
- Business & Money
- Management & Leadership

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery

Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: $35.10 $35.10 FREE delivery: Friday, April 5 Ships from: Amazon Sold by: ayvax
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used: $12.45
Other sellers on amazon.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

101 Case Studies in Construction Management 1st Edition
Purchase options and add-ons.
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years’ experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors, communications, quality and cost control, change orders, claims and disputes, safety, and close-outs. Other hot topics covered include BIM, sustainability, and lean.
Each case is written in straightforward language and designed to test the reader’s independent and critical thinking skills to develop their real-world problem-solving ability. The cases are open to interpretation, and students will need to develop their own opinions of what’s presented to them in order to reach a satisfactory solution.
The cases are ideal for use in the classroom or flipped classroom, for individual or group exercises, and to encourage research, writing, and presenting skills in all manner of applied construction management situations. Such a broad and useful selection of cases studies cannot be found anywhere else. While there is often no "right" answer, the author has provided model solutions to instructors through the online eResource.
- ISBN-10 081536198X
- ISBN-13 978-0815361985
- Edition 1st
- Publisher Routledge
- Publication date September 18, 2018
- Language English
- Dimensions 6.14 x 0.41 x 9.21 inches
- Print length 164 pages
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Similar items that may deliver to you quickly

Editorial Reviews
About the author.
Len Holm is a Senior Lecturer at the University of Washington, USA. He has over 40 years’ construction industry experience at all levels and owns his own construction management firm. He is the author of numerous books on construction, including Management of Construction Projects: A Constructor's Perspective , 2nd edition, also published by Routledge.
Product details
- Publisher : Routledge; 1st edition (September 18, 2018)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 164 pages
- ISBN-10 : 081536198X
- ISBN-13 : 978-0815361985
- Item Weight : 9.1 ounces
- Dimensions : 6.14 x 0.41 x 9.21 inches
- #334 in Technical Project Management (Books)
- #368 in Engineering Project Management
- #2,475 in Home Design & Construction (Books)
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
A Knowledgeable Partner Leveraging Innovative and Creative Solutions on Every Project
Whether it’s a government or a private sector client, OCMI takes a unique, 360-degree holistic approach that includes research, analysis and even challenging our own findings. This process has led to new ways of addressing our clients' challenges. Our teams collect and share their solutions, which has led to an unparalleled story of success for our clients. Explore some of the ways in which OCMI delivers unique, out-of-the-box approaches to resolve our client's challenges.

- Case Studies
- Join Our Team
© 2024 O'Connor Construction Management, Inc.
- Morris Wade Associates
- Cost Control
- Schedule Control
- Project & Construction Management

Browse Subjects
- Building Superintendence">Superintendence Superintendence > Case studies.">Case studies.
- Construction industry Management">Management Management > Case studies.">Case studies.
- Case studies.
Join TheConstructor to ask questions, answer questions, write articles, and connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits.
Confirm Password *
First Name *
Last Name *
Country Select a country… Åland Islands Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belau Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia Bonaire, Saint Eustatius and Saba Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory British Virgin Islands Brunei Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo (Brazzaville) Congo (Kinshasa) Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba CuraÇao Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Isle of Man Israel Italy Ivory Coast Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macao S.A.R., China Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island North Korea Norway Oman Pakistan Palestinian Territory Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Ireland Reunion Romania Russia Rwanda São Tomé and Príncipe Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin (Dutch part) Saint Martin (French part) Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia/Sandwich Islands South Korea South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom (UK) United States (US) Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican Venezuela Vietnam Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Western Samoa Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
By registering, you agree to the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . *
Log in to TheConstructor to ask questions, answer people’s questions, write articles & connect with other people. When you join you get additional benefits.
Join for free or log in to continue reading...
Username or email *
Forgot Password
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link and will create a new password via email.
Sorry, you do not have permission to ask a question, You must log in to ask a question. Join now!

