bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]


The 7 Best Business Plan Examples (2024)
As an aspiring entrepreneur gearing up to start your own business , you likely know the importance of drafting a business plan. However, you might not be entirely sure where to begin or what specific details to include. That’s where examining business plan examples can be beneficial. Sample business plans serve as real-world templates to help you craft your own plan with confidence. They also provide insight into the key sections that make up a business plan, as well as demonstrate how to structure and present your ideas effectively.
Start selling online now with Shopify

Example business plan
To understand how to write a business plan, let’s study an example structured using a seven-part template. Here’s a quick overview of those parts:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of your business and the contents of your business plan.
- Company description: More info about your company, its goals and mission, and why you started it in the first place.
- Market analysis: Research about the market and industry your business will operate in, including a competitive analysis about the companies you’ll be up against.
- Products and services: A detailed description of what you’ll be selling to your customers.
- Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market.
- Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background.
- Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even long-term) financial goals and the costs to run the business. If you’re looking for funding, this is the place to discuss your request and needs.
7 business plan examples (section by section)
In this section, you’ll find hypothetical and real-world examples of each aspect of a business plan to show you how the whole thing comes together.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary offers a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. You’ll want to include a brief description of your company, market research, competitor analysis, and financial information.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is three paragraphs and occupies nearly half the page:
- Company description
You might go more in-depth with your company description and include the following sections:
- Nature of the business. Mention the general category of business you fall under. Are you a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer of your products?
- Background information. Talk about your past experiences and skills, and how you’ve combined them to fill in the market.
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your company —as a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC, or other business type.
- Industry. Which business sector do you operate in? The answer might be technology, merchandising, or another industry.
- Team. Whether you’re the sole full-time employee of your business or you have contractors to support your daily workflow, this is your chance to put them under the spotlight.
You can also repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business. Hair extensions brand Luxy Hair has a blurb on it’s About page that could easily be repurposed as a company description for its business plan.

- Market analysis
Market analysis comprises research on product supply and demand, your target market, the competitive landscape, and industry trends. You might do a SWOT analysis to learn where you stand and identify market gaps that you could exploit to establish your footing. Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical ecommerce business:

You’ll also want to run a competitive analysis as part of the market analysis component of your business plan. This will show you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to gain an edge over the competition.
- Products and services
This part of your business plan describes your product or service, how it will be priced, and the ways it will compete against similar offerings in the market. Don’t go into too much detail here—a few lines are enough to introduce your item to the reader.
- Marketing plan
Potential investors will want to know how you’ll get the word out about your business. So it’s essential to build a marketing plan that highlights the promotion and customer acquisition strategies you’re planning to adopt.
Most marketing plans focus on the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. However, it’s easier when you break it down by the different marketing channels . Mention how you intend to promote your business using blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth marketing.
Here’s an example of a hypothetical marketing plan for a real estate website:

Logistics and operations
This section of your business plan provides information about your production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan (a.k.a. financial statement) offers a breakdown of your sales, revenue, expenses, profit, and other financial metrics. You’ll want to include all the numbers and concrete data to project your current and projected financial state.
In this business plan example, the financial statement for ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy includes forecasted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.

It then goes deeper into the financials, citing:
- Funding needs
- Project cash-flow statement
- Project profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
You can use Shopify’s financial plan template to create your own income statement, cash-flow statement, and balance sheet.
Types of business plans (and what to write for each)
A one-page business plan is a pared down version of a standard business plan that’s easy for potential investors and partners to understand. You’ll want to include all of these sections, but make sure they’re abbreviated and summarized:
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there’s a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example. Shopify has a great business plan template for startups that include all the below points:
- Market research: in depth
- Financials: in depth
Internal
Your internal business plan acts as the enforcer of your company’s vision. It reminds your team of the long-term objective and keeps them strategically aligned toward the same goal. Be sure to include:
- Market research
Feasibility
A feasibility business plan is essentially a feasibility study that helps you evaluate whether your product or idea is worthy of a full business plan. Include the following sections:
A strategic (or growth) business plan lays out your long-term vision and goals. This means your predictions stretch further into the future, and you aim for greater growth and revenue. While crafting this document, you use all the parts of a usual business plan but add more to each one:
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Market analysis: detailed analysis
- Marketing plan: detailed strategy
- Logistics and operations plan: detailed plan
- Financials: detailed projections
Free business plan templates
Now that you’re familiar with what’s included and how to format a business plan, let’s go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from.
Bplans’ free business plan template

Bplans’ free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business. It has many pages just for your financial plan and statements. Once you fill it out, you’ll see exactly where your business stands financially and what you need to do to keep it on track or make it better.
PandaDoc’s free business plan template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is detailed and guides you through every section, so you don’t have to figure everything out on your own. Filling it out, you’ll grasp the ins and outs of your business and how each part fits together. It’s also handy because it connects to PandaDoc’s e-signature for easy signing, ideal for businesses with partners or a board.
Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template

Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template helps you map out the essentials of your business, like partnerships, core activities, and what makes you different. It’s a collaborative tool for you and your team to learn how everything in your business is linked.
Better business planning equals better business outcomes
Building a business plan is key to establishing a clear direction and strategy for your venture. With a solid plan in hand, you’ll know what steps to take for achieving each of your business goals. Kickstart your business planning and set yourself up for success with a defined roadmap—utilizing the sample business plans above to inform your approach.
Business plan FAQ
What are the 3 main points of a business plan.
- Concept. Explain what your business does and the main idea behind it. This is where you tell people what you plan to achieve with your business.
- Contents. Explain what you’re selling or offering. Point out who you’re selling to and who else is selling something similar. This part concerns your products or services, who will buy them, and who you’re up against.
- Cash flow. Explain how money will move in and out of your business. Discuss the money you need to start and keep the business going, the costs of running your business, and how much money you expect to make.
How do I write a simple business plan?
To create a simple business plan, start with an executive summary that details your business vision and objectives. Follow this with a concise description of your company’s structure, your market analysis, and information about your products or services. Conclude your plan with financial projections that outline your expected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The optimal format for a business plan arranges your plan in a clear and structured way, helping potential investors get a quick grasp of what your business is about and what you aim to achieve. Always start with a summary of your plan and finish with the financial details or any extra information at the end.
Want to learn more?
- Question: Are You a Business Owner or an Entrepreneur?
- Bootstrapping a Business: 10 Tips to Help You Succeed
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: 20 Ways to Think Like an Entrepreneur
- 101+ Best Small Business Software Programs
Oberlo uses cookies to provide necessary site functionality and improve your experience. By using our website, you agree to our privacy policy.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14343635291-33bf053f368c43f6a792e94775285bbd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business
15+ Business Plan Examples to Win Your Next Round of Funding
By Jennifer Gaskin , Jun 09, 2021

“If you fail to plan, you are planning to fail,” according to words of wisdom dubiously attributed to Benjamin Franklin. While there’s no solid evidence that Franklin actually coined this phrase, the sentiment rings true for any business.
Not having a solid plan makes it unlikely you’ll achieve the goals you seek, whether the goals are getting your to-do list done or launching a successful organization.
In the early stages of a company, that means developing things like pitch decks, business plans, one-sheeters and more. With Venngage’s Business Plan Builder , you can easily organize your business plan into a visually appealing format that can help you win over investors, lenders or partners.
Learn more about how to create a business plan so you can hit the ground running after reading through this list for inspirational examples of business plans.
START CREATING FOR FREE
Click to jump ahead:
Simple business plan example, startup business plan example, small business plan example, nonprofit business plan example, strategic business plan example, market analysis business plan example, sales business plan example, organization and management business plan example, marketing and sales strategy business plan example, apple business plan example, airbnb business plan example, sequoia capital business plan example.
While your business plan should be supported by thorough and exhaustive research into your market and competitors, the resulting document does not have to be overwhelming for the reader. In fact, if you can boil your business plan down to a few key pages, all the better.

CREATE THIS PLAN TEMPLATE
The simple, bold visual aesthetic of this business plan template pairs well with the straightforward approach to the content and various elements of the business plan itself.
Use Venngage’s My Brand Kit to automatically add your brand colors and fonts to your business plan with just a few clicks.
Return to Table of Contents
An essential startup business plan should include a clear and compelling value proposition, market analysis, competitive analysis, target audience identification, financial projections, and a well-defined marketing and operational strategy.
For a typical startup, the need to appear disruptive in the industry is important. After all, if you’re not offering anything truly new, why would an investor turn their attention toward your organization. That means establishing a problem and the ways in which you solve it right away.

CREATE THIS PRESENTATION TEMPLATE
Whether it’s a full-scale business plan or, in this case, a pitch deck, the ideal way for a startup to make a splash with its plans is to be bold. This successful business plan example is memorable and aspirational.
In the Venngage editor, you can upload images of your business. Add these images to your plans and reports to make them uniquely your own.
All businesses start out small at first, but that doesn’t mean their communications have to be small. One of the best ways to get investors, lenders and talent on board is to show that you’ve done your due diligence.

In this small business plan example, the content is spread over many pages, which is useful in making lengthy, in-depth research feel less like a chore than packing everyone on as few pages as possible.
Organizations that set out to solve problems rather than earning profits also benefit from creating compelling business plans that stir an emotional response in potential donors, benefactors, potential staff members or even media.

