How to Set, Track, and Achieve Business Objectives with 60 Examples
By Kate Eby | April 10, 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Businesses that set objectives make better decisions. Business objectives allow companies to focus their efforts, track progress, and visualize future success. We’ve worked with experts to create the most comprehensive guide to business objectives.
Included in this article, you’ll find the differences between business objectives and business goals , the four main business objectives , and the benefits of setting business objectives . Plus, find 60 examples of business objectives , which you can download in Microsoft Word.

What Is a Business Objective?
A business objective is a specific, measurable outcome that a company works to achieve. Company leaders set business objectives that help the organization meet its long-term goals. Business objectives should be recorded so that teams can easily access them.
Business objectives cover many different factors of a company’s success, such as financial health, operations, productivity, and growth.
One easy way to make sure that you are setting the right business objectives is to follow the SMART goal framework . SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
To learn about setting project objectives using the SMART framework, see this comprehensive guide to writing SMART project objectives .
Business Objectives vs. Business Goal
A business goal is a broad, long-term outcome that a company works toward. Goals usually inform which strategies that department leaders will implement. A business objective , however, is a specific, short-term outcome or action that helps the company achieve long-term goals.
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, goals and objectives are not the same . In general, goals are broad in scope and describe an outcome, while objectives are narrow in scope and describe a specific action or step.
While these differences are important to understand, many of the common frameworks for successful goal-setting — such as SMART, objectives and key results ( OKRs ), and management by objectives (MBO) — can be useful when writing business objectives.
When deciding on objectives for a team or department, keep in mind the overarching goals of a business. Each objective should move the company closer to its long-term goals.
Project Goals and Objectives Template
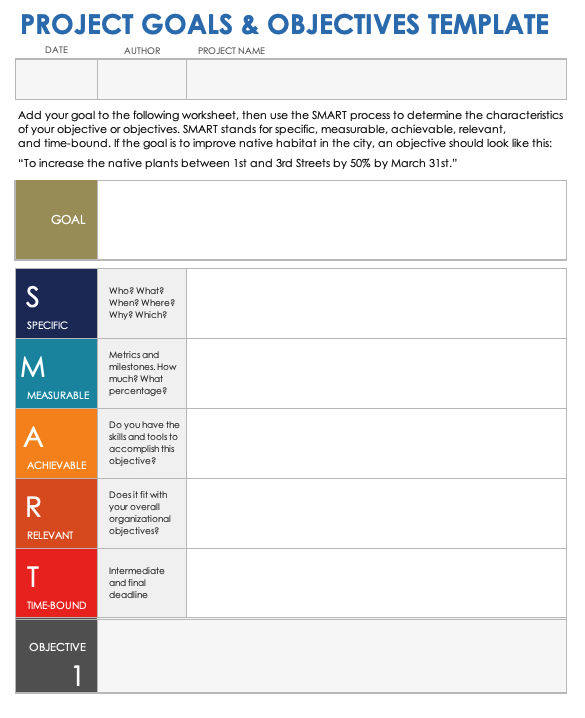
Download the Project Goals and Objectives Template for Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Use this free, printable template to learn how to break down project goals into individual objectives using the SMART framework. Write the primary goal at the top of the worksheet, then follow the SMART process to create one or more specific objectives that will help you achieve that goal.
For resources to help with setting and tracking goals at your company, see this all-inclusive list of goal tracking and setting templates .
What Are the Four Main Business Objectives?
The four main business objectives are economic, social, human, and organic. Each can help a business ensure their prolonged health and growth. For example, human objectives refer to employees’ well-being, while economic objectives refer to the company’s financial health.
These are the four main business objectives:
- Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
- Example: Reduce average customer wait times from eight minutes to four minutes.
- Example: Hire two new chemical engineers by the end of Q2.
- Example: Improve the efficiency of a specific software product by 15 percent.
Types of Business Objectives
There are many types of business objectives beyond the main four. These range from regulation objectives to environmental objectives to municipal objectives. For example, a global objective might be to distribute a product to a new country.
In addition to economic, social, human, and organic objectives, here are some other types of business objectives companies might set:
- Regulatory: These objectives relate to compliance requirements, such as meeting quality standards or conducting internal audits.
- National: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and how they contribute to the country they operate in, such as promoting social justice causes and creating employment opportunities.
- Global: These objectives relate to a company’s place in and its contribution to many countries, such as improving living standards and responding to global demands for products and services.
- Environmental: These objectives relate to a company’s environmental impact, such as reducing chemical waste or making eco-friendly investments.
- Healthcare: These objectives relate to the health and well-being of a population, whether within or outside an organization. These objectives might be improving healthcare benefit options for employees or refining a drug so that it has fewer side effects.
The Importance of Having Business Objectives
Teams need business objectives to stay focused on the company’s long-term goals. Business objectives help individual employees understand how their roles contribute to the larger mission of the organization. Setting business objectives facilitates effective planning.
Here are some benefits to setting business objectives:

- Develops Leadership: Company leaders are more effective when they have a clear vision and can delegate tasks to make it a reality. Setting objectives is a great way to improve one’s leadership skills.
- Increases Motivation: People tend to be more invested in work when they have clear, attainable objectives to achieve. Plus, each completed objective provides a morale boost to keep teams happy and productive.
- Encourages Innovation and Productivity: With increased motivation and workplace satisfaction come more innovations. Set attainable but challenging objectives, and watch teams come up with creative solutions to get things done.
- Improves Strategy: Setting objectives that align with overarching company goals means that everyone across the company can stay aligned on strategic implementation.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Overall customer satisfaction is more likely to increase over time when measurable quality improvements are in place.
- Improves Prioritization: When they are being able to see all of the current objectives, team members can more easily prioritize their work, which in turn makes their workloads feel more manageable.
- Improves Financial Health: Setting economic objectives in particular can help companies stay on top of their financial goals.
60 Examples of Business Objectives
Company leaders can use business objectives to improve every facet of an organization, from customer satisfaction to market share to employee well-being. Here are 60 examples of business objectives that can help a company achieve its goals.
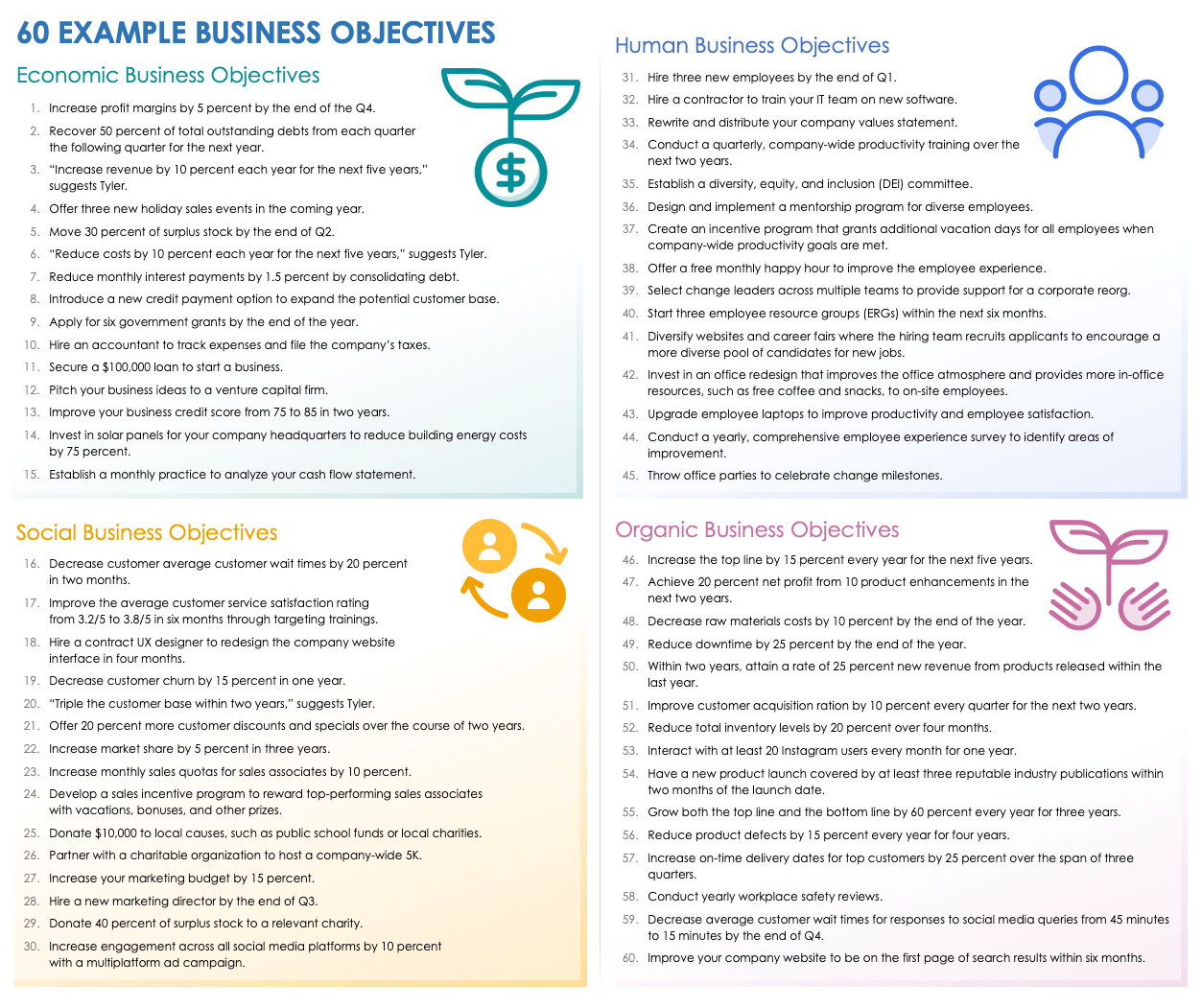
Economic Business Objectives
- Increase profit margins by 5 percent by the end of the Q4.
- Recover 50 percent of total outstanding debts from each quarter the following quarter for the next year.
- “Increase revenue by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer three new holiday sales events in the coming year.
- Move 30 percent of surplus stock by the end of Q2.
- “Reduce costs by 10 percent each year for the next five years,” suggests Tyler.
- Reduce monthly interest payments by 1.5 percent by consolidating debt.
- Introduce a new credit payment option to expand the potential customer base.
- Apply for six government grants by the end of the year.
- Hire an accountant to track expenses and file the company’s taxes.
- Secure a $100,000 loan to start a business.
- Pitch your business ideas to a venture capital firm.
- Improve your business credit score from 75 to 85 in two years.
- Invest in solar panels for your company headquarters to reduce building energy costs by 75 percent.
- Establish a monthly practice to analyze your cash flow statement.
Social Business Objectives
- Decrease customer average customer wait times by 20 percent in two months.
- Improve the average customer service satisfaction rating from 3.2/5 to 3.8/5 in six months through targeting trainings.
- Hire a contract UX designer to redesign the company website interface in four months.
- Decrease customer churn by 15 percent in one year.
- “Triple the customer base within two years,” suggests Tyler.
- Offer 20 percent more customer discounts and specials over the course of two years.
- Increase market share by 5 percent in three years.
- Increase monthly sales quotas for sales associates by 10 percent.
- Develop a sales incentive program to reward top-performing sales associates with vacations, bonuses, and other prizes.
- Donate $10,000 to local causes, such as public school funds or local charities.
- Partner with a charitable organization to host a company-wide 5K.
- Increase your marketing budget by 15 percent.
- Hire a new marketing director by the end of Q3.
- Donate 40 percent of surplus stock to a relevant charity.
- Increase engagement across all social media platforms by 10 percent with a multiplatform ad campaign.
Human Business Objectives
- Hire three new employees by the end of Q1.
- Hire a contractor to train your IT team on new software.
- Rewrite and distribute your company values statement.
- Conduct a quarterly, company-wide productivity training over the next two years.
- Establish a diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) committee.
- Design and implement a mentorship program for diverse employees.
- Create an incentive program that grants additional vacation days for all employees when company-wide productivity goals are met.
- Offer a free monthly happy hour to improve the employee experience.
- Select change leaders across multiple teams to provide support for a corporate reorg.
- Start three employee resource groups (ERGs) within the next six months.
- Diversify websites and career fairs where the hiring team recruits applicants to encourage a more diverse pool of candidates for new jobs.
- Invest in an office redesign that improves the office atmosphere and provides more in-office resources, such as free coffee and snacks, to on-site employees.
- Upgrade employee laptops to improve productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Conduct a yearly, comprehensive employee experience survey to identify areas of improvement.
- Throw office parties to celebrate change milestones.
Organic Business Objectives
- Increase the top line by 15 percent every year for the next five years.
- Achieve 20 percent net profit from 10 product enhancements in the next two years.
- Decrease raw materials costs by 10 percent by the end of the year.
- Reduce downtime by 25 percent by the end of the year.
- Within two years, attain a rate of 25 percent new revenue from products released within the last year.
- Improve customer acquisition ration by 10 percent every quarter for the next two years.
- Reduce total inventory levels by 20 percent over four months.
- Interact with at least 20 Instagram users every month for one year.
- Have a new product launch covered by at least three reputable industry publications within two months of the launch date.
- Grow both the top line and the bottom line by 60 percent every year for three years.
- Reduce product defects by 15 percent every year for four years.
- Increase on-time delivery dates for top customers by 25 percent over the span of three quarters.
- Conduct yearly workplace safety reviews.
- Decrease average customer wait times for responses to social media queries from 45 minutes to 15 minutes by the end of Q4.
- Improve your company website to be on the first page of search results within six months.
Download 60 Example Business Objectives for
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Track the Progress of Business Objectives with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Goals and Objectives for Business Plan with Examples
NOV.05, 2023

