Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456

Pollution of Air and Water
Introduction: what is air pollution and water pollution.
Air pollution has been the highlight of all major international level meetings, air is something we all share and cherish. The presence of breathable air is very important for leading a healthy life, the recent levels of air pollution witnessed around the world has been of serious concern for all the people, different environmentalists like Greta Thunberg, etc have raised their voices forcing the governments to change their policies regarding pollution. Public demand for this has also been very high and as a result, stricter policies have been coming up and all are made aware of the causes and concerns of air pollution.
Air pollution directly affects the health of humans and animals alike. The air humans and animals breathe is directed to the lungs and as such the pollutants present in the air directly get into the lungs and can lead to lung cancers. In the case of animals, several cases of deaths related to air pollution have been witnessed in different parts of the world. Also, birds have been severely affected by the air pollution because they have to be at the core of the polluted air. In recent times, air pollution has been of such several levels that breathing in that air was equivalent to smoking two packs of cigarettes in a day. Air pollution is also very harmful to crops and other agricultural products because when air is highly polluted and rain starts pouring, the rain pours in the form of Acid rain. The acid rain pours on people who are out, the crop produces and finally gets added into the ground. The acid rain can cause skin allergies if exposure to such rain is prolonged and can also damage the crop if caution is not exercised. The addition of acid rain into the groundwater disrupts the PH of the groundwater and as a result the groundwater also gets polluted.
Water pollution has also been of extreme concern for leaders and people around the globe. Several efforts are being implemented to reduce the water pollution levels to the minimum. It is found that the most polluted water bodies are those which are nearer to the residential or the commercial areas. While the water bodies near to the residential areas have got polluted due to the discharge of all the drainage waste into these waters, the one close to the commercial areas has witnessed the release of industrial waste into them as the main cause of water pollution in these areas. Several other water bodies have been witnessed as becoming municipal dumping sites.
Water pollution is a critical concern because the pollution in water bodies has an extremely severe effect on the lives of aquatic animals and it totally leads to the disruption of aquatic ecosystems there. The huge presence of plastics, water bottles, and polythenes can cause fatal conditions for aquatic animals. Also, the increased water pollution has disturbed the PH level of the water bodies and as a result, water at some points in these water bodies has become so poisonous or acidic that fishes, dolphins, and penguins have often been seen dead at the sea, river shores.
Air and Water pollution both are very harmful to human existence on this planet. Air and water are the most precious natural resources which are present in abundance but we misuse and abuse them. The pollution in any of these has a serious effect on the lives of humans and animals alike. Air and water pollution if abused to the maximum level can’t be turned back on immediately, several diseases and disorders previously unknown to humans have been identified as a consequence of air and water getting polluted with poisonous substances which are released from chemical and other such environment degrading industries. Like humans, the health of the planet is also getting affected when we choke the air it breezes and pollute the water that flows on it.
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the exhaustive presence of undesired gasses/particles in the atmosphere. The gasses may be released off due to natural causes like volcanic eruptions etc or maybe released off due to man-made causes like industries or vehicles. Both affect the air quality immensely and make it very harmful for breathing and sometimes extremely toxic.
Air pollution is caused by releasing various gasses into the atmosphere, finely divided solids, or finely dispersed liquid aerosols at rates that exceed the environment's natural capacity to dissipate and dilute or consume them. These compounds can achieve concentrations in the air that cause unwanted effects on health and the economy.
Air pollution is one of the prime concerns of all countries in the 21 st century, there have been several agreements between countries all over the globe to control their respective emissions and relatively lower the amount of air pollution. India has been severely affected by air pollution, the capital of the country has been reeling under severe air pollution levels where the AQI has been at times the maximum and in the range of hazardous.
Water Pollution
Water pollution is another type of pollution where the water has a heavy presence of undesired entities in it. From oil spills to commercial drainages all add up to destroy the precious water bodies. Water pollution has also been caused by the dumping of waste materials at the depths of rivers and lakes. The presence of plastic bags, bottles have also added up to the pollution of water.
Water pollution is caused by leaking different substances into subterranean groundwater or into lakes, streams, rivers, estuaries, and oceans to the point where the substances interfere with the beneficial use of water or with the natural functioning of ecosystems. Apart from releasing substances such as chemicals or microorganisms , water pollution may also include releasing energy into water bodies in the form of radioactivity or heat.
Causes of Air pollution
Combustion from Industry
Manufacturing processes can produce virtually all the common air pollutants. Some of these are created by the combustion of fossil fuels driving the manufacturing process, resulting in oxides of particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen.
Transportation Emissions
Popular forms of transport such as cars, planes, and ships typically use combustion to extract fossil-fuel electricity. The combustion process releases pollutants, such as particles and carbon monoxide, into the air and also releases rapidly forming substances into nitrogen oxides and ozone, which are important air pollutants.
Agriculture Side-Effects
Farmers use fossil-fuel-driven machines to plow fields and harvest crops, and animals raised in bulk for food often create their own kind of air pollution. Methane is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect causing global warming; it originates from intestinal gas released by livestock.
Volcano Eruptions
Natural processes emit plenty of polluting substances into the air. Sulfur dioxide is a major modern air pollutant and volcanoes can release enough sulfur dioxide into the air to affect global cooling, according to National Geographic.
Forest Fires
Forest fires release pollutants into the air in the same way as pollution produced by fireplaces that burn wood. They produce fine particles of smoke that are small enough to get into the lungs and damage the lungs and heart, according to the EPA.
Tobacco Smoke
Homes in the developing world may have visible smoke coming from the fire used to heat and cook the house. Tobacco smoke is commonly the only noticeable type of air pollution within the home in the developed world. Both sources of indoor smoking are linked with respiratory diseases.
Metal Smelting
Different industries produce specific profiles of air pollutants, and the major source of metal pollution such as lead is metal smelting, while niche applications of lead, such as in the manufacturing of certain aviation fuels, often contribute.
Aerosols and CFCs
Refrigerants are the most common emitter of CFCs, especially those used after the 1930s. When not properly disposed of the coolant used in old refrigerators, cars, air conditioners, and other machines, it leaks CFCs into the atmosphere as liquids evaporate or work their way into the soil.
Causes of Water Pollution
Industrial Waste
Industries produce enormous quantities of waste containing toxic chemicals and pollutants, which causes air pollution and harm to our atmosphere.
Many industries, lacking a proper waste management system, drain the waste into the freshwater that enters canals, rivers, and later into the sea.
Toxic chemicals can change watercolor, increase the number of minerals, called eutrophication, change water temperature, and pose a serious hazard to water organisms.
Sewage and Wastewater
The sewage and wastewater produced in each household is chemically treated and released into the sea along with fresh water. The sewage water contains toxins, a typical water pollutant, other harmful
Marine Dumping
The garbage produced by households in the form of paper, plastic, food, aluminum, rubber, glass, is collected and dumped into the sea in some countries. These items take 2 weeks to 200 years to decompose.
When such things enter the sea, they not only cause water pollution but also harm animals in the sea.
Accidental Oil Leakage
Oil spill poses an enormous threat to marine life as large quantities of oil spill into the sea and does not dissolve in water. It causes local marine wildlife issues involving fish, birds, and sea otters.
If an accident occurs a ship carrying a large amount of oil can spill oil. Such an oil spill can cause differing harm to ocean species, depending on the amount of oil spilled, pollutant toxicity, and the depth of the ocean.
The Burning of Fossil Fuels
When burnt, fossil fuels such as coal and oil produce considerable amounts of ash in the atmosphere. Particulate matter which contains toxic chemicals when combined with water vapor causes acid rain. Carbon dioxide is also released from fossil fuel burning which results in global warming.
Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides
The farmers use artificial fertilizers and pesticides to protect crops from insects and bacteria. They are important for the growth of a plant. But they create harmful pollutants for plants and animals when these contaminants are mixed with water.
Also, the chemicals mix up with rainwater when it rains and flow down into rivers and canals, and cause serious damage to aquatic animals.
Leakage from Sewer Lines
A small leak from the sewer lines will contaminate the groundwater and make drinking unsafe for the people. The leaking water can also spill onto the soil when not cleaned on time and can become a breeding ground for insects and mosquitoes.
Global Warming
As a result of the greenhouse effect, an increase in world temperature results in global warming. It increases the water temperature which leads to the death of aquatic animals and marine species resulting in water contamination later on.
Radioactive Waste
The production of nuclear energy is through nuclear fission or fusion. Uranium, which is a highly toxic chemical, is the element used in the production of nuclear energy.
Acid rain is in fact water pollution from air pollution. As air pollution combines the acidic pollutants released into the atmosphere with water vapor, it results in acid rain.
Eutrophication
The increased nutrient levels in bodies of water are known as eutrophication. It results in algae blooming in the atmosphere. It also depletes the amount of oxygen in the water that impacts fish and other aquatic animal populations adversely.
Effects of Air Pollution
Global warming is potentially one of the most troubling consequences for scientists and environmentalists alike. Global warming is a direct result of the greenhouse effect, produced by high CO 2 and methane emissions into the atmosphere. Most of these emissions are produced by manufacturing so that companies and factories can address this with social responsibility and action.
Climate Change
Climate change is yet another result of global warming. When the planet's temperature rises, the usual climatic cycles are disturbed, accelerating the changes of these cycles in an evident way.
Gasses emitted from industry, power stations, boilers, cooking, and transportation are highly toxic. Such gasses contain sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) released by burning fossil fuels into the atmosphere. When these compounds collect in the atmosphere and react with water, they form dilute nitric and sulphuric acid solutions, and when those amounts are air, both the environment and the surfaces suffer.
Smog Effect
The smog effect or beret effect happens when a sort of dark fog is spread over the towns and fields. The fog is a pollutant load and can be of two types: sulfurous smog and photochemical smog, both toxic and harmful to health. Both sources of smog are the product of industrial and urban practice.
Deterioration of Fields
Acid rain, climate change and smog cause damage to the surface of the Earth. Contaminated water and gasses flow into the earth, altering soil composition. That affects agriculture directly, the evolving crop cycles and the composition of the food we all consume.
Extinction of Animal Species
As the poles ' ice masses melt and sea levels increase, other animal species which rely on oceans and rivers to survive are endangered. Currents change, ocean temperatures rise and migratory patterns change, and in areas unfamiliar to them, many species are forced to look for food. Deforestation and low soil quality also mean the forests and biodiversity are vanishing. And, probably, a difference in many wild species' behavior.
Respiratory Health Problems
It is perhaps one of the most visible and troubling human effects. Pollutants can cause respiratory diseases and allergies ranging from asthma, cancer, or emphysema to coughs.
Inhalation of toxic agents affects the respiratory system specifically in the lungs and other tissues.
Deterioration in Building Materials
Air pollutants often deteriorate and change the constitution of building materials, thereby degrading, eroding, or damaging many buildings and infrastructure at an increased rate over time.
Effects of Water Pollution
Effects on Human Beings
One of the major effects of this is sickness. The World Health Organization states that around 120,000 deaths related to cholera occur annually. In fact, for example, the Fukushima disaster increased the prevalence of thyroid cancer in untreated children by 70 percent.
Death of Aquatic Life
Polluted water most affects animals and plants which depend on water for life. Statistics on the consequences of the Deep Horizon spill from the Center for Biological Diversity provide valuable insight into the impact of pollution on aquatic life. The 2010 Gulf of Mexico spill injured more than 82,000 birds, 25,900 marine animals, 6165 sea turtles, and an unknown number of fish and Invertebrates in the study.
Food Chain Disruption
Pollution interferes with the food chain by transferring the toxins from one level in the chain to another. Pollution can in some cases wash out a whole part of the food chain. These affect the other species either by causing excessive growth if the predator dies or dies (if the prey is wiped out)
Destruction of Ecosystems
The addition of certain microorganisms or their disappearance distorts the environment. For example, nutrient pollution leads to an increase in algae which depletes oxygen water and leads to the death of fish and other aquatic life.
Economic Effects
The management and restoration of polluted bodies of water are costly. For example, in 2019 Japan announced that storing the contaminated water after the Fukushima accident is running out of space. This currently contains more than one million tons of contaminated water stored in tanks. Research shows that cleanup of the disaster's effects would cost at least $660 billion.
FAQs on Pollution of Air and Water
1. What is the Main Cause of Air and Water Pollution?
The major causes of air pollution are coal and carbon combustion, manufacturing and chemical production, mining operations, indoor pollution, high-rate renewable gas emissions, etc. A lot of other causes lead to air and water pollution.
2. Explain how Air Pollution and Water Pollution affect the Environment?
Also, air pollution can have a direct impact on water pollution. If pollutants such as sulfur dioxide fall up into the air, they can combine to produce acid rain. Acid rain can turn waterways poisonous and can kill fish and other animals. Water pollution can have major environmental impacts.
3. Is Air Pollution or Water Pollution worse?
Air pollution will become a greater global killer than dirty water ' Urban air pollution is set to become the largest environmental cause of premature death in the coming decades.
Biology • Class 12

Air, Water, and Soil Pollution
Sep 02, 2014
480 likes | 1.1k Views
Air, Water, and Soil Pollution. A meta-study conducted in 2007 by David Pimentel at Cornell University suggests that as many as 40% of all deaths worldwide are linked to soil, water, and air pollution. Air pollution from smoke and various chemicals kills 3 million people a year worldwide.
Share Presentation
- particulate matter
- los angeles
- ground level
- ground level ozone
- controlling los angeles smog

Presentation Transcript
Air, Water, and Soil Pollution A meta-study conducted in 2007 by David Pimentel at Cornell University suggests that as many as 40% of all deaths worldwide are linked to soil, water, and air pollution. Air pollution from smoke and various chemicals kills 3 million people a year worldwide. In the United States alone about 3 million tons of toxic chemicals are released into the environment -- contributing to cancer, birth defects, immune system defects and many other serious health problems. Source: Pimentel, David. Cornell University. 2007.
Water and Air Pollution Air Pollution / Photochemical Smog • Ground-level Ozone • Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) • Particulate Matter (ash, smoke, dust, pollen) Soil Contamination • Acid Deposition/Acid Rain • DDT • Heavy Metals Water Pollution • Minamata Disease (methylmercury contamination) • bioaccumulation • Eutrophication and Dead Zones (excess nitrogen)
Air Pollution / Photochemical Smog Ground-level Ozone Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Particulate Matter (ash, smoke, dust, pollen)
Air pollution • Role of physical geography • Prevailing winds • Topography and inversions • Role of cultural geography • Use of fuels and solvents related to level of urbanization, industrialization, and regulations • Disruption of soil linked to particulate matter
Air pollution • A photochemical smog is the chemical reaction of sunlight, nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere, which leaves airborne particles (called particulate matter) and ground-level ozone. • 3 million deaths worldwide
Air Pollutants Defining Dirty Air • Smog is the general term used to describe a variety of air pollutants, including ground-level ozone (smog's main ingredient), particulate matter, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. It refers to air pollution that is formed when gases from many sources are released into the air and chemically react with each other in sunlight. • Ocean breezes sweep the smog inland toward the mountains where an inversion layer of warm air pushes it down, trapping the smog close to the ground where we live and breathe. Ground-level ozone (O3) is a colorless, odorless pollutant formed by a chemical reaction between volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the presence of sunlight. The primary source of VOCs and NOx is mobile sources, including cars, trucks, buses, plus agricultural and construction equipment. Particulate matter (PM) is the term used for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. It originates from a variety of sources, including motor vehicles, power plants, construction activities, soil dust, soot and industrial processes. Coarse particles (PM10) are generally emitted from sources such as windblown dust, vehicles traveling on unpaved roads, and crushing and grinding operations. Fine particles (PM2.5) can come from fuel combustion (motor vehicles, power generation, industrial facilities) and fugitive dust. PM2.5 is formed primarily in the atmosphere from gases such as sulfur oxides, NOx, and VOCs. Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas by-product of combustion produced primarily by motor vehicles. Burned wood and charcoal also emit carbon monoxide.
Ground-level Ozone – from combustion of fuels • Ozone is a strong irritant that can constrict the airways, forcing the respiratory system to work harder to provide oxygen. It also can cause: • Aggravated respiratory diseases such as emphysema, bronchitis and asthma • Damage to deep portions of the lungs, even after symptoms such as coughing or a sore throat disappear • Wheezing, chest pain, dry throat, headache, or nausea • Reduced resistance to infection and increased fatigue Particulate Matter – PM 2.5 (from combustion) and PM 10 (from loose dust) • A series of scientific studies have linked particulate matter, especially fine particles, with a variety of significant health problems: • Aggravated asthma, heart, or lung disease • Respiratory-related hospital admissions and emergency room visits • Acute respiratory symptoms, including severe chest pain, gasping, and aggravated coughing • Decreased lung function which can be experienced as shortness of breath • Chronic bronchitis • Premature death Carbon Monoxide – from combustion of fuels and wood • Carbon monoxide replaces oxygen in the body's red blood cells. People with heart disease are more susceptible to developing chest pains when exposed to low levels of carbon monoxide. Exposure to high levels of carbon monoxide can: • Slow reflexes and cause confusion and drowsiness • Result in death in confined spaces (i.e., an enclosed garage) at very high concentrations
Controlling Los Angeles Smog with Technology? Since smog was first recognized as a serious problem in 1947, inventors and engineers have proposed innovative ideas to get rid of it. • One was to connect all Los Angeles industries to a massive network of concrete exhaust pipes routed to the mountains where pollution could be released above the inversion layer. If it works for sewage, it will work for air pollution, thought the engineering firm that pioneered the "air sanitation system" concept. But the system would have required 89 miles of ductwork and the energy to move the large volumes of air would have been several times beyond what Hoover Dam could supply. Many other ideas surfaced in the 1950s and 1960s to purify, ventilate or wash the air over Los Angeles. • One was to cut holes in the mountains and install huge exhaust fans to blow smog out of the basin. However, blowing or washing away smog proved to be impractical since it involved a land mass of 1,600 square miles and over 200 million tons of air. The enormous energy requirements made the idea impossible. • One scientist suggested blackening whole sections of the eastern mountains so as to store heat and create thermal currents and westerly winds that would blow smog over the mountains
Particulate matter • Source: incomplete burning of fuel • Respiratory problems • Short transport distance • Closest to source = most affected
Source: AQMD, 2006
Source: AQMD
Photochemial smog • Sources: incomplete burning of fuel • Nitrogen dioxide, hydrocarbons, and sunlight • Forms ozone at ground level • Respiratory problems, damage to plants
Ozone non-attainment days, 1993-2002
Historic Smog Levels, Los Angeles
How to Control Los Angeles Smog? • 1970 Clean Air Act (amended repeatedly until 1990) sets standards for 6 key pollutants. States then implement plans to comply. • Key elements in California have been automobile smog checks, more refined gasoline required statewide, smokestack scrubbers which catch particulate and oxides of nitrogen and sulfur. • New management plans call for increased use of cleaner solvents that release fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Dry cleaning, manufacturing, etc.. • Scrubbers use lime or ammonia to remove NOx and SOx • Catalytic converters on automobiles remove NOx
Acid rain • Source: burning fossil fuels • Sulfur from coal becomes sulfuric acid • Terrestrial effects (forests, soils) • Aquatic effects (death of fish) • Material effects (buildings, monuments)
Sources of Acid Depostion Sources of nitrogen oxides (NOx) Sources of sulfer oxides (SOx)
Damage to vegetationDamage to vegetation and the dying of forests have long been associated with acid rain. The washing out of metal ions results in limited plant nutrients. Vegetation exposed to acid rain will therefore absorb less of these essential nutrients. The result is poorer quality of a plant’s proteins, stunted growth and exposure to diseases. Death of fishDeath of fish is the best known effect of acidification, and is therefore a reliable and frequently used indicator. There are two reasons for the death of fish. When the acidification reaches a certain level, the fry die. The most sensitive species are trout and salmon.
Acid Effect on Forest in Czech Republic, 2006
- More by User