CREATE THIS REPORT TEMPLATE
Simplicity is the goal for nonprofits when it comes to business plans, particularly in their early days. Explain the crisis at hand and exactly how your organization will make a difference, which will help donors visualize how their money will be used to help.
Business plans are also helpful for companies that have been around for a while. Whether they’re considering new products to launch or looking for new opportunities, companies can approach business plans from the strategy side of the equation as well.

Strategic business plans or strategy infographics should be highly focused on a single area or problem to be solved rather than taking a holistic approach to the entire business. Expanding scope too much can make a strategy seem too difficult to implement.
Easily share your business plan with Venngage’s multiple download options, including PNG, PNG HD, and as an interactive PDF.
One-page business plan example
For organizations with a simple business model, often a one-page business plan is all that’s needed. This is possible in any industry, but the most common are traditional ones like retail, where few complex concepts need to be explained.

This one-page strategic business plan example could be easily replicated for an organization that offers goods or services across multiple channels or one with three core business areas. It’s a good business plan example for companies whose plans can be easily boiled down to a few bullet points per area.
Especially when entering a saturated market, understanding the landscape and players is crucial to understanding how your organization can fit it—and stand out. That’s why centering your business plan around a market analysis is often a good idea.

In this example, the majority of the content and about half the pages are focused on the market analysis, including competitors, trends, pricing, demographics and more. This successful business plan example ensures the artwork and style used perfectly matches the company’s aesthetic, which further reinforces its position in the market.
You can find more memorable business plan templates to customize in the Venngage editor. Browse Venngage’s business plan templates to find plans that work for you and start editing.
Company description business plan example
Depending on the market, focusing on your company story and what makes you different can drive your narrative home with potential investors. By focusing your business plan on a company description, you center yourself and your organization in the minds of your audience.

This abbreviated plan is a good business plan example. It uses most of the content to tell the organization’s story. In addition to background about the company, potential investors or clients can see how this design firm’s process is different from their rivals.
With Venngage Business , you can collaborate with team members in real-time to create a business plan that will be effective when presenting to investors.
Five-year business plan example
For most startups or young companies, showing potential investors or partners exactly how and when the company will become profitable is a key aspect of presenting a business plan. Whether it’s woven into a larger presentation or stands alone, you should be sure to include your five-year business plan so investors know you’re looking far beyond the present.

CREATE THIS PROPOSAL TEMPLATE
With Venngage’s Business Plan Builder , you can customize a schedule like this to quickly illustrate for investors or partners what your revenue targets are for the first three to five years your company is in operation.
The lifeblood of any company is the sales team. These are the energetic folks who bring in new business, develop leads and turn prospects into customers. Focusing your energy on creating a sales business plan would prove to investors that you understand what will make your company money.
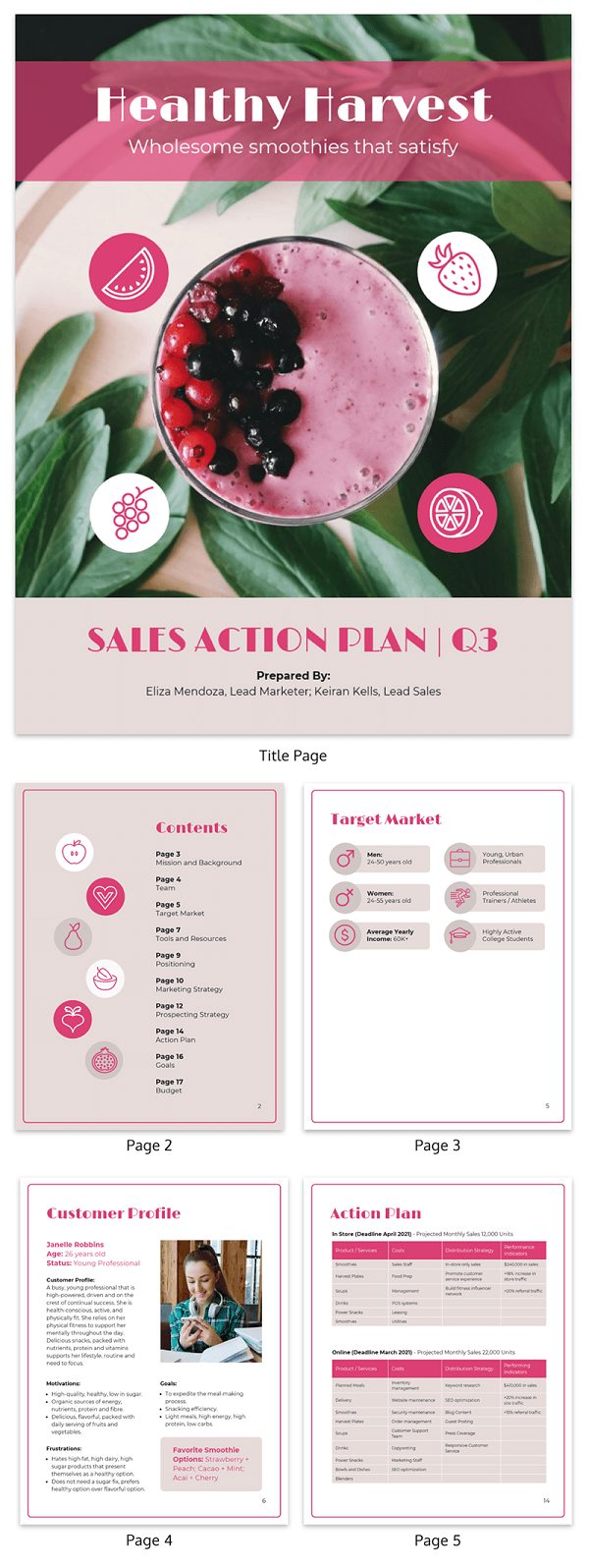
In this example sales business plan, several facets of ideal buyers are detailed. These include a perfect customer profile that helps to convey to your audience that customer relationships will be at the heart of your operation.
You can include business infographics in your plan to visualize your goals. And with Venngage’s gallery of images and icons, you can customize the template to better reflect your business ethos.
Company mergers and shakeups are also major reasons for organizations to require strong business planning. Creating new departments, deciding which staff to retain and charting a course forward can be even more complex than starting a business from scratch.

This organization and management business plan focuses on how the company can optimize operations through a few key organizational projects.
Executive summary for business plan example
Executive summaries give your business plan a strong human touch, and they set the tone for what’s to follow. That could mean having your executive leadership team write a personal note or singling out some huge achievements of which you’re particularly proud in a business plan infographic .

In this executive summary for a business plan, a brief note is accompanied by a few notable achievements that signal the organization and leadership team’s authority in the industry.
Marketing and sales are two sides of the same coin, and clever companies know how they play off each other. That’s why centering your business plan around your marketing and sales strategy can pay dividends when it comes time to find investors and potential partners.

This marketing and sales business plan example is the picture of a sleek, modern aesthetic, which is appropriate across many industries and will speak volumes to numbers-obsesses sales and marketing leaders.
Do business plans really help? Well, here’s some math for you; in 1981, Apple had just gone public and was in the midst of marketing an absolute flop , the Apple III computer. The company’s market cap, or total estimated market value, could hit $3 trillion this year.
Did this Apple business plan make the difference? No, it’s not possible to attribute the success of Apple entirely to this business plan from July 1981, but this ancient artifact goes to show that even the most groundbreaking companies need to take an honest stock of their situation.

Apple’s 1981 business plan example pdf covers everything from the market landscape for computing to the products that founder Steve Jobs expects to roll out over the next few years, and the advanced analysis contained in the document shows how strategic Jobs and other Apple executives were in those early days.
Inviting strangers to stay in your house for the weekend seemed like a crazy concept before Airbnb became one of the world’s biggest companies. Like all disruptive startups, Airbnb had to create a robust, active system from nothing.

As this Airbnb business plan pitch deck example shows, for companies that are introducing entirely new concepts, it’s helpful not to get too into the weeds. Explain the problem simply and boil down the essence of your solution into a few words; in this case, “A web platform where users can rent out their space” perfectly sums up this popular company.
Sequoia Capital is one of the most successful venture capital firms in the world, backing startups that now have a combined stock market value of more than $1 trillion, according to a Forbes analysis .
For young companies and startups that want to play in the big leagues, tailoring your pitch to something that would appeal to a company like Sequoia Capital is a good idea. That’s why the company has a standard business plan format it recommends .

