Communication
A collection of TED Talks (and more) on the topic of Communication.

Video playlists about Communication

The most popular TED Talks of 2022

The most popular TED Talks of 2021

Why do we tell stories?

The art of finding common ground
Talks about communication.

How to be an active citizen and spark change

A Palestinian and an Israeli, face to face

3 strategies to address the teacher shortage crisis

Ideas change everything — and what's next for TED

How to spot a cult

A comedian's take on how to save democracy

3 steps to better connect with your fellow humans

How to bridge political divides — from two friends on opposing sides

What makes someone vote against their political party?

How AI will help us connect with ourselves and each other

The magical AI assistants of the future — and the engineering behind them

How advanced is whale talk?

The unifying power of grace

True love — and the myth of "happily ever after"

How comedy helps us deal with hard truths

How to make learning as addictive as social media
Exclusive articles about communication, this writer analyzed 100 graduation speeches — here are the 4 tips they all share, 4 ways to make people feel valued at work, even when you’re not all together, kicking yourself for not saying something at a meeting here’s how to speak up skillfully.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Top Tips for Effective Presentations
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
How can you make a good presentation even more effective?
This page draws on published advice from expert presenters around the world, which will help to take your presentations from merely ‘good’ to ‘great’.
By bringing together advice from a wide range of people, the aim is to cover a whole range of areas.
Whether you are an experienced presenter, or just starting out, there should be ideas here to help you to improve.
1. Show your Passion and Connect with your Audience
It’s hard to be relaxed and be yourself when you’re nervous.
But time and again, the great presenters say that the most important thing is to connect with your audience, and the best way to do that is to let your passion for the subject shine through.
Be honest with the audience about what is important to you and why it matters.
Be enthusiastic and honest, and the audience will respond.
2. Focus on your Audience’s Needs
Your presentation needs to be built around what your audience is going to get out of the presentation.
As you prepare the presentation, you always need to bear in mind what the audience needs and wants to know, not what you can tell them.
While you’re giving the presentation, you also need to remain focused on your audience’s response, and react to that.
You need to make it easy for your audience to understand and respond.
3. Keep it Simple: Concentrate on your Core Message
When planning your presentation, you should always keep in mind the question:
What is the key message (or three key points) for my audience to take away?
You should be able to communicate that key message very briefly.
Some experts recommend a 30-second ‘elevator summary’, others that you can write it on the back of a business card, or say it in no more than 15 words.
Whichever rule you choose, the important thing is to keep your core message focused and brief.
And if what you are planning to say doesn’t contribute to that core message, don’t say it.
4. Smile and Make Eye Contact with your Audience
This sounds very easy, but a surprisingly large number of presenters fail to do it.
If you smile and make eye contact, you are building rapport , which helps the audience to connect with you and your subject. It also helps you to feel less nervous, because you are talking to individuals, not to a great mass of unknown people.
To help you with this, make sure that you don’t turn down all the lights so that only the slide screen is visible. Your audience needs to see you as well as your slides.
5. Start Strongly
The beginning of your presentation is crucial. You need to grab your audience’s attention and hold it.
They will give you a few minutes’ grace in which to entertain them, before they start to switch off if you’re dull. So don’t waste that on explaining who you are. Start by entertaining them.
Try a story (see tip 7 below), or an attention-grabbing (but useful) image on a slide.
6. Remember the 10-20-30 Rule for Slideshows
This is a tip from Guy Kawasaki of Apple. He suggests that slideshows should:
- Contain no more than 10 slides;
- Last no more than 20 minutes; and
- Use a font size of no less than 30 point.
This last is particularly important as it stops you trying to put too much information on any one slide. This whole approach avoids the dreaded ‘Death by PowerPoint’.
As a general rule, slides should be the sideshow to you, the presenter. A good set of slides should be no use without the presenter, and they should definitely contain less, rather than more, information, expressed simply.
If you need to provide more information, create a bespoke handout and give it out after your presentation.
7. Tell Stories
Human beings are programmed to respond to stories.
Stories help us to pay attention, and also to remember things. If you can use stories in your presentation, your audience is more likely to engage and to remember your points afterwards. It is a good idea to start with a story, but there is a wider point too: you need your presentation to act like a story.
Think about what story you are trying to tell your audience, and create your presentation to tell it.
Finding The Story Behind Your Presentation
To effectively tell a story, focus on using at least one of the two most basic storytelling mechanics in your presentation:
Focusing On Characters – People have stories; things, data, and objects do not. So ask yourself “who” is directly involved in your topic that you can use as the focal point of your story.
For example, instead of talking about cars (your company’s products), you could focus on specific characters like:
- The drivers the car is intended for – people looking for speed and adventure
- The engineers who went out of their way to design the most cost-effective car imaginable
A Changing Dynamic – A story needs something to change along the way. So ask yourself “What is not as it should be?” and answer with what you are going to do about it (or what you did about it).
For example…
- Did hazardous road conditions inspire you to build a rugged, all-terrain jeep that any family could afford?
- Did a complicated and confusing food labelling system lead you to establish a colour-coded nutritional index so that anybody could easily understand it?
To see 15 more actionable storytelling tips, see Nuts & Bolts Speed Training’s post on Storytelling Tips .
8. Use your Voice Effectively
The spoken word is actually a pretty inefficient means of communication, because it uses only one of your audience’s five senses. That’s why presenters tend to use visual aids, too. But you can help to make the spoken word better by using your voice effectively.
Varying the speed at which you talk, and emphasising changes in pitch and tone all help to make your voice more interesting and hold your audience’s attention.
For more about this, see our page on Effective Speaking .
9. Use your Body Too
It has been estimated that more than three quarters of communication is non-verbal.
That means that as well as your tone of voice, your body language is crucial to getting your message across. Make sure that you are giving the right messages: body language to avoid includes crossed arms, hands held behind your back or in your pockets, and pacing the stage.
Make your gestures open and confident, and move naturally around the stage, and among the audience too, if possible.
10. Relax, Breathe and Enjoy
If you find presenting difficult, it can be hard to be calm and relaxed about doing it.
One option is to start by concentrating on your breathing. Slow it down, and make sure that you’re breathing fully. Make sure that you continue to pause for breath occasionally during your presentation too.
For more ideas, see our page on Coping with Presentation Nerves .
If you can bring yourself to relax, you will almost certainly present better. If you can actually start to enjoy yourself, your audience will respond to that, and engage better. Your presentations will improve exponentially, and so will your confidence. It’s well worth a try.
Improve your Presentation Skills
Follow our guide to boost your presentation skills learning about preparation, delivery, questions and all other aspects of giving effective presentations.
Start with: What is a Presentation?
Continue to: How to Give a Speech Self Presentation
See also: Five Ways You Can Do Visual Marketing on a Budget Can Presentation Science Improve Your Presentation? Typography – It’s All About the Message in Your Slides
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

suicide prevention
8 templates

computer network
75 templates

spring season
28 templates

cybersecurity
6 templates

46 templates

18 templates
Communication Skills Training Workshop
Communication skills training workshop presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Communication Skills Training Workshops are perfect for individuals or groups who want to gain the knowledge and practice necessary to become better communicators. Here, attendees can learn about topics ranging from active listening to body language for effective communication. The workshops typically offer tips, activities, and other opportunities to practise these skills in a comfortable and supportive environment. Not only do participants learn important concepts of communication; they also get real-world experience putting them into practise as well. Learning better communication skills can be easy if you use creative templates like this one, full of editable, visual resources that will captivate your students
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 30 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Available in different formats
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online

Group Presentations
46 How to structure your presentation
Lucinda Atwood and Christian Westin
This chapter teaches you a quick, easy way to create effective presentations. You’ll also learn how to use valid resources and avoid plagiarism.
There are lots of ways to structure a presentation, but we like this one best. It’s clear, simple and fits most presentations.
In this part of your presentation, you’ll capture the audience’s attention, tell them who you are, and give them a preview of your presentation.
- Grabber/hook (Goes before or after the self-introduction) A very brief and interesting statement or question that grabs the audience’s attention. See Grabber Types below for more details.
- Self-introduction (Goes before or after the grabber ) Tell the audience your name and credentials. For example: I’m Minh and I’ve been a professional presenter for 10 years.
- Thesis The main point or argument of your presentation. Be brief and precise, not general or vague. For example: I’m going to show you how practicing your presentation 10 times will improve your grade by 20%.
- Overview of main points Briefly outline the main points that you’ll cover in your presentation. To help your audience, do list these in same order that you’ll deliver them later on. For example: First, we’ll talk about what makes presentations great, then I’ll share some data on how practice affects your confidence and performance, and finally we’ll look at how to practice.
In this part of your presentation, you’ll deliver the detailed information of your presentation.
- Key point 1 A major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
- Key point 2 Another major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
- Key point 3 The final major point that supports your thesis and may have supporting sub-points
In this part you’ll remind the audience of what you told them, and tell them what to do next.
- Summary of main points (Can be merged with your conclusion) Clearly restate your three main points in the same order you delivered them. It’s the same as your overview but in past tense. First, I described what makes presentations great, then I shared data on how practice affects confidence and performance, and finally we looked at how to practice.
- Conclusion Restate your thesis in past tense. For example: I’m showed you that practicing your presentation 10 times will improve your grade by 20%.
- Call to action Give your audience clear, active and compelling direction, based on what you told them. For example: Practice your presentations ten times and start collecting those A-plusses!
Grabber types
Remember that the grabber’s job is grabbing the audience’s attention, so it must be surprising, fascinating or intriguing. It must also be related to your presentation’s topic. Here are some descriptions and examples:
You can also mix and match grabbers. For example, you could show an image and ask the audience to guess what it is.
The length of your grabber is relative to your total presentation time. For a 2-minute presentation, it should be quite brief – maybe one sentence. For a 16-minute team presentation, a 45-60 second grabber would be appropriate.
Outline your presentation
The fastest way to create a successful presentation is to start with an outline. Y ou’ll need two outlines: a preparation outline, and a speaking outline.
Preparation outlines are comprehensive outlines that include all of the information in your presentation. Our presentation outline will consist of the content of what the audience will see and hear. Eventually, you will move away from this outline as you develop your materials and practice your presentation.
Your speaking outline will contain notes to guide you and is usually not shared with your audience. It will summarize the full preparation outline down to more usable notes. You should create a set of abbreviated notes for the actual delivery.
Use an outline, not a script; this will allow you to be more natural and let you look at the audience or camera. Reading is a guaranteed way to make your presentation boring.
The easiest way to create your outline is to work in this order:
- Determine your thesis and write this as a full sentence
- Determine your 3 Main Points
- Add key supporting points for each of your Main Points
- Complete the other parts – introduction, grabber, call to action, etc.
Working in this order is fast because it’s easier to create the conclusion and grabber when you’ve already decided on the content. Also, after you have the main structure it’s easy to add details, examples, and stories that make your presentation interesting and convincing.
You can use your presentation outline as a starting point to developing your speaking outline. It’s a good idea to make speaking notes to align with your main points and visuals in each section.
UNC Libraries Presentation Planning Worksheet
Using Examples and Scenarios
Presenters will often use examples and scenarios to help illustrate the their message. The main difference between examples and scenarios is that while both help “show” the audience what you mean, an example is the “thing” itself, while a scenario would include more detail about the sequence or development of events. Scenarios also tend to be longer and more nuanced.
An ‘example’ of a sales target might be: to sell 500 units in 30 days. A ‘scenario’ might be described as: Company A is selling vacuums to the Atlantic Canada region. They are trying to increase their sales, and so have set a target of 500 units in the region in 30 days, using a sales incentive program for employees and promoting a sale at local stores.
A Word About Storytelling
Storytelling can be an effective way to convey your message to your audience. Stories are a fundamental part of the human experience, and, if well-told, can resonate with listeners. Some of the most inspiring TEDTalks speakers use storytelling effectively in their presentations. You can find out more about how to incorporate storytelling techniques into presentations from the TEDTAlk speakers directly.

Read the following blog post from Nayomi Chibana (2015).
http://blog.visme.co/7-storytelling-techniques-used-by-the-most-inspiring-ted-presenters/
Test your knowledge
How to structure your presentation Copyright © by Lucinda Atwood and Christian Westin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
10 Simple Tips for a Great Presentation
January 10, 2022 - Dom Barnard
The way you speak to someone in private is not the same as addressing an audience during a presentation. Not least as that presentation may involve a diverse range of people, with differing interests and attention spans.
Nerves may take over, or at the very least you may realise that not everyone is listening, understanding or agreeing, and you need to work harder to engage them.
Elsewhere in our resources for effective business communications, we have stressed how important it is to either speak or write in a purposeful way. To be clear on your goals, whether that’s to inform, educate, seek approval/opinions, persuade, influence or sell. Communications can often have a mixture of those aims.
The only way to be purposeful and successful in presentations is to invest in the necessary communication skills. However, in this article, we list 10 simple tips for delivering a confident presentation, that achieves results.
1. See yourself as others see you. Hear yourself as others hear you
Visual elements of your presentation are crucial. Humans use visual references to process immeasurable amounts of information. We can reach opinions about a situation or person with a glance.
That makes it essential to focus on non-verbal communication.
To gain immediate credibility with your audience, think carefully about such factors as:
- Is your body language positive ?
- Are your presentation slides clear ?
- Are you dressed appropriately for the situation?
What does positive body language look like? It’s things such as smiling and standing or sitting straight, with your arms resting on a lectern, table or by your side. Lean slightly forward and use as much eye contact as possible. No slouching, hands in pockets, crossed arms, or constantly looking down!
Also, consider how you sound to the audience:
- Do you need to speak louder because the room is large?
- Are the audience native English speakers?
- Are you talking quickly because you are nervous?
- Are you amplifying your breathing and mouth noises by being too close to the microphone?
2. Know your objectives
There’s a widely accepted principle of presentations:
- Tell them what you are going to say
- Remind them what you just said
This is an oversimplification. However, it indicates how important it is to be 100% clear on what response you want from your audience and to communicate your desired outcome brilliantly.
If your presentation has no core purpose or ‘call to action’, it’s just a random string of words. Think about:
- What would a positive outcome be for you?
- Are you looking for new clients or funding?
- What message do you want your audience to take away with them?
Much depends on the nature of your audience of course. Take time to consider who you are talking to. Think about what is most likely to influence their behaviour and decision-making, and whether that are facts, figures or even words and phrases that support your presentation objective.
Also, to get the best results from presentations, consider what your audience will need to know about you. What expertise and insights should you mention, adding weight to your credibility?