Cruise Ship Pollution – Air and Water
Cruise Ship Pollution – Air and Water Teri Shore, Bluewater Network Tim Eichenberg, Oceana Cruise ships produce significant volumes of air pollution while in port and in transit. Air pollution from cruise ships can be reduced by using cleaner fuels and technologies
1.14k views • 23 slides

Air and Air Pollution
Air and Air Pollution. G. Tyler Miller, Jr.’s Environmental Science 10 th Edition Chapter 12. Key Concepts- Chapter Overview. Structure and composition of the atmosphere. Types and sources of outdoor air pollution. Types, formation, and effects of smog.
1.08k views • 33 slides

AIR and WATER POLLUTION
441 views • 21 slides

soil pollution
2???????(soil polluting property) (1) ????????(invisibility) (2)????????(persistence) (3)??????????(noxiousness). ?????????,????????????????????,????????????????????,???????????,?????????????. ?????????(self-purification) . . ???????????????? 1??????? 2????????(physical che
495 views • 26 slides

Air and Air Pollution. G. Tyler Miller’s Living in the Environment 13 th Edition Chapter 17. Dr. Richard Clements Chattanooga State Technical Community College. Key Concepts. Structure and composition of the atmosphere. Types and sources of outdoor air pollution.
398 views • 20 slides

Air, soil and water pollution in Hungary
Air, soil and water pollution in Hungary. Comenius project 2012/2014. Environmental problems. Rapid industrialization Emissions from automobiles Electric power Acid rain Sulfur dioxide in the air.
418 views • 17 slides

Air and Air Pollution. The Atmosphere. Stratosphere 11-30 miles Little water vapor Ozone layer UV filter Troposphere 11 mile at equator; 8 miles at poles weather breeder 78% N, 21% O Natural heating Solar radiation Greenhouse effect. The Atmosphere. Exosphere Thermosphere
757 views • 54 slides

Soil pollution
Soil pollution. SOIL POLLUTION Contamination of soil by human and natural activities which cause harmful effects on living beings. Sources of soil pollution. Industrial wastes Urban wastes Agricultural wastes Radioactive pollutants Biological agents. Industrial wastes. Paper mills
16.39k views • 16 slides

Water and soil pollution
Water and soil pollution.
361 views • 12 slides

PoLLutioN (water & air pollution)
PoLLutioN (water & air pollution). Kelompok 2: 1. Arif Fajar Utomo ( L2C008118) 2. Rohmat Figi Arto (L2C008148). Pollution.
333 views • 14 slides

Pollution of air, sea , water and soil in Poland
Pollution of air, sea , water and soil in Poland. Wojciech Olejniczak Publiczne Gimnazjum nr 2 w Staszowie kl. 2b . Poland. In the past Poland was a beautiful country. Crystal-clear water in lakes surrounded by lots of plants , being a home to countless animals ,. Poland.
362 views • 17 slides
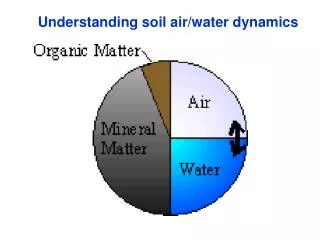
Understanding soil air/water dynamics
Understanding soil air/water dynamics. Porosity the soil’s respiratory and circulatory system. White zones are pores > 1mm. No-till soil. Tilled soil. (Young and Ritz, 2000). Soil pores come in many sizes and shapes. http://www.mtm.kuleuven.ac.be/Research/NDT/IDO_SHerman_final.ppt.
718 views • 43 slides

Water and Water Pollution
Water and Water Pollution. Chapter 11. Key Concepts. Why is water so important? How much water is available? How much water are we using? What causes water shortages and what can be done? What causes floods and how can they be avoided? Sources, types, and risks of water pollution
1.51k views • 78 slides

SOIL POLLUTION
SOIL POLLUTION. SUPERVISION Prof. Dr. Mervat Salah. What causes heavy metal pollution?. What is soil pollution?. Metals have unique chemical properties. Causes Of soil pollution. Leakages from sanitary sewage. Acid rains, when fumes released from industries get mixed with rains.
4.32k views • 27 slides

AIR AND WATER POLLUTION
AIR AND WATER POLLUTION. In Brunei Darussalam. Some Facts and Figures. Located on the north cost of the island of Borneo Surrounded by the state of Sarawak, Malaysia Population of 408,786 as at June 2012 Classified as a ‘ developing country ’. Towards Environmental Sustainability.
656 views • 34 slides

Air and Air Pollution. Key Concepts. Structure and composition of the atmosphere. Types and sources of outdoor air pollution. Types, formation, and effects of smog. Sources and effects of acid deposition. Effects of air pollution. Prevention and control of air pollution. The Atmosphere.
458 views • 21 slides

SOIL pollution
SOIL pollution. Causes of soil pollution.
1.93k views • 22 slides

Effects of Environmental Contaminants – Air and Soil Pollution
Effects of Environmental Contaminants – Air and Soil Pollution. pollutants can also be called contaminants: waste from human activities that may harm humans or other forms of life when released into the environment.
485 views • 15 slides

Air and Air Pollution. G. Tyler Miller’s Living in the Environment 13 th Edition Chapter 17. Modified by Charlotte Kirkpatrick Dr. Richard Clements Chattanooga State Technical Community College. Key Concepts. Structure and composition of the atmosphere.
289 views • 19 slides

About Air Pollution and water Pollution
let Describe about air pollution and water pollution as Pollution has many aspects. http://energy.wesrch.com
2k views • 17 slides

Cause Of Air And Water Pollution
You cannot imagine how many types of activities affect the air and water pollution in this world. Here mentioned some causes of air and water pollution. For more details check Prkruti.
586 views • 8 slides

Soil pollution. SOIL POLLUTANTS. Plastics Agro chemicals Fertilizers Heavy metals. Plastics. Major part of global domestic and industrial waste Not easily biodegraded Waste plastic accumulates much thus adds to severe pollution problem
823 views • 18 slides
- Random article
- Teaching guide
- Privacy & cookies

by Chris Woodford . Last updated: November 22, 2022.
Photo: Air pollution is obvious when it pours from a smokestack (chimney), but it's not always so easy to spot. This is an old photo of the kind of smoke that used to come from coal-fired power plants and, apart from soot (unburned carbon particles), its pollutants include sulfur dioxide and the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide. Thanks to tougher pollution controls, modern power plants produce only a fraction as much pollution. Modern pollution made by traffic consists of gases like nitrogen dioxide and "particulates" (microscopic soot and dust fragments) that are largely invisible.
What is air pollution?
Air pollution is a gas (or a liquid or solid dispersed through ordinary air) released in a big enough quantity to harm the health of people or other animals, kill plants or stop them growing properly, damage or disrupt some other aspect of the environment (such as making buildings crumble), or cause some other kind of nuisance (reduced visibility, perhaps, or an unpleasant odor).
Natural air pollution
Photo: Forest fires are a completely natural cause of air pollution. We'll never be able to prevent them breaking out or stop the pollution they cause; our best hope is to manage forests, where we can, so fires don't spread. Ironically, that can mean deliberately burning areas of forest, as shown here, to create firebreaks. Forests are also deliberately burned to regenerate ecosystems. Photo by courtesy of US Fish and Wildlife Service .
Top-ten kinds of air pollution Photo: Flying molecules—if you could see air pollution close up, this is what it would look like. Image courtesy of US Department of Energy. Any gas could qualify as pollution if it reached a high enough concentration to do harm. Theoretically, that means there are dozens of different pollution gases. It's important to note that not all the things we think of as pollution are gases: some are aerosols (liquids or solids dispersed through gases). In practice, about ten different substances cause most concern: Sulfur dioxide : Coal, petroleum, and other fuels are often impure and contain sulfur as well as organic (carbon-based) compounds. When sulfur (spelled "sulphur" in some countries) burns with oxygen from the air, sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) is produced. Coal-fired power plants are the world's biggest source of sulfur-dioxide air pollution, which contributes to smog, acid rain, and health problems that include lung disease. [5] Large amounts of sulfur dioxide are also produced by ships, which use dirtier diesel fuel than cars and trucks. [6] Carbon monoxide : This highly dangerous gas forms when fuels have too little oxygen to burn completely. It spews out in car exhausts and it can also build up to dangerous levels inside your home if you have a poorly maintained gas boiler , stove, or fuel-burning appliance. (Always fit a carbon monoxide detector if you burn fuels indoors.) [7] Carbon dioxide : This gas is central to everyday life and isn't normally considered a pollutant: we all produce it when we breathe out and plants such as crops and trees need to "breathe" it in to grow. However, carbon dioxide is also a greenhouse gas released by engines and power plants. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, it's been building up in Earth's atmosphere and contributing to the problem of global warming and climate change . [8] Nitrogen oxides : Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) and nitrogen oxide (NO) are pollutants produced as an indirect result of combustion, when nitrogen and oxygen from the air react together. Nitrogen oxide pollution comes from vehicle engines and power plants, and plays an important role in the formation of acid rain, ozone and smog. Nitrogen oxides are also "indirect greenhouse gases" (they contribute to global warming by producing ozone, which is a greenhouse gas). [9] Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) : These carbon-based (organic) chemicals evaporate easily at ordinary temperatures and pressures, so they readily become gases. That's precisely why they're used as solvents in many different household chemicals such as paints , waxes, and varnishes. Unfortunately, they're also a form of air pollution: they're believed to have long-term (chronic) effects on people's health and they play a role in the formation of ozone and smog. VOCs are also released by tobacco smoke and wildfires. [10] Particulates : There are many different kinds of particulates, from black soot in diesel exhaust to dust and organic matter from the desert. Airborne liquid droplets from farm pollution also count as particulates. Particulates of different sizes are often referred to by the letters PM followed by a number, so PM 10 means soot particles of less than 10 microns (10 millionths of a meter or 10µm in diameter, roughly 10 times thinner than a thick human hair). The smaller ("finer") the particulates, the deeper they travel into our lungs and the more dangerous they are. PM 2.5 particulates are much more dangerous (they're less than 2.5 millionths of a meter or about 40 times thinner than a typical hair). In cities, most particulates come from traffic fumes. [11] Ozone : Also called trioxygen, this is a type of oxygen gas whose molecules are made from three oxygen atoms joined together (so it has the chemical formula O 3 ), instead of just the two atoms in conventional oxygen (O 2 ). In the stratosphere (upper atmosphere), a band of ozone ("the ozone layer") protects us by screening out harmful ultraviolet radiation (high-energy blue light) beaming down from the Sun. At ground level, it's a toxic pollutant that can damage health. It forms when sunlight strikes a cocktail of other pollution and is a key ingredient of smog (see box below). [12] Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) : Once thought to be harmless, these gases were widely used in refrigerators and aerosol cans until it was discovered that they damaged Earth's ozone layer. We discuss this in more detail down below. [13] Unburned hydrocarbons : Petroleum and other fuels are made of organic compounds based on chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. When they burn properly, they're completely converted into harmless carbon dioxide and water ; when they burn incompletely, they can release carbon monoxide or float into the air in their unburned form, contributing to smog. Lead and heavy metals : Lead and other toxic "heavy metals" can be spread into the air either as toxic compounds or as aerosols (when solids or liquids are dispersed through gases and carried through the air by them) in such things as exhaust fumes and the fly ash (contaminated waste dust) from incinerator smokestacks. [14] What are the causes of air pollution?
Photo: Even in the age of electric cars, traffic remains a major cause of air pollution. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) (NREL photo id#46361).
Photo: Brown smog lingers over Denver, Colorado. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) (NREL photo id#56919).
Chart: Most of the world's major cities routinely exceed World Health Organization (WHO) air pollution guidelines, though progress is being made: you can see that the 2022 figures (green) show a marked improvement on the 2016 ones (orange) in almost every case. This chart compares annual mean PM 2.5 levels in 12 representative cities around the world with the recently revised (2021) WHO guideline value of 5μg per cubic meter (dotted line). PM 2.5 particulates are those smaller than 2.5 microns and believed to be most closely linked with adverse health effects. For more about this chart and the data sources used, see note [22] .
Photo: Smokestacks billowing pollution over Moscow, Russia in 1994. Factory pollution is much less of a problem than it used to be in the world's "richer" countries—partly because a lot of their industry has been exported to nations such as China, India, and Mexico. Photo by Roger Taylor courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) .
What effects does air pollution have?
Photo: Air pollution can cause a variety of lung diseases and other respiratory problems. This chest X ray shows a lung disease called emphysema in the patient's left lung. A variety of things can cause it, including smoking and exposure to air pollution. Photo courtesy of National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and National Institutes of Health.
" In 2016, 91% of the world population was living in places where the WHO air quality guidelines levels were not met." World Health Organization , 2018
Photo: For many years, the stonework on the Parthenon in Athens, Greece has been blackened by particulates from traffic pollution, but other sources of pollution, such as wood-burning stoves, are increasingly significant. Photo by Michael M. Reddy courtesy of U.S. Geological Survey .
How air pollution works on different scales
Indoor air pollution.
Photo: Air freshener—or air polluter?
Further reading
Acid rain—a closer look.
Photo: Acid rain can turn lakes so acidic that fish no longer survive. Picture courtesy of U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Division of Public Affairs. Why does that matter? Pure water is neither acidic nor alkaline but completely neutral (we say it has an acidity level or pH of 7.0). Ordinary rainwater is a little bit more acidic than this with about the same acidity as bananas (roughly pH 5.5), but if rain falls through sulfur dioxide pollution it can turn much more acidic (with a pH of 4.5 or lower, which is the same acidity as orange or lemon juice). When acid rain accumulates in lakes or rivers, it gradually turns the entire water more acidic. That's a real problem because fish thrive only in water that is neutral or slightly acidic (typically with a pH of 6.5–7.0). Once the acidity drops below about pH 6.0, fish soon start to die—and if the pH drops to about 4.0 or less, all the fish will be killed. Acid rain has caused major problems in lakes throughout North America and Europe. It also causes the death of forests, reduces the fertility of soil, and damages buildings by eating away stonework (the marble on the US Capitol in Washington, DC has been eroded by acid-rain, for example). One of the biggest difficulties in tackling acid rain is that it can happen over very long distances. In one notable case, sulfur dioxide air pollution produced by power plants in the UK was blamed for causing acid rain that fell on Scandinavian countries such as Norway, producing widespread damage to forests and the deaths of thousands of fish in acidified lakes. The British government refused to acknowledge the problem and that was partly why the UK became known as the "dirty man of Europe" in the 1980s and 1990s. [18] Acid rain was a particular problem in the last 30–40 years of the 20th century. Thanks to the decline in coal-fired power plants, and the sulfur dioxide they spewed out, it's less of a problem for western countries today. But it's still a big issue in places like India, where coal remains a major source of energy. Global air pollution It's hard to imagine doing anything so dramatic and serious that it would damage our entire, enormous planet—but, remarkable though it may seem, we all do things like this everyday, contributing to problems such as global warming and the damage to the ozone layer (two separate issues that are often confused). Global warming Every time you ride in a car, turn on the lights, switch on your TV , take a shower, microwave a meal, or use energy that's come from burning a fossil fuel such as oil, coal, or natural gas, you're almost certainly adding to the problem of global warming and climate change: unless it's been produced in some environmentally friendly way, the energy you're using has most likely released carbon dioxide gas into the air. While it's not an obvious pollutant, carbon dioxide has gradually built up in the atmosphere, along with other chemicals known as greenhouse gases . Together, these gases act a bit like a blanket surrounding our planet that is slowly making the mean global temperature rise, causing the climate (the long-term pattern of our weather) to change, and producing a variety of different effects on the natural world, including rising sea levels. Read more in our main article about global warming and climate change . Ozone holes
How can we solve the problem of air pollution?
Photo: Pollution solution: an electrostatic smoke precipitator helps to prevent air pollution from this smokestack at the McNeil biomass power plant in Burlington, VT. Photo by Warren Gretz courtesy of US DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
What can you do to help reduce air pollution?
Photo: Buying organic food reduces the use of sprayed pesticides and other chemicals, so it helps to reduce air (as well as water) pollution.
If you liked this article...
Find out more, on this site.
- Climate change and global warming
- Environmentalism (introduction)
- Land pollution
- Organic food and farming
- Renewable energy
- Water pollution

