Call Us (877) 968-7147
Most popular blog categories
- Payroll Tips
- Accounting Tips
- Accountant Professional Tips


How to Craft the Financial Section of Business Plan (Hint: It’s All About the Numbers)
Writing a small business plan takes time and effort … especially when you have to dive into the numbers for the financial section. But, working on the financial section of business plan could lead to a big payoff for your business.
Read on to learn what is the financial section of a business plan, why it matters, and how to write one for your company.
What is the financial section of business plan?
Generally, the financial section is one of the last sections in a business plan. It describes a business’s historical financial state (if applicable) and future financial projections. Businesses include supporting documents such as budgets and financial statements, as well as funding requests in this section of the plan.
The financial part of the business plan introduces numbers. It comes after the executive summary, company description , market analysis, organization structure, product information, and marketing and sales strategies.
Businesses that are trying to get financing from lenders or investors use the financial section to make their case. This section also acts as a financial roadmap so you can budget for your business’s future income and expenses.
Why it matters
The financial section of the business plan is critical for moving beyond wordy aspirations and into hard data and the wonderful world of numbers.
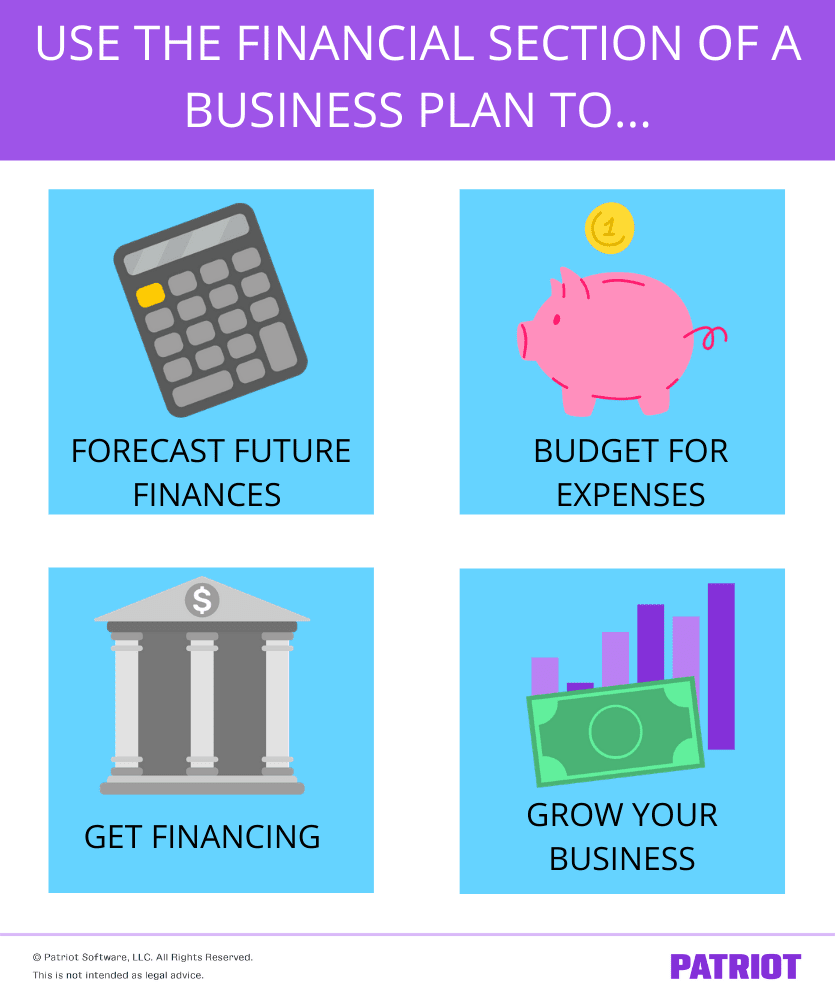
Through the financial section, you can:
- Forecast your business’s future finances
- Budget for expenses (e.g., startup costs)
- Get financing from lenders or investors
- Grow your business
- Growth : 64% of businesses with a business plan were able to grow their business, compared to 43% of businesses without a business plan.
- Financing : 36% of businesses with a business plan secured a loan, compared to 18% of businesses without a plan.
So, if you want to possibly double your chances of securing a business loan, consider putting in a little time and effort into your business plan’s financial section.
Writing your financial section
To write the financial section, you first need to gather some information. Keep in mind that the information you gather depends on whether you have historical financial information or if you’re a brand-new startup.
Your financial section should detail:
- Business expenses
Financial projections
Financial statements, break-even point, funding requests, exit strategy, business expenses.
Whether you’ve been in business for one day or 10 years, you have expenses. These expenses might simply be startup costs for new businesses or fixed and variable costs for veteran businesses.
Take a look at some common business expenses you may need to include in the financial section of business plan:
- Licenses and permits
- Cost of goods sold
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Payroll costs (e.g., salaries and taxes)
- Utilities
- Equipment
- Supplies
- Advertising
Write down each type of expense and amount you currently have as well as expenses you predict you’ll have. Use a consistent time period (e.g., monthly costs).
Indicate which expenses are fixed (unchanging month-to-month) and which are variable (subject to changes).
How much do you anticipate earning from sales each month?
If you operate an existing business, you can look at previous monthly revenue to make an educated estimate. Take factors into consideration, like seasonality and economic ups and downs, when basing projections on previous cash flow.
Coming up with your financial projections may be a bit trickier if you are a startup. After all, you have nothing to go off of. Come up with a reasonable monthly goal based on things like your industry, competitors, and the market. Hint : Look at your market analysis section of the business plan for guidance.
A financial statement details your business’s finances. The three main types of financial statements are income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Income statements summarize your business’s income and expenses during a period of time (e.g., a month). This document shows whether your business had a net profit or loss during that time period.
Cash flow statements break down your business’s incoming and outgoing money. This document details whether your company has enough cash on hand to cover expenses.
The balance sheet summarizes your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Balance sheets help with debt management and business growth decisions.
If you run a startup, you can create “pro forma financial statements,” which are statements based on projections.
If you’ve been in business for a bit, you should have financial statements in your records. You can include these in your business plan. And, include forecasted financial statements.

You’re just in luck. Check out our FREE guide, Use Financial Statements to Assess the Health of Your Business , to learn more about the different types of financial statements for your business.
Potential investors want to know when your business will reach its break-even point. The break-even point is when your business’s sales equal its expenses.
Estimate when your company will reach its break-even point and detail it in the financial section of business plan.
If you’re looking for financing, detail your funding request here. Include how much you are looking for, list ideal terms (e.g., 10-year loan or 15% equity), and how long your request will cover.
Remember to discuss why you are requesting money and what you plan on using the money for (e.g., equipment).
Back up your funding request by emphasizing your financial projections.
Last but not least, your financial section should also discuss your business’s exit strategy. An exit strategy is a plan that outlines what you’ll do if you need to sell or close your business, retire, etc.
Investors and lenders want to know how their investment or loan is protected if your business doesn’t make it. The exit strategy does just that. It explains how your business will make ends meet even if it doesn’t make it.
When you’re working on the financial section of business plan, take advantage of your accounting records to make things easier on yourself. For organized books, try Patriot’s online accounting software . Get your free trial now!
Stay up to date on the latest accounting tips and training
You may also be interested in:
Need help with accounting? Easy peasy.
Business owners love Patriot’s accounting software.
But don’t just take our word…

Explore the Demo! Start My Free Trial
Relax—run payroll in just 3 easy steps!
Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support. Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial.

Relax—pay employees in just 3 steps with Patriot Payroll!
Business owners love Patriot’s award-winning payroll software.

Watch Video Demo!
Watch Video Demo
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your startup and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
Projected Balance Sheet
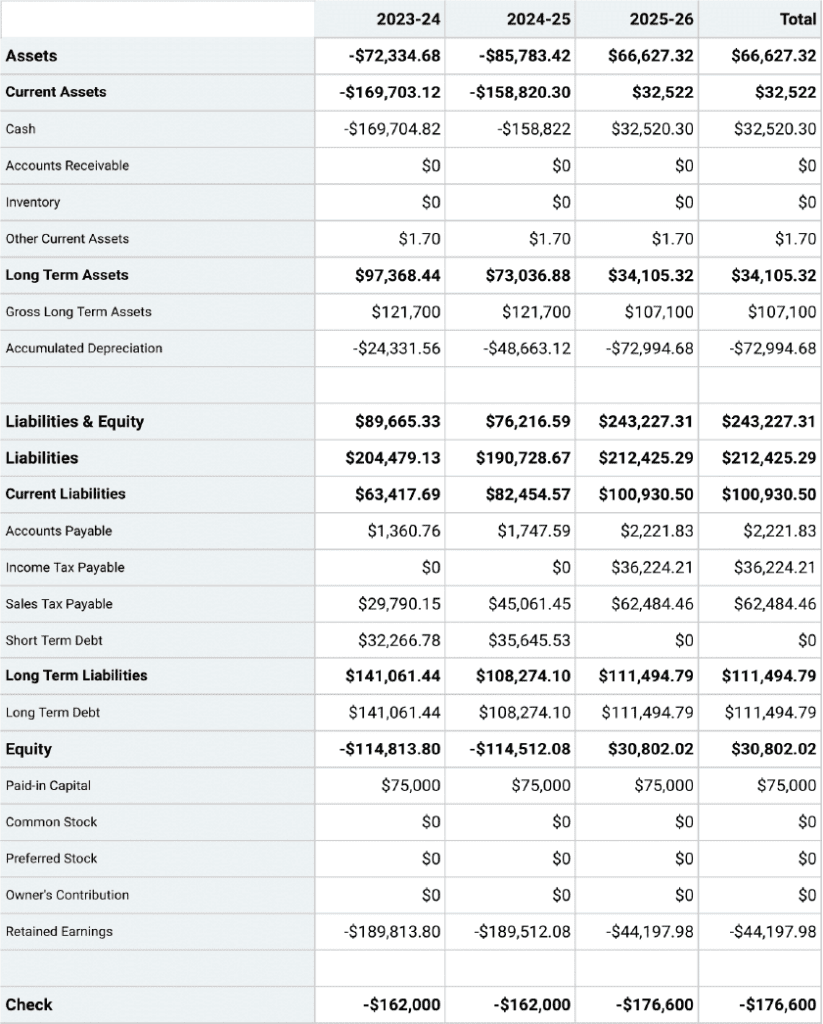
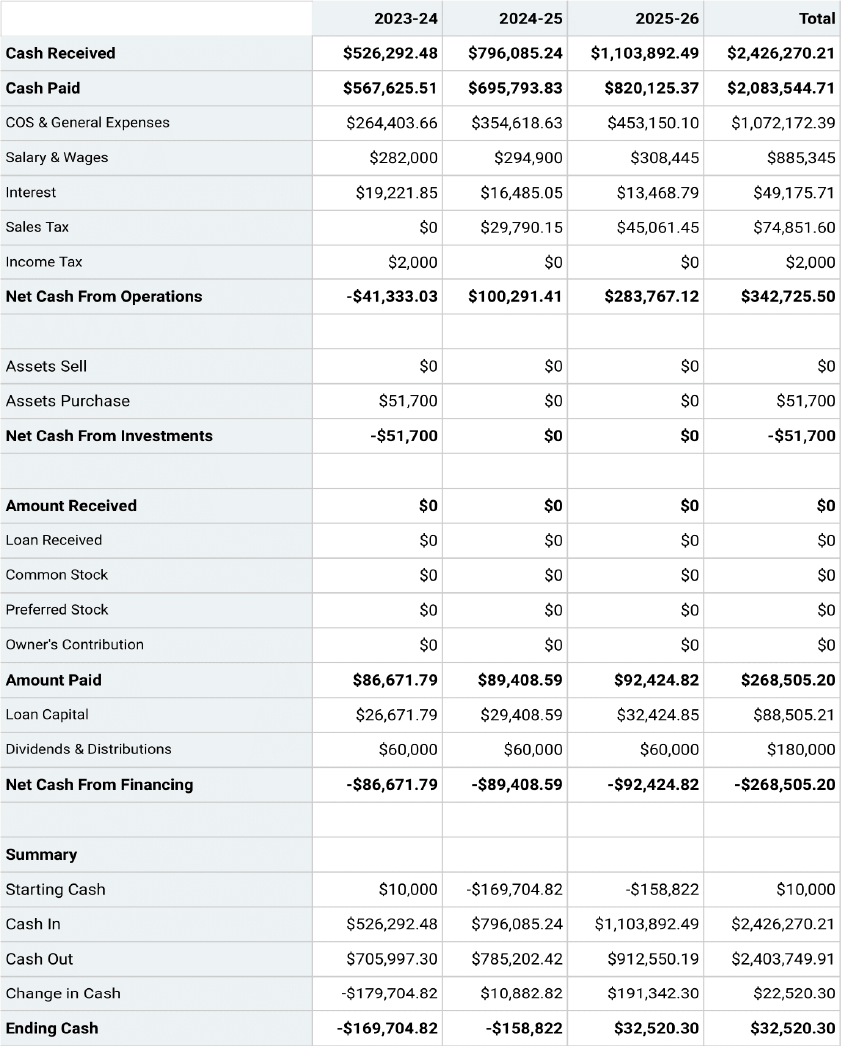
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
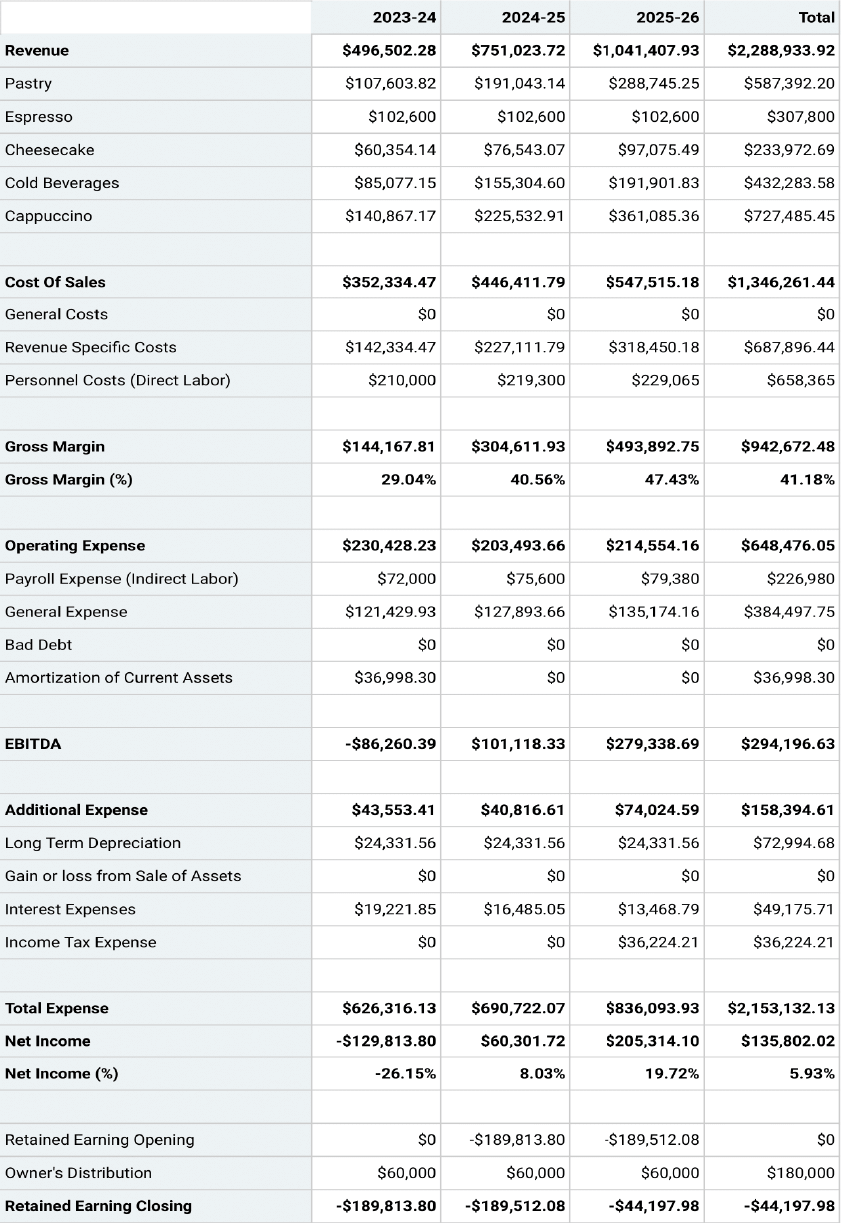
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
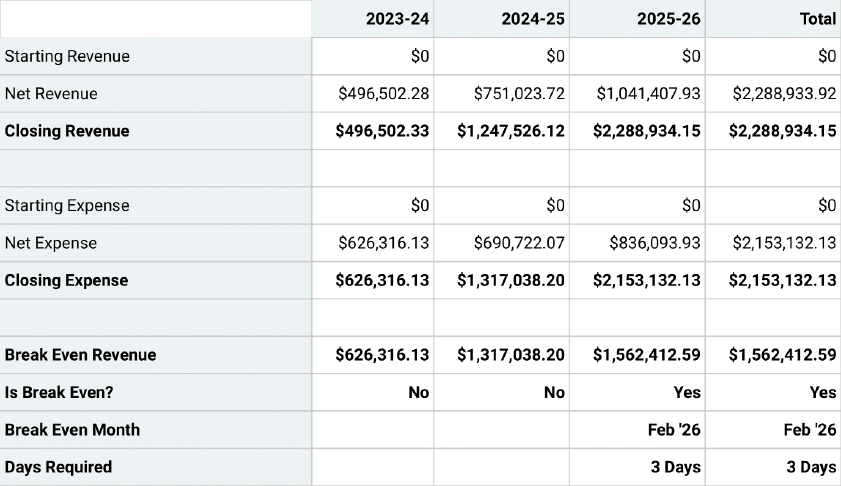
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Franchise Trends
- The Female Founder
- The Roadmap
- The Small Business Show
- U.S. Chamber of Commerce Small Business Update
- Company Culture
- Customer Experience
- Entrepreneurship
- Growth Strategy
- Recruitment
- Small Business Grants
- Social Media
- Contribute Content Request
- Show Appearance Request

