- Call to +1 844 889-9952

35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples
🔝 top-10 micro environmental analysis examples, 🤔 what is micro environment in business, 📊 what are micro environmental factors, 🔎 what is a micro environment analysis, 🔧 micro environment analysis tools, 💡 essay ideas on micro environmental analysis.
Today, several internal and external factors come into play to drive sustainable growth for businesses. It takes seamless coordination and implementation between these elements to nurture the future development of a company.
Micro environmental analysis refers to internal factors like employees, customers, suppliers, shareholders, and competitors that lead to failure or success. Keep reading to learn more about it and find some excellent micro environment essay examples.
- Marketing: Concept and Approaches
- Coca-Cola Middle East: Coke Zero Marketing Strategy
- Eastman Kodak Company's Marketing Analysis
- Lolous Company's Marketing Plan
- Atec Incorporation Marketing Plan
- Marketing Techniques and Segmentation in Examples
- Dior Company Marketing Strategies
- Marks and Spencer Company's Marketing Principles
- Toyota Motor Corporation's Marketing Plan
- Eye2Go Company's Three Year Marketing Plan
Micro environment pinpoints an organizational environment that can directly influence day-to-day operations. It involves several internal forces that can lead to the success or failure of a company. Depending on the organizational issue, these internal factors are unique in nature. In fact, they can impact the company’s performance potential over time.
In a competitive landscape, companies face a lot of challenges, and things get more complicated when internal micro environmental elements are distinctive.
Macro Vs. Micro Environment
Suppliers can impact a company’s delivery network and customer value . Their reliability determines whether or not the business can maintain smooth operations. Typically, managers have to exercise full control over suppliers’ costs and availability. If the supply shortages and expenses are under control, the company won’t have to deal with customer dissatisfaction and decreased sales.
The Company
When reviewing micro environmental factors, it is crucial to consider top management, HR, finance, accounting, and research and development departments . There’s no rocket science – managers have to collaborate and bring stakeholders on the same page to make informed decisions and follow strategic plans.
Competitors
Competitors or rivals propel companies to improve their customer satisfaction and overall value. Businesses have to meet customers’ increasing demands and expectations to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Marketing Intermediaries
In a standard value delivery network, marketing intermediaries play a crucial role for any company. Middlemen like merchants or agents help businesses find potential customers, whereas physical distribution entities like transportation and warehouses assist companies in stocking and moving goods.
In a company’s micro environment, customers are the most valuable actors. Companies need a solid value delivery system to engage customers and build long-term relationships to drive growth. Customer markets can include business, reseller, government, international, and consumer markets .
General Public
The general public is a potential group interested in the product or service offered by the company. The company can lose the general public’s interest if business offerings are not purposeful.
From a company’s perspective, the public falls into several categories:
- media public,
- citizen-action public,
- financial public,
- local public,
- general public,
- internal public.
A micro environment includes elements within a unique organizational environment. Micro doesn’t translate into a minor task or factor. It hints at one or more problems within a company and how often they can affect organizational growth .
Look at a micro environment analysis through the lens of the company rather than the industry. Technically, micro environment analysis refers to reviewed internal forces of a micro environment. It can be about the competitor, market, stakeholder, or supplier analyses.
A SWOT analysis is one of the most effective micro environment analysis tools. It helps you understand the strengths , opportunities , weaknesses , and threats of each internal force. You can use this method to paint a full picture of all internal elements that can influence the growth and performance of your business. SWOT analysis can work as a direct indicator to assess different organizational areas and determine if there’s been an improvement. An in-depth SWOT analysis helps organizations tackle challenges, threats, and avail opportunities.
Porter’s 5 Forces
Porter’s Five Forces refer to a model to review five key competitive factors that apply to all industries. This model makes it easier to spot the pros and cons of an industry. It includes the following:
- Competitive rivalry in the same industry
- Substitute threat of a product or service
- The bargaining influence of customers
- The bargaining influence of suppliers
- The potential threat of new players in the market
Need some additional information? Check our more micro environment essay examples on the web page below.
- Marketing Strategy and Development in the UAE Business essay sample: Companies' innovation shifts in modern times are outcomes of the game that compelled some firms to exit the market prematurely.
- Samsung Company: Contemporary Marketing Report Business essay sample: The political factors that influence the marketing of Samsung’s smartphones in the UK are associated with Brexit.
- McDonalds' Marketing Strategies in the UAE Business essay sample: This paper analyzes the marketing strategies of McDonald's in the UAE, its strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities, the micro-environmental and macro-environmental factors.
- "A Cut Above" Hairdressing Business' Marketing Management Business essay sample: The A Cut Above business has to introduce a new type of cutting and styling method to improve the good appearance and confidence of customers.
- Sony Ericsson Company's Marketing Plan Business essay sample: This marketing plan depicts the importance of situation analysis for setting the objectives and strategies, so Sony Ericsson will be able to target all segments in the UK.
- Marketing Environment Definition in the Marketing Sector Business essay sample: Marketing environment is a term used to define the factors that influence the marketing sector in a particular setting.
- Hong Kong Greenking Food Stuff Co Ltd.: Case Study Business essay sample: The company selected for analysis is Hong Kong Greenking Food Stuff Co Ltd. This company specializes in frozen food distributed through traditional stores and the Internet Web Site.
- Apple and Microsoft Companies' Marketing Approaches Business essay sample: Marketing strategy determines the choice of market segments that the company is targeting and it is part of the strategic direction of the company.
- Toyota Motor Corporation: Financial Strategies Business essay sample: Lowering the costs of the current products has no risks as long as the same quality standards are maintained, thus the company can increase its profits due to higher revenue.
- Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola Companies' Marketing Business essay sample: The two companies, Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola, depend on experienced employees, finance, and brand names as their strengths in competing for market share.
- Marketing Fundamentals to Magnolia Web Studio Business essay sample: Demonstration of the applicability of the marketing concepts to promote the website Magnolia Web Studio. The paper contains an overview of the general marketing concept
- Marketing Plan for Kraft Foods Business essay sample: The marketing plan relates to Kraft Foods Incorporation which is a firm that operates within the United States food processing industry.
- Toyota Prius, Green or Geek Machine-Case Study Business essay sample: The article examines the Toyota Prius hybrid car: what is the reason for its popularity, what challenges did Toyota face in its production and how it coped with them.
- BEA19 Technologies Ltd: Opportunities in Sports Coaching Business essay sample: Essential GPS tracking devices are currently used in sports coaching to monitor athletes’ distance traveled and speed during a training session.
- Australian Supermarket Industry Analysis Business essay sample: There are two dominant actors within the retail industry in Australia - Coles, and Woolworths. Together, they seem to possess about 80% of the whole market share.
- Business and Business Environment Business essay sample: The current report is going to explore the key impacts of micro- and macroeconomic factors on Tesla Inc. using PESLE and SWOT analyses.
- Macro and Micro Factors Leading to Credit Crunch Business essay sample: This paper is about the ongoing economic meltdown caused by the credit crunch in the US and UK economies since the winter of 2007.
- Global Marketing Environment Business essay sample: The paper states that the complexity of the global marketing environment is justified by the abundance of variables that influence marketing decisions.
- Strategic Management Analysis Nike Business essay sample: The paper gathered analyses and evaluates relevant information on both the Nike company and the industry it occupies.
- Analysis of Uber American Company Business essay sample: Uber is an American international public company from San Francisco that has created a mobile application for finding, calling, and paying for taxis or private drivers.
- The Walt Disney Company's Marketing Transformations Business essay sample: Disney's expansion into foreign markets has become more complex than before. To keep the high revenues and a good public image, the organization must adapt its approaches.
- Primark Stores Limited's Retail Theory and Practices Business essay sample: This report assesses the retail scenario, opportunities, and threats of Primark Stores Limited, as well as the company’s strategies to foster its growth and continuity.
- Influence of Leadership and Strategy on Decision-Making Process in Maxis Company Business essay sample: Organizational leadership and corporate strategy are significant components of any business company. They often shape the organization’s “economic appearance”.
- Colgate Palmolive Company: Colgate Toothpaste Products Business essay sample: Colgate toothpaste products are made for oral hygiene they include mouthwashes, toothpaste, dental floss, and toothbrushes.
- The Unilever Group's Strategies for the Next Five Years Business essay sample: This paper provides a detailed analysis of the Unilever Group to determine the best strategies for the next five years.
Cite this page
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2023, August 8). 35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples. https://business-essay.com/analyses/micro-environmental-analysis-research-paper-examples/
"35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples." BusinessEssay , 8 Aug. 2023, business-essay.com/analyses/micro-environmental-analysis-research-paper-examples/.
BusinessEssay . (2023) '35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples'. 8 August.
BusinessEssay . 2023. "35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples." August 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/analyses/micro-environmental-analysis-research-paper-examples/.
1. BusinessEssay . "35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples." August 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/analyses/micro-environmental-analysis-research-paper-examples/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "35 Micro Environmental Analysis Examples." August 8, 2023. https://business-essay.com/analyses/micro-environmental-analysis-research-paper-examples/.
- Product Lifecycle Analysis
- Organizational Analysis
- Stakeholders Analysis
- Market Structure Analysis
- STP Analysis
- Benchmarking Analysis
- Entrepreneur Feasibility Analysis
- Functional Job Analysis
- Spend Analysis
- Corporate Reputation Analysis

Analyzing the Organization’s Microenvironment
When we say microenvironment (or alternatively, Competitor Environment) we are referring primarily to an organization’s industry, and the upstream and downstream markets related to it. An industry is a group of firms producing products that are close substitutes. In the course of competition, these firms influence one another. Typically, industries include a rich mix of competitive strategies that companies use in pursuing strategic competitiveness and above-average returns. In part, these strategies are chosen because of the influence of an industry’s characteristics. [1] Upstream markets are the industries that provide the raw material or inputs for the focal industry, while downstream markets are the industries (sometimes consumer segments) that consume the industry outputs. For example, the oil production market is upstream of the oil-refining market (and, conversely, the oil refiners are downstream of the oil producers), which in turn is upstream of the gasoline sales market. Instead of upstream and downstream, the terms wholesale and retail are often used. Accordingly, the industry microenvironment consists of stakeholder groups that a firm has regular dealings with. The way these relationships develop can affect the costs, quality, and overall success of a business.
Porter’s Five-Forces Analysis of Market Structure
You can distill the results of PESTEL and microenvironment analysis to view the competitive structure of an industry using Michael Porter’s five forces, see Figure 3.1 . Here you will find that your understanding of the microenvironment is particularly helpful. Porter’s model attempts to analyze the attractiveness of an industry by considering five forces within a market. According to Porter, the likelihood of firms making profits in a given industry depends on five factors: (1) barriers to entry and new entry threats, (2) buyer and (3) supplier bargaining power, (4) threat from substitutes, and (5) the degree of rivalry of competitors in the industry. [2]
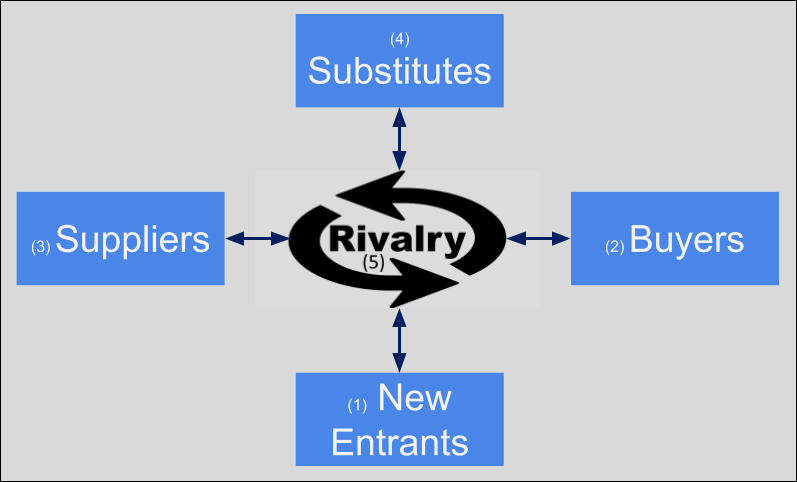
The industry environment has a more direct effect on the firm’s strategic competitiveness and above-average returns than the general environment. The intensity of industry competition and an industry’s profit potential (as measured by the long-run return on invested capital) are a function of these five forces of competition: the threats posed by new entrants, the power of suppliers, the power of buyers, product substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among competitors.
Porter’s five-forces model of competition expands the arena for competitive analysis. Historically, when studying the competitive environment, firms concentrated on companies with which they competed directly (competitor groups). However, firms must search more broadly to identify current and potential competitors by identifying potential customers as well as the firms serving them. Competing for the same customers and thus being influenced by how customers value location and firm capabilities in their decisions is referred to as the market microstructure. [3]
Example 3.2 Understanding an Industry Using Porter’s Five Forces
Looking at JPMorgan Chase, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis shows that the company’s strongest force is rivalry, as there is a huge variety of banking companies to compete with JPM. Bargaining power of buyers is important too, because of the various competitors the buyers could switch to, and so JPM combats this with special offers that attract consumers. Substitutions are a large factor in the banking industry as well, and like with buyers, consumers have a great level of bargaining power as a whole. New entrants, on the other hand, are a relatively low threat to JPMorgan Chase.