- Breathless: Why Air Pollution Matters—and How it Affects You by Chris Woodford. Icon, 2021. My new book explores the problem in much more depth than I've been able to go into here. You can also read a bonus chapter called Angels with dirty faces: How air pollution blackens our buildings and monuments .
- The Invisible Killer: The Rising Global Threat of Air Pollution and How We Can Fight Back by Gary Fuller. Melville House, 2018.
- Reducing Pollution and Waste by Jen Green. Raintree/Capstone, 2011. A 48-page introduction for ages 9–12. The emphasis here is on getting children to think about pollution: where it comes from, who makes it, and who should solve the problem.
- Pollution Crisis by Russ Parker. Rosen, 2009. A 32-page guide for ages 8–10. It starts with a global survey of the problem; looks at air, water, and land pollution; then considers how we all need to be part of the solution.
- Earth Matters by Lynn Dicks et al. Dorling Kindersley, 2008. This isn't specifically about pollution. Instead, it explores how a range of different environmental problems are testing life to the limit in the planet's major biomes (oceans, forests, and so on). I wrote the section of this book that covers the polar regions.
- State of Global Air : One of the best sources of global air pollution data.
- American Lung Association: State of the Air Report : A good source of data about the United States.
- European Environment Agency: Air quality in Europe : A definitive overview of the situation in the European countries.
- World Health Organization (WHO) Ambient (outdoor) air pollution in cities database : A spreadsheet of pollution data for most major cities in the world (a little out of date, but a new version is expected soon).
- Our World in Data : Accessible guides to global data from Oxford University.
- The New York Times Topics: Air Pollution
- The Guardian: Pollution
- Wired: Pollution
- 'Invisible killer': fossil fuels caused 8.7m deaths globally in 2018, research finds by Oliver Milman. The Guardian, February 9, 2021. Pollution of various kinds causes something like one in five of all deaths.
- Millions of masks distributed to students in 'gas chamber' Delhi : BBC News, 1 November 2019.
- 90% of world's children are breathing toxic air, WHO study finds by Matthew Taylor. The Guardian, October 29, 2018. The air pollution affecting billions of children could continue to harm their health throughout their lives.
- Pollution May Dim Thinking Skills, Study in China Suggests by Mike Ives. The New York Times, August 29, 2018. Long-term exposure to air pollution seems to cause a decline in cognitive skills.
- Global pollution kills 9m a year and threatens 'survival of human societies' by Damian Carrington. The Guardian, October 19, 2017. Air, water, and land pollution kill millions, cost trillions, and threaten the very survival of humankind, a new study reveals.
- India's Air Pollution Rivals China's as World's Deadliest by Geeta Anand. The New York Times, February 14, 2017. High levels of pollution could be killing 1.1 million Indians each year.
- More Than 9 in 10 People Breathe Bad Air, WHO Study Says by Mike Ives. The New York Times, September 27, 2016. New WHO figures suggest the vast majority of us are compromising our health by breathing bad air.
- Study Links 6.5 Million Deaths Each Year to Air Pollution by Stanley Reed. The New York Times, June 26, 2016. Air pollution deaths are far greater than previously supposed according to a new study by the International Energy Agency.
- UK air pollution 'linked to 40,000 early deaths a year' by Michelle Roberts, BBC News, February 23, 2016. Diesel engines, cigarette smoke, and even air fresheners are among the causes of premature death from air pollution.
- This Wearable Detects Pollution to Build Air Quality Maps in Real Time by Davey Alba. Wired, November 19, 2014. A wearable pollution gadget lets people track their exposure to air pollution through a smartphone app.
- Air pollution and public health: emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk by Frank J. Kelly and Julia C. Fussell, Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2015
- Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: lines that connect by C.A. Pope and D.W. Dockery. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2006
- Ambient and household air pollution: complex triggers of disease by Stephen A. Farmer et al, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2014
Text copyright © Chris Woodford 2010, 2022. All rights reserved. Full copyright notice and terms of use .
Rate this page
Tell your friends, cite this page, more to explore on our website....
- Get the book
- Send feedback
Home / Free Education Presentation templates / Free Water Pollution PPT Template and Google slides
Free Water Pollution PPT Template and Google slides

About the Template
Today one of the most pressing environmental concerns is water pollution. Download this water pollution ppt template and outline your thoughts on water pollution and what can you do to prevent it.
Today water pollution, Air Pollution is becoming a serious concern. Our Free Water Pollution PowerPoint Template features a thoughtfully crafted blend of eye-catching visuals, data-driven charts, and easy-to-read text. With a color scheme that evokes the tranquillity of clean waters and the urgency to protect them, this template sets the stage for impactful storytelling.
Key Features of this free Water Pollution Presentation template:
- Stunning Visuals: From polluted water bodies to images of eco-friendly practices, this PPT on water pollutions provides you wide range of high-quality visuals to support your message.
- Clear and Concise Text: The template’s text sections are formatted for maximum readability, making it easy to create informative content without overwhelming your audience.
- Environmental Icons: Included icons help in reinforcing environmental themes and are easily customizable.
- Section Breaks: Well-structured section breaks allows you to organize your presentation seamlessly, ensuring your content flows naturally.
- Editable and Customizable: The template is fully customizable, so you can tailor it to your specific needs, whether you’re a student, researcher, educator, or environmental advocate.
According to recent research conducted by Environment Protection Agency (EPA), water in many nations’ rivers and lakes and the reservoir is far from pure. Plus, the quality of the water tested is far from pure.
Water pollution is a massive global problem. Every year, millions of pollutants are dumped into our oceans, lakes, and rivers. This contamination can cause serious health problems for both people and wildlife. Thankfully, there are ways to help prevent water pollution from happening. With this water pollution PowerPoint presentation slide , educate your audience and make them understand the causes and essential steps to be taken to reduce the impact.
Water pollution can have a devastating impact on aquatic life and the environment. But together we can protect our waters and preserve our planet! So, what you are waiting for is to get this presentation on water pollution and create awareness in society for preserving the environment.
If you are looking for more environmental-related templates, check out our Creative templates library.
Google Slide,PowerPoint
100% Fully Customizable
Free to use
Free Active Template Library

Free Air Pollution PPT Template and Google Slides
Free Ecology PPT Template and Google Slides