Bofta Yimam reveals the power of storytelling in enhancing business visibility…
Scott mautz unveils the secrets to building mental strength, unlocking the power of authenticity on social media – corey perlman, 5 simple steps to earn your sales prospect’s trust — ursula….
- business plan
- small busienss
- balance sheet
How to Complete the Financial Section of Business Plan
A plan intends to explain the business, introduce critical contributors, products and, services and defines the goals for the future. It paints a picture of the founder’s expectations and helps others see their vision. The financial section of the plan provides the proof behind the story. It is the section that investors and lenders are most interested in, and often the first section they read, despite it being near the end of the plan. It also acts as a roadmap and a guide for the direction the company will take into the future.
Financial Section Elements
While it may sound complicated, the financial section of a business plan only contains three documents and a brief explanation of each. It is necessary to prepare an income statement, cash flow projection and a balance sheet either using spreadsheets, or software that does all of the calculations automatically. Before beginning this statement, it’s necessary to gather the following information:
Business Start-Up Expenses
This list of all of the costs associated with getting the business up and running comprises what primarily are one-time fees such as registering the company. Following is only a partial list of possible start-up costs, every business is unique, and the list may, or may not, contain these items and more.
- Business registration fees
- Licensing and permits
- Product inventory
- Deposit on rental property
- Down payment to purchase property
- Down payment on machines and equipment
- Set-up fees for utilities
Business Operating Costs
As the name implies, operating costs are the ongoing expenses that need to be paid to keep the business running. These expenses are usually monthly bills, and for a start-up, estimate six months worth of these costs. A company’s list of operating expenses might include:
- Monthly mortgage payment or rent
- Logistics and distribution
- Marketing and promotion
- Loan paymentsRaw materials
- Office supplies
- Building/vehicle maintenance
The Income Statement
This financial statement details the company’s revenues, expenses, and profit for a set period. Established businesses generated these annually, or semi-annually, based on actual performance. Start-ups with no previous years to look at have to use statistical data within the industry to make reasonable projections. A start-up will also produce monthly versions of this statement to show the forecast of growth. This section will include the data such as:
- Gross revenue (sales, interest income and sales of assets)
- General and administrative expenses (start-up and operating costs)
- Corporate tax rate (expected tax liabilities)
The math is simple here: subtract the expenditures from the revenue, and the remaining number is profit. When put into the proper format, an income statement gives a clear view of the financial viability of a company.
Cash-Flow Projection
This statement shows how you expect cash to flow in to, and out of, your business. It’s an essential internal cash management tool and a source of data that shows what your business’s capital needs will be in the near future. For investors and bank loan officers, it helps determine your creditworthiness and amount you can borrow. The cash-flow projection contains three parts:
- Cash revenues — This part details the incoming cash from sales for specific periods of time, usually monthly. It is an estimate, based upon past performance and future projections for current businesses, and industry averages for start-ups.
- Cash disbursements — Every monthly bill or other expense that is paid out in cash gets listed in this section. As with revenue, these are estimates, either based upon historical data, current data, or industry data.
- Cash flow projection — This merely is a reconciliation of the cash revenues to cash disbursements. Adding the current month’s revenues to the carried-over balance, then subtracting the month’s disbursements creates estimated cash flow.
The Balance Sheet
The final financial statement required for the business plan’s financial section is a balance sheet. This statement is a snapshot of the company’s net worth at a given point in time. Established businesses produce a balance sheet annually. Information from the income statement and cash flow projection are used to complete this statement. It summarizes the business’s financial data into three main categories:
- Assets — This is the total of all of the tangible items that the company owns that hold monetary value. That includes equipment, property, and cash-on-hand, for example.
- Liabilities — This is the total amount of debt that the company owes its creditors. You’ll include every debt, whether recurring, one-time, fixed, or variable.
- Equity — This is merely the difference between the company’s assets, including retained earnings and current earnings, and its liabilities.
Side-Notes and Details
In some cases, it may be necessary to explain details within the financial statements. Denote these instances within the statement and include a brief explanation sheet as an attachment. It may also be useful to add information on the process used to estimate revenues and expenses, which will show interested parties the intent and help them better understand the data.
Don’t Sweat the Process
It’s important to note that the order in which these financial statements is created may vary from the way they are presented here. This is to be expected. In fact, most business plan creators end up going back and forth with these statements as the numbers reveal the business’s financial reality. It paints a crystal clear picture of its economic viability, which can present to a lender, investor, or shareholder with confidence.
All of these financial documents can be created by using accounting and business software readily available online. Even so, some people aren’t entirely comfortable creating financial statements for their business plan, and outsource this critical task to a professional. Even the largest corporations struggle with financial planning and reporting, and they often hire the job out to someone more qualified. It’s merely a matter of making sure that the data is accurate, easy to track, and based on sound accounting practices.