The Constructor
3 important cases of building collapse due to poor construction management.
Do you need to remove the ads? Join now!
🕑 Reading time: 1 minute
Construction is perhaps the most critical stage in the life cycle of structures, mainly because of the danger of failure and the high chances of underestimating construction loads.
A report developed by the American Society of Civil Engineers, based on their study of around 600 failed structures, found that around 40% of the structures failed during the construction stage, 36% of the structures failed during the pre-construction stage due to flawed designs, and 24% failed during their operational stage.
The failure of a structure is described as the propagation of local collapse from one segment to another segment, eventually resulting in the failure of an entire building or its lopsided part. It could be a product of natural disasters, for example, seismic tremors, floods, or coincidental acts such as an explosion in the service system or terrorist bombings.

Analyzing the reasons for explicit structural failures and proposing measures to relieve their effects is a successful measure to lessen risks and improve the safety of structures. Therefore, this article discusses the failure of some major structures, their root causes, and the lessons learned.
1. The Skyline Plaza Apartment Building, Virginia, US
The design plan of the Skyline Plaza complex included six office buildings, eight apartment buildings, shops, and one hotel. The project was a $200 million residential-commercial complex and was situated in Fairfax County, Virginia. During the construction of the skyline plaza complex, one of the apartment buildings under construction collapsed. A total of 15 labors were killed, and 40 were injured.
Design drawings of the collapsed building included the construction of 26 stories, a penthouse, and a four-story storm basement for parking. The building design was of a reinforced concrete flat plate with a 200 mm thick concrete slab. The height between each story was 2.7 m.

1.1 Investigation Findings
On 2 nd March 1973, some portion of the apartment building collapsed during construction. The collapse began on the 23 rd floor when the slab of the 24 th floor was being cast. On the 23 rd floor, the slab started showing cracks and the failure of the building occurred vertically along the full height of the building, including the basement levels. Also, the adjacent post-tensioned reinforced concrete car parking structure collapsed.
Specialists concurred that the concrete had not acquired sufficient strength to carry the construction loads applied during the construction process. Investigators confirmed that the original design plan had no deficiencies. The most probable reason for the collapse of the building was the punching shear failure on the 23 rd floor of the building.
After the collapse, a team from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) came to the site and started an investigation. Further, a detailed investigation was conducted by the National Bureau of Standards (NBS).
NBS and OSHA mentioned in their reports that the collapse of the building was directly related to poorly managed construction processes. The court found that the contractor and the site engineer were guilty of negligence as the contractor didn't follow the building code requirement and the site engineer didn't inspect the work properly.
1.2 Lessons Learned
After the collapse of the Skyline Plaza apartment building, a series of changes were made in the building code related to the progressive collapse failure. Special inspection procedures were added in the inspection section of the building codes. Design criteria were also changed for effective planning to reduce the possibility of failure due to progressive collapse. The following points describe the violations of specified construction requirements and standard practices:
- Violation of prerequisites to completely shore the two stories underneath the floor being cast.
- Failure to permit legitimate curing time before removing shoring.
- Failure to conduct curing test on the concrete specimen in the field.
- Use of out-of-plumb shoring.
- Improper inspection during casting and formwork removal to check the strength of concrete.
- Improper installation of the climbing crane.
2. Ronan Point Tower, Canning Town , London
The need to give substitution lodging to homes destroyed in World War-II encouraged European engineers to develop innovative pre-assembled construction strategies. One such plan included the construction of high-rise buildings using pre-stressed concrete components made in factories.
The structural framework included the construction of load-bearing walls and each floor was directly stacked onto the walls. Grouted bearing surfaces were used to construct the joint between the wall and the floor. This process of construction was termed as system building. A skyscraper at Ronan Point, Canning Town, UK, was built using this system building technique.
On 16 th May 1968, a blast occurred due to gas leakage in the kitchen of a house on the 18 th floor. Just after the blast, the kitchen walls collapsed, and in-turn, the walls above the 18 th floor caved in. This impacted the floors beneath and obliterated the entire corner of the structure. A total of 14 people were injured and three were killed.

