

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how do you calculate your gpa step-by-step instructions.
Coursework/GPA

How exactly do you take a document that's as complicated as your transcript and shrink it all down to a single number? If you're wondering how to use the final grades you've gotten in high school to determine your GPA, then you've come to the right place. This article will show you how to make this calculation, step by step. But first, what exactly is a GPA?
What Is a GPA?
Most likely, in your high school classes, your final grades are awarded either as letters (A-, B+, etc.) or percents (92%, 85%, etc. out of 100%).
A GPA, or grade point average, converts those letters or percents into numbers and then averages these numbers together. Because it's made up of all your grades, your GPA is one of the most important factors for college admission. It's a good indicator of your intelligence, work ethic, perseverance, and willingness to push yourself.
GPAs are useful for colleges to easily compare you with other students who graduated from your school and with all the other applicants. But why?
Imagine you're an admissions officer who has to look at thousands of college applications. Would you rather go through each transcript individually, add up all the As and all the Bs, and then compare that to the next person, and so on? Or, would you rather have an easy summary number that could be used for a quick comparison across the board?
Your GPA is that quick summary number.

The Difference Between Weighted and Unweighted GPA
There are two main types of GPAs: weighted and unweighted.
An unweighted GPA is when a school uses a scale that goes from 0.0 to 4.0 and does not take into account the difficulty level of classes.
By contrast, a weighted GPA is when a school uses a scale that goes from 0.0 all the way up to 5.0 (or sometimes 6.0) and does take into account class difficulty. In this model, the school gives higher numerical values to grades earned in honors , AP , and/or IB classes .
Here's an example to help clarify the differences here. Say Jeremy gets an A in a standard-level US History class, whereas Lakshmi gets an A in AP US History . In the unweighted GPA model, both As are treated the same way, with each translating to a 4.0 .
But in the weighted GPA model, Jeremy's A would convert to a 4.0 and Lakshmi's A would convert to a 5.0 to show that her class took a lot more effort to ace .
See the difference?
Before we continue, it's important to understand that this article focuses mainly on explaining and calculating unweighted GPAs. (For more information on weighted GPAs, check out our other guide .)

How Do You Calculate Your Unweighted GPA?
The first thing to do in order to calculate a grade point average is to convert each of the final class grades you've gotten so far in high school into the correct decimal.
Here is the standard unweighted scale for doing this:
Next, perform the following calculation :
- Add all the converted decimal grades together—this is your sum
- Count the number of classes you've taken
- Divide the sum by the number of classes , and you have your unweighted GPA
In the following section, we'll go through an example calculation of an unweighted GPA.

Want to build the best possible college application?
We can help. PrepScholar Admissions is the world's best admissions consulting service. We combine world-class admissions counselors with our data-driven, proprietary admissions strategies . We've overseen thousands of students get into their top choice schools , from state colleges to the Ivy League.
We know what kinds of students colleges want to admit. We want to get you admitted to your dream schools .
Learn more about PrepScholar Admissions to maximize your chance of getting in.

Step-by-Step Example of an Unweighted GPA Calculation
Let me show you an example of how to calculate an unweighted GPA so you can see how this will look in practice. (To see how to calculate a weighted GPA, check out our other article .) We'll use a sample transcript for incognito CIA operative John Doe.
Be aware that for this example, we are assuming that all classes are worth the same number of credits (in other words, you can ignore the credit column in the transcript below).
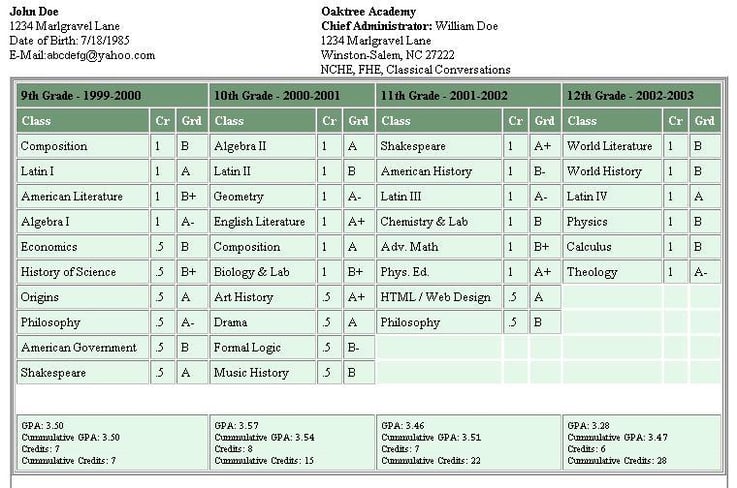
Step 1: Convert Grades Into Decimals
In order to learn how to calculate a GPA, let's first convert John's letter grades into numbers:
Let's also count how many classes he took each of those school years:
Step 2: Calculate Individual Year GPAs
To get each individual year's GPA, all we need to do is divide the sum by the number of classes . If this division ends up with a long decimal, simply round to the nearest hundredth:
Step 3: Calculate Cumulative High School GPA
To get a cumulative GPA for John's entire high school career, we simply add up the sums for all the years and divide by the number of classes he took over all those years:
35 + 35.7 + 27.7 + 19.7 = 118.1 (sum of all final grades)
10 + 10 + 8 + 6 = 34 (total number of classes taken)
118.1 / 34 = 3.47 (GPA)
So, his GPA for all of high school is 3.47.
Pro tip: The cumulative GPA is not an average of each year because the number of classes taken each year is different.
Step 4: Calculate GPA Submitted to Colleges (Optional)
Finally, if we wanted to figure out the GPA that John would send out on his college applications, we would do the same process, but leave off senior year. Since applications go out in the beginning of 12th grade, those final grades won't make it into the application GPA:
35 + 35.7 + 27.7 = 98.4 (sum of final grades from 9th to 11th grade)
10 + 10 + 8 = 28 (number of classes taken from 9th to 11th grade)
98.4 / 28 = 3.51 (college application GPA)
As you can see, John's college application GPA would be 3.51 .

