

Urdu Self-Introductions: “My Name is” in Urdu & More!

An appropriate and friendly introduction in the Urdu language to the natives can allow you to rub elbows with them without much effort. People always take pleasure and pride in speaking their language. To hear the local language from a foreigner’s mouth is a real-time exotic experience which evokes the interest of the locals and serves as the key to rapport-building with them.
Introducing yourself in Urdu won’t be a problem anymore; this article will trigger your first flight to the journey of Urdu -learning by familiarizing you with things like “My name is” in Urdu. Whether you need to learn how to introduce yourself in interview in Urdu or just talking about yourself in Urdu, you’ve come to the right place.
If you’re asking, “How can I talk about myself in Urdu language?” learning a few basic Urdu introductory sentences or lines to introduce yourself in Urdu can prove to be a good beginning for you. However, before proceeding further into how to introduce yourself in Urdu language, you’ll greatly benefit from firsthand knowledge about Pakistani Urdu culture.
Table of Contents
- Some Do’s and Don’ts in Pakistanti Urdu Culture
- Seek Attention with Greetings
- Inquiring After Someone’s Well-Being in Urdu
- Identifying Yourself
- Placing Yourself in Society
- Express Gratitude at the End of the Discussion
- Practice and Exercise: Write a Sample Essay to Introduce Yourself in Urdu
- How UrduPod101.com Can Help You

1. Some Do’s and Don’ts in Pakistani Urdu Culture
Before beginning, be sure to check out our “Urdu in Three Minutes: Introducing Yourself in Urdu” video above!
When visiting an Urdu-speaking society like Pakistan , you must keep some social, cultural , and religious factors in consideration. These factors will help you win the confidence of the natives and enjoy your stay there. Let’s have a cursory look at some of the salient factors in this regard.
- Avoid having consistent eye-contact with the opposite gender. It’s not advisable in Pakistani society, and is almost an offense in some cases.
- Avoid shaking hands with the opposite gender.
- Keep a reasonable physical distance from the opposite gender while talking.
In short, the list above indicates that you should always be considerate enough to use different body language for different genders, as this is a significant aspect of Pakistani Urdu culture.
Now that we’ve discussed a few important do’s and don’ts, below are a few magical sentences and phrases to equip you with answers to the most common questions. Here’s how to introduce yourself in the Urdu language, from self-introduction in Urdu for interviews to talking about where you are from in Urdu!
2. Seek Attention with Greetings
How to introduce yourself to someone in Urdu (or any language) begins with hello.
- السلام علیکم Assalam-o-Alaikum. “Hello.”
السلام علیکم ( Assalam-o-Alaikum ) is the most widely used greeting in Pakistan to seek attention and start a discussion with someone to introduce yourself in Urdu. It literally translates to: “Peace be upon you.” Although it doesn’t translate to the English greeting “ hello ” exactly, it’s the near equivalent to it. It’s the biggest icebreaker in the Urdu language. Once you can pronounce it properly, you’ve taken your first step toward mastering the best way to introduce yourself in Urdu.
Subsequently, to conclude a conversation with the phrase خدا حافظ ( Khuda Hafiz ) is the most appropriate ending. Literally, it means, “May God protect you.” It will always leave a good taste in the mouth of the person you’ve talked with. You may use these greetings for males and females both, without any gender discrimination.
Remember! During self-introduction in Urdu language, shaking hands with the same gender is desirable; however, always avoid shaking hands with the opposite gender.

3. Inquiring After Someone’s Well-being in Urdu

How to inquire about someone’s general well-being or health in Urdu is another thing which may be on your mind after meeting a native Urdu speaker. Following are the key sentences you can use to ask about someone’s well-being (or talk about your own).
If inquiring about the health of a male, you’ll use:
- آپ کیسے ہیں؟ Aap kaisay hain? “How are you?”
If inquiring about the health of a female, you’ll use:
- آپ کیسی ہیں؟ Aap kaisi hain? “How are you?”
Here’s the most suitable answer to the question:
- میں بالکل ٹھیک ہوں، شکریہ۔ Mein bilkul theek hun, shukriya. “I am perfectly alright. Thank you.”
تم کیسے ہو؟ ( Tum kaisay ho? ) when asking a male, and تم کیسی ہو؟ ( Tum kaisi ho? ) when asking a female, or “How are you?” is another sentence to ask about the well-being of someone while introducing yourself in Urdu. However, this sentence is an informal way of inquiring after people of your own age group or who are younger than you. If spoken to an elder or a senior , it’s taken as a sign of disrespect.
For new learners, the informal way of inquiring after someone isn’t recommended. Thus the tip of the day is to be as formal as you can at the beginning, for it will save you many embarrassing situations.
4. Identifying Yourself
The universal practice of naming is important to all human beings across the globe. Therefore, beginning to introduce yourself in Urdu by disclosing your name is the best possible strategy.
1- Talking About Your Name in Urdu

How to say my name in Urdu may be the most pertinent question in your mind after the greeting session. Here are three widely used ways of stating your name in Urdu, along with the question you can use to ask someone else’s name.
Let’s start with the question.
- آپ کا نام کیا ہے؟ Aap ka naam kya hai? “What is your name?”
There are three popular ways to state your name in Urdu.
1. میرا نام ۔۔۔۔۔ ہے۔ Mera naam …..hai. “My name is ……”
2. مجھے ۔۔۔۔۔ کہتے ہیں۔ Mujhe …… kehty hain. “I am known as ……”
3. میں ۔۔۔۔۔ ہوں۔ Mein ….. hun. “I am …..”
In all three cases, fill the blank space with your first name. If you’re wondering how to introduce yourself in an interview in Urdu, or about any other informal occasion of introducing yourself in Urdu, the above examples are a good way to go about this.

The first one is the most popular and recommended answer. Also, keep in mind to introduce yourself with your first name because it’s normative in Pakistan to call someone by their first name.
Now, let’s look at another advantageous sentence: the “Please introduce yourself,” meaning in Urdu. This is roughly equivalent to “Tell me about yourself,” in Urdu.
- مہربانی فرما کر، آپ اپنا تعارف کروائیں۔ Maharbani farma kar, apna taaruf karwain. “Please, introduce yourself.”
2- Talking About Your Age in Urdu
Telling your age or asking another’s is another way of keeping the discussion going and engaging someone in your introduction in the Urdu language. An Urdu-speaking person may ask your age as follows:
- آپ کی عمر کتنی ہے؟ Aap ki umer kitni hai? “How old are you?”
Here’s the most recommended way to reply:
1. میں ۔۔۔۔۔ سال کا ہوں۔ Mein …… ka hun “I am …… years old.” [Male]
2. میں ۔۔۔۔۔ سال کی ہوں۔ Main …… ki hun “I am …… years old.” [Female]
You can fill in the blank space with the exact digit or number in Urdu of your age. Please, keep in mind that the first sentence is for the masculine gender, and the second for the feminine gender. The Urdu words کا ( ka ) and کی ( ki ) show the masculine or feminine possession of something, respectively.
3- Nationality

If you find it necessary to disclose your nationality in Urdu , you can always benefit from the following sentences.
- آپ کون سے ملک سے ہیں؟ Aap kon say mulk say hain? “Which country are you from?”
1. میں جاپان سے ہوں۔ Mein Japan say hun. “I am from Japan.”
2. .میں جاپانی ہوں Mein Japani hun. “I am Japanese.”

Here, once again, we have two sentences to state our nationality; however, these sentences aren’t gender case sensitive. The basic difference between them is that if you want to use the name of your country in Urdu without any change, then you can opt for the first sentence.
However, if you want to state your nationality, go with the second sentence by mentioning your nationality in the blank space.
5. Placing Yourself in Society

1- Occupation: Talking About Your Job in Urdu
To state your profession or occupation in Urdu helps you to open new vistas for discussion, while simultaneously accelerating the process of socialization. Below are some sentences you can use to state your profession in the Urdu language.
- آپ کا پیشہ کیا ہے؟ Aap ka peisha kya hai? “ What is your profession ?”
1. میں پیشے سے ۔۔۔۔۔ ہوں۔ Mein peishy say ….. hun “By profession, I am a ……”
2. میں ایک ۔۔۔۔۔ ہوں۔ Mein aik ….. hun “I am a ……”
In both cases, you need to write down your exact profession, without any change (e.g. doctor, engineer, lawyer, etc.). This will clearly indicate your profession to the questioner.
2- Marital Status
Now, if you’ve become intimate enough with someone, it may be time to share your personal details with him/her. Telling about your marital status is one such personal share. Here are some phrases you can use to talk about your marital status in Urdu:
- کیا آپ شادی شدہ ہیں؟ Kya aap shadi shuda hain? “ Are you married ?”
1. جی ہاں، میں شادی شدہ ہوں۔ Jee haan, mein shadi shuda hun “Yes, I am married.”

2. جی نہیں، میں شادی شدہ نہیں ہوں۔ Jee nahi, mein shadi shuda nahi hun. “No, I am not married.”
The first reply affirms that you’re married, while the second one negates.
3- Talking About Your Family in Urdu: Family Details
If you want to extend the conversation and share some more information about your family members in Urdu , this is the right moment. Ask about the other person’s children, or tell about your own, as follows.
- آپ کے کتنے بچے ہیں؟ Aap kay kitnay bachay hain? “How many children do you have?”
- میرے ۔۔۔۔۔ بچے ہیں۔ Mery ….. bachay hain. “I have ….. children.”
In the blank space, plug in the number of children you have.
Finding someone with a mutual hobby is a very good omen in a foreign land. Always go for a hunt by discussing hobbies in the following manner.
- آپ کا مشغلہ کیا ہے؟ Aap ka mashghala kya hai? “What is your hobby?”
- میرا مشغلہ ۔۔۔۔۔۔ ہے۔ Mera mashghala ۔۔۔۔۔۔۔ hai. “…… is my hobby.”
Fill in the blank space with your hobby, and you’ve hit the bull’s eye!
6. Express Gratitude at the End of the Discussion

Giving a proper ending to your introduction is quite significant; it determines the nature of the future relationship between you and the other speaker. Don’t make haste, and rather try to give proper closure to the discussion.
- آپ کو یہاں آ کر کیسا لگا؟ Aap ko yahan aa kar kaisa laga? “How do you feel here?”
- مجھے یہاں آ کر بہت خوشی ہوئی۔ Mujhe yahan aa kar bohat khushi hui. “I am very happy to be here.”
Don’t forget to respond to thanks with thanks. This is the best available conclusion in Urdu. Besides the following expression, remember to have a look at the common ways to say thank you on UrduPod101.com , as well.
!شکریہ Shukriya! “Thank you!”
Reciprocate the compliment with the same vigor and grace, as this is considered courteous.
Yes, you have concluded your conversation perfectly!