Free Earth Day PowerPoint Template & Google Slides Themes for Presentation

Free In Loving Memory of Template PowerPoint & Google Slides

Free Google Slides Vintage Theme PowerPoint Template
Are you looking for custom presentation template designs.
It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when or randomised words which don’t look even slightly believable
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Public Health
Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review
Ioannis manisalidis.
1 Delphis S.A., Kifisia, Greece
2 Laboratory of Hygiene and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
Elisavet Stavropoulou
3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois (CHUV), Service de Médicine Interne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Agathangelos Stavropoulos
4 School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Eugenia Bezirtzoglou
One of our era's greatest scourges is air pollution, on account not only of its impact on climate change but also its impact on public and individual health due to increasing morbidity and mortality. There are many pollutants that are major factors in disease in humans. Among them, Particulate Matter (PM), particles of variable but very small diameter, penetrate the respiratory system via inhalation, causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, reproductive and central nervous system dysfunctions, and cancer. Despite the fact that ozone in the stratosphere plays a protective role against ultraviolet irradiation, it is harmful when in high concentration at ground level, also affecting the respiratory and cardiovascular system. Furthermore, nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), dioxins, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are all considered air pollutants that are harmful to humans. Carbon monoxide can even provoke direct poisoning when breathed in at high levels. Heavy metals such as lead, when absorbed into the human body, can lead to direct poisoning or chronic intoxication, depending on exposure. Diseases occurring from the aforementioned substances include principally respiratory problems such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, bronchiolitis, and also lung cancer, cardiovascular events, central nervous system dysfunctions, and cutaneous diseases. Last but not least, climate change resulting from environmental pollution affects the geographical distribution of many infectious diseases, as do natural disasters. The only way to tackle this problem is through public awareness coupled with a multidisciplinary approach by scientific experts; national and international organizations must address the emergence of this threat and propose sustainable solutions.
Approach to the Problem
The interactions between humans and their physical surroundings have been extensively studied, as multiple human activities influence the environment. The environment is a coupling of the biotic (living organisms and microorganisms) and the abiotic (hydrosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere).
Pollution is defined as the introduction into the environment of substances harmful to humans and other living organisms. Pollutants are harmful solids, liquids, or gases produced in higher than usual concentrations that reduce the quality of our environment.
Human activities have an adverse effect on the environment by polluting the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the soil in which plants grow. Although the industrial revolution was a great success in terms of technology, society, and the provision of multiple services, it also introduced the production of huge quantities of pollutants emitted into the air that are harmful to human health. Without any doubt, the global environmental pollution is considered an international public health issue with multiple facets. Social, economic, and legislative concerns and lifestyle habits are related to this major problem. Clearly, urbanization and industrialization are reaching unprecedented and upsetting proportions worldwide in our era. Anthropogenic air pollution is one of the biggest public health hazards worldwide, given that it accounts for about 9 million deaths per year ( 1 ).
Without a doubt, all of the aforementioned are closely associated with climate change, and in the event of danger, the consequences can be severe for mankind ( 2 ). Climate changes and the effects of global planetary warming seriously affect multiple ecosystems, causing problems such as food safety issues, ice and iceberg melting, animal extinction, and damage to plants ( 3 , 4 ).
Air pollution has various health effects. The health of susceptible and sensitive individuals can be impacted even on low air pollution days. Short-term exposure to air pollutants is closely related to COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, respiratory disease, and high rates of hospitalization (a measurement of morbidity).
The long-term effects associated with air pollution are chronic asthma, pulmonary insufficiency, cardiovascular diseases, and cardiovascular mortality. According to a Swedish cohort study, diabetes seems to be induced after long-term air pollution exposure ( 5 ). Moreover, air pollution seems to have various malign health effects in early human life, such as respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal disorders ( 3 ), leading to infant mortality or chronic disease in adult age ( 6 ).
National reports have mentioned the increased risk of morbidity and mortality ( 1 ). These studies were conducted in many places around the world and show a correlation between daily ranges of particulate matter (PM) concentration and daily mortality. Climate shifts and global planetary warming ( 3 ) could aggravate the situation. Besides, increased hospitalization (an index of morbidity) has been registered among the elderly and susceptible individuals for specific reasons. Fine and ultrafine particulate matter seems to be associated with more serious illnesses ( 6 ), as it can invade the deepest parts of the airways and more easily reach the bloodstream.
Air pollution mainly affects those living in large urban areas, where road emissions contribute the most to the degradation of air quality. There is also a danger of industrial accidents, where the spread of a toxic fog can be fatal to the populations of the surrounding areas. The dispersion of pollutants is determined by many parameters, most notably atmospheric stability and wind ( 6 ).
In developing countries ( 7 ), the problem is more serious due to overpopulation and uncontrolled urbanization along with the development of industrialization. This leads to poor air quality, especially in countries with social disparities and a lack of information on sustainable management of the environment. The use of fuels such as wood fuel or solid fuel for domestic needs due to low incomes exposes people to bad-quality, polluted air at home. It is of note that three billion people around the world are using the above sources of energy for their daily heating and cooking needs ( 8 ). In developing countries, the women of the household seem to carry the highest risk for disease development due to their longer duration exposure to the indoor air pollution ( 8 , 9 ). Due to its fast industrial development and overpopulation, China is one of the Asian countries confronting serious air pollution problems ( 10 , 11 ). The lung cancer mortality observed in China is associated with fine particles ( 12 ). As stated already, long-term exposure is associated with deleterious effects on the cardiovascular system ( 3 , 5 ). However, it is interesting to note that cardiovascular diseases have mostly been observed in developed and high-income countries rather than in the developing low-income countries exposed highly to air pollution ( 13 ). Extreme air pollution is recorded in India, where the air quality reaches hazardous levels. New Delhi is one of the more polluted cities in India. Flights in and out of New Delhi International Airport are often canceled due to the reduced visibility associated with air pollution. Pollution is occurring both in urban and rural areas in India due to the fast industrialization, urbanization, and rise in use of motorcycle transportation. Nevertheless, biomass combustion associated with heating and cooking needs and practices is a major source of household air pollution in India and in Nepal ( 14 , 15 ). There is spatial heterogeneity in India, as areas with diverse climatological conditions and population and education levels generate different indoor air qualities, with higher PM 2.5 observed in North Indian states (557–601 μg/m 3 ) compared to the Southern States (183–214 μg/m 3 ) ( 16 , 17 ). The cold climate of the North Indian areas may be the main reason for this, as longer periods at home and more heating are necessary compared to in the tropical climate of Southern India. Household air pollution in India is associated with major health effects, especially in women and young children, who stay indoors for longer periods. Chronic obstructive respiratory disease (CORD) and lung cancer are mostly observed in women, while acute lower respiratory disease is seen in young children under 5 years of age ( 18 ).
Accumulation of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide and smoke, reaching 1,500 mg/m3, resulted in an increase in the number of deaths (4,000 deaths) in December 1952 in London and in 1963 in New York City (400 deaths) ( 19 ). An association of pollution with mortality was reported on the basis of monitoring of outdoor pollution in six US metropolitan cities ( 20 ). In every case, it seems that mortality was closely related to the levels of fine, inhalable, and sulfate particles more than with the levels of total particulate pollution, aerosol acidity, sulfur dioxide, or nitrogen dioxide ( 20 ).
Furthermore, extremely high levels of pollution are reported in Mexico City and Rio de Janeiro, followed by Milan, Ankara, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Moscow ( 19 ).
Based on the magnitude of the public health impact, it is certain that different kinds of interventions should be taken into account. Success and effectiveness in controlling air pollution, specifically at the local level, have been reported. Adequate technological means are applied considering the source and the nature of the emission as well as its impact on health and the environment. The importance of point sources and non-point sources of air pollution control is reported by Schwela and Köth-Jahr ( 21 ). Without a doubt, a detailed emission inventory must record all sources in a given area. Beyond considering the above sources and their nature, topography and meteorology should also be considered, as stated previously. Assessment of the control policies and methods is often extrapolated from the local to the regional and then to the global scale. Air pollution may be dispersed and transported from one region to another area located far away. Air pollution management means the reduction to acceptable levels or possible elimination of air pollutants whose presence in the air affects our health or the environmental ecosystem. Private and governmental entities and authorities implement actions to ensure the air quality ( 22 ). Air quality standards and guidelines were adopted for the different pollutants by the WHO and EPA as a tool for the management of air quality ( 1 , 23 ). These standards have to be compared to the emissions inventory standards by causal analysis and dispersion modeling in order to reveal the problematic areas ( 24 ). Inventories are generally based on a combination of direct measurements and emissions modeling ( 24 ).
As an example, we state here the control measures at the source through the use of catalytic converters in cars. These are devices that turn the pollutants and toxic gases produced from combustion engines into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis through redox reactions ( 25 ). In Greece, the use of private cars was restricted by tracking their license plates in order to reduce traffic congestion during rush hour ( 25 ).
Concerning industrial emissions, collectors and closed systems can keep the air pollution to the minimal standards imposed by legislation ( 26 ).
Current strategies to improve air quality require an estimation of the economic value of the benefits gained from proposed programs. These proposed programs by public authorities, and directives are issued with guidelines to be respected.
In Europe, air quality limit values AQLVs (Air Quality Limit Values) are issued for setting off planning claims ( 27 ). In the USA, the NAAQS (National Ambient Air Quality Standards) establish the national air quality limit values ( 27 ). While both standards and directives are based on different mechanisms, significant success has been achieved in the reduction of overall emissions and associated health and environmental effects ( 27 ). The European Directive identifies geographical areas of risk exposure as monitoring/assessment zones to record the emission sources and levels of air pollution ( 27 ), whereas the USA establishes global geographical air quality criteria according to the severity of their air quality problem and records all sources of the pollutants and their precursors ( 27 ).
In this vein, funds have been financing, directly or indirectly, projects related to air quality along with the technical infrastructure to maintain good air quality. These plans focus on an inventory of databases from air quality environmental planning awareness campaigns. Moreover, pollution measures of air emissions may be taken for vehicles, machines, and industries in urban areas.
Technological innovation can only be successful if it is able to meet the needs of society. In this sense, technology must reflect the decision-making practices and procedures of those involved in risk assessment and evaluation and act as a facilitator in providing information and assessments to enable decision makers to make the best decisions possible. Summarizing the aforementioned in order to design an effective air quality control strategy, several aspects must be considered: environmental factors and ambient air quality conditions, engineering factors and air pollutant characteristics, and finally, economic operating costs for technological improvement and administrative and legal costs. Considering the economic factor, competitiveness through neoliberal concepts is offering a solution to environmental problems ( 22 ).
The development of environmental governance, along with technological progress, has initiated the deployment of a dialogue. Environmental politics has created objections and points of opposition between different political parties, scientists, media, and governmental and non-governmental organizations ( 22 ). Radical environmental activism actions and movements have been created ( 22 ). The rise of the new information and communication technologies (ICTs) are many times examined as to whether and in which way they have influenced means of communication and social movements such as activism ( 28 ). Since the 1990s, the term “digital activism” has been used increasingly and in many different disciplines ( 29 ). Nowadays, multiple digital technologies can be used to produce a digital activism outcome on environmental issues. More specifically, devices with online capabilities such as computers or mobile phones are being used as a way to pursue change in political and social affairs ( 30 ).
In the present paper, we focus on the sources of environmental pollution in relation to public health and propose some solutions and interventions that may be of interest to environmental legislators and decision makers.
Sources of Exposure
It is known that the majority of environmental pollutants are emitted through large-scale human activities such as the use of industrial machinery, power-producing stations, combustion engines, and cars. Because these activities are performed at such a large scale, they are by far the major contributors to air pollution, with cars estimated to be responsible for approximately 80% of today's pollution ( 31 ). Some other human activities are also influencing our environment to a lesser extent, such as field cultivation techniques, gas stations, fuel tanks heaters, and cleaning procedures ( 32 ), as well as several natural sources, such as volcanic and soil eruptions and forest fires.
The classification of air pollutants is based mainly on the sources producing pollution. Therefore, it is worth mentioning the four main sources, following the classification system: Major sources, Area sources, Mobile sources, and Natural sources.
Major sources include the emission of pollutants from power stations, refineries, and petrochemicals, the chemical and fertilizer industries, metallurgical and other industrial plants, and, finally, municipal incineration.
Indoor area sources include domestic cleaning activities, dry cleaners, printing shops, and petrol stations.
Mobile sources include automobiles, cars, railways, airways, and other types of vehicles.
Finally, natural sources include, as stated previously, physical disasters ( 33 ) such as forest fire, volcanic erosion, dust storms, and agricultural burning.
However, many classification systems have been proposed. Another type of classification is a grouping according to the recipient of the pollution, as follows:
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2 , NO, NO 2 , SO 3 , etc.
Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge ( 10 ) at high levels that affect the water quality ( 34 , 35 ).
Soil pollution occurs through the release of chemicals or the disposal of wastes, such as heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and pesticides.
Air pollution can influence the quality of soil and water bodies by polluting precipitation, falling into water and soil environments ( 34 , 36 ). Notably, the chemistry of the soil can be amended due to acid precipitation by affecting plants, cultures, and water quality ( 37 ). Moreover, movement of heavy metals is favored by soil acidity, and metals are so then moving into the watery environment. It is known that heavy metals such as aluminum are noxious to wildlife and fishes. Soil quality seems to be of importance, as soils with low calcium carbonate levels are at increased jeopardy from acid rain. Over and above rain, snow and particulate matter drip into watery ' bodies ( 36 , 38 ).
Lastly, pollution is classified following type of origin:
Radioactive and nuclear pollution , releasing radioactive and nuclear pollutants into water, air, and soil during nuclear explosions and accidents, from nuclear weapons, and through handling or disposal of radioactive sewage.
Radioactive materials can contaminate surface water bodies and, being noxious to the environment, plants, animals, and humans. It is known that several radioactive substances such as radium and uranium concentrate in the bones and can cause cancers ( 38 , 39 ).
Noise pollution is produced by machines, vehicles, traffic noises, and musical installations that are harmful to our hearing.
The World Health Organization introduced the term DALYs. The DALYs for a disease or health condition is defined as the sum of the Years of Life Lost (YLL) due to premature mortality in the population and the Years Lost due to Disability (YLD) for people living with the health condition or its consequences ( 39 ). In Europe, air pollution is the main cause of disability-adjusted life years lost (DALYs), followed by noise pollution. The potential relationships of noise and air pollution with health have been studied ( 40 ). The study found that DALYs related to noise were more important than those related to air pollution, as the effects of environmental noise on cardiovascular disease were independent of air pollution ( 40 ). Environmental noise should be counted as an independent public health risk ( 40 ).
Environmental pollution occurs when changes in the physical, chemical, or biological constituents of the environment (air masses, temperature, climate, etc.) are produced.
Pollutants harm our environment either by increasing levels above normal or by introducing harmful toxic substances. Primary pollutants are directly produced from the above sources, and secondary pollutants are emitted as by-products of the primary ones. Pollutants can be biodegradable or non-biodegradable and of natural origin or anthropogenic, as stated previously. Moreover, their origin can be a unique source (point-source) or dispersed sources.
Pollutants have differences in physical and chemical properties, explaining the discrepancy in their capacity for producing toxic effects. As an example, we state here that aerosol compounds ( 41 – 43 ) have a greater toxicity than gaseous compounds due to their tiny size (solid or liquid) in the atmosphere; they have a greater penetration capacity. Gaseous compounds are eliminated more easily by our respiratory system ( 41 ). These particles are able to damage lungs and can even enter the bloodstream ( 41 ), leading to the premature deaths of millions of people yearly. Moreover, the aerosol acidity ([H+]) seems to considerably enhance the production of secondary organic aerosols (SOA), but this last aspect is not supported by other scientific teams ( 38 ).
Climate and Pollution
Air pollution and climate change are closely related. Climate is the other side of the same coin that reduces the quality of our Earth ( 44 ). Pollutants such as black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and aerosols affect the amount of incoming sunlight. As a result, the temperature of the Earth is increasing, resulting in the melting of ice, icebergs, and glaciers.
In this vein, climatic changes will affect the incidence and prevalence of both residual and imported infections in Europe. Climate and weather affect the duration, timing, and intensity of outbreaks strongly and change the map of infectious diseases in the globe ( 45 ). Mosquito-transmitted parasitic or viral diseases are extremely climate-sensitive, as warming firstly shortens the pathogen incubation period and secondly shifts the geographic map of the vector. Similarly, water-warming following climate changes leads to a high incidence of waterborne infections. Recently, in Europe, eradicated diseases seem to be emerging due to the migration of population, for example, cholera, poliomyelitis, tick-borne encephalitis, and malaria ( 46 ).
The spread of epidemics is associated with natural climate disasters and storms, which seem to occur more frequently nowadays ( 47 ). Malnutrition and disequilibration of the immune system are also associated with the emerging infections affecting public health ( 48 ).
The Chikungunya virus “took the airplane” from the Indian Ocean to Europe, as outbreaks of the disease were registered in Italy ( 49 ) as well as autochthonous cases in France ( 50 ).
An increase in cryptosporidiosis in the United Kingdom and in the Czech Republic seems to have occurred following flooding ( 36 , 51 ).
As stated previously, aerosols compounds are tiny in size and considerably affect the climate. They are able to dissipate sunlight (the albedo phenomenon) by dispersing a quarter of the sun's rays back to space and have cooled the global temperature over the last 30 years ( 52 ).
Air Pollutants
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports on six major air pollutants, namely particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and lead. Air pollution can have a disastrous effect on all components of the environment, including groundwater, soil, and air. Additionally, it poses a serious threat to living organisms. In this vein, our interest is mainly to focus on these pollutants, as they are related to more extensive and severe problems in human health and environmental impact. Acid rain, global warming, the greenhouse effect, and climate changes have an important ecological impact on air pollution ( 53 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) and Health
Studies have shown a relationship between particulate matter (PM) and adverse health effects, focusing on either short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic) PM exposure.
Particulate matter (PM) is usually formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between the different pollutants. The penetration of particles is closely dependent on their size ( 53 ). Particulate Matter (PM) was defined as a term for particles by the United States Environmental Protection Agency ( 54 ). Particulate matter (PM) pollution includes particles with diameters of 10 micrometers (μm) or smaller, called PM 10 , and extremely fine particles with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers (μm) and smaller.
Particulate matter contains tiny liquid or solid droplets that can be inhaled and cause serious health effects ( 55 ). Particles <10 μm in diameter (PM 10 ) after inhalation can invade the lungs and even reach the bloodstream. Fine particles, PM 2.5 , pose a greater risk to health ( 6 , 56 ) ( Table 1 ).
Penetrability according to particle size.
Multiple epidemiological studies have been performed on the health effects of PM. A positive relation was shown between both short-term and long-term exposures of PM 2.5 and acute nasopharyngitis ( 56 ). In addition, long-term exposure to PM for years was found to be related to cardiovascular diseases and infant mortality.
Those studies depend on PM 2.5 monitors and are restricted in terms of study area or city area due to a lack of spatially resolved daily PM 2.5 concentration data and, in this way, are not representative of the entire population. Following a recent epidemiological study by the Department of Environmental Health at Harvard School of Public Health (Boston, MA) ( 57 ), it was reported that, as PM 2.5 concentrations vary spatially, an exposure error (Berkson error) seems to be produced, and the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects are not yet completely elucidated. The team developed a PM 2.5 exposure model based on remote sensing data for assessing short- and long-term human exposures ( 57 ). This model permits spatial resolution in short-term effects plus the assessment of long-term effects in the whole population.
Moreover, respiratory diseases and affection of the immune system are registered as long-term chronic effects ( 58 ). It is worth noting that people with asthma, pneumonia, diabetes, and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible and vulnerable to the effects of PM. PM 2.5 , followed by PM 10 , are strongly associated with diverse respiratory system diseases ( 59 ), as their size permits them to pierce interior spaces ( 60 ). The particles produce toxic effects according to their chemical and physical properties. The components of PM 10 and PM 2.5 can be organic (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, benzene, 1-3 butadiene) or inorganic (carbon, chlorides, nitrates, sulfates, metals) in nature ( 55 ).
Particulate Matter (PM) is divided into four main categories according to type and size ( 61 ) ( Table 2 ).
Types and sizes of particulate Matter (PM).
Gas contaminants include PM in aerial masses.
Particulate contaminants include contaminants such as smog, soot, tobacco smoke, oil smoke, fly ash, and cement dust.
Biological Contaminants are microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, and bacterial spores), cat allergens, house dust and allergens, and pollen.
Types of Dust include suspended atmospheric dust, settling dust, and heavy dust.
Finally, another fact is that the half-lives of PM 10 and PM 2.5 particles in the atmosphere is extended due to their tiny dimensions; this permits their long-lasting suspension in the atmosphere and even their transfer and spread to distant destinations where people and the environment may be exposed to the same magnitude of pollution ( 53 ). They are able to change the nutrient balance in watery ecosystems, damage forests and crops, and acidify water bodies.
As stated, PM 2.5 , due to their tiny size, are causing more serious health effects. These aforementioned fine particles are the main cause of the “haze” formation in different metropolitan areas ( 12 , 13 , 61 ).
Ozone Impact in the Atmosphere
Ozone (O 3 ) is a gas formed from oxygen under high voltage electric discharge ( 62 ). It is a strong oxidant, 52% stronger than chlorine. It arises in the stratosphere, but it could also arise following chain reactions of photochemical smog in the troposphere ( 63 ).
Ozone can travel to distant areas from its initial source, moving with air masses ( 64 ). It is surprising that ozone levels over cities are low in contrast to the increased amounts occuring in urban areas, which could become harmful for cultures, forests, and vegetation ( 65 ) as it is reducing carbon assimilation ( 66 ). Ozone reduces growth and yield ( 47 , 48 ) and affects the plant microflora due to its antimicrobial capacity ( 67 , 68 ). In this regard, ozone acts upon other natural ecosystems, with microflora ( 69 , 70 ) and animal species changing their species composition ( 71 ). Ozone increases DNA damage in epidermal keratinocytes and leads to impaired cellular function ( 72 ).
Ground-level ozone (GLO) is generated through a chemical reaction between oxides of nitrogen and VOCs emitted from natural sources and/or following anthropogenic activities.
Ozone uptake usually occurs by inhalation. Ozone affects the upper layers of the skin and the tear ducts ( 73 ). A study of short-term exposure of mice to high levels of ozone showed malondialdehyde formation in the upper skin (epidermis) but also depletion in vitamins C and E. It is likely that ozone levels are not interfering with the skin barrier function and integrity to predispose to skin disease ( 74 ).
Due to the low water-solubility of ozone, inhaled ozone has the capacity to penetrate deeply into the lungs ( 75 ).
Toxic effects induced by ozone are registered in urban areas all over the world, causing biochemical, morphologic, functional, and immunological disorders ( 76 ).
The European project (APHEA2) focuses on the acute effects of ambient ozone concentrations on mortality ( 77 ). Daily ozone concentrations compared to the daily number of deaths were reported from different European cities for a 3-year period. During the warm period of the year, an observed increase in ozone concentration was associated with an increase in the daily number of deaths (0.33%), in the number of respiratory deaths (1.13%), and in the number of cardiovascular deaths (0.45%). No effect was observed during wintertime.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide is produced by fossil fuel when combustion is incomplete. The symptoms of poisoning due to inhaling carbon monoxide include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, and, finally, loss of consciousness.
The affinity of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin is much greater than that of oxygen. In this vein, serious poisoning may occur in people exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide for a long period of time. Due to the loss of oxygen as a result of the competitive binding of carbon monoxide, hypoxia, ischemia, and cardiovascular disease are observed.
Carbon monoxide affects the greenhouses gases that are tightly connected to global warming and climate. This should lead to an increase in soil and water temperatures, and extreme weather conditions or storms may occur ( 68 ).
However, in laboratory and field experiments, it has been seen to produce increased plant growth ( 78 ).
Nitrogen Oxide (NO 2 )
Nitrogen oxide is a traffic-related pollutant, as it is emitted from automobile motor engines ( 79 , 80 ). It is an irritant of the respiratory system as it penetrates deep in the lung, inducing respiratory diseases, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea, bronchospasm, and even pulmonary edema when inhaled at high levels. It seems that concentrations over 0.2 ppm produce these adverse effects in humans, while concentrations higher than 2.0 ppm affect T-lymphocytes, particularly the CD8+ cells and NK cells that produce our immune response ( 81 ).It is reported that long-term exposure to high levels of nitrogen dioxide can be responsible for chronic lung disease. Long-term exposure to NO 2 can impair the sense of smell ( 81 ).
However, systems other than respiratory ones can be involved, as symptoms such as eye, throat, and nose irritation have been registered ( 81 ).
High levels of nitrogen dioxide are deleterious to crops and vegetation, as they have been observed to reduce crop yield and plant growth efficiency. Moreover, NO 2 can reduce visibility and discolor fabrics ( 81 ).
Sulfur Dioxide (SO 2 )
Sulfur dioxide is a harmful gas that is emitted mainly from fossil fuel consumption or industrial activities. The annual standard for SO 2 is 0.03 ppm ( 82 ). It affects human, animal, and plant life. Susceptible people as those with lung disease, old people, and children, who present a higher risk of damage. The major health problems associated with sulfur dioxide emissions in industrialized areas are respiratory irritation, bronchitis, mucus production, and bronchospasm, as it is a sensory irritant and penetrates deep into the lung converted into bisulfite and interacting with sensory receptors, causing bronchoconstriction. Moreover, skin redness, damage to the eyes (lacrimation and corneal opacity) and mucous membranes, and worsening of pre-existing cardiovascular disease have been observed ( 81 ).
Environmental adverse effects, such as acidification of soil and acid rain, seem to be associated with sulfur dioxide emissions ( 83 ).
Lead is a heavy metal used in different industrial plants and emitted from some petrol motor engines, batteries, radiators, waste incinerators, and waste waters ( 84 ).
Moreover, major sources of lead pollution in the air are metals, ore, and piston-engine aircraft. Lead poisoning is a threat to public health due to its deleterious effects upon humans, animals, and the environment, especially in the developing countries.
Exposure to lead can occur through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal absorption. Trans- placental transport of lead was also reported, as lead passes through the placenta unencumbered ( 85 ). The younger the fetus is, the more harmful the toxic effects. Lead toxicity affects the fetal nervous system; edema or swelling of the brain is observed ( 86 ). Lead, when inhaled, accumulates in the blood, soft tissue, liver, lung, bones, and cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems. Moreover, loss of concentration and memory, as well as muscle and joint pain, were observed in adults ( 85 , 86 ).
Children and newborns ( 87 ) are extremely susceptible even to minimal doses of lead, as it is a neurotoxicant and causes learning disabilities, impairment of memory, hyperactivity, and even mental retardation.
Elevated amounts of lead in the environment are harmful to plants and crop growth. Neurological effects are observed in vertebrates and animals in association with high lead levels ( 88 ).

Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(PAHs)
The distribution of PAHs is ubiquitous in the environment, as the atmosphere is the most important means of their dispersal. They are found in coal and in tar sediments. Moreover, they are generated through incomplete combustion of organic matter as in the cases of forest fires, incineration, and engines ( 89 ). PAH compounds, such as benzopyrene, acenaphthylene, anthracene, and fluoranthene are recognized as toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances. They are an important risk factor for lung cancer ( 89 ).
Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as toluene, benzene, ethylbenzene, and xylene ( 90 ), have been found to be associated with cancer in humans ( 91 ). The use of new products and materials has actually resulted in increased concentrations of VOCs. VOCs pollute indoor air ( 90 ) and may have adverse effects on human health ( 91 ). Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ). Predictable assessment of the toxic effects of complex VOC mixtures is difficult to estimate, as these pollutants can have synergic, antagonistic, or indifferent effects ( 91 , 93 ).
Dioxins originate from industrial processes but also come from natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanic eruptions. They accumulate in foods such as meat and dairy products, fish and shellfish, and especially in the fatty tissue of animals ( 94 ).
Short-period exhibition to high dioxin concentrations may result in dark spots and lesions on the skin ( 94 ). Long-term exposure to dioxins can cause developmental problems, impairment of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems, reproductive infertility, and cancer ( 94 ).
Without any doubt, fossil fuel consumption is responsible for a sizeable part of air contamination. This contamination may be anthropogenic, as in agricultural and industrial processes or transportation, while contamination from natural sources is also possible. Interestingly, it is of note that the air quality standards established through the European Air Quality Directive are somewhat looser than the WHO guidelines, which are stricter ( 95 ).
Effect of Air Pollution on Health
The most common air pollutants are ground-level ozone and Particulates Matter (PM). Air pollution is distinguished into two main types:
Outdoor pollution is the ambient air pollution.
Indoor pollution is the pollution generated by household combustion of fuels.
People exposed to high concentrations of air pollutants experience disease symptoms and states of greater and lesser seriousness. These effects are grouped into short- and long-term effects affecting health.
Susceptible populations that need to be aware of health protection measures include old people, children, and people with diabetes and predisposing heart or lung disease, especially asthma.
As extensively stated previously, according to a recent epidemiological study from Harvard School of Public Health, the relative magnitudes of the short- and long-term effects have not been completely clarified ( 57 ) due to the different epidemiological methodologies and to the exposure errors. New models are proposed for assessing short- and long-term human exposure data more successfully ( 57 ). Thus, in the present section, we report the more common short- and long-term health effects but also general concerns for both types of effects, as these effects are often dependent on environmental conditions, dose, and individual susceptibility.
Short-term effects are temporary and range from simple discomfort, such as irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, throat, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness, and breathing difficulties, to more serious states, such as asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung and heart problems. Short-term exposure to air pollution can also cause headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
These problems can be aggravated by extended long-term exposure to the pollutants, which is harmful to the neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems and causes cancer and even, rarely, deaths.
The long-term effects are chronic, lasting for years or the whole life and can even lead to death. Furthermore, the toxicity of several air pollutants may also induce a variety of cancers in the long term ( 96 ).
As stated already, respiratory disorders are closely associated with the inhalation of air pollutants. These pollutants will invade through the airways and will accumulate at the cells. Damage to target cells should be related to the pollutant component involved and its source and dose. Health effects are also closely dependent on country, area, season, and time. An extended exposure duration to the pollutant should incline to long-term health effects in relation also to the above factors.
Particulate Matter (PMs), dust, benzene, and O 3 cause serious damage to the respiratory system ( 97 ). Moreover, there is a supplementary risk in case of existing respiratory disease such as asthma ( 98 ). Long-term effects are more frequent in people with a predisposing disease state. When the trachea is contaminated by pollutants, voice alterations may be remarked after acute exposure. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be induced following air pollution, increasing morbidity and mortality ( 99 ). Long-term effects from traffic, industrial air pollution, and combustion of fuels are the major factors for COPD risk ( 99 ).
Multiple cardiovascular effects have been observed after exposure to air pollutants ( 100 ). Changes occurred in blood cells after long-term exposure may affect cardiac functionality. Coronary arteriosclerosis was reported following long-term exposure to traffic emissions ( 101 ), while short-term exposure is related to hypertension, stroke, myocardial infracts, and heart insufficiency. Ventricle hypertrophy is reported to occur in humans after long-time exposure to nitrogen oxide (NO 2 ) ( 102 , 103 ).
Neurological effects have been observed in adults and children after extended-term exposure to air pollutants.
Psychological complications, autism, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight seem to be related to long-term air pollution ( 83 ). The etiologic agent of the neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's and Parkinson's) is not yet known, although it is believed that extended exposure to air pollution seems to be a factor. Specifically, pesticides and metals are cited as etiological factors, together with diet. The mechanisms in the development of neurodegenerative disease include oxidative stress, protein aggregation, inflammation, and mitochondrial impairment in neurons ( 104 ) ( Figure 1 ).

Impact of air pollutants on the brain.
Brain inflammation was observed in dogs living in a highly polluted area in Mexico for a long period ( 105 ). In human adults, markers of systemic inflammation (IL-6 and fibrinogen) were found to be increased as an immediate response to PNC on the IL-6 level, possibly leading to the production of acute-phase proteins ( 106 ). The progression of atherosclerosis and oxidative stress seem to be the mechanisms involved in the neurological disturbances caused by long-term air pollution. Inflammation comes secondary to the oxidative stress and seems to be involved in the impairment of developmental maturation, affecting multiple organs ( 105 , 107 ). Similarly, other factors seem to be involved in the developmental maturation, which define the vulnerability to long-term air pollution. These include birthweight, maternal smoking, genetic background and socioeconomic environment, as well as education level.
However, diet, starting from breast-feeding, is another determinant factor. Diet is the main source of antioxidants, which play a key role in our protection against air pollutants ( 108 ). Antioxidants are free radical scavengers and limit the interaction of free radicals in the brain ( 108 ). Similarly, genetic background may result in a differential susceptibility toward the oxidative stress pathway ( 60 ). For example, antioxidant supplementation with vitamins C and E appears to modulate the effect of ozone in asthmatic children homozygous for the GSTM1 null allele ( 61 ). Inflammatory cytokines released in the periphery (e.g., respiratory epithelia) upregulate the innate immune Toll-like receptor 2. Such activation and the subsequent events leading to neurodegeneration have recently been observed in lung lavage in mice exposed to ambient Los Angeles (CA, USA) particulate matter ( 61 ). In children, neurodevelopmental morbidities were observed after lead exposure. These children developed aggressive and delinquent behavior, reduced intelligence, learning difficulties, and hyperactivity ( 109 ). No level of lead exposure seems to be “safe,” and the scientific community has asked the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to reduce the current screening guideline of 10 μg/dl ( 109 ).
It is important to state that impact on the immune system, causing dysfunction and neuroinflammation ( 104 ), is related to poor air quality. Yet, increases in serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM) and the complement component C3 are observed ( 106 ). Another issue is that antigen presentation is affected by air pollutants, as there is an upregulation of costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 on macrophages ( 110 ).
As is known, skin is our shield against ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and other pollutants, as it is the most exterior layer of our body. Traffic-related pollutants, such as PAHs, VOCs, oxides, and PM, may cause pigmented spots on our skin ( 111 ). On the one hand, as already stated, when pollutants penetrate through the skin or are inhaled, damage to the organs is observed, as some of these pollutants are mutagenic and carcinogenic, and, specifically, they affect the liver and lung. On the other hand, air pollutants (and those in the troposphere) reduce the adverse effects of ultraviolet radiation UVR in polluted urban areas ( 111 ). Air pollutants absorbed by the human skin may contribute to skin aging, psoriasis, acne, urticaria, eczema, and atopic dermatitis ( 111 ), usually caused by exposure to oxides and photochemical smoke ( 111 ). Exposure to PM and cigarette smoking act as skin-aging agents, causing spots, dyschromia, and wrinkles. Lastly, pollutants have been associated with skin cancer ( 111 ).
Higher morbidity is reported to fetuses and children when exposed to the above dangers. Impairment in fetal growth, low birth weight, and autism have been reported ( 112 ).
Another exterior organ that may be affected is the eye. Contamination usually comes from suspended pollutants and may result in asymptomatic eye outcomes, irritation ( 112 ), retinopathy, or dry eye syndrome ( 113 , 114 ).
Environmental Impact of Air Pollution
Air pollution is harming not only human health but also the environment ( 115 ) in which we live. The most important environmental effects are as follows.
Acid rain is wet (rain, fog, snow) or dry (particulates and gas) precipitation containing toxic amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. They are able to acidify the water and soil environments, damage trees and plantations, and even damage buildings and outdoor sculptures, constructions, and statues.
Haze is produced when fine particles are dispersed in the air and reduce the transparency of the atmosphere. It is caused by gas emissions in the air coming from industrial facilities, power plants, automobiles, and trucks.
Ozone , as discussed previously, occurs both at ground level and in the upper level (stratosphere) of the Earth's atmosphere. Stratospheric ozone is protecting us from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. In contrast, ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and is a pollutant. Unfortunately, stratospheric ozone is gradually damaged by ozone-depleting substances (i.e., chemicals, pesticides, and aerosols). If this protecting stratospheric ozone layer is thinned, then UV radiation can reach our Earth, with harmful effects for human life (skin cancer) ( 116 ) and crops ( 117 ). In plants, ozone penetrates through the stomata, inducing them to close, which blocks CO 2 transfer and induces a reduction in photosynthesis ( 118 ).
Global climate change is an important issue that concerns mankind. As is known, the “greenhouse effect” keeps the Earth's temperature stable. Unhappily, anthropogenic activities have destroyed this protecting temperature effect by producing large amounts of greenhouse gases, and global warming is mounting, with harmful effects on human health, animals, forests, wildlife, agriculture, and the water environment. A report states that global warming is adding to the health risks of poor people ( 119 ).
People living in poorly constructed buildings in warm-climate countries are at high risk for heat-related health problems as temperatures mount ( 119 ).
Wildlife is burdened by toxic pollutants coming from the air, soil, or the water ecosystem and, in this way, animals can develop health problems when exposed to high levels of pollutants. Reproductive failure and birth effects have been reported.
Eutrophication is occurring when elevated concentrations of nutrients (especially nitrogen) stimulate the blooming of aquatic algae, which can cause a disequilibration in the diversity of fish and their deaths.
Without a doubt, there is a critical concentration of pollution that an ecosystem can tolerate without being destroyed, which is associated with the ecosystem's capacity to neutralize acidity. The Canada Acid Rain Program established this load at 20 kg/ha/yr ( 120 ).
Hence, air pollution has deleterious effects on both soil and water ( 121 ). Concerning PM as an air pollutant, its impact on crop yield and food productivity has been reported. Its impact on watery bodies is associated with the survival of living organisms and fishes and their productivity potential ( 121 ).
An impairment in photosynthetic rhythm and metabolism is observed in plants exposed to the effects of ozone ( 121 ).
Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are involved in the formation of acid rain and are harmful to plants and marine organisms.
Last but not least, as mentioned above, the toxicity associated with lead and other metals is the main threat to our ecosystems (air, water, and soil) and living creatures ( 121 ).
In 2018, during the first WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, the WHO's General Director, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, called air pollution a “silent public health emergency” and “the new tobacco” ( 122 ).
Undoubtedly, children are particularly vulnerable to air pollution, especially during their development. Air pollution has adverse effects on our lives in many different respects.
Diseases associated with air pollution have not only an important economic impact but also a societal impact due to absences from productive work and school.
Despite the difficulty of eradicating the problem of anthropogenic environmental pollution, a successful solution could be envisaged as a tight collaboration of authorities, bodies, and doctors to regularize the situation. Governments should spread sufficient information and educate people and should involve professionals in these issues so as to control the emergence of the problem successfully.
Technologies to reduce air pollution at the source must be established and should be used in all industries and power plants. The Kyoto Protocol of 1997 set as a major target the reduction of GHG emissions to below 5% by 2012 ( 123 ). This was followed by the Copenhagen summit, 2009 ( 124 ), and then the Durban summit of 2011 ( 125 ), where it was decided to keep to the same line of action. The Kyoto protocol and the subsequent ones were ratified by many countries. Among the pioneers who adopted this important protocol for the world's environmental and climate “health” was China ( 3 ). As is known, China is a fast-developing economy and its GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is expected to be very high by 2050, which is defined as the year of dissolution of the protocol for the decrease in gas emissions.
A more recent international agreement of crucial importance for climate change is the Paris Agreement of 2015, issued by the UNFCCC (United Nations Climate Change Committee). This latest agreement was ratified by a plethora of UN (United Nations) countries as well as the countries of the European Union ( 126 ). In this vein, parties should promote actions and measures to enhance numerous aspects around the subject. Boosting education, training, public awareness, and public participation are some of the relevant actions for maximizing the opportunities to achieve the targets and goals on the crucial matter of climate change and environmental pollution ( 126 ). Without any doubt, technological improvements makes our world easier and it seems difficult to reduce the harmful impact caused by gas emissions, we could limit its use by seeking reliable approaches.
Synopsizing, a global prevention policy should be designed in order to combat anthropogenic air pollution as a complement to the correct handling of the adverse health effects associated with air pollution. Sustainable development practices should be applied, together with information coming from research in order to handle the problem effectively.
At this point, international cooperation in terms of research, development, administration policy, monitoring, and politics is vital for effective pollution control. Legislation concerning air pollution must be aligned and updated, and policy makers should propose the design of a powerful tool of environmental and health protection. As a result, the main proposal of this essay is that we should focus on fostering local structures to promote experience and practice and extrapolate these to the international level through developing effective policies for sustainable management of ecosystems.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
IM is employed by the company Delphis S.A. The remaining authors declare that the present review paper was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.

Air Pollution
Our overview of indoor and outdoor air pollution.
By Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser
This article was first published in October 2017 and last revised in February 2024.
Air pollution is one of the world's largest health and environmental problems. It develops in two contexts: indoor (household) air pollution and outdoor air pollution.
In this topic page, we look at the aggregate picture of air pollution – both indoor and outdoor. We also have dedicated topic pages that look in more depth at these subjects:
Indoor Air Pollution
Look in detail at the data and research on the health impacts of Indoor Air Pollution, attributed deaths, and its causes across the world
Outdoor Air Pollution
Look in detail at the data and research on exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution, its health impacts, and attributed deaths across the world
Look in detail at the data and research on energy consumption, its impacts around the world today, and how this has changed over time
See all interactive charts on Air Pollution ↓
Other research and writing on air pollution on Our World in Data:
- Air pollution: does it get worse before it gets better?
- Data Review: How many people die from air pollution?
- Energy poverty and indoor air pollution: a problem as old as humanity that we can end within our lifetime
- How many people do not have access to clean fuels for cooking?
- What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?
- What the history of London’s air pollution can tell us about the future of today’s growing megacities
- When will countries phase out coal power?
Air pollution is one of the world's leading risk factors for death
Air pollution is responsible for millions of deaths each year.
Air pollution – the combination of outdoor and indoor particulate matter and ozone – is a risk factor for many of the leading causes of death, including heart disease, stroke, lower respiratory infections, lung cancer, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), in its Global Burden of Disease study, provides estimates of the number of deaths attributed to the range of risk factors for disease. 1
In the visualization, we see the number of deaths per year attributed to each risk factor. This chart shows the global total but can be explored for any country or region using the "change country" toggle.
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for death. In low-income countries, it is often very near the top of the list (or is the leading risk factor).
Air pollution contributes to one in ten deaths globally
In recent years, air pollution has contributed to one in ten deaths globally. 2
In the map shown here, we see the share of deaths attributed to air pollution across the world.
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for disease burden
Air pollution is one of the leading risk factors for death. But its impacts go even further; it is also one of the main contributors to the global disease burden.
Global disease burden takes into account not only years of life lost to early death but also the number of years lived in poor health.
In the visualization, we see risk factors ranked in order of DALYs – disability-adjusted life years – the metric used to assess disease burden. Again, air pollution is near the top of the list, making it one of the leading risk factors for poor health across the world.
Air pollution not only takes years from people's lives but also has a large effect on the quality of life while they're still living.
Who is most affected by air pollution?
Death rates from air pollution are highest in low-to-middle-income countries.
Air pollution is a health and environmental issue across all countries of the world but with large differences in severity.
In the interactive map, we show death rates from air pollution across the world, measured as the number of deaths per 100,000 people in a given country or region.
The burden of air pollution tends to be greater across both low and middle-income countries for two reasons: indoor pollution rates tend to be high in low-income countries due to a reliance on solid fuels for cooking, and outdoor air pollution tends to increase as countries industrialize and shift from low to middle incomes.
A map of the number of deaths from air pollution by country can be found here .
How are death rates from air pollution changing?
Death rates from air pollution are falling – mainly due to improvements in indoor pollution.
In the visualization, we show global death rates from air pollution over time – shown as the total air pollution – in addition to the individual contributions from outdoor and indoor pollution.
Globally, we see that in recent decades, the death rates from total air pollution have declined: since 1990, death rates have nearly halved. But, as we see from the breakdown, this decline has been primarily driven by improvements in indoor air pollution.
Death rates from indoor air pollution have seen an impressive decline, while improvements in outdoor pollution have been much more modest.
You can explore this data for any country or region using the "change country" toggle on the interactive chart.
Interactive charts on air pollution
Murray, C. J., Aravkin, A. Y., Zheng, P., Abbafati, C., Abbas, K. M., Abbasi-Kangevari, M., ... & Borzouei, S. (2020). Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 . The Lancet , 396 (10258), 1223-1249.
Here, we use the term 'contributes,' meaning it was one of the attributed risk factors for a given disease or cause of death. There can be multiple risk factors for a given disease that can amplify one another. This means that in some cases, air pollution was not the only risk factor but one of several.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.