Source: Investopedia, Analyzing Porter’s Five Forces on JPMorgan (JPM) , 2018Fa
Understanding this area is particularly important because, in recent years, industry boundaries have become blurred. For example, in the electrical utilities industry, cogenerators (firms that also produce power) are competing with regional utility companies. Moreover, telecommunications companies now compete with broadcasters, software manufacturers provide personal financial services, airlines sell mutual funds, and automakers sell insurance and provide financing. [4] In addition to focusing on customers rather than specific industry boundaries to define markets, geographic boundaries are also relevant. Research suggests that different geographic markets for the same product can have considerably different competitive conditions. [5]
Example 3.3 Forward or Backward Integration
In August 2017, the e-commerce giant Amazon acquired Whole Foods Market Inc. for $13.7 Billion. This acquisition allowed Amazon to gain 400 physical stores and get access to large data of consumers’ grocery buying habits, patterns, and preferences.
Source: Doctor Vidya Hattangadi, What is a business integration strategy? , 2018Fa
The five-forces model recognizes that suppliers can become a firm’s competitors (by integrating forward), as can buyers (by integrating backward). Several firms have integrated forward in the pharmaceutical industry by acquiring distributors or wholesalers. In addition, firms choosing to enter a new market and those producing products that are adequate substitutes for existing products can become competitors of a company.
Another way to think about industry market structure is that these five sets of stakeholders are competing for profits in the given industry. For instance, if a supplier to an industry is powerful, they can charge higher prices. If the industry can’t pass its higher costs onto their buyers in the form of higher prices, industry members make less profit. For example, if you have a jewelry store, but are dependent on a monopolist like De Beers for diamonds, then De Beers actually is extracting more relative value from your industry (i.e., the retail jewelry business).
Threat of New Entrants
The likelihood of new entry is a function of the extent to which barriers to entry exist. Evidence suggests that companies often find it difficult to identify new competitors. [6] Identifying new entrants is important because they can threaten the market share of existing competitors. One reason new entrants pose such a threat is that they bring additional production capacity. Unless the demand for a good or service is increasing, additional capacity holds consumers’ costs down, resulting in less revenue and lower returns for competing firms. Often, new entrants have a keen interest in gaining a large market share. As a result, new competitors may force existing firms to be more effective and efficient and to learn how to compete on new dimensions (for example, using an Internet-based distribution channel).
Example 3.4 New Entrant
Amazon’s recent acquisition of PillPack is threatening pharmaceutical market share, potentially altering the landscape of medication home delivery. Amazon serves as a threat due to its power and capacity to provide service. Existing local pharmaceutical companies now competing with home delivery will have to add tools to keep customers satisfied and to maintain trust.
Source: Pharmacy Today, Will recent announcements alter medication home delivery? , Sarah Cushing, 2018Fa
The more difficult it is for other firms to enter a market, the more likely it is that existing firms can make relatively high profits. The likelihood that firms will enter an industry is a function of two factors: barriers to entry and the retaliation expected from current industry participants. Entry barriers make it difficult for new firms to enter an industry and often place them at a competitive disadvantage even when they are able to enter. As such, high-entry barriers increase the returns for existing firms in the industry. [7]
The threat of new entrants is high when:
- Barriers to entry are low (initial capital costs, costs to scale efficiently.)
- There are no network effects (a good or service is more valuable when more people use it, e.g., the internet was of little value until more people started to use it.)
- Customer switching costs are low.
- Incumbents do not possess brand loyalty, proprietary technology, preferential access to raw materials or distribution channels, favorable geographic location, or cumulative experience.
- There are no restrictive government regulations.
- A low expectation that incumbents in the industry cannot or will not retaliate.
Buyer Bargaining Power
The stronger the power of buyers in an industry, the more likely it is that they will be able to force down prices and reduce the profits of firms that provide the product. Firms seek to maximize the return on their invested capital. Alternatively, buyers (customers of an industry or firm) want to buy products at the lowest possible price—the point at which the industry earns the lowest acceptable rate of return on its invested capital. To reduce their costs, buyers bargain for higher-quality, greater levels of service, and lower prices. These outcomes are achieved by encouraging competitive battles among the industry’s firms.
Example 3.5 Buyer Bargaining Power
Tenants and buyer of real estate in Abu Dhabi are experiencing greater bargaining power due to the oversupply of apartments and villas in the city and driving down purchase prices by 9% and rental prices by 12% overall. With more units coming on the market in 2019, this trend is expected to remain for the foreseeable future. Meanwhile, buyers and tenants are expected to move to bigger and better apartments as property owners seek their investments.
Source: Khaleej Times, Tenants, buyers have more bargaining power in Abu Dhabi , 2019Wi
The bargaining power of buyers is high when:
- Only a few buyers exist and those buyers purchase relatively large quantities relative to the size of any single seller.
- When the industry’s products are commodities or standardized.
- Switching costs are low or non-existent.
- Buyers can reasonably threaten backward integration into the industry.
Supplier Bargaining Power
The stronger the power of suppliers in an industry, the more difficult it is for firms within that sector to make a profit because suppliers can determine the terms and conditions on which business is conducted. Increasing prices and reducing the quality of its products are potential means used by suppliers to exert power over firms competing within an industry. If a firm is unable to recover cost increases by its suppliers through its pricing structure, its profitability is reduced by its suppliers’ actions.
Example 3.6 Supplier Bargaining Power
Apple plans to move away from its Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) antenna technology toward a newer modified polyimide (MPI) for all phones built starting in 2019. The newer material is performs as well as the older one but has a much higher yield rate, making it more effective. The older LCP process was complicated to manufacture, prone to defects, and could be accomplished by a limited number of suppliers. Because there will be five new suppliers of the MPI antennae, Apple has greater bargaining power, will get comparable performance with fewer failures, and expects to pay lower prices.
Source: 9to5Mac, 2019 iPhones to use new combination of antenna technology , Ziqi Cao, 2018Fa
The bargaining power of suppliers is high when:
- The industry of the suppliers is more concentrated than that of the industry to which it sells.
- Suppliers do not rely on the industry as their sole source of revenue.
- Switching costs are high.
- The products offered by the supplier is highly differentiated.
- No readily available substitutes are available.
- The threat of forward integration into the industry by suppliers is reasonable.
Threat of Substitutes
This measures the ease with which buyers can switch to another product that does the same thing, such as using aluminum cans rather than glass or plastic bottles to package a beverage. The ease of switching depends on what costs would be involved (e.g., while it may be easy to sell Coke or Pepsi in bottles or cans, transferring all your data to a new database system and retraining staff could be expensive) and how similar customers perceive the alternatives to be. Substitute products are goods or services from outside a given industry that perform similar or the same functions as a product that the industry produces. For example, as a sugar substitute, NutraSweet places an upper limit on sugar manufacturers’ prices—NutraSweet and sugar perform the same function but with different characteristics.
Example 3.7 Substitution
Boxed is a new online, membership-free wholesale retailer that allows you to buy in bulk from the comfort of your home without any membership fees. They have a curated range of products that allow them to be the low cost leader which makes for direct competition with other wholesalers such as Costco or Sam’s club. As switching costs are minimal to almost non-existent, it is very easy for customers to switch to Boxed as they not only offer the best prices, but also offer free shipping on orders over 49 dollars.
Source: Fox 4 News, On Your Side: ‘Boxed’ Bulk Delivery Service , Ariadna Archibald, 2018Fa
Other product substitutes include fax machines instead of overnight deliveries, plastic containers rather than glass jars, and tea substituted for coffee. Recently, firms have introduced to the market several low-alcohol fruit-flavored drinks that many customers substitute for beer. For example, Smirnoff Ice was introduced with substantial advertising of the type often used for beer. Other firms have introduced lemonade with 5% alcohol (e.g., Doc Otis Hard Lemon) and tea and lemon combinations with alcohol (e.g., BoDean’s Twisted Tea). These products are increasing in popularity, especially among younger people, and, as product substitutes, have the potential to reduce overall sales of beer. [8] In general, differentiating a product along dimensions that customers value (such as price, quality, service after the sale, and location) reduces a substitute’s attractiveness.
The threat of substitute products is high when:
- The substitute offers an attractive price-to-performance trade-off.
- The substitute product’s price is lower or its quality and performance capabilities are equal to or greater than those of the competing product.
- Customers face few, if any, switching costs.
Degree of Rivalry
This measures the degree of competition between existing firms. The higher the degree of rivalry, the more difficult it is for existing firms to generate high profits.
The degree of rivalry is highest when:
- There are numerous competitors or competitors are equally balanced.
- The industry is experiencing slow growth.
- Fixed costs are high in the industry.
- The industry’s products lack differentiation
- Rivals in the industry have high strategic stakes.
- Leaving the industry comes with high exit barriers.
Numerous or Equally Balanced Competitors
Example 3.8 numerous or balanced rivalry.
Coca-Cola and Pepsi have been in the “Cola Wars” for a long time. Although their portfolios are no longer limited to soft drinks, their continuing battle on a full spectrum of growth and earnings measures shows the intensity of rivalry that continues between the two. Pepsi seems to currently lead in consumer demand, showing a 43% higher return over the last five years. And while consumers are shifting their preferences to healthier options, so are these two rivals as they attempt to modify consumer perceptions of their brands. Pepsi acquired Naked, Kevita and Soda Stream. Meanwhile Coca-Cola acquired Honest Tea, Costa Coffee, MOJO Kombucha, and a minority stake in the growing Gatorade competitor Body Armor.
Source: Yahoo Finance, The Cola Wars: Pepsi vs. Coke , 2019Sp
Intense rivalries are common in industries with many companies. With multiple competitors, it is common for a few firms to believe that they can act without eliciting a response. However, evidence suggests that other firms generally are aware of competitors’ actions, often choosing to respond to them. At the other extreme, industries with only a few firms of equivalent size and power also tend to have strong rivalries. The large and often similar-sized resource bases of these firms permit vigorous actions and responses. The Fuji/Kodak and Airbus/Boeing competitive battles exemplify intense rivalries between pairs of relatively equivalent competitors.
Example 3.9 Slow Growing Industry
With the growing concern of vehicle carbon emissions, the advent of electric cars for consumer use has become inevitable. While the need for a change is clear, the market is clearly developing slowly because there isn’t the proper infrastructure for the charging of electric vehicles like the network of gas stations that currently exist. Until companies can differentiate through an increased range and charging options, the industry will continue to develop slowly.
Source: Phys.org, ‘Not right away’: Electric cars still have long road ahead , 2018Fa
Slow Industry Growth
When a market is growing, firms try to use resources effectively to serve an expanding customer base. Growing markets reduce the pressure to take customers from competitors. However, rivalry in non-growth or slow-growth markets becomes more intense as firms battle to increase their market shares by attracting their competitors’ customers.
Typically, battles to protect market shares are fierce. Certainly, this has been the case with Fuji and Kodak. The instability in the market that results from these competitive engagements reduce profitability for firms throughout the industry, as is demonstrated by the commercial aircraft industry. The market for large aircraft is expected to decline or grow only slightly over the next few years. To expand market share, Boeing and Airbus will compete aggressively in terms of the introduction of new products, and product and service differentiation; both firms are likely to win and lose battles; however, as of this writing Boeing is the current leader.
High Fixed Costs or High Storage Costs
Example 3.10 high fixed costs.
Approach Resources, an independent oil and gas company, is an example of a company hindered by high fixed costs in 2018. G&A and interest costs are the main reason these fixed costs are so high, and need to be reduced if the company wants to remain competitive. It is likely that in the future they will use some sort of debt restructuring to try and drive down these costs compared to other companies in their industry.
Source: Seeking Alpha, Approach Resources: Hindered By High Fixed Costs , 2018Fa
When fixed costs account for a large part of total costs, companies try to maximize the use of their productive capacity. Doing so allows the firm to spread costs across a larger volume of output. However, when many firms attempt to maximize their productive capacity, excess capacity is created on an industry-wide basis. To then reduce inventories, individual companies typically cut the price of their product and offer rebates and other special discounts to customers. These practices, however, often intensify competition. The pattern of excess capacity at the industry level followed by intense rivalry at the firm level is observed frequently in industries with high storage costs. Perishable products, for example, lose their value rapidly with the passage of time. As their inventories grow, producers of perishable goods often use pricing strategies to sell products quickly.
Lack of Differentiation or Low Switching Costs
When buyers find a differentiated product that satisfies their needs, they frequently purchase the product faithfully over time. Industries with many companies that have successfully differentiated their products have less rivalry, resulting in lower competition for individual firms. [9] However, when buyers view products as commodities (as products with few differentiated features or capabilities), rivalry intensifies. In these instances, buyers’ purchasing decisions are based primarily on price and, to a lesser degree, service. Film for cameras is an example of a commodity. Thus, the competition between Fuji and Kodak is expected to be strong.
Example 3.11 Commodities
Commodities are grouped into three main categories – agriculture, energy, and metals. The term “agriculture” leads one to think about this category as items such as lumber or fibers that we create clothes out of, but it also pertains to drinks, grains, and animals that are specifically raised for food. Low product differentiation and low prices are both characteristics of commodities.
Based on this definition, buying a soft drink at grocery store presents two options — to buy a commodity or a branded item. If the customer perceives Pepsi or Coca-Cola as providing a higher quality than the generic store brand (also known as a dealer brand) of “cola”, they will pay a premium for the product. However, if the customer doesn’t perceive a value distinction then the cola is simply a commodity and they will purchase the lowest cost alternative.
