

A typical PhD student schedule [Free template download]
A PhD student’s schedule is very different to anything that people have experienced in undergraduate or masters level education. Depending on the country that you are doing your PhD in, you may have classes alongside your dedicated research time. It is likely that you will work many hours more than a typical full-time job and may have some other administrative or teaching duties alongside your research.
A typical PhD student schedule involves turning up to the Department between 8 AM and 9 PM, and performing research activities during the day such as reading, writing, analyzing and reporting on literature and experiments.
The schedule of a PhD student also changes depending on the culture in your research group. Some supervisors require PhD students to turn up 6 to 7 days a week and spend up to 12 hours a day doing research. In my experience, this is very rare but a horror story that often gets passed around.
Most PhD supervisors are much more moderate when it comes to the commitments of their students and this article will cover the typical PhD student schedule and what you can expect if you enter a PhD.
A typical PhD daily schedule
A typical PhD student’s daily schedule will vary depending on the subject area, supervisor, and stage of your PhD. However, there are some things that are done consistently throughout the process of a PhD.
Here is a typical daily schedule of a PhD student.
The above timetable can also include:
- teaching activities
- group meetings
- departmental meetings
- other administrative tasks
- training, and much more
There are so many facets to a PhD students daily schedule that it changes almost every day depending on the demands of the research and the supervisor.
Here are some of the activities that a typical PhD student schedule contains. I have also looked at some of the specifics of different subject fields.
Common PhD student activities
A PhD is a training ground for academia.
Throughout a PhD, you will learn to perform the tasks of an academic such as reading literature, writing reports, analysing data, reporting and communicating your results, and presenting or attending different scientific talks and presentations.

Reading is the cornerstone of a PhD.
Learning to find the appropriate literature for your research and coming up with a method for reading, taking notes, and synthesising conclusions will be what sets out the top 10% of PhD students from the rest.
Many PhD students forget to set aside enough time for reading and it can severely impact their progress.
Reading wasn’t my favourite part of doing a PhD and I probably ignored it more than I should have. Nonetheless, ensuring you read regularly in and around your subject area will keep you up-to-date with the latest advancements in your field.
Supervisor meetings
Meeting regularly with your supervisor will keep your PhD on track.
Open communication between a PhD supervisor and the student ensures timely completion and help when things aren’t going so well.
My favourite frequency for supervisor meetings was fortnightly.
Every two weeks means I had enough time to plan, execute, and analyse data based on our previous meeting.
During supervisor meetings, you should share everything that has happened since the previous meeting. Importantly, you should share what has gone right, and wrong, and where you are going next. Head into supervisor meetings with solutions to problems and be sure to take criticism with an open mind.
Depending on your research area it may be more appropriate to meet up with your supervisor weekly to report your progress.
Writing during a PhD is often left until the last year but it is important to write regularly throughout your PhD.
Regular writing (even if it is just methods) will help you when you come to write your thesis or peer-reviewed paper.
During a PhD there are often different writing milestones that you need to achieve including:
- literature reviews
- conference abstracts
- technical reports for collaborators
- progress reports for grant funders
- peer review paper writing
- thesis or dissertation writing
As you can see, there are lots of different times when a PhD student will be set at their desk writing up results for a variety of audiences.
Formulating your own ideas and contributing to an academic field means analysing data and literature.
Many hours of PhD student time are dedicated to the analysis of other people’s ideas, data collected in the lab, and stress testing their own hypotheses.
Analysis is another cornerstone of a PhD.
Reporting your research findings is incredibly important. Communication is what keeps research rolling.
There are several ways that PhD students have to report their results. They may be reporting to their supervisor, collaborators, others in their field, all the general public.
One thing I loved about my PhD was the ability to communicate my research to a general and broad audience.
Writing reports, producing presentations, and writing performance reports for grant funding bodies are all important parts of a PhD student’s typical schedule.
Group/department meetings
After starting my PhD I was amazed at the amount of group and departmental meetings that I was expected to attend.
They seem to always be scheduled at a really inappropriate time and can cut your working day in half. Nonetheless, they are an important part of the PhD process.
Group meetings are for people in the same research group to share their findings and help each other with their work.
Departmental meetings may have an external presenter (from another university or Department) and so they must be well attended to give the appearance of an active and vibrant research community. You’ll get loads of emails reminding you about a meeting if there is a guest lecturer.
Topic-specific activities
Depending on the topic of your PhD you may have some other regular activities.
Humanities students will spend a fair amount of time in the library and reading academic texts. Looking for rare books, papers, and collections in the deepest darkest areas of the library are where you will find many humanity PhD’s.
Science, technology, engineering and maths PhD students will spend a lot of time performing experiments in a laboratory environment.
They will also help train masters and undergraduate students on particular instruments or techniques and be responsible for Occupational Health & Safety in the labs.
Because of the nature of a stem PhD, a science, technology, engineering or maths PhD student will spend many hours alone working in the depths of a university lab.
Social Sciences
Social sciences are likely to be conducting research using surveys or interviews and handling large amounts of data.
Making sure that they have ethical approval for their research can take a bit of time too.
Collecting enough data through questionnaires and surveys is always an issue for social science PhD students so they will be out collecting data as often as possible. They may have research assistants and undergraduates that can help them with their work.
Number of hours that PhD students work
There is no one answer to the number of hours that PhD students work. The number of hours is determined by the culture of the lab and the stage of the PhD.
On average a PhD student will work 40 – 60 hours per week.
Most will try to keep a regular 9 – 5 schedule whilst others will work when they are at their most productive. I know of one PhD student who would come into the lab at 5 PM and stay until one or two in the morning.
The great thing about doing a PhD is that you quite often get to choose your schedule. You may want to work early in the morning or late at night depending on when you feel most awake.
Also, you get to choose where you perform your PhD studies, as long as you do not need to be in a lab or present in the department.
What does a great PhD schedule look like?
A PhD student’s schedule can easily become unproductive if they go with the flow.
I believe that a strong daily schedule and commitment to at least two hours of focused work every single day will lead you to a much more rewarding and efficient.
I released a YouTube video that talks about the components of a failproof PhD daily schedule and you can watch it here:
I also include links to my daily schedule template that you can also get for free by clicking the image below:

Wrapping up
This article has been through everything you need to know about the typical PhD student schedule and how many hours you are expected to be in your office or department.
Having a frank conversation with your PhD supervisor will allow you to understand their expectations of their PhD students. It varies wildly from supervisor to supervisor – so it’s very good to be on the same page as soon as you start.
Remember to download my free daily schedule template to boost your productivity!