Using Sequoia Capital’s business plan example means being simple and clear with your content, like the above deck. Note how no slide contains much copy, and even when all slides appear on the screen at once, the text is legible.
In summary: Use Venngage to design business plans that will impress investors
Not every business plan, pitch deck or one-sheeter will net you billions in investment dollars, but every entrepreneur should be adept at crafting impressive, authoritative and informative business plans.
Whether you use one of the inspirational templates shared here or you want to go old school and mimic Apple’s 1981 business plan, using Venngage’s Business Plan Builder helps you bring your company’s vision to life.
24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
Free Business Plan Template
.png)
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
Thank you for downloading the offer.
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
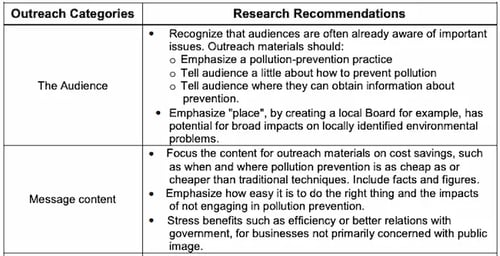
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
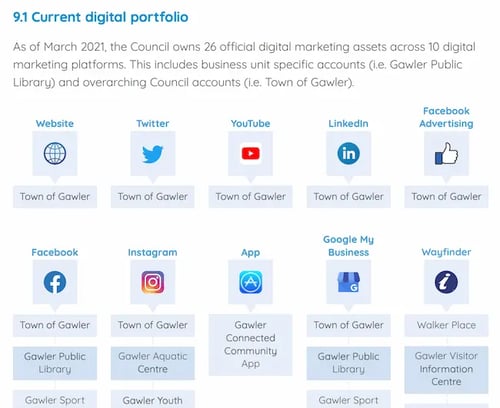
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
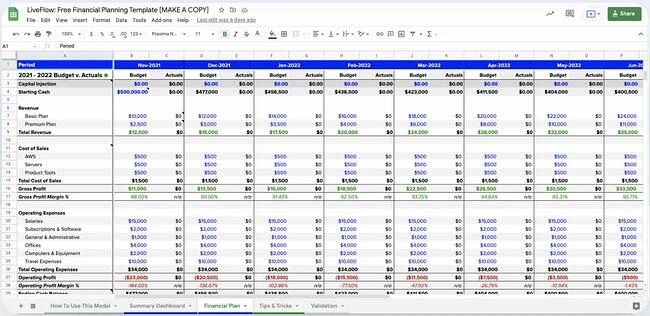
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![better name for business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

19 Best Sample Business Plans & Examples to Help You Write Your Own

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![better name for business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![better name for business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Learn to Build a Better Business Plan

Sample Business Plan Gallery
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples to kickstart your own plan.
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples.

How to Write a Business Plan
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business quickly and efficiently.
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business.

Business Plan Template
Build your business using the proven planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.
Use the planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.

Subscribe to Bplans business insights
Stay up to date with the latest business planning, management, growth, and funding trends from bplans..
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Popular Downloads

SWOT Analysis
Easily evaluate your competitive position and develop effective growth strategies.
Refine your competitive strategy using a SWOT analysis.

Cash Flow Forecast
Improve the health of your business by easily estimating your business’s financial future.
Estimate and improve the financial health of your business.

Lean Business Plan Template
Fast, simple, and shareable. Start with a one-page plan to grow alongside your business.
Start with a simple one-page plan to grow alongside your business…
Start Your Business

Business Startup Guide
Get everything in order to start your business and write your business plan.
Get everything in order to start your business.

How to start a business with no money
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this proven process to get your business…
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this�…

Startup Checklist
Break down the startup process and check all the necessary boxes.

Estimating Startup Costs
What will it cost to start your business? These are the expenses you will need to consider.
Do you know what it will cost to start your business?

Write Your Business Plan

Business Planning in Under an Hour
Learn how to write your business plan in under an hour.

1-Page Business Plan Template
A faster, more efficient way to develop your business strategy.
Perfect Your Elevator Pitch

Pitch Guide
Learn how to create a winning elevator pitch deck and speech that will impress investors.
Impress investors with a winning pitch deck and elevator pitch.


Elements of the Elevator Pitch
If you're pitching to investors or building a pitch deck, here are the 7 things you need.
Here are the 7 things you need to include in your elevator pitch.

Investor-Ready Pitch Gallery
Explore our gallery of sample pitch decks, including a curated collection of startup pitches like Ub…
Explore our gallery of sample pitch decks, including a curated co…

Investor Pitch Template
Start your pitch off right with a proven pitch deck template.

Get Your Business Funded

Funding Guide
Learn how to prepare your business plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.
Prepare your plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.

Ways to Fund Your Business
When it comes to funding, there isn't a one-size-fits-all method. Here are your options.
Find out what funding options are available for your business.
Grow Your Business

How to Grow Your Business
Growing your business can be just as difficult as starting. Here are proven ways to grow.
Try these proven methods to continue growing your business.

Grow Using Your Business Plan
Turn your business plan into a growth-oriented business strategy.

Set Clear and Actionable Goals
Grow your business by setting clear goals and establishing key metrics for success.
Learn to set clear and actionable goals to grow your business.

How to Forecast Cash Flow
Create a cash flow forecast to help keep your business healthy and plan for the future.
Keep your business healthy using a cash flow forecast.

Tim Berry Blog
Learn from renowned business planning expert and founder of Bplans, Tim Berry.

Business Glossary
Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.

What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
How to Write a Business Plan Cover Letter That Wins Investors

