Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples

How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
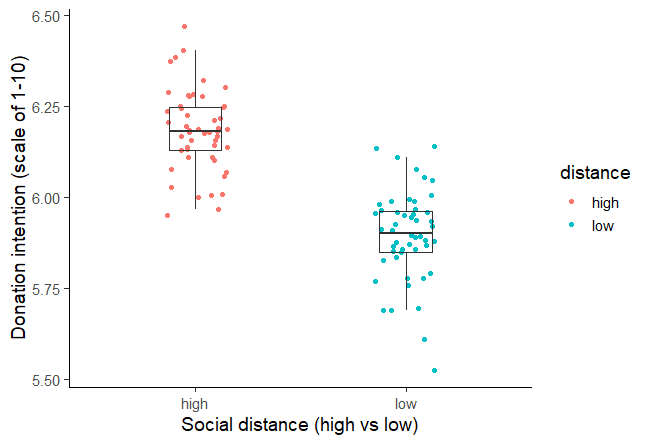
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, what is your plagiarism score.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
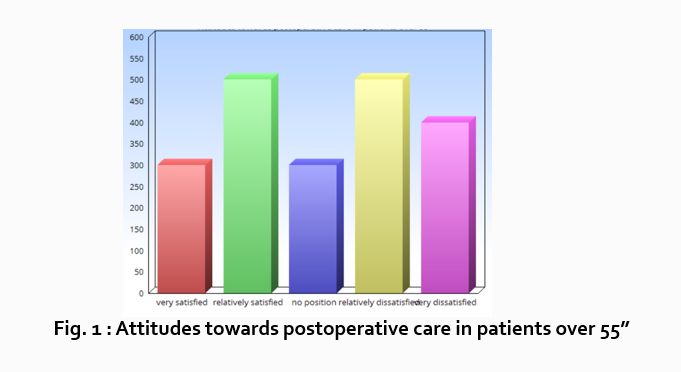
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
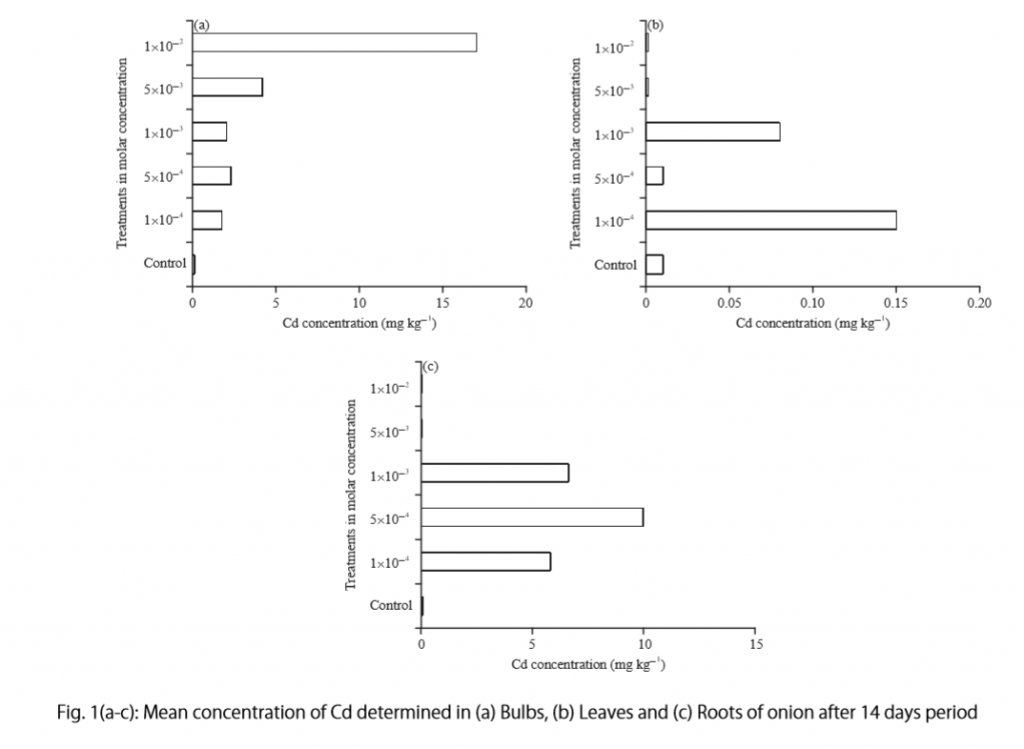
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" results section
Figures and Captions in Lab Reports
"Results Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
Additional tips for results sections.
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is the core of the paper. Don't start the results sections with methods you left out of the Materials and Methods section. You need to give an overall description of the experiments and present the data you found.
- Factual statements supported by evidence. Short and sweet without excess words
- Present representative data rather than endlessly repetitive data
- Discuss variables only if they had an effect (positive or negative)
- Use meaningful statistics
- Avoid redundancy. If it is in the tables or captions you may not need to repeat it
A short article by Dr. Brett Couch and Dr. Deena Wassenberg, Biology Program, University of Minnesota
- Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary.
- Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained.
- Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting results in chronological order rather than logical order; ignoring results that do not support the conclusions;
- Number tables and figures separately beginning with 1 (i.e. Table 1, Table 2, Figure 1, etc.).
- Do not attempt to evaluate the results in this section. Report only what you found; hold all discussion of the significance of the results for the Discussion section.
- It is not necessary to describe every step of your statistical analyses. Scientists understand all about null hypotheses, rejection rules, and so forth and do not need to be reminded of them. Just say something like, "Honeybees did not use the flowers in proportion to their availability (X2 = 7.9, p<0.05, d.f.= 4, chi-square test)." Likewise, cite tables and figures without describing in detail how the data were manipulated. Explanations of this sort should appear in a legend or caption written on the same page as the figure or table.
- You must refer in the text to each figure or table you include in your paper.
- Tables generally should report summary-level data, such as means ± standard deviations, rather than all your raw data. A long list of all your individual observations will mean much less than a few concise, easy-to-read tables or figures that bring out the main findings of your study.
- Only use a figure (graph) when the data lend themselves to a good visual representation. Avoid using figures that show too many variables or trends at once, because they can be hard to understand.
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion
- << Previous: METHODS
- Next: DISCUSSION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
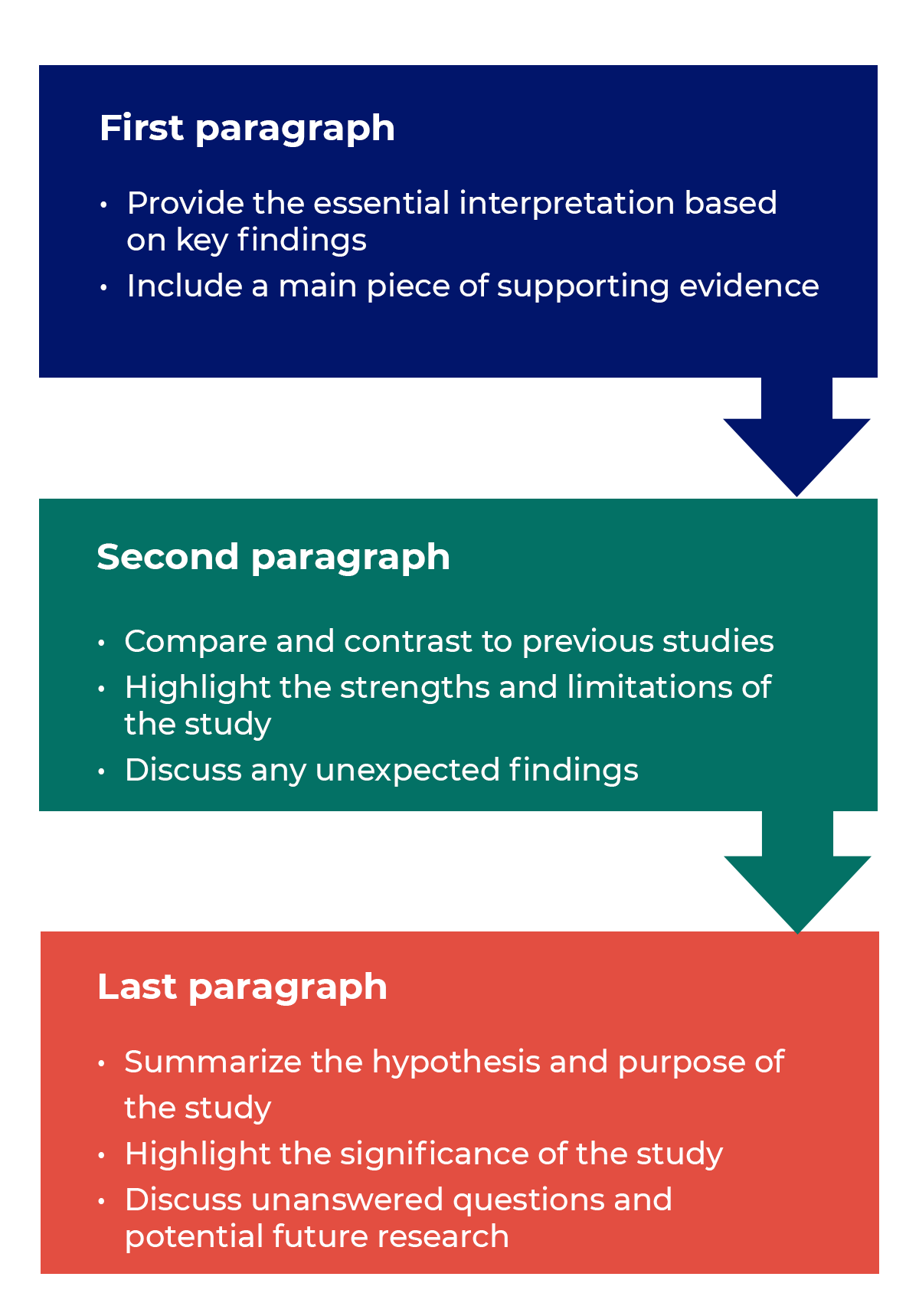
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 53.5K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing

Path to An Impactful Paper: Common Manuscript Writing Patterns and Structure
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The results section is where you report the findings of your study based upon the methodology [or methodologies] you applied to gather information. The results section should state the findings of the research arranged in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation. A section describing results should be particularly detailed if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Findings can only confirm or reject the hypothesis underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise. Use non-textual elements appropriately, such as figures and tables, to present findings more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish information that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other content that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data that has not been summarized should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good strategy is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper that follows].
Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Brett, Paul. "A Genre Analysis of the Results Section of Sociology Articles." English for Specific Speakers 13 (1994): 47-59; Go to English for Specific Purposes on ScienceDirect;Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit; "Reporting Findings." In Making Sense of Social Research Malcolm Williams, editor. (London;: SAGE Publications, 2003) pp. 188-207.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Organization and Approach
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results . Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach.
- Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings . This approach can be used to highlight important findings. For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is appropriate to highlight this finding in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a result and then explain it, before presenting the next result then explaining it, and so on, then end with an overall synopsis . This is the preferred approach if you have multiple results of equal significance. It is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it is helpful to provide a brief conclusion that ties each of the findings together and provides a narrative bridge to the discussion section of the your paper.
NOTE : Just as the literature review should be arranged under conceptual categories rather than systematically describing each source, you should also organize your findings under key themes related to addressing the research problem. This can be done under either format noted above [i.e., a thorough explanation of the key results or a sequential, thematic description and explanation of each finding].
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following:
- Introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem underpinning your study . This is useful in re-orientating the reader's focus back to the research problem after having read a review of the literature and your explanation of the methods used for gathering and analyzing information.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate key findings, if appropriate . Rather than relying entirely on descriptive text, consider how your findings can be presented visually. This is a helpful way of condensing a lot of data into one place that can then be referred to in the text. Consider referring to appendices if there is a lot of non-textual elements.
- A systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation . Not all results that emerge from the methodology used to gather information may be related to answering the " So What? " question. Do not confuse observations with interpretations; observations in this context refers to highlighting important findings you discovered through a process of reviewing prior literature and gathering data.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported . However, focus on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem. It is not uncommon to have unanticipated results that are not relevant to answering the research question. This is not to say that you don't acknowledge tangential findings and, in fact, can be referred to as areas for further research in the conclusion of your paper. However, spending time in the results section describing tangential findings clutters your overall results section and distracts the reader.
- A short paragraph that concludes the results section by synthesizing the key findings of the study . Highlight the most important findings you want readers to remember as they transition into the discussion section. This is particularly important if, for example, there are many results to report, the findings are complicated or unanticipated, or they are impactful or actionable in some way [i.e., able to be pursued in a feasible way applied to practice].
NOTE: Always use the past tense when referring to your study's findings. Reference to findings should always be described as having already happened because the method used to gather the information has been completed.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save this for the discussion section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to the work of Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings. This should have been done in your introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need for additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Writing up research is rarely a linear process. Always revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . A negative result generally refers to a finding that does not support the underlying assumptions of your study. Do not ignore them. Document these findings and then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, can give you an opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be hesitant to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater than other variables..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...." Subjective modifiers should be explained in the discussion section of the paper [i.e., why did one variable appear greater? Or, how does the finding demonstrate a promising trend?].
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you want to highlight a particular finding, it is appropriate to do so in the results section. However, you should emphasize its significance in relation to addressing the research problem in the discussion section. Do not repeat it in your results section because you can do that in the conclusion of your paper.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. Don't call a chart an illustration or a figure a table. If you are not sure, go here .
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers. Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit ; Ng, K. H. and W. C. Peh. "Writing the Results." Singapore Medical Journal 49 (2008): 967-968; Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in scholarly social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings with a discussion about their significance and implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two distinct sections for each section in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret the information and answer the "So What?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you can consider melding the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
Driscoll, Dana Lynn and Aleksandra Kasztalska. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Insiderness
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 9:59 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an APA Results Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
What to Include in an APA Results Section
- Justify Claims
- Summarize Results
Report All Relevant Results
- Report Statistical Findings
Include Tables and Figures
What not to include in an apa results section.
Psychology papers generally follow a specific structure. One important section of a paper is known as the results section. An APA results section of a psychology paper summarizes the data that was collected and the statistical analyses that were performed. The goal of this section is to report the results of your study or experiment without any type of subjective interpretation.
At a Glance
The results section is a vital part of an APA paper that summarizes a study's findings and statistical analysis. This section often includes descriptive text, tables, and figures to help summarize the findings. The focus is purely on summarizing and presenting the findings and should not include any interpretation, since you'll cover that in the subsequent discussion section.
This article covers how to write an APA results section, including what to include and what to avoid.
The results section is the third section of a psychology paper. It will appear after the introduction and methods sections and before the discussion section.
The results section should include:
- A summary of the research findings.
- Information about participant flow, recruitment, retention, and attrition. If some participants started the study and later left or failed to complete the study, then this should be described.
- Information about any reasons why some data might have been excluded from the study.
- Statistical information including samples sizes and statistical tests that were used. It should report standard deviations, p-values, and other measures of interest.
Results Should Justify Your Claims
Report data in order to sufficiently justify your conclusions. Since you'll be talking about your own interpretation of the results in the discussion section, you need to be sure that the information reported in the results section justifies your claims.
When you start writing your discussion section, you can then look back on your results to ensure that all the data you need are there to fully support your conclusions. Be sure not to make claims in your discussion section that are not supported by the findings described in your results section.
Summarize Your Results
Remember, you are summarizing the results of your psychological study, not reporting them in full detail. The results section should be a relatively brief overview of your findings, not a complete presentation of every single number and calculation.
If you choose, you can create a supplemental online archive where other researchers can access the raw data if they choose.
How long should a results section be?
The length of your results section will vary depending on the nature of your paper and the complexity of your research. In most cases, this will be the shortest section of your paper.
Just as the results section of your psychology paper should sufficiently justify your claims, it should also provide an accurate look at what you found in your study. Be sure to mention all relevant information.
Don't omit findings simply because they failed to support your predictions.
Your hypothesis may have expected more statistically significant results or your study didn't support your hypothesis , but that doesn't mean that the conclusions you reach are not useful. Provide data about what you found in your results section, then save your interpretation for what the results might mean in the discussion section.
While your study might not have supported your original predictions, your finding can provide important inspiration for future explorations into a topic.
How is the results section different from the discussion section?
The results section provides the results of your study or experiment. The goal of the section is to report what happened and the statistical analyses you performed. The discussion section is where you will examine what these results mean and whether they support or fail to support your hypothesis.
Report Your Statistical Findings
Always assume that your readers have a solid understanding of statistical concepts. There's no need to explain what a t-test is or how a one-way ANOVA works. Your responsibility is to report the results of your study, not to teach your readers how to analyze or interpret statistics.
Include Effect Sizes
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association recommends including effect sizes in your results section so that readers can appreciate the importance of your study's findings.
Your results section should include both text and illustrations. Presenting data in this way makes it easier for readers to quickly look at your results.
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
Only include tables and figures if you are going to talk about them in the body text of your results section.
In addition to knowing what you should include in the results section of your psychology paper, it's also important to be aware of things that you should avoid putting in this section:
Cause-and-Effect Conclusions
Don't draw cause-effect conclusions. Avoid making any claims suggesting that your result "proves" that something is true.
Interpretations
Present the data without editorializing it. Save your comments and interpretations for the discussion section of your paper.
Statistics Without Context
Don't include statistics without narration. The results section should not be a numbers dump. Instead, you should sequentially narrate what these numbers mean.
Don't include the raw data in the results section. The results section should be a concise presentation of the results. If there is raw data that would be useful, include it in the appendix .
Don't only rely on descriptive text. Use tables and figures to present these findings when appropriate. This makes the results section easier to read and can convey a great deal of information quickly.
Repeated Data
Don't present the same data twice in your illustrative materials. If you have already presented some data in a table, don't present it again in a figure. If you have presented data in a figure, don't present it again in a table.
All of Your Findings
Don't feel like you have to include everything. If data is irrelevant to the research question, don't include it in the results section.
But Don't Skip Relevant Data
Don't leave out results because they don't support your claims. Even if your data does not support your hypothesis, including it in your findings is essential if it's relevant.
More Tips for Writing a Results Section
If you are struggling, there are a few things to remember that might help:
- Use the past tense . The results section should be written in the past tense.
- Be concise and objective . You will have the opportunity to give your own interpretations of the results in the discussion section.
- Use APA format . As you are writing your results section, keep a style guide on hand. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Visit your library . Read some journal articles that are on your topic. Pay attention to how the authors present the results of their research.
- Get a second opinion . If possible, take your paper to your school's writing lab for additional assistance.
What This Means For You
Remember, the results section of your paper is all about providing the data from your study. This section is often the shortest part of your paper, and in most cases, the most clinical.
Be sure not to include any subjective interpretation of the results. Simply relay the data in the most objective and straightforward way possible. You can then provide your own analysis of what these results mean in the discussion section of your paper.
Bavdekar SB, Chandak S. Results: Unraveling the findings . J Assoc Physicians India . 2015 Sep;63(9):44-6. PMID:27608866.
Snyder N, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. How to write an effective results section . Clin Spine Surg . 2019;32(7):295-296. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
Purdue Online Writing Lab. APA sample paper: Experimental psychology .
Berkeley University. Reviewing test results .
Tuncel A, Atan A. How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):16-19. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.048
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources

Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
APA Results Section – Explanation & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The APA results section summarizes data and includes reporting statistics in a quantitative research study. The APA results section is an essential part of your research paper and typically begins with a brief overview of the data followed by a systematic and detailed reporting of each hypothesis tested. The interpreted results will then be presented in the discussion sections. Ensure you adhere to APA style guidelines consistently throughout the paper.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 APA Results Section – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: APA results section
- 3 What’s included in the APA results section?
- 4 APA results section: Introducing the data
- 5 APA results section: Summarizing the data
- 6 APA results section: Reporting the results
- 7 APA results section: Formatting numbers
- 8 APA results section: Don’t include these
APA Results Section – In a Nutshell
- The APA results section of empirical manuscripts reports the quantitative results of a study conducted on a data set.
- The APA results section provides concrete evidence to disprove or confirm the hypothesis.
Definition: APA results section
The American Psychological Association recommends the APA style guide for presenting results in a manuscript. A research manuscript’s APA results section describes the researcher’s findings following a thorough data analysis and interpretation of the results. It uses obtained data to test or refute the theory of a research study.
What’s included in the APA results section?
The APA results section includes preliminary details on the data, participants, statistics , and the results of the explanatory analysis , as discussed below.
- Participants – The number of participants is reported at every study stage
- Missing data – Identifying the amount of data excluded from the final analysis.
- Adverse effects – Report any unforeseen events for clinical studies
- Descriptive statistics – Summarize the secondary and primary outcomes of a study
- Inferential statistics – Helps researchers draw conclusions and make predictions from the data.
- Confidence interval and effect size – Confidence intervals are a range of possible values for the data set mean.
- Results of explanatory analysis – An exploratory research investigates data to test a hypothesis, check assumptions, and find anomalies.
APA results section: Introducing the data
Before you discuss your research findings, start by clearly describing the participants at each study stage. If any data was excluded from the eventual analysis, indicate that too.
Participants
Recruitment, participant flow, and attrition should be reported. Attrition bias affects external and internal validity and produces erroneous results.
A flow chart is often the best way to report the number of participants per group per stage and their reasons for attrition. Below is an example of how to report participant flow.
- 25% of the 400 participants who signed up and completed the first survey were eliminated for not fitting the research criteria.
- 15% didn’t use fiber optics internet exclusively.
- 10% did not have internet access.
- 300 participants progressed to the final survey round for a gift bag.
- 52 people didn’t complete the survey.
This resulted in 248 research participants.
Missing data & adverse effects
In any study, missing data must be reported. Unexpected events, poor storage, and equipment failures can cause missing data. In any instance, clearly explain why you couldn’t use the data.
Data outliers can be excluded from the final study, but you must explain why. Include how you handled missing data. Standard procedures include mean-value imputation, interpolation, extrapolation, and substitution.
- Results of 33 participants were excluded from the study as they did not meet the research criteria.
- The data for another 4 participants were lost due to human error.
APA results section: Summarizing the data
It is important to note that you should provide a summary of your study’s results. However, you can create a supplemental archive for other researchers to access raw data. 2
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are concise coefficients that summarize a specific data collection , such as a population sample or APA results section. APA results section can include descriptive statistics such as:
- Central tendency measures describe a data set by identifying the center of the data set. ( mode , median, mean )
- Measures of variability describe the score dispersion within a data set. ( standard deviation , range, variance , and interquartile range )
- Sample sizes
- Variables of interest, which are measured, changing quantities in experimental studies. Be sure to explain how you operationalized any variable of interest you use.
- 20 athletes in five trials were given 400 mg of a performance-enhancing substance to measure their speed (m/s ) and reaction time(s).
- After averaging each athlete’s speed and response time, the group’s averages were calculated.
The group that used the performance-enhancing drug had a higher speed (m/s) than the group that did not use the drug ( M = 4, SD=1.25 )
APA results section: Reporting the results
APA journal standards require all the appropriate hypothesis tests, confidence intervals, and effect size estimates to be reported in the APA results section.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics help researchers draw conclusions and make predictions based on the data.
When you are reporting the inferential statistics in the APA results section, use the following:
- Degrees of freedom
- Test statistic (includes the z-score, t-value, and f-ratio )
- Error term (if needed, though it is not included in correlations and non-parametric tests.)
- The exact p-value (unless . 001)
In keeping with the hypotheses, athletes who take performance-enhancing drugs have increased reaction times, and speeds, t (20) = 1s , p .001
Confidence intervals & effect sizes
A confidence interval can be described as a range of possible values for the mean derived from the sample data. It helps show the variability that is around point estimates. You should include confidence intervals any time you report estimates for population parameters.
Night guards consume an average of 600 mg of caffeine weekly, 93% CI [90, 200}
Effect size measures an experiment’s magnitude. It explains the research’s significance. Since effect size is an estimate, confidence intervals should be included.
Moderate amounts of performance-enhancing drugs increase speed significantly, Cohen’s d =1.4, 93% CI [0.92, 1.57]
Subgroup & exploratory analyses
Exploratory analysis tests a hypothesis, checks assumptions , and finds patterns and anomalies in data . If you find notable results, report them as exploratory, not confirming, to avoid overstating their value.
APA results section: Formatting numbers
Use figures, text, and tables to show numbers in APA results sections properly.
✓ For three or fewer numbers, use a sentence, a table for 4 and 20 numbers, and a figure for more than 20 .
✓ Number and title the APA tables and figures , as well as relevant notes. If you have already presented the data in a table, do not repeat it in a figure and vice versa.
✓ Statistics in your APA results section must be abbreviated, capitalized, and italicized.
✓ Use APA norms for reporting statistics and writing numbers.
✓ Look up these guidelines if you are unsure how to present certain symbols.

APA results section: Don’t include these
Besides knowing what to include in an APA results section, it is just as important to know what not to have. Below is an outline of what you should exclude from an APA results section.
What should be included in the APA results section?
The APA results section should include details on the participants, descriptive statistics and inferential statistics , missing data , and the results of any exploratory analysis.
What tense should I use to write my results?
Write the APA results section in the past tense.
When should I include tables and figures?
Include tables and figures if you will discuss them in the body text of the APA results section.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be written in the past tense. A section describing results [a.k.a., "findings"] is particularly necessary if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Research results can only confirm or reject the research problem underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise, using non-textual elements, such as figures and tables, if appropriate, to present results more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish material that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other material that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good rule is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper].
Bates College; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
For most research paper formats, there are two ways of presenting and organizing the results .
- Present the results followed by a short explanation of the findings . For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is correct to point this out in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists, and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening, belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a section and then discuss it, before presenting the next section then discussing it, and so on . This is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it can be helpful to provide a brief conclusion in the results section that ties each of the findings together and links to the discussion.
NOTE: The discussion section should generally follow the same format chosen in presenting and organizing the results.
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following elements:
- An introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem that underpins the purpose of your study.
- A summary of your key findings arranged in a logical sequence that generally follows your methodology section.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate the findings, if appropriate.
- In the text, a systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation [remember that not all results that emerge from the methodology that you used to gather the data may be relevant].
- Use of the past tense when refering to your results.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported. However, focus only on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem.
Using Non-textual Elements
- Either place figures, tables, charts, etc. within the text of the result, or include them in the back of the report--do one or the other but never do both.
- In the text, refer to each non-textual element in numbered order [e.g., Table 1, Table 2; Chart 1, Chart 2; Map 1, Map 2].
- If you place non-textual elements at the end of the report, make sure they are clearly distinguished from any attached appendix materials, such as raw data.
- Regardless of placement, each non-textual element must be numbered consecutively and complete with caption [caption goes under the figure, table, chart, etc.]
- Each non-textual element must be titled, numbered consecutively, and complete with a heading [title with description goes above the figure, table, chart, etc.].
- In proofreading your results section, be sure that each non-textual element is sufficiently complete so that it could stand on its own, separate from the text.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save all this for the next section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings ; this should have been done in your Introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need to provide additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . If some of your results fail to support your hypothesis, do not ignore them. Document them, then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, often provides you with the opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be afraid to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater or lesser than..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...."
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you feel the need to highlight something, you will have a chance to do that in the discussion section.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. If you are not sure, look up the term in a dictionary.
Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers . Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results . Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings from the study with a discussion about their implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two sections for each element in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret your data and answer the "so what?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you may want to meld the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
- << Previous: Quantitative Methods
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen . Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean – any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs discussion vs conclusion, checklist: research results, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like ‘appears’ or ‘implies’.
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe shop: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the trainers, boots, sandals, etc.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualise trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarise or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.

Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organisations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
‘I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.’
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Swaen, B. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/results-section/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
What is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Write a Results Section for a Dissertation or Research Paper: Guide & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Write a Results Section for a Dissertation or Research Paper: Guide & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A results section is a crucial part of a research paper or dissertation, where you analyze your major findings. This section goes beyond simply presenting study outcomes. You should also include a comprehensive statistical analysis and interpret the collected data in detail.
Without dissertation research results, it is impossible to imagine a scientific work. Your task here is to present your study findings. What are qualitative or quantitative indicators? How to use tables and diagrams? How to describe data? Our article answers all these questions and many more. So, read further to discover how to analyze and describe your research indexes or contact or professionals for dissertation help from StudyCrumb.
What Is a Results Section of Dissertation?
The results section of a dissertation is a data statement from your research. Here you should present the main findings of your study to your readers. This section aims to show information objectively, systematically, concisely. It is allowed using text supplemented with illustrations. In general, this section's length is not limited but should include all necessary data. Interpretations or conclusions should not be included in this section. Therefore, in theory, this is one of your shortest sections. But it can also be one of the most challenging sections. The introduction presents a research topic and answers the question "why?". The Methods section explains the data collection process and answers "how?". Meanwhile, the result section shows actual data gained from experiments and tells "what?" Thus, this part plays a critical role in highlighting study's relevance. This chapter gives reader study relevance with novelty. So, you should figure out how to write it correctly. Here are main tasks that you should keep in mind while writing:
- Results answer the question "What was found in your research?"
- Results contain only your study's outcome. They do not include comments or interpretations.
- Results must always be presented accurately & objectively.
- Tables & figures are used to draw readers' attention. But the same data should never be presented in the form of a table and a figure. Don't repeat anything from a table also in text.
Dissertation: Results vs Discussion vs Conclusion
Results and discussion sections of a dissertation are often confused among researchers. Sometimes both these parts are mixed up with a conclusion for thesis . Figured out what is covered in each of these important chapters. Your readers should see that you notice how different they are. A clear understanding of differences will help you write your dissertation more effectively. 5 differences between Results VS Discussion VS Conclusion:
Wanna figure out the actual difference between discussion vs conclusion? Check out our helpful articles about Dissertation Discussion or Dissertation Conclusion.
Present Your Findings When Writing Results Section of Dissertation
Now it's time to understand how to arrange the results section of the dissertation. First, present most general findings, then narrow it down to a more specific one. Describe both qualitative & quantitative results. For example, imagine you are comparing the behavior of hamsters and mice. First, say a few words about the behavioral type of mammals that you studied. Then, mention rodents in general. At end, describe specific species of animals you carried out an experiment on.
Qualitative Results Section in Dissertation
In your dissertation results section, qualitative data may not be directly related to specific sub-questions or hypotheses. You can structure this chapter around main issues that arise when analyzing data. For each question, make a general observation of what data show. For example, you may recall recurring agreements or differences, patterns, trends. Personal answers are the basis of your research. Clarify and support these views with direct quotes. Add more information to the thesis appendix if it's needed.
Quantitative Results Section in a Dissertation
The easiest way to write a quantitative dissertation results section is to build it around a sub-question or hypothesis of your research. For each subquery, provide relevant results and include statistical analysis . Then briefly evaluate importance & reliability. Notice how each result relates to the problem or whether it supports the hypothesis. Focus on key trends, differences, and relationships between data. But don't speculate about their meaning or consequences. This should be put in the discussion vs conclusion section. Suppose your results are not directly related to answering your questions. Maybe there is additional information that helps readers understand how you collect data. In that case, you can include them in the appendix. It is often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables. But only if they accurately support your results and add value.
Tables and Figures in Results Section in Dissertation
We recommend you use tables or figures in the dissertation results section correctly. Such interpretation can effectively present complex data concisely and visually. It allows readers to quickly gain a statistical overview. On the contrary, poorly designed graphs can confuse readers. That will reduce the effectiveness of your article. Here are our recommendations that help you understand how to use tables and figures:
- Make sure tables and figures are self-explanatory. Sometimes, your readers may look at tables and figures before reading the entire text. So they should make sense as separate elements.
- Do not repeat the content of tables and figures in text. Text can be used to highlight key points from tables and figures. But do not repeat every element.
- Make sure that values or information in tables and text are consistent. Make sure that abbreviations, group names, interpretations are the same as in text.
- Use clear, informative titles for tables and figures. Do not leave any table or figure without a title or legend. Otherwise, readers will not be able to understand data's meaning. Also, make sure column names, labels, figures are understandable.
- Check accuracy of data presented in tables and figures. Always double-check tables and figures to make sure numbers converge.
- Tables should not contain redundant information. Make sure tables in the article are not too crowded. If you need to provide extensive data, use Appendixes.
- Make sure images are clear. Make sure images and all parts of drawings are precise. Lettering should be in a standard font and legible against the background of the picture.
- Ask for permission to use illustrations. If you use illustrations, be sure to ask copyright holders and indicate them.
Tips on How to Write a Results Section
We have prepared several tips on how to write the results section of the dissertation! Present data collected during study objectively, logically, and concisely. Highlight most important results and organize them into specific sections. It is an excellent way to show that you have covered all the descriptive information you need. Correct usage of visual elements effectively helps your readers with understanding. So, follow main 3 rules for writing this part:
- State only actual results. Leave explanations and comments for Discussion.
- Use text, tables, and pictures to orderly highlight key results.
- Make sure that contents of tables and figures are not repeated in text.
In case you have questions about a conceptual framework in research , you will find a blog dedicated to this issue in our database.
What to Avoid When Writing the Results Section of a Dissertation
Here we will discuss how NOT to write the results section of a dissertation. Or simply, what points to avoid:
- Do not make your research too complicated. Your paper, tables, and graphs should be clearly marked and follow order. So that they can exist independently without further explanation.
- Do not include raw data. Remember, you are summarizing relevant results, not reporting them in detail. This chapter should briefly summarize your findings. Avoid complete introduction to each number and calculation.
- Do not contradict errors or false results. Explain these errors and contradictions in conclusions. This often happens when different research methods have been used.
- Do not write a conclusion or discussion. Instead, this part should contain summaries of findings.
- Do not tend to include explanations and inferences from results. Such an approach can make this chapter subjective, unclear, and confusing to the reader.
- Do not forget about novelty. Its lack is one of the main reasons for the paper's rejection.

Dissertation Results Section Example
Let's take a look at some good results section of dissertation examples. Remember that this part shows fundamental research you've done in detail. So, it has to be clear and concise, as you can see in the sample.
Final Thoughts on Writing Results Section of Dissertation
When writing a results section of a dissertation, highlight your achievements by data. The main chapter's task is to convince the reader of conclusions' validity of your research. You should not overload text with too detailed information. Never use words whose meanings you do not understand. Also, oversimplification may seem unconvincing for readers. But on the other hand, writing this part can even be fun. You can directly see your study results, which you'll interpret later. So keep going, and we wish you courage!
Writing any academic paper is long and thorough work. But StudyCrumb got you back! Our professional writers will deliver any type of work quickly and excellently!

