Solar System Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on solar system.
Our solar system consists of eight planets that revolve around the Sun, which is central to our solar system . These planets have broadly been classified into two categories that are inner planets and outer planets. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are called inner planets. The inner planets are closer to the Sun and they are smaller in size as compared to the outer planets. These are also referred to as the Terrestrial planets. And the other four Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are termed as the outer planets. These four are massive in size and are often referred to as Giant planets.

The smallest planet in our solar system is Mercury, which is also closest to the Sun. The geological features of Mercury consist of lobed ridges and impact craters. Being closest to the Sun the Mercury’s temperature sores extremely high during the day time. Mercury can go as high as 450 degree Celsius but surprisingly the nights here are freezing cold. Mercury has a diameter of 4,878 km and Mercury does not have any natural satellite like Earth.
Venus is also said to be the hottest planet of our solar system. It has a toxic atmosphere that always traps heat. Venus is also the brightest planet and it is visible to the naked eye. Venus has a thick silicate layer around an iron core which is also similar to that of Earth. Astronomers have seen traces of internal geological activity on Venus planet. Venus has a diameter of 12,104 km and it is just like Mars. Venus also does not have any natural satellite like Earth.
Earth is the largest inner planet. It is covered two-third with water. Earth is the only planet in our solar system where life is possible. Earth’s atmosphere which is rich in nitrogen and oxygen makes it fit for the survival of various species of flora and fauna. However human activities are negatively impacting its atmosphere. Earth has a diameter of 12,760 km and Earth has one natural satellite that is the moon.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and it is often referred to as the Red Planet. This planet has a reddish appeal because of the iron oxide present on this planet. Mars planet is a cold planet and it has geological features similar to that of Earth. This is the only reason why it has captured the interest of astronomers like no other planet. This planet has traces of frozen ice caps and it has been found on the planet. Mars has a diameter of 6,787 km and it has two natural satellites.
It is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter has a strong magnetic field . Jupiter largely consists of helium and hydrogen. It has a Great Red Spot and cloud bands. The giant storm is believed to have raged here for hundreds of years. Jupiter has a diameter of 139,822 km and it has as many as 79 natural satellites which are much more than of Earth and Mars.
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun. It is also known for its ring system and these rings are made of tiny particles of ice and rock. Saturn’s atmosphere is quite like that of Jupiter because it is also largely composed of hydrogen and helium. Saturn has a diameter of 120,500 km and It has 62 natural satellites that are mainly composed of ice. As compare with Jupiter it has less satellite.
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is the lightest of all the giant and outer planets. Presence of Methane in the atmosphere this Uranus planet has a blue tint. Uranus core is colder than the other giant planets and the planet orbits on its side. Uranus has a diameter of 51,120 km and it has 27 natural satellites.
Neptune is the last planet in our solar system. It is also the coldest of all the planets. Neptune is around the same size as the Uranus. And it is much more massive and dense. Neptune’s atmosphere is composed of helium, hydrogen, methane, and ammonia and it experiences extremely strong winds. It is the only planet in our solar system which is found by mathematical prediction. Neptune has a diameter of 49,530 km and it has 14 natural satellites which are more than of Earth and Mars.
Scientists and astronomers have been studying our solar system for centuries and then after they will findings are quite interesting. Various planets that form a part of our solar system have their own unique geological features and all are different from each other in several ways.

Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Main Registration
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- GATE 2024 Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- XAT Cut Off 2024
- XAT Score vs Percentile 2024
- CAT Score Vs Percentile
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Essay on Solar System
We see the sun every day shining in the sky and at night, we see the moon. Many other heavy bodies like satellites, meteoroids, and asteroids not visible to our naked eyes also make up the solar system. The sun and its planets together form the Solar System. The existence of the Solar System is about 4.6 billion years old.
100 Words Essay on The Solar System
200 words essay on the solar system, 500 words essay on the solar system.

The solar system comprises all the planets that revolve around the sun. The solar system also contains moons, asteroids, comets, minor planets, and different types of gases and dust.
The planets are categorised into two categories: internal planets and outer planets. Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupyter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are called inner planets . Earlier, there were nine planets considered till 2006, but now, Pluto does not lie in the list of planets, it does not meet the standard set for the planets.
It is now termed a dwarf planet. In our solar system, the earth is the only planet where life exists. There are many solar systems that exist in the universe, it is more than 500. Our solar system includes the Kuiper belt that lies past Neptune’s orbit.
The Sun is a star that is made up of massive hot gas that gives us heat and light . The Sun is the focal point of the solar system, every substance in the solar system revolves around the Sun. There are eight planets in the solar system, Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and the smallest planet in the solar system whereas Neptune is the farthest one and Jupiter is the biggest planet in the solar system.
Only Earth has a supportive environment for living creatures. The Earth rotates around its own axis and revolves around the Sun, similarly the moon orbits around the Earth. For complete rotation the earth takes one day and for completing one cycle around the sun it takes 365 days. It is what we call one year and due to gravity we all are stuck to the surface of the Earth.
A Comet is a large body in space made of rocks, ice, and frozen gas. The centre of a comet is called the nucleus. Asteroids are also large bodies in space made of rocks and minerals, they mostly orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter in an area called the Asteroid Belt.
The solar system comprises eight planets, about 170 natural planetary satellites, and uncountable asteroids, meteorites, and comets. The solar system is situated within the Orion-Cygnus arm of the Milky way galaxy . Alpha Centauri made up of the stars Proxima Centauri, Alpha Centauri A, and Alpha Centauri B are the closest star systems to the solar system. The sun which is located at the centre of the solar system affects the motion of the body through its gravitational force. It contains more than 99% mass of the system.
Planets and Their Moons
Mercury | Mercury is the closest and smallest plate in the solar system, it orbits around the Sun and takes 87.97 earth days, it spins around slowly compared to Earth and it is slightly bigger than earth. It has a solid surface that is covered with craters and has a thin surface.
Venus | Venus is the second closest planet to the Sun. Venus is very similar to the earth in shape and densityVenus is the hottest planet in the solar system, it has a thick and toxic atmosphere covered with carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid in the form of yellowish clouds, and trapped heat.
Earth | Earth is the only planet that has a livable environment that sustains life and the ecosystem. It is the third closest and fifth largest planet in the solar system. On earth, life is possible for various reasons, but the most essential thing is the availability of water and the presence of oxygen. Earth is also known as the ‘Blue Planet’ because 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with seas, oceans, and large rivers of water
Mars | Mars is the fourth planet from the sun in the solar system. It appears as a red, orange, and radish ball because of the presence of iron oxide which is why Mars is also known as the ‘Red Planet’. Mars is positioned just next to the Earth. The evidence of water and oxygen raised hopes about the possibility of life on Mars.
Jupiter | Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system and the first of the four gas giants. It is the fifth planet from the Sun. Jupiter also has a ring system like all the large gas planets, although these rings are not famous or as visible as Saturn’s ring.
Saturn | Saturn is the second largest and least dense planet in the solar system. Saturn can float in water because Saturn is made of gases, it's a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of earth. Saturn has rings that are made of gas and dust.
Uranus | Uranus is the coldest planet in the solar system, it revolves around the sun and takes 84 earth years to complete one rotation around the earth. Uranus is called an ‘Ice Giant’ planet because it is covered with ice and Hydrogen gas.
Neptune | Neptune is the eighth planet and farthest planet from the sun in the solar system, its atmosphere is made of hydrogen, helium, and methane gas. Neptune is a dark, cold, and very windy planet in the solar system.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Geotechnical engineer
The role of geotechnical engineer starts with reviewing the projects needed to define the required material properties. The work responsibilities are followed by a site investigation of rock, soil, fault distribution and bedrock properties on and below an area of interest. The investigation is aimed to improve the ground engineering design and determine their engineering properties that include how they will interact with, on or in a proposed construction.
The role of geotechnical engineer in mining includes designing and determining the type of foundations, earthworks, and or pavement subgrades required for the intended man-made structures to be made. Geotechnical engineering jobs are involved in earthen and concrete dam construction projects, working under a range of normal and extreme loading conditions.
Cartographer
How fascinating it is to represent the whole world on just a piece of paper or a sphere. With the help of maps, we are able to represent the real world on a much smaller scale. Individuals who opt for a career as a cartographer are those who make maps. But, cartography is not just limited to maps, it is about a mixture of art , science , and technology. As a cartographer, not only you will create maps but use various geodetic surveys and remote sensing systems to measure, analyse, and create different maps for political, cultural or educational purposes.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Product Manager
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Operations manager.
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Bank Probationary Officer (PO)
Investment director.
An investment director is a person who helps corporations and individuals manage their finances. They can help them develop a strategy to achieve their goals, including paying off debts and investing in the future. In addition, he or she can help individuals make informed decisions.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
An expert in plumbing is aware of building regulations and safety standards and works to make sure these standards are upheld. Testing pipes for leakage using air pressure and other gauges, and also the ability to construct new pipe systems by cutting, fitting, measuring and threading pipes are some of the other more involved aspects of plumbing. Individuals in the plumber career path are self-employed or work for a small business employing less than ten people, though some might find working for larger entities or the government more desirable.
Construction Manager
Individuals who opt for a career as construction managers have a senior-level management role offered in construction firms. Responsibilities in the construction management career path are assigning tasks to workers, inspecting their work, and coordinating with other professionals including architects, subcontractors, and building services engineers.
Urban Planner
Urban Planning careers revolve around the idea of developing a plan to use the land optimally, without affecting the environment. Urban planning jobs are offered to those candidates who are skilled in making the right use of land to distribute the growing population, to create various communities.
Urban planning careers come with the opportunity to make changes to the existing cities and towns. They identify various community needs and make short and long-term plans accordingly.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Naval Architect
A Naval Architect is a professional who designs, produces and repairs safe and sea-worthy surfaces or underwater structures. A Naval Architect stays involved in creating and designing ships, ferries, submarines and yachts with implementation of various principles such as gravity, ideal hull form, buoyancy and stability.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Veterinary Doctor
Pathologist.
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Speech Therapist
Gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
Hospital Administrator
The hospital Administrator is in charge of organising and supervising the daily operations of medical services and facilities. This organising includes managing of organisation’s staff and its members in service, budgets, service reports, departmental reporting and taking reminders of patient care and services.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Videographer
Multimedia specialist.
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Linguistic meaning is related to language or Linguistics which is the study of languages. A career as a linguistic meaning, a profession that is based on the scientific study of language, and it's a very broad field with many specialities. Famous linguists work in academia, researching and teaching different areas of language, such as phonetics (sounds), syntax (word order) and semantics (meaning).
Other researchers focus on specialities like computational linguistics, which seeks to better match human and computer language capacities, or applied linguistics, which is concerned with improving language education. Still, others work as language experts for the government, advertising companies, dictionary publishers and various other private enterprises. Some might work from home as freelance linguists. Philologist, phonologist, and dialectician are some of Linguist synonym. Linguists can study French , German , Italian .
Public Relation Executive
Travel journalist.
The career of a travel journalist is full of passion, excitement and responsibility. Journalism as a career could be challenging at times, but if you're someone who has been genuinely enthusiastic about all this, then it is the best decision for you. Travel journalism jobs are all about insightful, artfully written, informative narratives designed to cover the travel industry. Travel Journalist is someone who explores, gathers and presents information as a news article.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
Merchandiser.
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Metallurgical Engineer
A metallurgical engineer is a professional who studies and produces materials that bring power to our world. He or she extracts metals from ores and rocks and transforms them into alloys, high-purity metals and other materials used in developing infrastructure, transportation and healthcare equipment.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
ITSM Manager
Information security manager.
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
Business Intelligence Developer
Applications for admissions are open..

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN

NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score upto 100% marks

JEE Main high scoring chapters and topics
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Study 40% syllabus and score upto 100% marks in JEE
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications
We Appeared in
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Solar System Essay

Introduction to Essay Writing on Solar System on Vedantu
An essay is a piece of writing where an author expresses in detail all the information on a particular topic. An essay differs from other writing because it is more structured and it provides the author with their own perspective. In this particular essay, we shall know in detail about the solar system. Use this essay as a reference essay and try writing an essay on the solar system.
Let us begin our learning!
Essay on Solar System
The solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, and sixty-seven satellites of the planets, and a large number of small bodies (comets and asteroids). Earlier, Pluto was considered the smallest planet but now Pluto is not recognized anymore as a planet. The inner solar system comprises Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune form the outer solar system. These four planets are massive in size; hence they are called Giant Planets. Each planet revolves around the sun in its own orbits at its own speed.
Let us explore all the celestial bodies present in the Solar system.
The Sun was born 4.6 billions of years ago and it was formed from a giant rotating cloud of gasses and dust known as solar Nebula. The sun is the biggest star present at the center of the solar system. It is a self-luminous sphere of gasses. Its gravitational force holds the entire solar system. It has a radius of 695,508 kilometers and is 150 million kilometers away from Earth.
Mercury is the smallest and closest planet to the sun. It is also called Swift planet because it completes its revolution in 88 earth days. Its diameter is only one third of Earth but its density is about the same. The temperature of this planet is as high as 450 degrees Celsius in the mornings and nights are freezing cold. The surface of this planet is filled with craters, mountains and valleys.
Venus is the second closest planet to the sun and the hottest. Venus is the brightest planet and hence called the morning star. Venus is named after the Roman Goddess of love and beauty. Venus completes one revolution around the sun in 255 earth days. Venus spins clockwise on its orbits unlike other planets. Its surface is covered with clouds, craters, mountains and lava plains.
The third planet in the solar system is Earth. This is the only planet that sustains life. It is called the Blue planet because 70% of the earth's surface is covered with water. Earth takes 365 days to complete one revolution around the sun. This planet has only one natural satellite, the Moon.
The fourth planet from the sun in the solar system is Mars. It appears as a red-orange ball because of the presence of iron oxide and so it is called the Red planet. It is the second smallest planet after Mercury. Mars is named after the Roman God of war. Its surface is covered with volcanoes, craters all over.
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system. Jupiter is rich in hydrogen and helium gas and so it is also called a Gas Giant planet. Jupiter takes 4333 earth days to complete one revolution around the sun. This planet has 79 satellites. Jupiter has four rings.
Saturn is the least dense planet in the solar system. It is the second-largest planet. Saturn can float in water because it is made up of gasses like helium. The beautiful rings around the planet are made up of bits of ice, rock, and dust. Saturn revolves very slowly around the sun. This planet is named after the Roman God of agriculture and wealth.
Uranus is the coldest planet in the solar system. It takes 84 earth years to complete one revolution around the sun. Uranus is called an ice giant planet because its layer is made of ice and hydrogen, helium and methane. Uranus looks blue in color because of the presence of methane. Uranus has 27 satellites.
Neptune is the eighth and the farthest planet from the sun in the solar system. Neptune is named after the Roman God of the sea. Its atmosphere is made up of hydrogen, helium and methane and the presence of methane gives the color blue to the planet. It takes 165 earth years to complete one revolution. Neptune has 6 rings.
Comets and Asteroids:
Comets and Asteroids are the small celestial bodies that rotate around the sun. Asteroids are made up of rocks, metals and water. Comets are made up of frozen ammonia, methane and small amounts of rocky material.