Business Plan Cover Pages
Ayush Jalan
- December 12, 2023

Writing a business plan cover letter is an important part of presenting your business plan to potential lenders and investors when seeking investment. It’s the first thing an interested investor will read, and it’s your chance to make a good first impression.
In this article, we’ll see an overview of what a business plan cover letter is, why it’s important, and how to write it. We’ll also share a template, some examples, and useful tips you can use to write a formal cover letter for your own business plan and make it stand out.
What is a business plan cover letter?
A business plan cover letter is a formal document that accompanies your business plan and serves the purpose of introducing you and your business venture to potential investors or lenders. In other words, it’s a way for you to sell your business idea and show why you believe in it.
In the same way that a job seeker presents a cover letter alongside their resume to an employer in order to get hired, you need a cover letter to go alongside your business plan in order to secure funding or a business loan.
Why is a business plan cover letter important?
Through a cover letter, you show the investor why you are a good fit, what value your business can bring to them, and why they should invest in your company instead of your competitor.
To increase your chances of getting funding, it’s wise to tailor your cover letter based on the investor reading it. This means researching the companies the investor has previously invested in, their risk tolerance, and the values they look for in a business partner.
Although your business plans already details all crucial data, the cover letter should provide a glimpse into the current financial position of your company, including its profitability, debt, projections, and more.
The idea here is to let the investor know what they are getting into and reduce uncertainties. If they like your cover letter, they will be more interested to go through the whole business plan and ask questions before investing .
How to write a business plan cover letter?
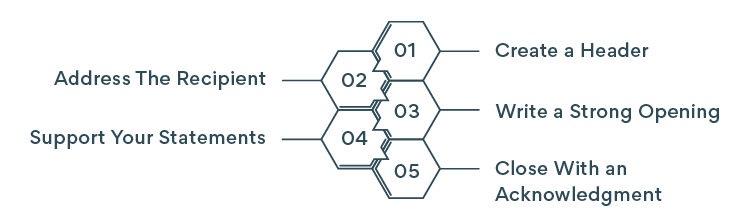
Before you start writing a cover letter, make sure you’re done preparing a business plan and that there are no errors in it. A well-written cover letter isn’t going to get you very far if the business plan itself is not properly made.
Once your business plan is ready, follow these steps to write a cover letter:
Step 1. Create a header
The header of your business plan cover letter should include your name, the name of your business, your address, and your contact information. Next, write the date. And finally, write the name of the investor, the institution they are affiliated with, and their address.
If you’re sending the document via email, there’s no need to write a header, and you can jump to addressing the recipient with a formal greeting.
Step 2. Address the recipient
Unless you don’t know the name of the recipient, don’t make the mistake of addressing them as “Dear Investor” as that may give the impression that you haven’t researched the person you’re sending your business plan to.
Addressing the name of the recipient such as “Dear Mr. Green” or “Dear Ms. Jones” sets a good tone and is preferred over a generic greeting.
Step 3. Write a strong opening
The first paragraph of your letter should immediately grab the reader’s attention. This means stating the intent of the letter, the reason you want to work with this investor, and how you will use their money to scale the business.
Explain why you think your business is a good investment opportunity, and mention details such as the type of ownership, legal formation, the structure of the business , its history, and any notable achievements.
Step 4. Support your statements
Claims made without evidence don’t mean much, so you’re going to need to provide some form of data or facts to prove that you’re worth the risk.
This is admittedly hard to do if you’re a startup since most startups fail. That’s why it’s a good idea to track these key startup metrics to assess your financial position and the overall viability of your business idea.
Step 5. Close with an acknowledgment
The last paragraph of a cover letter should emphasize three things: your interest in working with the investor, the value of this opportunity, and the timeline of how you’re expecting things to happen.
Once done, thank the reader for their time, express your eagerness to see their response, and request a meeting to discuss things further. End the letter with a formal sign-off.
Tips for writing a business plan cover letter
Here are some tips for writing a business plan cover letter:
- Keep the letter short and descriptive, no more than one or two pages.
- Use a formal, conversational tone, and avoid using slang, jargon, and contractions. The easier it is to read your letter, the better.
- Address the reader by name, and avoid using “To Whom It May Concern.”
- Mention your professional background, the competency of the management team, and how it all benefits the business.
- If you’ve acquired funding in the past, highlight the individuals, institutions, or banks that have invested in your company.
Business plan cover letter template
[Your Name] [Your Company’s Name] [Your Address] [Your Contact Information] [Date]
[Investor’s Name] [Investor’s Company Name] [Investor’s Address] Dear [Name of Investor],
I am writing to request your investment in [Your Business Name]. We are [ brief overview of your business ] and we believe that [Your Business Name] has great potential to be a valuable addition to your portfolio.
[Provide a brief description of your current financial situation and how the funds will be used]
[Mention your unique selling proposition]
Please find attached a copy of our business plan which provides more information on our company and product offerings. We would appreciate it if you could take the time to review our plan and offer your feedback. We look forward to working with you.
Thank you for your time and consideration.
Sincerely, [Your Name].
Business plan cover letter example
William Cutler Cutler and Colors Co. 132, My Street, Kingston New York 12401 [email protected] February 17, 2023
James F. Miller Miller Industries Pvt. Ltd. 1234 NW Bobcat Lane, St. Robert, Missouri Dear Mr. Miller,
Cutler and Colors is an emerging fashion retailer in New York City specializing in men’s garments, and we’re looking to expand to six more cities in the U.S. by the end of 2023. With your financial support, we project to double our production and strengthen our supply chain efficiency.
We believe Cutler and Colors will be a valuable addition to your portfolio. We currently have $220,000 of our own funds invested in the business and are looking to raise an additional $500,000. The money will be used to hire more staff, set up new stores, purchase new equipment, and advertise online.
By streamlining our supply chain, we intend to undercut our competitors and offer high-quality garments at an affordable price.
Please find attached a copy of our business plan which provides more information on our company and product offerings. We would appreciate it if you could take the time to review our plan and provide us with your feedback. We look forward to working with you.
Sincerely, William Cutler
Lure investors with a great first impression
Writing a good cover letter is key when presenting your business plan to potential lenders and investors. Your cover letter should be well-written, professional-looking, and tailored to the interests of the investor reading your business plan.
Be mindful of the length of your cover letter; it should be short enough to retain the reader’s interest and long enough to cover the subject. If you’re sending the cover letter over email, it’s a good idea to follow up after some time in case you don’t get a response.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a business plan cover letter be.
Ideally, your cover letter should not exceed one page; if there’s more to add, a maximum of two pages is considered permissible. That said, it’s usually better to write a shorter cover letter than a longer one.
Can I include statistics in a business plan cover letter?
Yes, you can mention data in your cover letter to support your claims, but don’t overdo it since your business plan already highlights your financials and future projections in great detail.
Can I skip writing a business plan cover letter?
If you’re sending a physical copy of your business plan to an investor or lender, it’s absolutely crucial that you attach a cover letter with it. However, a cover letter is not that necessary if you’re sending it via email as you can simply write a note in the body of the email.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
How to Write a Business Plan [Complete Guide]
Last Updated on – Aug 8, 2023 @ 3:22 pm
Preparing to write your business plan? You’re already one step ahead of other entrepreneurs who don’t see its value.
A well-thought-out and well-written plan for starting and running your business helps you focus on what you need to do to make your business idea work. It can also boost your chance of getting investments and loans to finance your business .
Did you know that half of small businesses fail in their first four years? Planning is such a crucial step to reducing the risks of managing an enterprise. Turn your business idea from something abstract and uncertain into a successful venture. It starts with drafting a good business plan.
Here’s your definitive guide to writing a business plan that speaks for itself.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that details what a business is, what direction it will take, and how you’ll get it there.
Practically speaking, the business plan evaluates your business’ viability. As the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) puts it , the document allows entrepreneurs to find out whether or not their business idea will bring in more money than how much it costs to start and run it.
More than just a document, the business plan helps business owners to figure out the key aspects of an enterprise, including the following:
- Business goals and strategies to meet them
- Competitive edge and how to leverage it
- Potential problems and how to solve them
- Funding required to start the business
- Equipment, facilities, and manpower needed for operations
Who Needs a Business Plan and What Is It Used For?
Every aspiring entrepreneur who will spend a great amount of money, time, and energy to earn a profit needs a business plan.
Business planning is a crucial part of starting an entrepreneurial journey, no matter how small or big a business is. Never skip this step—as they say, failing to plan is planning to fail.
Here are some examples of business types that benefit much from business planning:
Founders of startup businesses seek funds to begin their new venture. Business plans help them persuade investors and lenders to provide the funding they need.
For startups, a business plan explains the nature of the new venture, how it will achieve its goals, and why the founders are the best people to lead the company. The startup business plan should also specify the capital needed to jumpstart the new business.
Related: Fast-Growing Startups in the Philippines
Existing Businesses
Not only do startups gain advantage from a business plan—existing enterprises need it, too.
But business plans for growing businesses serve a different purpose. Usually, a business plan helps a middle-stage business raise funds for additional facilities, equipment, manpower, and others needed for expansion. This document also defines strategies for growth and allocates resources based on strategic priorities.
Growing businesses also use business plans to communicate their vision to various stakeholders such as customers, business partners, potential investors and lenders, employees, and suppliers.
For such needs, a business plan for existing businesses lays out the goals, strategies, metrics to evaluate success, responsibilities, and resource allocation.
Social Enterprises
Social enterprises may not be as profit-driven as other business types, but that doesn’t mean they need business planning any less.
A social enterprise needs to prepare a business plan to achieve its social objectives and keep empowering the communities it’s supporting. This document is what government agencies and donor agencies require and evaluate when approving grants for funding a social project .
A social enterprise business plan determines the social issue that a business idea will solve, its beneficiaries, products or services, target market, and sales projections, among many others.
Non-Profit Organizations/NGOs
Like social enterprises, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can also use business plans to source funds for their campaigns and projects.
A nonprofit business plan discusses the problems an NGO is trying to solve through a certain project, as well as how it will do that and how much resources are needed.
It also helps the organization and its board members to prepare for risks by making projections on how likely the activities will push through and how the current sources of funds will continue to yield a certain level of revenue. Most importantly, the business plan defines the Plan B if the original plan ends up failing.
Business Plan Format and Its Components
How does a business plan exactly look like? There’s no recommended universal format for business plans. Ideally, yours is customized according to the nature of your business and what you’re going to use the plan for.
However, all business plans have sections in common. Here’s a quick walkthrough of the six components that make up a business plan.
1. Executive Summary
Like an abstract of a college thesis or a foreword of a book, the executive summary is meant to provide a brief overview of the document. It presents the highlights of a business plan in a page or two.
The executive summary the first thing that readers see, so keep it short yet engaging and compelling enough to make them want to view more details in your plan.
2. Company Profile
The company profile is your chance to introduce yourself and your business to people outside your company. It’s also called the company summary, company information, business description, and business profile.
This section quickly answers the five Ws and one H of your business: who, what, when, where, why, and how.
Think of it as your business calling card. Being the shortest section of the business plan, the company profile provides a quick overview of the business—who the owner and founder is, management team, business goals, business address, product or service, and what makes it unique.
3. Operations Plan
The operations plan explains how you’ll run your business, focusing on the different aspects of manufacturing your product. This section includes the following information, among many others:
- Type of business (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation , or non-profit)
- How the product is made or the service completed
- Necessary materials, equipment, and facilities to manufacture the product or complete the service
- Any subcontractors needed
- Quality control system
4. Organizational Plan
Your people should play a major role in your business plan, just as how they’re important to your business success . The organizational plan includes a chart that shows how your company is structured according to key departments or functions such as administration, production/manufacturing, marketing, and finance. This organizational chart not only presents the levels of authority in a company but also clarifies who is responsible for which people and function.
Aside from the organizational chart, the organizational plan also includes these details:
- Number of employees to hire
- Responsibilities of each job role
- Qualifications of workers who will perform each role
- Salaries and benefits per job assignment
5. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan and the succeeding chapters are the heart and soul of your business plan, explaining the things that will make your business work. This section details how you plan to promote your product or service in the market.
Specifically, the marketing plan covers the following:
- How the product or service will work and how it will benefit customers
- Target market and its profile
- Strategies for packaging, advertising, public relations, and distribution
- Competitive advantage
6. Financial Plan
A critical section in your business plan, the financial plan helps you assess how much money you’ll need to start or grow your enterprise and identify your funding sources to get your business off the ground and sustain its operations. This is where you’ll provide financial estimates that cover at least one year of running your business.
Investors and lenders specifically look for these financial details in business plans:
- How much you’re going to borrow, what you’ll use the loan for, and how you’ll pay it back
- How much profit you’re expecting to make (through an income statement and balance sheet)
- How you can finance your business operations (through a cash flow statement)
- Whether to keep the business going or close it down to cut losses (through a break-even analysis)
Related: How to Write a Business Proposal
Should You Use a Business Plan Template?
Business plan templates identify what information to put into each section and how it should be structured.
They provide instructions to guide entrepreneurs through the process. This way, nothing is missed out while writing the plan.
Thus, using a business plan template is a great idea, especially if this is your first time to prepare a plan for starting or growing your enterprise.
Helpful as it as may be, a business plan template doesn’t make business planning 100% effortless. While it provides the outline that makes writing the plan easy and quick, you still need to do your homework.
For example, a template won’t compute the financial projections for you—it’s a task you have to complete either on your own or with the help of a professional.
So before you use a business plan template, manage your expectations first and be prepared to do a lot of math!
8 Free Business Plan Templates
Yes, you read it right—you can download free online business plan templates. Some of these templates are designed for a specific niche, while others offer sample business plans for a wide range of business categories and industries.
Start off by choosing any of these free templates that suit your business planning needs.
1. Business Plan Format by the DTI
DTI has a wealth of useful information for micro, small, and medium businesses in the Philippines. Of course, it’s free to access since it comes from the government.
On the DTI website, simply look for the Business Planning section and download the business plan format in a PDF file. This document not only lists down all the information to be included in every section of a business plan, but it also provides guide questions per section—making business planning easier for first-timers.
If you want a more detailed discussion of what should go into each component of your business plan plus sample scenarios, check the DTI’s Negosyo Center e-book that fleshes out things for small business owners.
2. Simple Business Plan Template by The Balance Small Business
The Balance is an online resource for small business owners. It has a free business plan template that’s simple and easy to understand for beginners, with instructions on how to use it. Broken down into sections, the simple business plan template tells you what to include in each component of the plan.
Simply copy the free template and paste it into a word document or spreadsheet. From there, you can start drafting your business plan with the template as a guide.
3. Free Sample Business Plans by Bplans
This website features a collection of over 500 free business plan samples for various industries, including restaurants, e-commerce, real estate, services, nonprofit, and manufacturing.
Under each category are links to many sample business plans for specific types of business. Each sample comes with a plan outline, too. For example, under the Services category, you’ll find sample plans for businesses like auto repair shops, advertising agencies, catering companies, health spas, photography studios, and more.
4. Business Plan Samples by LivePlan
More than 500 free sample business plans are available at the LivePlan website, so you’re likely to find one that suits your business best. The samples allow users to know how other businesses structured and worded each component of their business plans. You can copy and paste the sections into your own plan.
To download a full business plan sample, you’ll have to sign up by submitting your name and email address through the website.
5. Business Plan Templates by PandaDoc
PandaDoc offers free business plan templates for NGOs, startups, restaurants, cafes, bakeries, hotels, and salons. These documents can be downloaded in PDF format.
But if you want a customizable template, you can download the PandaDoc template for a 14-day free trial. This template allows you to edit the document, choose a theme that matches your branding, and add pictures and videos.
The website also has free templates for executive summaries and business letters.
6. The One-Page Business Plan by The $100 Startup
If your business has a simple concept, then a one-page business plan template is ideal to use. This downloadable PDF file is a very simple outline made up of a few sections with questions that you have to answer in just a short sentence or two.
7. Business Plans by Microsoft
Microsoft provides a broad selection of templates for its users, including business plan templates in Word, business plan presentations in PowerPoint, and business plan checklists in Excel.
- Sample business plan template (Word) – Provides the steps in writing a complete business plan
- Business plan presentation template (PowerPoint) – Consists of slides for different sections of a business plan that highlight the key points for viewers
- Business plan checklist template (Excel) – Enumerates the important things to do when writing a business plan, using the Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threat (SWOT) analysis framework
The advantage of using a template from Microsoft is having a professional-looking document, slideshow presentation, or spreadsheet. No need to do the formatting by yourself because the template is already formatted. All you have to do is enter the necessary information into the template to complete your business plan.
8. Social Business Plan Guidelines by the Ateneo de Manila
This free business plan format for social entrepreneurs comes from the Ateneo de Manila University’s John Gokongwei School of Management. In a glimpse, it provides the basic information you need to plan a social enterprise.
It also has more detailed business plan guidelines you can refer to. Simply click the link to the word document at the bottommost part of the page.
Related: 11 Best MBA Programs & Schools in the Philippines
How to Write a Business Plan
An outstanding business plan covers everything your stakeholders need to know about your business. So don’t just wing it—put a lot of thought into this critical document.
Let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of drafting a business plan, whether you’ll use a template or not.
1. Brainstorm about your business idea
You may have a very promising business idea, but it won’t fly unless you develop it into a clear-cut concept.
Brainstorm with your team about everything you can think of about starting and running the business. Then list them all down.
Be as creative as possible. No need to be too critical at this point.
While brainstorming, aim to answer these key questions:
- Why do you want to start the business? What has inspired you to go for it?
- What product or service do you plan to sell?
- Who will be your target customers? What are their problems that you’re hoping to solve through your product or service? How will you promote your offerings to them?
- What will be your business branding ? How will you position your brand in the industry?
- What is your competitive advantage? What makes your business unique?
- Where do you see your business within a year?
2. Validate your business idea
Research on the specifics of your business idea—paying special attention to your product or service, target market, and competitors.
According to entrepreneurship experts, it’s best to spend twice as much time on this step as spending the time to the actual drafting of the business plan.
Here are some ways to validate your business idea:
- Read studies and research to find information and trends about your industry .
- Conduct market research to gather insights from industry leaders, potential customers, and suppliers . You can do this through surveys, focus group discussions, and one-on-one interviews with your stakeholders.
- Collect data about your competitors , especially the product or service they offer and how they reach their customers. Consider buying from them or visiting their store to get a feel of their products and customer experience.