Every business needs a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and how it plans to get there. A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and actions to achieve them. A well-written business plan from business plan specialists can help a business attract investors, secure funding, and guide its growth.
Understanding Business Objectives
Business objectives are S pecific, M easurable, A chievable, R elevant, and T ime-bound (SMART) statements that describe what a business wants to accomplish in a given period. They are derived from the overall vision and mission of the business, and they support its strategic direction.
Business plan objectives can be categorized into different types, depending on their purpose and scope. Some common types of business objectives are:
- Financial objectives
- Operational objectives
- Marketing objectives
- Social objectives
For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be:
- To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year.
- To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months.
- To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
- To improve its customer satisfaction rating by 15% in the next month.
The Significance of Business Objectives
Business objectives are important for several reasons. They help to:
- Clarify and direct the company and stakeholders
- Align the company’s efforts and resources to a common goal
- Motivate and inspire employees to perform better
- Measure and evaluate the company’s progress and performance
- Communicate the company’s value and advantage to customers and the market
For example, by setting a revenue objective, a bakery can focus on increasing its sales and marketing efforts, monitor its sales data and customer feedback, motivate its staff to deliver quality products and service, communicate its unique selling points and benefits to its customers, and adjust its pricing and product mix according to market demand.
Advantages of Outlining Business Objectives
Outlining business objectives is a crucial step in creating a business plan. It serves as a roadmap for the company’s growth and development. Outlining business objectives has several advantages, such as:
- Clarifies the company’s vision, direction, scope, and boundaries
- Break down the company’s goals into smaller tasks and milestones
- Assigns roles and responsibilities and delegates tasks
- Establishes standards and criteria for success and performance
- Anticipates risks and challenges and devises contingency plans
For example, by outlining its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer in its business plan, a bakery can:
- Attract investors with its viable business plan for investors
- Secure funding from banks or others with its realistic financial plan
- Partner with businesses or organizations that complement or enhance its products or services
- Choose the best marketing, pricing, product, staff, location, etc. for its target market and customers
Setting Goals and Objectives for a Business Plan
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan is not a one-time task. It requires careful planning, research, analysis, and evaluation. To set effective goals and objectives for a business plan, one should follow some best practices, such as:
OPTION 1: Use the SMART framework. A SMART goal or objective is clear, quantifiable, realistic, aligned with the company’s mission and vision, and has a deadline. SMART stands for:
- Specific – The goal or objective should be clear, concise, and well-defined.
- Measurable – The goal or objective should be quantifiable or verifiable.
- Achievable – The goal or objective should be realistic and attainable.
- Relevant – The goal or objective should be aligned with the company’s vision, mission, and values.
- Time-bound – The goal or objective should have a deadline or timeframe.
For example, using the SMART criteria, a bakery can refine its business objective for increasing the average revenue per customer as follows:
- Specific – Increase revenue with new products and services from $5 to $5.50.
- Measurable – Track customer revenue monthly with sales reports.
- Achievable – Research the market, develop new products and services, and train staff to upsell and cross-sell.
- Relevant – Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, profitability and cash flow, and market competitiveness.
- Time-bound – Achieve this objective in six months, from January 1st to June 30th.
OPTION 2: Use the OKR framework. OKR stands for O bjectives and K ey R esults. An OKR is a goal-setting technique that links the company’s objectives with measurable outcomes. An objective is a qualitative statement of what the company wants to achieve. A key result is a quantitative metric that shows how the objective will be achieved.
OPTION 3: Use the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for S trengths, W eaknesses, O pportunities, and T hreats. A SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps the company assess the internal and external factors that affect its goals and objectives.
- Strengths – Internal factors that give the company an advantage over others.
- Weaknesses – Internal factors that limit the company’s performance or growth.
- Opportunities – External factors that allow the company to improve or expand.
- Threats – External factors that pose a risk or challenge to the company.
For example, using these frameworks, a bakery might set the following goals and objectives for its SBA business plan :
Objective – To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
Key Results:
- Research gluten-free cake market demand and preferences by month-end.
- Create and test 10 gluten-free cake recipes by next month-end.
- Make and sell 100 gluten-free cakes weekly online or in-store by quarter-end.
SWOT Analysis:
- Expertise and experience in baking and cake decorating.
- Loyal and satisfied customer base.
- Strong online presence and reputation.
Weaknesses:
- Limited production capacity and equipment.
- High production costs and low-profit margins.
- Lack of knowledge and skills in gluten-free baking.
Opportunities:
- Growing demand and awareness for gluten-free products.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
- Potential partnerships and collaborations with health-conscious customers and organizations.
- Increasing competition from other bakeries and gluten-free brands.
- Changing customer tastes and preferences.
- Regulatory and legal issues related to gluten-free labeling and certification.
Examples of Business Goals and Objectives
To illustrate how to write business goals and objectives for a business plan, let’s use a hypothetical example of a bakery business called Sweet Treats. Sweet Treats is a small bakery specializing in custom-made cakes, cupcakes, cookies, and other baked goods for various occasions.
Here are some examples of possible startup business goals and objectives for Sweet Treats:
Earning and Preserving Profitability
Profitability is the ability of a company to generate more revenue than expenses. It indicates the financial health and performance of the company. Profitability is essential for a business to sustain its operations, grow its market share, and reward its stakeholders.
Some possible objectives for earning and preserving profitability for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase the gross profit margin by 5% in the next quarter by reducing the cost of goods sold
- To achieve a net income of $100,000 in the current fiscal year by increasing sales and reducing overhead costs
Ensuring Consistent Cash Flow
Cash flow is the amount of money that flows in and out of a company. A company needs to have enough cash to cover its operating expenses, pay its debts, invest in its growth, and reward its shareholders.
Some possible objectives for ensuring consistent cash flow for Sweet Treats are:
- Increase monthly operating cash inflow by 15% by the end of the year by improving the efficiency and productivity of the business processes
- Increase the cash flow from investing activities by selling or disposing of non-performing or obsolete assets
Creating and Maintaining Efficiency
Efficiency is the ratio of output to input. It measures how well a company uses its resources to produce its products or services. Efficiency can help a business improve its quality, productivity, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Some possible objectives for creating and maintaining efficiency for Sweet Treats are:
- To reduce the production time by 10% in the next month by implementing lean manufacturing techniques
- To increase the customer service response rate by 20% in the next week by using chatbots or automated systems
Winning and Keeping Clients
Clients are the people or organizations that buy or use the products or services of a company. They are the source of revenue and growth for a company. Therefore, winning and keeping clients is vital to generating steady revenue, increasing customer loyalty, and enhancing word-of-mouth marketing.
Some possible objectives for winning and keeping clients for Sweet Treats are:
- To acquire 100 new clients in the next quarter by launching a referral program or a promotional campaign
- To retain 90% of existing clients in the current year by offering loyalty rewards or satisfaction guarantees
Building a Recognizable Brand
A brand is the name, logo, design, or other features distinguishing a company from its competitors. It represents the identity, reputation, and value proposition of a company. Building a recognizable brand is crucial for attracting and retaining clients and creating a loyal fan base.
Some possible objectives for building a recognizable brand for Sweet Treats are:
- To increase brand awareness by 50% in the next six months by creating and distributing engaging content on social media platforms
- To improve brand image by 30% in the next year by participating in social causes or sponsoring events that align with the company’s values
Expanding and Nurturing an Audience with Marketing
An audience is a group of people interested in or following a company’s products or services. They can be potential or existing clients, fans, influencers, or partners. Expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing is essential for increasing a company’s visibility, reach, and engagement.
Some possible objectives for expanding and nurturing an audience with marketing for Sweet Treats are:
- To grow the email list by 1,000 subscribers in the next month by offering a free ebook or a webinar
- To nurture leads by sending them relevant and valuable information through email newsletters or blog posts
Strategizing for Expansion
Expansion is the process of increasing a company’s size, scope, or scale. It can involve entering new markets, launching new products or services, opening new locations, or forming new alliances. Strategizing for expansion is important for diversifying revenue streams, reaching new audiences, and gaining competitive advantages.
Some possible objectives for strategizing for expansion for Sweet Treats are:
- To launch a new product or service line by developing and testing prototypes
- To open a new branch or franchise by securing funding and hiring staff
Template for Business Objectives
A template for writing business objectives is a format or structure that can be used as a guide or reference for creating your objectives. A template for writing business objectives can help you to ensure that your objectives are SMART, clear, concise, and consistent.
To use this template, fill in the blanks with your information. Here is an example of how you can use this template:
Example of Business Objectives
Our business is a _____________ (type of business) that provides _____________ (products or services) to _____________ (target market). Our vision is to _____________ (vision statement) and our mission is to _____________ (mission statement).
Our long-term business goals and objectives for the next _____________ (time period) are:
S pecific: We want to _____________ (specific goal) by _____________ (specific action).
M easurable: We will measure our progress by _____________ (quantifiable indicator).
A chievable: We have _____________ (resources, capabilities, constraints) that will enable us to achieve this goal.
R elevant: This goal supports our vision and mission by _____________ (benefit or impact).
T ime-bound: We will complete this goal by _____________ (deadline).
Repeat this process for each goal and objective for your business plan.
How to Monitor Your Business Objectives?
After setting goals and objectives for your business plan, you should check them regularly to see if you are achieving them. Monitoring your business objectives can help you to:
- Track your progress and performance
- Identify and overcome any challenges
- Adjust your actions and strategies as needed
Some of the tools and methods that you can use to monitor your business objectives are:
- Dashboards – Show key data and metrics for your objectives with tools like Google Data Studio, Databox, or DashThis.
- Reports – Get detailed information and analysis for your objectives with tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or SEMrush.
- Feedback – Learn from your customers and their needs and expectations with tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Google Forms.
Strategies for Realizing Business Objectives
To achieve your business objectives, you need more than setting and monitoring them. You need strategies and actions that support them. Strategies are the general methods to reach your objectives. Actions are the specific steps to implement your strategies.
Different objectives require different strategies and actions. Some common types are:
- Marketing strategies
- Operational strategies
- Financial strategies
- Human resource strategies
- Growth strategies
To implement effective strategies and actions, consider these factors:
- Alignment – They should match your vision, mission, values, goals, and objectives
- Feasibility – They should be possible with your capabilities, resources, and constraints
- Suitability – They should fit the context and needs of your business
How OGSCapital Can Help You Achieve Your Business Objectives?
We at OGSCapital can help you with your business plan and related documents. We have over 15 years of experience writing high-quality business plans for various industries and regions. We have a team of business plan experts who can assist you with market research, financial analysis, strategy formulation, and presentation design. We can customize your business plan to suit your needs and objectives, whether you need funding, launching, expanding, or entering a new market. We can also help you with pitch decks, executive summaries, feasibility studies, and grant proposals. Contact us today for a free quote and start working on your business plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the goals and objectives in business.
Goals and objectives in a business plan are the desired outcomes that a company works toward. To describe company goals and objectives for a business plan, start with your mission statement and then identify your strategic and operational objectives. To write company objectives, you must brainstorm, organize, prioritize, assign, track, and review them using the SMART framework and KPIs.
What are the examples of goals and objectives in a business plan?
Examples of goals and objectives in a business plan are: Goal: To increase revenue by 10% each year for the next five years. Objective: To launch a new product line and create a marketing campaign to reach new customers.
What are the 4 main objectives of a business?
The 4 main objectives of a business are economic, social, human, and organic. Economic objectives deal with financial performance, social objectives deal with social responsibility, human objectives deal with employee welfare, and organic objectives deal with business growth and development.
What are goals and objectives examples?
Setting goals and objectives for a business plan describes what a business or a team wants to achieve and how they will do it. For example: Goal: To provide excellent customer service. Objective: To increase customer satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the quarter.
At OGSCapital, our business planning services offer expert guidance and support to create a realistic and actionable plan that aligns with your vision and mission. Get in touch to discuss further!
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- 22 types of business objectives to meas ...
22 types of business objectives to measure success