7. Practice and Exercise: Write a Sample Essay to Introduce Yourself in Urdu
No one can undermine the significance of a good introduction, because it’s your first impression on others. Here, you’ve been informed with a few tips, techniques, and sentences that may help you in leaving a good, sound, and memorable impression on native Urdu speakers.
To become fully confident in answering the question of how to introduce yourself to someone in Urdu, try to do different exercises with the help of our website: UrduPod101.com .
Now, how to go about introducing yourself in Urdu?
Initially, writing an essay titled “Myself in Urdu” is a workable suggestion to start with. Practice saying “My name is” in Urdu, and much more in your essay. Here’s a sample essay to provide you with a road map to writing your comprehensive introduction.
1- Sample Essay
میرا نام ہاروکی موراکامی ہے۔ میں ایک جاپانی لکھاری ہوں۔ میں کیوٹو، جاپان میں پیدا ہوا۔ میں ایک جاز بار اور کافی ہاؤس کا مالک ہوں۔ میری عمر ستر سال ہے۔ میں نے ٹوکیو میں واقع وسیڈا یونیورسٹی سے تعلیم حاصل کی۔ میراتھن ریس میرا مشغلہ ہے۔
Mera naam Haruki Murakami hai. Mein ek Japani likhari hun. Mein Kyoto, Japan mein paida hua. Mein ek jazz bar aur coffee house ka malik hun. Meri umer sattar saal hai. Mein nay Tokyo mein waqay weseda university say taleem hasil ki. Marathon race mera mashghala hai.
“My name is Haruki Murakami. I am a Japanese writer. I was born in Kyoto, Japan. I am the owner of a Jazz bar and coffee house in Tokyo. I am seventy years old. I studied drama at Waseda University located in Tokyo. The marathon race is my hobby.”
8. How UrduPod101.com Can Help You

Everyone knows the famous proverbial rule that practice makes a man perfect. If you want to interact with an Urdu-speaking person or community frequently, and you want to get mastery over this art, join us at UrduPod101.com . We’ll give you the best experience of reading and learning something significant about how to introduce yourself in Urdu, and beyond.
Here, you’ll find a few key phrases and sentences to familiarize you with the art of introducing yourself in the Urdu language. In addition, UrduPod101.com has also introduced a series of comprehensive video lectures on Urdu language-learning strategies .
Until next time, let us know how you feel about these phrases and simple introduction etiquettes! Do you feel more confident now? What are the similarities and differences to those in your own country? We’d love to hear from you!
Very Happy Urdu Learning!
Or sign up using Facebook
Got an account? Sign in here

How To Say ‘Thank you’ in Urdu

How to Say Hello in Urdu: Make the Perfect First Impression

How to Say I Love You in Urdu – Romantic Word List

Pakistani National Anthem: Qaumi Taraanah

Classroom Classics: A Companion to Unignorable Urdu Phrases

A Set of Widely Used Unmistakable Urdu Restaurant Phrases
How to celebrate april fools’ day in urdu.
- General Announcements
- Advanced Urdu
- Tips & Techniques
- Urdu Alphabet
- Urdu Grammar
- Urdu Lessons
- Urdu Online
- Urdu Phrases
- Urdu Podcasts
- Pakistani Holidays
- Feature Spotlight
- Success Stories
- Teaching Urdu
- Team UrduPod101
- Uncategorized
- Urdu Language
- Urdu Translation
- Word of the Day
- Working Abroad
Copyright © 2024 Innovative Language Learning. All rights reserved. UrduPod101.com Privacy Policy | Terms of Use . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- , February 23, 2024
Remarkable Ways To Introduce Yourself In Urdu – #1 Guide

If you are soon traveling to or staying in Pakistan, you should know how to introduce yourself in Urdu. Confidence in body language and an efficient introduction to the locals can help you get along with Urdu native speakers.
If you are a travel enthusiast, then you can understand the importance of knowing a second language. If you want to communicate with the native speakers of a particular language, you can always start with a self-introduction. Urdu is the official language of Pakistan, a South-Asian country. Seventy million people speak Urdu as their first language, while 100 million people speak it as a second language. You can learn this highly spoken language through the Ling app .
Express Gratitude With Basic Urdu Greetings
People enjoy and take pride in speaking their native tongue. Hearing a foreign person that speaks a native language is an unusual experience. It serves as a foundation in creating an understanding with them.
The majority of Pakistanis are Muslims. The first step to start the convo is by saying لسلام علیکم ( Assalam-u-Alaikum ) which means “Peace be unto you”. Whenever or wherever Muslims are gathered, the greeting is commonly used. If you are greeting a native speaker, try the following words before starting a conversation or introduce yourself in Urdu.
Keeping in view the Pakistani religion and culture notes, you should follow some basic rules while greeting someone. Don’t make consistent eye contact or shake hands with the opposite gender. It’s frowned upon in Pakistani society. Also, when conversing with the other gender, maintain a reasonable distance.
Sentences To Introduce Yourself In Urdu
Before starting, first, develop confident body language and then speak in a kind manner. It will help you to introduce yourself in a better way. Start with your name and then talk about your age, family, profession, and favorite hobby. Read the following sentences and learn Urdu words and vocabulary.
Common Words And Phrases After You Introduce Yourself In Urdu
Talking to someone in their native language is not as easy as it seems. You should know some basic vocabulary words that will help you in writing and speaking the Urdu language. Here are a few of them.
End Of The Conversation In Urdu
A strong conclusion shapes the nature of your future relationship with the other speaker. Don’t rush things; instead, attempt to bring the conversations to a logical conclusion. So, mastering these examples sentences might help you in making a long-lasting impression on another person.
Learn Urdu With Ling App
Now you can talk to any Urdu native speaker in formal and informal situations and introduce yourself in Urdu. Learning Urdu is not a big deal as long as you have a good tutor. Why pay for courses when you can learn Urdu through the Ling app? A language learning app developed by Simya solutions . Through its audio and video recording, you can grasp your target language quickly.
You can learn Urdu verbs, adjectives, nouns, and alphabet and spellings. Look at our blogs on “ Happy new year in Urdu ” and “ Basic Urdu words and phrases ” to understand the Urdu language better. If you want to learn multiple foreign languages or need more information, open your browser and visit the Ling app website (free) and start your language learning journey today.
Updated by Samawiyah Hasnain
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

People also read

5+ Best Ukrainian Proverbs For Total Beginners

No Ukrainian On Rosetta Stone: Try The 2 Best Resources

60+ Wonderful Names In Ukrainian For Babies

3+ Best And Fun Ways To Say Cheers In Ukrainian!

Greetings In Ukrainian You Should Know: #1 Guide

Happy Birthday In Ukrainian: 10+ Easy Ways!
What makes learning with ling special, interactive exercises.
Improve your pronunciation by starting a conversation with our app’s interactive chatbot
Engaging activities
Practice your skills with mini-games and track your progress with fun quizzes
Mix of languages
Choose from over 60 languages, both big and small, and listen to audio from native speakers
Proven results
Backed by linguistic research, our learning methods can help you achieve fluency in record time
Southeast Asia
East europe.
© 2024 Simya Solutions Ltd.

- _وضاحتی مضامین
- _مختصر مضامین
Few Lines on Myself in Urdu | 10 Lines on Myself in Urdu
آج ہم اُردو میں میرے تعارف پر دس سطریں فراہم کرنے جا رہے ہیں۔ یہ مختصر مضمون یاد رکھنے میں بھی آسان ہے۔ اس مضمون کو آسان اور سادہ الفاظ میں لکھا گیا ہے لہذا کوئی بھی طالب علم اس موضوع پر لکھ سکتا ہے۔ اُردو میں میرے تعارف پر یہ مختصر مضمون عام طور پر پہلی، دوسری اور تیسری جماعت کے بچوں کے لیے کافی مفید ہے۔

میرے تعارف پر دس سطریں
میرے تعارف پر دس سطریں درج ذیل ہیں:
1) میرا نام محمد علی ہے۔
2) میں پاکستان کے دوسرے بڑے شہر لاہور میں اپنے خاندان کے ساتھ رہتا ہوں۔
3) میری عمر دس سال ہے۔
4) میرے والد کا نام محمد عبدللہ ہے۔
5) میری والدہ کا نام زینب عبدللہ ہے۔
6) میرے والد ایک ڈاکٹر ہیں اور میری والدہ گھریلو خاتون ہیں۔
7) میں آرمی پبلک سکول میں چوتھی جماعت کا طالب علم ہوں۔
8) میں وقت کا بہت پابند اور محنتی ہوں۔
9) شام کو میں اپنے دوستوں کے ساتھ کھیلتا ہوں۔
10) میں اپنے بزرگوں، والدین اور اساتذہ کی اطاعت کرتا ہوں۔
ایک تبصرہ شائع کریں
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- College essay
How to Write About Yourself in a College Essay | Examples
Published on September 21, 2021 by Kirsten Courault . Revised on May 31, 2023.
An insightful college admissions essay requires deep self-reflection, authenticity, and a balance between confidence and vulnerability. Your essay shouldn’t just be a resume of your experiences; colleges are looking for a story that demonstrates your most important values and qualities.
To write about your achievements and qualities without sounding arrogant, use specific stories to illustrate them. You can also write about challenges you’ve faced or mistakes you’ve made to show vulnerability and personal growth.

Table of contents
Start with self-reflection, how to write about challenges and mistakes, how to write about your achievements and qualities, how to write about a cliché experience, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about college application essays.
Before you start writing, spend some time reflecting to identify your values and qualities. You should do a comprehensive brainstorming session, but here are a few questions to get you started:
- What are three words your friends or family would use to describe you, and why would they choose them?
- Whom do you admire most and why?
- What are the top five things you are thankful for?
- What has inspired your hobbies or future goals?
- What are you most proud of? Ashamed of?
As you self-reflect, consider how your values and goals reflect your prospective university’s program and culture, and brainstorm stories that demonstrate the fit between the two.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing about difficult experiences can be an effective way to show authenticity and create an emotional connection to the reader, but choose carefully which details to share, and aim to demonstrate how the experience helped you learn and grow.
Be vulnerable
It’s not necessary to have a tragic story or a huge confession. But you should openly share your thoughts, feelings, and experiences to evoke an emotional response from the reader. Even a cliché or mundane topic can be made interesting with honest reflection. This honesty is a preface to self-reflection and insight in the essay’s conclusion.
Don’t overshare
With difficult topics, you shouldn’t focus too much on negative aspects. Instead, use your challenging circumstances as a brief introduction to how you responded positively.
Share what you have learned
It’s okay to include your failure or mistakes in your essay if you include a lesson learned. After telling a descriptive, honest story, you should explain what you learned and how you applied it to your life.
While it’s good to sell your strengths, you also don’t want to come across as arrogant. Instead of just stating your extracurricular activities, achievements, or personal qualities, aim to discreetly incorporate them into your story.
Brag indirectly
Mention your extracurricular activities or awards in passing, not outright, to avoid sounding like you’re bragging from a resume.
Use stories to prove your qualities
Even if you don’t have any impressive academic achievements or extracurriculars, you can still demonstrate your academic or personal character. But you should use personal examples to provide proof. In other words, show evidence of your character instead of just telling.
Many high school students write about common topics such as sports, volunteer work, or their family. Your essay topic doesn’t have to be groundbreaking, but do try to include unexpected personal details and your authentic voice to make your essay stand out .
To find an original angle, try these techniques:
- Focus on a specific moment, and describe the scene using your five senses.
- Mention objects that have special significance to you.
- Instead of following a common story arc, include a surprising twist or insight.
Your unique voice can shed new perspective on a common human experience while also revealing your personality. When read out loud, the essay should sound like you are talking.
If you want to know more about academic writing , effective communication , or parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Transition words
- Passive voice
- Paraphrasing
Communication
- How to end an email
- Ms, mrs, miss
- How to start an email
- I hope this email finds you well
- Hope you are doing well
Parts of speech
- Personal pronouns
- Conjunctions
First, spend time reflecting on your core values and character . You can start with these questions:
However, you should do a comprehensive brainstorming session to fully understand your values. Also consider how your values and goals match your prospective university’s program and culture. Then, brainstorm stories that illustrate the fit between the two.
When writing about yourself , including difficult experiences or failures can be a great way to show vulnerability and authenticity, but be careful not to overshare, and focus on showing how you matured from the experience.
Through specific stories, you can weave your achievements and qualities into your essay so that it doesn’t seem like you’re bragging from a resume.
Include specific, personal details and use your authentic voice to shed a new perspective on a common human experience.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Courault, K. (2023, May 31). How to Write About Yourself in a College Essay | Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/college-essay/write-about-yourself/
Is this article helpful?