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5 Writing the Results Section
5.1 The Results Section
This section explains what you found; i.e., the answer to your research question. The Results and the Discussion (of the results) sections are the two most often mixed up sections by those who are new to this structure of writing. Just remember that Results is where you objectively summarize and present the data.
Generally, this section will begin with a brief overview of the results, then cover each of the main results from the data. Objectively point out the main ideas and use tables, figures, and other graphics as necessary to present the data. This section also discusses any limitations of the study. Fig. 2.6 shows an example of the Results section.
Writing tips:
If you are writing a purely research paper you can present your findings using verbs of attribution: words that point out that these are someone else’s ideas. For example, you could write:
- The author stated
- This article points out
- The results of the PCR analysis showed that
- Model results can be seen in Table X
Just remember not to interpret the information. For writing an experimental report here are some tips:
- Report results and show supporting data
- Order results from most to least complex
- Describe results in past tense
- Be concise: Examining patterns for 38,646 measurements of foliar δ 15 N from non-N 2 -fixing species, mean foliar δ 15 N was 0.4‰ (Table 1).
- Interpret results
- Repeat all the data from the table, instead select important results to report
- Be verbose: Table 1 indicates that after examining patterns for 38,646 measurements of foliar δ 15 N from non-N 2 -fixing species the mean foliar δ 15 N was 0.4‰.
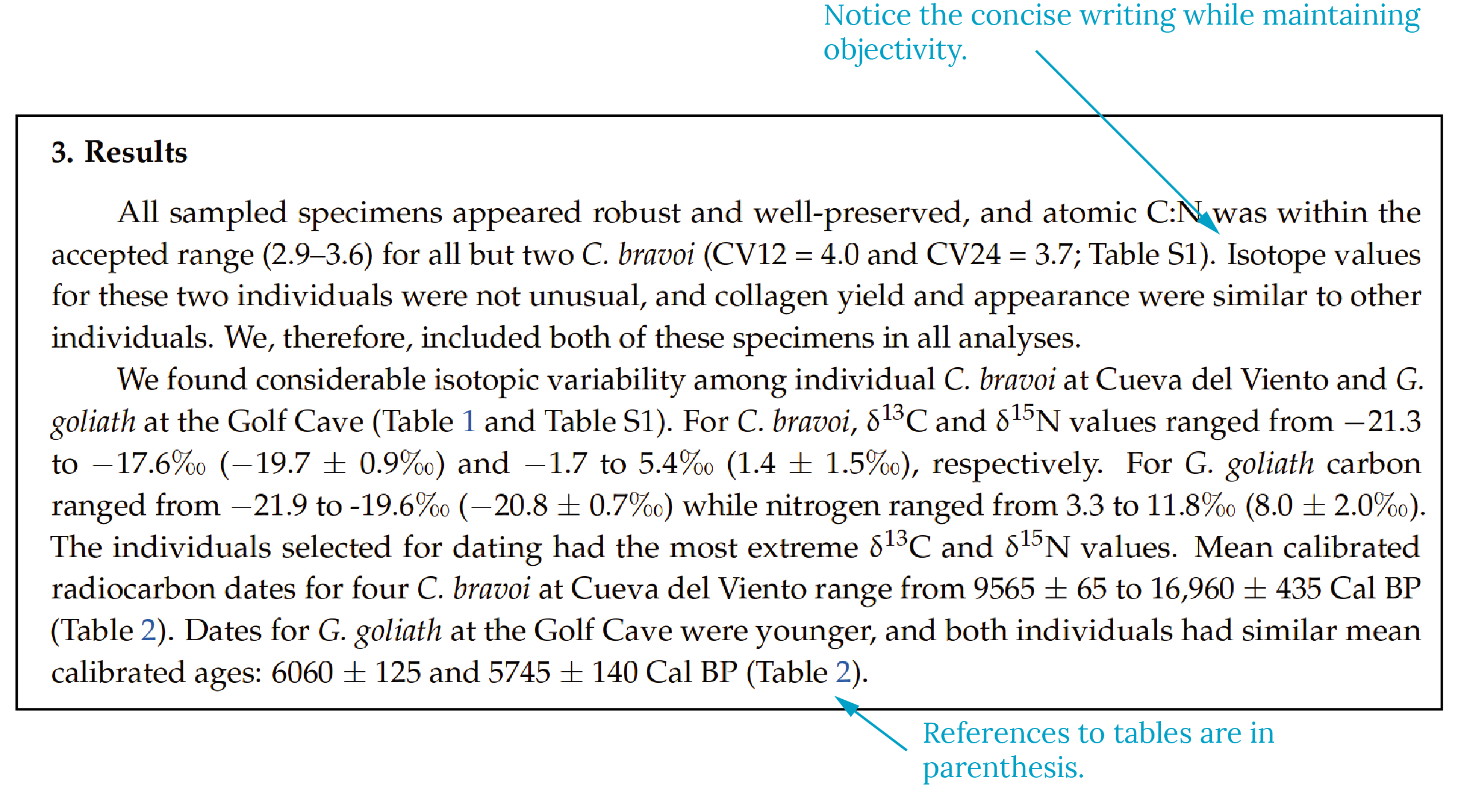
5.2 Figures and Tables
The word figure is used to describe any graphic in the document that is not a table. It can refer to photographs, drawings, diagrams, maps, and other type of illustrations. Fig. 2.7 shows a table and Fig. 2.8 shows results with a figure.
Writing Tips:
Be consistent in formatting for all figures and tables. Figure numbers and titles are listed in the caption below the figure. Table numbers and titles are listed above the table. Notes or source information are placed in the caption below the table. Figures and tables should be placed in the text where they are referred to and the reference to the figure or table should be in parenthetical text. Captions should be concise yet contain enough information for the reader to understand what the figure is about. Graphs should have clearly labeled legends.
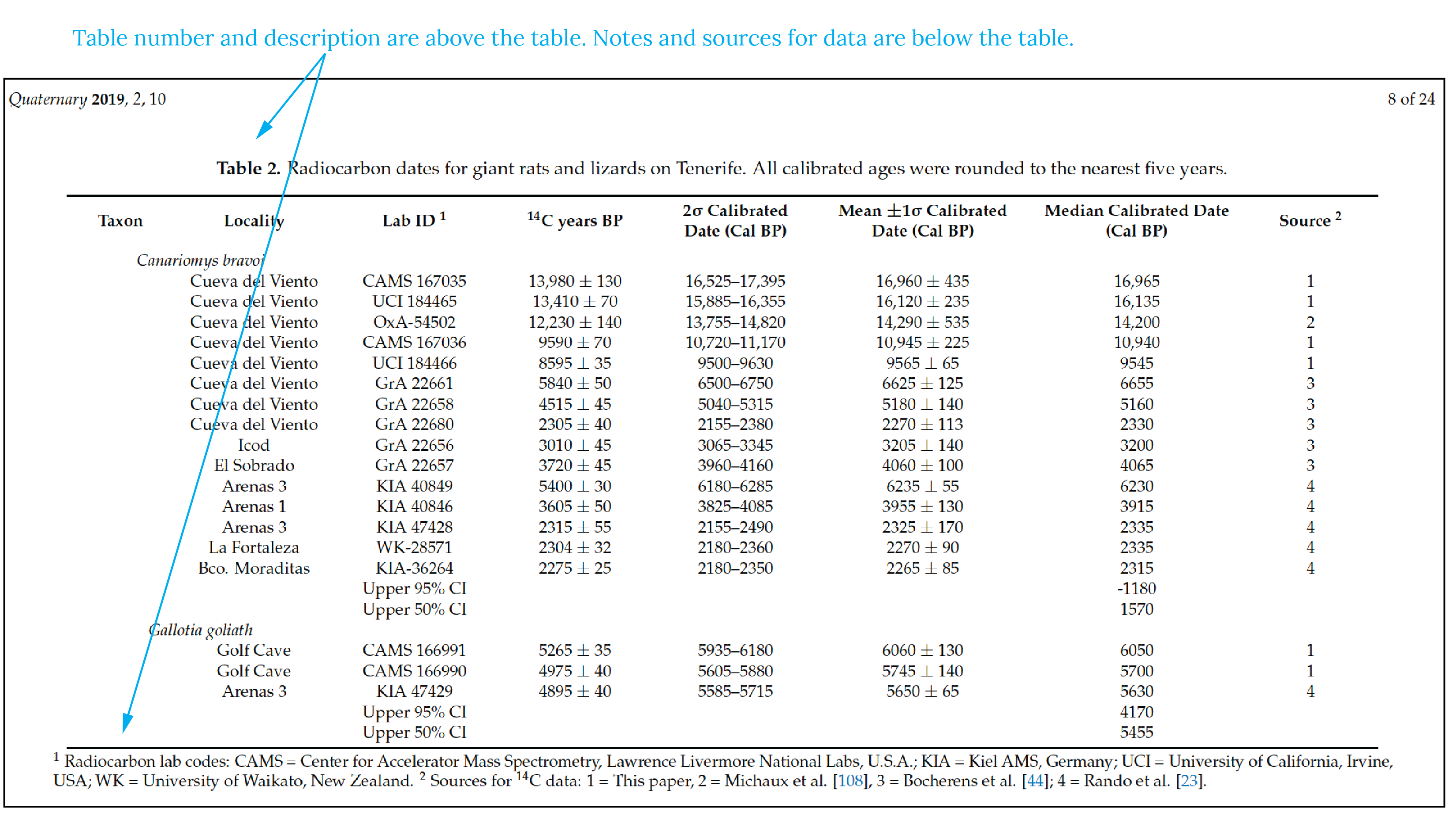
Technical Writing @ SLCC Copyright © 2020 by Department of English, Linguistics, and Writing Studies at SLCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Results Section Of A Research Paper: How To Write It Properly

The results section of a research paper refers to the part that represents the study’s core findings from the methods that the researcher used to collect and analyze data. This section presents the results logically without interpretation or bias from the author.
Thus, this part of a research paper sets up the read for evaluation and analysis of the findings in the discussion section. Essentially, this section breaks down the information into several sentences, showing its importance to the research question. Writing results section in a research paper entails summarizing the gathered data and the performed statistical analysis. That way, the author presents or reports the results without subjective interpretation.
What Is The Results Section Of A Research Paper?
In its simplest definition, a research paper results section is where the researcher reports the findings of a study based on the applied methodology for gathering information. It’s the part where the author states the research findings in a logical sequence without interpreting them. If the research paper has data from actual research, this section should feature a detailed description of the results.
When writing a dissertation, a thesis, or any other academic paper, the result section should come third in sections’ sequence. It should follow the Methods and Materials presentation and the Discussion section comes after it. But most scientific papers present the Results and Discussion sections together. However, the results section answers the question, “What did your research uncover?”
Ideally, this section allows you to report findings in research paper, creating the basis for sufficiently justified conclusions. After writing the study findings in the results section, you interpret them in the subsequent discussion part. Therefore, your results section should report information that will justify your claims. That way, you can look back on the results section when writing the discussion part to ensure that your report supports your conclusions.
What Goes in the Results Section of a Research Paper?
This section should present results in research paper. The findings part of a research paper can differ in structure depending on the study, discipline, and journal. Nevertheless, the results section presents a description of the experiment while presenting the research results. When writing this part of your research paper, you can use graphs and tables if necessary.
However, state the findings without interpreting them. For instance, you can find a correlation between variables when analyzing data. In that case, your results section can explain this correlation without speculating about the causes of this correlation.
Here’s what to include in the results section of research paper:
A brief introductory of the context, repeating the research questions to help the readers understand the results A report about information collection, participants, and recruitment: for instance, you can include a demographic summary with the participants’ characteristics A systematic findings’ description, with a logical presentation highlighting relevant and crucial results A contextual data analysis explaining the meaning in sentences Information corresponding to the primary research questions Secondary findings like subgroup analysis and secondary outcomes Visual elements like charts, figures, tables, and maps, illustrating and summarizing the findings
Ensure that your results section cites and numbers visual elements in an orderly manner. Every table or figure should stand alone without text. That means visual elements should have adequate non-textual content to enable the audiences to understand their meanings.
If your study has a broad scope, several variables, or used methodologies that yielded different results, state the most relevant results only based on the research question you presented in your Introduction section.
The general rule is to leave out any data that doesn’t present your study’s direct outcome or findings. Unless the professor, advisor, university faulty, or your target journal requests you to combine the Results and Discussion sections, omit the interpretations and explanations of the results in this section.
How Long Should A Results Section Be?
The findings section of a research paper ranges between two and three pages, with tables, text, and figures. In most cases, universities and journals insist that this section shouldn’t exceed 1,000 words over four to nine paragraphs, usually with no references.
But a good findings section occupies 5% of the entire paper. For instance, this section should have 500 words if a dissertation has 10,000 words. If the educator didn’t specify the number of words to include in this chapter, use the data you collect to determine its length. Nevertheless, be as concise as possible by featuring only relevant results that answer your research question.
How To Write Results Section Of Research Paper
Perhaps, you have completed researching and writing the preceding sections, and you’re now wondering how to write results. By the time you’re composing this section, you already have findings or answers to your research questions. However, you don’t even know how to start a results section. And your search for guidelines landed you on this page.
Well, every research project is different and unique. That’s why researchers use different strategies when writing this section of their research papers. The scientific or academic discipline, specialization field, target journal, and the author are factors influencing how you write this section. Nevertheless, there’s a general way of writing this section, although it might differ slightly between disciplines. Here’s how to write results section in a research paper.
Check the instructions or guidelines. Check their instructions or guidelines first, whether you’re writing the research paper as part of your coursework or for an academic journal. These guidelines outline the requirements for presenting results in research papers. Also, check the published articles to know how to approach this section. When reviewing the procedures, check content restrictions and length. Essentially, learn everything you can about this section from the instructions or guidelines before you start writing. Reflect on your research findings. With instructions and guidelines in mind, reflect on your research findings to determine how to present them in your research paper. Decide on the best way to show the results so that they can answer the research question. Also, strive to clarify and streamline your report, especially with a complex and lengthy results section. You can use subheadings to avoid peripheral and excessive details. Additionally, consider breaking down the content to make it easy for the readers to understand or remember. Your hypothesis, research question, or methodologies might influence the structure of the findings sections. Nevertheless, a hierarchy of importance, chronological order, or meaningful grouping of categories or themes can be an effective way of presenting your findings. Design your visual presentations. Visual presentations improve the textual report of the research findings. Therefore, decide on the figures and styles to use in your tables, graphs, photos, and maps. However, check the instructions and guidelines of your faculty or journal to determine the visual aids you can use. Also, check what the guidelines say about their formats and design elements. Ideally, number the figures and tables according to their mention in the text. Additionally, your figures and tables should be self-explanatory. Write your findings section. Writing the results section of a research paper entails communicating the information you gathered from your study. Ideally, be as objective and factual as possible. If you gathered complex information, try to simplify and present it accurately, precisely, and clearly. Therefore, use well-structured sentences instead of complex expressions and phrases. Also, use an active voice and past tense since you’ve already done the research. Additionally, use correct spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Take your time to present the findings in the best way possible to focus your readers on your study objectives while preparing them for the coming speculations, interpretations, and recommendations. Edit Your Findings Section. Once you’ve written the results part of your paper, please go through it to ensure that you’ve presented your study findings in the best way possible. Make sure that the content of this section is factual, accurate, and without errors. You’ve taken a considerable amount of time to compose the results scientific paper audiences will find interesting to read. Therefore, take a moment to go through the draft and eliminate all errors.
Practical Tips on How to Write a Results Section of a Research Paper
The results part of a research paper aims to present the key findings objectively in a logical and orderly sequence using text and illustrative materials. A common mistake that many authors make is confusing the information in the discussion and the results sections. To avoid this, focus on presenting your research findings without interpreting them or speculating about them.
The following tips on how to write a results section should make this task easier for you:
Summarize your study results: Instead of reporting the findings in full detail, summarize them. That way, you can develop an overview of the results. Present relevant findings only: Don’t report everything you found during your research. Instead, present pertinent information only. That means taking time to analyze your results to know what your audiences want to know. Report statistical findings: When writing this section, assume that the audiences understand statistical concepts. Therefore, don’t try to explain the nitty-gritty in this section. Remember that your work is to report your study’s findings in this section. Be objective and concise: You can interpret the findings in the discussion sections. Therefore, focus on presenting the results objectively and concisely in this section. Use the suitable format: Use the correct style to present the findings depending on your study field.
Get Professional Help with the Research Section
Maybe you’re pursuing your graduate or undergraduate studies but cannot write the results part of your paper. Perhaps, you’re done researching and analyzing information, but this section proves too tricky for you to write. Well, you’re not alone because many students across the world struggle to present their research findings.
Luckily, our highly educated, talented, and experienced writers are always ready to assist such learners. If you are stuck with the results part of your paper, our professionals can help you . We offer high-quality, custom writing help online. We’re a reliable team of experts with a sterling reputation for providing comprehensive assistance to college, high school, and university learners. We deliver highly informative academic papers after conducting extensive and in-depth research. Contact us saying something like, “please do my thesis” to get quality help with your paper!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
- Quantitative research results
- Qualitative research results
- Step-by-Step guide
Results writing checklist
- Results section formats
- Results section example

How to write the results section of a research paper?
- You must add collected, analyzed, and interpreted data or any statistical analyses performed.
- The section should be written clearly and easily, without technical jargon or unnecessary details.
- The results section should also include tables, graphs, or figures that help to illustrate the findings.
Reporting quantitative research results
- When you write the results section of a research paper, it is essential to focus on the key findings and provide clear and concise explanations of the statistical analysis used.
- It is vital to use appropriate graphs and tables to present the data visually and make it easier to understand.
- When describing the results, talk about the problems you encountered and the limitations that may affect future studies.
Reporting qualitative research results
Step-by-step guide to results section creating, step 1. review your research., step 2. reread the purpose of your research and write it in the results section., step 3. describe the methods you used., step 4: organize and structure your notes..
- What did you research?
- Why did you research?
- What method did you explore?
- What did you get as a result?
Step 5. Remove everything you don’t need.
Step 6. get rid of all errors, typos, and inaccuracies..
- You have read your paper and marked the main results and statistics;
- You have written the primary purpose of the study;
- You specified what methods were used;
- You have structured your results section in a logical sequence;
- You confirmed each of your hypotheses described in the work with the results of the research;
- You have read the text ready and removed all unnecessary;
- You eliminated any errors, typos, and inaccuracies in the text.
Results section formats you can use
Results section of a research paper example.
The results of the study indicated that there was a significant correlation between the level of stress and the frequency of exercise. Participants who reported higher stress levels also reported exercising less frequently than those who reported lower stress levels.
Additionally, there was a significant difference in self-reported overall well-being between those who engaged in regular exercise and those who did not. Those who exercised regularly reported higher overall well-being levels than those who did not. These findings suggest that regular exercise may be an effective strategy for reducing stress and improving overall well-being.