Clear business objectives help you achieve your mission statement and long-term company vision. These objectives can range from financial objectives to organization specific objectives. Take a look at 22 types of business objectives you can set—plus, learn when to use business objectives vs. 14 other goal frameworks.
Whether you work at a small business, a start up, or as a team lead at a larger enterprise, as a key business owner, you’re responsible for identifying the business objectives that will help your organization hit its long-term goals. Setting goals and strategic objectives is the best way to know where you’re going and how to get there.
In this article, learn about 22 different types of business objectives and how to make them achievable. Then, take a look at the 15 different types of goals you can set, depending on why you’re setting those goals.
What is a business objective?
Business objectives are the results you are aiming to achieve in order to accomplish your longer-term company vision. Think of business objectives as metrics to measure your overall business success.
Hitting your business objectives means you’re on the path towards achieving larger company goals. As such, business objectives should focus on large-scale organizational impact. Good business objectives are measurable, specific, and time-bound.
22 types of business objectives
Set business objectives based on factors that measure and impact your organization’s success. For example, you might set the following business objectives:
Financial business objectives
1. Profitability: A profitability-focused business objective is important if your company is relying on outside investors. Achieving—and maintaining—profitability ensures your long-term success so you can make progress towards your overall company mission.
2. Revenue: Revenue-focused business objectives help you balance your income with your costs in order to stay in business. You might set business objectives to achieve a certain annual revenue goal, or to increase revenue by a certain percentage over a period of time.
3. Costs: Costs refer to how much money you’re spending on your business. Reducing costs can help you increase revenue and achieve profitability. Business objectives related to cost can help you control production or operations cost to improve your business’s financial performance.
4. Cash flow: Cash flow refers to the money moving into and out of your business. Cash flow can be positive—when you’re making more than you’re spending—or negative—when you’re spending more than you’re making. Similar to profitability, a cash flow-oriented business objective can help set you up for long term financial success.
5. Sustainable growth: In order to grow as a business, you need to grow sustainably. Setting business objectives around sustainable growth can help you plan your financial projections, employee costs, and other financial considerations.
Customer-centric business objectives
6. Competitive positioning: A big element of your business strategy is thinking about how your product or service compares to others in the same market. By setting a business objective focused on competitive positioning, you can ensure your product or service reaches parity with what’s expected in the market, or use competitive positioning to outdo your competitors in a key area.
8. Customer satisfaction: In order to succeed as a business, you need happy customers. Focusing on a customer satisfaction-based business objective can help you better serve your customers. Depending on the business objective, this might focus on a customer advocacy program, a better help desk, or something similarly customer-facing.
9. Brand awareness: Your brand is what makes your organization stand out from the crowd. Brand awareness is an important way to understand how your customers think of your brand, and how aware they are of your distinct brand vs. your competitors. Understanding—and increasing—brand awareness is a key part of your long-term marketing strategy .
10. Sales: You’ll often find business objectives related to improving or refining the sales cycle. This could include anything from reducing customer acquisition cost (CAC), developing better lead tracking, increasing cross-selling, or something else.
11. Churn: In business, your churn rate refers to how many customers you lose over a set period of time. Reducing churn is a great way to increase your revenue and ensure your customers are satisfied with the product or service you provide.
Internal business objectives
12. Employee satisfaction and engagement: Part of your business is how your employees feel about working there, too. Increasing employee satisfaction and engagement leads to happier employees, reduced burnout , and more effective teams.
13. Employee retention: A key internal business objective is how long your employees spend at your company. Increasing tenure and reducing turnover can help you achieve more complex projects with knowledgeable employees.
14. Company growth: In order to grow your business, you also need to grow the number of people you employ. Growing your company sustainably can be difficult—which is why businesses often set company growth as a key business objective.
15. Organizational culture: Organizational culture is the ideals, values, and group norms that shape how team members interact within your company. Good culture drives employee engagement and increases retention, which is one of the key reasons so many companies set organizational culture-focused business objectives.
16. Change management: Smoothly implement large-scale organizational change with change management . Though you typically won’t see organizations set this type of business objective year after year, it can be a helpful objective to set if you have large changes on the horizon.
17. Productivity: At Asana, we don’t think of productivity as “doing the most you can,” but rather as a way to optimize your time and get your best work done. Increasing employee productivity can help your teams achieve their high-impact work more efficiently.
18. Employee effectiveness: Teams don’t just need to be efficient—they also need to know the right things to work on. The best companies aim for efficiency and effectiveness—which is where an effectiveness-based business objective comes into play. To learn more, read our article about the difference between efficiency and effectiveness .
19. Diversity and inclusion: A big part of a welcoming company culture is making sure your employees feel like they belong. Investing in diversity and inclusion programs can help your business be more welcoming to your current and potential employees.
Regulation related business objectives
20. Quality control: Implementing quality control measures as a business objective can help you ensure your product or services are at the level you want them to be. This in turn leads to better customer relationships and overall increase in revenue.
21. Compliance: If your business has any compliance needs to meet in the near future, setting those compliance requirements as a business objective will ensure you hit your targets on time.
22. Sustainability or waste reduction: Some businesses set business objectives to reduce waste or increase sustainability. While this may not directly impact your business, proving that you’re environmentally minded can help you reach specific audiences you’re targeting.
Which goal framework is right for you?
Figuring out exactly what type of goal you need to set can be tricky. Each goal framework is slightly different—and implementing the right one can help you achieve success.
The type of goal you set will depend on the business activities you’re running and the specific goals you have. If your goals have a set time frame, you may want to go with short-term objectives, whereas larger goals have their own unique frameworks.
If you’re not sure where to start, check out these 15 goal frameworks for different situations:
1. Business objectives: Set goals based on operating factors that impact your company’s long-term success.
2. Business plan : Also called a business strategy plan. Document your business’ goals and plan out how you’ll get there.
3. Vision statement : Set an organization-wide North Star.
4. Big Hairy Audacious Goals (BHAGs) : Set organization-sized stretch goals .
5. Company values : Align your team around core principles.
6. Strategic plan : Clarify your three to five year company goals during the strategic planning process.
7. Strategic goal : Set the goals you want to achieve by the end of your strategic plan.
8. Critical success factors : Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals.
9. Strategic management : Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals.
10. Business goals : Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time.
11. Objectives and key results (OKRs) : Set and communicate annual company goals.
12. Key performance indicators (KPIs) : Set quantitative goals.
13. Project objectives : Share what you want to achieve by the end of a project.
14. Project deliverables : Identify a project’s output.
15. Project milestones : Mark specific checkpoints along a project’s timeline.
More goal setting resources
Clear goals are critical to keep your organization functioning. In addition to business objectives, check out our goal setting resource hub for tips on setting goals and achieving high-impact results. Then when you’re ready, get started with Asana for goal tracking. With Asana , you can connect your company goals to the work that supports them—all in one place.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to effectively manage goals