Source: The Balance, What Commodities Are and How Its Trading Market Works , 2019Wi
The effect of switching costs is identical to that described for differentiated products. The lower the buyer’s’ switching costs, the easier it is for competitors to attract buyers through pricing and service offerings. High switching costs, however, at least partially insulate the firm from rivals’ efforts to attract customers. Interestingly, the switching costs—such as pilot and mechanic training—are high in aircraft purchases, yet, the rivalry between Boeing and Airbus remains intense because the stakes for both are extremely high.
High Strategic Stakes
Competitive rivalry is likely to be high when it is important for several of the competitors to perform well in the market. For example, although it is diversified and is a market leader in other businesses, Samsung has targeted market leadership in the consumer electronics market. This market is quite important to Sony and other major competitors such as Hitachi, Matsushita, NEC, and Mitsubishi. Thus, we can expect substantial rivalry in this market over the next few years.
Example 3.12 High Stakes Rivalry
After acquiring Uber’s local business in Indonesia, Grab, a top ride-hailing firm based in South East Asia, formed a joint venture with ZhongAn International and insurance company to add insurance and loan financing products for its drivers. This action by Grab is part of their ambition to become the leading South East Asia irval to Go-Jek (an Indonesian ride-hailing firm).
In recent years, these two companies have battled to provide services beyond ride-hailing. For its part, Go-Jek is expanding its business to Vietnam and Thailand compete with Grab. This rivalry has escalated since 2018 as Grab has raised $3 billion of a $5 billion capital goal while Go-Jek is close to raising $2 billion to strengthen their balance sheet.
Source: TechCrunch, Grab moves to Offer Digital Insurance Services in Southeast Asia , 2019Wi
High strategic stakes can also exist in terms of geographic locations. For example, Japanese automobile manufacturers are committed to a significant presence in the U.S. marketplace. A key reason for this is that the United States is the world’s single largest market for auto manufacturers’ products. Because of the stakes involved in this country for Japanese and U.S. manufacturers, rivalry among firms in the U.S. and global automobile industry is highly intense. While close proximity tends to promote greater rivalry, physically proximate competition has potentially positive benefits as well. For example, when competitors are located near one another, it is easier for suppliers to serve them and they can develop economies of scale that lead to lower production costs. Additionally, communications with key industry stakeholders such as suppliers are facilitated and more efficient when they are close to the firm. [10]
High Exit Barriers
Sometimes companies continue competing in an industry even though the returns on their invested capital are low or negative. Firms making this choice likely face high exit barriers, which include economic, strategic, and emotional factors, causing companies to remain in an industry when the profitability of doing so is questionable.
Example 3.13 Exit Barriers to Rivalry
Earn credit, add your own example !
Attractiveness and Profitability
Using Porter’s analysis, firms are likely to generate higher profits (and be considered attractive) if the industry:
- Is difficult to enter
- There is limited rivalry
- Buyers are relatively weak
- Suppliers are relatively weak
- There are few substitutes
Profits are likely to be low (and the industry considered unattractive) if:
- The industry is easy to enter
- There is a high degree of rivalry between firms within the industry
- Buyers are strong
- Suppliers are strong
- It is easy to switch to alternatives
Effective industry analyses are products of careful study and interpretation of data and information from multiple sources. A wealth of industry-specific data is available to be analyzed. Because of globalization, international markets and rivalries must be included in the firm’s analyses. In fact, research shows that in some industries, international variables are more important than domestic ones as determinants of strategic competitiveness. Furthermore, because of the development of global markets, a country’s borders no longer restrict industry structures. In fact, movement into international markets enhances the chances of success for new ventures as well as more established firms. [11]
Following a study of the five forces of competition, the firm can develop the insights required to determine an industry’s attractiveness in terms of its potential to earn adequate or superior returns on its invested capital. In general, the stronger competitive forces are, the lower the profit potential for an industry’s firms. An unattractive industry has low entry barriers, suppliers and buyers with strong bargaining positions, strong competitive threats from product substitutes, and intense rivalry among competitors. These industry characteristics make it very difficult for firms to achieve strategic competitiveness and earn above-average returns. Alternatively, an attractive industry has high entry barriers, suppliers and buyers with little bargaining power, few competitive threats from product substitutes, and relatively moderate rivalry. [12]
- Spanos, Y. E., & Lioukas, S. (2001). An examination into the causal logic of rent generation: Contrasting Porter’s competitive strategy framework and the resource-based perspective. Strategic Management Journal, 22, 907–934. ↵
- Porter, M. E. (1980). Competitive strategy. New York: Free Press. ↵
- Zaheer, S., & Zaheer, A. (2001). Market microstructure in a global b2b network, Strategic Management Journal, 22, 859–873. ↵
- Hitt, M. A., Ricart I Costa, J., & Nixon, R. D. (1999). New managerial mindsets. New York: Wiley. ↵
- Pan, Y., & Chi, P. S. K. (1999). Financial performance and survival of multinational corporations in China. Strategic Management Journal, 20, 359–374; Brooks, G. R. (1995). Defining market boundaries Strategic Management Journal, 16, 535–549. ↵
- Geroski, P. A. (1999). Early warning of new rivals. Sloan Management Review, 40(3), 107–116. ↵
- Robinson, K. C., & McDougall, P. P. (2001). Entry barriers and new venture performance: A comparison of universal and contingency approaches. Strategic Management Journal, 22, 659–685. ↵
- Khermouch, G. (2001, March 5). Grown-up drinks for tender taste buds. Business Week, p. 96. ↵
- Deephouse, D. L. (1999). To be different, or to be the same? It’s a question (and theory) of strategic balance. Strategic Management Journal, 20, 147–166. ↵
- Chung, W., & Kalnins, A. (2001). Agglomeration effects and performance: Test of the Texas lodging industry Strategic Management Journal, 22, 969–988. ↵
- Kuemmerle, W. (2001). Home base and knowledge management in international ventures. Journal of Business Venturing, 17, 99–122; Lorenzoni, G., & Lipparini, A. (1999). The leveraging of interfirm relationships as a distinctive organizational capability: A longitudinal study. Strategic Management Journal, 20, 317–338. ↵
Strategic Management Copyright © 2020 by John Morris is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.4 A Firm’s Micro Environment: Porter’s Five Forces
A firm’s micro environment is directly connected to the firm in some way, and firms must understand the micro environment in order to successfully compete in an industry. All firms are part of an industry —a group of firms all making similar products or offering similar services, for example, automobile manufacturers or airlines. Firms in an industry may or may not compete directly against one another, as we’ll discuss shortly, but they all face similar situations in terms of customer interests, supplier relations, and industry growth or decline.
Harvard strategy professor Michael Porter developed an analysis tool to evaluate a firm’s micro environment. Porter’s Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry (Figure 5.4). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that affects a firm’s potential to be successful in its industry. It is important to note that this tool is different than Porter’s generic strategy typology that we will discuss later.
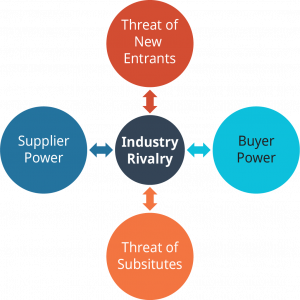
Industry Rivalry
Industry rivalry , the first of Porter’s forces, is in the centre of the diagram. Note that the arrows in the diagram show two-way relationships between rivalry and all of the other forces. This is because each force can affect how hard firms in an industry must compete against each other to gain customers, establish favourable supplier relationships, and defend themselves against new firms entering the industry.
When using Porter’s model, an analyst will determine if each force has a strong or weak impact on industry firms. In the case of rivalry, the question of strength focuses on how hard firms must fight against industry rivals (competitors) to gain customers and market share. Strong rivalry in an industry reduces the profit potential for all firms because consumers have many firms from which to purchase products or services and can make at least part of their purchasing decisions based on prices. An industry with weak rivalry will have few firms, meaning that there are enough customers for everyone, or will have firms that have each staked out a unique position in the industry, meaning that customers will be more loyal to the firm that best meets their particular needs.
The Threat of New Entrants
In an industry, there are incumbent (existing) firms that compete against each other as rivals. If an industry has a growing market or is very profitable, however, it may attract new entrants . These either are firms that start-up in the industry as new companies or are firms from another industry that expand their capabilities or target markets to compete in an industry that is new to them.
Different industries may be easier or harder to enter depending on barriers to entry , and factors that prevent new firms from successfully competing in the industry. Common barriers to entry include cost, brand loyalty, and industry growth. For example, the firms in the airline industry rarely face threats from new entrants because it is very expensive to obtain the equipment, airport landing rights, and expertise to start up a new airline.
Brand loyalty can also keep new firms from entering an industry, because customers who are familiar with a strong brand name may be unwilling to try a new, unknown brand. Industry growth can increase or decrease the chances a new entrant will succeed. In an industry with low growth, new customers are scarce, and a firm can only gain market share by attracting customers from other firms. Think of all the ads you see and hear from competing cell phone providers. Cell phone companies are facing lower industry growth and must offer consumers incentives to switch from another provider. On the other hand, high-growth industries have an increasing number of customers, and new firms can successfully appeal to new customers by offering them something existing firms do not offer. It is important to note that barriers to entry are not always external, firms often lobby politicians for regulations that can be a barrier to entry. These types of barriers will be covered in greater depth in more upper-level courses.
Threat of Substitutes
In the context of Porter’s model, a substitute is any other product or service that can satisfy the same need of a customer as an industry’s offerings. Be careful not to confuse substitutes with rivals. Rivals offer similar products or services and directly compete with one another. Substitutes are completely different products or services that consumers would be willing to use instead of the product they currently use. For example, the fast-food industry offers quickly prepared, convenient, low-cost meals. Customers can go to McDonald’s, Wendy’s, Burger King, or Taco Bell—all of these firms compete against each other for business. However, their customers are really just hungry people. What else could you do if you were hungry? You could go to the grocery store and buy food to prepare at home. McDonald’s does not directly compete against Kroger for customers because they are in different industries, but McDonald’s does face a threat from grocery stores because they both sell food. How does McDonald’s defend itself from the threat of Kroger as a substitute? By making sure their food is already prepared and convenient to purchase—your burger or salad is ready to eat and available without even getting out of your car.
Supplier Power
Virtually all firms have suppliers who sell parts, materials, labour, or products. Supplier power refers to the balance of power in the relationship between firms and their suppliers in an industry. Suppliers can have the upper hand in a relationship if they offer specialized products or control rare resources. For example, when Sony develops a new PlayStation model, it often works with a single supplier to develop the most advanced processor chip it can for their game console. That means its supplier will be able to command a fairly high price for the processors, an indication that the supplier has power. On the other hand, a firm that needs commodity resources such as oil, wheat, or aluminum in its operations will have many suppliers to choose from and can easily switch suppliers if price or quality is better from a new partner. Commodity suppliers usually have low power.
Buyer Power
The last of Porter’s forces is buyer power , which refers to the balance of power in the relationship between a firm and its customers. If a firm provides a unique good or service, it will have the power to charge its customers premium prices, because those customers have no choice but to buy from the firm if they need that product. In contrast, when customers have many potential sources for a product, firms will need to attract customers by offering better prices or better value for the money if they want to sell their products. One protection firms have against buyer power is switching costs , the penalty consumers face when they choose to use a particular product made by a different company. Switching costs can be financial (the extra price paid to choose a different product) or practical (the time or hassle required to switch to a different product). For example, think about your smartphone. If you have an iPhone now, what would be the penalty for you to switch to a non-Apple smartphone? Would it just be the cost of the new phone? Smartphones are not inexpensive, but even when cell phone service providers offer free phones to new customers, many people still don’t switch. The loss of compatibility with other Apple products, the need to transfer apps and phone settings to another system, and the loss of favourite iPhone features, such as iMessage, are enough to keep many people loyal to their iPhones.
Principles of Management – Chapter 8.4 by David S. Bright, et al., © Open Stax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , unless otherwise noted.
5.4 A Firm’s Micro Environment: Porter’s Five Forces Copyright © 2022 by Lina Manuel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Micro Environment Definition, Factors & Example
The micro environment in marketing includes all those micro factors that affect business strategy, decision making and performance. It is vital for business success to conduct macro environment and micro environment analysis before decision-making process. Macro environment f actors include political, economic, social, technological, and legal factors. On the other hand, company micro environment factors include customers, suppliers, competitors, employees, shareholders and media.
Table of Contents
How Micro Environment Affect Business Decisions
Mostly, in the marketing environment, micro factors do not affect all the businesses in the industry in the same manner. The reason is that every business is different in size, capacity, financial resources, human resources and overall strategies.
For example, competitors affect the business decision-making process. MacBook Pro is a well-known brand of Apple Inc. Dell XPS 13 and HP Spectre 13 Laptops are giving Apple Inc. a tough time and certainly affect its decision making. Apple is already introduced a functional keys touch bar. It is possible that Apple Inc. introduces MacBook Pro with Intel Coffee Lake Processor in mid 2018 to compete with its rivals and sustain the customer base.
Examples of Micro Environment Factors Affect Business
The customers are the central part of any business as they tend to attract and retain most of the customers to generate revenue. Therefore, organizations must adopt a marketing strategy that attracts the potential customers and retains the existing customers by taking into consideration the wants and needs of customers and by providing the after sales services and value-added services.
