Science Essay

Learn How to Write an A+ Science Essay
11 min read

People also read
150+ Engaging Science Essay Topics To Hook Your Readers
8 Impressive Science Essay Examples for Students
Science Fiction Essay: Examples & Easy Steps Guide
Essay About Science and Technology| Tips & Examples
Essay About Science in Everyday Life - Samples & Writing Tips
Check Out 5 Impressive Essay About Science Fair Examples
Did you ever imagine that essay writing was just for students in the Humanities? Well, think again!
For science students, tackling a science essay might seem challenging, as it not only demands a deep understanding of the subject but also strong writing skills.
However, fret not because we've got your back!
With the right steps and tips, you can write an engaging and informative science essay easily!
This blog will take you through all the important steps of writing a science essay, from choosing a topic to presenting the final work.
So, let's get into it!
- 1. What Is a Science Essay?
- 2. How To Write a Science Essay?
- 3. How to Structure a Science Essay?
- 4. Science Essay Examples
- 5. How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
- 6. Science Essay Topics
- 7. Science Essay Writing Tips
What Is a Science Essay?
A science essay is an academic paper focusing on a scientific topic from physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific field.
Science essays are mostly expository. That is, they require you to explain your chosen topic in detail. However, they can also be descriptive and exploratory.
A descriptive science essay aims to describe a certain scientific phenomenon according to established knowledge.
On the other hand, the exploratory science essay requires you to go beyond the current theories and explore new interpretations.
So before you set out to write your essay, always check out the instructions given by your instructor. Whether a science essay is expository or exploratory must be clear from the start. Or, if you face any difficulty, you can take help from a science essay writer as well.
Moreover, check out this video to understand scientific writing in detail.
Now that you know what it is, let's look at the steps you need to take to write a science essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Write a Science Essay?
Writing a science essay is not as complex as it may seem. All you need to do is follow the right steps to create an impressive piece of work that meets the assigned criteria.
Here's what you need to do:
Choose Your Topic
A good topic forms the foundation for an engaging and well-written essay. Therefore, you should ensure that you pick something interesting or relevant to your field of study.
To choose a good topic, you can brainstorm ideas relating to the subject matter. You may also find inspiration from other science essays or articles about the same topic.
Conduct Research
Once you have chosen your topic, start researching it thoroughly to develop a strong argument or discussion in your essay.
Make sure you use reliable sources and cite them properly . You should also make notes while conducting your research so that you can reference them easily when writing the essay. Or, you can get expert assistance from an essay writing service to manage your citations.
Create an Outline
A good essay outline helps to organize the ideas in your paper. It serves as a guide throughout the writing process and ensures you don’t miss out on important points.
An outline makes it easier to write a well-structured paper that flows logically. It should be detailed enough to guide you through the entire writing process.
However, your outline should be flexible, and it's sometimes better to change it along the way to improve your structure.
Start Writing
Once you have a good outline, start writing the essay by following your plan.
The first step in writing any essay is to draft it. This means putting your thoughts down on paper in a rough form without worrying about grammar or spelling mistakes.
So begin your essay by introducing the topic, then carefully explain it using evidence and examples to support your argument.
Don't worry if your first draft isn't perfect - it's just the starting point!
Proofread & Edit
After finishing your first draft, take time to proofread and edit it for grammar and spelling mistakes.
Proofreading is the process of checking for grammatical mistakes. It should be done after you have finished writing your essay.
Editing, on the other hand, involves reviewing the structure and organization of your essay and its content. It should be done before you submit your final work.
Both proofreading and editing are essential for producing a high-quality essay. Make sure to give yourself enough time to do them properly!
After revising the essay, you should format it according to the guidelines given by your instructor. This could involve using a specific font size, page margins, or citation style.
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified.
In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA , Chicago , or Harvard . Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your essay looks professional.
Following these steps will help you create an informative and well-structured science essay that meets the given criteria.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Structure a Science Essay?
A basic science essay structure includes an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Let's look at each of these briefly.
- Introduction
Your essay introduction should introduce your topic and provide a brief overview of what you will discuss in the essay. It should also state your thesis or main argument.
For instance, a thesis statement for a science essay could be,
"The human body is capable of incredible feats, as evidenced by the many athletes who have competed in the Olympic games."
The body of your essay will contain the bulk of your argument or discussion. It should be divided into paragraphs, each discussing a different point.
For instance, imagine you were writing about sports and the human body.
Your first paragraph can discuss the physical capabilities of the human body.
The second paragraph may be about the physical benefits of competing in sports.
Similarly, in the third paragraph, you can present one or two case studies of specific athletes to support your point.
Once you have explained all your points in the body, it’s time to conclude the essay.
Your essay conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and leave the reader with a sense of closure.
In the conclusion, you reiterate your thesis and sum up your arguments. You can also suggest implications or potential applications of the ideas discussed in the essay.
By following this structure, you will create a well-organized essay.
Check out a few example essays to see this structure in practice.
Science Essay Examples
A great way to get inspired when writing a science essay is to look at other examples of successful essays written by others.
Here are some examples that will give you an idea of how to write your essay.
Science Essay About Genetics - Science Essay Example
Environmental Science Essay Example | PDF Sample
The Science of Nanotechnology
Science, Non-Science, and Pseudo-Science
The Science Of Science Education
Science in our Daily Lives
Short Science Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a short science essay:
Want to read more essay examples? Here, you can find more science essay examples to learn from.
How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
Choosing the right science essay topic is a critical first step in crafting a compelling and engaging essay. Here's a concise guide on how to make this decision wisely:
- Consider Your Interests: Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the realm of science. Selecting a topic that genuinely fascinates you will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and motivated.
- Relevance to the Course: Ensure that your chosen topic aligns with your course or assignment requirements. Read the assignment guidelines carefully to understand the scope and focus expected by your instructor.
- Current Trends and Issues: Stay updated with the latest scientific developments and trends. Opting for a topic that addresses contemporary issues not only makes your essay relevant but also demonstrates your awareness of current events in the field.
- Narrow Down the Scope: Science is vast, so narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Instead of a broad subject like "Climate Change," consider a more specific angle like "The Impact of Melting Arctic Ice on Global Sea Levels."
- Available Resources: Ensure that there are sufficient credible sources and research materials available for your chosen topic. A lack of resources can hinder your research efforts.
- Discuss with Your Instructor: If you're uncertain about your topic choice, don't hesitate to consult your instructor or professor. They can provide valuable guidance and may even suggest specific topics based on your academic goals.
Science Essay Topics
Choosing an appropriate topic for a science essay is one of the first steps in writing a successful paper.
Here are a few science essay topics to get you started:
- How space exploration affects our daily lives?
- How has technology changed our understanding of medicine?
- Are there ethical considerations to consider when conducting scientific research?
- How does climate change affect the biodiversity of different parts of the world?
- How can artificial intelligence be used in medicine?
- What impact have vaccines had on global health?
- What is the future of renewable energy?
- How do we ensure that genetically modified organisms are safe for humans and the environment?
- The influence of social media on human behavior: A social science perspective
- What are the potential risks and benefits of stem cell therapy?
Important science topics can cover anything from space exploration to chemistry and biology. So you can choose any topic according to your interests!
Need more topics? We have gathered 100+ science essay topics to help you find a great topic!
Continue reading to find some tips to help you write a successful science essay.
Science Essay Writing Tips
Once you have chosen a topic and looked at examples, it's time to start writing the science essay.
Here are some key tips for a successful essay:
- Research thoroughly
Make sure you do extensive research before you begin writing your paper. This will ensure that the facts and figures you include are accurate and supported by reliable sources.
- Use clear language
Avoid using jargon or overly technical language when writing your essay. Plain language is easier to understand and more engaging for readers.
- Referencing
Always provide references for any information you include in your essay. This will demonstrate that you acknowledge other people's work and show that the evidence you use is credible.
Make sure to follow the basic structure of an essay and organize your thoughts into clear sections. This will improve the flow and make your essay easier to read.
- Ask someone to proofread
It’s also a good idea to get someone else to proofread your work as they may spot mistakes that you have missed.
These few tips will help ensure that your science essay is well-written and informative!
You've learned the steps to writing a successful science essay and looked at some examples and topics to get you started.
Make sure you thoroughly research, use clear language, structure your thoughts, and proofread your essay. With these tips, you’re sure to write a great science essay!
Do you still need expert help writing a science essay? Our science essay writing service is here to help. With our team of professional writers, you can rest assured that your essay will be written to the highest standards.
Contact our online writing service now to get started!
Also, do not forget to try our essay typer tool for quick and cost-free aid with your essays!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
How to Write a Scientific Essay

