows what the level of the audience’s knowledge of the topic/issue is).

The body of the presentation begins with what you want the audience to know, and presents the instruction.
The conclusion of the presentation briefly summarizes the steps in the body.
An instructional report simply gives instruction. Do not add your opinion regarding benefits or consequences. Just give the instructions on how to do something.
See the following example:
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/oerfiles/technical+writing/Example+Informative+Oral+Presentation+Installing+a+hard+drive.doc
- Technical Writing. Authored by : Dr. Elizabeth Lohman. Provided by : Tidewater Community College. Located at : http://www.tcc.edu/ . Project : Z Degree Program. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of woman speaking. Authored by : Erin and Joe. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9kZBdV . License : CC BY: Attribution

Business English Lesson: Presentations
This lesson introduces students to the parts of a presentation (introduction, body, conclusion), tips for effective presentations, and peer evaluations of class presentations.
Download lesson as pdf
14.1. Warm-up Questions
1. Are you a good public speaker? Why or why not?
2. What can you do to relax while giving a presentation or speech?
3. In your country, what is considered polite behavior while listening to a presentation or speech?
4. Make a list of what you think constitutes a good business presentation.
a. Maintain eye contact.
b. _____________________________________________________________________________
c. _____________________________________________________________________________
d. _____________________________________________________________________________
e. _____________________________________________________________________________
f. _____________________________________________________________________________
14.2a. Parts of a Presentation
There are 3 main parts of a presentation: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion.
The Introduction: You should introduce yourself and your topic. You also want to grab the audience’s attention by asking a question, telling a story, or giving an interesting fact about your topic. You should also outline what you will talk about.
The Body: The body should support your introduction by giving facts, opinions, or reasons to support your topic. In this section, you discuss your main points in more detail.
The Conclusion: The conclusions should restate your main points without the examples. This is a brief summary of what you want the audience to remember. You can finish with a personal thought, recommendation, or a question.
14.2b. Read through the following phrases and decide if they belong in the introduction, body, or conclusion. Write ‘I’, ‘B’, or ‘C’.
1. Good morning everyone. __________
2. To sum up. ________________
3. I would like to thank you for coming here today. ____________
4. My next point deals with… ___________
5. Moving on to… _____________
6. To conclude… _____________
7. First, I will talk about… __________
8. Does anyone have any questions? _____________
9. Let’s begin with… ____________
10. Last but not least… ___________
11. Thank you for listening. ________
12. Let’s move on to my next point. __________
13. Today I will be discussing… __________
14. I’d like to expand on this by saying… _________
15. Let me go back to an earlier point. __________
In the body, there are 3 main ways of talking about your points: introduce a new point, expand on a point, and go back to a point. Read the following phrases and decide if the speaker wants to introduce, expand, or go back.
1. I want to expand on this point. ________________________
2. Let me go back to an earlier point. _______________________
3. Let’s move on to… ________________________________
4. I would like to return to… _________________________________
5. Let me tell you more about that. __________________________
6. Let’s proceed to… ___________________________________
7. I’ll change direction by saying… _____________________________
8. Next, I’d like to point out… _________________________________
9. In addition to this point… __________________________________
10. Let’s continue by considering… ______________________________
14.3a. Activity
As a class make a list of possible topics for presentations. Then, choose a topic to present to the class. As a class, create the guidelines for the presentations.
1. Time limit? __________________________________________________________________
2. PowerPoint? ________________________________________________
3. Visual Aides? ________________________________________________________________
4. Handouts? ________________________________________
5. Memorized or with note cards? ___________________________________
Tips for Effective Presentations
1. Allow plenty of time for preparation.
2. Structure your presentation into Introduction, Body, and Conclusion.
3. Make notes based on key words.
4. Rehearse your presentation several times.
5. Make clear visual aids that do not overload your audience.
6. Use clear language and use active verbs.
7. Explain the structure of your presentation in the introduction.
8. Signpost your presentation so the audience knows where you are. (first, next, finally)
9. Relax, and communicate with your audience.
10. Be aware of your body language.
11. Maintain interest by varying the speed, pitch, and tone of your voice.
12. Answer questions politely.
14.3b. Alternate Activity
For each presentation, have the students fill out peer evaluations (on the following page). This is a good way to get feedback from classmates and will help the students realize their strengths and weaknesses. The evaluations may remain anonymous if the students prefer.
Peer Evaluation Form
Presenter _____________________________
Topic ___________________________________
Rate the presenter on a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 indicates a need for improvement and 5 indicates a job well done.
1. The presenter spoke clearly. ___________________
2. The presenter spoke at an appropriate volume. ___________________
3. The presenter spoke at a good pace, not too fast or slow. ________________
4. The presenter appeared to be relaxed. ________________
5. The presenter interacted with the audience. ________________
6. The presenter had appropriate body language. _______________
7. The presenter maintained eye contact with the audience. _____________
8. The topic was interesting. _______________
9. The presentation had clear organization. _______________
10. The presentation was prepared well. _______________
11. The details were relevant to the topic. _______________
12. The presentation was easy to follow. ________________
13. The language was clear and concise. ________________
14. The presentation had few grammar mistakes. _____________
15. The presenter answered questions politely. _______________
Related Posts