3. Have an overall picture in mind before starting on details
Once you have focused on your audience and the purpose of your presentation, the planning continues. That’s because successful presentations rely on extensive preparation.
Planning would need to include the nuts-and-bolts aspects of this task, such as:
- How long does the presentation need to be?
- What is the audience size and demographic?
- The audience size and demographic
- Are you part of a panel, solo or some other format?
- Is there a Question and Answer session at the end?
- Would it be better to have questions throughout?
- What technology will you need?
4. Work out the framework for your presentation
That doesn’t mean hammering away on your keyboard and wildly jotting down everything you want to say though. The best presentations are succinct, well structured and hold the audience’s attention by design (more on this below).
You could start by considering factors such as:
- What three things do you want your audience to remember?
- How can you design your presentation around these points?
- How can you explain these points in the introduction and conclusion
- Should you cover the three points together or in a logical order?
5. Lead the audience along with you
You need to make sure your audience is engaged throughout your presentation. You are talking to them, not over or around them. The central pillar of this is effective presentation content that speaks directly to them , and which is varied and interesting.
Keep facts, figures and technical jargon to a minimum, and explain it (never assume they understand). Weave in storytelling techniques , anecdotes, audience questions and pauses to ‘punctuate’ your presentation.
Visual aids are a superb way to hold attention during presentations and can add to your confidence and flow. When used correctly!
They should not contain a massive amount of detail, especially information that expands on what you are saying. If your audience is trying to read and understand your media content or handouts, they are not listening to you.
You can use presentation folders or follow-up emails and website links to add more information. For now, use slides/handouts to structure your content and move your audience from topic to topic.
Or, to reinforce especially important messages.
Breaking up the presentation into a small number of sections – with the current section stated on each slide – helps you to stay focused too.
The following tips will help:
- Whether to include a table of contents to help the audience follow along?
- Breaking up the presentation into a small number of sections, with the current section stated on each slide
- After each section, show which sections have been completed and which are coming up
- How much time will you leave for questions? Will you allow questions throughout the presentation or only at the end?
6. Rehearse aloud and get feedback
Practice is the key to a great presentation.
If possible, rehearse with a colleague or friend. This can be in person, using video conferencing simulator or online meeting tools. Ask them for honest feedback.
- Practice Exercises for Presentations
At the very least, record yourself using your preferred technology, so you can play it back and look for ways to improve your presentation skills.
When you practice, avoid distractions that could throw you off, and do it as realistically as possible, including any time constraints.
Things to look for include:
- Content that is complex and trips you up. Can you simply it?
- Places where you ad-lib too much and go off track
- Lack of clarity on your purpose and call to action
- Visual materials that don’t synch with your spoken content
- Physical habits that can be distracting, such as rocking, touching your face or filling hesitations with errs and umms
7. Win hearts then minds
The reason that eye contact is important in presentations is that it creates a vital connection between you and your audience. This is also reinforced by asking rhetorical questions, pausing to look around, smiling when appropriate and adding the human touch to your content.
This links to the contemporary emphasis on emotional intelligence – showing understanding and empathy, staying calm and positive and managing your own reactions. Both your verbal and non-verbal communications should be warm, responsive and sincere.
This includes valued gestures in the art of presentations. Such as:
- Greeting your audience and introducing yourself with humility.
- Thanking them for their attention.
- Making yourself available for questions or post-presentation discussions.
- Using your hands in a controlled way for non-verbal communications.
- If you are standing, move around the stage to engage all areas of the presentation space.
It also means that you should be polite when answering audience questions, no matter how hostile they are.

8. Keep it simple
When drafting and practising a successful presentation, put yourself in the audience! This connects to the empathy mentioned above, and the need to choose impactful content to create the right outcome. If you were listening to this presentation, would you be engaged and informed?
No matter how complex your presentation is, use words and analogies everyone in the audience will understand.
Keep to the following:
- Clarity of narrative with an easy-to-understand presentation structure
- No (or few) acronyms or technical terms if possible
- Explain your visual aids, especially diagrams and graphs
However, keep an eye on your audience too. Do they look like they are losing attention or getting confused? You may need to go back over something, or even ask for a show of hands to indicate something that needs additional explanation.
Try to read body language without losing the thread of your presentation. This is especially relevant if you are addressing smaller groups, and you can see a decision-maker slumping, checking the time or looking blank. You may need to address a question directly to them or highlight something that draws their attention back.
9. Be enthusiastic
If you’re not interested in your own speech, why should the audience be?
It’s particularly important to start and end with a flourish. So, make sure when you prepare that you really focus on your introduction and conclusion, finishing with a strong call to action.
Also, modulate your tone and emphasis regularly. A monotone voice can send an audience to sleep even when the content is outstanding!
Sustain energy throughout the speech, but don’t race through your presentation. Pauses help you keep on track, boost audience attention and make the flow more natural.
10. Be yourself
That may seem like a long list of ways to make presentations more successful and productive.
However, it can all be summed up by doing as much preparation and planning as possible, so you feel confident and relaxed.
Especially focusing on:
- Where you are
- What you are doing
- Why you are saying what you are saying
- Why the audience needs to hear what you are saying
If you follow these simple tips for a great presentation, you should be able to deliver your spoken communication in a responsive and effective way.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Great Leaders Communicate
- Carmine Gallo

Four strategies to motivate and inspire your team.
Transformational leaders are exceptional communicators. In this piece, the author outlines four communication strategies to help motivate and inspire your team: 1) Use short words to talk about hard things. 2) Choose sticky metaphors to reinforce key concepts. 3) Humanize data to create value. 4). Make mission your mantra to align teams.
In the age of knowledge, ideas are the foundation of success in almost every field. You can have the greatest idea in the world, but if you can’t persuade anyone else to follow your vision, your influence and impact will be greatly diminished. And that’s why communication is no longer considered a “soft skill” among the world’s top business leaders. Leaders who reach the top do not simply pay lip service to the importance of effective communication. Instead, they study the art in all its forms — writing, speaking, presenting — and constantly strive to improve on those skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Powerful and Effective Presentation Skills: More in Demand Now Than Ever

When we talk with our L&D colleagues from around the globe, we often hear that presentation skills training is one of the top opportunities they’re looking to provide their learners. And this holds true whether their learners are individual contributors, people managers, or senior leaders. This is not surprising.
Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way.
For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget, or explain a new product to a client or prospect. Or you may want to build support for a new idea, bring a new employee into the fold, or even just present your achievements to your manager during your performance review.
And now, with so many employees working from home or in hybrid mode, and business travel in decline, there’s a growing need to find new ways to make effective presentations when the audience may be fully virtual or a combination of in person and remote attendees.
Whether you’re making a standup presentation to a large live audience, or a sit-down one-on-one, whether you’re delivering your presentation face to face or virtually, solid presentation skills matter.
Even the most seasoned and accomplished presenters may need to fine-tune or update their skills. Expectations have changed over the last decade or so. Yesterday’s PowerPoint which primarily relied on bulleted points, broken up by the occasional clip-art image, won’t cut it with today’s audience.
The digital revolution has revolutionized the way people want to receive information. People expect presentations that are more visually interesting. They expect to see data, metrics that support assertions. And now, with so many previously in-person meetings occurring virtually, there’s an entirely new level of technical preparedness required.
The leadership development tools and the individual learning opportunities you’re providing should include presentation skills training that covers both the evergreen fundamentals and the up-to-date capabilities that can make or break a presentation.
So, just what should be included in solid presentation skills training? Here’s what I think.
The fundamentals will always apply When it comes to making a powerful and effective presentation, the fundamentals will always apply. You need to understand your objective. Is it strictly to convey information, so that your audience’s knowledge is increased? Is it to persuade your audience to take some action? Is it to convince people to support your idea? Once you understand what your objective is, you need to define your central message. There may be a lot of things you want to share with your audience during your presentation, but find – and stick with – the core, the most important point you want them to walk away with. And make sure that your message is clear and compelling.
You also need to tailor your presentation to your audience. Who are they and what might they be expecting? Say you’re giving a product pitch to a client. A technical team may be interested in a lot of nitty-gritty product detail. The business side will no doubt be more interested in what returns they can expect on their investment.
Another consideration is the setting: is this a formal presentation to a large audience with questions reserved for the end, or a presentation in a smaller setting where there’s the possibility for conversation throughout? Is your presentation virtual or in-person? To be delivered individually or as a group? What time of the day will you be speaking? Will there be others speaking before you and might that impact how your message will be received?
Once these fundamentals are established, you’re in building mode. What are the specific points you want to share that will help you best meet your objective and get across your core message? Now figure out how to convey those points in the clearest, most straightforward, and succinct way. This doesn’t mean that your presentation has to be a series of clipped bullet points. No one wants to sit through a presentation in which the presenter reads through what’s on the slide. You can get your points across using stories, fact, diagrams, videos, props, and other types of media.
Visual design matters While you don’t want to clutter up your presentation with too many visual elements that don’t serve your objective and can be distracting, using a variety of visual formats to convey your core message will make your presentation more memorable than slides filled with text. A couple of tips: avoid images that are cliched and overdone. Be careful not to mix up too many different types of images. If you’re using photos, stick with photos. If you’re using drawn images, keep the style consistent. When data are presented, stay consistent with colors and fonts from one type of chart to the next. Keep things clear and simple, using data to support key points without overwhelming your audience with too much information. And don’t assume that your audience is composed of statisticians (unless, of course, it is).
When presenting qualitative data, brief videos provide a way to engage your audience and create emotional connection and impact. Word clouds are another way to get qualitative data across.
Practice makes perfect You’ve pulled together a perfect presentation. But it likely won’t be perfect unless it’s well delivered. So don’t forget to practice your presentation ahead of time. Pro tip: record yourself as you practice out loud. This will force you to think through what you’re going to say for each element of your presentation. And watching your recording will help you identify your mistakes—such as fidgeting, using too many fillers (such as “umm,” or “like”), or speaking too fast.
A key element of your preparation should involve anticipating any technical difficulties. If you’ve embedded videos, make sure they work. If you’re presenting virtually, make sure that the lighting is good, and that your speaker and camera are working. Whether presenting in person or virtually, get there early enough to work out any technical glitches before your presentation is scheduled to begin. Few things are a bigger audience turn-off than sitting there watching the presenter struggle with the delivery mechanisms!
Finally, be kind to yourself. Despite thorough preparation and practice, sometimes, things go wrong, and you need to recover in the moment, adapt, and carry on. It’s unlikely that you’ll have caused any lasting damage and the important thing is to learn from your experience, so your next presentation is stronger.
How are you providing presentation skills training for your learners?
Manika Gandhi is Senior Learning Design Manager at Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
- Back to All Programs /
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Gain skills and techniques to engage, inform and inspire others, improving your ability to communicate as a leader.
All Start Dates
8:30 AM – 4:30 PM ET
2 consecutive days
Registration Deadline
June 30, 2024
November 24, 2024
Communication Strategies Program Overview
Communication strategies: presenting with impact, a public speaking course.
Public speaking—whether delivering a presentation, making a pitch, or leading a group discussion—can cause even the most confident leader to break a sweat. Yet communicating your message with poise, confidence, and conviction is an essential leadership skill. Mastering your public speaking and presentation skills will enable you to inspire your audience as well as build trust and credibility.
Through oral presentations and small group activities, you will put proven public speaking techniques and tools into practice, test out new approaches, and learn to communicate clearly and confidently. Discover the powerful impact of storytelling and practical persuasion skills to authentically illustrate your message. Learn how to effectively organize materials to blend analytical and emotional content into a compelling story, and incorporate dynamic introductions and memorable endings into your presentations.
Who Should Register for this Public Speaking Course
This communication program is appropriate for business professionals at all levels of experience who would like to enhance their communication skills to succeed in delivering impactful presentations. It is ideal for anyone in a role that requires ceremonial speaking, persuasive speaking, or any other type of public speaking, regardless of industry or years of experience.
All participants will earn a Certificate of Participation from the Harvard Division of Continuing Education
Participants must be fluent in English to participate fully in fast-moving discussions and exercises.
Benefits of Communication Strategies: Presenting With Impact
This communication strategies program is designed to offer new techniques to improve your public speaking skills. Key takeaways from the program will help you improve your ability to persuade and influence your audience in large- and small-group settings.
During this public speaking training course, you will:
- Learn guiding principles of making effective presentations
- Build confidence in your presentation abilities
- Cultivate your personal leadership and communication style
- Learn strategies on handling hostile audiences
“Jill [Slye] shared invaluable tips that have helped me to reduce my anxiety and negative self-talk around my presentations while conveying a message that encourages others to affect change through empowering presentations.” — Lizbeth Sanches-Acre
The curriculum for this communication strategies program is designed to be interactive and hands-on. You will practice the skills and techniques you are learning in real-time through small group activities and oral presentations during the program.
The curriculum will cover topics such as:
- Effective delivery skills involving presence, vocal variety, body language, narratives and humor, and handling nerves
- Crafting clear and concise messages
- Understanding and connecting with your audience
- Techniques for effective handling of Q&A sessions
- Ways to gain buy-in and influence your audience
- Strategies for online communications, webinars, podcasts, Zoom platforms, etc.
This public speaking course is offered as a two-day on-campus program in our state-of-the-art classroom space in the heart of historic Harvard University. Program tuition is $2,990 plus the cost of travel.
Considering this program?
Send yourself the details.
Related Programs
- Effective Organizational Communication
- Influence and Persuasion in Leadership
- Becoming a Leader: Developing Your Style and Making Sound Decisions
July Schedule
- Communication Overview
- Honing Your Personal Communication Style
- Developing Audience Centered Content
- Presentations
- Strategies for Online Communications
- Leadership Communication Model
December Schedule
Jill abruzese slye, certificates of leadership excellence.
The Certificates of Leadership Excellence (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills.
This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get started earning your certificate.
How will this program help me improve my public speaking skills?
This program will help you improve your public speaking skills through hands-on practice of communication techniques and new approaches. As part of the program, you will engage in group exercises and oral presentations where you will receive feedback from the instructor and your peers to help you improve your skills in real time.
How will improving public speaking help me advance my career?
Public speaking is an important skill for any business professional, regardless of industry or role. To advance your career, you must possess the ability to convey your message with clarity and lead group discussions with confidence, regardless of the specific situation. Developing the techniques and strategies to communicate effectively will help build trust in your leadership skills more broadly.
What skills or experience is needed before enrolling in this program?
Participants do not need any specific experience or skills to enroll in this program. It is open to any business professional interested in improving their public speaking skills and their ability to communicate effectively and persuasively.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Oral Presentations
Presentation basics, key elements of good presentations.
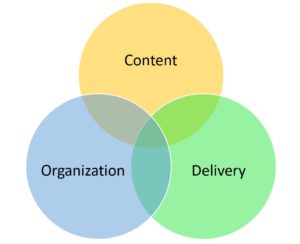
There are three key elements of good presentations: Content, Organization, Delivery. Your audience needs interesting and appropriate content in order to pay attention, especially at the start of a presentation. Logical organization helps retain your audience’s attention – they need to be able to follow your train of thought and predict where you are going with your ideas. Delivery also is important, as your own engagement with the information helps your audience engage.
Content deals with the substance of your presentation. Your ideas and information should be original and significant. Use accepted and relevant sources in your research, and reference those sources as needed. Offer a clear analysis that’s comprehensive and concise at the same time – strive for the right amount of information for your audience’s needs and the allotted presentation time. Make sure that your content is relevant to your audience, so that they understand immediately why they should pay attention to your presentation.
Garr Reynolds, in his book Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery , identifies characteristics of presentation content that create what he calls SUCCES(s): [1]
- Simplicity – reduce information to key points and essential meanings
- Unexpectedness – pose questions, offer interesting statistics, “make the audience aware that they have a gap in their knowledge and then fill that gap”
- Concreteness – use specific language, provide real-life examples
- Credibility – use sources, facts, statistics to back up your content; deliver information confidently; know your information well
- Emotions – engage your audience to feel something about your content
- Stories – use examples and illustrations to create a “story element” to the presentation
Finally, to make your content effective, repeat key information throughout your presentation. A memory research pioneer, German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, found that we forget approximately 50 percent of new information within 18 minutes, with retention falling to 35 percent after a week. However, Ebbinghaus also discovered that repetition of the new information at key intervals can change this trajectory, a discovery known as the spacing effect. The lesson for presenters: work repetition into your presentation content.
Organization
Good organization requires a clear beginning, middle, and end. Link your ideas logically throughout the presentation to lead to an ending that resolves the problem or summarizes the situation you presented at the start. If you’re presenting based on a formal report or proposal, you may want to follow the order of the longer written document, but you don’t have to; as long as you include main ideas, it’s up to you to determine your presentation’s organization based on your audience and purpose. Strive for clear transitions between individual points, slides, and topics.