When writing any essay it’s important to always keep the end goal in mind. You want to produce a document that is detailed, factual, about the subject matter and most importantly to the point.
Writing scientific essays will always be slightly different to when you write an essay for say English Literature . You need to be more analytical and precise when answering your questions. To help achieve this, you need to keep three golden rules in mind.
- Analysing the question, so that you know exactly what you have to do
Planning your answer
- Writing the essay
Now, let’s look at these steps in more detail to help you fully understand how to apply the three golden rules.
Analysing the question
- Start by looking at the instruction. Essays need to be written out in continuous prose. You shouldn’t be using bullet points or writing in note form.
- If it helps to make a particular point, however, you can use a diagram providing it is relevant and adequately explained.
- Look at the topic you are required to write about. The wording of the essay title tells you what you should confine your answer to – there is no place for interesting facts about other areas.
The next step is to plan your answer. What we are going to try to do is show you how to produce an effective plan in a very short time. You need a framework to show your knowledge otherwise it is too easy to concentrate on only a few aspects.
For example, when writing an essay on biology we can divide the topic up in a number of different ways. So, if you have to answer a question like ‘Outline the main properties of life and system reproduction’
The steps for planning are simple. Firstly, define the main terms within the question that need to be addressed. Then list the properties asked for and lastly, roughly assess how many words of your word count you are going to allocate to each term.
Writing the Essay
The final step (you’re almost there), now you have your plan in place for the essay, it’s time to get it all down in black and white. Follow your plan for answering the question, making sure you stick to the word count, check your spelling and grammar and give credit where credit’s (always reference your sources).