Related Articles
Bofta yimam reveals the power of storytelling in enhancing business visibility and authenticity.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .
Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
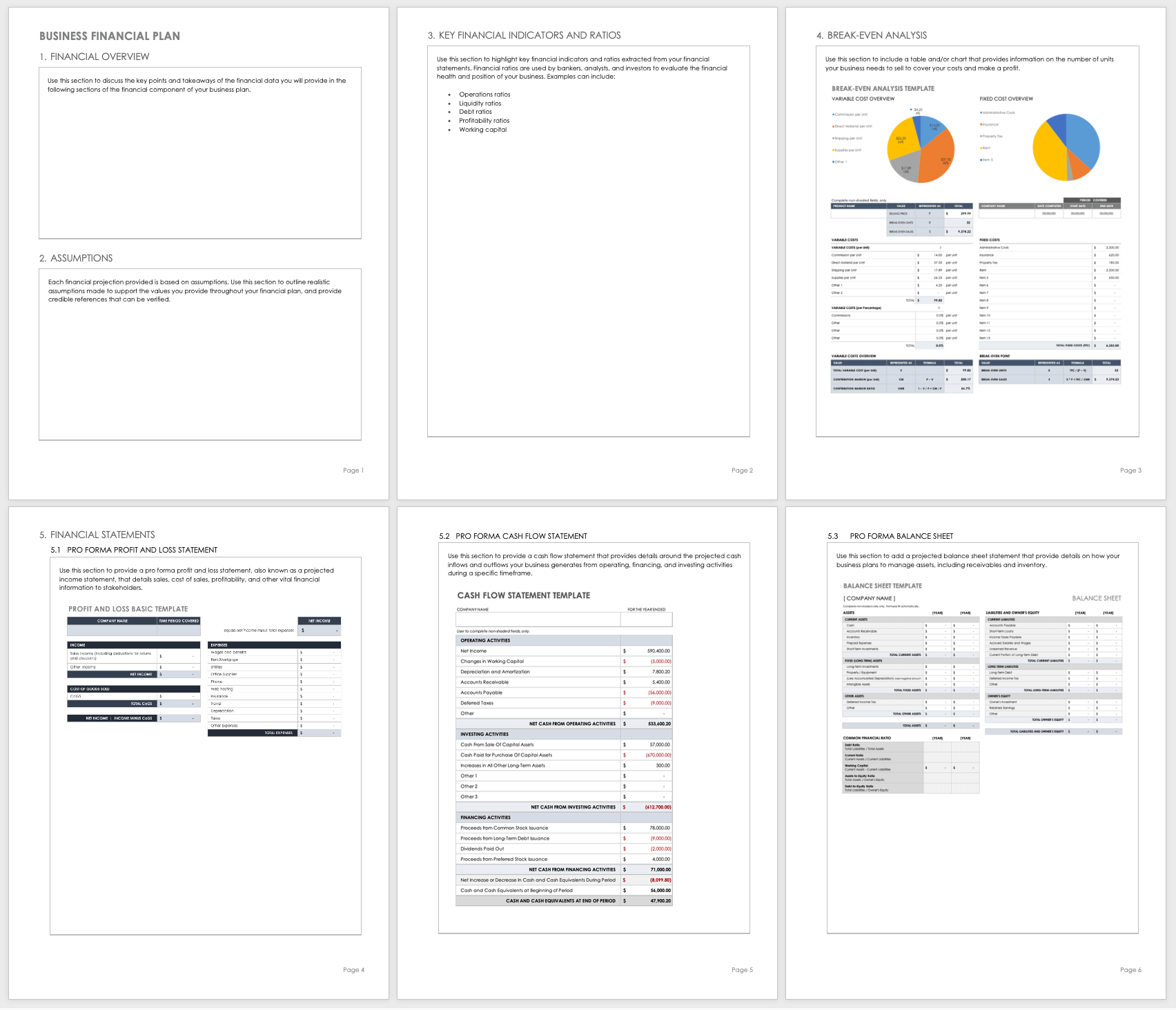
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
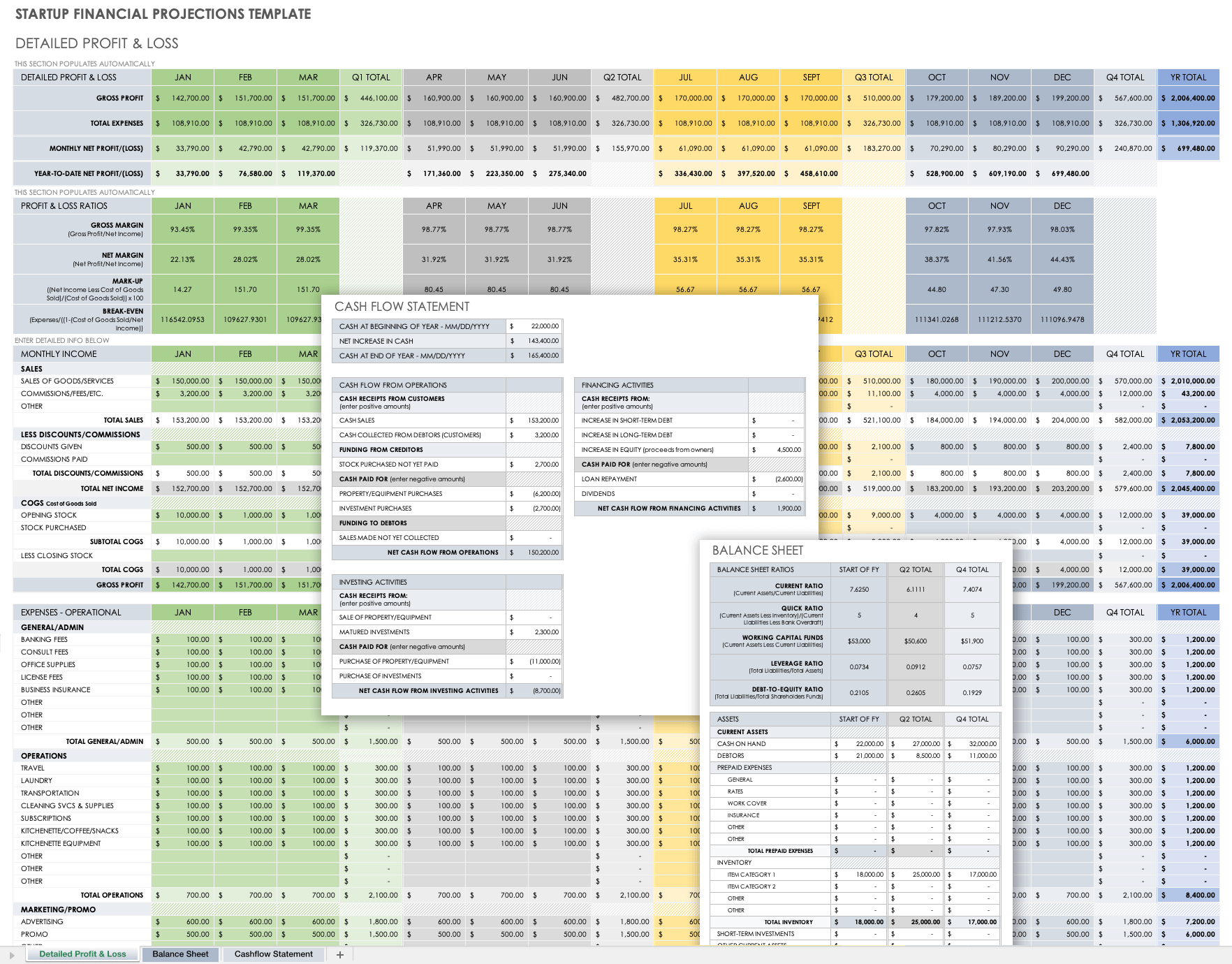
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
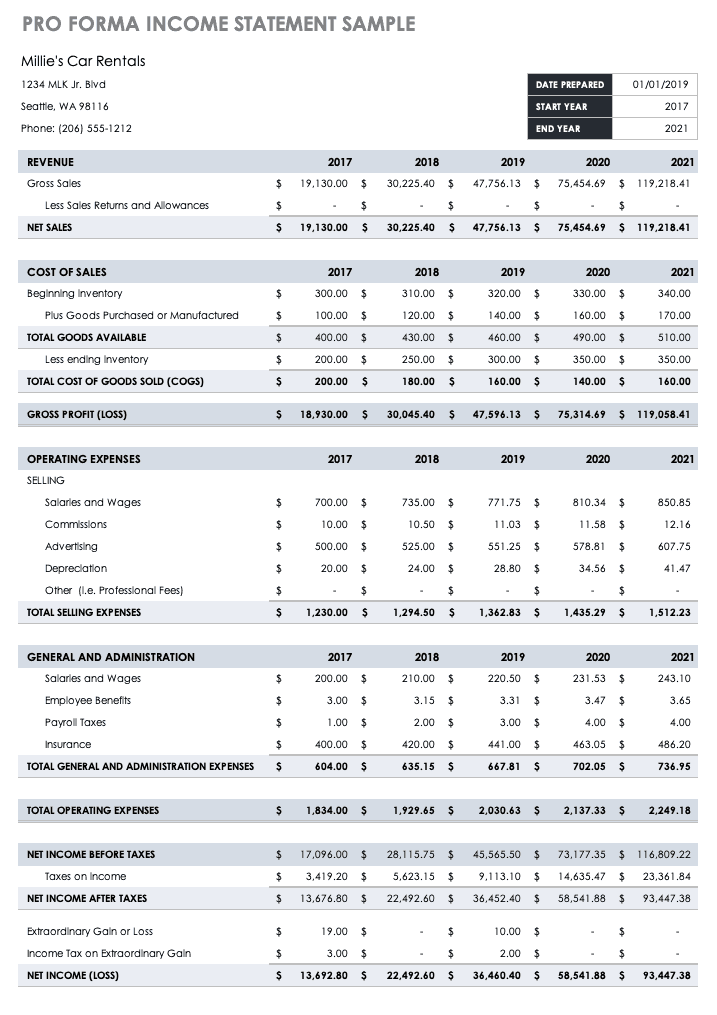
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
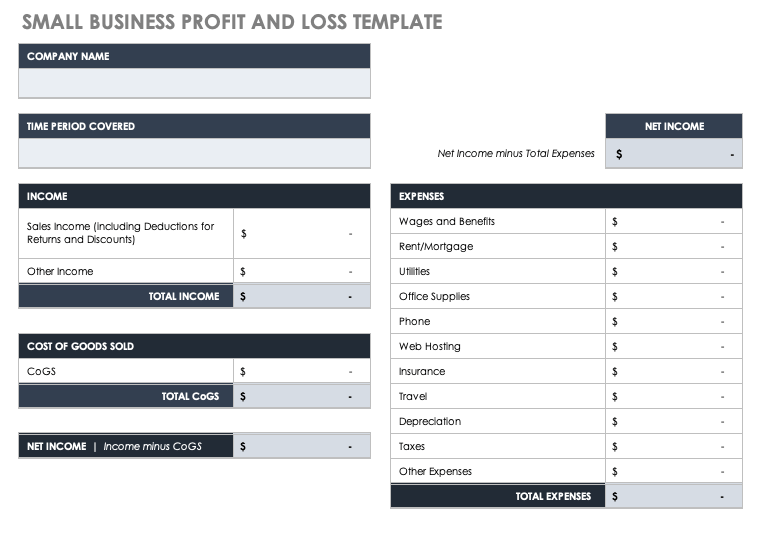
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
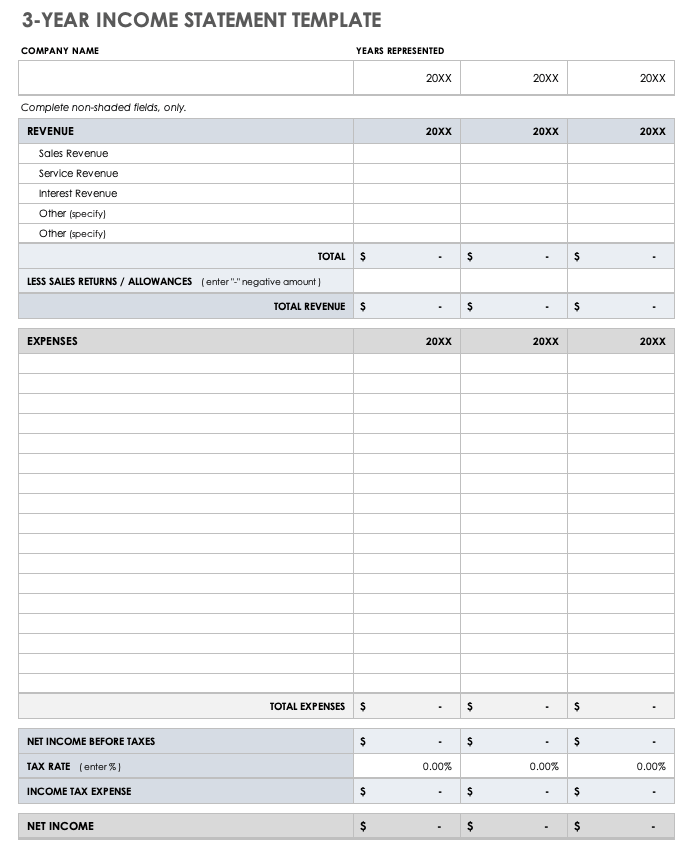
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
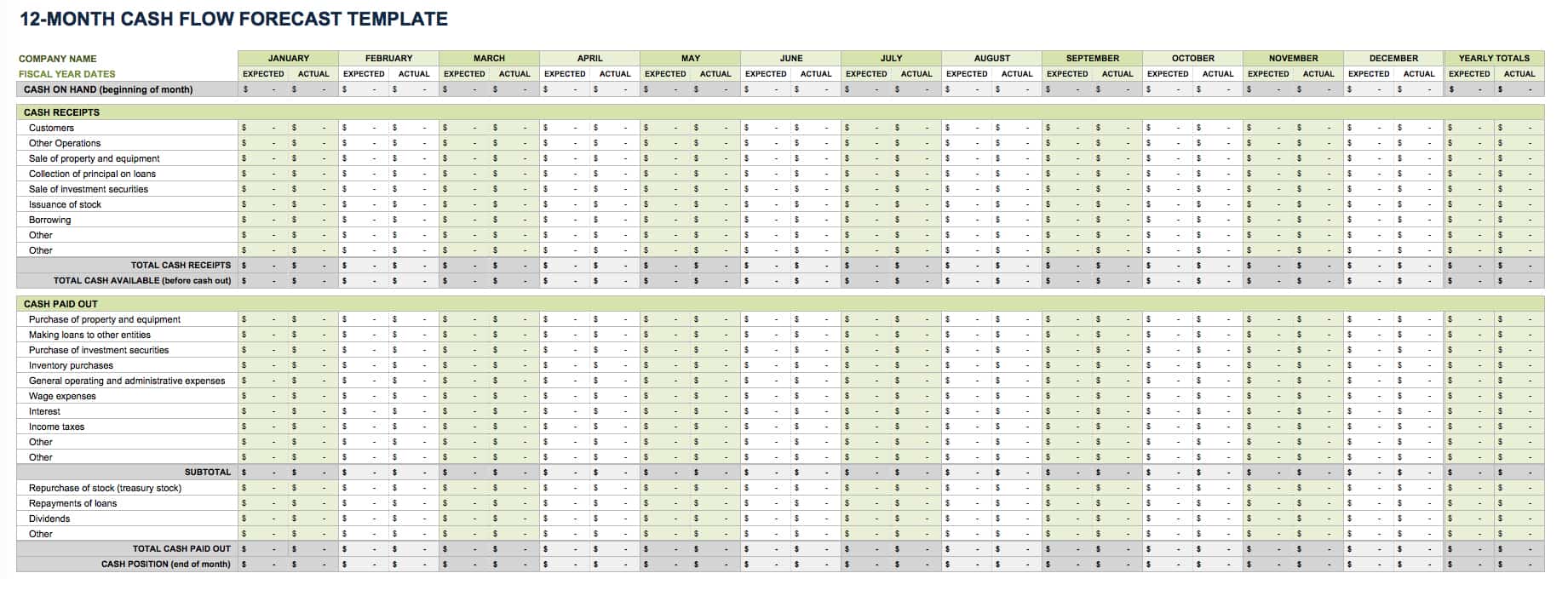
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
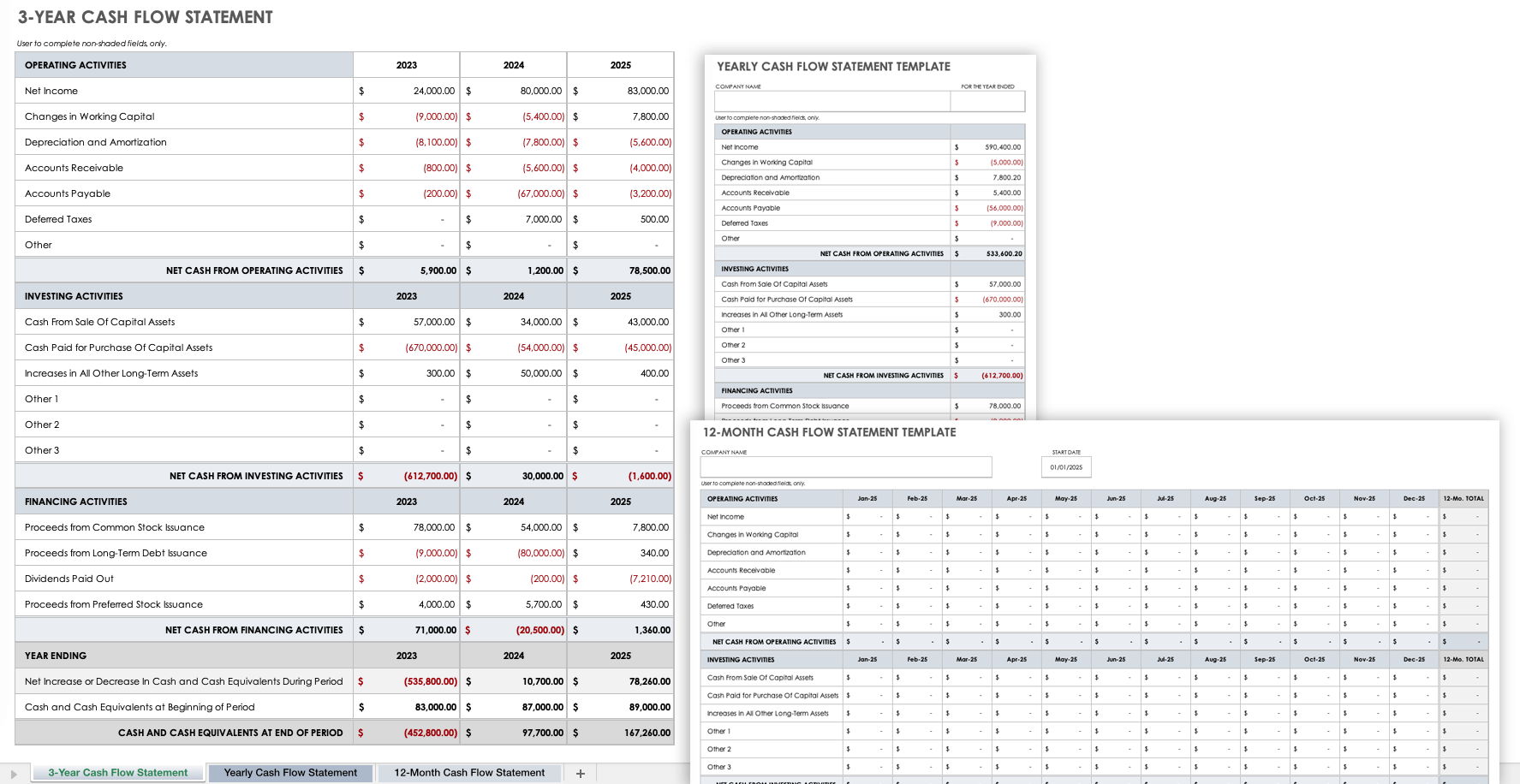
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
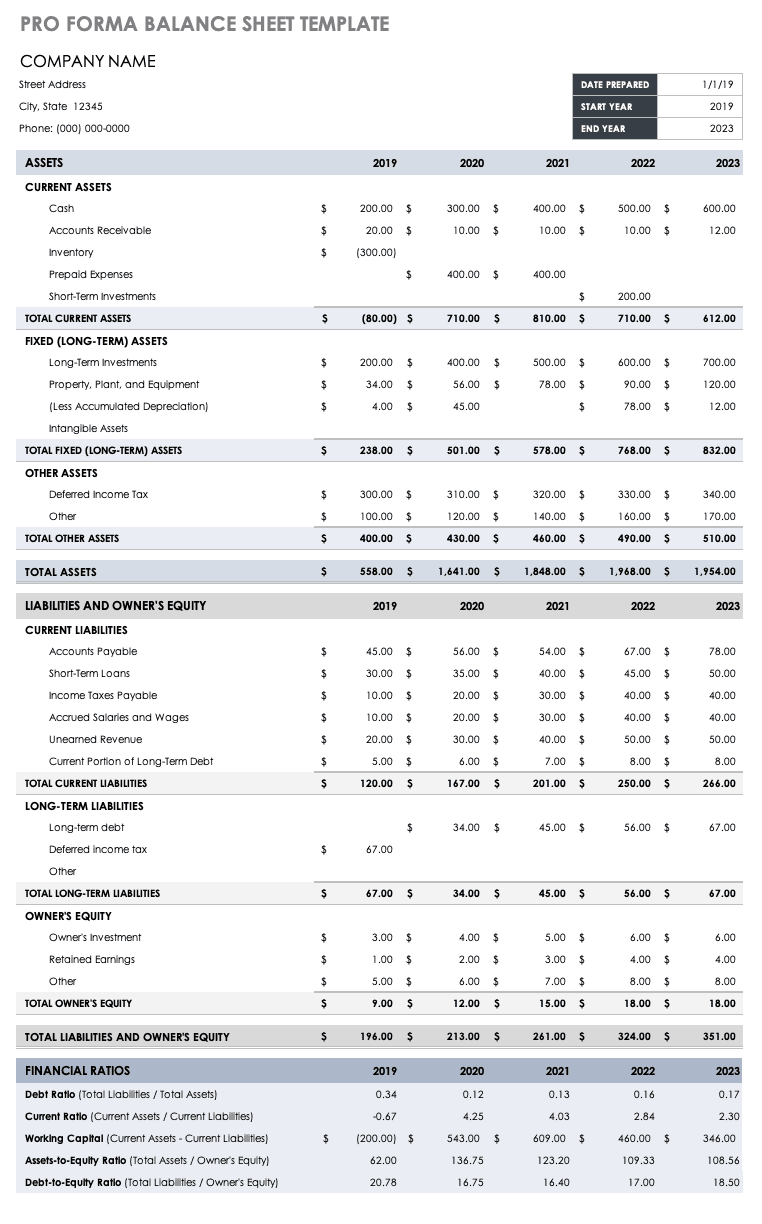
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
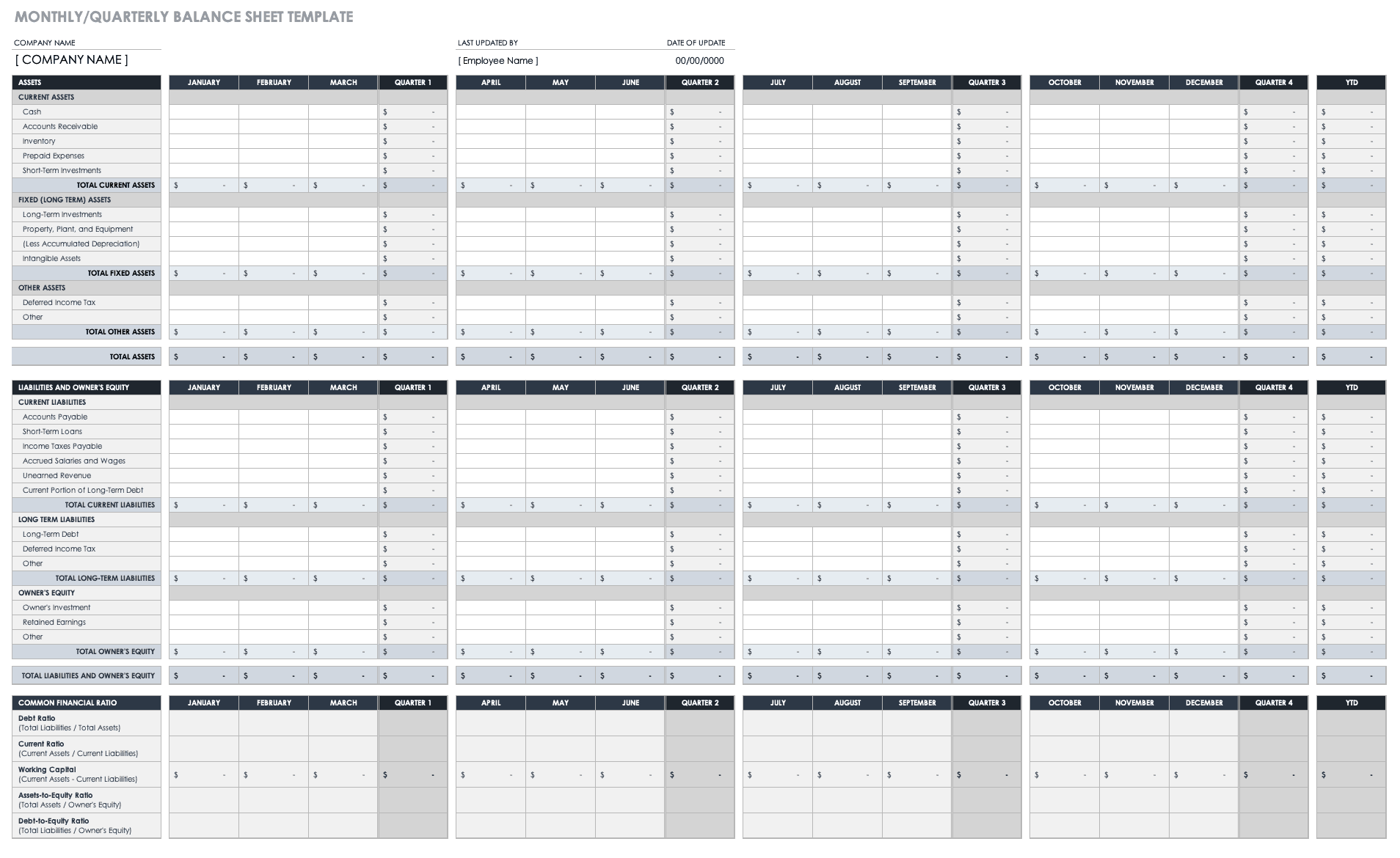
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
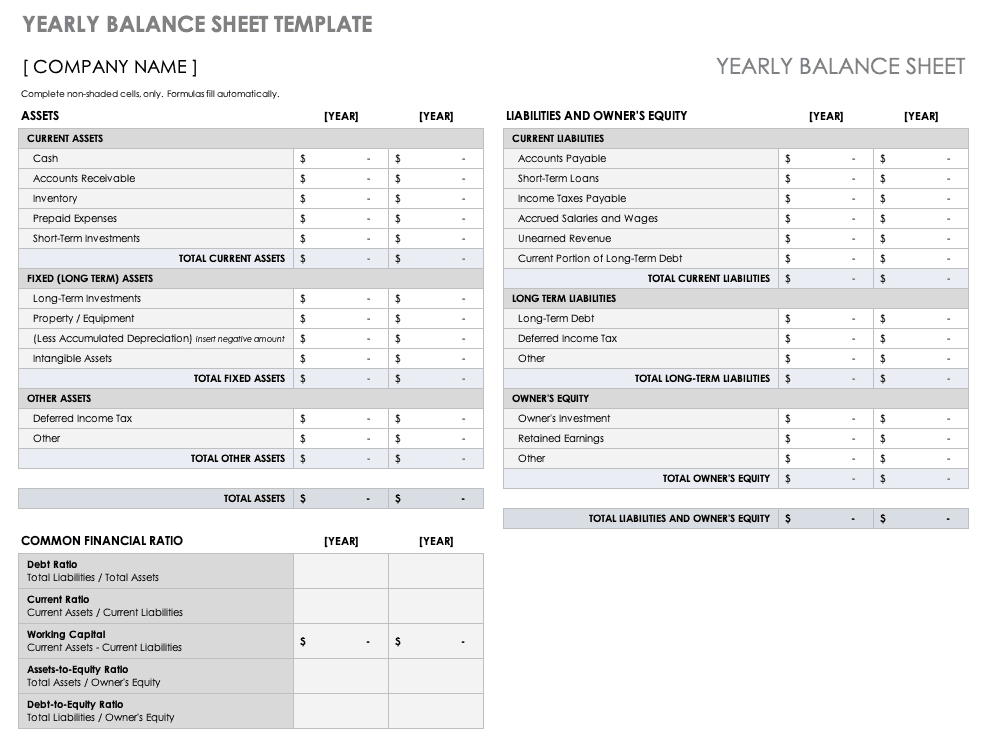
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
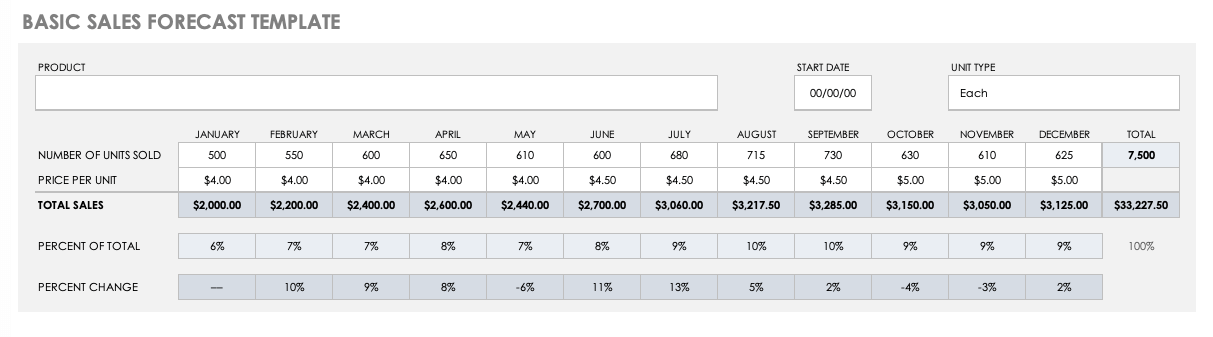
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
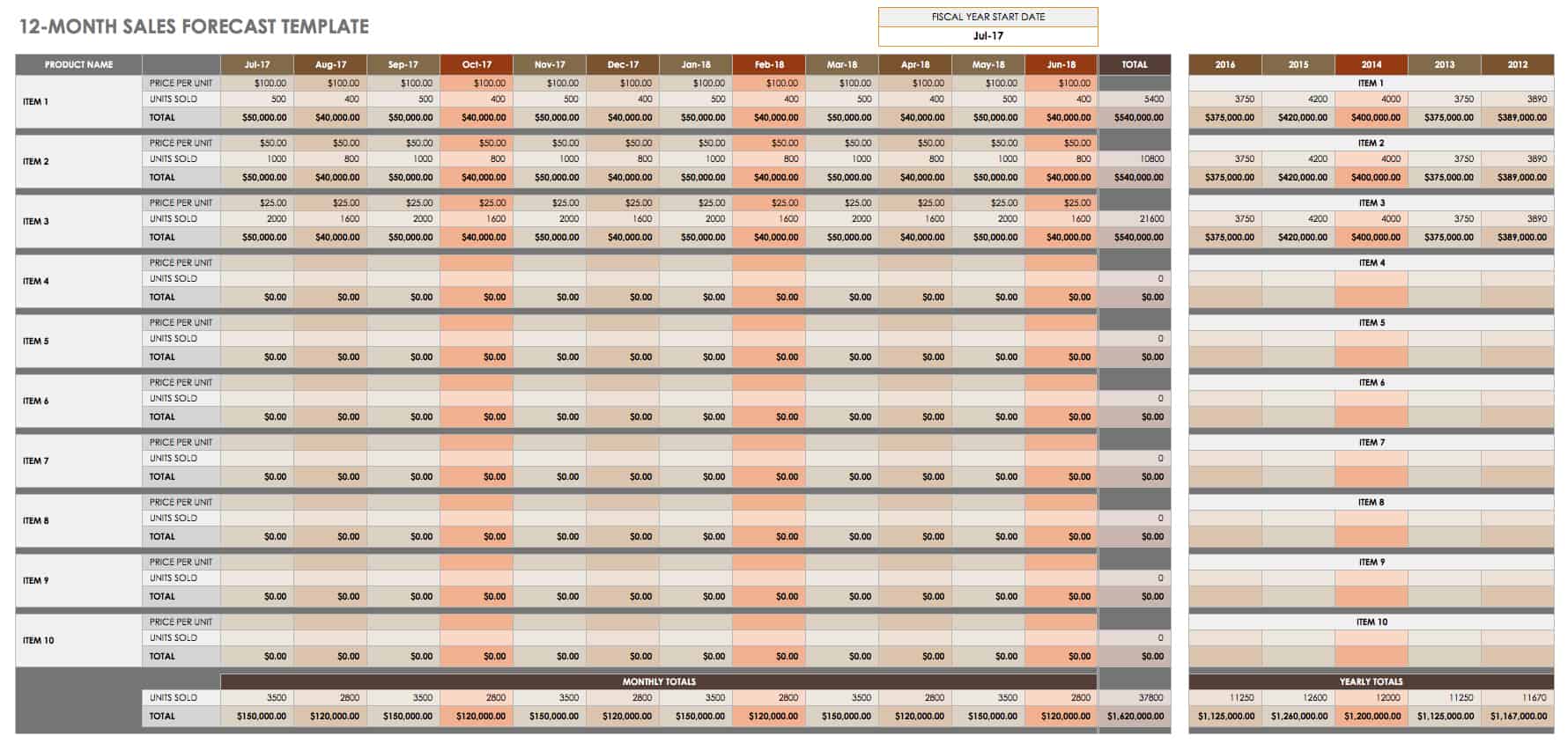
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
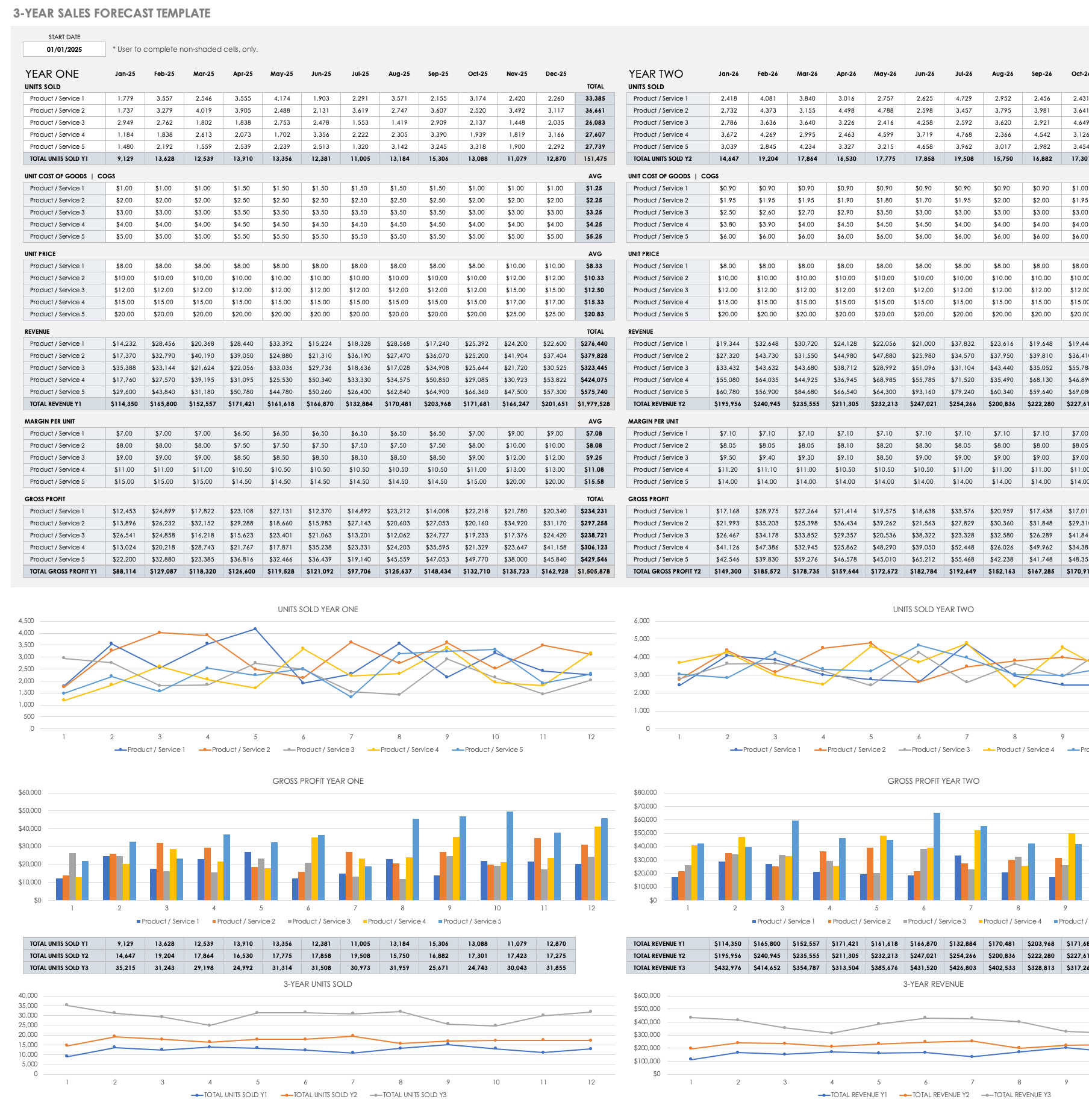
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
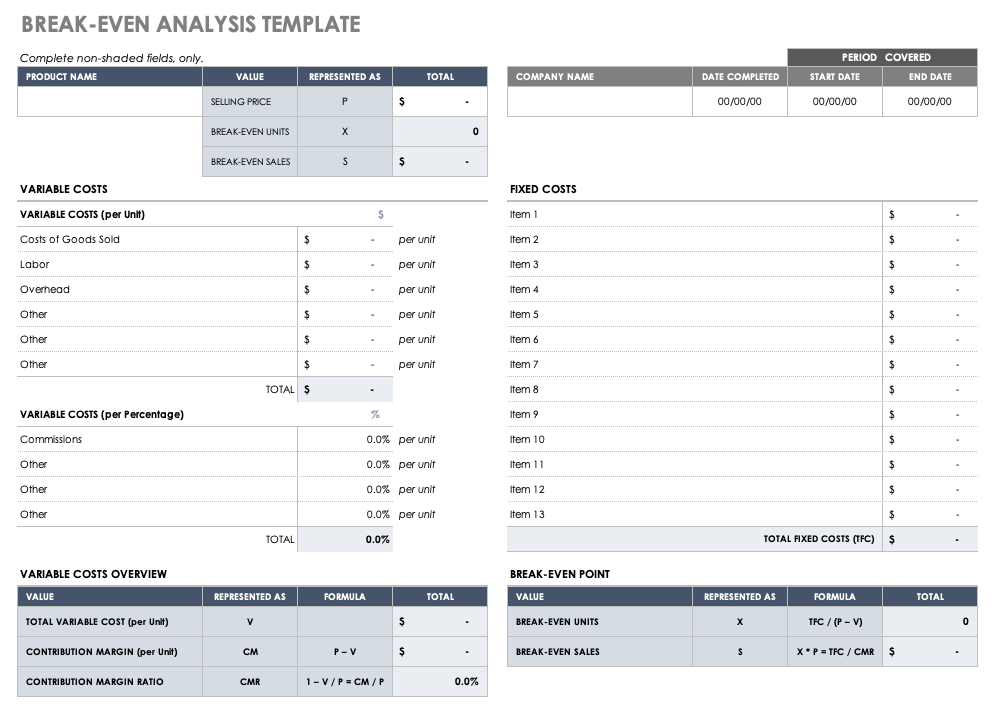
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
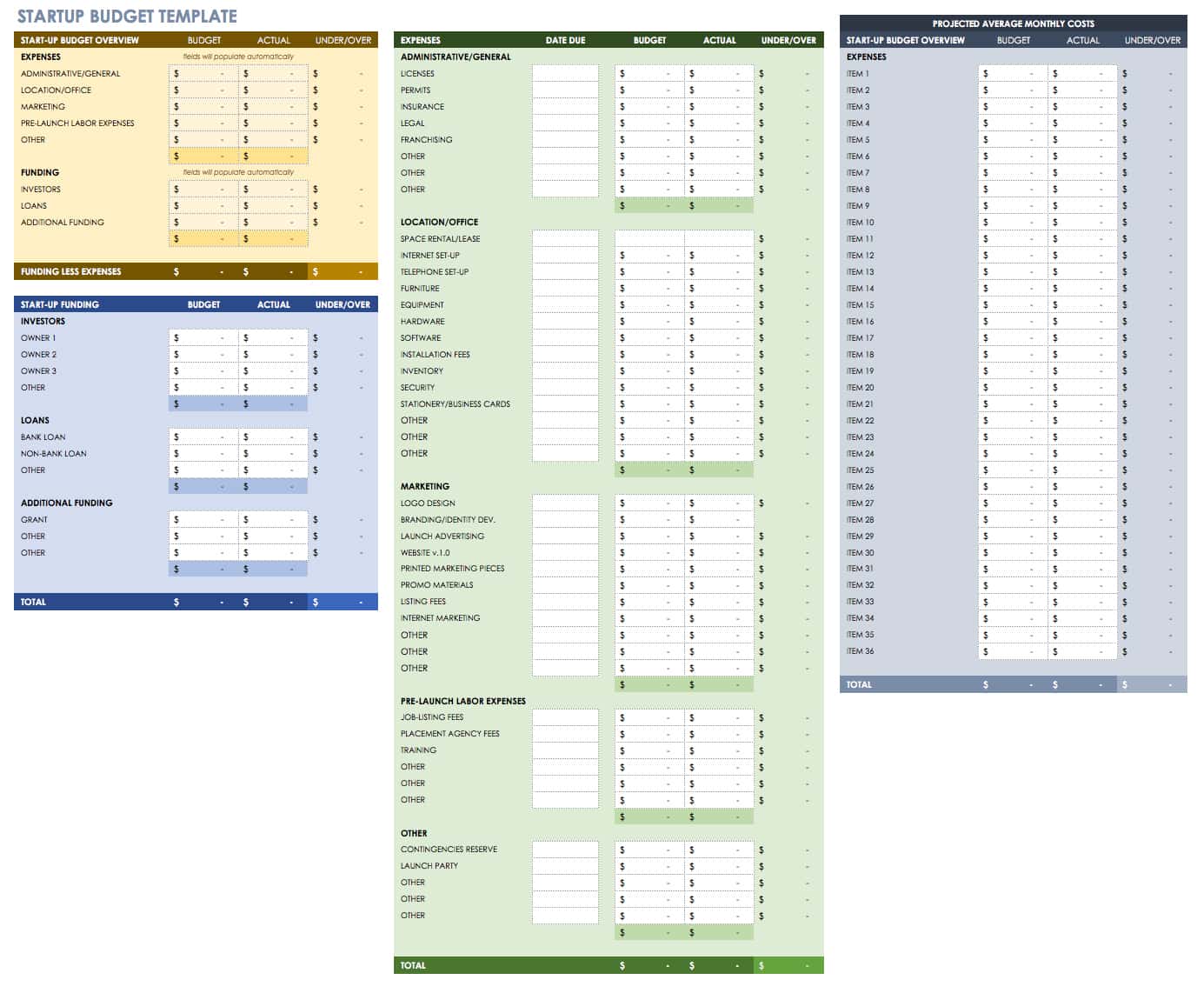
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
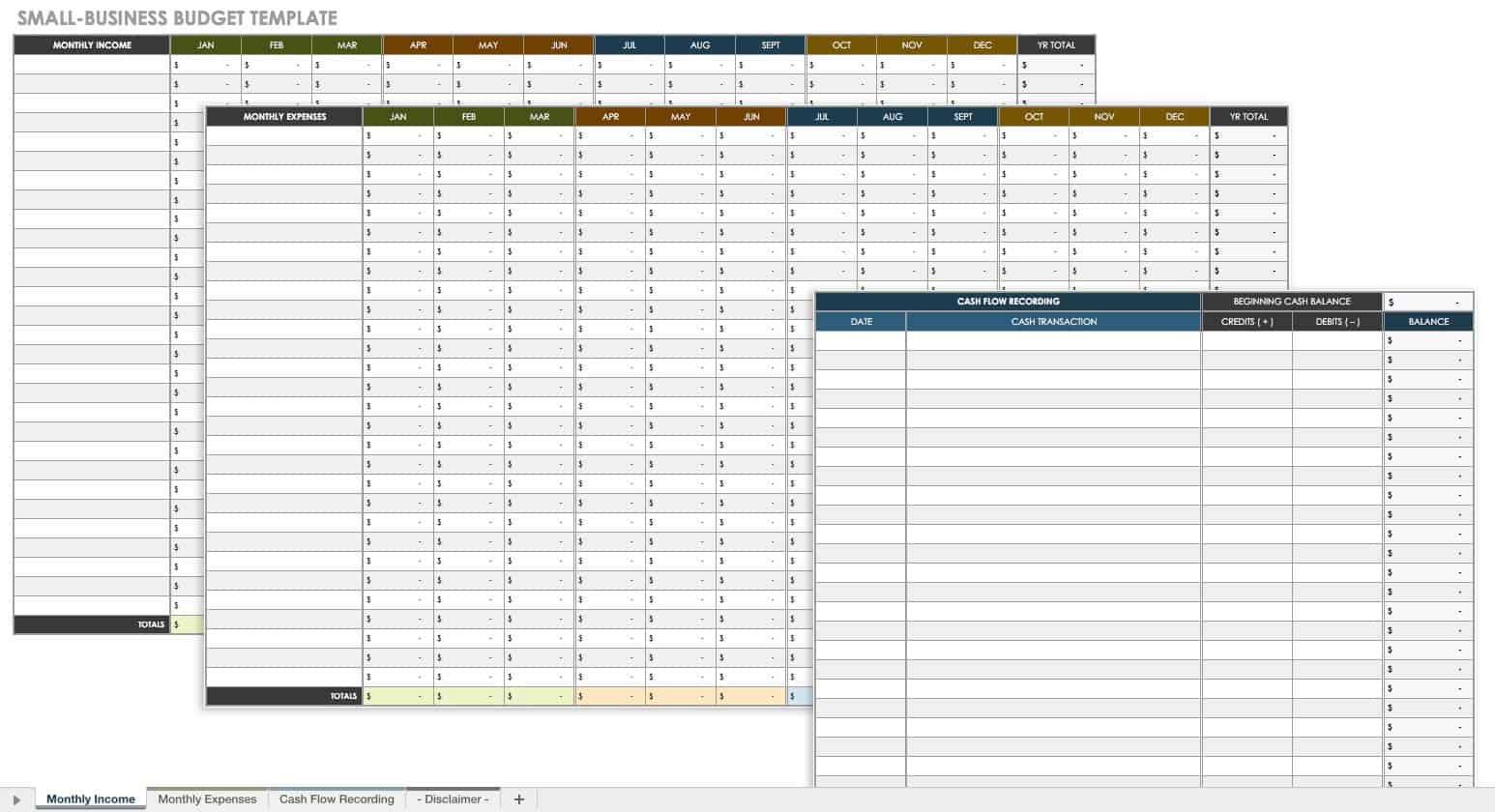
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
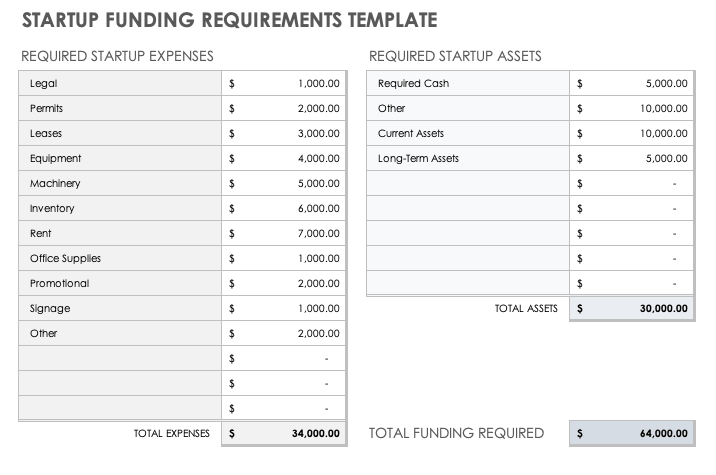
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
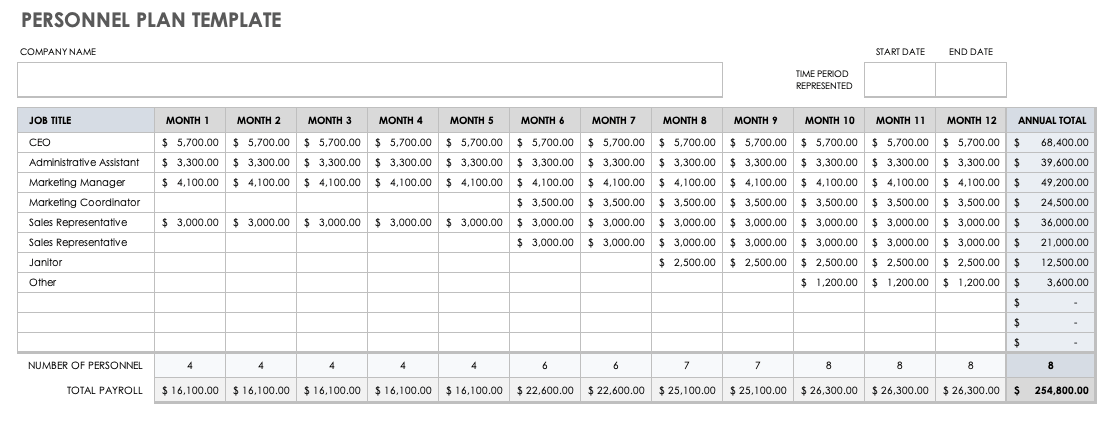
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Simple Business Plan Template for Startups, Small Businesses & Entrepreneurs
Financial plan, what is a financial plan.
A business’ financial plan is the part of your business plan that details how your company will achieve its financial goals. It includes information on your company’s projected income, expenses, and cash flow in the form of a 5-Year Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. The plan should also detail how much funding your company needs and the key uses of these funds.
The financial plan is an important part of the business plan, as it provides a framework for making financial decisions. It can be used to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Why Your Financial Plan is Important
The financial section of your business plan details the financial implications of running your company. It is important for the following two reasons:
Making Informed Decisions
A financial plan provides a framework for making decisions about how to use your money. It can help you determine whether or not you can afford to make a major purchase, such as a new piece of equipment.
It can also help you decide how much money to reinvest in your business, and how much to save for paying taxes.
A financial plan is like a roadmap for your business. It can help you track your progress and make adjustments as needed. The plan can also help you identify potential problems before they arise.
For example, if your sales are below your projections, you may need to adjust your budget accordingly.
Your financial plan helps you understand how much outside funding is required, when your levels of cash might fall low, and what sales and other goals you need to hit to become financially viable.
Securing Funding
This section of your plan is absolutely critical if you are trying to secure funding. Your financial plan should include information on your revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
This information will help potential investors or lenders understand your business’s financial situation and decide whether or not to provide funding.
Include a detailed description of how you plan to use the funds you are requesting. For example, what are the key uses of the funds (e.g., purchasing equipment, paying staff, etc.) and what are the future timings of these financial outlays.
The financial information in your business plan should be realistic and accurate. Do not overstate your projected revenues or underestimate your expenses. This can lead to problems down the road.
Potential investors and lenders will be very interested in your future projections since it indicates whether you will be able to repay your loans and/or provide a nice return on investment (ROI) upon exit.
Financial Plan Template: 4 Components to Include in Your Financial Plan
The financial section of a business plan should have the following four sub-sections:
Revenue Model
Here you will detail how your company generates revenues. Oftentimes this is very straightforward, for instance, if you sell products. Other times, your answer might be more complex, such as if you’re selling subscriptions (particularly at different price/service levels) or if you are selling multiple products and services.
Financial Overview & Highlights
In developing your financial plan, you need to create full financial forecasts including the following financial statements.
5-Year Income Statement / Profit and Loss Statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), shows how much revenue your business has generated over a specific period of time, and how much of that revenue has turned into profits. The statement includes your company’s revenues and expenses for a given time period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It can also show your company’s net income, which is the amount of money your company has made after all expenses have been paid.
5-Year Balance Sheet
A balance sheet shows a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. The balance sheet lists a company’s assets (what it owns), its liabilities (what it owes), and its equity (the difference between its assets and its liabilities).
The balance sheet is important because it shows a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. A strong balance sheet indicates that a company has the resources it needs to grow and expand. A weak balance sheet, on the other hand, may indicate that a company is struggling to pay its bills and may be at risk of bankruptcy.
5-Year Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement shows how much cash a company has on hand, as well as how much cash it is generating (or losing) over a specific period of time. The statement includes both operating and non-operating activities, such as revenue from sales, expenses, investing activities, and financing activities.
While your full financial projections will go in your Appendix, highlights of your financial projections will go in the Financial Plan section.
These highlights include your Total Revenue, Direct Expenses, Gross Profit, Other Expenses, EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization), and Net Income projections. Also include key assumptions used in creating these future projections such as revenue and cost growth rates.
Funding Requirements/Use of Funds
In this section, you will detail how much outside funding you require, if any, and the core uses of these funds.
For example, detail how much of the funding you need for:
- Product Development
- Product Manufacturing
- Rent or Office/Building Build-Out
Exit Strategy
If you are seeking equity capital, you need to explain your “exit strategy” here or how investors will “cash out” from their investment.
To add credibility to your exit strategy, conduct market research. Specifically, find other companies in your market who have exited in the past few years. Mention how they exited and the amounts of the exit (e.g., XYZ Corp. bought ABC Corp. for $Y).
Business Plan Financial Plan FAQs
What is a financial plan template.
A financial plan template is a pre-formatted spreadsheet that you can use to create your own financial plan. The financial plan template includes formulas that will automatically calculate your revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections.
How Can I Download a Financial Plan Template?
Download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template which includes a complete financial plan template and more to help you write a solid business plan in hours.
How Do You Make Realistic Assumptions in Your Business Plan?
When forecasting your company’s future, you need to make realistic assumptions. Conduct market research and speak with industry experts to get a better idea of the key trends affecting your business and realistic growth rates.
You should also use historical data to help inform your projections. For example, if you are launching a new product, use past sales data to estimate how many units you might sell in Year 1, Year 2, etc.
Learn more about how to make the appropriate financial assumptions for your business plan.
How Do You Make the Proper Financial Projections for Your Business Plan?
Your business plan’s financial projections should be based on your business model and your market research. The goal is to make as realistic and achievable projections as possible.
To create a good financial projection, you need to understand your revenue model and your target market. Once you have this information, you can develop assumptions around revenue growth, cost of goods sold, margins, expenses, and other key metrics.
Once you have your assumptions set, you can plug them into a financial model to generate your projections.
Learn more about how to make the proper financial projections for your business plan.
What Financials Should Be Included in a Business Plan?
There are a few key financials that should be included in a traditional business plan format. These include the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement.
Income Statements, also called Profit and Loss Statements, will show your company’s expected income and expense projections over a specific period of time (usually 1 year, 3 years, or 5 years). Balance Sheets will show your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Cash Flow Statements will show how much cash your company has generated and used over a specific period of time.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template includes a complete financial plan template to easily create these financial statements and more so you can write a great business plan in hours.
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE OUTLINE
- Business Plan Template Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
- 10. Appendix
- Business Plan Summary
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Writing a Business Plan—Financial Projections
Spell out your financial forecast in dollars and sense
Creating financial projections for your startup is both an art and a science. Although investors want to see cold, hard numbers, it can be difficult to predict your financial performance three years down the road, especially if you are still raising seed money. Regardless, short- and medium-term financial projections are a required part of your business plan if you want serious attention from investors.
The financial section of your business plan should include a sales forecast , expenses budget , cash flow statement , balance sheet , and a profit and loss statement . Be sure to follow the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board , a private-sector organization responsible for setting financial accounting and reporting standards in the U.S. If financial reporting is new territory for you, have an accountant review your projections.
Sales Forecast
As a startup business, you do not have past results to review, which can make forecasting sales difficult. It can be done, though, if you have a good understanding of the market you are entering and industry trends as a whole. In fact, sales forecasts based on a solid understanding of industry and market trends will show potential investors that you've done your homework and your forecast is more than just guesswork.