Kirsten Courault
Other students also liked, style and tone tips for your college essay | examples, what do colleges look for in an essay | examples & tips, how to make your college essay stand out | tips & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
My Self Essay in English: The Journey of Self-Discovery
Hello everyone! I hope you are doing well and great. Today, I want to share something special with you. It’s a PDF about an essay in English titled My Self. Let’s dive into why the journey of self-discovery is so essential and how it can light up our ways in life.
Understanding Why My Self (Self Discovery) Matter:
Self-discovery means understanding who are you, and what makes you different from others, well, you! It’s like finding pieces in the puzzle that fit together to create the big picture of who you are. When you know yourself, you can make better decisions in your life and feel happier because you are living in a way that is right for you.
My Self Essay in English PDF:
The PDF includes:
- An essay about someone’s journey to discover themselves that what he is.
- Why it’s okay to not have all the answers right away?
- How facing challenges can help you grow in your life?
How to Download:
To download the PDF about an amazing essay on My Self, click on the “Download” button given above.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Self Discovery is like going on a great and interesting adventure. It’s all about exploring different parts of yourself and seeing what makes you different from others.
Thanks for reading and taking the time to this article and PDF. I hope you enjoyed our PDF Essay and discovered a lot of info about the importance of Self Discovery. May this essay inspire you to embrace the beauty of your own unfolding story?
More Valuable PDFs:
We have more amazing PDFs available, So, don’t forget to take a look there and I hope you will enjoy them too .
- Taleem e Niswan Essay in Urdu .
- Dr Aafia Siddiqui Story in Urdu .
- My Last Day at School Quotations .
- Pollution Essay in English .
- My Favorite Personality Essay in English .
Related Posts

Do Good Have Good Story: A Heartwarming Tale of Kindness

My Aim in Life Essay Quotations: Inspiring Reflections
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Things you buy through our links may earn Vox Media a commission
- The Case for Marrying an Older Man
A woman’s life is all work and little rest. An age gap relationship can help.

In the summer, in the south of France, my husband and I like to play, rather badly, the lottery. We take long, scorching walks to the village — gratuitous beauty, gratuitous heat — kicking up dust and languid debates over how we’d spend such an influx. I purchase scratch-offs, jackpot tickets, scraping the former with euro coins in restaurants too fine for that. I never cash them in, nor do I check the winning numbers. For I already won something like the lotto, with its gifts and its curses, when he married me.
He is ten years older than I am. I chose him on purpose, not by chance. As far as life decisions go, on balance, I recommend it.
When I was 20 and a junior at Harvard College, a series of great ironies began to mock me. I could study all I wanted, prove myself as exceptional as I liked, and still my fiercest advantage remained so universal it deflated my other plans. My youth. The newness of my face and body. Compellingly effortless; cruelly fleeting. I shared it with the average, idle young woman shrugging down the street. The thought, when it descended on me, jolted my perspective, the way a falling leaf can make you look up: I could diligently craft an ideal existence, over years and years of sleepless nights and industry. Or I could just marry it early.
So naturally I began to lug a heavy suitcase of books each Saturday to the Harvard Business School to work on my Nabokov paper. In one cavernous, well-appointed room sat approximately 50 of the planet’s most suitable bachelors. I had high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out. Apologies to Progress, but older men still desired those things.
I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence. Each time I reconsidered the project, it struck me as more reasonable. Why ignore our youth when it amounted to a superpower? Why assume the burdens of womanhood, its too-quick-to-vanish upper hand, but not its brief benefits at least? Perhaps it came easier to avoid the topic wholesale than to accept that women really do have a tragically short window of power, and reason enough to take advantage of that fact while they can. As for me, I liked history, Victorian novels, knew of imminent female pitfalls from all the books I’d read: vampiric boyfriends; labor, at the office and in the hospital, expected simultaneously; a decline in status as we aged, like a looming eclipse. I’d have disliked being called calculating, but I had, like all women, a calculator in my head. I thought it silly to ignore its answers when they pointed to an unfairness for which we really ought to have been preparing.
I was competitive by nature, an English-literature student with all the corresponding major ambitions and minor prospects (Great American novel; email job). A little Bovarist , frantic for new places and ideas; to travel here, to travel there, to be in the room where things happened. I resented the callow boys in my class, who lusted after a particular, socially sanctioned type on campus: thin and sexless, emotionally detached and socially connected, the opposite of me. Restless one Saturday night, I slipped on a red dress and snuck into a graduate-school event, coiling an HDMI cord around my wrist as proof of some technical duty. I danced. I drank for free, until one of the organizers asked me to leave. I called and climbed into an Uber. Then I promptly climbed out of it. For there he was, emerging from the revolving doors. Brown eyes, curved lips, immaculate jacket. I went to him, asked him for a cigarette. A date, days later. A second one, where I discovered he was a person, potentially my favorite kind: funny, clear-eyed, brilliant, on intimate terms with the universe.
I used to love men like men love women — that is, not very well, and with a hunger driven only by my own inadequacies. Not him. In those early days, I spoke fondly of my family, stocked the fridge with his favorite pasta, folded his clothes more neatly than I ever have since. I wrote his mother a thank-you note for hosting me in his native France, something befitting a daughter-in-law. It worked; I meant it. After graduation and my fellowship at Oxford, I stayed in Europe for his career and married him at 23.
Of course I just fell in love. Romances have a setting; I had only intervened to place myself well. Mainly, I spotted the precise trouble of being a woman ahead of time, tried to surf it instead of letting it drown me on principle. I had grown bored of discussions of fair and unfair, equal or unequal , and preferred instead to consider a thing called ease.
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon. When a 50-year-old man and a 25-year-old woman walk down the street, the questions form themselves inside of you; they make you feel cynical and obscene: How good of a deal is that? Which party is getting the better one? Would I take it? He is older. Income rises with age, so we assume he has money, at least relative to her; at minimum, more connections and experience. She has supple skin. Energy. Sex. Maybe she gets a Birkin. Maybe he gets a baby long after his prime. The sight of their entwined hands throws a lucid light on the calculations each of us makes, in love, to varying degrees of denial. You could get married in the most romantic place in the world, like I did, and you would still have to sign a contract.
Twenty and 30 is not like 30 and 40; some freshness to my features back then, some clumsiness in my bearing, warped our decade, in the eyes of others, to an uncrossable gulf. Perhaps this explains the anger we felt directed at us at the start of our relationship. People seemed to take us very, very personally. I recall a hellish car ride with a friend of his who began to castigate me in the backseat, in tones so low that only I could hear him. He told me, You wanted a rich boyfriend. You chased and snuck into parties . He spared me the insult of gold digger, but he drew, with other words, the outline for it. Most offended were the single older women, my husband’s classmates. They discussed me in the bathroom at parties when I was in the stall. What does he see in her? What do they talk about? They were concerned about me. They wielded their concern like a bludgeon. They paraphrased without meaning to my favorite line from Nabokov’s Lolita : “You took advantage of my disadvantage,” suspecting me of some weakness he in turn mined. It did not disturb them, so much, to consider that all relationships were trades. The trouble was the trade I’d made struck them as a bad one.
The truth is you can fall in love with someone for all sorts of reasons, tiny transactions, pluses and minuses, whose sum is your affection for each other, your loyalty, your commitment. The way someone picks up your favorite croissant. Their habit of listening hard. What they do for you on your anniversary and your reciprocal gesture, wrapped thoughtfully. The serenity they inspire; your happiness, enlivening it. When someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them.
When I think of same-age, same-stage relationships, what I tend to picture is a woman who is doing too much for too little.
I’m 27 now, and most women my age have “partners.” These days, girls become partners quite young. A partner is supposed to be a modern answer to the oppression of marriage, the terrible feeling of someone looming over you, head of a household to which you can only ever be the neck. Necks are vulnerable. The problem with a partner, however, is if you’re equal in all things, you compromise in all things. And men are too skilled at taking .
There is a boy out there who knows how to floss because my friend taught him. Now he kisses college girls with fresh breath. A boy married to my friend who doesn’t know how to pack his own suitcase. She “likes to do it for him.” A million boys who know how to touch a woman, who go to therapy because they were pushed, who learned fidelity, boundaries, decency, manners, to use a top sheet and act humanely beneath it, to call their mothers, match colors, bring flowers to a funeral and inhale, exhale in the face of rage, because some girl, some girl we know, some girl they probably don’t speak to and will never, ever credit, took the time to teach him. All while she was working, raising herself, clawing up the cliff-face of adulthood. Hauling him at her own expense.
I find a post on Reddit where five thousand men try to define “ a woman’s touch .” They describe raised flower beds, blankets, photographs of their loved ones, not hers, sprouting on the mantel overnight. Candles, coasters, side tables. Someone remembering to take lint out of the dryer. To give compliments. I wonder what these women are getting back. I imagine them like Cinderella’s mice, scurrying around, their sole proof of life their contributions to a more central character. On occasion I meet a nice couple, who grew up together. They know each other with a fraternalism tender and alien to me. But I think of all my friends who failed at this, were failed at this, and I think, No, absolutely not, too risky . Riskier, sometimes, than an age gap.