Competitors
The competitors of an organization can have a direct impact on business strategies. The organization must know how to do a competitive analysis of competitors and have a competitive advantage. An organization must understand, what value added services their competitor is providing or the unique selling point of their competitors. How they can differentiate from their competitors. What benefits a company can offer to the customers which competitors does not offer.
In other words, understand competitors marketing mix strategy i.e. product, price, placement, promotion, people, process and physical evidence. Other approaches for market competitive analysis is PEST Analysis , PESTLE Analysis and SWOT Analysis as well.
An organization must understand that unawareness of competitors can make it difficult beat the competitors and lead the market. It must know how competitors react when there is a change in market environment such as political and legal changes, technological change, change in consumers behaviours can impact their business. They should also analyze how their competitors are responding to market changes and what tactics they are using to come up with better planning to these changes.
For Instance, Videocon, BPL, Onida and others are competitors of Philip Television in Television Market. The other form of competition is “Product Form” in which customer seeks different features and functions in a product. For example, a customer is willing to purchase a two-wheeler car which can come with gears and without gear, automatic or manual. These are the features of product and services which customer would be considered during the purchase process.
Skilled employees can help an organization to achieve organizational goals and objectives. As skilled and experienced employees has expertise to support organization to get success. This begins with the hiring process and continues through regular and timely training and development sessions. The training and development process helps the employees to work effectively and efficiently in order to achieve the organizational goals, specifically in service sector.
To some extent employees affect business environment. If there is low motivation and low skilled employees, business would suffer as the employees would be least motivated towards sales.
Actions of a supplier can influence the business strategy, as they provide the materials for production. For instance, if their services will not reasonable and timely that will affect the production time and the sales due to delayed process of production.
If the supplier increases the prices of raw material they provide to the company, it will impact the marketing mix strategy of an organization, which will end-up with the increase in price of finished goods. Therefore keeping a strong relation with supplier can help a company in getting an edge over competitors.
Shareholders
Shareholders of an organization have an influence as the company want investors to increase for this they might make a decision to increase money by buoyant on stock market, i.e. shifting to public from private ownership. This change will pressure the company as the public shareholders seek returns on their investment.
The shareholders’ demand for raise in profit can influence the business success in longer-run. Therefore, it is important for top management to keep strong and better relations with shareholders to have a successful business on long-term basis.
Media and Social Media
The way media acts can make or break an organization. Organization should manage to keep a good relationship with media as whatever it shows will directly influence the organization business. If media will show positive aspect, this will increase the business of organization and vice-versa. In order to maintain good relations with media some organization do maintain a public relation department who manage events and deal with media on behalf of company
Organizations must understand the ways which they can reach their customers and have positive company and brand image in their mind. For this, some organization approaches newspapers to let people know about their business and some approach consumer television programs to have the attention of a large number of direct audience. These days social media applications are a good idea to reach customers in a more appropriate way i.e. Facebook, Youtube, Twitter and Instagram etc.
A story that has been done by the media on a one-off, could impact on a firms’ daily operations thus becoming that firms micro environment. However, a firm could be influenced to have long term operational decisions in a bid to avoid negative media stories.
It is not necessary that business will control microenvironment factors all the time. Since micro and macro environment affect marketing campaigns, companies should conduct environmental analysis before developing marketing strategy.
About The Author
Umar Farooq
8.4 A Firm's Micro Environment: Porter's Five Forces
- What makes up a firm’s external micro environment, and what tools do strategists use to understand it?
A firm’s micro environment is illustrated in the green circle in Exhibit 8.4 . These entities are all directly connected to the firm in some way, and firms must understand the micro environment in order to successfully compete in an industry. All firms are part of an industry —a group of firms all making similar products or offering similar services, for example automobile manufacturers or airlines. Firms in an industry may or may not compete directly against one another, as we’ll discuss shortly, but they all face similar situations in terms of customer interests, supplier relations, and industry growth or decline.
Harvard strategy professor Michael Porter developed an analysis tool to evaluate a firm’s micro environment. Porter’s Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry ( Exhibit 8.6 ). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that affects a firm’s potential to be successful in its industry. It is important to note that this tool is different than Porter’s generic strategy typology that we will discuss later.
Industry Rivalry
Industry rivalry , the first of Porter’s forces, is in the center of the diagram. Note that the arrows in the diagram show two-way relationships between rivalry and all of the other forces. This is because each force can affect how hard firms in an industry must compete against each other to gain customers, establish favorable supplier relationships, and defend themselves against new firms entering the industry.
When using Porter’s model, an analyst will determine if each force has a strong or weak impact on industry firms. In the case of rivalry, the question of strength focuses on how hard firms must fight against industry rivals (competitors) to gain customers and market share. Strong rivalry in an industry reduces the profit potential for all firms because consumers have many firms from which to purchase products or services and can make at least part of their purchasing decisions based on prices. An industry with weak rivalry will have few firms, meaning that there are enough customers for everyone, or will have firms that have each staked out a unique position in the industry, meaning that customers will be more loyal to the firm that best meets their particular needs.
The Threat of New Entrants
In an industry, there are incumbent (existing) firms that compete against each other as rivals. If an industry has a growing market or is very profitable, however, it may attract new entrants . These either are firms that start up in the industry as new companies or are firms from another industry that expand their capabilities or target markets to compete in an industry that is new to them.
Different industries may be easier or harder to enter depending on barriers to entry , factors that prevent new firms from successfully competing in the industry. Common barriers to entry include cost, brand loyalty, and industry growth. For example, the firms in the airline industry rarely face threats from new entrants because it is very expensive to obtain the equipment, airport landing rights, and expertise to start up a new airline.
Brand loyalty can also keep new firms from entering an industry, because customers who are familiar with a strong brand name may be unwilling to try a new, unknown brand. Industry growth can increase or decrease the chances a new entrant will succeed. In an industry with low growth, new customers are scarce, and a firm can only gain market share by attracting customers of other firms. Think of all the ads you see and hear from competing cell phone providers. Cell phone companies are facing lower industry growth and must offer consumers incentives to switch from another provider. On the other hand, high-growth industries have an increasing number of customers, and new firms can successfully appeal to new customers by offering them something existing firms do not offer. It is important to note that barriers to entry are not always external, firms often lobby politicians for regulations that can be a barrier to entry. These types of barriers will be covered in greater depth in more upper level courses.
Threat of Substitutes
In the context of Porter’s model, a substitute is any other product or service that can satisfy the same need for a customer as an industry’s offerings. Be careful not to confuse substitutes with rivals. Rivals offer similar products or services and directly compete with one another. Substitutes are completely different products or services that consumers would be willing to use instead of the product they currently use. For example, the fast food industry offers quickly prepared, convenient, low-cost meals. Customers can go to McDonald’s, Wendy’s, Burger King, or Taco Bell—all of these firms compete against each other for business. However, their customers are really just hungry people. What else could you do if you were hungry? You could go to the grocery store and buy food to prepare at home. McDonald’s does not directly compete against Kroger for customers, because they are in different industries, but McDonald’s does face a threat from grocery stores because they both sell food. How does McDonald’s defend itself from the threat of Kroger as a substitute? By making sure their food is already prepared and convenient to purchase—your burger or salad is ready to eat and available without even getting out of your car.
Supplier Power
Virtually all firms have suppliers who sell parts, materials, labor, or products. Supplier power refers to the balance of power in the relationship between firms and their suppliers in an industry. Suppliers can have the upper hand in a relationship if they offer specialized products or control rare resources. For example, when Sony develops a new PlayStation model, it often works with a single supplier to develop the most advanced processor chip it can for their game console. That means its supplier will be able to command a fairly high price for the processors, an indication that the supplier has power. On the other hand, a firm that needs commodity resources such as oil, wheat, or aluminum in its operations will have many suppliers to choose from and can easily switch suppliers if price or quality is better from a new partner. Commodity suppliers usually have low power.
Buyer Power
The last of Porter’s forces is buyer power , which refers to the balance of power in the relationship between a firm and its customers. If a firm provides a unique good or service, it will have the power to charge its customers premium prices, because those customers have no choice but to buy from the firm if they need that product. In contrast, when customers have many potential sources for a product, firms will need to attract customers by offering better prices or better value for the money if they want to sell their products. One protection firms have against buyer power is switching costs , the penalty consumers face when they choose to use a particular product made by a different company. Switching costs can be financial (the extra price paid to choose a different product) or practical (the time or hassle required to switch to a different product). For example, think about your smartphone. If you have an iPhone now, what would be the penalty for you to switch to a non-Apple smartphone? Would it just be the cost of the new phone? Smartphones are not inexpensive, but even when cell phone service providers offer free phones to new customers, many people still don’t switch. The loss of compatibility with other Apple products, the need to transfer apps and phone settings to another system, and the loss of favorite iPhone features, such as iMessage, are enough to keep many people loyal to their iPhones.
Concept Check
- Describe each of Porter’s Five Forces. What information does each provide a manager trying to understand her firm’s micro environment?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: David S. Bright, Anastasia H. Cortes
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Management
- Publication date: Mar 20, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/8-4-a-firms-micro-environment-porters-five-forces
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Calculators
- Swot Analysis
- Pestle Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Organizational Structure
- Copywriting
- Research Topics
- Student Resources
Services We Provide

Resources We Provide

Login / Register

- Every Thing You Need to Know About Micro-environment!
The business world as we see it today is more intense and competitive than ever before. In other words, the stakes for businesses were never this high and competition only gets fiercer each day. In such a scenario, organizations’ effectiveness in terms of strategic planning becomes a critical success factor for them.
Table of Contents
- What is micro environment
Micro environment in business
- Micro environment in marketing
Speaking of strategic planning, there are various dimensions that businesses take into account while realizing their strategic goals and objectives. These strategic goals explain the long-term plans that organizations have to ensure swift advancement and dominance in the industry. While there are various major considerations with respect to strategic planning, environmental analysis is a key objective for companies.
To explain, a lucid understanding of the internal environment, as well as the external environment corresponding to a company or industry, aids in setting business objectives and realizing the future course of action. The fact of the matter is that the external environment factors define the overall scenario in a specific industry as influenced by the macro environment.
In this blog, we delve further into understanding the conceptualization of the micro environment, the factors that are a part of the micro environment, and how they affect businesses. The blog highlights all the intricacies of micro environment in business and micro environment in marketing. So, let us get started with micro environment definition and contextual understanding.
What is micro environment?
Micro environment is a business term that refers to the direct factors existing within the company that can directly impact the operations and decision-making of the company. These factors play a crucial role in the context of a firm's business strategies and the setting of strategic business goals.
When a business creates a favourable operating environment, this will highlight various business opportunities for a firm, on the other hand, an unfavourable operating environment will point at the prevailing threats that a business needs to mitigate.
To further explain, the micro environment of an enterprise is inclusive of five prominent factors that include the following:
- Competitors
- Market intermediaries
As you can clearly identify, each of the above dimensions of micro-environment-factors is a crucial determinant in giving companies a clear direction with respect to strategic planning . Also, these factors directly affect the success and authority of a business in its corresponding industry.
This explains why organizations or business leaders associate such great significance with micro environment analysis to identify the immediate threats and opportunities in the operating environment. In fact, in this context, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis proves to be a highly effective and reliable strategic planning tool for the worthwhile assessment of the micro environment.
Probing further, the subsequent sections explain micro-environment-factors and sheds light on the influence of each micro environment factor on business strategies and business success.

For any business big or small, it is essential that the top management has great awareness of the operating environment. Any threat that a business does not identify in a timely manner can doom the business at a later stage. Similarly, any missed opportunity in the immediate environment could imply that the business missed out on scaling new heights. Having said that, for businesses, it is important to conduct a well-detailed micro environment analysis at regular intervals.
The bottom line is that an effective micro environment analysis facilitates strategic change management that could transform the destiny of an organization for the better. The role of the top management is not limited to realizing the threats and opportunities existing in the micro environment. The ultimate objective is to act upon those opportunities or threats to make a real difference in terms of business performance and success.
Now, let us comprehend how each dimension of micro-environment-factors can directly or indirectly impact an organization’s prospects of success. Besides, it also offers a lucid understanding of the reasons why organizations need to have their strategic goals and plans in alignment with the present state of micro environment factors.

Micro environment factors and their influence
Well, we already listed out the six verticals of micro environment that hold the key to micro environment analysis and subsequently, business planning. Now, let us find out in detail how each of these factors has a considerable influence.
1. Competitors
Competitor analysis not only helps companies to understand what is working well for their competitors but also helps them to realize the existing gaps in their own strategies. Having said that, for any firm, competitors make a vital part of the operating environment. Businesses can always learn from the strengths and weaknesses of their competitors.
Moreover, identifying and analyzing the competitors also helps companies to determine the degree of rivalry in the market. When the degree of competition or rivalry is high, the stakes are high too and there is no margin for error. For any firm, it is important to understand the magnitude of rivalry in the market or the operating environment so that they can set attainable goals for developing competitive advantages.
Moving forward, for a business, competition exists not only in the form of business rivals but also in terms of products and services. In a perfect competition market wherein all enterprises are offering identical products or services, consumers have readily available substitutes. Consumers can easily switch to new businesses or products when the threat of substitutes is high and consumer switching costs are low.