Business English Lesson: The Stock Market

Business English Lesson: Business and Culture
Business english lesson: characteristics of an entrepreneur.
Comments are closed.
- Business English
- Phrasal Verbs
- ESL Library
- Online ESL Curriculum
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement Archive
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback

Introduction, Body, and Conclusion
Jul 23, 2014
330 likes | 1.6k Views
Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Chapter Four The Third Step in Essay Writing. Step Three: Organize and Connect the Specific Evidence. Organize and connect your supporting material by using: common methods of organization effective transitions other connecting words.
Share Presentation
- common methods
- conclusions
- unusual hours
- student zombies note
- loud sports jackets
- high prices

Presentation Transcript
Introduction, Body, and Conclusion Chapter Four The Third Step in Essay Writing
Step Three: Organize and Connect the Specific Evidence • Organize and connect your supporting material by using: • common methods of organization • effective transitions • other connecting words
Common Methods of Organization • Time Order • Emphatic Order
Time Order Also referred to as “chronological order” Details are listed as they occur intime. Firstthisis done; nextthis;thenthis; after that,this; and so on. Example:To exercise successfully, you should follow a simple plan consisting of arranging the time, making preparations, and warming up properly.
Emphatic Order Also referred to as “saving the best for last” Emphasisis placed on the most important detailby positioning it near the endof a paragraph or an essay. • Example: Celebrities lead very stressful lives. They work long, unusual hours. In addition, they have to manage their images. Most important, celebrities must deal with the stress of being in constant danger.
Transitional Words Transitionssignal thedirectionof a writer’s thoughts. They are likeroad signsthat guide travelers. • Example:Afteryou’ve snagged the job of TV sports reporter, you have to begin working on the details of your image. First,invest in two or three loud sports jackets [. . .].
Transitional Sentences Transitional, orlinking, sentencesare used between paragraphs to help tie them smoothly together. • Example:Many of the other patrons are even more of a problem than the concession stand. • (Concession standreminds us of the previous supporting paragraph, while many of the other patronsintroduces the point to be developed next.)
Other Connecting Words • Repeated Words • Pronouns • Synonyms
RepeatedWords Repeating key words helps tie together the flow of thoughts in a paper. Example: One reason for studying psychology is [. . .]. Psychology is also useful in [. . .].
Pronouns Pronouns (he, she, it, you, they, this, that, and others) connect ideas and help you avoid needless repetition. Example: Another way for people to economize at an amusement park is to bring their own food. If they pack a lunch, they will avoid high prices.
Synonyms Synonymsare words that are alike in meaning, like pretty and attractive. They can be used to help writing flow. (They also add variety and interest to your sentences.) Example:There are several methods of fund-raising [. . .]. One technique is to hold an auction [. . .].
Introductions, Conclusions, and Titles A well-developed introduction, conclusion, and title can also help organize and connect your essay…
Methods of Introduction • 1: Begin with a general statement of your topic. • 2: Start with an idea or a situation that is the opposite of the one you will develop. • 3: Explain the importance of the topic to your reader. • 4: Use an incident or a brief story. • 5: Ask one or more questions. • 6: Use a quotation.
Common Methods of Conclusion • 1: End with a summary and a final thought. • 2: Include a thought-provoking question. • 3: End with a prediction or recommendation.
Titles Titles are brief summaries of what your paper is about. Examples: How to Complain; Student Zombies Note: You should not underline or put “quotation marks” around the title, but you should CAPITALIZE all but small connecting words.
- More by User