2.1 Investigation Findings
The investigation team revealed that the building collapsed due to the non-availability of an alternative load path when one portion of the external wall collapsed. After the demolition of the building, it was also revealed that the quality of the grouted bearing surface for the joints between floors and the walls was poor.
Because of the unprecedented collapse, the government examined the safety of other buildings constructed using the same concept as the Ronan Point Tower. Many buildings were demolished well ahead of their life span.
The concept of progressive collapse of structures was not much known to the engineers before the failure of the Ronan Point Tower. In such collapses, a local failure is followed by widespread collapse through a chain reaction. What was irregular on account of the failure of the Ronan Point Tower was that a minor gas blast set off the collapse of a huge portion of a finished structure.
2.2 Lessons Learned
The experience due to the failure of Ronan Point Tower re-emphasized the following points:
- Progressive failure can also occur in fully constructed structures.
- A structure should have redundancies to reduce the possibility of progressive failure.
- Quality control should strictly be followed in the construction processes.

3. 2000 Commonwealth Avenue, Boston, US
On 25 th January 1971, a two-third portion of a 16-story residential building known as 2000-Commonwealth Avenue in Boston collapsed during construction, leading to the death of four workers. The building was under construction for more than six years. The collapse of the building generated approximately 8000 tons of debris. Luckily, the failure of the building was gradual, giving the workers some time to escape from the building site.
The building was designed as a reinforced concrete structure and flat slabs were used for the roofing system with an elevator shaft provided in the center. This type of structural design is mainly famous for multi-story construction as it reduces the thickness of the slab and overall height between the floors. The thickness of flat slabs was between 160-190 mm for all the building areas except near the elevator core where it was 230 mm thick. The arrangement of the structural component constituted a height of 2.7 m for all the floors.
The building, situated at 2000 Commonwealth Avenue, was intended to be 16 stories high with a mechanical room of height 1.5 m for the working of the lift at the rooftop. The plan area of the structure was 56 x 21 m 2 . The building additionally had underground parking of two levels. A pool, auxiliary spaces, and one flat were situated on the first floor, and a total of 132 flats were on the second through sixteen floors. At first, these flats were to be leased. However, the proprietors later chose to advertise them as apartment suites.
At the hour of the collapse of the building, construction work was almost completed. The brickwork was finished up to the sixteenth floor, and the structure was generally encased from the second to the fifteenth floor. Heating, plumbing, and ventilation frameworks were introduced all through different floors of the structure. The interior work had also started on the lower floors. A temporary lift was constructed to help in moving equipment to various floors. It was assessed that 100 individuals were working in or around the structure at the hour of the collapse.
The collapse of the building occurred in three stages. These stages were, failure due to punching shear in the rooftop at section E5, the failure of the slab, and in the end, the progressive failure of the structure.