Delivery involves a range of factors from body language and word choice to vocal variety. A good presenter has a passion for the subject and an ability to convey and perhaps elicit that emotion in the audience. Audience engagement through eye contact, facial expression, gestures, and/or vocal tone contributes to an effective presentation. Delivery also deals with the confidence and professionalism with which you deliver the presentation. Hesitations, “ums,” and other types of vocal fumbling will distract your audience, while a clear, confident presentation helps to engage them.
Content, organization, and delivery work together and are equally important aspects of presentations.
The following two videos provide basic tips for creating effective presentations in terms of content, organization, and delivery. As you view them, consider their similarity of information and dissimilarity in presentation style. What can you infer about the presenter and intended audience of each presentation? Which video resonates more fully with you personally, and why? In terms of conveying information to a general audience, which video do you think is most effective, and why?
Planning Presentations
As you can see based on the video examples, presentations always require a situational analysis in the planning stage. Identify your audience, purpose, context, and all of the communication variables that you need to consider in order to make choices that will result in an effective presentation for your purpose and audience. For example, your purpose – the one, main idea that you want to convey through your presentation – can influence your content, organization, delivery, and overall approach. Identifying your audience can help you with what may be the most critical aspect of your presentation, making your information relevant to your audience. Analyzing communication variables for your presentation also will help you determine if you need supplemental materials or handouts, how to arrange a room for an in-person presentation, how best to structure a virtual presentation, and more.
Even if you are creating a presentation based on a formal report or proposal for which you have already done a situational analysis, do another situational analysis for your presentation, as your audience, organization, language, and overall approach may differ based on the different communication mode.
Planning Online Presentations
In addition to doing a situational analysis, online presentations may require some additional planning time in terms of how you present information. A real-time, in-person audience may pay attention to your presentation simply because you are present, and you may be able to adapt your presentation to audience reaction. However, it’s more difficult to capture the attention of a virtual audience, either real-time or asynchronous, so online presentations need to be thought through very deliberately in terms of their content, organization, look, and approach.
The following video, while written for online instructors, nonetheless offers important points to consider for any type of virtual, online presentation.
Understanding Presentation Audiences
Audiences are egocentric, meaning that they operate under the principle of WIIFM: what’s in it for them. Don’t expect your audience to meet you where you are; meet them where they are and then take them where you want to go together. According to Lucas, audiences “pay closest attention to messages that affect their own values, beliefs, and well being. Listeners approach speeches with one question uppermost in mind: ‘Why is this important to me?’ … What do these psychological principles mean to you as a speaker? First, they mean that your listeners will hear and judge what you say on the basis of what they already know and believe. Second, they mean you must relate your message to your listeners–show how it pertains to them, explain why they should care about it as much as you do.” [2]
Also, audiences have relatively short attention spans, and often decide whether or not to give you their attention within the first minute or so of a presentation. Various research studies indicate a five – twenty minute attention span for any type of presentation (note that results of studies vary). An article titled “ Neuroscience Proves You Should Follow TED’s 18-Minute Rule to Win Your Pitch ” discusses the concept of “cognitve backlog,” or the idea that the more information you provide, the more information your audience will tune out and not remember. [3]

These audience characteristics lay the groundwork for presentation strategies identified in the videos, strategies such as starting with and continuing a story, engaging attention with an interesting statistic, and more. The point to remember is that you need to make conscious, reasoned decisions about ways to engage your audience. Keeping audience attention span and egocentrism in mind, strive for the following presentation basics:
- Conciseness
- Connection with audience
Expectations for Presentations
The 10/20/30 rule, generally attributed to venture capitalist Guy Kawasaki, is a good guideline to help you achieve a “just right” balance in your presentations. Geared for entrepreneurs pitching their business, his advice is a discipline that would improve the quality—and, effectiveness—of most presentations. In brief, 10/20/30 translates to a maximum of 10 slides, a maximum of 20 minutes and a minimum of 30 point font. [4]
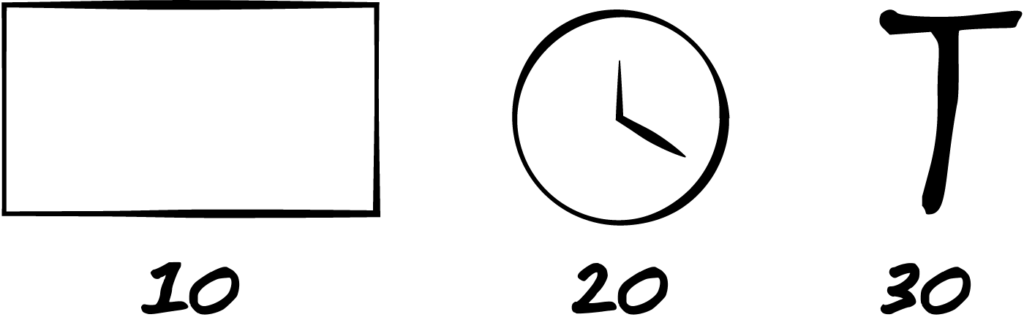
While this rule is a good starting point, it does not overrule your audience analysis or understanding of your purpose. Sometimes, you may need more slides or have a more involved purpose—like training people in new software or presenting the results of a research study—that takes more than 30 minutes to address. In that case, go with what your audience needs and what will make your presentation most effective. The concept behind the 10/20/30 rule—to make new learning easy for your audience to take in, process and remember—should still be your guide even if you don’t follow the rule exactly.
One last way to gauge presentations is to consider most audiences’ expectations for good presentations:
- main ideas are compelling and relevant
- information is organized with a clear beginning, middle, and end; audience can follow where the ideas are leading
- delivery shows the presenter’s enthusiasm and engagement
- visuals apply good design practices
- presentation length is appropriate for audience, purpose, and context
The following video summarizes characteristics that create effective presentations.
[1] Reynolds, Garr. (2012) Presentation Zen: Simple Ideas on Presentation Design and Delivery. 2nd ed. New Riders, Pearson Education. Information from pages 78- 81. http://ptgmedia.pearsoncmg.com/images/9780321811981/samplepages/0321811984.pdf
[2] Lucas, Stephen E. (2020) The Art of Public Speaking (13th edition).
[3] Gallo, Carmine. “Neuroscience Proves You Should Follow TED’s 18-Minute Rule to Win Your Pitch.” Inc. , https://www.inc.com/theupsstore/small-biz-ings.html
[4] Kawasaki, Guy. The 10/20/30 Rule of PowerPoint . December 2005. ↵
- Presentation Basics, original material and material adapted from Business Communication Skills for Managers, see attributions below. Authored by : Susan Oaks. Project : Communications for Professionals. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Making a Presentation for a Meeting. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/making-a-presentation-for-a-meeting/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- image of professional making a presentation. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/agreement-brainstorming-business-3408113/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- video Create an Effective Business Presentation. Authored by : Nick Morgan. Provided by : Harvard Business Review. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HTRt0zkD73M . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video How to Give a Great Presentation - 7 Presentation Skills and Tips to Leave an Impression. Provided by : Practical Psychology. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MnIPpUiTcRc . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Teaching Tip: Designing Online Lectures and Recorded Presentations. Authored by : Greg Steinke and Jill Zimmerman. Provided by : CCAPS Teaching Tips, University of Minnesota. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GCAaRZJFJAU . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of businesswoman presenting to an audience. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/analyzing-audience-board-3565815/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Visual Aids. Authored by : Nina Burokas. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/visual-aids/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- video Five Simple Rules for Creating World Changing Presentations. Authored by : Nancy Duarte. Provided by : Duarte Inc.. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hT9GGmundag . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video

Privacy Policy
Nonverbal Communication and Body Language
Improving emotional intelligence (eq), conflict resolution skills.
- Empathy: How to Feel and Respond to the Emotions of Others
Anger Management
Managing conflict with humor.
- The 5 Love Languages and Their Influence on Relationships
- Gaslighting: Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Childhood Issues
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Aging Issues
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- Senior Housing
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
What is effective communication?
Effective communication skill 1: become an engaged listener, skill 2: pay attention to nonverbal signals, skill 3: keep stress in check, skill 4: assert yourself, effective communication.
Want to communicate better? These tips will help you avoid misunderstandings, grasp the real meaning of what’s being communicated, and greatly improve your work and personal relationships.

Effective communication is about more than just exchanging information. It’s about understanding the emotion and intentions behind the information. As well as being able to clearly convey a message, you need to also listen in a way that gains the full meaning of what’s being said and makes the other person feel heard and understood.
Effective communication sounds like it should be instinctive. But all too often, when we try to communicate with others something goes astray. We say one thing, the other person hears something else, and misunderstandings, frustration, and conflicts ensue. This can cause problems in your home, school, and work relationships.
For many of us, communicating more clearly and effectively requires learning some important skills. Whether you’re trying to improve communication with your spouse, kids, boss, or coworkers, learning these skills can deepen your connections to others, build greater trust and respect, and improve teamwork, problem solving, and your overall social and emotional health.
What’s stopping you from communicating effectively?
Common barriers to effective communication include:
Stress and out-of-control emotion. When you’re stressed or emotionally overwhelmed, you’re more likely to misread other people, send confusing or off-putting nonverbal signals, and lapse into unhealthy knee-jerk patterns of behavior. To avoid conflict and misunderstandings, you can learn how to quickly calm down before continuing a conversation.
Lack of focus. You can’t communicate effectively when you’re multitasking. If you’re checking your phone , planning what you’re going to say next, or daydreaming, you’re almost certain to miss nonverbal cues in the conversation. To communicate effectively, you need to avoid distractions and stay focused.
Inconsistent body language. Nonverbal communication should reinforce what is being said, not contradict it. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will likely feel that you’re being dishonest. For example, you can’t say “yes” while shaking your head no.
[Read: Nonverbal Communication and Body Language]
Negative body language. If you disagree with or dislike what’s being said, you might use negative body language to rebuff the other person’s message, such as crossing your arms, avoiding eye contact, or tapping your feet. You don’t have to agree with, or even like what’s being said, but to communicate effectively and not put the other person on the defensive, it’s important to avoid sending negative signals.
When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the speaker is trying to convey.
There’s a big difference between engaged listening and simply hearing. When you really listen—when you’re engaged with what’s being said—you’ll hear the subtle intonations in someone’s voice that tell you how that person is feeling and the emotions they’re trying to communicate. When you’re an engaged listener, not only will you better understand the other person, you’ll also make that person feel heard and understood, which can help build a stronger, deeper connection between you.
By communicating in this way, you’ll also experience a process that lowers stress and supports physical and emotional well-being. If the person you’re talking to is calm, for example, listening in an engaged way will help to calm you, too. Similarly, if the person is agitated, you can help calm them by listening in an attentive way and making the person feel understood.
If your goal is to fully understand and connect with the other person, listening in an engaged way will often come naturally. If it doesn’t, try the following tips. The more you practice them, the more satisfying and rewarding your interactions with others will become.
Tips for becoming an engaged listener
Focus fully on the speaker. You can’t listen in an engaged way if you’re constantly checking your phone or thinking about something else. You need to stay focused on the moment-to-moment experience in order to pick up the subtle nuances and important nonverbal cues in a conversation. If you find it hard to concentrate on some speakers, try repeating their words over in your head—it’ll reinforce their message and help you stay focused.
Favor your right ear. As strange as it sounds, the left side of the brain contains the primary processing centers for both speech comprehension and emotions. Since the left side of the brain is connected to the right side of the body, favoring your right ear can help you better detect the emotional nuances of what someone is saying.
Avoid interrupting or trying to redirect the conversation to your concerns. By saying something like, “If you think that’s bad, let me tell you what happened to me.” Listening is not the same as waiting for your turn to talk. You can’t concentrate on what someone’s saying if you’re forming what you’re going to say next. Often, the speaker can read your facial expressions and know that your mind’s elsewhere.
Show your interest in what’s being said. Nod occasionally, smile at the person, and make sure your posture is open and inviting. Encourage the speaker to continue with small verbal comments like “yes” or “uh huh.”
Try to set aside judgment. In order to communicate effectively with someone, you don’t have to like them or agree with their ideas, values, or opinions. However, you do need to set aside your judgment and withhold blame and criticism in order to fully understand them. The most difficult communication, when successfully executed, can often lead to an unlikely connection with someone.
[Read: Improving Emotional Intelligence (EQ)]
Provide feedback. If there seems to be a disconnect, reflect what has been said by paraphrasing. “What I’m hearing is,” or “Sounds like you are saying,” are great ways to reflect back. Don’t simply repeat what the speaker has said verbatim, though—you’ll sound insincere or unintelligent. Instead, express what the speaker’s words mean to you. Ask questions to clarify certain points: “What do you mean when you say…” or “Is this what you mean?”
Hear the emotion behind the words . It’s the higher frequencies of human speech that impart emotion. You can become more attuned to these frequencies—and thus better able to understand what others are really saying—by exercising the tiny muscles of your middle ear (the smallest in the body). You can do this by singing, playing a wind instrument, or listening to certain types of high-frequency music (a Mozart symphony or violin concerto, for example, rather than low-frequency rock, pop, or hip-hop).
The way you look, listen, move, and react to another person tells them more about how you’re feeling than words alone ever can. Nonverbal communication, or body language, includes facial expressions, body movement and gestures, eye contact, posture, the tone of your voice, and even your muscle tension and breathing.
Developing the ability to understand and use nonverbal communication can help you connect with others, express what you really mean, navigate challenging situations, and build better relationships at home and work.
- You can enhance effective communication by using open body language—arms uncrossed, standing with an open stance or sitting on the edge of your seat, and maintaining eye contact with the person you’re talking to.
- You can also use body language to emphasize or enhance your verbal message—patting a friend on the back while complimenting him on his success, for example, or pounding your fists to underline your message.
Improve how you read nonverbal communication
Be aware of individual differences. People from different countries and cultures tend to use different nonverbal communication gestures, so it’s important to take age, culture, religion, gender, and emotional state into account when reading body language signals. An American teen, a grieving widow, and an Asian businessman, for example, are likely to use nonverbal signals differently.
Look at nonverbal communication signals as a group. Don’t read too much into a single gesture or nonverbal cue. Consider all of the nonverbal signals you receive, from eye contact to tone of voice to body language. Anyone can slip up occasionally and let eye contact go, for example, or briefly cross their arms without meaning to. Consider the signals as a whole to get a better “read” on a person.
Improve how you deliver nonverbal communication
Use nonverbal signals that match up with your words rather than contradict them. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will feel confused or suspect that you’re being dishonest. For example, sitting with your arms crossed and shaking your head doesn’t match words telling the other person that you agree with what they’re saying.
Adjust your nonverbal signals according to the context. The tone of your voice, for example, should be different when you’re addressing a child than when you’re addressing a group of adults. Similarly, take into account the emotional state and cultural background of the person you’re interacting with.
Avoid negative body language. Instead, use body language to convey positive feelings, even when you’re not actually experiencing them. If you’re nervous about a situation—a job interview, important presentation, or first date, for example—you can use positive body language to signal confidence, even though you’re not feeling it. Instead of tentatively entering a room with your head down, eyes averted, and sliding into a chair, try standing tall with your shoulders back, smiling and maintaining eye contact, and delivering a firm handshake. It will make you feel more self-confident and help to put the other person at ease.
How many times have you felt stressed during a disagreement with your spouse, kids, boss, friends, or coworkers and then said or done something you later regretted? If you can quickly relieve stress and return to a calm state, you’ll not only avoid such regrets, but in many cases you’ll also help to calm the other person as well. It’s only when you’re in a calm, relaxed state that you’ll be able to know whether the situation requires a response, or whether the other person’s signals indicate it would be better to remain silent.
In situations such as a job interview, business presentation, high-pressure meeting, or introduction to a loved one’s family, for example, it’s important to manage your emotions, think on your feet, and effectively communicate under pressure.
Communicate effectively by staying calm under pressure
Use stalling tactics to give yourself time to think. Ask for a question to be repeated or for clarification of a statement before you respond.
Pause to collect your thoughts. Silence isn’t necessarily a bad thing—pausing can make you seem more in control than rushing your response.
Make one point and provide an example or supporting piece of information. If your response is too long or you waffle about a number of points, you risk losing the listener’s interest. Follow one point with an example and then gauge the listener’s reaction to tell if you should make a second point.
Deliver your words clearly. In many cases, how you say something can be as important as what you say. Speak clearly, maintain an even tone, and make eye contact. Keep your body language relaxed and open.
Wrap up with a summary and then stop. Summarize your response and then stop talking, even if it leaves a silence in the room. You don’t have to fill the silence by continuing to talk.
Quick stress relief for effective communication
When a conversation starts to get heated, you need something quick and immediate to bring down the emotional intensity. By learning to quickly reduce stress in the moment, you can safely take stock of any strong emotions you’re experiencing, regulate your feelings, and behave appropriately.
Recognize when you’re becoming stressed. Your body will let you know if you’re stressed as you communicate. Are your muscles or stomach tight? Are your hands clenched? Is your breath shallow? Are you “forgetting” to breathe?
Take a moment to calm down before deciding to continue a conversation or postpone it.
Bring your senses to the rescue. The best way to rapidly and reliably relieve stress is through the senses—sight, sound, touch, taste, smell—or movement. For example, you could pop a peppermint in your mouth, squeeze a stress ball in your pocket, take a few deep breaths, clench and relax your muscles, or simply recall a soothing, sensory-rich image. Each person responds differently to sensory input, so you need to find a coping mechanism that is soothing to you.
[Read: Quick Stress Relief]
Look for humor in the situation. When used appropriately, humor is a great way to relieve stress when communicating . When you or those around you start taking things too seriously, find a way to lighten the mood by sharing a joke or an amusing story.
Be willing to compromise. Sometimes, if you can both bend a little, you’ll be able to find a happy middle ground that reduces the stress levels for everyone concerned. If you realize that the other person cares much more about an issue than you do, compromise may be easier for you and a good investment for the future of the relationship.
Agree to disagree, if necessary, and take time away from the situation so everyone can calm down. Go for a stroll outside if possible, or spend a few minutes meditating. Physical movement or finding a quiet place to regain your balance can quickly reduce stress.
Find your space for healing and growth
Regain is an online couples counseling service. Whether you’re facing problems with communication, intimacy, or trust, Regain’s licensed, accredited therapists can help you improve your relationship.
Direct, assertive expression makes for clear communication and can help boost your self-esteem and decision-making skills. Being assertive means expressing your thoughts, feelings, and needs in an open and honest way, while standing up for yourself and respecting others. It does NOT mean being hostile, aggressive, or demanding. Effective communication is always about understanding the other person, not about winning an argument or forcing your opinions on others.
To improve your assertiveness
Value yourself and your options. They are as important as anyone else’s.
Know your needs and wants. Learn to express them without infringing on the rights of others.
Express negative thoughts in a positive way. It’s okay to be angry , but you must remain respectful as well.
Receive feedback positively. Accept compliments graciously, learn from your mistakes, ask for help when needed.
Learn to say “no.” Know your limits and don’t let others take advantage of you. Look for alternatives so everyone feels good about the outcome.
Developing assertive communication techniques
Empathetic assertion conveys sensitivity to the other person. First, recognize the other person’s situation or feelings, then state your needs or opinion. “I know you’ve been very busy at work, but I want you to make time for us as well.”
Escalating assertion can be employed when your first attempts are not successful. You become increasingly firm as time progresses, which may include outlining consequences if your needs are not met. For example, “If you don’t abide by the contract, I’ll be forced to pursue legal action.”
Practice assertiveness in lower risk situations to help build up your confidence. Or ask friends or family if you can practice assertiveness techniques on them first.
More Information
- Effective Communication: Improving Your Social Skills - Communicate more effectively, improve your conversation skills, and become more assertive. (AnxietyCanada)
- Core Listening Skills - How to be a better listener. (SucceedSocially.com)
- Effective Communication - How to communicate in groups using nonverbal communication and active listening techniques. (University of Maine)
- Some Common Communication Mistakes - And how to avoid them. (SucceedSocially.com)
- 3aPPa3 – When cognitive demand increases, does the right ear have an advantage? – Danielle Sacchinell | Acoustics.org . (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2022, from Link
- How to Behave More Assertively . (n.d.). 10. Weger, H., Castle Bell, G., Minei, E. M., & Robinson, M. C. (2014). The Relative Effectiveness of Active Listening in Initial Interactions. International Journal of Listening , 28(1), 13–31. Link
More in Communication
How to read body language to build better relationships at home and work