Writing the Introduction and Conclusion
Writing the Introduction and Conclusion. Diagram of the Introduction. 1 st sentence: Topic sentence to establish time frame (e.g. great depression) and the effect this has on the individual. 2 nd sentence: MUST include novel and central character and is written exactly like this:
232 views • 7 slides

Introduction and Conclusion Paragraphs
Introduction and Conclusion Paragraphs. No pain for me this time…. The Introduction Paragraph. The first paragraph in a paper that introduces your topic and thesis statement Contains 3 main parts: Attention-Getter / Hook Lead-in Thesis statement. A Visual.
559 views • 11 slides

Introduction and Conclusion
9/18/2012. Prof. Teel English Composition . 2. Goals:. Introduction: to get your reader's attention and to arouse interest in your topicConclusion: to emphasize the main point you have made and to help the reader remember it. 9/18/2012. Prof. Teel English Composition . 3. A Good Introducti
304 views • 8 slides

What Makes a Good Introduction and Conclusion?
What Makes a Good Introduction and Conclusion?. Ms.Wetzel’s Language Arts Class. Expository Writing Introductions What are expository writers trying to accomplish in introductions?. To tell the reader what they are writing about.
261 views • 16 slides

Speech Organization: Intro + Body + Conclusion
Speech Organization: Intro + Body + Conclusion. Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture/ Recap (also tying in Chapters 7 and 8—because of snow days). What does “Strategic Organization” Mean?. Necessary for Public Speaking? (Why/Why not?). Review. General Purpose: To Inform
543 views • 23 slides

Introduction, Body, and conclusion: The basic structure of a research paper
Introduction, Body, and conclusion: The basic structure of a research paper. Ms. Calabrese. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Hook Capture the readers attention Set the scene Different types of Hooks Use a quote Ask a question Use a shocking fact Use a statistic
454 views • 16 slides
LOOK AT THE MARK SCHEME USE THE BOOKLET. Link back to question (Introduction/conclusion and at the end of a thematic paragraph). Useful key terms to show judgement in your essay. Disparity Perpetuate Exemplify Consolidate Profound Coherent. Clear themes.
116 views • 2 slides

Introduction and Conclusion Paragraphs. “The Landlady”. The Introduction. The introduction has a “hook or grabber” to catch the reader’s attention. Some “grabbers” include opening with a: strong statement/headline Quotation Anecdote/story Statistic/fact Rhetorical question
747 views • 18 slides

Character Sketch: Introduction and Conclusion
Character Sketch: Introduction and Conclusion. Ms. Marshall. Character Sketch: Introduction and Conclusion September 12, 2011. 14.
182 views • 7 slides

How to: Write an Introduction and Conclusion
How to: Write an Introduction and Conclusion. November 22 nd , 2010 . Writing an Essay . The most important factors to consider when writing an essay are a proper introduction and conclusion. These two paragraphs are the backbone of the essay. They could “make or break” an essay.
2.51k views • 17 slides

Introduction & Conclusion notes
Introduction & Conclusion notes. Your introduction should . . . Begin with a broad statement that applies to life in general and has to do with the ideas in your thesis statement. Mention the title and author of the text.
146 views • 4 slides

Writing a Research Paper – Part 4: Introduction, Conclusion, and Body Paragraphs
Writing a Research Paper – Part 4: Introduction, Conclusion, and Body Paragraphs. Mr. White’s History Class. Objectives. What do we want to know how to do? Write an introduction Write a conclusion Write body paragraphs. Paragraphs – What are they?.
289 views • 17 slides