Gather all relevant information and analyze your findings to assess whether the business idea is feasible or not. You may need to tweak your business idea based on your evaluation of its feasibility.
3. Define the purpose of your business plan
It’s extremely difficult to carry out anything if you aren’t sure about why you’re doing it in the first place. Without a clear purpose, you’re like driving a car without knowing where you’re headed to.
When it comes to writing your business plan, you should have its purpose in mind from the get-go. It can be one or more of the following:
- Create a roadmap to provide the directions the business must take to achieve your goals and overcome challenges. This is ideal for bootstrapping or self-funding startups.
- Seek investments and loans to finance a business. If this is your purpose for making a business plan, it should be compelling enough to attract investors and lenders.
- Set your targets, budget, timelines, and milestones. When you put them all in writing, it’s so much easier to evaluate and measure your business’ actual performance versus your goals.
- Communicate your vision and strategic priorities with the management team. With this purpose, your business plan must establish specific goals for your managers so that they have something to commit to, you can track progress, and get them to follow through on their commitments. Also, having a business plan for this purpose ensures that everybody involved in running your business is on the same page.
- Minimize risks. Running a business in itself involves a lot of risks, and it gets riskier with a poorly researched business idea. A business plan can help entrepreneurs mitigate them by organizing activities and preparing for contingencies.
4. Create an outline for the executive summary
The first section of any business plan is the executive summary. You don’t have to draft it yet at this point, but it helps to write an outline for it before you proceed with the rest of the sections.
In a sentence or two, describe these key aspects of your business:
- Product or service
- Target market
- Competitors
- Unique value proposition (how you set your business apart from the competition)
- Management team
- Short-term and long-term business goals
- Possible sources of revenue
5. Describe your business
The next step is to write your company profile. Get your readers to become familiar with your business and realize why they should be interested in it.
If you have no idea what specifically goes into this crucial business plan section, you can check the company profiles of businesses in your industry. Usually, you can find them on their websites at the About Us or About the Company page. Take note of the information included and how they’re written.
Here are the must-haves of a great company profile:
- Brief history of the company
- Mission and vision
- Product or service lineup
- Target market and audience
- How the business will address the customers’ pain points
- What makes the business unique
6. Provide details about your operations and organizational structure
Anyone who will read your business plan needs to know what they should expect when they deal with you. They need to see a solid plan for your operations and the people who make up your team. So give your operations plan and organizational plan a careful thought.
For your operations plan, choose carefully the right legal structure for your business. Will you be a sole proprietor? Or will you partner with someone or form a corporation? Your choice will have an impact not only on your business operations but also on the taxes you’ll pay and your personal liability .
As for the organizational plan, it’s where you put your organizational chart that shows a glimpse of the hierarchy within your organization. You can easily create this chart in Microsoft Word, Excel, or PowerPoint.
Also introduce the people who comprise your management team—their relevant experience, qualifications, and expertise . The organizational plan must also include information of the support personnel, as well as who reports to whom and who manages whom.
If you’ll be outsourcing some of your business functions, add them to your organizational plan, too. These may include consultants , accountants , lawyers , logistics specialists, and IT specialists. This way, you’re showing that you’re planning to fill in any expertise and skill gaps in your in-house team.
Also Read: Business Process Outsourcing to the Philippines [Complete Guide]
7. Compose your marketing plan
Make this section of your business plan as comprehensive and detailed as possible. You’d want to prove that you’ll take a strategic and aggressive approach to reach your target customers and promote your brand and product or service to them.
Divide your marketing plan into five subsections: objectives, product/service description, target market profile, competition profile, and promotional activities.
A. Objectives
Zero in on the what and the why of your marketing activities. Under the marketing objectives section, list down all your goals and the strategies you’ll implement to meet them.
Your marketing goals can be any of the following:
- Raise brand awareness
- Introduce a new product or service
- Regain or get more customers for an existing product or service
- Secure long-term contracts with your ideal clients
- Increase sales in a certain market, product, or price point
- Improve product manufacturing or product/service delivery
- Increase prices without affecting sales
B. Product/Service Description
Describe each product or service you’ll offer, including its features and benefits. You can use storytelling , images, charts, tables, or any visual element that best illustrates how each item will work to the benefit of your target customers.
C. Target Market Profile
Present as much relevant data as you can about your potential customers. Make sure to include the following:
- Demographic profile: age range, gender, income level, education, interests, etc.
- Buying behaviors
- Factors that influence their buying decisions: purchasing power, personal preferences, economic conditions, marketing campaigns, social factors (such as peer pressure and social media influencers ), cultural factors, etc.
D. Competition Profile
Your marketing plan must focus not only on your own business but also those of your competitors. List down the similar products or services that they offer to your target customers.
Also, provide an assessment of your competitors’ performance. Which areas are they doing well? How can you improve on their strengths and weaknesses? How can your business stand out? Is it your more competitive pricing? Better customer service? Superior product quality?
To come up with a good competition profile, take the time to research about your competitors. When interviewing your target customers, ask them about the brands they use or businesses they deal with.
You can also do an online search of your competitors. For example, if you’ll run a pet supplies store in Pasig, search for “pet stores Pasig” on Google. The search engine results page may show you the different stores that sell the same products as the ones you plan to offer. Read customer reviews online to get deeper insights on how these businesses serve their clients.
Consider doing a “secret shopping” in your competitor’s store. This way, you can experience firsthand how they treat their customers and how they market and sell their products or services. You might even be able to get information about their product lineup and pricing.
E. Promotional Activities
The last subsection of your marketing plan must discuss how you’ll promote your brand and products or services and connect with customers. Also, be ready to allocate budget for each marketing activity you identify in your plan.
Create a list of marketing activities you plan to implement. Will you reach your audience through SEO (organic online search), paid advertising, and/or social media? Or will you go the traditional route through print and TV advertising or joining expos, exhibits, and trade shows? The right choice depends on the nature of your business and the type of audience you’re trying to reach.
8. Develop your financial plan
The financial plan is the section where you’ll crunch the numbers. Unless you’re really good at math, it’s best to hire an accountant or business consultant who will work with you to develop a foolproof financial plan.
Put simply, a financial plan explains how a business will spend money and make more money. It also estimates the amount of time it will take for the business to earn a profit.
Here are the specifics of a good financial plan:
- Total capital requirement
- Business financing plan and any loan requirement
- Collateral to put up for a business loan
- Schedule for loan repayment
- Financial statements : cash flow statement, income statement/profit and loss statement, and balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Financial analysis
Ultimately, these financial projections answer the question, “Is your business financially feasible?”
9. Back up your business plan with supporting documents
Books and theses have an appendix section at the end that provides additional resources. Your business plan should have one, too. This final section consists of documents, surveys, studies, charts, tables, images, and other elements that provide supporting data.
Depending on the information you’ve presented in the other sections of the plan, your appendix may include these things:
- Market research data and findings
- Resumes of the management team
- Relevant financial documents
- Lease agreements
- Bank statements
- Licenses and permits
10. Review and refine your business plan
Your business plan is almost done at this point. Now all you have to do is go over the document once more to ensure you’ve covered everything and nothing crucial is left out.
Check your final draft and be sure it has the following:
- Sound business idea – If you’ve done Step 2 properly (validating business idea), you can be confident that you have a sound business idea.
- Comprehensive and in-depth look into your business in a professional format
- Thorough understanding of your target customers , their behaviors, interests, and needs
- Competent management team – The people who make up your team must possess the skills and expertise that complement yours.
- Business focus or specialization
Aside from yourself, ask a business partner, proofreader, and accountant or financial expert to review your business plan and spot any errors and inconsistencies. You’d want to make sure that it looks professional and is accurate.
11. Write the executive summary
Lastly, get back to the outline you created in Step 4 and write it based on your final draft. Make sure to craft an engaging executive summary that hooks people into reading the rest of the plan.
6 Actionable Tips on Writing a Business Plan
Anyone can write a business plan—but it takes more than great writing skills to create an exceptional one.
Here are some tips to help you prepare an effective business plan that goes beyond the ordinary.
1. Write with your audience in mind
When drafting your business plan, you’re writing not for yourself but for people who will play key roles in starting and running your enterprise. This is why it’s important that you know whom you’re writing for and keep them in mind while preparing your business plan.
If you think you can’t create a plan that caters to all your audience groups, consider having different versions of the document. For example, you can come up with a business plan for investors, another for lenders, one for employees, and so on. But keep the data consistent across all versions.
To write a business plan that suits a particular audience, you have to use the right language, highlight the parts that interest them, and adjust the format accordingly.
A. Use the Right Language
One of the most important rules in business writing: use the language that your target audience easily understands. If you’re writing for engineers, finance people, or lawyers, your language can be technical—meaning you can use jargons and terminologies familiar to them.
However, if you’re writing for investors who barely have technical knowledge, tweak your language in simple terms that are easy to grasp and appreciate.
Likewise, if you’re writing a business plan to communicate internally with managers and employees your company’s direction and strategies, it’s best to use more casual language than you would when writing for high-level, external stakeholders.
B. Appeal to Your Audience’s Interests
It also helps to understand what interests your audience because they will influence how you’ll write your business plan.
Your management team, for instance, will be interested in knowing your business goals and strategies so that they can help you steer the company in the right direction.
Investors and lenders look at the business plan differently—they’ll be more interested in your financial statements to determine your financial health, like if your business is worth investing in or has the ability to pay back a loan.
C. Adopt a Suitable Business Plan Format
There’s no one-size-fits-all format for business plans because it depends mainly on your audience, aside from the nature of your business.
Let’s say you’ll set up a restaurant, and you’re drafting a business plan to apply for a business loan. To convince lenders that your business is viable, details such as your restaurant’s location and possible renovations are crucial.
Meanwhile, if you’re writing the plan for potential big-time investors, you’ll take a different approach. A good restaurant business plan focuses on the business aspects that will lead to growth and profitability (Remember that investors are interested in how they’ll make money from partnering with you).
2. Keep it concise
How long should a business plan be? According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , it depends on various factors such as the specific audience it’s written for and the nature of a business. The SBA cites surveys that found the ideal length to be at least 25 to 100 pages.
Sounds a lot? If you have a simple business idea and you’re writing a business plan for busy people who don’t have time to pore over hundreds of pages, then one page up to 20 pages should be fine.
However, you may need to provide more explanation (which will take up more pages in your business plan) if you’re planning to build a new kind of business, and a risky one at that.
The size of your business also affects the length of your business plan. Business plans for small businesses need not exceed 30 pages. Corporate business plans are expected to be longer.
What matters more than length is how concise your business plan is. Meaning, it provides all the necessary information—including solid research and analysis—using the fewest words possible. No place for wordiness here!
3. Document everything related to your business
Support your claims in the business plan with solid facts and proof. Investors, for instance, need an assurance that they won’t lose their investment when they trust you with their money. This is where documenting your business thoroughly plays a crucial role.
What kinds of documentation can you include in your business plan?
- Industry forecast or projections
- Licensing agreements
- Location strategy
- Prototype of your product or service
- Survey and FGD results
- Resumes of your management team
4. Show your passion and dedication to your business
Although business plans have straightforward, matter-of-fact content, you can still establish an emotional connection with your readers through your plan. After all, your readers are humans with feelings and motivations.
No need to be dramatic about it—you can show your passion and dedication while still sounding professional in your business plan. Write about the mistakes you’ve had (like a failed business in the past), what you’ve learned from the experience, the values you hold, and the problems of your customers you want to solve through your product or service.
5. Know your competition and how you’ll stand out
Your business won’t be the single player in your industry. Other businesses in the same niche have started way ahead of you, and some new ones will also compete for business in the future.
Write your business plan in such a way that you know your competitors so well. Identify all of them and what makes your business unique compared with the rest without belittling them.
6. Be realistic and conservative in all your estimates
In any aspect of your business, it’s better to underpromise and overdeliver than the other way around. This also holds true when writing a business plan. You wouldn’t want to set unrealistic expectations that will lead to disappointments and worse, losses, when you fail to deliver on your promise.
There’s no place for too much optimism in your business plan. Your budget allocation, timelines, capital requirements, sales and revenue targets, and financial projections must be reasonable, realistic, and conservative. These will lend credibility to your business plan and yourself as an entrepreneur. Because there are a lot of factors beyond your control, always assume that things will get completed longer and cost more ( consider inflation over time! ).
This is where your research prior to writing the draft comes extremely helpful. You have something solid and factual to benchmark against. For example, if your analysis based on the facts you’ve gathered indicates that you’ll be able to get 40% share off the market in your first year of operations, consider making your estimates a bit more conservative and attainable.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Business Valuation in the Philippines
10 Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Business Plan
Now, let’s explore the mistakes entrepreneurs often commit when writing a business plan. Listing them all down here to let you know what to avoid.
1. Prioritizing Form Over Substance
Spend most of your time and energy on building solid research and facts rather than obsessing about which font type or background color will look best for your document.
2. Overthinking
Many entrepreneurs take too long to complete their business plans because they worry too much about it. Don’t get intimidated by business planning—you don’t have to be an expert or a degree holder in business management or business administration to be able to write an outstanding business plan. Overthinking will just lead to analysis paralysis and get nothing done.
As long as you know your business well and are passionate about it, then writing a business plan won’t be as difficult as you think, especially if you’re using a template.
3. Submitting the Document Without Proofreading It
If your business plan is filled with typos and grammatical errors, readers will get distracted even if you’re presenting substantial information. It may also give your audience an impression that you’re careless—and who wants to deal with a person who isn’t professional and careful enough?
Even if it costs you money, pay a professional proofreader to check your work and correct any errors so that the message you wanted to convey through your business plan will get across.
4. Making Empty Claims
Any statement that isn’t sufficiently supported by solid research or documentation has to go. For example, if you want to claim to be the top player in your industry but you don’t have any evidence to back it up, rethink about including it in your business plan.
5. Writing an Overly Long and Wordy Plan
Make sure that everything you put into your business plan is relevant and serves your purpose. Otherwise, remove unnecessary statements that just add fluff to the document.
Also, don’t waste your readers’ time by using too many words—including highfalutin ones. Remember, your goal is to make your audience understand your business, not to impress them with beautiful or complex prose.
6. Using Too Many Superlatives
Even if you really feel that your business, business idea, or projection is incredible, amazing, the best, great, fantastic, or one of a kind, avoid using these superlatives because they aren’t appropriate for formal documents like a business plan.
7. Doing the Financial Projections on Your Own
Unless you’re an accountant yourself, it’s best that you get a professional to do the job for you. It will save you time and the headache of dealing with numbers and formatting your financial plan properly.
8. Overestimating Your Projections
The business plan is not a place to make impossible promises—while they look good on paper, you might run into trouble fulfilling them. To avoid this mistake, always do your research. Find out how other businesses do it and what the typical timeframes and financial projections are before you come up with your estimates.
9. Long-Term Business Planning
As much as possible, limit your projections to only a year. A lot of things can happen and make your business different from how you initially planned it. Stick with your short-term or one-year targets and estimates, then just tweak your business plan as time goes by.
10. Including Unfounded Rumors About Your Competitors
Not only do rumors make your business plan look unprofessional, but they also distract your readers from your intended message, which is to highlight what makes your business different from the competition. Avoid including details based only on hearsay. Everything in your plan must be backed up by solid, quantifiable facts.
Key Takeaway
A business plan is more than just a document that you prepare once and will never look at again. Rather, it’s a strategic tool that you should use from time to time to guide your business operations, get the buy-in of your stakeholders, and grow your business over time.
Once you’re done with writing your business plan, make the most of it for your business. Use it and modify it as often as needed!
Ready and confident to start writing your business plan? Share your thoughts and questions below!
Other Useful Business Resources from Grit PH:
- How to Sell a Business in the Philippines
About Venus Zoleta
Venus Zoleta is an experienced writer and editor, specializing in personal finance and digital marketing.
She has been a regular columnist for some of the biggest business & finance publications in the Philippines, such as MoneyMax.ph and Filipiknow.net.
Hoping to retire early, she started investing and bought a home in her early 20s. This crazy cat mom eats ramen like there's no tomorrow.
Education: University of the Philippines (B.A. Journalism) Focus: Personal Finance, Personal Development, and Entrepreneurship
Reader Interactions
March 3, 2020 at 10:00 am
I like it, and i want to learn more about for business
March 6, 2020 at 9:46 am
Hello Ms. Venus, Rise Against Hunger Philippines, N.G.O. , branching out into a new high ways… and i am newly hired as a social enterprise development officer… whose main tasks to launch a product line; an up-cycled tarpaulin bags.. manufactured by a group of community women (skills training’s, coordinated by life coached; aiming w-holistic transformation and sustainability program.. . with such a big tasks, i need a step by step guides, and if possible a coach for i cannot do it alone… thank you, henry reandino chua
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
We need your help!
Our team is currently conducting research for an upcoming guide focusing on starting a business in the Philippines . We would greatly appreciate your contribution, which should only require a few seconds of your time.
Thank you in advance!
- Digital Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Digital PR & Link Building
- Social Media Marketing
- Digital Advertising (PPC & Social)
- Content Marketing
- Copywriting
- Email Marketing
- Conversion Optimization
- Web/App Development
- Ecommerce Development
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Location of Business * Number of Employees * 1 - 10 11 -50 51 - 100 100 - 500 500+ Phone Number * Email * Insurance Company Standard Insurance AXA Philippines BDO AIG Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Full Name * Company Name * Mobile Number * Email Address * Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Contact Number * Email Address * Target Location Preferred Developer * Ayala Land SM Prime Megaworld Alveo Land DMCI Homes Federal Land Robinsons Land Corp Vista Land and Lifescapes Filinvest Land Shang Properties Century Properties Empire East Rockwell Land Name Submit
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident real estate agents can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed property developments you’re interested to invest in.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Age * Location* Phone Number * Email Address * Insurance Company Sun Life Financial Pru Life U.K. AXA Philippines AIA Philippines Manulife Insular Life BPI-AIA BDO Life Etiqa FWD Insurance Allianz PNB Life Phone Get a Quote
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident financial advisors can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed insurance company you’re interested in.
Results Showcase
14 Surprising Ideas for Naming Membership Tiers