How Tutors Breakdown Essays
An exceptional essay
- reflects the detail that could be expected from a comprehensive knowledge and understanding of relevant parts of the specification
- is free from fundamental errors
- maintains appropriate depth and accuracy throughout
- includes two or more paragraphs of material that indicates greater depth or breadth of study
A good essay
An average essay
- contains a significant amount of material that reflects the detail that could be expected from a knowledge and understanding of relevant parts of the specification.
In practice this will amount to about half the essay.
- is likely to reflect limited knowledge of some areas and to be patchy in quality
- demonstrates a good understanding of basic principles with some errors and evidence of misunderstanding
A poor essay
- contains much material which is below the level expected of a candidate who has completed the course
- Contains fundamental errors reflecting a poor grasp of basic principles and concepts
Privacy Overview
- Communicating in STEM Disciplines
- Features of Academic STEM Writing
- STEM Writing Tips
- Academic Integrity in STEM
- Strategies for Writing
- Science Writing Videos – YouTube Channel
- Educator Resources
- Lesson Plans, Activities and Assignments
- Strategies for Teaching Writing
- Grading Techniques
Science Essay Writing (First-Year Undergraduates)
Writing an Argumentative Science Essay
These resources have been designed to help teach students how to write a well-structured argumentative science essay (approximately 1,250 words) over the course of a term. They will take part in four interactive in-class activity sessions (intended to last 50 – 60 min each) that each focus on a different, critical theme in writing essays, and which are designed to supplement pre-class homework readings and short activities.
Student essays can be written to address any brief. An example is:
Identify a current controversy in science that interests you. State your opinion, and present the evidence that justifies your position.
The four in-class activity sessions will help students develop their essays (see Table 1).
Table 1: The four topics that will be covered in in-class activity sessions will help students develop their essays over the term. ‘PRE’ classes refer to readings and very short activities that must be completed before they come to the in-class sessions.
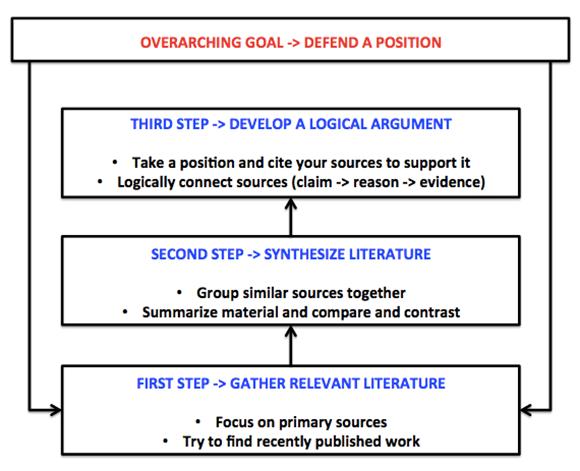
Figure 1. Essay Writing Framework
- Pre-Class Activity
- In-Class Activity
- Activity Solutions
The Fundamental Components of a Good Essay Structure
A good essay requires a good structure; it needs to be clear and concise, and it needs to integrate ‘signposts’ throughout so that a reader is able to follow the logical argument that the author is making. There is no room for an author’s thoughts to wander away from the purpose of the essay, because such misdirection will lead to the reader becoming confused. To stop this confusion arising, various writing and reading conventions have developed over time. One of these conventions is the internal structure of an academic essay.
This internal structure resembles an ‘ ɪ ’ shape. The top horizontal bar represents the thesis , or part of the essay that will comprise a thesis statement and one or more development statements. The thesis statement is the claim of the argument presented in the essay. Without this, the reader would not know what to expect the rest of the essay to develop. The development statement(s) are also crucial as they tells a reader which points will be used to support the argument, and also which order they will be presented in. If some of these points are not listed – or presented in a different order to the one stated – the reader might fail to understand the author’s intent, or even discount the steps used to support the argument.
The vertical bar of the ‘ ɪ ’ represents the main body of the essay, where each of the points presented in the development part of the thesis should be presented and discussed. Examples and references (citations) are generally included in these paragraphs, but it is important to note that each paragraph should contain only one main idea with examples or references that justify it. This main idea should be presented in a topic sentence at the beginning of the paragraph; these topic sentences act as signposts throughout the main body of the essay.
The bottom horizontal bar of the ‘ ɪ ’ represents the summary/conclusion of the essay. Here the thesis (main claim) and pieces of supporting evidence (different points that developed the argument) are restated briefly to show the reader why/how everything fits together. No new information should be added to the essay at this point.
** Materials adapted from those provided by Joanne Nakonechny, UBC Skylight **
Thesis and Development Statements Recap:
How to write a good thesis statement
Your defining sentence/sentences must clearly state the main idea of your writing. You must include the subject you will discuss and the points that you will make about that subject in the order in which you will write about them.
The value of development statements
These list the different reasons (which will be accompanied with evidence) that the writer is going to use to support his/her claim. These narrowed or more focused points provide the steps of the argument to establish the validity of the thesis statement.
Note that if these reasons are too broad, the essay will be vague, because not all aspects of them can be addressed.
Vague development example:
“Science can solve starvation, disease and crime.”
Stronger development example:
“Science, through genetically modified foods and better crop fertilizers, can contribute to solving starvation.”
Note that this second example provides the reader with information about the specific steps the writer is going to use to support the thesis that science can contribute to solving starvation; genetically modified foods and better crop fertilizers are the reasons that the author is going to expand on to support his/her claim that science can contribute to solving starvation.
Activity 1 (complete before the in-class session)
Throughout these classes, you will develop an argumentative essay in which you state a clear thesis, make claims and supply reasons and evidence to support these reasons, and write a sound conclusion. To begin with, you must:
- Identify a current controversy in science that interests you.
- State your opinion and some of the reasons that you can use as evidence to support your position.
- Come to class prepared to speak about these with a partner.
The Fundamentals of a Good Essay Structure [In-Class Session]
Activity 1 (5 minutes)
Produce short written responses that show:
- One idea in the reading that you already use in your essay writing
- One idea in the reading that you will now use in your essay writing
Activity 2 (10 minutes)
Take part in a class discussion about the structure that a good essay should take. Specifically, think about and discuss:
#What is a thesis statement? #What are development statements? How are they linked to the thesis statement? #What is the purpose of these parts of an essay? #How should the main body of an essay be organized? #What is a topic sentence? Is it the same as a development statement? #What sort of information should appear in the conclusion to an essay?
Activity 3 (10 minutes)
As a general rule, thesis statements in many essays are too general, which means it is not possible for the author to fully address them with reasons and evidence in his/her writing. Stronger thesis statements should provide narrowed or more focused points.
Rank the following four thesis statements (from best to worst) and justify your decisions:
Activity 4 (15 minutes)
In the homework, you were asked to identify a current controversy in science that interests you, and to state your opinion and think of some of the reasons that you could use to support your position.
Choose a partner and briefly speak to them about this (you should both aim to have spoken about your interests and opinions within five minutes).
Now, in the next five minutes, try to write a thesis statement and one or more development statements that you will use to begin your argumentative essay.
And, in the last five minutes, talk to your partner about your thesis statement and development statement(s) and see if you can help each other improve them.
Hint: Are your statements too broad/vague, and do they list enough reasons that you will use to support the main claim made in the thesis statement. Re-writing a thesis statement can take some time, but revision is an important part of the writing process. Try to settle on a good thesis and development statement by the next class but don’t rush things – in many ways, these are the most important parts of an essay.
The suggested solutions of these activities require a password for access. We encourage interested instructors to contact Dr. Jackie Stewart and the ScWRL team to obtain access. Please fill out the Access Request and Feedback Form to inquire about resources you are interested in.
Click here for suggested solutions password protected page for: Activity solutions
Searching the Literature and Including Citations and References
Effective Searching
For tips on how to search the literature effectively, to find useful material that could support the development of your essay, and on how to integrate these into your essay, we advise you to read our guides here and here .
Avoiding Plagiarism
Before coming to class, we also ask you to read the following information about plagiarism, so that you know how to identify the different types – and, more importantly, avoid them in your own writing; after all, it is your responsibility to know what plagiarism is and how to avoid it.
To start, review the information in this website link: http://help.library.ubc.ca/planning-your-research/academic-integrity-plagiarism/ , before reading more at this one: http://learningcommons.ubc.ca/resource-guides/avoiding-plagiarism/
You should come to class with an idea about how to avoid each of the three types of plagiarism noted here, ready to participate in a discussion about the main issues. Make some brief notes if you feel they will help you.
Identifying Different Types of Sources
Read the following website link to learn how to differentiate between different types of sources and evaluate how appropriate and useful they are for your essay here: http://help.library.ubc.ca/evaluating-and-citing-sources/evaluating-information-sources/ Make sure you read the information about ‘Primary Sources’ and the related link to ‘Learn about finding…’.
You are also encouraged to watch the following Grammar Squirrel videos to help you solidify these concepts:
- Citing Sources in Science Writing
Make some brief notes on the main differences between primary, secondary and tertiary resources and come to class ready to discuss these.
Searching the Literature
To help you start gathering material for your essay, you should start searching for appropriate literature to support your thesis and the reasons that you are going to develop in the main body of your writing. For a guide on how best to do this, see here .
Before class, find one example of each of primary, secondary and tertiary sources that relate to your essay. On a single sheet of paper, for each resource, write notes on the following, and bring these with you to the in-class session.
- Is this a primary, secondary or tertiary source? Why?
- How might you use this resource in your essay?
For your homework, you were asked to review information about the three main types of plagiarism, and how these can be avoided. You were also asked to read information and watch videos about identifying different types of sources.
Activity 1 (10 minutes)
Take part in a discussion with your classmates and instructor(s) about the three main types of plagiarism. What are they? Have you ever committed any of these before without realizing? How can you avoid plagiarism in your essays?
Activity 2 (15 minutes)
First, take part in a brief discussion with your classmates and instructor(s) about the differences between primary, secondary and tertiary sources. Why are primary sources usually preferred for use in essays and scholarly writing? Are any tertiary sources useful or reliable? Why/why not?