Writing an Introduction and Conclusion
Writing an Introduction and Conclusion. To Kill a Mockingbird Theme Analysis Paper. Introduction .
275 views • 10 slides

Speech Organization: Intro + Body + Conclusion. Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture/Recap. Examples of Informative Speeches. Good or bad organization?. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YivQYeI0vys http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ck5vVU8qQWA. What does “Strategic Organization” Mean?.
434 views • 26 slides

The introduction and the conclusion
The introduction and the conclusion . Granville Lily 2010. The introduction and the conclusion are key elements in the structure of your essay writing. They are the bookends that stop the bits in the middle collapsing, if you like.
231 views • 10 slides

Speech Organization: Intro + Body + Conclusion. Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture/Recap. Examples of Informative Speeches. Good or bad organization?. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YivQYeI0vys http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ck5vVU8qQWA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iADcfffP4wE.
486 views • 26 slides

Introduction Results Discussion Conclusion
M. D. Ballmer, J. van Hunen, G. Ito, P. J. Tackley and T. A. Bianco Intraplate volcano chains originating from small-scale sublithospheric convection. OUTLINE OUTLINE OUTLINE OUTLINE OUTLINE. Introduction Results Discussion Conclusion. Motivation
909 views • 34 slides

Introduction Simulation Results Conclusion
Hybrid Source Studies. Olivier Dadoun. A. Variola , F. Poirier , I. Chaikovska, J. Bonis R.Chehab L. Rinofli , A. Vivoli, V. Strakhovenko. Introduction Simulation Results Conclusion. [email protected] www.dadoun.net. Positron sources using channeling. Baseline for CLIC :
316 views • 16 slides

Introduction | Process | | Conclusion | Resources |
Seashore Web Quest. Introduction | Process | | Conclusion | Resources |. A Web Quest for 2 nd Grade Marine Activities, Resources and Education (MARE) Designed by Sue Priolo …[email protected]. INTRODUCTION. Introduction | Process | Conclusion | Resources |.
174 views • 7 slides

Three Parts of an Essay: Introduction, Body, Conclusion
Three Parts of an Essay: Introduction, Body, Conclusion. An essay has three basic parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion . Each part has a specific purpose. A good introductory paragraph does several things: It tells what your topic and main ideas are (specific)
1.64k views • 10 slides

Writing- Introduction and Conclusion
Writing- Introduction and Conclusion. ENGL 101 Mrs. Eleftheriades. Monday, April 28. Aim: What is the function of the introduction and conclusion paragraph in an argumentative essay ? Objectives: To become familiar with strategies for writing effective introductions and conclusions
310 views • 11 slides

