How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.

Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures.

Chapter 21. Conclusion: The Value of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is engaging research, in the best sense of the word.
A few of the meanings of engage = to attract or hold by influence or power; to hold the attention of; to induce to participate; to enter into contest with; to bring together or interlock; to deal with at length; to pledge oneself; to begin and carry on an enterprise; to take part or participate; to come together; engaged = to be actively involved in or committed; to greatly interest; to be embedded with. ( Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary )
There really is no “cookbook” for conducting qualitative research. Each study is unique because the social world is rich and full of wonders, and those of us who are curious about it have our own position in that world and our own understandings and experiences we bring with us when we seek to explore it. And yet even though our reports may be subjective, we can do what we can to make them honest and intelligible to everyone else. Learning how to do that is learning how to be a qualitative researcher rather than simply an amateur observer. Helping you understand that and getting you ready for doing so have been the goal of this book.

According to Lareau ( 2021:36 ), excellent qualitative work must include all the following elements: a clear contribution to new knowledge, a succinct assessment of previous literature that shows the holes in the literature, a research question that can be answered with the data in hand, a breadth and depth in the data collection, a clear exposition of the results, a deep analysis that links the evidence to the interpretation, an acknowledgment of disconfirming evidence, a discussion that uses the case as a springboard to reflect on more general concerns, and a full discussion of implications for ideas and practices. The emphasis on rigor, the clear contribution to new knowledge, and the reflection on more general concerns place qualitative research within the “scientific” camp vis-à-vis the “humanistic inquiry” camp of pure description or ideographic approaches. The attention to previous literature and filling the holes in what we know about a phenomenon or case or situation set qualitative research apart from otherwise excellent journalism, which makes no pretensions of writing to or for a larger body of knowledge.
In the magnificently engaging untextbook Rocking Qualitative Social Science , Ashley Rubin ( 2021 ) notes, “Rigorous research does not have to be rigid” ( 3 ). I agree with her claim that there are many ways to get to the top of the mountain, and you can have fun doing so. An ardent rock climber, Rubin calls her approach the Dirtbagger approach, a way of climbing the mountain that is creative, flexible, and definitely outside proscribed methods. Here are eleven lessons offered by Rubin in paraphrase form with commentary and direct quotes noted:
- There is no right way to do qualitative social science, “and people should choose the approach that works for them, for the particular project at hand, given whatever constraints and opportunities are happening in their life at the time. ( 252 )”
- Disagreements about what is proper qualitative research are distracting and misleading.
- Even though research questions are very important, they can and most likely will change during data collection or even data analysis—don’t worry about this.
- Your findings will have a bigger impact if you’ve connected them to previous literature; this shows that you are part of the larger conversation. This “anchor” can be a policy issue or a theoretical debate in the literature, but it need not be either. Sometimes what we do is really novel (but rarely—so always poke around and check before proceeding as if you are inventing the wheel).
- Although there are some rules you really must follow when designing your study (e.g., how to obtain informed consent, defining a sample), unexpected things often happen in the course of data collection that make a mockery of your original plans. Be flexible.
- Sometimes you have chosen a topic for some reason you can’t yet articulate to yourself—the subject or site just calls to you in some way. That’s fine. But you will still need to justify your choice in some way (hint: see number 4 above).
- Pay close attention to your sample: “Think about what you are leaving out, what your data allow you to observe, and what you can do to fill in some of those blanks” (252). And when you can’t fill them in, be honest about this when writing about the limitations of your study.
- Even if you are doing interviews, archival research, focus groups, or any other method of data collection that does not actually require “going into the field,” you can still approach your work as fieldwork. This means taking fieldnotes or memos about what you are observing and how you are reacting and processing those observations or interviews or interactions or documents. Remember that you yourself are the instrument of data collection, so keep a reflective eye on yourself throughout.
- Memo, memo, memo. There is no magic about how data become findings. It takes a lot of work, a lot of reflection, a lot of writing. Analytic memos are the helpful bridge between all that raw data and the presented findings.
- Rubin strongly rejects the idea that qualitative research cannot make causal claims. I would agree, but only to a point. We don’t make the kinds of predictive causal claims you see in quantitative research, and it can confuse you and lead you down some unpromising paths if you think you can. That said, qualitative research can help demonstrate the causal mechanisms by which something happens. Qualitative research is also helpful in exploring alternative explanations and counterfactuals. If you want to know more about qualitative research and causality, I encourage you to read chapter 10 of Rubin’s text.
- Some people are still skeptical about the value of qualitative research because they don’t understand the rigor required of it and confuse it with journalism or even fiction writing. You are just going to have to deal with this—maybe even people sitting on your committee are going to question your research. So be prepared to defend qualitative research by knowing the common misconceptions and criticisms and how to respond to them. We’ve talked a bit about these in chapter 20, and I also encourage you to read chapter 10 of Rubin’s text for more.

Hopefully, by the time you have reached the end of this book, you will have done a bit of your own qualitative research—maybe you’ve conducted an interview or practiced taking fieldnotes. You may have read some examples of excellent qualitative research and have (hopefully!) come to appreciate the value of this approach. This is a good time, then, to take a step back and think about the ways that qualitative research is valuable, distinct and different from both quantitative methods and humanistic (nonscientific) inquiry.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study?
Across all Western countries, we can observe a strong statistical relationship between young people’s educational attainment and their parent’s level of education. If you have at least one parent who went to university, your own chances of going to and graduating from university are much higher compared to not having university-educated parents. Why this happens is much less clear… This is where qualitative research becomes important: to help us get a clearer understanding of the dynamics that lead to this observed statistical relationship.
In my own research, I go a step further and look at young men and women who have crossed this barrier: they have become the first in their family to go to university. I am interested in finding out why and how first-in-family university students made it to university and how being at university is experienced. In-depth interviews allow me to learn about hopes, aspirations, fears, struggles, resilience and success. Interviews give participants an opportunity to tell their stories in their own words while also validating their experiences.
I often ask the young people I interview what being in my studies means to them. As one of my participants told me, it is good to know that “people like me are worth studying.” I cannot think of a better way to explain why qualitative research is important.
-Wolfgang Lehman, author of Education and Society: Canadian Perspectives
For me personally, the real value of the qualitative approach is that it helps me address the concerns I have about the social world—how people make sense of their lives, how they create strategies to deal with unfair circumstances or systems of oppression, and why they are motivated to act in some situations but not others. Surveys and other forms of large impersonal data collection simply do not allow me to get at these concerns. I appreciate other forms of research for other kinds of questions. This ecumenical approach has served me well in my own career as a sociologist—I’ve used surveys of students to help me describe classed pathways through college and into the workforce, supplemented by interviews and focus groups that help me explain and understand the patterns uncovered by quantitative methods ( Hurst 2019 ). My goal for this book has not been to convince you to become a qualitative researcher exclusively but rather to understand and appreciate its value under the right circumstances (e.g., with the right questions and concerns).
In the same way that we would not use a screwdriver to hammer a nail into the wall, we don’t want to misuse the tools we have at hand. Nor should we critique the screwdriver for its failure to do the hammer’s job. Qualitative research is not about generating predictions or demonstrating causality. We can never statistically generalize our findings from a small sample of people in a particular context to the world at large. But that doesn’t mean we can’t generate better understandings of how the world works, despite “small” samples. Excellent qualitative research does a great job describing (whether through “thick description” or illustrative quotes) a phenomenon, case, or setting and generates deeper insight into the social world through the development of new concepts or identification of patterns and relationships that were previously unknown to us. The two components—accurate description and theoretical insight—are generated together through the iterative process of data analysis, which itself is based on a solid foundation of data collection. And along the way, we can have some fun and meet some interesting people!

Supplement: Twenty Great (engaging, insightful) Books Based on Qualitative Research
Armstrong, Elizabeth A. and Laura T. Hamilton. 2015. Paying for the Party: How College Maintains Inequality . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Bourgois, Phillipe and Jeffrey Schonberg. 2009. Righteous Dopefiend . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
DiTomaso, Nancy. 2013. The American Non-dilemma: Racial Inequality without Racism . Thousand Oaks, CA; SAGE.
Ehrenreich, Barbara. 2010. Nickel and Dimed: On (Not) Getting By in America . New York: Metropolitan Books.
Fine, Gary Alan. 2018. Talking Art: The Culture of Practice and the Practice of Culture in MFA Education . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ghodsee, Kristen Rogheh. 2011. Lost in Transition: Ethnographies of Everyday Life after Communism . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Gowan, Teresa. 2010. Hobos, Hustlers, and Backsliders: Homeless in San Francisco . Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Graeber, David. 2013. The Democracy Project: A History, a Crisis, a Movement . New York: Spiegel & Grau.
Grazian, David. 2015. American Zoo: A Sociological Safari . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Hartigan, John. 1999. Racial Situations: Class Predicaments of Whiteness in Detroit . Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press.
Ho, Karen Zouwen. 2009. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street. Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Hochschild, Arlie Russell. 2018. Strangers in Their Own Land: Anger and Mourning on the American Right . New York: New Press.
Lamont, Michèle. 1994. Money, Morals, and Manners: The Culture of the French and the American Upper-Middle Class . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Lareau, Annette. 2011. Unequal Childhoods: Class, Race, and Family Life. 2nd ed with an Update a Decade Later. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Leondar-Wright, Betsy. 2014. Missing Class: Strengthening Social Movement Groups by Seeing Class Cultures . Ithaca, NY: ILR Press.
Macleod, Jay. 2008. Ain’t No Makin’ It: Aspirations and Attainment in a Low-Income Neighborhood . 3rd ed. New York: Routledge.
Newman, Katherine T. 2000. No Shame in My Game: The Working Poor in the Inner City . 3rd ed. New York: Vintage Press.
Sherman, Rachel. 2006. Class Acts: Service and Inequality in Luxury Hotels . Berkeley: University of California Press.
Streib, Jessi. 2015. The Power of the Past: Understanding Cross-Class Marriages . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Stuber, Jenny M. 2011. Inside the College Gates: How Class and Culture Matter in Higher Education . Lanham, Md.: Lexington Books.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
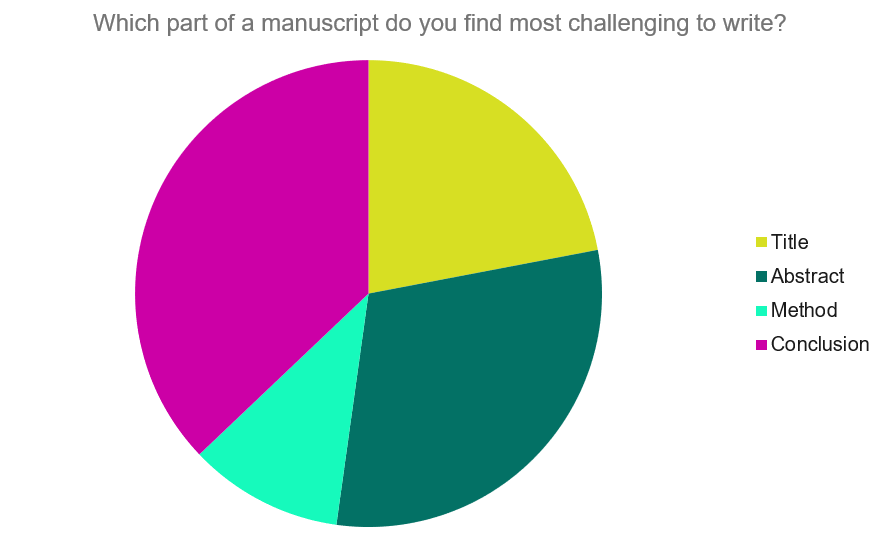
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
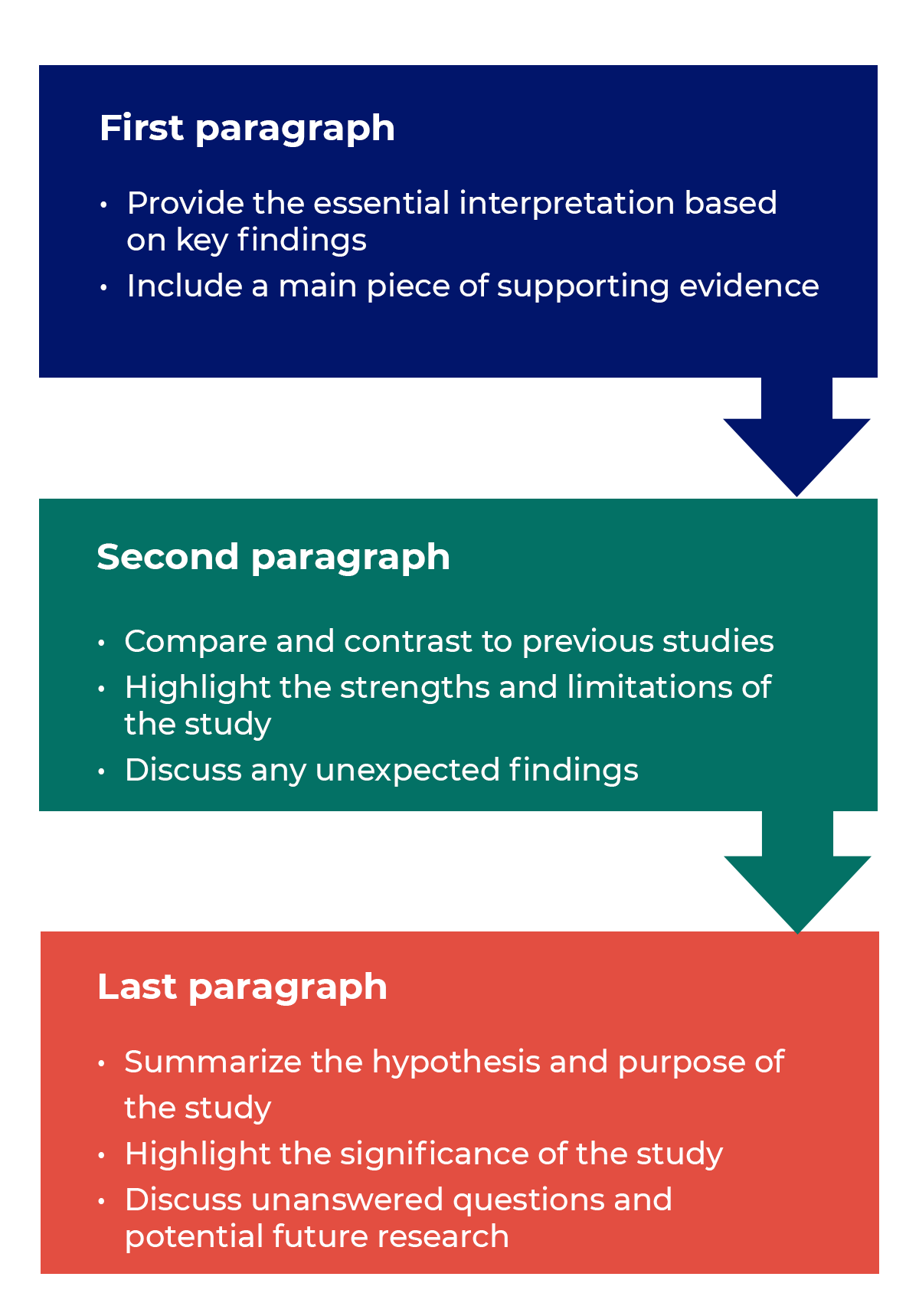
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Culture
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

A newer edition of this book is available.
- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

31 Writing Up Qualitative Research
Jane F. Gilgun, School of Social Work, University of Minnesota, Twin Cities
- Published: 04 August 2014
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter provides guidelines for writing journal articles based on qualitative approaches. The guidelines are part of the tradition of the Chicago School of Sociology and the author’s experience as a writer and reviewer. The guidelines include understanding experiences in context, immersion, interpretations grounded in accounts of informants’ lived experiences, and research as action-oriented. The chapter also covers writing articles that report findings based on ethnographies, autoethnographies, performances, poetry, and photography and other graphic media.
How researchers write up results for journal publications depends on the purposes of the research and the methodologies they use. Some topics are standard, such as statements about methods and methodologies, but how to represent other topics, like related research and theory, reflexivity, and informants’ accounts, may vary. For example, articles based on ethnographic research may be structured differently from writing up research whose purpose is theory development. Journal editors and reviewers often are familiar with variations in style of write-ups, but, when they are not, they may ask for modifications that violate the methodological principles of the research. A common reviewer request is for percentages, which has little meaning in almost all forms of qualitative research because the purpose of the research is to identify patterns of meanings and not distributions of variables. For example, Irvine’s (2013) ethnography of the meanings of pets to homeless people shows a variety of meaning without giving the number of participants from which she drew.