FAQs on Solar System Essay
1. How many planets are there in the solar system?
There are eight planets in the solar system.
2. Is the sun a planet or star?
The sun is a big star located at the centre of the solar system.
3. Which planet sustains life?
The Earth planet sustains life.
4. Which is the coldest planet in the solar system?
Uranus is the coldest planet in the solar system.
5. How to write well on any topic?
It is very important for the students to learn to write on their own. To write a good essay students should follow the following steps -
Try to understand the topic you want to write about
Read from multiple sources to get an idea of the topic
Prepare a structure that is what all you want to cover in your writing
Note down all the important points according to your structure
Arrange the collected information in the pre-decided structure
Remember to keep your readers engaged in your essay
Try to use idea and words which doesn't hurt anyone's emotions
Start writing and with time you would get better in the process
You can also send us your essays or writing which will be evaluated by the faculty.
6. What should be the structure on which an essay can be written?
Like every writing, an essay also has three parts that are the introduction, body, and conclusion. Keep the introduction very interesting, get the attention of your reader by starting with a short story then gradually introduce your topic through that story. Secondly, make the audience aware of the keywords of the topic. In the body, write in detail about the topic like state the historical, economical, social, environmental, cultural factors of your topic. And then conclude your essay by summarizing the key message and the takeaways of the essay. Try to practice with this framework and in due course of time, you will be able to write an excellent essay. Also, try to read from some great essays.
7. What is the process of planet formation called?
The process by which planets are formed is called planetesimals. In the process, the clouds of gasses came together due to gravitational differences . The area of more clouds had higher gravitation and thus attracted more clouds towards them. The ball of clouds takes a round shape through the process of accretion.
Read the article on Solar systems on the website of Vedantu.
8. What are terrestrial and jovian planets?
Terrestrial planets are planets closer to the Sun, it is also called inner planets. These planets are also called Earth-like planets as their features are similar to the Earth. It includes four planets which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Whereas jovian planets are the outer planets which are farther from the Sun. They are also called Jupiter-like planets as they share features similar to Jupiter. It includes Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
9. Can we draw diagrams in an essay?
Some diagrammatic representation in an essay can be done. However, it is recommended that we should avoid drawing diagrams in an essay as it breaks the flow of the writing. Read some good essays to improve your writing style.

Solar System and Planets Essay
Our solar system consists of a sun, eight planets, satellites, dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids and comets. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Earlier it had nine planets. However, Pluto, the ninth planet does not meet the latest standards set for the planets. It has now been termed as a dwarf planet thereby increasing the count of the dwarf planets in our solar system to five.
Long and Short Essays on Solar System and Planets in English
Here are long and short essay on solar system and planets in English, to help you with the topic in your exams or essay writing/debate competitions.
After going through these solar system and planets essay, you will know about the formation of solar system, when the planets were discovered, the dwarf planets, satellites and characteristics of individual planets etc.
All in all, these Solar System and Planets Essays will make you familiar with the universe we are a part of, so much so, that you can confidently take part in debates, talk shows and discussions, on our solar system and its planets. Please go through these essays to select your needed ones:
Short Essay on Solar System and Planets (200 words)
The universe is massive. It is much bigger than we can imagine and our solar system is just a small part of it. Our solar system houses a big, bright star called the Sun. The Sun is a rich source of electromagnetic energy that it exudes in the form of light and heat. There are eight planets in our solar system namely, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path referred to as the orbit. Several other smaller objects also move around the sun.
Many planets in our solar system have natural satellites called the moon. While Earth has one moon, Mars has two, Neptune has 14 moons, Uranus has 27 moons, Saturn has 62 moons and Jupiter has as many as 79 moons. Even the dwarf planet Pluto has 5 moons. Mercury and Venus, on the other hand, do not have any moon. Just as the planets move around the Sun in a fixed path, moons orbit around their respective planets.
In addition to the Sun, planets and moons, our solar system consists of several other celestial bodies called the comets, asteroids and meteoroids. While our solar system has only one star, many other solar systems are known to have at least two stars.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (300 words)
Introduction
Our solar system was formed billions of years ago. It consists of numerous celestial bodies including planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, meteorites and a massive star. Our solar system forms a part of the Milky Way Galaxy. Various celestial bodies in our solar system revolve around the Sun directly or indirectly.
The Formation of the Solar System
It is believed that around 4.6 billion years ago, the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud gave shape to our solar system. Major part of the collapsing mass collated at the centre, that formed the Sun. The remaining mass flattened into a proto planetary disk and formed the planets, satellites and other objects in the solar system. Planet Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system, contains major chunk of the remaining mass.
Our solar system is believed to have evolved substantially since its inception. Many new moons have come into shape from the gases and dust around the planets. Several collisions among the celestial bodies have also occurred and still continue to occur thereby contributing to the evolution of the solar system.
The Discovery of Planets
For thousands of years astronomers believed that Earth was stationary and formed the centre of the universe. It was in the 18 th century that the astronomers accepted that Earth orbits around the Sun.
In 2 nd millennium BC, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn were identified by ancient Babylonian astronomers. Later, Nicolaus Copernicus also identified them. Uranus was discovered by famous astronomer, Sir William Herschel in 1781. Neptune was discovered by English astronomer and mathematician, John Couch Adams in the year 1846. It was in the year 1930 that the ninth planet, Pluto was discovered. Astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovered Pluto which is now identified as a dwarf planet.
The study of the universe and heavenly bodies is one of the most fascinating studies. Through continuous research, astronomers have found out several surprising facts about the universe and our solar system. Our solar system is ever evolving and newer facts are being discovered and studied by researchers year after year.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (400 words)
Celestial bodies are objects that naturally occur in the observable universe. These include the stars, natural satellites, planets, asteroids, galaxies, comets and meteorites. Our solar system consists of a Sun, eight planets their moons, five dwarf planets and asteroids among other celestial bodies. Brief information about each of the celestial bodies present in our solar system is given below.
The Sun is the only star on our solar system. It is stationary and the other objects in our solar system revolve around it. It is the most massive component of our solar system. Research states that it comprises of 99.86% of the entire mass of our solar system.
The Planets
There are eight planets in the solar system. These are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The planets have been divided into two groups – Terrestrial Planets and Giant Planets. Planets vary based on their size, geological features, mass, number of satellites and various other factors. No traces of life have been found on any planet apart from Earth.
The Dwarf Planets
There are five dwarf planets in our solar system. These are Pluto, Ceres, Haumea, Eris and Makemake. While Ceres is situated in the asteroid belt others are located in the outer solar system. Dwarf planets are quite like the full size planets. The only difference is that the full size planets have cleared the objects in the area of their orbit whereas the dwarf planets have not.
Astronomers claim that there are six other objects in our solar system that are akin to the dwarf planets. These may be officially recognized as dwarf planets in the times to come.
There are a total of 193 moons in our solar system as per a research conducted in the year 2008. Out of these, 185 moons orbit around the full size planets and 8 moons revolve around the dwarf planets. Moons come in various sizes and shapes. They differ from each other in various ways. Most of the moons are airless. However, there are some that have atmosphere. Some even have hidden oceans. Each planet has different number of moons. Earth has just one moon while Jupiter has the highest number of moons. It has a total of 79 moons. Moons orbit around their respective planets.
In addition to the aforementioned, there are many other celestial bodies in our solar system. These include the Interplanetary Medium, Kuiper Belt, Oort Cloud, asteroids and meteoroids. The Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud comprise of billions of icy objects. Each celestial body in our solar system is unique with its own set of features.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (500 words)
Our Solar System – A Small Part of the Universe
Our solar system is huge but nothing compared to the size of the universe. The universe is humongous and is believed to encompass numerous solar systems consisting of several planets, stars and other heavenly bodies. The universe is all space and time and it is not possible to calculate its spatial size. The size of the observable universe is estimated to be 93 billion light years.
The Galaxies and Solar Systems
Research shows that just like our solar system there are numerous other solar systems in the universe. The universe consists of billions of galaxies. Each of these galaxies has uncountable stars and many of these stars are said to have solar systems of their own. The size of the stars, the number of planets, the geological features of the planets, the number and size of the natural satellites vary from solar system to solar system.
Our solar system is a part of the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way Galaxy is huge. It has more than 100 billion stars. More than 2500 stars with planets orbiting around them have been discovered in the Milky Way Galaxy. The study in this field is going on constantly. There are numerous planetary systems that the scientists and astronomers are yet to discover.
Our Solar System
Our solar system encompasses Sun which is a big ball of fire. Sun is stationary and forms the centre of our solar system. Eight planets namely, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune revolve around the Sun. Each of these planets move in a fixed path in its own set speed. The geological features of each of these planets are different. While Neptune is freezing cold, Venus is scorching hot. Similarly, while Jupiter is massively big, Mercury is comparatively very small in size. The planet is even smaller than some of the moons in our solar system. The atmosphere of each of the planets is different. Planets have been divided into two groups and the features of the planets within each group also vary vastly.
Earth is the only planet in our solar system which is known to have life. It is filled with vast oceans and gases such as oxygen and nitrogen that render life. Mars is said to share some similarities with Earth. Evidences of ice have been found on the planet. The planet is extremely cold and thus life there seems impossible. However, it is believed that the planet was once wet and warm and life existed here. Astronomers are studying this planet closely and have found many interesting facts about the same. These planets have different numbers of natural satellites.
Apart from this, there are five dwarf planets in our solar system. These are Ceres, Haumea, Makemake, Eris and Pluto. Earlier there were nine planets in our solar system and Pluto was one among them. However, it has now been termed as a dwarf planet.
The Universe is vast and there is a lot to study and discover. Scientists have studied our solar system deeply for centuries and are now moving beyond to study other solar systems and galaxies. A lot of interesting facts about this enchanting universe are likely to surface in the times to come.
Long Essay on Solar System and Planets (600 words)
Our solar system consists of eight planets that revolve around the Sun, which is central to our solar system. These planets have broadly been classified into two categories – inner planets and outer planets. There are four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The inner planets are closer to the Sun and smaller in size as compared to the outer planets. These are also referred to as the Terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are termed as the outer planets. These are massive in size and are often referred to as Giant planets.
Here is brief information about each of these planets:
The smallest planet in our solar system, Mercury is also the closest to the Sun. Its geological features consist of lobed ridges and impact craters. Being closest to the Sun, Mercury’s temperature sores extremely high during the day time. It can go as high as 450 degree Celsius. Surprisingly, the nights here are freezing cold.
Mercury has a diameter of 4,878 km. It does not have any natural satellite.
Venus is said to be the hottest planet of our solar system. It has a toxic atmosphere that traps heat. It is also the brightest planet and is visible to the naked eye. It has a thick silicate layer around an iron core which is similar to that of Earth. Astronomers have seen traces of internal geological activity on this planet.
Venus has a diameter of 12,104 km. Just like Mars, Venus also does not have any natural satellite.
Earth is the largest inner planet. Two-third of this planet is covered with water. It is the only planet in our solar system where life is known to exist. Earth’s atmosphere, which is rich in nitrogen and oxygen, makes it fit for the survival of various species of flora and fauna. However, human activities are having negative impact on its atmosphere.
Earth has a diameter of 12,760 km. It has one natural satellite, the moon.
Mars, the fourth planet from Sun, is often referred to as the Red Planet. The iron oxide present on this planet gives it a reddish appeal. The planet is cold and has geological features similar to that of Earth. This is the reason why it has captured the interest of astronomers like no other planet. Traces of frozen ice caps have been found on the planet.
Mars has a diameter of 6,787 km and two natural satellites.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. It has a strong magnetic field. It largely consists of helium and hydrogen. It has a Great Red Spot and cloud bands. A giant storm is believed to have raged here for hundreds of years.
Jupiter has a diameter of 139,822 km and has as many as 79 natural satellites.
Saturn is known for its ring system. These rings are made of tiny particles of ice and rock. Its atmosphere is quite like that of Jupiter as it is also largely composed of hydrogen and helium.
Saturn has a diameter of 120,500 km. It has 62 natural satellites that are mainly composed of ice.
Uranus, the seventh planet from Sun, is the lightest of all the giant, outer planets. It has a blue tint which is because of the presence of Methane in the atmosphere. Its core is colder than the other giant planets. The planet orbits on its side.
Uranus has a diameter of 51,120 km and 27 natural satellites.
The last planet in our solar system, Neptune is also the coldest of all. It is around the same size as the Uranus but is much more massive and dense. Neptune’s atmosphere is composed of helium, hydrogen, methane and ammonia. It experiences extremely strong winds. It is the only planet in our solar system which is found by mathematical prediction.
Neptune has a diameter of 49,530 km. It has 14 natural satellites.
Scientists and astronomers have been studying our solar system for centuries and the findings are quite interesting. Various planets that form a part of our solar system have their own unique geological features and are different from each other in several ways.
More Information:
Essay on Role of Science in Making India
Essay on Wonders of Science
Essay on Science and Technology
Related Posts
Money essay, music essay, importance of education essay, education essay, newspaper essay, my hobby essay.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Solar System for School Students
- Updated on
- Dec 23, 2023