Boost your emotional intelligence to help you be happy and successful

Tips for handling conflicts, arguments, and disagreements

How to feel and respond to the emotions of others

Tips and techniques for getting anger under control

Using laughter and play to resolve disagreements

The 5 Love Languages
What they are and how they influence relationships

Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
5 ways to deal with gaslighting

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
120 Presentation Topic Ideas Help You Hook Your Audience
Updated: January 15, 2024
Published: August 09, 2023
Cooking is easy. The puzzle is figuring out what to eat. As soon as you know that, you can get started. The same holds for presentations. The sooner you can whip up a good, informative, and catchy topic, the easier the rest of the process becomes.

Pick a good topic that resonates with you and your audience to set a strong foundation. But select the wrong topic, and it becomes difficult to connect with your audience, find mutual interests, or hold their attention.
So, let’s learn how to develop thought-provoking and relevant topics for your presentations. You’ll also find some best practices to make your presentation memorable.


10 Free PowerPoint Templates
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
- Creative templates.
- Data-driven templates.
- Professional templates.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Table of Contents
How to Choose a Great Presentation Topic in 5 Steps
120 presentation topic ideas, 5 presentation tips.

4. Choose an appropriate presentation style.
There are many ways to present a topic. Your personality, the topic at hand, and your audience’s personas will help you determine which style would best fit you and your audience.
Select a presentation style that will communicate the main idea clearly and have a lasting impact on your audience.
For instance, explore a freeform style presenter by Sir Ken Robinson.
5. Engage with your audience.
Work on your presentation skills to make a strong connection with your audience, get through to them and leave a mark.
Think of the presenter as the link between the topic and the audience. A strong or a weak presenter can make a difference between a presentation being a thriving success or a boring failure.
Hone your skills by engaging and interacting with your audience. Make them feel like a part of the presentation and not just spectators. 70% of marketers have found presentations with interactive content to be more effective than those without.
Here are a few ways you can make your presentation interactive:
- Start your speech with uncommon questions to your audience. Involve them from the get-go, like ask to raise their hands if X.
- Make eye contact to build credibility and show confidence. Don’t stare at your slides or notes. Smile occasionally and talk to the audience directly.
- Have an active and confident body language. Don’t stand in the same place the entire time. Move around the stage.
- Don’t be monotonous. Speak as you would to a colleague — with enthusiasm.
- Ask close-ended questions in between to keep the audience engaged without losing time. Address them using their names to keep things interesting.
- Share personal experiences and stories that your audience will find fascinating and relatable.
- Practice thoroughly before you present so you’re fluent with the material and delivery.
- Energy and excitement can be quite contagious. Make sure you exude enough to spread some to your audience.
Feeling Inspired Yet?
Now you have all the right ingredients for choosing amazing topics and a hundred ideas to drive inspiration from. So, go ahead and start cooking presentations that will blow your audience away.
Don’t forget to choose a super-relevant topic and add meaty information. Do it with excitement to make it enjoyable for you and your audience. Best of luck!
![presentation regarding communication Blog - Beautiful PowerPoint Presentation Template [List-Based]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/013286c0-2cc2-45f8-a6db-c71dad0835b8.png)
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![presentation regarding communication How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ecommerce%20business%20plan.png)
How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]
![presentation regarding communication How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Make-infographic-hero%20%28598%20%C3%97%20398%20px%29.jpg)
How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]
![presentation regarding communication 20 Great Examples of PowerPoint Presentation Design [+ Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint-presentation-examples.webp)
20 Great Examples of PowerPoint Presentation Design [+ Templates]

Get Buyers to Do What You Want: The Power of Temptation Bundling in Sales

How to Create an Engaging 5-Minute Presentation
![presentation regarding communication How to Start a Presentation [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-start-presenting.webp)
How to Start a Presentation [+ Examples]
![presentation regarding communication 17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips to Make More Creative Slideshows [+ Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint-design-tricks_7.webp)
17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips to Make More Creative Slideshows [+ Templates]
![presentation regarding communication How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Powerpoint%20presentation.jpg)
How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]

The Presenter's Guide to Nailing Your Next PowerPoint
![presentation regarding communication How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/presentation-cover-page_3.webp)
How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