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
Understanding and solving intractable resource governance problems.
- In the Press
- Conferences and Talks
- Exploring models of electronic wastes governance in the United States and Mexico: Recycling, risk and environmental justice
- The Collaborative Resource Governance Lab (CoReGovLab)
- Water Conflicts in Mexico: A Multi-Method Approach
- Past projects
- Publications and scholarly output
- Research Interests
- Higher education and academia
- Public administration, public policy and public management research
- Research-oriented blog posts
- Stuff about research methods
- Research trajectory
- Publications
- Developing a Writing Practice
- Outlining Papers
- Publishing strategies
- Writing a book manuscript
- Writing a research paper, book chapter or dissertation/thesis chapter
- Everything Notebook
- Literature Reviews
- Note-Taking Techniques
- Organization and Time Management
- Planning Methods and Approaches
- Qualitative Methods, Qualitative Research, Qualitative Analysis
- Reading Notes of Books
- Reading Strategies
- Teaching Public Policy, Public Administration and Public Management
- My Reading Notes of Books on How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation/How to Conduct PhD Research
- Writing a Thesis (Undergraduate or Masters) or a Dissertation (PhD)
- Reading strategies for undergraduates
- Social Media in Academia
- Resources for Job Seekers in the Academic Market
- Writing Groups and Retreats
- Regional Development (Fall 2015)
- State and Local Government (Fall 2015)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2016)
- Regional Development (Fall 2016)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2018)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2019)
- Public Policy Analysis (Spring 2016)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Summer Session 2011)
- POLI 352 Comparative Politics of Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 2)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Term 1)
- POLI 332 Latin American Environmental Politics (Term 2, Spring 2012)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
Planning the timeline and progress of your doctoral dissertation (or Masters/undergraduate thesis)
One of my PhD students lamented this week with me that she had a lot to juggle (taking children to and from schools and to and from activities, etc.) and that she needed a strategy to make her research move forward. I had been planning to write this blog post for a while, since this is the one question I get asked the most by doctoral students (“ how do I plan my unstructured time over the summer ” being the other one).
Do you have one like this but for dissertations? From how to pick your topic to how to plan your chapters or something similar? 🙂 — Mariana Miguélez (@Scherezadda) March 27, 2018
I had to rush to get this blog post done because my student is 2 years away from the deadline her university has imposed for her thesis defence, which is why I sat down with her last night to show her how I do things. I have two other PhD students at exactly the same stage (2 years to defense) so I figured I might as well finish this blog post.
While I’ve suggested that people read one (or more) of the books that I’ve digested myself (check my Writing a Doctoral Dissertation page), one of the main things I teach my students is how to apply backcasting techniques to develop a project plan . I was trained as a project manager, and I worked in that capacity for a number of years, so I understand exactly the kind of work that needs to be done to develop good project plans.
There are a few resources for students, which I mentioned on Twitter earlier today (October 5th, 2018), many of which are listed in the thread that will appear if you click anywhere on the tweet shown below. Thanks to everyone who responded to my query, though I think many of them were professors describing their own process, which is not the same as having a doctoral dissertation (ONE GOAL) to finish in X number of years. My students are doing theirs in the 3 papers’ model, which is a bit closer to the day-to-day life of a professor, but still, the trajectory is quite different. Anyhow, here are some recommendations (click on the tweet to expand the entire thread).
Everyone: one of my PhD students today asked me how to plan her day/week/month/time table. Can you tweet me your process before I tweet/thread mine? Thanks! (I'm off to dinner because I've already written 460 words). — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 3, 2018
The core planning strategy I would thus recommend doctoral, masters and undergraduate students is to engage in a combination of Gantt Chart Design and project backcasting techniques .
The Gantt chart is a technique I learned in graduate school when I took project management courses. This is a hypothetical Gantt chart for my doctoral student, covering about 15 months.
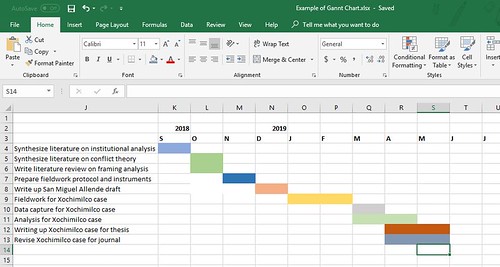
What I suggested to her was to use backcasting techniques to plan backwards from her goal (PhD thesis defense) to intermediate goals. This post explains how I backcast a project https://t.co/wAmyejeoa0 since her dissertation is a 3-papers one, I suggested she uses that model. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
For Gantt Chart templates, you can see Dr. Emma Sheppard’s here.
Project planning for research students https://t.co/ku7shfB5uL excellent template by @DrESheppard which may be of interest to students from undergrad, Masters and PhD levels. pic.twitter.com/ujQVlYocH7 — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) September 3, 2018
Here is another resource that you can use to create Gantt Charts.
To do Gantt charts you can use Excel or Microsoft Project (which is how I learned to do them), or Visio (which has been bought by the evil company and is now Microsoft Visio). I liked this detailed approach that uses connectors between milestones and tasks https://t.co/xVjNmM1q7c — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
Hugh Kearns and Maria Gardiner have lots of resources on their site, and have published books on this as well.
I just realised @ithinkwell and @ithinkwellHugh have excellent FREE templates on their website https://t.co/Q859jNiM6Q for PhD students to plan their trajectories, etc. #PhDChat (thanks, Maria and Hugh!) — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
Dr. Patrick Dunleavy’s book “ Authoring a PhD ” is incredible and really does help students who are planning their PhD process. I recommend it to my own doctoral students.
And of course I would be remiss if I forgot to recommend Dr. Ellie Mackin Roberts (my coauthor for a forthcoming book on research planning) and her website. Ellie has A TON of downloadable printables for you to plan your own research. She is fantastic.
Both for doctoral students AND for post-PhD folks, my coauthor Dr. @EllieMackin has an entire website for research planning https://t.co/unXMqmaf2Z she offers FREE downloadable printable templates that you can use to plan your own research. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
In the end, the process I recommended to my students and that I do myself is – set a target defense date and then work backwards and plan tasks, activities, and intermediate goals. For example, I have asked my students to plan submission dates for their 3 papers (to be sent to journals) and then schedule fieldwork and data analysis accordingly. This process has worked well, and I hope my description of the process will help my students and others!
In a subsequent blog post I’ll describe how to go from long-term goals (submit paper X by Y date) to daily tasks. That blog post will definitely apply to doctoral students and post-PhD folks.
If you liked this blog post, you may also be interested in my Resources for Graduate Students page, and on my reading notes of books I’ve read on how to do a doctoral degree.
You can share this blog post on the following social networks by clicking on their icon.
Posted in academia .
No comments
By Raul Pacheco-Vega – October 6, 2018
0 Responses
Stay in touch with the conversation, subscribe to the RSS feed for comments on this post .
Leave a Reply Cancel Some HTML is OK
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
or, reply to this post via trackback .
About Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
Find me online.
My Research Output
- Google Scholar Profile
- Academia.Edu
- ResearchGate
My Social Networks
- Polycentricity Network
Recent Posts
- “State-Sponsored Activism: Bureaucrats and Social Movements in Brazil” – Jessica Rich – my reading notes
- Reading Like a Writer – Francine Prose – my reading notes
- Using the Pacheco-Vega workflows and frameworks to write and/or revise a scholarly book
- On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- The Abstract Decomposition Matrix Technique to find a gap in the literature
Recent Comments
- Hazera on On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- Kipi Fidelis on A sequential framework for teaching how to write good research questions
- Razib Paul on On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- Jonathan Wilcox on An improved version of the Drafts Review Matrix – responding to reviewers and editors’ comments
- Catherine Franz on What’s the difference between the Everything Notebook and the Commonplace Book?
Follow me on Twitter:
Proudly powered by WordPress and Carrington .
Carrington Theme by Crowd Favorite

UCL Ear Institute
- Typical timetable for full-time PhD student (3 ...

Typical timetable for full-time PhD student (3 Year)
Students and studentships.

Find out what our current cohort of research students are getting up to, where our past students have ended up and whether we have any Studentships currently advertised on our jobs page:
- Current students
- Alumni testimonials
- Studentships (Jobs page)
- Resources for students/supervisors
8 Rules to write a PhD Thesis
Rule 4: make a phd timetable.
A PhD thesis can not be written in one week. Get this through your head. It is hard, maybe even the hardest thing you have to do during your PhD. It is going to be a painful task for most of you (it was for me). So schedule it in a proper time-wise manner. Do not wait until it’s just two weeks before the deadline to start writing. Here is a proposal: make a document with your PhD plan . Write down in that document the important things that need to be done in the last six months of your PhD, preferably in some chronological order. 3 Examples of things to write can be submission of papers, finishing data analyses or other leftover work, writing the thesis, preparing for the defence, sending some important emails, etc. Allocate at least two months of your time for the writing of the thesis . That’s a minimum proposed time frame and it might be far from ideal for you. Time equals money as they say, and that’s definitively the case for the PhD. So you might not want to spend too much of your time in thesis writing. On the other hand, you surely don’t want to underestimate the time that is required for such a colossal task. Therefore, you need to make a well-balanced estimate and plan your thesis writing accordingly. How can then someone derive such an estimate ?
For starters, you need to understand that the exact amount of time that is necessary to finish the thesis writing is hard to predict. The reason for this is that during such a large time period, your life is going to be influenced by a lot of factors. Some of these factors are uncontrollable and there is no way to prepare for them (the phenomenon also simply known as “ life happens ”). Some other factors are directly related to the practical task at hand and can thus be more easily predicted and regulated to your advantage. Using this knowledge, you can make a rough calculation of how much time it will take to write your PhD thesis. I personally think three factors are of significant importance to derive such an estimate. First, the format of the thesis , i.e. a paper-based thesis or a monograph, the latter of which will surely require more time to finish. Second, your personal writing speed , measured in the amount of chapters that you will be able to write on average in a specified time period (usually a week). Third, the number of chapters you need to write. Choosing the format of the thesis should be fairly obvious, based on common practices in your research field, the regulations of your academic institution and the existence or not of published PhD work (papers). Moreover, you should already have a pretty good estimate on the amount of total chapters, based on the modular way of constructing your PhD story as was explained in Rule 3 . Then all that is left, is for you to make an educated guess of your writing speed. The combination of the aforementioned three factors will then help you make a realistic estimation of how long the PhD thesis writing will take.
Let me share with you my personal experience on this matter. My thesis was paper-based. Following the rules in the section During writing , I was writing one to two thesis chapters per week. These were chapter drafts, so definitely not polished material. Therefore, my minimum writing speed was around one chapter per week . Continuing, I had a total of eight chapters to write + the abstract (derived from my initial story structure), which let’s say was equivalent to approximately nine chapters. Worst case scenario, I write one chapter per week, so a total of nine weeks are required. Best case scenario, I write two chapters per week, so a total of five weeks are required (rounding it up). Chapter size plays a huge role as you can probably guess. The proposed estimate of two months time is somewhere between five and nine weeks and closer to the second (the maximum of the two). So, eight weeks, equal to two months, sounded like a good deadline for my writing project. In the end, I finished the thesis writing in seven weeks, which was one week before the deadline. That included also reviewing the edits and comments from my supervisor and several rewrites. The important thing to remember here is that the calculation of your thesis time frame is going to be a personal rough estimate . Therefore, using an average writing speed of one chapter per week without further thought is justifiable (see Rule 7 on how to have more control over this). To summarize, my advice is to 1) calculate the number of chapters you are going to write 2) directly translate that number to weeks and 3) round it up to months. 4
Responsibly follow the time schedule you set up for yourself and be aware to not procrastinate on your thesis writing. This has also been stated more empirically as the notion that “ work expands to fill the time available for its completion ” (Parkinson’s Law). Procrastination can lead to unpleasant and stressful days before the thesis submission, that anyone would gladly dispense with. I have seen people doing rewrites, last minute additions, or otherwise work that could have been done a week or so ago, if properly scheduled. I have heard of people literally running to submit a printed copy in their respective department one hour before the deadline. Doesn’t sound too good to me. It’s a million times better to be prepared and follow your time plan religiously . Try to schedule your thesis writing in an anticipatory manner. This will happen when unfortunate scenarios that you can personally deal with, are managed to a satisfying degree. See also related discussion in the Epilogue .
Make a PhD timetable and allocate a realistic time frame for your thesis writing.
Of course you can make such a plan document from the start of your PhD. I just want to stress here the importance of including in this document what needs to be done during the last stages of your PhD. ↩︎
Remember to round up the resulting number to months! A basic arithmetic example is appropriate here. If you have a total of \(11\) chapters, the time required to write them down would be calculated as follows: \(\frac{11 \text{ chapters }}{1 \text{ chapter/week }}=11 \text{ weeks } \approx 12 \text{ weeks }\) (closest multiple of \(4\) ), which is equal to \(3\) months, assuming that \(1\) month is equal to \(4\) weeks. ↩︎
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Create a Research Timeline for Your Thesis