Essay on Solar System: Our solar system consists of one Sun and eight (formerly nine) planets. These eight planets are gravitationally bound by the Sun on their orbits. Apart from these eight planets, there are more than 210 known planetary satellites, asteroids, comets, and other icy bodies that are assembled in the Solar system.
The first four planets are called terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) the two gas planets (Jupiter and Saturn), and the other remaining ones are ice giants (Neptune and Uranus.)
This Blog Includes:
Inner planets (terrestrial planets):, outer planets (gas giants).
Learn about the smallest planet in our solar system
The Sun is the primary source of light and energy and is about 93 million miles from the Earth. It is the only star in our solar system and one of the more than 100 billion stars in the Milky Way. The surface of the Sun is about 5,500 degrees Celsius (10,000 degrees Fahrenheit) hot and the temperature reaches 15 million Celsius (27 million Fahrenheit).
In terms of age and size, the Sun is 4.5 billion years old, composed of hydrogen and helium with a diameter of about 865,000 miles which is approximately 1.4 million kilometres.
The planets that are made of rocks and metals are known as Inner Planets or Terrestrial Planets. These planets are comparatively small in size compared to the other outer planets. The description of these four planets is as follows:
1. Mercury—The Swift Planet
Mercury is the swiftest planet in our solar system which completes an orbit around the Sun in just 88 Earth days. Its proximity to the Sun contributes to extreme temperature variations, from scorching highs to freezing lows.
With minimal atmosphere, Mercury lacks the protective blanket found on the Earth, exposing its surface to harsh solar radiation.
2. Venus—The Evening Star or Morning Star
Venus, which is often referred to as the evening star or morning star, depends on its position relative to the Sun. When Venus is trailing the Sun, it is the evening star, visible after the sunset. Conversely, when ahead of the Sun, it is the morning star, appearing before sunrise.
This dual identity arises from Venus´s orbit, positioning it closer to the Sun than Earth and causing varied visibility during different parts of the orbital journey.
3. Earth—Blue Planet
The home planet to all living things is Earth. It is the only planet that is known for the existence of life.
The surface of the Earth is made up of the crust, the core, and the mantle. It is a giant rocky planet with a circumference of about 40,075 kilometers; 71 percent or ¾ th of the Earth is covered with oceans and seas. A large area covered with water makes this planet a Blue Planet.
4. Mars—Red Planet
The fourth planet of the solar system, Mars, is the most explored planet by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA.) The reason behind so many missions or research for Mars is to hope for the existence of extraterrestrial life on the planet.
Apart from the possibility of life on Mars, the planet is also known for its presence of iron oxide that turns the planet reddish in appearance.
Want to know more about our Planet Earth? Read Essay on Earth for more information.
5. Jupiter—King of Planets
Jupiter is the first planet of our solar system in the category of outer planets, also known as gas giants. According to NASA, the U.S. government agency, the planet’s size is more than twice that of all other planets combined.
Except for Jupiter’s size, the solar system’s first outer planet is made up of leftover gases from the formation of the Sun.
6. Saturn—Ringed Planet
The sixth planet from the Sun is Saturn. It is also known as the ringed planet and the second-largest solar system planet.
The three distinctive features that make Saturn different from other planets are its huge 145 moons, visibility from the Earth with the naked eye, and the seven main rings named D, C, B, A, F, G, and E from the outward side of the planet.
7. Uranus—Ice Giant
The seventh planet from the Sun, Uranus, is one of the two ice giants in the list of the outer solar system. The planet is featured with the third largest diameter which makes the planet the third largest in the solar system.
Other than massive size, Uranus is made up of three dense icy materials, methane, ammonia, and water – above all a small rocky core.
8. Neptune—Blue Giant
The third largest and eighth planet of the solar system is Neptune. According to NASA, the farthest planet from the Sun is more than 17 times Earth’s size and nearly 58 times the dimensions of Earth’s volume.
The cool blue planet, due to the absorption of infrared light by the planet’s Methane atmosphere, comprises a core with the capacity to pick up a lot of gas, making Neptune impossible for the existence of life.
Also Read: Essay on Space Exploration
Our Solar system is incomplete without the Moon, a planetary large natural object that travels around the Earth. However, the Moon does not make its light but it reflects the light of the sunlight.
The total number of moons in our Solar system is 290, out of which one Moon belongs to Earth, two to Mars, 27 to Uranus, 95 to Jupiter, 146 to Saturn, 5 to dwarf planet Pluto, and 14 to Neptune.
The solar system consists of the Sun, terrestrial planets, gas giants, Earth’s Moon, celestial bodies , and various other objects. The unique formation and dynamics continue to amaze scientists offering a glimpse into the vastness and beauty of our cosmic neighbourhood.
Ans: The Nebular Theory, which states that the solar system is made up of interstellar clouds of dust and gas, is the best theory for the solar system.
Ans: Arybhatta, the mathematician and astronomer was the first to discover that the Earth revolves around the Sun.
Ans: There is only one solar system in the universe.
Ans: Our solar system consists of only stars and we know it as The Sun.
Ans: The size of the solar system is almost 12 trillion miles, nearly 2 light years.
Related Articles:
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Deepika Joshi
Deepika Joshi is an experienced content writer with expertise in creating educational and informative content. She has a year of experience writing content for speeches, essays, NCERT, study abroad and EdTech SaaS. Her strengths lie in conducting thorough research and ananlysis to provide accurate and up-to-date information to readers. She enjoys staying updated on new skills and knowledge, particulary in education domain. In her free time, she loves to read articles, and blogs with related to her field to further expand her expertise. In personal life, she loves creative writing and aspire to connect with innovative people who have fresh ideas to offer.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet

When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

- Vishal's account
Essay On Solar System – 10 Lines, Short and Long Essay for Children and Students
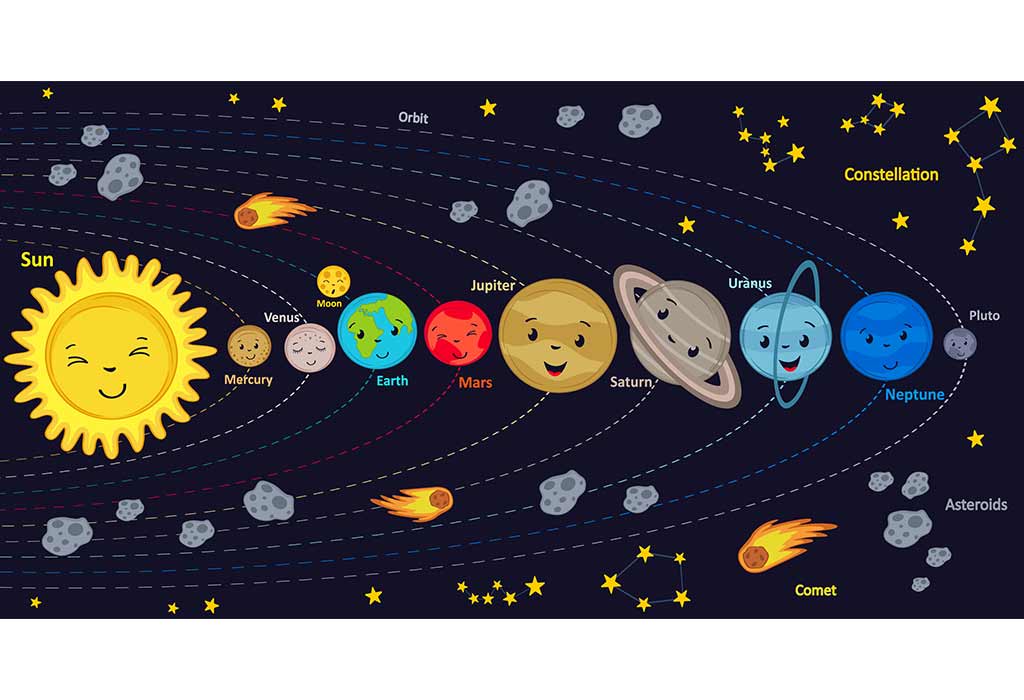

Key Points to Remember When Writing an Essay on the Solar System
10 lines on solar system, a paragraph on solar system, short essay on solar system, long essay of the solar system in english, what will your child learn from the essay on the solar system.
Writing essays can be an incredible journey of exploration, especially when diving into fascinating topics like the solar system. A solar system essay, like the one we’re about to embark on, provides an opportunity to understand the vast universe we are a part of. By attempting this essay in English, students can improve their language skills, enhance their creativity, and develop a deeper appreciation for the wonders beyond our planet. Now, let’s travel through space and time to understand the marvellous entity we call the solar system.
When you embark on the enlightening journey of writing an essay on the solar system, it’s essential to remember some fundamental aspects to make your essay stand out. These points ensure that your content is rich and informative and captivates your readers.
- Research Thoroughly: Before starting, gather information from credible sources. The solar system is vast, and discoveries are made regularly.
- Keep It Organised: Structure your essay with a proper introduction, body, and conclusion. This will help readers follow your thoughts.
- Use Simple Language: If it’s meant for children and students, keep your language simple and avoid jargon.
- Include Visuals: Include images or diagrams of planets, orbits, or other celestial bodies to make your essay more engaging and to help explain complex concepts.
- Discuss Recent Discoveries: Astronomy is a constantly evolving field. To keep your essay current, mention any new findings or missions.
- Maintain Accuracy: When mentioning facts or figures, ensure they are accurate. Mistakes in such essays can misinform readers.
- Personal Touch: Share anecdotes or experiences related to stargazing or space exploration. This adds a warm, personal touch to the essay.
- Include Interesting Facts: Sprinkle your essay with fascinating tidbits about the solar system , like the storms on Jupiter or the possibility of water on Mars .
- Stay Updated: The realm of space exploration and astronomy is constantly advancing. Ensure you are updated with the latest information.
- Proofread: After finishing your essay, review it for any grammatical or factual errors. A well-polished essay makes a better impression.
For primary class students just beginning their exploration into the vast wonders of space, breaking down the vastness of the solar system into digestible bites is essential. The solar system can be awe-inspiring with its planets, moons, and other celestial wonders. Here’s a simple solar system 10-line essay perfect for budding astronomers and an essay for primary-class students.
1. The solar system comprises the sun and all the celestial objects around it.
2. There are eight planets: Mercury , Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn , Uranus, and Neptune.
3. The sun is a giant star that gives us light and warmth.
4. Earth , our home, is the third planet from the sun and the only one known to have life.
5. The moon is Earth’s natural satellite and orbits around us.
6. Jupiter , the largest planet, has a giant red storm raging for centuries.
7. Between Mars and Jupiter, there’s an asteroid belt filled with rocky objects (4) .
8. The solar system also includes comets with tails that glow when close to the sun.
9. Neptune, the farthest planet, has strong winds and dark storms (5) .
10. Exploring our solar system helps us learn more about our place in the universe.
Young students can use these lines as a foundation and further expand their knowledge by exploring each point in depth as they grow.
Writing an essay for classes 1 & 2 can be a great way for young students to understand the solar system. To help them grasp the essentials, here’s a short essay in 100 words tailored to their comprehension level.
The solar system is like a big family in space. At the centre is the sun , shining bright and giving us light. Around the sun, eight planets move in circles called orbits. Earth is one of them, and it’s where we live. Some planets have rings, like Saturn, and some have many moons. There are also tiny rocks called asteroids and icy bodies known as comets. Every member of this space family has its own unique story. By reading and learning about the solar system, kids can begin to understand the vast world beyond our blue sky.
The allure of the night sky, dotted with twinkling stars and distant planets, has always been a source of wonder for humans. Exploring the solar system’s mysteries offers profound insights into the cosmos and our place within it. The following essay, in 200 words, captures the essence of this mesmerising expanse.
Our solar system is a cosmic marvel, a vast expanse dominated by the sun’s brilliant glow. The centre of the solar system is occupied by the sun, a colossal sphere of fiery gas that makes up over 99% of the solar system’s total mass (3) . Orbits around this central star are eight diverse planets with unique features and mysteries. The rocky planets Mercury, Venus , Earth, and Mars are nearest to the sun. These are followed by the gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn, and the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune.
In contrast, each planet provides a distinct study, from Mercury and Venus’s scorching surfaces to Neptune’s frozen realms. Beyond the planets, the solar system also shelters asteroids, comets, and dwarf planets like Pluto. As we send probes and satellites farther into space, our understanding of this vast system deepens, revealing secrets that challenge our understanding of existence. The solar system, with its intricate dance of celestial bodies, is a testament to the grandeur of the universe, beckoning us to explore and discover.
For every student and reader, understanding our solar system is the first step towards unravelling the deeper mysteries of the cosmos.
The cosmos has always fascinated mankind. Its vastness and mysteries have piqued our curiosity for centuries. To comprehend the universe’s grandeur, we must begin with our neighbourhood in space: the solar system. This solar system essay for class 3 and above offers more profound insights into our cosmic home.
What Is the Solar System?
The solar system comprises various celestial bodies held together by the sun’s gravitational pull, which sits at its centre. This dynamic system is located in the Milky Way galaxy and spans a distance of billions of miles. The major constituents of the solar system are the sun, eight planets, their moons, and a range of smaller objects like asteroids, comets, and dwarf planets. It is an intricate dance of objects revolving around the sun, each following its unique path and exhibiting individual characteristics.
How Does the Solar System Work?
The sun is the heart of the solar system, a colossal ball of gas undergoing nuclear fusion. It emits immense heat and light, making life possible on Earth. The sun’s gravitational force is so strong that it keeps all the planets and celestial bodies in their orbits.
The planets orbit the sun in elliptical paths. Like Mercury and Venus, those closest to the sun complete their orbits quicker than those farther away, such as Neptune . The force of gravity also ensures that moons orbit planets. For example, our Earth has one moon, while Jupiter boasts 79 known moons!
The balance of gravity and the momentum of celestial objects keep everything in place. Without the sun’s gravitational pull, planets would drift away into the vastness of space.
Celestial Bodies Exist in the Solar System
Our solar system’s central star provides energy and light that drive life on Earth.
There are eight in total. The inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) are rocky, while the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) are gas giants or ice giants.
Natural satellites that orbit planets. Their number varies from planet to planet.
4. Asteroids
Rocky fragments remain from the formation of the solar system. Most are found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Comets are icy bodies that come from the solar system’s outer regions. When they approach the sun, they develop glowing tails.
6. Dwarf Planets
These celestial bodies orbit the sun and have enough mass for their self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces (2) . However, they still need to clear their neighbouring region of other objects. Pluto is the most famous dwarf planet.
7. Kuiper Belt & Oort Cloud
These are regions beyond Neptune filled with millions of icy objects. The Kuiper Belt is closer than the Oort Cloud and is the birthplace of short-term comets (1) .
Our solar system is breathtakingly vast and dynamic, filled with various celestial bodies. Its complex mechanisms and operations provide invaluable insights into the universe’s workings. Understanding the solar system is not just a part of the curriculum for students in class 3 and above; it is a journey into the wondrous realm of space. This essay aims to be a guide, igniting young minds’ curiosity and exploration.
Through the essay on the solar system, your child will gain a foundational understanding of our cosmic neighbourhood, grasping the vastness and intricacies of space. Beyond mere facts, the essay fosters curiosity, inspiring them to dig deeper into the mysteries of the universe and comprehend the grandeur and significance of the celestial dance above us.
1. Where is the solar system situated?
The solar system is in the Milky Way galaxy, in one of its spiral arms called the Orion Arm.
2. How many total solar systems exist?
Numerous solar systems exist, with billions believed to reside in our Milky Way galaxy alone. This showcases the vast expanse and diversity of solar systems.
The solar system’s myriad celestial bodies and dynamic interplays provide a window into the cosmos’s infinite wonders. Understanding and appreciating its grandeur satiates our innate curiosity and helps us find our humble place within the vast tapestry of the universe.
References/Resources
1. Relationship of the Kuiper Belt to the Oort Cloud; The European Space Agency; https://esahubble.org/images/opo0204i/
2. What is a Dwarf Planet?; Jet Propulsion Laboratory; https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/infographics/what-is-a-dwarf-planet ; April 2015
3. Our Sun: Facts; NASA; https://science.nasa.gov/sun/facts/
4. Asteroids: Facts; NASA; https://science.nasa.gov/solar-system/asteroids/facts/
5. Neptune Facts; NASA; https://science.nasa.gov/neptune/facts/
Also Read:
Facts About Space for Children
- RELATED ARTICLES
- MORE FROM AUTHOR

15 Popular Chapter Books For Third Graders

Teach Your Kids About Zoo Animals With Pictures

Speech on Patriotism in English for Students and Children

List Of Christmas Words That Start With N

What's the Christmas Story, Mamma?