What If My Classes Are Worth Different Amounts of Credits?
In the example above, we calculated John's GPA with the assumption that every took was worth the same amount of credits. If this isn't the case for you, you'll need to add in an extra step.
To calculate your GPA when your classes are worth different amounts of credits, you'll need to multiply your grade for each class by the number of credits it was worth and sum those together (instead of just summing all your grades together) and divide that sum by the total number of credits you took (rather than just the total number of classes you took).
As a quick example, let's take another look at John's junior year grades, this time with the number of credits each class was worth.
Here we can see that the last two classes John took were each only worth half a credit. In the table, the third column, "Quality Points," shows the product of John's GPA in each class with the number of credits that class was worth.
To find John's GPA (based solely on these eight classes), all you need to do now is sum the number of quality points and divide them by the number of credits John took:
GPA = (4.0+2.7+3.7+3.0+3.3+4.0+2.0+1.5) / (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 0.5 + 0.5)
GPA = 24.2/7 = 3.46 .
What's Next?
Interested in diving even deeper into the differences between weighted and unweighted GPA? Then check out our guide to the benefits and drawbacks of both .
Want to see step-by-step weighted GPA calculation? Let us show you how it's done .
Curious how your GPA compares? Learn what a good or bad GPA is and then see how you stack up against the average high school student .
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
What is Cumulative GPA? How Do You Calculate it?
What’s covered:, what is a cumulative gpa, how to calculate your cumulative gpa, my cumulative gpa seems wrong – did i make a mistake.
- What is a Good GPA for College Admissions?
Your GPA is an important part of your college application, so naturally, you want to know where you stand. But there’s also a lot of confusion about what it actually means and how to figure yours out.
What is a cumulative GPA? And how do you calculate yours? We’ve got your answers!
GPAs (Grade Point Averages) are used to express a student’s academic strength in a single numerical value. There are many kinds of GPAs: cumulative, semester, weighted, unweighted.
Your semester GPA is an average of the grades you received in a given semester. Meanwhile, your cumulative GPA is an average of all the grades you’ve received in all your courses throughout high school.
Each course is assigned a certain number of credits, with those with a higher number of credits carrying more value than those with a lower number of credits. Using the formula outlined below, a GPA is the calculated average of the corresponding numerical value of your grades (that’s why it stands for “Grade Point Average”). The standardized scale is 0.0-4.0, with a 4.0 equaling an A and a 0 equaling an F. For weighted GPAs, you add an extra half- or full-point to more difficult courses.
Briefly, to calculate your unweighted GPA, follow these steps:
- Multiply the credits for each course by the corresponding numerical grade point of the grade you earned. (See chart below for grades and their numerical values.)
- Add the total grade points together.
- Add together the number of credits you earned.
- Divide the grade point total by the total number of credits, rounding to the nearest hundredth.
To calculate your weighted GPA, the only change is that in the first step, you’ll add the following to each grade point:
- 0.0 for regular courses.
- 0.5 for Honors, IB SL, and dual enrollment courses.
- 1.0 for AP, post-AP, IB HL, and college courses.
Here’s an example schedule of a student that has completed their freshman year. Let’s calculate the unweighted GPA first.
Calculating Unweighted Cumulative GPA: Example
So, we take the raw value and divide it by the number of credits: 63.2/17 = 3.72. This is the student’s semester 1 unweighted GPA.
This student’s semester 2 GPA is 66.2/17 = 3.89
Their cumulative GPA would be the sum of the raw values divided by the sum of the credits.
So, this would be (63.2+66.2)/(17+17) = 3.81
Since both semesters have the same credit value, you can also just average together the semester GPAs and get the same number: (3.89+3.72)/2 = 3.81 (rounded).
If the credit values are different, however, you’ll want to sum raw values and divide them by the total number of credits.
Keep in mind that you don’t have to do this semester by semester. If you’re calculating cumulative GPA, you can just sum together the raw values for ALL of your courses, and divide them by the total number of credits. We’ve broken this up by semester to keep it simpler for this example.
Calculating Weighted Cumulative GPA: Example
So how do you calculate weighted cumulative GPA, then? We have to add the extra points for course type. Since the student has 2 honors courses, we’d add .5 to their Grade Point before multiplying it by the number of credits.
So, we take the raw value and divide it by the number of credits: 66.2/17 = 3.89. This is the student’s semester 1 weighted GPA.
The student’s semester 2 weighted GPA is 69.2/17 = 4.07
Their cumulative GPA is (69.2+66.2)/(17+17) = 3.98
When juggling a bunch of numbers and moving through several calculations, it can be easy to make a mistake. If the number you’ve arrived at seems too low, too high, or even outside the range of possibility, there are a few places you can check for common mistakes.
Forgetting a + or –
An A- may still be in the A-range, or a C+ may feel so close to the B-range that it’s unimportant, but these distinctions do matter when calculating your cumulative GPA. Go through your calculations and make sure that you’ve accounted for the pluses and minuses that may be part of your grade.
Not Weighting a Class Correctly
Maybe you looked at the wrong line, or forgot to add the boost that an Honors or IB class gives you. Go through the initial weighting of each class again, and see if there’s a place you may have gotten it wrong. Remember that different subjects are weighted differently.
Forgetting to Account for Credits
If your GPA comes out unrealistically high, you may have forgotten to divide by the number of credits somewhere along the way. On the other hand, if it’s unrealistically low, you may have forgotten to multiply by the number of credits. It may seem counterintuitive, but to get your correct cumulative GPA, you need to first multiply each class by the number of credits, and then divide the number you get overall by the number of credits total.
Remember that some classes count for more credits than others. Make sure that you have the correct number for each class.
Simple Arithmetic Errors
When calculating your cumulative GPA, you’re juggling a lot of numbers, so it’s easy to make a simple arithmetic error. Rounding decimals incorrectly, copying something wrong, or even leaving out a number or adding it twice can happen if you’re trying to keep track of too much in your head. If you can’t find a place where you made the error, start again from the beginning, with a pencil and paper, and go through your calculations slowly and methodically.
What is a Good Cumulative GPA for College Admissions?
While GPAs on a 4-point scale are standardized, their relative strength varies by school to school. An A- at school 1 might be more comparable to a B at school 2. Similarly, a B+ in one class may be an A in another course. That means that evaluating a “good” GPA is subjective.
To better understand your GPA and how it compares to those of other applicants at your target colleges, consider factors like:
- Your school
- The average GPA in your class year
- The rigor of your schedule (measured against the courses available at your school)
- Whether your grades are weighted or unweighted
- Your target colleges
- Your demographics ( the average GPA varies by ethnic group )
For example, if you’re hoping to attend Harvard, your GPA should be at or higher than the average of their incoming freshman class, which is roughly a 3.95 unweighted. Meanwhile, Temple University’s average GPA is around a 3.5, so you wouldn’t need as high a GPA if this were your target school.
If you’re just starting to create your college list, our posts about grades and GPA are a good place to start exploring once you know your cumulative GPA. Knowing your own GPA will help you figure out at which schools gaining admission might be easier or tougher. Keep in mind that admissions are holistic, so having a lower GPA doesn’t necessarily spell the end of your dream school.
Don’t worry if your school is particularly rigorous and it’s very difficult to attain a 4.0; colleges will look at you in the context of your specific class and note if you rank highly compared to your classmates. Similarly, if you come from an underrepresented or low-income background, colleges may be more forgiving of a lower GPA.
Cumulative GPA and Scholarships
You may be considering applying for scholarships to help cover the significant costs of college. Some scholarships have GPA requirements, so researching what these are and calculating your own GPA accurately are essential steps in applying. Even for scholarships that don’t have specific GPA requirements, it’s best to aim for the highest GPA possible to improve your chances. A high GPA is always impressive, especially when applying for a selective scholarship.
How Your GPA Impacts Your College Chances
GPA does play a big role in the admissions process, as it factors into your Academic Index (AI). AI is a single number that reflects the strength of your GPA and test scores. Many selective colleges use AI to weed out applicants before even considering qualitative factors like extracurriculars and essays.
If you’re not sure whether your GPA is good enough, you can use our free chancing engine . This tool will let you know your chances of acceptance at over 1,500 colleges, and will also give you tips for improving your profile. We highly recommend testing it out to get a jumpstart on your college strategy!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