Authors sometimes move easily through the review process, but most often they do not, not only because reviewers might not “get it,” but also because authors have left out, underemphasized, or been less than clear about aspects of their research that reviewers and editors believe are important. Working with editors and reviewers frequently results in improved articles.
The purpose of this chapter is to provide guidelines for writing journal articles based on qualitative approaches. My intended audience is composed of researchers, reviewers for journals, and journal editors. Reviewers for funding agencies may also find this chapter useful. I use the terms “journal article” and “research report” as synonyms, even though some journal articles are not reports of research. I have derived the guidelines from ideas associated with the Chicago School of Sociology and my experience as an author and reviewer. Although the Chicago School was, as Becker (1999) wrote, “open to various ways of doing sociology” (p. 10), the ideas in this chapter are part of the tradition, but they are not representative of the entire tradition. Furthermore, the ideas are not fixed but are open-ended because they evolve over time. I have followed the principles of the Chicago School of Sociology throughout my career, augmented by updates to these ideas, experiments with other traditions, and the sense I make of my own experiences as researcher, author, and reviewer.
The ideas on which I draw include understanding experiences in context, immersion, interpretations grounded in accounts of informants’ lived experiences, and research as action-oriented ( Bulmer, 1984 ; Faris, 1967 ; Gilgun, 1999 d ; 2005 a ; 2012 a ; 2013 b ). To follow these principles, researchers do in-depth studies that take into account the multiple contextual factors that influence meanings and interpretations, seek multiple points of view, and often use multiple methods such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. Researchers do this style of research not only because what they learn is interesting, but because they want to do useful research; that is, research that leads to social actions and even transformations in policies, programs, and interventions. Authors and reviewers pay attention to these principles. Authors convey them in their write-ups, and reviewers look for them as they develop their appraisals.
Excellent writing up of qualitative research matches these principles. In other words, write-ups convey lived experience within multiple contexts, multiple points of view, and analyses that deepen understandings. In addition, if the research is applied, then authors write about how findings may contribute to quality of life. Qualitative researchers from other traditions may follow similar or different guidelines in their write-ups, and I sometimes note other styles of write-ups. Often these variations are related to terminology and not procedures. The reach of the Chicago School of Sociology is wide and deep.
Following these guidelines does not guarantee an easy review process, but this article will be helpful to researchers as they plan and craft their articles and as they respond to reviewers’ and editors’ comments. After almost thirty years of publishing research based on qualitative approaches, almost as many years as a reviewer, and the editing of three collections of qualitative research reports ( Gilgun, Daly, & Handel, 1992 ; Gilgun & Sussman, 1996 : Gilgun & Sands, 2012 ), I am positioned to offer helpful guidelines, not only to authors but also to reviewers and journal editors.
I begin this chapter with a discussion of general principles and then cover the content of typical sections of research reports. Some of the general material fits into various sections of reports, such as methods and findings. In those cases, I do not repeat material already covered and assume that my writing is clear enough so that readers know how the general material fits into particular sections of articles.
Although most of this chapter addresses the writing of conventional research reports, I also cover writing articles that report findings through ethnographies, autoethnographies, performances, poetry, and photography and other graphic media. Ethnographies are based on researchers’ immersion in the field, where they do extensive observations, interviews, and often document analysis (see Block, 2012 ). Geertz’s (1973) notion of “thick description” is associated with ethnographies. Thick description is characterized by research reports that show the matrix of meanings that researchers identify and attempt to represent in their reports. Autoethnographies are in-depth reflective accounts of individual lives that the narrators themselves write ( Ellis, 2009 ). Ethnographies and autoethnographies involve reflections on meanings, contexts, and other wider influences on individual lives. They are studies of intersections of individual lives and wider cultural themes and practices. Reports of these types of research can look different from conventional research reports in that they appear less formal; the usual sections of methods, literature review, findings, and analysis may have different names; and the sections may be in places that fit the logical flow of the research and not the typical structure of introductory material, methods, results, and discussion. Despite these superficial differences, researchers who write these kinds of articles seek to deepen understandings and hope to move audiences to action through conveying lived experience in context and through multiple points of view. They also typically seek transformations of persons and societies. Links between these forms of research and Chicago School traditions are self-evident.
Some General Principles
Research reports that have these characteristics depend on the quality of the data on which the reports are based, the quality of the analysis, and the skills of researchers in conveying the analysis concisely and with “grab” ( Glaser, 1978 ), which means writing that is vivid and memorable ( Gilgun, 2005 b ). Grab brings findings to life. With grab, human experiences jump off the page. Priority is given to the voices of research participants, whom I call informants, with citations and the wisdom of other researchers providing important contextual information. The voices and analyses of researchers do not dominate ( Gilgun, 2005 c ), except in some articles whose purpose is theory development or the presentation of a theory. Researcher analyses often are important, especially in putting forth social action recommendations that stem from the experiences of informants.
A well-done report shows consistency between research traditions and the writing-up of research. For example, reflexivity statements, writing with grab, and copious excerpts from fieldnotes, interviews, and documents of various sorts are consistent with phenomenological approaches whose emphasis is on lived experience and interpretations that informants make of their experiences. Researchers new to qualitative research, however, often mix their traditions without realizing it, which works when the traditions are compatible. When the traditions are not compatible, the write-ups can be confusing and even contradictory ( Gilgun, 2005 d ). Some authors may write in distanced, third-person styles while attempting to convey informants’ lived experiences. These scholars may, therefore, have difficulty getting their articles accepted. Hopefully, this chapter will facilitate the writing of research reports that show consistency across their many parts and save scholars from rejections of work over which they have taken much care.
Details on These General Principles
In this section, I provide more detail on writing up qualitative research. I begin with a discussion of the need for high-quality data, high-quality analysis, and grab. I then move on to the details of the report, such as the place of prior research and theory, contents of methods sections, organization of findings, and the balance between descriptive material and authors’ interpretations. Dilemmas abound. Writing up qualitative research is not for the faint of heart.
High-Quality Data
Since qualitative researchers seek to understand the subjective experiences of research informants in various contexts, high-quality data result in large part from the degree that researchers practice immersion and to the degree that both researchers and informants develop rapport and engage with each other. Through active engagement, informants share their experiences with the kind of detail that brings their experiences to life. How to develop rapport is beyond the scope of this article, but openness and acceptance of whatever informants say are fundamental to engagement. Interviewers do not have to agree with the values that informants’ accounts convey, as when I interview murderers and rapists ( Gilgun, 2008 ), but we do maintain a neutrality that allows the dialogue to continue ( Gilgun & Anderson, 2013 ). The content of interviews is not about us and our preferences, but about understanding informants.
Prolonged engagement can result in quality data. In interview research, prolonged engagement allows for informants’ multiple perspectives to emerge, including inconsistencies, contradictions, ambiguities, and ambivalences. In addition, prolonged engagement facilitates the kind of trust needed for informants to share personal, sensitive information in detail, which are the kinds of data that qualitative researchers seek. Prolonged engagement also gives researchers time to reflect on what they are learning and experiencing through the interviews. This provides opportunities to develop new understandings and test new understandings through subsequent research. Their understandings thus deepen and broaden. Informants, too, can reflect, reconsider, and deepen the accounts they share.
Prolonged engagement means in-depth interviews, typically multiple interviews of more than an hour each. As mentioned earlier, time between interviews allows researchers and informants to reflect on the previous interview and prepare for the next. Researchers can do background reading, discuss emerging ideas with others, and formulate pertinent new questions. Informants may retrieve long-forgotten memories and interpretations through interviews. If they have only one interview, they have no opportunity to share with researchers the material that arises after the single interview is concluded.
There are exceptions to multiple interviews as necessary for immersion and high-quality data. When researchers have expertise in interviewing and when the topic is focused, one interview of between ninety minutes to two hours could provide some depth. Even under these conditions, however, more than one interview is ideal. I did a study that involved one ninety-minute interview with perpetrators of child sexual abuse in order to understand the circumstances under which their abusive behaviors became known to law enforcement. Thus, the interview was focused. The interviewees were volunteers who had talked about the topic many times in the course of their involvement in sex abuse treatment programs. They shared their stories with depth and breadth. I, too, was well-prepared. By then, I had had about twenty-five years of experience interviewing people about personal, sensitive topics. The informants provided accounts not only because the topic was focused, but because they were willing to share and I was willing to listen and to ask questions about their sexually abusive behaviors. With one interview, however, I knew relatively little about their social histories and general worldviews. Thus, I did not have the specifics necessary to place their accounts into context. The material they provided remained valuable and resulted in one publication ( Sharma & Gilgun, 2008 ) and others in planning stages. I prefer two or more interviews because of the importance of contextual data.
In observational studies, prolonged engagement means that researchers do multiple observations over time to obtain the nuances and details that compose human actions. Observational studies often have interview components and also may have document analysis as well. In document analysis, prolonged engagement means researchers base their analyses on an ample storehouse of documents and not just flit in and out of the documents. The quality of document analysis depends on whether the analysis shows multiple perspectives, patterns, and variations within patterns. Ethnographies have these characteristics. Block’s (2012) ethnographic research on AIDS orphans in Lesotho, Africa, is an example of a well-done ethnography.
Sample Size
In principle, the size of the sample and the depth of the interview affect whether researchers can claim immersion. The more depth and breadth each case in a study has, the smaller the sample size can be. For example, researchers can engage in immersion through a single in-depth case study when they do multiple interviews and if multiple facets of the case are examined. Case studies are investigations of single units. The case can be composed of an individual, a couple, a family, a group, a nation, or a region. Single case studies are useful in the illustration, development, and testing of theories, as well as in in-depth descriptions.
The more focused the questions, the larger the sample will be. A study on long-term marriage would require a minimum of two or three interviews because the topic is complicated. The sample would include at least ten participants and up to twenty or thirty, depending on the number of interviews, to account for some of the many patterns that are likely to emerge in a study of a topic this complex. In the one-interview study I did of how sexual abuse came to the notice of law enforcement, one interview was adequate because of the tight focus of the question. Yet, I used a sample size of thirty-two to maximize the possibility of identifying a variety of patterns, which the study accomplished. As mentioned, the one interview, however, did not allow me to contextualize the stories the informants told. Fortunately, I have another large sample that involved multiple, in-depth interviews in which informants discussed multiple contexts over time. This other study was helpful to me in understanding the accounts from the single-interview study.
Recruitment can be difficult. When it is, researchers may not be able to obtain an adequate sample. For example, a sample of seven participants engaging in a single sixty- to ninety-minute interview may not provide enough data on which to base a credible analysis. In a similar vein, articles based on a single or even a few focus groups may not provide enough depth to be informative. Some depth is possible if, in a single-interview study of less than fifteen or twenty interviewees, researchers meet with informants a second time to go over what researchers understand about informants’ accounts. This sometimes is called member-checking , and it provides additional data on which to base the analysis. In summary, the more depth and breadth to a study, the smaller the sample size can be—even as small as one or two—depending on the questions and the complexity of the cases.
Quality of the Analysis
A quality analysis begins with initial planning of the research and continues until the article is accepted for publication. An excellent research report has transparency , meaning the write-up is clear in what researchers did, how they did it, and why. I often tell students they can do almost anything reasonable and ethical, as long as they make a clear account in the write-up.
During planning, some researchers identify those concepts that they can use as sensitizing concepts once in the field. Transparency about the sources of sensitizing concepts characterizes well-done reports. The sources are literature reviews and reflexivity statements. Most researchers, however, have only a limited awareness of the importance of being clear about the sources of sensitizing concepts and other notions that become part of research coding schemes. Sensitizing concepts are notions that researchers identify before beginning their research and that help researchers notice and name social processes that they might not have noticed otherwise ( Blumer, 1986 ). Other researchers wait until data analysis to begin to identify concepts that they may use as codes and that may also become core concepts that organize findings. Either approach is acceptable and depends on purpose and methodologies.
During data collection, researchers reflect on what they are learning, typically talk to other researchers about their emerging understandings, and read relevant research and theory to enlarge and deepen their understandings. Researchers also keep fieldnotes that are a form of reflection. Based on their various reflections, researchers can reformulate interview and research questions and formulate new ones, do within—and across—case comparisons while in the field, and develop new insights into the meanings of the material.
Also, while in the field, researchers identify promising patterns of meanings and identify tentative core concepts, sometimes called categories , which are ideas that organize the copious material that they amass. Once researchers identify tentative core concepts, they seek to test whether they hold up, and, when they do, they further develop the patterns and concepts. Sometimes researchers think they have “struck gold” when they identify a possible core concept or pattern, only to find that the data—or metaphorical vein of gold—peter out (Phyllis Stern, personal communication, November 2002). They then go on to identify and follow-up on other concepts and patterns that show promise of becoming viable.
Core concepts become viable when researchers are able to dimensionalize them ( Schatzman, 1991 ) through selective coding ( Corbin & Strauss, 2008 ). This means that researchers have found data that show the multiple facets of concepts, such as patterns and exceptions to any general patterns. Authors may use other terms to describe what they did, such as thematic analysis. What is important is to describe the processes and produces; and what researchers call them is of less importance.
Core concepts may begin as sensitizing concepts. Researchers sometimes identify, name, and code core concepts through notions that are part of their general stores of knowledge but were not part of the literature review or reflexivity statement. Glaser (1978) called the practice “theoretical sensitivity.” The names researchers choose may be words or phrases informants have used. However derived, core concepts are central to the organization of findings ( Gilgun, 2012 a ).
At some point, data collection stops, but analysis does not. Researchers carry analysis that occurred in the field into the next phases of the research. Immersion at this point means that researchers read and code transcripts of interviews, observations, and any documentary material they find useful. They carry forward the core concepts they identified in the field. An example of a core concept is “resilience,” which in my own research organized a great deal of interview material. The concept of resilience has been an organizing idea in several of the articles I have written and plan to write ( Gilgun, 1996 a ; 1996 b ; 2002 a ; 2002 b ; 2004 a ; 2004 b ; 2005 a ; 2006 , 2008 ; 2010 ; Gilgun & Abrams, 2005 ; Gilgun, Keskinen, Marti, & Rice, 1999 ; Gilgun, Klein, & Pranis, 2000 ).
Corbin and Strauss (2008) stated that selective coding helps researchers to decide if a concept can become a core concept, meaning it organizes a great deal of data that have multiple dimensions. An example of dimensionalization is a study of social workers in Australia whose clients were Aboriginal people. The researchers identified several core concepts, among them critical self-awareness ( Bennet, Zubrzycki, & Bacon, 2011 ). The dimensions of critical self-awareness included understanding motivations to work with Aboriginal people, fears of working with Aboriginal people, and personalization and internalization of the anger that some Aboriginal people express.
Like many other researchers, Bennet et al. (2011) were not working within an explicit Chicago School tradition. They therefore do not use terms such as core concepts, dimensionalization, and selective coding. Instead, they described their procedures as thematic analysis, conceptual mapping, and a search for meaning. However, they did use the term “saturation,” which is part of the Chicago School tradition.
A single core concept or multiple related core concepts compose research reports. The Bennet et al. (2011) article, for example, linked multiple core concepts. The authors showed how critical self-awareness leads to meaningful relationships that in turn connect to “acquiring Aboriginal knowledge” (p. 30).
With viable core concepts and rich data, researchers are positioned to present their findings in ways that are memorable and interesting; that is, with “grab” ( Glaser, 1978 ). “Grab” requires compelling descriptive material: excerpts from interviews, field notes, and various types of documents, as well as researchers’ paraphrases of these materials. An example of a research report with grab is Irvine’s (2013) account of her study of the meanings of pets to homeless people. She provided vivid descriptions of her interactions with the participants and compelling quotes that show what pets mean. Here, an example from Denise’s account of her relationship with her cat Ivy:
I have a history with depression up to suicide ideation, and Ivy, I refer to her as my suicide barrier. And I don’t say that in any light way. I would say, most days, she’s the reason why I keep going.... She is the only source of daily, steady affection and companionship that I have. (p. 19)
These and other quotes, as well as Irvine’s well-written, detailed descriptive material, show what grab means.
Grab equates with excellence in writing. Irvine’s (2013) article is an example. In terms of the grab of her article, her work is in the Chicago School tradition. She wrote in the first person. She told complete stories in which she quoted extensively from the interviews, described the persons she interviewed and the settings in which she interviewed them, and provided biographical sketches. Robert Park and Ernest Burgess, both of whom trained generations of graduate students in qualitative research at the University of Chicago in the first quarter of the twentieth century, held seminars on the use of literary techniques, such as those used in novels and autobiographies, in writing up research ( Bulmer, 1984 ; Gilgun, 1999 d ; 2012 a ). These educators wanted researchers to report on their “first-hand observation.” Park told a class of graduate students to
[g]o and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesk. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seat of your pants dirty. ( McKinney, 1966 , p. 71)
Park suggested to Pauline Young (1928 ; 1932) to “think and feel” like the residents of Russian Town, the subject of her dissertation, published in 1932 ( Faris, 1967 ). Irvine’s work shows these qualities. She immersed herself in the settings, she conducted in-depth interviews, and she conveyed her first-hand experiences in vivid terms.