5-minute read
- 21st May 2023
Beginning a dissertation can feel both thrilling and overwhelming. One of the best things you can do to prepare for the exciting journey of doing a dissertation is to design a comprehensive timeline as your guide. Here we will take you step by step through creating your thesis timeline and provide some example templates, so you’ll be well-prepared to begin your dissertation work.
Reasons for Creating a Timeline
There are many benefits to crafting a detailed dissertation timeline. In addition to helping with time management and meeting crucial deadlines, your timeline will also help you stay motivated by reviewing the tasks you have completed as you progress. A thorough timeline will be valuable during your dissertation proposal and useful if you are applying for grants or other additional funding.
Ste0ps for Creating a Timeline for Your Thesis:
- Research and record all requirements and deadlines.
Before you write out your timeline, ensure you know all of your program’s requirements and deadlines. Academic institutions often require you to complete your dissertation within a specified timeframe.
There are likely several recommended or mandatory deadlines for approval of certain items by your adviser (and possibly the rest of your committee members). Gather all these dates beforehand so you can allot an appropriate amount of time to meet your deadlines.
It will be beneficial to meet with your adviser to understand when you are expected to complete the major phases of your dissertation work and to confirm that there aren’t any other requirements or deadlines that you may not be aware of.
- List all of your tasks and bundle them into phases.
Now that you’ve assembled your dates, working backward from your deadlines is a good rule of thumb. List all of the required tasks that must be completed to meet each milestone, from coming up with your research questions to writing each chapter of your dissertation .
Even though your list will be unique to your research project, it can help to refer to a thesis checklist . It’s also helpful to assemble tasks into different phases (e.g., dissertation proposal, research recruitment). Grouping tasks into phases gives anyone looking at your timeline a quick overview of your research plan.
- Organize your tasks into a schedule and assign task deadlines.
Now it’s time to build your timeline. There are many different free templates available online, from straightforward lists of deliverables to colorful options with room for notes and customization.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
A popular organizational approach for thesis timelines is a Gantt chart , which is a type of bar chart often used in project management in which the length of the bar corresponds to the time the task will take. The best choice for you will depend on the specifics of your research study and personal preferences. Whichever option you select, make sure you can easily edit and revise it as need be.
Sanity-Saving Tips:
● Pay attention to your work style. Some people are more productive when writing in short bursts, while others write better after taking time to get into the zone. Some people choose to start writing parts of their thesis while still conducting research, while others prefer to focus on one phase at a time. Set yourself up for success by reflecting on what type of schedule will help you create the best quality work.
● Schedule breaks. Almost everyone will work better after a well-deserved break. Make sure to schedule regular breaks into your timeline, as well as provide enough time to sleep, eat well, and do anything else you need to do to safeguard your well-being.
● Always have a plan B. Your dissertation is an extensive endeavor with many moving parts. It’s impossible to anticipate and plan for every conceivable event, but it’s helpful to expect something may occur that will cause a deviation from your original timeline. Perhaps study recruitment takes longer than you expected, or one of your committee members gets sick and you have to postpone your dissertation proposal. After you draft your timeline, check that it is not so strict that any disruption will cause a total derailment of your plan. Aim to strike a balance between goals that will inspire you to progress steadfastly and have some leeway in your timeline for the inevitable curveball that life will throw at you somewhere along the way.
Following these three steps will help you draft a timeline to steer the course of your dissertation work: research and record all requirements and deadlines; work backward from your dissertation deadline and assemble your task lists; and organize your tasks into a timeline.
Don’t forget to include ample time for editing and proofreading your dissertation . And if you are interested in any help from us, you can try a sample of our services for free . Best of luck in writing your dissertation!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- PhD Overview and Timeline
Given here are School-wide graduate degree policies and guidance. Program-specific degree options, requirements, and model programs can be found on the "Graduate Programs" pages under each of the subject areas listed in Academics .
General Ph.D. Requirements
- 10 semester-long graduate courses, including at least 8 disciplinary. At least 5 of the 10 should be graduate-level SEAS "technical" courses (or FAS graduate-level technical courses taught by SEAS faculty), not including seminar/reading/project courses. Undergraduate-level courses cannot be used. For details on course requirements, see the school's overall PhD course requirements and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Program Plan (i.e., the set of courses to be used towards the degree) approval by the Committee on Higher Degrees (CHD).
- Minimum full-time academic residency of two years .
- Serve as a Teaching Fellow (TF) in one semester of the second year.
- Oral Qualifying Examination Preparation in the major field is evaluated in an oral examination by a qualifying committee. The examination has the dual purpose of verifying the adequacy of the student's preparation for undertaking research in a chosen field and of assessing the student's ability to synthesize knowledge already acquired. For details on arranging your Qualifying Exam, see the exam policies and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Committee Meetings : PhD students' research committees meet according to the guidelines in each area's "Committee Meetings" listing. For details see the "G3+ Committee Meetings" section of the Policies of the CHD and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Final Oral Examination (Defense) This public examination devoted to the field of the dissertation is conducted by the student's research committee. It includes, but is not restricted to, a defense of the dissertation itself. For details of arranging your final oral exam see the Ph.D. Timeline page.
- Dissertation Upon successful completion of the qualifying examination, a committee chaired by the research supervisor is constituted to oversee the dissertation research. The dissertation must, in the judgment of the research committee, meet the standards of significant and original research.
Optional additions to the Ph.D. program
Harvard PhD students may choose to pursue these additional aspects:
- a Secondary Field (which is similar to a "minor" subject area). SEAS offers PhD Secondary Field programs in Data Science and in Computational Science and Engineering . GSAS lists secondary fields offered by other programs.
- a Master of Science (S.M.) degree conferred en route to the Ph.D in one of several of SEAS's subject areas. For details see here .
- a Teaching Certificate awarded by the Derek Bok Center for Teaching and Learning .
SEAS PhD students may apply to participate in the Health Sciences and Technology graduate program with Harvard Medical School and MIT. Please check with the HST program for details on eligibility (e.g., only students in their G1 year may apply) and the application process.
PhD Timeline
--> Also see the separate pages with on-boarding information for new PhD students <-- Information and Resources for New Graduate Students Wiki site for incoming PhD students (behind Harvard Key)
First Year (G1)
- Notify your financial aid officers of any external funding. Contact: Erin Bishop in SEAS Finance and Emily Fingerle in GSAS Financial Aid.
- Make note of the course registration deadline. (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Register for courses before the deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day")
- Mid-January: Deadline for submitting materials to be reviewed at the January CHD meetings .
- Late-January: Course registration deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day").
- G1s: Your Prospective Program Plan due to the Office of Academic Programs on this day.
- Transfer of up to 3 classes of coursework may be allowed. Include the Application for Credit for Work Done Elsewhere with your Prospective Program Plan.
- April 1: Research Advisor Selection Form /Research Assistant appointment form due to Office of Academic Programs.
- Note: The April CHD meeting is the last CHD meeting in all academic year. CHD does not meet over the summer. Remember to plan ahead.
Second year (G2)
Throughout year.
- G2’s are required to serve as a Teaching Fellow in either the Fall or Spring semester.
- Make sure you complete the TF form once you line up a TF position!
- G2’s are required to take their qualifying exam in either the Fall or Spring terms.
- Email quals_defenses@seas to book a room. If you book your own room (e.g., external to SEAS) you must still email quals_defenses@seas well in advance in order for your required documentation to be ready, else your exam cannot take place.
- Upon completion of the exam, students are required to submit the Designation of Research Committee form to OAP.
- If you plan to request a delay of the qualifying exam, complete a Request to Delay Qual Exam form. Note that delays until September (i.e. start of G3 year) are typically approved as a matter of course
- Mid-September: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Mid-October : Final Program Plan due to OAP; see the CHD page for dates.
- Late-January : Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- May 1 : Advising Agreement form due to OAP.
- May: Commencement and diploma options for Masters en Route / Continuing Master’s students - You can apply to receive your S.M. degree en route to your PhD after you have completed eight of your core courses (this requirement may depend on area). You will receive your S.M. diploma, and participate in the Commencement if you choose to. However since you will be considered a non-terminal degree recipient, you will not be able to join the ceremony in Sander's Theater.
Third year (G3+) and beyond
- Meet with your Research Committee at least annually, as indicated by your area's expectations.
- Send any changes to your Final Program Plan to the CHD for review. See the CHD page for submission dates. Note that the Committee on Higher Degrees expects students not to petition for a revised Program Plan less than a year prior to the final defense in case additional coursework is required, so it's important to keep your plan up to date with your courses as actually taken.
- Inform OAP of any changes to your research committee .
- PhD candidates can review their eligibility to receive an SM en route .
- Early-September: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar.
- Late-January: Course Registration Deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). See the GSAS Policies Academic Calendar
- May 1 : RA reappointment form due to OAP.
Completing your degree
Degree application.
- Check out FAS degree-completion information here (Registrar) and deadlines here (GSAS calendar)
- Complete the degree application via my.harvard by the Registrar's deadline.
- If you schedule your own room (e.g., external to SEAS) you must still email quals_defenses@seas well in advance in order for your required documentation to be ready, else your defense cannot take place. You must also get agreement from your full committee to hold your defense in a non-SEAS room.
Dissertation Submission and Commencement
- The best way to share your dissertation with others is by linking to the DASH copy. DASH uses persistent URLs and provides you with download statistics, and the DASH copy of your PDF will not include the signed Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC). If you choose to post or share your PDF in some other way, you should remove the DAC page so that readers do not have access to the scanned signatures.
- Get ready for commencement by updating your email and other contact information via my.harvard.edu .
In Academic Programs
- Non-Resident and Part-Time Study
- CHD Meeting Schedule
- PhD Course Requirements
- PhD Program Plans
- Teaching: G2 year
- Qualifying Exam: by end of G2 year
- Research Advisors, Committees, and Meetings
- Dissertation and Final Oral Exam
- SM and ME Course Requirements
- SM and ME Program Plans
- Masters Thesis and Supervisor
- SM degree en route to the PhD
- Graduate Student Forms
- Teaching Fellows
- External Fellowships List
- COVID-19 Graduate Program Changes (archived)

- Code of Ethics
- Dissertation Editing
- Dissertation Coaching
- Free Consultation
How to Create a Dissertation Timeline (With Examples + Tempate)
When it’s time to start thinking about writing your dissertation, it is vital to put together a dissertation timeline. This will help you map out the months you will be spending on your dissertation, and ensure that you’re staying on track. A specific and detailed dissertation timeline will serve as an outline to guide you, step by step, through what can be a long and challenging process.
While we often refer to a dissertation in a way that makes it sound like a monolith, in reality, a dissertation consists of many moving parts. A dissertation timeline includes a series of milestones that leads up to the dissertation defense , revisions, and final submission of your dissertation. Constructing an outline of every step in the dissertation process , including rough estimates of how long each will take, will give you a realistic picture of where you are in the process at any given time.
Before embarking on your dissertation, it is a good idea to meet with your dissertation advisor and sketch out a dissertation timeline that is realistic for the size and scope of your project and includes deadlines. This will provide you with much-needed structure and a sense of what will happen next. To get an idea of what a completed dissertation looks like and the components your program requires, ask to see samples from recent graduates in your department.
These are a few frequently asked questions about crafting a dissertation timeline:
- What does a dissertation timeline look like?
- What goes in a dissertation timeline?
- How structured should a dissertation timeline be?
- What do you do with a dissertation timeline?