You’re planning your membership program, but you’re stumped on naming membership tiers so your offer doesn’t look like everyone else’s.
In this article, we are going to share insights about designing membership levels and the best way to come up with creative tier names that will make potential customers hit that “sign up” button fast.
Coming up with creative membership level names
You’ve seen the membership tier cliches, and you don’t want your membership program to fall into that trap.
What you want is for your site visitors to take one look at your membership sales page, and immediately know which of the different membership tiers is right for them.
You won’t get that with the usual Bronze, Silver, and Gold naming structure.
The best way to come up with a creative naming structure for your membership levels is to tie it into the topic of your membership site.
For example, if you have a membership teaching people how to play a musical instrument then some great tiers might be:
- Musician in the Making
- Concert Ready
Take a few minutes to jot down membership level names that are specific to your niche. Catchy creative level names are all around when you get brainstorming. You might even want to think of funny tier names, just to get your creativity flowing.
Your new members need to be able to identify which option is right for them based on the level name, but you will also be able to explain the value in your pricing page .
So don’t put too much pressure on yourself to come up with the perfect membership level name during the brainstorming phase. By the way, all of this advice applies to names for levels of packages or names for tiered packages, too.
We’re going to dive deeper into more membership tier naming in a minute. But first, let’s decide how many tiers you need.
How many membership tiers should you offer?
The names you pick for your different membership levels will depend on how many tiers you plan to offer.
The rule of thumb here is to offer no more than 4 membership levels, and preferably just 3.
Why is it better to offer fewer membership levels? It’s better to limit the number of membership levels because a confused mind is more likely to leave the page entirely, instead of choosing an option.
Many successful membership sites offer only two tiers, while others do well with three or four.
Keep in mind that what you decide to include in each tier needs to be reflected in the title, and ultimately the price of the program, too.
Pricing your membership site levels
Pricing a membership site is an art and a science, and you can get more advice on how to do it right in our membership pricing guide . Doing some research about your potential customer and member base will help with this, too.
However, it’s important to consider the price of your different membership levels because the name you choose for each tier needs to be in alignment.
For example, you wouldn’t want to name your membership levels Rose at $50/month, Petunia at $100/month, and Dandelion at $300/month.
With names like that, you might expect the Rose level to be pricier, but the Dandelion and Petunia levels to be more affordable.
Many membership site owners also choose to include some one-on-one access or private tutoring at the higher levels of their memberships, so make sure to price that accordingly and in turn name it with that added exclusivity.
Naming your membership levels based on the benefits and services included is the smart thing to do. For example, your free member level could just be called the free tier on your website, to reduce confusion and entice more members to join.
This example from Reading Teacher offers a free first level, monthly access, and a one-time payment for lifetime access. Here the names for tiered packages are very straightforward.
Membership levels for different types of membership sites
It’s time to look at the different options for naming membership levels, based on the exact type of membership you are offering. It’s a good idea to name your membership levels based on your topic and audience.
Yes, you could pick a brand name for your membership and then have tiers based on the payment duration. Many online membership sites offer monthly and annual subscriptions.
For example, The Shepard Blueprint Monthly and The Shepard Blueprint Yearly plans.
That works fine if you only have two options, but if you really want to encourage people to pick a certain tier then follow the advice below for your particular membership style.
It’s a great idea to offer a price break for customers who upgrade from a monthly subscription to an annual one. Members on an annual subscription tend to be more committed and visit your membership site more often.
Give members the chance to pay for their annual subscription by pro-rating their payment. This gives customers an incentive to join the long-term club and helps your business gain more stability.
1. Skill-based learning memberships
Many membership programs are designed to support people who are starting out and want to improve their skills.
Examples of these types of membership levels include language learning, professional development, crafting, sports, music, writing, coding, gardening, and everything in between.
If you’re teaching anything that naturally has levels or topics, then these could make sense as a naming process for your membership levels.
For example, a martial arts membership program might offer 4 tiers:
- White belt membership
- Green belt membership
- Black belt membership
- Master black belt membership
These are fun names for membership levels, and whether the content is directly tied to the belt level or not, you’re able to convey that the skill level increases with each tier.
Other examples of skill-based memberships include:
- Intermediate
You can also follow the Treehouse example , and offer one monthly membership price but give people a chance to choose the focus of their learning.
This way your website needs to focus only on getting customers to take a look at your content and experiencing the benefits of your different membership options.
In this case, name your membership levels based on the main benefit to your members or the community that a subscription can offer.