The Chicago School also encouraged students to write in the first person. A good example is a report by Dollard (1937) , who was concerned about the racial practices of the Southern town where he was doing fieldwork. He said he was afraid that other white people watched as he talked to “Negroes” on his front porch, when he knew that custom regarding the “proper” place of “Negroes” was at the back door. He wrote
My Negro friend brought still another Negro up on the porch to meet me. Should we shake hands? Would he be insulted if I did not, or would he accept the situation? I kept my hands in pockets and did not do it, a device that was often useful in resolving such a situation. (p. 7)
This description is a portrait of a pivotal moment in Dollard’s fieldwork, and it is full of connotations about the racist practices of the time ( Gilgun, 1999 d ; 2012 a ).
Irvine (2013) also wrote in the first person. Here’s an example:
I met Trish on a cold December day in Boulder. She stood on the median at the exit of a busy shopping center with her Jack Russell Terrier bundled up in a dog bed beside her. She was “flying a sign,” or panhandling, with a piece of cardboard neatly lettered in black marker to read, “Sober. Doing the best I can. Please help.” (p. 14)
These two excerpts illustrate a methodological point Small (1916) made in his chapter on the first fifty years of sociological research in the United States: namely, the importance of going beyond “technical treatises” and providing first-person “frank judgments” that can help future generations interpret sociology. Without such contexts, “the historical significance of treatises will be misunderstood” (p. 722). Throughout his chapter, Small wrote in the first-person and provided his views—or frank judgments—on the events he narrated. From then until now, research reports in the Chicago tradition are vivid and contextual, conveying to the extent possible what it was like to be persons in situations.
There are many other examples of well-done research reports. Eck’s (2013) article on never-married men includes the basic elements that are present in almost all reports based on qualitative methods. It is transparent in its procedures, situated within scholarly traditions, well-organized, vivid, and instructive both for those new to qualitative research and for long-term researchers like me. The other articles I cite in this chapter also show many desirable qualities in research reports.
Research Report Sections
The main sections of standard reports based on qualitative methods are the same as for articles based on other types of methods: Introduction, Methods, Findings, and Discussion. The American Psychological Association (APA) manual (2009) provides information on what goes into each of these sections. Research reports in sociology journals follow a similar format, although the citation style is slightly different. The American Sociological Association uses first and last names in the reference section, a practice I support. In articles based on qualitative approaches, researchers sometimes change the names of sections, add or omit some, or reorder them. When changes are made, the general guideline is whether the changes make sense and are consistent with the purpose of the research. As Saldaña (2003) pointed out, researchers choose how to present their findings on the basis of credibility, vividness, and persuasive qualities and not for the sake of novelty. Because some articles report findings as fictionalized accounts, poetry, plays, songs, and performances (including plays), it makes sense that the sections on these findings vary from the standard format that I discuss here.
Although there are no rigid rules about how to write journal articles based on qualitative research, much depends on the methodological perspectives, purposes of the research, and the editorial guidelines of particular journals. For example, if researchers want to develop a theory, it is important to be clear from the beginning of the article to state this as the purpose of the research. The entire article should then focus on how the authors developed the theory. Research and theory cited in the literature review should have direct relevance to the substantive area on which the authors theorized. The methods section should explain what the researchers did to develop the theory. The findings section should begin with a statement of the theory that the researchers developed. The rest of the findings section should usually be composed of three parts. The first is composed of excerpts from those data that support the concepts of the theory. This is the grounding of the theory in something clear and concrete. The second is the authors’ thinking or interpretation of the meanings of each of the concepts. The third is an analysis of how the theory contributes to what is already known, such as how the findings elaborate on and call into question what is known. Thus, a research report on the development of a theory should contain a lot of scholarship that others have developed.
A report based on narrative principles or one based on an ethnography should contain copious excerpts from interviews, citing less scholarship than an article whose purpose is to develop theory. However, it is good practice to bring in related research and theory in the results section when this literature helps in interpretation, when findings have connections to other bodies of thought, and when findings are facets of a larger issue. In my now older publication on incest perpetrators ( Gilgun, 1995 ), the editors suggested that I show that when therapists engage in sexual relationships with clients, they are engaging in abuses of power similar to those of incest perpetrators. I was at first indignant that the editors wanted me to do even more work on the article, but I soon was glad they did. It is important to show that incest or any human phenomenon is not isolated from other phenomenon but is part of a larger picture. Doing so fit my purposes, which was to show how to do theory-testing/theory-guided qualitative research. Showing how findings fit into related research and theory is part of this type of research.
Whenever researchers are ready to submit an article for publication, it is wise to read recent issues of journals in which they would like to publish. If they can identify an article whose structure, methodologies, and general purpose are similar to theirs, they could study how those authors presented their material. If, for example, in a report on narrative research, the introductory material is relatively brief, and the findings and discussion sections compose most of the pages, researchers would do well to format their articles in similar ways. I study journals in which I have interest and model much of my own articles after those published in these journals. I make sure, however, that I cover topics that in my judgment are important to cover.
Prior Research and Theory
In my experience, something as simple as the place of prior research and theory can get complicated in the writing of reports based on qualitative research, even when the purpose of the article is primarily descriptive and is not to construct an explicit theory. In general, related research and theory literature can be presented at the beginning of a report as part of a review of pertinent research and theory, in the findings section when prior work helps in the interpretation and analysis of findings, or in the discussion section, where authors may reflect on how their findings add to, undermine, or correct what is known and even add something new.
Readers expect and journal editors typically want articles to begin with literature review, with some exceptions. A perusal of journals that publish qualitative studies shows this. Yet there are exceptions. Valásquez (2011) began her report on her encounter with scientology with an extended and rather meandering first-person narrative. Her literature review began toward the end of the article. She tailored the review to the report that preceded it. In this article and others, the literature review helped in the interpretation of findings and helped to situate the report in its scholarly contexts. In other articles, the literature review appears in the introductory section. This sets the scholarly context of the research, highlights the significance of topics, and identifies gaps in knowledge. Neither authors nor reviewers should have rigid expectations about where the scholarship of others belongs. It belongs where it makes the most sense and has the most impact.
For many, the placement of literature reviews seems self-evident. Yet, some well-known approaches, such as grounded theory, can set authors up for confusion about where the literature review belongs. This can result in delays in writing up their results. The procedures of grounded theory are open-ended and designed to find new aspects of phenomena—often underresearched—and then develop theories from the findings. At the outset of their work, researchers cannot anticipate what they will find. Therefore, teachers such as Strauss and Glaser advised students not to do literature reviews until they had identified basic social processes that become the focus of the research ( Covan, 2007 ; Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ).
How, then, do researchers write up research reports when they are doing an open-ended study that, by definition, will culminate in unanticipated findings? Do they write their reports as records on how they proceeded chronologically, or do they follow APA style and the dominant tradition that says the literature review comes first? For the most part, I follow the tradition, as, apparently, do most researchers. However, to structure reports in this way sometimes feels strained and artificial. I would prefer to write a more chronological account, in which I can share with readers the lines of inquiry and procedures I followed. The literature review at the beginning of the report, therefore, would be brief. The methods section is quite detailed in how I went about developing the theory. The findings section would have the three-part format I discussed earlier: statement of the theory, presentations of excerpts that support assertions that certain concepts compose the theory, my interpretation of the meanings of the concepts and the excerpts that support them, and then the use of related research and theory to further develop the theory and to situate it in its scholarly traditions.
In all but one of the research reports that I have published, I did the literature after I had identified findings. The one exception was research I did based on the method of analytic induction, in which researchers can use literature reviews to focus their research from the outset ( Gilgun, 1995 , 2007 ). In this research, I used concepts from theories on justice and care to analyze transcripts of interviews I had previously conducted on how perpetrators view child sexual abuse. Even though I was familiar with the transcripts, I found that the concepts of justice and care and their definitions sensitized me to see things in the material that I had not noticed as I did data collection and during previous analyses of the data.
Furthermore, in writing up the results, I brought in research that was not part of the literature review to help me to interpret findings and to show how findings fit with and added to what was already known. I did not place this material in the introductory literature review. Placing related research and theory as parts of the results and discussion sections is common and may be necessary in articles that are reporting on a theory that the authors developed. For descriptive studies whose purpose is not theory-building, such as ethnographies, some findings sections include the addition of research and theory not present in the introductory section. Often, however, authors do not follow this pattern. An example is found in Ahmed (2013) , who described how migrants experience settling into a new country. She presents excerpts from interviews and her interpretation of them, including organizing them into a typology, but she does not bring additional research and theory into her interpretations.
Tensions can arise between how much space to give to literature reviews and how much to allot to presentation of informants’ accounts/findings ( Gilgun, 2005 c ). This happened in the most recent article I co-wrote, which is on mothers’ perspectives on the signs of child sexual abuse ( Gilgun & Anderson, 2013 ). We believed the literature review was important because it not only set up our research but summarized a great deal of information that was important to our intended audience of social service professionals. We also wanted to anticipate the expectations of reviewers and the journal editor. Yet, we put much effort into making the literature review as concise as possible in order to have reasonable space for findings. We wrote the literature review before we did data analysis. When we wrote up the results, the first draft was probably three times longer than any journal article could be.
We had written case studies first to be sure that we understood each case in detail. We had wanted to share what the women said in the kind of detail that had helped us deepen our own understandings, so we cut back on the case material. The article was still too long. We decided to exclude the few instances we had in which women knew of the abuse but tried to handle it themselves or did not believe the children when told. We did more summarizing of the literature review. We eliminated many references.
After much effort, we finally had a manuscript that was the required length of twenty-two pages. It included a literature review that set up the research in good form, an adequate accounting of the method, and findings that conveyed with grab the complexities of the signs and lack of signs of child sexual abuse. We wove points made in the literature review into our interpretations, yet we had to leave out important patterns for the sake of space. The editor’s decision was a revise and resubmit, which we did. The main recommendation was to elaborate on applications. This was a great suggestion, and we dug deep to think about this. We are pleased with the results. We had to do further reading on topics we had not anticipated at the onset of our project, and we squeezed in a few new citations in the discussion section that related to implications of the research. This additional material greatly enhanced the meanings and usefulness of the research.
There is much more to say about qualitative research and literature reviews. Sometimes researchers get stuck, as I have more than once. I have research that I have not yet published because I have been unable to figure out how to do the multiple literature reviews I think I must show how my theory builds on, adds to, and challenges what is already known. I have written up this research as conference papers, where expectations about literature reviews are more relaxed ( Gilgun, 1996c , 1998 , 1999c , 2000 ). One of these. papers was on a comprehensive theory of interpersonal violence ( Gilgun, 2000 ). I wanted to write my theory first and then show how the findings contribute to what is already known. Doing so doesn’t seem so outlandish today, and I now can imagine writing it up exactly as I would want to. At the same time, I wonder if I would? I really don’t know if any journal that would publish a theory of violence would also accept an article that places a literature review after findings. Furthermore, my writing up of the theory would take so many pages that I would not have enough space to do a comprehensive literature review. As of today, the theory I am developing has links to sixteen or more bodies of literature. No way can I publish a journal-length article that will accommodate that much research and theory!
So, here I am, many years into the development of a comprehensive theory, still reflecting on how to create journal articles out of my analysis. I have published many articles in social media outlets exploring ideas that are the basis for the theory. I have put these articles into collections that are available on the internet ( Gilgun, 2012 b ; 2012 c ; 2013 a ). The theory is so complex that writing bits and pieces over the years and having a place to put them have been very helpful.
Finally, some articles may cite few if any related research and theory. This may fit articles whose purpose is to convey lived experience that stands on its own. These articles feature performances, plays, autoethnographies, fictionalized accounts, poetry, and song, among others. Egbe (2013) wrote two poems that she explained were accounts of her experiences of doing research in Nigeria with young smokers. She said she was “dazed by the vast opportunity this method gives a researcher to dig deep into a research problem and be submerged into the world of participants” (p. 353). Her two-page article is composed of two poems and her explanation. The article showed grab, evidence of immersion, experiences in contexts, and multiple perspectives. Her work, therefore, followed well-established guidelines for writing up qualitative research. Egbe not only omitted a literature review, but she did not write about how to use the results of her research, assuming that its uses are self-evident. Obviously, she thought a literature review unnecessary; the reviewers and journal editors agreed with her.
Reflexivity Statements
A growing number of journals encourage researchers to include reflexivity statements in research reports. Researchers may place these in the introductory material of an article, after the literature review and before the methods section; this probably is the most important place to put them because reflexivity statements often influence the focus and design of the research, including the choice of sensitizing concepts and codes. Reflexivity statements may also appear in the methods and findings and methods sections when important. Reflexivity statements are accounts of researchers’ experiences with the topic of research; accounts of their expectations regarding informant issues and their relationships to informants, especially in regard to power differentials and other ethical concerns; and accounts of their reflections on various issues related to possible experiences that informants may have had. They also may include the experience they had while participating in the research ( D’Cruz, Gillingham, & Melendez, 2007 ; Presser, 2005 ). My article on doing research on violence is an extended reflexivity statement ( Gilgun, 2008 ). There appears to be no standard content for reflexivity statements and no standard places for them to appear. Personal and professional experiences and reflections on power differentials may be the emergent standard. Whatever decisions researchers make about reflexivity statements, they alert audiences to researchers’ perspectives, which can be helpful to readers as they attempt to make sense of research reports.
An example of a reflexivity statement is found in Winter (2010) work. Winter is a practitioner turned researcher who had a previous relationship as a guardian ad litem with the children with whom she later conducted the research that she was reporting. Winter was reflexive about the implications of her prior relationship with these children. I imagine, based on my own experience, that she put only a fraction of her thinking into her article. Not only did she write in her reflexivity statement that she had a prior relationship with the children, but she also wrote about the ethical issues involved.
Ethical issues have a place in reflexivity statements. I have run into ethical questions over the course of my research career. One situation that stands out is the encounter I had with a mother and her eleven-year-old daughter who had participated in my dissertation research on child sexual abuse ( Gilgun, 1983 ). The mother cried and told her daughter how sorry she was that she had been unable to protect her from sexual abuse. The girl was touched but did not seem to know what to do. I suggested that she go stand by her mother. When she got close, the mother and daughter hugged each other and cried. This is a significant event with ethical implications that I included in the findings section of my dissertation and in a subsequent research report ( Gilgun, 1984 ). The ethical issue is, first, whether I should have stepped out of my role as detached researcher and guided the girl to go to her mother, and, second, whether I should have made my blurring of boundaries public by publishing them.
As far as the placement of reflexivity statements, the initial statement has a logical location after the literature review because the reflexivity statement contributes to the development of the research questions, the identification of sensitizing concepts, the interview schedule, and the overall design of research procedures. Accounts of ongoing reflexivity could be part the findings section and of the discussion section. Reflexivity statements are not a standard part of research reports, but they can contribute to readers’ understandings of the research.
Along with the literature review, reflexivity statements contribute to practical and applied significance statements and may also help to identify gaps in knowledge. Literature reviews and reflexivity statements contain key concepts. The concepts that researchers define at the end of introductory sections typically become codes during analysis, although researchers may not label the concepts as codes either in the introductory section or in the methods section. I am unsure why such labeling has not become routine. When concepts carry the label code , this clarifies where codes come from. Without naming codes and stating where they come from, much of analysis is mystified. Many reports read as if the codes appear out of nowhere during analysis. Even Glaser’s (1978) notion of theoretical sensitivity mystifies the origins of codes. How, for example, do researchers become theoretically sensitive? What if researchers are beginning their scholarly careers? How theoretically sensitive are they ( Covan, 2007 )? What are the implications for the quality of the analysis?
Research Questions, Hypotheses, and Definitions
The final part of the introductory section of a research report is devoted to research questions, hypotheses to be tested (if any), and definitions of core concepts. In general, in qualitative research, hypotheses are statements of relationships between concepts. Theories usually are composed of two or more hypotheses, although, at times, some researchers may use the term theory to designate a single hypothesis ( Gilgun, 2005 b ). Concepts are extractions from concrete data. Sometimes concepts are called second-order concepts and data first-order concepts .
Research questions may be absent. In their place are purpose statements that make the focus of the report clear. Hypotheses are rarely present in qualitative research. When they are, the purpose of the research is to test them and typically to develop them more fully. This type of research has in the past been called analytic induction ( Gilgun, 1995 e), whereas a more up-to-date version of qualitative hypothesis testing and theory-guided research is called deductive qualitative analysis ( Gilgun, 2005 d ; 2013 ). Analytic induction and deductive qualitative analysis are part of the Chicago School tradition.