Second, form groups of 4-6 people, and take turns to fill out a table of primary, secondary, and tertiary sources that you each found to support the development of your essays.
When filling out the second column (How might you use this?) , think about how the information contained in this source applies to the scientific controversy that you are writing about; specifically, try to outline how you could use this source to provide a reason and evidence to support the thesis of your argument. You should explain this to your classmates as you fill in the table.
Take part in a discussion with all of your classmates and instructor(s) about the sources that you found. Are they suitable for inclusion in your essays? Why/why not? How are you going to find more sources to help add content depth to your essays?
Activity 4 (10 minutes)
Work with a partner to try to paraphrase some of the information in one of your sources (preferably your primary source); remember the video you watched before class about integrating sources in your work – it is important in science essays to reword what has been written in a source and then attribute the idea to the author(s) of that source.
For now, try to just reword the key information so that it could be included in the main body of your essay. For a more complete guide to attributing the information to the author(s) of the source from which it came, please read the following if you have not already done so: Integrating and Citing Sources .
It is important that you learn the correct format for including citations in your essay, and for compiling the references list at the end.
Click here for suggested solutions password protected page for: Activity Solutions
Paragraph Structure, Topic Sentences and Transitions
Good essays are easy to read and follow a logical development. Structuring the content of your essay in an organized way is thus critical to making sure your reader(s) understand the argument you are making. Even the most content-rich essay can be misinterpreted if it is not structured properly.
A good structure relies upon effective paragraphing. You should try to only include one main content point per paragraph, even if this means some paragraphs are much smaller than others; the key when writing an essay that defends a thesis statement is to use one paragraph for each reason that you present to provide support for your main claim.
Once you have split your essay into discrete paragraphs, you should add in topic sentences to begin each one; these sentences should act as signposts for your reader(s), telling them clearly and succinctly what they can expect to read about in the following paragraph. You can think of them as mini development statements that map the logical development of your essay from paragraph to paragraph.
Finally, you should add in transitions (little words and phrases) that link each sentence together smoothly and make everything easy to read. Words such as ‘initially’, ‘secondly’, ‘however’, ‘furthermore’ and ‘lastly,’ and phrases such as ‘as a result’, ‘on the other hand’ and ‘in addition’ are typical examples that you probably already use on a day-to-day basis.
For more information on effective paragraphing, we advise you to read the following student guide before coming to class: Organizing
Think about the different elements that make a piece of writing effective, and come to class prepared to discuss some of these.
Also, make sure that you bring at least two primary sources that you have found to use in your essay; you will work on writing paragraphs about these with a partner in class.
To prepare you for this class, you should have read the student guide about organizing your writing (how to paragraph effectively). Remember that you must present your essay in a logical way if it is to be interpreted as you mean it to be by your reader(s). A big part of this is invested in writing paragraphs that each present one main idea.
Take part in a class discussion by thinking about the following question: “What makes a good piece of writing?” Hint: Think of as many things as possible (not just those that relate to paragraphing, and structure).
Your instructor will brainstorm the class ideas on the blackboard/whiteboard, but you should do the same so that you can refer to your notes later.
Activity 2 (25 minutes)
Take out the sources that you brought with you (which relate to the current scientific controversy that you are going to discuss in your essay); you should have brought at least two, and these should preferably be primary sources.
Take 10 minutes to write a paragraph about each one so that it could fit into the essay you are writing. Use the brainstorm/notes you took from Activity 1 to help guide your writing. Do not worry too much about writing long paragraphs at this point, but try to make sure you only talk in depth about the one main point of the source you are using in each one.
In the remaining five minutes, try to write a topic sentence for each paragraph; remember that this should act as a mini development statement (or a signpost) that tells a reader what they can expect to read about in the coming paragraph. Lastly, try to add some transition words/phrases to link all the sentences smoothly together.
Make sure you include a citation for your sources (at least one per paragraph)
Activity 3 (15 minutes)
Swap your writing with a partner, and read each other’s work. In the first 10 minutes, make notes on their writing (being constructive) that will help them improve it. Some things to focus on include:
- Is there only one main point per paragraph?
- Does each topic sentence serve as a good signpost? Is it clear from this one sentence alone what the author is going to talk about in that paragraph?
- Does each sentence transition smoothly into the next one?
- Are any of the transition words/phrases confusing?
- Does the writing follow a logical path?
- Are there any confusing terms used (overly complex words, or science jargon)?
- Are the citations formatted correctly?
For the last five minutes, you should take your piece of writing back and begin to improve it based on the feedback your partner gave you. If you do not finish all of these improvements by the end of class, you should complete them as homework; you should try to complete a first draft of your essay soon after this class anyway.
The Importance of Peer Review
When a researcher, or team of researchers, finishes a stage of work, they usually write a paper presenting their methods, findings and conclusions. They then send the paper to a scientific journal to be considered for publication. If the journal’s editor thinks it is suitable for their journal he/she will send the paper to other scientists, who research and publish in the same field and ask them to:
- Comment on its validity – are the research results credible; is the design and methodology appropriate?
- Judge the significance – is it an important finding?
- Determine its originality – are the results new? Does the paper refer properly to work performed by others?
- Give an opinion as to whether the paper should be published, improved or rejected (usually to be submitted elsewhere).
This process is called peer review, and it is incredibly important in making sure that only high-quality written work appears in the literature , but it also allows authors to improve their original work based on the feedback of others.
Did you know?
There are around 21,000 scholarly and scientific journals that use the peer-review system. A high proportion of these are scientific, technical or medical journals, which together publish over 1,000,000 research papers each year.
By the way...
Peer review is also used to assess scientists’ applications for research funds. Funding bodies, such as medical research charities, seek expert advice on a scientist’s proposal before agreeing to pay for it. Peer review in this instance is used to judge which applications have the best potential to help an organization achieve its objectives.
Peer Review – Your Essay
You are not reporting the results of experiments in a journal article or applying for funding, but are writing an essay about a current controversy in science that interests you.
The process of peer review that you will undertake is very similar, however; by hearing what your peers think about your work before you hand it in, you should gain a valuable insight into how they interpret it, and where they think it can be improved. If you make suggested improvements, it is very likely that it will receive a higher grade when you hand it to your instructors.
You already have some experience of the peer-review system, because you provided feedback on a partner’s two paragraphs in the last class, and had them provide you with feedback on your own writing.
For some further tips on how to give effective feedback, make sure you read the following guide before coming to class: How to Give and Receive Effective Feedback , and arrive ready to participate in a discussion about peer review and its importance.
Make sure you also bring a draft of your essay to class; you will be working with a partner to provide feedback on these essays.
Peer review ensures that only high-quality work appears in the science literature; it also allows a writer to improve his/her work based on feedback provided by someone within his/her field. Today you will get the chance to provide constructive feedback on someone else’s essay, while having them comment on yours. This exchange should help you improve your work greatly.
Take part in a class discussion about peer review and its importance. Some specific questions to think about include:
- What would happen if scientists didn't have their work reviewed by their peers?
- Are they any downsides? What happens if there is a disagreement?
- What sort of feedback is the best to give/receive?
Activity 2 (30 minutes)
Choose a partner (preferably someone you haven’t worked with before) and swap your essay drafts. First of all, read through their essay in its entirety before going back and reading it in smaller chunks. Comment on it by annotating the work where you are confused, or where you think improvements can be made. Rather than editing it, suggest other options that would lead to improvements (e.g. don’t make the improvements yourself).
Pay extra attention to the most important elements that dictate whether an essay has a good structure and reads well:
- Are the thesis and development statements clear? Are they too narrow or too broad?
- Is the work split up into paragraphs that focus on one main point each?
- Does the essay follow a logical path of development? Do the reasons that are supplied to support the original thesis follow the order that they were set out in the original development statement(s)?
- Are topic sentences used effectively so that someone who was lost (just started reading halfway through) would understand the route being taken (what the author was going to elaborate on in a given paragraph)?
- Are transition words and phrases used effectively so that each sentence transitions smoothly into the next one?
- Is the conclusion clear and concise? Does the author introduce any new material here that is confusing in any way?
- Is the essay interesting? Do you feel you have learned something new? Do you agree with the thesis statement now that you have read the whole essay (have you been convinced by the author’s argument)?
Read through the comments you have received from your partner and make sure you understand them all. Once you are satisfied that you do, spend the remaining time making improvements based on their feedback. You will not be able to finish all of these in class, but you can take the feedback away with you and use it to improve your essay before handing it in.
Essay Writing Introduction
Essay Structure: Pre-Class Activity | In-Class Activity
Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism: Pre-Class Activity | In-Class Activity
Paragraphing: Pre-Class Activity | In-Class Activity
Peer Review: Pre-Class Activity | In-Class Activity
Click here for suggested solutions password protected page for: Pre-class activity and In-class activity solutions