15 Useful Presentation Topics for Business Communication
By: Author Shrot Katewa
If you are on this page, we know that you are a change maker in your business! We know that you understand the role that business communication plays in any professional setup. So, we want to give our best to enable you to make this change happen. Today, we want to talk about 15 useful topics for Business Communication that you can present in your organisation and empower others.
But first, let’s start with What is business communication? Business communication, in rudimentary terms, can be defined as a form of formal communication among professionals who are working for a common business objective.
While communication, in general, is important for any business to survive and thrive, in order to achieve success in business and for its respective teams, business communication becomes absolutely critical as success can’t be achieved without interacting with each other and having a common goal and objective in mind.
It is important to keep in mind that business communication is not just between your subordinates or your boss, you need to consider all stakeholders associated with your business. It can be one to many, one on one or many to one. Furthermore, it can involve various forms for communication medium such as email, telephone, intranet, presentations, video, social media, magazines, meetings, interviews, discussions etc.
So, what are some of the topics for business communication that you can give a presentation for your team? Let’s have a look –
A Quick Note Before We Begin – if you want to make jaw-dropping presentations, I would recommend using one of these Presentation Designs . The best part is – it is only $16.5 a month, but you get to download and use as many presentation designs as you like! I personally use it from time-to-time, and it makes my task of making beautiful presentations really quick and easy!
1. How to communicate business decisions during a crisis
Crisis management is one of the key moments when clear and coherent communication is of utmost importance. Any lack of communication or miscommunication during a crisis can lead to tragic circumstances for the business. A great topic for teams and companies to debate and create guidelines and response mechanisms to combat such issues.
2. Importance of Intranet
Intranet is a perfect platform to communicate business news and updates. As an internal business communication tool, it provides opportunities for information to be shared with the employees. Its importance can not be doubted. Taking up a topic like this one can help your team and colleagues truly understand the purpose behind deploying and managing the intranet within organisations.
3. Townhall and its benefits
This is often a forgotten mode of communication in many organisations. In today’s modern day of social media and other platforms, it is easy to forget the impact that a townhall can have on the employees of an organisation. An interesting presentation topic for business communication.
4. How to give an effective feedback
Giving feedback to your colleagues or team members can constitute one of the most essential types of communication as it ensures that the team has a healthy work relationship and there is no hindrance on the journey of achieving the common goal of the organisation. The best part about such a topic is that it is applicable across divisions and teams and can be useful irrespective for the background of your audience.
5. How to crack a business deal
Every organisation needs clients. Converting a potential lead into a successful client needs a lot more than business communication. However, understanding the need of your audience and communicating the right message, product or service that fulfils the requirement plays a key role in cracking a deal. It serves as a great topic for discussion on the importance of business communication among the sales team.
6. Managing relationship with you boss
There are many among us who don’t like their boss. Trust me, it is not uncommon! 🙂 But, part of the reason for the failure of a healthy relationship with your boss is business communication or the lack of it. A topic like this may not only enable you to come across colleagues who may resonate with your ideas, but also help improve relationships of your colleagues with their respective bosses.
7. Email Etiquettes
Let’s face it – email is the most common mode of communication among all employees in an organisation. Thus, it is of utmost importance that messages sent over an email communicate what was intended and not anything else. It is a great business communication presentation topic especially for the new employees who have recently joined your office.
8. How to communicate with your peers
Another important topic for most business settings. It is important for the employees to really understand the company’s policy on the work environment and communication among the employees. Having a presentation session on this business topic can be really helpful in setting up a healthy work environment for your employees.
9. Role of millennials in your brand success
I view this as a very interesting presentation topic for business communication. Why? Because, the role of millennials in the success of a brand is often not completely understood. With the onset of social media, millennials are finding it more and more easy to voice their opinion and impact a brand. This topic could serve as an interesting business communication presentation.
10. Is the newsletter dead?
In this modern age where more and more information is consumed over digital mediums and the attention span of your audience is only diminishing, the importance of newsletter can form a good topic for not just a business presentation, but also include an interesting debate as an activity post your presentation.
11. Tips for successful business relationships with customers
Having a successful business relationship with customers goes way beyond just converting a potential lead into a customer. This is often a part of the business that gets missed out. Thus, considering this topic for your business communication presentation can be really fruitful.
12. Role of influencers for building a brand –
Social media has played a pivotal role of distributing the power to influence others from celebrities to individuals known as influencers. The role of an influencer is often not completely understood even though there are several influencers who now have the authority to influence your brand both positively and negatively. The lack of this understanding can impact the communication strategy of your brand. Thus, a very carefully curated session with this presentation topic for business communication can be highly effective in reaching success and achieving the goals of your business.
13. Brand guidelines and its importance
When we are talking about business communication, brand guidelines is a perfect topic as it sets the method of ensuring that the messaging and communication is consistent irrespective of which employee is engaging with a stakeholder outside your organisation. It is also really important that all employees understand the importance of consistent messaging.
14. Impact of social media for employees
We’ve come across several organisations that are struggling with leveraging their own employees across social media to create an awesome brand image. Furthermore, the impact of identifying the opportunities to leverage your employees towards a focused campaign is barely understood. Thus, considering this topic for your business communication presentation can be an eye opener for many within your organisation including business leaders.
15. Significance of company blogs
If you are a business communicator, you surely understand that each medium of communication is important as it often has its own pros and cons. Many believe that a company blog is turning out to be irrelevant. However, if a company blog is created with a correct strategy that is specific to a business, it can not just be successful but also push across customers. Taking up this presentation topic for business communication can, again, be a very interesting one. It may lead to an open debate and also help to work around and build upon your company’s existing communication strategy.
So there you have it. There is a lot to talk about when we need to share something useful on business communication. I would like you to consider these topics only as a conversation starter and build up from the brief pointers that we have mentioned. I also hope that you find the above topics really something that you can use and is effective in your business setting. Do let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
Our goal on this blog is to create content that helps YOU create fantastic presentations; especially if you have never been a designer. We’ve started our blog with non-designers in mind, and we have got some amazing content on our site to help YOU design better.
If you have any topics in mind that you would want us to write about, be sure to drop us a comment below. In case you need us to work with you and improve the design of your presentation, write to us on [email protected] . Our team will be happy to help you with your requirements.
Lastly, your contribution can make this world a better place for presentations . All you have to do is simply share this blog in your network and help other fellow non-designers with their designs!
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
Strategies in Communication: Your Guide to Better Connections
In today’s world, communication skills are essential. Whether you're talking on the phone or meeting someone face to face, these strategies can help you better connect with others.
![presentation regarding communication [Featured image] Three employees communicate during a casual meeting in their office.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/3Fa3Y1BLaIytL7sWGmJsvM/6da9fed4b993c3ba5dfdee85644e0408/iStock-641970956_super.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
Effective communication is foundational to healthy working and personal relationships. People communicate in various ways, and understanding how and when to use each type of communication can benefit your ability to communicate effectively.
In addition to strengthening your communication skills, you can also find better connections in your personal and professional life by learning strategies to address common communication barriers that may involve cultural or linguistic differences.
In this article, you'll learn strategies for more effective communication and explore different communication styles.
Importance of effective strategies in communication
Good communication helps prevent conflicts that may arise in the ambiguity of miscommunication. Effective communication skills are foundational to any good personal or professional relationship. Learning successful strategies in communication can impact your ability to motivate others, have more engaging conversations, share information, and practice more efficient problem-solving.
Effective organizational communication strategies can help employees and coworkers understand what is expected of them, meet goals, and boost motivation. Communication skills are essential if you're in a leadership position or manage a team where you must delegate responsibilities while maintaining a respectful relationship.
7 effective strategies in communication
Building your communication skills takes practice, but it is entirely possible and worth it. Find your weaknesses and consider focusing on one or two strategies at a time. To improve communication skills, notice your current communication style. With time and effort, you’ll convey better ideas, thoughts, actions, and opinions in your personal and professional life. Use the following strategies to get started.
1. Convey important points clearly and concisely.
It may be tempting to insert additional information, include popular phrases to relate to the listener, or fall back on filler words that lack true meaning. However, this could be perceived as clutter when you want others to understand your message fully. Many people read or listen to tons of communications all day, so it's important to choose your words wisely and organize your thoughts in a way that's easy to follow.
Use these tips to improve the clarity and conciseness of your communication:
Use action verbs when possible.
Offer tangible and concrete terms instead of ambiguous ones. For example, instead of, “Let’s touch base sometime later in the week,” say, “Would Thursday at 3 p.m. work to check in on this project?"
Leave out filler words and clichés that lack meaning.
End with a clear call to action if the communication requires the listener to do something.
In written communication, use bullet points and avoid long streams of text.
Consider using visual aids to support your points.
2. Use multiple modes of communication.
We often communicate to others using a wide range of different communication styles without even noticing it. In an email to a coworker, you may include a screenshot of a document—a visual and written method of communication. When you speak to someone face-to-face, meanwhile, you likely use nonverbal communication with your body language and verbal communication as you’re speaking.
Intentionally using multiple modes of communication can add clarity to what you’re trying to convey. Match the modes of communication you choose to the type of communication and listener. Consider the best way to communicate based on the end goal and needs of the listener, and prepare to use multiple modes of communication if sharing with a group.
3. Be mindful of your tone.
The way in which you say something – and the medium through which you do it – affects how your communication is received by others. As a result, the tone of your voice or your written communication should appropriately match what you’re trying to convey.
Think about how the interaction would be received if you were on the receiving end. If you’re communicating a policy change to a group of employees, think about their pain points, any questions they may have, and their needs. In your communication, build in that information with a tone of understanding and openness so that employees who may be anxious about such changes are calmed.
When emotions get involved, it may be hard to maintain the tone you intend. Take time to think through what you’ll say and how you’ll say it to maintain better control of your emotions.
4. Maintain awareness of your body language and nonverbal cues.
Similar to tone, it’s vital that you are aware of what your body language and gestures convey to listeners. It may be challenging to control certain nonverbal cues, especially if you struggle with emotions tied to the conversation. Practice being aware of your body and facial expressions in your daily communication to start understanding where you can improve. Ask for feedback if appropriate.
Practice these ways to use body language to improve your communication skills:
Uncross your arms to maintain a more “open” position.
Speak at a steady pace and avoid talking and moving quickly or erratically.
Match your eye level with the listener—if they are sitting down, sit with them.
Maintain eye contact.
Shift your posture and gestures to match that of the listener if needed.
Stand facing the person you’re speaking with.
5. Know your audience.
To know your audience is to understand their thoughts and feelings—it involves perspective and will take time and thoughtfulness. Modulate your tone, gestures, and body language to help your audience perceive your motives and intentions. Before you send an email, approach a coworker, or walk into a meeting, take the time to understand the audience and consider how they may feel or react to what you’re about to communicate to them.
6. Focus on what others say and acknowledge it.
When you can focus on what you are saying and what others say in response, you can tailor your communication style and content appropriately. Referred to as active listening , this technique shows you are listening through nonverbal communication.
You may be more effective in your communication when you can acknowledge the perception of others and respond appropriately to their feedback, questions, or suggestions. Be open and listen, avoiding defensiveness and interrupting. If you don’t know how to respond, simply tell the other person that you'll get back to them once you've given it greater consideration. There is no harm in asking for time to provide a thoughtful response.
7. Request and provide feedback.
Asking for feedback can be helpful if you’re struggling with effective communication. It can also help you build useful communication strategies in a leadership role.
Ask a boss or coworker to provide constructive feedback, or record yourself and watch for any nonverbal communication that could negatively affect your ability to transmit your message successfully. Manage your emotions and pride to accept and implement constructive criticism. When you ask for feedback, invite the listener to point out things you might be struggling with, thank them, and be mindful of their time.
Overcoming potential barriers to effective communication
Communication barriers can be anything that negatively impacts your ability to communicate appropriately with others. From the tools you use to communicate to your methods of communication, barriers may be physical, emotional, cultural, or linguistic. Fortunately, there are ways to address these barriers and improve your ability to communicate in varying scenarios.
Sometimes, emotions can cloud your ability to communicate effectively and actively listen. Emotions like anger or disappointment can affect your ability to communicate because your brain struggles to process what is being said, especially if you're experiencing stress or anxiety at that time.
To mitigate the impact of your emotions, wait until you’ve managed them before choosing the best method and environment to speak with a person or group of people. You can also involve a mediator or neutral third party.
Perception
How others perceive you and the motives behind your words and actions can help or hinder your communication ability. To avoid negative perception, be sure your intention is clearly stated and understood, have open body language, and make time for follow-up questions.
Social differences among cultures can create misunderstandings that impede effective communication.
It’s important, particularly in the workplace, to ask questions about communication standards, norms, and preferences if you suspect a cultural-based communication barrier. Companies can be sensitive and respectful to other cultures by communicating the desire to meet the communication needs of all employees.
Language barriers don’t just refer to speaking different languages entirely, but also regional and dialectal differences between people and how they each understand the same language. For example, there may be two ways to say the same word, associations tied to certain words or phrases, or colloquialisms in one part of the United States that don’t exist in other regions, among other things.
To overcome language barriers, avoid jargon, clichés, phrases, or slang that may not translate well without further explanation. In other words, know your audience. Also, some technical terms may be appropriate if you're writing an email to a coworker or supervisor, but not when speaking at a conference for a group of students.
Interpersonal
Interpersonal barriers refer to the relationship between you and the person or people with whom you’re communicating. Interpersonal barriers can be a lack of trust, engagement, or a difference of opinion. You can more clearly communicate in these instances if you can be transparent, open to criticism, and keep strong emotions at bay. Understand that when interpersonal barriers are present, you may need to compromise, offer solutions, and even step away and take time to consider the situation.
4 types of communication
The four main types of communication are verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual. Any time you communicate with someone, you use at least one of these types of communication, but you often rely on several types at once.
For example, consider when you walk into a colleague’s office to discuss a project. You're communicating with the words you say but also your tone of voice, body language, and expressions. You may also bring a visual aid like a copy of the project details or send a follow-up email after you chat with them. All of these means of communication help get your point across.
To improve your strategies in communication, focus on each type of communication and consider ways you can build upon your skills in that area. If you have a strength in one area, assess what makes you most effective as you build upon other types of communication. One important note: The type of communication you choose should be appropriate for the situation.
1. Verbal communication
Verbal communication is the actual words you speak and how you say them.
This can mean your pitch, volume, cadence, and more. Improve your verbal communication skills by being clear and concise, and avoid unnecessary filler words, such as “um,” “yeah,” “like,” and “you know.” Read the other person or people you’re communicating with using good active listening skills. Be confident in your speech and know when to listen and when to talk.
Read more: 10 Tips to Improve Public Speaking Skills
2. Nonverbal communication
Nonverbal communication refers to the nuisances that you may not even be aware of when speaking with someone or a group of people.
Your gestures, body language, and facial expressions are all means of nonverbal communication. Ironically, watching others is one of the best ways to improve nonverbal communication. Do they make eye contact? Are their arms crossed? Are they talking with their hands a lot? Being aware of others' nonverbal communication can help create awareness of your own, and you may be able to control your body language better when communicating.
3. Visual communication
Visual communication is considered anything you use to convey information that the eyes can see. This can be a visual aid like a presentation, document, image, infographic, and so on.
Visual communication can supplement what you say and give listeners a tangible example. For instance, if you’re writing a group email to your team about the timeline of a project instead of writing it all out, create a bar graph to show improvement and attach it to the email. This would be a visual way to communicate the needs of the project.
4. Written communication
Written communication encompasses anything written or typed—from text messages to memos and reports to emails. To improve your written communication, use templates for reference and keep samples of good writing pieces you’ve done in the past. Remember, you can’t always read the tone of written communication, so rely on punctuation and simplicity, and avoid jokes or sarcasm to prevent miscommunication.
Read more: 7 Ways to Improve Your Writing Skills
Common modes of communication
A mode of communication refers to the medium used by the sender of a message to deliver the communication to the receiver, how we deliver a message, and how the message is received. This could be email, text, or speech. Three standard modes of communication are presentational, interpersonal, and interpretive.
Presentational and interpretive modes of communication are referred to as one-way communication since it typically involves delivering a message in a way that does not facilitate or encourage interaction or exchange from the receiver.
Interpretive communication may occur in a classroom where a teacher presents information to students. Students must interpret the content based on the medium and the speaker’s communication cues like body language, tone, and other means of communication used. Presentational communication may occur in a seminar or more formal setting where the speaker presents rehearsed, scripted content to a group of listeners.
Interpersonal communication is different. When we engage in interpersonal modes of communication, we interact with the recipient of our message. In this relational-based mode, we use verbal and nonverbal means of communication. Examples of interpersonal communication could be a phone conversation or texting.
Take the next steps to improve your communication development in your personal and professional life by applying these strategies in the real world. Effective communication is a critical life skill that is highly prized in the workplace. Invest in your communication skills to build and maintain healthy relationships and positively impact your career and personal life.
Need resources to get started? Enroll in an online course like the University of Pennsylvania's Improving Communication Skills or the University of Colorado's Teamwork Skills: Communicating Effectively in Groups , both offered on Coursera. These courses can provide professional guidance and helpful resources to improve your communication.
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

Importance of communication skills in presentation

Effective communication, fresh perspectives, and enhanced teamwork have created some of the world’s best projects. People who can communicate their desires, goals, and wishful outcomes are game-changers, and those people are valuable for any architectural company. It’s hard to talk about where you could be in 10 or 20 years. However, focusing on mastering your communication skills while you’re still young and improving intellectually, will make you ideally suited for future leadership positions.
Words depict your personality
What makes architects unique is the way we think, and to let the world know what your ideas are about, you must know how to communicate well. The building design has evolved to incorporate innovative design, construction methods, and social elements, resulting in the opportunity for architects to integrate knowledge from various fields into the design process. Sometimes trying to convey everything in a particular design can create chaos. What I mean by that is if you’re trying to cram 8 ideas into one project, it muddles the water and none of your ideas are accurately communicated. Instead, try to focus on solving the problem with one or two ideas. You will meet a lot of new people from all walks of life. Take advantage of these opportunities to reflect on your career progress and learn from them.

Socialize and Influence people.
Great pioneers of businesses, organizations, institutions are all very clear on what they want and are very good at communicating these ideas efficiently to people and get work done. People of varying knowledge and experience levels should be able to understand what you’re talking about. The real challenge is to be brief but comprehensive; try to be as detailed as possible whilst using as little words as possible. Plus, Staying empathetic will help you get along with everyone in the workplace. Become a person they can turn to openly share their notions without judgment. In this way, you provide the support, opportunity, and ensure the maximum results.

When you present, you are in charge of the room.
Jurors and critics want to hear and discuss big ideas. Good communication skills can ease these interactions, and ensure that you can get your point across calmly and clearly, and also take on board the responses. The purpose of a presentation is to get them to understand the concept and approach and to engage the space in their minds. Anything you are trying to convince a jury in words has to be correlated to the illustrations.
So, there should be enough visual material on the wall to make your life easy explaining it during design juries. The words that we choose can make a big difference in whether your project is understood.

Comprehend the Feedback

The jury process is not always about your presentation skills but an opportunity to improve your active listening skills. Listening is an active form of communication. Listen to what people tell you. Design jurors and reviewers only want to explore the ideas behind the project. Give them what they want, and don’t refrain from talking about the process and how the structure has been developed. Concentrate on what they are saying and avoid interruptions until they are through speaking. Seek feedback and ask questions when in the position to speak. As we know, Practice makes you perfect. Form a group like mock viva with your friends, and invite them to critique your work. This will not only allow you to see your idea from a different angle but also allow you to prevent mistakes and practice for the day.

In the field of architecture, communication between the architect and his organization is based on everything from verbal communication to computer-generated architectural drawings and images. Architect’s duties require specific skills for any project—designing, engineering, managing, supervising, and communicating with clients and builders. It eventually comes down to teamwork and execution. Coordinating the responsibilities of all members is crucial for a successful design. Communication makes it easier to function collectively, and also makes use of the strength of each individual to meet the project deadlines. It’s all about getting the right information to the right people at the right time. Misunderstanding is a common distraction from design intentions among teams that do not take the time to understand one another.

Clients, Us and the project
The collective vision among the architect and client is directly related to the success of a project. The choice of an architect by the client depends on his satisfaction gathered during the discussion where conversation skills play a vital role. The client needs to set up confidence and trust in the architect and good communication is the key to land your dream project. We should convey the value we are bringing to the project in terms they understand. If they’re figures-oriented, talk of budget savings.
If they’re aesthetically minded, talk of beauty. If they’re rational types, talk of energy efficiency.
As architects, you’ll know there are a million variables in play when it comes to planning and constructing a building. Your clients might not. So it’s up to us to be clear and show them the way.

Sneha Kannan, a young architect, Interior designer based in Chennai. Her work involves creating spaces with strong visual and social identity. As an architectural writer and graphic designer in practice, she believes graduation is just a start to life. Developing a strong interest in aesthetics and management, she is working her way towards becoming a multi-faceted individual.

The state of Architectural Journalism in India vs the world

Cyberwalk By Design Forum International
Related posts.