Methods Section
Most methods sections for reports based on qualitative approaches have the same elements as any other research report. Descriptions of the sample, recruitment, interview schedule, and plans for data analysis are standard. The APA manual provides guidelines ( American Psychological Association, 2009 ) that fit many types of qualitative research reports. However, reports based on autoethnographies, poetry, and performances may have brief or no methods sections. As is clear by now, the report’s contents depend on the purposes and methodologies of the research and on the editorial requirements of journals.
Accounts of Methodologies
In writing up qualitative research, methods sections usually contain a brief overview of the research methodology, which is the set of principles that guided the research. The following is an account of the methodology used in a research report on cancer treatment in India:
For this project we drew upon interpretive traditions within qualitative research. This involved us taking an in-depth exploratory approach to data collection, aimed at documenting the subjective and complex experiences of the respondents. Our aim was to achieve a detailed understanding of the varying positions adhered to, and to locate those within a broader spectrum underlying beliefs and/or agendas. ( Broom & Doron, 2013 , p. 57)
Sometimes, statements of methodology are much more elaborate, but in research reports, such a statement is sufficient, again depending on the editorial policies of particular journals. A few citations, which this article had, round out an adequate statement of methodology.
However, many reports are written in a clear and straightforward way with scant or no account of methodologies. Examples are the work of Eck (2013) and Spermon, Darlington, and Gibney (2013) . These kinds of well-done write-ups might eventually be considered generic. Spermon et al. said their study was phenomenological, which sets up assumptions that the report will be primarily descriptive. In actuality, the intent was to develop theory. Such mixing of methodologies may be the wave of the future; in many ways, distinctions between phenomenological studies whose purposes are descriptive and those whose purposes are to build theory are blurred. Such blurring may have been the case for decades because it is possible and often desirable to build theories based on phenomenological perspectives; that is, in-depth descriptions of lived experience. However, authors are wise to state in one place what their methodologies are and how they put them to use, such as for descriptive purposes or for theory-building.
Description of Sample
Placing descriptions of sample size and the demographics of the sample in the methods sections is typical. As mentioned earlier, evaluation of sample size depends on the depth and breadth of the study. The more depth a study has, the smaller the number of cases can be. The more breadth and the sharper the focus, the larger sample sizes typically are. Samples on which a study is based must provide enough material on which to base a credible article. A sample size of one may be adequate if researchers show their work demonstrates the basic principles of almost all forms of qualitative research: perspectives of persons who participate in the research, researcher immersion into the settings or the life stories of persons interviewed, multiple perspectives, contextual information of various types, and applications. Autoethnographies often have an n of one, but joint autoethnographies are possible. Ethnographies may not give a sample size, as was the case in the performance ethnography of Valásquez (2011) who wrote in the first person about her experience with scientology. In her first-person ethnography, Irvine (2013) also did not mention sample size. She said that the narratives she used for the article were from a larger study on the meanings of animals to people who have no homes. She did not describe the usual demographics of age, gender, social class, and ethnicity.
Most articles describe the demographics of the sample. In a recently accepted article ( Gilgun & Anderson, 2013 ), I saw no relevance in mentioning the size of the larger sample from which we drew in order to tell the stories of how mothers responded to their learning that their husbands or life partners had sexually abused their children. We included an exact count of the larger sample because we assumed that it would be the journal’s expectations. We also gave particulars of the demographics. Except for social class and ethnicity, we saw little relevance for the other descriptors. These status variables were relevant to us because most of the sample was white and middle or upper class. This is important because much research on child sexual abuse is done with poor people, and there are stereotypes that poor families and families of color are more likely to experience incest than are white middle and upper class families. Overall, as with some other issues related to writing, the adequacy of the sample description depends on the methodological principles of the research and the journal’s editorial policies.
Recruitment
Accounts of recruitment procedures are important because researchers want to show that their work is ethical. Respect for the autonomy or freedom of choice of participants needs to be demonstrated. In addition, often the persons in whose lives we are interested have vulnerabilities. To show that the research procedures have not exploited these vulnerabilities is part of ethical considerations. Most articles have these accounts. Furthermore, when there are accounts of recruitment procedures, it becomes obvious why the sample is not randomly selected. Irvine’s (2013) account of recruitment is exemplary. She recruited through veterinary clinics that took care of the pets of homeless persons. She did not approach potential participants herself. Doing so risked making refusals difficult. The staff informed persons of the research and its purposes. If individuals said they were interested, they gave permission for the staff to give their names to researchers. The research interviews took place in the clinics.
The ethics of recruitment revolve around values, such as respect for autonomy, dignity, and worth. Other ethical issues that are important to mention in reports include the use of incentives for participation. Although many human subjects committees now require monetary incentives for participation, this has ethical implications. Irvine (2013) solved this by giving gift cards after the interviews were completed. Reports on ethical issues have a place in methods sections.
Data Collection and Analysis
Accounts of data collection and analysis are part of the methods section. Data collection procedures should be detailed for many reasons. Primary among them is the need for transparency in terms of the ethical standards the researchers followed, as well as the need to allow for replication of the study. Such details also provide guidelines for others who might be interested in using the methods. In addition, there are many different schools of thought and procedures for each of the methods used with the three general types of data collection: interviews, observations, and documents. It is helpful to state which particular data collection procedures the researchers used. Researchers often provide examples of the kinds of questions asked and procedures used for recording observations and excerpts from documents. Some researchers may omit such an accounting, as with some autoethnographies and articles that turn research material into performances.
How researchers analyzed data is part of the methods sections. As with data collection, there are so many types of analysis that researchers need to describe the particular forms that they used. For figuring out how to report on data analysis, researchers would do well to study articles in journals in which they want to publish. Irvine (2013) used a method of analysis I have never heard of called “personal narrative analysis” (p. 8). She gave enough detail to provide the general idea of what she did and a sufficient number of citations for additional information.
The level of detail can vary. In some sociology journals, for example, researchers may say little about analysis and sometimes little about data collection. This is because the journal editors, reviewers, and those who publish in and read the articles have assumptions that they for the most part take for granted. Even in these journals, however, researchers may want to account for their analytic procedures, especially if they are writing on topics outside of what is usual in such journals.
Other journals require a great deal of detail. In those instances, researchers first decide what they think is essential and then shape their accounts to fit what appears to be usual practice in the journal. The following paragraphs describe data analysis in a recently accepted article on signs of child sexual abuse in families ( Gilgun & Anderson, 2013 ).
Data Analysis
In the analysis of data, the first author read the transcripts multiple times and coded them for instances related to disclosures of child sexual abuse and associated signs of the abuse, such as how and when the women first learned of the abuse or suspected it was occurring in their families, their responses, and their reflections on the signs of abuse they might have missed, as well as child and perpetrator behaviors that they did not realize were related to child sexual abuse. Their initial and longer term responses and reflections were also coded. The second author independently read and coded about one-third of the transcripts using this coding scheme to arrive at a 100 percent agreement.
Sources of the codes were our professional experiences in the area of child sexual abuse, the review of research, and the first author’s familiarity with the content of the interviews because she had been the interviewer. These codes served as sensitizing concepts, which, as Blumer (1986) explained, are ideas that guide researchers to see aspects of phenomena that they might otherwise not notice. Although altering researchers’ ideas to what might be significant serves an obvious useful purpose, sensitizing concepts might also may blind researchers to other aspects of phenomena that might be important. Therefore, we also used negative case analysis, which is a procedure that guides researchers to look for aspects of phenomena that contradict or do not fit with emerging understandings. In this way, researchers are positioned to see patterns, variations within patterns, exceptions, and contradictions in findings ( Becker et al., 1961 ; Bogdan & Biklen, 2007 ; Cressey, 1953 ; Lindesmith, 1947 ).
As we wrote this section, we were aware of the limited space that we had to fill. Yet we were committed to accounting for where our codes came from for reviewers and editors who may be unfamiliar with pre-established codes. As discussed earlier, many reports are written as if codes appear by magic. We decided that, in this report, we would be as clear as possible about where our codes came from. We also reasoned that we would have to call on the authority of well-respected methodologists if reviewers and editors had questions about what we had done. Furthermore, we were aware of the dated nature of the references; we could do nothing about that because there has not been much written recently about pre-established codes. I have written about this quite a bit, but as one of the authors, I not only had to be anonymous during the review process, but I could not be the sole authority.
Generalizability
Many reviewers and editors have questions about the generalizability of the results of qualitative research. Authors themselves sometimes question the generalizability of their own findings. That’s why it remains important to provide clear guidelines in research reports about how the authors view the usefulness of their findings. The following ideas may be helpful to authors as they write their reports and to reviewers who are positioned as gatekeepers. The results of qualitative research are not meant to be generalized in a probabilistic sense. But because dropouts and refusals limit the randomness of samples, most forms of research can’t be generalized in a probabilistic sense.
Conversely, as Cronbach (1975) wrote almost forty years ago, the results of any form of research are working hypotheses that must be tested in local settings. Thus, the applicability of qualitative or any other kind of research can be demonstrated only through attempts at application. Do the findings illuminate other situations? Do the results provide researchers, policy makers, and direct practitioners with ideas on how to proceed? Those who apply the research expect to have to adjust findings to fit particular new situations. Many researchers and some journal editors and reviewers know through common sense and everyday experience how to use the results of qualitative research. Our personal lives are extended case studies. What we learn in one situation, we carry over into another. We know we have to test what we have learned in past situations for fit with new situations. If we do not, we impose our ideas on situations that may demand new perspectives. This common practice of applying results to all situations is disrespectful of local conditions and autonomy of persons. We want to avoid such disrespect in how we suggest readers use the results of our research.
Trustworthiness and Authenticity
Pointing out the trustworthiness of procedures and the findings that result from them sometimes are parts of methods sections. Related to trustworthiness are issues of authenticity ( Guba & Lincoln, 2005 ). Both trustworthiness and authenticity arise from immersion, seeking to understand the perspectives of others in context, reflexivity, and seeking multiple points of view. Researchers who have applied these principles will produce reports that are trustworthy and authentic. In addition, the reports will have grab. Extended discussions related to these issues are beyond the scope of this chapter and the scope of research reports as well.
I get more requests for revisions of methods sections, especially for accounts of data collection and analysis, than for any other parts of a manuscript. This is not surprising, given the multiple possible variations. I never know who the reviewers will be and what their expectations are. I rely first on my beliefs about what I want in the procedures section and then I study articles the journal has already publishes. I include what journal editors appear to expect, but I also add information that I think is important, even when it is not part of what I see in methods sections.
Findings Sections
Findings sections in research reports include both descriptive and conceptual material. Descriptive material is composed of researchers’ paraphrasing and summarizing of what they found and excerpts from interviews, fieldnotes, and documents. The descriptive material, at its best, is detailed and lively; it not only is informative, it has grab. This material contributes to understandings of human experiences in context. In addition, descriptive material is the basis of researchers’ theorizing and it also provides documentation and illustrations of assertions that researchers make.
Conceptual material comprises the analysis and is made up of inferences such as the general statements, concepts, and hypotheses that researchers develop from the material (data). One way to think about the relationship between descriptive and conceptual material is to think of descriptive material as composed of first-order concepts and conceptual material as composed of second-order concepts. Each type depends on the other. Credible conceptual material is based on descriptive material, some of which is contained in the article. Qualitative research yields mountains of data, a fraction of which can be placed into a published article.
As with other sections of research reports, findings sections have many possible variations that depend on the purpose of the research and the methodologies on which the research is based. Thus, the findings can range from heavily descriptive to heavily conceptual. Heavily conceptual research reports arise from research whose purpose is theoretical, in which researchers set out to test, refine, reformulate, or develop theory. Theoretical reports require some descriptive material to show the basis of theoretical statements, but they are often relatively short on descriptive material.
Reports that are primarily descriptive are composed of excerpts from data. Theoretical material appears in often subtle ways, such as in the form of concepts that organize findings. Irvine’s (2013) study of homeless people and their pets is largely descriptive, composed of excerpts from the interviews and Irvine’s paraphrases and narration of what she did, how, and when. The findings were narrative case studies based on interviews and observations. The details of the narratives were vivid and had the kind of grab that Glaser (1978) recommended. They showed multiples perspectives and variations on what it meant to homeless informants to have pets in their lives. The first three pages were a review of relevant literature and a presentation of method. The last five pages were a discussion of the findings.
As lengthy as the descriptive material is, conceptual material frames the entire report. In the literature review, Irvine introduced notions of positive identity, generativity, and redemption. She used them to analyze her data and organize findings, which were the narrative case studies. She used the concept of redemption as the core or organizing concept, going into some detail about how the research material supports the significance of this idea of pets as redemptive for homeless people.
This analysis is based squarely on the descriptive material. For instance, Irvine wrote that in the stories she presented in her article, “animals provide the vehicle for redemption.” She illustrated this point with a quote from one of the narratives and then reminded readers that the narratives “contain variations on the theme” of “ life is better because this animal is in it ” (p. 20; emphasis in original). Readers do not take this on faith because the basis of this general statement in presented multiple times in the case studies. Irvine has much more material on which she based these ideas, but there is not enough room in a journal-length article to show all of her evidence.
An example of an article that is theoretical in purpose and short on descriptive material is found in the work of Cordeau (2012) . She developed a grounded theory of the “transition from student to professional nurse” when student nurses work with “mannequins as simulated patients” (p. 90). Based on interviews, observations, and reports that the students wrote on their clinical experiences, the study was composed of about 10 percent descriptive material. This material included excerpts interviews and student reports. In the results section, she used this descriptive material to illustrate and possibly document the grounded theory she constructed. The theory’s “core category” was “linking,” which had four components, called properties. She documented the properties, primarily with her own thinking about her research material and also with excerpts from interviews, observations, and student reports.
Like Irvine’s (2013) study, the purpose of Cordeau’s (2012) work was applied where she wanted to build theory that would contribute to the development of clinical expertise in nursing students. She also devoted about one page of her study to applications.
Core Concepts
I’ve previously provided an extended discussion of core concepts. This section highlights some key points and illustrates them. Core concepts, often called core categories , organize findings. I prefer the term concept because concept is the term used in discussing theory, such as “concepts are the building blocks of theory,” and theory is one of several possible products of qualitative research. Researchers decide on which concepts are core in the course of analysis. Researchers are ready to write up their reports when they have settled on, named, and dimensionalized one or more core concepts. The terms “core concepts” and “core categories” are associated with grounded theory ( Charmaz, 2006 ; Corbin & Strauss, 2008 ), but they are useful in other types of qualitative research, such as interpretive phenomenology and narrative analysis. Core concepts both organize findings and, typically, bring together a great deal of information. The term “dimension” means that researchers account for as many aspects of the core concepts as they can in order to show the multiple perspectives and patterns that typically compose concepts.
In reporting on core concepts, I recommend that researchers name them, introduce them, describe them using excerpts from the research material, comment on them, and then situate each of the concepts and their commentaries within their scholarly contexts. As discussed earlier, this shows how the findings fit with what is already known, or add to, force modification of, or refute what is known. Although many researchers, do not situate findings in their scholarly contexts, they usually cover the other topics.
No matter how authors report findings, they should do so with grab. An example of a report exemplary for its grab is the work of Scott (2003) on what it means to be a professional with a physical disability. Scott began her article not with a literature review but with three reviewer comments on other articles she had written. She then stated that the present article was a response to these comments. She followed up with a description of three male students who waited to speak to her after class about her disability and the notion of embodiment that she discussed in class. She brought in related literature throughout the article. Through her own reflections, reports on how others have responded to her, reports on the accounts that three other women with disabilities gave to her as a person with cerebral palsy, and her literature review, Scott not only showed the meanings of disabilities to persons who have them, but also what others say about their own disabilities, what some people who are able-bodied say about women with disabilities, and how all of this connects to what is known about disabilities and to wide-spread beliefs about disabilities. Her article is full of grab, such as the header that read, “The Day I Became Human.” With the authors’ own experience as the centerpiece, this article exemplifies write-ups that demonstrate the meanings of lived experience in various contexts, immersion, grab, and implications for social action. The analysis she presented as part of her findings is exemplary.
In the production of quality research, no matter the type of write-up, there are no short cuts. Research reports based on poetry, for example, are held to the same standards as any other article: grab, immersion, lived experience in context, and implications for action. In addition, such research reports typically locate themselves within social and human sciences traditions. Furman’s (2007) reflections and analysis of poetry that he wrote over the course of many years provide an example of how poetry can be used in qualitative analysis. This kind of research is a type of document analysis. In performance studies, researchers create a theater production of informant’s accounts of their experiences whose purpose is to transform audiences and move them to action ( Saldaña, 2003 ). The performances are the equivalent of research reports and when they are effective, they have the four characteristics of qualitative research under discussion.