- For Authors
- Collaboration
- Privacy Policy

- Conferences & Symposiums
Tools & Methods
How to successfully write a scientific essay.
Posted by Cody Rhodes
If you are undertaking a course which relates to science, you are more or less apt to write an essay on science. You need to know how to write a science essay irrespective of whether your professor gives you a topic or you come up with one. Additionally, you need to have an end objective in mind. Writing a science essay necessitates that you produce an article which has all the details and facts about the subject matter and it ought to be to the point. Also, you need to know and understand that science essays are more or less different from other types of essays. They require you to be analytical and precise when answering questions. Hence, this can be quite challenging and tiresome. However, that should not deter you from learning how to write your paper. You can always inquire for pre-written research papers for sale from writing services like EssayZoo.
Also, you can read other people’s articles and find out how they produce and develop unique and high-quality papers. Moreover, this will help you understand how to approach your essays in different ways. Nonetheless, if you want to learn how to write a scientific paper in a successful manner, consider the following tips.

Select a topic for your article Like any other type of essay, you need to have a topic before you start the actual writing process. Your professor or instructor may give you a science essay topic to write about or ask you to come up with yours. When selecting a topic for your paper, ensure that you choose one you can write about. Do not pick a complex topic which can make the writing process boring and infuriating for you. Instead, choose one that you are familiar with. Select a topic you will not struggle gathering information about. Also, you need to have an interest in it. If you are unable to come up with a good topic, trying reading other people’s articles. This will help you develop a topic with ease.
Draft a plan After selecting a topic, the next step is drafting a plan or an outline. An outline is fundamental in writing a scientific essay as it is the foundation on which your paper is built. Additionally, it acts as a road map for your article. Hence, you need to incorporate all the thoughts and ideas you will include in your essay in the outline. You need to know what you will include in the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Drafting a plan helps you save a lot of time when writing your paper. Also, it helps you to keep track of the primary objective of your article.
Start writing the article After drafting a plan, you can begin the writing process. Writing your paper will be smooth and easier as you have an outline which helps simplify the writing process. When writing your article, begin with a strong hook for your introduction. Dictate the direction your paper will take. Provide some background information and state the issue you will discuss as well as the solutions you have come up with. Arrange the body of your article according to the essay structure you will use to guide you. Also, ensure that you use transitory sentences to show the relationship between the paragraphs of your article. Conclude your essay by summarizing all the key points. Also, highlight the practical potential of our findings and their impacts.
Proofread and check for errors in the paper Before submitting or forwarding your article, it is fundamental that you proofread and correct all the errors that you come across. Delivering a paper that is full of mistakes can affect your overall performance in a negative manner. Thus, it is essential you revise your paper and check for errors. Correct all of them. Ask a friend to proofread your paper. He or she may spot some of the mistakes you did not come across.
In conclusion, writing a scientific essay differs from writing other types of papers. A scientific essay requires you to produce an article which has all the information and facts about the subject matter and it ought to be to the point. Nonetheless, the scientific essay formats similar to the format of any other essay: introduction, body, and conclusion. You need to use your outline to guide you through the writing process. To learn how to write a scientific essay in a successful manner, consider the tips above.

Related Articles:
One response to how to successfully write a scientific essay.
Hai…you have posted great article, it really helpful to us.. I will refer this page to my friends; I hope you will like to read – scientific research paper writing service
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Top Keywords
Diabetes | Alzheimer’s disease Cancer | Breast cancer | Tumor Blood pressure | Heart Brain | Kidney | Liver | Lung Stress | Pain | Therapy Infection | Inflammation | Injury DNA | RNA | Receptor | Nanoparticles Bacteria | Virus | Plant
See more …

Proofread or Perish: Editing your scientific writing for successful publication

Lab Leader makes software applications for experiment design in life science

Cyagen Biosciences – Helping you choose the right animal model for your research
Labcollector lims and eln for improving productivity in the lab.

Image Cytometer – NucleoCounter® NC-3000™
Recent posts.
- Sleep abnormalities in different clinical stages of psychosis
- A compact high yield isotope enrichment system
- Late second trimester miscarriages
- Making Christmas trees under duress, or how cells regulate the production of ribosomal RNA
- Rabbits with mammary carcinomas as a model for comparative pathology and translational science in breast cancer research

School of Biological Sciences
University of Manchester
Tutorial – Appendix 2: A Practical Guide to Writing Essays – Level 1
Appendix 2: a practical guide to writing essays.