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper?
The writing of the results section of a scientific paper is very important for the readers for clearly understanding of the study. This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures.
Introduction
Medical articles consist of review articles, case reports, and letters to the editor which are prepared with the intention of publishing in journals related to the medical discipline of the author. For an academician to be able to progress in carreer, and make his/her activities known in the academic environment, require preparation of the protocol of his/her academic research article, and acquiring sufficient information, and experience related to the composition of this article. In this review article, the information related to the writing of the ‘Results’ section, and use of tables, and figures will be presented to the attention of the readers.
Writing the ‘Results’ section
The ‘Results’ section is perhaps the most important part of a research article. In fact the authors will share the results of their research/study with their readers. Renown British biologist Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895) indicated his feelings as “The great tragedy of science: the slaying of a beautiful hypothesis by an ugly fact.” which emphasizes the importance of accurately, and impressively written results.
In essence results provide a response for the question” What is found in the research performed?”. Therefore, it is the most vital part of the article. As a priority, while drafting the ‘Results’ section of a manuscript one should not firstly write down methods in the ‘Material and Method’ section. The first sentence should give information about the number of patients who met the inclusion criteria, and thus enrolled in the study. [ 1 ] Besides information about the number of patients excluded from the study, and the reasons for exclusion is very important in that they will enlighten the readers, and reviewers who critically evaluate the manuscript, and also reflect the seriousness of the study. On the other hand, the results obtained should be recorded in chronological order, and without any comments. [ 2 ] In this section use of simple present tense is more appropriate. The findings should be expressed in brief, lucid, and explicable words. The writing style should not be boring for the reader. During writing process of a research article, a generally ill-conceived point is that positive, and significant findings are more important, attractive, and valuable, while negative, and insignificant findings are worthless, and less attractive. A scientific research is not performed to confirm a hypothesis, rather to test it. Not only positive, and significant results are worth writing, on the other hand negative or statistically insignificant result which support fallacy of a widely accepted opinion might be valuable. Therefore, all findings obtained during research should be inclıuded in the ‘Results’ section. [ 1 ]
While writing the ‘Results’ section, the sequence of results, tabulated data, and information which will be illustrated as figures should be definitively indicated. In indicating insignificant changes, do not use expressions as “decreased” or “increased”, these words should be reserved for significant changes. If results related to more than one parameter would be reported, it is appropriate to write the results under the subheading of its related parameter so as to facilitate reading, and comprehension of information. [ 2 ] Only data, and information concerning the study in question should be included in the ‘Results’ section. Results not mentioned in this section should not be included in the ‘Discussion’ and ‘Summary’ sections. Since the results obtained by the authors are cited in the ‘Results’ section, any reference should not be indicated in this section. [ 3 ]
In the ‘Results’ section, numerical expressions should be written in technically appropriate terms. The number of digits (1, 2 or 3 digits) to be written after a comma (in Turkish) or a point (in especially American English) should be determined The number of digits written after the punctuation marks should not be changed all throughout the text. Data should be expressed as mean/median ± standard deviation. Data as age, and scale scores should be indicated together with ranges of values. Absolute numerical value corresponding to a percentage must be also indicated. P values calculated in statistical analysis should be expressed in their absolute values. While writing p values of statistically significant data, instead of p<0.05 the actual level of significance should be recorded. If p value is smaller than 0.001, then it can be written as p <0.01. [ 2 ] While writing the ‘Results’ section, significant data which should be recalled by the readers must be indicated in the main text. It will be appropriate to indicate other demographic numerical details in tables or figures.
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23) is presented below:
“A total of 9 (56.2%) female, and 7 (43.8%) male patients with were included in this study. Mean age of all the patients was 44.3±13.8 (17–65) years, and mean dimensions of the adrenal mass was 4.5±3.4 (1–14) cm. Mean ages of the male, and female patients were 44.1 (30–65), and 42.4 (17–64) years, while mean diameters of adrenal masses were 3.2 (1–5), and 4.5 (1–14) cm (p age =0.963, p mass size =0.206). Surgical procedures were realized using transperitoneal approach through Chevron incision in 1 (6.2%), and retroperitoneal approach using flank incision with removal of the 11. rib in 15 (93.7%) patients. Right (n=6; 37.5%), and left (n=2; 12.5%) adrenalectomies were performed. Two (12.5%) patients underwent bilateral adrenalectomy in the same session because of clinical Cushing’s syndrome persisted despite transsphenoidal hipophysectomy. Mean operative time, and length of the hospital stay were 135 (65–190) min, and 3 (2–6) days, respectively. While resecting 11. rib during retroperitoneal adrenalectomy performed in 1 patient, pleura was perforated for nearly 1.5 cm. The perforated region was drained, and closed intraoperatively with 4/0 polyglyctan sutures. The patient did not develop postoperative pneumothorax. In none of the patients postoperative complications as pneumothorax, bleeding, prolonged drainage were seen. Results of histopathological analysis of the specimens retrieved at the end of the operation were summarized in Table 1 .” Table 1. Histopathological examination results of the patients Histopathological diagnosis Men n (%) Women n (%) Total n (%) Adrenal cortical adenoma 5 (31.3) 6 (37.6) 11 (68.8) Pheochromocytoma 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) 2 (12.6) Ganglioneuroma 1 (6.2) - 1 (6.2) Myelolipoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Adrenal carcinoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Total 7 (43.7) 9 (56.2) 16 (100) Open in a separate window
Use of tables, and figures
To prevent the audience from getting bored while reading a scientific article, some of the data should be expressed in a visual format in graphics, and figures rather than crowded numerical values in the text. Peer-reviewers frequently look at tables, and figures. High quality tables, and figures increase the chance of acceptance of the manuscript for publication.
Number of tables in the manuscript should not exceed the number recommended by the editorial board of the journal. Data in the main text, and tables should not be repeated many times. Tables should be comprehensible, and a reader should be able to express an opinion about the results just at looking at the tables without reading the main text. Data included in tables should comply with those mentioned in the main text, and percentages in rows, and columns should be summed up accurately. Unit of each variable should be absolutely defined. Sampling size of each group should be absolutely indicated. Values should be expressed as values±standard error, range or 95% confidence interval. Tables should include precise p values, and level of significance as assessed with statistical analysis should be indicated in footnotes. [ 2 ] Use of abbreviations in tables should be avoided, if abbreviations are required they should be defined explicitly in the footnotes or legends of the tables. As a general rule, rows should be arranged as double-spaced Besides do not use pattern coloring for cells of rows, and columns. Values included in tables should be correctly approximated. [ 1 , 2 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23).is shown in Table 1 .
Most of the readers priorly prefer to look at figures, and graphs rather than reading lots of pages. Selection of appropriate types of graphs for demonstration of data is a critical decision which requires artist’s meticulousness. As is the case with tables, graphs, and figures should also disploay information not provided in the text. Bar, line, and pie graphs, scatter plots, and histograms are some examples of graphs. In graphs, independent variables should be represented on the horizontal, and dependent variables on the vertical axis. Number of subjects in every subgroup should be indicated The labels on each axis should be easily understandable. [ 2 ] The label of the Y axis should be written vertically from bottom to top. The fundamental point in writing explanatory notes for graphs, and figures is to help the readers understand the contents of them without referring to the main text. Meanings of abbreviations, and acronyms used in the graphs, and figures should be provided in explanatory notes. In the explanatory notes striking data should be emphasized. Statistical tests used, levels of significance, sampling size, stains used for analyses, and magnification rate should be written in order to facilitate comprehension of the study procedures. [ 1 , 2 ]
Flow diagram can be utilized in the ‘Results’ section. This diagram facilitates comprehension of the results obtained at certain steps of monitorization during the research process. Flow diagram can be used either in the ‘Results’ or ‘Material and Method’ section. [ 2 , 3 ]
Histopathological analyses, surgical technique or radiological images which are considered to be more useful for the comprehension of the text by the readers can be visually displayed. Important findings should be marked on photos, and their definitions should be provided clearly in the explanatory legends. [ 1 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the ‘Results’ section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17–22.) are shown in Figures 1 , and and2 2 .

a The mean SHIM scores of the groups before and after treatment. SHIM sexual health inventory for male. b The mean IPSS scores of the groups before and after treatment. IPSS international prostate symptom score

Flowchart showing patients’ progress during the study. SHIM sexual health inventory for male, IIEF international index of erectile function, IPSS international prostate symptom score, QoL quality of life, Q max maximum urinary flow rate. PRV post voiding residual urine volume
In conclusion, in line with the motto of the famous German physicist Albert Einstein (1879–1955). ‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor .’ results obtained in a scientific research article should be expressed accurately, and with a masterstroke of a tailor in compliance with certain rules which will ensure acceptability of the scientific manuscript by the editorial board of the journal, and also facilitate its intelligibility by the readers.
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
Crafting a comprehensive research paper can be daunting. Understanding diverse citation styles and various subject areas presents a challenge for many.
Without clear examples, students often feel lost and overwhelmed, unsure of how to start or which style fits their subject.
Explore our collection of expertly written research paper examples. We’ve covered various citation styles and a diverse range of subjects.
So, read on!
- 1. Research Paper Example for Different Formats
- 2. Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
- 3. Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
- 4. Research Paper Example Outline
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
Following a specific formatting style is essential while writing a research paper . Knowing the conventions and guidelines for each format can help you in creating a perfect paper. Here we have gathered examples of research paper for most commonly applied citation styles :
Social Media and Social Media Marketing: A Literature Review
APA Research Paper Example
APA (American Psychological Association) style is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, and education. This format is recognized for its clear and concise writing, emphasis on proper citations, and orderly presentation of ideas.
Here are some research paper examples in APA style:
Research Paper Example APA 7th Edition
Research Paper Example MLA
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is frequently employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. An MLA research paper might explore literature analysis, linguistic studies, or historical research within the humanities.
Here is an example:
Found Voices: Carl Sagan
Research Paper Example Chicago
Chicago style is utilized in various fields like history, arts, and social sciences. Research papers in Chicago style could delve into historical events, artistic analyses, or social science inquiries.
Here is a research paper formatted in Chicago style:
Chicago Research Paper Sample
Research Paper Example Harvard
Harvard style is widely used in business, management, and some social sciences. Research papers in Harvard style might address business strategies, case studies, or social policies.
View this sample Harvard style paper here:
Harvard Research Paper Sample
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper has different parts. Each part is important for the overall success of the paper. Chapters in a research paper must be written correctly, using a certain format and structure.
The following are examples of how different sections of the research paper can be written.
Research Proposal
The research proposal acts as a detailed plan or roadmap for your study, outlining the focus of your research and its significance. It's essential as it not only guides your research but also persuades others about the value of your study.
Example of Research Proposal
An abstract serves as a concise overview of your entire research paper. It provides a quick insight into the main elements of your study. It summarizes your research's purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions in a brief format.
Research Paper Example Abstract
Literature Review
A literature review summarizes the existing research on your study's topic, showcasing what has already been explored. This section adds credibility to your own research by analyzing and summarizing prior studies related to your topic.
Literature Review Research Paper Example
Methodology
The methodology section functions as a detailed explanation of how you conducted your research. This part covers the tools, techniques, and steps used to collect and analyze data for your study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper
The conclusion summarizes your findings, their significance and the impact of your research. This section outlines the key takeaways and the broader implications of your study's results.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
Research papers can be about any subject that needs a detailed study. The following examples show research papers for different subjects.
History Research Paper Sample
Preparing a history research paper involves investigating and presenting information about past events. This may include exploring perspectives, analyzing sources, and constructing a narrative that explains the significance of historical events.
View this history research paper sample:
Many Faces of Generalissimo Fransisco Franco
Sociology Research Paper Sample
In sociology research, statistics and data are harnessed to explore societal issues within a particular region or group. These findings are thoroughly analyzed to gain an understanding of the structure and dynamics present within these communities.
Here is a sample:
A Descriptive Statistical Analysis within the State of Virginia
Science Fair Research Paper Sample
A science research paper involves explaining a scientific experiment or project. It includes outlining the purpose, procedures, observations, and results of the experiment in a clear, logical manner.
Here are some examples:
Science Fair Paper Format
What Do I Need To Do For The Science Fair?
Psychology Research Paper Sample
Writing a psychology research paper involves studying human behavior and mental processes. This process includes conducting experiments, gathering data, and analyzing results to understand the human mind, emotions, and behavior.
Here is an example psychology paper:
The Effects of Food Deprivation on Concentration and Perseverance
Art History Research Paper Sample
Studying art history includes examining artworks, understanding their historical context, and learning about the artists. This helps analyze and interpret how art has evolved over various periods and regions.
Check out this sample paper analyzing European art and impacts:
European Art History: A Primer
Research Paper Example Outline
Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper.
Here is an outline of a research paper example:
Here is a downloadable sample of a standard research paper outline:
Research Paper Outline
Want to create the perfect outline for your paper? Check out this in-depth guide on creating a research paper outline for a structured paper!
Good Research Paper Examples for Students
Here are some more samples of research paper for students to learn from:
Fiscal Research Center - Action Plan
Qualitative Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example Introduction
How to Write a Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example for High School
Now that you have explored the research paper examples, you can start working on your research project. Hopefully, these examples will help you understand the writing process for a research paper.
If you're facing challenges with your writing requirements, you can hire our essay writing service .
Our team is experienced in delivering perfectly formatted, 100% original research papers. So, whether you need help with a part of research or an entire paper, our experts are here to deliver.
So, why miss out? Place your ‘ write my research paper ’ request today and get a top-quality research paper!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
4 Examples of Academic Writing
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
The best way to understand what effective academic writing looks like is to review academic writing examples.
Let's begin with four of the most common types of academic writing: research proposals, dissertations, abstracts, and academic articles. We'll be examining each type of writing and providing academic writing samples of each.
Whether you aim to earn funding for a passion project or are stymied by how to format an abstract, these academic writing examples will help you nail your next undertaking.
Academic Writing Example 1: Research Proposals
A research proposal is an outline of the proposed research of a PhD candidate, a private researcher, or someone hoping to obtain a research grant .
Your proposal should put your best foot forward: It details your intended research question and how it relates to existing research, makes an argument for why your research should be chosen for advancement or funding, and explains the deliverables you hope to achieve with your research.
A more detailed look at what proposal writing is and what goes into a research proposal may also be beneficial. Every proposal is different because every project is different. Proposal requirements also differ according to the university or funding agency that reviews the proposal.
Research Proposal Structure
A cover letter summarizing your proposal and showcasing why you should be chosen
An introduction or abstract
An explanation of the background, purpose, and significance of your research
A research plan or methodology that includes a timeline (a Gantt chart may be beneficial)
A projected budget, if applicable
Academic Writing Sample: Research Proposal Excerpt
Building on the work of the three foundational sociological theorists—Marx, Weber, and Durkheim—and Mark Traugott's theory of the "insurgent barricade," this proposed research will analyze the appearance, use, and disappearance of barricade warfare as an effective battle strategy.
Focusing on these three theorists, this research will determine which theory or theories best explain the life cycle of barricade warfare, focusing in particular on its disappearance. A brief but comprehensive history of barricade warfare will be provided in addition to the theoretical explanations of barricade warfare's utility.
Research Proposal Writing Tips
Before you format your proposal, contact your targeted university, private organization, or funding agency to confirm what they require for proposals. Then, try to follow this format as closely as possible.
Be detailed when outlining your goals and your funding needs. Connect the objectives of the research to the resources you're requesting.
Be realistic in what you ask for as far as resources—don't ask for more or less than you need, and show evidence to justify your choices.
Don't dedicate too much text in your proposal to describing past research. A summary of key points, arguments, theories, and how your research will build on them should suffice.
Remember that no matter how good your proposal is, it might be rejected. You're likely up against dozens or even hundreds of other candidates who have equally sound proposals. Don't be discouraged if this happens. See it as a learning opportunity for your next proposal.
Academic Writing Example 2: Dissertations
A dissertation is a body of writing that represents original research and is generally written as part of a PhD or master's program.
Typically, it builds on previous research in the field to make a significant contribution or advancement. You may benefit from more detailed information on what a dissertation is , how to write a dissertation , and how to edit a dissertation .
Dissertation Structure
Introduction/background and the significance of the study
Literature review
Methodology
Results/findings
Conclusion/contribution to the body of research
Academic Writing Sample: Dissertation Excerpt
There are two options for choosing a unit of analysis for this phenomenon: the social artifact (erected barricades) or the social interaction (the collaboration of insurgents engaged in barricade warfare). The best choice is social interaction.
Most individual occurrences of barricade warfare involve the construction of more than one barricade, and the number of barricades is not necessarily a valid indicator of the sociological magnitude of an insurgence. The most relevant choice is an insurgence, the event of a conflict involving barricade warfare.
Dissertation Writing Tips
Remember to bear in mind the significance of your study. It doesn't have to be paradigm shifting, but you want to infuse the dissertation with reminders of why your research is important.
Don't get bogged down in trying to show that your research is one of a kind or uniquely contributive to the body of research. It likely isn't, and it's more effective to show how you are building on previous research .
Remember to check with your college or university to ensure that you're formatting your dissertation according to the school's expectations.
Ask your advisor questions when you need to.
Be prepared to make alterations to your dissertation according to your thesis committee's suggestions. This doesn't mean you did a bad job—it just means there's room for improvement.
Academic Writing Example 3: Abstracts
The abstract is actually a component of other forms of academic writing, such as scholarly articles and dissertations. The abstract acts as a comprehensive outline of your paper in paragraph form.
Abstract Structure
Results
You may want to read more about what abstracts are and why they are important in preparing yourself for writing one.
Academic Writing Sample: Abstract
Barricade warfare has occurred across several spectra, but most notably, it occurred almost exclusively in a 300-year period between the 16th and 19th centuries. Each instance had an inciting incident, but a common thread was the culture of revolution: a revolutionary tradition based on the belief that injustice was being carried out and that, in this case, barricade insurgence was the way to resolve it.
This study uses the theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim to analyze barricade warfare, its appearance, and its disappearance. Ultimately, neither theory can independently explain this phenomenon.
Marx offers a reasonable explanation for why barricade warfare may have died, but his theory is difficult to test empirically and fails to explain the absence of recurrences. Conversely, Durkheim's theory is much easier to observe and can explain why barricade warfare has not experienced a renaissance. However, he offered no reason as to why it died in the first place.
These two theoretical orientations complement each other nicely and, ultimately, neither can stand alone.
Notice that this abstract comes in at under 200 words (a common limit) but nevertheless covers the background of the study, how it was approached, and the results and conclusions of the research.
If you are struggling to meet a word count, check out 10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need .
Abstract Writing Tips
Be conscious of your word count. Stay under the limit.
Check with your school or target journal to make sure special formatting is not required.
Don't use abbreviations or citations in the abstract.
Don't simply restate your thesis or copy your introduction. Neither of these is an abstract.
Remember that your abstract often gives readers their first impressions of your work. Despite its short length, it deserves a lot of attention.
Academic Writing Example 4: Articles
Academic articles are pieces of writing intended for publication in academic journals or other scholarly sources. They may be original research studies, literature analyses, critiques , or other forms of scholarly writing.
Article Structure
Abstract and keywords
Introduction
Materials and methods
References and appendices
Academic Writing Sample: Article Excerpt
"Those great revolutionary barricades were places where heroes came together" (Hugo, 2008). This description by Victor Hugo of the 1832 June Rebellion in Paris comes from his seminal work of fiction, Les Miserables.
Although the account is fictionalized, it is deeply representative of what historian Mark Traugott (2010, p. 225) terms the "culture of revolution." This spirit of heroic response to social injustice swept across Europe during the second half of the millennium and was characterized in part by barricade warfare.
The phenomenon of the insurgent barricade has essentially disappeared, however, leaving no trace of its short-lived but intense epoch, and the question of why this happened remains a mystery. The theories of Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim, when taken together, provide a compelling explanation for the disappearance of barricade warfare, and the tenets of each theory will be examined to explain this phenomenon.
Article Writing Tips
Follow these detailed steps for writing an article and publishing it in a journal .
Make sure that you follow all of your target journal's guidelines.
Have a second set of educated eyes look over your article to correct typos, confusing language, and unclear arguments.
Don't be discouraged if your article is not chosen for publication. As with proposal writing, you are up against countless others with equally compelling research.
Don't be discouraged if the journal asks you to make changes to your article. This is common. It means they see value in your article, as well as room for improvement.
Whether you're applying for funding, earning an advanced degree, aiming to publish in a journal, or just trying to cram your 4,000-word study into a 150-word abstract, hopefully these academic writing examples have helped get your creative juices flowing.
Go out there and write! With these academic writing samples at your side, you are sure to model your academic writing appropriately.
Achieve Your Academic Goals
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need