Beat thrash for good: 4 organizational planning challenges and solutions
Use critical success factors to support your strategic plan
Business growth
Business tips
Business objectives: How to set them (with 5 examples and a template)
As anyone who played rec league sports in the '90s might remember, being on a team for some reason required you to sell knockoff candy bars to raise funds. Every season, my biggest customer was always me. Some kids went door-to-door, some set up outside local businesses, some sent boxes to their parents' jobs—I just used my allowance to buy a few for myself.
Aside from initiative, what my approach lacked was a plan, a goal, and accountability. A lot to ask of an unmotivated nine-year-old, I know, but 100% required for anyone who runs an actual business.
Business objectives help companies avoid my pitfalls by laying the groundwork for all the above so they can pursue achievable growth.
Table of contents:
The benefits of setting business objectives
How to set business objectives, examples of business objectives and goals, business objective template, tips for achieving business objectives.
Zapier is the leader in workflow automation—integrating with 6,000+ apps from partners like Google, Salesforce, and Microsoft. Use interfaces, data tables, and logic to build secure, automated systems for your business-critical workflows across your organization's technology stack. Learn more .
What are business objectives?
Business objectives are specific, written steps that guide company growth in measurable terms. A good business objective is concise, actionable, and assigned definite metrics for tracking progress and measuring success. Coming up with effective objectives requires a strong understanding of:
What you want the company to achieve
How you can measure success
Which players are involved in driving success
The timelines needed to plan, initiate, and implement steps
How you can improve or better support business processes , personnel, logistics, and management
How, if successful, these actions can be integrated sustainably going forward
Business objectives vs. goals
Where a business objective is an actionable step taken to make improvements toward growth, a business goal is the specific high-level growth an objective helps a company reach. Business objectives are often used interchangeably with business goals, but an objective is in service of a goal.
Here's what that breakdown could have looked like for nine-year-old me selling candy for my little league team:
Business objective: I will increase my sales output by learning and implementing point-of-sale conversion frameworks. I'll measure success by comparing week-over-week sales growth to median sales across players on my baseball team.
Business goal: I will sell more candy bars than anyone on my team and earn the grand prize: a team party at Pizza Hut.
You might think it's good enough to continue working status quo toward your goals, but as the cliche goes, good enough usually isn't. Establishing and following defined, actionable steps through business objectives can:
Help establish clear roadmaps: You can translate your objectives into time-sensitive sequences to chart your path toward growth.
Set groundwork for culture: Clear objectives should reflect the culture you envision, and, in turn, they should help guide your team to foster it.
Influence talent acquisition: Once you know your objectives, you can use them to find the people with the specific skills and experiences needed to actualize them.
Encourage teamwork: People work together better when they know what they're working toward.
Promote sound leadership: Clear objectives give leaders opportunities to get the resources they need.
Establish accountability: By measuring progress, you can see where errors and inefficiencies come from.
Drive productivity: The endgame of an objective is to make individual team members and processes more effective.
Setting business objectives takes a thoughtful, top-to-bottom approach. At every level of your business—whether you're a massive candy corporation or one kid selling chocolate almond bars door-to-door—there are improvements to make, steps to take, and players with stakes (or in my case, bats) in the game.

1. Establish clear goals
You can't hit a home run without a fence, and you can't reach a goal without setting it. Before you start brainstorming your objectives, you need to know what your objectives will help you work toward.
Analytical tactics like a SWOT analysis and goal-setting frameworks like SMART can be extremely useful at this stage, as you'll need to be specific about what you want to achieve and honest about what is achievable. Here are a few example goals:
Increase total revenue by 25% over the next two years
Reduce production costs by 10% by the end of the year
Provide health insurance for employees by next fiscal year
Grow design department to 10+ employees this year
Reach 100k Instagram followers ahead of new product launch
Implement full rebrand before new partnership announcement
Once you have these goals in place, you can establish individual objectives that position your company to reach them.
2. Set a baseline
Like a field manager before a game, you've got to set your baselines. (Very niche pun, I know.) With a definite goal in mind, the only way to know your progress is to know where you're starting from.
If you want to increase conversions on a specific link by X percent, look beyond current conversion percentage to the myriad factors going into it. Log the page traffic, clicks, ad performance, time on page, bounce rate, and other engagement metrics historically to this point. Your objectives will dig deeper into that one outcome to address deficiencies in the sales funnel , so every figure is important.
Analyzing your baselines could also help you recalibrate your goals. You may have decided abstractly that you want conversion rates to double in six months, but is that really possible? If your measurables show there's potentially a heavier lift involved than you expected, you can always roll back the goal performance or expand the timeline.
3. Involve players at all levels in the conversation
Too often, the most important people are left out of conversations about goals and objectives. The more levels of complexity and oversight, the more important it is to hear from everyone—yet the more likely it is that some will be excluded.
Let's say you want to reduce overhead by 5% over the next two years for your sporting goods manufacturing outfit. At a high level, your team finds you can reduce production costs by using cheaper materials for baseball gloves. A member of your sales team points out that the reduction in quality, which your brand is famous for, could lead to losses that offset those savings. Meanwhile, a factory representative points out that replacing outdated machines would be expensive initially but would increase efficiency, reduce defects, and cut maintenance costs, breaking even in four years.
By involving various teams at multiple levels, you find it's worth it to extend timelines from two to four years. Your overhead reduction may be lower than 5% by year two but should be much higher than that by year four based on these changes.
The takeaway from this pretty crude example is that it's helpful to make sure every team that touches anything related to your objective gets consulted. They should give valuable, practical input thanks to their boots- (or cleats-) on-the-ground experience.
4. Define measurable outcomes
An objective should be exactly that. Using KPIs (key performance indicators) to apply a level of objectivity to your action steps allows you to measure their progress and success over time and either adapt as you go along or stay the course.
How do you know if your specific objectives are leading to increased web traffic, or if that's just natural (or even incidental) growth? How do you know if your recruiting efforts lead to better candidates, or whether your employees are actually more satisfied? Here are a few examples of measurable outcomes to show proof:
Percentage change (15% overall increase in revenue)
Goal number (10,000 subscribers)
Success range (five to 10 new clients)
Clear change (new company name)
Executable action (weekly newsletter launch)
Your objectives should have specific, measurable outcomes. It's not enough to have a better product, be more efficient, or have more brand awareness . Your objective should be provable and grounded in data.
5. Outline a roadmap with a schedule
You've got your organizational goals defined, logged your baselines, sourced objectives from across your company, and know your metrics for defining success. Now it's time to set an actionable plan you can execute.
Your objectives roadmap should include all involved team members and departments and clear timelines for reaching milestones. Within your objectives, set action items with deadlines to stay on track, along with corresponding progress markers. For the objective of "increase lead conversion efficiency by 10%," that could look like:
May 15: Begin time logging
June 1: Register team members for productivity seminar
June 15: Integrate Trello for managing processes
June 15: Audit time log
July 1: Implement lead automation
August 1: Audit time log—goal efficiency increase of 5%
6. Integrate successful changes
You've successfully achieved your objectives—great! But as Yogi Berra famously said, "It ain't over till it's over," and it ain't over yet.
Don't let this win be a one-off accomplishment. Berra also said "You can observe a lot by just watching," and applying what you observed from this process will help you continue growing your company. Take what worked, and integrate it into your business processes for sustainable improvement. Then create new objectives, so you can continue the cycle.
Business objectives aren't collated plans or complicated flowcharts—they're short, impactful statements that are easy to memorize and communicate. There are four basic components every business objective should have:
A growth-oriented intention (improve efficiency)
One or more actions (implement monthly training sessions)
A measurement for success (20% increase)
A timeline to reach success (by end of year)
For this year's summer swimwear line, we will increase sales by 15% over last year's line through customer relationship marketing. We will execute distinct email campaigns by segmenting last year's summer swimwear customers and this year's spring casualwear customers and offering season-long discount codes.
Our SaaS product's implementation team will grow to five during the next fiscal year. This will require us to submit a budget proposal by the end of the quarter and look into restructured growth tracks, new job posting templates, and revised role descriptions by the start of next fiscal year.
We will increase customer satisfaction for our mobile app product demonstrably by the end of the year by integrating a new AI chatbot feature. To measure the change in customer satisfaction, we will monitor ratings in the app store, specifically looking for decreases in rates of negative reviews by 5%-10% as well as increases in overall positive reviews by 5%-10%.
Each of our water filtration systems will achieve NSF certification ahead of the launch of our rebranding campaign. Our product team will establish a checklist of changes necessary for meeting certification requirements and communicate timelines to the marketing team.
HR will implement bi-annual performance reviews starting next year. Review timelines will be built into scheduling software, and HR will automate email reminders to managers to communicate to their teams.
Business objectives can be as simple as one action or as complex as a multi-year roadmap—but they should be able to fall into a clear, actionable framework.
Calling your shot to the left centerfield wall and hitting a ball over that wall are two different things—the same goes for setting an objective and actualizing it.
Start with clear, attainable goals: Objectives should position your business to reach broader growth goals, so start by establishing those.
Align decisions with objectives: Once you set objectives, they should inform other decisions. Decision-makers should think about how changes they make along the way affect their objectives' timelines and execution.
Stick to the schedule or adjust it: Schedules should propel change, not rush it. Work toward meeting milestones and deadlines, but understand that they can always be moved if complications or new priorities arise. Remember, it's ok to fall short on goals .
Listen to team members at all levels: Those most affected by organizational changes can be the ones with the least say in the matter. Great ideas and insights can come from any level—even if they're only tangentially related to an outcome.
Implement automation: Automation keeps systems running smoothly—business objectives are no exception. Make a plan to bring no-code automation into workflows with Zapier to move your work forward, faster.
What makes business objectives so useful is that they can help you build a plan with defined steps to reach obtainable growth goals. As (one more time) Yogi Berra also once said, "You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there."
As you outline your objectives, here are some guides that can help you find KPIs and improvement opportunities:
How to conduct your own market research survey
6 customer satisfaction metrics to start measuring
Streamline work across departments with automation
Measuring SaaS success: 5 essential product-led growth metrics to track
12 value proposition templates—and how to write your own
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Bryce Emley
Currently based in Albuquerque, NM, Bryce Emley holds an MFA in Creative Writing from NC State and nearly a decade of writing and editing experience. His work has been published in magazines including The Atlantic, Boston Review, Salon, and Modern Farmer and has received a regional Emmy and awards from venues including Narrative, Wesleyan University, the Edward F. Albee Foundation, and the Pablo Neruda Prize. When he isn’t writing content, poetry, or creative nonfiction, he enjoys traveling, baking, playing music, reliving his barista days in his own kitchen, camping, and being bad at carpentry.
- Small business
- Sales & business development
Related articles
How to create a sales plan (and 3 templates that do it for you)
How to create a sales plan (and 3 templates...
How to build a B2B prospecting list for cold email campaigns
How to build a B2B prospecting list for cold...
The only Gantt chart template you'll ever need for Excel (and how to automate it)
The only Gantt chart template you'll ever...
6 ways to break down organizational silos
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Setting Business Goals & Objectives: 4 Considerations