Writing an essay is a big task that will be easier to manage if you break it down into five main tasks as shown below:
An essay-writing Model in 5 steps
- Analyse the question
What is the topic?
What are the key verbs?
Question the question—brainstorm and probe
What information do you need?
How are you going to find information?
Find the information
Make notes and/or mind maps
- Plan and sort
Arrange information in a logical structure
Plan sections and paragraphs
Introduction and conclusion
- Edit (and proofread)
For sense and logical flow
For grammar and spelling
My Learning Essentials offers a number of online resources and workshops that will help you to, understand the importance of referencing your sources, use appropriate language and style in your writing, write and proofread your essays. For more information visit the writing skills My Learning Essentials pages: http://www.library.manchester.ac.uk/services-and-support/students/support-for-your-studies/my-learning-essentials/
1. Analyse the question
Many students write great essays — but not on the topic they were asked about. First, look at the main idea or topic in the question. What are you going to be writing about? Next, look at the verb in the question — the action word. This verb, or action word, is asking you to do something with the topic.
Here are some common verbs or action words and explanations:
2. Research
Once you have analysed the question, start thinking about what you need to find out. It’s better and more efficient to have a clear focus for your research than to go straight to the library and look through lots of books that may not be relevant.
Start by asking yourself, ‘What do I need to find out?’ Put your ideas down on paper. A mind map is a good way to do this. Useful questions to start focusing your research are: What? Why? When? How? Where? Who?
My Learning Essentials offer a number of online resources and workshops to help you to plan your research. Visit the My Learning Essentials page: http://www.library.manchester.ac.uk/services-and-support/students/support-for-your-studies/my-learning-essentials/workshops-and-online-resources/
3. Plan and sort
First, scan through your source . Find out if there’s any relevant information in what you are reading. If you’re reading a book, look at the contents page, any headings, and the index. Stick a Post-It note on useful pages.
Next, read for detail . Read the text to get the information you want. Start by skimming your eyes over the page to pick our relevant headings, summaries, words. If it’s useful, make notes.
Making notes
There are two rules when you are making notes:
- page reference
- date of publication
- publisher’s name (book)
- place where it was published (book or journal)
- the journal number, volume and date (journal)
- Make brief notes rather than copy text, but if you feel an extract is very valuable put it in quotation marks so that when you write your essay, you’ll know that you have to put it in your own words. Failing to rewrite the text in your own words would be plagiarism.
For more information on plagiarism, refer to the semester 1 section of this handbook, the First Level Handbook, and the My Learning Essentials Plagiarism Resource http://libassets.manchester.ac.uk/mle/avoiding-plagiarism/
Everyone will make notes differently and as it suits them. However, the aim of making notes when you are researching an essay is to use them when you write the essay. It is therefore important that you can:
- Read your notes
- Find their source
- Determine what the topics and main points are on each note (highlight the main ideas, key points or headings).
- Compose your notes so you can move bits of information around later when you have to sort your notes into an essay.
For example:
- Write/type in chunks (one topic for one chunk) with a space between them so you can cut your notes up later, or
- write the main topics or questions you want to answer on separate pieces of paper before you start making notes. As you find relevant information, write it on the appropriate page. (This takes longer as you have to write the source down a number of times, but it does mean you have ordered your notes into headings.)
Sort information into essay plans
You’ve got lots of information now: how do you put it all together to make an essay that makes sense? As there are many ways to sort out a huge heap of clothes (type of clothes, colour, size, fabric…), there are many ways of sorting information. Whichever method you use, you are looking for ways to arrange the information into groups and to order the groups into a logical sequence . You need to play around with your notes until you find a pattern that seems right and will answer the question.
- Find the main points in your notes, put them on a separate page – a mind map is a good way to do this – and see if your main points form any patterns or groups.
- Is there a logical order? Does one thing have to come after another? Do points relate to one another somehow? Think about how you could link the points.
- Using the information above, draw your essay plan. You could draw a picture, a mind map, a flow chart or whatever you want. Or you could build a structure by using bits of card that you can move around.
- Select and put the relevant notes into the appropriate group so you are ready to start writing your first draft.
The essay has four main parts:
- introduction
- references.
People usually write the introduction and conclusion after they have written the main body of the essay, so we have covered the essay components in that order below.
For more information on essay writing visit the My Learning Essentials web pages:
http://www.library.manchester.ac.uk/services-and-support/students/support-for-your-studies/my-learning-essentials/workshops-and-online-resources/?level=3&level1Link=3&level2Links=writing
Structure . The main body should have a clear structure. Depending on the length of the essay, you may have just a series of paragraphs, or sections with headings, or possibly even subsections. In the latter case, make sure that the hierarchy of headings is obvious so that the reader doesn’t get lost.
Flow . The main body of the essay answers the question and flows logically from one key point to another (each point needs to be backed up by evidence [experiments, research, texts, interviews, etc …] that must be referenced). You should normally write one main idea per paragraph and the main ideas in your essay should be linked or ‘signposted’. Signposts show readers where they are going, so they don’t get lost. This lets the reader know how you are going to tackle the idea, or how one idea is linked with the one before it or after it.
Some signpost words and phrases are:
- ‘These changes . . . “
- ‘Such developments
- ‘This
- ‘In the first few paragraphs . . . “
- ‘I will look in turn at. . . ‘
- ‘However, . . . “
- ‘Similarly’
- ‘But’.
Figures: purpose . You should try to include tables, diagrams, and perhaps photographs in your essay. Tables are valuable for summarising information, and are most likely to impress if they show the results of relevant experimental data. Diagrams enable the reader to visualise things, replacing the need for lengthy descriptions. Photographs must be selected with care, to show something meaningful. Nobody will be impressed by a picture of a giraffe – we all know what one looks like, so the picture would be mere decoration. But a detailed picture of a giraffe’s markings might be useful if it illustrates a key point.
Figures: labelling, legends and acknowledgment . Whenever you use a table, diagram or image in your essay you must:
- cite the source
- write a legend (a small box of text that describes the content of the figure).
- make sure that the legend and explanation are adapted to your purpose.
For example: Figure 1. The pathway of synthesis of the amino acid alanine, showing… From Bloggs (1989). [When using a figure originally produced by someone else, never use the original legend, because it is likely to have a different Figure number and to have information that is not relevant for your purposes. Also, make sure that you explain any abbreviations or other symbols that your reader needs to know about the Figure, including details of different colours if they are used to highlight certain aspects of the Figure].
Checklist for the main body of text
- Does your text have a clear structure?
- Does the text follow a logical sequence so that the argument flows?
- Does your text have both breadth and depth – i.e. general coverage of the major issues with in-depth treatment of particularly important points?
- Does your text include some illustrative experimental results?
- Have you chosen the diagrams or photographs carefully to provide information and understanding, or are the illustrations merely decorative?
- Are your figures acknowledged properly? Did you label them and include legend and explanation?
Introduction