My younger brother is in his early 20s, handsome, successful, but in many ways: an endearing disaster. By his age, I had long since wisened up. He leaves his clothes in the dryer, takes out a single shirt, steams it for three minutes. His towel on the floor, for someone else to retrieve. His lovely, same-age girlfriend is aching to fix these tendencies, among others. She is capable beyond words. Statistically, they will not end up together. He moved into his first place recently, and she, the girlfriend, supplied him with a long, detailed list of things he needed for his apartment: sheets, towels, hangers, a colander, which made me laugh. She picked out his couch. I will bet you anything she will fix his laundry habits, and if so, they will impress the next girl. If they break up, she will never see that couch again, and he will forget its story. I tell her when I visit because I like her, though I get in trouble for it: You shouldn’t do so much for him, not for someone who is not stuck with you, not for any boy, not even for my wonderful brother.
Too much work had left my husband, by 30, jaded and uninspired. He’d burned out — but I could reenchant things. I danced at restaurants when they played a song I liked. I turned grocery shopping into an adventure, pleased by what I provided. Ambitious, hungry, he needed someone smart enough to sustain his interest, but flexible enough in her habits to build them around his hours. I could. I do: read myself occupied, make myself free, materialize beside him when he calls for me. In exchange, I left a lucrative but deadening spreadsheet job to write full-time, without having to live like a writer. I learned to cook, a little, and decorate, somewhat poorly. Mostly I get to read, to walk central London and Miami and think in delicious circles, to work hard, when necessary, for free, and write stories for far less than minimum wage when I tally all the hours I take to write them.
At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self, couldn’t imagine doing it in tandem with someone, two raw lumps of clay trying to mold one another and only sullying things worse. I’d go on dates with boys my age and leave with the impression they were telling me not about themselves but some person who didn’t exist yet and on whom I was meant to bet regardless. My husband struck me instead as so finished, formed. Analyzable for compatibility. He bore the traces of other women who’d improved him, small but crucial basics like use a coaster ; listen, don’t give advice. Young egos mellow into patience and generosity.
My husband isn’t my partner. He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did. Adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations. But his logistics ran so smoothly that he simply tacked mine on. I moved into his flat, onto his level, drag and drop, cleaner thrice a week, bills automatic. By opting out of partnership in my 20s, I granted myself a kind of compartmentalized, liberating selfishness none of my friends have managed. I am the work in progress, the party we worry about, a surprising dominance. When I searched for my first job, at 21, we combined our efforts, for my sake. He had wisdom to impart, contacts with whom he arranged coffees; we spent an afternoon, laughing, drawing up earnest lists of my pros and cons (highly sociable; sloppy math). Meanwhile, I took calls from a dear friend who had a boyfriend her age. Both savagely ambitious, hyperclose and entwined in each other’s projects. If each was a start-up , the other was the first hire, an intense dedication I found riveting. Yet every time she called me, I hung up with the distinct feeling that too much was happening at the same time: both learning to please a boss; to forge more adult relationships with their families; to pay bills and taxes and hang prints on the wall. Neither had any advice to give and certainly no stability. I pictured a three-legged race, two people tied together and hobbling toward every milestone.
I don’t fool myself. My marriage has its cons. There are only so many times one can say “thank you” — for splendid scenes, fine dinners — before the phrase starts to grate. I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that shapes the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him. He doesn’t have to hold it over my head. It just floats there, complicating usual shorthands to explain dissatisfaction like, You aren’t being supportive lately . It’s a Frenchism to say, “Take a decision,” and from time to time I joke: from whom? Occasionally I find myself in some fabulous country at some fabulous party and I think what a long way I have traveled, like a lucky cloud, and it is frightening to think of oneself as vapor.
Mostly I worry that if he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive, but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials, the way Renaissance painters hid in their paintings their faces among a crowd. I wonder if when they looked at their paintings, they saw their own faces first. But this is the wrong question, if our aim is happiness. Like the other question on which I’m expected to dwell: Who is in charge, the man who drives or the woman who put him there so she could enjoy herself? I sit in the car, in the painting it would have taken me a corporate job and 20 years to paint alone, and my concern over who has the upper hand becomes as distant as the horizon, the one he and I made so wide for me.
To be a woman is to race against the clock, in several ways, until there is nothing left to be but run ragged.
We try to put it off, but it will hit us at some point: that we live in a world in which our power has a different shape from that of men, a different distribution of advantage, ours a funnel and theirs an expanding cone. A woman at 20 rarely has to earn her welcome; a boy at 20 will be turned away at the door. A woman at 30 may find a younger woman has taken her seat; a man at 30 will have invited her. I think back to the women in the bathroom, my husband’s classmates. What was my relationship if not an inconvertible sign of this unfairness? What was I doing, in marrying older, if not endorsing it? I had taken advantage of their disadvantage. I had preempted my own. After all, principled women are meant to defy unfairness, to show some integrity or denial, not plan around it, like I had. These were driven women, successful, beautiful, capable. I merely possessed the one thing they had already lost. In getting ahead of the problem, had I pushed them down? If I hadn’t, would it really have made any difference?
When we decided we wanted to be equal to men, we got on men’s time. We worked when they worked, retired when they retired, had to squeeze pregnancy, children, menopause somewhere impossibly in the margins. I have a friend, in her late 20s, who wears a mood ring; these days it is often red, flickering in the air like a siren when she explains her predicament to me. She has raised her fair share of same-age boyfriends. She has put her head down, worked laboriously alongside them, too. At last she is beginning to reap the dividends, earning the income to finally enjoy herself. But it is now, exactly at this precipice of freedom and pleasure, that a time problem comes closing in. If she would like to have children before 35, she must begin her next profession, motherhood, rather soon, compromising inevitably her original one. The same-age partner, equally unsettled in his career, will take only the minimum time off, she guesses, or else pay some cost which will come back to bite her. Everything unfailingly does. If she freezes her eggs to buy time, the decision and its logistics will burden her singly — and perhaps it will not work. Overlay the years a woman is supposed to establish herself in her career and her fertility window and it’s a perfect, miserable circle. By midlife women report feeling invisible, undervalued; it is a telling cliché, that after all this, some husbands leave for a younger girl. So when is her time, exactly? For leisure, ease, liberty? There is no brand of feminism which achieved female rest. If women’s problem in the ’50s was a paralyzing malaise, now it is that they are too active, too capable, never permitted a vacation they didn’t plan. It’s not that our efforts to have it all were fated for failure. They simply weren’t imaginative enough.
For me, my relationship, with its age gap, has alleviated this rush , permitted me to massage the clock, shift its hands to my benefit. Very soon, we will decide to have children, and I don’t panic over last gasps of fun, because I took so many big breaths of it early: on the holidays of someone who had worked a decade longer than I had, in beautiful places when I was young and beautiful, a symmetry I recommend. If such a thing as maternal energy exists, mine was never depleted. I spent the last nearly seven years supported more than I support and I am still not as old as my husband was when he met me. When I have a child, I will expect more help from him than I would if he were younger, for what does professional tenure earn you if not the right to set more limits on work demands — or, if not, to secure some child care, at the very least? When I return to work after maternal upheaval, he will aid me, as he’s always had, with his ability to put himself aside, as younger men are rarely able.
Above all, the great gift of my marriage is flexibility. A chance to live my life before I become responsible for someone else’s — a lover’s, or a child’s. A chance to write. A chance at a destiny that doesn’t adhere rigidly to the routines and timelines of men, but lends itself instead to roomy accommodation, to the very fluidity Betty Friedan dreamed of in 1963 in The Feminine Mystique , but we’ve largely forgotten: some career or style of life that “permits year-to-year variation — a full-time paid job in one community, part-time in another, exercise of the professional skill in serious volunteer work or a period of study during pregnancy or early motherhood when a full-time job is not feasible.” Some things are just not feasible in our current structures. Somewhere along the way we stopped admitting that, and all we did was make women feel like personal failures. I dream of new structures, a world in which women have entry-level jobs in their 30s; alternate avenues for promotion; corporate ladders with balconies on which they can stand still, have a smoke, take a break, make a baby, enjoy themselves, before they keep climbing. Perhaps men long for this in their own way. Actually I am sure of that.
Once, when we first fell in love, I put my head in his lap on a long car ride; I remember his hands on my face, the sun, the twisting turns of a mountain road, surprising and not surprising us like our romance, and his voice, telling me that it was his biggest regret that I was so young, he feared he would lose me. Last week, we looked back at old photos and agreed we’d given each other our respective best years. Sometimes real equality is not so obvious, sometimes it takes turns, sometimes it takes almost a decade to reveal itself.
More From This Series
- Can You Still Sell Out in This Economy?
- 7 Stories of Dramatic Career Pivots
- My Mother’s Death Blew Up My Life. Opening a Book and Wine Store Helped My Grief
- newsletter pick
- first person
- relationships
- the good life
- best of the cut
The Cut Shop
Most viewed stories.
- This Mercury Retrograde in Aries Will Be Peak Chaos
- Madame Clairevoyant: Horoscopes for the Week of March 31–April 6
- What We Know About the Mommy Vlogger Accused of Child Abuse
- Random Punching Attacks Rattle New York City Women
- When Your Kid Is the Classroom Problem Child
Editor’s Picks