20 Creative Back-to-school Bulletin Boards
Popular on parenting.

245 Rare Boy & Girl Names with Meanings

Top 22 Short Moral Stories For Kids

170 Boy & Girl Names That Mean 'Gift from God'

800+ Unique & Cute Nicknames for Boys & Girls
Latest posts.

Cookie Monster Coloring Pages - Free Printable Pages For Kids
Robot Coloring Pages - Free Printable Pages For Kids

Cheerleading Coloring Pages - Free Printable Pages For Kids

Essay On Holi - 10 lines, Short and Long Essay for Students and Children

Solar System Essay in English For School Students
Unlock the secrets of our solar system with our comprehensive Solar System essay on its formation, structure, and fascinating celestial bodies.
November 1, 2023

Table of Contents
The solar system essay is a remarkable and awe-inspiring essay about encompassing the Sun and its eight major planets, their moons, countless asteroids, and a myriad of comets. At its center is the Sun – a blazing ball of nuclear fusion that sustains life on Earth and all other celestial bodies nearby. Orbiting this source of energy are diverse planets, each with unique characteristics and mysteries waiting to be unraveled. From Mercury’s scorching inferno to Neptune’s icy desolation, our system showcases a wide range of environments.
Our home planet, Earth, stands out as the only known place in the universe where life thrives – making it particularly intriguing to both scientists and philosophers alike. The natural satellites of these planets – such as Earth’s Moon, Ganymede, and Titan – provide valuable insights into their parent bodies’ history and geology. In addition to these planets and their moons, the solar system also hosts numerous asteroids and comets which have played significant roles in shaping Earth’s past through impact events. Studying this vast system not only expands our understanding of the cosmos but also offers the potential for answers about the origin of life and habitable worlds beyond our own. As we continue exploring this wonderous celestial arrangement, it
It is a large celestial body that revolves in a fixed orbit around the Sun. It doesn’t have its lights and uses sunlight to reflect light. Because planets are closer to us, they don’t twinkle as stars. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars remain in the inner solar system, while Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are in the outer solar system.
Our Solar System
There are eight planets are divided into two groups: inner planets and outer planets. Inner planets, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, are more minor and closer to the Sun. The remaining four planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune – are much larger and often called Giant planets.

The most minor planet in our solar system is Mercury, which is also closest to the Sun. Mercury’s geological features include lobed ridges and impact craters. Mercury has a very high surface temperature due to its proximity to the Sun. It can reach temperatures of 450 degrees Celsius during the daytime, but at night, Mercury is cold. Mercury’s diameter is 4,878 kilometres, and it lacks a natural satellite.
As well as being the hottest planet in our solar system, Venus has a toxic atmosphere always traps heat. Venus is also the brightest planet and can be seen from the ground. Venus has the same iron core as Earth and has a thick silicate layer surrounding it. The Venus planet has a diameter of 12,104 km and is similar to Mars. Astronomers have seen evidence of internal geological activity. As with Mars, Venus does not have any natural satellites like Earth.
During the Earth’s lifetime, life is possible because it is covered two-thirds with water. The atmosphere on Earth, which is rich in nitrogen and oxygen, makes it an ideal place for various flora and fauna to survive. Earth has a diameter of 12,760 km and one natural satellite, the moon.
Often referred to as the Red Planet, Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. This planet is cold and has similar geological features to Earth.This is the only reason why it has captured the interest of astronomers like no other planet. An ice cap has been discovered on this planet.
Jupiter has a strong magnetic field and is primarily made up of helium and hydrogen. It also has a Great Red Spot and cloud bands. This giant storm is believed to have raged here for hundreds of years. There are 79 natural satellites on Jupiter, which is much more than there are on Earth and Mars combined. Jupiter has a diameter of 139,822 km.
As the sixth planet from the Sun, Saturn is also known for its ring system, composed primarily of ice and rock particles. Saturn’s atmosphere is quite like Jupiter’s because it is mostly made up of hydrogen and helium. Saturn has a diameter of 120,500 km and has 62 natural satellites, most of which are made up of ice. Saturn has fewer satellites than Jupiter.
The seventh planet from the Sun, Uranus, is the lightest. Uranus has a blue tint due to methane in its atmosphere. Its core is colder than the other giant planets, and it orbits on its side.
It is the coldest, Neptune is the largest and densest. Neptune has an atmosphere made up of helium, hydrogen, methane, and ammonia and has extremely strong winds. It is the only planet in our solar system that was discovered mathematically. Neptune has a diameter of 49,530 km and has 14 natural satellites, which is more than Earth or Mars combined.
Solar System Essay FAQs
Solar system essays examine the sun, planets, moons, asteroids, and comets of our celestial neighbourhood. They explore their characteristics, orbits, and the vastness of space.
The solar system is a collection of celestial bodies centred around the sun. It includes eight major planets, their moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects. The sun's gravity holds these bodies in orbit, creating a complex and fascinating cosmic neighbourhood.
Our solar system consists of the sun, a star at the centre, and various celestial objects orbiting it. This includes eight planets, their moons, asteroids, and comets. Earth, our home, is one of these planets and supports life as we know it.
The solar system comprises:
The sun is a massive star at the centre. Eight significant planets, including Earth, orbiting the sun. Numerous moons orbiting these planets. Asteroids are rocky objects, some of which are found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Comets are icy bodies that travel in elliptical orbits around the sun, occasionally becoming visible from Earth.
T Distribution Formula, Definition, Table, Applications
Standard Form Formula, Definition, Solved Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

.st1{display:none} Related Articles
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024-25 Released Download PDF
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus 2024-2025 Released Download PDF
- UP Board 12th Result 2024, Check UP Board Class 12 Result Details
- CBSE Class 7 Maths Notes Chapter 15 Visualising Solid Shapes
- Bihar Board 10th Result 2024 Out Soon @biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in
- ISC Class 12 Biology Paper 1 Exam Analysis 2024
- PSEB Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2023-24 PDF Download
- PSEB Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus, Check Updated Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper 2023-24

Essay on Solar System and Planets in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Our solar system consists of a sun, eight planets, satellites, dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids and comets. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Earlier it had nine planets. However, Pluto, the ninth planet does not meet the latest standards set for the planets. It has now been termed as a dwarf planet thereby increasing the count of the dwarf planets in our solar system to five.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essays on Solar System and Planets in English
Here are long and short essay on solar system and planets in English, to help you with the topic in your exams or essay writing/debate competitions.
After going through these solar system and planets essay, you will know about the formation of solar system, when the planets were discovered, the dwarf planets, satellites and characteristics of individual planets etc.
All in all, these Solar System and Planets Essays will make you familiar with the universe we are a part of, so much so, that you can confidently take part in debates, talk shows and discussions, on our solar system and its planets. Please go through these essays to select your needed ones:
Short Essay on Solar System and Planets (200 words)
The universe is massive. It is much bigger than we can imagine and our solar system is just a small part of it. Our solar system houses a big, bright star called the Sun. The Sun is a rich source of electromagnetic energy that it exudes in the form of light and heat. There are eight planets in our solar system namely, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path referred to as the orbit. Several other smaller objects also move around the sun.
Many planets in our solar system have natural satellites called the moon. While Earth has one moon, Mars has two, Neptune has 14 moons, Uranus has 27 moons, Saturn has 62 moons and Jupiter has as many as 79 moons. Even the dwarf planet Pluto has 5 moons. Mercury and Venus, on the other hand, do not have any moon. Just as the planets move around the Sun in a fixed path, moons orbit around their respective planets.
In addition to the Sun, planets and moons, our solar system consists of several other celestial bodies called the comets, asteroids and meteoroids. While our solar system has only one star, many other solar systems are known to have at least two stars.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (300 words)
Introduction
Our solar system was formed billions of years ago. It consists of numerous celestial bodies including planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, meteorites and a massive star. Our solar system forms a part of the Milky Way Galaxy. Various celestial bodies in our solar system revolve around the Sun directly or indirectly.
The Formation of the Solar System
It is believed that around 4.6 billion years ago, the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud gave shape to our solar system. Major part of the collapsing mass collated at the centre, that formed the Sun. The remaining mass flattened into a proto planetary disk and formed the planets, satellites and other objects in the solar system. Planet Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system, contains major chunk of the remaining mass.
Our solar system is believed to have evolved substantially since its inception. Many new moons have come into shape from the gases and dust around the planets. Several collisions among the celestial bodies have also occurred and still continue to occur thereby contributing to the evolution of the solar system.
The Discovery of Planets
For thousands of years astronomers believed that Earth was stationary and formed the centre of the universe. It was in the 18 th century that the astronomers accepted that Earth orbits around the Sun.
In 2 nd millennium BC, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn were identified by ancient Babylonian astronomers. Later, Nicolaus Copernicus also identified them. Uranus was discovered by famous astronomer, Sir William Herschel in 1781. Neptune was discovered by English astronomer and mathematician, John Couch Adams in the year 1846. It was in the year 1930 that the ninth planet, Pluto was discovered. Astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovered Pluto which is now identified as a dwarf planet.
The study of the universe and heavenly bodies is one of the most fascinating studies. Through continuous research, astronomers have found out several surprising facts about the universe and our solar system. Our solar system is ever evolving and newer facts are being discovered and studied by researchers year after year.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (400 words)
Celestial bodies are objects that naturally occur in the observable universe. These include the stars, natural satellites, planets, asteroids, galaxies, comets and meteorites. Our solar system consists of a Sun, eight planets their moons, five dwarf planets and asteroids among other celestial bodies. Brief information about each of the celestial bodies present in our solar system is given below.
The Sun is the only star on our solar system. It is stationary and the other objects in our solar system revolve around it. It is the most massive component of our solar system. Research states that it comprises of 99.86% of the entire mass of our solar system.
The Planets
There are eight planets in the solar system. These are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The planets have been divided into two groups – Terrestrial Planets and Giant Planets. Planets vary based on their size, geological features, mass, number of satellites and various other factors. No traces of life have been found on any planet apart from Earth.
The Dwarf Planets
There are five dwarf planets in our solar system. These are Pluto, Ceres, Haumea, Eris and Makemake. While Ceres is situated in the asteroid belt others are located in the outer solar system. Dwarf planets are quite like the full size planets. The only difference is that the full size planets have cleared the objects in the area of their orbit whereas the dwarf planets have not.
Astronomers claim that there are six other objects in our solar system that are akin to the dwarf planets. These may be officially recognized as dwarf planets in the times to come.
There are a total of 193 moons in our solar system as per a research conducted in the year 2008. Out of these, 185 moons orbit around the full size planets and 8 moons revolve around the dwarf planets. Moons come in various sizes and shapes. They differ from each other in various ways. Most of the moons are airless. However, there are some that have atmosphere. Some even have hidden oceans. Each planet has different number of moons. Earth has just one moon while Jupiter has the highest number of moons. It has a total of 79 moons. Moons orbit around their respective planets.
In addition to the aforementioned, there are many other celestial bodies in our solar system. These include the Interplanetary Medium, Kuiper Belt, Oort Cloud, asteroids and meteoroids. The Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud comprise of billions of icy objects. Each celestial body in our solar system is unique with its own set of features.
Essay on Solar System and Planets (500 words)
Our Solar System – A Small Part of the Universe
Our solar system is huge but nothing compared to the size of the universe. The universe is humongous and is believed to encompass numerous solar systems consisting of several planets, stars and other heavenly bodies. The universe is all space and time and it is not possible to calculate its spatial size. The size of the observable universe is estimated to be 93 billion light years.
The Galaxies and Solar Systems
Research shows that just like our solar system there are numerous other solar systems in the universe. The universe consists of billions of galaxies. Each of these galaxies has uncountable stars and many of these stars are said to have solar systems of their own. The size of the stars, the number of planets, the geological features of the planets, the number and size of the natural satellites vary from solar system to solar system.
Our solar system is a part of the Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way Galaxy is huge. It has more than 100 billion stars. More than 2500 stars with planets orbiting around them have been discovered in the Milky Way Galaxy. The study in this field is going on constantly. There are numerous planetary systems that the scientists and astronomers are yet to discover.
Our Solar System
Our solar system encompasses Sun which is a big ball of fire. Sun is stationary and forms the centre of our solar system. Eight planets namely, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune revolve around the Sun. Each of these planets move in a fixed path in its own set speed. The geological features of each of these planets are different. While Neptune is freezing cold, Venus is scorching hot. Similarly, while Jupiter is massively big, Mercury is comparatively very small in size. The planet is even smaller than some of the moons in our solar system. The atmosphere of each of the planets is different. Planets have been divided into two groups and the features of the planets within each group also vary vastly.
Earth is the only planet in our solar system which is known to have life. It is filled with vast oceans and gases such as oxygen and nitrogen that render life. Mars is said to share some similarities with Earth. Evidences of ice have been found on the planet. The planet is extremely cold and thus life there seems impossible. However, it is believed that the planet was once wet and warm and life existed here. Astronomers are studying this planet closely and have found many interesting facts about the same. These planets have different numbers of natural satellites.
Apart from this, there are five dwarf planets in our solar system. These are Ceres, Haumea, Makemake, Eris and Pluto. Earlier there were nine planets in our solar system and Pluto was one among them. However, it has now been termed as a dwarf planet.
The Universe is vast and there is a lot to study and discover. Scientists have studied our solar system deeply for centuries and are now moving beyond to study other solar systems and galaxies. A lot of interesting facts about this enchanting universe are likely to surface in the times to come.
Long Essay on Solar System and Planets (600 words)
Our solar system consists of eight planets that revolve around the Sun, which is central to our solar system. These planets have broadly been classified into two categories – inner planets and outer planets. There are four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The inner planets are closer to the Sun and smaller in size as compared to the outer planets. These are also referred to as the Terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are termed as the outer planets. These are massive in size and are often referred to as Giant planets.
Here is brief information about each of these planets:
The smallest planet in our solar system, Mercury is also the closest to the Sun. Its geological features consist of lobed ridges and impact craters. Being closest to the Sun, Mercury’s temperature sores extremely high during the day time. It can go as high as 450 degree Celsius. Surprisingly, the nights here are freezing cold.
Mercury has a diameter of 4,878 km. It does not have any natural satellite.
Venus is said to be the hottest planet of our solar system. It has a toxic atmosphere that traps heat. It is also the brightest planet and is visible to the naked eye. It has a thick silicate layer around an iron core which is similar to that of Earth. Astronomers have seen traces of internal geological activity on this planet.
Venus has a diameter of 12,104 km. Just like Mars, Venus also does not have any natural satellite.
Earth is the largest inner planet. Two-third of this planet is covered with water. It is the only planet in our solar system where life is known to exist. Earth’s atmosphere, which is rich in nitrogen and oxygen, makes it fit for the survival of various species of flora and fauna. However, human activities are having negative impact on its atmosphere.
Earth has a diameter of 12,760 km. It has one natural satellite, the moon.
Mars, the fourth planet from Sun, is often referred to as the Red Planet. The iron oxide present on this planet gives it a reddish appeal. The planet is cold and has geological features similar to that of Earth. This is the reason why it has captured the interest of astronomers like no other planet. Traces of frozen ice caps have been found on the planet.
Mars has a diameter of 6,787 km and two natural satellites.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. It has a strong magnetic field. It largely consists of helium and hydrogen. It has a Great Red Spot and cloud bands. A giant storm is believed to have raged here for hundreds of years.
Jupiter has a diameter of 139,822 km and has as many as 79 natural satellites.
Saturn is known for its ring system. These rings are made of tiny particles of ice and rock. Its atmosphere is quite like that of Jupiter as it is also largely composed of hydrogen and helium.
Saturn has a diameter of 120,500 km. It has 62 natural satellites that are mainly composed of ice.
Uranus, the seventh planet from Sun, is the lightest of all the giant, outer planets. It has a blue tint which is because of the presence of Methane in the atmosphere. Its core is colder than the other giant planets. The planet orbits on its side.
Uranus has a diameter of 51,120 km and 27 natural satellites.
The last planet in our solar system, Neptune is also the coldest of all. It is around the same size as the Uranus but is much more massive and dense. Neptune’s atmosphere is composed of helium, hydrogen, methane and ammonia. It experiences extremely strong winds. It is the only planet in our solar system which is found by mathematical prediction.
Neptune has a diameter of 49,530 km. It has 14 natural satellites.
Scientists and astronomers have been studying our solar system for centuries and the findings are quite interesting. Various planets that form a part of our solar system have their own unique geological features and are different from each other in several ways.
More Information:
- Essay on Role of Science in Making India
- Essay on Wonders of Science
- Essay on Science and Technology
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