21 Legit Research Databases for Free Journal Articles in 2022

Grant Writing Basics
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

How To Write A Research Paper
Find Sources For A Research Paper

How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
10 min read
Published on: Mar 26, 2024
Last updated on: Mar 25, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
Share this article
Research papers are an essential part of academic life, but one of the most challenging aspects can be finding credible sources to support your arguments.
With the vast amount of information available online, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, by following some simple steps, you can streamline the process of finding reliable sources for your research paper .
In this guide, we'll break down the process into easy-to-follow steps to help you find the best sources for your paper.
On This Page On This Page -->
Step 1: Define Your Topic and Research Questions
Before you venture into your quest for sources, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your research topic and the specific questions you aim to address. Define the scope of your paper and identify keywords and key concepts that will guide your search for relevant sources.
Step 2: Utilize Academic Databases
Academic databases are treasure troves of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic journals covering a wide range of subjects. Institutions often provide access to these databases through their libraries. Some popular academic databases include:
- IEEE Xplore
- Google Scholar
These databases allow you to search for peer-reviewed articles and academic papers related to your topic.
Use advanced search features to narrow down your results based on publication date, author, and keywords .
Academic Resources Classified by Discipline
Here's a breakdown of prominent databases categorized by academic discipline:
Step 3: Explore Library Catalogs
Your university or local library's catalog is another valuable resource for finding sources. Library catalogs contain books, periodicals, and other materials that may not be available online.
Use the catalog's search function to locate relevant books, journals, and other materials that can contribute to your research.
Step 4: Consult Bibliographies and References
When you find a relevant source, take note of its bibliography or make a list of sources for the research paper. These lists often contain citations to other works that may be useful for your research.
By exploring the references cited in a particular source, you can uncover additional resources and expand your understanding of the topic.
Step 5: Boolean Operators for Effective Searches
Boolean operators are words or symbols used to refine search queries by defining the relationships between search terms. The three primary operators include "AND," which narrows searches by requiring all terms to be present; "OR," which broadens searches by including either term or both; and "NOT," which excludes specific terms to refine results further.
Most databases provide advanced search features for seamless application of Boolean logic.
Step 6: Consider Primary Sources
Depending on your research topic, primary sources such as interviews, surveys, archival documents, and original data sets can provide valuable insights and support for your arguments.
Primary sources offer firsthand accounts and original perspectives on historical events, social phenomena, and scientific discoveries.
Step 7: Evaluate the Credibility of Sources
Not all sources are created equal, and it's crucial to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you encounter.
Consider the author's credentials, the publication venue, and whether the source is peer-reviewed. Look for evidence of bias or conflicts of interest that may undermine the source's credibility.
Step 8: Keep Track of Your Sources
As you gather sources for your research paper, maintain a systematic record of the materials you consult. Keep track of bibliographic information, including author names, publication dates, titles, and page numbers . This information will be invaluable when citing your sources and creating a bibliography or works cited page.
Other Online Sources
In addition to academic databases and library catalogs, exploring popular online sources can provide valuable insights and perspectives on your research topic. Here are some types of online sources you can consider:
Websites hosted by reputable organizations, institutions, and experts (such as the New York Times) can offer valuable information and analysis on a wide range of topics. Look for websites belonging to universities, research institutions, government agencies, and established non-profit organizations.
Crowdsourced Encyclopedias like Wikipedia
While Wikipedia can provide a broad overview of a topic and lead you to other sources, it's essential to verify the information found there with more authoritative sources.
Use Wikipedia as a starting point for your research, but rely on peer-reviewed journal articles and academic sources for in-depth analysis and evidence.
Tips for Assessing the Credibility of Online Sources
When using online sources, it's important to exercise caution and critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of the information you find. Here are some tips for assessing the credibility of online sources:
- Check the Domain Extension: Look for websites with domain extensions that indicate credibility. URLs ending in .edu are educational resources, while URLs ending in .gov are government-related resources. These sites often provide reliable and authoritative information.
- Look for DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers): DOIs are unique alphanumeric strings assigned to scholarly articles and indicate that the article has been published in a peer-reviewed, scientific journal. Finding a DOI can help you assess the scholarly rigor of the source.
- Evaluate the Authorship and Credentials: Consider the qualifications and expertise of the author or organization behind the website or blog. Look for information about the author's credentials, affiliations, and expertise in the subject matter.
- Consider the Currency and Relevance: Assess how up-to-date the information is and whether it aligns with the scope and focus of your research. Look for recent publications and timely analyses that reflect current trends and developments in the field.
Wrapping it up!
Finding sources for your research paper may seem like a challenge, but by following these steps, you can locate credible sources to support your arguments and enhance the quality of your paper.
By approaching the research process systematically and critically evaluating the information you encounter, you can produce a well-researched and compelling research paper.
If you are struggling with finding credible sources or have time constraints, do not hesitate to seek writing help for your research papers . CollegeEssay.org has professional writers ready to assist you.
Connect with our essay writing service now and receive expert guidance and support to elevate your research paper to the next level.
Cathy A. (Law)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 19 March 2024
TacticAI: an AI assistant for football tactics
- Zhe Wang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0748-5376 1 na1 ,
- Petar Veličković ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2820-4692 1 na1 ,
- Daniel Hennes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3646-5286 1 na1 ,
- Nenad Tomašev ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1624-0220 1 ,
- Laurel Prince 1 ,
- Michael Kaisers 1 ,
- Yoram Bachrach 1 ,
- Romuald Elie 1 ,
- Li Kevin Wenliang 1 ,
- Federico Piccinini 1 ,
- William Spearman 2 ,
- Ian Graham 3 ,
- Jerome Connor 1 ,
- Yi Yang 1 ,
- Adrià Recasens 1 ,
- Mina Khan 1 ,
- Nathalie Beauguerlange 1 ,
- Pablo Sprechmann 1 ,
- Pol Moreno 1 ,
- Nicolas Heess ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7876-9256 1 ,
- Michael Bowling ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2960-8418 4 ,
- Demis Hassabis 1 &
- Karl Tuyls ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7929-1944 5
Nature Communications volume 15 , Article number: 1906 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
26k Accesses
255 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Computational science
- Information technology
Identifying key patterns of tactics implemented by rival teams, and developing effective responses, lies at the heart of modern football. However, doing so algorithmically remains an open research challenge. To address this unmet need, we propose TacticAI, an AI football tactics assistant developed and evaluated in close collaboration with domain experts from Liverpool FC. We focus on analysing corner kicks, as they offer coaches the most direct opportunities for interventions and improvements. TacticAI incorporates both a predictive and a generative component, allowing the coaches to effectively sample and explore alternative player setups for each corner kick routine and to select those with the highest predicted likelihood of success. We validate TacticAI on a number of relevant benchmark tasks: predicting receivers and shot attempts and recommending player position adjustments. The utility of TacticAI is validated by a qualitative study conducted with football domain experts at Liverpool FC. We show that TacticAI’s model suggestions are not only indistinguishable from real tactics, but also favoured over existing tactics 90% of the time, and that TacticAI offers an effective corner kick retrieval system. TacticAI achieves these results despite the limited availability of gold-standard data, achieving data efficiency through geometric deep learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Artificial intelligence and illusions of understanding in scientific research
Lisa Messeri & M. J. Crockett

Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold
John Jumper, Richard Evans, … Demis Hassabis