In practical terms, your forecast should be broken down by monthly sales with entries showing which units are being sold, their price points, and how many you expect to sell. When getting into the second year of your business plan and beyond, it's acceptable to reduce the forecast to quarterly sales. In fact, that's the case for most items in your business plan.
Expenses Budget
What you're selling has to cost something, and this budget is where you need to show your expenses. These include the cost to your business of the units being sold in addition to overhead. It's a good idea to break down your expenses by fixed costs and variable costs. For example, certain expenses will be the same or close to the same every month, including rent, insurance, and others. Some costs likely will vary month by month such as advertising or seasonal sales help.
Cash Flow Statement
As with your sales forecast, cash flow statements for a startup require doing some homework since you do not have historical data to use as a reference. This statement, in short, breaks down how much cash is coming into your business on a monthly basis vs. how much is going out. By using your sales forecasts and your expenses budget, you can estimate your cash flow intelligently.
Keep in mind that revenue often will trail sales, depending on the type of business you are operating. For example, if you have contracts with clients, they may not be paying for items they purchase until the month following delivery. Some clients may carry balances 60 or 90 days beyond delivery. You need to account for this lag when calculating exactly when you expect to see your revenue.
Profit and Loss Statement
Your P&L statement should take the information from your sales projections, expenses budget, and cash flow statement to project how much you expect in profits or losses through the three years included in your business plan. You should have a figure for each individual year as well as a figure for the full three-year period.
Balance Sheet
You provide a breakdown of all of your assets and liabilities in the balances sheet. Many of these assets and liabilities are items that go beyond monthly sales and expenses. For example, any property, equipment, or unsold inventory you own is an asset with a value that can be assigned to it. The same goes for outstanding invoices owed to you that have not been paid. Even though you don't have the cash in hand, you can count those invoices as assets. The amount you owe on a business loan or the amount you owe others on invoices you've not paid would count as liabilities. The balance is the difference between the value of everything you own vs. the value of everything you owe.
Break-Even Projection
If you've done a good job projecting your sales and expenses and inputting the numbers into a spreadsheet, you should be able to identify a date when your business breaks even—in other words, the date when you become profitable, with more money coming in than going out. As a startup business, this is not expected to happen overnight, but potential investors want to see that you have a date in mind and that you can support that projection with the numbers you've supplied in the financial section of your business plan.
Additional Tips
When putting together your financial projections, keep some general tips in mind:
- Get comfortable with spreadsheet software if you aren't already. It is the starting point for all financial projections and offers flexibility, allowing you to quickly change assumptions or weigh alternative scenarios. Microsoft Excel is the most common, and chances are you already have it on your computer. You can also buy special software packages to help with financial projections.
- Prepare a five-year projection . Don’t include this one in the business plan, since the further into the future you project, the harder it is to predict. However, have the projection available in case an investor asks for it.
- Offer two scenarios only . Investors will want to see a best-case and worst-case scenario, but don’t inundate your business plan with myriad medium-case scenarios. They likely will just cause confusion.
- Be reasonable and clear . As mentioned before, financial forecasting is as much art as science. You’ll have to assume certain things, such as your revenue growth, how your raw material and administrative costs will grow, and how effective you’ll be at collecting on accounts receivable. It’s best to be realistic in your projections as you try to recruit investors. If your industry is going through a contraction period and you’re projecting revenue growth of 20 percent a month, expect investors to see red flags.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
First Steps: Writing the Financials Section of Your Business Plan This quick guide offers tips that will help you create the financials section for your business plan.
By The Staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. • Jan 4, 2015
In their book Write Your Business Plan , the staff of Entrepreneur Media, Inc. offer an in-depth understanding of what's essential to any business plan, what's appropriate for your venture, and what it takes to ensure success. In this edited excerpt, the authors outline what type of information you should include in the financials section of your business plan.
Financial data is always at the back of the business plan, but that doesn't mean it's any less important than such up-front material as the description of the business concept and the management team. Astute investors look carefully at the charts, tables, formulas and spreadsheets in the financial section because they know this information is like the pulse, respiration rate and blood pressure in a human being—it shows the condition of the patient. In fact, you'll find many potential investors taking a quick peak at the numbers before reading the plan.
Financial statements come in threes: income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Taken together they provide an accurate picture of a company's current value, plus its ability to pay its bills today and earn a profit going forward. This information is very important to business plan readers.
You can typically gather information and use Excel or another financial program to create your spreadsheets. You'll also find them available in most business plan software; these programs also do the calculations.
Income statement.
An income statement shows whether you're making any money. It adds up all your revenue from sales and other sources, subtracts all your costs, and comes up with the net income figure, also known as the bottom line.
Income statements are called various names—profit and loss statement (P&L) and earnings statement are two common alternatives. They can get pretty complicated in their attempt to capture sources of income, such as interest, and expenses, such as depreciation. But the basic idea is pretty simple: If you subtract costs from income, what you have left is profit.
To figure your income statement, you need to gather a bunch of numbers, including your gross revenue, which is made up of sales and any income from interest or sales of assets; your sales, general and administrative (SG&A) expenses; what you paid out in interest and dividends, if anything; and your corporate tax rate. If you have those, you're ready to go.
If you're a startup and don't have any prior years' figures to look at, look for statistics about other businesses within your industry. The most important question to ask is: What has been the experience of similar companies? If you know that car dealers across the nation have averaged 12 percent annual sales gains, that's a good starting point for figuring your company's projections.
Balance sheet.
If the income sheet shows what you're earning, the balance sheet shows what you're worth. A balance sheet can help an investor see that a company owns valuable assets that don't show up on the income statement or that it may be profitable but is heavily in debt. It adds up everything your business owns, subtracts everything the business owes, and shows the difference as the net worth of the business.
Actually, accountants put it differently and, of course, use different names. The things you own are called assets. The things you owe money on are called liabilities. And net worth is referred to as equity.
A balance sheet shows your condition on a given date, usually the end of your fiscal year. Sometimes balance sheets are compared. That is, next to the figures for the end of the most recent year, you place the entries for the end of the prior period. This gives you a snapshot of how and where your financial position has changed.
A balance sheet also places a value on the owner's equity in the business. When you subtract liabilities from assets, what's left is the value of the equity in the business owned by you and any partners. Tracking changes in this number will tell you whether you're getting richer or poorer.
Balance sheets can also be projected into the future, and the projections can serve as targets to aim for or benchmarks to compare against actual results. Balance sheets are affected by sales, too. If your accounts receivable go up or inventory increases, your balance sheet reflects this. And, of course, increases in cash show up on the balance sheet. So it's important to look ahead to see how your balance sheet will appear given your sales forecast.
Cash flow statement.
The cash flow statement monitors the flow of cash over a period of time (a year, a quarter, a month) and shows you how much cash you have on hand at the moment.
The cash flow statement, also called the statement of changes in financial position, probes and analyzes changes that have occurred on the balance sheet. It's different from the income statement, which describes sales and profits but doesn't necessarily tell you where your cash came from or how it's being used.
A cash flow statement consists of two parts. One follows the flow of cash into and out of the company. The other shows how the funds were spent. The two parts are called, respectively, sources of funds and uses of funds. At the bottom is, naturally, the bottom line, called net changes in cash position. It shows whether you improved your cash position and by how much during the period.
Other Financial Information
If you're seeking investors for your company, you'll probably need to provide quite a bit more financial information than what is in the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements. For instance, a personal finance statement may be needed if you're guaranteeing loans yourself. Applying business data to other ratios and formulas will yield important information on what your profit margin is and what level of sales it will take for you to reach profitability. Still other figures, such as the various ratios, will help predict whether you'll be able to pay your bills for long. These bits of information are helpful to you as well as to investors, it should be noted. Understanding and, if possible, mastering them, will help you run your business more smoothly.
Entrepreneur Staff
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Bantam Bagels' Founder Fell Into a Mindset Trap 'People Don't Talk About' After Selling the Now-Defunct Business for $34 Million — Here's What Happened
- Lock This Startup Wants to Grow Your Side Hustle for You , While Cutting You a Monthly Check
- I Designed My Dream Home for Free With an AI Architect — Here's How It Works
- Renowned Psychologist Adam Grant Says This 3-Step Leadership Method Will Help Fight Employee Burnout
- Lock Most Americans Don't Think Higher Education Is Worth the Cost — But This State-By-State Breakdown of College Graduates' Salaries Tells a Different Story
- Lock Watch Now: Tapping into Your Unconventional Thinking and Using It to Create a Million-Dollar Business
Most Popular Red Arrow
He took his side hustle full-time after being laid off from meta in 2023 — now he earns about $200,000 a year: 'sweet, sweet irony'.
When Scott Goodfriend moved from Los Angeles to New York City, he became "obsessed" with the city's culinary offerings — and saw a business opportunity.