Discussion Sections
In traditional research reports, the discussion section follows the results section. In discussion sections, authors reflect on findings, including what the findings are, how findings contribute to understandings of phenomena of interest, the lines of inquiry the results open up, and implications for policy and practice. Other generic topics to consider are those related to the focus of the journal. For example, if the journal’s focus is related to health, then authors show how findings are related to health.
Discussion sections present the author with opportunities to advocate for how his or her research can be used. The applied purposes of Irvine’s (2013) research come through when she devoted an entire page to make observations about implications. She pointed out how her research contributes to a transformation of images of homeless persons as isolated to images of them as engaged in relationships not only with their pets but with other persons, too. She noted that rehousing homeless persons requires a change in policy that would allow them to have pets. Furthermore, she said that caring for a pet “can turn things around” (p. 24).
In the discussion section I wrote with Anderson ( Gilgun & Anderson, 2013 ), we addressed methodological issues, such as the probable existence of other patterns in addition to those we identified and the nonrandom nature of our sample. We also acknowledged the difficulties in working with families in which child sexual abuse has occurred. Since qualitative researchers want to understand lived experiences, we had to prepare ourselves to deal effectively in research areas that are difficult emotionally for us as researchers. Although we may acknowledge the emotional challenges of some topics in reflexivity statements, discussion sections are opportunities for authors to acknowledge the difficulties of using the results we produce. In the article I wrote with Anderson, we made such an acknowledgment, one that we hoped would facilitate more effective practice. We wrote
Practitioners themselves may experience shock, rage, and disgust. The practice of neutrality, in its therapeutic sense, is important in these cases ( Gil & Johnson, 1993 ; Rober, 2011 ). Neutrality means that practitioners maintain their analytic stances while at the same time they remain attuned not only to service users but also to themselves. When practicing neutrality, service providers regulate their own emotional responses in order to remain emotionally available to service users. Neutrality also means that service providers remain open-minded so that they can hear stories that they may not expect to hear; in other words, to make room for the unexpected ( Rober, 2011 ). Attunement to inner processes is a form of reflection that can facilitate the development of trust between service users and providers. When providers are reflective, they are less likely to tune out, close down, and otherwise stop listening to what services users express. When they listen and hear what service users say, they are more likely to facilitate the best possible outcomes in difficult situations ( Weingarten, 2012 ).
Doing research on lived experience can be difficult for informants and for researchers. Acknowledgment of the implications of these difficulties for users of the research has a place in discussion sections.
In summary, most articles are fairly straightforward in their write-ups: focused literature reviews, reflexivity statements in many cases, clear statements of purpose, clarity about sources of research questions and/or hypotheses, identification and definition of key concepts, identification of codes the researcher develops from literature reviews and reflexivity statements, succinct accounting of methods, and findings organized logically by core concepts around which the researcher organizes the multiple dimensions of those concepts. Excellent writing makes articles interesting and accessible. Some kinds of write-ups deviate from these components, but they are held to the same standards of immersion, experiences in context, multiple perspectives, and implications for action and other applications. When authors have the good fortune to have a recommendation to revise and resubmit, suggestions for revisions often improve the quality of the article.
The seemingly endless variations that are possible in the write-up of qualitative research makes writing and reviewing manuscripts challenging, especially when compared to traditions in which rigid rules prevail. However, it is important that approaches to qualitative research continue to evolve to meet with our ever-changing understandings of human phenomena. The clarity and transparency of reports are the fundamental guidelines for making judgments about quality. I often tell my students that the guidelines for doing qualitative research are flexible, and what is important is to be clear about what you did, why you did it, and what you came up with.
The notion of grab is central to write-up. Since qualitative research seeks to understand lived experiences, it is logical that findings report on the lived experiences in vivid terms, replete with quotes from data. This is not to undermine the importance of analysis, but grab is possible even in write-ups that require a great deal of analysis. Grab becomes possible because researchers must provide the evidence for the theories and concepts they develop.
When there are questions about priorities related to informants’ voices, researchers’ interpretations, and prior research, I hope that authors, reviewers, and editors remember that as important as analysis and previous work may be, the voices of informants bring these other important parts of manuscripts to life. Researchers make decisions about whose voices take priority.
There is no one way to respond to these dilemmas. Authors must make their own decisions about what is important to them and then search for journals that will welcome what they want to convey. It’s important to consider pushing the boundaries and writing an article in a way that the researcher thinks will best convey his or her findings.
The importance of quality data, quality analysis, and “grab” are foundational. I began this chapter with a discussion of the balance between description and analysis. I then considered core concepts as organizers of findings, the place of literature reviews, styles of presenting methods and methodologies, and the balance between the voices of informants and researchers. I concluded with the many variations in types of reports that result from the various purposes that qualitative research projects can have. There are many different types of qualitative research and many styles of write-ups. This chapter may sensitize readers to enduring issues in the writing of research reports. Like qualitative research itself, there are multiple points of view on how to write up qualitative research.
Ahmed, A. ( 2013 ). Structural narrative analysis: Understanding experiences of lifestyle migration through two plot typologies. Qualitative Inquiry , 19 , 231–243.
Google Scholar
American Psychological Association. ( 2009 ). The publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Google Preview
Becker, H. S. ( 1999 ). The Chicago School, so-called. Qualitative Sociology , 22 (1), 3–12.
Becker, H. S. , Geer, B. , Hughes, E. C. , & Strauss, A. L. ( 1961 ). Boys in white: Student culture in medical school . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Block, E. ( 2012 ). “That’s what I see:” Enhancing AIDS intervention research through deep ethnography. Qualitative Social Work 14 ( 4 ), 379–394.
Bogdan, R. C. , & Biklen, S. K. ( 2007 ). Qualitative research for education: An introduction to theories and methods (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Bennet, B. , Zubrzycki, J. , & Bacon, V. ( 2011 ). What do we know? The experiences of social workers working alongside aboriginal people. Australian Social Work , 64 (1), 20–37.
Blumer, H. ( 1986 ). The methodological position of symbolic interactionism. In H. Blumer (Ed.), Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method (pp. 1–60). Berkeley: University of California Press.
Bulmer, M. ( 1984 ). The Chicago School of Sociology: Institutionalization, diversity, and the rise of sociological research . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Broom, A. F. , & Doron, A. ( 2013 ). Traditional medicines, collective negotiation, and representations of risks in Indian cancer care. Qualitative Health Research , 23 (1), 54–65.
Charmaz, K. ( 2006 ). Constructing Grounded Theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis . London: Sage.
Corbin, J. , & Straus, A. ( 2008 ). Basics of qualitative research (3rd. ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Cordeau, M. A. ( 2012 ). Linking the transition: A substantive theory of high stakes clinical simulation. Advances in Nursing Science , 35 (3), E90–E102.
Covan, E. K. ( 2007 ). The discovery of grounded theory in practice: The legacy of multiple methods. In A. Bryant & K. Charmaz (Eds.), The Sage handbook of grounded theory (pp. 58–93). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Cressey, D. R. ( 1953 ). Other people’s money . Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Cronbach, L. ( 1975 ). Beyond the two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist , 30 , 116–127.
D’Cruz, H. , Gillingham, P. , & Melendez, S. ( 2007 ). Reflexivity, its meanings and relevance for social work: A critical review of the literature. British Journal of Social Work , 37 (1), 73–90.
Dollard, J. ( 1937 ). Caste and class in a southern town . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Eck, B. ( 2013 ). How never-married men make sense of an unintended identity. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography , 42 (1), 31–63.
Egbe, C. O. ( 2013 ). Descriptive poems on a qualitative research with young smokers in southern Nigeria (2013). Qualitative Inquiry , 19 (5), 353–354.
Ellis, C. ( 2009 ). Revision: Autoethnographic reflections on life and work . Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press.
Faris, R. E. L. ( 1967 ). Chicago sociology 1920-1932 . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Furman, R. ( 2007 ). Poetry and narrative as qualitative data: Explorations into existential theory. The Indo-Pacific Journal of Phenomenology , 7 , 1–9.
Geertz, C. ( 1973 ). The interpretation of culture . New York: Basic.
Gil, E. , & Johnson, T. C. ( 1993 ). Sexualized children: Assessment and treatment of sexualized children and children who molest . Rockville, MD: Launch Press.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 1983 ). The sexual abuse of the young female in life course perspective. 3058 . Ann Arbor, MI: Dissertations Abstracts International.
Gilgun, J. F. (1984). A non-coercive method of helping children discuss their own sexual abuse. Part II: An example of intervention by multiple qualitative case studies. Scribd.com . Retrieved from http://www.scribd.com/doc/117051267/A-Non-Coercive-Method-of-Helping-Children-Discuss-Their-Own-Sexual-Abuse .
Gilgun, J. F. ( 1995 ). “We shared something special”: The moral discourse of incest perpetrators. Journal of Marriage and the Family , 57 , 265–281.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 1996 a). Human development and adversity in ecological perspective: Part 1: A conceptual framework. Families in Society , 77 , 395–402.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 1996 b). Human development and adversity in ecological perspective, Part 2: Three patterns. Families in Society , 77 , 459–576.
Gilgun, Jane F. (l996c November). The phenomenology of family violence. Paper presented at the Preconference Workshop on Theory Construction and Research Methodology, National Council on Family Relations, Kansas City, MO, November 5.
Gilgun, J. F. (1998, November). A comprehensive theory of family violence. Paper presented at the 28th Preconference Workshop on Theory Construction and Research Methodology, National Council on Family Relations , Milwaukee, WI.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 1999 a). CASPARS: New tools for assessing client risks and strengths. Families in Society , 80 (5), 450–459.
Gilgun, J. F. (1999c, November). In their own words: Men talk about their violence . Paper presented at the 29th Preconference Workshop on Theory Construction and Research Methodology, National Council on Family Relations , Irvine, CA.
Gilgun, Jane F. ( 1999 d ). Methodological pluralism and qualitative family research. In Suzanne K. Steinmetz , Marvin B. Sussman , and Gary W. Peterson (Eds.), Handbook of Marriage and the Family (2nd ed.) (pp. 219–261). New York: Plenum.
Gilgun, J. F. (2000, June 25–28). A comprehensive theory of interpersonal violence . Paper presented at the Victimization of Children and Youth: An International Research Conference, Durham, NH .
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2002 a). Completing the circle: American Indian medicine wheels and the promotion of resilience in children and youth in care. Journal of Human Behavior and the Social Environment , 6 (2), 65–84.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2002 b). Social work and the assessment of the potential for violence. In T. N. Tiong & I. Dodds (Eds.), Social work around the world II (pp. 58–74). Berne, Switzerland: International Federation of Social Workers.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2004 a). A strengths-based approach to child and family assessment. In D. R. Catheral (Ed.), Handbook of stress, trauma and the family (pp. 307–324). New York: Bruner-Routledge.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2004 b). The 4-D: Strengths-based assessments for youth who’ve experienced adversities. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment , 10 (4), 51–73 .
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2005 a). Evidence-based practice, descriptive research, and the resilience-schema-gender-brain (RSGB) assessment. British Journal of Social Work , 35 (6), 843–862.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2005 b). “ Grab” and good science: Writing up the results of qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research , 15 (2), 256–262.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2005 c). Lighten up! The citation dilemma in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research , 15 (5), 721–725.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2005 d). Qualitative research and family psychology. Journal of Family Psychology , 19 (1), 40–50.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2006 ). Children and adolescents with problematic sexual behaviors: Lessons from research on resilience. In R. Longo & D. Prescott (Eds.), Current perspectives on working with sexually aggressive youth and youth with sexual behavior problems (pp. 383–394). Holyoke, MA: Neari Press.
Gilgun, Jane F. (2007, November). The legacy of the Chicago School of Sociology for family theory-building, Pre-Conference Workshop on Theory Construction and Research Methodology, National Council on Family Relation, Pittsburgh, PA, November 7.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2008 ). Lived experience, reflexivity, and research on perpetrators of interpersonal violence. Qualitative Social Work , 7 (2), 181–197.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2010 ). Reflections on 25 years of research on violence. Reflections: Narratives of Professional Helping , 16 (4), 50–59.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2012 a). Enduring themes in qualitative family research. Journal of Family Theory and Review , 4 , 80–95.
Gilgun, J. F. (2012b). School shootings are not senseless and other essays on violence . Amazon. http://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_noss?url=search-alias%3Ddigital-text&field-keywords=school+shootings+are+not+senseless . Retrieved 2 January 2014.
Gilgun, J. F. (2012c). The thin blue line of police brutality & other essays . Amazon. http://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_noss?url=search-alias%3Ddigital-text&field-keywords=the+thin+blue+line+of+police+brutality&rh=n%3A133140011%2Ck%3Athe+thin+blue+line+of+police+brutality . Retrieved 2 January 2014.
Gilgun, J. F. (2013a). The logic of murderous rampages & other essays on violence and its prevention (2nd ed.). Amazon. http://www.amazon.com/Murderous-Rampages-Essays-Violence-Prevention-ebook/dp/B00AYPR18A/ref=sr_1_2?s=digital-text&ie=UTF8&qid=1388681278&sr=1-2&keywords=the+logic+of+murderous+rampages . Retrieved 2 January 2014.
Gilgun, J. F. ( 2013 b). Qualitative family research: Enduring themes and contemporary variations. In G. F. Peterson & K. Bush (Eds.), Handbook of marriage and the family (3rd ed., pp. 91–119). New York: Plenum.
Gilgun, J. F. , & Abrams, L. S. ( 2005 ). Gendered adaptations, resilience, and the perpetration of violence. In M. Ungar (Ed.), Handbook for working with children and Youth: Pathways to resilience across cultures and context (pp. 57–70). Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Gilgun, J. F. , & Anderson, G. ( 2013 ). Mothers’ perspectives on signs of child sexual abuse in their families. Families in Society , 94 (4), 259–267.
Gilgun, J. F. , Daly, K. , & Handel, G. (Eds.). ( 1992 ). Qualitative methods in family research . Newbury Park, CA: SAGE Publications.
Gilgun, J. F. , Keskinen, S. , Marti, D. J. , & Rice, K. ( 1999 ). Clinical applications of the CASPARS instruments: Boys who act out sexually. Families in Society , 80 (6), 629–641.
Gilgun, J. F. , Klein, C. , & Pranis, K. ( 2000 ). The significance of resources in models of risk. Journal of Interpersonal Violence , 14 , 627–646.
Gilgun, J. F. , & Sands, R. G. (Eds.). ( 2012 ). Special issue: The contributions of qualitative approaches to developmental intervention research. Qualitative Social Work: Research and Practice , 11 (4), 80–95.
Gilgun, J. F. , & Sussman, M. B. (Eds.). ( 1996 ). The methods and methodologies of qualitative family research . New York: Haworth. Also published as a special issue of Marriage and Family Review , 41 (1–2).
Glaser, B. ( 1978 ). Theoretical sensitivity . Mill Valley, CA: Sociology Press.
Glaser, B. , & Strauss, A. ( 1967 ). The discovery of grounded theory . Chicago: Aldine.
Guba, E. G. , & Lincoln, Y. S. ( 2005 ). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Irvine, L. ( 2013 ). Animals as lifechangers and lifesavers: Pets in the redemptive narratives of homeless people. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography , 42 (1), 3–30.
Lindesmith, A. ( 1947 ). Opiate addictions . Bloomington, IN: Principia.
McKinney, J. C. ( 1966 ). Constructive typology and social theory . New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Presser, L. ( 2005 ). Negotiating power and narrative in research: Implications for feminist methodology. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 30 (4), 2067–2090.
Rober, P. ( 2011 ). The therapist’s experiencing in family therapy practice. Journal of Family Therapy , 33 , 233–255.
Saldaña, J. ( 2003 ). Dramatizing data: A primer. Qualitative Inquiry , 9 , 218–236.
Schatzman, L. ( 1991 ). Dimensional analysis: Notes on an alternative approach to the grounding of theory in qualitative research. In D. R. Maines (Ed.), Social organizations and social process: Essays in honor of Anselm Strauss (pp. 303–314). New York: Aldine de Gruyter.
Scott, J. A. ( 2003 ). Problematizing a researcher’s performance of “insider status:” An autoethnography of “designer disabled” identity. Qualitative Inquiry , 19 , 101–115.
Sharma, A. , & Gilgun, J. F. ( 2008 ). What perpetrators say about child sexual abuse. Indian Journal of Social Work , 69 (3), 321–338.
Small, A. W. ( 1916 ). Fifty years of sociology in the United States, 1865–1915. American Journal of Sociology , 21 , 712–864.
Spermon, D. Darlington, Y , & Gibney, P. ( 2013 ). Complex posttraumatic stress disorder: Voice of healing. Qualitative Health Research , 24 (1), 43–53.
Velásquez, G. ( 2011 ). Inside the Church of Scientology: An ethnographic performance script. Qualitative Inquiry , 17 , 824–836.
