The top list of academic search engines

1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
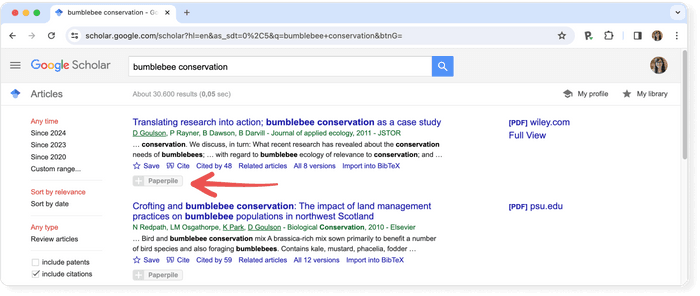
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
Stand on the shoulders of giants
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions, from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other web sites. Google Scholar helps you find relevant work across the world of scholarly research.

How are documents ranked?
Google Scholar aims to rank documents the way researchers do, weighing the full text of each document, where it was published, who it was written by, as well as how often and how recently it has been cited in other scholarly literature.
Features of Google Scholar
- Search all scholarly literature from one convenient place
- Explore related works, citations, authors, and publications
- Locate the complete document through your library or on the web
- Keep up with recent developments in any area of research
- Check who's citing your publications, create a public author profile

Disclaimer: Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
- Privacy & Terms
A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Neil McWilliam
- Parliamentary System
New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI.
🇺🇦 make metadata, not war
A comprehensive bibliographic database of the world’s scholarly literature
The world’s largest collection of open access research papers, machine access to our vast unique full text corpus, core features, indexing the world’s repositories.
We serve the global network of repositories and journals
Comprehensive data coverage
We provide both metadata and full text access to our comprehensive collection through our APIs and Datasets
Powerful services
We create powerful services for researchers, universities, and industry
Cutting-edge solutions
We research and develop innovative data-driven and AI solutions
Committed to the POSI
Cost-free PIDs for your repository
OAI identifiers are unique identifiers minted cost-free by repositories. Ensure that your repository is correctly configured, enabling the CORE OAI Resolver to redirect your identifiers to your repository landing pages.
OAI IDs provide a cost-free option for assigning Persistent Identifiers (PIDs) to your repository records. Learn more.
Who we serve?
Enabling others to create new tools and innovate using a global comprehensive collection of research papers.

“ Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can ... ” Show more
Gareth Malcolm, Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Academic institutions.
Making research more discoverable, improving metadata quality, helping to meet and monitor open access compliance.

“ CORE’s role in providing a unified search of repository content is a great tool for the researcher and ex... ” Show more
Nicola Dowson, Library Services Manager at Open University
Researchers & general public.
Tools to find, discover and explore the wealth of open access research. Free for everyone, forever.

“ With millions of research papers available across thousands of different systems, CORE provides an invalu... ” Show more
Jon Tennant, Rogue Paleontologist and Founder of the Open Science MOOC
Helping funders to analyse, audit and monitor open research and accelerate towards open science.

“ Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, hel... ” Show more
Ben Johnson, Research Policy Adviser at Research England
Our services, access to raw data.
Create new and innovative solutions.
Content discovery
Find relevant research and make your research more visible.
Managing content
Manage how your research content is exposed to the world.
Companies using CORE

Gareth Malcolm
Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can utilise in our plagiarism detection software.
Academic institution using CORE
Kathleen Shearer
Executive Director of the Confederation of Open Access Repositories (COAR)
CORE has significantly assisted the academic institutions participating in our global network with their key mission, which is their scientific content exposure. In addition, CORE has helped our content administrators to showcase the real benefits of repositories via its added value services.
Partner projects

Ben Johnson
Research Policy Adviser
Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, helping to turn the promise of a 'research commons' into a reality. The aggregation services that CORE provides therefore make a very valuable contribution to the evolving open access environment in the UK.

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Download 55 million PDFs for free
Explore our top research interests.