James Clear Explains Why the 'Two Minute Rule' Is the Key to Long-Term Habit Building
The hardest step is usually the first one, he says. So make it short.
Get Your Business a One-Year Sam's Club Membership for Just $14
Shop for office essentials, lunch for the team, appliances, electronics, and more.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
United Airlines Is Offering Taylor Swift Fans a 13% Discount on Select Flights — Here's How to Cash In
13 is famously Swift's favorite (and lucky) number.
Microsoft's New AI Can Make Photographs Sing and Talk — and It Already Has the Mona Lisa Lip-Syncing
The VASA-1 AI model was not trained on the Mona Lisa but could animate it anyway.
Successfully copied link
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, business plan financials: 3 statements to include.
The finance section of your business plan is essential to securing investors and determining whether your idea is even viable. Here's what to include.

If your business plan is the blueprint of how to run your company, the financials section is the key to making it happen. The finance section of your business plan is essential to determining whether your idea is even viable in the long term. It’s also necessary to convince investors of this viability and subsequently secure the type and amount of funding you need. Here’s what to include in your business plan financials.
[Read: How to Write a One-Page Business Plan ]
What are business plan financials?
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you’ll need to plan for your business’s future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any funding requests in this part of your business plan.
Business plan financials are vital because they allow you to budget for existing or future expenses, as well as forecast your business’s future finances. A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Sections to include in your business plan financials
Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan:
Profit and loss statement
A profit and loss statement , also known as an income statement, identifies your business’s revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company’s overall financial health in a given time period. While profit and loss statements are typically prepared quarterly, you will need to do so at least annually before filing your business tax return with the IRS.
Common items to include on a profit and loss statement :
- Revenue: total sales and refunds, including any money gained from selling property or equipment.
- Expenditures: total expenses.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): the cost of making products, including materials and time.
- Gross margin: revenue minus COGS.
- Operational expenditures (OPEX): the cost of running your business, including paying employees, rent, equipment and travel expenses.
- Depreciation: any loss of value over time, such as with equipment.
- Earnings before tax (EBT): revenue minus COGS, OPEX, interest, loan payments and depreciation.
- Profit: revenue minus all of your expenses.
Businesses that have not yet started should provide projected income statements in their financials section. Currently operational businesses should include past and present income statements, in addition to any future projections.
[Read: Top Small Business Planning Strategies ]
A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company’s finances, allowing you to keep track of earnings and expenses. It includes what your business owns (assets) versus what it owes (liabilities), as well as how much your business is currently worth (equity).
On the assets side of your balance sheet, you will have three subsections: current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Current assets include cash or its equivalent value, while fixed assets refer to long-term investments like equipment or buildings. Any assets that do not fall within these categories, such as patents and copyrights, can be classified as other assets.
On the liabilities side of your balance sheet, include a total of what your business owes. These can be broken down into two parts: current liabilities (amounts to be paid within a year) and long-term liabilities (amounts due for longer than a year, including mortgages and employee benefits).
Once you’ve calculated your assets and liabilities, you can determine your business’s net worth, also known as equity. This can be calculated by subtracting what you owe from what you own, or assets minus liabilities.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement shows the exact amount of money coming into your business (inflow) and going out of it (outflow). Each cost incurred or amount earned should be documented on its own line, and categorized into one of the following three categories: operating activities, investment activities and financing activities. These three categories can all have inflow and outflow activities.
Operating activities involve any ongoing expenses necessary for day-to-day operations; these are likely to make up the majority of your cash flow statement. Investment activities, on the other hand, cover any long-term payments that are needed to start and run your business. Finally, financing activities include the money you’ve used to fund your business venture, including transactions with creditors or funders.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
More tips for your startup
How to change your ein, or how to fix an incorrect ein, micro-business vs. startup: what’s the difference, micro businesses: what are they and how do you start one.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Maintenance break
Wednesday (20.03.2024), 06:30 - 8:30 UTC
Our system will be temporarily unavailable due to new features implementation
- What should a financial section of a business plan include?
- Blog , Launch your startup