The introduction comes at the start of the essay and sets the scene for the reader. It usually defines clearly the subject you will address (e.g. the adaptations of organisms to cold environments), how you will address this subject (e.g. by using examples drawn principally from the Arctic zone) and what you will show or argue (e.g. that all types of organism, from microbes through to mammals, have specific adaptations that fit them for life in cold environments). The length of an introduction depends on the length of your essay, but is usually between 50 to 200 words.
Remember that reading the introduction constitutes the first impression on your reader (i.e. your assessor). Therefore, it should be the last section that you revise at the editing stage, making sure that it leads the reader clearly into the details of the subject you have covered and that it is completely free of typos and spelling mistakes.
Check-list for the Introduction
- Does your introduction start logically by telling the reader what the essay is about – for example, the various adaptations to habitat in the bear family?
- Does your introduction outline how you will address this topic – for example, by an overview of the habitats of bears, followed by in-depth treatment of some specific adaptations?
- Is it free of typos and spelling mistakes?
Conclusion
An essay needs a conclusion. Like the introduction, this need not be long: 50 to 200 words is sufficient, depending on the length of the essay. It should draw the information together and, ideally, place it in a broader context by personalising the findings, stating an opinion or supporting a further direction which may follow on from the topic. The conclusion should not introduce facts in addition to those in the main body.
Check-list for the Conclusion
- Does your conclusion sum up what was said in the main body?
- If the title of the essay was a question, did you give a clear answer in the conclusion?
- Does your conclusion state your personal opinion on the topic or its future development or further work that needs to be done? Does it show that you are thinking further?
In all scientific writing you are expected to cite your main sources of information. Scientific journals have their own preferred (usually obligatory) method of doing this. The piece of text below shows how you can cite work in an essay, dissertation or thesis. Then you supply an alphabetical list of references at the end of the essay. The Harvard style of referencing adopted at the University of Manchester will be covered in the Writing and Referencing Skills unit in semester 2. For more information refer to the Referencing Guide from the University Library (http://subjects.library.manchester.ac.uk/referencing/referencing-harvard).
Citations in the text
Jones and Smith (1999) showed that the ribosomal RNA of fungi differs from that of slime moulds. This challenged the previous assumption that slime moulds are part of the fungal kingdom (Toby and Dean, 1987). However, according to Bloggs et al . (1999) the slime moulds can still be accommodated in the fungal kingdom for convenience. Slime moulds are considered part of the Eucarya domain by Todar (2012).
Reference list at the end of the essay:
List the references in alphabetical order and if you have several publications written by the same author(s) in the same year, add a letter (a,b,c…) after the year to distinguish between them.
Bloggs, A.E., Biggles, N.H. and Bow, R.T. (1999). The Slime Moulds . 2 nd edn. London and New York: Academic Press.
[ Guidance: this reference is to a book. We give the names of all authors, the publication date, title, name of publisher and place of publication. Note that we referred to Bloggs et al .(1999) in the text. The term “ et al .” is an abbreviation of the Latin et alia (meaning “and others”). Note also that within the text “Bloggs et al .” is part of a sentence, so we put only the date in parentheses for the citation in the text. If you wish to cite the entire book, then no page numbers are listed. To cite a specific portion of a book, page numbers are added following the book title in the reference list (see Toby and Dean below).
Todar K. (2012) Overview Of Bacteriology. Available at: http://textbookofbacteriology.net, [Accessed 15 November 2013].
Jones, B.B. and Smith, J.O.E. (1999). Ribosomal RNA of slime moulds, Journal of Ribosomal RNA 12, 33-38.
Toby F.S. and Dean P.L. (1987). Slime moulds are part of the fungal kingdom, in Edwards A.E. and Kane Y. (eds.) The Fungal Kingdom. Luton: Osbert Publishing Co., pp. 154-180 .
EndNote: This is an electronic system for storing and retrieving references. It is very powerful and simple to use, but you must always check that the output is consistent with the instructions given in this section. EndNote will be covered (and assessed) in the Writing and Referencing Skills online unit in Semester 2 to help you research and reference your written work.
Visit the My Learning Essentials online resource for a guide to using EndNote: https://www.escholar.manchester.ac.uk/learning-objects/mle/endnote-guide/ (we recommend EndNote online if you wish to use your own computer).
Note that journals have their own house style so there will be minor differences between them, particularly in their use of punctuation, but all reference lists for the same journal will be in the same format.
First Draft
When you write your first draft, keep two things in mind:
- Length: you may lose marks if your essay is too long. Ensure therefore that your essay is within the page limit that has been set.
- Expression: don’t worry about such matters as punctuation, spelling or grammar at this stage. You can get this right at the editing stage. If you put too much time into getting these things right at the drafting stage, you will have less time to spend on thinking about the content, and you will be less willing to change it when you edit for sense and flow at the editing stage.
Writing style
The style of your essay should fit the task or the questions asked and be targeted to your reader. Just as you are careful to use the correct tone of voice and language in different situations so you must take care with your writing. Generally writing should be:
- Make sure that you write exactly what you mean in a simple way.
- Write briefly and keep to the point. Use short sentences. Make sure that the meaning of your sentences is obvious.
- Check that you would feel comfortable reading your essay if you were actually the reader.
- Make sure that you have included everything of importance. Take care to explain or define any abbreviations or specialised jargon in full before using a shortened version later. Do not use slang, colloquialisms or cliches in formal written work.
When you are editing your essay, you will need to bear in mind a number of things. The best way to do this, without forgetting something, is to edit in ‘layers’, using a check-list to make sure you have not forgotten anything.
Check-list for Style
- Tone – is it right for the purpose and the receiver?
- Clarity – is it simple, clear and easy to understand?
- Complete – have you included everything of importance?
Check-list for Sense
- Does your essay make sense?
- Does it flow logically?
- Have you got all the main points in?
- Are there bits of information that aren’t useful and need to be deleted?
- Are your main ideas in paragraphs?
- Are the paragraphs linked to one another so that the essay flows rather than jumps from one thing to another?
- Is the essay within the page limit?
Check-list for Proofreading
- Are the punctuation, grammar, spelling and format correct?
- If you have written your essay on a word-processor, run the spell check over it.
- Have you referenced all quotes and names correctly?
- Is the essay written in the correct format? (one and a half line spacing, margins at least 2.5cm all around the text, minimum font size 10 point).
School Writer in Residence
The School has three ‘Writers in Residence’ who are funded by The Royal Literary Fund.
Susan Barker – Monday and Friday
Tania Hershman – Tuesday
Katherine Clements – Wednesday and Thursday
The Writers in Residence are based in the Simon Building. Please see the BIOL10000 Blackboard site for further information about the writers’ expertise and instructions for appointment booking.
- ← Tutorial – Appendix 5: A practical guide to writing essays – Level 2
- Tutorial Guide – Employability Skills P2 – Level 2 →
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Biology library
Course: biology library > unit 1.
- Preparing to study biology
- Biology overview
What is life?
Introduction, properties of life, 1. organization, 2. metabolism, 3. homeostasis, 5. reproduction, 6. response, 7. evolution, is this the definitive list, separating living and non-living things, what counts as life is still being defined., what do you think, works cited:.
- Eveleth, R. "There Are 37.2 Trillion Cells in Your Body." Smithsonian.com. October 24, 2013. http://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/there-are-372-trillion-cells-in-your-body-4941473/?no-ist .
- Koshland, D. E. "The Seven Pillars of Life." Science 295, no. 5563 (2002): 2215-216. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1068489 .
- Mullen, L. "Defining Life: Q&A with Scientist Gerald Joyce." Space.com. August 1, 2013. http://www.space.com/22210-life-definition-gerald-joyce-interview.html .
References:
Suggestions for further reading, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