Weingarten, K. ( 2012 ). Sorrow: A therapist’s reflection on the inevitable and the unknowable. Family Process , 51 (4), 440–455.
Winter, K. ( 2010 ). The perspectives of young children in care. Child and Family Social Work , 15 , 186–195.
Young, P. V. (l928). The reorganization of Jewish family life in America. Social Forces , 7 , 238–243.
Young, P. V. (l932). The Pilgrims of Russian Town . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Qualitative Methods
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The word qualitative implies an emphasis on the qualities of entities and on processes and meanings that are not experimentally examined or measured [if measured at all] in terms of quantity, amount, intensity, or frequency. Qualitative researchers stress the socially constructed nature of reality, the intimate relationship between the researcher and what is studied, and the situational constraints that shape inquiry. Such researchers emphasize the value-laden nature of inquiry. They seek answers to questions that stress how social experience is created and given meaning. In contrast, quantitative studies emphasize the measurement and analysis of causal relationships between variables, not processes. Qualitative forms of inquiry are considered by many social and behavioral scientists to be as much a perspective on how to approach investigating a research problem as it is a method.
Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. “Introduction: The Discipline and Practice of Qualitative Research.” In The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman. K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. 3 rd edition. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005), p. 10.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Below are the three key elements that define a qualitative research study and the applied forms each take in the investigation of a research problem.
- Naturalistic -- refers to studying real-world situations as they unfold naturally; non-manipulative and non-controlling; the researcher is open to whatever emerges [i.e., there is a lack of predetermined constraints on findings].
- Emergent -- acceptance of adapting inquiry as understanding deepens and/or situations change; the researcher avoids rigid designs that eliminate responding to opportunities to pursue new paths of discovery as they emerge.
- Purposeful -- cases for study [e.g., people, organizations, communities, cultures, events, critical incidences] are selected because they are “information rich” and illuminative. That is, they offer useful manifestations of the phenomenon of interest; sampling is aimed at insight about the phenomenon, not empirical generalization derived from a sample and applied to a population.
The Collection of Data
- Data -- observations yield a detailed, "thick description" [in-depth understanding]; interviews capture direct quotations about people’s personal perspectives and lived experiences; often derived from carefully conducted case studies and review of material culture.
- Personal experience and engagement -- researcher has direct contact with and gets close to the people, situation, and phenomenon under investigation; the researcher’s personal experiences and insights are an important part of the inquiry and critical to understanding the phenomenon.
- Empathic neutrality -- an empathic stance in working with study respondents seeks vicarious understanding without judgment [neutrality] by showing openness, sensitivity, respect, awareness, and responsiveness; in observation, it means being fully present [mindfulness].
- Dynamic systems -- there is attention to process; assumes change is ongoing, whether the focus is on an individual, an organization, a community, or an entire culture, therefore, the researcher is mindful of and attentive to system and situational dynamics.
The Analysis
- Unique case orientation -- assumes that each case is special and unique; the first level of analysis is being true to, respecting, and capturing the details of the individual cases being studied; cross-case analysis follows from and depends upon the quality of individual case studies.
- Inductive analysis -- immersion in the details and specifics of the data to discover important patterns, themes, and inter-relationships; begins by exploring, then confirming findings, guided by analytical principles rather than rules.
- Holistic perspective -- the whole phenomenon under study is understood as a complex system that is more than the sum of its parts; the focus is on complex interdependencies and system dynamics that cannot be reduced in any meaningful way to linear, cause and effect relationships and/or a few discrete variables.
- Context sensitive -- places findings in a social, historical, and temporal context; researcher is careful about [even dubious of] the possibility or meaningfulness of generalizations across time and space; emphasizes careful comparative case study analysis and extrapolating patterns for possible transferability and adaptation in new settings.
- Voice, perspective, and reflexivity -- the qualitative methodologist owns and is reflective about her or his own voice and perspective; a credible voice conveys authenticity and trustworthiness; complete objectivity being impossible and pure subjectivity undermining credibility, the researcher's focus reflects a balance between understanding and depicting the world authentically in all its complexity and of being self-analytical, politically aware, and reflexive in consciousness.
Berg, Bruce Lawrence. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences . 8th edition. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2012; Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. Handbook of Qualitative Research . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000; Marshall, Catherine and Gretchen B. Rossman. Designing Qualitative Research . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1995; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 2009.
Basic Research Design for Qualitative Studies
Unlike positivist or experimental research that utilizes a linear and one-directional sequence of design steps, there is considerable variation in how a qualitative research study is organized. In general, qualitative researchers attempt to describe and interpret human behavior based primarily on the words of selected individuals [a.k.a., “informants” or “respondents”] and/or through the interpretation of their material culture or occupied space. There is a reflexive process underpinning every stage of a qualitative study to ensure that researcher biases, presuppositions, and interpretations are clearly evident, thus ensuring that the reader is better able to interpret the overall validity of the research. According to Maxwell (2009), there are five, not necessarily ordered or sequential, components in qualitative research designs. How they are presented depends upon the research philosophy and theoretical framework of the study, the methods chosen, and the general assumptions underpinning the study. Goals Describe the central research problem being addressed but avoid describing any anticipated outcomes. Questions to ask yourself are: Why is your study worth doing? What issues do you want to clarify, and what practices and policies do you want it to influence? Why do you want to conduct this study, and why should the reader care about the results? Conceptual Framework Questions to ask yourself are: What do you think is going on with the issues, settings, or people you plan to study? What theories, beliefs, and prior research findings will guide or inform your research, and what literature, preliminary studies, and personal experiences will you draw upon for understanding the people or issues you are studying? Note to not only report the results of other studies in your review of the literature, but note the methods used as well. If appropriate, describe why earlier studies using quantitative methods were inadequate in addressing the research problem. Research Questions Usually there is a research problem that frames your qualitative study and that influences your decision about what methods to use, but qualitative designs generally lack an accompanying hypothesis or set of assumptions because the findings are emergent and unpredictable. In this context, more specific research questions are generally the result of an interactive design process rather than the starting point for that process. Questions to ask yourself are: What do you specifically want to learn or understand by conducting this study? What do you not know about the things you are studying that you want to learn? What questions will your research attempt to answer, and how are these questions related to one another? Methods Structured approaches to applying a method or methods to your study help to ensure that there is comparability of data across sources and researchers and, thus, they can be useful in answering questions that deal with differences between phenomena and the explanation for these differences [variance questions]. An unstructured approach allows the researcher to focus on the particular phenomena studied. This facilitates an understanding of the processes that led to specific outcomes, trading generalizability and comparability for internal validity and contextual and evaluative understanding. Questions to ask yourself are: What will you actually do in conducting this study? What approaches and techniques will you use to collect and analyze your data, and how do these constitute an integrated strategy? Validity In contrast to quantitative studies where the goal is to design, in advance, “controls” such as formal comparisons, sampling strategies, or statistical manipulations to address anticipated and unanticipated threats to validity, qualitative researchers must attempt to rule out most threats to validity after the research has begun by relying on evidence collected during the research process itself in order to effectively argue that any alternative explanations for a phenomenon are implausible. Questions to ask yourself are: How might your results and conclusions be wrong? What are the plausible alternative interpretations and validity threats to these, and how will you deal with these? How can the data that you have, or that you could potentially collect, support or challenge your ideas about what’s going on? Why should we believe your results? Conclusion Although Maxwell does not mention a conclusion as one of the components of a qualitative research design, you should formally conclude your study. Briefly reiterate the goals of your study and the ways in which your research addressed them. Discuss the benefits of your study and how stakeholders can use your results. Also, note the limitations of your study and, if appropriate, place them in the context of areas in need of further research.
Chenail, Ronald J. Introduction to Qualitative Research Design. Nova Southeastern University; Heath, A. W. The Proposal in Qualitative Research. The Qualitative Report 3 (March 1997); Marshall, Catherine and Gretchen B. Rossman. Designing Qualitative Research . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1999; Maxwell, Joseph A. "Designing a Qualitative Study." In The SAGE Handbook of Applied Social Research Methods . Leonard Bickman and Debra J. Rog, eds. 2nd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2009), p. 214-253; Qualitative Research Methods. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Yin, Robert K. Qualitative Research from Start to Finish . 2nd edition. New York: Guilford, 2015.

Strengths of Using Qualitative Methods
The advantage of using qualitative methods is that they generate rich, detailed data that leave the participants' perspectives intact and provide multiple contexts for understanding the phenomenon under study. In this way, qualitative research can be used to vividly demonstrate phenomena or to conduct cross-case comparisons and analysis of individuals or groups.
Among the specific strengths of using qualitative methods to study social science research problems is the ability to:
- Obtain a more realistic view of the lived world that cannot be understood or experienced in numerical data and statistical analysis;
- Provide the researcher with the perspective of the participants of the study through immersion in a culture or situation and as a result of direct interaction with them;
- Allow the researcher to describe existing phenomena and current situations;
- Develop flexible ways to perform data collection, subsequent analysis, and interpretation of collected information;
- Yield results that can be helpful in pioneering new ways of understanding;
- Respond to changes that occur while conducting the study ]e.g., extended fieldwork or observation] and offer the flexibility to shift the focus of the research as a result;
- Provide a holistic view of the phenomena under investigation;
- Respond to local situations, conditions, and needs of participants;
- Interact with the research subjects in their own language and on their own terms; and,
- Create a descriptive capability based on primary and unstructured data.
Anderson, Claire. “Presenting and Evaluating Qualitative Research.” American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 74 (2010): 1-7; Denzin, Norman. K. and Yvonna S. Lincoln. Handbook of Qualitative Research . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 2009.
Limitations of Using Qualitative Methods
It is very much true that most of the limitations you find in using qualitative research techniques also reflect their inherent strengths . For example, small sample sizes help you investigate research problems in a comprehensive and in-depth manner. However, small sample sizes undermine opportunities to draw useful generalizations from, or to make broad policy recommendations based upon, the findings. Additionally, as the primary instrument of investigation, qualitative researchers are often embedded in the cultures and experiences of others. However, cultural embeddedness increases the opportunity for bias generated from conscious or unconscious assumptions about the study setting to enter into how data is gathered, interpreted, and reported.
Some specific limitations associated with using qualitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include the following:
- Drifting away from the original objectives of the study in response to the changing nature of the context under which the research is conducted;
- Arriving at different conclusions based on the same information depending on the personal characteristics of the researcher;
- Replication of a study is very difficult;
- Research using human subjects increases the chance of ethical dilemmas that undermine the overall validity of the study;
- An inability to investigate causality between different research phenomena;
- Difficulty in explaining differences in the quality and quantity of information obtained from different respondents and arriving at different, non-consistent conclusions;
- Data gathering and analysis is often time consuming and/or expensive;
- Requires a high level of experience from the researcher to obtain the targeted information from the respondent;
- May lack consistency and reliability because the researcher can employ different probing techniques and the respondent can choose to tell some particular stories and ignore others; and,
- Generation of a significant amount of data that cannot be randomized into manageable parts for analysis.
Research Tip
Human Subject Research and Institutional Review Board Approval
Almost every socio-behavioral study requires you to submit your proposed research plan to an Institutional Review Board. The role of the Board is to evaluate your research proposal and determine whether it will be conducted ethically and under the regulations, institutional polices, and Code of Ethics set forth by the university. The purpose of the review is to protect the rights and welfare of individuals participating in your study. The review is intended to ensure equitable selection of respondents, that you have met the requirements for obtaining informed consent , that there is clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university [read: no lawsuits!], and that privacy and confidentiality are maintained throughout the research process and beyond. Go to the USC IRB website for detailed information and templates of forms you need to submit before you can proceed. If you are unsure whether your study is subject to IRB review, consult with your professor or academic advisor.
Chenail, Ronald J. Introduction to Qualitative Research Design. Nova Southeastern University; Labaree, Robert V. "Working Successfully with Your Institutional Review Board: Practical Advice for Academic Librarians." College and Research Libraries News 71 (April 2010): 190-193.
Another Research Tip
Finding Examples of How to Apply Different Types of Research Methods
SAGE publications is a major publisher of studies about how to design and conduct research in the social and behavioral sciences. Their SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases database includes contents from books, articles, encyclopedias, handbooks, and videos covering social science research design and methods including the complete Little Green Book Series of Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences and the Little Blue Book Series of Qualitative Research techniques. The database also includes case studies outlining the research methods used in real research projects. This is an excellent source for finding definitions of key terms and descriptions of research design and practice, techniques of data gathering, analysis, and reporting, and information about theories of research [e.g., grounded theory]. The database covers both qualitative and quantitative research methods as well as mixed methods approaches to conducting research.
SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases
NOTE : For a list of online communities, research centers, indispensable learning resources, and personal websites of leading qualitative researchers, GO HERE .
For a list of scholarly journals devoted to the study and application of qualitative research methods, GO HERE .
- << Previous: 6. The Methodology
- Next: Quantitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How To Write The Conclusion Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD Cand). Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021
So, you’ve wrapped up your results and discussion chapters, and you’re finally on the home stretch – the conclusion chapter . In this post, we’ll discuss everything you need to know to craft a high-quality conclusion chapter for your dissertation or thesis project.
Overview: Dissertation Conclusion Chapter
- What the thesis/dissertation conclusion chapter is
- What to include in your conclusion chapter
- How to structure and write up your conclusion chapter
- A few tips to help you ace the chapter
What exactly is the conclusion chapter?
The conclusion chapter is typically the final major chapter of a dissertation or thesis. As such, it serves as a concluding summary of your research findings and wraps up the document. While some publications such as journal articles and research reports combine the discussion and conclusion sections, these are typically separate chapters in a dissertation or thesis. As always, be sure to check what your university’s structural preference is before you start writing up these chapters.
So, what’s the difference between the discussion and the conclusion chapter?
Well, the two chapters are quite similar , as they both discuss the key findings of the study. However, the conclusion chapter is typically more general and high-level in nature. In your discussion chapter, you’ll typically discuss the intricate details of your study, but in your conclusion chapter, you’ll take a broader perspective, reporting on the main research outcomes and how these addressed your research aim (or aims) .
A core function of the conclusion chapter is to synthesise all major points covered in your study and to tell the reader what they should take away from your work. Basically, you need to tell them what you found , why it’s valuable , how it can be applied , and what further research can be done.
Whatever you do, don’t just copy and paste what you’ve written in your discussion chapter! The conclusion chapter should not be a simple rehash of the discussion chapter. While the two chapters are similar, they have distinctly different functions.

What should I include in the conclusion chapter?
To understand what needs to go into your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to understand what the chapter needs to achieve. In general, a good dissertation conclusion chapter should achieve the following:
- Summarise the key findings of the study
- Explicitly answer the research question(s) and address the research aims
- Inform the reader of the study’s main contributions
- Discuss any limitations or weaknesses of the study
- Present recommendations for future research
Therefore, your conclusion chapter needs to cover these core components. Importantly, you need to be careful not to include any new findings or data points. Your conclusion chapter should be based purely on data and analysis findings that you’ve already presented in the earlier chapters. If there’s a new point you want to introduce, you’ll need to go back to your results and discussion chapters to weave the foundation in there.
In many cases, readers will jump from the introduction chapter directly to the conclusions chapter to get a quick overview of the study’s purpose and key findings. Therefore, when you write up your conclusion chapter, it’s useful to assume that the reader hasn’t consumed the inner chapters of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, craft your conclusion chapter such that there’s a strong connection and smooth flow between the introduction and conclusion chapters, even though they’re on opposite ends of your document.
Need a helping hand?
How to write the conclusion chapter
Now that you have a clearer view of what the conclusion chapter is about, let’s break down the structure of this chapter so that you can get writing. Keep in mind that this is merely a typical structure – it’s not set in stone or universal. Some universities will prefer that you cover some of these points in the discussion chapter , or that you cover the points at different levels in different chapters.
Step 1: Craft a brief introduction section
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the conclusions chapter needs to start with a brief introduction. In this introductory section, you’ll want to tell the reader what they can expect to find in the chapter, and in what order . Here’s an example of what this might look like:
This chapter will conclude the study by summarising the key research findings in relation to the research aims and questions and discussing the value and contribution thereof. It will also review the limitations of the study and propose opportunities for future research.
Importantly, the objective here is just to give the reader a taste of what’s to come (a roadmap of sorts), not a summary of the chapter. So, keep it short and sweet – a paragraph or two should be ample.
Step 2: Discuss the overall findings in relation to the research aims
The next step in writing your conclusions chapter is to discuss the overall findings of your study , as they relate to the research aims and research questions . You would have likely covered similar ground in the discussion chapter, so it’s important to zoom out a little bit here and focus on the broader findings – specifically, how these help address the research aims .