3.1 Investigation Findings
The civic chairman of Boston appointed a commission to inquire about the collapse of the building. The commission discovered the following critical observations:
- There was no signature of an architect or engineer found on a single drawing of the building.
- The design engineer didn't give the computations supporting his structural drawings to the commission. No head or representative of the team of contractors held a building construction license of Boston city.
- Ownership of the venture changed a few times, with changes in planners and architects. This scenario added to the general disarray and contributed to the abnormalities referred above.
- The general contractual worker just had a solitary representative on location. Most subcontracts were given directly by the owner to the subcontractors and bypassed the general contractor. A total of seven subcontractors were involved in the construction.
- The subcontractor, who was assigned to conduct the cold weather protection work on the structural concrete didn't carry out the assigned work. However, the structural engineer had indicated these measures.
- There was no proof of any inspection of the work by a specialist despite the fact that the project particulars needed this.
- The quality of construction material and quality inspections were poor.
- The collapse of the building occurred due to the development of punching shear mechanism around column E5. Punching shear developed the flexural cracks around the roof slab located near the elevator core. Thus, the slab collapsed due to flexural yielding.
- The design manual indicated a 28-day strength of 25 MPa. However, at the failure time, 47 days after casting work, the concrete couldn't seem to attain the necessary 28-day strength.
- The most critical inadequacies were an absence of shoring under the slab at the roof and the quality of the concrete.
3.2 Lessons Learned
The following key factors describe the collapse of the multi-story building situated at 2000 Commonwealth Avenue:
- Authorized design engineers should be chosen for the development of working drawings for construction.
- Engineers and architects should be responsible for all the design-related calculations and their design work must be examined by the experts in that field from a government organization.
- Ownership of a project should not change multiple times to reduce the confusion between the previous engineer and the newly appointed engineer.
- Inspection at the construction site should be conducted regularly by government organizations, especially for cold weather work.
- The quality of concrete work should be monitored throughout the project.
- The construction work should conform to design documents and construction procedures.
The collapse of a building is characterized as the propagation of an initial local collapse from component to component, ultimately resulting in the collapse of a whole structure or a disproportionately large portion of it.
Construction is one of the most critical phases in the life cycle of buildings due to the risk of failure and the possibility of underestimating construction loads.
The structural framework included the construction of load-bearing walls and each floor was directly stacked on the walls. Grouted bearing surfaces were used to construct the joint between the wall and the floor. This process of construction was termed system building.
Top 5 Biggest Dam Failures in the World
5 Disastrous Foundation Failures in New York City
Top 6 Energy-Efficient High-Rise Buildings in the World

Ravi Panwar
Related posts.

Design of Steel Tanks

Filler Slabs: Material and Advantages
- Help & FAQ
Communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing: a case study in construction management
- Department of Management
- Monash University Accident Research Centre
Research output : Contribution to journal › Article › Research › peer-review
Purpose: This paper aims to examine four key management processes, namely, communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing, to determine how these impact on transportation infrastructure project success. The context for this study is the construction of a major highway in the United Arab Emirates. Design/methodology/approach: Multiple sources of data are used in this case study that include the following: examination of various documents relating to the project in question; interviews with ten key stakeholders involved with the construction of the project; observations made during the site visit and interviews conducted with four site engineers; a focus group conducted with six key stakeholders involved in the project; and finally interviews conducted with the Minister of Public Works and the Director-General of the Ministry of Public Works. Analysis was conducted using NVivo. Findings: Identification and involvement of key stakeholders, particularly in the early phases of a construction project, is found to be highly critical. Managers must develop detailed understanding of stakeholders’ influence in terms of their legitimacy, power and urgency in achieving effectiveness of the management processes. Originality/value: The study highlights how different stakeholders influence communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing at different stages of the construction project. Hence, understanding stakeholder’s level of legitimacy, power and urgency across the different stages of a project is highly critical.
- Communication
- Construction industry
- Coordination
- Decision making
- Knowledge sharing
Access to Document
- 10.1108/JKM-08-2018-0503
Other files and links
- Link to publication in Scopus
T1 - Communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing
T2 - a case study in construction management
AU - Al Nahyan, Moza Tahnoon
AU - Sohal, Amrik
AU - Hawas, Yaser
AU - Fildes, Brian
N2 - Purpose: This paper aims to examine four key management processes, namely, communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing, to determine how these impact on transportation infrastructure project success. The context for this study is the construction of a major highway in the United Arab Emirates. Design/methodology/approach: Multiple sources of data are used in this case study that include the following: examination of various documents relating to the project in question; interviews with ten key stakeholders involved with the construction of the project; observations made during the site visit and interviews conducted with four site engineers; a focus group conducted with six key stakeholders involved in the project; and finally interviews conducted with the Minister of Public Works and the Director-General of the Ministry of Public Works. Analysis was conducted using NVivo. Findings: Identification and involvement of key stakeholders, particularly in the early phases of a construction project, is found to be highly critical. Managers must develop detailed understanding of stakeholders’ influence in terms of their legitimacy, power and urgency in achieving effectiveness of the management processes. Originality/value: The study highlights how different stakeholders influence communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing at different stages of the construction project. Hence, understanding stakeholder’s level of legitimacy, power and urgency across the different stages of a project is highly critical.
AB - Purpose: This paper aims to examine four key management processes, namely, communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing, to determine how these impact on transportation infrastructure project success. The context for this study is the construction of a major highway in the United Arab Emirates. Design/methodology/approach: Multiple sources of data are used in this case study that include the following: examination of various documents relating to the project in question; interviews with ten key stakeholders involved with the construction of the project; observations made during the site visit and interviews conducted with four site engineers; a focus group conducted with six key stakeholders involved in the project; and finally interviews conducted with the Minister of Public Works and the Director-General of the Ministry of Public Works. Analysis was conducted using NVivo. Findings: Identification and involvement of key stakeholders, particularly in the early phases of a construction project, is found to be highly critical. Managers must develop detailed understanding of stakeholders’ influence in terms of their legitimacy, power and urgency in achieving effectiveness of the management processes. Originality/value: The study highlights how different stakeholders influence communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing at different stages of the construction project. Hence, understanding stakeholder’s level of legitimacy, power and urgency across the different stages of a project is highly critical.
KW - Communication
KW - Construction industry
KW - Coordination
KW - Decision making
KW - Knowledge sharing
UR - http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?scp=85060941425&partnerID=8YFLogxK
U2 - 10.1108/JKM-08-2018-0503
DO - 10.1108/JKM-08-2018-0503
M3 - Article
AN - SCOPUS:85060941425
SN - 1367-3270
JO - Journal of Knowledge Management
JF - Journal of Knowledge Management