LIFE SCIENCES ESSAYS GRADE 10-12

The document provides a clear structure on how to write the essays. This document has been created from information available from the internet and it is not meant for any business purposes (FREE SUPPLY) but to help South African Life sciences Learners by gathering all the important information together. Not for market purposes only meant at assisting the Learners with a simple clear alternative in the essay writing, With a compilation of essays from Grade 12-10. You have to read the essays with understanding and never try to memorize them, as that is never part of learning. We aimed at creating independent and innovative thinkers of the south African as non-profit organization. Sources 1. I’solezwe lesiXhosa, 17 September, 2015 page 11 2. Life Sciences Academics (Facebook page), DR Marian Ross 3. http://www.testtakingpa.com/study/ 4. South African Department Basic Education Exam question papers and memorandums available from WWW.dbe.gov.za 5. Mr. Chaple's Science Class Blog http://chaplescienceclass.blogspot.com/2017/09/dnastructure.html 6. Eastern Cape Department of Education https://www.ecexams.co.za/ExaminationPapers.htm
Related Papers
Life Sciences have always been a fundamental area of science. The exponential increase in the quantity of scientific information and the rate, at which new discoveries are made, require very elaborate, interdisciplinary and up-to-date information and their understanding. This fourth edition of Life sciences, Fundamentals and practice includes extensive revisions of the previous edition. We have attempted to provide an extraordinarily large amount of information from the enormous and ever-growing field in an easily retrievable form. It is written in clear and concise language to enhance self-motivation and strategic learning skill of the students and empowering them with a mechanism to measure and analyze their abilities and the confidence of winning. We have given equal importance to text and illustrations. The fourth edition has a number of new figures to enhance understanding. At the same time, we avoid excess detail, which can obscure the main point of the figure. We have retained the design elements that have evolved through the previous editions to make the book easier to read. Sincere efforts have been made to support textual clarifications and explanations with the help of flow charts, figures and tables to make learning easy and convincing. The chapters have been supplemented with self-tests and questions so as to check one’s own level of understanding. Although the chapters of this book can be read independently of one another, they are arranged in a logical sequence. Each page is carefully laid out to place related text, figures and tables near one another, minimizing the need for page turning while reading a topic. I have given equal importance to text and illustrations as well. We hope you will find this book interesting, relevant and challenging.
Life Sciences have always been a fundamental area of science. The exponential increase in the quantity of scientific information and the rate, at which new discoveries are made, require very elaborate, interdisciplinary and up-to-date information and their understanding. This fourth edition of Life sciences, Fundamentals and practice includes extensive revisions of the previous edition. We have attempted to provide an extraordinarily large amount of information from the enormous and ever-growing field in an easily retrievable form. It is written in clear and concise language to enhance self-motivation and strategic learning skill of the students and empowering them with a mechanism to measure and analyze their abilities and the confidence of winning. We have given equal importance to text and illustrations. The fourth edition has a number of new figures to enhance understanding. At the same time, we avoid excess details, which can obscure the main point of the figure. We have retained the design elements that have evolved through the previous editions to make the book easier to read. Sincere efforts have been made to support textual clarifications and explanations with the help of flow charts, figures and tables to make learning easy and convincing. The chapters have been supplemented with self-tests and questions so as to check one’s own level of understanding. We hope you will find this book interesting, relevant and challenging.
Halus Satriawan
Bekele Gebreamanule
Joyce Wawira
By the end of the course, the learner should be able to: 1. communicate biological information in a precise, clear and logical manner 2. develop an understanding of interrelationships between plants and animals and between humans and their environment 3. apply the knowledge gained to improve and maintain the health of the individual, family and the community 4. relate and apply relevant biological knowledge and understanding to social and economic situations in rural and urban settings 5. observe and identify features of familiar and unfamiliar organisms, record the observations and make deductions about the functions of parts of organisms 6. develop positive attitudes and interest towards biology and the relevant practical skills 7. demonstrate resourcefulness, relevant technical skills and scientific thinking necessary for economic development 8. design and carry out experiments and projects that will enable them understand biological concepts 9. create awareness of the value of cooperation in solving problems 10. acquire a firm foundation of relevant knowledge, skills and attitudes for further education and for training in related scientific field.
Science & Education
Eneku Ronald
Farah Ramzi
TRISNA AMELIA
This book contains concept of biology and the exercise in English language that can help the readers to improve their English skill in biology. There are eight main contents in this book, which are the chemistry of life, an introduction of metabolisms, biotechnology, mechanisms of evolution, classification of living things,reproduction in plant, thermoregulation, and ecology. Hopefully, this book can help the readers to expand their knowledge about English for Biology.
Nature Reviews Genetics
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dr Peter Judge | Tutorial Essays for Science Subjects 1 Tutorial Essays for Science Subjects This guide is designed to provide help and advice on scientific writing. Although students studying Medical and Life Sciences are most likely to have to write essays for tutorials at Oxford, it is important all scientists
It follows a different format and deviates in structure from how we were initially taught to write, or even how we currently write for English, history, or social science classes. ... T. Torello, M. Bucheli, D. Lohman, and R. Jue. 2007. A student's guide to writing in the life sciences. The President and Fellows of Harvard University ...
How to Structure a Science Essay? A basic science essay structure includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. ... Essay About Science in Everyday Life - Samples & Writing Tips. 5 min read. Check Out 5 Impressive Essay About Science Fair Examples. Browse All (+1) 888 687 4420;
A new initiative, Writing in the Life Sciences, began at Harvard University in response to the recognition of the importance of writing in science and the lack of a consis-tent, clear, articulated writing curriculum for undergraduate science students. While much thought and energy have been put into the undergraduate science curriculum, a parallel,
Life Science Topic Style Suggested Grammar 1 Life on Earth strong verb/quality adjective verbs 2 I/II Life Sciences "-ly" words adverbs 3 II Classification who/which adjectives/phrases 4 II Cell Structure decoration: simile/metaphor 5 II DNA www.asia commas 6 III Cells Discovery run-ons, fragments
How to write the Introduction in a Life Science Paper: 1.5 - 2 pages One thing that is quite common is a lack of distinction between the introduction and the discussion sections of a life science paper. So just as a brief reminder, the introduction provides a very brief background and context for this specific line of research.
For example, when writing an essay on biology we can divide the topic up in a number of different ways. So, if you have to answer a question like 'Outline the main properties of life and system reproduction' The steps for planning are simple. Firstly, define the main terms within the question that need to be addressed.
Review . Relevant Literature . Present : Relevant . Data . Interpret the Data . Synthesise : Data and Theories . Refute : the Major View . Clarify : Research/ Data
Writing an Argumentative Science Essay. These resources have been designed to help teach students how to write a well-structured argumentative science essay (approximately 1,250 words) over the course of a term. They will take part in four interactive in-class activity sessions (intended to last 50 - 60 min each) that each focus on a ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
depend heavily upon the review, either for argument or overall structure, you must also cite the review article. This is one of the most common mistakes made by life sciences students. Students who rely upon a review article and do not cite it are sometimes accused of trying to hide the review as a source. One
Writing is an integral part of science at every stage; it is how we outline a project idea, communicate with collaborators, draft a grant application, synthesize our insights into a manuscript, and share science beyond academia. ... and peers, we emphasize the mechanics: how to structure a manuscript, the style conventions of scientific writing ...
This video explains how to write an argumentative essay for Life Sciences Paper II. It gives tips on format, structure, content, mark allocation and planning...
Conclude your essay by summarizing all the key points. Also, highlight the practical potential of our findings and their impacts. Proofread and check for errors in the paper. Before submitting or forwarding your article, it is fundamental that you proofread and correct all the errors that you come across.
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
Figures: labelling, legends and acknowledgment. Whenever you use a table, diagram or image in your essay you must: cite the source. write a legend (a small box of text that describes the content of the figure). make sure that the legend and explanation are adapted to your purpose. For example: Figure 1.
You yourself started out as a single cell and now have tens of trillions of cells in your body 1 ! Growth depends on anabolic pathways that build large, complex molecules such as proteins and DNA, the genetic material. 5. Reproduction. Living organisms can reproduce themselves to create new organisms.
Essays on Life Sciences, with Related Science Fiction Stories 3 world and all living forms once and for all. It would have been blasphemy to challenge such a simple truth. It took a British naturalist, Charles Darwin, in a book published in 1859, to turn blasphemy into science. Darwin rejected the idea that living forms
Essay about Life Science. "Lab Assignment #2 (Horse Evolution)" Through fossil records from Hyracotherium to Mesohippus to Merychippus to Pleshippus to the Equus, one can see the development of dentition, limbs and skull based on the environment that the horses adapted to with time. Environmental changes from the Eocene to the Holocene ...
It's our hope that Working Life stories are similarly thought-provoking for our readers. As the year draws to a close, we've put together a list of the most read essays of 2022, featuring a mortifying interview, unconventional lab meetings, career twists, and more. Why I teach my students about scientific failure
The document provides a clear structure on how to write the essays. This document has been created from information available from the internet and it is not meant for any business purposes (FREE SUPPLY) but to help South African Life sciences. ... LIFE SCIENCES ESSAYS GRADE 10-12 4 Source: Department of Basic Education 2014 Mind the Gap CAPS ...
Earth and Life Science is a fascinating field of study that helps us understand our world and the life forms that live in it. It is a combination of two major sciences. Earth Science studies the Earth, its structure, and how it changes over time. Life Science, on the other hand, focuses on living things, their functions, and their interactions ...