No matter how good your business idea is and how much money you manage to invest in it, the foundation of the company is its financial stability. Especially in the business plan, you need to show that in the foreseeable future your startup will get off the ground and become profitable. How to write the financial section of a business plan? Read our article to find out.
Financial section of a business plan – table of contents:
What is a financial section, the income statement, the balance sheet, break-even point (bep), benefits of a financial plan.
What exactly is the financial section in a business plan? In the financial section you should focus on forecasting the startup’s financial situation as it is mainly needed to attract investors or take out a loan. When creating such a section, you can better understand the functioning of your company and learn about the prospects of how the company can manage in the future.
It is a good idea to start building a financial plan by setting goals for the company. Goals can be divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term. The first are usually set for no more than 5 years. Here we can outline, for example, repayment of debts and loans, but also the purchase of new assets or increase of market presence. Medium-term plans are usually implemented in 5 up to 10 years, and these are larger investments. Everything that we want to realize in more than 10 years is referred to as long-term goals – difficult, often costly, but important for the development of the company.
Next, it is worth including an income statement in your financial plan. This will give the reader of the business plan an insight into expenses, revenues, and profit for a particular period. This will also allow you to assess the most important financial results and get an idea of what condition your startup is currently in – whether it is making a profit or a loss.
In a financial plan, it is also important to include a balance sheet which shows how much equity the company has in a given period. This is a kind of summary of the financial situation. On the one hand, you need to determine the company’s assets, that is, everything the startup owns. On the other hand, you have liabilities, that is debts owed to the creditor of the company. Learning the exact value of assets and liabilities, you can determine the amount of equity. You simply have to subtract the liabilities from the assets.
Another element that must be included in the financial section of the business plan is the cash flow projection. It shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of the company. In this way you can easily determine when expenses become too high and when you should think about external funding. Thanks to the cash flow projection, potential investors reading the business plan can tell whether the company has enough cash, and whether it is worth investing in it.
In the financial plan, it is also worth defining the break-even point. What is it? The break-even point is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal, meaning there is no loss or gain for your business. If your company exceeds a break-even point, it means it has started making a profit. Determining the break-even point comes in handy when analyzing sales figures, when analyzing costs, and when setting prices. Thanks to a break-even analysis, you can think about what to do to increase profitability and reduce the time to reach this threshold.
What are the benefits of a financial plan? With such an analysis, you can clearly set the company’s goals. A financial plan will allow you to manage your cash flow more sensibly, enabling you to better allocate your company’s budget. Such a plan also helps to identify and reduce costs. This, in turn, minimizes financial risks. Above all, however, a financial plan increases the chances of raising capital.
If you like our content, join our busy bees community on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, Pinterest.
Author: Andy Nichols A problem solver with 5 different degrees and endless reserves of motivation. This makes him a perfect Business Owner & Manager. When searching for employees and partners, openness and curiosity of the world are qualities he values the most. View all posts
Launch your startup:
- What is a startup?
- Pros and cons of creating a startup
- 8 best industries for startups
- Top 5 skills every highly successful startup founder needs
- How to create a startup? 7 simple and easy steps
- 6 essential startup development stages
- How to create a startup growth strategy?
- General startup statistics you need to know
- Startup vs. corporate job. Which is right for you?
- 5 incredible companies that started in a garage
- How to find a business idea?
- How to check if your startup idea already exists?
- How to name a startup? Useful tips and strategies
- How to gain business knowledge quickly? 5 best practices
- Why do startups fail? 6 startup ideas you should avoid
- 5 weird business ideas that made millions
- Top 6 most profitable small businesses
- 7 questions to determine if your business idea is worth pursuing
- What is a buyer persona? 5 benefits of creating a buyer persona
- How to validate your business idea? 3 easy steps
- Should you follow your passion? The importance of passion in business
- What is market reseach and why is it important?
- Using social media in business
- What to do when you have too many business ideas?
- How to write a good problem statement for your startup?
- How to test your business idea for real?
- How to create a prototype for a product?
- How to build an MVP?
- How to use surveys for testing your business idea?
- 10 useful tools to validate your business idea
- What is a business plan? 4 types of business plans
- What should be included in a business plan?
- What should a product description include?
- Competitor analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Traditional business plan vs. lean startup plan
- Implementation plan. What is it and how to create it?
- Everything you need to know about patents
- Financial management for startups
- What permits and licenses does my startup need?
- What is the average startup founder salary?
- 4 startup taxes you need to pay
- Which legal structure is best for your business?
- Startup costs. How much money will you need?
- Protection of intellectual property in a startup
- Family funding vs. self-funding
- What is a shareholders’ agreement?
To-do Lists
Stay on top of your most important issues and track project progress thanks to task priorities & statuses .
- Cooperation models
- Human Resources
- User Experience
- Project management
Recent posts