De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion
Joseph L. Watson, David Juergens, … David Baker
Introduction
Association football, or simply football or soccer, is a widely popular and highly professionalised sport, in which two teams compete to score goals against each other. As each football team comprises up to 11 active players at all times and takes place on a very large pitch (also known as a soccer field), scoring goals tends to require a significant degree of strategic team-play. Under the rules codified in the Laws of the Game 1 , this competition has nurtured an evolution of nuanced strategies and tactics, culminating in modern professional football leagues. In today’s play, data-driven insights are a key driver in determining the optimal player setups for each game and developing counter-tactics to maximise the chances of success 2 .
When competing at the highest level the margins are incredibly tight, and it is increasingly important to be able to capitalise on any opportunity for creating an advantage on the pitch. To that end, top-tier clubs employ diverse teams of coaches, analysts and experts, tasked with studying and devising (counter-)tactics before each game. Several recent methods attempt to improve tactical coaching and player decision-making through artificial intelligence (AI) tools, using a wide variety of data types from videos to tracking sensors and applying diverse algorithms ranging from simple logistic regression to elaborate neural network architectures. Such methods have been employed to help predict shot events from videos 3 , forecast off-screen movement from spatio-temporal data 4 , determine whether a match is in-play or interrupted 5 , or identify player actions 6 .
The execution of agreed-upon plans by players on the pitch is highly dynamic and imperfect, depending on numerous factors including player fitness and fatigue, variations in player movement and positioning, weather, the state of the pitch, and the reaction of the opposing team. In contrast, set pieces provide an opportunity to exert more control on the outcome, as the brief interruption in play allows the players to reposition according to one of the practiced and pre-agreed patterns, and make a deliberate attempt towards the goal. Examples of such set pieces include free kicks, corner kicks, goal kicks, throw-ins, and penalties 2 .
Among set pieces, corner kicks are of particular importance, as an improvement in corner kick execution may substantially modify game outcomes, and they lend themselves to principled, tactical and detailed analysis. This is because corner kicks tend to occur frequently in football matches (with ~10 corners on average taking place in each match 7 ), they are taken from a fixed, rigid position, and they offer an immediate opportunity for scoring a goal—no other set piece simultaneously satisfies all of the above. In practice, corner kick routines are determined well ahead of each match, taking into account the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing team and their typical tactical deployment. It is for this reason that we focus on corner kick analysis in particular, and propose TacticAI, an AI football assistant for supporting the human expert with set piece analysis, and the development and improvement of corner kick routines.
TacticAI is rooted in learning efficient representations of corner kick tactics from raw, spatio-temporal player tracking data. It makes efficient use of this data by representing each corner kick situation as a graph—a natural representation for modelling relationships between players (Fig. 1 A, Table 2 ), and these player relationships may be of higher importance than the absolute distances between them on the pitch 8 . Such a graph input is a natural candidate for graph machine learning models 9 , which we employ within TacticAI to obtain high-dimensional latent player representations. In the Supplementary Discussion section, we carefully contrast TacticAI against prior art in the area.
A How corner kick situations are converted to a graph representation. Each player is treated as a node in a graph, with node, edge and graph features extracted as detailed in the main text. Then, a graph neural network operates over this graph by performing message passing; each node’s representation is updated using the messages sent to it from its neighbouring nodes. B How TacticAI processes a given corner kick. To ensure that TacticAI’s answers are robust in the face of horizontal or vertical reflections, all possible combinations of reflections are applied to the input corner, and these four views are then fed to the core TacticAI model, where they are able to interact with each other to compute the final player representations—each internal blue arrow corresponds to a single message passing layer from ( A ). Once player representations are computed, they can be used to predict the corner’s receiver, whether a shot has been taken, as well as assistive adjustments to player positions and velocities, which increase or decrease the probability of a shot being taken.
Uniquely, TacticAI takes advantage of geometric deep learning 10 to explicitly produce player representations that respect several symmetries of the football pitch (Fig. 1 B). As an illustrative example, we can usually safely assume that under a horizontal or vertical reflection of the pitch state, the game situation is equivalent. Geometric deep learning ensures that TacticAI’s player representations will be identically computed under such reflections, such that this symmetry does not have to be learnt from data. This proves to be a valuable addition, as high-quality tracking data is often limited—with only a few hundred matches played each year in every league. We provide an in-depth overview of how we employ geometric deep learning in TacticAI in the “Methods” section.
From these representations, TacticAI is then able to answer various predictive questions about the outcomes of a corner—for example, which player is most likely to make first contact with the ball, or whether a shot will take place. TacticAI can also be used as a retrieval system—for mining similar corner kick situations based on the similarity of player representations—and a generative recommendation system, suggesting adjustments to player positions and velocities to maximise or minimise the estimated shot probability. Through several experiments within a case study with domain expert coaches and analysts from Liverpool FC, the results of which we present in the next section, we obtain clear statistical evidence that TacticAI readily provides useful, realistic and accurate tactical suggestions.
To demonstrate the diverse qualities of our approach, we design TacticAI with three distinct predictive and generative components: receiver prediction, shot prediction, and tactic recommendation through guided generation, which also correspond to the benchmark tasks for quantitatively evaluating TacticAI. In addition to providing accurate quantitative insights for corner kick analysis with its predictive components, the interplay between TacticAI’s predictive and generative components allows coaches to sample alternative player setups for each routine of interest, and directly evaluate the possible outcomes of such alternatives.
We will first describe our quantitative analysis, which demonstrates that TacticAI’s predictive components are accurate at predicting corner kick receivers and shot situations on held-out test corners and that the proposed player adjustments do not strongly deviate from ground-truth situations. However, such an analysis only gives an indirect insight into how useful TacticAI would be once deployed. We tackle this question of utility head-on and conduct a comprehensive case study in collaboration with our partners at Liverpool FC—where we directly ask human expert raters to judge the utility of TacticAI’s predictions and player adjustments. The following sections expand on the specific results and analysis we have performed.
In what follows, we will describe TacticAI’s components at a minimal level necessary to understand our evaluation. We defer detailed descriptions of TacticAI’s components to the “Methods” section. Note that, all our error bars reported in this research are standard deviations.
Benchmarking TacticAI
We evaluate the three components of TacticAI on a relevant benchmark dataset of corner kicks. Our dataset consists of 7176 corner kicks from the 2020 to 2021 Premier League seasons, which we randomly shuffle and split into a training (80%) and a test set (20%). As previously mentioned, TacticAI operates on graphs. Accordingly, we represent each corner kick situation as a graph, where each node corresponds to a player. The features associated with each node encode the movements (velocities and positions) and simple profiles (heights and weights) of on-pitch players at the timestamp when the corresponding corner kick was being taken by the attacking kicker (see the “Methods” section), and no information of ball movement was encoded. The graphs are fully connected; that is, for every pair of players, we will include the edge connecting them in the graph. Each of these edges encodes a binary feature, indicating whether the two players are on opposing teams or not. For each task, we generated the relevant dataset of node/edge/graph features and corresponding labels (Tables 1 and 2 , see the “Methods” section). The components were then trained separately with their corresponding corner kick graphs. In particular, we only employ a minimal set of features to construct the corner kick graphs, without encoding the movements of the ball nor explicitly encoding the distances between players into the graphs. We used a consistent training-test split for all benchmark tasks, as this made it possible to benchmark not only the individual components but also their interactions.
Accurate receiver and shot prediction through geometric deep learning
One of TacticAI’s key predictive models forecasts the receiver out of the 22 on-pitch players. The receiver is defined as the first player touching the ball after the corner is taken. In our evaluation, all methods used the same set of features (see the “Receiver prediction” entry in Table 1 and the “Methods” section). We leveraged the receiver prediction task to benchmark several different TacticAI base models. Our best-performing model—achieving 0.782 ± 0.039 in top-3 test accuracy after 50,000 training steps—was a deep graph attention network 11 , 12 , leveraging geometric deep learning 10 through the use of D 2 group convolutions 13 . We supplement this result with a detailed ablation study, verifying that both our choice of base architecture and group convolution yielded significant improvements in the receiver prediction task (Supplementary Table 2 , see the subsection “Ablation study” in the “Methods” section). Considering that corner kick receiver prediction is a highly challenging task with many factors that are unseen by our model—including fatigue and fitness levels, and actual ball trajectory—we consider TacticAI’s top-3 accuracy to reflect a high level of predictive power, and keep the base TacticAI architecture fixed for subsequent studies. In addition to this quantitative evaluation with the evaluation dataset, we also evaluate the performance of TacticAI’s receiver prediction component in a case study with human raters. Please see the “Case study with expert raters” section for more details.
For shot prediction, we observe that reusing the base TacticAI architecture to directly predict shot events—i.e., directly modelling the probability \({\mathbb{P}}(\,{{\mbox{shot}}}| {{\mbox{corner}}}\,)\) —proved challenging, only yielding a test F 1 score of 0.52 ± 0.03, for a GATv2 base model. Note that here we use the F 1 score—the harmonic mean of precision and recall—as it is commonly used in binary classification problems over imbalanced datasets, such as shot prediction. However, given that we already have a potent receiver predictor, we decided to use its output to give us additional insight into whether or not a shot had been taken. Hence, we opted to decompose the probability of taking a shot as
where \({\mathbb{P}}(\,{{\mbox{receiver}}}| {{\mbox{corner}}}\,)\) are the probabilities computed by TacticAI’s receiver prediction system, and \({\mathbb{P}}(\,{{\mbox{shot}}}| {{\mbox{receiver}}},{{\mbox{corner}}}\,)\) models the conditional shot probability after a specific player makes first contact with the ball. This was implemented through providing an additional global feature to indicate the receiver in the corresponding corner kick (Table 1 ) while the architecture otherwise remained the same as that of receiver prediction (Supplementary Fig. 2 , see the “Methods” section). At training time, we feed the ground-truth receiver as input to the model—at inference time, we attempt every possible receiver, weighing their contributions using the probabilities given by TacticAI’s receiver predictor, as per Eq. ( 1 ). This two-phased approach yielded a final test F 1 score of 0.68 ± 0.04 for shot prediction, which encodes significantly more signal than the unconditional shot predictor, especially considering the many unobservables associated with predicting shot events. Just as for receiver prediction, this performance can be further improved using geometric deep learning; a conditional GATv2 shot predictor with D 2 group convolutions achieves an F 1 score of 0.71 ± 0.01.
Moreover, we also observe that, even just through predicting the receivers, without explicitly classifying any other salient features of corners, TacticAI learned generalisable representations of the data. Specifically, team setups with similar tactical patterns tend to cluster together in TacticAI’s latent space (Fig. 2 ). However, no clear clusters are observed in the raw input space (Supplementary Fig. 1 ). This indicates that TacticAI can be leveraged as a useful corner kick retrieval system, and we will present our evaluation of this hypothesis in the “Case study with expert raters” section.
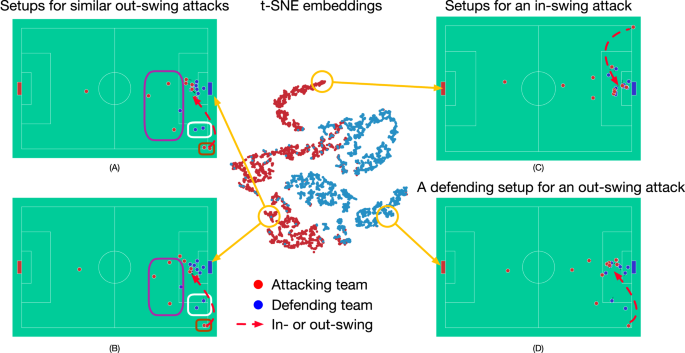
We visualise the latent representations of attacking and defending teams in 1024 corner kicks using t -SNE. A latent team embedding in one corner kick sample is the mean of the latent player representations on the same attacking ( A – C ) or defending ( D ) team. Given the reference corner kick sample ( A ), we retrieve another corner kick sample ( B ) with respect to the closest distance of their representations in the latent space. We observe that ( A ) and ( B ) are both out-swing corner kicks and share similar patterns of their attacking tactics, which are highlighted with rectangles having the same colours, although they bear differences with respect to the absolute positions and velocities of the players. All the while, the latent representation of an in-swing attack ( C ) is distant from both ( A ) and ( B ) in the latent space. The red arrows are only used to demonstrate the difference between in- and out-swing corner kicks, not the actual ball trajectories.
Lastly, it is worth emphasising that the utility of the shot predictor likely does not come from forecasting whether a shot event will occur—a challenging problem with many imponderables—but from analysing the difference in predicted shot probability across multiple corners. Indeed, in the following section, we will show how TacticAI’s generative tactic refinements can directly influence the predicted shot probabilities, which will then corresponds to highly favourable evaluation by our expert raters in the “Case study with expert raters” section.
Controlled tactic refinement using class-conditional generative models
Equipped with components that are able to potently relate corner kicks with their various outcomes (e.g. receivers and shot events), we can explore the use of TacticAI to suggest adjustments of tactics, in order to amplify or reduce the likelihood of certain outcomes.
Specifically, we aim to produce adjustments to the movements of players on one of the two teams, including their positions and velocities, which would maximise or minimise the probability of a shot event, conditioned on the initial corner setup, consisting of the movements of players on both teams and their heights and weights. In particular, although in real-world scenarios both teams may react simultaneously to the movements of each other, in our study, we focus on moderate adjustments to player movements, which help to detect players that are not responding to a tactic properly. Due to this reason, we simplify the process of tactic refinement through generating the adjustments for only one team while keeping the other fixed. The way we train a model for this task is through an auto-encoding objective: we feed the ground-truth shot outcome (a binary indicator) as an additional graph-level feature to TacticAI’s model (Table 1 ), and then have it learn to reconstruct a probability distribution of the input player coordinates (Fig. 1 B, also see the “Methods” section). As a consequence, our tactic adjustment system does not depend on the previously discussed shot predictor—although we can use the shot predictor to evaluate whether the adjustments make a measurable difference in shot probability.
This autoencoder-based generative model is an individual component that separates from TacticAI’s predictive systems. All three systems share the encoder architecture (without sharing parameters), but use different decoders (see the “Methods” section). At inference time, we can instead feed in a desired shot outcome for the given corner setup, and then sample new positions and velocities for players on one team using this probability distribution. This setup, in principle, allows for flexible downstream use, as human coaches can optimise corner kick setups through generating adjustments conditioned on the specific outcomes of their interest—e.g., increasing shot probability for the attacking team, decreasing it for the defending team (Fig. 3 ) or amplifying the chance that a particular striker receives the ball.
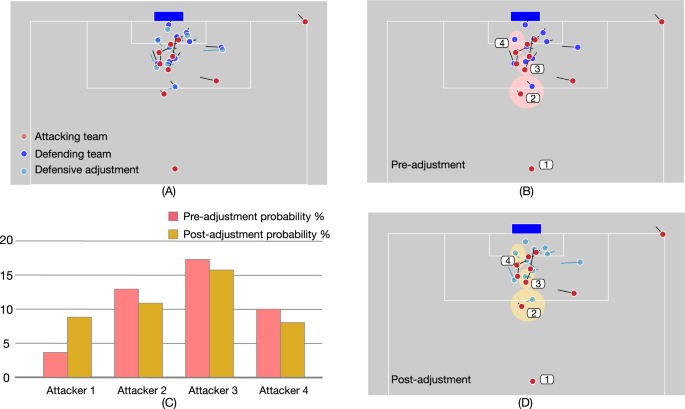
TacticAI makes it possible for human coaches to redesign corner kick tactics in ways that help maximise the probability of a positive outcome for either the attacking or the defending team by identifying key players, as well as by providing temporally coordinated tactic recommendations that take all players into consideration. As demonstrated in the present example ( A ), for a corner kick in which there was a shot attempt in reality ( B ), TacticAI can generate a tactically-adjusted setting in which the shot probability has been reduced, by adjusting the positioning of the defenders ( D ). The suggested defender positions result in reduced receiver probability for attacking players 2–5 (see bottom row), while the receiver probability of Attacker 1, who is distant from the goalpost, has been increased ( C ). The model is capable of generating multiple such scenarios. Coaches can inspect the different options visually and additionally consult TacticAI’s quantitative analysis of the presented tactics.
We first evaluate the generated adjustments quantitatively, by verifying that they are indistinguishable from the original corner kick distribution using a classifier. To do this, we synthesised a dataset consisting of 200 corner kick samples and their corresponding conditionally generated adjustments. Specifically, for corners without a shot event, we generated adjustments for the attacking team by setting the shot event feature to 1, and vice-versa for the defending team when a shot event did happen. We found that the real and generated samples were not distinguishable by an MLP classifier, with an F 1 score of 0.53 ± 0.05, indicating random chance level accuracy. This result indicates that the adjustments produced by TacticAI are likely similar enough to real corner kicks that the MLP is unable to tell them apart. Note that, in spite of this similarity, TacticAI recommends player-level adjustments that are not negligible—in the following section we will illustrate several salient examples of this. To more realistically validate the practical indistinguishability of TacticAI’s adjustments from realistic corners, we also evaluated the realism of the adjustments in a case study with human experts, which we will present in the following section.
In addition, we leveraged our TacticAI shot predictor to estimate whether the proposed adjustments were effective. We did this by analysing 100 corner kick samples in which threatening shots occurred, and then, for each sample, generated one defensive refinement through setting the shot event feature to 0. We observed that the average shot probability significantly decreased, from 0.75 ± 0.14 for ground-truth corners to 0.69 ± 0.16 for adjustments ( z = 2.62, p < 0.001). This observation was consistent when testing for attacking team refinements (shot probability increased from 0.18 ± 0.16 to 0.31 ± 0.26 ( z = −4.46, p < 0.001)). Moving beyond this result, we also asked human raters to assess the utility of TacticAI’s proposed adjustments within our case study, which we detail next.
Case study with expert raters
Although quantitative evaluation with well-defined benchmark datasets was critical for the technical development of TacticAI, the ultimate test of TacticAI as a football tactic assistant is its practical downstream utility being recognised by professionals in the industry. To this end, we evaluated TacticAI through a case study with our partners at Liverpool FC (LFC). Specifically, we invited a group of five football experts: three data scientists, one video analyst, and one coaching assistant. Each of them completed four tasks in the case study, which evaluated the utility of TacticAI’s components from several perspectives; these include (1) the realism of TacticAI’s generated adjustments, (2) the plausibility of TacticAI’s receiver predictions, (3) effectiveness of TacticAI’s embeddings for retrieving similar corners, and (4) usefulness of TacticAI’s recommended adjustments. We provide an overview of our study’s results here and refer the interested reader to Supplementary Figs. 3 – 5 and the Supplementary Methods for additional details.
We first simultaneously evaluated the realism of the adjusted corner kicks generated by TacticAI, and the plausibility of its receiver predictions. Going through a collection of 50 corner kick samples, we first asked the raters to classify whether a given sample was real or generated by TacticAI, and then they were asked to identify the most likely receivers in the corner kick sample (Supplementary Fig. 3 ).
On the task of classifying real and generated samples, first, we found that the raters’ average F 1 score of classifying the real vs. generated samples was only 0.60 ± 0.04, with individual F 1 scores ( \({F}_{1}^{A}=0.54,{F}_{1}^{B}=0.64,{F}_{1}^{C}=0.65,{F}_{1}^{D}=0.62,{F}_{1}^{E}=0.56\) ), indicating that the raters were, in many situations, unable to distinguish TacticAI’s adjustments from real corners.
The previous evaluation focused on analysing realism detection performance across raters. We also conduct a study that analyses realism detection across samples. Specifically, we assigned ratings for each sample—assigning +1 to a sample if it was identified as real by a human rater, and 0 otherwise—and computed the average rating for each sample across the five raters. Importantly, by studying the distribution of ratings, we found that there was no significant difference between the average ratings assigned to real and generated corners ( z = −0.34, p > 0.05) (Fig. 4 A). Hence, the real and generated samples were assigned statistically indistinguishable average ratings by human raters.
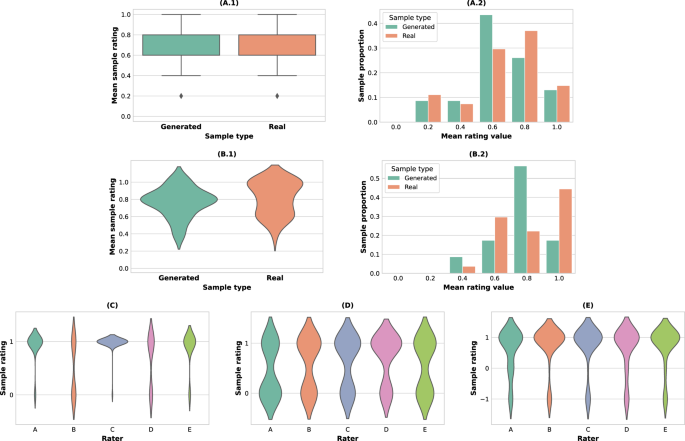
In task 1, we tested the statistical difference between the real corner kick samples and the synthetic ones generated by TacticAI from two aspects: ( A.1 ) the distributions of their assigned ratings, and ( A.2 ) the corresponding histograms of the rating values. Analogously, in task 2 (receiver prediction), ( B.1 ) we track the distributions of the top-3 accuracy of receiver prediction using those samples, and ( B.2 ) the corresponding histogram of the mean rating per sample. No statistical difference in the mean was observed in either cases (( A.1 ) ( z = −0.34, p > 0.05), and ( B.1 ) ( z = 0.97, p > 0.05)). Additionally, we observed a statistically significant difference between the ratings of different raters on receiver prediction, with three clear clusters emerging ( C ). Specifically, Raters A and E had similar ratings ( z = 0.66, p > 0.05), and Raters B and D also rated in similar ways ( z = −1.84, p > 0.05), while Rater C responded differently from all other raters. This suggests a good level of variety of the human raters with respect to their perceptions of corner kicks. In task 3—identifying similar corners retrieved in terms of salient strategic setups—there were no significant differences among the distributions of the ratings by different raters ( D ), suggesting a high level of agreement on the usefulness of TacticAI’s capability of retrieving similar corners ( F 1,4 = 1.01, p > 0.1). Finally, in task 4, we compared the ratings of TacticAI’s strategic refinements across the human raters ( E ) and found that the raters also agreed on the general effectiveness of the refinements recommended by TacticAI ( F 1,4 = 0.45, p > 0.05). Note that the violin plots used in B.1 and C – E model a continuous probability distribution and hence assign nonzero probabilities to values outside of the allowed ranges. We only label y -axis ticks for the possible set of ratings.
For the task of identifying receivers, we rated TacticAI’s predictions with respect to a rater as +1 if at least one of the receivers identified by the rater appeared in TacticAI’s top-3 predictions, and 0 otherwise. The average top-3 accuracy among the human raters was 0.79 ± 0.18; specifically, 0.81 ± 0.17 for the real samples, and 0.77 ± 0.21 for the generated ones. These scores closely line up with the accuracy of TacticAI in predicting receivers for held-out test corners, validating our quantitative study. Further, after averaging the ratings for receiver prediction sample-wise, we found no statistically significant difference between the average ratings of predicting receivers over the real and generated samples ( z = 0.97, p > 0.05) (Fig. 4 B). This indicates that TacticAI was equally performant in predicting the receivers of real corners and TacticAI-generated adjustments, and hence may be leveraged for this purpose even in simulated scenarios.
There is a notably high variance in the average receiver prediction rating of TacticAI. We hypothesise that this is due to the fact that different raters may choose to focus on different salient features when evaluating the likely receivers (or even the amount of likely receivers). We set out to validate this hypothesis by testing the pair-wise similarity of the predictions by the human raters through running a one-away analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a Tukey test. We found that the distributions of the five raters’ predictions were significantly different ( F 1,4 = 14.46, p < 0.001) forming three clusters (Fig. 4 C). This result indicates that different human raters—as suggested by their various titles at LFC—may often use very different leads when suggesting plausible receivers. The fact that TacticAI manages to retain a high top-3 accuracy in such a setting suggests that it was able to capture the salient patterns of corner kick strategies, which broadly align with human raters’ preferences. We will further test this hypothesis in the third task—identifying similar corners.