Construction management case study
The use of construction management can offer a flexible procurement method that supports the changing nature of the brief and the potential for the design to evolve.
You can download the construction management case study here or find the full text below.
Construction management is a procurement where the ‘traditional builder’ is replaced by a construction management organisation. Their responsibility is to work directly for the client in the management of the construction phase. A construction manager has expertise in both building and management and is contracted to the client to provide management services only. The works are completed by a series of trade contracts arranged by the construction manager, but entered into directly between each trade contractor and the client. A significant aspect of construction management is that the construction manager has no direct involvement in the payments to the trade contractors. The role of the design team and its relationship with the client and construction manager is very similar to the traditional contracts between architect, client and contractor. The design team is commonly novated to the construction manager.
Action to benefit good design
- Early involvement of the construction manager to assess buildability prior to commencing design development.
- Engage independent design advice from either a design champion, design quality team (DQT) or the OVGA to assist with design quality management in preparing the brief and contract development and at key project milestones.
- An established and positive working relationship between the construction management organisation and the sub-contractors.
- Ensure that the construction management fee is subject to achieving design benchmarks or assessment via Key Result Areas (KRAs) as assisted by independent design advice.
- Ensure that each trade contract agreement specifically refers to design quality and explains how it will be delivered.
Case study: Sidney Myer Music Bowl, Kings Domain, Melbourne
Project background.
Originally opened in 1959, the Sidney Myer Music Bowl is a celebrated, rare survivor of Melbourne’s heroic postwar period of architecture and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. Over time the Bowl was in need of significant restoration
and upgrade required to address its substantial functional deficiencies which made it inadequate to support performances. The upgrade required a change to sightlines, regarding of the grassy berm and flexibility in delivery of the project to avoid impacting the operation of key annual events, specifically the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind’s Carols by Candlelight.
The brief required an upgrade of all facilities to integrate back of house production, catering artist change and warm up, theatre infrastructure and technologies, commercially supportive facilities, hire-out function spaces and a cafe. The refurbishment needed to respect the heritage value of the original structure, while rejuvenating its cultural life as one of Melbourne’s most loved venues. Apart from the original cable network and supporting columns, the existing fabric has been restored and reconstructed. The new work extends the original footprint, mainly underground. Major areas for refurbishment included replacing the canopy damaged by prolonged water penetration through the edges of the ‘Alumply’ panels which caused deterioration of the plywood, and some delamination of the aluminum cladding. The entire canopy was replaced with a new cladding system. The use of construction management offered a flexible procurement method that supported the changing nature of the brief and the potential for the design to evolve.