1 (page 3) p. 3 The Solar System
- Published: November 2010
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
‘The Solar System’ investigates how long people have been aware of the planets, when planets were first identified, when their distance from Earth was first estimated, and how. What is a planet? How are planets made? What are migrating planets? At what point did we realize that the planets, including Earth, travel around the Sun? Who was Johannes Kepler, and what is the significance of his three laws of planetary motion? An overview is given of the Solar System, the Sun and the planets. The importance of planets' satellites is explored and objects of other types, such as asteroids, trans-Neptunian objects, and comets are placed in context.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Paragraph Writing
- Paragraph On Solar System
Paragraph on Solar System - Check Samples for 100, 150, 200, 250 Words
The eight planets, the sun and the satellites constitute the solar system. Previously, there were nine planets, but Pluto is no longer recognised as a planet now. The sun is at the centre of the solar system, and all eight planets revolve around it. The rotation and revolution of the planets cause the change of the season and day and night.
Table of Contents
Paragraph on solar system in 100 words, paragraph on solar system in 150 words, paragraph on solar system in 200 words, paragraph on solar system in 250 words, frequently asked questions on solar system.
Our solar system is unique in that it supports life on its third planet. Children are taught about the solar system in their schools as it is an important part of our lives. In order to write about the solar system, you can refer to the samples provided below.
As per our knowledge, there are approximately 500 solar systems in the universe. The solar system consists of the sun, the eight planets and the satellites. Other than these, there are asteroids, comets, dust, minor planets, and gas. The Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars constitute the inner solar system, and the asteroid belt lies between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are the outer solar system planets. The rotation of the planets causes the day and night, and the revolution of planets around the sun causes the change of seasons. Our solar system is present in the Milkyway galaxy. As per astronomers and scientists, the earth is the only planetary body that supports life.
The sun, eight planets, and satellites make up the solar system. Asteroids, comets, dust, small planets, and gas are among the other objects found in space. The Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars make up the inner solar system, whereas the asteroid belt is between Mars and Jupiter’s orbit. According to our knowledge, there are around 500 solar systems in the universe. The outer solar system planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the planets revolve around it in their own orbits. The rotation of the planets causes the days and nights, and the changing of seasons is caused by the revolution of the planets around the sun. Our solar system exists in the Milkyway galaxy. According to scientists and astronomers, the earth is the only planetary body where life can exist. But this can be proven wrong after more discoveries about the universe.
The solar system comprises the sun, eight planets (Pluto is considered as a dwarf planet), and satellites. Other than these, there are also asteroids, comets, dust, small planets, and gases found in space. The sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars make up the inner solar system and Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are in the outer solar system. The asteroid belt lies in between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The sun is the biggest star in the solar system, which is at the centre of the solar system and the planets orbit around the sun. The planets rotate on their own axis and revolve around the sun in their own orbits. The rotation causes days and nights, whereas the revolution causes the change of seasons in the planets. The research on our universe is still going on, but there are around 500 solar systems present in our universe, as per the little information we have gathered. Our solar system lies in the Milkyway Galaxy, which appears like a white band in the night sky and is therefore named as Milkyway Galaxy. According to scientists and astronomers, the earth is the only planetary body where life can exist. But this can be proven wrong after other discoveries about the universe.
The sun, eight planets (including Pluto, which is a dwarf planet), and satellites make up the solar system. The inner solar system is made up of the sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, whereas the outer solar system is made up of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Between Mars and Jupiter’s orbits is where the asteroid belt lies. Asteroids, comets, dust, tiny planets, and gases are among the other objects that can be found in space. The sun is the largest star in the solar system, located at the centre of the system, around which all the eight planets revolve. Planets rotate in their own axes and follow their own orbits around the sun. The rotation of the planets in their own axes causes the change of day and night, and the revolution causes the change of seasons throughout the year. Research about the universe is still a vast ongoing process, but different scientists and researchers have come to various conclusions about the solar system. It has been found that the solar system lies in the Milkyway Galaxy. The Milkyway galaxy got its name from the Romans, who thought the earth’s nighttime skyline looked like a band and a patch of milk. As per our little knowledge, we know that there are about 500 solar systems in the universe, but later, there might be some additions. As per scientists and astronomers, the earth is the only planetary body where life can exist, but this can be proven wrong after more research and discoveries about the universe.
What are the components of the solar system?
The solar system consists of the sun, eight planets, satellites, asteroids, gases, comets, and dust particles.
How are days and nights caused?
Days and nights are caused due to the rotation of the planets in their own axes. It will be a day on the sun-facing side of the planet and a night on the other side.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Your Article Library
Short essay on solar system.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here is your essay on Solar System!
The Solar System is made up of all the planets that orbit our Sun. In addition to planets, the Solar System also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, minor planets, dust and gas. The inner solar system contains the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The main asteroid belt lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The planets of the outer solar system are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune (Pluto is now classified as a dwarf planet).

Image Courtesy : upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/a9/Planets2013.jpg
Everything in the Solar System orbits or revolves around the Sun. The Sun contains around 98% of all the material in the Solar System. The larger an object is, the more gravity it has. Because the Sun is so large, its powerful gravity attracts all the other objects in the Solar System towards it. At the same time, these objects, which are moving very rapidly, try to fly away from the Sun, outward into the emptiness of outer space.
The result of the planets trying to fly away, at the same time that the Sun is trying to pull them inward is that they become trapped half-way in between. Balanced between flying towards the Sun and escaping into space, they spend eternity orbiting around their parent star.
The Planets orbit in the same direction (counter-clockwise looking down from above the Sun’s North Pole); all but Venus, Uranus and Pluto also rotate in that same sense. Mercury has the fastest elliptical orbit,
48 km per second. It has the shortest revolution at 88 days. Pluto has an orbital speed of 5 km per second. It takes 248 years for Pluto to make one complete revolution.
Related Articles:
- Paragraphs on Solar System (601 Words)
- Solar System: Keynotes on our Solar System
Solar System
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
CBSE Library

Essay On Solar System and Planets | Solar System and Planets Essay for Students and Children in English
Essay On Solar System and Planets: Essay On Solar System and Planets: Our solar system consists of eight planets and the various satellites associated with it. There were nine planets before, but pluto was derecognised as a planet. In this essay on solar systems and planets, we will be talking about each planet and its properties and unique facts. We have the sun around which all the eight planets revolve. An informative and comprehensive essay on solar systems and planets will be provided below.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Solar System and Planets for Students and Kids in English
We have provided 600-word long essay on solar system and planets and a short essay on solar system and planets with a word limit of 200. These essays can be used by school students and children for project works, assignments, holidays homework, test, exam, quiz and essay writing competition.
Long Essay On Solar System And Planets 500 Words in English
Find below a long essay on solar system and planets with a word limit of 600 is helpful for students of classes 7,8,9 and 10.
The universe consists of more than 500 solar systems as of now or as of our limited knowledge on the universe. Our solar system is present inside the Milkyway galaxy. The Milkyway galaxy is called so because the Romans named it as they found the earth’s skyline at night to resemble that of a band and a patch of milk. The solar system is the most important part of our Milkyway galaxy. According to experts and astronomers, the solar system is the only planetary body in the universe that supports life. And earth, a part of the solar system, is the only planet that supports life in the universe. But this can easily be false since man has not discovered all the aspects of our universe.
Solar systems consist of eight planets, which are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Pluto was also a planet but it was derecognized a few years ago because of its size. The main criteria for being a planet are it should orbit around the sun, it should have sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium and it should have a clearly defined neighborhood around its orbit. Pluto failed in the second criterion. But Pluto is known as a dwarf planet. All these decisions of naming, recognizing and derecognizing of planetary objects are taken by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Basically, IAU is an international body that consists of astronomers and scientists all across the world with the main objective and goal of promoting and safeguarding the astronomical sciences in every sphere, through collective international cooperation.
Each planet present in the solar systems revolves around the sun inside their own orbits at their own speed. This is an essential criterion to be declared as a planet in the solar system.
Each of the planets that we mentioned has its own characteristics, which is given below
Characteristics of the Planets in the Solar System
- Mercury: Mercury also knows as the swift planet, is the smallest, hottest and the closet planet to the sun in the solar system. The temperature on Mercury can go as high as 450-degree Celcius on normal days but the nights are freezing cold. Mercury completes one revolution in 88 earth days. With a diameter of 4878 kilometers and a distance of 35 million miles from the sun, mercury is the fastest planet in the solar system
- Venus: Venus also called as a morning star, is the second closet planet to the sun in the solar system. With a distance of 67 million miles from the sun, Venus completes one complete revolution around the sun in 255 earth days. It is also known as the hottest planet in the solar system. On bright days, Venus is visible through the naked eye because it also one of the brightest planets
- Earth: The third planet in the solar system is the only known planet in the whole universe which can sustain life. Nicknamed as the blue planet, Earth completes one revolution around the sun in 365 earth days and is at a distance of 93 million miles from the sun. With a diameter of 12760 kilometres, the earth is covered with two-thirds of water on its surface. The presence of water and oxygen is what makes earth sustain life.
- Mars: Also known as the red planet is the fourth planet from the sun. It is called a red planet because of the presence of iron oxide on the Martian surface which gives it the red tinge. With a distance of 142 million miles from the sun, Mars completes one full revolution around the sun in 687 earth days. It is considered to be a cold planet and has certain physical and geographical features that are similar to the earth. It is most likely to be the next home for human beings after the Earth
- Jupiter: Nick-named as the giant planet of the solar system is fourth in line from the Sun and is the biggest known planet soo far. With a huge diameter of 139,822 kilometers and a distance of 484 million miles from the sun, Jupiter takes almost 4333 earth days to complete one revolution around the sun. Jupiter is known to have 79 natural satellites revolving around it. It also has great red spots and cloud bands surrounding the planet.
- Saturn: Known as the ringed planet, because of the numerous rings around it, which are made up of ice particles. Saturn is at a distance of 887 million miles from the sun and takes 10,759 earth days to complete one complete revolution around the sun. It has 62 natural satellites composed of ice
- Uranus: Uranus is the second largest planet with a diameter of 51,120 kilometers and takes 30,687 earth days to complete one revolution. It is also the coldest planet in the solar system
- Neptune: The last planet in the line is Neptune also called a big blue planet. It is 2.8 billion miles away from the sun and takes 60,190 earth days to complete one revolution.