Engineering

Anthropology

- Earth Sciences

- Computer Science

- Mathematics

- Health Sciences

Join 256 million academics and researchers
Accelerate your research, streamline your discovery of relevant research.
Get access to 55+ million research papers and stay informed with important topics through courses.
Grow Your Audience
Build your success and track your impact.
Share your work with other academics, grow your audience, and track your impact on your field with our robust analytics.
Unlock the most powerful tools with Academia Premium

Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools
Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts.
- Advanced Search
- PDF Packages of 37 papers
- Summaries and Search Alerts

Share your work, track your impact, and grow your audience
Get notified when other academics mention you or cite your papers. Track your impact with in-depth analytics and network with members of your field.
- Mentions and Citations Tracking
- Advanced Analytics
- Publishing Tools
Real stories from real people

Used by academics at over 16,000 universities

Get started and find the best quality research
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Cognitive Science
- Academia ©2024

- Advanced search
- Peer review

Discover relevant research today

Advance your research field in the open

Reach new audiences and maximize your readership
ScienceOpen puts your research in the context of
Publications
For Publishers
ScienceOpen offers content hosting, context building and marketing services for publishers. See our tailored offerings
- For academic publishers to promote journals and interdisciplinary collections
- For open access journals to host journal content in an interactive environment
- For university library publishing to develop new open access paradigms for their scholars
- For scholarly societies to promote content with interactive features
For Institutions
ScienceOpen offers state-of-the-art technology and a range of solutions and services
- For faculties and research groups to promote and share your work
- For research institutes to build up your own branding for OA publications
- For funders to develop new open access publishing paradigms
- For university libraries to create an independent OA publishing environment
For Researchers
Make an impact and build your research profile in the open with ScienceOpen
- Search and discover relevant research in over 93 million Open Access articles and article records
- Share your expertise and get credit by publicly reviewing any article
- Publish your poster or preprint and track usage and impact with article- and author-level metrics
- Create a topical Collection to advance your research field
Create a Journal powered by ScienceOpen
Launching a new open access journal or an open access press? ScienceOpen now provides full end-to-end open access publishing solutions – embedded within our smart interactive discovery environment. A modular approach allows open access publishers to pick and choose among a range of services and design the platform that fits their goals and budget.
Continue reading “Create a Journal powered by ScienceOpen”
What can a Researcher do on ScienceOpen?
ScienceOpen provides researchers with a wide range of tools to support their research – all for free. Here is a short checklist to make sure you are getting the most of the technological infrastructure and content that we have to offer. What can a researcher do on ScienceOpen? Continue reading “What can a Researcher do on ScienceOpen?”
ScienceOpen on the Road
Upcoming events.
- 20 – 22 February – ResearcherToReader Conferece
Past Events
- 09 November – Webinar for the Discoverability of African Research
- 26 – 27 October – Attending the Workshop on Open Citations and Open Scholarly Metadata
- 18 – 22 October – ScienceOpen at Frankfurt Book Fair.
- 27 – 29 September – Attending OA Tage, Berlin .
- 25 – 27 September – ScienceOpen at Open Science Fair
- 19 – 21 September – OASPA 2023 Annual Conference .
- 22 – 24 May – ScienceOpen sponsoring Pint of Science, Berlin.
- 16-17 May – ScienceOpen at 3rd AEUP Conference.
- 20 – 21 April – ScienceOpen attending Scaling Small: Community-Owned Futures for Open Access Books .
- 18 – 20 April – ScienceOpen at the London Book Fair .
What is ScienceOpen?
- Smart search and discovery within an interactive interface
- Researcher promotion and ORCID integration
- Open evaluation with article reviews and Collections
- Business model based on providing services to publishers
Live Twitter stream
Some of our partners:.

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
Ocular blood flow in preterm neonates
- Ronald H. Silverman
- Leora Pinto
Lengthened circadian rhythms in mice with self-controlled ambient light intensity
- Jun Ogasawara
- Nobuyoshi Matsumoto
- Yuji Ikegaya
Association between atherosclerosis and height loss among older individuals
- Yuji Shimizu
- Kazuhiko Arima
- Takahiro Maeda
Graphical user interface-based convolutional neural network models for detecting nasopalatine duct cysts using panoramic radiography
- Naohisa Hirahara
- Takashi Kaneda
Prevalence of impaired renal function among childless men as compared to fathers: a population-based study
- Michael Kitlinski
- Aleksander Giwercman
- Angel Elenkov
Measurement of relative transition strengths of 133 Cs Rydberg D states using electromagnetically induced transparency
- Shanxia Bao
- Suotang Jia
Impact of drainage retinotomy on surgical outcomes of retinal detachment: insights from the Japan-Retinal Detachment Registry
- Hisashi Fukuyama
- Hiroto Ishikawa
- Shin Yamane