AR-Adapted Warehome for Sale

Alchemy of Architecture: How Does Architecture Impact the Daily Lives of People

Architecture in the 5th dimension

Architectural Anthropology: Understanding People for Better Designs
- Architectural Community
- Architectural Facts
- RTF Architectural Reviews
- Architectural styles
- City and Architecture
- Fun & Architecture
- History of Architecture
- Design Studio Portfolios
- Designing for typologies
- RTF Design Inspiration
- Architecture News
- Career Advice
- Case Studies
- Construction & Materials
- Covid and Architecture
- Interior Design
- Know Your Architects
- Landscape Architecture
- Materials & Construction
- Product Design
- RTF Fresh Perspectives
- Sustainable Architecture
- Top Architects
- Travel and Architecture
- Rethinking The Future Awards 2022
- RTF Awards 2021 | Results
- GADA 2021 | Results
- RTF Awards 2020 | Results
- ACD Awards 2020 | Results
- GADA 2019 | Results
- ACD Awards 2018 | Results
- GADA 2018 | Results
- RTF Awards 2017 | Results
- RTF Sustainability Awards 2017 | Results
- RTF Sustainability Awards 2016 | Results
- RTF Sustainability Awards 2015 | Results
- RTF Awards 2014 | Results
- RTF Architectural Visualization Competition 2020 – Results
- Architectural Photography Competition 2020 – Results
- Designer’s Days of Quarantine Contest – Results
- Urban Sketching Competition May 2020 – Results
- RTF Essay Writing Competition April 2020 – Results
- Architectural Photography Competition 2019 – Finalists
- The Ultimate Thesis Guide
- Introduction to Landscape Architecture
- Perfect Guide to Architecting Your Career
- How to Design Architecture Portfolio
- How to Design Streets
- Introduction to Urban Design
- Introduction to Product Design
- Complete Guide to Dissertation Writing
- Introduction to Skyscraper Design
- Educational
- Hospitality
- Institutional
- Office Buildings
- Public Building
- Residential
- Sports & Recreation
- Temporary Structure
- Commercial Interior Design
- Corporate Interior Design
- Healthcare Interior Design
- Hospitality Interior Design
- Residential Interior Design
- Sustainability
- Transportation
- Urban Design
- Host your Course with RTF
- Architectural Writing Training Programme | WFH
- Editorial Internship | In-office
- Graphic Design Internship
- Research Internship | WFH
- Research Internship | New Delhi
- RTF | About RTF
- Submit Your Story
Looking for Job/ Internship?
Rtf will connect you with right design studios.


Communication Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 – 5)
By Status.net Editorial Team on July 26, 2023 — 6 minutes to read
Effective communication is a crucial skill in the workplace: it fosters healthy relationships, clear information exchange, and a positive work environment. Although some employees excel at communication instinctively, others may need guidance in refining their skills. Performance reviews provide an ideal avenue for evaluating and guiding employee communication skills on a regular basis. To assist managers and supervisors during these assessments, this article offers an organized structure of performance review phrases and paragraphs examples with a focus on communication skills.
By following the provided examples and breaking down the various aspects of communication skills, managers and supervisors can ensure that performance reviews are effective and consistent. The aim is to promote growth, constructive feedback, and a better understanding of workplace communication expectations for every employee, thus resulting in a more successful and harmonious work environment.
Questions to determine an employee’s performance review rating for communication skills:
- Does the employee communicate effectively with team members, managers, and clients?
- Does the employee actively listen and provide thoughtful responses?
- Does the employee express ideas and opinions clearly and concisely?
- Does the employee use appropriate tone and language in written and verbal communication?
- Does the employee adapt their communication style to different situations and audiences?
Based on your assessment of the employee’s performance in these areas, you can assign a rating that reflects their communication skills. For example, if the employee consistently communicates effectively, listens actively, and adapts their communication style to different situations, they may receive a high rating. Conversely, if the employee struggles to communicate clearly or appropriately, they may receive a lower rating.
Performance Review Phrases and Paragraphs Examples for Communication Skills
5 – outstanding, phrases examples.
- Exceptional ability to convey complex ideas in a simple and easily understandable manner
- Consistently demonstrates active listening skills and responds appropriately
- Facilitates open and honest discussion, promoting a positive work environment
- Frequently praised for engaging communication style and active listening skills
- Leveraged excellent communication skills to resolve conflicts effectively and efficiently
- Regularly sought out for advice regarding effective communication strategies
- Demonstrated exceptional skill in written and verbal communication across multiple channels
Paragraph Example 1
“John consistently demonstrates outstanding communication skills. His ability to articulate complex concepts in a simple and understandable manner is truly exceptional. He actively listens during conversations and is well-regarded for his engaging communication style. His skills in conflict resolution and providing guidance in effective communication strategies are frequently sought out by his peers. John has shown mastery in communicating across multiple channels, with excellent verbal and written communication.”
Paragraph Example 2
“Jane consistently displays outstanding communication skills. She is able to take complex ideas and present them in a simple, easy to understand manner, allowing her team to effectively grasp new concepts. She actively listens to others, showing genuine interest in their input and responds with thoughtfulness. Her ability to facilitate open and honest discussion fosters a positive and inclusive work environment.”
4 – Exceeds Expectations
- Effectively conveys thoughts and ideas, making sure everyone is on the same page
- Often engages in active listening, providing constructive feedback when necessary
- Promotes a positive work environment by openly communicating with team members
- Continuously expanded communication skills through self-learning and workshops
- Mastered the art of tailoring communication to suit diverse audiences
- Took initiative to lead presentations and meetings with clarity and confidence
- Enhanced team communication by introducing new collaboration tools and techniques
- Created a positive and inclusive environment by communicating effectively with team members
“Jane has exceeded expectations in communication skills. She continually improves her abilities through self-learning and attending workshops. Jane has a strong command of tailoring her communication to suit diverse audiences, routinely leading presentations and meetings with confidence. She was instrumental in enhancing team communication by introducing new collaboration tools and techniques. Jane’s effective communication skills create a positive and inclusive environment that fosters strong team relationships.”
“John exceeds expectations in his communication skills. He effectively shares his thoughts and ideas, ensuring everyone on the team is aligned and informed. John actively listens to his colleagues, offering constructive feedback and support. His open communication style contributes to a positive work environment and strong team dynamics.”
3 – Meets Expectations
- Adequately communicates thoughts and ideas with coworkers
- Typically engages in active listening and responds to feedback
- Contributes to a positive work environment by maintaining open lines of communication
- Consistently communicates information in a clear and concise manner
- Effectively balances active listening and speaking during discussions
- Demonstrates good written and verbal communication skills
- Proactively seeks to improve communication skills through feedback from colleagues
- Successfully adapts communication style to various situations and audiences
“Sam meets expectations in his communication skills. He consistently communicates information clearly and concisely in both written and verbal communication forms. Sam is effective in his ability to balance active listening and speaking during discussions, and he adapts his communication style as needed to diverse situations and audiences. He takes feedback from colleagues seriously and proactively works to improve his communication skills.”
“Susan meets expectations in her communication skills. She adequately conveys her thoughts and ideas to coworkers, and generally engages in active listening, responding to feedback when necessary. Susan keeps open lines of communication with her team members and contributes to a positive work environment.”
2 – Needs Improvement
- Struggles to clearly convey thoughts and ideas to coworkers
- Has difficulty engaging in active listening and responding appropriately to feedback
- Could improve upon fostering a positive work environment through better communication
- Struggles to clearly articulate thoughts and ideas
- Difficulty in adapting communication style to different audiences
- Limited development of written communication skills
- Inconsistent in providing timely responses to messages and inquiries
- Needs to improve active listening skills during meetings and discussions
“James requires improvement in his communication skills. His ability to articulate thoughts and ideas is not clear, and he has difficulty adapting his communication style to different audiences. James should focus on improving his written communication skills and ensuring that he is consistent in providing timely responses to messages and inquiries. Additionally, it is vital for James to enhance his active listening skills during meetings and discussions.”
“Tom’s communication skills need improvement. He often struggles to clearly express his thoughts and ideas to his coworkers, leading to confusion and misunderstandings. When engaged in conversation, Tom has difficulty actively listening and responding appropriately to feedback. An improvement in Tom’s communication would help foster a more positive work environment.”
1 – Unacceptable
- Consistent failure to convey information accurately and effectively
- Unable to adapt communication style to suit the audience or the situation
- Ignored or dismissed valuable feedback from colleagues regarding communication issues
- Disrespectful and unprofessional communication with peers and supervisors
- Habitual absence or disengagement during team meetings and discussions
- Frequently fails to effectively communicate thoughts and ideas.
- Does not engage in active listening or provide appropriate responses to feedback.
- Negatively impacts the work environment through a lack of effective communication.
“Lucy’s communication skills are currently unacceptable. She frequently fails to effectively articulate her thoughts and ideas, causing disconnects within the team. Lucy does not engage in active listening and often provides inappropriate responses to feedback. Her lack of communication has a negative impact on the work environment, and it’s crucial for her to address this issue.”
“Sara’s communication skills are unacceptable. She consistently fails to accurately and effectively convey information, and she is unable to adapt her communication style to suit various audiences or situations. Sara has also dismissed valuable feedback from her colleagues regarding communication issues. She exhibits disrespectful and unprofessional communication with peers and supervisors. It is crucial that Sara takes immediate steps to improve her communication skills, including addressing her habitual absence and disengagement in team meetings and discussions.”
- Decision Making Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Listening Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Supervision Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Problem Solving Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Mentoring Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
- Planning Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5)
Top 20 Presentation Interview Questions & Answers
Master your responses to Presentation related interview questions with our example questions and answers. Boost your chances of landing the job by learning how to effectively communicate your Presentation capabilities.

Mastering the art of delivering a captivating presentation is an invaluable skill that transcends industries and job titles. Whether you’re pitching to potential clients, sharing insights with colleagues, or inspiring an audience at a large conference, your ability to communicate clearly, engage listeners, and convey information effectively can be a game-changer in your professional journey.
But what makes a great presentation? How do you prepare content that resonates, design slides that captivate, and deliver your message with confidence? In this article, we delve into the key components of crafting and executing a powerful presentation. We’ll provide you with strategic insights, practical tips, and answers to common questions that will help elevate your public speaking skills and enable you to present like a seasoned pro.
Common Presentation Interview Questions
1. how do you tailor a presentation to an audience with varied levels of expertise.
Delivering effective presentations requires understanding the range of expertise within your audience. A speaker must strike a balance, ensuring the content is accessible to novices without being overly simplistic for experts. This question reveals the candidate’s ability to assess audience needs, adapt their message accordingly, and communicate complex ideas in an inclusive manner that engages all participants. Mastery of this skill demonstrates an awareness of the diversity within any group and a commitment to inclusive communication, which is crucial for successful knowledge transfer and audience engagement.
When responding, outline your approach to audience analysis, such as conducting pre-presentation surveys or interviews to gauge expertise levels. Discuss how you would structure your presentation to introduce fundamental concepts while also providing depth for those more knowledgeable. Share techniques for interactive elements that can engage all levels, such as Q&A sessions, and how you might provide supplemental materials for further learning. Highlight past experiences where you successfully managed such a scenario, underscoring your adaptability and consideration for audience diversity.
Example: “ In tailoring a presentation to a diverse audience, I begin with a thorough audience analysis, often leveraging pre-presentation surveys to understand the varying degrees of expertise. This data informs the structure of my presentation, ensuring I lay a foundational narrative that is accessible to novices while incorporating advanced insights to challenge and engage experts. I carefully craft the content to enable a layered approach, where core concepts are clear and additional complexity is introduced progressively.
Interactive elements are pivotal; I integrate Q&A sessions at strategic intervals, which allow for real-time assessment and adaptation to audience needs. These sessions serve a dual purpose: they clarify uncertainties for beginners and open the floor to deeper discussions for seasoned attendees. To cater to ongoing learning, I provide supplemental materials post-presentation, such as advanced reading lists or access to online resources. This approach not only accommodates all levels of expertise during the session but also extends the learning experience beyond the presentation itself. My experience with this method has consistently yielded positive feedback, demonstrating its effectiveness in engaging and educating heterogeneous groups.”
2. What strategies do you employ for maintaining audience engagement during a lengthy presentation?
To keep an audience attentive and invested throughout lengthy presentations, a presenter must understand audience psychology, content structuring, and dynamic delivery. It’s not merely about disseminating information; it’s about crafting a narrative that resonates, using pacing techniques to maintain energy, and incorporating interactive elements to foster active participation. An effective presenter must be adept at reading the room and adapting on the fly, ensuring the material remains relevant and the delivery compelling.
When responding to this question, focus on concrete strategies you use, such as breaking up the presentation into digestible segments, using storytelling techniques, incorporating multimedia, and facilitating audience interaction through questions or activities. Discuss how you monitor audience body language and feedback to make real-time adjustments, ensuring your presentation is a dialogue rather than a monologue. Highlight your ability to weave in anecdotes or analogies that relate to your audience’s interests or experiences, which can create a more personalized and memorable presentation experience.
Example: “ To maintain audience engagement during a lengthy presentation, I segment the content into digestible parts, each with a clear focus and purpose. This modular approach not only helps in keeping the audience’s attention but also makes it easier for them to process and remember the information. I integrate multimedia elements strategically, such as short videos or interactive graphics, to provide a visual break and reinforce key points.
I employ storytelling techniques, crafting a narrative that connects the dots between the data and the real-world implications. This not only humanizes the content but also makes it more relatable and engaging. To ensure the presentation remains a dialogue, I incorporate moments for audience interaction. This could be through direct questions, quick polls, or even small group discussions if the format allows. I’m always attuned to the audience’s body language and feedback, ready to adjust the pace or dive deeper into topics that resonate. By weaving in relevant anecdotes and analogies, I create a personalized experience, making the content stick and the presentation memorable.”
3. Describe your process for distilling complex information into understandable slides.
Bridging the gap between intricate, detailed data and the audience’s comprehension is a key aspect of presentations. The ability to synthesize and simplify complex information is not just about making slides—it’s about grasping the essence of the data, identifying the key messages, and crafting a narrative that resonates. This skill demonstrates a presenter’s capacity to think critically, focus on what’s most important, and communicate effectively, ensuring that the audience walks away with the intended knowledge without being overwhelmed by technicalities or jargon.
When responding, outline a structured approach that starts with thoroughly understanding the complex material yourself. Emphasize how you prioritize the most relevant points for your audience’s needs and interests. Discuss your method for creating a storyline or framework that guides the presentation, and mention any tools or techniques you use to make data visually appealing and digestible, such as infographics, analogies, or real-world examples. Be prepared to provide a specific example of a time you successfully transformed a complicated subject into an engaging and informative presentation.
Example: “ My process begins with a deep dive into the material to ensure I have a solid grasp of the subject matter. Once I fully understand the complexities, I identify the key messages that are most pertinent to the audience’s needs. This involves discerning the essential information from the peripheral details, which often requires a critical evaluation of the data’s relevance and impact.
Next, I construct a narrative that not only conveys these key points but also tells a compelling story. This narrative framework is crucial as it provides a logical flow that guides the audience through the information without overwhelming them. To enhance comprehension, I employ visual aids such as infographics, which distill data into a more accessible format. I also use analogies and real-world examples to create relatable touchpoints for the audience. For instance, when presenting a complex financial strategy, I once used a simple kitchen recipe analogy to illustrate the step-by-step process, which resonated well with the audience and made the strategy easy to understand and remember.”
4. In what ways have you utilized storytelling within a professional presentation?
Transforming a mundane topic into a captivating journey is the hallmark of an adept storyteller within presentations. Storytelling is not merely a method of conveying information; it’s a powerful tool for engagement, making complex data relatable, and driving a message home. Employers seek individuals who can harness the art of narrative to communicate ideas compellingly, ensuring that key points resonate with their audience long after the presentation concludes.
When responding to this question, articulate how you’ve woven narratives into your presentations to illustrate concepts, humanize data, and create memorable moments. Share specific examples where your storytelling skills have enhanced understanding, fostered emotional connections, or inspired action. It’s essential to convey that your use of storytelling is strategic, intentionally crafted to support the presentation’s objectives and cater to the interests and needs of your audience.
Example: “ In leveraging storytelling, I’ve found that anchoring complex data within relatable narratives significantly enhances comprehension and retention. For instance, when presenting market analysis, I’ve utilized customer journey stories that encapsulate data points within the lived experiences of representative personas. This approach not only humanizes abstract figures but also fosters empathy, enabling stakeholders to grasp the practical implications of trends and figures.
Additionally, I’ve employed storytelling to catalyze action, particularly during strategic pitches. By crafting a narrative arc that mirrors the classic hero’s journey, I’ve positioned the product or initiative as the ‘hero’ equipped to overcome the audience’s challenges, which are framed as the ‘villain’. This technique not only makes the presentation more engaging but also aligns the audience’s emotional investment with the desired outcome, often resulting in a compelling call to action that resonates on both an intellectual and emotional level.”
5. Share an example where you had to adjust your presentation style on the fly due to unforeseen circumstances.
Adaptability and audience engagement are critical components of effective presentation skills. When unforeseen circumstances arise—such as technical difficulties, an unexpected change in audience demographics, or a drastic shift in the mood of the room—presenters must be capable of pivoting quickly and effectively. This question allows interviewers to assess a candidate’s ability to think on their feet, demonstrate flexibility, and maintain composure under pressure. It also reveals how a candidate can tailor their communication to suit the audience’s needs and still achieve the presentation’s objectives, even when conditions are less than ideal.
When responding, it’s crucial to describe a specific instance that showcases your adaptability without losing sight of your presentation goals. Begin by outlining the initial plan and the unexpected issue that arose. Then, detail the changes you implemented, explaining why you chose that particular adjustment and how you kept your audience engaged. Conclude with the outcome, emphasizing how your quick thinking and flexibility led to a successful presentation despite the challenges.
Example: “ In one instance, I was delivering a presentation to a diverse group of stakeholders when I noticed a significant portion of the audience was not fully engaged, likely due to varying levels of familiarity with the topic. Recognizing this, I pivoted from the planned technical deep-dive to a more high-level approach, interspersing relatable analogies and interactive elements to foster a more inclusive atmosphere. This shift not only recaptured the audience’s attention but also encouraged a dialogue that allowed for a more tailored and dynamic presentation.
The adjustment resulted in a positive shift in the room’s energy, with increased participation and pertinent questions that enriched the session. Post-presentation feedback underscored the effectiveness of the adaptation, with attendees expressing appreciation for the accessible content and the interactive nature of the experience. The ability to read the room and seamlessly modify the delivery ensured that the presentation’s objectives were met and the message was successfully conveyed to all participants.”
6. Outline your approach to handling challenging questions from the audience post-presentation.
Fielding challenging questions after delivering a presentation is where a presenter demonstrates their depth of knowledge and composure. This question is a litmus test for a candidate’s expertise on the subject matter, their critical thinking skills, and their capacity to maintain professionalism under pressure. It also reveals how well they can think on their feet and manage potentially adversarial situations, ensuring that the presentation’s objectives are not undermined by a tough Q&A session.
When responding to this question, articulate a structured approach that includes active listening, acknowledging the questioner, and providing a clear, concise, and confident answer. If unsure about a question, it’s acceptable to admit it and offer to follow up with a more informed response later. It’s vital to stay calm and respectful, using the opportunity to further demonstrate your expertise and enhance the audience’s understanding of the topic.
Example: “ In addressing challenging questions post-presentation, my initial step is to ensure that I fully comprehend the inquiry by actively listening and, if necessary, seeking clarification. This not only shows respect to the questioner but also allows me to tailor my response more effectively. I acknowledge the question and the individual asking it, which maintains a positive and engaging atmosphere.
When formulating a response, I prioritize clarity and conciseness, drawing upon relevant data and examples to substantiate my points. If the question touches on an area outside my immediate expertise, I maintain transparency by acknowledging the limits of my current knowledge. In such cases, I commit to providing a detailed follow-up after consulting additional resources or colleagues. This approach not only upholds my credibility but also demonstrates a commitment to accuracy and ongoing learning. Throughout the interaction, I remain composed and courteous, leveraging challenging questions as opportunities to deepen the audience’s understanding and to reinforce key messages from my presentation.”
7. What is your experience with using interactive elements in presentations?
Enhancing understanding, retention, and participation are the goals of incorporating interactive elements in presentations. They transform passive listeners into active participants, fostering a dynamic exchange of ideas and ensuring the message is not just heard but experienced. Employers are looking for individuals who can leverage these tools to create memorable and effective presentations that stand out in an era where attention spans are short and the need to impactfully convey information is high.
When responding to this question, it’s essential to provide concrete examples of when you have incorporated interactive elements such as real-time polls, Q&A sessions, or interactive demonstrations. Discuss the impact these elements had on the presentation’s effectiveness, how they helped you achieve your objectives, and the feedback received. This demonstrates your understanding of the value of interactivity and your ability to successfully implement it.
Example: “ Incorporating interactive elements into presentations has been a key strategy in my approach to engaging audiences and reinforcing key messages. For instance, I’ve utilized real-time polls during market analysis presentations to gauge audience sentiment, which not only captures attention but also provides immediate data to tailor the discussion. The dynamic nature of the poll results sparks a conversation and allows me to address specific interests or concerns on the spot, making the presentation more relevant and impactful.
Additionally, I’ve leveraged Q&A sessions effectively by integrating them at strategic points in the presentation rather than leaving them for the end. This ensures that the content remains fresh in the audience’s mind and encourages a more active participation, leading to a deeper understanding of the material. The feedback from these sessions has consistently highlighted their effectiveness in making the presentations more memorable and informative, as they foster a two-way dialogue that enriches the experience for both the audience and myself as the presenter.”
8. Detail how you measure the effectiveness of a presentation.
Gauging the effectiveness of a presentation is essential for continuous improvement and ensuring that the intended message resonates with the audience. Effectiveness can be measured through various quantitative and qualitative metrics, such as audience engagement, comprehension, feedback, and the subsequent actions taken by attendees. A skilled presenter knows that the success of a presentation extends beyond the applause—it’s about the lasting impact and the ability to drive the audience toward a desired outcome or understanding.
When responding to this question, you should discuss specific methods you use to evaluate your presentations. For instance, you might mention using real-time polls or surveys to gather immediate audience reactions, employing Q&A sessions to gauge understanding, or analyzing post-presentation feedback forms. You could also talk about tracking the implementation of ideas or strategies presented, or following up with attendees to see how the information has impacted their work or perspective. It’s important to convey that you have a systematic approach to evaluation and that you use these insights to refine your presentation skills and content.
Example: “ To measure the effectiveness of a presentation, I employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative metrics. Immediately following the presentation, I utilize real-time audience engagement tools, such as polls or interactive Q&A sessions, to assess understanding and retention of the content. This provides instant feedback on the clarity and impact of the presentation, allowing me to gauge whether the audience is aligning with the intended message.
In the days following the presentation, I distribute post-presentation surveys to collect more reflective feedback on the content, delivery, and overall value provided. I analyze this data to identify patterns and areas for improvement. Additionally, I track the long-term effects by following up with attendees to understand how they have applied the information or strategies discussed. This not only helps in assessing the practical impact of the presentation but also informs future presentations, ensuring that they are tailored to foster actionable outcomes and sustained engagement.”
9. Have you ever experienced technical difficulties during a presentation and how did you handle it?
Handling technical difficulties during presentations is a common challenge that can test a presenter’s composure and problem-solving skills. The ability to handle such disruptions showcases flexibility, preparedness, and professionalism. Employers are interested in how potential candidates deal with unexpected challenges and maintain their ability to communicate effectively under pressure. They also look for evidence of a candidate’s technical acumen and whether they have a plan B, such as backup materials or alternative methods to convey their message when technology fails.
When responding, it’s crucial to recount a specific instance where you faced technical difficulties, emphasizing your thought process and actions taken to resolve the issue. Highlight your calm demeanor, your quick thinking to implement a solution, or your decision to proceed without the aid of technology, if necessary. If you had contingency plans in place, such as printed handouts or a whiteboard illustration, mention these. Demonstrating that you can keep your audience engaged despite setbacks will illustrate your resilience and capability as a presenter.
Example: “ Absolutely, technical difficulties are almost an inevitable part of modern presentations. On one occasion, I was in the midst of a critical presentation when the projector suddenly failed. Without skipping a beat, I shifted to a whiteboard to illustrate the key points while the technical issue was being addressed. This not only demonstrated my ability to adapt quickly but also my preparation; I had ensured that the main points could be communicated without reliance on slides. Meanwhile, I engaged the audience with relevant questions to maintain their attention and encourage participation, turning the potential disruption into an interactive discussion.
In another instance, the presentation software crashed, and it was clear that a quick fix was not available. I had anticipated such a scenario and brought printed copies of the slides as a backup. I distributed these to the audience and proceeded with the presentation, effectively turning it into a guided discussion. These experiences have reinforced the importance of always having a Plan B, whether it’s a hard copy of the presentation or an alternative method of delivery, ensuring that the message is conveyed effectively regardless of technological challenges.”
10. Which software platforms are you proficient in for creating compelling visual aids?
Crafting compelling visual aids is a crucial aspect of presentations, as they are the visual voice of the speaker’s ideas. Proficiency in a range of software platforms demonstrates versatility and the capacity to tailor the presentation to the audience’s needs and the context of the information. It also suggests an awareness of current technologies and an aptitude for visual storytelling, which are valuable in creating engaging, informative, and memorable presentations.
When responding to this question, it’s best to list the specific software platforms you’re skilled in, such as PowerPoint, Prezi, Keynote, Adobe Creative Suite, Canva, or any other specialized tools you might use. Provide examples of presentations you’ve created using these platforms and discuss how you leveraged their unique features to enhance your message. If possible, share anecdotes about how your visual aids positively influenced the outcome of a presentation or helped convey complex information in an accessible manner.
Example: “ I am proficient in a variety of software platforms that are essential for creating compelling visual aids, including PowerPoint, Prezi, Keynote, and Adobe Creative Suite, with a particular emphasis on Illustrator and Photoshop for custom graphics. Additionally, I am adept at using Canva for quick yet professional designs when time is of the essence.
In leveraging PowerPoint, I have utilized its advanced animation and transition capabilities to craft a narrative flow that underscores key points, ensuring the audience remains engaged throughout the presentation. With Prezi, I’ve created dynamic, non-linear presentations that are particularly effective for storytelling and keeping viewers intrigued by the spatial journey. For executive briefings, I’ve turned to Keynote for its clean design aesthetics and seamless integration with Apple products, which often match the technological preferences of the audience. Adobe Creative Suite has been my go-to for developing high-quality, original graphics and editing images to a professional standard, ensuring that every visual element is tailored to the presentation’s message. These tools, combined with a strategic approach to visual storytelling, have consistently led to successful outcomes, such as securing stakeholder buy-in or simplifying the communication of complex data.”
11. Relate a time when you had to present a topic outside your area of expertise.
Showcasing flexibility, the ability to research comprehensively, and the skill to learn quickly are essential when conveying information on unfamiliar topics. It also demonstrates confidence and the competence to step outside one’s comfort zone, which are indicative of a growth mindset and leadership potential. Interviewers are looking for evidence of how you approach the challenge of presenting on an unknown subject, the strategies you use to become knowledgeable, and how you ensure that the information is understood by your audience.
When responding to this question, focus on a specific instance where you had to present on an unfamiliar topic. Detail the steps you took to familiarize yourself with the subject matter, including any research or learning methods you employed. Discuss how you ensured your presentation was engaging and understandable, and reflect on the outcome. Highlight any feedback you received and what you learned from the experience, emphasizing your adaptability and commitment to professional development.
Example: “ When tasked with presenting a topic outside my expertise, I immediately immersed myself in intensive research, seeking out the most current and relevant information from credible sources. I prioritized understanding the fundamental concepts and terminology to ensure I could speak with confidence and clarity. To make the material engaging, I employed storytelling techniques, relating the new information to common experiences and using analogies that resonated with the audience’s background.
During the presentation, I focused on interactive elements, such as Q&A sessions, to foster a collaborative learning environment. This approach not only enhanced audience engagement but also allowed me to gauge their understanding in real-time, adjusting my delivery as needed. The feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with attendees appreciating the digestible format and the clear conveyance of complex material. This experience underscored the importance of thorough preparation and the ability to translate intricate concepts into accessible content, reinforcing my adaptability and dedication to continuous learning.”
12. How do you ensure that your body language positively contributes to your message delivery?
Nonverbal cues like body language play a significant role in engaging the audience and reinforcing the message during presentations. Your stance, gestures, and facial expressions can either distract from or enhance the clarity and impact of your communication. Presenters who are self-aware and intentionally use their body to add depth to their message ensure that it resonates more powerfully with their audience.
When responding, it’s essential to highlight your awareness of common body language principles, such as maintaining eye contact, using gestures to emphasize points, and adopting an open stance to appear approachable and confident. Discuss your strategies for practicing these techniques, perhaps through videotaping your rehearsals or receiving feedback from peers. Emphasize your commitment to continuous improvement and how you actively work to align your nonverbal communication with your spoken words to deliver a coherent and compelling presentation.
Example: “ In ensuring that my body language aligns positively with my message delivery, I prioritize the synchronization of verbal and nonverbal cues. This involves maintaining steady eye contact to foster engagement and demonstrate confidence, as well as utilizing purposeful gestures that underscore key points, thereby enhancing the audience’s comprehension and retention of the content. An open stance is adopted not only to appear approachable but also to project an aura of confidence and authority.
To refine these techniques, I engage in deliberate practice, often recording my presentations to critically evaluate my body language and its impact on the message conveyed. This self-review is complemented by seeking candid feedback from peers, which provides external perspectives on my nonverbal communication. This iterative process of rehearsal, feedback, and adjustment fosters a heightened awareness of my physical presence and ensures that my body language consistently reinforces the clarity and persuasiveness of my presentations.”
13. What techniques do you use to open and close a presentation memorably?
Understanding the psychological impact of a strong start and finish is crucial for presenters. The opening and closing of a presentation are pivotal moments that can captivate an audience or leave them with a lasting impression. A powerful opening can hook the audience’s attention, while an effective closing can reinforce the key message and call to action, ensuring the presentation’s objectives are achieved.
When responding, highlight specific techniques you employ to engage your audience from the outset, such as starting with a thought-provoking question, a relevant anecdote, or an interesting statistic. Explain how you establish the relevance of your topic to your audience’s interests and needs. For concluding your presentation, discuss methods you use to summarize the main points succinctly and clearly, possibly circling back to your opening hook for a cohesive effect. Mention any strategies you use to inspire or motivate your audience to take action, reflecting on how you ensure your final words resonate and drive home the purpose of your presentation.
Example: “ To open a presentation memorably, I often begin with a compelling hook that directly relates to the core message—this could be a surprising statistic that challenges common perceptions, a brief story that illustrates the stakes involved, or a question that prompts the audience to think critically about the topic. This technique not only captures attention but also sets the stage for the narrative arc of the presentation. It’s crucial to establish the relevance of the topic early on, so I make sure to articulate how the content will address the audience’s interests or solve a problem they care about.
Closing a presentation is just as critical as the opening, as it’s the last opportunity to reinforce the key message. I employ a strategy of bookending, where I circle back to the opening hook, creating a sense of closure and reinforcing the central theme. I summarize the main points succinctly, ensuring they are clear and memorable, and end with a call to action that is both inspiring and practical. This could be an invitation to adopt a new perspective, a challenge to apply the information presented, or a tangible next step they can take. By doing so, I ensure the presentation has a lasting impact and drives the audience toward the intended outcome.”
14. How do you incorporate feedback from previous presentations into future ones?
Incorporating feedback into presentations is an exploration into your ability to self-reflect, adapt, and evolve your approach. It demonstrates whether you see feedback as a gift for growth or as criticism to be dismissed. Employers are looking for individuals who actively seek out and apply constructive criticism to enhance their performance, ensuring their message resonates more effectively with each iteration.
To respond, outline a systematic approach: First, explain how you solicit feedback, whether through formal surveys, informal conversations, or even by observing audience engagement during the presentation. Then, discuss how you analyze this information to identify patterns or specific areas for enhancement. Finally, share examples of how you’ve altered your presentation style, content, or delivery method based on this feedback, leading to tangible improvements in audience reception or desired outcomes.
Example: “ Incorporating feedback into future presentations is a critical aspect of refining and improving the effectiveness of my communication. Following each presentation, I actively seek out both qualitative and quantitative feedback through structured surveys and open-ended discussions. This dual approach allows me to gather specific insights and gauge the emotional resonance of the content with the audience.
Upon collecting the feedback, I conduct a thorough analysis to identify recurring themes or suggestions for improvement. For instance, if multiple participants point out that certain sections were too complex or not sufficiently engaging, I prioritize those areas for modification. I then iterate on the content, simplifying complex ideas or incorporating storytelling elements to enhance engagement. Additionally, if the feedback indicates that the pacing was off or that the visuals were not impactful, I adjust the tempo of my delivery and redesign the visual aids accordingly. This process of continuous refinement, guided by targeted feedback, has consistently led to more dynamic presentations and measurable increases in audience understanding and interaction.”
15. When have you successfully adapted a presentation for multicultural audiences?
Adapting content, tone, and delivery to suit multicultural audiences is paramount when delivering presentations. The ability to navigate the subtleties of cross-cultural interactions ensures your message resonates with everyone in the room, regardless of their background. This skill is particularly valuable in a globalized business environment where teams and clientele are often international.
When responding to this question, recount a specific instance where you tailored a presentation to cater to a multicultural audience. Detail the research and preparation you undertook to understand the cultural expectations and norms of the audience. Explain how you adjusted your language, examples, humor, and even visual aids to be culturally sensitive and engaging. Highlight the feedback you received and how it informed your approach to future presentations, demonstrating continuous learning and adaptability.
Example: “ In preparation for a presentation to a multicultural audience, I conducted thorough research to understand the cultural nuances and communication styles of the participants. Recognizing the diversity in the room, I carefully selected universal themes and designed the content to resonate across cultural boundaries. I avoided idioms and region-specific references that could lead to misunderstandings, and instead, used clear, concise language.
I adapted visual aids to include a variety of cultural contexts, ensuring that imagery and examples were inclusive and relatable. Humor was used judiciously, with a focus on light, universally understandable jokes that did not hinge on cultural knowledge. The success of this approach was evident in the engaged reactions during the presentation and the positive feedback afterward, which highlighted the clarity and inclusiveness of the content. This experience reinforced the importance of cultural sensitivity and has since guided my approach to crafting and delivering presentations to diverse groups.”
16. Describe how you prioritize content when faced with strict time constraints.
Distilling complex ideas into digestible, impactful points is essential when presenting information under tight time constraints. This question serves to reveal your critical thinking and content curation skills. It also sheds light on your understanding of the audience’s needs and your ability to focus on key messages that align with the objectives of the presentation. Employers are looking for your capability to identify what’s most important and to convey it in a clear, concise manner that respects the audience’s time and attention span.
To respond, illustrate your process for determining the priority of content, which might involve identifying the core message, understanding the audience’s level of knowledge on the topic, and considering the outcomes you want to achieve. Share a specific example of a time when you successfully navigated this challenge, explaining how you decided what to include, what to leave out, and how you structured your presentation to ensure it was effective within the allotted time.
Example: “ When prioritizing content under time constraints, my approach is to distill the presentation down to its essence by focusing on the objectives of the presentation and the key takeaways for the audience. I start by identifying the core message and the most critical pieces of information that support that message. I then assess the audience’s existing knowledge and tailor the content to fill gaps or build on their understanding, ensuring that the content is neither too basic nor too complex.
For example, in a recent high-stakes presentation with a 10-minute limit, I was tasked with conveying the potential impact of a new technology. I honed in on the three most compelling benefits of the technology, supported by succinct data points that underscored its value. I omitted technical jargon and detailed methodology, which would have taken up valuable time and potentially lost the audience’s interest. Instead, I structured the presentation to open with a strong, relatable narrative that illustrated the technology’s significance, followed by the key benefits and closing with a clear call to action. This approach kept the presentation within the time frame and resonated well with the audience, leading to a successful outcome.”
17. What methods do you use to foster collaboration during group presentations?
Transforming a collection of individual contributions into a cohesive, impactful performance is the essence of effective collaboration in group presentations. Beyond assessing your skills in orchestrating a group effort, this question seeks to understand your ability to harness diverse perspectives, navigate interpersonal dynamics, and leverage each team member’s strengths to achieve a common goal. It’s about your approach to leadership, your capacity for empathy, and your strategic planning to ensure all voices are heard and integrated into the final product.
When responding, outline a structured approach: start by explaining how you set clear objectives and expectations from the outset. Discuss the importance of creating an inclusive environment where all participants feel valued, mentioning specific techniques like round-robin brainstorming or utilizing digital collaboration tools. Highlight any processes you implement to ensure accountability, such as regular check-ins or progress reports. Lastly, share a brief example from your experience where your methods led to a successful group presentation outcome, emphasizing the positive feedback and results achieved through your facilitation of teamwork.
Example: “ To foster collaboration during group presentations, I begin by establishing clear objectives and expectations, ensuring that each team member understands the goals and their role in achieving them. I create an inclusive environment by employing techniques such as round-robin brainstorming, which guarantees that everyone has a voice, and by leveraging digital collaboration tools like shared documents and real-time editing platforms to facilitate seamless communication and idea sharing.
Accountability is maintained through regular check-ins and progress reports, which help keep the team aligned and focused. For instance, in a recent project, this approach led to the development of a highly engaging presentation that received commendable feedback for its cohesiveness and the way it leveraged each team member’s strengths. The success was evident not just in the outcome, but also in the team’s increased confidence and the client’s satisfaction with our collaborative process.”
18. Give an instance where persuasive presentation skills led to a tangible outcome.
Influencing and persuading an audience to take action or to view a topic from a different perspective is a key element of effective presentation skills. Employers seek individuals who can not only present information clearly but who can also compel stakeholders, sway opinions, secure buy-in, or drive organizational change through their presentations. This question is designed to assess a candidate’s ability to impact decision-making and achieve real-world results through their communication prowess.
When responding, select a specific example that showcases your ability to craft and deliver a persuasive presentation. Focus on the preparation work, the audience analysis you conducted, and how you tailored your message for maximum impact. Discuss the strategies you used to engage the audience, any visual or data-driven aids that supported your case, and how you handled objections or questions. Conclude with the outcome, detailing how your presentation directly influenced a decision, action, or shift in perspective, and, if possible, mention any measurable results that followed.
Example: “ In a recent instance, I developed a presentation aimed at persuading a panel of stakeholders to adopt a new software solution that promised to enhance operational efficiency. I began by conducting a thorough audience analysis, identifying the key concerns and motivations of each stakeholder. This enabled me to tailor the content, focusing on the software’s ability to address specific pain points such as reducing manual errors and streamlining workflow processes.
I employed a narrative structure, anchoring the presentation around a central story of a hypothetical yet relatable scenario where the software dramatically improved productivity. To bolster my argument, I integrated compelling data visualizations that clearly demonstrated the potential return on investment and comparative analyses with existing systems. Throughout the presentation, I engaged the audience with rhetorical questions and interactive elements, maintaining their attention and fostering a collaborative atmosphere.
When faced with skepticism, I addressed questions with evidence-based responses, reinforcing the software’s benefits with real-world success stories from similar organizations. The outcome was a unanimous decision to proceed with implementation, and within six months, the organization reported a 25% increase in operational efficiency, validating the effectiveness of the persuasive strategies employed in the presentation.”
19. How do you maintain coherence when integrating data and statistics into your narrative?
Weaving data and statistics into a narrative without losing the audience’s attention or confusing them is an art form. It requires a clear understanding of the story you’re trying to tell and the role that data plays in that story. It’s not just about presenting numbers; it’s about making those numbers meaningful and relevant to your audience. Employers are looking for individuals who can take complex information and distill it into a compelling, accessible format that supports the overarching message. This skill demonstrates critical thinking, analytical prowess, and the capacity to engage and persuade an audience.
When responding to this question, emphasize your approach to storytelling with data. Discuss how you prioritize the most impactful statistics, use analogies or visual aids to illustrate your points, and ensure each piece of data reinforces the narrative thread. Mention any techniques you use to make complex data more digestible, such as breaking it down into simpler terms, building it up piece by piece, or relating it to something familiar to the audience. The goal is to show that you can make data a tool for storytelling rather than a stumbling block.
Example: “ To maintain coherence when integrating data and statistics into a narrative, I prioritize selecting data points that directly support the story’s core message. This involves a careful curation process where I identify the most impactful statistics that align with the narrative’s objective and resonate with the intended audience. I also use analogies and visual aids to contextualize the data, grounding abstract numbers in concrete and relatable terms. For instance, if I’m presenting on the growth of renewable energy, I might compare the increase in solar panel installations to a familiar concept, like the growth of a city’s population, to make the scale more understandable.
In addition, I employ a progressive disclosure technique, introducing data in layers to avoid overwhelming the audience. I start with a high-level overview, then gradually delve into more detailed statistics as the story unfolds, ensuring each data point is a logical extension of the previous information. This scaffolding approach helps the audience to assimilate complex data in manageable increments. By using these strategies, I ensure that data enhances the narrative, providing evidence and clarity, rather than detracting from the story’s flow and coherence.”
20. Reflect on a moment when you effectively used silence as a tool in your presentation.
Controlling the room and the audience’s attention can be achieved by mastering the art of silence in a presentation. Effective use of silence can emphasize important points, give the audience time to absorb information, and create a dynamic rhythm that keeps listeners engaged. It demonstrates a presenter’s confidence and comfort with the material and the presentation space. Silence can also serve as a non-verbal cue, signaling to the audience that something significant is being communicated, which can heighten interest and focus.
When responding to this question, you should recount a specific instance where you strategically employed a pause. Describe the lead-up to the moment of silence, the audience’s reaction, and the impact it had on the overall presentation. Explain your thought process behind the decision to use silence at that particular juncture and how it contributed to the effectiveness of your communication. Your response should convey your understanding of pacing and your ability to use silence not as an absence of words, but as a powerful communication tool in itself.
Example: “ In a recent presentation on the impact of strategic pauses in speech, I deliberately incorporated a prolonged silence following a key point about the power of pausing to enhance audience engagement. After discussing the cognitive overload that can occur with a constant stream of information, I paused for a full ten seconds. This silence not only allowed the audience to digest the information but also served as a live demonstration of the concept. The room’s dynamic shifted palpably; attendees leaned forward, anticipation built, and when I resumed speaking, the engagement was markedly heightened. This silence punctuated the importance of the point and underscored the effectiveness of the technique.
The decision to use silence at that moment was informed by the understanding that strategic pauses can act as an auditory underline, giving weight to the preceding statement. It was a calculated risk, but the payoff was evident in the audience’s renewed focus and the lively Q&A session that followed. This approach reinforced the message that silence, when used purposefully, is not a void but a tool for emphasizing content and facilitating deeper comprehension.”
Top 20 Facility Management Interview Questions & Answers
Top 20 insurance claims interview questions & answers, you may also be interested in..., top 20 safeguarding interview questions & answers, top 20 mechanical engineering interview questions & answers, top 20 lean six sigma interview questions & answers, top 20 succession planning interview questions & answers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Download the "Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 11th Grade" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Try incorporating their feedback into your next chat, brainstorming session, or video conference. 4. Prioritize interpersonal skills. Improving interpersonal skills —or your ability to work with others—will feed into the way you communicate with your colleagues, managers, and more.
9 talks. The art of finding common ground. Disagreements, miscommunications, opposing beliefs -- oh my! Whether at work, with strangers or over family dinner, these talks will help you traverse the rugged terrain of heated conversation and map out the best ways to see eye-to-eye. See all playlists on Communication.
Try a story (see tip 7 below), or an attention-grabbing (but useful) image on a slide. 6. Remember the 10-20-30 Rule for Slideshows. This is a tip from Guy Kawasaki of Apple. He suggests that slideshows should: Contain no more than 10 slides; Last no more than 20 minutes; and. Use a font size of no less than 30 point.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Communication Skills Training Workshops are perfect for individuals or groups who want to gain the knowledge and practice necessary to become better communicators. Here, attendees can learn about topics ranging from active listening to body language for effective communication.
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. Communication occurs in many forms, including verbal and non-verbal, written, visual, and ...
Determine your 3 Main Points. Add key supporting points for each of your Main Points. Complete the other parts - introduction, grabber, call to action, etc. Working in this order is fast because it's easier to create the conclusion and grabber when you've already decided on the content. Also, after you have the main structure it's easy ...
1. See yourself as others see you. Hear yourself as others hear you. Visual elements of your presentation are crucial. Humans use visual references to process immeasurable amounts of information. We can reach opinions about a situation or person with a glance. That makes it essential to focus on non-verbal communication.
Summary. Transformational leaders are exceptional communicators. In this piece, the author outlines four communication strategies to help motivate and inspire your team: 1) Use short words to talk ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
This is not surprising. Effective communications skills are a powerful career activator, and most of us are called upon to communicate in some type of formal presentation mode at some point along the way. For instance, you might be asked to brief management on market research results, walk your team through a new process, lay out the new budget ...
Cultivate your personal leadership and communication style; Learn strategies on handling hostile audiences "Jill [Slye] shared invaluable tips that have helped me to reduce my anxiety and negative self-talk around my presentations while conveying a message that encourages others to affect change through empowering presentations."
Planning Presentations. As you can see based on the video examples, presentations always require a situational analysis in the planning stage. Identify your audience, purpose, context, and all of the communication variables that you need to consider in order to make choices that will result in an effective presentation for your purpose and audience.
Effective communication skill 1: Become an engaged listener. When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the ...
Communication skills take on heightened importance for leaders. In fact, take a few minutes to think of a person you consider to be an effective leader. I bet communication skills are one of their traits. Such skills are essential to conveying and showcasing leadership ability. It doesn't necessarily mean the person is overly loquacious.
Step 3: Be novel. Make sure you either select a new topic or bring an entirely new and unique perspective to an already covered issue. For instance, don't make a presentation on the "best lead generation strategies.". Your audience has probably heard those dozens of times already. Corny.
3. Townhall and its benefits. This is often a forgotten mode of communication in many organisations. In today's modern day of social media and other platforms, it is easy to forget the impact that a townhall can have on the employees of an organisation. An interesting presentation topic for business communication. 4.
Practice being aware of your body and facial expressions in your daily communication to start understanding where you can improve. Ask for feedback if appropriate. Practice these ways to use body language to improve your communication skills: Uncross your arms to maintain a more "open" position.
Importance of communication skills in presentation. Effective communication, fresh perspectives, and enhanced teamwork have created some of the world's best projects. People who can communicate their desires, goals, and wishful outcomes are game-changers, and those people are valuable for any architectural company.
back. Communication Skills: Performance Review Examples (Rating 1 - 5) Effective communication is a crucial skill in the workplace: it fosters healthy relationships, clear information exchange, and a positive work environment. Although some employees excel at communication instinctively, others may need guidance in refining their skills.
These tools, combined with a strategic approach to visual storytelling, have consistently led to successful outcomes, such as securing stakeholder buy-in or simplifying the communication of complex data.". 11. Relate a time when you had to present a topic outside your area of expertise.