“We are all developers”. How can citizen developers help your company? | AI in business #74

1 big truth about software errors | #2 First steps in software testing

10 Best Content Creation Tools

10 best Google Chrome extensions for productivity

10 best platforms for selling ebooks – Create & sell digital products #13

10 best websites for small business owners

Set and accomplish your
Team goals with firmbee.
years of experience
users trusted our solutions
team of experts
processed documents yearly
Start working with Firmbee to elevate your firm's efficiency. Manage teams and tasks with our project management module . Use CRM tools , regain finance control , and issue invoices with our free invoicing app .
- Polski ( Polish )
- Freelancer Management System
- Recruitment Software
- Free Invoicing App
- Project Management
- HR Management System
Useful links
- Help Center
- Terms And Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Please sign in
You need to log in to use the bookmarking feature.

- Baker Library
- Special Collections
- Fast Answers
- All Services
- Plan Your Visit
- Working Knowledge
- Academic Programs
- Faculty & Research
- Harvard Business Review
- Initiatives
- Map / Directions
How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Advice on how to include financial information in a business plan, including things like a sales forecast, expense budget, and cash-flow statement.
Author/Editor (By:)
Elizabeth Wasserman
Contributor
Corporate author, related organizations, citation type.
Business Plans
Periodical Title
Periodical audience type.
Popular, Practitioner
How to Improve the Accuracy of Financial Forecasts
5 min. read
Updated April 22, 2024
Every spring, I read and review dozens of business plans as a member of an angel investment group and a judge at several business plan contests. I love it.
The plans I’ve seen are better than ever this year. But, for some reason, their financial projections are the worst I’ve seen.
How can the plans be better while their financials are worse?
I think product/market fit, defensibility, scalability, market need, and management experience are much harder to fix than bad financials. A good business with poor financial projections will survive and grow.
Still, it’s a shame. The worst, and by far the most common mistake , is absurdly high profitability. So, in honor of this epidemic of bad financials, here’s my five-step plan for better financial projections.
1. Start with a sales forecast
Make it bottoms-up, always; never tops-down. This means you start with unit and price details and build up to sales from specific, concrete assumptions.
For example, if it’s a website, base your forecast on metrics you and others can compare to other websites, such as unique visits, page views, and conversions. If it’s a product going through distributors to retail stores, look at the number of stores you can reach and the distributors required to reach them, and forecast units per store per month.
Never get caught forecasting a market by assuming the total market size and then projecting your market share. That doesn’t work. Nobody who matters believes it.
Do it monthly for 12 months, then annually for the second and third year. Think of it as a spreadsheet with months and years horizontally across the top and category names vertically along the left-hand side.
Your sales forecast should include your direct costs (also called unit costs) and costs of goods sold (or COGS). This is how much it costs you in direct costs, unit costs, per units sold. These are costs you don’t pay if you don’t sell. They go up and down as sales go up and down.
If you have no idea, don’t throw your arms up in frustration; don’t say “but it’s a new business, how could I know?” Break it into unit economics and unit assumptions.
Get some comparisons from similar industries to show you what gross margin (sales less costs of sales) might be, and average profitability. Google “standard financial ratios” for leads, and don’t expect to pay more than $100 for one industry profile.
And if you still have no idea, then:
1. keep your day job; or 2. find some partners who know the industry.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. Forecast running expenses
We call these operating expenses , such as rent, utilities, payroll, advertising, websites, travel and so forth. Again, if you have no idea, you need to find financial profiles, take in a partner, talk to somebody who’s done it before, or maybe keep your day job. You don’t want to have no idea.
This is also a spreadsheet, with the same months and years as in the Sales Forecast horizontally across the top, and the categories vertically down the left side.
By the time you’re done with expenses, you’ve got everything you need to do an estimated profit or loss analysis. The standard format starts with sales, then subtracts direct costs to calculate gross margin. Then you subtract operating expenses to calculate profit before interest and taxes (called EBIT, with the E standing for “earnings.”)
If your projections have profits higher than 10 or so percent of sales, you’re not done. Either you have underestimated your costs or expenses, or you have an unusually strong business. It’s almost always the former.
Hint: No matter what industry you’re in, if your pretax profits are more than 15 percent, then I suggest you subtract 15 percent from your projected profits and add that amount back into operating expenses as marketing expense.
Having profits too high usually means you aren’t projecting all your expenses. And marketing is where most people underestimate expenses. Besides, in a real business, well-spent marketing expenses are better than profits because they grow your business, which makes it more valuable over the long term.
3. Startup costs
Make a list of expenses you’ll have to pay before you start. Common startup expenses are legal expenses, website development, logos, signage, fixing up a location, computers and so on. Then make a list of assets you’ll need.
Those are things like vehicles, equipment, furniture, startup inventory, and starting cash in the bank.
The cash in the bank is the toughest. If you look at your running profit and loss , that will give you an idea. You have to have money to support your early losses. Read the next step and then revisit it.
4. Understand cash flow
Unfortunately, making a profit doesn’t mean you have cash in the bank. The biggest problems here are business-to-business sales, which typically mean you get paid a month later, and product businesses, which normally have to buy things to sell before they sell them.
If you’re a business that paid two months ago for what you sell today and will be paid for that three months from now, then cash flow is both critical and unintuitive. You’re going to need money in the bank (you can call that working capital) to handle running expenses while you wait to sell stuff and get paid for it.
On the other hand, If you’re selling to people who pay immediately in cash, check, or credit card, especially if you’re not putting money into buying and keeping products, then cash flow is more predictable.
Ironically, some of the worst cash-flow problems come with high growth rates.
If you have no idea, and you do have business-to-business sales and inventory, then look at templates, software, books, tutorials, or somebody who can help you. Don’t take cash flow for granted, even if you expect to be profitable.
5. Review and revise regularly
Yes, you should forecast for 12 months and the two following years, but no, don’t expect your forecast to be accurate. They never are.
You do the financial forecasts so you can set expectations and link spending to sales, but that’s just the start. Review your results every month. Compare actual results to what you had planned. And make corrections.
Final thought: all financial projections are wrong, by definition. We’re human and we don’t predict the future accurately. So don’t expect accuracy.
Go for plausibility, and then follow up with a regular plan versus actual analysis , review, and revisions. We call that management.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- 1. Start with a sales forecast
- 2. Forecast running expenses
- 3. Startup costs
- 4. Understand cash flow
- 5. Review and revise regularly
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What Is a Break-Even Analysis?