Activity-stability trade-off observed in variants at position 315 of the GH10 xylanase XynR
- Tomoka Nakamura
- Teisuke Takita
- Kiyoshi Yasukawa
Multifunctional carbon nanotubes coated stainless steel mesh for electrowetting, hydrophobic, and dye absorption behavior
- Hyeong Kwang Benno Park
- Imen Kebaili
- Anuruddh Kumar
An observational study to identify causative factors for not using hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus
- Atsushi Manabe
- Ryuichi Minoda Sada
- Kazuhiro Hatta
Investigation of class-F power amplifier in the presence of the second and fourth harmonics of input voltage
- Parastoo Rostami
- Akram Sheikhi
Modulation efficiency of clove oil nano-emulsion against genotoxic, oxidative stress, and histological injuries induced via titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mice
- Hanan R. H. Mohamed
- Sawsan El-Shamy
- Haidan El-Shorbagy
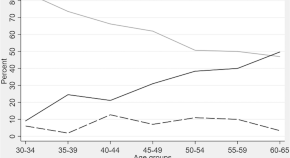
A household survey of the prevalence of subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment among urban community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 65
- Kanokporn Pinyopornpanish
- Nida Buawangpong
- Chaisiri Angkurawaranon
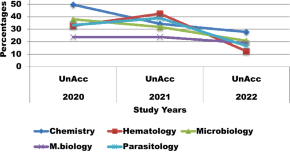
Performances and determinants of proficiency testing in clinical laboratory services at comprehensive specialized hospitals, northwest Ethiopia
- Negesse Cherie
- Bisrat Birke Teketelew
- Dereje Mengesha Berta
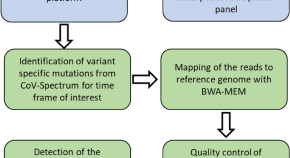
Detection of SARS-COV-2 variants and their proportions in wastewater samples using next-generation sequencing in Finland
- Anssi Lipponen
- Aleksi Kolehmainen
- Carita Savolainen-Kopra
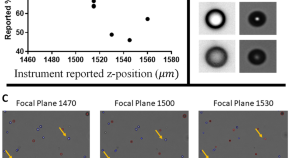
Establishing a reference focal plane using convolutional neural networks and beads for brightfield imaging
- Joe Chalfoun
- Steven P. Lund
- Sumona Sarkar
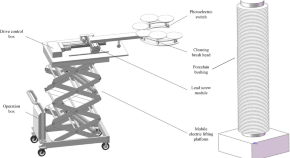
Design of robotic arm for the porcelain bushing in substation
- Zhaoxing Ma
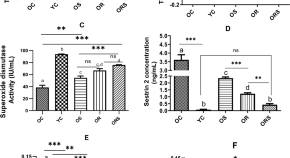
Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
- Majid Mohabbat
- Hamid Arazi
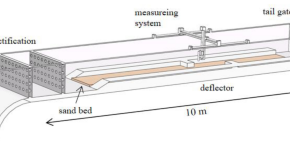
Velocity field and turbulence structure of the meandering flow produced by alternating deflectors
- Jie-min Zhan
- Wing-hong Onyx Wai
- Ying-ying Luo
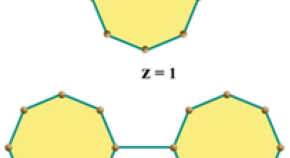
Computation of expected values of some connectivity based topological descriptors of random cyclooctane chains
- Shamaila Yousaf
- Zaffar Iqbal
- Abudulai Issa
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Search Results
Working papers
Our working paper series disseminates economic research relevant to the various tasks and functions of the ECB , and provides a conceptual and empirical basis for policy-making. The working papers constitute “work in progress”. They are published to stimulate discussion and contribute to the advancement of our knowledge of economic matters. They are addressed to experts, so readers should be knowledgeable in economics.
The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the ECB.
All pages in this section
Our website uses cookies.
We are always working to improve this website for our users. To do this, we use the anonymous data provided by cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies
We have updated our privacy policy
We are always working to improve this website for our users. To do this, we use the anonymous data provided by cookies. See what has changed in our privacy policy
Your cookie preference has expired
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
Research Identifies Characteristics of Cities That Would Support Young People’s Mental Health
Survey responses from global panel that included young people provide insights into what would make cities mental health-friendly for youth
As cities around the world continue to draw young people for work, education, and social opportunities, a new study identifies characteristics that would support young urban dwellers’ mental health. The findings, based on survey responses from a global panel that included adolescents and young adults, provide a set of priorities that city planners can adopt to build urban environments that are safe, equitable, and inclusive.
To determine city characteristics that could bolster youth mental health, researchers administered an initial survey to a panel of more than 400, including young people and a multidisciplinary group of researchers, practitioners, and advocates. Through two subsequent surveys, participants prioritized six characteristics that would support young city dwellers’ mental health: opportunities to build life skills; age-friendly environments that accept young people’s feelings and values; free and safe public spaces where young people can connect; employment and job security; interventions that address the social determinants of health; and urban design with youth input and priorities in mind.