What Does a Dissertation Timeline Look Like?
One way to think about a dissertation timeline is as a kind of outline. While the outlining process is unique to each writer, there are commonalities shared by all of them. Likewise, when writing a dissertation timeline, you’ll want to include all of the basic elements of your dissertation as well as the amount of time you think you’ll need to execute them.
The best dissertation timeline format is the one that works for you. Though I’ve reformed somewhat over the years, for a long time I wasn’t a fan of intensely detailed outlines. Many people don’t like outlines. And that’s okay! However, writing a dissertation is not the time to be flying by the seat of your pants. To get started, a simple, linear timeline that projects the amount of time you think you’ll need to write your dissertation will suffice.
Example Dissertation Timeline
Below, you’ll find an example of a dissertation timeline, which you can view as an image in your browser or download as a spreadsheet. Feel free to use the spreadsheet as a template as you build your own dissertation timeline.
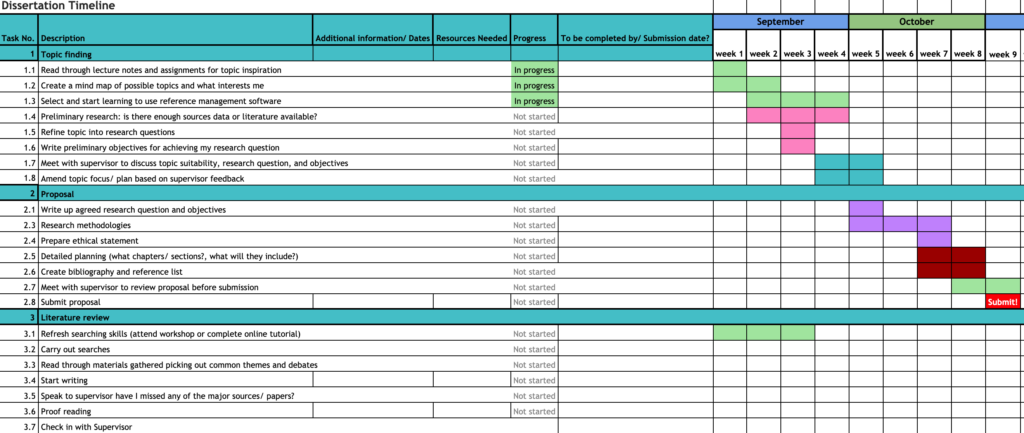
Or download the spreadsheet below:
Inclusion in a Dissertation Timeline
When constructing your dissertation timeline, include every element of the dissertation from the abstract to the conclusion. Keep in mind that you may not be writing your chapters in chronological order. For instance, after completing their first round of research and writing their research question, most graduate students will tackle their literature review next, even though it comes after the abstract and introduction in the final document.
Depending on the field being studied, most dissertations will also include sections for methodology, results, and discussion. Many programs also require a detailed conclusion that alludes to future research possibilities. Every dissertation also has an extensive list of references (pro tip: write this as you’re writing your dissertation), as well as appendices for charts, graphs, and other ephemera. And don’t forget your acknowledgments!
Dissertation Timeline Structure
The structure of your dissertation timeline will take shape once you’re engaged in the research process. While a road map may seem like an apt metaphor for a dissertation, once you get started you may notice a lot of starts and stops and circling back. After you’ve begun researching, you may realize that you need to allot more time for digging through the databases, or you may discover that you need to reformulate your research question entirely.

I’ve seen many of my own graduate students use calendars to great effect, giving themselves hard and fast deadlines to meet. Many students also build out their dissertation timelines as they progress, attaching working drafts of their abstract, introduction, and literature review to their timeline within a giant spreadsheet that links to multiple documents and sources. All of these methods are valid. Devise one that works for you.
Using a Dissertation Timeline
So once you have a thoughtful, soundly-constructed dissertation timeline, what do you do with it? First, and most importantly, try your best to adhere to it. Check in with your dissertation timeline regularly, and use it to keep yourself on track. Also, make adjustments to it as needed. If you find yourself breezing through your preliminary research but needing a bit more time for your literature review, consult your timeline and adjust accordingly.
While meeting your deadlines is important, also construct your dissertation timeline with an understanding that many graduate students face delays once they start working on their dissertation. These can include hold-ups at the department or university level in the form of late IRB approval or limited lab space or grant funding that gets cut. Anything can happen, but having a dissertation timeline will help you get back on track as soon as the storm passes.
In my own experience, I also found my dissertation timeline to be a great document to share and discuss with my dissertation chair and committee. Once I finished my comprehensive exams, I met with members of my dissertation committee and got feedback on my rough dissertation timeline to make sure my goals for submitting my dissertation and graduating were realistic. This also ensured that we were all on the same page.
When writing a dissertation, timing is everything. Creating a dissertation timeline gives you definitive time limits for research and writing, and it also influences several other major decisions that you’ll need to make. These include preparation to go on the job market, which often coincides with writing your dissertation. There is no doubt that this will be a hectic time in your graduate school career, but having a well-organized dissertation timeline is a good way to keep everything in perspective.
Related posts:

Courtney Watson, Ph.D.
Courtney Watson, Ph.D. is an Associate Professor of English at Radford University Carilion, in Roanoke, Virginia. Her areas of expertise include undergraduate and graduate curriculum development for writing courses in the health sciences and American literature with a focus on literary travel, tourism, and heritage economies. Her writing and academic scholarship has been widely published in places that include Studies in American Culture , Dialogue , and The Virginia Quarterly Review . Her research on the integration of humanities into STEM education will be published by Routledge in an upcoming collection. Dr. Watson has also been nominated by the State Council for Higher Education of Virginia’s Outstanding Faculty Rising Star Award, and she is a past winner of the National Society of Arts & Letters Regional Short Story Prize, as well as institutional awards for scholarly research and excellence in teaching. Throughout her career in higher education, Dr. Watson has served in faculty governance and administration as a frequent committee chair and program chair. As a higher education consultant, she has served as a subject matter expert, an evaluator, and a contributor to white papers exploring program development, enrollment research, and educational mergers and acquisitions.
Comments are closed.
How to Finish Your Dissertation in Half the Time
Learn how to avoid the pitfalls preventing you from finishing your dissertation faster.

Subscribe to get the free eBook!
Dr. Courtney Watson In the News
“ See It for Yourself ” in With Good Reason: Beyond the Book July 22, 2022
“ I Thought You’d Never Ask: Consent in Contemporary Romance ” in New Frontiers in Popular Romance (McFarland) June 13, 2022
- Common Errors
- Dissertation Success
- Presentation
- Quantitative Analysis
- Surviving Grad School
“How to Finish Your Dissertation in Half the Time”