Key initiatives to protect the design quality
- Design advice early in the procurement process supported the management of design quality in contract and brief development.
- An early understanding of the complexity and heritage sensitivities of the site.
- Independent advice from the original architect Barry Patten.
- An “open book” approach offered transparency with preliminaries and profits declared.
- Use of Hooker Cockram as experienced sub-contractors, as the construction management organisation.
Constraints
- The breakdown of the project into two separate stages to facilitate the continuity of use for the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind’s Carols by Candlelight.
- Unexpected change to the brief for required patron sightlines to the stage area.
- Unforseen industrial issues beyond the control of the client or construction management organisation.
- A change in government halfway through the project.
What worked well
- The flexibility of construction management as a procurement method supported the design changes required, including adjustment to audience sightlines, the need to raise the berm and additional fill.
- Efficient and effective resourcing of the project by Hooker Cockram as the construction management organisation.
- Major Projects Victoria (MPV) acting as design champion.
Updated 5 July 2023
JavaScript must be enabled for this website to reliably work
For instructions on how to enable JavaScript, please visit enable-javascript.com .

Case Studies
At Morgan Sindall Construction, our purpose is to create inspiring places that enhance the communities in which we all live, learn, work, play, care and protect.
Take a look at the case studies of just some of the projects our teams have delivered for our customers.

Centre for Sustainable Chemistry, University of Nottingham

Collaborative Teaching Laboratory

Highfields Spencer Academy

Enterprise Centre, University of East Anglia

Potteries Museum and Art Gallery

Barbara Hepworth Building (School of Art & Design)
Named after local Wakefield-born sculptor, Barbara Hepworth, the new building has allowed the University of Huddersfield’s Art, Design and Architecture Schools to be housed in one creative and technologically advanced hub.

Lambeth Town Hall
The ‘Your New Town Hall’ project has rejuvenated Lambeth’s historic Grade II-listed, Edwardian town hall, driven by the Council’s ambition to provide a modern, energy efficient worksplace while increasing public access and community use.

Woodside & Gorbals Health & Care Centres
Morgan Sindall Construction delivered two brand-new primary care facilities to modernise the services available to patients in the Glasgow and Clyde area.

Theatre extension and refurbishment, James Padget Hospital
In response to population growth and increased operation numbers, the James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust commissioned the extension and refurbishment of its theatre complex at the James Paget Hospital in Great Yarmouth.

Hackney Britannia project

55 Colmore Row
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Lydon Solutions
Construction Project Management Software Solutions