For instance, the degree of competition is high in the consumer goods market as all companies are equally placed and sell similar products. If you use the products of Unilever Global , making the switch to Procter & Gamble will not make much of a difference.
All in all, an analysis of competitors helps companies to recognize their competitive positioning in the market, the degree of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes from other companies or products. In accordance with the same, businesses formulate their strategies for expansion and growth. Lastly, with respect to assessing the competition in the market, realizing the threat posed by new players or emerging businesses is also vital.
2. Consumers
Let’s start with a simple question, can a business advance without consumers? Can a business scale new heights without acquiring new customers at all times? Certainly, the answer to both these questions is well known to all of us.
One of the most important objectives of any business is to create incremental consumer demand. As it is often said, “consumers are the king” and this fact will stay forever. With respect to the analysis of micro-environment-factors, it is not only important to realize consumer preferences and needs but also to recognize the bargaining power of consumers. If we look at the state of affairs in the contemporary business world, everything revolves around consumer experiences. Businesses are paying more heed to consumer feedback than ever before in the bid to acquire and retain customers with exceptional experiences.
However, in the context of micro-environment-factors specifically, the primary objective of an enterprise is to analyze the bargaining power of consumers. To explain, the bargaining power of consumers is a direct measure of the kind of influence that consumers can have on a company’s product quality, pricing strategies, and functional efficiency.
When consumers assume enormous bargaining power, they can exert massive influence on companies to offer the highest quality at the lowest possible price. But the real question is, under what conditions is the bargaining power of consumers high? What are the substantial determinants of the bargaining power of buyers?
The factors that influence the bargaining power of buyers are listed below:
1. The number of buyers
When there is a large number of buyers in the market, the bargaining power of buyers is low. However, when there are only a few buyers and each buyer holds a substantial market share, the bargaining power of buyers is very high.
2. Switching costs
Consumer switching cost simply refers to the additional costs that consumers will have to incur when they switch to a new brand or product. For consumers, switching costs is a major consideration. Having said that, if the switching cost is low, consumers assume a greater bargaining power as they can switch to a new brand or product easily. On the contrary, if switching costs are too high, the bargaining power of consumers reduces significantly.
For instance, the switching costs for buyers are almost negligible in the consumer goods and grocery market. However, in the automobile market or the consumer electronics market, the switching costs can be too overwhelming for consumers.
3. The threat of backward integration
The bargaining power of consumers is high when buyers can exert great influence in terms of forcing backward integration. To explain, backward integration is the process by which companies buy suppliers or vendors in the supply chain.
4. Nature of commodities
In a market with standardized products, the bargaining power of buyers is high as the switching costs are low. However, in a market with large scale product differentiation, the consumer switching costs are high and hence the bargaining power is low.
3. Suppliers
Every business has a large magnitude of dependence on supply chain management and this is where the relationship between businesses and suppliers holds immense significance. Further, in the operational environment of a given firm, the bargaining power of suppliers can largely affect business operations and strategic planning for a sustainable future.
To explain, the bargaining power of suppliers in micro environment explains the extent to which suppliers in an industry can influence product quality, supply chain operations, and prices of firms. In contemporary times, we often hear about a global supply chain crisis that is affecting supply chains and production across all industries. In times like these where companies are at a disadvantage, suppliers assume massive bargaining power.
However, that is just one aspect of the various factors that determine the bargaining power of suppliers. These factors are listed below:
1. Availability of substitutes
The bargaining power of suppliers will be next to negligible if there is a large number of suppliers in the industry and replacements are easily available. However, when there are only a few suppliers and substitutes are not easily available, suppliers will have a much greater influence on companies
2. Reliance of suppliers on the industry
In case the suppliers rely solely on one industry for their profitability, their bargaining power will be low while the bargaining power of companies in the industry will be very high. On the flip side, the suppliers get revenue from various industries and are not entirely dependent on one market, the bargaining power of the suppliers will be high.
3. Switching costs for enterprises
Switching cost is not only a consideration for consumers but also for businesses. For enterprises, switching costs exist in terms of the additional costs to be incurred when they switch from one supplier to another. Having said that, if the switching costs are too high for companies, suppliers will assume greater bargaining power. Alternatively, if the switching costs are low and there are plenty of suppliers to choose from, the bargaining power of the suppliers will be low.
4. The threat of forwarding integration
Another major consideration with respect to the analysis of suppliers is whether they can exert the risk of forward integration or not. To explain, forward integration is the process through which companies look to reduce operational costs by purchasing supplier firms. By doing so, companies can eliminate third-party reliance on suppliers for distribution.
In the context of the operating environment of a company, the micro environment factor of people pertains to the local public, consumer rights groups, environmentalists, and other segments of the general public that can potentially affect a business and its success metrics.
Having said that, it is important for companies to maintain a positive relationship with the segments of the general public for positive public perception and to manage business reputation effectively. When businesses have a positive reputation among the general public inclusive of various interest groups, it is likely to attract new customers.
On the contrary, a negative public perception can dent the business and it may end up losing investors’ and customers’ trust. For instance, Starbucks has drawn a lot of flak in the past from environmental groups for its disposable plastic cups adding immensely to pollution. The criticism of Starbucks majorly led by environmentalist groups compelled the eco-friendly customers to switch to other brands. Hence, the company had to address the ethical issues pertaining to environmental neglect with immediate effect and introduce reusable paper cups.
5. Marketing intermediaries
Marketing intermediaries include middlemen or intermediary agencies that assist businesses in terms of promotion, selling, and distribution of their products. To further elaborate, marketing intermediaries include sellers, resellers, wholesalers, and other agents in the distribution channel.
Now, it is a well-known fact that businesses need to maintain an extensive network of sellers and wholesalers to ensure smooth distribution channels that are vital for revenue generation. Hence, companies need to analyze the marketing intermediaries and the value drawn from them on a regular basis to remain competitive. Also, they need to review their relationship with the marketing intermediaries at regular intervals to plug the gaps in the best interest of business objectives.
Now you will definitely have a crystal clear idea of the significance and impact of each factor that is taken into account while analyzing micro-environment-factors. In addition to the macro environment in business, it is equally important for businesses to analyze the micro environment that gives a clear picture of the immediate operating environment.
Proceeding further, the purpose of analyzing the micro environment is not limited to refining or developing operational strategies. Even from the marketing perspective, the analysis of the micro environment is imperative. Having said that, the ensuing section sheds light on all that you need to know about the micro environment in marketing.
What is micro environment in marketing?
The 4 Ps of Marketing also called the marketing mix include Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Having said that, from the marketing perspective, each marketing strategy is centered around these 4 Ps. What we need to acknowledge is that the micro-environment factors mentioned above also have a huge impact on the 4Ps of marketing.
Needless to say, marketing is one of the core functionalities of every business. If we look around, the most successful business organizations in contemporary times also have the most innovative marketing strategies. The bottom line is that irrespective of whether it is a highly established brand like Nike or an emerging startup, effective marketing is indispensable.
For businesses to acquire new leads and convert customers at a swift pace, they need to work consistently on marketing objectives that include enhanced market share, increased brand awareness, product launch, market penetration, and so on. These marketing SMART Goals are directly linked with greater business success in terms of customer acquisition, revenue generation, and profitability.
What we need to understand is how the micro environment factors influence the product or service being offered by a business, the pricing strategies linked to the product, the places where the product is promoted, and the promotional strategies implemented by a company. So, let us comprehend in detail how each factor can have a substantial influence on a brand’s marketing.
The product quality of competitors and how competitors promote their products directly impact the marketing strategies of a company. Also, competitors’ pricing strategies influence a company’s pricing strategies.
Hence, in the formulation of marketing plans, companies undertake the objective of competitor analysis to identify the marketing channels that competitor firms are using. In fact, companies analyze the 4 Ps marketing mix of competitor firms on a regular basis to constantly optimize their marketing.
In contemporary marketing, companies are very watchful of each other’s digital marketing strategies and promotional offers. For instance, when one major firm in the industry runs discount campaigns, other companies also come up with special promotional offers for customers. For instance, when Zara is selling its products at discounted rates, the likes of H&M will follow the same strategy along with other apparel brands. This is how competitor firms influence each other’s marketing strategies and brand positioning.
As discussed above, consumers directly influence the product quality and pricing strategies of a firm. For any brand, it is important to not only analyze the bargaining power of customers but also to identify the changing consumer needs and offer them the best-fit products or services.
Having said that, as per the bargaining power of the customers, companies decide their pricing strategies. Companies are less likely to introduce products or services with premium pricing where the bargaining power of customers is too high. Moreover, subject to the changing preferences of the consumer and their expectations of quality, companies change their product development strategies.
Companies look to consistently optimize their products or introduce new products in the market to stay ahead of the changing consumer preferences. This explains why automotive companies introduce facelifts of their best-performing cars after every two to three years to cater to the changing consumer preferences.
Moreover, based on consumer behavior, companies decide their promotional strategies. For instance, if a substantial proportion of consumer interactions start online or through social media, companies will lay greater emphasis on SEO, social media marketing, and other digital marketing strategies for customer acquisition. To gain further insights into optimizing your social media marketing efforts, you can read more about the services offered by a reputable social media marketing agency.
Like consumers, suppliers can also have a direct influence on product quality and pricing strategies. In a market where suppliers have enormous bargaining power, they can exploit the pricing strategies of companies.
Let us try to understand this by taking the example of the current scenario in the automotive industry. As most of us know, the global automotive industry is facing unprecedented losses because of supply chain bottlenecks primarily related to semiconductor shortages. In times when the industry is largely hit by semiconductor shortages, suppliers are assuming greater power and are exploiting the input costs for companies. Consequently, there is a price hike in the industry and hence a downfall in sales.
Through this example, we can clearly comprehend how suppliers can make a massive difference in the marketing micro environment. If suppliers choose to hoard back the supplies, it will put immense pressure on the supply chain operations of a firm. Consequently, it will directly impact product strategies and pricing strategies.
In the modern era, most companies want to position themselves as a sustainable brand that cares for the environment. Marketing on the lines of being a purpose driven brand has become the need of the hour for companies. This is for the simple reason that brands’ public perception is directly linked to their growth and the sustenance of their competitive advantages.
When brands promote their products along the lines of sustainability, they try to set a positive narrative among the general public and environmentalist groups. The preferences of the modern consumers are changing and they are being more watchful of brand perceptions than in the past. To substantiate, as per Business Wire , almost 80 percent of modern consumers want to buy from brands that are perceived as environment-friendly.
This explains why most brands and businesses are now promoting greater transparency in their sustainable approaches. Almost every business now provides a sustainability report in the public domain and has set targets for carbon neutrality. In fact, sustainability or CSR initiatives are now at the epicenter of marketing campaigns for most businesses.
To cite an example, big brands like Adidas are running exclusive sustainability campaigns for proactive marketing. Brands are now using sustainability as a unique selling proposition and to maintain a positive brand image among the general public and environmental activists. They realize that not doing so may harm the perception of their business and they may begin to lose customers to relatively more sustainable brands.
To cite another example, in recent times, PETA, a globally renowned animal rights organization, launched a campaign against Gucci for exploiting animals and treating them unethically for their exotic skins. Given the fact that PETA enjoys global recognition and influence, the campaign dented the public image of Gucci, the consequences of which would have surely been felt in terms of customer attrition. Again, very recently, Gucci was under criticism one more time as PETA called out the brand for using wild animals for its advertising campaigns.
Hence, while setting marketing objectives and formulating marketing plans, companies need to be considerate of the public view as that may have a significant impact on the achievement of marketing goals. Marketing dashboards examples can provide valuable insights into public perception and help companies make informed decisions.
As discussed above, marketing intermediaries have a direct correlation with the promotion and distribution of products. Companies’ relationship with the network of wholesalers, sellers, distributors and retailers is a key determinant of marketing and related operations. Also, the marketing intermediaries may have a substantial influence on the product and pricing strategies.
To explain, if a company is selling inferior products with an overpriced strategy, most wholesalers, distributors, or retailers would not want to deal with the company. On the other hand, if a company is selling a high-quality product with a penetration pricing strategy , most retailers and wholesalers will happily associate with that product.
For wholesalers, retailers, and distributors, the sole purpose of collaboration will be their own profitability rather than the company’s profitability. Having said that, they will only be interested in qualities that have substantial demand in the market for their quality and unique features.
Recommended Readings
What is macro environment?
Change management models businesses should know
To encapsulate, while macro environment factors offer an in-depth understanding of the overall industrial environment with respect to a country or market, the micro environment factors explain the immediate operating environment that surrounds a firm. For effective strategic planning, substantial analysis of both macro environment and micro environment is necessary. The findings of environmental analysis help the companies not only identify the threats or opportunities but also to chart a course of action for the future.
What is the difference between micro and macro environment?
The term "micro environment" describes the immediate context in which a firm operates, including elements like suppliers, clients, rival businesses, and other stakeholders. It is the particular setting in which an organisation runs and over which it has some degree of power or influence.
On the other hand, the term "macro environment" refers to the broader, uncontrollable external elements, such as economic, technological, demographic, political, and cultural aspects, that have an impact on the business environment. These variables are frequently out of the company's hands, yet they can have a big impact on how it runs and how well it performs.
What are the tools used to analyse the micro environment?