6 Min. Read
How to Forecast Sales for a Subscription Business

<1 Min. Read

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- What is a Business Plan
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Mission Statement
- Marketing Section
- Operating Plan
- Management & Staffing Section
- Financial Section
- Business Plan Tips
- Income Statement
- Balance Sheet
- Cash Flow Statement
- Break-even Analysis
- Ratio Analysis
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Notes to Financials
- Financial Budgets
- Forecasting Cash Flow
- Break-Even Analysis
- Operation Issues
- Marketing Issues
- Licenses, Permits, Inspections & Taxes
- Management/Staffing
- Financial Issues
Main Menu Items
Home Writing a Business Plan Financial Statements Forecasting Statements Business Checklist
Example of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
- Email a Friend
FINANCIAL SECTION OF YOUR BUSINESS PLAN
The Financial Section, in many cases, is the most scrutinized section of your business plan. In short, it provides details on how potentially profitable the business will be, how much debt and equity capital is required for the business venture, and when debts are scheduled to be repaid to investors. In addition, this section includes your financial statement forecasts, and the assumptions made when creating your financial projections.
The Financial Section of your business plan relies on Forecasted Financial Statements. Forecasted financial statements help an entrepreneur determine the feasibility of his/her business venture. Also, forecasted financial statements help to estimate the amount of money an entrepreneur will need in order to successfully launch and operate the proposed endeavor. In addition, these statements help investors determine the plan's feasibility and its potential profitability. It is for these reasons that many refer the financial section as the "heart of a business plan". All other sections of the plan (operations section, management section, marketing section, etc) show an investor whether or not an entrepreneurs' financial projections can materialize as envisioned.
The structure of the financial section generally includes the following items:
Part A. Introduction to the Financial Plan Part B. Forecasted Financial Statements Part C. Notes to the Forecasted Financial Statements
Click on the above links for information on each item of the Financial Plan. Examples are also provided.
Below provides examples of Financial Plans. (Please note, the financial statements and analysis for two of the examples below; namely " The Internet Company " and " Scholarship Information Services " provide forecasted financial statements for a two year period. Your forecasted financial statements and analysis, however, should generally provide projections for at least a three year period.
EXAMPLES OF THE FINANCIAL PLAN SECTION OF A BUSINESS PLAN
J&B Incorporated Scholarship Information Services The Internet Company The Maple Syrup Company
Sign up for the newsletter!
FREE Marketing Guide
© Copyright 2009 - Business Plan Hut - All Rights Reserved
About - Contact Us - Privacy Policy - Disclaimer - Sitemap - Login - Admin

Netherlands
- Knowledge base
Introduction
Crafting a business plan is akin to architecting the future of your enterprise. It functions as a compass to help you navigate the treacherous seas of entrepreneurship. The foundational components of a business plan are key to success whether you are a seasoned business owner or a budding entrepreneur.
In this thorough guide, we’ll examine every important component, empowering you to construct a robust blueprint for success.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary, which provides a succinct synopsis of the main ideas of your firm, acts as the gateway to your business plan . It summarizes your company’s unique selling proposition (USP), market potential, financial forecasts, and team experience. Even though it comes first, it’s usually written last, condensing the main ideas of your plan into an engaging story that attracts stakeholders and investors.
2. Company Description
This part gives a thorough overview of your company, outlining its goals, values, mission, and organizational structure. It explains how your business separates from the competition by outlining your industry, target market, and competitive landscape. Defining your company’s mission statement lays the foundation for building investor interest and credibility.
3. Market Analysis
Comprehending your target audience is essential for long-term expansion. The market study section explores competition dynamics, customer demographics, and industry trends. You can find opportunities, foresee problems, and improve your value proposition to appeal to your target market by carrying out in-depth market research. This part gives prospective investors confidence by demonstrating your keen grasp of market subtleties.
4. Organization & Management
Your team is the lifeblood of your enterprise, embodying its vision and driving its execution. An introduction to notable individuals, including their positions, duties, and credentials, is provided here. By demonstrating the knowledge and cooperation among members of your team, you inspire confidence in your capacity to overcome obstacles and seize opportunities. This part of your business plan is crucial since investors want reassurance regarding the skill and unity of the management team.
5. Product or Service Line
Every successful business endeavour starts with a compelling solution that fills a real gap in the market. This part explains your product or service, emphasizing its attributes, advantages, and special selling points. You may distinguish your brand and strengthen its market positioning by clearly stating how your service solves problems and provides clients with real value. To help investors understand the core of your business and its potential market, it is imperative that you be as detailed and clear as possible.
6. Marketing & Sales Strategy
To succeed in the market, even the most inventive goods and services need to employ smart sales and marketing techniques. This part outlines your strategy for attracting and keeping consumers. It covers branding, pricing, distribution methods, and sales techniques. You show insight and flexibility in responding to changing market conditions by providing a thorough and data-driven marketing plan. Investors carefully examine this part to determine your capacity for revenue generation and long-term growth.
7. Funding Request
Every entrepreneurial journey requires financial fuel to propel it forward. The funding request segment articulates your capital requirements, delineating how funds will be allocated to fuel growth and achieve key milestones. It is crucial to maintain clarity and transparency while looking for financing from financial institutions, angel investors, or venture capitalists. You can encourage trust in the viability and scalability of your company model by making a strong case for investment and laying out the possible returns.
8. Financial Projections
Numbers tell a story, illuminating the financial trajectory of your venture and its potential for profitability. This section presents detailed financial projections, including income statements, cash flow forecasts, as well as balance sheets. By showcasing revenue streams, cost structures, and growth metrics, you provide investors with a clear roadmap for financial success. Accuracy, realism, and conservatism are key, to instilling trust and credibility in your projections.
A well-written business plan is more than simply a paper; it’s a strategic instrument that gives entrepreneurs the clarity and confidence to successfully negotiate the complexity of the commercial world. By meticulously addressing each component, you lay the foundation for success, inspiring investor confidence and charting a course for sustainable growth. As you embark on your entrepreneurial journey, remember that a robust business plan is not merely a static blueprint but a dynamic roadmap that evolves with your venture, guiding you towards your goals and aspirations.
A business plan acts as a road map for your project, assisting in stakeholder communication and directing strategic decision-making. It aids in streamlining your company’s concept, spotting possibilities and obstacles, and setting up a path for long-term success.
While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, a typical business plan ranges from 20 to 40 pages. It must be succinct but thorough, focusing on key insights and strategies while avoiding unnecessary fluff.
Although templates might offer a useful structure, it’s vital to customize your business plan to the particular requirements and circumstances of your endeavour. For optimum impact, personalize each segment to match your vision, objectives, and market conditions.

Our Services
- Netherlands Company Formation
- Singapore Company Formation
- Poland Company Formation
- Canada Company Formation
- Dubai Company Formation
- Company Registration in Australia
Headquarters
Woxa IT Park, 463, Udyog Vihar, Phase 5, Gurugram 122016
Privacy Policy
Terms and conditions, ©2024 ondemand international llp, privacy policy terms and conditions, ©2021 odint consulting llp.
Please update your browser.
We don't support this browser version anymore. Using an updated version will help protect your accounts and provide a better experience.
Update your browser
We don't support this browser version anymore. Using an updated version will help protect your accounts and provide a better experience.
We’ve signed you out of your account.
You’ve successfully signed out
We’ve enhanced our platform for chase.com. For a better experience, download the Chase app for your iPhone or Android. Or, go to System Requirements from your laptop or desktop.
Credit Cards
Checking Accounts
Savings Accounts
Mortgage & Home Equity
Chase for Business
Commercial Banking
- ATM & branch
Please turn on JavaScript in your browser
It appears your web browser is not using JavaScript. Without it, some pages won't work properly. Please adjust the settings in your browser to make sure JavaScript is turned on.
Chase Survey
Your feedback is important to us. Will you take a few moments to answer some quick questions?
You're now leaving Chase
Chase's website and/or mobile terms, privacy and security policies don't apply to the site or app you're about to visit. Please review its terms, privacy and security policies to see how they apply to you. Chase isn’t responsible for (and doesn't provide) any products, services or content at this third-party site or app, except for products and services that explicitly carry the Chase name.
Introduction
Strategies for early repayment, potential penalties and considerations, debt repayment strategies, a guide to paying off your personal loan early.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate personal loans to write unbiased product reviews.
- Refinancing your loans could get you a better interest rate and shorter repayment term.
- Two common repayment strategies are the debt avalanche and the debt snowball.
- If you can make more frequent payments on your debt, you'll save on interest costs.
The benefits of paying off a personal loan early
With loans available for everything from paying for college to buying a new car or renovating your home, you can find yourself facing a growing pile of debt before you know it. Paying off those loans as quickly as possible saves you money in the long run and frees up your cash to put toward other financial goals.
Understanding your loan terms
Most loans come with interest , the additional charge a borrower pays to use the lender's money. The faster you pay off a loan, the less in total interest you need to pay.
Reducing your loan balances more quickly than scheduled is possible, and it doesn't have to be that complicated. These tips can help you do it, says Gabe Krajicek, CEO of Kasasa, a fintech company that provides financial products and marketing services to community banks and credit unions
Making extra payments
If you're financially able, you can reduce the cost of your loan fast by making more payments than the ones scheduled. Or, you can make larger payments at the same cadence as you've already been paying.
"The faster you pay down your loans, the more money you will save in interest, but be careful not sacrifice your safety net," Krajicek says. "Life's surprise expenses don't stop just because you are on a mission to pay off your debt."
Consolidate payments
You may be able to consolidate multiple loans into one with a single monthly payment, which can make it easier to keep track of your loan balance. You may even be able to get a lower interest rate, although that's more common with loan refinancing.
Krajicek recommends consulting with a local community bank or credit union. Depending on the type of loan, you may also be able to refinance with an online lender or a large-scale bank. The best personal loan for you will depend on your credit score.
Refinancing for a lower interest rate
Refinancing your loans can get you a lower interest rate , which will save you on interest on your loan. You may also be able to shorten your repayment term length, which will make your monthly payments higher but cost you less in overall interest.
There are several options to lower your payments, get assistance paying off your loans, or even get loans forgiven altogether. This could be through government programs or local organizations. You may also ask family and friends for money to help pay off your debt, and then pay them back at a lower interest rate or with no interest at all.
Prepayment penalties
The biggest con of paying off a loan early is that you'll have to make higher monthly payments than you initially budgeted for to do so. Additionally, some lenders may charge prepayment penalties, though that is rare. Generally speaking, it's not bad to pay off a loan too early. The exceptions are if you can't afford the higher monthly payments or if the lender charges a prepayment penalty.
Assessing financial impact
Your credit score may drop when you pay off a loan. Your credit score is made up of many factors, including your credit mix and the length of your credit history. When you close a loan, you'll impact these factors.
Among the two most popular strategies to pay down loan debt are the debt avalanche and the debt snowball .
Debt avalanche
With a debt avalanche, you pay off your loan with the highest interest rate first. Once your highest interest rate debt is paid off, you move on to the next-highest interest rate, and so on down the line. By doing so, you'll save more money over the course of the loan, says Forrest McCall, personal finance expert and owner of the finance blog, " Don't Work Another Day ."
Debt snowball
The debt snowball method has you start by paying down your smallest debt first. You will pay the most on the smallest debt and the minimum on the rest. "After this initial debt is paid off, you put the full amount of what you were paying on this debt toward the next smallest amount," Krajicek says. "And of course, limit accumulating more debt as you work to pay off current debt.
Paying off a personal loan early may temporarily impact your credit score due to the closure of an active account. However, your credit score will benefit in the long run by reducing your debt-to-income ratio and demonstrating your creditworthiness.
Find out if there's a prepayment penalty by reviewing your loan agreement or contacting your lender directly. Understanding the terms of your loan is a crucial step to take before making those extra payments.
Generally, it's best to pay off the debt with the highest interest rate first, which is usually credit card debt. However, freeing yourself from a personal loan can also provide psychological and financial relief.
Lump sum payments are made on top of your regular payments, and are applied directly to the principal amount of your loan. This reduces the overall balance more quickly and decreases the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Yes, refinancing can help you pay off your loan early if you secure a lower interest rate or more favorable terms. This will let more of your payment go towards the principal rather than interest.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The financial section of a business plan is one of the most essential components of the plan, as you will need it if you have any hope of winning over investors or obtaining a bank loan. Even if ...
Generally, the financial section is one of the last sections in a business plan. It describes a business's historical financial state (if applicable) and future financial projections. Businesses include supporting documents such as budgets and financial statements, as well as funding requests in this section of the plan. The financial part of ...
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders ...
The financial plan section of a business plan is a look into the future of the business and its ability to generate profits, pay its bills and create wealth. Its main documents are income statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. There may be several versions of these, each demonstrating the likely effects of various scenarios. ...
The financials section of your business plan tells you and your potential investors, loan providers or partners whether your business idea makes economic sense. Without an impressive financials ...
7. Build a Visual Report. If you've closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using "what-if" scenarios. Now, we'll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
The final financial statement required for the business plan's financial section is a balance sheet. This statement is a snapshot of the company's net worth at a given point in time. Established businesses produce a balance sheet annually. Information from the income statement and cash flow projection are used to complete this statement.
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors. ...
Financial ratios and metrics. With all of your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios. While these metrics are entirely optional to include in your plan, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
A business' financial plan is the part of your business plan that details how your company will achieve its financial goals. It includes information on your company's projected income, expenses, and cash flow in the form of a 5-Year Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement. The plan should also detail how much funding your ...
The financial section of your business plan should include a sales forecast, expenses budget, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and a profit and loss statement. Be sure to follow the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, a private-sector organization responsible for setting ...
Here are some steps that you can take to create the financial section of a business plan: 1. Create a sales forecast. The first document to create for the financial section is the sales forecast. This is a document that highlights the sales that you might project the business to achieve over the next three years.
Financial statements come in threes: income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Taken together they provide an accurate picture of a company's current value, plus its ability to pay ...
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
8. Financial Plan. The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations.
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you'll need to plan for your business's future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any ...
6. Financials. The financial section of your business plan is critical, especially if you want to circulate the plan to investors or lenders. The purpose of this section is threefold: to 1) outline your business's financial plan, 2) demonstrate your profit potential, and 3) share your financing needs.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Another element that must be included in the financial section of the business plan is the cash flow projection. It shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of the company. In this way you can easily determine when expenses become too high and when you should think about external funding. Thanks to the cash flow projection, potential ...
The market analysis section of your business plan is where you demonstrate your in-depth knowledge of the industry, your target market, and your competitors. ... Balance sheet: A balance sheet offers a snapshot of your business's financial position at a specific point in time, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity.
The Financial Statement. First, a financial plan should include a financial statement that consists of the following three parts. Income statement: Also called the profit and loss statement, or P&L, it details the profit or loss the business will generate. Cash flow statement: Functioning a little like a check register for a checking account ...
3. Products & Services. This section allows for a more complete explanation of the kinds of goods or services the business will be selling or providing. Make the descriptions compelling and ...
FINANCIAL SECTION OF YOUR BUSINESS PLAN. The Financial Section, in many cases, is the most scrutinized section of your business plan. In short, it provides details on how potentially profitable the business will be, how much debt and equity capital is required for the business venture, when debts are scheduled to be repaid to investors, your financial statement forecasts, and the assumptions ...
How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan /citations/how-to-write-the-financial-section-of-a-business-plan Advice on how to include financial information in a business plan, including things like a sales forecast, expense budget, and cash-flow statement.
So, in honor of this epidemic of bad financials, here's my five-step plan for better financial projections. 1. Start with a sales forecast. Make it bottoms-up, always; never tops-down. This means you start with unit and price details and build up to sales from specific, concrete assumptions.
FINANCIAL SECTION OF YOUR BUSINESS PLAN. The Financial Section, in many cases, is the most scrutinized section of your business plan. In short, it provides details on how potentially profitable the business will be, how much debt and equity capital is required for the business venture, and when debts are scheduled to be repaid to investors. ...
The executive summary, which provides a succinct synopsis of the main ideas of your firm, acts as the gateway to your business plan. It summarizes your company's unique selling proposition (USP), market potential, financial forecasts, and team experience. Even though it comes first, it's usually written last, condensing the main ideas of ...
Step 1: Create a sales projection. Sales projections are an important component of your financial projections. For existing businesses, you can base your projections on past performance obtained ...
You should consult your own tax, legal and accounting advisors before engaging in any financial transaction. J.P. Morgan Wealth Management is a business of JPMorgan Chase & Co., which offers investment products and services through J.P. Morgan Securities LLC (JPMS), a registered broker-dealer and investment adviser, member FINRA and SIPC.
Debt avalanche. With a debt avalanche, you pay off your loan with the highest interest rate first. Once your highest interest rate debt is paid off, you move on to the next-highest interest rate ...