GPA Calculator
What is gpa gpa meaning, gpa scale — gpa converter chart, how to calculate my gpa, cumulative gpa, grade point average calculator — how to use.
If you're searching for an easy and quick way of calculating your GPA, you've come to the right place — our GPA calculator is the perfect tool for you. Whether you're a high school or a college student , if you want to calculate your GPA with or without credits (including any extra-graded courses ), or even find your cumulative GPA ... we've got you covered. Also, if you want to know the GPA meaning, or how to calculate GPA manually, we've prepared introductory paragraphs to both these topics as well.
Since you've come to this page, that means you're into educational calculators! Have a look at two other handy tools, both for teachers and students — maybe they'll free up your valuable time?
Final grade calculator helps you estimate what grade you need on the final exam to reach your target.
Test grade calculator to set a grading scale adjusted to your needs.
GPA stands for Grade Point Average . It's a score that measures your academic achievement and is used throughout your educational career: in middle school, high school, and college. The basic formula for calculating GPA is to divide the total points earned in a program by the total number of courses. If your courses have credits, or if they are graded differently (e.g., honors courses), you need to compute the weighted average . Scroll down to read more about GPA weighting.
If you're searching for a GPA converter, you're most likely looking for a GPA scale table, which shows the grade point equivalents:
The table above presents one of the standard 4.0 GPA scales. However, different schools may use different systems; unfortunately, it's not universal by any means. Before using our GPA calculator, make sure this is the grading scale your school has adopted.
We're here to convince you that calculating your GPA is not nearly as difficult as you think! Let's have a look at an example grade card:
To calculate the GPA, you first need to convert your grades (expressed in letters) into a numerical scale . For that, use the GPA scale table from the previous paragraph:
That wasn't so difficult, was it?
Then, depending on your educational stage, some extra grade weighting may need to be done:
High school GPA
In high school education, some courses take class difficulty into account, so they're graded differently. When taking classes from a higher level, the extra points can be added to your grade, e.g.:
- 1 extra point for AP Courses (Advanced Placement Courses), IB Courses (International Baccalaureate Courses), and College Preparatory Classes.
- 0.5 additional points for Honors Courses (this rule may vary between schools, awarding, e.g., 1 point for this type of course).
So you either need to take those extra courses into account or can ignore them completely:
Only regular classes (unweighted GPA )
Let's repeat the table with the example grades:
These are the only values you need to calculate your unweighted high school GPA:
where GPE \text{GPE} GPE is the grade point equivalent .
Have you noticed that it's just the regular old average?
Courses with extra points (weighted GPA)
If you've taken some special courses, you'll probably want to calculate the weighted GPA:
GPE weighted \text{GPE}_{\text{weighted}} GPE weighted stands for weighted grade point equivalent . Notice that GPA is usually rounded to 2 digits.
Sometimes there are also credits tied to high school courses - for a more detailed explanation, check out our dedicated high school GPA calculator .
College GPA
College courses usually have credits. Assume that our result card looks like this:
All you need to do now is sum the products of the course grade point equivalents and their corresponding credit points and divide that value by the sum of all obtained credits:
where CP \text{CP} CP are credit points .
So in this example, we have:
If your courses don't have credits (or all of them are worth the same amount), GPA is the ratio of the sum of your grade point equivalents and the number of courses taken (it's the GPA formula previously seen in High school GPA — unweighted GPA):
If you want to learn more about estimating your college GPA and how to interpret your results, make sure to check our college GPA calculator .
A cumulative GPA is a grade point average calculated across multiple semesters or terms. It is a weighted average of your results, which may be calculated differently depending on the types of courses and credits you take:
- Cumulative GPA with courses credits is calculated as:
For example, assume that you took 15 credits in the fall semester, and your GPA was 3.65. In the spring semester, your results were even better, and you obtained 3.83 from 18 course credits. How would you find the cumulative GPA for those two semesters?
Your total credits are
And so our formula becomes:
Substituting the numbers gives us:
Your cumulative GPA is 3.75.
Cumulative GPA without courses credits
However, if your classes don't have course credits (or they are all worth the same amount of credits), you only need to know your prior GPA and the number of courses taken:
where n c \text{n}_{\text{c}} n c is the number of classes .
Let's say that your friend obtained a GPA of 3.65 from 5 courses in the fall semester, and in the spring semester, they got a 3.83 GPA from 10 courses:
Therefore, we get:
Their cumulative GPA is 3.77. If you're in high school, this GPA may be called your unweighted cumulative GPA .
To calculate your weighted cumulative GPA , do the same as in the above examples, but instead of using the standard grade point equivalents, use the weighted ones (e.g., 4.5 for grade A for the honors course instead of the standard 4.0).
Now that we have provided the GPA meaning and a detailed set of instructions on how to calculate GPA manually, let's come to the heart of the matter: how to quickly find GPA using this grade point average calculator! We're pretty sure it's rather self-explanatory, but, just in case, let's have a look at some step-by-step instructions:
Choose the type of school you're attending . We are assuming that you're a high school student, so we pick that option from the drop-down list.
Decide on which grade options suit you best . You need to answer the following questions:
Do you attend different types of courses (like regular/honors/AP/IB/College)?
Do the courses have credits?
Do you want to calculate cumulative GPA?
We will assume that you've attended one honor and one AP course, that your courses don't have credits, and you'd like to find your cumulative GPA
Prior results: previously you got GPA = 3.5 from 5 courses.
Input the grades and other necessary values into the appropriate fields. In our case, you need to enter your grades, course type, and prior results. Remember that you can enter up to 30 courses. Also, it's ok if you want to enter less than three courses - the calculator will ignore the blank boxes.
And there you go — in the blink of an eye, our GPA calculator displays your results :
You've entered 4 courses.
Your GPA: 3.63. This is GPA weighted by course difficulty. It's usually simply called your weighted GPA.
(Of course, you'd get the same result if you calculated the result manually)
Your cumulative GPA: 3.56
How do I calculate GPA?
To calculate your G rade P oint A verage ( GPA ):
- Assign each of your final grades a numerical value. For example, A=4, B=3, C=2, D=1, F=0.
- Multiply each course's numerical grade by its credit hours.
- Sum these values.
- Divide this sum by the total number of credit hours taken.
The result is your GPA .
What is a good GPA?
Generally, a GPA of 3.0 or above is considered good , with 3.5 to 4.0 being excellent. A GPA closer to 4.0 is often seen as ideal for highly competitive programs or schools. Remember, different schools and employers may have their own definitions of a "good" GPA.
What does GPA stand for?
GPA stands for G rade P oint A verage. It's a numerical calculation representing your average performance across all your courses. Each grade you receive in a class is assigned a point value , like an A might be 4 points. Your GPA is calculated by taking the average of these points , giving you a number that typically ranges from 0 to 4.0, showing how well you've performed academically.
How do I calculate cumulative GPA?
To calculate your cumulative GPA , which is different from your semester GPA (GPA is calculated for one semester, and cumulative GPA is for all semesters):
- Sum the total credit hours for all courses taken across all semesters.
- Divide the total grade points by the total credit hours.
The result is your cumulative GPA , representing your overall academic performance.
Black Friday
Delay and reverb, pcb impedance.
- Biology (99)
- Chemistry (98)
- Construction (144)
- Conversion (292)
- Ecology (30)
- Everyday life (261)
- Finance (569)
- Health (440)
- Physics (508)
- Sports (104)
- Statistics (182)
- Other (181)
- Discover Omni (40)
GPA Calculator
Use this calculator to calculate grade point average (GPA) and generate a GPA report. If you use percentage grades, have grades on a different scale or in high school with AP/IB classes, please change the "Settings" to input specific values. Also use the settings to group courses into semesters or to include past GPA.
GPA Planning Calculator
The calculator can be used to determine the minimum GPA required in future courses to raise GPA to a desired level or maintain the GPA above a certain level.
Related Grade Calculator