Businesses use a number of micro environment tools, such as SWOT analysis , Porter's Five Forces analysis, PESTEL analysis , and customer analysis, to analyse their microenvironment. Businesses can discover their internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and dangers by using a SWOT analysis.
By analysing the bargaining power of suppliers and customers, the threat posed by new competitors, the threat posed by substitutes, and the level of existing rivalry, Porter's Five Forces study aids firms in understanding the competitive environment. The political, economic, social, technical, environmental, and legal elements that could have an impact on the firm are taken into account by PESTEL analysis. Understanding a customer's requirements and preferences can help a business build better products and more effective marketing plans.
Copyright © 2023 CrowJack. All Rights Reserved
- Micro Environment
As an organization, understanding the environment in which you function is an extremely important exercise. It could be the difference between success and failure. Let us study in detail the different factors of micro environment that affect an organization.
Suggested Videos
The micro environment is the operating environment of the firm. This is because the functioning of the micro environment has a direct and immediate bearing on the company . They are more interlinked with the company than macro environmental factors.
Let us take a look at some of the most important and common elements of the micro environment. These elements are different for different organizations. But the following ones are usually found in almost all companies.
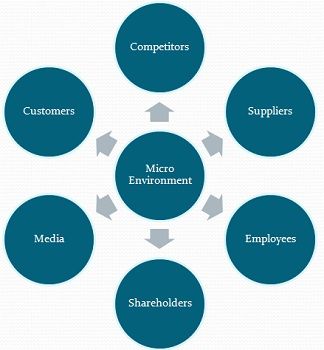
(Source: KeyDifferences)
Learn Macro Environment here.
1] Customers
The main purpose for the existence of most organizations is to satisfy the needs and wants of the customers. The enterprise aims to please the customer and earn a profit in return.
So the ultimate aim is to provide the best products /services to the customer at the best prices. Failure to do so may result in failure of the business .
This is why it has become increasingly important to listen to customers and value their feedback. This is why customer consumer surveys have increasing importance in today’s markets .
2] Competitors
There are no pure monopolies in the world. Every organization, whether big or small, has competition and competitors. So the company has to keep a constant check on their competitors.
The company must ensure that their products have a USP that makes them different and unique in the market. The products offered must also be better and cheaper than those of the competition.
3] Employees
Employees or labor is one of the most important factor of production for a company. Human resources are a significant factor in the success (or failure) of a firm. Hence employing the correct people, best suited to your firm is of vital importance.
And training and development of these employees is also essential. If care is not taken in this matter the organization can never succeed, because employees are the back bone of every organization.
4] Shareholders
Shareholders invest in the company, but they are not merely investors. They own shares of the company, so they are actually owners of the company in a way. This means they get a say in the running of a company.
Shareholders will also demand a return on their investment. So it is the company’s duty to earn profits and pass on this benefits to the shareholders. They have to create wealth for these shareholders.
To keep their interest dividends also have to be paid. So the company must find the right balance between the health of the company and the benefits to the shareholders.
5] Suppliers
Suppliers provide the firm with the materials and factors of production they need to run the business. The relation between the company and the suppliers is a power equation. Both depend on each other for their survival.
So it is necessary for the company to have healthy and amenable relations with their suppliers. This is essential to the smooth running of the organization. For example if the company has a falling out with one raw material supplier it could delay their whole production process by days.
Every company is going to need media to promote their brand and market their products. So it is necessary that the company maintain their relationship and their status quo with the media.
Any negative coverage in the media can lead to huge losses for the company. This is why companies hire PR managers to help them use the media to a positive effect.
Learn the vision and mission statement here in detail.
Solved Question on Micro Environment
Q: In any market, ____ is king and they are the organizations most important micro economic factor.
Ans: The correct option is A. Customer is the king, and the reason for the existence of the firm is to satisfy the wants and needs of the customers. They are the most important element of their micro environment.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Introduction to Business Environment
- Vision and Mission Statements
- Global Integration and Business Environment
- Macro Environment
One response to “Micro Environment”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Business Jargons
A Business Encyclopedia
Micro Environment
Definition : Micro Environment, refers to the environment comprising of all the actors of an organization’s immediate environment which influences the performance of the company, as they have a direct bearing on the firm’s regular business operations.
The micro environment is popularly referred to as task environment or operating environment.
Elements of Micro Environment
The elements of the micro environment are closely associated with the company and they do not affect all the companies operating in the industry, in a similar manner, as some factors are specific to the firm.
So we can say that the micro environment is one which the firm addresses in its specific arena, such as the industry or the strategic group.

Competitors
Competition is what keeps the firm thriving. Competitors are the rival sellers operating in the same industry. It must be noted that the nature and intensity of competition highly influence the firm’s products and services. Product Differentiation is something that helps the firm to beat the cut-throat competition in the market.
For a firm to survive competition it is required to keep a close watch on the competitors (both existing and potential) future moves and actions, so as to prepare in advance, as well as to predict the response of competitors to company’s moves. Moreover, competitor analysis also helps in maintaining or improving market share and position.
Suppliers are the one who provides inputs such as material, components, labour and other stock of goods to the firm, which is required to undertake manufacturing activities. when there is uncertainty as to the supply constraints, it usually builds pressure on the firms and they are required to maintain high inventories, which leads to cost increases.
Suppliers have the power to change the firm’s position in the market and its capabilities.
The relationship amidst the firm and its suppliers represents a power equation, based on the industry conditions and their dependence on each other.
The success of the organization greatly depends on how effectively the firm fulfils the needs and wants of the customers, which is profitable to the firm and also provides value to the customer. The firm needs to analyze what the customers expect from their products and services so that the firm can satisfy them.
It must be noted that without customers no business can survive for a long time. So, the primary objective of the firm is to create and retain customers, to keep itself going.
Intermediaries
Intermediaries refer to marketing intermediaries which cover agents, merchants, distributors, dealers, wholesalers, etc. that participate in the company’s supply chain, in stocking and transporting the goods from their source location to their destination.
It acts as a link between the business organization and the ultimate consumer.
Shareholders
Shareholders are the real owners of the company who invest their money in the company’s business, by purchasing the shares, for which they are paid a dividend every year as a return. Shareholders have the right to vote in the company’s general meeting.
Placing the right person at the right job and retaining them for the long term by keeping the staff motivated is very important for the strategic planning process. Training and development act as a guide to the firm’s employees which ensures an up-to-date workforce.
A qualified and competent workforce can help the firm to achieve success with little efforts.
We all know the power of media these days, it can make or break an organization or its products/services overnight.
Management of media whether electronic media, press media or social media is really important not just to create a positive and clean image of the company and its products in front of the audience but also to support the firm in building a good reputation in the market. The right use of media can do wonders for the company and boost its sales.
When the firm competes with the firm operating in the same industry, with the same micro environmental factors, the relative success of the company is based on the relative effectiveness of the company in dealing with these factors.
Related terms:
- Monopolistic Competition
- Porter’s Five Forces Model
- Business Environment
- Internal Environment
- Macro Environment
Reader Interactions
Kwanele says
April 24, 2021 at 6:43 pm
Who is the author of this article and when was it published?
Surbhi S says
April 26, 2021 at 9:39 am
The author of this article is Surbhi S. and it was published on Feb 14, 2020
Jorge Morais Diamantino says
November 6, 2021 at 8:12 pm
THANKS FOR THIS
February 6, 2023 at 8:30 pm
Thank you very much!
harry machamanda says
January 31, 2022 at 3:21 am
great explanation
Heather Mpala says
November 3, 2022 at 2:02 pm
Thank you for helping us understand business jargons
sema crist says
November 23, 2022 at 2:04 pm
Sodia Saunta says
August 18, 2023 at 8:19 am
I like this video
m.dokata says
November 17, 2023 at 12:50 pm
thank you for great support keep it up
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report
Marketing form an essential part of all business ventures. The Kentucky Fried Chicken is one such commercial undertaking that fulfils society needs through merchandizing fast foods and side dishes. Their delicacies attract the milieu and numerous persons outside Australia.
n an industrial setting, a quality SWOT analysis is advisable (Segal-Horn, & Faulkner, pg. 28). The strengths and weaknesses are internal to the organization while the opportunities and strengths are outside forces from the company’s control. In discussing these elements, the paper will focus on the micro-environmental and macro-environmental marketing factors that impact on an organization. KFC has been on the public limelight for both affirmative and negative concerns.
All these are central to their ability to capitalize on a strong corporate image as stipulated by a careful assessment on marketing techniques. Micro-environmental factors symbolize issues pertinent to the company. They directly impact on KFC from a personal perspective. It could be stakeholder response, customer satisfaction, employee grievances, or competition. These are issues that can easily be handled by the company without help from consultants.
Macro- environmental factors on the other hand, create as an enormous challenge to the company because they are bigger issues beyond interior control. They include demographics, technology, social factors, and legislative issues among others. Consequently, they probably affect the company over the long term. Collective effort in handling the two forces ensures a company’s ability to maintain an enviable customer base.
Managers pre-eminently address such concerns through a series of situation analyses that correlates the two scenarios whilst at the same time seeks to find long lasting remedies. An environmental scan aids in attending to issues effectively in order to avoid crises in the future (Groucutt, et al. pg.43).
KFC influence on microenvironment factors within Australia
All competitive markets are volatile and prone to change. KFC thus requires strategy transformation and plan update depending on the revolution exhibited in the market. Issues occurring within this business entity require internal attention as such; KFC can influence its internal activities through multiple means including the incorporation of the techniques discussed.
They represent KFC’s image and they can be controlled by it. Customer attraction, access and retention become the full responsibility of the service provider. For KFC in Australia, home deliveries will maximize the customer base. Alternatively, self-service measures will work well for them. This is so because customers like choosing what they want to eat in their preferred portions. Secondly, it creates enough time to serve everyone. KFC should implement a customer relations desk through which their complaints can be redressed efficiently.
Shareholders
Shareholders represent the second most important asset of a business entity. They should be treated with uttermost respect to prevent them from defecting from the company (Carroll, pg.7). When this occurs, the share value reduces and it daunts the company image. KFC should inform them of any changes in management and they should maintain consistency in communication in order to make the stakeholders feel Important.
A good relationship with suppliers means a quality feedback from the consumers. When the suppliers of various fast foods receive good treatment from KFC they most likely will reciprocate with goodwill. Suppliers ensure that no food poisoning cases occur and that quality meals reach the public through KFC.
Employees form an imperative part of the firm. For KFC to succeed in a competitive market, it should realize that employee-handling techniques reflect through service delivery. As such, the employees must receive salaries in good time. They should make a decent living out of the wages. They must be able to afford necessities. This is to ensure that psychological factors do not cause them to treat customers unfairly.
Competition
Australia poses a competitive environment especially when fast food joints come into the picture. World known McDonald’s, Chicken inn and Vissalis reside in Australia. They offer almost same food quality. To ensure success, KFC must develop a strategy to gain the competitive advantage.
Essentially, they should maximize on excellent customer care, increase food varieties, maintain good relations with the media and work on an eminent corporate image. Additional, Sanders must invest on franchising in marginalized sections of the globe like Latin America and Africa since they also pose as superior market destinations (Havaldar, & Havaldar, pg. 29).
The media poses a vital part of a marketing strategy. KFC must take special concern when media issues arise. They should use media for positive publicity and avoid contact with the media during scandals. So far, for KFC in Australia the media has been of tremendous help especially for advertising. The internal memos, press releases and conferences also act as the best forum for publicity and creation of awareness.
Macro-environmental trends
Macro-environmental factors require exceptional consideration since most of them impact negatively on the firm. The worst part of this is that their impacts last for a long time and often call for financial rejuvenation and image restoration efforts. Macro-environmental factors (Kirst-Ashman, pg.100) revolve around the treats and opportunities of the business empire.
The purpose of the assignment is to capitalize on the opportunities while reducing the threats. KFC’s location at Guilford was based on a strategic plan in the 18 th century. Changes within the society result in a complete transformation in how things occur. Two centuries down the line, KFC faces multiple threats
Various environmental front groups accuse KFC of ecological degradation (Carroll, pg.9). They claim the rain forests face extinction based on the amount of wrapping material used cover their products.
The paper that serves this purpose is manufactured from the same forest trees and thus KFC is in the verge of a sue trail by environmentalists. Secondly, the foods contain a large portion of oil, which poses as an enormous risk to health, and weight related complications. Finally, the vegans also threaten to sue KFC because they do not protect animals.
Investing in franchising (Segal-Horn, & Faulkner, pg. 19) within and outside Australia is a huge task requiring excellent skills and financial empowerment. KFC might face collapse if they fail to formulate a proper monetary plan to aid in future planning. Additionally, KFC will require enough money for marketing and settling up a crisis control unit in order to deviate from crisis situations. Without such a plan then they will likely fall victim of numerous circumstances.
Issues revolving around disputes, publicity, law, and controversies encompass political environment. A case of a teenage girl suffering effects of food poisoning from KFC products badly destroys the firm’s image. The Sydney incident really took a toll on KFC making it spend over eight million in compensation and huge sums of money in image restoration activities.
An accusation of racial stereotype in Australia also leaves this company struggling to win consumer goodwill. All these events plus others not highlighted that are politically instigated, pause a major threat to the firm’s success.