For the third task, we asked the human raters to judge 50 pairs of corners for their similarity. Each pair consisted of a reference corner and a retrieved corner, where the retrieved corner was chosen either as the nearest-neighbour of the reference in terms of their TacticAI latent space representations, or—as a feature-level heuristic—the cosine similarities of their raw features (Supplementary Fig. 4 ) in our corner kick dataset. We score the raters’ judgement of a pair as +1 if they considered the corners presented in the case to be usefully similar, otherwise, the pair is scored with 0. We first computed, for each rater, the recall with which they have judged a baseline- or TacticAI-retrieved pair as usefully similar—see description of Task 3 in the Supplementary Methods . For TacticAI retrievals, the average recall across all raters was 0.59 ± 0.09, and for the baseline system, the recall was 0.36 ± 0.10. Secondly, we assess the statistical difference between the results of the two methods by averaging the ratings for each reference–retrieval pair, finding that the average rating of TacticAI retrievals is significantly higher than the average rating of baseline method retrievals ( z = 2.34, p < 0.05). These two results suggest that TacticAI significantly outperforms the feature-space baseline as a method for mining similar corners. This indicates that TacticAI is able to extract salient features from corners that are not trivial to extract from the input data alone, reinforcing it as a potent tool for discovering opposing team tactics from available data. Finally, we observed that this task exhibited a high level of inter-rater agreement for TacticAI-retrieved pairs ( F 1,4 = 1.01, p > 0.1) (Fig. 4 D), suggesting that human raters were largely in agreement with respect to their assessment of TacticAI’s performance.
Finally, we evaluated TacticAI’s player adjustment recommendations for their practical utility. Specifically, each rater was given 50 tactical refinements together with the corresponding real corner kick setups—see Supplementary Fig. 5 , and the “Case study design” section in the Supplementary Methods . The raters were then asked to rate each refinement as saliently improving the tactics (+1), saliently making them worse (−1), or offering no salient differences (0). We calculated the average rating assigned by each of the raters (giving us a value in the range [− 1, 1] for each rater). The average of these values across all five raters was 0.7 ± 0.1. Further, for 45 of the 50 situations (90%), the human raters found TacticAI’s suggestion to be favourable on average (by majority voting). Both of these results indicate that TacticAI’s recommendations are salient and useful to a downstream football club practitioner, and we set out to validate this with statistical tests.
We performed statistical significance testing of the observed positive ratings. First, for each of the 50 situations, we averaged its ratings across all five raters and then ran a t -test to assess whether the mean rating was significantly larger than zero. Indeed, the statistical test indicated that the tactical adjustments recommended by TacticAI were constructive overall ( \({t}_{49}^{{{{{{{{\rm{avg}}}}}}}}}=9.20,\, p \, < \, 0.001\) ). Secondly, we verified that each of the five raters individually found TacticAI’s recommendations to be constructive, running a t -test on each of their ratings individually. For all of the five raters, their average ratings were found to be above zero with statistical significance ( \({t}_{49}^{A}=5.84,\, {p}^{A} \, < \, 0.001;{t}_{49}^{B}=7.88,\; {p}^{B} \, < \, 0.001;{t}_{49}^{C}=7.00,\; {p}^{C} \, < \, 0.001;{t}_{49}^{D}=6.04,\; {p}^{D} \, < \, 0.001;{t}_{49}^{E}=7.30,\, {p}^{E} \, < \, 0.001\) ). In addition, their ratings also shared a high level of inter-agreement ( F 1,4 = 0.45, p > 0.05) (Fig. 4 E), suggesting a level of practical usefulness that is generally recognised by human experts, even though they represent different backgrounds.
Taking all of these results together, we find TacticAI to possess strong components for prediction, retrieval, and tactical adjustments on corner kicks. To illustrate the kinds of salient recommendations by TacticAI, in Fig. 5 we present four examples with a high degree of inter-rater agreement.
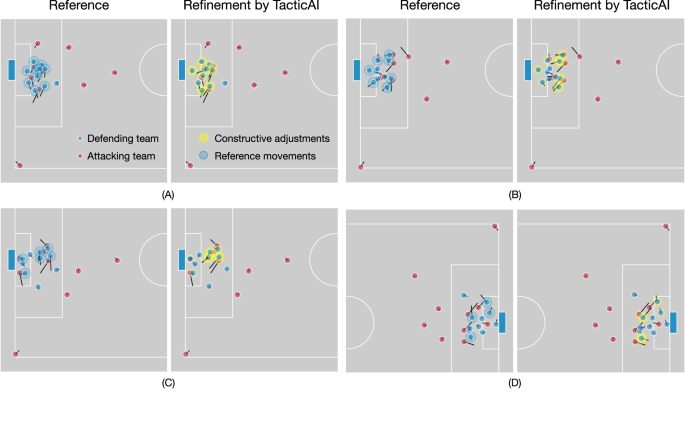
These examples are selected from our case study with human experts, to illustrate the breadth of tactical adjustments that TacticAI suggests to teams defending a corner. The density of the yellow circles coincides with the number of times that the corresponding change is recognised as constructive by human experts. Instead of optimising the movement of one specific player, TacticAI can recommend improvements for multiple players in one generation step through suggesting better positions to block the opposing players, or better orientations to track them more efficiently. Some specific comments from expert raters follow. In A , according to raters, TacticAI suggests more favourable positions for several defenders, and improved tracking runs for several others—further, the goalkeeper is positioned more deeply, which is also beneficial. In B , TacticAI suggests that the defenders furthest away from the corner make improved covering runs, which was unanimously deemed useful, with several other defenders also positioned more favourably. In C , TacticAI recommends improved covering runs for a central group of defenders in the penalty box, which was unanimously considered salient by our raters. And in D , TacticAI suggests substantially better tracking runs for two central defenders, along with a better positioning for two other defenders in the goal area.
We have demonstrated an AI assistant for football tactics and provided statistical evidence of its efficacy through a comprehensive case study with expert human raters from Liverpool FC. First, TacticAI is able to accurately predict the first receiver after a corner kick is taken as well as the probability of a shot as the direct result of the corner. Second, TacticAI has been shown to produce plausible tactical variations that improve outcomes in a salient way, while being indistinguishable from real scenarios by domain experts. And finally, the system’s latent player representations are a powerful means to retrieve similar set-piece tactics, allowing coaches to analyse relevant tactics and counter-tactics that have been successful in the past.
The broader scope of strategy modelling in football has previously been addressed from various individual angles, such as pass prediction 14 , 15 , 16 , shot prediction 3 or corner kick tactical classification 7 . However, to the best of our knowledge, our work stands out by combining and evaluating predictive and generative modelling of corner kicks for tactic development. It also stands out in its method of applying geometric deep learning, allowing for efficiently incorporating various symmetries of the football pitch for improved data efficiency. Our method incorporates minimal domain knowledge and does not rely on intricate feature engineering—though its factorised design naturally allows for more intricate feature engineering approaches when such features are available.
Our methodology requires the position and velocity estimates of all players at the time of execution of the corner and subsequent events. Here, we derive these from high-quality tracking and event data, with data availability from tracking providers limited to top leagues. Player tracking based on broadcast video would increase the reach and training data substantially, but would also likely result in noisier model inputs. While the attention mechanism of GATs would allow us to perform introspection of the most salient factors contributing to the model outcome, our method does not explicitly model exogenous (aleatoric) uncertainty, which would be valuable context for the football analyst.
While the empirical study of our method’s efficacy has been focused on corner kicks in association football, it readily generalises to other set pieces (such as throw-ins, which similarly benefit from similarity retrieval, pass and/or shot prediction) and other team sports with suspended play situations. The learned representations and overall framing of TacticAI also lay the ground for future research to integrate a natural language interface that enables domain-grounded conversations with the assistant, with the aim to retrieve particular situations of interest, make predictions for a given tactical variant, compare and contrast, and guide through an interactive process to derive tactical suggestions. It is thus our belief that TacticAI lays the groundwork for the next-generation AI assistant for football.
We devised TacticAI as a geometric deep learning pipeline, further expanded in this section. We process labelled spatio-temporal football data into graph representations, and train and evaluate on benchmarking tasks cast as classification or regression. These steps are presented in sequence, followed by details on the employed computational architecture.
Raw corner kick data
The raw dataset consisted of 9693 corner kicks collected from the 2020–21, 2021–22, and 2022–23 (up to January 2023) Premier League seasons. The dataset was provided by Liverpool FC and comprises four separate data sources, described below.
Our primary data source is spatio-temporal trajectory frames (tracking data), which tracked all on-pitch players and the ball, for each match, at 25 frames per second. In addition to player positions, their velocities are derived from position data through filtering. For each corner kick, we only used the frame in which the kick is being taken as input information.
Secondly, we also leverage event stream data, which annotated the events or actions (e.g., passes, shots and goals) that have occurred in the corresponding tracking frames.
Thirdly, the line-up data for the corresponding games, which recorded the players’ profiles, including their heights, weights and roles, is also used.
Lastly, we have access to miscellaneous game data, which contains the game days, stadium information, and pitch length and width in meters.
Graph representation and construction
We assumed that we were provided with an input graph \({{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}=({{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}},\,{{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}})\) with a set of nodes \({{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\) and edges \({{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}}\subseteq {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\times {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\) . Within the context of football games, we took \({{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\) to be the set of 22 players currently on the pitch for both teams, and we set \({{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}}={{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\times {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\) ; that is, we assumed all pairs of players have the potential to interact. Further analyses, leveraging more specific choices of \({{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}}\) , would be an interesting avenue for future work.
Additionally, we assume that the graph is appropriately featurised. Specifically, we provide a node feature matrix, \({{{{{{{\bf{X}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times k}\) , an edge feature tensor, \({{{{{{{\bf{E}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times | {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times l}\) , and a graph feature vector, \({{{{{{{\bf{g}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{m}\) . The appropriate entries of these objects provide us with the input features for each node, edge, and graph. For example, \({{{{{{{{\bf{x}}}}}}}}}_{u}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\) would provide attributes of an individual player \(u\in {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}\) , such as position, height and weight, and \({{{{{{{{\bf{e}}}}}}}}}_{uv}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{l}\) would provide the attributes of a particular pair of players \((u,\, v)\in {{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}}\) , such as their distance, and whether they belong to the same team. The graph feature vector, g , can be used to store global attributes of interest to the corner kick, such as the game time, current score, or ball position. For a simplified visualisation of how a graph neural network would process such an input, refer to Fig. 1 A.
To construct the input graphs, we first aligned the four data sources with respect to their game IDs and timestamps and filtered out 2517 invalid corner kicks, for which the alignment failed due to missing data, e.g., missing tracking frames or event labels. This filtering yielded 7176 valid corner kicks for training and evaluation. We summarised the exact information that was used to construct the input graphs in Table 2 . In particular, other than player heights (measured in centimeters (cm)) and weights (measured in kilograms (kg)), the players were anonymous in the model. For the cases in which the player profiles were missing, we set their heights and weights to 180 cm and 75 kg, respectively, as defaults. In total, we had 385 such occurrences out of a total of 213,246( = 22 × 9693) during data preprocessing. We downscaled the heights and weights by a factor of 100. Moreover, for each corner kick, we zero-centred the positions of on-pitch players and normalised them onto a 10 m × 10 m pitch, and their velocities were re-scaled accordingly. For the cases in which the pitch dimensions were missing, we used a standard pitch dimension of 110 m × 63 m as default.
We summarised the grouping of the features in Table 1 . The actual features used in different benchmark tasks may differ, and we will describe this in more detail in the next section. To focus on modelling the high-level tactics played by the attacking and defending teams, other than a binary indicator for ball possession—which is 1 for the corner kick taker and 0 for all other players—no information of ball movement, neither positions nor velocities, was used to construct the input graphs. Additionally, we do not have access to the player’s vertical movement, therefore only information on the two-dimensional movements of each player is provided in the data. We do however acknowledge that such information, when available, would be interesting to consider in a corner kick outcome predictor, considering the prevalence of aerial battles in corners.
Benchmark tasks construction
TacticAI consists of three predictive and generative models, which also correspond to three benchmark tasks implemented in this study. Specifically, (1) Receiver prediction, (2) Threatening shot prediction, and (3) Guided generation of team positions and velocities (Table 1 ). The graphs of all the benchmark tasks used the same feature space of nodes and edges, differing only in the global features.
For all three tasks, our models first transform the node features to a latent node feature matrix, \({{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}={f}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}({{{{{{{\bf{X}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{E}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{g}}}}}}}})\) , from which we could answer queries: either about individual players—in which case we learned a relevant classifier or regressor over the h u vectors (the rows of H )—or about the occurrence of a global event (e.g. shot taken)—in which case we classified or regressed over the aggregated player vectors, ∑ u h u . In both cases, the classifiers were trained using stochastic gradient descent over an appropriately chosen loss function, such as categorical cross-entropy for classifiers, and mean squared error for regressors.
For different tasks, we extracted the corresponding ground-truth labels from either the event stream data or the tracking data. Specifically, (1) We modelled receiver prediction as a node classification task and labelled the first player to touch the ball after the corner was taken as the target node. This player could be either an attacking or defensive player. (2) Shot prediction was modelled as graph classification. In particular, we considered a next-ball-touch action by the attacking team as a shot if it was a direct corner, a goal, an aerial, hit on the goalposts, a shot attempt saved by the goalkeeper, or missing target. This yielded 1736 corners labelled as a shot being taken, and 5440 corners labelled as a shot not being taken. (3) For guided generation of player position and velocities, no additional label was needed, as this model relied on a self-supervised reconstruction objective.
The entire dataset was split into training and evaluation sets with an 80:20 ratio through random sampling, and the same splits were used for all tasks.
Graph neural networks
The central model of TacticAI is the graph neural network (GNN) 9 , which computes latent representations on a graph by repeatedly combining them within each node’s neighbourhood. Here we define a node’s neighbourhood, \({{{{{{{{\mathcal{N}}}}}}}}}_{u}\) , as the set of all first-order neighbours of node u , that is, \({{{{{{{{\mathcal{N}}}}}}}}}_{u}=\{v\,| \,(v,\, u)\in {{{{{{{\mathcal{E}}}}}}}}\}\) . A single GNN layer then transforms the node features by passing messages between neighbouring nodes 17 , following the notation of related work 10 , and the implementation of the CLRS-30 benchmark baselines 18 :
where \(\psi :{{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{l}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{m}\to {{\mathbb{R}}}^{{k}^{{\prime} }}\) and \(\phi :{{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{{k}^{{\prime} }}\to {{\mathbb{R}}}^{{k}^{{\prime} }}\) are two learnable functions (e.g. multilayer perceptrons), \({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}_{u}^{(t)}\) are the features of node u after t GNN layers, and ⨁ is any permutation-invariant aggregator, such as sum, max, or average. By definition, we set \({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}_{u}^{(0)}={{{{{{{{\bf{x}}}}}}}}}_{u}\) , and iterate Eq. ( 2 ) for T steps, where T is a hyperparameter. Then, we let \({{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}={f}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}({{{{{{{\bf{X}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{E}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{g}}}}}}}})={{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}^{(T)}\) be the final node embeddings coming out of the GNN.
It is well known that Eq. ( 2 ) is remarkably general; it can be used to express popular models such as Transformers 19 as a special case, and it has been argued that all discrete deep learning models can be expressed in this form 20 , 21 . This makes GNNs a perfect framework for benchmarking various approaches to modelling player–player interactions in the context of football.
Different choices of ψ , ϕ and ⨁ yield different architectures. In our case, we utilise a message function that factorises into an attentional mechanism, \(a:{{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{k}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{l}\times {{\mathbb{R}}}^{m}\to {\mathbb{R}}\) :
yielding the graph attention network (GAT) architecture 12 . In our work, specifically, we use a two-layer multilayer perceptron for the attentional mechanism, as proposed by GATv2 11 :
where \({{{{{{{{\bf{W}}}}}}}}}_{1},\, {{{{{{{{\bf{W}}}}}}}}}_{2}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{k\times h}\) , \({{{{{{{{\bf{W}}}}}}}}}_{e}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{l\times h}\) , \({{{{{{{{\bf{W}}}}}}}}}_{g}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{m\times h}\) and \({{{{{{{\bf{a}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{h}\) are the learnable parameters of the attentional mechanism, and LeakyReLU is the leaky rectified linear activation function. This mechanism computes coefficients of interaction (a single scalar value) for each pair of connected nodes ( u , v ), which are then normalised across all neighbours of u using the \({{{{{{{\rm{softmax}}}}}}}}\) function.
Through early-stage experimentation, we have ascertained that GATs are capable of matching the performance of more generic choices of ψ (such as the MPNN 17 ) while being more scalable. Hence, we focus our study on the GAT model in this work. More details can be found in the subsection “Ablation study” section.
Geometric deep learning
In spite of the power of Eq. ( 2 ), using it in its full generality is often prone to overfitting, given the large number of parameters contained in ψ and ϕ . This problem is exacerbated in the football analytics domain, where gold-standard data is generally very scarce—for example, in the English Premier League, only a few hundred games are played every season.
In order to tackle this issue, we can exploit the immense regularity of data arising from football games. Strategically equivalent game states are also called transpositions, and symmetries such as arriving at the same chess position through different move sequences have been exploited computationally since the 1960s 22 . Similarly, game rotations and reflections may yield equivalent strategic situations 23 . Using the blueprint of geometric deep learning (GDL) 10 , we can design specialised GNN architectures that exploit this regularity.
That is, geometric deep learning is a generic methodology for deriving mathematical constraints on neural networks, such that they will behave predictably when inputs are transformed in certain ways. In several important cases, these constraints can be directly resolved, directly informing neural network architecture design. For a comprehensive example of point clouds under 3D rotational symmetry, see Fuchs et al. 24 .
To elucidate several aspects of the GDL framework on a high level, let us assume that there exists a group of input data transformations (symmetries), \({\mathfrak{G}}\) under which the ground-truth label remains unchanged. Specifically, if we let y ( X , E , g ) be the label given to the graph featurised with X , E , g , then for every transformation \({\mathfrak{g}}\in {\mathfrak{G}}\) , the following property holds:
This condition is also referred to as \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -invariance. Here, by \({\mathfrak{g}}({{{{{{{\bf{X}}}}}}}})\) we denote the result of transforming X by \({\mathfrak{g}}\) —a concept also known as a group action. More generally, it is a function of the form \({\mathfrak{G}}\times {{{{{{{\mathcal{S}}}}}}}}\to {{{{{{{\mathcal{S}}}}}}}}\) for some state set \({{{{{{{\mathcal{S}}}}}}}}\) . Note that a single group element, \({\mathfrak{g}}\in {\mathfrak{G}}\) can easily produce different actions on different \({{{{{{{\mathcal{S}}}}}}}}\) —in this case, \({{{{{{{\mathcal{S}}}}}}}}\) could be \({{\mathbb{R}}}^{| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times k}\) ( X ), \({{\mathbb{R}}}^{| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times | {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}| \times l}\) ( E ) and \({{\mathbb{R}}}^{m}\) ( g ).
It is worth noting that GNNs may also be derived using a GDL perspective if we set the symmetry group \({\mathfrak{G}}\) to \({S}_{| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}}|\) , the permutation group of \(| {{{{{{{\mathcal{V}}}}}}}}|\) objects. Owing to the design of Eq. ( 2 ), its outputs will not be dependent on the exact permutation of nodes in the input graph.
Frame averaging
A simple mechanism to enforce \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -invariance, given any predictor \({f}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}({{{{{{{\bf{X}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{E}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{g}}}}}}}})\) , performs frame averaging across all \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -transformed inputs:
This ensures that all \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -transformed versions of a particular input (also known as that input’s orbit) will have exactly the same output, satisfying Eq. ( 5 ). A variant of this approach has also been applied in the AlphaGo architecture 25 to encode symmetries of a Go board.
In our specific implementation, we set \({\mathfrak{G}}={D}_{2}=\{{{{{{{{\rm{id}}}}}}}},\leftrightarrow,\updownarrow,\leftrightarrow \updownarrow \}\) , the dihedral group. Exploiting D 2 -invariance allows us to encode quadrant symmetries. Each element of the D 2 group encodes the presence of vertical or horizontal reflections of the input football pitch. Under these transformations, the pitch is assumed completely symmetric, and hence many predictions, such as which player receives the corner kick, or takes a shot from it, can be safely assumed unchanged. As an example of how to compute transformed features in Eq. ( 6 ), ↔( X ) horizontally reflects all positional features of players in X (e.g. the coordinates of the player), and negates the x -axis component of their velocity.
Group convolutions
While the frame averaging approach of Eq. ( 6 ) is a powerful way to restrict GNNs to respect input symmetries, it arguably misses an opportunity for the different \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -transformed views to interact while their computations are being performed. For small groups such as D 2 , a more fine-grained approach can be assumed, operating over a single GNN layer in Eq. ( 2 ), which we will write shortly as \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}^{(t)}={g}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}^{(t-1)},\, {{{{{{{\bf{E}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{\bf{g}}}}}}}})\) . The condition that we need a symmetry-respecting GNN layer to satisfy is as follows, for all transformations \({\mathfrak{g}}\in {\mathfrak{G}}\) :
that is, it does not matter if we apply \({\mathfrak{g}}\) it to the input or the output of the function \({g}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}\) —the final answer is the same. This condition is also referred to as \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -equivariance, and it has recently proved to be a potent paradigm for developing powerful GNNs over biochemical data 24 , 26 .