A Case Study on Using Microsoft 365 for Construction Project Management
Many organizations want to use Microsoft 365 to manage their construction projects. Unfortunately, figuring out where to start and how to bring all the Microsoft applications together into a cohesive solution can be overwhelming. We posted a three-part blog a little while back that includes some tips and considerations to help you on your way. You can check out that series here:
- How to Start Managing Construction Projects in Microsoft 365 – Part 1
- How to Start Managing Construction Projects in Microsoft 365 – Part 2
- How to Start Managing Construction Projects in Microsoft 365 – Part 3
Starting with this new post, we are kicking off a new series to describe a case study of a real-world implementation of Microsoft 365 for construction project management. We will detail the challenges, explain some of our decisions, provide sample deliverables, and reiterate critical takeaways that might help your organization develop its construction program management solution in Microsoft 365. In this first post, we will discuss the client’s challenge and then provide a detailed analysis in follow-up posts.
The client’s challenge: How to use Microsoft 365 for effective project management
The client in this case study contracted Lydon Solutions to develop a Microsoft 365 project management solution for a multi-billion-dollar program with over eighty active projects. Meeting the client’s requirements required re-engineering their current processes and tools to deliver a solution using out-of-the-box Microsoft 365 applications effectively.
Below are the requests by the client, the systems they were using, and the Microsoft 365 applications and approaches we are implementing to solve their unique challenges.
Before we dive into the solution space, we cannot stress enough the importance of collecting requirements. Without detailed requirements , it’s like building a house without a design. In many cases, we don’t have the luxury to perform a complete requirement gathering session since clients want a solution sooner rather than later, don’t have the resources to support the effort, and often see requirements gathering as unnecessary costs. Fortunately, we have the experience to work with whatever clients can provide and fill in the gaps where needed. But if you use a third-party vendor without this type of experience, you will end up with a disjointed solution that costs an arm and a leg to build.
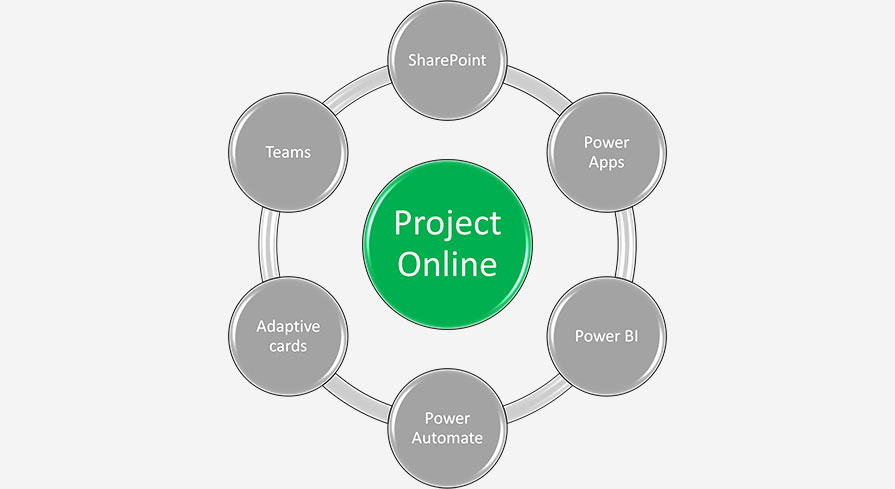
In the next post, we will discuss how we approached and implemented a Project Online solution.
Lydon Solutions has been developing and implementing construction management solutions in Microsoft 365 since its inception way back in 2011. We also provide a turnkey construction management product called Construction Viz that can be quickly deployed into a client’s Microsoft 365 or hosted externally. You can check out a video of the CMAA product demo here .
Related Posts