Short Essay On Solar System and Planets 200 Words in English
Find below a short essay on solar system and planets with a word limit of 200 is helpful for students of classes 1,2,3,4,5 and 6.
Our solar system is made up of eight planets, which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Each of these planets has unique characteristics and properties. Pluto is known as a dwarf planet which as at the farthest distance from the sun.
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun at a distance of 35 million miles from the sun. It is nicknamed as the swift planet. The second in line is the Venus, also knows as the morning star, is the brightest planet in the solar system which can be seen by human beings from earth. The third in line is Earth, known as the blue planet, which is the only known planet in the universe that supports life. The fourth in line is the Jupiter which is the biggest planet in the solar system with a diameter of 139,822 kilometres. The fifth in line is the Saturn known to be the ice planet of our solar system is at a distance of 887 million miles from the sun. The sixth in line is the Uranus which is the 2nd largest planet and is full of methane in its atmosphere. The last planet in the solar system is Neptune which is at a distance of 4.5 billion kilometres from the sun and has helium, hydrogen, ammonia and methane in its atmosphere.
10 Lines On Solar System and Planets Essay
- The Solar system consists of 8 planets and one Sun
- The 8 planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
- For a planetary body to be called a planet, it needs to fulfil the criteria given by IAU (International Astronomical Union)
- Internation Astronomical Union is responsible for discovering, naming and taking care of the science of astronomy in the world
- There are more than 500 solar systems in the universe.
- Each planet has its own properties and characteristics
- Earth is the only known planet to support life
- Jupiter is the biggest planet in the solar system
- Mercury is the smallest known planet
- Sun is not a planet but is considered as a star.

FAQ’s on Essay On Solar System and Planets
Question 1. How many planets are there?
Answer: There are 8 planets
Question 2. Is the sun a star or a planet?
Answer: Sun is a star located at the centre of our solar system
Question 3. What is the most Earth-like planet?
Answer: Kepler-452b is the most Earth-like planet in the universe
Question 4. What is the difference between a galaxy and a universe?
Answer: Galaxy is a cluster of stars while the universe consists of planets and celestial bodies.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
The Origins of the Solar System Essay
Introduction.
The origin of the Sun and its orbiting planets has been a point of hypothesis and conjecture ever since man looked upon the stars and planets and wondered about their origins. For the ancient Greek and Roman civilization the celestial bodies they observed in the sky were thought of as Gods and Goddesses, looking down up the Earth from some form of godlike platform. Today, it is an established fact that the heavenly bodies we see in the night sky are composed of planets and stars, celestial bodies of rock, gas and varying forms of elements that were formed billions of years ago. Even though such objects have been observed for hundreds of years it is only within the last 200 that humanity has begun to understand their unique qualities. While there have been conjectures, varying hypothesis and age old established theories what must be understood is that as the science of astronomy evolves humanity begins to slowly adapt to new information, new discoveries and subsequent re-evaluations of what we knew of as fact. For example, early studies of astronomy adopted the geocentric model in that they believed that the sun, planets, moon and stars revolved around the Earth, not only that there was also the belief that the Earth was in fact flat (Copernicus, 2009: 83). It is based on this that when examining the established theories on the origins of the solar system one must do so with both an open yet skeptical mind, taking into account the given data and observations yet not clearly adhering to any one theory as being definitive proof.
Another interesting topic that should be taken note of is the origin of the Earth itself for just as there have been numerous theories as to the origin of the solar system there have been a plethora of theories which have attempted to determine the origin of the Earth itself. Our home planet is unique in that it is the only planet within our solar system that has sufficiently developed to be able to support life. While there have been varying accounts of how life came to be on Earth, with religion and science vying for attention, the fact remains that the uniqueness of our planet should not be underestimated and as such bodes a certain degree of curiosity as to the origins of the unique circumstances that enabled Earth to become what it is today. It is based on the various questions presented that this paper will explore the origins of the solar system and of Earth itself in order to attain a clear picture of where it came from and what its possible end could be.
The Nebular Hypothesis

Currently, one of the most widely accepted theories regarding the formation of the solar system is that of the nebular hypothesis which states that the solar system originated from a molecular cloud wherein through the introduction of an external force caused a gravitational collapse of the fragment resulting in the creation of A pre-solar nebula that would eventually become our solar system (Glassmeier, 2006: 1 – 5). While there has been no definitive evidence as to the exact origin of the external force that caused a section of the molecular cloud to collapse rather than dispersing it into space it is theorized that the energy from a nearby supernova produced sufficient enough force to cause the collapse and help trigger the necessary events needed to create the solar system. While few studies dispute the nebular hypothesis several do call into question the theory that a supernova caused the initial collapse. Studies such as those by Woolfson (2010) state that the energies from a supernova instead of causing a section of the molecular cloud to collapse would have actually dispersed a majority of the cloud into space thus preventing the formation of the solar system (Woolfson, 2000: 1 – 15). Furthermore, while the nebular hypothesis has been well established as a guiding concept in understanding the creation of celestial bodies little is known as to the precise origins of the molecular cloud that gave birth to the solar system itself. Several scientists such as Lognonne et al. (2007) state that origin of the Sun and its surrounding planets was a molecular cloud and go to great lengths explaining how it led to the creation of the solar system yet a lot of studies neglect to mention how the molecular cloud came to be in the first place (Lognonne et al., 2007: 1 -3)
Origin of the Molecular Cloud
While this paper has so far expounded on the nebular theory involving the Solar system’s origins as coming from a giant molecular cloud a rather interesting question comes to mind, “if the origin of the solar system is that of a giant molecular cloud where did the molecular cloud come from?”. Studies such as those by Sorrell (2008) explain that while our own sun is 4.5 billion years old the age of the universe itself has been estimated at roughly 13.75 billion years (estimate subject to change due to varying accounts as to the proper calculation) (Sorrell, 2008: 45 – 49). Furthermore it must be noted that our sun is not the oldest sun in the universe let alone in our galaxy and in fact can be considered in the prime of its “youth” as a main sequence star (Naylor, 2009: 432). It has been theorized by researchers such as Freire (2008) that a few billion years after the Big Bang, Super Massive stars, many times the temperature of our current sun and several times its size, were among the first stars to form within the universe (Freire, 2008: 459-460). These celestial bodies were able to grow to such great size due to less “competition” for available materials in order to coalesce into stars; it must be noted though that at this point in time planets were unable to form due to the lack of heavier elements in which a sufficient enough solid mass could coalesce into a planet (Dessart, 2010: 2113-2125).
Rather interestingly, it was actually due to the inherent instability of Super Massive stars that the universe became what it is today; this is due to the theory that as a direct result of their internal instability most of the original Super Massive stars became supernovas which actually caused the original molecular clouds in the universe to form (Dessart et al., 2010: 2120 – 2125). The original state of the universe was actually more “pure” in the sense that there was a distinct lack of heavier elements, as such the question of “where did the heavier elements come from?” comes to mind. This is actually resolved by looking at the activity of our own sun wherein through a process called stellar nucleosynthesis in which the nuclear reactions within the sun itself is able to help build the nuclei of elements that are heavier than hydrogen (Chiosi, 2010).
Runaway Star Hypothesis
In relation to the explanation of the origins of the molecular cloud as coming from the debris from Super Massive stars Courtland (2010) presents a new theory that details exactly how the molecular cloud that spawned the solar system came to be. In her study which involved the examination of various meteorites she discovered that sealed within the rock were calcium-aluminum rich incisions (Al-26) that could only have been formed by stars that were at least 10 times as massive as the sun (Courtland, 2010: 8). Due to the fact that Super Massive stars usually form within clusters with Al 26 usually decaying rapidly due to the intense heat within such clusters it is hypothesized by Courtland (2010) that a run away must have been tossed out of its orbit as a direct result of either an explosion of a nearby Super Massive star or due to combined gravitational push by its sibling stars within the cluster (Courtland, 2010: 8). Due to Super Massive stars having a relatively short life cycle when the star became a supernova the dispersed molecules and elements became the molecular cloud that we know of today as being the primary basis of the nebular hypothesis.
Formation of the Sun and Planets
Creation of the sun.
Since this paper has now established the various theories which attempt to explain the origins of the molecular cloud that brought about the creation of the solar it is now necessary to explain the current prevailing theory on how the planets and the creation of the sun came about. As mentioned earlier, in the section detailing the nebular theory, it was explained that as a direct result of a gravitational collapse of a section of the molecular cloud this precipitated the creation of the solar system (Boeyens, 2009: 493-499). A better explanation of this would be that as section of the nebula collapsed this produced a certain degree of angular momentum wherein the nebula actually began to spin faster as it collapsed in on itself. This spinning combined within the collapse produced a great deal of kinetic energy within the core of the molecular cloud until the result was a contraction of the center of the molecular cloud, which had now become a disc shaped object, into what is known as a proto-star, namely a star that has yet to have hydrogen fusion occur at its core (Boeyens, 2009: 493-499). Within 50 million years the internal temperature and pressure of the core itself was able to build to sufficient levels resulting in the start of hydrogen fusion marking the entry of the sun into its life as a main sequence star (Boeyens, 2009: 493-499)
Theory of Accretion
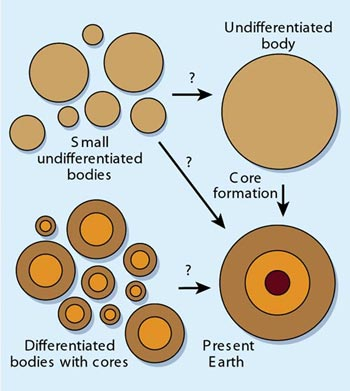
The theory of accretion is currently the most widely accepted theory proposing the creation of the planets, in it the theory indicates that the leftover material from the sun’s creation continued to spin around the sun slowly clumping together piece by piece until larger dust shaped particles were created (Ogihara et al., 2007: 522-530). Gradually these dust particles also began clumping together resulting in the creation of larger and larger objects until finally the entire solar system was composed of literally dozens of moon sized objects that crashed into each over a period of several million years (Ogihara et al., 2007: 522-530). It must be noted that the reason why such a process didn’t just create a system of bits and pieces of rock is due to the fact that these moon sized objects actually had viscous outer cores in the sense that their composition was similar to lava due to the high temperatures of the sun at the time and the process of accretion itself. As such when the objects collided what resulted was not a titanic clash that mutually shattered the objects but rather a process where both objects combined to form a larger structure or surfaces were “swapped” in the sense that certain parts of either proto-planet’s surface accreted to the colliding object (Ogihara et al., 2007: 522-530).
Creation of the Earth
Originally the Earth was a proto-planet no bigger than the moon yet over several million years the process of accretion was able to slowly build up the Earth to its present shape. It must be noted though that the early outer core of the planet was fluid in that due to the intense heat present at the time metals that had accumulated on the planet’s surface slowly submerged into the inner core creating the metallic core that is present today (Robin, 2008: 4061 -4075). Within 150 million years of the planet reaching its current mass the surface sufficiently cooled resulting in the creation of a primitive crust, yet unlike today the surface of the Earth is estimated by studies as being roughly 1600 degrees Celsius with numerous volcanoes dotting the landscape releasing gases into the atmosphere which formed the initial atmosphere of the planet which was kept in place by Earth’s inherent gravity (Robin, 2008: 4061 -4075).
Formation of the Oceans: Comet/Proto-planet Impact Theory
Most scientists agree that the presence of water on the Earth was the pivotal necessity necessary in order for life to start on the planet. When examining the process of Earth’s creation though there seems to be few indicators of water actually forming directly from the process of creation or within the Earth itself (Robin, 2008: 4061 -4075). One theory that attempts to explain this is the comet/proto-planet impact theory which states that proto-planets, planetoids and comets that were composed of ice were actually prevalent in the inner system during the later stages of the process of accretion. (Robin, 2008: 4061 -4075) As such as the Earth continued to orbit around the sun it supposedly impact millions of comets along with several icy proto-planets to create the water that can be seen in the oceans today. In fact, 4.4 billion years after the creation of the sun the Earth had actually sufficiently cooled enough to actually create clouds, rain, and the even oceans on the planets surface (Robin, 2008: 4061 -4075). This particular period marks the creation of the atmosphere that is present in the world today which is a combination of oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases.
By the end of this paper it has become apparent that the process of creation of our solar system and even of our planet has been an accumulation of fortunate incidents that culminated in humanity evolving into its present state. When examining the theories explaining the creation of the molecular cloud, how Courtland (2010) presented the notion that the molecular cloud our present system came from originated from a rogue Super Massive star that coincidentally was shot out of its group by gravitational forces, that it was able to travel far enough to an area ideal enough for uninterrupted growth, that the creation of our planet was in the right place, at the right time with readily available water literally crashing into the planet in order to support life; a combination of all of these completely coincidental factors almost leads one to believe that the creation of humanity itself was no accident but on purpose. On the other hand there are quite literally billions upon billions of solar systems within the universe and it might actually be the case that the process that created the Earth is not so coincidental and that somewhere out there life similarly exists on thousands of planetary systems with the exact same composition as that of humanity yet far away enough that we cannot see the similarities at the present.
Reference List
Boeyens, JA 2009, ‘Commensurability in the solar system’, Physics Essays , 22, 4, pp. 493-499, Academic Search Premier.
‘Copernicus’ 2009, American Heritage Student Science Dictionary , p. 83, Science Reference Center.
Courtland, R 2010, ‘Runaway star may have spawned the solar system’, New Scientist , 205, 2754, p. 8, Academic Search Premier.
Chiosi, C 2010, ‘Primordial and Stellar Nucleosynthesis Chemical Evolution of Galaxies’, AIP Conference Proceedings , 1213, 1, pp. 42-63, Academic Search Premier.
Dessart, L, Livne, E, & Waldman, R 2010, ‘Shock-heating of stellar envelopes: a possible common mechanism at the origin of explosions and eruptions in massive stars’, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , 405, 4, pp. 2113-2131, Academic Search Premier.
Fazekas, A, (2010), Hubble telescope catches superfast runaway star . Web.
Freire, PC 2008, ‘Super-Massive Neutron Stars’, AIP Conference Proceedings , 983, 1, pp. 459-463, Academic Search Premier.
Glassmeier, K, Boehnhardt, H, Koschny, D, Kührt, E, & Richter, I 2006, ‘The Rosetta Mission: Flying Towards the Origin of the Solar System’, Space Science Reviews , 128, 1-4, pp. 1-21, Academic Search Premier.
Lognonne, P, Des Marais, D, Raulin, F, & Fishbaugh, K 2007, ‘Epilogue: The Origins of Life in the Solar System and Future Exploration’, Space Science Reviews , 129, 1-3, pp. 301-304, Academic Search Premier.
McFadden, L, Weissman, P, & Johnson, T 2007, Encyclopedia of the Solar System , Elsevier LTD., eBook Collection. Web.
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan. (N.I.). Hd 141569a’s disk . Web.
Naylor, T 2009, ‘Are pre-main-sequence stars older than we thought?’, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , 399, 1, pp. 432-442, Academic Search Premier.
N.I.. (2010). The Creation of the Earth. Web.
Ogihara, M, Ida, S, & Morbidelli, A 2007, ‘Accretion of terrestrial planets from oligarchs in a turbulent disk’, ICARUS , 188, 2, pp. 522-534, Academic Search Premier.
Photo Journal. (2007). Pia09967: water’s early journey in a solar system (artist concept) . Web.
Robin M., C 2008, ‘Accretion of the Earth’, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical & Engineering Sciences , 366, 1883, pp. 4061-4075, Academic Search Premier.
Sorrell, WH 2008, ‘The cosmic age crisis and the Hubble constant in a non-expanding universe’, Astrophysics & Space Science , 317, 1/2, pp. 45-58, Academic Search Premier.
Woolfson, M 2000, ‘The origin and evolution of the solar system’, Astronomy & Geophysics , 41, 1, pp. 1.12-1.19, Academic Search Premier.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, March 28). The Origins of the Solar System. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-origins-of-the-solar-system/
"The Origins of the Solar System." IvyPanda , 28 Mar. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/the-origins-of-the-solar-system/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'The Origins of the Solar System'. 28 March.
IvyPanda . 2022. "The Origins of the Solar System." March 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-origins-of-the-solar-system/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Origins of the Solar System." March 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-origins-of-the-solar-system/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Origins of the Solar System." March 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-origins-of-the-solar-system/.
- The Solar System’s Nebular Model
- Nebular Model of the Solar system
- Succesorship vs. Accretion
- Proto-Nationalism in Premodern Korea and Since 1780
- “Mars the Abode of Life” by Percival Lowell
- Proto-Nationalism in Korea and Other Nations Since 1780
- What Aspects of Our Behaviour May Have Changed Little Since the Time of Our Proto-Human Ancestors?
- Solar System Formation
- "Proto-Peasant Revolts?" by Craton
- Active Galactic Nucleus: Phenomenon and Detection Methods
- Copernican Model of the Solar System
- Infinite and Non-Expanding Universe
- Astronomy and Astrology Comparison
- Observations and Explorations of Venus
- “In the Beginning” by Cardinal Joseph
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Solar system planets in order: A complete guide
The best facts about all the planets closest to Earth.
Photo credit: Getty/NASA
Toby Saunders
Whether you're a budding astronomer, space enthusiast, or revising for a school exam, knowing the planets in order throughout our Solar System can be incredibly useful.
The most common way of deciding the order of planets is based on the distance of each planet from the Sun . To measure these colossal distances between each planet and the Sun, scientists use Astronomical Units (AU), rather than kilometres. An AU is the distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is a staggering 1.5x10 8 km (149597870.691km, to be exact).
You can also order the planets in terms of size (we’re using diameter to measure this). Either way, you may need to come up with a planet order mnemonic to help remember it (we've got you covered below).
Order of the planets from the Sun