In practical terms, it’s useful to start this section by reminding your reader of your research aims and research questions, so that the findings are well contextualised. In this section, phrases such as, “This study aimed to…” and “the results indicate that…” will likely come in handy. For example, you could say something like the following:
This study aimed to investigate the feeding habits of the naked mole-rat. The results indicate that naked mole rats feed on underground roots and tubers. Further findings show that these creatures eat only a part of the plant, leaving essential parts to ensure long-term food stability.
Be careful not to make overly bold claims here. Avoid claims such as “this study proves that” or “the findings disprove existing the existing theory”. It’s seldom the case that a single study can prove or disprove something. Typically, this is achieved by a broader body of research, not a single study – especially not a dissertation or thesis which will inherently have significant and limitations. We’ll discuss those limitations a little later.

Step 3: Discuss how your study contributes to the field
Next, you’ll need to discuss how your research has contributed to the field – both in terms of theory and practice . This involves talking about what you achieved in your study, highlighting why this is important and valuable, and how it can be used or applied.
In this section you’ll want to:
- Mention any research outputs created as a result of your study (e.g., articles, publications, etc.)
- Inform the reader on just how your research solves your research problem , and why that matters
- Reflect on gaps in the existing research and discuss how your study contributes towards addressing these gaps
- Discuss your study in relation to relevant theories . For example, does it confirm these theories or constructively challenge them?
- Discuss how your research findings can be applied in the real world . For example, what specific actions can practitioners take, based on your findings?
Be careful to strike a careful balance between being firm but humble in your arguments here. It’s unlikely that your one study will fundamentally change paradigms or shake up the discipline, so making claims to this effect will be frowned upon . At the same time though, you need to present your arguments with confidence, firmly asserting the contribution your research has made, however small that contribution may be. Simply put, you need to keep it balanced .
Step 4: Reflect on the limitations of your study
Now that you’ve pumped your research up, the next step is to critically reflect on the limitations and potential shortcomings of your study. You may have already covered this in the discussion chapter, depending on your university’s structural preferences, so be careful not to repeat yourself unnecessarily.
There are many potential limitations that can apply to any given study. Some common ones include:
- Sampling issues that reduce the generalisability of the findings (e.g., non-probability sampling )
- Insufficient sample size (e.g., not getting enough survey responses ) or limited data access
- Low-resolution data collection or analysis techniques
- Researcher bias or lack of experience
- Lack of access to research equipment
- Time constraints that limit the methodology (e.g. cross-sectional vs longitudinal time horizon)
- Budget constraints that limit various aspects of the study
Discussing the limitations of your research may feel self-defeating (no one wants to highlight their weaknesses, right), but it’s a critical component of high-quality research. It’s important to appreciate that all studies have limitations (even well-funded studies by expert researchers) – therefore acknowledging these limitations adds credibility to your research by showing that you understand the limitations of your research design .
That being said, keep an eye on your wording and make sure that you don’t undermine your research . It’s important to strike a balance between recognising the limitations, but also highlighting the value of your research despite those limitations. Show the reader that you understand the limitations, that these were justified given your constraints, and that you know how they can be improved upon – this will get you marks.

Next, you’ll need to make recommendations for future studies. This will largely be built on the limitations you just discussed. For example, if one of your study’s weaknesses was related to a specific data collection or analysis method, you can make a recommendation that future researchers undertake similar research using a more sophisticated method.
Another potential source of future research recommendations is any data points or analysis findings that were interesting or surprising , but not directly related to your study’s research aims and research questions. So, if you observed anything that “stood out” in your analysis, but you didn’t explore it in your discussion (due to a lack of relevance to your research aims), you can earmark that for further exploration in this section.
Essentially, this section is an opportunity to outline how other researchers can build on your study to take the research further and help develop the body of knowledge. So, think carefully about the new questions that your study has raised, and clearly outline these for future researchers to pick up on.
Step 6: Wrap up with a closing summary
Quick tips for a top-notch conclusion chapter
Now that we’ve covered the what , why and how of the conclusion chapter, here are some quick tips and suggestions to help you craft a rock-solid conclusion.
- Don’t ramble . The conclusion chapter usually consumes 5-7% of the total word count (although this will vary between universities), so you need to be concise. Edit this chapter thoroughly with a focus on brevity and clarity.
- Be very careful about the claims you make in terms of your study’s contribution. Nothing will make the marker’s eyes roll back faster than exaggerated or unfounded claims. Be humble but firm in your claim-making.
- Use clear and simple language that can be easily understood by an intelligent layman. Remember that not every reader will be an expert in your field, so it’s important to make your writing accessible. Bear in mind that no one knows your research better than you do, so it’s important to spell things out clearly for readers.
Hopefully, this post has given you some direction and confidence to take on the conclusion chapter of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re still feeling a little shaky and need a helping hand, consider booking a free initial consultation with a friendly Grad Coach to discuss how we can help you with hands-on, private coaching.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

17 Comments
Really you team are doing great!
Your guide on writing the concluding chapter of a research is really informative especially to the beginners who really do not know where to start. Im now ready to start. Keep it up guys
Really your team are doing great!
Very helpful guidelines, timely saved. Thanks so much for the tips.
This post was very helpful and informative. Thank you team.
A very enjoyable, understandable and crisp presentation on how to write a conclusion chapter. I thoroughly enjoyed it. Thanks Jenna.
This was a very helpful article which really gave me practical pointers for my concluding chapter. Keep doing what you are doing! It meant a lot to me to be able to have this guide. Thank you so much.
Nice content dealing with the conclusion chapter, it’s a relief after the streneous task of completing discussion part.Thanks for valuable guidance
Thanks for your guidance
I get all my doubts clarified regarding the conclusion chapter. It’s really amazing. Many thanks.
Very helpful tips. Thanks so much for the guidance
Thank you very much for this piece. It offers a very helpful starting point in writing the conclusion chapter of my thesis.
It’s awesome! Most useful and timely too. Thanks a million times
Bundle of thanks for your guidance. It was greatly helpful.
Wonderful, clear, practical guidance. So grateful to read this as I conclude my research. Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Buy Custom Assignment
- Custom College Papers
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Research Papers
- Buy Custom Term Papers
- Cheap Custom Term Papers
- Custom Courseworks
- Custom Thesis Papers
- Custom Expository Essays
- Custom Plagiarism Check
- Cheap Custom Essay
- Custom Argumentative Essays
- Custom Case Study
- Custom Annotated Bibliography
- Custom Book Report
- How It Works
- +1 (888) 398 0091
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Topics
- Uncategorized
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Qualitative Research Paper
October 25, 2023
A qualitative research paper is a type of academic paper that focuses on exploring and understanding a phenomenon in depth, often using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of textual or visual data. Unlike quantitative research which relies on numerical data and statistical analysis, a qualitative research paper aims to provide detailed insights, interpretations, and subjective understandings of the research topic. The purpose of writing a qualitative research paper is to delve into the complexity of the subject matter and provide a rich and comprehensive understanding of it. To write a qualitative research paper effectively, it is crucial to carefully select a research topic, formulate pertinent research questions, conduct a thorough literature review, select an appropriate methodology, collect and analyze data, and present well-supported interpretations and conclusions.
Choosing a Research Topic
Choosing a research topic is a critical first step in writing a qualitative research paper. The topic should be of interest to the researcher and align with their expertise and passion. It is important to select a topic that is specific, manageable, and aligned with the research objectives. One approach is to identify gaps in existing literature and areas that require further exploration. Brainstorming, consulting with peers and mentors, and reviewing recent publications can help in generating ideas.
Once potential topics are identified, it is necessary to evaluate their feasibility and relevance. Consideration should be given to the availability of resources, access to data, ethical considerations, and potential impact. The research topic should be significant, addressing a research gap or contributing to the existing body of knowledge. It is also beneficial to choose a topic that allows for in-depth exploration and provides opportunities for meaningful analysis and interpretation.
Narrow down the topic by clarifying the research questions and objectives. This will refine the focus and guide the research process. It is essential to ensure that the chosen topic is ethically sound and aligns with the research guidelines and regulations. By carefully selecting a research topic, researchers can lay a solid foundation for their qualitative research paper and set themselves up for a successful and impactful study.
Qualitative Research Paper Topics Examples:
- The lived experiences of nursing home residents
- An exploration of the impact of social media on mental health
- Understanding the perspectives of parents of children with autism spectrum disorder
- The influence of cultural values on leadership styles in multinational organizations
- The role of spirituality in addiction recovery
- A phenomenological study of the experience of chronic pain
- Investigating the benefits and drawbacks of remote working for employees
- The experiences of international students in higher education
- The impact of mindfulness practices on stress and anxiety
- Exploring the factors that contribute to a positive work-life balance in healthcare professionals.
Formulating Research Questions and Objectives
Formulating clear research questions and objectives is a crucial step in writing a qualitative research paper. These questions and objectives guide the research process and provide focus for the study. Here are some tips for formulating research questions and objectives:
- Start with a broad research question: This will allow for exploration of the research topic and help in identifying key areas of focus.
- Refine the research question: Narrow down the research question by considering its relevance, feasibility, and practicality.
- Consider the research objectives: The research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Use the SMART criteria to refine the research objectives.
- Ensure coherence between research questions and objectives: The research questions and objectives should work together to provide clarity and direction for the research.
- Use open-ended questions: Qualitative research involves exploring in-depth subjective experiences and perspectives. Open-ended questions allow for this exploration and provide rich data.
- Keep the target audience in mind: Formulate research questions and objectives that are relevant and meaningful to the intended audience.
Examples of research questions and objectives:
Research question: How do teachers cope with the challenges of remote teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Research objectives:
- To explore the experiences of teachers with remote teaching during the pandemic.
- To identify the strategies used by teachers to overcome the challenges of remote teaching.
- To understand the impact of remote teaching on the well-being of teachers.
Conducting a Literature Review
Conducting a literature review is a critical aspect of writing a qualitative research paper. It involves reviewing existing literature on the chosen research topic and identifying gaps or areas that require further exploration. Here are some tips for conducting a literature review:
- Develop a search strategy: It is essential to develop a search strategy to ensure that relevant literature is captured. Databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and PsycINFO can be used to search for relevant literature.
- Use keywords: Keywords are essential for ensuring that relevant literature is identified. Start with a broad search, and then narrow down the search using specific keywords.
- Review the literature: Review the identified literature and assess its quality, relevance, and validity. Identify and summarize key themes, concepts, and findings.
- Identify gaps in the literature: Identify areas where further research is required. This will provide a basis for formulating research questions and objectives.
- Document all sources: Keep accurate records of all sources reviewed, including the author, title, publication date, and source.
- Evaluate the relevance of the literature: Ensure that reviewed literature is relevant by evaluating the date of publication and the credibility of the author and publisher.
Conducting a literature review is a crucial step in writing a qualitative research paper. The review provides a basis for understanding existing knowledge and identifying areas for future research. By carefully reviewing literature, researchers can ensure that their writing is informed and current, and that their research objectives are relevant and significant.
Selecting a Methodology
Selecting the appropriate methodology is a critical step in writing a qualitative research paper. The methodology chosen should align with the research questions and objectives and provide a suitable approach to collect relevant data. Qualitative research methodologies include ethnography, case study, grounded theory, phenomenology, and content analysis.
Researchers need to consider which methodology is best suited for their research questions and objectives. Ethnography and grounded theory are useful when researchers need to explore and describe complex social phenomena. Phenomenology is suited for understanding how individuals perceive or experience specific phenomena. Case study research is appropriate when researchers need to understand or explain a specific case or context. Content analysis is helpful when researchers need to analyze textual or visual data.
Selecting an appropriate methodology is essential to ensure high-quality research that can effectively answer the research questions and objectives. Careful consideration of the strengths and weaknesses of each methodology will ensure that the chosen methodology is best suited to the research project for writing a qualitative research paper.
Collecting Data
Collecting data is a crucial step in a qualitative research project. Data collection methods should be carefully chosen, based on the research questions, objectives, and methodology selected. The most common data collection methods in qualitative research include interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis.
Interviews are common in qualitative research and gather data through structured, semi-structured, or unstructured questions. Focus groups use group discussions to gather data from participants on specific topics. Observation involves collecting data through direct observation of behavior, while document analysis involves analyzing existing documents such as newspapers, journals, or reports.
When selecting a data collection method, it is essential to consider the research question and objective, the availability of participants, and the time and resources available. It is important to ensure that the data collection method is ethical and respects participants’ privacy and confidentiality.
In addition to collecting data, it is essential to document the data obtained. Data documentation should include information such as the date and time of data collection, the data collection method used, the participants’ demographics, and their responses. Further, it is crucial to ensure that the data collected is reliable and valid.
Overall, collecting data is a critical step in a qualitative research project, and researchers must carefully select appropriate data collection methods and document and analyze their data accurately.
Analyzing Data
Analyzing data is a crucial step in writing a qualitative research paper. It involves reviewing and interpreting the data collected to answer the research questions and objectives. Researchers must ensure that the data is analyzed consistently, systematically, and accurately.
Qualitative data analysis methods include thematic analysis, content analysis, and narrative analysis. Thematic analysis involves identifying themes and patterns within the data, while content analysis involves analyzing the frequency and distribution of specific words or phrases. Narrative analysis involves analyzing and interpreting the stories told by participants in the research project.
During data analysis, the researcher must document and track the findings and conclusions in a clear and concise manner. Writing can help to organize thoughts and ideas, making it easier to identify and summarize key themes and patterns.
It is essential to maintain transparency throughout the data analysis process, clearly outlining the steps taken to analyze the data. Researchers must also ensure that the analysis remains true to the data collected and avoid introducing personal bias.
Overall, analyzing data is a critical step in writing a qualitative research paper. By carefully analyzing and interpreting data, researchers can answer research questions and objectives and provide new insights into a specific topic or phenomenon. Writing is crucial throughout the process as it guides the analysis and ensures that the findings are documented and transparent.
Interpreting Results
Interpreting results is a crucial step in writing a qualitative research paper. It involves analyzing the data, identifying key themes, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Researchers must ensure that the results are accurately and transparently reported.
During the interpretation of results, it is essential to keep an open mind, question assumptions, and support findings with strong evidence from the data collected. The analysis should consider different perspectives, such as the participants’ views and cultural background.
Qualitative research is often subjective, and interpretations of results can vary widely. Therefore, it is crucial to incorporate alternative interpretations and acknowledge any potential limitations or biases in the research process.
Researchers should use writing to convey the findings clearly and concisely, including a comprehensive summary of key themes and conclusions drawn from the data. The discussion of results should connect the research findings to previous literature and highlight the study’s contributions to the field.
In addition, researchers must also consider any practical implications of the research, including suggestions for future research and recommendations for policy or practice. Finally, researchers should ensure that the results are presented in a way that is accessible to a wide audience, including both academic and non-academic communities.
In conclusion, interpreting results from qualitative research is a multi-step process that involves analyzing the data collected, drawing conclusions and taking into account the research limitations, and presenting the findings in a clear, concise, and accessible manner.
Sociology Research Topics Ideas
Importance of Computer in Nursing Practice Essay
History Research Paper Topics For Students
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
Latest Articles
Navigating the complexities of a Document-Based Question (DBQ) essay can be daunting, especially given its unique blend of historical analysis...
An introduction speech stands as your first opportunity to connect with an audience, setting the tone for the message you...
Embarking on the journey to write a rough draft for an essay is not just a task but a pivotal...
I want to feel as happy, as your customers do, so I'd better order now
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on 10 October 2022.
The conclusion is the very last part of your thesis or dissertation . It should be concise and engaging, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your main findings, as well as the answer to your research question .
In it, you should:
- Clearly state the answer to your main research question
- Summarise and reflect on your research process
- Make recommendations for future work on your topic
- Show what new knowledge you have contributed to your field
- Wrap up your thesis or dissertation
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Discussion vs. conclusion, how long should your conclusion be, step 1: answer your research question, step 2: summarise and reflect on your research, step 3: make future recommendations, step 4: emphasise your contributions to your field, step 5: wrap up your thesis or dissertation, full conclusion example, conclusion checklist, frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
While your conclusion contains similar elements to your discussion section , they are not the same thing.
Your conclusion should be shorter and more general than your discussion. Instead of repeating literature from your literature review , discussing specific research results , or interpreting your data in detail, concentrate on making broad statements that sum up the most important insights of your research.
As a rule of thumb, your conclusion should not introduce new data, interpretations, or arguments.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count.
An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research. A humanities topic or systematic review , on the other hand, might require more space to conclude its analysis, tying all the previous sections together in an overall argument.
Your conclusion should begin with the main question that your thesis or dissertation aimed to address. This is your final chance to show that you’ve done what you set out to do, so make sure to formulate a clear, concise answer.
- Don’t repeat a list of all the results that you already discussed
- Do synthesise them into a final takeaway that the reader will remember.