How to Prepare a PhD Research Plan/Schedule?
PhD research plan is a structured schedule for completing different objectives and milestones during a given timeframe. Scholars are usually unaware of it. Let us find out how to prepare it.
Between March 2021 to 2022, I read almost 15 different research proposals from students (for their projects) and only a single one, I found, with a comprehensive research plan for 3 years. Which is still not, kind of practical, probably copied from other students.
Such entities are not known to over 90% of students, if some know that because their university asked for but unfortunately, this basic procedure lacks penetration among students. I don’t know the exact reason, but students lack a basic understanding of the research process.
Meaning, that they don’t know or perhaps don’t complete their course work needly. PhD research requires many documents, SOPs and write-ups, before even starting it. For example, a rough research plan, research proposal, initial interview, competence screening, grant proposal and so on.
However, the requirement varies among universities and thus knowledge regarding basic procedures often also varies among students. So I’m not blaming students but certainly, it is the fault of the university side, as well.
When you come up with a research proposal with a research schedule or entire plant, certainly it will create a positive image and good reputation. So it is important. But how to prepare it?
Hey, there I’m Dr Tushar, a PhD tutor and coach. In this article, we will understand how we can prepare a structured plan for the PhD research and how to execute it.
So let’s get started.
How to prepare a PhD research plan/schedule?
A PhD research plan or schedule can be prepared using the GANTT chart which includes a month, semester or year-wise planning of the entire PhD research work.
First, enlist goals and objectives.
It’s not about your research objective enlisted in your proposal. I’m talking about the objectives of your PhD. Take a look at some of the objectives.
Note that these are all the objectives that should be completed during the PhD, but not limited to a specific subject. Note you have to show how you can complete or achieve each objective during the entire tenure of your work.
And that is what the plan/schedule is all about. Next, explain the time duration. The time required to complete each goal, roughly. For example, a semester or a year to complete the course work or 4 to 8 months for completion of ethical approval.
Now two things must be known to you, at this point in time.
- First, enlist the time required to complete each objective, as aforementioned.
- Second, what goals would you complete during each semester?
For instance, course work takes a semester to complete, but during the period a scholar can also craft their PhD research title, research proposal, ethical approval and grant proposals.
Now it is also crucial to know that there is no time bound to complete goals, but it should be completed as you explained. Let’s say you can plant it for 3 years, 4 or even 5 years depending on the weightage of your work.
In summary, the answer to the question of how to prepare a research plan is,
- Enlist your goals or objectives.
- Decide the time required to complete each goal.
- Prepare a GANTT chart.
Now you have prepared zero-date planning for your research but how to present it? The answer is a GANTT chart.
GANTT chart for PhD research plan:
GANTT chart is a task manager and graphical presentation of how and how many tasks are completed or should be completed against a given time duration. Take a look at the image below.
How can you prepare one?
Open MS Excel (on Windows) or numbers (on Mac).
Enlist goals or objectives in a column.
Enlist years (duration of PhD) in a row and bifurcate them into individual semesters. You can also prepare a month-wise plan, that’s totally up to you. In my opinion, semester-wise planning is good because research is a lengthy and time-consuming process. So monthly planning would not work.
To make a chart more attractive and readable use colors, as I used. Now mark a ‘cell’ against a column and row showing the objective which you are going to complete in a semester. Take a look.
After the end of this, your GANTT chart would look like this.
You can prepare a month-wise planning, individual semester-wise planning and goal-wise planning etc. I will explain these things in upcoming articles on 5 different types of GANTT charts for PhD.
Custom writing services:
If you find difficulties in preparing a research plan, synopsis, proposal or GANTT chart. We can work on behalf of you. Our costume services are,
- Synopsis writing
- Project writing
- Research proposal writing
- Research planning and GANTT chart preparation.
You can contact us at [email protected] or [email protected] to get more information.
Wrapping up:
Planning and executing a research schedule are two different things. Oftentimes, students just prepare as per the requirements and then do work as per their convenience. Then they are stuck in one place and just work around the time.
Plan things. Make your own GANTT chart, put it on your work table or stick it on a wall so that you can see it daily. Try to achieve each goal in time. Trust me things will work and you will complete your PhD before anyone else.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author


Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.

Why is it called a Doctor of Philosophy?

Preparing for a PhD Viva
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
- FAQs for Prospective Students
- How to Apply
- Master’s & PhD Program
- Tuition & Fees
- Awards and Funding
- Role of the Supervisor
- Conflict within Committee
- Student Responsibilities
- Incoming Students
- Thesis, Defence and Graduation
- Master’s
- Doctoral (PhD)
- RES Forms & Policies
- Finance/HR Forms
- Core Faculty
- Administrative Staff
- Postdoctoral Fellows and Research Associates
- Master’s of Arts and Science Students
- PhD Students
- Alumni Interviews
- IRES Student Society
- Research Themes
- Theses & Dissertations
- IRES and Open Access
- Information for Authors
- Research Map
- RES Graduate Courses
- Methods Courses
- Undergraduate Courses taught by IRES Core Faculty
- Non-RES Courses
- Non-UBC Courses
- Vancouver Summer Program
- IRES Newsletter
- Seminar Videos
- Media Coverage
- External Opportunities
- Departmental Award Recipients
Graduate Program
Doctoral thesis timeline, ideal timeline for res phd students, year 1: september - april.
- Attend UBC Graduate Student Orientation in late August.
- You have until the second week of term to add/drop courses most courses.
- Begin your courses and attend the IRES Orientation/Welcome Back BBQ during the first Sept!
- Apply for Awards and Funding starting in late summer and continuing through the fall.
- Is a potential supervisory committee member a non-G+PS Member? If so, you must complete a Recommendation for a Non-G+PS member to serve as part of your supervisory committee .
- You must complete and submit an RES Supervisory Committee Composition Form to the Graduate Program Manager once your committee is confirmed.
- An RES Committee Meeting Report form must be submitted to the IRES Graduate Program Manager for each committee meeting held.
- Your first Committee Meeting Report Form and the Committee Composition form are due to the Graduate Program Manager by the end of May of your first year in program.
- complete your required coursework
- form your supervisory committee
- when supervisory committee meetings should be held
- hold your Comprehensive Exams
- complete your Thesis Proposal
- Advance to Candidacy
- conduct any fieldwork
- write up your thesis
- Go through the External Examination and Final Oral Defence process
Year 2: September - April
- Complete any outstanding course requirements.
- If you haven't already, form your supervisory committee and complete the RES Supervisory Committee Composition Form
- Committee Meeting Report Forms are due at the end of May of each year of your program once your supervisory committee is formed.
- Hold your Comprehensive Exams - this must be completed no later than 30th month in program.
- ensure both student and supervisor(s) are clear of the program requirements, expectations and the student is on-track to complete their program (ideally) within 4 years.
- provide an opportunity for the student to voice any questions or concerns they may have and be able to provide feedback on the program, the courses they have taken, how their last year has been, etc.
- provide an opportunity for the supervisor(s) to comment on the student's progress in program and ask any questions.
- Towards the end of the meeting, the supervisor(s) will be asked to leave the meeting to allow for a discussion with only the student, Graduate Advisor and Graduate Program Manager. This time can be used to provide any additional feedback the student may have.
- An email confirmation from your supervisor(s) to the Graduate Program Manager is sufficient to confirm that your thesis proposal has been approved by your supervisory committee step - no form to fill out!
- you must Advance to Candidacy by the end of your 36th month in program, but ideally this is done in your second year in program (within 12-24 months).
Year 3: September - April
- Hold the RES Fall - Year 3 Review . All third-year PhD students must fill out the required form, together with their supervisors, and submit the completed form to the Graduate Program Manager. While there is no mandatory meeting, students may request to schedule a meeting with the Graduate Advisor and the Graduate Program Manager to discuss their program.
- Committee Meeting Report(s) due at the end of May (or shortly after a meeting is held).
- Conduct any fieldwork for your doctoral dissertation.
- Start planning in detail when these steps will be taken to complete your program on time.
- Doctoral Exam Timeline
- Doctoral Exams FAQ's
- Doctoral Exams Deadlines
Year 4: September - April
- Under normal circumstances, this process takes about four months to complete.
- Use the Doctoral Exam Timeline to plan your submission and the Doctoral Exams tools to help you complete all steps.
- Post-Final Oral Defence - Doctoral Forms: Mandatory
- Provided you have met all other degree requirements, your program will be closed as of the date on your G+PS thesis receipt (email).
- Please contact the Tuition Fee Payment Office at Brock Hall to request a refund of any remaining portion of the term's tuition fees. Only full months of tuition can be refunded.Tuition Fee Payment Office 2016–1874 East Mall Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z1 604.822.9836
- students are able to have their degrees awarded on any one of four dates in a given year; dates in September, November, February, and May. Once the degree has been awarded by the UBC Senate, a notation will appear on the transcript. However, formal conferral at Congregation ceremonies and official degree parchments will remain available in May and November only.
- Doctoral Citations for Graduation
- Graduation Ceremonies - held in May and November of each year.

- Jul 29, 2020
How I Made My PhD Completion Plan on Excel (With Template)
Updated: Dec 12, 2023
For the last few weeks, I've been working on my PhD completion plan. It's basically an excel spreadsheet that I'm using to track my progress and plan my time for the remainder of my PhD. My thesis is due August of next year (with a 6 month extension) so the clock is definitely ticking. But what started as a quick and basic gantt chart has quickly turned into a more complicated excel spreadsheet - and I love it so much I thought I'd share it with you all!
If you want to skip to accessing the excel template click the link below. But if you want to see how I made the document and how to use it, then keep on reading!
Basically, to make the Gantt charts I followed this Youtube tutorial:
I really wanted a Gantt chart that showed percentage progress as well as a general timeline, so I thought this tutorial was really useful for showing me how to do this!
If you start playing around with the Gantt charts in the template I've provided and run into any difficulties, particularly with things like changing the dates displayed on each chart, this is a good reference point as to how to fix problems that may arise. But of course, if you reach out to me for assistance with editing the spreadsheet, I'll do my best to help too!
The basic set up is that I have a colour coded table to the left of each Gantt chart within my file, that lists off each task with both my planned dates and my actual dates of start and completion for each task. Therefore, as I go along, if the dates that I actually do things don't correlate with my planned timeline, then I have a space to put the new dates down without losing my originally planned timeline. Basically, this set up allows me to have two options for what my Gantt chart looks like, I have the "Plan" view and the "Actual" view. I also have a column for % completion, so that on the "Actual" Gantt chart, it'll show me how far through I am with each task with a dark bar.