Letter grade and the numerical equivalents used for this calculator
Grade point average (GPA) is a commonly used indicator of an individual's academic achievement in school. It is the average of the grades attained in each course, taking course credit into consideration. Grading systems vary in different countries, or even schools. This calculator accepts letter grades as well as numerical inputs. These letter grades are translated into numerical values as shown below.
Most schools, colleges, and universities in the United States use a grading system based on the letters above, though E is sometimes used instead of F. Grading systems do differ however based on what constitutes an A or B, and some do not include grades such as an A+ or a B-. Others may attribute more weight to certain courses, and thus whatever grade is attained in the course will have a larger effect on overall GPA. The calculator can account for this based on the number of credits attributed to a course, where credit is the "weighting" of the course, as shown in the examples below.
Guidelines for raising GPA
There is no sure formula for raising a person's GPA, and strategies that work for one person may not work for another. However, there are some common guidelines and study habits that can be helpful when trying to raise GPA. The guidelines below are mostly anecdotal and are not intended as fail-safe ways to raise one's GPA, but are generally good habits that can have positive effects on learning, which may in turn increase GPA.
Actively attending classes:
Classes are being paid for likely either by a student or their parent, and not attending classes is both a financial loss, as well as a loss in potential education. While a student may decide that attending a particular class is not beneficial to their learning, or not a good use of their time, even if the professor is largely ineffective, there is usually valuable information that can be obtained simply by attending class. Not attending class for example, could result in negative effects on a student's GPA if for some reason the student misses information about a change in exam location or material.
Furthermore, while it may be true that professors largely repeat notes in class that are often later posted to a website, skipping classes can result in missed opportunities. Questions from students in class, as well as the explanations that may follow can provide seemingly inconsequential bits of information that can in fact make a large difference on tests. This is because interaction with the professor and other students can increase a person's depth of knowledge on a subject, or may provide the small tip necessary to solidify a student's understanding of a topic.
In addition, attending class, particularly if the class is smaller in size, can allow the professor to link a name, a face, and a grade, particularly if the student actively participates. Professors that see attentive and involved students are more inclined to be understanding of any potential issues that may arise such as emergencies resulting in missed due dates. Along with this, active participation is more likely to engage a student's mind in regards to the subject matter than reading online notes or a textbook, and points of confusion can also be clarified on the spot. These can in turn affect a person's grade and overall GPA.
Every student has his or her own learning style. Some like to work for hours at a time to complete an assignment, while others may take many breaks. There is no ideal strategy, and how a person approaches learning is highly dependent on learning style, as well as adhering to a study strategy that complements their schedule and desires. The method that maximizes the value of the time spent is likely the most effective for improving learning, and subsequently, GPA.
Organization of work that needs to be done, as well as notes taken is also important. It is as important to be able to find relevant information as it is to take notes in class. Notes are most valuable when they can be used to supplement learning. Professors present large amounts of information during the course of a lecture, not all of which a student may have time to process. It is important to practice taking notes in a manner that enables the student to look back and learn (or lookup) the information.
Time management is also an important aspect of planning. There are only 24 hours in a day, not all of which a person can use effectively. While learning is important, taking more courses or activities than a person can handle can be detrimental both to learning, as well as to average GPA. Once all courses have been selected, budgeting and scheduling time for each course can help to put the amount of work and time necessary into perspective. While the amount of work necessary for a number of courses may initially seem daunting, planning how and when to approach the work for each course may help reduce stress and improve efficiency once the work is quantified (or could help a person realize that they are tackling more than they can handle).
Reviewing work regularly, in terms of studying, is another aspect of time management. A substantial amount of information is covered in a course by the time of the final exam, and reviewing some of the information regularly over a period of time is often more effective than attempting to memorize all of the information right before an exam. Learning the information through periodic review can ultimately save a person more time, and potentially position them to perform better on an exam, and thereby improve GPA.
GPA Calculator: Accurate, Quick, And Reliable GPA Calculating