The paper was published online February 21 in Nature .
The study’s lead author is Pamela Collins, MD, MPH, chair of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health’s Department of Mental Health. The study was conducted while Collins was on the faculty at the University of Washington. The paper was written by an international, interdisciplinary team, including citiesRISE, a global nonprofit that works to transform mental health policy and practice in cities, especially for young people.
Cities have long been a draw for young people. Research by UNICEF projects that cities will be home to 70 percent of the world’s children by 2050. Although urban environments influence a broad range of health outcomes, both positive and negative, their impacts manifest unequally. Mental disorders are the leading causes of disability among 10- to 24-year-olds globally. Exposure to urban inequality, violence, lack of green space, and fear of displacement disproportionately affects marginalized groups, increasing risk for poor mental health among urban youth.
“Right now, we are living with the largest population of adolescents in the world’s history, so this is an incredibly important group of people for global attention,” says Collins. “Investing in young people is an investment in their present well-being and future potential, and it’s an investment in the next generation—the children they will bear.”
Data collection for the study began in April 2020 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. To capture its possible impacts, researchers added an open-ended survey question asking panelists how the pandemic influenced their perceptions of youth mental health in cities. The panelists reported that the pandemic either shed new light on the inequality and uneven distribution of resources experienced by marginalized communities in urban areas, or confirmed their preconceptions of how social vulnerability exacerbates health outcomes.
For their study, the researchers recruited a panel of more than 400 individuals from 53 countries, including 327 young people ages 14 to 25, from a cross-section of fields, including education, advocacy, adolescent health, mental health and substance use, urban planning and development, data and technology, housing, and criminal justice. The researchers administered three sequential surveys to panelists beginning in April 2020 that asked panelists to identify elements of urban life that would support mental health for young people.
The top 37 characteristics were then grouped into six domains: intrapersonal, interpersonal, community, organizational, policy, and environment. Within these domains, panelists ranked characteristics based on immediacy of impact on youth mental health, ability to help youth thrive, and ease or feasibility of implementation.
Taken together, the characteristics identified in the study provide a comprehensive set of priorities that policymakers and urban planners can use as a guide to improve young city dwellers' mental health. Among them: Youth-focused mental health and educational services could support young people’s emotional development and self-efficacy. Investment in spaces that facilitate social connection may help alleviate young people’s experiences of isolation and support their need for healthy, trusting relationships. Creating employment opportunities and job security could undo the economic losses that young people and their families experienced during the pandemic and help cities retain residents after a COVID-era exodus from urban centers.
The findings suggest that creating a mental health-friendly city for young people requires investments across multiple interconnected sectors like transportation, housing, employment, health, and urban planning, with a central focus on social and economic equity. They also require urban planning policy approaches that commit to systemic and sustained collaboration, without magnifying existing privileges through initiatives like gentrification and developing green spaces at the expense of marginalized communities in need of affordable housing.
The authors say this framework underscores that responses by cities should include young people in the planning and design of interventions that directly impact their mental health and well-being.
“ Making cities mental health friendly for adolescents and young adults ” was co-authored by an international, interdisciplinary team of 31 researchers led by the University of Washington Consortium for Global Mental Health, Urban@UW, the University of Melbourne, and citiesRISE. Author funding is listed in the Acknowledgements section of the paper.
Related Content