The Introduction & Conclusion
The Introduction & Conclusion. Aloha and Adios. The Purpose. To grab the reader's attention, raise his level of interest This is often called "the hook ” To introduce the reader to the topic and prepare him for what follows in the body of the paper. Easy Checklist.
219 views • 7 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hrideep Barot. Presentation, Public Speaking, Speech Writing. A presentation structure includes an introduction, context, main body, conclusion, and scope for questions. Depending on the type of presentation you're doing, this format can change. The article discusses various considerations for each section of a presentation structure.
Typical Presentation Structure . In general, the contents of a presentation include an introduction, body, and conclusion. At times, it may include visual aids. This is the usual flow for crafting an effective presentation structure: from introduction to conclusion, which covers all the necessary sections and allows the audience to follow along ...
1. Open - Body - Conclusion. The Open - Body - Conclusion approach is one of the most practical structures you can use for presentations. (Click here to download a worksheet that helps you use it.) People often call it the "tell 'em" approach, because you: Tell audience members what you're going to tell them (introduction). Tell them ...
This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there. Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". 5.
The easiest way to study a presentation structure is to subdivide it into sections. Basically, every presentation has a structure that follows this formula: Introduction > Body > Conclusion. Introduction. The introduction is the first section of the presentation and sets the tone for the rest of the presentation.
Parts of a Presentation. All types of presentations consist of three basic parts: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. In general, the introduction should be about 10-15% of your speaking time, the body around 75%, and the conclusion only 10%. The old adage is that in the introduction you tell them what you will tell them; in the ...
2. Use the Outline View. One other way to structure a PowerPoint presentation in the editing mode is to use Outline View. You can choose it from the VIEW tab. This view doesn't display sections, but it shows the title and main text of each slide, which can give you a quick overview of the presentation contents.
Let's take a look at the three parts that make up the structure of any presentation: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Introductions. The introduction of a talk is an opportunity to get your audience interested in your talk as well as prepare them for the journey. You'll want to use the brief time that you devote to the introduction wisely.
In the introduction, you tell your audience what your message is going to be. In the body, you tell your audience your real message. In the conclusion, you summarize what your message was. We will now consider each of these parts in more detail. Introduction. The introduction is a very important - perhaps the most important - part of your ...
Let's break down the typical structure into three main parts: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Introduction. The introduction is like the opening act of a performance, and it's super important because it tells your audience what they'll learn from your presentation. Here are the different slides you need to include in the beginning ...
An eye-catching introduction, a body and a conclusion emphasizing your primary ideas are the three essential components of a successful speech. Here's what you should include while creating the structure of your presentation. An introduction; The body; Conclusion; 3. Flesh out Your Outline
How to create an engaging introduction. Consider using the tips below to engage your audience before your next presentation: 1. Tell your audience who you are. Introduce yourself, and then once your audience knows your name, tell them why they should listen to you. Example: "Good morning. My name is Miranda Booker, and I'm here today to ...
Based on the above, all presentations can be divided into three parts: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Transition statements and transition words can be used to maintain flow. Introduction. The way you begin determines how your audience will respond throughout your presentation.
Use transitions between sections of your presentation (introduction, body, and conclusion) as well as between points in your main body section. The Writing Studio's handout on Roadmaps ... Conclusion - Examples of conclusions should include a signal that it is the conclusion, summary of points, and an appropriate ending (such as "Thank ...
Introductions; Bodies; Conclusions; Below is a sample outline that can be used for most speeches and presentations. For each of these general elements, a number of specific elements are found. Not all presentations will require each of these specific items but they are covered here in the event you need a full-content presentation.
In this article, we will look at presentation structure, focusing on the three parts: Introduction, main body, and conclusion of a presentation. We will explore what each part does and specific tips to help structure these parts of the presentation in the best possible way. The Agenda. Part 1: The introduction of a presentation.
30 Example Phrases: How to Conclude a Presentation. 1. "In summary, let's revisit the key takeaways from today's presentation.". 2. "Thank you for your attention. Let's move forward together.". 3. "That brings us to the end. I'm open to any questions you may have.".
A presentation: has an introduction, body and conclusion; may include visual aids; is usually followed by questions and discussions; may also have a handout for the audience to take away. Introduction. The introduction should orient the audience to your subject and purpose. To capture interest and set up rapport, it should tell the audience ...
As with any effective essay, an oral presentation needs an introduction, a body and a conclusion. The Introduction An introduction is essential. It allows you to engage your audience and set the scene for the talk which follows. Without an introduction, your audience will not know where you are taking them and what your main points will be.
The format for the Instructional Oral Presentation is Introduction, Body and Conclusion. In the introduction, you must. tell your expertise regarding the topic/issue. The presentation of these steps is referred to as the MORE (+E) principle: M eaningful to audience, O penness of speaker, R elates to past experiences, E xpertise of the speaker ...
14.2a. Parts of a Presentation. There are 3 main parts of a presentation: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. The Introduction: You should introduce yourself and your topic. You also want to grab the audience's attention by asking a question, telling a story, or giving an interesting fact about your topic.
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
Methods of Introduction • 1: Begin with a general statement of your topic. • 2: Start with an idea or a situation that is the opposite of the one you will develop. • 3: Explain the importance of the topic to your reader. • 4: Use an incident or a brief story. • 5: Ask one or more questions. • 6: Use a quotation.