- 31 Oct 2023
Setting business goals and objectives is important to your company’s success. They create a roadmap to help you identify and manage risk , gain employee buy-in, boost team performance , and execute strategy . They’re also an excellent marker to measure your business’s performance.
Yet, meeting those goals can be difficult. According to an Economist study , 90 percent of senior executives from companies with annual revenues of one billion dollars or more admitted they failed to reach all their strategic goals because of poor implementation. In order to execute strategy, it’s important to first understand what’s attainable when developing organizational goals and objectives.
If you’re struggling to establish realistic benchmarks for your business, here’s an overview of what business goals and objectives are, how to set them, and what you should consider during the process.
Access your free e-book today.
What Are Business Goals and Objectives?
Business objectives dictate how your company plans to achieve its goals and address the business’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. While your business goals may shift, your objectives won’t until there’s an organizational change .
Business goals describe where your company wants to end up and define your business strategy’s expected achievements.
According to the Harvard Business School Online course Strategy Execution , there are different types of strategic goals . Some may even push you and your team out of your comfort zone, yet are important to implement.
For example, David Rodriguez, global chief human resources officer at Marriott, describes in Strategy Execution the importance of stretch goals and “pushing people to not accept today's level of success as a final destination but as a starting point for what might be possible in the future.”
It’s important to strike a balance between bold and unrealistic, however. To do this, you must understand how to responsibly set your business goals and objectives.
Related: A Manager’s Guide To Successful Strategy Implementation
How to Set Business Goals and Objectives
While setting your company’s business goals and objectives might seem like a simple task, it’s important to remember that these goals shouldn’t be based solely on what you hope to achieve. There should be a correlation between your company’s key performance indicators (KPIs)—quantifiable success measures—and your business strategy to justify why the goal should, and needs to, be achieved.
This is often illustrated through a strategy map —an illustration of the cause-and-effect relationships that underpin your strategy. This valuable tool can help you identify and align your business goals and objectives.
“A strategy map gives everyone in your business a road map to understand the relationship between goals and measures and how they build on each other to create value,” says HBS Professor Robert Simons in Strategy Execution .
While this roadmap can be incredibly helpful in creating the right business goals and objectives, a balanced scorecard —a tool to help you track and assess non-financial measures—ensures they’re achievable through your current business strategy.
“Ask yourself, if I picked up a scorecard and examined the measures on that scorecard, could I infer what the business's strategy was,” Simon says. “If you've designed measures well, the answer should be yes.”
According to Strategy Execution , these measures are necessary to ensure your performance goals are achieved. When used in tandem, a balanced scorecard and strategy map can also tell you whether your goals and objectives will create value for you and your customers.
“The balanced scorecard combines the traditional financial perspective with additional perspectives that focus on customers, internal business processes, and learning and development,” Simons says.
These four perspectives are key considerations when setting your business goals and objectives. Here’s an overview of what those perspectives are and how they can help you set the right goals for your business.
4 Things to Consider When Setting Business Goals and Objectives
1. financial measures.
It’s important to ensure your plans and processes lead to desired levels of economic value. Therefore, some of your business goals and objectives should be financial.
Some examples of financial performance goals include:
- Cutting costs
- Increasing revenue
- Improving cash flow management
“Businesses set financial goals by building profit plans—one of the primary diagnostic control systems managers use to execute strategy,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “They’re budgets drawn up for business units that have both revenues and expenses, and summarize the anticipated revenue inflows and expense outflows for a specified accounting period.”
Profit plans are essential when setting your business goals and objectives because they provide a critical link between your business strategy and economic value creation.
According to Simons, it’s important to ask three questions when profit planning:
- Does my business strategy generate enough profit to cover costs and reinvest in the business?
- Does my business generate enough cash to remain solvent through the year?
- Does my business create sufficient financial returns for investors?
By mapping out monetary value, you can weigh the cost of different strategies and how likely it is you’ll meet your company and investors’ financial expectations.
2. Customer Satisfaction
To ensure your business goals and objectives aid in your company’s long-term success, you need to think critically about your customers’ satisfaction. This is especially important in a world where customer reviews and testimonials are crucial to your organization’s success.
“Everything that's important to the business, we have a KPI and we measure it,” says Tom Siebel, founder, chairman, and CEO of C3.ai, in Strategy Execution . “And what could be more important than customer satisfaction?”
Unlike your company’s reputation, measuring customer satisfaction has a far more personal touch in identifying what customers love and how to capitalize on it through future strategic initiatives .
“We do anonymous customer satisfaction surveys every quarter to see how we're measuring up to our customer expectations,” Siebel says.
While this is one example, your customer satisfaction measures should reflect your desired market position and focus on creating additional value for your audience.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Internal Business Processes
Internal business processes is another perspective that should factor into your goal setting. It refers to several aspects of your business that aren’t directly affected by outside forces. Since many goals and objectives are driven by factors such as business competition and market shifts, considering internal processes can create a balanced business strategy.
“Our goals are balanced to make sure we’re holistically managing the business from a financial performance, quality assurance, innovation, and human talent perspective,” says Tom Polen, CEO and president of Becton Dickinson, in Strategy Execution .
According to Strategy Execution , internal business operations are broken down into the following processes:
- Operations management
- Customer management
While improvements to internal processes aren’t driven by economic value, these types of goals can still reap a positive return on investment.
“We end up spending much more time on internal business process goals versus financial goals,” Polen says. “Because if we take care of them, the financial goals will follow at the end of the day.”
4. Learning and Growth Opportunities
Another consideration while setting business goals and objectives is learning and growth opportunities for your team. These are designed to increase employee satisfaction and productivity.
According to Strategy Execution , learning and growth opportunities touch on three types of capital:
- Human: Your employees and the skills and knowledge required for them to meet your company’s goals
- Information: The databases, networks, and IT systems needed to support your long-term growth
- Organization: Ensuring your company’s leadership and culture provide people with purpose and clear objectives
Employee development is a common focus for learning and growth goals. Through professional development opportunities , your team will build valuable business skills and feel empowered to take more risks and innovate.
To create a culture of innovation , it’s important to ensure there’s a safe space for your team to make mistakes—and even fail.
“We ask that people learn from their mistakes,” Rodriguez says in Strategy Execution . “It's really important to us that people feel it’s safe to try new things. And all we ask is people extract their learnings and apply it to the next situation.”