Student Spotlight: Glendedora Dolce

Study Estimates Nearly 70 Percent of Children Under Six in Chicago May Be Exposed to Lead-Contaminated Tap Water

Hidden Food Insecurity: The Adolescents Who Aren’t Getting Enough to Eat

A Zero-Emissions Transition Would Save Kids’ Lives

Child Diarrhea Has a Cheap and Easy Fix—Why Isn’t It Reaching Patients?
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Operating Systems
Title: aios: llm agent operating system.
Abstract: The integration and deployment of large language model (LLM)-based intelligent agents have been fraught with challenges that compromise their efficiency and efficacy. Among these issues are sub-optimal scheduling and resource allocation of agent requests over the LLM, the difficulties in maintaining context during interactions between agent and LLM, and the complexities inherent in integrating heterogeneous agents with different capabilities and specializations. The rapid increase of agent quantity and complexity further exacerbates these issues, often leading to bottlenecks and sub-optimal utilization of resources. Inspired by these challenges, this paper presents AIOS, an LLM agent operating system, which embeds large language model into operating systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. Specifically, AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, and maintain access control for agents. We present the architecture of such an operating system, outline the core challenges it aims to resolve, and provide the basic design and implementation of the AIOS. Our experiments on concurrent execution of multiple agents demonstrate the reliability and efficiency of our AIOS modules. Through this, we aim to not only improve the performance and efficiency of LLM agents but also to pioneer for better development and deployment of the AIOS ecosystem in the future. The project is open-source at this https URL .
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Large language models use a surprisingly simple mechanism to retrieve some stored knowledge
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Large language models, such as those that power popular artificial intelligence chatbots like ChatGPT, are incredibly complex. Even though these models are being used as tools in many areas, such as customer support, code generation, and language translation, scientists still don’t fully grasp how they work.
In an effort to better understand what is going on under the hood, researchers at MIT and elsewhere studied the mechanisms at work when these enormous machine-learning models retrieve stored knowledge.
They found a surprising result: Large language models (LLMs) often use a very simple linear function to recover and decode stored facts. Moreover, the model uses the same decoding function for similar types of facts. Linear functions, equations with only two variables and no exponents, capture the straightforward, straight-line relationship between two variables.
The researchers showed that, by identifying linear functions for different facts, they can probe the model to see what it knows about new subjects, and where within the model that knowledge is stored.
Using a technique they developed to estimate these simple functions, the researchers found that even when a model answers a prompt incorrectly, it has often stored the correct information. In the future, scientists could use such an approach to find and correct falsehoods inside the model, which could reduce a model’s tendency to sometimes give incorrect or nonsensical answers.
“Even though these models are really complicated, nonlinear functions that are trained on lots of data and are very hard to understand, there are sometimes really simple mechanisms working inside them. This is one instance of that,” says Evan Hernandez, an electrical engineering and computer science (EECS) graduate student and co-lead author of a paper detailing these findings .
Hernandez wrote the paper with co-lead author Arnab Sharma, a computer science graduate student at Northeastern University; his advisor, Jacob Andreas, an associate professor in EECS and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL); senior author David Bau, an assistant professor of computer science at Northeastern; and others at MIT, Harvard University, and the Israeli Institute of Technology. The research will be presented at the International Conference on Learning Representations.
Finding facts
Most large language models, also called transformer models, are neural networks . Loosely based on the human brain, neural networks contain billions of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that are grouped into many layers, and which encode and process data.