Earth Day Match: Donate to Defend Our Planet
Drilling on public lands, mass wildlife extinctions, worsening climate change—our planet is in crisis. Help us fight back this Earth Day and your gift will be matched $1 for $1.
Air Pollution: Everything You Need to Know
How smog, soot, greenhouse gases, and other top air pollutants are affecting the planet—and your health.
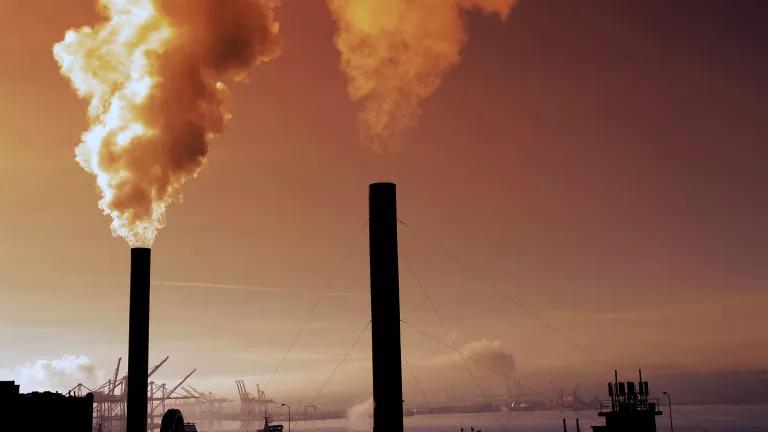

- Share this page block
What is air pollution?
What causes air pollution, effects of air pollution, air pollution in the united states, air pollution and environmental justice, controlling air pollution, how to help reduce air pollution, how to protect your health.
Air pollution refers to the release of pollutants into the air—pollutants that are detrimental to human health and the planet as a whole. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) , each year, indoor and outdoor air pollution is responsible for nearly seven million deaths around the globe. Ninety-nine percent of human beings currently breathe air that exceeds the WHO’s guideline limits for pollutants, with those living in low- and middle-income countries suffering the most. In the United States, the Clean Air Act , established in 1970, authorizes the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to safeguard public health by regulating the emissions of these harmful air pollutants.
“Most air pollution comes from energy use and production,” says John Walke , director of the Clean Air team at NRDC. Driving a car on gasoline, heating a home with oil, running a power plant on fracked gas : In each case, a fossil fuel is burned and harmful chemicals and gases are released into the air.
“We’ve made progress over the last 50 years in improving air quality in the United States, thanks to the Clean Air Act. But climate change will make it harder in the future to meet pollution standards, which are designed to protect health ,” says Walke.
Air pollution is now the world’s fourth-largest risk factor for early death. According to the 2020 State of Global Air report —which summarizes the latest scientific understanding of air pollution around the world—4.5 million deaths were linked to outdoor air pollution exposures in 2019, and another 2.2 million deaths were caused by indoor air pollution. The world’s most populous countries, China and India, continue to bear the highest burdens of disease.
“Despite improvements in reducing global average mortality rates from air pollution, this report also serves as a sobering reminder that the climate crisis threatens to worsen air pollution problems significantly,” explains Vijay Limaye , senior scientist in NRDC’s Science Office. Smog, for instance, is intensified by increased heat, forming when the weather is warmer and there’s more ultraviolet radiation. In addition, climate change increases the production of allergenic air pollutants, including mold (thanks to damp conditions caused by extreme weather and increased flooding) and pollen (due to a longer pollen season). “Climate change–fueled droughts and dry conditions are also setting the stage for dangerous wildfires,” adds Limaye. “ Wildfire smoke can linger for days and pollute the air with particulate matter hundreds of miles downwind.”
The effects of air pollution on the human body vary, depending on the type of pollutant, the length and level of exposure, and other factors, including a person’s individual health risks and the cumulative impacts of multiple pollutants or stressors.
Smog and soot
These are the two most prevalent types of air pollution. Smog (sometimes referred to as ground-level ozone) occurs when emissions from combusting fossil fuels react with sunlight. Soot—a type of particulate matter —is made up of tiny particles of chemicals, soil, smoke, dust, or allergens that are carried in the air. The sources of smog and soot are similar. “Both come from cars and trucks, factories, power plants, incinerators, engines, generally anything that combusts fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, or natural gas,” Walke says.
Smog can irritate the eyes and throat and also damage the lungs, especially those of children, senior citizens, and people who work or exercise outdoors. It’s even worse for people who have asthma or allergies; these extra pollutants can intensify their symptoms and trigger asthma attacks. The tiniest airborne particles in soot are especially dangerous because they can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream and worsen bronchitis, lead to heart attacks, and even hasten death. In 2020, a report from Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health showed that COVID-19 mortality rates were higher in areas with more particulate matter pollution than in areas with even slightly less, showing a correlation between the virus’s deadliness and long-term exposure to air pollution.
These findings also illuminate an important environmental justice issue . Because highways and polluting facilities have historically been sited in or next to low-income neighborhoods and communities of color, the negative effects of this pollution have been disproportionately experienced by the people who live in these communities.
Hazardous air pollutants
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead , dioxins, and benzene. “These are also most often emitted during gas or coal combustion, incineration, or—in the case of benzene—found in gasoline,” Walke says. Benzene, classified as a carcinogen by the EPA, can cause eye, skin, and lung irritation in the short term and blood disorders in the long term. Dioxins, more typically found in food but also present in small amounts in the air, is another carcinogen that can affect the liver in the short term and harm the immune, nervous, and endocrine systems, as well as reproductive functions. Mercury attacks the central nervous system. In large amounts, lead can damage children’s brains and kidneys, and even minimal exposure can affect children’s IQ and ability to learn.
Another category of toxic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are by-products of traffic exhaust and wildfire smoke. In large amounts, they have been linked to eye and lung irritation, blood and liver issues, and even cancer. In one study , the children of mothers exposed to PAHs during pregnancy showed slower brain-processing speeds and more pronounced symptoms of ADHD.
Greenhouse gases
While these climate pollutants don’t have the direct or immediate impacts on the human body associated with other air pollutants, like smog or hazardous chemicals, they are still harmful to our health. By trapping the earth’s heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases lead to warmer temperatures, which in turn lead to the hallmarks of climate change: rising sea levels, more extreme weather, heat-related deaths, and the increased transmission of infectious diseases. In 2021, carbon dioxide accounted for roughly 79 percent of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions, and methane made up more than 11 percent. “Carbon dioxide comes from combusting fossil fuels, and methane comes from natural and industrial sources, including large amounts that are released during oil and gas drilling,” Walke says. “We emit far larger amounts of carbon dioxide, but methane is significantly more potent, so it’s also very destructive.”
Another class of greenhouse gases, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) , are thousands of times more powerful than carbon dioxide in their ability to trap heat. In October 2016, more than 140 countries signed the Kigali Agreement to reduce the use of these chemicals—which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators—and develop greener alternatives over time. (The United States officially signed onto the Kigali Agreement in 2022.)
Pollen and mold
Mold and allergens from trees, weeds, and grass are also carried in the air, are exacerbated by climate change, and can be hazardous to health. Though they aren’t regulated, they can be considered a form of air pollution. “When homes, schools, or businesses get water damage, mold can grow and produce allergenic airborne pollutants,” says Kim Knowlton, professor of environmental health sciences at Columbia University and a former NRDC scientist. “ Mold exposure can precipitate asthma attacks or an allergic response, and some molds can even produce toxins that would be dangerous for anyone to inhale.”
Pollen allergies are worsening because of climate change . “Lab and field studies are showing that pollen-producing plants—especially ragweed—grow larger and produce more pollen when you increase the amount of carbon dioxide that they grow in,” Knowlton says. “Climate change also extends the pollen production season, and some studies are beginning to suggest that ragweed pollen itself might be becoming a more potent allergen.” If so, more people will suffer runny noses, fevers, itchy eyes, and other symptoms. “And for people with allergies and asthma, pollen peaks can precipitate asthma attacks, which are far more serious and can be life-threatening.”

More than one in three U.S. residents—120 million people—live in counties with unhealthy levels of air pollution, according to the 2023 State of the Air report by the American Lung Association (ALA). Since the annual report was first published, in 2000, its findings have shown how the Clean Air Act has been able to reduce harmful emissions from transportation, power plants, and manufacturing.
Recent findings, however, reflect how climate change–fueled wildfires and extreme heat are adding to the challenges of protecting public health. The latest report—which focuses on ozone, year-round particle pollution, and short-term particle pollution—also finds that people of color are 61 percent more likely than white people to live in a county with a failing grade in at least one of those categories, and three times more likely to live in a county that fails in all three.
In rankings for each of the three pollution categories covered by the ALA report, California cities occupy the top three slots (i.e., were highest in pollution), despite progress that the Golden State has made in reducing air pollution emissions in the past half century. At the other end of the spectrum, these cities consistently rank among the country’s best for air quality: Burlington, Vermont; Honolulu; and Wilmington, North Carolina.
No one wants to live next door to an incinerator, oil refinery, port, toxic waste dump, or other polluting site. Yet millions of people around the world do, and this puts them at a much higher risk for respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease, neurological damage, cancer, and death. In the United States, people of color are 1.5 times more likely than whites to live in areas with poor air quality, according to the ALA.
Historically, racist zoning policies and discriminatory lending practices known as redlining have combined to keep polluting industries and car-choked highways away from white neighborhoods and have turned communities of color—especially low-income and working-class communities of color—into sacrifice zones, where residents are forced to breathe dirty air and suffer the many health problems associated with it. In addition to the increased health risks that come from living in such places, the polluted air can economically harm residents in the form of missed workdays and higher medical costs.
Environmental racism isn't limited to cities and industrial areas. Outdoor laborers, including the estimated three million migrant and seasonal farmworkers in the United States, are among the most vulnerable to air pollution—and they’re also among the least equipped, politically, to pressure employers and lawmakers to affirm their right to breathe clean air.
Recently, cumulative impact mapping , which uses data on environmental conditions and demographics, has been able to show how some communities are overburdened with layers of issues, like high levels of poverty, unemployment, and pollution. Tools like the Environmental Justice Screening Method and the EPA’s EJScreen provide evidence of what many environmental justice communities have been explaining for decades: that we need land use and public health reforms to ensure that vulnerable areas are not overburdened and that the people who need resources the most are receiving them.
In the United States, the Clean Air Act has been a crucial tool for reducing air pollution since its passage in 1970, although fossil fuel interests aided by industry-friendly lawmakers have frequently attempted to weaken its many protections. Ensuring that this bedrock environmental law remains intact and properly enforced will always be key to maintaining and improving our air quality.
But the best, most effective way to control air pollution is to speed up our transition to cleaner fuels and industrial processes. By switching over to renewable energy sources (such as wind and solar power), maximizing fuel efficiency in our vehicles, and replacing more and more of our gasoline-powered cars and trucks with electric versions, we'll be limiting air pollution at its source while also curbing the global warming that heightens so many of its worst health impacts.
And what about the economic costs of controlling air pollution? According to a report on the Clean Air Act commissioned by NRDC, the annual benefits of cleaner air are up to 32 times greater than the cost of clean air regulations. Those benefits include up to 370,000 avoided premature deaths, 189,000 fewer hospital admissions for cardiac and respiratory illnesses, and net economic benefits of up to $3.8 trillion for the U.S. economy every year.
“The less gasoline we burn, the better we’re doing to reduce air pollution and the harmful effects of climate change,” Walke explains. “Make good choices about transportation. When you can, ride a bike, walk, or take public transportation. For driving, choose a car that gets better miles per gallon of gas or buy an electric car .” You can also investigate your power provider options—you may be able to request that your electricity be supplied by wind or solar. Buying your food locally cuts down on the fossil fuels burned in trucking or flying food in from across the world. And most important: “Support leaders who push for clean air and water and responsible steps on climate change,” Walke says.
- “When you see in the news or hear on the weather report that pollution levels are high, it may be useful to limit the time when children go outside or you go for a jog,” Walke says. Generally, ozone levels tend to be lower in the morning.
- If you exercise outside, stay as far as you can from heavily trafficked roads. Then shower and wash your clothes to remove fine particles.
- The air may look clear, but that doesn’t mean it’s pollution free. Utilize tools like the EPA’s air pollution monitor, AirNow , to get the latest conditions. If the air quality is bad, stay inside with the windows closed.
- If you live or work in an area that’s prone to wildfires, stay away from the harmful smoke as much as you’re able. Consider keeping a small stock of masks to wear when conditions are poor. The most ideal masks for smoke particles will be labelled “NIOSH” (which stands for National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) and have either “N95” or “P100” printed on it.
- If you’re using an air conditioner while outdoor pollution conditions are bad, use the recirculating setting to limit the amount of polluted air that gets inside.
This story was originally published on November 1, 2016, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