An empirical thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
A case study –based thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
In the second example, the research aim is not directly restated, but rather added implicitly to the statement. To avoid repeating yourself, it is helpful to reformulate your aims and questions into an overall statement of what you did and how you did it.
Your conclusion is an opportunity to remind your reader why you took the approach you did, what you expected to find, and how well the results matched your expectations.
To avoid repetition , consider writing more reflectively here, rather than just writing a summary of each preceding section. Consider mentioning the effectiveness of your methodology , or perhaps any new questions or unexpected insights that arose in the process.
You can also mention any limitations of your research, but only if you haven’t already included these in the discussion. Don’t dwell on them at length, though – focus on the positives of your work.
- While x limits the generalisability of the results, this approach provides new insight into y .
- This research clearly illustrates x , but it also raises the question of y .
You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms.
- Based on these conclusions, practitioners should consider …
- To better understand the implications of these results, future studies could address …
- Further research is needed to determine the causes of/effects of/relationship between …
When making recommendations for further research, be sure not to undermine your own work. Relatedly, while future studies might confirm, build on, or enrich your conclusions, they shouldn’t be required for your argument to feel complete. Your work should stand alone on its own merits.
Just as you should avoid too much self-criticism, you should also avoid exaggerating the applicability of your research. If you’re making recommendations for policy, business, or other practical implementations, it’s generally best to frame them as ‘shoulds’ rather than ‘musts’. All in all, the purpose of academic research is to inform, explain, and explore – not to demand.
Make sure your reader is left with a strong impression of what your research has contributed to the state of your field.
Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Returning to your problem statement to explain how your research helps solve the problem
- Referring back to the literature review and showing how you have addressed a gap in knowledge
- Discussing how your findings confirm or challenge an existing theory or assumption
Again, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already covered in the discussion in your conclusion. Instead, pick out the most important points and sum them up succinctly, situating your project in a broader context.
The end is near! Once you’ve finished writing your conclusion, it’s time to wrap up your thesis or dissertation with a few final steps:
- It’s a good idea to write your abstract next, while the research is still fresh in your mind.
- Next, make sure your reference list is complete and correctly formatted. To speed up the process, you can use our free APA citation generator .
- Once you’ve added any appendices , you can create a table of contents and title page .
- Finally, read through the whole document again to make sure your thesis is clearly written and free from language errors. You can proofread it yourself , ask a friend, or consider Scribbr’s proofreading and editing service .
Here is an example of how you can write your conclusion section. Notice how it includes everything mentioned above:
V. Conclusion
The current research aimed to identify acoustic speech characteristics which mark the beginning of an exacerbation in COPD patients.
The central questions for this research were as follows: 1. Which acoustic measures extracted from read speech differ between COPD speakers in stable condition and healthy speakers? 2. In what ways does the speech of COPD patients during an exacerbation differ from speech of COPD patients during stable periods?
All recordings were aligned using a script. Subsequently, they were manually annotated to indicate respiratory actions such as inhaling and exhaling. The recordings of 9 stable COPD patients reading aloud were then compared with the recordings of 5 healthy control subjects reading aloud. The results showed a significant effect of condition on the number of in- and exhalations per syllable, the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable, and the ratio of voiced and silence intervals. The number of in- and exhalations per syllable and the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable were higher for COPD patients than for healthy controls, which confirmed both hypotheses.
However, the higher ratio of voiced and silence intervals for COPD patients compared to healthy controls was not in line with the hypotheses. This unpredicted result might have been caused by the different reading materials or recording procedures for both groups, or by a difference in reading skills. Moreover, there was a trend regarding the effect of condition on the number of syllables per breath group. The number of syllables per breath group was higher for healthy controls than for COPD patients, which was in line with the hypothesis. There was no effect of condition on pitch, intensity, center of gravity, pitch variability, speaking rate, or articulation rate.
This research has shown that the speech of COPD patients in exacerbation differs from the speech of COPD patients in stable condition. This might have potential for the detection of exacerbations. However, sustained vowels rarely occur in spontaneous speech. Therefore, the last two outcome measures might have greater potential for the detection of beginning exacerbations, but further research on the different outcome measures and their potential for the detection of exacerbations is needed due to the limitations of the current study.
Checklist: Conclusion
I have clearly and concisely answered the main research question .
I have summarized my overall argument or key takeaways.
I have mentioned any important limitations of the research.
I have given relevant recommendations .
I have clearly explained what my research has contributed to my field.
I have not introduced any new data or arguments.
You've written a great conclusion! Use the other checklists to further improve your dissertation.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples.

9 methodologies for a successful qualitative research assignment
Qualitative research is important in the educational and scientific domains. It enables a deeper understanding of phenomena, experiences, and context. Many researchers employ such research activities in the fields of history, sociology, and anthropology. For such researchers, learning quality analysis insights is crucial. This way, they can perform well throughout their research journey. Writing a qualitative research assignment is one such way to practice qualitative interpretations. When students address various qualitative questions in these projects, they become efficient in conducting these activities at a higher level, such as for a master’s or Ph.D. thesis.
The FormPlus highlights why researchers prefer qualitative research over quantitative research. It is faster, scientific, objective, focused, and acceptable. Researchers who don’t know what to expect from the research outcomes usually choose qualitative research. In this guide, we will discuss the top methodologies that students can employ while writing their qualitative research assignments. This way, you can write an appealing document that perfectly demonstrates your qualitative research skills.
However, being stressed with academic and daily life commitments, if you find it challenging to manage time exclusively for such projects, availing of assignment writing services can make it manageable. Instead of doing anything wrong in the hustle, get it done by the professionals specifically working to handle these academic write-ups. Now, let’s define quality research before we discuss the actual topic.
What is meant by qualitative research?
Quality research is a market research method that gathers data from conversational and open-ended communication. In simple words, it is about what people think and why they think so. It relates to the nature or standard of something rather than dealing with its quantity. Such researchers collect nonnumerical data to understand opinions, concepts, and ideas.
How do you write a qualitative research assignment? Top 9 methodologies
Writing an assignment requires your command of various tasks. Qualitative research assignment design involves research, writing, structuring, and providing citations of the resources used. Assignment writing plays a crucial role in upgrading your grades.
So, you must make it accurate and authentic. Write it with the utmost care without skipping any important aspects. Sometimes, it can be hard, but it becomes easy if you correctly use effective methodologies. This is why we have brought together some of the common methodologies you can use to write your qualitative research assignments.
1. Interviews
A qualitative interview is mostly used in projects that involve market research. In this study personal interaction is required to collect in-depth information of the participants. In qualitative research for assignment, consider the interview as a personal form of research agenda rather than a focused group study. A qualitative interview requires careful planning so that you can gather meaningful data.
Here are the simple steps to consider for its implementation in a qualitative research assignment:
- Define research objectives.
- Identify the target population.
- Obtain informed consent of participants.
- Make an interview guideline.
- Select a suitable location.
- Conduct the interview.
- Show respect for participant’s perspectives.
- Analyse the data.
2. Observation
In qualitative observation, the researcher gathers data from five senses: sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. It is a subject approach that depends on the sensory organ of the researcher. This method allows you to better understand the culture, process, and people under study. Some of its characteristics to consider for writing a qualitative research assignment include,
- It is a naturalistic inquiry of the participants in a natural environment.
- This approach is subjective and depends on the researcher’s observation.
- It does not seek a definite answer to a query.
- The researcher can recognise their own biases when compiling findings.
3. Questionnaires
In this type of survey, the researcher asks open-ended questions to participants. This way, they price the long written or typed document. In writing qualitative research assignments, these questions aim to reveal the participants’ narratives and experiences. Once you know what type of information you need, you can start curating your questionnaire form. The questions must be specific and clear enough that the participants can comprehend them.
Below are the main points that must be considered when creating qualitative research questionnaires.
- Avoid jargon and ambiguity in the questions.
- Each question should contribute to the research objectives.
- Use simple language.
- The questions should be neutral and unbiased.
- Be precise, as the complex questions can overwhelm the respondents.
- Always conduct a pilot test.
- Put yourself in the respondent’s shoes while asking questions.
4. Case Study
A case study is a detailed analysis of a person, place, thing, organisation, or phenomenon. This method is appropriate when you want to gain a contextual, concrete, and in-depth understanding of the real-world problem for writing your qualitative research assignment. This method is especially helpful when you need more time to conduct large-scale research activities.
The four crucial steps below can be followed up with this methodology.
- Select a case that has the potential to provide new and unexpected insights into the subject.
- Make a theoretical framework.
- Collect your data from various primary and secondary resources.
- Describe and analyse the case to provide a clear picture of the subject.
5. Focus Groups
Focused group research has some interesting properties. In this method, a planned interview is conducted within a small group. For this purpose, some of the participants are sampled from the study population to record data for writing a qualitative research assignment. Typically, a focused group has features like,
- At least four to ten participants must meet for up to two hours.
- There must be a facilitator who can guide the discussion by asking open-ended questions.
- The emphasis must be put on the group discussion rather than the discussion of the group members with the facilitator.
- The discussion should be recorded and transcribed by the researchers.
6. Ethnographic Research
It is the most in-depth research method that involves studying people in their natural environment. It requires the researcher to adopt the target audience environment. The environment can be anything from an organisation to a city or any remote location.
However, the geographical constraints can be a problem in this study. For students who are writing their qualitative research assignment, some of the features of ethnographic research to write in their document include,
- The researcher can get a more realistic picture of the study.
- It uncovers extremely valuable insights.
- Provides accurate predictions.
- You can extend the observation to create more in-depth data.
- You can interact with people within a particular context.
7. Record Keeping
This method is similar to going to the library to collect data from books. You consult various relayed books, note the important points, and take note of the referencing. So, the researcher uses already existing data rather than introducing new things in the field.
Later on, this data can be used to conduct new research. Yet, when faced with the vast resources available in your institution’s library, seeking assistance from UK-based assignment writing services is an excellent solution if you need help pinpointing the most relevant information for your topic. Proficient in data gathering and adept at structuring qualitative research assignments, these professionals can significantly elevate your academic results.
This method is mostly used by companies to understand a group of customers’ behaviour, characteristics, and motivation. It allows respondents to ask in-depth questions about their experience. In a business market, it helps you understand how your customers make decisions. The intent is to understand them at their level and make related changes in your setup. The researcher must ask generic and precise questions that have a clear purpose.
Consider the below examples of qualitative survey questions. It can be useful in recording data and writing qualitative research assignments.
- Why did you buy this skin care product?
- What is the overall narrative of this brand?
- How do you feel after buying this product?
- What sets this brand apart from others?
- How will this product fulfil your needs?
- What are the things that you expect from this brand to grant you?
9. Action Research
This method involves collaboration and empowerment of the participants. It is mostly appropriate for marginalised groups where there is no flexibility.
The primary characteristics of the action research that can be quoted in your qualitative research assignment include,
- It is action-oriented, and participants are actively involved in the research.
- There is a collaborative process between participants and researchers.
- The nature of action research is flexible to the changing situation.
However, the survey also accompanies some of the limitations, including,
- The researcher can misinterpret the open-ended questions.
- The data ownership between the researcher and participants needs to be negotiated.
- The ethical considerations must be kept.
- It is not considered a scientific method as it is fluid in data collection. Consequently, it may not attract the finding.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative research?
Both research types share the common aim of knowledge acquisition. In quantitative research, the use of numbers and objective measures is used. It seeks answers to questions like when and where.
On the other hand, in qualitative research, the researcher is concerned with subjective phenomena. Such data can’t be numerically measured. For example, you might conduct a survey to analyse how different people experience grief.
What are the 4 types of qualitative research?
There are various types of qualitative research. It may include,
● Phenomenological studies:
It examines the human experience via description provided by the people involved. These are the lived experiences of the people. It is usually used in research areas where little knowledge is known.
● Ethnographic studies:
It involves the analysis of data about cultural groups. In such analysis, the researcher mostly lives with different communities and becomes part of their culture to provide solid interpretations.
● Grounded theory studies:
In this qualitative approach, the researcher collects and analyses the data. Later on, a theory is developed that is grounded in the data. It used both inductive and deductive approaches for theory development.
● Historical studies:
It is concerned with the location, identification, evaluation, and synthesis of data from the past. These researchers are not concerned with discovering past events but with relating these events to the present happenings.
The Research Gate provides a flow chart illustrating various qualitative research methods.
What are The 7 characteristics of qualitative research?
The following are some of the distinct features of qualitative research. You can write about them in your qualitative research assignment, as they are collected from reliable sources.
- It can even capture the changing attitude within the target group.
- It is beyond the limitations associated with quantitative research
- It explains something that numbers alone can’t describe.
- It is a flexible approach to improve the outcomes.
- A researcher is not supposed to become more speculative about the results.
- This approach is more targeted.
- It keeps the cost of data collection down.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research?
The pros of qualitative research can’t be denied. However, some cons are also associated with this research.
- Explore attitudes and behaviours in depth.
- It encourages discussions for better results.
- Generate descriptive data that can formulate new theories.
- The small sample size can be a problem.
- Bias in the sample collection.
- Lack of privacy if you are covering a sensitive topic.
Qualitative research assignment examples
The Afe Babalola University ePortal provides an example of a qualitative assignment. Here is the description of quality questions and related answers. You can get an idea about how to handle your quality research assignment project with this sample.
The questions asked in the paper are displayed below.
The Slide Team presents a template for further compressing other details, such as the qualitative research assignment template. You can use it to make your presentation look professional.
Writing a qualitative research assignment is crucial, especially if you want to engage in research activities for your master’s thesis. Most researchers choose this method because of the associated credibility and reliability of the results. In the above guide, we have discussed some of the prominent features of this method. All of the given data can help you in writing your assignments. We have discussed the benefits of each methodology and a brief account of how you can carry it.
However, even after going through this whole guideline, if the concepts of the Qualitative Research methods assignment seem ambiguous and you think you can’t write a good project, then ask professional to “ write my assignment .” These experts can consult the best sources for the data collection of your project. Consequently, they will deliver you the winning document that can stand out among other write-ups.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Having said that, the conclusion of a qualitative study can at times be quite detailed. This would depend on the complexity of the study. A questionnaire about likes and dislikes is simpler to score, interpret, and infer than a focus group, interview, or case study. In the case of a simpler study, you may reiterate the key findings of the study ...
Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on 'generate'. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline. Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion.
That said, qualitative research can help demonstrate the causal mechanisms by which something happens. Qualitative research is also helpful in exploring alternative explanations and counterfactuals. If you want to know more about qualitative research and causality, I encourage you to read chapter 10 of Rubin's text.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Abstract. This chapter provides guidelines for writing journal articles based on qualitative approaches. The guidelines are part of the tradition of the Chicago School of Sociology and the author's experience as a writer and reviewer. The guidelines include understanding experiences in context, immersion, interpretations grounded in accounts ...
In this post, we'll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can: · Reword your thesis statement. · Highlight the significance of your research. · Discuss limitations. · Connect to the introduction. · End with a thought-provoking statement.
4. Provide a summary of the literature relating to the topic and what gaps there may be. Rationale for study. 5. Identify the rationale for the study. The rationale for the use of qualitative methods can be noted here or in the methods section. Objective. 6. Clearly articulate the objective of the study.
Purpose - This paper aims to offer junior scholars a front-to-back guide to writing an academic, theoretically positioned, qualitative research article in the social sciences. Design/methodology ...
Objective To provide an overview of qualitative methods, particularly for reviewers and authors who may be less familiar with qualitative research.Methods A question and answer format is used to address considerations for writing and evaluating qualitative research.Results and Conclusions When producing qualitative research, individuals are encouraged to address the qualitative research ...
Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions (phenomenological research questions), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process (grounded theory questions), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes (qualitative case study ...
Conclusion Although Maxwell does not mention a conclusion as one of the components of a qualitative research design, you should formally conclude your study. ... 2009), p. 214-253; Qualitative Research Methods. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Yin, Robert K. Qualitative Research from Start to Finish. 2nd edition. New York: Guilford, 2015 ...
In general, a good dissertation conclusion chapter should achieve the following: Summarise the key findings of the study. Explicitly answer the research question (s) and address the research aims. Inform the reader of the study's main contributions. Discuss any limitations or weaknesses of the study.
We partnered with NVivo to host a free webinar on how to write conclusions based on your qualitative research findings. Join research methodologist Dr. Veron...
To write a qualitative research paper effectively, it is crucial to carefully select a research topic, formulate pertinent research questions, conduct a thorough literature review, select an appropriate methodology, collect and analyze data, and present well-supported interpretations and conclusions. Choosing a Research Topic.
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
Step 3: Make future recommendations. You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms. Example: Recommendation sentence.
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Conclusion . Writing a qualitative research assignment is crucial, especially if you want to engage in research activities for your master's thesis. Most researchers choose this method because ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.