Much of the knowledge stored in a transformer can be represented as relations that connect subjects and objects. For instance, “Miles Davis plays the trumpet” is a relation that connects the subject, Miles Davis, to the object, trumpet.
As a transformer gains more knowledge, it stores additional facts about a certain subject across multiple layers. If a user asks about that subject, the model must decode the most relevant fact to respond to the query.
If someone prompts a transformer by saying “Miles Davis plays the. . .” the model should respond with “trumpet” and not “Illinois” (the state where Miles Davis was born).
“Somewhere in the network’s computation, there has to be a mechanism that goes and looks for the fact that Miles Davis plays the trumpet, and then pulls that information out and helps generate the next word. We wanted to understand what that mechanism was,” Hernandez says.
The researchers set up a series of experiments to probe LLMs, and found that, even though they are extremely complex, the models decode relational information using a simple linear function. Each function is specific to the type of fact being retrieved.
For example, the transformer would use one decoding function any time it wants to output the instrument a person plays and a different function each time it wants to output the state where a person was born.
The researchers developed a method to estimate these simple functions, and then computed functions for 47 different relations, such as “capital city of a country” and “lead singer of a band.”
While there could be an infinite number of possible relations, the researchers chose to study this specific subset because they are representative of the kinds of facts that can be written in this way.
They tested each function by changing the subject to see if it could recover the correct object information. For instance, the function for “capital city of a country” should retrieve Oslo if the subject is Norway and London if the subject is England.
Functions retrieved the correct information more than 60 percent of the time, showing that some information in a transformer is encoded and retrieved in this way.
“But not everything is linearly encoded. For some facts, even though the model knows them and will predict text that is consistent with these facts, we can’t find linear functions for them. This suggests that the model is doing something more intricate to store that information,” he says.
Visualizing a model’s knowledge
They also used the functions to determine what a model believes is true about different subjects.
In one experiment, they started with the prompt “Bill Bradley was a” and used the decoding functions for “plays sports” and “attended university” to see if the model knows that Sen. Bradley was a basketball player who attended Princeton.
“We can show that, even though the model may choose to focus on different information when it produces text, it does encode all that information,” Hernandez says.
They used this probing technique to produce what they call an “attribute lens,” a grid that visualizes where specific information about a particular relation is stored within the transformer’s many layers.
Attribute lenses can be generated automatically, providing a streamlined method to help researchers understand more about a model. This visualization tool could enable scientists and engineers to correct stored knowledge and help prevent an AI chatbot from giving false information.
In the future, Hernandez and his collaborators want to better understand what happens in cases where facts are not stored linearly. They would also like to run experiments with larger models, as well as study the precision of linear decoding functions.
“This is an exciting work that reveals a missing piece in our understanding of how large language models recall factual knowledge during inference. Previous work showed that LLMs build information-rich representations of given subjects, from which specific attributes are being extracted during inference. This work shows that the complex nonlinear computation of LLMs for attribute extraction can be well-approximated with a simple linear function,” says Mor Geva Pipek, an assistant professor in the School of Computer Science at Tel Aviv University, who was not involved with this work.
This research was supported, in part, by Open Philanthropy, the Israeli Science Foundation, and an Azrieli Foundation Early Career Faculty Fellowship.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Evan Hernandez
- Jacob Andreas
- Language and Intelligence Group
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Computer science and technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Human-computer interaction
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Demystifying machine-learning systems
AI agents help explain other AI systems