As I said, this all allows me to have two options for what my Gantt chart looks like, with both a planned and an actual dates option, I can control what I'm seeing on the chart using this nifty little drop down box:

By picking either actual or plan from the drop down box, it changes the display of the Gantt chart and what values come up in the second table entitled "Data Prep". You don't need to enter anything in the Data Prep table or do anything to it, it's all set up to get all the information it needs from the colour-coded table.
Then the sheet is set up to automatically create a Gantt chart like this one:

I've colour coded the chart based on three PhD Aims and general thesis writing. You'll notice that the dark bars indicate my percentage progress like I mentioned earlier, so if a bar is half way across, then the task is 50% complete. However, this will only show on the actual view, not the plan view.
If you change the dates for any of the planned or actual dates, it'll automatically update the Data Prep table and the corresponding Gantt chart.
Within the document, I have an overall Gantt chart to chart the whole PhD, but then I've also made tabs for each aim, where you can break each task down into smaller more actionable tasks and have a Gantt chart that displays those in detail. I've personally found this really useful so that I can both get an overall picture of my PhD, but also go into more detail for each aim or project when I need it.
I've also included a "Calendar View" option tab in the document. I don't think there's a way to automatically import dates of all your various tasks into the calendar, so you'll have to do it manually if this is a set up that would be beneficial for you. But personally, I liked being able to plan my day to day out on a calendar in order to know when I could put down tasks as planning to be performed on my Gantt charts. So I filled this calendar view out before I did any date planning on the charts. I obviously colour code these tasks for each aim and then general thesis writing in the same colours I've used to make the overall Gantt chart to make things easier to navigate and know what's going on at first glance.
I haven't included this in the template, but in my personal PhD completion plan document, I also have more tabs with experimental information like my immunohistochemistry antibody panels, so that I can quickly refer back to them while I'm looking at the timelines of completing my lab work for each project.
To access the most up-to-date version of this template, head to my new website at:
This excel sheet looks incredible and I cannot wait to use it: thanks for creating and sharing it with us!
Hello Lily,
My name is Hida and I am thankful for your kind sharing of this template. You have done a good deed and I also hope I can enjoy sharing my knowledge with others too. Thanks 😘
Love from Malaysia,
Hello, thank you so much for sharing this! very beneficial indeed. I need a little help, in extending the timeline beyond December 2021. Can you help me with it? Thanks a lot!
Hi Siti, the date axis are simply the dates on the gantt chart (top of the chart). If you click on those, the date axis will be selected
Hi, thanks for sharing and providing resources. Now that you are using notion how does this planning fit with that software? Or are you still using the gantt chart as your overall planning tool. Many thanks

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
Wharton Stories
What to expect from a phd schedule.
Take a look at a current student’s schedule and get the insider perspective from doctoral students and coordinators on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
The life of a PhD candidate can be stressful as you adjust to a rigorous academic and research schedule. Penn and Wharton offer a variety of resources to help support you in the transition to PhD life.
Wharton’s sense of community offers a level of comfort when reaching out to faculty as well as fellow students to help solve problems. Doctoral students and coordinators give the insider view on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
Class and Research First
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small , the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program , said, “It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses. Second year they still have a lot of coursework to do, but more of that is elective with a focus more on their interests. During those years they’re expected to get started on research.”
In addition to taking classes and getting started with research, the Marketing program requires students to write two papers. The first research paper is due at the end of the second year, the other is due at the end of the third year.
The Real Estate and Business Economics and Public Policy programs run like the Marketing program. Fernando Ferreira , coordinator for the programs, said, “During the first year they complete six core courses. In the second year, the focus shifts to field courses and to independent research. They have two professors advising them in that year.”
After completing the main courses, students shift to conducting independent research. For REAL and BEPP students this means writing three dissertation chapters during the third and fourth years.
Time for Conferences and Seminars
Because coursework is usually completed by the second half of the program, there’s time for students to attend lectures and seminars. Andrea Contigiani , a fifth year student in the Management program, said, “In my fourth year, I usually attended a seminar around lunchtime. Wharton has an incredible seminar series throughout the year, with a good seminar happening almost everyday. Occasionally, I attended other events, like MBA events or speaker series. I then go back to research for most of the afternoon.”
Prof. Small said, “Students are expected to actively participate in seminars and activities. They’re also encouraged to go to academic conferences and try to present their work at those conferences. It is similar to the expectations of being a faculty member, minus teaching.”
Classes take up the majority of the first two years of the programs. When the focus then switches to research, you’re expected to work independently. Sometimes that can be intimidating. You become your own boss, which is an adjustment from being told what to do and when to do it.
So how do you manage it? Get advice from students and coordinators.
Posted: August 4, 2017
- Work/Life Balance
Doctoral Programs
Matthew caulfield.
Hometown Ocean City, New Jersey
Concentration Management and Legal Studies & Business Ethics
Doctoral Stage Second Year
Typical Day at a Glance
8:30 am Wake up and get ready for the day
9:15 am Get to PhD Offices, respond to emails, check philosophy blogs and read news
10:30 am Journal article readings
11:30 am Meet with advisor
12:00 pm Attend departmental seminar speaker and lunch
1:30 pm Attend Wharton Social Impact Doctoral Community meeting
3:00 pm Attend business ethics seminar
5:00 pm Read for class
7:00 pm Meet with nonparametric statistics study group
8:00 pm Complete homework
12:00 am Go home
1:00 am Bedtime
What is your favorite part about Wharton?
First, the faculty are excellent. They are often leading experts in their fields, and they can offer advice that would be hard to find elsewhere.
Second, the other PhD students are just as passionate about research as you would hope. A huge part of my scholarly development has been due to the discussions I have had with other graduate students.
Third, the Wharton name can offer you serious advantages. In the course of research, I think industry practitioners as well as other academics have been more willing to talk or correspond with me because I am a graduate student at Wharton.
Related Content

Prof. Zhao’s International Strategy Course Examines What It Takes to Go Global

How Do Wharton’s East and West Coast EMBA Classes Mix?

What this Faculty Member Wants Students to Get Out of His Entrepreneurship Classes

San Francisco Student Explores Ways to Address Challenges for Nonprofits

3 Benefits You’ll Get from Taking a Global Modular Course at Wharton

How This Wharton MBA is Paving His Future in Clean Energy Through the Kleinman Certificate Program

Women of Wharton Events Provide Valuable Opportunities to Connect

PhD Candidate Matthew Caulfield Became an Election Technology Expert — As an Undergrad

8 Wharton Faculty to Follow on LinkedIn

Five EMBA Parents Share Their Advice, Their Experience in the Program, and Their Child Care Solutions

How to Prepare a Strong PhD Application

Prof. Corinne Low Teaches Business Principles to Wharton MBAs and Zambian 8th Graders

Temporary Shift or New Reality? How Work May Change Post-Pandemic

Paving the Way for More Women in Real Estate

Welcome Back to Campus: 7 Social Impact Programs for Student Changemakers

Tips for Completing Your PhD Thesis on Time
Completing a PhD course is undoubtedly one of the most fulfilling pursuits for academics. Recently, however, a new term arose: ABD (“All but Dissertation”). ABD refers to students who have completed their coursework and passed the exam, but have yet to complete and defend their theses. Indeed, ABD students are more common than previously thought. The PhD Completion Project revealed that the ten-year cumulative completion rate for PhD students ranges from 64% (engineering) to 49% (humanities). While not all students advance to the doctoral writing stage before dropping out, a significant portion do, based on these numbers. Leaving graduate school without finishing your thesis has psychological and occupational consequences. Completing your thesis on time is, therefore, essential for career advancement and personal growth.
Overcoming a Time Crunch
Being pressed for time will likely happen, especially if you are holding down a part-time job during your doctoral studies. The pressure to finish is greatest during the last year of your PhD and this is usually the time when conflicts and tensions arise. There are tips that can help you finish your PhD on time , even when you’re pressed for it.
- Prepare an action plan for your last year. This will help you optimize the time that you have left and avoid feeling overwhelmed by all the things that you have to do.
- Clarify your priorities. Ask yourself what you intend to finish first and stick to it. It may be helpful to break down your priorities into smaller and simpler tasks.
- “The truth can wait.” That is, it is vital to start writing your doctoral thesis once you have your data, even if more can be done.
- Know all the rules and regulations of the university. Prepare a list of all the documents and papers that you will need before you need them. This will help you avoid pitfalls in your last year.
- Familiarize yourself with software. Producing scientific documents entails the use of specific programs, such as LaTeX. While the program may not be as easy to understand as other editors, there are marked advantages such as ease in publication and faster manipulation of images.
- Pay attention to your career. While you may think that this is not the best time to think about your career , it is. Your career should follow suit after your doctoral studies, and focusing on what lies ahead will help you frame the current situation.
Key Tasks for Finishing Your PhD on Time
Finishing your PhD thesis on time is not as daunting as it sounds. Although many students will be pressed for time, completing your study is possible with a little ingenuity from your part.
- First, ensure that you meet all the PhD requirements set by your institution. Never presume anything without double-checking with your institution and your supervisor. This can save you from a lot of wasted time and stress.
- Keep a good perspective. Your peers are unlikely to read your thesis , but they are likely to read journals and articles resulting from it.
- Contrary to what most people say, your introduction should be written last. Breaking your thesis into defined stages is important for success. On that same note, your conclusion also should be written last.
- Get familiar with project management applications, such as Trello.
- Buy your own laser printer. This will save you from having to rush elsewhere to have your drafts printed. It will save you time and money as well.
- Get feedback on the entire thesis—from start to finish. Getting feedback for individual chapters is fine, but you should aim to get feedback on the entire work.
- “Begin with the end in mind.” Make sure you know when your doctoral studies are supposed to end, and when your work will be considered as done.
Planning and Writing Your Thesis
Breaking down your tasks into manageable blocks is one way to ensure that you actually finish the entire thing. There are plenty of techniques to help you along the way, such as the 25-minute Pomodoro for academic writing. Undoubtedly, writing your thesis is at least as hard as performing the actual study, but it is never impossible. With the right tools at your disposal and a positive mindset, you can finish your PhD on time. Below is a checklist of things that you need to do to get to graduation day.
- Draft your proposal and research design
- Acquire IRB consent
- Pilot study
- Gather data and information for your study
- Analyze your data
- Write, write, and write some more . Ideally, aim to write for a minimum of 30 minutes a day
- Defend your thesis
Completing your PhD paper on time is definitely possible. Knowing the tips and tricks of the trade can help you to get on your way towards a life in academia.
Thanks for the very useful article to complete the Ph.D. thesis before the deadline. The doctorate course is very difficult for the student so the student could not able to complete the work on time. But your article helps to finish the article to complete the work for the students.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

- AI in Academia
- Reporting Research
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without AI-assistance
Imagine you’re a scientist who just made a ground-breaking discovery! You want to share your…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia…
How to Manage Your PhD Timeline for Smoother Research Completion
7 Steps of Writing an Excellent Academic Book Chapter
Top 12 Potential PhD Viva Questions and How to Answer Them