- Grade calculator
- Final grade calculator
- GPA calculator
The GPA Calculator helps students calculate their current GPA accurately and immediately . The GPA, a pivotal metric in a student's academic profile, is intricately woven from the grades earned in each course, coupled with the corresponding credit hours and their respective weights.
What is the GPA Calculator
Before using the GPA Calculator , let's first understand what GPA is. The A Grade Point Average (GPA) is a numerical score of a student's performance throughout their academic semester. A student’s GPA is typically measured on a scale ranging from 0 to 4.0 or 5.0 (depending on the weighted or unweighted scaling system).
The GPA Calculator is an academic tool assisting students to determine their Grade Point Average (GPA). By inputting their grades and associated credits for each course, you can quickly and accurately evaluate academic performance over a specific period. Streamlining the process of GPA calculation, the GPA Calculator saves time for manual calculations.
While GPA Calculator provides an overview of a student's performance across multiple courses, the Grade Calculator is used to assess their performance on a specific course. To achieve a high GPA, it's essential to estimate your grade in each course. Use the Grade Calculator to calculate your average score. If your current average is not what you desire , you can use the Final Grade Calculator to determine the grade you need on upcoming assignments or exams to reach your goal.
How to Use the GPA Calculator
Utilizing a GPA calculator is a straightforward procedure that involves entering the grades and credit hours for each course. Here's a comprehensive step-by-step guide to using the GPA calculator:
GPA Calculator key terms
Before delving into the intricacies of any calculator, and specifically the gpa calculator, it is crucial to comprehend the following key terms: .
Course Name: This term refers to the distinct title assigned to a course, such as Mathematics, Marketing, Literatures, or History. The course name varies depending on the academic institution.
Grade: The academic performance in a given course, typically represented by letter grades such as A+, B-, C, etc. When using the GPA Calculator, selecting the appropriate grade for each class is fundamental to calculating an accurate GPA.
Credits: The assigned weight or value to a course, reflecting the time and effort required for its completion. Credits, or credit hours,are often specified in the course syllabus or can be found on the academic transcript. Inputting the correct credit hours into the GPA Calculator ensures a precise calculation of the overall GPA.
Weighted: An option in GPA calculation that represents the course difficulty. When a GPA is weighted, the level of complexity or difficulty of each course distinguishes between regular, honors, or Advanced Placement (AP) courses. The weighted GPA provides a more exact reflection of a student's achievement in their academic pursuit. Weighted scoring involves prioritizing courses by assigning a bonus score based on their difficulty.
Step-by-step guides on how to use the GPA Calculator
Step 1: Type the name of the Course
Begin by inputting the names of your courses. For instance, enter titles like Math, Marketing, History, etc. to distinctly identify each course.
Step 2: Input the Course’s grade
Next, input the appropriate letter grades for each course, choosing from options like A+, B, C-, and so on.
Step 3: Input the Credit
Note the credit hours assigned to each course. This information is usually accessible in your course syllabus or on your academic transcript.
Step 4: Select Weighting option
Depending on your academic institution's requirements, you might need to indicate whether you prefer a weighted or unweighted GPA. If your courses vary in difficulty levels, additional information such as the course level (regular, honors, or AP) may be required to calculate a weighted GPA.
Step 5: Initiate calculation
Once all the necessary data has been input, initiate the calculation process. The GPA calculator will typically offer the option to generate either an unweighted or a weighted GPA based on the information provided.
Note: You can add more semesters as needed.
GPA Calculation: Formula and Example
To compute the GPA (grade point average), you must assign numerical values to letter grades and subsequently average them, resulting in an overall measure of academic performance. Here's a basic guide to the GPA calculation:
GPA Calculation Formula
The GPA is determined through a weighted average of grades, with the number of credits serving as the weight. The numeric grade is derived from the GPA table. Mathematically, the GPA is expressed as the sum of the product of the credits (c) and the corresponding grade (g):
GPA = c 1× g 1+ c 2× g 2+ c 3× g 3 +... + cn × gn ) / (c 1 +c 2 +c 3 +...+ cn )
In which:
c: The credits
g: The course’s grade
Examples of GPA Calculations
The calculation of unweighted GPA and weighted GPA is a bit different. While unweighted GPA treats all courses equally, weighted GPA considers the difficulty and complexity of the courses and assigns additional points accordingly.
Example 1: Unweighted GPA
In an unweighted GPA system, every course holds the same weight, irrespective of its level of difficulty.
If your school used an unweighted GPA system, your grades might look like this:
- Literature: A (equivalent to 4.00), with a credit value of 2.
- Physics: A- (equivalent to 3.67), with a credit value of 3.
- Math: B- (equivalent to 2.67), with a credit value of 4.
Your unweighted GPA is calculated by:
Unweighted GPA = 2 × 4.00 + 3 × 3.67 + 4 × 2.67) / (2 + 3 + 4) = 29.69 / 9 = 3.29
So, the GPA is 3.29, equivalent to grade B on the letter scale.
Example 2: Weighted GPA
The scale for weighted GPAs may extend beyond 4.0 to account for these extra points. The specific weighting system can vary by institution, but it often adds extra points to the GPA for honors or AP courses, reflecting the increased difficulty.
For example, if an AP course has a grade point of 3.0, then the “real” grade will be 3.00 + 1.00 = 4.00.
Let's examine this scenario:
- Business: A- (equivalent to 3.67), with a credit value of 2.
- AP Accounting: B (equivalent to 4.00; as for an AP class, B = 3.00 + 1.00 = 4.00), with a credit value of 3.
- IB Economics: B+ (equivalent to 4.33; as for an IB class, B+ = 3.33 + 1.00 = 4.33), with a credit value of 2.
Your unweighted GPA is determined by
Unweighted GPA = (2 × 3.67 + 3 × 4.00 + 2 × 4.33) / (2 + 3 + 2) = 28 / 7 = 4.00
So, the GPA is 4.00, equivalent to grade A on the letter scale.
To determine the additional weighted bonus for each category, consult the following table:
GPA Table: Converting Grade Letters to Grade Points
The table presented below illustrates the conversion of your letter grades into numeric grades (percentages) and corresponding GPAs on a 4.0 scale.
Say goodbye to the days of calculating GPA manually; the process of computing GPA is now simplified with the help of GPA Calculator. There is no exaggeration to say that GPA calculators have become indispensable companions in the student’s educational journey.
Grade Point Average - Frequently Asked Questions
How to calculate your gpa on a 4.0 scale , to calculate your gpa on a 4.0 scale, follow the below steps: .
Step 1: Assign each of your letter grades a numerical value based on the 4.0 scale (for example: A = 4.0, B = 3.0)
Step 2: Multiply each grade's value by the course's credit hours.
Step 3: Add the results for all courses.
Step 4: Divide the total by the total credit hours.
For example:
- On Math (3 credits) you got an A
- On Literature (4 credits) you got a B
- On History (2 credits) you got a C
Your GPA calculation would be:
(4.0 * 3 + 3.0 * 4 + 2.0 * 2) / (3 + 4 + 2) = (12 + 12 + 4) / 9 = 28 / 9 = 3.11
How to raise your GPA ?
To raise your gpa, focus on improving your grades in current and future courses. here are some tips to help you raise your gpa: .
- Manage your time : Create a study schedule that allows you to allocate sufficient time to each subject. Avoid procrastination and stay organized with your assignments and study materials.
- Seek help when needed : If you're struggling with a particular subject, don't hesitate to seek help from your teachers, tutors, or classmates. Understanding difficult concepts early can prevent them from affecting your overall GPA.
- Review and practice : Regularly review your notes and textbooks to reinforce your understanding of the material. Practice problems and quizzes can help you assess your comprehension and improve your performance.
- Take advantage of extra credit : If your courses offer extra credit opportunities, take advantage of them to boost your grades.
- Consider retaking courses : If you've performed poorly in a course that is essential to your GPA, consider retaking it to improve your grade.
What is the difference between weighted and unweighted GPA?
Unweighted GPA : This GPA scale doesn't consider the difficulty of the courses. Each course is given the same weight when calculating GPA.
Weighted GPA : Th is GPA scale considers the difficulty of the courses. Courses such as honors, AP (Advanced Placement), or IB (International Baccalaureate) are given extra weight, usually on a scale of 4.0 to 5.0 or higher. This means that an A in an honors or AP course might be worth more than 4.0 on a 4.0 scale.
- Utility Menu
Committee on Degrees in Social Studies
- Grading and Honors
Social Studies theses are sent to two readers, who provide grades and comments. Graders use a Latin scale, with honors grades ranging from a very rare straight “summa” (the equivalent of an A+) to a “cum minus” (the equivalent of a B-). It is also possible to receive non-honors grades (which revert to a letter grade scale). If the first two grades are more than a Latin grade apart (e.g., “magna plus” and “cum”) the thesis will be sent out for a third reading.
You must pass your thesis and complete both parts of the oral exam in order to graduate with a degree in Social Studies. Every student in recent memory who has submitted a thesis has passed and graduated.
Social Studies uses a formula to calculate honors recommendations that takes into account course grades, thesis grades, and oral exam grades. If a thesis has received two readings, both readings will be weighted equally. If a thesis has received three readings, the median grade will be weighted 50% and the two outliers 25% each.
All courses in our five overlapping social science departments (anthropology, economics, government, history, and sociology) count for concentration credit, whether or not they are part of a student’s focus field. In addition, we will count courses outside of these departments that were successfully petitioned to count towards a focus field. We only count course grades earned in the first seven semesters, as we do not have access to eighth semester grades when we determine honors.
Our recommendations are “English Honors” and they are necessary but not sufficient for college-wide Latin Honors, which are based on all eight semesters of grades and are subject to college-wide GPA cutoffs. You can learn more about the honors process at the college level by reading the Harvard College Handbook for Students .
Regardless of your Latin Honors outcome, you may list any English Honors you earned in Social Studies on your resume.
- Concentration Requirements
- Supervisor Database
- Thesis Supervisor Form
- Methods Resources
- Thesis Formatting
- Late Policy
- Past Thesis Titles
- Advice from the Class of 2016
- Senior Thesis Reflections
- Study Abroad
No results found
We can’t find anything with that term at the moment, try searching something else.
GPA Calculator
This GPA calculator computes your GPA and creates a report based on your course credits and grade. Both numerical and letter grades are accepted.
Prior Semester
Prior Semester's GPA (optional)
Completed Credits (optional)
Grade Format
Related Calculators
There was an error with your calculation.
Table of Contents
Gpa planning calculator, this calculator uses letter grades and their numerical counterparts, improve your gpa, regular class attendance.
This calculator computes a student’s grade point average (GPA). If you’re in high school and taking AP/IB classes, you’ll need to adjust the “Settings” to input the grades in percentages or on a different scale. It’s possible to incorporate previous GPA or group courses by semester.
You may use the calculator to estimate the minimum GPA needed in future courses to achieve the target GPA or maintain the desired GPA.
There are several grading systems in use across the world and in schools. One of the most often used measures of academic accomplishment is a student’s grade point average (GPA). Course credit is considered when calculating a student’s overall grade average.
It is possible to enter letters and numbers into this calculator. The list below shows that the letter grades correspond to the number values.
- F = 0 grade points
- D- = 0.7 grade points
- D = 1 grade point
- D+ = 1.3 grade points
- C- = 1.7 grade points
- C = 2 grade points
- C+ = 2.3 grade points
- B- = 2.7 grade points
- B = 3 grade points
- B+ = 3.3 grade points
- A- = 3.7 grade points
- A = 4 grade points
- A+ = 4.3 grade points
P (pass), NP (not pass), I (incomplete), and W (withdrawal) have no impact.
Most students in American schools are graded according to the system outlined above. However, F is sometimes substituted for E. Some grading systems contain grades such as an A+ or a B-, and some don’t.
Some students may place greater value on specific courses than others. The calculator can consider this if a class has a "weighting" of a certain number of credits. It makes their grade in a course more significant in determining their total grade point average.
Tactics that work for one student may not be effective for another, so there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Some tips below can help raise your GPA. These suggestions may not be reliable ways to increase your grade point average. But in general, they can help you develop good habits and positively impact your studies by raising your GPA.
Classes are usually paid for either by the students or their parents. Sometimes students may decide a course is useless to their education or is a waste of time. Dropping a class entails a financial loss and a loss of a chance to get an education.
But even just attending a class can provide important information. Suppose a student doesn't get information about a change in an exam or a course because they didn't attend class. In this case, the student's grade point average might suffer.
Teachers periodically give lectures, which will be available online. But not attending a course may result in a lack of additional information. Interacting with the professor and other students can help a student gain a deeper understanding of the course. Live interaction will help the student better grasp certain concepts. Answering seemingly insignificant questions that students ask in class and the following explanations can significantly impact test scores.
Students that actively participate help the instructor connect names, faces, and grades, especially in small classes. Professors who find their students interested and attentive are likelier to show understanding in critical situations like missing deadlines.
Active participation will engage the student better in the course than reading online notes or a textbook, and a teacher can clarify unclear points immediately on the spot. This can affect a student's grade and grade point average.
Every student absorbs information differently. Some prefer to work methodically for long periods, while others prefer to rest frequently. There is no one-size-fits-all method of learning. Each person's learning style and schedule determine their approach to learning.
Learning and record keeping accompany each other. A student may not have enough time to absorb all the information presented by the instructor during a lecture, so it is better to take notes during lectures. Studying notes will allow you to return to the notes later and refresh your knowledge.
Time management is essential for planning. There are only 24 hours a day, and we can't effectively use all of them. Yes, studying is crucial. But taking more courses or classes than a person can handle can hurt their grades and grade point average.
The volume of classes in some subjects can seem daunting. But planning how and when to work on each discipline or course can reduce stress and increase productivity. Once all the classes have been chosen, budgeting and scheduling classes can help you estimate the amount of work and time involved.
Regularly reviewing syllabus work is another essential time-management item. The final exam covers a lot of information in a course. Studying information methodically and regularly is often more effective than memorizing all the information in a week or a few days before an exam.
Consistent study of information can ultimately save time, help you pass the exam better, and improve your grade point average.
GPA Calculator
Use this college GPA calculator to easily calculate the cumulative grade point average (GPA) for a given semester. Enter letter grades (A, B-, C+, etc.) achieved on all relevant courses, as well as the credits for each course. The GPA is then weighted based on the number of credits.
Related calculators
- How to calculate your GPA
- High school GPA vs college GPA
- How to convert a letter grade to points
- Frequently asked questions
Do P/NP (Pass/No Pass) courses get factored in GPA?
Do incompletes (i) or withdrawals (w) receive grade points, how are advanced placement or honors courses counted, how to calculate your gpa.
With the help of this GPA calculator you can calculate your GPA weighted by the number of credits for each course. This is often referred to as CGPA which may stand for "cumulative GPA" or "college GPA". GPA itself stands for Grade Point Average. The software will also compute the sum total of credits from all courses.
To use the calculator, enter the number of courses you have completed (or intend to complete) and then for each course enter the letter grade or expected grade as well as the number of credits it contributes. The overall GPA is weighted based on the number of credits. This means that if you have special courses which are weighted more heavily, you can alter the number of credits to get an exact calculation. For example, if a course has double the weight, just double its credits. Likewise, if it only weighs half as much as other courses, slash the number of credits in half.