3 Questions: Jacob Andreas on large language models

Solving a machine-learning mystery
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Designing solutions to ensure equity in health care
Read full story →

Training manufacturing technologists to be future shop floor leaders
Characterizing social networks

MIT economics to launch new predoctoral fellowship program
Programming functional fabrics
Does technology help or hurt employment?
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
https://www.nist.gov/publications/legacy-charlotte-moore-sitterly-internet-age
Legacy of Charlotte Moore Sitterly in the Internet Age
Download paper, additional citation formats.
- Google Scholar

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. From one place, you can search across many disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court ...
Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual. Try it for select papers. Learn More. Semantic Scholar uses groundbreaking AI and engineering to understand the semantics of scientific literature to help Scholars discover relevant research.
Keep up to date with health and medical developments to stimulate research and improve patient care. Search our books and journals covering education, reference information, decision support and more. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (English Edition), Volume 111, Issue 4. Resuscitation, Volume 83, Issue 11. FEBS Letters, Volume 584, Issue 9.
Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, helping to turn the promise of a 'research commons' into a reality. The aggregation services that CORE provides therefore make a very valuable contribution to the evolving open access environment in the UK. Show all.
Browse, search, and explore journals indexed in the Web of Science. The Master Journal List is an invaluable tool to help you to find the right journal for your needs across multiple indices hosted on the Web of Science platform. Spanning all disciplines and regions, Web of Science Core Collection is at the heart of the Web of Science platform. Curated with care by an expert team of in-house ...
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
Accelerating research discovery to shape a better future . ... Search the Wiley Online Library Search term. Advanced Search. 1,700+ Journals 260+ Reference Works. 27,000+ Online Books Resources Researchers Researchers ... Submit a paper; Track your article; Learn about Open Access; Subjects Agriculture, Aquaculture & Food Science ...
With Connected Papers you can just search and visually discover important recent papers. No need to keep lists. Create the bibliography for your thesis Start with the references that you will definitely want in your bibliography and use Connected Papers to fill in the gaps and find the rest! Discover the most relevant prior and derivative works
Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools. Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts. Advanced Search. PDF Packages of 37 papers.
Elsevier Journal Finder helps you find journals that could be best suited for publishing your scientific article. Journal Finder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper's abstract to scientific journals.
RefSeek - Academic Search Engine. Web. Documents. Type 2 or more characters for results. Learn about: Pluto, Gravity. Browse the Reference Site Directory. Academic search engine for students and researchers. Locates relevant academic search results from web pages, books, encyclopedias, and journals.
arXiv is a free distribution service and an open-access archive for nearly 2.4 million scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics.
Search Millions of Research Papers. This fulltext search index includes over 35 million research articles and other scholarly documents preserved in the Internet Archive. The collection spans from digitized copies of eighteenth century journals through the latest Open Access conference proceedings and preprints crawled from the World Wide Web.
Make an impact and build your research profile in the open with ScienceOpen. Search and discover relevant research in over 93 million Open Access articles and article records; Share your expertise and get credit by publicly reviewing any article; Publish your poster or preprint and track usage and impact with article- and author-level metrics; Create a topical Collection to advance your ...
Design, synthesis and bioactivity study on oxygen-heterocyclic-based pyran analogues as effective P -glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance in MCF-7/ADR cell. Ashraf H. F. Abd El-Wahab. Rita M ...
ERIC is an online library of education research and information, sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education.
Scinapse Trends. Paper Search. Collections. Favorites. History. Submit Feedback. Presenting a whole new perspective on research discovery services. Intelligent data and quick access to state-of-the-art insights.
Our working paper series disseminates economic research relevant to the various tasks and functions of the ECB, and provides a conceptual and empirical basis for policy-making.The working papers constitute "work in progress". They are published to stimulate discussion and contribute to the advancement of our knowledge of economic matters.
The study was conducted while Collins was on the faculty at the University of Washington. The paper was written by an international, interdisciplinary team, including citiesRISE, a global nonprofit that works to transform mental health policy and practice in cities, especially for young people. Cities have long been a draw for young people.
A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 6, entitled, "Altered brain morphology ...
Reference resolution is an important problem, one that is essential to understand and successfully handle context of different kinds. This context includes both previous turns and context that pertains to non-conversational entities, such as entities on the user's screen or those running in the background. While LLMs have been shown to be extremely powerful for a variety of tasks, their use in ...
The integration and deployment of large language model (LLM)-based intelligent agents have been fraught with challenges that compromise their efficiency and efficacy. Among these issues are sub-optimal scheduling and resource allocation of agent requests over the LLM, the difficulties in maintaining context during interactions between agent and LLM, and the complexities inherent in integrating ...
The research will be presented at the International Conference on Learning Representations. Finding facts. Most large language models, also called transformer models, are neural networks. Loosely based on the human brain, neural networks contain billions of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that are grouped into many layers, and which encode ...
Abstract Most (yet not all) results of atomic physics research of Charlotte Moore Sitterly (CMS), which was closely connected to astrophysics, are now incorporated in online databases, one of which is the Atomic Spectra Database of the National Institute of Standards and Technology.