The Particulars of PM 2.5

What Are the Effects of Climate Change?
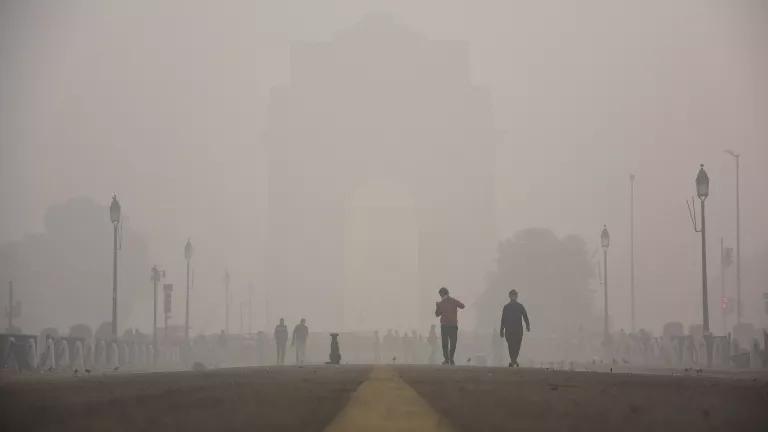

Fossil Fuel Air Pollution Kills One in Five People
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Biology, Ecology, Health, Earth Science, Geography
Loading ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants . Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash . They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land. Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides —chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects— seep into waterways and harm wildlife . All living things—from one-celled microbes to blue whales—depend on Earth ’s supply of air and water. When these resources are polluted, all forms of life are threatened. Pollution is a global problem. Although urban areas are usually more polluted than the countryside, pollution can spread to remote places where no people live. For example, pesticides and other chemicals have been found in the Antarctic ice sheet . In the middle of the northern Pacific Ocean, a huge collection of microscopic plastic particles forms what is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . Air and water currents carry pollution. Ocean currents and migrating fish carry marine pollutants far and wide. Winds can pick up radioactive material accidentally released from a nuclear reactor and scatter it around the world. Smoke from a factory in one country drifts into another country. In the past, visitors to Big Bend National Park in the U.S. state of Texas could see 290 kilometers (180 miles) across the vast landscape . Now, coal-burning power plants in Texas and the neighboring state of Chihuahua, Mexico have spewed so much pollution into the air that visitors to Big Bend can sometimes see only 50 kilometers (30 miles). The three major types of pollution are air pollution , water pollution , and land pollution . Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible . A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible . Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants are invisible. It can make people’s eyes burn and make them have difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of lung cancer . Sometimes, air pollution kills quickly. In 1984, an accident at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, released a deadly gas into the air. At least 8,000 people died within days. Hundreds of thou sands more were permanently injured. Natural disasters can also cause air pollution to increase quickly. When volcanoes erupt , they eject volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere . Volcanic ash can discolor the sky for months. After the eruption of the Indonesian volcano of Krakatoa in 1883, ash darkened the sky around the world. The dimmer sky caused fewer crops to be harvested as far away as Europe and North America. For years, meteorologists tracked what was known as the “equatorial smoke stream .” In fact, this smoke stream was a jet stream , a wind high in Earth’s atmosphere that Krakatoa’s air pollution made visible. Volcanic gases , such as sulfur dioxide , can kill nearby residents and make the soil infertile for years. Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy, famously erupted in 79, killing hundreds of residents of the nearby towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Most victims of Vesuvius were not killed by lava or landslides caused by the eruption. They were choked, or asphyxiated , by deadly volcanic gases. In 1986, a toxic cloud developed over Lake Nyos, Cameroon. Lake Nyos sits in the crater of a volcano. Though the volcano did not erupt, it did eject volcanic gases into the lake. The heated gases passed through the water of the lake and collected as a cloud that descended the slopes of the volcano and into nearby valleys . As the toxic cloud moved across the landscape, it killed birds and other organisms in their natural habitat . This air pollution also killed thousands of cattle and as many as 1,700 people. Most air pollution is not natural, however. It comes from burning fossil fuels —coal, oil , and natural gas . When gasoline is burned to power cars and trucks, it produces carbon monoxide , a colorless, odorless gas. The gas is harmful in high concentrations , or amounts. City traffic produces highly concentrated carbon monoxide. Cars and factories produce other common pollutants, including nitrogen oxide , sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbons . These chemicals react with sunlight to produce smog , a thick fog or haze of air pollution. The smog is so thick in Linfen, China, that people can seldom see the sun. Smog can be brown or grayish blue, depending on which pollutants are in it. Smog makes breathing difficult, especially for children and older adults. Some cities that suffer from extreme smog issue air pollution warnings. The government of Hong Kong, for example, will warn people not to go outside or engage in strenuous physical activity (such as running or swimming) when smog is very thick.
When air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide mix with moisture, they change into acids . They then fall back to earth as acid rain . Wind often carries acid rain far from the pollution source. Pollutants produced by factories and power plants in Spain can fall as acid rain in Norway. Acid rain can kill all the trees in a forest . It can also devastate lakes, streams, and other waterways. When lakes become acidic, fish can’t survive . In Sweden, acid rain created thousands of “ dead lakes ,” where fish no longer live. Acid rain also wears away marble and other kinds of stone . It has erased the words on gravestones and damaged many historic buildings and monuments . The Taj Mahal , in Agra, India, was once gleaming white. Years of exposure to acid rain has left it pale. Governments have tried to prevent acid rain by limiting the amount of pollutants released into the air. In Europe and North America, they have had some success, but acid rain remains a major problem in the developing world , especially Asia. Greenhouse gases are another source of air pollution. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane occur naturally in the atmosphere. In fact, they are necessary for life on Earth. They absorb sunlight reflected from Earth, preventing it from escaping into space. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, they keep Earth warm enough for people to live. This is called the greenhouse effect . But human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has increased the greenhouse effect, and average temperatures across the globe are rising. The decade that began in the year 2000 was the warmest on record. This increase in worldwide average temperatures, caused in part by human activity, is called global warming . Global warming is causing ice sheets and glaciers to melt. The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise at a rate of two millimeters (0.09 inches) per year. The rising seas will eventually flood low-lying coastal regions . Entire nations, such as the islands of Maldives, are threatened by this climate change . Global warming also contributes to the phenomenon of ocean acidification . Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Fewer organisms can survive in warmer, less salty waters. The ocean food web is threatened as plants and animals such as coral fail to adapt to more acidic oceans. Scientists have predicted that global warming will cause an increase in severe storms . It will also cause more droughts in some regions and more flooding in others. The change in average temperatures is already shrinking some habitats, the regions where plants and animals naturally live. Polar bears hunt seals from sea ice in the Arctic. The melting ice is forcing polar bears to travel farther to find food , and their numbers are shrinking. People and governments can respond quickly and effectively to reduce air pollution. Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a dangerous form of air pollution that governments worked to reduce in the 1980s and 1990s. CFCs are found in gases that cool refrigerators, in foam products, and in aerosol cans . CFCs damage the ozone layer , a region in Earth’s upper atmosphere. The ozone layer protects Earth by absorbing much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation . When people are exposed to more ultraviolet radiation, they are more likely to develop skin cancer, eye diseases, and other illnesses. In the 1980s, scientists noticed that the ozone layer over Antarctica was thinning. This is often called the “ ozone hole .” No one lives permanently in Antarctica. But Australia, the home of more than 22 million people, lies at the edge of the hole. In the 1990s, the Australian government began an effort to warn people of the dangers of too much sun. Many countries, including the United States, now severely limit the production of CFCs. Water Pollution Some polluted water looks muddy, smells bad, and has garbage floating in it. Some polluted water looks clean, but is filled with harmful chemicals you can’t see or smell. Polluted water is unsafe for drinking and swimming. Some people who drink polluted water are exposed to hazardous chemicals that may make them sick years later. Others consume bacteria and other tiny aquatic organisms that cause disease. The United Nations estimates that 4,000 children die every day from drinking dirty water. Sometimes, polluted water harms people indirectly. They get sick because the fish that live in polluted water are unsafe to eat. They have too many pollutants in their flesh. There are some natural sources of water pollution. Oil and natural gas, for example, can leak into oceans and lakes from natural underground sources. These sites are called petroleum seeps . The world’s largest petroleum seep is the Coal Oil Point Seep, off the coast of the U.S. state of California. The Coal Oil Point Seep releases so much oil that tar balls wash up on nearby beaches . Tar balls are small, sticky pieces of pollution that eventually decompose in the ocean.
Human activity also contributes to water pollution. Chemicals and oils from factories are sometimes dumped or seep into waterways. These chemicals are called runoff. Chemicals in runoff can create a toxic environment for aquatic life. Runoff can also help create a fertile environment for cyanobacteria , also called blue-green algae . Cyanobacteria reproduce rapidly, creating a harmful algal bloom (HAB) . Harmful algal blooms prevent organisms such as plants and fish from living in the ocean. They are associated with “ dead zones ” in the world’s lakes and rivers, places where little life exists below surface water. Mining and drilling can also contribute to water pollution. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a major contributor to pollution of rivers and streams near coal mines . Acid helps miners remove coal from the surrounding rocks . The acid is washed into streams and rivers, where it reacts with rocks and sand. It releases chemical sulfur from the rocks and sand, creating a river rich in sulfuric acid . Sulfuric acid is toxic to plants, fish, and other aquatic organisms. Sulfuric acid is also toxic to people, making rivers polluted by AMD dangerous sources of water for drinking and hygiene . Oil spills are another source of water pollution. In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to gush from the ocean floor. In the following months, hundreds of millions of gallons of oil spewed into the gulf waters. The spill produced large plumes of oil under the sea and an oil slick on the surface as large as 24,000 square kilometers (9,100 square miles). The oil slick coated wetlands in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi, killing marsh plants and aquatic organisms such as crabs and fish. Birds, such as pelicans , became coated in oil and were unable to fly or access food. More than two million animals died as a result of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Buried chemical waste can also pollute water supplies. For many years, people disposed of chemical wastes carelessly, not realizing its dangers. In the 1970s, people living in the Love Canal area in Niagara Falls, New York, suffered from extremely high rates of cancer and birth defects . It was discovered that a chemical waste dump had poisoned the area’s water. In 1978, 800 families living in Love Canal had to a bandon their homes. If not disposed of properly, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants can escape into the environment. Radioactive waste can harm living things and pollute the water. Sewage that has not been properly treated is a common source of water pollution. Many cities around the world have poor sewage systems and sewage treatment plants. Delhi, the capital of India, is home to more than 21 million people. More than half the sewage and other waste produced in the city are dumped into the Yamuna River. This pollution makes the river dangerous to use as a source of water for drinking or hygiene. It also reduces the river’s fishery , resulting in less food for the local community. A major source of water pollution is fertilizer used in agriculture . Fertilizer is material added to soil to make plants grow larger and faster. Fertilizers usually contain large amounts of the elements nitrogen and phosphorus , which help plants grow. Rainwater washes fertilizer into streams and lakes. There, the nitrogen and phosphorus cause cyanobacteria to form harmful algal blooms. Rain washes other pollutants into streams and lakes. It picks up animal waste from cattle ranches. Cars drip oil onto the street, and rain carries it into storm drains , which lead to waterways such as rivers and seas. Rain sometimes washes chemical pesticides off of plants and into streams. Pesticides can also seep into groundwater , the water beneath the surface of the Earth. Heat can pollute water. Power plants, for example, produce a huge amount of heat. Power plants are often located on rivers so they can use the water as a coolant . Cool water circulates through the plant, absorbing heat. The heated water is then returned to the river. Aquatic creatures are sensitive to changes in temperature. Some fish, for example, can only live in cold water. Warmer river temperatures prevent fish eggs from hatching. Warmer river water also contributes to harmful algal blooms. Another type of water pollution is simple garbage. The Citarum River in Indonesia, for example, has so much garbage floating in it that you cannot see the water. Floating trash makes the river difficult to fish in. Aquatic animals such as fish and turtles mistake trash, such as plastic bags, for food. Plastic bags and twine can kill many ocean creatures. Chemical pollutants in trash can also pollute the water, making it toxic for fish and people who use the river as a source of drinking water. The fish that are caught in a polluted river often have high levels of chemical toxins in their flesh. People absorb these toxins as they eat the fish. Garbage also fouls the ocean. Many plastic bottles and other pieces of trash are thrown overboard from boats. The wind blows trash out to sea. Ocean currents carry plastics and other floating trash to certain places on the globe, where it cannot escape. The largest of these areas, called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. According to some estimates, this garbage patch is the size of Texas. The trash is a threat to fish and seabirds, which mistake the plastic for food. Many of the plastics are covered with chemical pollutants. Land Pollution Many of the same pollutants that foul the water also harm the land. Mining sometimes leaves the soil contaminated with dangerous chemicals. Pesticides and fertilizers from agricultural fields are blown by the wind. They can harm plants, animals, and sometimes people. Some fruits and vegetables absorb the pesticides that help them grow. When people consume the fruits and vegetables, the pesticides enter their bodies. Some pesticides can cause cancer and other diseases. A pesticide called DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) was once commonly used to kill insects, especially mosquitoes. In many parts of the world, mosquitoes carry a disease called malaria , which kills a million people every year. Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize for his understanding of how DDT can control insects and other pests. DDT is responsible for reducing malaria in places such as Taiwan and Sri Lanka. In 1962, American biologist Rachel Carson wrote a book called Silent Spring , which discussed the dangers of DDT. She argued that it could contribute to cancer in humans. She also explained how it was destroying bird eggs, which caused the number of bald eagles, brown pelicans, and ospreys to drop. In 1972, the United States banned the use of DDT. Many other countries also banned it. But DDT didn’t disappear entirely. Today, many governments support the use of DDT because it remains the most effective way to combat malaria. Trash is another form of land pollution. Around the world, paper, cans, glass jars, plastic products, and junked cars and appliances mar the landscape. Litter makes it difficult for plants and other producers in the food web to create nutrients . Animals can die if they mistakenly eat plastic. Garbage often contains dangerous pollutants such as oils, chemicals, and ink. These pollutants can leech into the soil and harm plants, animals, and people. Inefficient garbage collection systems contribute to land pollution. Often, the garbage is picked up and brought to a dump, or landfill . Garbage is buried in landfills. Sometimes, communities produce so much garbage that their landfills are filling up. They are running out of places to dump their trash. A massive landfill near Quezon City, Philippines, was the site of a land pollution tragedy in 2000. Hundreds of people lived on the slopes of the Quezon City landfill. These people made their living from recycling and selling items found in the landfill. However, the landfill was not secure. Heavy rains caused a trash landslide, killing 218 people. Sometimes, landfills are not completely sealed off from the land around them. Pollutants from the landfill leak into the earth in which they are buried. Plants that grow in the earth may be contaminated, and the herbivores that eat the plants also become contaminated. So do the predators that consume the herbivores. This process, where a chemical builds up in each level of the food web, is called bioaccumulation . Pollutants leaked from landfills also leak into local groundwater supplies. There, the aquatic food web (from microscopic algae to fish to predators such as sharks or eagles) can suffer from bioaccumulation of toxic chemicals. Some communities do not have adequate garbage collection systems, and trash lines the side of roads. In other places, garbage washes up on beaches. Kamilo Beach, in the U.S. state of Hawai'i, is littered with plastic bags and bottles carried in by the tide . The trash is dangerous to ocean life and reduces economic activity in the area. Tourism is Hawai'i’s largest industry . Polluted beaches discourage tourists from investing in the area’s hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Some cities incinerate , or burn, their garbage. Incinerating trash gets rid of it, but it can release dangerous heavy metals and chemicals into the air. So while trash incinerators can help with the problem of land pollution, they sometimes add to the problem of air pollution. Reducing Pollution Around the world, people and governments are making efforts to combat pollution. Recycling, for instance, is becoming more common. In recycling, trash is processed so its useful materials can be used again. Glass, aluminum cans, and many types of plastic can be melted and reused . Paper can be broken down and turned into new paper. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and waterways. Austria and Switzerland have the highest recycling rates. These nations recycle between 50 and 60 percent of their garbage. The United States recycles about 30 percent of its garbage. Governments can combat pollution by passing laws that limit the amount and types of chemicals factories and agribusinesses are allowed to use. The smoke from coal-burning power plants can be filtered. People and businesses that illegally dump pollutants into the land, water, and air can be fined for millions of dollars. Some government programs, such as the Superfund program in the United States, can force polluters to clean up the sites they polluted. International agreements can also reduce pollution. The Kyoto Protocol , a United Nations agreement to limit the emission of greenhouse gases, has been signed by 191 countries. The United States, the world’s second-largest producer of greenhouse gases, did not sign the agreement. Other countries, such as China, the world’s largest producer of greenhouse gases, have not met their goals. Still, many gains have been made. In 1969, the Cuyahoga River, in the U.S. state of Ohio, was so clogged with oil and trash that it caught on fire. The fire helped spur the Clean Water Act of 1972. This law limited what pollutants could be released into water and set standards for how clean water should be. Today, the Cuyahoga River is much cleaner. Fish have returned to regions of the river where they once could not survive. But even as some rivers are becoming cleaner, others are becoming more polluted. As countries around the world become wealthier, some forms of pollution increase. Countries with growing economies usually need more power plants, which produce more pollutants. Reducing pollution requires environmental, political, and economic leadership. Developed nations must work to reduce and recycle their materials, while developing nations must work to strengthen their economies without destroying the environment. Developed and developing countries must work together toward the common goal of protecting the environment for future use.
How Long Does It Last? Different materials decompose at different rates. How long does it take for these common types of trash to break down?
- Paper: 2-4 weeks
- Orange peel: 6 months
- Milk carton: 5 years
- Plastic bag: 15 years
- Tin can: 100 years
- Plastic bottle: 450 years
- Glass bottle: 500 years
- Styrofoam: Never
Indoor Air Pollution The air inside your house can be polluted. Air and carpet cleaners, insect sprays, and cigarettes are all sources of indoor air pollution.
Light Pollution Light pollution is the excess amount of light in the night sky. Light pollution, also called photopollution, is almost always found in urban areas. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems by confusing the distinction between night and day. Nocturnal animals, those that are active at night, may venture out during the day, while diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, may remain active well into the night. Feeding and sleep patterns may be confused. Light pollution also indicates an excess use of energy. The dark-sky movement is a campaign by people to reduce light pollution. This would reduce energy use, allow ecosystems to function more normally, and allow scientists and stargazers to observe the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution Noise pollution is the constant presence of loud, disruptive noises in an area. Usually, noise pollution is caused by construction or nearby transportation facilities, such as airports. Noise pollution is unpleasant, and can be dangerous. Some songbirds, such as robins, are unable to communicate or find food in the presence of heavy noise pollution. The sound waves produced by some noise pollutants can disrupt the sonar used by marine animals to communicate or locate food.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

- In PowerPoint Downloads
- On July 10, 2021
Air Pollution PPT | Free Download | 17 Slides
Table of contents.
To live, we need to breathe. To breathe, we need fresh air. Fresh air is one of the basic and essential things we need to live on earth. Fresh air is equally important to every one us as food and water. Even plants need oxygen to convert food into energy. From these things, we can understand the importance of oxygen and fresh air. A place without oxygen will be a dead zone with no humans, animals, and plants. Without oxygen, nobody can survive on earth.
All these facts point the fingers at the importance of keeping air pollution-free. But the truth is, the air is getting polluted at a massive rate every day. There are hundreds of causes. In these, there are some which are very harmful to us. But how can we reduce the rate of air pollution? Well, there are different ways that we could try to stop air pollution. Before that, let us find out what are the utmost causes of air pollution. Here are they.
What Do We Mean By Air Pollution?
It’s simple. Air pollution refers to the release of pollutants into the air like Nitrogen Oxide, Volatile Organic Compounds, Carbon Dioxide, Sulphur Oxide, dioxins, and other harmful gases. Once these gases are released, they become a colossal threat to the environment and human health.
How Do We Know the Quality of Air?
The purity of air measured using an AQI thermometer that runs on a scale from 0 to 500. The AQI refers to Air Quality Index. It measures how pure or polluted the surrounding air is. If the numeric value on the scale is between 0-50, the quality of the surrounding air is considered healthy and satisfactory. As the values increase, the quality of the air decreases. If AQI is showing a value of 500, that means you are standing in a hazardous surrounding. Have a look at the AQI chart below for more details.
Major Causes Of Air Pollution
It is well known to everyone how air pollution happens. It happens in many ways. Sometimes careless and reckless human activities lead to the major reasons for air pollution. Even though, here are some of the common causes of air pollution.
Burning of Plastic Wastes.
How do we avoid plastics from our houses? Either we throw them or light them up, right? These careless acts will lead to the worst pollution ever. Burning them releases toxic gases like dioxins, furans, mercury, and polychlorinated. These gases are a threat to the atmosphere, vegetation, humans, and animal health. If we throw them out, they can remain in the soil for 20-500 years before fully decomposing based on the material and structure. Over these years, it pollutes the soil and harms the earth.
So, burning and throwing plastic does not work and leads to air pollution or soil pollution in the long term perspective. Then what will we do? Well, we can recycle and reuse plastic to an extent. But once the plastic is melted and reformed into new products, the quality of plastic gets reduced. In addition, the quality of plastic will keep reducing with every successive recycling. Furthermore, recycling is limited to a number 3 or 4 times because of the quality compromise of plastic.
In fact, we only have a limited number of opportunities in the case of plastic. Either we reduce the use of plastic or recycle and reuse them as much as we can.
Limiting the use of plastic seems more practical and smooth in our day-to-day life. There are many instances where we can reduce the use of plastic. Here are some of the tracts where we can instantly act to limit the usages of plastic
- Use cloth bags instead of plastics bags while going to the shops.
- Use paper plates and tumblers instead of plastic ones when you arrange a tea party or get-togethers.
- Use paper straws in restaurants and coffee shops.
- Use paper bottled soft drinks.
There are more and more situations where we can reduce the unnecessary use of plastic covers and materials. It can turn out well when more people come forward with the same mindset of bringing down plastic use.
Are there any alternatives for plastic?
Yes, there are. But literally, there are no materials with the exact matching properties with plastic. For instance, properties like durability, strength, water-resistant, lightweight, and inexpensive are rare to find in materials without polymer as an ingredient. Scientists and researchers are trying to formulate materials with the matching properties as plastic but with less pollution.
As said earlier, there are many instances where we can reduce the use of plastic and always try to avoid it as much as we can. Even if they are baby steps towards reducing plastic, take it and help our environment. Moreover, be a part of keeping the city and your premises clean.
Industrial Emission
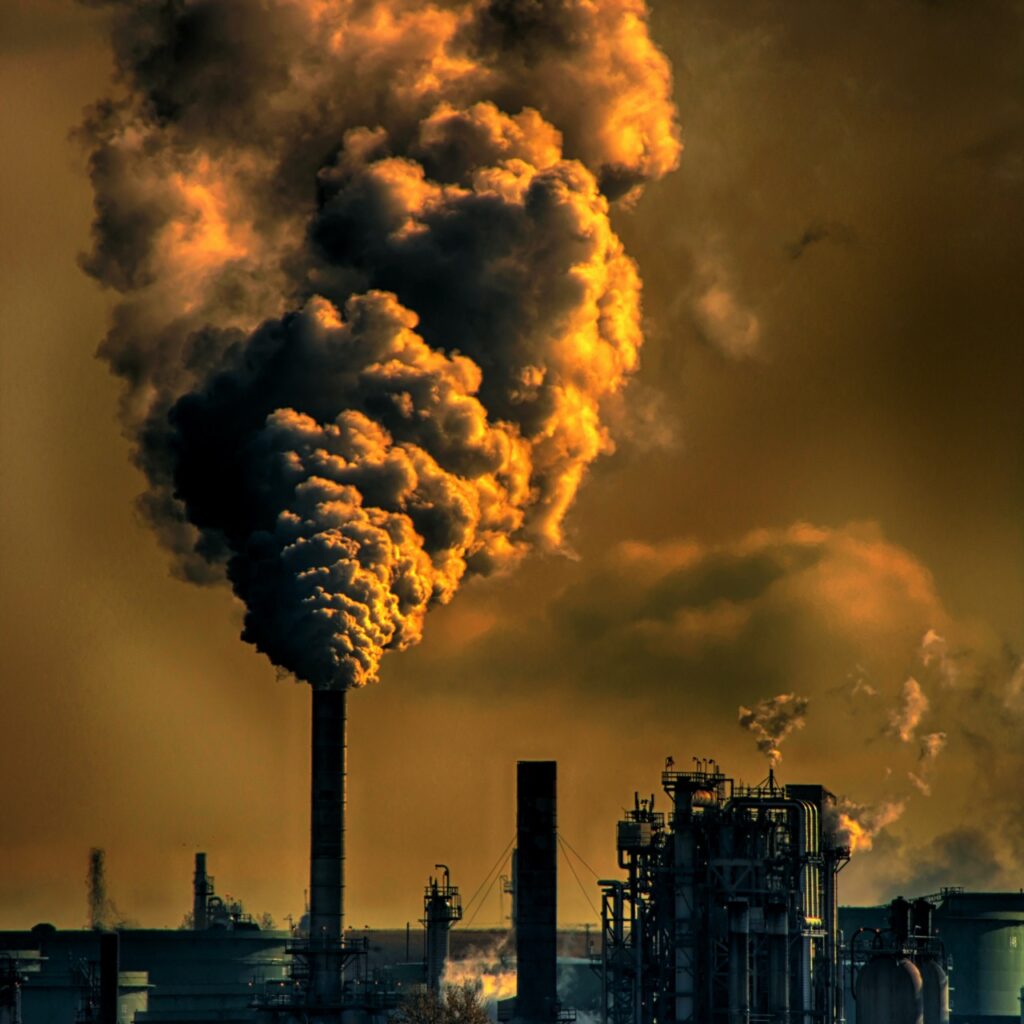