Response to the macro-environmental trends
The conditions earlier mentioned occur from time to time. Responding to them needs an individual to be in control especially when the media are involved. This is because they always have a way of blowing things out of proportion. To avoid future problems, KFC should invest in regular advertisements. This aids them to remain relevant within a changing environment.
They should not change their logo frequently in order to create consistency and to avoid consumer apathy and confusion. Secondly, consumer lobby groups help in brand positioning products so that when legislative issues arise, they come out strongly to defend their cause (Kirst-Ashman, pg .89).
The most important aspect of future reaction lies within a relevant Public Relation team and a crisis management unit. These two will always help KFC find a good solution to problems while at the same time control media coverage. Finally, KFC needs a superior company attorney who will handle all the corporate and legal matters. When they face jurisdiction, then the attorney advices them on the right steps to take.
In conclusion, KFC like many other companies dealing in fast foods, face many challenges both internal and external. A quality strategic plan aids in giving them a scope and direction over the long-term and essentially offers them a rejoinder in times of need. The strategy should also be review every three months to improve it based on the changes within the two environments (Groucutt, et al. pg.54).
Carroll, A 2009, Business & Society: Ethics & Stakeholder Management , South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason, OH.
Groucutt, J, Forsyth, P & Leadley, P 2004, Marketing: Essential Principles, New Realities , Kogan Page, London.
Havaldar, K & Havaldar, K 2010, Business Marketing Text and Cases , Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Ltd, New Delhi.
Kirst-Ashman, K 2011, Human Behavior in the Macro Social Environment: An Empowerment Approach to Understanding Communities, Organizations, and Groups , Brooks/Cole, Australia.
Segal-Horn, S & Faulkner, D 2008, International Strategy , Thomson Learning, London.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 28). KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report. https://ivypanda.com/essays/microenvironment-and-the-macro-environment/
"KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report." IvyPanda , 28 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/microenvironment-and-the-macro-environment/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report'. 28 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/microenvironment-and-the-macro-environment/.
1. IvyPanda . "KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/microenvironment-and-the-macro-environment/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "KFC Micro- and Macro-Environment Report." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/microenvironment-and-the-macro-environment/.
- Micro- and Macro-Related Aspects of Social Practice
- Factors Explaining Exports and Imports
- Riding the Waves of Culture: Chapter IX Reflection
- KFC in Australia: The Particular Features of the Marketing Environment
- Technology as a Macro-environmental Force that Affect Marketing Related Decision
- Apple Inc.'s Macroenvironmental Analysis
- Macro-Environment Analysis of ‘A Horror Show at the Cinemaplex’ Using PESTE Approach
- International Verses Domestic Strategic Management
- Macro-Environment (PESTLE Analysis) of Target Corporation
- Ditra Company's Macro-environment, Competitive Environment and Internal Environment
- United Arab Emirates: Achieving High Development
- Dubai Aluminum: Opening a Branch in Saudi Arabia
- Food and Well Being
- Rice Production in China
- Analysis of the French Wine Sector
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Business
Micro-Environmental Analysis Of Apple Inc Essay Sample
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Business , Market , Customers , Steve Jobs , Products , Apple , Company , Marketing
Published: 03/10/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Apple is an American multinational company formed in 1976 by Steve Jobs and his friends S. Wozniak, and R. Wayne. Apple’s products brought revolution in personal computer and consumer electronic industry. Apple is well-known in world market for its innovative products. Micro-environmental analysis of the Apple will help in understanding direct impact of micro environment factors on the company, its operations and business performance. This paper discusses the impact of micro-environmental factors on the Apple Inc.
A micro-environmental analysis will analyze all internal and micro factors such as company, employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, and publics/ media.
The Company: Apple has achieved new heights of success under the guidance of Steve Jobs. Steve was great a leader with extraordinary management skills. The leadership style of Steve was mix of situational and transformational. Steve was aware how make employees efficient and satisfied. Steve developed a collaborative organizational environment where all employees can share their ideas freely and participate in decision-making process. Collaborative environment of Apple not only empowered employees but also helped organization in bringing innovation to market before its competitors (Badenhorst-Weiss et al.). Presently Apple is growing under the guidance of Tim Cook who is also following the steps of Steve Jobs and taking his legacy forward. Apple is holding strong financial position in the market with annual revenue of around 183 billion US$ (2014) (Apple Press). Net income of the company is around 40 billion US$ for 2014. Recent success of i6 and iOS 8 across the world also positively impacted brand image and cash flow of the company. Apple is always on the top in bringing innovative technology to the consumers, which has proven on various instances. Apple involved in offering large variety of consumer electronics and computers that fulfill different needs of the customers. The offerings of Apple includes: Mac, iPod, iPad, iPhone, iTunes, Apple watch, and Apple store. Innovations drives success of the organization, and all offerings of the Apple are one step ahead of its competitors (Apple). Human Resource/ Employees: Apple is aware that success of any organization cannot be achieved without effective human resource management. Each employee at Apple has clear allocation of responsibilities; they understand their role and deliver the service as per the standards established by the Apple. All managers treat their employees with respect and dignity. Managers coach their team members and provide all type of support, training to drive customer satisfaction and organizational growth. Apple also ensures that it provide ample opportunity of growth and learnings to its employees. Employees at Apple can freely share their problems and issues with their seniors. A healthy working environment at Apple resulted in mutual growth of stakeholders (Fernando). Suppliers: Apple has large supplier base which provides company high bargaining power. The suppliers of the company are located in different parts of the world i.e. China, India, and South Africa. Apple believe in empowering its suppliers by organizing capacity building and training programs. A healthy and close relationship with its suppliers enables company to manage supply chain efficiently and gain competitive advantages. Apple developed strict code of conduct for its suppliers which need to follow by the suppliers. Apple ensure that all suppliers follow code of conduct by conducting various audits through the year and across the locations. Apple ensures that even small components is best in quality (Apple). Customers: Apple delivers what it promise to its customers i.e. good quality, innovative technology, excellent functioning and competitive pricing. According to a study conducted J.D. Power, Apple scores highest when it comes to customer satisfaction with 85 percent delighted customers (GSM Arena). Apple achieved customer satisfaction by efficiently managing all processes starting from procuring equipment, production of goods, retailing of the products and after sales services. Competitors: Apple is operating in very competitive market. Major competitors of Apple are Samsung, Microsoft and Google. In Smartphone market Motorola, HP, HCL and Blackberry also giving competition to the Apple. In developing countries Apple’s products are considered as premium products due to high pricing, however, Samsung has variety of products that are capable to fulfill needs of the customers and suitable on their pockets. Developing countries have wide untapped market and huge potential of growth that is presently not targeted by the Apple. It is important for the Apple to increase its product range and develop products in low price range in order to gain market share. Presently Samsung is holding top position when it comes to market share in Smart phone market. Apple needs to work strategically in order to regain its top position especially when product life cycle is too short and dynamics of market are continuously changing. Publics: media, government, financial bodies, and other general public falls into this factor. Apple is effectively dealing government bodies by adhering with all rules and regulations established by the authorities. Media may have mix opinion towards Apple by criticizing its products. However, customers like Apple and feel proud after owning its products.
Works Cited
"Apple Press." October 2014. Apple. 21 October 2014. Badenhorst-Weiss, H., Brevis, T., and Cant, M. Business Management: A Contemporary Approach. Cape Town: Juta and Company Ltd., 2008. Fernando, A.C. Business Environment. New Delhi: Pearson Education India, 2011. "Supplier Responsibility." 2014. Apple. Online. 21 October 2014. "US customer satisfaction led by Apple, Samsung close second." 25 April 2014 . GSM Arena. 21 October 2014.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 2171
This paper is created by writer with
ID 272004699
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Approach essays, legal drinking age essays, different styles essays, obese essays, scarce resources essays, war ii essays, the play essays, harsh essays, psychosocial essays, effective leadership essays, music theory essays, essay on after school delinquency prevention program, free research paper on follow up compliance with pre arranged primary care providers post emergency room, health care essay sample, cyber bullying essay, republican and liberal democratic positions essay sample, low back pain cost of illness essay sample, code of ethics for physical therapists without the use of drugs essay, report on internal briefing paper, research paper on procedures in the physical sciences, powers of congress essay, sample essay on receiving feedback, culturally responsive teachers in todays diverse classroom essay samples, example of objectives report, literary analysis assignment essay example, good chinese immigration to the united states of america research paper example, free report about comparison between social identity and realistic conflict theories, hand washing and bacteria report sample, example of the andrea yates case essay, free literature review on differential effects of egfr ligands on endocytic, external analysis of hd motorcycle manufacturer case study sample, good example of mathematics paper report, example of interactive advertisin campaign course work, essay on e business, free art architecture research paper example, art in the middle east research papers example, invasion of privacy case studies, public debt case studies, fatality case studies, timeliness case studies, cruise ship case studies, incapacity case studies, tracheostomy case studies.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.5: A Firm's Micro Environment- Porter's Five Forces
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 12953

Learning Objectives
- What makes up a firm’s external micro environment, and what tools do strategists use to understand it?
A firm’s micro environment is illustrated in the green circle in Exhibit 8.4. These entities are all directly connected to the firm in some way, and firms must understand the micro environment in order to successfully compete in an industry. All firms are part of an industry —a group of firms all making similar products or offering similar services, for example automobile manufacturers or airlines. Firms in an industry may or may not compete directly against one another, as we’ll discuss shortly, but they all face similar situations in terms of customer interests, supplier relations, and industry growth or decline.
Harvard strategy professor Michael Porter developed an analysis tool to evaluate a firm’s micro environment. Porter’s Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry (Exhibit 8.6). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that affects a firm’s potential to be successful in its industry. It is important to note that this tool is different than Porter’s generic strategy typology that we will discuss later.

Industry Rivalry
Industry rivalry , the first of Porter’s forces, is in the center of the diagram. Note that the arrows in the diagram show two-way relationships between rivalry and all of the other forces. This is because each force can affect how hard firms in an industry must compete against each other to gain customers, establish favorable supplier relationships, and defend themselves against new firms entering the industry.
When using Porter’s model, an analyst will determine if each force has a strong or weak impact on industry firms. In the case of rivalry, the question of strength focuses on how hard firms must fight against industry rivals (competitors) to gain customers and market share. Strong rivalry in an industry reduces the profit potential for all firms because consumers have many firms from which to purchase products or services and can make at least part of their purchasing decisions based on prices. An industry with weak rivalry will have few firms, meaning that there are enough customers for everyone, or will have firms that have each staked out a unique position in the industry, meaning that customers will be more loyal to the firm that best meets their particular needs.
The Threat of New Entrants
In an industry, there are incumbent (existing) firms that compete against each other as rivals. If an industry has a growing market or is very profitable, however, it may attract new entrants . These either are firms that start up in the industry as new companies or are firms from another industry that expand their capabilities or target markets to compete in an industry that is new to them.
Different industries may be easier or harder to enter depending on barriers to entry , factors that prevent new firms from successfully competing in the industry. Common barriers to entry include cost, brand loyalty, and industry growth. For example, the firms in the airline industry rarely face threats from new entrants because it is very expensive to obtain the equipment, airport landing rights, and expertise to start up a new airline.
Brand loyalty can also keep new firms from entering an industry, because customers who are familiar with a strong brand name may be unwilling to try a new, unknown brand. Industry growth can increase or decrease the chances a new entrant will succeed. In an industry with low growth, new customers are scarce, and a firm can only gain market share by attracting customers of other firms. Think of all the ads you see and hear from competing cell phone providers. Cell phone companies are facing lower industry growth and must offer consumers incentives to switch from another provider. On the other hand, high-growth industries have an increasing number of customers, and new firms can successfully appeal to new customers by offering them something existing firms do not offer. It is important to note that barriers to entry are not always external, firms often lobby politicians for regulations that can be a barrier to entry. These types of barriers will be covered in greater depth in more upper level courses.
Threat of Substitutes
In the context of Porter’s model, a substitute is any other product or service that can satisfy the same need for a customer as an industry’s offerings. Be careful not to confuse substitutes with rivals. Rivals offer similar products or services and directly compete with one another. Substitutes are completely different products or services that consumers would be willing to use instead of the product they currently use. For example, the fast food industry offers quickly prepared, convenient, low-cost meals. Customers can go to McDonald’s, Wendy’s, Burger King, or Taco Bell—all of these firms compete against each other for business. However, their customers are really just hungry people. What else could you do if you were hungry? You could go to the grocery store and buy food to prepare at home. McDonald’s does not directly compete against Kroger for customers, because they are in different industries, but McDonald’s does face a threat from grocery stores because they both sell food. How does McDonald’s defend itself from the threat of Kroger as a substitute? By making sure their food is already prepared and convenient to purchase—your burger or salad is ready to eat and available without even getting out of your car.

Supplier Power
Virtually all firms have suppliers who sell parts, materials, labor, or products. Supplier power refers to the balance of power in the relationship between firms and their suppliers in an industry. Suppliers can have the upper hand in a relationship if they offer specialized products or control rare resources. For example, when Sony develops a new PlayStation model, it often works with a single supplier to develop the most advanced processor chip it can for their game console. That means its supplier will be able to command a fairly high price for the processors, an indication that the supplier has power. On the other hand, a firm that needs commodity resources such as oil, wheat, or aluminum in its operations will have many suppliers to choose from and can easily switch suppliers if price or quality is better from a new partner. Commodity suppliers usually have low power.