Achieve Your Business Goals
Business goals aren’t all about your organization’s possible successes. It’s also about your potential failures.
“When we set goals, we like to imagine a bright future with our business succeeding,” Simons says in Strategy Execution . “But to identify your critical performance variables, you need to engage in an uncomfortable exercise and consider what can cause your strategy to fail.”
Anticipating potential failures isn’t easy. Enrolling in an online course—like HBS Online’s Strategy Execution —can immerse you in real-world case studies of past strategy successes and failures to help you better understand where these companies went wrong and how to avoid it in your business.
Do you need help setting your business goals and objectives? Explore Strategy Execution —one of our online strategy courses —and download our free strategy e-book to gain the insights to create a successful strategy.

About the Author

Business Plan Goals and Examples for Success
Written by Dave Lavinsky

A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs and businesses to achieve their objectives. One crucial aspect of a business plan is outlining clear and measurable goals. Business plan goals are the specific targets and milestones that a company aims to achieve within a defined timeframe. They provide a direction and purpose for the business, guiding decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning. In this article, we will explore the importance of setting business plan goals and provide examples of common goals.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Why are Business Plan Goals Important?
Business plan goals are essential for several reasons:
- Strategic Focus : Goals help businesses define their strategic direction and focus their efforts on what matters most. They align the company’s efforts and resources towards achieving specific objectives, ensuring that everyone is working towards a common purpose.
- Measurable Outcomes : Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By setting SMART goals, businesses can track progress, measure success, and identify areas for improvement.
- Motivation and Accountability : Goals provide motivation and drive for entrepreneurs and employees. They create a sense of purpose and urgency, encouraging individuals to work towards achieving the desired outcomes. Goals also establish accountability, as progress is monitored and reviewed regularly.
- Decision-Making : Goals serve as a reference point for decision-making. They help businesses prioritize initiatives, allocate resources, and evaluate opportunities based on their alignment with the established goals.
Examples of Business Plan Goals
Business plan goals can vary depending on the nature, size, and stage of the business. Here are some common examples of business plan goals:
Financial Goals:
- Achieve a specific revenue target within a defined timeframe.
- Increase profitability by a certain percentage or dollar amount.
- Reduce costs or increase efficiency in a particular area of the business.
- Secure funding or investment to support business growth.
Market Penetration Goals:
- Expand market share in a specific geographic region or target market.
- Increase brand awareness and recognition among the target audience.
- Launch new products or services in the market.
- Increase customer retention or loyalty.
Operational Goals:
- Improve production or service delivery processes to enhance quality or reduce lead times.
- Enhance supply chain management to optimize inventory levels or reduce costs.
- Implement new technologies or systems to streamline operations or improve customer experience.
- Achieve certifications or industry standards to improve credibility and competitiveness.
Human Resources Goals:
- Hire and retain top talent to support business growth.
- Provide training and development opportunities for employees to enhance their skills and performance.
- Improve employee engagement and satisfaction levels.
- Establish a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Social Responsibility Goals:
- Implement environmentally sustainable practices in the business operations.
- Contribute to the local community through philanthropic initiatives or social impact programs.
- Promote diversity, equity, and inclusion within the organization.
- Establish ethical and responsible business practices.
Business Plan Goals Conclusion
Business plan goals are critical for defining the direction and purpose of a business. They provide measurable outcomes, motivation, and accountability, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. Examples of business plan goals can include financial, market penetration, operational, human resources, and social responsibility objectives. When setting business plan goals, it’s essential to make them SMART – specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound – to increase their effectiveness in driving business success. Regular monitoring and review of progress towards these goals can help businesses stay on track and adapt their strategies as needed to achieve their desired outcomes.

6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Table of Contents
1) Becoming and staying profitable
2) maintaining cash flow , 3) establishing and sustaining productivity , 4) attracting and retaining customers , 5) developing a memorable brand and marketing strategy, 6) planning for growth , track your business objectives and more with countingup.
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as it helps you set up your business and secure the necessary funding. A major part of this plan is your objectives or the outcomes you aim to reach. If you’re unsure where to start, this list of business objective examples can help.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- Becoming and staying profitable
- Maintaining cash flow
- Establishing and sustaining productivity
- Attracting and retaining customers
- Developing a memorable brand
- Reaching and growing an audience through marketing
- Planning for growth
One of the key objectives you may consider is establishing and maintaining profitability . In short, you’ll aim to earn more than you spend and pay off your startup costs. To do this, you’ll need to consider your business’s starting budget and how you’ll stick to it.
To create an objective around profitability, you’ll need to calculate how much you spend to start your business and how much you’ll have to spend regularly to run it. Knowing these numbers will help you determine the earnings you’ll need to become profitable. From there, you can factor in the pricing of your products or services and create sales goals .
For example, say you spend £2,000 on startup costs and expect to spend about £200 monthly to cover business expenses. To earn a profit, you’ll first need to earn back that £2,000 then make more than £200 monthly.
Once you know what you’ll need to earn to become profitable, you can create a realistic timeline to achieve it. If demand and sales forecasts suggest you could earn about £700 monthly, you may create a timeline of 5 months to become profitable.
Maintaining cash flow is another financial objective you could include in your business plan. While profitability means you’ll make more money than you spend, cash flow is the cash running in and out of your business over a given time. This flow is crucial to your company’s success because you need available cash to cover business expenses .
When you complete services, clients may not pay out an invoice right away, meaning you won’t see the cash until they do. If you make enough sales but have low cash flow, you’ll struggle to run your business. So, create an achievable and measurable plan for how you’ll maintain the cash flow you need.
For example, if you spend £500 monthly, you’ll need to ensure you have at least that much available cash. On top of that, anticipate and save for unexpected or emergency expenses, such as broken equipment. To maintain your cash flow, you may want to prioritise cash payments, introduce a realistic deadline for invoices, or create a system to turn your profit to cash.
Aside from financial objectives, another example of objectives for a business plan is sustaining productivity . When you run a business, it can be overwhelming and challenging to stay on top of all the tasks you have to get done. But, if you aim to remain productive and create a clear plan as to how, you can better manage your to-do list.
For example, you may find project management tools that can help you track what you need to do and how to organise your priorities. You may also plan to outsource some aspects of your business eventually, such as investing in an accountant.
Other than planning how you’ll get things done, you may want to create an objective for developing and retaining a customer base. Here, you may outline your efforts to find leads and recruit customers. So, establish goals for how many customers you want to find in your business’s first month, quarter, or year. Your market research can help you understand demand and create realistic sales goals.
If you start a business that customers regularly need, like hairdressing, you may also want to create a strategy for how you’ll retain customers you earn. For example, you could introduce a loyalty program or prioritise customer service to build strong relationships.
Another example of objectives for a business plan is to develop a memorable brand and overall marketing strategy . Your brand is how you present your business to the public, including its unique tone and design. So, here you might research how to make a brand memorable and consider what colour scheme and style will best reach your target audience.
To measure your brand’s progress, you could hold focus groups on understanding what people think of your overall look. Then, surveys can help you grasp the reach of your reputation over time.
Aside from tracking the success of your brand strategy, you may want to consider your business’s marketing approach. For example, you might invest in paid advertising and use social media. You can measure the progress of this over time by using tools like Google Analytics to track your following and reach.
Finally, creating an objective for your company’s growth will help you understand and plan for where you want to go. For example, you may want to expand your services or open a second location for a shop. Whatever ideas you have for the future of your business, try to create a clear, measurable way of getting there, including a timeline. You may also want to include steps towards this goal and savings goals for growth.
To achieve and track your business plan objectives, you’ll need to organise your finances well. But, financial management can be stressful and time-consuming when you’re self-employed. That’s why thousands of business owners use the Countingup app to make their financial admin easier.
Countingup is the business account with built-in accounting software that allows you to manage all your financial data in one place. With the cash flow insights feature, you can confidently keep on top of your finances wherever you are. Plus, the app lets you track and manage what you spend on your business with automatic expense categorisation. This way, you can stick to your budget and plan to accomplish your objectives.

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
How to throw a launch party for a new business.
So your business is all set up and you’re ready to launch in
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best side hustle ideas to start in 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to Register A Company in the UK
There are over four million companies registered in the UK – could your
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
How to start a successful business during a recession
Starting a business during a recession may sound like madness, but some big
What is a mission statement (and how to write one)
When starting a small business, you’ll need a plan to get things up