Most Popular
What is your email.
This email will be used to sign into all New York sites. By submitting your email, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy and to receive email correspondence from us.
Sign In To Continue Reading
Create your free account.
Password must be at least 8 characters and contain:
- Lower case letters (a-z)
- Upper case letters (A-Z)
- Numbers (0-9)
- Special Characters (!@#$%^&*)
As part of your account, you’ll receive occasional updates and offers from New York , which you can opt out of anytime.

Urdu Essays List 3
Essay on discipline in urdu, essay on city life in urdu, essay on good citizen in urdu, essay on doctor profession in urdu, essay on co-education in urdu, essay on zindagi in urdu, essay on juma in urdu, essay on first aid in urdu, essay on doctor in urdu, mera yadgar safar essay in urdu, essay on fashion in urdu, essay on water pollution in urdu, essay on my family in urdu, essay on women’s rights in urdu, essay on vegetables in urdu, essay on democracy in urdu, essay on uswa hasana in urdu, essay on father in urdu, essay on four seasons in urdu, dehati zindagi essay in urdu, تغیر کے موضوع پر ایک مضمون, اولمپک کھیل پر مختصر نوٹ, “چوری ایک بری عادت ہے” مضمون, عورتوں کی حالت پر ایک مختصر مضمون, benefits of knowledge urdu | تعلیم کے فوائد پر ایک مضمون, عمل سے زندگی بنتی ہے جنت بھی جہنم بھی مضمون, ہمت مرداں مدد خدا مضمون, علم روشنی ہے مضمون, sohanjana plant benefits in urdu | سوہانجنا کے فوائد, essay on sword in urdu | تلوار پر مضمون, essay on badshahi mosque in urdu, essay on anti corruption in urdu, essay on fateh makkah in urdu, essay on ramzan in urdu, essay on police in urdu, meri pasandeeda kitab mazmoon , essay on subah ki sair in urdu, essay on seerat-e-nabvi in urdu, essay on childhood in urdu, essay on tree plantation in urdu, how to become a successful person essay in urdu, essay on bijli in urdu, essay on cleanliness in urdu, essay on bulb in urdu, essay on indian army in urdu, essay on beauty of j&k in urdu, essay on qur’an in urdu, essay on patriotism in urdu, essay on parents in urdu, essay on drugs in urdu, essay on badminton in urdu, meri maa essay in urdu, my father my hero essay in urdu, essay on eidain in urdu, essay on election in urdu, essay on eid milad un nabi in urdu, essay on agriculture in pakistan in urdu, essay on electricity in urdu, essay on hajj in urdu, essay on alodgi in urdu, essay on qutub minar in urdu, essay on quran in urdu, aab e zam zam essay in urdu, my hobby essay in urdu, kitab insan ki behtreen dost hai essay, lalach buri bala hai essay in urdu, mobile phone essay in urdu, dehshat gardi essay in urdu, urdu essay allah ki naimat, ajaib ghar essay in urdu, tandrusti hazar naimat hai | تندرستی ہزار نعمت ہے, minar e pakistan essay in urdu | مینار پاکستان پر مضمون, national river of pakistan in urdu | پاکستان کا قومی دریا, qaumi parchan mazmoon | پاکستان کا قومی پرچم, جوانی زندگی کا بہترین وقت مضمون, essay on shahadat in urdu, waqia karbala in urdu, essay on shaheed in urdu, pollution essay in urdu, qaumi ittehad essay in urdu, hubul watni mazmoon in urdu, benefits of banana in urdu, great wall of china history in urdu, essay on ramzan ki barkatain in urdu, role of media essay in urdu, role of media in pakistan in urdu, taleem essay in urdu, benefits of strawberry in urdu, benefits of pomegranate in urdu, essay on lahore in urdu, essay on karachi in urdu, barsat ka mausam essay in urdu, adab e zindagi essay in urdu, superstition essay in urdu, short essay on population problem in india, berozgari essay in urdu, media ki azadi essay in urdu, how to achieve world peace essay, masla e kashmir essay in urdu, mera school essay in urdu, essay on jahez in urdu, essay on school uniform in urdu, essay on forest in urdu, what is global warming in urdu, causes of global warming in urdu, کامیابی کے اصول, ٹک ٹاک ایپلیکیشن کی حقیقت, khush ikhlaqi essay in urdu, essay on insaaf in urdu, essay on respect of teacher in urdu, essay on insaniyat in urdu, essay on zil hajj in urdu, akhbar bini essay in urdu, language of jammu and kashmir, essay on dengue in urdu, ilm e deen ki ahmiyat essay, غزوۂ بدر پر مضمون, اگر میں وزیر تعلیم ہوتا, میری پسندیدہ شخصیت حضرت محمد ﷺ, اسلام زندہ ہوتا ہے ہر کربلا کے بعد مضمون, عزم کامرانی کی کنجی ہے, انسداد گداگری مضمون, کرونا وائرس اور ہماری ذمہ داریاں, ماں پر مضمون.
- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
That Viral Essay Wasn’t About Age Gaps. It Was About Marrying Rich.
But both tactics are flawed if you want to have any hope of becoming yourself..
Women are wisest, a viral essay in New York magazine’s the Cut argues , to maximize their most valuable cultural assets— youth and beauty—and marry older men when they’re still very young. Doing so, 27-year-old writer Grazie Sophia Christie writes, opens up a life of ease, and gets women off of a male-defined timeline that has our professional and reproductive lives crashing irreconcilably into each other. Sure, she says, there are concessions, like one’s freedom and entire independent identity. But those are small gives in comparison to a life in which a person has no adult responsibilities, including the responsibility to become oneself.
This is all framed as rational, perhaps even feminist advice, a way for women to quit playing by men’s rules and to reject exploitative capitalist demands—a choice the writer argues is the most obviously intelligent one. That other Harvard undergraduates did not busy themselves trying to attract wealthy or soon-to-be-wealthy men seems to flummox her (taking her “high breasts, most of my eggs, plausible deniability when it came to purity, a flush ponytail, a pep in my step that had yet to run out” to the Harvard Business School library, “I could not understand why my female classmates did not join me, given their intelligence”). But it’s nothing more than a recycling of some of the oldest advice around: For women to mold themselves around more-powerful men, to never grow into independent adults, and to find happiness in a state of perpetual pre-adolescence, submission, and dependence. These are odd choices for an aspiring writer (one wonders what, exactly, a girl who never wants to grow up and has no idea who she is beyond what a man has made her into could possibly have to write about). And it’s bad advice for most human beings, at least if what most human beings seek are meaningful and happy lives.
But this is not an essay about the benefits of younger women marrying older men. It is an essay about the benefits of younger women marrying rich men. Most of the purported upsides—a paid-for apartment, paid-for vacations, lives split between Miami and London—are less about her husband’s age than his wealth. Every 20-year-old in the country could decide to marry a thirtysomething and she wouldn’t suddenly be gifted an eternal vacation.
Which is part of what makes the framing of this as an age-gap essay both strange and revealing. The benefits the writer derives from her relationship come from her partner’s money. But the things she gives up are the result of both their profound financial inequality and her relative youth. Compared to her and her peers, she writes, her husband “struck me instead as so finished, formed.” By contrast, “At 20, I had felt daunted by the project of becoming my ideal self.” The idea of having to take responsibility for her own life was profoundly unappealing, as “adulthood seemed a series of exhausting obligations.” Tying herself to an older man gave her an out, a way to skip the work of becoming an adult by allowing a father-husband to mold her to his desires. “My husband isn’t my partner,” she writes. “He’s my mentor, my lover, and, only in certain contexts, my friend. I’ll never forget it, how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it, and I did.”
These, by the way, are the things she says are benefits of marrying older.
The downsides are many, including a basic inability to express a full range of human emotion (“I live in an apartment whose rent he pays and that constrains the freedom with which I can ever be angry with him”) and an understanding that she owes back, in some other form, what he materially provides (the most revealing line in the essay may be when she claims that “when someone says they feel unappreciated, what they really mean is you’re in debt to them”). It is clear that part of what she has paid in exchange for a paid-for life is a total lack of any sense of self, and a tacit agreement not to pursue one. “If he ever betrayed me and I had to move on, I would survive,” she writes, “but would find in my humor, preferences, the way I make coffee or the bed nothing that he did not teach, change, mold, recompose, stamp with his initials.”
Reading Christie’s essay, I thought of another one: Joan Didion’s on self-respect , in which Didion argues that “character—the willingness to accept responsibility for one’s own life—is the source from which self-respect springs.” If we lack self-respect, “we are peculiarly in thrall to everyone we see, curiously determined to live out—since our self-image is untenable—their false notions of us.” Self-respect may not make life effortless and easy. But it means that whenever “we eventually lie down alone in that notoriously un- comfortable bed, the one we make ourselves,” at least we can fall asleep.
It can feel catty to publicly criticize another woman’s romantic choices, and doing so inevitably opens one up to accusations of jealousy or pettiness. But the stories we tell about marriage, love, partnership, and gender matter, especially when they’re told in major culture-shaping magazines. And it’s equally as condescending to say that women’s choices are off-limits for critique, especially when those choices are shared as universal advice, and especially when they neatly dovetail with resurgent conservative efforts to make women’s lives smaller and less independent. “Marry rich” is, as labor economist Kathryn Anne Edwards put it in Bloomberg, essentially the Republican plan for mothers. The model of marriage as a hierarchy with a breadwinning man on top and a younger, dependent, submissive woman meeting his needs and those of their children is not exactly a fresh or groundbreaking ideal. It’s a model that kept women trapped and miserable for centuries.
It’s also one that profoundly stunted women’s intellectual and personal growth. In her essay for the Cut, Christie seems to believe that a life of ease will abet a life freed up for creative endeavors, and happiness. But there’s little evidence that having material abundance and little adversity actually makes people happy, let alone more creatively generativ e . Having one’s basic material needs met does seem to be a prerequisite for happiness. But a meaningful life requires some sense of self, an ability to look outward rather than inward, and the intellectual and experiential layers that come with facing hardship and surmounting it.
A good and happy life is not a life in which all is easy. A good and happy life (and here I am borrowing from centuries of philosophers and scholars) is one characterized by the pursuit of meaning and knowledge, by deep connections with and service to other people (and not just to your husband and children), and by the kind of rich self-knowledge and satisfaction that comes from owning one’s choices, taking responsibility for one’s life, and doing the difficult and endless work of growing into a fully-formed person—and then evolving again. Handing everything about one’s life over to an authority figure, from the big decisions to the minute details, may seem like a path to ease for those who cannot stomach the obligations and opportunities of their own freedom. It’s really an intellectual and emotional dead end.
And what kind of man seeks out a marriage like this, in which his only job is to provide, but very much is owed? What kind of man desires, as the writer cast herself, a raw lump of clay to be molded to simply fill in whatever cracks in his life needed filling? And if the transaction is money and guidance in exchange for youth, beauty, and pliability, what happens when the young, beautiful, and pliable party inevitably ages and perhaps feels her backbone begin to harden? What happens if she has children?
The thing about using youth and beauty as a currency is that those assets depreciate pretty rapidly. There is a nearly endless supply of young and beautiful women, with more added each year. There are smaller numbers of wealthy older men, and the pool winnows down even further if one presumes, as Christie does, that many of these men want to date and marry compliant twentysomethings. If youth and beauty are what you’re exchanging for a man’s resources, you’d better make sure there’s something else there—like the basic ability to provide for yourself, or at the very least a sense of self—to back that exchange up.
It is hard to be an adult woman; it’s hard to be an adult, period. And many women in our era of unfinished feminism no doubt find plenty to envy about a life in which they don’t have to work tirelessly to barely make ends meet, don’t have to manage the needs of both children and man-children, could simply be taken care of for once. This may also explain some of the social media fascination with Trad Wives and stay-at-home girlfriends (some of that fascination is also, I suspect, simply a sexual submission fetish , but that’s another column). Fantasies of leisure reflect a real need for it, and American women would be far better off—happier, freer—if time and resources were not so often so constrained, and doled out so inequitably.
But the way out is not actually found in submission, and certainly not in electing to be carried by a man who could choose to drop you at any time. That’s not a life of ease. It’s a life of perpetual insecurity, knowing your spouse believes your value is decreasing by the day while his—an actual dollar figure—rises. A life in which one simply allows another adult to do all the deciding for them is a stunted life, one of profound smallness—even if the vacations are nice.
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries

The Hardships and Dreams of Asian Americans Living in Poverty
Illustrations by Jing Li
Asian Americans are often portrayed as economically and educationally successful.
In reality, about one-in-ten Asian Americans live in poverty. Asian Americans also have the most income inequality of any major racial or ethnic group in the United States.
Without closely examining the diversity of Asian American experiences, it’s easy to miss the distinct stories of Asian Americans living with economic hardship.
To understand more about this population, Pew Research Center conducted 18 focus groups in 12 languages to explore the stories and experiences of Asian Americans living in poverty.
Table of Contents
Of the 24 million Asians living in the United States, about 2.3 million live in poverty . Many are working to overcome the economic hardships they encounter and achieve their American dream. But they face challenges along the way, from Asian immigrants grappling with language barriers to U.S.-born Asians navigating pathways to success.
In February 2023, Pew Research Center conducted 18 focus groups with adult participants from 11 Asian origin groups in different regions across the U.S. These are among the most likely Asian origin groups to experience economic hardship in the U.S. Focus groups included those whose approximate family income is at or below 140%-250% of the 2022 federal poverty line, depending on their location. Accompanying these focus group findings are results from a Pew Research Center survey about the hardships and dreams of Asians living in poverty, conducted from July 2022 to January 2023.
Some common themes that focus group participants shared include day-to-day financial difficulties, assumptions by others that they do not need help because they are Asian, and the importance of financial security in achieving the American dream.
Related: 1 in 10: Redefining the Asian American Dream (Short Film)
Focus groups also reveal that Asian Americans’ experiences with economic hardship differ by whether they were born in the U.S. or outside the country. Some immigrants not only experience difficulties making ends meet, but also face challenges that come with living in a new, unfamiliar country. These include learning English, navigating daily life in a new place and finding a stable job.
Even though U.S.-born Asians grew up in this country and speak English, they talk about the challenges of understanding what it takes to succeed in America. This includes getting the “right” education, getting access to the “right” knowledge and knowing the “right” people to succeed.
The findings in this data essay reveal what participants shared about their experiences with economic hardship, overcoming challenges, and their views of the American dream and social mobility in America.
The terms Asians and Asian Americans are used interchangeably throughout this data essay to refer to those who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.
The terms living in poverty, living near or below the federal poverty line and living with economic hardship are used interchangeably throughout this essay to refer to adults whose family income is close to or below the 2022 federal poverty line.
- For results on Asian adults from the focus groups, this refers to adults whose approximate family income is at or below 140%-250% of the federal poverty line. Thresholds varied by focus group recruitment locations to account for differences in the cost of living.
- For results on Asian adults from the survey , this refers to adults whose approximate family income falls at or below 100% of the federal poverty line.
- For data on the total U.S. Asian population from the U.S. Census Bureau , this refers to all Asian Americans whose family income is at or below 100% of the federal poverty line.
The terms federal poverty line and poverty line are used interchangeably to refer to the federal poverty guidelines published yearly by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The term U.S. born refers to people born in 50 U.S. states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories.
The term immigrant refers to people who were born outside the 50 U.S. states or the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories.
Asian Americans and financial struggles
Financial difficulties are part of many Asian Americans’ day-to-day lives, according to the 2022-23 survey. Asian adults were asked if they had experienced any of the following financial challenges in the past 12 months: gotten food from a food bank or a charitable organization, lost their health insurance, had problems paying for their rent or mortgage, had trouble paying for medical care for themselves or their family, had trouble paying their bills, or been unable to save money for emergencies.
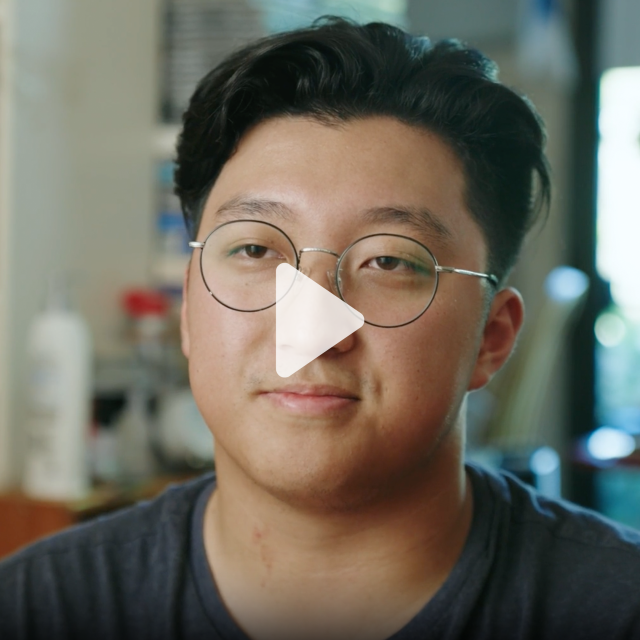