Buyer Power
The last of Porter’s forces is buyer power , which refers to the balance of power in the relationship between a firm and its customers. If a firm provides a unique good or service, it will have the power to charge its customers premium prices, because those customers have no choice but to buy from the firm if they need that product. In contrast, when customers have many potential sources for a product, firms will need to attract customers by offering better prices or better value for the money if they want to sell their products. One protection firms have against buyer power is switching costs , the penalty consumers face when they choose to use a particular product made by a different company. Switching costs can be financial (the extra price paid to choose a different product) or practical (the time or hassle required to switch to a different product). For example, think about your smartphone. If you have an iPhone now, what would be the penalty for you to switch to a non-Apple smartphone? Would it just be the cost of the new phone? Smartphones are not inexpensive, but even when cell phone service providers offer free phones to new customers, many people still don’t switch. The loss of compatibility with other Apple products, the need to transfer apps and phone settings to another system, and the loss of favorite iPhone features, such as iMessage, are enough to keep many people loyal to their iPhones.
Concept Check
- Describe each of Porter’s Five Forces. What information does each provide a manager trying to understand her firm’s micro environment?
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Micro and Macro Environment
While microenvironment has a direct impact on business activities, the macro environment is a general business environment, which influences all business groups at large. It is important to learn the business environment, so as to understand the effect of various forces on business. Take a read of the given article to know the difference between microenvironment and macro environment.
Content: Micro Environment Vs Macro Environment
Comparison chart, definition of micro environment.
Microenvironment refers to the environment which is in direct contact with the business organization and can affect the routine activities of business straight away. It is associated with a small area in which the firm functions.
The microenvironment is a collection of all the forces that are close to the firm. These forces are very particular for the said business only. They can influence the performance and day to day operations of the company, but for the short term only. Its elements include suppliers, competitors, marketing intermediaries, customers and the firm itself.

Micro Environment
- Suppliers are the ones who provide inputs to the business like raw material, equipment and so on.
- Competitors are the rivals, which compete with the firm in the market and resources as well.
- Marketing intermediaries may include wholesalers, distributors, and retailers that make a link between the firm and the customers.
- Customers / Consumers are the ones who purchase the goods for their own consumption. They are considered as the king of business.
- The firm itself is an aggregate of a number of elements like owners like shareholders or investors, employees and the board of directors.
Definition of Macro Environment
The general environment within the economy that influences the working, performance, decision making and strategy of all business groups at the same time is known as Macro Environment. It is dynamic in nature. Therefore it keeps on changing.
It constitutes those outside forces that are not under the control of the firm but have a powerful impact on the firm’s functioning. It consists of individuals, groups, organizations, agencies and others with which the firm deals during the course of its business.
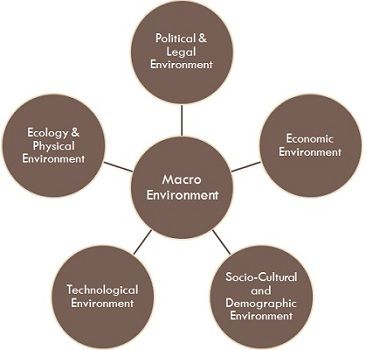
Macro Environment
The study of Macro Environment is known as PESTLE Analysis. PESTLE stands for the variables that exist in the environment, i.e. Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Legal and Environmental. These variables, consider both economic and non-economic factors like social concerns, government policies, family structure, population size, inflation, GDP aspects, income distribution, ethnic mix, political stability, taxes, and duties, etc.
Key Differences Between Micro Environment and Macro Environment
The following are the major difference between micro and macro environment:
- The microenvironment is the environment which is in immediate contact with the firm. The environment which is not specific to a particular firm but can influence the working of all the business groups is known as Macro Environment.
- The factors of the microenvironment affect the particular business only, but the macro-environmental factors affect all the business entities.
- The microenvironmental factors are controllable by the business but to some extent only. However, the macroeconomic variables are uncontrollable.
- The elements of the microenvironment affect directly and regularly to the firm which is just opposite in the case of the macro environment.
- The study of the microenvironment is described as COSMIC analysis. Conversely, PESTLE Analysis is a study of the macro environment.
Video: Micro Vs Macro Environment
Microenvironment and macro environment, both cover the overall environment of business. So, they are more complementary rather than contradictory. The study of these environments will help to know the strength, weakness, opportunity and threat of business.
You Might Also Like:
Preksha says
January 12, 2017 at 11:34 am
Wonderfully written.
January 12, 2017 at 11:35 am
In which category would service provider come?
Surbhi S says
January 12, 2017 at 12:15 pm
samuel onyema says
March 23, 2019 at 3:11 am
can you help me with the Harvard referencing of your journal Difference between micro and macro environment
luthando says
January 23, 2017 at 12:48 am
Wonderfully written it makes sense
Timothy says
March 4, 2017 at 9:03 pm
Adane zewude says
March 22, 2023 at 5:24 am
Good view and written excellent definition
ntongo dianah says
May 31, 2017 at 2:49 pm
thank you it was on important value for my research
Siddharth Deshpande says
December 20, 2017 at 8:19 pm
Thank you so much for the article! Very well stated!
Arjit Sawhney says
February 19, 2018 at 3:56 pm
Far better than reading boring books with so much repetition. Thank you 🙂
Sesilie says
February 23, 2018 at 4:48 pm
Its helpful for my assignment
Henrietta Freeman says
April 11, 2018 at 10:22 pm
Well written & easy to understand
February 11, 2019 at 2:56 pm
Well written and it will definitely assist with my strategy module this year. thank you.
February 23, 2019 at 4:30 am
Quiet helpful.
April 9, 2019 at 11:23 am
Easy and well written. It helped me a lot with my midterms, thank you :”D
July 2, 2019 at 3:08 pm
It is very useful
Malith says
July 8, 2019 at 1:04 am
This is very nice and easy to understand. This helps me a lot to do my assignment
Maureen says
August 17, 2019 at 10:30 pm
The micro and macro environment that influence the business. I require reasons. please help me sir.
March 25, 2020 at 10:34 pm
helpfull but i have to relate this to law enforcement enviroment
help with Havard referencing
Isagani says
November 27, 2020 at 5:26 am
Thank you. It’s a big help to my research
November 29, 2020 at 5:51 pm
This is a very, very clear article that has clarified the differences between the micro and macro environment. I found the advice to think of the environments as complementary rather than contradictory to be especially helpful. Thank you!
Matildah Chileshe says
December 8, 2020 at 8:34 am
wonderfully written and easy to understand.
Bright Musonda Kaoma says
February 7, 2022 at 12:00 pm
Thank you so much, this has added value to my assignment
March 3, 2022 at 3:30 am
It is short and well-structured. Very useful for beginners!
Donewell Chauke says
June 16, 2022 at 1:48 am
good deal,,i found everything i have been gasping for,,
Thank yóu Author ❤️❤️❤️
Mary khoviwa says
July 17, 2022 at 4:44 pm
It is well explained. It has covered all elements needed in the topic. It is indeed helpful for all business players
wahab cheema says
December 2, 2022 at 11:53 am
Thanks for your information. I am read your article and I am very impressed.
Arielle Boyd says
January 16, 2023 at 6:08 am
Thanks for your information. I have read your article and I think there was a lot of information provided.
Tucker@mubs says
January 21, 2023 at 5:55 am
Very helpful summarized information. Thank you 😊
M.Tanvir says
January 30, 2023 at 1:48 pm
Thanks , This information is very helpful for everyone
Muhammad Adnan says
March 19, 2023 at 12:41 pm
Zara Monster says
October 16, 2023 at 3:16 pm
This was good
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Marketing and Micro Environment. Marketing is a process of creating, communicating, and delivering value to the customer. It is a set of activities that are designed to create a specific outcome. The Marketing Mix consists of four key elements: product, price, promotion, and place. Effective marketing incorporates macro and micro-marketing ...
Business essay sample: The current report is going to explore the key impacts of micro- and macroeconomic factors on Tesla Inc. using PESLE and SWOT analyses. Business essay sample: This paper is about the ongoing economic meltdown caused by the credit crunch in the US and UK economies since the winter of 2007.
MACRO MICRO MARKET MACRO Figure 1.1 An overview of the business environment UNIT The 1: micro environment of an organisation The micro environment is also known as the internal environment. Within this environment, the organisation creates its character or ethos from certain elements.
Analyzing the Organization's Microenvironment. When we say microenvironment (or alternatively, Competitor Environment) we are referring primarily to an organization's industry, and the upstream and downstream markets related to it. An industry is a group of firms producing products that are close substitutes. In the course of competition ...
The micro environment is also known as Porter's Five Forces of Competition. The macro environment is primarily concerned with major issues and upcoming changes in the environment. The analysis looks at five areas of interest, which are 1) Power of the Buyers; 2) Power of the Suppliers; 3) Threat of Substitute Products; 4) Threat of New ...
Harvard strategy professor Michael Porter developed an analysis tool to evaluate a firm's micro environment. Porter's Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry (Figure 5.4). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that ...
The micro environment in marketing includes all those micro factors that affect business strategy, decision making and performance. It is vital for business success to conduct macro environment and micro environment analysis before decision-making process. Macro environment f actors include political, economic, social, technological, and legal ...
Harvard strategy professor Michael Porter developed an analysis tool to evaluate a firm's micro environment. Porter's Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry (Exhibit 8.6). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that ...
Micro environment factors and their influence. Well, we already listed out the six verticals of micro environment that hold the key to micro environment analysis and subsequently, business planning. Now, let us find out in detail how each of these factors has a considerable influence. 1. Competitors.
Changes in the factors of a macro environment cannot be controlled but efforts can be made to minimize its negative impact. A micro environment consists of forces close to the company that affects a company's ability to serve its customers. In case of Sony Bravia, its Porters 5 forces and Stakeholders. These 5 forces are external influences ...
The micro environment is the operating environment of the firm. This is because the functioning of the micro environment has a direct and immediate bearing on the company. They are more interlinked with the company than macro environmental factors. Let us take a look at some of the most important and common elements of the micro environment.
Micro Environment. Definition: Micro Environment, refers to the environment comprising of all the actors of an organization's immediate environment which influences the performance of the company, as they have a direct bearing on the firm's regular business operations. The micro environment is popularly referred to as task environment or ...
Marketing will act as a media between companies and consumers to interact and create a long term relationship. Marketing is influenced by both Micro & Micro environment which includes various aspects like Political, Economical and Socio-cultural, Technological & Legal and Environmental. The marketing techniques include choosing target market ...
In discussing these elements, the paper will focus on the micro-environmental and macro-environmental marketing factors that impact on an organization. KFC has been on the public limelight for both affirmative and negative concerns. All these are central to their ability to capitalize on a strong corporate image as stipulated by a careful ...
A micro-environmental analysis will analyze all internal and micro factors such as company, employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, and publics/ media. The Company: Apple has achieved new heights of success under the guidance of Steve Jobs. Steve was great a leader with extraordinary management skills.
1. The Company's Microenvironment. a. The Company. The first factor is the company itself. 1). Top management is responsible for setting the company's mission, objectives, broad strategies, and policies. 2). Marketing managers must make decisions within the parameters established by top management.
Porter's Five Forces is a tool used to examine different micro-environmental groups in order to understand the impact each group has on a firm in an industry (Exhibit 8.6). Each of the forces represents an aspect of competition that affects a firm's potential to be successful in its industry. It is important to note that this tool is ...
Micro environment. Question 5: Essay questions. 5 Phiwe heard that there is a new Consumer Protection Act and a National Credit Act. She needs to known how these Acts will affect the purchasing department. Discuss the National Consumer Protection Act and the National Credit Act and how they will affect the purchasing function.
Micro environmental factors create one of two parts of the external environment of a company. Micro environmental factors include suppliers, resellers, customers, competition and the general public (Marketing Environment Definition Factors & Examples, 2016). Market competition has played a tremendous role in Walmart's success.
The Macro and micro environment Analysis. Paper Type: Free Essay: Subject: Business: Wordcount ... This type of ordering has gone up in a significant way. Environment of outside is very dynamic and is rapidly changing, everything which is outside the boundary of the business would be counted as an external source. ... From simple essay plans ...
Micro Environment. MICRO ENVIRONMENT includes the following factors. 1.SUPPLIERS : Suppliers are those people who are responsible for supplying necessary inputs to the organization and ensure the smooth flow of production. 2.COMPETITORS : Competitors can be called the close rivals and in order to survive the competition one has to keep a close ...
Micro environment is defined as the nearby environment, under which the firm operates. Macro environment refers to the general environment, that can affect the working of all business enterprises. COSMIC, i.e. Competitors, Organization itself, Suppliers, Market, Intermediaries and Customers. PESTLE, i.e. Political, Economic, Socio-cultural ...
This paper assesses the state and resilience of corporate and banking sectors in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) in a "higher-for-longer" interest rate environment using granular micro data to conduct the first cross-country corporate and banking sector stress tests for the MENA region. The results suggest that corporate sector debt at risk may increase sizably from 12 to 30 ...
Micro Environment Essay. Decent Essays. 744 Words; 3 Pages; Open Document. I believe Micro-environment is what our status role is, whereas a macro -environment is more of social hierarchy and socialization. There are many social institutions that can shape a person, just as one family can shape the same person in another way.