Industries play a colossal role in all kinds of pollutions. They contribute almost one-third to the overall when we compare industrial pollution with other causes. Industries will be the 2nd largest cause of air pollution, water pollution, and sound pollution. Pollutants like carbon monoxide, Nitrogen dioxide, and Sulfur dioxide are released when they operate factories and industries. The volume of pollutants released into the atmosphere is way more than we imagine and the problems they can make are huge.
It is necessary to know where the pollution happens and who pollutes the air the most. Studies say that industries that produce electricity pollute the atmosphere more than any other industry.
A considerable amount of pollutants is kicked from the industries when the continuous burning of fossil fuels happened. These emitted gases make the most of the troubles to the ozone layer and cause ozone layer depletion. We need both electricity and the earth. We can not avoid one or the other for any reason. The only way is to protect both without harming each other. The only solution for this will be the rise of green energy. Only the challenge facing is the continuous supply of energy. Green energy like solar and wind are very cost-effective and pollution-free when comparing to the traditional ones.
Each and every individual can contribute and can be a part of saving the earth from air pollution and global warming. Switch to green energy as much as we can and reduce the consumption of traditional electricity from the government or private companies. Nowadays, everybody has inverters in the home as a standard facility. It will not cost you much to connect 2 or 3 solar panels to the battery and save 60% power usage from the traditional electric supply.
How can we reduce industrial air pollution?
As we said earlier, industries and factories are essential for the growth of the people and nation. We can’t stop factories in the name of air pollution. What we can do is, we can find some ways to reduce the amount of air pollution. For instance, we should try to convert these harmful gases to regular gases with the help of proper techniques and setups.
Most importantly, people living near industrial areas are very likely to have many allergies and lung diseases. Always wear a mask when you are going out or going near industrial and factory areas. If you are working in an industrial area, always wear a mask and other safety gear to ensure maximum safety.

Wildfires can take place at any time. It is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire caused by lightning strikes. As the name says, it occurs largely in forest areas. Mostly, the lighting strikes on the trees, branches, dry grass, and then the fire is generated. Eventually, this fire will spread to other trees, branches, and grasses and becomes wildfires, and causes air pollution.
Wildfires are common forested areas of the United States and Canada. It is one of the causes of air pollution, deforestation, and animal extinction. In a wildfire, many animals lose their lives and shelter. Some get burns and wounds in the running through the wildfire.
All these will continue until fire settles down. Sometimes it takes 2-3 days to settle down completely. But in the end, we lose animals, trees, the environment, and what not?
Also, sometimes the causes of wildfire can be different. Sometimes it happens due to the carelessness of people living around the forest. For instance, even trash burning and campfires can spread fire if not concerned well. So it is always recommended to take precautions while doing wildfire potential activities.
Wildfires get worse when unattended. If you notice any fires or burns that need attention, call the authorities. Sometimes the fire can be controlled before getting worse.
Transportation
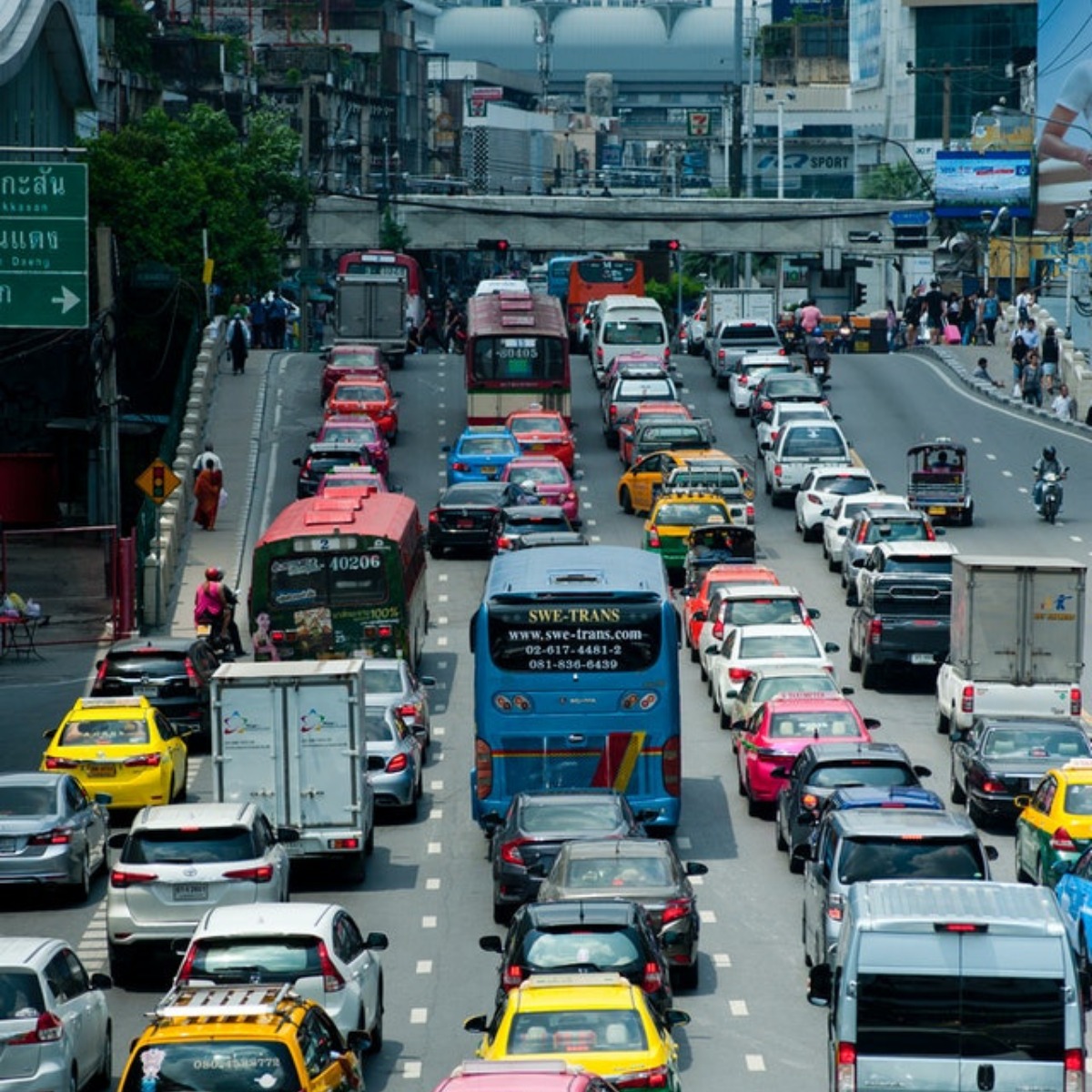

Transportation holds a neck-to-neck position with industries in the rate of air pollution. As we all know, the number of vehicles on the road is increasing day by day. Just look around, we could see houses with more than three vehicles even if they don’t need all of them. As the number of vehicles increases, the rate of pollution also tends to be increased. Old model vehicles are more likely to produce more pollution than new ones. Because when the vehicles get older and older, the amount of carbon emission increases. The rate of pollution is still on the rise even after the government and authorities made pollution laws strict.
Every country has its own vehicle emission standards or norms for the safety of the environment and people living in the country. But still, transportation holds the position for the majority of air pollutions happening around the world.
How can we reduce pollution caused by vehicles?
Earlier, it was challenging to find an alternative for fuels like petrol or diesel. Right now, technology has improved – researchers found a better alternative solution for the petrol and diesel engines for automobiles. Yes, they are EV’s. Electric vehicles are completely different from traditional vehicles. They are pollution-free and highly efficient than fuel engines. Electric vehicles can be charged from the house or charging stations in and around the city. EV’s have 5x efficiency more than the regular diesel or petrol-fueled automobiles and 4x lesser reduced pollution.
EV’s are on the rise. By 2025, at least 50% of the new vehicles coming out from the factories will be electric vehicles. It will seriously help to reduce the rate of pollution to some extend. People will switch to EV’s when companies launch better models with luxury and comfort.
It may sound crazy to most of us. But think about walking a little every day and avoid taking cars or bikes for smaller distances. Or, use a bicycle to travel nearby. It will help us to improve both our health and the earth’s health.
What are the health issues due to air pollution?
The quality of the air we breathe is very crucial. Poor quality can cause many health diseases in both adults and kids. Especially to the people living in cities, the chances of getting a disease like heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, and acute lower respiratory infections are very high.
Long-term exposure to polluted air in kids can lead to loss of lung capacity, asthma and emphysema. In addition, senior citizens are more likely to get allergies and breathing difficulties since they are less immune to the conditions. As a precaution to all of these, we can wear a mask while going out and traveling. If you are living in a highly polluted area, consider buying an air purifier for your home. An air purifier can help to improve the quality of air by filtering and thereby enabling a healthy environment inside our home for everyone.
How does air pollution affect environmental health?
The toxic gases also affect the environment in the same way. As the amount of harmful gases increases in the earth, the uncertainty of the environment’s health also increases. Changes in climates like temperature hikes, monsoon pattern shifts, and unexpected cyclones are a few examples. In these, ozone layer depletion is being the most complicated one.
We already know what is an ozone layer, and whats does it do? Let’s recall them for a while. The ozone layer is a part of the earth’s atmosphere, and it absorbs almost all of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet light. Guess what will happen when the ozone layer gets holes. All the harmful rays will fall into the animals, plants, and people on earth through the ozone layer holes. Studies say that by 2064 the ozone layer concentration levels may come to zero if the rate of pollution continues invariably. If that happens, the earth will not be a suitable place to live. The fun factor is, we don’t have any space other than earth to live right now. So, we have to protect the planet from being a desert.
Day by day, the rate of pollution is increasing. The hard truth is, nobody is really caring about the future of our planet. Even the government and authorities are keeping their eyes closed on social issues like global warming, air pollution, and soil erosion. If it keeps going like this, the earth will become uninhabitable.
Protecting the earth from pollutions is not deputed on somebody else. Each one of us should take responsibility and behave sensibly to protect the earth from pollution.
Download Free PPT
Jinu Varghese
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper matti pibus leo.
Get Started
- Brand Assets
- Flex UI Kit
- Modern UI Kit
- Framer UI Kit
- Gradients UI Kit
- Black & White UI Kit
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

49 templates

18 templates

40 templates

american football
16 templates

41 templates

tropical rainforest
29 templates
Action Plan for Water Pollution Prevention Infographics
Free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Welcome to this comprehensive collection of infographics focused on the vital topic of water pollution prevention! In a world where water is our most precious resource, understanding the causes, effects, and preventive measures is crucial. These infographics are thoughtfully designed to provide you with clear insights into the sources of water pollution, its impact on ecosystems, and actionable steps we can take to preserve and protect our waters for generations to come. And what’s more, they integrate seamlessly into our “Action Plan for Water Pollution Prevention” presentation! Download and join in the fight against water pollution.
Features of these infographics
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 32 different infographics to boost your presentations
- Include icons and Flaticon’s extension for further customization
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Include information about how to edit and customize your infographics
- Supplemental infographics for the template Action Plan for Water Pollution Prevention
How can I use the infographics?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute the infographics?
Combines with:
This template can be combined with this other one to create the perfect presentation:

Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The air pollution from factories, industries, thermal power stations, oil refineries, etc can be controlled by washing their smoke and waste gases with jets of water. The air pollution can be controlled by using non-polluting sources of energy like solar energy, wind energy and hydro energy for generating electricity. 19
Download for Free: This creative pollution Google Slides themes and PowerPoint template is available as a free download, making it accessible to anyone committed to addressing environmental pollution. Use it to champion environmental causes and advocate for change. Air pollution is sneaky; it's hard to see and even harder to measure.
Air pollutants often deteriorate and change the constitution of building materials, thereby degrading, eroding, or damaging many buildings and infrastructure at an increased rate over time. Effects of Water Pollution. Effects on Human Beings. One of the major effects of this is sickness.
Download the "Raising Awareness on Transport Pollution" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different... Multi-purpose.
Presentation Transcript. Air, Water, and Soil Pollution A meta-study conducted in 2007 by David Pimentel at Cornell University suggests that as many as 40% of all deaths worldwide are linked to soil, water, and air pollution. Air pollution from smoke and various chemicals kills 3 million people a year worldwide.
What is air pollution? Air lets our living planet breathe—it's the mixture of gases that fills the atmosphere, giving life to the plants and animals that make Earth such a vibrant place. Broadly speaking, air is almost entirely made up of two gases (78 percent nitrogen and 21 percent oxygen), with a few other gases (such as carbon dioxide and argon) present in much smaller quantities.
Air pollution consists of chemicals or particles in the air that can harm the health of humans, animals, and plants. It also damages buildings. Pollutants in the air take many forms. They can be gases, solid particles, or liquid droplets. Sources of Air Pollution Pollution enters the Earth's atmosphere in many different ways. Most air pollution is created by people, taking the form of ...
Air pollution is a critical issue that has a significant impact on our environment and health. One of the most damaging consequences of air pollution is acid rain, which can cause damage to trees, crops, and waterways. The meaning of this is a serious one, so wait no more to raise awareness about this issue.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. It is clear that air pollution needs to be addressed in our modern society, so organizing a meet up to talk about this environmental issue is certainly a good idea. For such an overwhelming task, having a presentation to follow makes everything much easier. This template here comes complete with ...
Today one of the most pressing environmental concerns is water pollution. Download this water pollution ppt template and outline your thoughts on water pollution and what can you do to prevent it.. Today water pollution, Air Pollution is becoming a serious concern. Our Free Water Pollution PowerPoint Template features a thoughtfully crafted blend of eye-catching visuals, data-driven charts ...
This video helps to learn how to create a PowerPoint Presentation.This video content is example so,what you want type it.Air Pollution ppthttps://learnbypkte...
Environmental pollution has many facets, and the resultant health risks include diseases in almost all organ systems. Thus, a chapter on air and water pollution control links with chapters on, for instance, diarrheal diseases (chapter 19), respiratory diseases in children and adults (chapters 25 and 35), cancers (chapter 29), neurological disorders (chapter 32), and cardiovascular disease ...
What is air pollution? Learn how greenhouse gases, smog, and toxic pollutants effect climate change, and human health. ... If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. ... Ways to Give Apply for a Grant Careers ...
Air pollution is determined as the presence of pollutants in the air in large quantities for long periods. Air pollutants are dispersed particles, hydrocarbons, CO, CO 2, NO, NO 2, SO 3, etc. Water pollution is organic and inorganic charge and biological charge at high levels that affect the water quality (34, 35).
Air pollution is a health and environmental issue across all countries of the world but with large differences in severity. In the interactive map, we show death rates from air pollution across the world, measured as the number of deaths per 100,000 people in a given country or region.
A number of air pollutants pose severe health risks and can sometimes be fatal, even in small amounts. Almost 200 of them are regulated by law; some of the most common are mercury, lead, dioxins ...
Traffic-Related Air Pollution (TRAP), a mixture of gasses and particles, has most of the elements of human-made air pollution: ground-level ozone, various forms of carbon, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and fine particulate matter. Ozone, an atmospheric gas, is often called smog ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash. They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land.
Water pollutants come from either point sources or dispersed sources. A point source is a pipe or channel, such as those used for discharge from an industrial facility or a city sewerage system.A dispersed (or nonpoint) source is a very broad unconfined area from which a variety of pollutants enter the water body, such as the runoff from an agricultural area.
Air Pollution PPT | Free Download | 17 Slides. To live, we need to breathe. To breathe, we need fresh air. Fresh air is one of the basic and essential things we need to live on earth. Fresh air is equally important to every one us as food and water. Even plants need oxygen to convert food into energy. From these things, we can understand the ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. There are many different types of pollution and it is important to know how we can reduce the ecological impact we can cause with each of them, any help is good! If you are also environmentally conscious, we bring you this template with a collection of infographics about air pollution. Inside ...
These infographics are thoughtfully designed to provide you with clear insights into the sources of water pollution, its impact on ecosystems, and actionable steps we can take to preserve and protect our waters for generations to come. And what's more, they integrate seamlessly into our "Action Plan for Water Pollution Prevention ...