How does self-employment work?
The decision to become self-employed is not one to take lightly, and you
Tips for choosing a company name
It can be difficult to choose the right company name. Read these simple tips to make your decision easier.
550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
The Main Objectives of a Business Plan Here's what a business plan will reveal and how it can save you time and resources.
By Eric Butow • Oct 27, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 11 / 11 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 1: The Foundation of a Business Plan series.
You need to think of what you want and whether your plan's findings suggest you'll get it. For instance, is your objective to gain freedom from control by other people? If your plan shows that you'll have to take on several equity partners, each of whom will desire a chunk of ownership , you may need to come up with a business that does not require intensive capital needs .
Perhaps you want a company that will let you do your work and get home at a reasonable hour, even a business you can run from home. There are so many options when it comes to starting a business , including the size, location, and, of course, the reason for existence. You will be able to determine all of these and so many more aspects of business with the help of your business plan . It forces you to think through all of the areas that form the main concept to the smallest details. This way you don't find yourself remembering at the last minute that your website is still not developed or that you still have most of your inventory in a warehouse and no way to ship it.
Related: How To Access The Potential Of Your Business Idea
Clarify Your Future Outlook
It may seem odd to say that a business plan can't predict the future. What are all those projections and forecasts for if they are not attempts to predict the future? The fact is, no projection or forecast is really a hard-and-fast prediction of the future. Not even the French seer Nostradamus could tell you for sure how your business will be doing in five years. The best you can do is have a plan in which you logically and systematically attempt to show what will happen if a particular scenario occurs. That scenario has been determined by your research and analysis to be the most likely one of the many that may occur. But it's still just a probability, not a guarantee.
You can, however, use your research, sales forecasts, market trends, and competitive analysis to make well-thought-out predictions of how you see your business developing if you are able to follow a specified course. To some extent, you can create your future rather than simply trying to predict it by the decisions you make. For example, you may not have a multimillion-dollar business in ten years if you are trying to start and run a small family business. Your decision on growth would therefore factor into your predictions and the outcome.
Related: Create A Business Plan Investors Will Love
Find Funding
There are all kinds of reasons why a venture capitalist, banker, or other investor may refuse to fund your company. It may be that there's no money to give out at the moment. It may be that the investor just backed a company very similar to your own and now wants something different. Perhaps the investor has just promised to back her brother-in-law's firm or is merely having a bad day and saying no to everything that crosses her desk. The point is that the quality of your plan may have little or nothing to do with your prospects of getting funded by a particular investor.
But what about the investment community as a whole? Surely if you show a well-prepared plan to a lot of people, someone will be willing to back you, right? Again, not necessarily. Communities, as well as people, are subject to fads, and your idea may be yesterday's fad. Conversely, it may be too far ahead of its time. It also may be an idea that comes about in a shaky economy or a saturated market. Timing is sometimes a factor that is out of your control.
Related: How To Use Your Business Plan
The same is true of the availability of funds. At times, banks everywhere seem to clamp down on lending, refusing to back even clearly superior borrowers. In many countries, there is no network of venture capitalists to back fledgling companies.
Open Negotiations
A business plan cannot guarantee that you will raise all the money you need at any given time, especially during the startup phase. Even if you are successful in finding an investor, the odds are good that you won't get quite what you asked for. There may be a big difference in what you have to give up, such as majority ownership or control, to get the funds. Or you may be able to make minor adjustments if you cannot snare as large a chunk of cash as you want.
Related: What To Include And Not To Include In A Business Plan
In a sense, a business plan used for seeking funding is part of a negotiation taking place between you and your prospective financial backers. The part of the plan where you describe your financial needs can be considered your opening bid in this negotiation. The other information it contains, from market research to management bios, can be considered supporting arguments. If you look at it that way, a business plan is an excellent opening bid. It's definite, comprehensive, and clear.
But it's still just a bid, and you know what happens to bids in negotiations. They get whittled away, the terms get changed, and, sometimes, the whole negotiation breaks down under the force of an ultimatum from one of the parties involved. Does this mean you should ask for a good deal more money than you actually need in your plan? Actually, that may not be the best strategy either. Investors who see a lot of plans are going to notice if you're asking for way too much money. Such a move stands a good chance of alienating those who might otherwise be enthusiastic backers of your plan. It's probably a better idea to ask for a little more than you think you can live with, plus slightly better terms than you really expect.
Related: How To Craft A Business Plan to Turn Investor's Heads
Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
A professional financier such as a bank loan officer or a venture capitalist will see literally hundreds of business plans in the course of a year. After this has gone on for several years, and the financier has backed some percentage of those plans and seen how events have turned out, he or she becomes very good at weeding out plans with inconsistencies or overblown projections and zeroing in on weaknesses, including some you'd probably rather not see highlighted.
If you've seen Shark Tank , you'll understand how shrewd those individuals with the dollars can be. In short, most financiers are expert plan analyzers. You have little chance of fooling one of them with an overly optimistic or even downright dishonest plan. That doesn't mean you shouldn't make the best case you honestly can for your business. But the key word is "honestly."
Related: How to Find Funding
You certainly shouldn't play down your strengths in a plan, but don't try to hide your weaknesses either. Intelligent, experienced financiers will see them anyway. Let's say you propose to open a small health food store at an address a block away from a Whole Foods. An investor who knows this fact but doesn't see any mention of it in your plan may suspect you've lost your senses—and who could blame her?
Now think about the effect if your plan notes the existence of that big grocery store. That gives you a chance to differentiate yourself explicitly, pointing out that you'll be dealing only in locally produced foods—which the superstore doesn't carry but many of its customers may want. Suddenly that high-volume operator becomes a helpful traffic builder, not a dangerous competitor.
Related: The Ultimate Business Plan Book
So, recognize and deal appropriately with the weaknesses in your plan rather than sweeping them under the rug. If you do it right, this troubleshooting can become one of the strongest parts of the whole plan.
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
People with goals succeed because they know where they are going...It's as simple as that."

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
- Business Aims and Objectives
- Explanations
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- Business Case Studies
- Business Development
- Business Operations
- Change Management
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Performance
- Human Resources
- Influences On Business
- Intermediate Accounting
- Introduction to Business
- Managerial Economics
- External Environment
- Forms of Business
- Franchising
- Key Business Terms
- Limited Liability
- Shareholder
- Sole Trader
- Operational Management
- Organizational Behavior
- Organizational Communication
- Strategic Analysis
- Strategic Direction
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
People with goals succeed because they know where they are going...It's as simple as that."
- Earl Nightingale
As with people, successful businesses also have clearly defined aims and objectives. Let's take a look at what these are exactly and why it is essential for businesses to have them.
Business aims and objectives definition
Business aims and objectives help guide a company's decisions and play a big part in deciding if the business will be successful.
Business aims are the broad, general goals that summarize what a company wants to achieve, while business objectives are specific, measurable targets that help a company achieve its aims.
Together, b usiness aims and objectives provide a clear direction for the company and help in setting priorities and goals, as well as making informed decisions.
Setting business aims and objectives
If business objectives are specific and measurable targets that help achieve business aims, we can consider them as steps taken by a company to reach its business aims . Objectives guide the next step to be taken to move closer to the company's aim. Objectives are also measured to make sure that all the right steps are orderly executed to achieve the aims.
To help managers and employees develop, manage and track objectives the right way, they create SMART objectives. This is a smarter way of creating objectives as it helps to put together an action plan, increase productivity, and track progress. SMART is an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-oriented.

Examples of aims and objectives
Financial aim - make a profit of £24,000 by the next financial year.
The objective for this aim would be: make profits of £2,000 for the next 12 months.
Financial aim - increase revenue in the next five years.
Objectives for this aim would be as follows:
Increase product awareness
Acquire new customer
Create or improve digital platform
Increase conversion rate
Reduce overhead costs
Non-financial aim - Become the most sustainable company in the industry.
Use recycled raw materials
Use production methods that reduce CO2 emissions
Some common aims and objectives
Some of the common financial aims and objectives are:
Increase revenue
Increase profit margins
Earn a return on investment
Attain financial stability
Some of the common non-financial aims and objectives are:
Employee satisfaction
Customer satisfaction
Social responsibility
Relation with suppliers
Importance of business aims and objectives
Setting business aims and objectives is important for a couple of reasons:
- It provides clarity of direction, helping to prioritise efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- It helps measure company's success , allowing to track progress and make better decisions
- It increases motivation of the employees, by helping them understand long-term goals
- It improves decision-making process at all levels of the organisation.
In conclusion, setting aims and objectives is a critical part of effective business management . It provides direction, focuses efforts, and drives continuous progress, helping businesses to attain their goals and succeed in the long term.
Advantages of setting aims and objectives
Setting aims and objectives are very important for a company, as it is a key component in ensuring success. It guides the course of action and helps to keep employees focused and act responsibly. It ensures clarity within the whole organisation. It also has many other advantages.
Providing direction
A set aim guides a company and its employees in making the right decisions . It directs the company in the right manner.
Business planning
A goal or aim helps to understand what the right next step is . It helps in planning every step of the business.
Employee motivation
Having a goal to reach can improve employee motivation. It can be further improved by having an incentive system in place for the first employee to reach an objective.
Less stress
Having set objectives gives employees a means to measure how much they have done and keep track of their performance . This helps to avoid unnecessary stress which employees face when they are unaware of their overall performance rate.
Less wastage of time
Setting steps (objectives) to accomplish an aim helps to achieve the aim faster . Setting objectives tells an employee exactly what is to be done next, and this saves a lot of time and prevents the employee from performing any unnecessary tasks.
Business aims and objectives examples
Let's take a look at some examples of business aims and objectives for Amazon.
Examples of Amazon's business aims:
- Be the world's most customer-centric company
- Increase market share in e-commerce and become number-one company in the world
- Constantly improve customer experience through innovation
Examples of Amazon's business objectives:
- increase Prime membership by 10% in the next year
- launch two new products every year
- expand the international delivery network
As you can see, each objective helps to achieve the different business aims of the company. Of course, in reality, the relationships between goals and objectives are more complex.
Business Aims and Objectives - Key takeaways
- Business aims are the long-term goals a company sets for itself.
- Business objectives are steps taken by a company to achieve its business aims.
- Objectives should be specific and measurable.
- Aims and objectives can be financial or non-financial.
- Setting aims and objectives guides a company’s course of action.
Frequently Asked Questions about Business Aims and Objectives
--> what are the aims and objectives of business.
Business aims and objectives provide a clear direction for the company and help in setting priorities and goals, as well as making informed decisions.
Business aims are the broad, general goals that summarize what a company wants to achieve, while business objectives are specific, measurable targets that help a company achieve its aims.
--> What are the advantages of setting business objectives?
Providing direction, business planning, employee motivation, less stress, and less wastage of time are the advantages of setting business objectives.
--> What is an example of a business objective?
An example of a business objective of a service company could be to increase customer satisfaction ratings from 3/5 to 4/5 in the next 6 months.
Usually, objectives should be related to business aims. For example, an increase in customer satisfaction helps to achieve the aim of creating a welcoming and friendly atmosphere.
--> What are the challenges of setting business aims and objectives?
The following are some of the challenges of setting business aims and objectives:
- Goals are too high to achieve.
- Difficulty adapting to change.
- Stress on employees.
- Unequal allocation of goals.
--> What is the difference between aims and objectives in business?
Business aims are more broad, general statements that summarize what a company wants to achieve, while business objectives are more specific, measurable steps that help a company accomplish its aims.
--> Why do businesses set aims and objectives?
Business set aims and objectives to:
- provide direction
- allocate resources
- measure success
- improve performance
- motivate employees
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards
Which of the following means long-term target?
Which of the following is a financial aim?
Which of the following best describes an aim?
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 79 business aims and objectives flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
List at least 4 advantages of setting aims and objectives.
1) Provisioning direction
2) Employee motivation
3) Business planning
4) Less stress
5) Less wastage of time
Company mission
Increase revenue by 40% in the next 5 years.
Long-term goal, a short statement written in broad terms
What is marginal revenue and what is the formula to calculate it?
Marginal Revenue (MR) is defined as the change (increase) in total revenue by producing one additional unit of output.
Marginal Revenue = Change in Revenue / Change in Quantity
What are the revenue taxes used for?
Revenue taxes are spent on social security, medical aid, child nutrition programmes, house assistance, and several other welfare programmes.