“It got really bad to the point where a simple bowl of rice, we weren’t even able to afford that. So there were times where a bowl of rice would be a meal for all three meals, or we just simply did not eat.” NOLAN , FILM PARTICIPANT
The most common financial difficulty experienced is being unable to save for emergencies. More than half of Asian adults living in poverty (57%) said this had happened to them. By comparison, fewer Asian adults living above the poverty line (40%) said this.
Note: “Asian adults living in poverty” refers to survey respondents whose approximate family income is at or below 100% of the federal poverty line. Share of respondents who didn’t offer an answer or answered “no” not shown.
Source: Survey of Asian American adults conducted July 5, 2022-Jan. 27, 2023. “The Hardships and Dreams of Asian Americans Living in Poverty”
Some focus group participants shared how challenging it was for them to save because of their earnings and their family needs. Participants also talked about the urgency they feel to save for their children and retirement:
“I feel a bit helpless [about my financial situation]. … I don’t want to be in debt. I have to save money to raise my kids, but I don’t have money to save.”
–Immigrant man of Korean origin in early 30s (translated from Korean)
“[I save money] to go to Pakistan. Because I have four children … I needed five or six tickets, in case my husband traveled with us, and it required a lot of money. We used to save for one whole year, and when we were back from Pakistan, we were usually empty-handed. Then the cycle started again.”
–Immigrant woman of Pakistani origin in late 40s (translated from Urdu)
“You’re not going to work forever. No one is going to work forever. You want to have savings … for your rent [or] in case of medical bills [if] something happens. [You] might as well [save for] some trips down the while when you [can] travel still. But you’re not going to be working at 80 years old, are you?”
–U.S.-born man of Chinese origin in early 40s
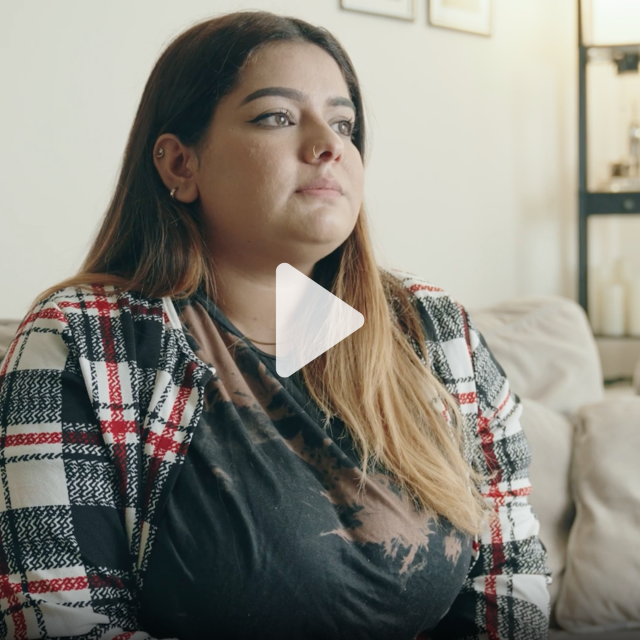

“We were all four of us in one apartment, four siblings, plus the parents, so that’s six people in a house, which was very, very cramped.” SABA , FILM PARTICIPANT
Other common difficulties for Asian Americans living near or below the poverty line include having trouble paying their bills (42%), needing to get food from a food bank or a charitable organization (38%) and having problems paying their rent or mortgage (33%), the survey found. Smaller shares of Asian adults living above the poverty line say they experienced difficulties paying their bills (17%), got food from a food bank or a charity (6%) or had trouble paying their rent or mortgage (11%).
These findings were echoed in our focus groups, where participants recalled the stress and tension their families felt when things like this happened to them:
“My dad lost his car a couple of times. There was this one time where I remember it was nighttime. All of a sudden, a cop comes over to our home [with another person]. … And my dad was forced to give up his car to this stranger … because, I don’t know, he wasn’t paying off the car or something. And it was very humiliating, and my brothers wanted to get physical with that person because he was acting very arrogantly. My dad was able to eventually pay back the car and somehow get it back. But there were many times when we might not have had a roof over our heads.”
–U.S.-born man of Pakistani origin in late 20s
Asian immigrants face challenges navigating life and employment in the U.S.
Immigrant and U.S.-born Asians experience economic hardship in different ways. Asian immigrants in the focus groups discussed how a lack of English proficiency, navigating transportation and getting a good job all shape their experiences with economic hardship.
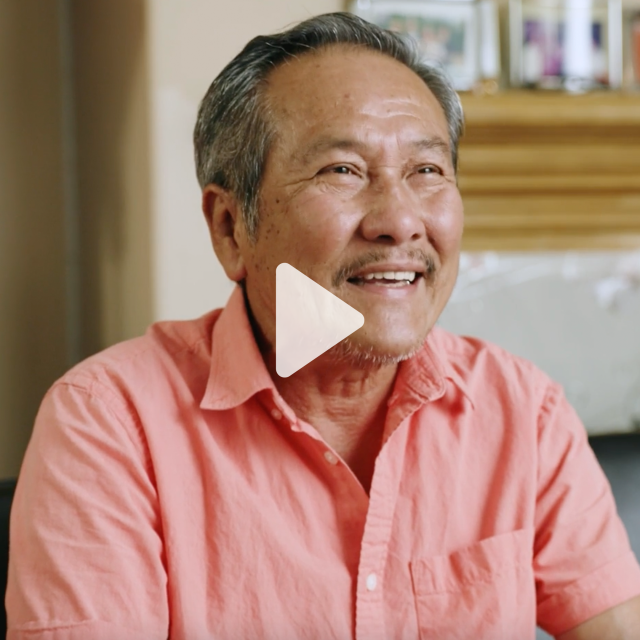

“I felt sad about life, didn’t know the language, didn’t know the roads. I had no friends, so I felt very sad.” PHONG , FILM PARTICIPANT (TRANSLATED FROM VIETNAMESE)
For example, not knowing English when they first arrived in the country created extra challenges when using local transportation systems and meeting basic daily life needs such as shopping for groceries:
“When we were very young, the most difficult thing we faced [after coming to the U.S.] was not being able to speak the language. Unless you lived in those times, you wouldn’t know. We didn’t know how to buy food. … We didn’t know the language and there was no interpreter available. … I didn’t know how to take the bus, I didn’t know where to go, or to which place they were taking me to school. When we were asked to go to the classroom, we didn’t know where to go. … There was no other way, because there was no communication.”
–Immigrant woman of Hmong origin in late 50s (translated from Hmong)
Language barriers also brought extra hurdles for Asian immigrants in the job market. Some focus group participants said it was hard to explain their skills to potential employers in English effectively, even if they had the relevant education or skills for the job and had learned English before they immigrated:
“After coming [to the U.S.], there were many problems to face, first … the language problem. We have read English … but we are not used to speaking. … We also had education … but since we can’t explain ourselves in English – what we can do, what we know … we are getting rejected [from jobs] as we cannot speak. … Another problem was that I had a child. My child was small. I could not go to work leaving him. At that time, my husband was working. He also had the same thing – he had education, but he could not get a good job because of the language. [As another participant] said, we had to work below the minimum wage.”
–Immigrant woman of Bangladeshi origin in late 30s (translated from Bengali)
Not wanting to be a burden influenced life choices of many U.S.-born participants
For many U.S.-born focus group participants, concerns about being a burden to their families shaped their childhoods and many of their life decisions:
“It’s difficult to talk to [my parents] because you grew up here and it’s just totally different from them growing up in Vietnam. … It’s the same like what [another participant] was saying, when you take off the burden to your parents, right? So I dropped out of college, just because I didn’t want them paying anymore. I just didn’t think that I was going to do or be anything in college, right? So I would rather work. So I started taking responsibility of my own and you start working really hard and you getting out of the house and helping them pay for bills.”
–U.S.-born man of Vietnamese origin in mid-40s
“My family’s struggling. Is education more important, [or] is working more important? I really felt that growing up because a lot of my friends, education – going to college and going to a techno school – wasn’t really on their radar, it wasn’t really something on their plan. I think talking to a lot of the folks and a lot of my friends during their time, they felt like they had to grow up to provide for their family or for you to find some type of income to kind of help their family. And so that really drove the direction of at least one of my friends, or a lot of my friends.”
–U.S.-born man of Hmong origin in mid-30s
Some U.S.-born focus group participants said that when reflecting on their childhoods, they could see the financial burden they had on their families in a way they did not realize as a child:
“At a certain point you become very aware of how much of a financial burden you are. You don’t ask for anything you want. Like, you don’t ask for prom. You don’t ask to join clubs. You don’t ask to go on field trips, things like that. You just know that it’s going to cause so much drain on your parents.”
–U.S.-born woman of Vietnamese origin in mid-20s
“[My parents] had like a lot of responsibilities, like … giving money back to their father, and then their sisters and brothers, helping them out back [in Pakistan]. … [My father] had to support us and then send money back constantly there. I didn’t know that until now, basically. … We would hardly see him. Maybe like on Sunday, we would see him a couple of hours. But it was on the weekdays, we would hardly see our father. He was always working.”
–U.S.-born woman of Pakistani origin in early 30s
Overcoming economic challenges
The survey found that when Asian adults living in poverty have needed help with bills, housing, food or seeking a job, about six-in-ten (61%) say they’ve turned to family or friends.
Some focus group participants mentioned that families and friends in their ethnic community were a great source of financial help. For others, the limited size of their ethnic community in the U.S. posed obstacles in obtaining assistance.