To satisfy D 2 -equivariance, we apply the group convolution approach 13 . Therein, views of the input are allowed to directly interact with their \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -transformed variants, in a manner very similar to grid convolutions (which is, indeed, a special case of group convolutions, setting \({\mathfrak{G}}\) to be the translation group). We use \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{{\mathfrak{g}}}^{(t)}\) to denote the \({\mathfrak{g}}\) -transformed view of the latent node features at layer t . Omitting E and g inputs for brevity, and using our previously designed layer \({g}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}\) as a building block, we can perform a group convolution as follows:
Here, ∥ is the concatenation operation, joining the two node feature matrices column-wise; \({{\mathfrak{g}}}^{-1}\) is the inverse transformation to \({\mathfrak{g}}\) (which must exist as \({\mathfrak{G}}\) is a group); and \({{\mathfrak{g}}}^{-1}{\mathfrak{h}}\) is the composition of the two transformations.
Effectively, Eq. ( 8 ) implies our D 2 -equivariant GNN needs to maintain a node feature matrix \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{{\mathfrak{g}}}^{(t)}\) for every \({\mathfrak{G}}\) -transformation of the current input, and these views are recombined by invoking \({g}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}\) on all pairs related together by applying a transformation \({\mathfrak{h}}\) . Note that all reflections are self-inverses, hence, in D 2 , \({\mathfrak{g}}={{\mathfrak{g}}}^{-1}\) .
It is worth noting that both the frame averaging in Eq. ( 6 ) and group convolution in Eq. ( 8 ) are similar in spirit to data augmentation. However, whereas standard data augmentation would only show one view at a time to the model, a frame averaging/group convolution architecture exhaustively generates all views and feeds them to the model all at once. Further, group convolutions allow these views to explicitly interact in a way that does not break symmetries. Here lies the key difference between the two approaches: frame averaging and group convolutions rigorously enforce the symmetries in \({\mathfrak{G}}\) , whereas data augmentation only provides implicit hints to the model about satisfying them. As a consequence of the exhaustive generation, Eqs. ( 6 ) and ( 8 ) are only feasible for small groups like D 2 . For larger groups, approaches like Steerable CNNs 27 may be employed.
Network architectures
While the three benchmark tasks we are performing have minor differences in the global features available to the model, the neural network models designed for them all have the same encoder–decoder architecture. The encoder has the same structure in all tasks, while the decoder model is tailored to produce appropriately shaped outputs for each benchmark task.
Given an input graph, TacticAI’s model first generates all relevant D 2 -transformed versions of it, by appropriately reflecting the player coordinates and velocities. We refer to the original input graph as the identity view, and the remaining three D 2 -transformed graphs as reflected views.
Once the views are prepared, we apply four group convolutional layers (Eq. ( 8 )) with a GATv2 base model (Eqs. ( 3 ) and ( 4 )) as the \({g}_{{{{{{{{\mathcal{G}}}}}}}}}\) function. Specifically, this means that, in Eqs. ( 3 ) and ( 4 ), every instance of \({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}_{u}^{(t-1)}\) is replaced by the concatenation of \({({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}_{{\mathfrak{h}}}^{(t-1)})}_{u}\parallel {({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}_{{{\mathfrak{g}}}^{-1}{\mathfrak{h}}}^{(t-1)})}_{u}\) . Each GATv2 layer has eight attention heads and computes four latent features overall per player. Accordingly, once the four group convolutions are performed, we have a representation of \({{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{4\times 22\times 4}\) , where the first dimension corresponds to the four views ( \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{{{{{{{{\rm{id}}}}}}}}},\, {{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{\leftrightarrow },\, {{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{\updownarrow },\, {{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{\leftrightarrow \updownarrow }\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{22\times 4}\) ), the second dimension corresponds to the players (eleven on each team), and the third corresponds to the 4-dimensional latent vector for each player node in this particular view. How this representation is used by the decoder depends on the specific downstream task, as we detail below.
For receiver prediction, which is a fully invariant function (i.e. reflections do not change the receiver), we perform simple frame averaging across all views, arriving at
and then learn a node-wise classifier over the rows of \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}^{{{{{{{{\rm{node}}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{22\times 4}\) . We further decode H node into a logit vector \({{{{{{{\bf{O}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{22}\) with a linear layer before computing the corresponding softmax cross entropy loss.
For shot prediction, which is once again fully invariant (i.e. reflections do not change the probability of a shot), we can further average the frame-averaged features across all players to get a global graph representation:
and then learn a binary classifier over \({{{{{{{{\bf{h}}}}}}}}}^{{{{{{{{\rm{graph}}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{4}\) . Specifically, we decode the hidden vector into a single logit with a linear layer and compute the sigmoid binary cross-entropy loss with the corresponding label.
For guided generation (position/velocity adjustments), we generate the player positions and velocities with respect to a particular outcome of interest for the human coaches, predicted over the rows of the hidden feature matrix. For example, the model may adjust the defensive setup to decrease the shot probability by the attacking team. The model output is now equivariant rather than invariant—reflecting the pitch appropriately reflects the predicted positions and velocity vectors. As such, we cannot perform frame averaging, and take only the identity view’s features, \({{{{{{{{\bf{H}}}}}}}}}_{{{{{{{{\rm{id}}}}}}}}}\in {{\mathbb{R}}}^{22\times 4}\) . From this latent feature matrix, we can then learn a conditional distribution from each row, which models the positions or velocities of the corresponding player. To do this, we extend the backbone encoder with conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE 28 , 29 ). Specifically, for the u -th row of H id , h u , we first map its latent embedding to the parameters of a two-dimensional Gaussian distribution \({{{{{{{\mathcal{N}}}}}}}}({\mu }_{u}| {\sigma }_{u})\) , and then sample the coordinates and velocities from this distribution. At training time, we can efficiently propagate gradients through this sampling operation using the reparameterisation trick 28 : sample a random value \({\epsilon }_{u} \sim {{{{{{{\mathcal{N}}}}}}}}(0,1)\) for each player from the unit Gaussian distribution, and then treat μ u + σ u ϵ u as the sample for this player. In what follows, we omit edge features for brevity. For each corner kick sample X with the corresponding outcome o (e.g. a binary value indicating a shot event), we extend the standard VAE loss 28 , 29 to our case of outcome-conditional guided generation as
where h u is the player embedding corresponding to the u th row of H id , and \({\mathbb{KL}}\) is Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence. Specifically, the first term is the generation loss between the real player input x u and the reconstructed sample decoded from h u with the decoder p ϕ . Using the KL term, the distribution of the latent embedding h u is regularised towards p ( h u ∣ o ), which is a multivariate Gaussian in our case.
A complete high-level summary of the generic encoder–decoder equivariant architecture employed by TacticAI can be summarised in Supplementary Fig. 2 . In the following section, we will provide empirical evidence for justifying these architectural decisions. This will be done through targeted ablation studies on our predictive benchmarks (receiver prediction and shot prediction).
Ablation study
We leveraged the receiver prediction task as a way to evaluate various base model architectures, and directly quantitatively assess the contributions of geometric deep learning in this context. We already see that the raw corner kick data can be better represented through geometric deep learning, yielding separable clusters in the latent space that could correspond to different attacking or defending tactics (Fig. 2 ). In addition, we hypothesise that these representations can also yield better performance on the task of receiver prediction. Accordingly, we ablate several design choices using deep learning on this task, as illustrated by the following four questions:
Does a factorised graph representation help? To assess this, we compare it against a convolutional neural network (CNN 30 ) baseline, which does not leverage a graph representation.
Does a graph structure help? To assess this, we compare against a Deep Sets 31 baseline, which only models each node in isolation without considering adjacency information—equivalently, setting each neighbourhood \({{{{{{{{\mathcal{N}}}}}}}}}_{u}\) to a singleton set { u }.
Are attentional GNNs a good strategy? To assess this, we compare against a message passing neural network 32 , MPNN baseline, which uses the fully potent GNN layer from Eq. ( 2 ) instead of the GATv2.
Does accounting for symmetries help? To assess this, we compare our geometric GATv2 baseline against one which does not utilise D 2 group convolutions but utilises D 2 frame averaging, and one which does not explicitly utilise any aspect of D 2 symmetries at all.
Each of these models has been trained for a fixed budget of 50,000 training steps. The test top- k receiver prediction accuracies of the trained models are provided in Supplementary Table 2 . As already discussed in the section “Results”, there is a clear advantage to using a full graph structure, as well as directly accounting for reflection symmetry. Further, the usage of the MPNN layer leads to slight overfitting compared to the GATv2, illustrating how attentional GNNs strike a good balance of expressivity and data efficiency for this task. Our analysis highlights the quantitative benefits of both graph representation learning and geometric deep learning for football analytics from tracking data. We also provide a brief ablation study for the shot prediction task in Supplementary Table 3 .
Training details
We train each of TacticAI’s models in isolation, using NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs. To minimise overfitting, each model’s learning objective is regularised with an L 2 norm penalty with respect to the network parameters. During training, we use the Adam stochastic gradient descent optimiser 33 over the regularised loss.
All models, including baselines, have been given an equal hyperparameter tuning budget, spanning the number of message passing steps ({1, 2, 4}), initial learning rate ({0.0001, 0.00005}), batch size ({128, 256}) and L 2 regularisation coefficient ({0.01, 0.005, 0.001, 0.0001, 0}). We summarise the chosen hyperparameters of each TacticAI model in Supplementary Table 1 .
Data availability
The data collected in the human experiments in this study have been deposited in the Zenodo database under accession code https://zenodo.org/records/10557063 , and the processed data which is used in the statistical analysis and to generate the relevant figures in the main text are available under the same accession code. The input and output data generated and/or analysed during the current study are protected and are not available due to data privacy laws and licensing restrictions. However, contact details of the input data providers are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Code availability
All the core models described in this research were built with the Graph Neural Network processors provided by the CLRS Algorithmic Reasoning Benchmark 18 , and their source code is available at https://github.com/google-deepmind/clrs . We are unable to release our code for this work as it was developed in a proprietary context; however, the corresponding authors are open to answer specific questions concerning re-implementations on request. For general data analysis, we used the following freely available packages: numpy v1.25.2 , pandas v1.5.3 , matplotlib v3.6.1 , seaborn v0.12.2 and scipy v1.9.3 . Specifically, the code of the statistical analysis conducted in this study is available at https://zenodo.org/records/10557063 .
The International Football Association Board (IFAB). Laws of the Game (The International Football Association Board, 2023).
Tuyls, K. et al. Game plan: what AI can do for football, and what football can do for AI. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 71 , 41–88 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Goka, R., Moroto, Y., Maeda, K., Ogawa, T. & Haseyama, M. Prediction of shooting events in soccer videos using complete bipartite graphs and players’ spatial–temporal relations. Sensors 23 , 4506 (2023).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Omidshafiei, S. et al. Multiagent off-screen behavior prediction in football. Sci. Rep. 12 , 8638 (2022).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lang, S., Wild, R., Isenko, A. & Link, D. Predicting the in-game status in soccer with machine learning using spatiotemporal player tracking data. Sci. Rep. 12 , 16291 (2022).
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C. & Baskurt, A. Action classification in soccer videos with long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (eds Diamantaras, K., Duch, W. & Iliadis, L. S.) pages 154–159 (Springer, 2010).
Shaw, L. & Gopaladesikan, S. Routine inspection: a playbook for corner kicks. In Machine Learning and Data Mining for Sports Analytics: 7th International Workshop, MLSA 2020, Co-located with ECML/PKDD 2020 , Proceedings, Ghent, Belgium, September 14–18, 2020, Vol . 7 , 3–16 (Springer, 2020).
Araújo, D. & Davids, K. Team synergies in sport: theory and measures. Front. Psychol. 7 , 1449 (2016).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Veličković, P. Everything is connected: graph neural networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 79 , 102538 (2023).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bronstein, M. M., Bruna, J., Cohen, T. & Veličković, P. Geometric deep learning: grids, groups, graphs, geodesics, and gauges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.13478 (2021).
Brody, S., Alon, U. & Yahav, E. How attentive are graph attention networks? In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=F72ximsx7C1 .
Veličković, P. et al. Graph attention networks. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2018). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJXMpikCZ .
Cohen, T. & Welling, M. Group equivariant convolutional networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Balcan, M. F. & Weinberger, K. Q.) 2990–2999 (PMLR, 2016).
Honda, Y., Kawakami, R., Yoshihashi, R., Kato, K. & Naemura, T. Pass receiver prediction in soccer using video and players’ trajectories. In 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW) 3502–3511 (2022). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9857310 .
Hubáček, O., Sourek, G. & Železný, F. Deep learning from spatial relations for soccer pass prediction. In MLSA@PKDD/ECML (eds Brefeld, U., Davis, J., Van Haaren, J. & Zimmermann, A.) Vol. 11330, (Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, Cham, 2018).
Sanyal, S. Who will receive the ball? Predicting pass recipient in soccer videos. J Visual Commun. Image Represent. 78 , 103190 (2021).
Gilmer, J., Schoenholz, S. S., Riley, P. F., Vinyals, O. & Dahl, G. E. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. In International Conference on Machine Learning (Precup, D. & Teh, Y. W.) 1263–1272 (PMLR, 2017).
Veličković, P. et al. The CLRS algorithmic reasoning benchmark. In International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Chaudhuri, K. et al.) 22084–22102 (PMLR, 2022).
Vaswani, A. et al. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (eds Guyon, I. et al.) Vol. 30 (Curran Associates, Inc., 2017).
Veličković, P. Message passing all the way up. In ICLR 2022 Workshop on Geometrical and Topological Representation Learning (GTRL, 2022). https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bc8GiEZkTe5 .
Baranwal, A., Kimon, F. & Aukosh, J. Optimality of message-passing architectures for sparse graphs. In Thirty-seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2023). https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/hash/7e991aa4cd2fdf0014fba2f000f542d0-Abstract-Conference.html .
Greenblatt, R. D., Eastlake III, D. E. & Crocker, S. D. The Greenblatt chess program. In Proc. Fall Joint Computer Conference , 14–16 , 801–810 (Association for Computing Machinery, 1967). https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1465611.1465715 .
Schijf, M., Allis, L. V. & Uiterwijk, J. W. Proof-number search and transpositions. ICGA J. 17 , 63–74 (1994).
Fuchs, F., Worrall, D., Fischer, V. & Welling, M. SE(3)-transformers: 3D roto-translation equivariant attention networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 33 , 1970–1981 (2020).
Google Scholar
Silver, D. et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529 , 484–489 (2016).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Satorras, V. G., Hoogeboom, E. & Welling, M. E ( n ) equivariant graph neural networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning (eds Meila, M. & Zhang, T.) 9323–9332 (PMLR, 2021).
Cohen, T. S. & Welling, M. Steerable CNNs. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR, 2017). https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJQKYt5ll .
Kingma, D. P. & Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. In 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2014, Banff, AB, Canada, April 14–16, 2014, Conference Track Proceedings (ICLR, 2014). https://openreview.net/forum?id=33X9fd2-9FyZd .
Sohn, K., Lee, H. & Yan, X. Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (eds Cortes, C, Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M. & Garnett, R.) Vol. 28 (Curran Associates, Inc., 2015).
Fernández, J. & Bornn, L. Soccermap: a deep learning architecture for visually-interpretable analysis in soccer. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Applied Data Science and Demo Track: European Conference, ECML PKDD 2020, Ghent, Belgium, September 14–18, 2020, Proceedings, Part V (eds Dong, Y., Ifrim, G., Mladenić, D., Saunders, C. & Van Hoecke, S.) 491–506 (Springer, 2021).
Zaheer, M. et al. Deep sets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems Vol. 30 (eds Guyon, I., et al.) (Curran Associates, Inc., 2017).
Gilmer, J., Schoenholz, S. S., Riley, P. F., Vinyals, O. & Dahl, G. E. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. In Proc. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning , Vol. 70 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 6–11 Aug 2017 (eds Precup, D. & Whye Teh, Y) 1263–1272 (PMLR, 2017).
Kingma, G. E. & Ba, J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In ICLR (Poster) , (eds Bengio, Y. & LeCun, Y.) (International Conference of Learning Representations (ICLR), 2015). https://openreview.net/forum?id=8gmWwjFyLj .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support of James French, Timothy Waskett, Hans Leitert and Benjamin Hervey for their extensive efforts in analysing TacticAI’s outputs. Further, we are thankful to Kevin McKee, Sherjil Ozair and Beatrice Bevilacqua for useful technical discussions, and Marc Lanctôt and Satinder Singh for reviewing the paper prior to submission.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Zhe Wang, Petar Veličković, Daniel Hennes.
Authors and Affiliations
Google DeepMind, 6-8 Handyside Street, London, N1C 4UZ, UK
Zhe Wang, Petar Veličković, Daniel Hennes, Nenad Tomašev, Laurel Prince, Michael Kaisers, Yoram Bachrach, Romuald Elie, Li Kevin Wenliang, Federico Piccinini, Jerome Connor, Yi Yang, Adrià Recasens, Mina Khan, Nathalie Beauguerlange, Pablo Sprechmann, Pol Moreno, Nicolas Heess & Demis Hassabis
Liverpool FC, AXA Training Centre, Simonswood Lane, Kirkby, Liverpool, L33 5XB, UK
William Spearman
Liverpool FC, Kirkby, UK
University of Alberta, Amii, Edmonton, AB, T6G 2E8, Canada
Michael Bowling
Google DeepMind, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Z.W., D. Hennes, L.P. and K.T. coordinated and organised the research effort leading to this paper. P.V. and Z.W. developed the core TacticAI models. Z.W., W.S. and I.G. prepared the Premier League corner kick dataset used for training and evaluating these models. P.V., Z.W., D. Hennes and N.T. designed the case study with human experts and Z.W. and P.V. performed the qualitative evaluation and statistical analysis of its outcomes. Z.W., P.V., D. Hennes, N.T., L.P., M. Kaisers, Y.B., R.E., L.K.W., F.P., W.S., I.G., N.H., M.B., D. Hassabis and K.T. contributed to writing the paper and providing feedback on the final manuscript. J.C., Y.Y., A.R., M. Khan, N.B., P.S. and P.M. contributed valuable technical and implementation discussions throughout the work’s development.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Zhe Wang , Petar Veličković or Karl Tuyls .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests but the following competing interests: TacticAI was developed during the course of the Authors’ employment at Google DeepMind and Liverpool Football Club, as applicable to each Author.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Communications thanks Rui Luo and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, peer review file, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wang, Z., Veličković, P., Hennes, D. et al. TacticAI: an AI assistant for football tactics. Nat Commun 15 , 1906 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45965-x
Download citation
Received : 13 October 2023
Accepted : 08 February 2024
Published : 19 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45965-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Example of Research Results in Research Paper: Results: Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables ...
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting ...
the results of your research, ... Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper. Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don't undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution. ... (e.g. shampoo bottles), for example by refilling or ...
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results. Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach. Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings. This approach can be used to highlight important findings.
One important section of a paper is known as the results section. An APA results section of a psychology paper summarizes the data that was collected and the statistical analyses that were performed. The goal of this section is to report the results of your study or experiment without any type of subjective interpretation.
The Results (also sometimes called Findings) section in an empirical research paper describes what the researcher(s) found when they analyzed their data. Its primary purpose is to use the data collected to answer the research question(s) posed in the introduction, even if the findings challenge the hypothesis.
The APA results section summarizes data and includes reporting statistics in a quantitative research study. The APA results section is an essential part of your research paper and typically begins with a brief overview of the data followed by a systematic and detailed reporting of each hypothesis tested. The interpreted results will then be presented in the discussion sections.
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be ...
Build coherence along this section using goal statements and explicit reasoning (guide the reader through your reasoning, including sentences of this type: 'In order to…, we performed….'; 'In view of this result, we ….', etc.). In summary, the general steps for writing the Results section of a research article are:
Step 4. Outlining the results section based on the research findings. Once you have organized your outcomes and figures, you should start writing your results section to clearly and precisely present complex information. Writing concise and precise sentences is the most effective way to accomplish this.
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
The easiest way to write a quantitative dissertation results section is to build it around a sub-question or hypothesis of your research. For each subquery, provide relevant results and include statistical analysis. Then briefly evaluate importance & reliability.
Generally, this section will begin with a brief overview of the results, then cover each of the main results from the data. Objectively point out the main ideas and use tables, figures, and other graphics as necessary to present the data. This section also discusses any limitations of the study. Fig. 2.6 shows an example of the Results section.
The results section of a research paper refers to the part that represents the study's core findings from the methods that the researcher used to collect and analyze data. This section presents the results logically without interpretation or bias from the author. Thus, this part of a research paper sets up the read for evaluation and analysis ...
Results section of a research paper example. Here is a short sample of the results section for the research paper on psychology: The results of the study indicated that there was a significant correlation between the level of stress and the frequency of exercise. Participants who reported higher stress levels also reported exercising less ...
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the 'Results' section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17-22.) are shown in Figures 1, and and2 2.
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
Psychology Research Paper Sample. Writing a psychology research paper involves studying human behavior and mental processes. This process includes conducting experiments, gathering data, and analyzing results to understand the human mind, emotions, and behavior. Here is an example psychology paper:
Academic Writing Example 1: Research Proposals. ... The abstract acts as a comprehensive outline of your paper in paragraph form. Abstract Structure. Background. ... how it was approached, and the results and conclusions of the research. If you are struggling to meet a word count, check out 10 Academic Phrases Your Writing Doesn't Need ...
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats ; How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples ; How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers ... How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips. 10 min read. How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps.
Identifying key patterns of tactics implemented by rival teams, and developing effective responses, lies at the heart of modern football. However, doing so algorithmically remains an open research ...