For example, say there are four college courses, two of which are worth 3 credits and two are worth 4 credits. Additionally, one of the latter is considered a special course worth 1.5 times a regular course. If you had A-, B, A and B+ respectively, enter these grades and then enter the weights 3, 3, 4, 6 (4 x 1.5 = 6). This way the weighted GPA will correctly reflect the differential contribution of each course.
High school GPA vs college GPA
This calculator can be used for computing both high-school GPA and college GPA, as long as they use the same GPA scale. If you enter grade points directly, then it makes zero difference what kind of grade point average you are looking to get as it becomes a simple weighted average math, no conversion is involved.
How to convert a letter grade to points
Our GPA calculator uses the following table to convert letter grades to grade points for the purpose of computing their weighted average.
If you know the grade points instead of the letter grades, it is preferable to enter them directly. This will ensure the best possible alignment with the GPA scale used by your educational institution.
Frequently asked questions
Below are answer to the most common questions students have when calculating their GPA.
No, P/NP (Pass /No Pass) courses should not be factored in the calculation of a student’s grade point average. Such courses do not result in letter grades or grade points and hence cannot be used in the calculation.
No. Such do not receive grade points or letter grades and therefore have no effect on a student's weighted GPA.
Different educational institutions would have different rules for factoring these in. Some would add half a point or a whole point to the course grade, whereas others would adjust the credits for the course by a multiplier. You should contact the college or university you are interested in for information on this before using our tool.
Cite this calculator & page
If you'd like to cite this online calculator resource and information as provided on the page, you can use the following citation: Georgiev G.Z., "GPA Calculator" , [online] Available at: https://www.gigacalculator.com/calculators/gpa-calculator.php URL [Accessed Date: 30 Mar, 2024].
Other calculators