“My dad arrived in the U.S. when he was 26 years old, and I’m now 29 years old. … I have seven siblings and my parents who support me. And my parents didn’t have that, they didn’t have their parents to support them.” TANG , FILM PARTICIPANT
“It was very difficult during [my] study [at university]. … I had a scholarship, most of the part was scholarship; however, I had to pay something between $10,000 and $15,000 per semester. And I had to eat, I had to pay rent, I had to do everything. At the same time, there are many other things too, aren’t there? And there was always a stress about money. This semester is over now, how do I pay for the next? I had no clarity about what to do and not to do. In that situation, I approached those friends studying there or who came there a little earlier and were working to borrow money. … I [was] offered help by some friends and in finding a job and being helped for my needs.”
–Immigrant man of Nepalese origin in early 40s (translated from Nepali)
“We didn’t have a large Burmese community to ask for such help. It was not yet present. As we had no such community, when we had just arrived, we told close friends, got directions and went to ask for help.”
–Immigrant woman of Burmese origin in late 40s (translated from Burmese)
However, not all Asians living with economic hardship have asked for or received help. In the focus groups, participants shared why they or their families sometimes did not do so or felt hesitant. Fear of gossip and shame were mentioned multiple times:
“[I experienced financial difficulties after I first arrived in the U.S.] because I came here as a student. … It’s because I had to pay monthly rent and I paid for living expenses. I felt a little pressured when the monthly payment date approached. I had no choice but to ask my parents in Korea for money even as an adult, so I felt a sense of shame.”
–Immigrant woman of Korean origin in early 40s (translated from Korean)
“My cousin will [help me financially] without judgment. But, like, my aunt and elders – if it gets back to them [that I asked for help], it’s going to for sure come with judgment. And if I could figure it out myself, I will take the way without judgment.”
“To add on to what [another participant] said, if you go to the community [for help] or whatever, you know, by tomorrow everybody’s going to know it’s your problem.”
–U.S.-born woman of Pakistani origin in early 40s
Immigrants who came to the U.S. because of conflict are more familiar with government aid programs
Asian immigrants come to this country for a variety of reasons. In the focus groups, immigrant participants who came to the U.S. due to conflict or war in their origin countries referenced government assistance programs more often than those who came for other reasons.
This reflects a broader pattern among Asian immigrants overall: Those who came because of conflict or persecution have turned to federal, state or local governments for help with living expenses or employment more often than immigrants who came for economic or educational opportunities, according to the survey.
Focus group participants reflected on differences in the amount of government help available. Sometimes, they expressed a sense of unequal treatment:
“Vietnamese have this program where people got sponsored because of the war. So for other Asians, they feel that we are more privileged. Because from what I know, the Koreans and the Japanese, they must have money in order to come to America. As for us, we can come here through the refugee program, we can come here through the political program. They feel that we got more preferential treatment than other Asians in that regard.”
–Immigrant man of Vietnamese origin in early 40s (translated from Vietnamese)
“During the pandemic, I had to go through housing assistance and everything [to pay my rent]. Something like that with EBT [Electronic Benefits Transfer], how they send you stimulus checks. Korea doesn’t have any of that stuff.”
–U.S.-born woman of Korean origin in late 40s
“I think my community is relatively traditional. Because 20 years ago, we went straight to Chinatown fresh off the plane [after immigrating]. I still remember being in [the local] hospital, lots of social workers were there to help out, including with a medical insurance card, and applying for service, most importantly medical insurance. We all went to [the same] street. We relied on other Chinese people.”
–Immigrant man of Chinese origin in late 30s (translated from Mandarin)
Family ties contribute to increased awareness of government programs. For example, when asked how they learned about using government programs for help, some U.S.-born participants said:
“[I learned about the government programs from] my parents. I had to translate for them.”
–U.S.-born woman of Cambodian origin in mid-30s
“I was working at [a smoothie shop], and I was 17 and a half. … My college loan was like $50,000 [and I was] making $12.50 [an hour], how the hell am I supposed to be paying that month to month? Because my month-to-month was damn near $300, $500. My $12.50 an hour does not even cover for it, any of it, whatsoever. And, you know, me [having] been kicked out of home … I was living with my aunt. … I don’t want to burden her. So I had to go and ask her. She told me, ‘Hey, you should go and apply for food stamps.’”
–U.S.-born woman of Laotian origin in mid-30s
U.S.-born and immigrant focus group participants hold different views on education’s role in achieving a better future

“My friend, he started out at internship … I was too naive. I was laughing at the time, like, ‘Man you spend your time? You took buses there every day? No pay?’ … I just didn’t know the big picture behind [it]. I wish I could plan for [it] just like how they did.” PHUOC , FILM PARTICIPANT
Reflecting on what could lead to success and achieving the American dream, focus group participants who were born in or grew up in the U.S. emphasized the value of getting connected to the “right” opportunities:
“[You don’t have] to go to school to be successful. I mean, they say there are people who are book smart and just people who are street smart, you know. [As long as you] grow up and you know the right people … networking on the right people to get into things. Or, you know, the right people to do the right things to get to where you want to be in life.”
–U.S.-born man of Hmong origin in late 20s
Other participants said it would have helped if their families had a deeper understanding of how the education system prepares them for good careers:
“I feel if my parents were educated and they could have guided me in the right direction [for college] – although, they tried their best. I’m not blaming them. But, you know, if I had someone of a more academic background who knew the system … I will try my best to help my daughter out in college or help her choose what her major is going to be. [My parents couldn’t provide] that kind of help that really helped me in choosing my major. … And so I think just the background that we come from was not the best – or not having the full grasp of this system. … Versus someone who’s had parents here for multiple years, and their parents are now telling them, like, ‘Hey, this is not the right decision for you. Try doing this. This will be better in the long run.’”
–U.S.-born man of Pakistani origin in early 30s
Some also said firsthand knowledge of how to invest and how the U.S. financial system works would have helped:
“[In] the newer generation, we have access to learn all the things we need to, right? [I watch videos] that talk about, like, ‘These are the things you need to do in order to be financially successful. You need to invest your money, get into stocks,’ and stuff like that. And I know that not even 1% of my Hmong community knows anything about that stuff. … So I think we can be more financially successful, including myself, if we were to look more deeply into those things.”
–U.S.-born woman of Hmong origin in late 20s
“If you’re educated and know how, like, let’s say investments work, if you know how that’s done and then you apply it actually going through [someone] like investors or even stockbrokers, then you’ll see the fruits of your labor, or at least experience that, as opposed to not even having the knowledge or even the experience to begin with.”
–U.S.-born man of Cambodian origin in mid-30s
Some participants shared that even when they have some knowledge of financial institutions, they feel the system is working against them:
“I think systematic racism [is a barrier to achieving the American dream]. … I mean, if you own a car, you got to get the bank to approve you. … And they charge people with, like, no credit the highest fee, the most percentage, which are a lot of the folks [like] us trying to achieve the American dream. And then we go to neighborhoods that have the highest crime rate, we also have the most premiums. … And so I think that, one, we’re paying a lot more with much less … the system [was] set up well before minorities, and I think we’re pretty much going to fall behind.”
Many focus group participants also see the value of education, especially a college one, in leading toward a better future and achieving the American dream:
“[When I think of the American dream, it means] if you work hard enough, you can succeed. … You can get an education or a higher education. Then you have so many choices here and exposure to so many ideas and concepts that you wouldn’t otherwise.”

“The bachelor’s degree was important to me in the sense that I needed it so that I could apply for the jobs I wanted. … I guess it made things a bit easier.” THET , FILM PARTICIPANT (TRANSLATED FROM BURMESE)
But this sentiment resonated more with immigrant participants than those born in the U.S.:
“It is the education and the relevant knowledge I think that our Hmong people must have. We’ve been living in this country for the last 45 years. I think that to live in this country, it is very important for some people. I do not think everyone has a ‘lawyer’ or a ‘doctor’ in their house. If it happens, maybe we will reach our goal and the poverty will gradually disappear from our lives.”
–Immigrant woman of Hmong origin in mid-30s (translated from Hmong)
“I think if I obtain any degree, I would perhaps be able to do something.”
Assumptions about Asians hurt their chances of overcoming challenges
Participants shared that other people’s assumptions about Asians complicate their experience of living with economic hardship. Asians are often characterized as a “model minority” and portrayed as educationally and financially successful when compared with other groups.
Some participants shared how the assumption that all Asians are doing well hurt their ability to seek help:
“I have a daughter … she’s the only Asian in class. … Everybody tends to think, ‘She’s Asian; she’s so smart; her mommy has money. So you got to invite her to your birthday party because her mom is rich. [Her] mom will buy you a present.’ … I’m not rich, but because we’re Asian … she’s invited to all these parties.”
–U.S.-born woman of Hmong origin in early 30s
“What I can assume is that outside of our community, especially at the government level, [including] state level and central federal level here, we are missing out or not eligible for benefits. In their opinion, we are rich, no matter if we are working or not. [They may think] our stories may not be genuine. They may think we are making up a story [if we apply for benefits].”
Striving for the American dream
Freedom was a recurring theme in how focus group participants define their American dream. Two aspects were mentioned. The first was freedom from debt and stress over making ends meet, such as paying for everyday basic needs including rent and food. The second was the ability to make life choices freely without financial constraints, enabling them to live the life they aspire to.
Reaching the American dream
Half of Asians living near or below the federal poverty line say they believe they have achieved the American dream or are on their way to achieving it, the survey found. This includes 15% who say they have achieved it and 36% who say they are on their way. By comparison, among those living above the poverty line, 27% say they’ve achieved the American dream, and another 46% say they are on their way.
“Before I came to America, I had never heard of the American dream. … But because I was able to at least bring my son along, not only my life but also his education has improved significantly.” THEIN , FILM PARTICIPANT (TRANSLATED FROM BURMESE)
Among focus group participants, many were optimistic about reaching the American dream for themselves:
“[To me, the American dream is] the opportunity to come to America. I’ve learned a lot after reaching here. And I’ve been able to help my parents and relatives. Despite facing some troubles here, I’ve [provided them a] little financial assistance. I would’ve been unable to help them if I had been in Bhutan.”
–Immigrant woman of Bhutanese origin in late 40s (translated from Dzongkha)
Some participants were also hopeful that the next generation can achieve their American dream, even when they themselves are not there yet:
“When I think about the American dream, I look back at myself, because I belong to the first generation that came to this country. We all started very late. I know that this country will help you, but really it will not be easy for us. … What I think will help me to be happy is to ‘reach the American dream.’ If I can’t achieve it, then I will support my children so that they can reach the dream and I will be happy with them. I will give my children money to help them study.”
“If I can’t get [the American dream] for myself, it is okay. No matter how I am, I’ve already reached half of my life. But I’ve done as much as I can do for [my children], so my responsibility is done. If it’s their turn, I believe they will be able to do all that I couldn’t. I believe it.”

“I would like to own a home one day. And at this rate, and like many of my peers, that’s not a reachable goal right now. I don’t see it being a reachable goal for me for a very, very, very long time.” TANG , FILM PARTICIPANT
Still, the survey found that 47% of Asian adults living in poverty say the American dream is out of reach for them, higher than the share among those living above the poverty line (26%). Not all Asians living in poverty feel the same way about achieving the American dream, with U.S.-born Asians in the focus groups being less optimistic about reaching the American dream than immigrant Asians.
“In a certain era with the U.S. and the immigrants coming, the American dream [was] you come, you study, you do this, you can climb up the ladder, etc., etc. That was the big American dream. And I think there was a period where that was possible. Not any longer.”
Others also shared worries about their prospects of reaching the American dream because of different immigration histories and economic concerns such as inflation:
“I think I was conditioned to think too small to have the American dream. … Vietnamese Americans came over here at a very specific time. … There were Chinese Americans that came here like centuries ago, and they had the time to build generational wealth. We know that Vietnamese people came here in the ’70s. That’s not enough time to grow generational wealth.”
–U.S.-born woman of Vietnamese origin in late 20s
“I have kids. … They’re spoiled. … Now with inflation, houses are more expensive now [than 10, 20 years ago], right? Let’s say 20 years from now, when they buy a house, [the American dream] is going to be unachievable, you know what I mean? Like, unless they are a TikTok star or an entertainer or some kind. … [It’s] going to be tough.”
–U.S.-born man of Chinese origin in late 30s
Freedom from debt
For many participants, being debt-free is important to their vision of the American dream and promotes a life with more financial stability and independence:
“[If I could choose one dream in America, it would be to have] no debt. … When buying something, they always say, ‘Be careful, or you’ll be in debt.’ … And that is what got stuck in my throat.”
–Immigrant woman of Laotian origin in mid-30s (translated from Lao)
“[I haven’t achieved the American dream because I’m not] debt-free, you know, just trying to have extra money, instead of living paycheck to paycheck.”
“[My dream in America is] to be independent, for example, we always lived with the money of mom and dad. One is to be independent when you come here. Let me earn so much money that if I go to the store and buy something, I don’t even have to look at the price tag. That [is] my dream.”
–Immigrant woman of Nepalese origin in early 40s (translated from Nepali)
Participants shared that being debt-free also means having less stress and worry about making ends meet so that they can have extra resources and bandwidth to help their families:
“[The most important thing to achieving the American dream is] being debt-free and having real estate and income steadiness. … If you have rent income, you’re not trading in your time for money, so you have real estate. … You’re not stressing, you have time for your kids more, and your family. You’re probably a little bit happier.”
–Immigrant man of Cambodian origin in mid-20s
“The main thing is that I want to fully support my father and mother, and that I don’t have to worry about [how] I will support myself, or how I will pay my house rent. This is my number one.”
–Immigrant woman of Bangladeshi origin in late 20s (translated from Bengali)
For others, having a stable job is an important step to reaching the American dream:
“I want to have a job, and if I have a job, I’ll have money. I’m only working three and a half days a week right now, and I want to work more. I want more jobs the most, right now. I don’t need anything in America. Just a job.”
Freedom to dream
Focus group participants mentioned having the financial ability to not only meet their basic needs, but also pursue their dreams. Asians born in the U.S. mentioned the freedom to chase one’s aspirations without financial constraints more often than immigrants. Regardless of nativity, the ability to live the life they want is fundamental to many focus group participants’ definitions of the American dream:
“[When] everyone around you is immigrants and you’re all just trying to survive, the only thing you’re trained to think about is survival. But you’re not thinking about investment. Like, when you grow older and you start thinking, ‘Okay, I need to spend money to make money,’ that’s when you start thinking bigger. Yeah, I’m not just thinking about like having one home, I want 10 homes.”
“[Financial] stability is you have nothing but you could survive. [Financial] freedom is you have enough that you can do anything you want. That’s my financial freedom.”