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
How to develop an awesome PhD timeline step-by-step
A successful PhD journey begins with a solid plan that includes a PhD timeline . A thought-through and well-designed PhD timeline requires some time but can be accomplished in a few simple steps.
Why a clear PhD research timeline matters
Step 1: decide what to include in your phd timeline, step 2: discuss your provisional phd timeline with your supervisor/s, step 3: design your phd timeline, step 4: regularly update your phd timeline.
Doing a PhD means committing to a challenging project that spans several years. Therefore, it is no surprise that doing a PhD can feel quite overwhelming. How do you even begin to tackle such a huge project?
A PhD timeline breaks down the daunting task of doing a PhD into an actionable plan with tasks and milestones along the way.
Even if not everything will go as planned (which is normal and no problem!), a PhD timeline can give PhD students peace of mind. A good plan, worked out in a PhD timeline, helps them to structure their time, communicate their goals and work toward specific targets.
Some PhD students are required to create a PhD timeline as part of their programme. Yet, even if PhD students are not required to do so, it is highly recommended to create a PhD timeline!
PhD timelines should be as diverse as PhD research projects: What you decide to include in your timeline should fit to your situation, goals and your programmes’ requirements.
Common elements included in a PhD timeline are the following:
- Data collection : How, when and where are you collecting your research data?
- Fieldwork : Is your data collection spread out or are you spending several weeks doing fieldwork? If so, when is this scheduled and how can you avoid overlaps with other requirements, such as coursework?
- Experiments : Are you running experiments for your PhD research? If so, when? And how long do you estimate this will take you?
- Data analysis : Once you have your data, be it quantitative or qualitative data, when and how do you analyse it? How much time do you block for this task?
- Writing plan : When are you writing down your results? How can you break down writing into different parts, for instance, writing goals per chapter or article?
- Publications : Publication requirements differ from PhD programme to programme. Even if you write your PhD as a monograph (instead of a selection of articles) , you should try to publish something during your PhD. When would you have an opportunity to do so, and how much time does it require?
- Conferences : Every PhD student should present at a conference during their PhD trajectory. Which conferences are you interested in? When do they take place, and when would you have findings to share at a conference?
- Coursework : What are your PhD programme’s coursework requirements? What courses are you interested in, and when are they offered?
- Other activities : Are there any other activities that are crucial for your PhD project? Think, for instance, about an extensive dissemination campaign, collaboration with external partners, internships, online activities etcetera.
Make a draft plan, including dates and times. Then move to Step 2: Discussing it with your supervisor/s!
Proactively creating your PhD timeline is a good step as a PhD student. However, you should share your thoughts and ideas with your PhD supervisor/s and get their input.
If possible, set up a meeting with your supervisor/s that is entirely dedicated to your PhD timeline. During this meeting, you can share what you created so far.
Then, you should discuss the following questions:
- Is there anything missing in the PhD timeline?
- Is the PhD timeline realistic?
- Should anything be removed from the PhD timeline to prioritise other tasks?
- Does the PhD timeline meet all the formal requirements to graduate within the designated amount of time?
- Is there institutional support and sufficient financial resources for activities such as fieldwork, conference attendance, etcetera?
Make sure to take notes during the meeting, as you will need the answers to these questions to edit your provisional PhD timeline.
Not only will this discussion help you to finalise your PhD timeline. It will also help you to get clarity on your supervisor/s’ expectations!
You may also like: Planning your PhD research: A 3-year PhD timeline example
Following the input of your supervisor/s, your PhD timeline will reach a more final stage. Now it is time to think about designing your PhD timeline:
A well-designed PhD timeline is not just pretty for the eyes, but it makes it much easier to have a good overview of all plans and milestones ahead.
Yet, it would be wrong to argue that there is a one-size-fits all solution to designing a perfect PhD timeline.
Maybe you are a very visual person and would prefer your timeline to illustrate a broad overview of the upcoming years. Maybe you are encouraged by checking things off your to-do list. In that case, a more detailed PhD timeline with many different tasks and milestones may be more suitable for you.
A common way to design PhD timelines is via Gantt charts. If you want to learn more about Gantt charts for your PhD timeline, check out my post on how to design Gantt charts in Microsoft Excel, Power Point and Word.
A PhD timeline is there to keep you on track and to showcase the milestones that you reached in your journey so far. However, while it is good to have a solid plan, the future is impossible to predict.
Your PhD timeline should be a living document or chart. Update it regularly!
For instance, a conference may be cancelled. You may have a period of sick leave. An experiment may not work out as planned. Or writing a paper takes longer than expected.
Successful PhD students remain flexible and don’t panic as soon as something does not work out as planned.
So, use your PhD timeline to regularly reflect on your progress and your current situation. Update your PhD timeline when needed, to prioritise tasks and set more concrete and achievable goals for the upcoming months.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
Left your dissertation too late? Ways to take action now
The best email signatures for graduate students (with examples), related articles.

How to paraphrase a quote: 4 simple strategies

Revise and resubmit: Sample peer review comments and examples

13 great academic phrases to write your discussion (+ published examples)

Introduce yourself in a PhD interview (4 simple steps + examples)
- University News
- Academic Departments A-Z
- Map & Directions
- Careers at HKUST
- Faculty Profiles
- About HKUST
- HKUST Fok Ying Tung Graduate School
- Administration
- PG Facts and Figures
- Publications
- Postgrad Channel
About FYTGS

- Program Types
- Areas of Studies
- PG Prospectus and Booklets
- Continuing and Professional Education
- Programs and Courses
- HKUST College of LifeLong Learning
- Useful Links
- How to Apply
- Admission Requirements
- Admission Timeline
- Documents Required
- Scholarships & Fees
- Online Application
- Accepting an Offer
- Submitting Official Documents
- Applying for Student Visa
- Handy Resources for Preparing Your Studies
- Moving to Hong Kong (for Non-Local Students)
- PG Visiting Internship Students (Research Only)
- Visiting PG Students (Coursework Only)
- PG Exchange Students
- Associate Postgraduate Students
- Preparing your Short-Term Study @HKUST

- Aims and Objectives of Research Postgraduate Education
- Strategic Framework for Taught Postgraduate Education
- Programs & Courses
- Academic Standards
- Code of Practice for RPg Thesis Supervision
- Academic Requirements for RPg Students
Handbook for Research Postgraduate Studies
- Handbook for Taught Postgraduate Studies
- Scholarships for Admission
- Hong Kong PhD Fellowship Scheme
- Targeted Taught Postgraduate Programmes Fellowships Scheme
- Other Funding & Scholarships
Scholarship
- Guidelines & Forms
- Online Systems
- Program/Course Guidelines and Proposals
- Introduction
- Meeting Schedules
- Meeting Documents
- Circulation
- Annual Reports
- Annual Reporting of Self-financing Programs
- Working Schedule
- Student Surveys and Statistics
- Training Series for HKUST(GZ)
- PG Outreach and Admissions
- Quick Access
- Download Prospectus
- University Governance
- Student Conduct and Academic Integrity
- Policies and Practices Governing Research Activities
- Scholarships, Awards and Financial Assistance
- Registration in Programs
- Study Commitment
- Curriculum Requirements (with guidelines on thesis research)
- Course Registration
- Course Substitution and Credit Transfer
- Course Grading
- Progression and Academic Standing
- Appeals and Grievance Channels
- Glossary of Terms
Guidelines for Scheduling, Preparing for and Executing PhD Thesis Examinations
A. student responsibilities.
- By the proposed examination date, the student will have completed all coursework requirements for the degree.
- The online proforma indicating the proposed examination date as described below must be submitted at least six weeks in advance. Inadequate notice served for taking the thesis examination will result in postponement of the thesis examination.
- The examination should not be scheduled on a Sunday or public holiday in order to encourage the participation of members of the University community.
- Avoid scheduling a thesis examination toward the end of a term, in order to allow sufficient time for revisions and other post-examination arrangements to avoid unnecessary delay in graduation.
- Form submission. The student must submit an online proforma via the Thesis Examination System of the Student Information System (SIS), accessible via Student Intranet . The proforma must be submitted to supervisor(s) and Department for endorsement no less than six weeks before the proposed examination date.
- Thesis submission. Students are required to submit the thesis copies to the iThenticate platform for originality check. The iThenticate report together with sufficient hard or electronic thesis copies ready for examination purpose should be submitted to the Department no less than four weeks before the thesis examination. Students failing to deliver these copies before the submission deadline may be required to postpone the thesis examination.
B. Supervisor Responsibilities
- Patent protection. If the contents of the thesis involve commercially sensitive information, the thesis supervisor(s) is/are advised to approach the Office of Knowledge Transfer well in advance to discuss the possibility of obtaining patent protection before the Department announces the thesis examination to the public.
- Originality Check. As students are required to submit the thesis copies to the iThenticate platform for originality check, supervisors should advise students on whether it is appropriate to exclude bibliography and works cited including the students' own previously published papers from the checking.
C. Department/School Responsibilities
- Liaison with examiners to make arrangements for the thesis examination should not be done by the candidate being examined.
- Approval from FYTGS on the proposed membership of the TEC should be sought no less than four weeks before the proposed examination date.
- If a Chairperson or examiner declines the appointment to serve on the TEC, the School/Department is responsible for nominating a replacement Chairperson/examiner for the consideration of FYTGS as soon as possible. FYTGS may request the thesis examination to be postponed if the time allowed for the replacement Chairperson/examiner to review the student’s thesis prior to the thesis examination is considered insufficient.
- Receipt of thesis copies. The Department should confirm and record the actual date of receipt of the thesis copies in the Thesis Examination System.
- Chairperson and members of the PhD TEC, such that members are given sufficient time to review the thesis.
- A thesis copy will be made available at the Department for perusal by faculty, students, other University members, and members of the public.
- Announcements. After receipt of the thesis copies has been entered in the Thesis Examination System, announcements will be automatically posted on the Thesis Defense Calendar . Other forms of posting, such as emails and/or posters, should also be made as appropriate.
- TEC appointment. Upon approval of the TEC membership and students’ submission of the thesis copies for examination purpose, the Department will formally issue an appointment to the Chairperson and examiners of the TEC.
- Email reminder. At least one working day before the thesis examination is held, the Department is required to send an email reminder to members of the PhD TEC and relevant parties of the School/Department, specifying the TEC membership and details of the thesis examination.
D. FYTGS Responsibilities
After the Department Head/Program Director and the Dean or the Dean’s designee have endorsed the proposed membership of the TEC, the proforma will be forwarded to FYTGS for approval.
- If the proposed membership is in line with the guidelines, a confirmation email will be sent to the student, copying the thesis supervisor(s), the Department and the School, normally no less than four weeks before the examination date.
- If deviations from the University guidelines are identified, postponement or withdrawal of the thesis examination (regardless of whether the student has duly submitted the thesis or not) will be requested/required until the clearance and approval of FYTGS has been sought.
E. Safety Assessment
Upon receiving the proforma via the Thesis Examination System, the Health, Safety and Environment Office (HSEO) will conduct risk assessment. HSEO will notify the student if a safety check is required.
F. Changes to Approved Proforma
After the proforma has been approved, any changes initiated by the Department, student’s supervisor, or student must be approved by FYTGS before the changes can be effected.
G. Further Enquiries
All enquiries regarding the arrangements for scheduling PhD thesis examinations, should be submitted to the Department.
Biostatistics Graduate Program
Shengxin tu dissertation defense – may 10.
Posted by duthip1 on Friday, April 26, 2024 in News .
PhD candidate Shengxin Tu will defend her dissertation on Friday, May 10, at 8 a.m. Central Time, at 2525 West End Avenue, in the 11th floor large conference room (suite 1100, room 11105). Her advisor is Bryan Shepherd . All are invited and encouraged to attend.
Rank-Based Analyses and Designs with Clustered Data
Clustered data are common in biomedical research. It is often of interest to evaluate the correlations within clusters and between variables with clustered data. Conventional approaches, including intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Pearson correlations, are commonly used in analyses with clustered data. However, these conventional approaches are sensitive to extreme values and skewness. They also depend on the scale of the data and are not applicable to ordered categorical data. In this dissertation, we define population parameters for the rank ICC and between- and within-cluster Spearman rank correlations. These definitions are natural extensions of the conventional correlations to the rank scale. We show that the total Spearman rank correlation approximates a weighted sum of between- and within-cluster Spearman rank correlations, with weights determined by the rank ICCs of the two random variables. We also describe estimation and inference for these four rank-based correlations, conduct simulations to evaluate the performance of our estimators, and illustrate their use with real data examples. Furthermore, we apply the rank ICC in the design of clustered randomized controlled trials (RCTs), proposing unified and simple sample size calculations for cluster RCTs with skewed or ordinal outcomes. Our calculation involves inflating the sample size for an adequately powered individual RCT for an ordinal outcome with a design effect that incorporates the rank ICC. For continuous outcomes, our calculation sets the number of distinct ordinal levels to the sample size. We show that with continuous data, our calculations closely approximate more complicated sample size calculations based on clustered Wilcoxon rank-sum tests. We conduct simulations to evaluate our calculations’ performance and illustrate their use in the design of two cluster RCTs, one with a skewed continuous outcome and a non-inferiority trial with an irregularly distributed count outcome.