The Sun, while not a planet, is what our Solar System’s bodies orbit around. The Sun is so large that you can fit over 1.3 million planet Earths inside of it. It's so big that it actually accounts for over 99 per cent of the Solar System’s total mass.
How hot is the Sun ? At its core, the Sun is around 15 million°C (27 million°F) while its outer atmosphere measures around 2 million°C (3.6 million°F) on average. Some areas of its atmosphere can reach a staggering 20 million°C (36 million°F).
What’s more, the Sun converts 600 million tonnes of hydrogen into four million tonnes of energy every second . It’s also estimated to have become about 30 per cent brighter since its formation around 4.6 billion years ago.
Fun fact: The Sun isn’t actually yellow/orange, as you might think from its various illustrations, including the one above. The actual colour of the Sun is white .
Strangely, there is such a thing as a day on the Sun – this is measured as the time it takes for the Sun to complete one full rotation relative to its distant stars.
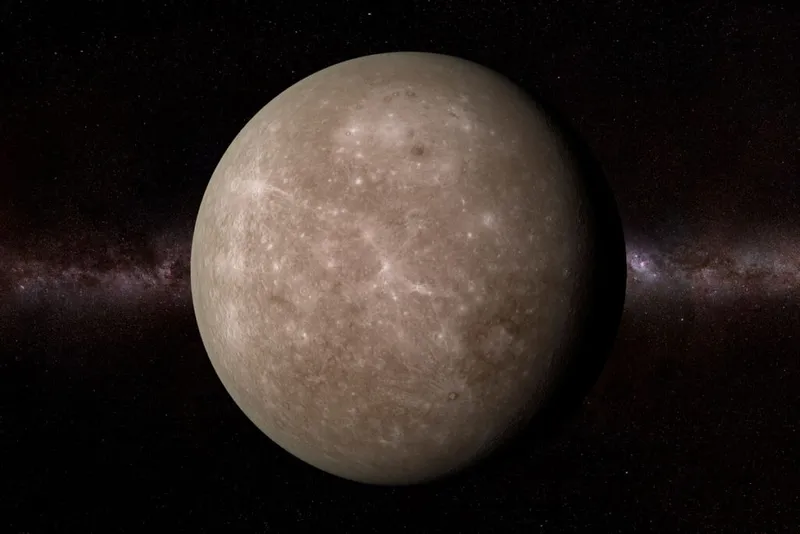

Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and is the smallest planet in our Solar System after Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. Mercury circles around the Sun in an egg-shaped orbit.
Thanks to its egg-shaped orbit, Mercury is also the closest planet to Earth , on average. Venus is on average 1.14 AU from Earth, while Mercury is a little closer at 1.04 AU on average.
Its rocky surface is reminiscent of the Moon’s – it is loaded with canyons – astronomers have even discovered a massive 250-mile-wide trench on the planet. This canyon may suggest that Mercury is getting smaller.
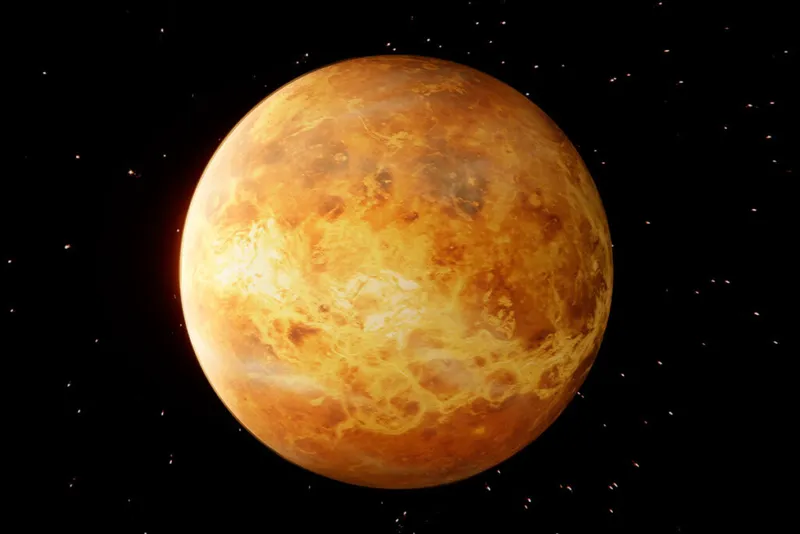

Venus is closest to Earth in size and gets closer to us during its orbit than any other of our Solar System’s planets (although Mercury is closest, on average). Although it is similar enough in terms of size and makeup, Venus can get extremely hot – it is generally the hottest in the Solar System.
The planet's heat, remarkable atmospheric pressure (over 90 times that on Earth) and corrosive acid rain mean that – despite its distance to us – Venus is not a good candidate for an off-world colony. Additionally, the planet's atmosphere is toxic and is around 96 per cent carbon dioxide.
Venus and Earth are remarkably similar planets – both planets feature an iron core and rocky exterior crusts. Volcanoes erupt on both Venus and Earth (not a common feature on planets in our Solar System). As of July 2020, Venus has at least 37 volcanoes that are active.
Fun fact: Venus has its own kind of rainbow , caused by the interference of light waves within droplets. In the form of a series of coloured concentric rings, they are called ‘glories’.
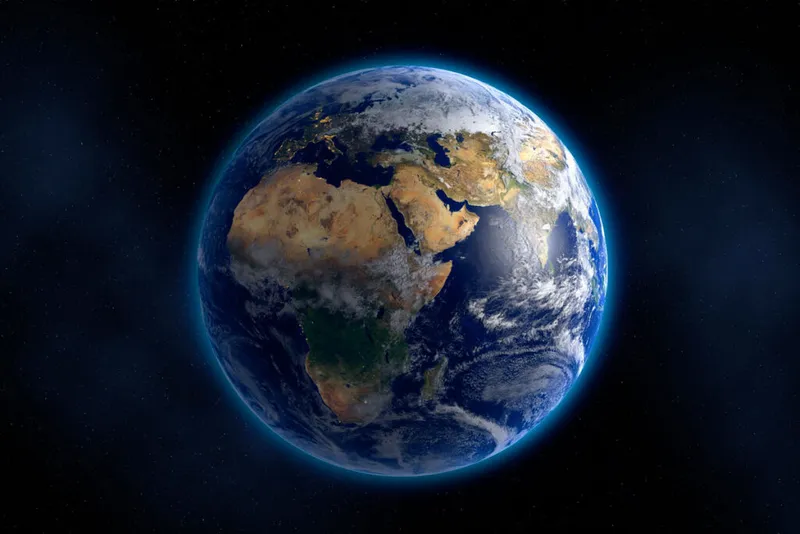

The Earth , our home planet, is the only planet in the Solar System to have just one moon . It is also the only world covered in liquid water and life (that we know).
The Earth is losing around 50,000 tonnes of mass annually. But, given its current mass, it would take close to 120,000 trillion years for it to completely disappear.
Its name originated from the Indo-European base ‘er’, which gave us the Germanic noun ‘ertho’, modern German ‘erde’ and the English ‘earth’.
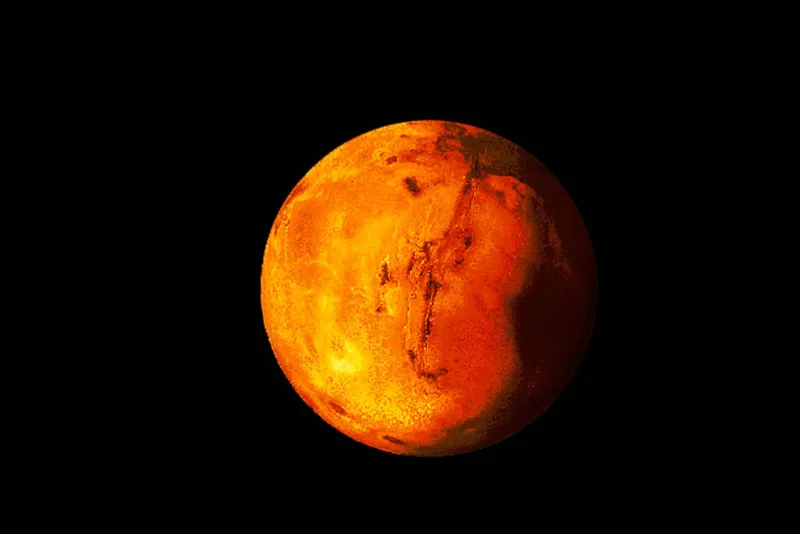

Mars , the Red Planet, gets its red appearance due to the rusting of iron found in rocks and dust. Mars is a surprisingly cold planet, with high temperatures of just 20 °C (70 °F) on its surface – its average is a chilly -63 °C (-81.4 °F).
Although we all know Mars as the dusty red planet, it is thought to have had a very watery past. Kasei Valles, the expansive system of channels that stretch across the Martian surface, was likely formed by multiple floods caused by volcanic activity over three billion years ago.
Mars is home to the tallest mountain in the Solar System , Olympus Mons. The huge volcano measures around 21.9 km from base to peak.
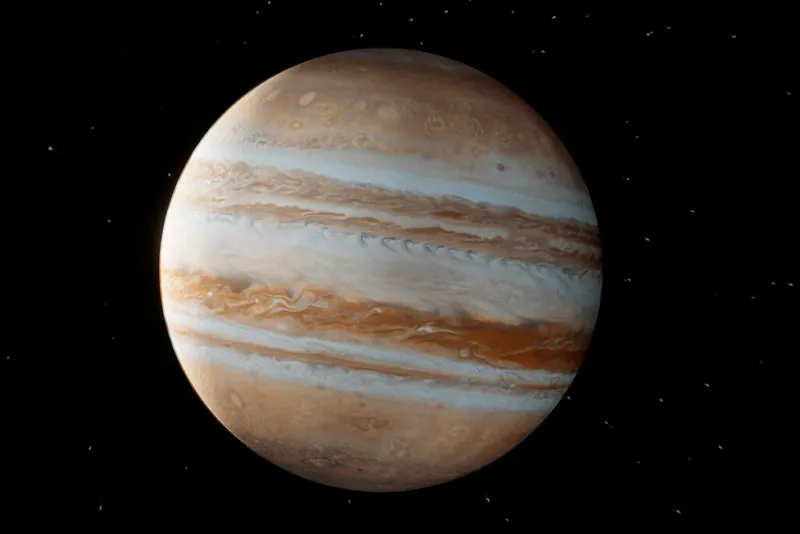

Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar System and the first of the gas giants. The fifth planet from the Sun is mostly swirling gases and liquids, meaning it doesn’t have a true surface. Those swirling gases and liquids help create the planet's stripy appearance .
Often referred to as a failed star, Jupiter’s atmosphere is mostly hydrogen-based . Even though it is massive, the gas giant isn’t big enough to commence thermonuclear reactions in its core and thus become a real star.
The Great Red Spot of Jupiter, which has astounded and confounded astronomers in equal measures since time began, is colder at the top and warmer at the bottom. It’s an ‘anticyclone’ that rotates in a clockwise manner. NASA’s Juno spacecraft revealed that the spot likely has a depth of around 500 km.
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and is famous for its large rings. It is the second-largest planet in our Solar System behind Jupiter. Rings aren’t unique to it (rings can be found around all four of the gas giants, including Jupiter), but Saturn’s are the most noticeable and striking.
Saturn’s rings are composed mostly of water ice and almost completely devoid of dirt . This implies that the rings of this gas giant are relatively young, potentially forming from the destruction of a moon that took place due to the tidal forces of the planet.
Since Saturn’s axis is tilted by 26.73 degrees to the Sun (similar to Earth's 23.5-degree tilt), the planet experiences seasons.
Saturn has 146 officially recognised moons. The number is set to grow, too, with more expected to be officially confirmed and named by the International Astronomical Union.