“As it was so hard at that time … what motivated you to keep going and work so hard?” “My strength, my mindset was I wanted to earn money so that my children could have a bright future.” PHUOC AND PHONG , FILM PARTICIPANTS (TRANSLATED FROM VIETNAMESE)
The American dream, to some focus group participants, is about more than financial achievements. Finding happiness and helping others, ultimately leading them to live the life they desire, are key parts of their American dream.
“I want to thank [another participant] for saying ‘self-actualization,’ because personally I think it’s really powerful to be able to know what you want. Because then you’ll know what kind of job you want, what kind of house you want, whether you want to be in politics or not. Like, loving yourself and understanding yourself to your core, then that will be the [deciding factor].”
–Immigrant man of Cambodian origin in early 40s
“I think for me [the American dream] is that there is a house for me, with no interest, I do not owe any loan, my parents could live there comfortably, their struggle is over, and also I have enough … to be able to do something for Pakistan later [in life], God willing.”
–Immigrant woman of Pakistani origin in mid-20s (translated from Urdu)
“[Some people define success as having] lots of money, kids, cars, right? But that’s not really … what I would consider success. Success is something that – does it make you happy? … Are you happy every day going to work? Does it make you happy? When you come home, are you happy?”
About this project
Pew Research Center designed these focus groups and survey questions to better understand the experiences of Asian Americans living with economic hardship. By including participants who are among the Asian origin groups most likely to experience poverty, the focus groups aimed to capture, in their own words, their experiences and challenges in America today. The discussions in these groups may or may not resonate with all Asians living in poverty in the United States.
The project is part of a broader research portfolio studying the diverse experiences of Asians living in the U.S.
Survey and demographic analysis of Asians living in poverty
For a comprehensive examination of Asian adults’ experiences with economic hardship from Pew Research Center’s 2022-23 survey of Asian Americans, as well as a demographic analysis of the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2022 American Community Survey, read “Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty.”
Videos throughout this data essay illustrate what focus group participants discussed. Individuals recorded in these video clips did not participate in the focus groups but were selected based on similar demographic characteristics and thematically relevant stories.
Watch the short film related to the themes in the data essay.
Methodological note
This multi-method research project examines the many facets of living with economic hardship among Asian Americans today.
The qualitative analysis is based on 18 focus groups conducted in February 2023 in 12 languages with 144 participants across four locations. Recruited participants had an approximate family income that is at or below 140%-250% of the federal poverty line, depending on the location. More information about the focus group methodology and analysis can be found in the focus group methodology .
The survey analysis included in this data essay is based on 561 Asian adults living near or below the poverty line from Pew Research Center’s 2022-23 survey of Asian Americans, the largest nationally representative survey of Asian American adults of its kind to date, conducted in six languages. For more details, refer to the survey methodology . For questions used in this analysis, refer to the topline questionnaire .
Acknowledgments
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. The Center’s Asian American portfolio was funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from The Asian American Foundation; Chan Zuckerberg Initiative DAF, an advised fund of the Silicon Valley Community Foundation; the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation; the Henry Luce Foundation; the Doris Duke Foundation; The Wallace H. Coulter Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Long Family Foundation; Lu-Hebert Fund; Gee Family Foundation; Joseph Cotchett; the Julian Abdey and Sabrina Moyle Charitable Fund; and Nanci Nishimura.
We would also like to thank the Leaders Forum for its thought leadership and valuable assistance in helping make this survey possible.
The strategic communications campaign used to promote the research was made possible with generous support from the Doris Duke Foundation.
This is a collaborative effort based on the input and analysis of a number of individuals and experts at Pew Research Center and outside experts.
- In this data essay, definitions of “living near or below the poverty line” and related terms differ between survey respondents and focus group participants. Refer to the terminology box for details. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on my self in Urdu- In this article we are going to read Essay on my self in Urdu | اپنے بارے میں مضمون , introduce myself meaning in urdu, میرا نام عفت نثار انصاری ہے۔ میری پیدائش الہ آباد شہر کے شیش محل بہادرگنج محلے میں ہوئی۔ میرے والد کا نام حافظ نثار احمد اور ماں ...
Self Introduction In Urdu Language- How to introduce yourself in urdu language, read 10 points to introduce yourself in urdu , tell me about yourself in urdu, how to introduce yourself in urdu, self introduction in urdu for interview, 10 lines on myself in urdu, my self essay in urdu for class 2
2. Seek Attention with Greetings. How to introduce yourself to someone in Urdu (or any language) begins with hello. السلام علیکم. Assalam-o-Alaikum. "Hello.". السلام علیکم ( Assalam-o-Alaikum) is the most widely used greeting in Pakistan to seek attention and start a discussion with someone to introduce yourself in Urdu.
Learn to Write an Essay on My Self in Urdu🔴 RECOMMENDED VIDEOS 🎥 https://youtu.be/vdEjv0Oohec🎥 https://youtu.be/NoCXFnI6tic🎥 https://youtu.be/I4rOqzo8bBI...
Back to: Urdu Essays List 2. 0. خود اعتمادی خود یقینی کا دوسرا نام ہے۔. یہ خوبی انسان کے بہترین اوصاف میں شمار ہوتی ہے۔. جس آدمی میں خود اعتمادی کی صفت ہو وہ بہترین انسان سمجھا جاتا ہے۔. خود اعتمادی والا ...
In this video, you will learn 10 Lines on My Self in Urdu. ABOUT THIS VIDEO My Self Essay in Urdu 10 Lines on My Self in Urdu Short Urdu Essay on My Self#M...
mera taruf essay in urdu. mazmoon in urdu.10 Lines On Myself.Myself Essay.Short Essay on Myself In urdu.self introduction in urdu for students.introduction i...
The first step to start the convo is by saying لسلام علیکم ( Assalam-u-Alaikum) which means "Peace be unto you". Whenever or wherever Muslims are gathered, the greeting is commonly used. If you are greeting a native speaker, try the following words before starting a conversation or introduce yourself in Urdu. English.
8) میں وقت کا بہت پابند اور محنتی ہوں۔. 9) شام کو میں اپنے دوستوں کے ساتھ کھیلتا ہوں۔. 10) میں اپنے بزرگوں، والدین اور اساتذہ کی اطاعت کرتا ہوں۔. Tags: 10 Lines on Myself in Urdu مختصر مضامین Few Lines on Myself in Urdu. جدید ...
Writing a self-portrait essay begins with describing the writer's personality, experiences, background history, beliefs and other relevant information. The essay must describe how the person reacts, thinks and believes.... Spoken by more than 100 million people, Urdu is the official language of Pakistan. It's also widely spoken in India and places that have large numbers of expats from ...
CHE PHYSICAL C. DeaconOyster4062. 12/31/2023. View full document. Essay on "Myself" Complete Essay for Class 10, Class 12 and Graduation and other classes. Essay No. 01 It is very easy to say something about others and even to pass one's comments on their activities, good or bad. But it is very difficult to say anything about oneself.
My Self Essay In Urdu | 5 lines on my self | My self | short essay on my self | Handwriting essayEssay on my self in Urdu Ten lines Essay | my self| 500 Word...
Urdu Self-Introductions: "My Name is" in Urdu & More! An appropriate and friendly introduction in the Urdu language to the natives can allow you to rub elbows with them withou
My Hobby Essay In Urdu- In this article we are writing an essay on my hobby writing,mera pasandida mashghala essay in urdu writing, ہر انسان کی طرح میرے بھی کئی مشاغل ہیں لیکن میرے فارغ وقت کا زیادہ تر حصہ میں اپنے پسندیدہ ترین مشغلے میں صرف کرتا ہوں۔ میرا پسندیدہ ترین مشغلہ ...
Good example. I peel off my varsity basketball uniform and jump into the shower to wash away my sweat, exhaustion, and anxiety. As the hot water relaxes my muscles from today's 50 suicide drills, I mull over what motivating words I should say to my teammates before next week's championship game against Westmont High.
Tandrusti Hazar Naimat hai Essay in Urdu: Health Importance; Hazrat Muhammad (ﷺ) Essay in Urdu: A Lesson of Kindness; My Self Essay in English: The Journey of Self-Discovery; Taleem e Niswan Essay in Urdu: Women's Education Importance; Federal Board Past Papers Class 9 English
There are always several meanings of each word in Urdu, the correct meaning of Myself in Urdu is میں ہی, and in roman we write it Mein He. The other meanings are Mein He and Khud Mein Nay. Myself is an pronoun, plural ourselves [ahr-selvz, ouuh r-, ou-er-] /ɑrˈsɛlvz, aʊər-, ˌaʊ ər-/ (Show IPA) according to parts of speech.
Urdu Self-Introductions: "My Name is" in Urdu & More! An appropriate and friendly introduction in the Urdu language to the natives can allow you to rub elbows with them withou
My Self Essay in Urdu for class prep.My Self Essay in Urdu for class one.My Self Essay in Urdu for class two.My Self Essay in Urdu for class three.if you lik...
The reception of a particular age-gap relationship depends on its obviousness. The greater and more visible the difference in years and status between a man and a woman, the more it strikes others as transactional. Transactional thinking in relationships is both as American as it gets and the least kosher subject in the American romantic lexicon.
ماں پر مضمون. 0. Urdu Essays List 3- Here is the list of 100 topics of urdu mazameen in urdu, اردو مضامین, اردو ادبی مضامین, اسلامی مقالات اردو, urdu essay app, essays in urdu on different topics , free online urdu essays, siyasi mazameen, mazmoon nawesi, urdu mazmoon nigari.
Women are wisest, a viral essay in New York magazine's the Cut argues, to maximize their most valuable cultural assets— youth and beauty—and marry older men when they're still very young ...
Introduction in Urdu | Urdu Introduction Myself in Urdu | Mera taaruf | Apna Taaruf | Myself essay in urdu | Meri zaat urdu mazmoon | Essay on myself in urdu...
The terms Asians and Asian Americans are used interchangeably throughout this data essay to refer to those who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.. The terms living in poverty, living near or below the federal poverty line and living with economic hardship are used interchangeably throughout this essay to refer to adults whose family ...
Myself Essay in Urdu Meri Zaat Urdu Mazmoon#urduessay #urdumazmoon #mazmoonnigariWebsite: https://urduessaypoint.blogspot.com/Watch Our Other Important Essay...