2. Access to different content levels
If you’re selling online memberships that contain different levels of access, then naming your tiers based on the amount of access is a logical plan.
Something as simple as this could work:
Of course, there is always room to jazz up your membership level names. Get creative by borrowing from other markets, like an ice cream shop.
- One spoonful (free plan)
- One scoop (paid plan)
- Banana Split Sunday (all-access)
Or a buffet:
- Membership sampler (free plan)
- A la carte (pay for specific content)
- All you can eat buffet (all-access)
Think about the type of content you’re providing, and what would make it enticing to your prospective members! Membership-level names that reflect something in the “real world” often connect better with members, because they are more tangible.
Your aim needs to be to provide a wide variety of options that cater to different needs and preferences, making it easier for individuals to find the membership level that suits them best.
Example from Data School
3. Different groups of people inside the same members area
If your membership site caters to different types of people, based on their roles, then naming your membership levels based on who they are for is a great way to go.
For example, you might have the following tiers for a school setting:
- Student tier
- Teacher tier
- Parent tier
Or for selling training to corporations , you might look at the following examples:
You can achieve this type of bulk course enrollment for membership levels with a learning management system ( what is an LMS ?) like AccessAlly.
These membership tier names are straightforward, and a customer can easily self-identify based on the structure.
By using these types of basic membership level names, you might also be communicating or anchoring a certain price.
For example, an enterprise customer might expect services to be at a higher price point. Whereas an individual member might want a monthly subscription that is more affordable, and easy to cancel.
4. Patrons or different supporter levels
If your membership program is geared toward patrons or supporters of your work, then naming your tiers based on their level of contribution is a great approach.
You want to make people feel special when they sign up to support your work. Remember that all contributions make a difference, even if they are small, so don’t forget to name your lower-level tiers just as sweetly as for your higher-level donors.
Creating an effective membership program goes beyond just offering valuable content and perks. To truly engage your audience and foster long-term loyalty, you need to establish an emotional connection with your members.
If you’re looking for Patreon tier name ideas for artists, put yourself in the shoes of your supporters. Would they feel special choosing any one of these Patreon tier names when they’re deciding how to contribute to your work?
Some examples to get your wheels turning include:
- Supporter of the arts
- Patron of the arts
- Benefactor of the arts
If your brand is focused on hard-hitting independent journalism, or keeping the press free from bias, you might take a look at this structure:
- Journalism Junkie
- Bias Guardian
- Independent Voice Defender
Your membership level naming strategy should match the value you bring, and what people can expect from supporting your work. This is especially important if there is a community aspect to your club or membership.
Example from Dr. Lana Wellness
5. Access to additional support
Another popular membership model strategy is to offer different levels of access to you as the teacher or mentor.
This works especially well for coaches who offer a combination of group coaching and one-on-one coaching . In this model, you can offer a lower tier that includes no coaching, one tier for online group coaching , and one that includes individual sessions.
Sometimes when we’re choosing names for tiers of service, we want to make all of the levels sound equally amazing. Try to resist that urge and focus on the benefits people get at each tier, so that you don’t wind up underselling your top tiers or bottom tiers, which tend to be easier to fulfill.
These might be named something like this (these might not be the most creative tiered package names, but they work):
- Self-serve training
- Group training
- Individual training
Or for more of a coaching slant in a tiered structure:
- Solo practice
- Group coaching
- VIP Coaching
Obviously, you can always dress these membership levels up with your brand’s specific vibe. For example in the health coaching space:
- Wellness Foundations
- Holistic Health Coaching
- Individual Health Assessment and Coaching
Go ahead and start to play with the different words and concepts that apply to your unique membership experience, and see what you come up with.
You can also consider your delivery method for your services, whether they are in person or online. Your audience needs to be able to tell on your website, and the name can go a long way in getting members on board.
Sometimes some of the best membership level names are pretty basic. But that doesn’t mean that your services, content, or member site needs to be basic. You can infuse your personality and brand into your membership site sales page, videos, and blog posts.
Moving between membership levels
One thing that can also make or break your membership tier naming convention is how easy it is to move between tiers.
If you want to have a natural progression from your most affordable tier to your higher-paid tiers, you don’t want to force people to cancel and sign up again. Or worse, have to email you to move them to a new plan manually.