of the users don't pass the Business Aims and Objectives quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free business-studies cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App

Privacy Overview
Setting goals is critical for every organisation because goals determine the broad vision and direction for any business plan. The best goals will align with the company mission, vision and culture and describe the business' longer term aspirations before laying out specific actions.
Do you know the difference between goals and objectives and how they are related? Without objectives, company goals have little support and can be difficult to reach. While the terms 'goals' and 'objectives' are often used interchangeably, they have major differences and important implications for organisations.
What Are Goals?
Goals can be somewhat abstract and big picture, but they set a wide, overarching target for the company to set their eyes on as a whole. Goals define the general intentions and ambitions of the business but can be difficult to measure. Setting goals is an important step of business planning, as a well-defined broad primary outcome will have an impact on areas including your mission statement, financial objectives, corporate culture and marketing strategy.
For example, a person could have a goal to become a successful published author. While this is a good goal, there are no specific actions or time frames associated with general goals like this. What defines a 'successful author’? How would they know when they've reached their goal? A generic action or project goal is motivating, but adding in precise targets or objectives will help the would-be author to reach their goal effectively.
Goal setting helps individuals and organisations motivate themselves towards a destination or achievement. In a positive work environment, developing lofty goals can boost employee engagement and create excitement that spurs action. Keep reading to learn how goals and objectives work together and how you can generate business results with goal-tracking tools.
What Are Objectives and How Are They Different?

Once a core goal is set, setting business objectives is the next step towards fostering a clear understanding of how to reach the desired outcome. The main difference between objectives and goals is that objectives are precise actions or measurable steps individuals and groups take to move closer to the goal. They are specific targets that typically have a time-bound schedule or timeline for completion.
For example, a company may have a goal of becoming the most profitable advertising agency in the country. Objectives related to this goal might include increasing their new business sales by five percent each quarter, growing their market share by a set time frame, improving client retention rates by 10 percent each month or adding two new products to their product line by the end of the fiscal year.
Examples of Business Goals vs. Objectives
While goals and objectives work in harmony to maximise your business strategy and produce results, they have clear differences that must be recognised to use them effectively.
- Broad in nature
- Valuable for setting a general direction or vision
- Difficult to measure
- Abstract ideas
- Longer term
- The end result
Examples of goals include:
- I want to become known as an expert in business strategy
- I will commit to my career development and learn how to increase sales
- I want to be more confident
Objectives are:
- Narrow in scope
- Specific steps
- Associated with a schedule and time frame
- The means to the end result
- Easy to measure
- Short term or medium term
Examples of objectives include:
- I will speak at five conferences in the next year
- I will read one book about sales strategy every month
- I will work with a coach to practise my networking skills by the end of this month
While goals create a vision with a wide range, objectives focus on the individual, achievable outcomes. Objectives are the concrete deliverables that make the goal come to life. Progress towards them helps measure advancement to reaching the larger end goal.
How Goals and Objectives Work Together

Setting goals without assigning measurable objectives will likely lead to goals that never get accomplished. Creating objectives without a broad goal or target lacks meaning. Goals can seem impossible or overwhelming without breaking them down into measurable tasks with objectives.
Many companies use the S.M.A.R.T. goal setting method to lay out specific objectives towards reaching each goal. Whether you are self-employed, have a small business or are part of a large organisation, your goals need to be supported with precise objectives.
Anytime an individual or employee undertakes a long-term goal, it can feel intimidating to put a plan together to make it happen. The S.M.A.R.T method helps make goals achievable by breaking the goal down and assigning responsibility to team members — they describe who will do what, by when.
S.M.A.R.T goals are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely. For example, the same scenario of the person with a goal of becoming a successful published author could use S.M.A.R.T. goal planning to outline key objectives towards the goal like this:
Specific: I will create and brand a nonfiction book series about healthy diets and publish at least one book per year.
Measurable: I will write 10–15 pages of copy per day and will work with my publishing agent five hours per week.
Attainable: I will hire an editor to review my writing before it is published.
Relevant: Publishing a book series will help establish me as an influencer in my industry and create awareness around nutrition and wellness.
Timely: I will publish one book per year for five years by having each draft ready in nine months.
Tracking Progress Towards Goals
Once you've established your business goals and mapped out specific objectives, you have to measure your progress towards them to stay on track towards your targets. Teams often use a variety of goal-tracking methods, tools and software to help measure progress towards specific outcomes and increase accountability of tasks.
Goal setting is only meaningful when you have a system in place to hold yourself and employees accountable for fulfilling objectives. When people make commitments to complete tasks in a transparent work environment, they experience the effect of social discipline and feel obligated to follow through to protect their integrity. No one wants to be the person that lets the team down or misses an important deadline!
Many organisations use performance management programs or teamwork software to make creating and measuring goal advancement easier. Software can help to foster accountability and responsibility towards goals within teams. Everyone can view progress towards one another's goals and targets, so there's no question about who is responsible for completing certain tasks within specific time frames.
Other benefits of using teamwork software include the ability to help teams communicate more effectively , provide greater visibility into performance and productivity issues, and have tools to reward employees or teams who are high achievers.
With these tools at your disposal, you’ll be able to track your progress against your objectives, stay motivated and demonstrate your ability to work towards a goal. A visual reminder that you’ve completed an objective can be a powerful way to help you reach your end goal faster. To help you stay focused on your goals, try these tips to improve your work performance and productivity .
Looking for more good stuff? We have plenty.
The latest from Samewave
Sign up to get updates when we publish new blog posts, news & insight.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Economic Business Objective: Also called financial objectives, economic objectives relate to the financial health and growth of the company. These objectives can involve profits, revenue, costs, cash flow, sustainable growth, debt management, and investments. Example: Reduce spending on paid advertisements by 20 percent.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
8. Critical success factors: Clarify the high-level goals you need to achieve in order to achieve your strategic goals. 9. Strategic management: Execute against your strategic plan in order to achieve your company goals. 10. Business goals: Set predetermined targets to achieve in a set period of time. 11.
Business objectives vs. goals. Where a business objective is an actionable step taken to make improvements toward growth, a business goal is the specific high-level growth an objective helps a company reach. Business objectives are often used interchangeably with business goals, but an objective is in service of a goal.
4 Things to Consider When Setting Business Goals and Objectives. 1. Financial Measures. It's important to ensure your plans and processes lead to desired levels of economic value. Therefore, some of your business goals and objectives should be financial. Some examples of financial performance goals include:
Here are four examples of business objectives in different categories. Example #1: Customer service business objective. Our business will reduce customer complaints by 25% this year. To accomplish this goal, we will hire three new team members to decrease time spent on hold for customers, add an online chat support option, and invest in ...
Here are some common examples of business plan goals: Financial Goals: Achieve a specific revenue target within a defined timeframe. Increase profitability by a certain percentage or dollar amount. Reduce costs or increase efficiency in a particular area of the business. Secure funding or investment to support business growth.
Aside from financial objectives, another example of objectives for a business plan is sustaining productivity. When you run a business, it can be overwhelming and challenging to stay on top of all the tasks you have to get done. But, if you aim to remain productive and create a clear plan as to how, you can better manage your to-do list.
To plan your plan, you'll first need to decide what your goals and objectives in business are. As part of that, you'll assess the business you've chosen to start, or are already running, to see ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
In addition to providing a framework for innovation at every level of a company's operations, business objectives can help: Increase revenue. Recruit and retain high-quality employees. Enhance customer satisfaction. Improve company culture. Maximize workplace safety. Develop leadership. Expand productivity. Increase product quality.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Customer Satisfaction. Your business is nothing without your customers. Customer satisfaction objectives help you improve the customer experience, build loyalty with your audience, and improve your brand reputation. Example: Achieve a customer satisfaction score of 80% by improving support services and collecting regular customer feedback.
Focus on the basics first: Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business. Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to ...
In the OKR system, the O (objective) is representative of a larger goal, while the KR (key results) represent the smaller objectives you use to measure your progress. Here's an OKR model for your computer sales goal. O: Increase profitability for the computer company. KR1: Make $300,000 in gross profit for the year.
Business Definition: Concept and Future Definition of Business Objectives "A business objective is a detailed picture of a step you plan to take to achieve a stated aim." Business objectives are a company's specific, measurable, and time-bound goals to achieve its broader mission and vision.
The Main Objectives of a Business Plan Here's what a business plan will reveal and how it can save you time and resources. The Main Objectives of a Business Plan. Opinions expressed by ...
Step 2: Align with Your Mission. Ensure that your objectives align seamlessly with your company's mission statement and core values. This alignment helps maintain consistency in your organization's actions and goals, reinforcing your commitment to your mission. Step 3: Be SMART.
To improve brand and reputation. To grow production size to meet demand. 4. Social objectives. Social business objectives are created to help or give back to society in some way. Businesses often set social goals: To ensure better quality products for customers.
Examples of Amazon's business aims: Be the world's most customer-centric company. Increase market share in e-commerce and become number-one company in the world. Constantly improve customer experience through innovation. Examples of Amazon's business objectives: increase Prime membership by 10% in the next year.
Examples of Business Goals vs. Objectives . While goals and objectives work in harmony to maximise your business strategy and produce results, they have clear differences that must be recognised to use them effectively. ... Anytime an individual or employee undertakes a long-term goal, it can feel intimidating to put a plan together to make it ...