- Grade Calculators
Cumulative GPA Calculator

Need to calculate your cumulative GPA? The calculator below is super flexible allowing you to calculate it in a variety of ways depending on what information you have available. You can use some or all of the sections (steps) below as needed. Enjoy!
The grade chart below shows the scale that will be used to calculate your grade point average. You only need to worry about selecting your grade scale if you intend to enter information in step 4 below.
If you have completed some classes and know your cumulative GPA, enter this information below. If you don't know this information, skip to step 3 or step 4.
Cumulative GPA
Cumulative Credits
If you know your GPA by semester, you can enter this information below. If not, skip down to step 4.
Semester GPA
Semester Credits
Use this section to enter grades and credit hours for classes completed.
This is where the magic happens. Once you have entered your information, press the calculate button to calculate your cumulative GPA.
Calculator Instructions
This cumulative GPA calculator is extremely flexible allowing you to enter information into any or all of the steps above depending on what information you have available.
- Start by selecting the grade scale to use. Many schools utilize different grade scales, so pick the correct one. If you don't see your grade scale, send us an email and we will add it. NOTE: You only need to select the grade scale in step 1 if you intend to enter individual class grades in step 4 of the calculator. Otherwise, don't worry about selecting the grade scale.
- Next, enter your old cumulative GPA and cumulative credits in step 2 of the calculator. This is useful if you know your cumulative GPA but maybe it doesn't include the semester you just completed. If you don't have this information, no problem. Proceed to step 3 of the calculator.
- If you don't have your cumulative GPA but you do have your GPA for each semester, then enter this information in step 3 of the calculator. Feel free to give the semester a name if you wish, but this is not required. Press the "Add Semester" button to add a new semester input field. If you don't have your GPA by semester, skip to step 4 of the calculator.
- In step 4 of the calculator, you can enter grade and credit-hour information for each class completed. You can also enter the class name (e.g. History 101) if you wish, but this is not required. If you have more than 5 courses that you need to enter, press the "Add Course" button and additional input fields will be added.
- Finally, press the "Calculate" button and your cumulative grade point average will be displayed in the results area.
Let's pretend that you know your old cumulative GPA and credit hours, but you just completed another semester and now need to calculate your new cumulative GPA. Your old GPA is 3.50 after having completed 34 credit hours of classwork. Enter these values in Step 2 of the calculator. For the semester you just completed, you only took two classes. Each class was worth 3 credit hours. In your first class, you got a "B". In your second class, you barely survived to get a "C". Enter these values in step 4 of the calculator and press the "Calculate" button. Your new cumulative GPA is 3.35 having completed 40 credit hours.
You Might Like These Too

Final Grade Calculator

College GPA Calculator
Test Grade Calculator
How can we improve this page.
Cumulative GPA Calculator
Calculate your cumulative GPA, and see how your current (and future) grades will affect your performance.
Current GPA (Optional)
How to use the cumulative gpa calculator.
Your cumulative GPA is the score typically used for college applications or entering the workforce. It's an average of averages, combining all your semester GPAs into a single, overall GPA. Want to figure out yours? Let's take a look.
Step-by-Step Tutorial
Not into videos? Check out the list below to follow along and figure out your cumulative GPA.
Enter your current GPA
In the first field, enter your most recent cumulative GPA along with the corresponding credit hours.
Enter your course name
Give each of your courses a name so that you'll be able to enter your grades in the proper row (it'll look nice too).
Enter your course grade
Select a letter grade for each of your courses from the dropdown. Note, A and A+ both have the value of 4.0.
Enter your course credits
For each course enter the amount of credit hours you completed during the semester. Don't forget labs and studios.
Add another course (optional)
Taking a heavy course load? Add as many extra classes as you need using the blue "add course" button near the bottom.
Add another semester (optional)
If your current GPA doesn't include all your semesters feel free to create more, and add in the rest of your courses.
Stay Up-to-date
Your cumulative GPA is one of the most important academic metrics out there, so it's important you keep abreast of any changes. The last thing you want is one class dragging your hard-earned 4.0 down to a B+. It pays to be diligent; bookmark this page and keep your GPA updated regularly. Not as high as you'd like? Then check out our pro-tips on how to raise your GPA . See you next time!
- Letter A+ A A- B+ B B- C+ C C- D+ D D- F Percent 100 99 98 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60
- Grade A+ A A- B+ B B- C+ C C- D+ D D- F Weight Regular Honors AP / IB College