Tags: clustered data , dissertation defense , RCTs , sample size calculations
Leave a Response
You must be logged in to post a comment

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The following PhD timeline example describes the process and milestones of completing a PhD within 3 years. Contents. Elements to include in a 3-year PhD timeline. The example scenario: Completing a PhD in 3 years. Example: planning year 1 of a 3-year PhD. Example: Planning year 2 of a 3-year PhD. Example: Planning year 3 of a 3-year PhD.
Submit the finalized thesis. PhD Thesis: Graduation: Complete any remaining formalities. PhD Awarded: Free Gantt chart excel template. ... The key to a smooth and efficient doctoral journey lies in well-planned time management—a structured PhD timeline. This blog serves as an invaluable guide, offering detailed tips for planning out each ...
A typical PhD student schedule involves turning up to the Department between 8 AM and 9 PM, and performing research activities during the day such as reading, writing, analyzing and reporting on literature and experiments. ... will help you when you come to write your thesis or peer-reviewed paper. During a PhD there are often different writing ...
January 15 Schedule meeting with chair to evaluate timeline & progress February 1 Submit revised dissertation (complete) to entire committee March Incorporate final revisions to full dissertation based on committee's feedback March 18, Wednesday Final date for May Doctoral Candidates' oral dissertation defense
I had to rush to get this blog post done because my student is 2 years away from the deadline her university has imposed for her thesis defence, which is why I sat down with her last night to show her how I do things. I have two other PhD students at exactly the same stage (2 years to defense) so I figured I might as well finish this blog post.
Transfer of registration from MPhil to PhD (between 9-18 months, but as. early as reasonable). 24 months: Submission and assessment of second year progress report on research log. Agreement of thesis structure and strict timetable. for thesis writing . 30 months (not less than 4 months before expected date of submission
Rule 4: Make a PhD timetable. A PhD thesis can not be written in one week. Get this through your head. It is hard, maybe even the hardest thing you have to do during your PhD. It is going to be a painful task for most of you (it was for me). So schedule it in a proper time-wise manner. Do not wait until it's just two weeks before the deadline ...
In my department, theses must be no longer than 175 pages plus front matter and appendices. They can be written in either the so-called "traditional thesis format," which largely consists of a general introduction, a literature review, an overall description of the materials and methods, a presentation of all the results, and a general ...
Milestone 7: Once the external expert/s reviews and approves the value, logic, and results of the doctoral thesis, the doctoral office allows the PhD candidate to take the thesis defense as the next course. In this defense, PhD candidates must pass a 2.5-3-hour oral examination based on their thesis in front of the doctoral examination panel.
Conclusion. Following these three steps will help you draft a timeline to steer the course of your dissertation work: research and record all requirements and deadlines; work backward from your dissertation deadline and assemble your task lists; and organize your tasks into a timeline. Don't forget to include ample time for editing and ...
Late-January: Course registration deadline (previously known as "Study Card Day"). Mid-February: Deadline for submitting materials to be reviewed at the March CHD meetings. G1s: Your Prospective Program Plan due to the Office of Academic Programs on this day. Transfer of up to 3 classes of coursework may be allowed.
A dissertation timeline includes a series of milestones that leads up to the dissertation defense, revisions, and final submission of your dissertation. Constructing an outline of every step in the dissertation process, including rough estimates of how long each will take, will give you a realistic picture of where you are in the process at any ...
Depending on your schedule, this might be across a full week or a few days. ... but generally speaking you can expect between 25 and 30 days of annual leave if you're a full-time PhD student, in addition to public holidays. ... The PhD thesis is the most important part of a doctoral degree. This page will introduce you to what you need to ...
Next, explain the time duration. The time required to complete each goal, roughly. For example, a semester or a year to complete the course work or 4 to 8 months for completion of ethical approval. Now two things must be known to you, at this point in time. First, enlist the time required to complete each objective, as aforementioned.
With apologies for the attention-grabbing title: of course I am not actually asking you to tell me when I, specifically, should schedule my defense. But I have heard very plausible-sounding rumors that the time of day at which a PhD candidate holds their thesis defense can have an impact on the difficulty and even the candidate's chance of passing.
Year 1: September - April. Attend UBC Graduate Student Orientation in late August. Confirm your RES course requirements and course schedule with your supervisor (s). You have until the second week of term to add/drop courses most courses. Begin your courses and attend the IRES Orientation/Welcome Back BBQ during the first Sept!
Manually creating a PhD timeline Gantt chart in PowerPoint is a bit easier than in Excel. Therefore, I will explain the process here. First, you need to open a blank PowerPoint slide. Then click on Insert (1.), then Chart (2.). A popup will appear.
How I Made My PhD Completion Plan on Excel (With Template) For the last few weeks, I've been working on my PhD completion plan. It's basically an excel spreadsheet that I'm using to track my progress and plan my time for the remainder of my PhD. My thesis is due August of next year (with a 6 month extension) so the clock is definitely ticking.
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small, the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program, said, "It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses.
Gather data and information for your study. Analyze your data. Write, write, and write some more. Ideally, aim to write for a minimum of 30 minutes a day. Defend your thesis. Finish. Completing your PhD paper on time is definitely possible. Knowing the tips and tricks of the trade can help you to get on your way towards a life in academia.
A successful PhD journey begins with a solid plan that includes a PhD timeline. A thought-through and well-designed PhD timeline requires some time but can be accomplished in a few simple steps. Contents Why a clear PhD research timeline mattersStep 1: Decide what to include in your PhD timelineStep 2: Discuss your provisional PhD timeline
Thesis distribution. The Department should immediately distribute the thesis copies and the iThenticate report to the following and record the actual dispatch date in the Thesis Examination System: Chairperson and members of the PhD TEC, such that members are given sufficient time to review the thesis.
writing of the thesis This is an example how a time and work plan can be designed. Of course, every work plan is individual. Also, the number and type of courses that are attended is just an example. It is the purpose of a time and work plan to be reviewed and adapted during the doctoral project. Example 1 (work and time schedule):
Shengxin Tu dissertation defense - May 10. Posted by duthip1 on Friday, April 26, 2024 in News.. PhD candidate Shengxin Tu will defend her dissertation on Friday, May 10, at 8 a.m. Central Time, at 2525 West End Avenue, in the 11th floor large conference room (suite 1100, room 11105). Her advisor is Bryan Shepherd.All are invited and encouraged to attend.
Pre-Fall & Fall 2024 course registration begins Wednesday, May 1, 2024 via Banner.