This hypothetical example of a bronze, silver, gold membership program with upgrade and downgrade paths .
Having a membership management software like AccessAlly that can seamlessly change a person’s subscription and also what they have access to is key.
Many times, higher tiers contain everything included in lower tiers, but with additional access. Find out what membership tools allow you to create the type of membership levels you have in mind, without creating a headache for you or your members.
You will also likely want to be able to pro-rate any past payments toward an upgrade or a downgrade in membership plans, so keep that in mind.
Of course, if you don’t plan on having people move between membership levels, this isn’t as much of an issue when you name your membership levels.
Name your membership levels in line with your brand
You probably have a lot of ideas by this point. Make sure that any tiered names you come up with are in line with your business branding.
How can you confirm that?
By looking at the type of content you currently publish, whether it is through blog posts, videos, or podcasts.
Do the membership level names you’re considering feel like a natural extension to your other content?
Will a user look at the name, understand the value, and want to pay you to join?
If not, then your business branding is not clear enough.
Another great litmus test is to see if a customer or friend can explain why it’s worth signing up for your memberships in a few words or less.
It’s time to start naming membership levels
I hope this article gave you some inspiration and a few fresh membership level names to inspire your subscription programs. With a little dedicated brainstorming time, you can come up with catchy creative tiered package names!
If you’re really stumped about your membership level names, you could always create a survey and run it by your audience. Sometimes a quick post or contest to get potential members involved in your business can make people feel like they are a part of something bigger.
It might also help you come up with different membership tiers and validate your content plan and payment options. Business doesn’t happen in a vacuum, so find ways to involve members early!
Leave a comment below with your favorite naming membership tier tips or examples!
I’m a writer, technologist, and regenerative farmer. I founded AccessAlly with my husband in one frantic weekend to solve my immediate course platform issues. Over a decade later the company has grown, and our product has evolved to serve millions of learners across the globe.
Unleash your online course potential with the free AccessAlly demo sandbox.
You might also like...

Create a WordPress Membership Site Dashboard to Increase Sales and Retention

7 Reasons To Hire a Freelancer To Build Your Membership Site and Help Scale Your Business
The Membership Site Software Debate: Platform or Plugin

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Synonyms for business plan include course of action, plan, option, method, strategy, procedure, alternative, system, course and policy. Find more similar words at wordhippo.com!
Start your plan by outlining the purpose and goals of your company. Include a summary of your business objectives, products, and services, along with a realistic description of market ...
Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market. Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background. Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even ...
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Determine how you can best reach potential customers. Evaluate your competition. Your marketing plan must set you apart from your competition, and you can't stand out unless you know your ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
That market research you've done will come in handy for the market analysis section of your business plan. This section should include your analysis of your target market, your competition's strengths and weaknesses, and relevant industry trends. When outlining your target market, make sure to include detailed descriptions of demographics ...
Return to Table of Contents. Startup business plan example. An essential startup business plan should include a clear and compelling value proposition, market analysis, competitive analysis, target audience identification, financial projections, and a well-defined marketing and operational strategy.. For a typical startup, the need to appear disruptive in the industry is important.
8. Panda Doc's Free Business Plan Template. PandaDoc's free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Business Glossary. Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know. Bplans offers free business plan samples and templates, business planning resources, how-to articles, financial calculators, industry reports and entrepreneurship webinars.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Create a Brief Business Plan. Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business.
It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It's more than just a stack of paper and can be ...
1. Executive Summary. A snapshot of your business plan as a whole, touching on your company's profile, mission, and the main points of your plan. Think of it as an elevator pitch that presents ...
The Best Business Plan Software of 2024. Wrike: Best overall. Smartsheet: Best for goal management. LivePlan: Best for financial forecasting. Aha!: Best for roadmapping. Bizplan: Best for ...
Once your business plan is ready, follow these steps to write a cover letter: Step 1. Create a header. The header of your business plan cover letter should include your name, the name of your business, your address, and your contact information. Next, write the date. And finally, write the name of the investor, the institution they are ...
2. Validate your business idea. Research on the specifics of your business idea—paying special attention to your product or service, target market, and competitors. According to entrepreneurship experts, it's best to spend twice as much time on this step as spending the time to the actual drafting of the business plan.
2. Access to different content levels. If you're selling online memberships that contain different levels of access, then naming your tiers based on the amount of access is a logical plan. Something as simple as this could work: Free; Paid; All-Access; Of course, there is always room to jazz up your membership level names.
Empire Business & Tax Advisors, LLC. Business Services, Tax Return Preparation, Business Consultant ... BBB Rating: A+. (407) 613-0850. 120 Broadway Ste 302, Kissimmee, FL 34741-5706. Get a Quote.