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Unweighted High School GPA. A basic GPA is calculated by converting every letter grade to a grade point number and then finding the average. So after the letter grades are converted to numbers, simply add up all of the grade points and then divide by the number of classes. Total Grade Points ÷ Total Number of Classes = GPA.
Step 3: Calculate Cumulative High School GPA. To get a cumulative GPA for John's entire high school career, we simply add up the sums for all the years and divide by the number of classes he took over all those years:. 35 + 35.7 + 27.7 + 19.7 = 118.1 (sum of all final grades) 10 + 10 + 8 + 6 = 34 (total number of classes taken) 118.1 / 34 = 3.47 (GPA) So, his GPA for all of high school is 3.47.
Academic performance is assessed using the GPA calculation. Calculating your grade point average can be an intimidating process, but you don't have to go at it alone. While studying and essay writing isn't an exact science, GPA calculation is, and leaves little room for interpretation. Get your lab coat ready and follow along as we break ...
To calculate your weighted GPA, use our calculator or…. 1. Add the following points to your original values AND then multiply the grade point for each class by its credit value. 0.0 for regular and ACP courses. 0.5 for Honors, IB SL, and dual enrollment courses. 1.0 for AP, post-AP, IB HL, and college courses. 2.
Below 65%. 0.0. Add the total grade points together. Add together the number of credits you earned. Divide the grade point total by the total number of credits, rounding to the nearest hundredth. To calculate your weighted GPA, the only change is that in the first step, you'll add the following to each grade point: 0.0 for regular courses.
B+=3.3, B=3.0, B-=2.7. Each class grade is multiplied by the credit for each class and added together to determine an unweighted GPA. Alternatively, some schools will calculate weighted GPAs, which give more importance to honors, accelerated, AP and IB classes.
Easily convert your letter grade or percentage to a grade point average (GPA), using our 4-point GPA scale. Understand the 4.0 scale and how to raise your GPA. ... based on a person's letter grade. For example, the letter grade of an "A" has a number value. Likewise, calculating a letter grade is usually done by looking at a particular ...
Understanding and Calculating your GPA What is GPA? • GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a standard way of measuring academic ... Divide total credits by total quality points to find your Semester GPA. Example: Course Grade Credits Quality Points Credits x Quality Points BIOL 150 B 3 3 9 ENGL 110 A 3 4 12 MATH 103 C 3 2 6 ...
Final Grade Calculator. Use this calculator to find out the grade needed on the final exam in order to get a desired grade in a course. It accepts letter grades, percentage grades, and other numerical inputs. The calculators above use the following letter grades and their typical corresponding numerical equivalents based on grade points.
GPA stands for Grade Point Average. It's a score that measures your academic achievement and is used throughout your educational career: in middle school, high school, and college. The basic formula for calculating GPA is to divide the total points earned in a program by the total number of courses. If your courses have credits, or if they are ...
Our University uses a 4.0 scale for calculation of Grade Point Average (GPA). How GPA is calculated For undergraduate students, only grades earned at A&M-Corpus Christi will be used to calculate your GPA at the University as used in determination of your academic rank and eligibility for graduation. If you are a graduate student, your GPA is computed both on all graduate work taken at this ...
The thesis letter grade is calculated in the final GPA up to 15 credits (but the letter grade "J/A" will be displayed in each semester). For example, if a person has 20 credits of J/A altogether, only the 15 credit from it will be calculate as A when it comes to the total GPA calculation.
Letter grade and the numerical equivalents used for this calculator. Grade point average (GPA) is a commonly used indicator of an individual's academic achievement in school. It is the average of the grades attained in each course, taking course credit into consideration. Grading systems vary in different countries, or even schools. This ...
To calculate your GPA on a 4.0 scale, follow the below steps: Step 1: Assign each of your letter grades a numerical value based on the 4.0 scale (for example: A = 4.0, B = 3.0) Step 2: Multiply each grade's value by the course's credit hours. Step 3: Add the results for all courses.
Social Studies uses a formula to calculate honors recommendations that takes into account course grades, thesis grades, and oral exam grades. If a thesis has received two readings, both readings will be weighted equally. If a thesis has received three readings, the median grade will be weighted 50% and the two outliers 25% each.
GPA calculation. This calculator uses the (4.0) four point GPA scale outlined in the tables below in order to convert your letter grades to numerical points. Your semester's GPA is calculated as the sum all the points earned, divided by the total number of course credits taken.
This calculator computes a student's grade point average (GPA). If you're in high school and taking AP/IB classes, you'll need to adjust the "Settings" to input the grades in percentages or on a different scale. It's possible to incorporate previous GPA or group courses by semester.
GPA Calculator. Use this college GPA calculator to easily calculate the cumulative grade point average (GPA) for a given semester. Enter letter grades (A, B-, C+, etc.) achieved on all relevant courses, as well as the credits for each course. The GPA is then weighted based on the number of credits.
Calculator Instructions. This cumulative GPA calculator is extremely flexible allowing you to enter information into any or all of the steps above depending on what information you have available. Start by selecting the grade scale to use. Many schools utilize different grade scales, so pick the correct one. If you don't see your grade scale ...
Look no further. Our easy-to-use high school GPA calculator will help you calculate your high school GPA in just minutes. Whether your goal is to earn a scholarship or get accepted at a prestigious college or university, we've got you covered. Pro Tip: Try our grade calculator to …. High School GPA Calculator.
Thesis/Dissertation or Readings and Research. • "SP" indicates progress toward project or research completion, but carries no credit. • "P" indicates satisfactory completion of course but carries no credit and the grade is not calculated in the GPA. "F" grades in a P/F course and credits attempted in such courses are included.
Add Course. Quickly calculate your cumulative GPA with our easy to use cumulative GPA calculator! Understand the differences between term, semester, year and overall GPA, and how each affects your high school or college career. Enter a current GPA to jump start your calculations, and get tips on how to bring up a mid or low GPA.
lower than the original, will be used in calculating the student's grade point average (GPA). While we can exclude grades for prior attempts (repeat/delete) when calculating a student's GPA, we must include the credits from all attempts when assessing if the student meets the quantitative SAP standard. Course Withdrawal
Instead of applying to grad programs that require a minimum 3.0 to 3.5 GPA, consider applying to programs with lower grade point average requirements. Additionally, some programs offer conditional ...