Microsoft 365 Horror Stories

How to Use Tags to Organize Files in Microsoft 365

Surface Duo: Microsoft Thunk Differently
Products & services.
- Construction Viz
- Professional Services
- Business Consulting
- Microsoft 365 Managed Services
- Government Agencies
News & Events
Join our mailing list.
- This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from . an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating,
If students ha ve a basic understanding of lean construction, users of the case study may wish to skip Section 1. In Section 2 of the case study, J. E. Dunn Construction has a contract for the renovation of three student housing buildings at Pittsburg State University. Situations are presented during preconstruction and project execution.
Construction case studies: Project management, financials, materials and more. To stay competitive, construction businesses should stay on top of the latest trends and best practices in the industry. One of the best ways to do this is by studying real-life examples of construction projects, processes and businesses.
ABSTRACT. This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling ...
This paper presents a practical, experience-based, step-by-step guide to select, conduct and complete a case study research in construction management. The paper justifies the rationale for ...
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors, communications, quality and cost control, change ...
AbstractConstruction engineering and management research faces a fundamental dilemma: projects are designed and built just once. Case studies, a qualitative research method, are an appealing choice that is suited to this unique reality. But the analytical ...
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors, communications, quality and cost control, change ...
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors ...
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors, communications, quality and cost control, change orders ...
Thus, when studying construction culture through a case study approach, it is critical to establish concise guidelines that can be referred to and followed. The proposed methodology is described in detail, from conceptualizing the research problem to reporting the findings, and is illustrated with an example application to a building ...
A Case Study for Improving Construction Project Management Amine Ghanem, Ph.D., P.E. Roger Williams University Bristol, RI Meghan Hogan Gilbane Building Company Providence, RI Mohamed El-Gafy, Ph.D., P.E. Michigan State University East Lansing, MI Every construction project generates an enormous amount of data. The need to be more
Case Studies in Construction Materials provides a forum for the rapid publication of short, structured Case Studies on construction materials and related Short Communications, specialising in actual case studies involving real construction projects. Now by popular demand, CSCM has expanded the scope of the journal to also enable longer papers to be submitted for publication.
Our teams collect and share their solutions, which has led to an unparalleled story of success for our clients. Explore some of the ways in which OCMI delivers unique, out-of-the-box approaches to resolve our client's challenges. See O'Connor Construction Management's case studies from our years of exemplary work including project management ...
This book provides 101 real-life construction management case studies from an author with over 40 years' experience in the construction industry and as a lecturer in construction management. Over 14 chapters, Len Holm has included case studies from real jobsites that cover organization, procurement, estimating, scheduling, subcontractors, communications, quality and cost control, change orders ...
Case study. Angus Cowan Constructions | A Total Shift from multiple Software to Buildern. Angus Cowan Constructions has been in the residential construction business for over 25 years. The recent years have been transformative for them, as innovative technologies in the construction business management completely changed the company's workflows.
3. 2000 Commonwealth Avenue, Boston, US. On 25 th January 1971, a two-third portion of a 16-story residential building known as 2000-Commonwealth Avenue in Boston collapsed during construction, leading to the death of four workers. The building was under construction for more than six years.
Communication, coordination, decision-making and knowledge-sharing: a case study in construction management. Moza Tahnoon Al Nahyan, Amrik Sohal, Yaser Hawas, Brian Fildes. Department of Management; Monash University Accident Research Centre; Research output: Contribution to journal › Article › Research › peer-review.
provided to assist in using the case study. 4. Subcontractor Management This case study involves the construction of a major academic building on a university campus. Because of the design of the building envelope, a major subcontractor on the project is the masonry subcontractor. The case study covers subcontractor risk
Construction Management - Case Study. PDF 133.46 KB (opens in a new window) Construction management is a procurement where the 'traditional builder' is replaced by a construction management organisation. Their responsibility is to work directly for the client in the management of the construction phase. A construction manager has expertise ...
The thesis begins with the Guggenheim Museum case study, and then considers the San Roque Power Facility case study. The project delivery methods of both studies are evaluated in light of six basic delivery alternatives: general contractor, construction manager, multiple primes, design-build, turnkey and build-operate-transfer.
Case Studies. At Morgan Sindall Construction, our purpose is to create inspiring places that enhance the communities in which we all live, learn, work, play, care and protect. Take a look at the case studies of just some of the projects our teams have delivered for our customers.
The client in this case study contracted Lydon Solutions to develop a Microsoft 365 project management solution for a multi-billion-dollar program with over eighty active projects. Meeting the client's requirements required re-engineering their current processes and tools to deliver a solution using out-of-the-box Microsoft 365 applications ...
Case study: Resource Allocation in Project Management Dramatically Improves Productivity. Intentionally planning your resource allocation can transform an outdated approach to project management into an efficient, streamlined process that fuels company growth. Such was the case with ProPoint Graphics. The design agency attempted to use a ...
Based on these locations with a relatively large proportion of deployment, it can be determined that special attention should be paid to spatial positions in LID planning and construction. This study provides valuable insights for solving combined sewer overflow problems and optimizing urban drainage management and provides guidance for future ...
The results of this study can provide a reference for the management and sustainable use of land resources during the construction of water conservancy and other projects. ... (which includes the Xingou River project, Xinmeng River project and Zoumatang River project) as a case study, this paper firstly constructs an integrated value accounting ...