Uranus is the seventh planet in order from the Sun in our Solar System. What’s special about this gas giant is that it orbits the Sun on its side . This could be because it collided with a massive object not long after its formation.
The first planet to be discovered via the use of a telescope, by William Herschel in 1781, Uranus gets its (hilarious to some) name from the Greek god of the sky. It’s also just one of two planets (along with Venus) that spins in a different direction from the rest.
Uranus’s core should consist largely of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, just as Neptune does, too. However, because of the extreme pressure on Uranuas, which measures several million atmospheres, unexpected and strange compounds should form on its surface.
Fun fact: The moons of Uranus are named after the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope, rather than coming from Greek or Roman mythology. Moon names include Titania (from Shakespeare play A Midsummer Night's Dream ) and Miranda (from The Tempest ).

Neptune is the eighth and final of the planets in our Solar System. The last of the gas giants, Neptune could have been discovered as early as 1612 by Galileo. It is named after the Roman god of the sea.
Interestingly, as the planet has a similar tilt to Earth, Neptune also experiences seasons. However, since one year on the gas giant is around 165 years on Earth, one season lasts for over 40 years.
‘Planet Nine’
There is a theoretical ‘Planet Nine’ (not you, Pluto) that is estimated to exist at the fringes of the Solar System. If it exists, it would have to be around 600 AU away from the Sun and have a mass at least 10 times that of Earth’s. Planet Nine is also known as Nibiru and Planet X.
Astronomers noticed something peculiar while analysing the “motions of objects at the furthest edge of the Solar System.” It was discovered that “the elliptical orbits of many of these objects all seemed to line up in the same direction.” This could mean, then, that a sizeable ninth planet exists out there.
It’s theorised, too, that Planet Nine’s orbit around the Sun would take 20,000 years to complete.
Astrophysicists, meanwhile, have suggested that Planet Nine could in fact be a primordial black hole . This black hole could theoretically be the size of a grapefruit but with a mass that’s five to ten times that of Earth’s.
How to remember the planets in order
To remember the Solar System planets in order, it’s probably best to use a mnemonic. A mnemonic is a handy way to remember things if you need to learn a particular order or list of a set of items. Use the first letter of each planet’s name to develop a phrase, the sillier the better.
So take the first letter of each planet in our Solar System in order: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune – M, V, E, M, J, S, U, N. Use these letters to create a phrase that’s silly enough for you to remember.
Popular mnemonics for remembering the Solar System planets in order include:
- My Very Excellent Mother Just Served Us Noodles
- My Very Easy Method Just Speeds Up Naming
- Most Very Elderly Men Just Slept Under Newspapers
If these mnemonics don’t work for you, try creating your own! Many Very Excellent Methods Just Spring Up Names, after all.
Order of the planets by size
The order of the planets in our Solar System by size (smallest to biggest) is as follows:
- Mercury | 3,457 km diameter
- Mars | 6,792 km diameter
- Venus | 12,104 km diameter
- Earth | 12,756 km diameter
- Neptune | 49,528 km diameter
- Uranus | 51,118 km diameter
- Saturn | 120,536 km diameter
- Jupiter | 142,984 km diameter
Is Pluto a planet?

Pluto is not a planet but is instead a dwarf planet. This was decided by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) back in 2006 when Pluto was reclassified. It’s no longer considered the ninth planet in our Solar System.
The IAU decided that for something to be considered a planet it must meet three criteria. It must...
- Orbit its host star (In our Solar System that’s the Sun).
- Be mostly round.
- Be big enough that its gravity cleared away any other objects of similar size near its orbit around the Sun. This means their gravity should be strong enough to be the dominant object in their orbit, sweeping up or influencing most other objects around them.
It was decided that Pluto is not big enough for its gravity to clear away other objects of similar size in its orbit.
It's argued that if Pluto was declared a planet, three other recently similar bodies (known as Quaoar, Sedna, and Eris) should also be declassified.
Despite this, a planetary scientist, Paul Byrne, thinks Pluto should still be considered our ninth planet . Byrne reasons that “out in the Kuiper Belt, where neighbouring bodies are far, far more distant than in the inner Solar System, Earth would not necessarily be able to clear its neighbourhood.”
By this metric, it could be argued that the Earth would also not be considered a planet if it were located in the same area of space as Pluto.
Pluto fact file:
- Size: 2,370 km diameter
- Mass: 0.01303 x 10 24 kg (around 0.2 per cent of Earth)
- Distance from the Sun: 39 AU average
- Length of day: About 153 hours (roughly 6.4 Earth days)
- Surface temperature: -226 to -240 ℃ (-375 to -400 ℉)
- Number of moons: Five (Charon, Nix, Hydra, Kerberos and Styx)
- Gravity compared to Earth: Around 1/15 compared to Earth (something weighing 100 pounds on Earth would weigh about seven on Pluto)
What dwarf planets are in our Solar System?
There are five officially recognised dwarf planets in our Solar System. Yes, Pluto now counts as a dwarf planet (get over it, it’s been classified as one since 2006).
Here are the officially recognised dwarf planets in our Solar System:
To be considered a dwarf planet, the celestial object must orbit the Sun, be nearly round, but “have not been able to clear their orbit of debris”, according to NASA.
As of writing, the International Astronomical Union has only verified five dwarf planets in our Solar System. There may be over 100 more dwarf planets waiting to be discovered by astronomers, however.
Share this article

You may also like
Science focus, 15 of the best space and astronomy books 2024, 20 of the most amazing moons in the solar system, comets and asteroids: five things you (probably) didn't know about them.

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
Gather Lessons
15 Questions about the Solar System
There are many planetary systems and ours is called the Solar System because our sun is named Sol, after the Latin word for Sun and anything related to the Sun we call “solar.”
Our solar system consists of our star, the Sun the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, dwarf planets such as Pluto, dozens of moons and millions of asteroids, comets and meteoroids.
Table of Contents
These are the 15 most important questions about the solar system
#1 How many planets are there in the Solar System?
There are eight planets in the solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
#2 What’s the nearest planet to the sun?
Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, and it’s also the smallest, only a little bit larger than Earth’s moon.
#3 What’s the second nearest planet to the sun?
Venus is the second planet from the sun, Venus is Earth’s twin in size
#4 What’s the third planet from the sun?
The Earth is the third planet from the sun, Earth is a waterworld, with two-thirds of the planet covered by ocean.
#5 What’s the fourth planet from the sun?
What We Know About the Red Planet . Mars is the fourth planet from the sun.
#6 What’s the fifth planet from the sun?
Jupiter is the fifth planet from our Sun and is, by far, the largest planet in the solar system – more than twice as massive as all the other planets combined.
#7 What’s the sixth planet from the sun?
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in our solar system .
#8 What’s the seventh planet from the sun?
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun . Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky
#9 What’s the eight planet from the sun?
The eighth planet from the sun, Neptune is about the size of Uranus and is known for supersonic strong winds.
#10 How old is our Solar System?
Our solar system formed about 4.5 billion years ago from a dense cloud of interstellar gas and dust
#11 What’s the coldest planet in our solar system?
The seventh planet from the sun, Uranus has the coldest atmosphere of any of the planets in the solar system
#12 What’s the smallest planet in our solar system?
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system—only slightly larger than Earth’s Moon.
#13 How many moons are there in out solar system?
There are more than 200 moons in our solar system. Most orbit the giant planet with Saturn and Jupiter leading moon counts
#14 What planet in the solar system has the most volcanic activity?
The surface of Venus is dominated by volcanic features and has more volcanoes than any other planet in the Solar System
#15 Which planet has the largest ring system?
Saturn’s ring system is the most extensive and complex in our solar system; it extends hundreds of thousands of kilometers from the planet.
#16 Which planet has the most moons?
Jupiter has the most moons of any planet in the Solar System
I am Jose Manuel, English professor and creator of EnglishPost.org, a blog whose mission is to share lessons for those who want to learn and improve their English
Related Posts

Discussion Questions about Transportation

Conversation Questions about School

Conversation Questions about Ethics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Solar System. Our solar system consists of eight planets that revolve around the Sun, which is central to our solar system. These planets have broadly been classified into two categories that are inner planets and outer planets. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are called inner planets. The inner planets are closer to the Sun ...
Short Essay On Solar System and Planets 200 Words in English. Find below a short essay on solar system and planets with a word limit of 200 is helpful for students of classes 1,2,3,4,5 and 6. Our solar system is made up of eight planets, which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. ...
500+ Words Essay on Solar System. The Sun and all other planets and celestial bodies that revolve around it are together called a solar system. Our solar system consists of eight planets and an asteroid belt. These planets are termed inner and outer planets. Earth, Venus, Mercury and Mars are considered inner planets closer to the Sun and ...
Essay on Solar System. We see the sun every day shining in the sky and at night, we see the moon. Many other heavy bodies like satellites, meteoroids, and asteroids not visible to our naked eyes also make up the solar system. The sun and its planets together form the Solar System. The existence of the Solar System is about 4.6 billion years old.
The eight planets of our solar system are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Pluto, which was earlier classified as a planet, is now considered a dwarf planet. There are nearly 200 moons and countless asteroids varying in size. Let us understand about the planets of our solar system and their characteristics.
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. Our solar system is a region of space. It has no atmosphere. But it contains many worlds - including Earth - with many kinds of atmospheres. The planets of our solar system - and even many asteroids - hold hundreds of moons in their orbits. The four giant planets - and at least one asteroid - have ...
The inner solar system comprises Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune form the outer solar system. These four planets are massive in size; hence they are called Giant Planets. Each planet revolves around the sun in its own orbits at its own speed. Let us explore all the celestial bodies present in the Solar ...
Short Essay on Solar System and Planets (200 words) The universe is massive. It is much bigger than we can imagine and our solar system is just a small part of it. Our solar system houses a big, bright star called the Sun. The Sun is a rich source of electromagnetic energy that it exudes in the form of light and heat.
Any natural solar system object other than the Sun, a planet, a dwarf planet, or a moon is called a small body; these include asteroids, meteoroids, and comets.Most of the more than one million asteroids, or minor planets, orbit between Mars and Jupiter in a nearly flat ring called the asteroid belt. The myriad fragments of asteroids and other small pieces of solid matter (smaller than a few ...
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. The largest of these objects are the eight planets, which in order from the Sun are four terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars); two gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn); and two ice giants (Uranus and Neptune).The Solar System developed 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a ...
Learn about the smallest planet in our solar system. Sun. The Sun is the primary source of light and energy and is about 93 million miles from the Earth. It is the only star in our solar system and one of the more than 100 billion stars in the Milky Way. The surface of the Sun is about 5,500 degrees Celsius (10,000 degrees Fahrenheit) hot and the temperature reaches 15 million Celsius (27 ...
The solar system, with its planets, moons, and other celestial wonders, can be truly awe-inspiring. Here's a simple solar system 10 lines essay perfect for budding astronomers and essay for primary class students. 1. The solar system is made up of the sun and all the celestial bodies that orbit around it. 2.
The solar system essay is a remarkable and awe-inspiring essay about encompassing the Sun and its eight major planets, their moons, countless asteroids, and a myriad of comets. At its center is the Sun - a blazing ball of nuclear fusion that sustains life on Earth and all other celestial bodies nearby.
Solar System Processes Research. The disk was formed because of the pulling action of the gravitational force between the nebula particles that acted towards the center of the disk. The Solar System Definition. A 'Shoot for the Moon' is a revelation of the first maiden journey to space by the Americans in the 1960s.
Short Essay on Solar System and Planets (200 words) The universe is massive. It is much bigger than we can imagine and our solar system is just a small part of it. Our solar system houses a big, bright star called the Sun. The Sun is a rich source of electromagnetic energy that it exudes in the form of light and heat.
The Sun. In the centre of the Solar System is the Sun, which is a fairly ordinary star, powered by the conversion of hydrogen into helium by nuclear fusion in its core. The Sun's diameter is 109 times and p. 8 its mass is nearly 333,000 times greater than the Earth's.
Short Essay on Solar System and Planets (200 words) The universe is massive. It is much bigger than we can imagine and our solar system is just a small part of it. Our solar system houses a big, bright star called the Sun. The Sun is a rich source of electromagnetic energy that it exudes in the form of light and heat.
Paragraph on Solar System in 250 Words. The sun, eight planets (including Pluto, which is a dwarf planet), and satellites make up the solar system. The inner solar system is made up of the sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, whereas the outer solar system is made up of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Between Mars and Jupiter's orbits ...
Here is your essay on Solar System! The Solar System is made up of all the planets that orbit our Sun. In addition to planets, the Solar System also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, minor planets, dust and gas. The inner solar system contains the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The main asteroid belt lies between the orbits of Mars ...
Short Essay On Solar System and Planets 200 Words in English. Find below a short essay on solar system and planets with a word limit of 200 is helpful for students of classes 1,2,3,4,5 and 6. Our solar system is made up of eight planets, which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. ...
For example, early studies of astronomy adopted the geocentric model in that they believed that the sun, planets, moon and stars revolved around the Earth, not only that there was also the belief that the Earth was in fact flat (Copernicus, 2009: 83). It is based on this that when examining the established theories on the origins of the solar ...
1354 Words6 Pages. The Solar System. Our solar system comprises of a normal star we call the Sun, the planets Neptune, Uranus, Saturn, Jupiter, Mars, Earth, Venus, and Mercury. It incorporates the satellites of the planets; various comets, asteroids, and meteoroids; and the interplanetary medium. The Sun is the wealthiest origin of ...
Here's everything you need to know about the order of planets in our Solar System. Facts about them and how to remember the order are within.
But the total mass of a solar system's planets never adds up to the total mass of gas and dust available around the young star. ... in short, the outcome of planet formation depends on the ...
15 Questions about the Solar System. Manuel Campos. January 9, 2024. There are many planetary systems and ours is called the Solar System because our sun is named Sol, after the Latin word for Sun and anything related to the Sun we call "solar.". Our solar system consists of our star, the Sun the planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter ...