
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Your Guide From Start to Finish

Today, we're swamped with information, like reading 174 newspapers every day. It comes from all over—news, social media, science, and more. This flood might make you feel overwhelmed and lost in a sea of facts and opinions. But being able to make sense of it all is crucial.
This guide isn't just about handling all that info; it's about using it to write awesome essays. We'll show you step by step how to pick a topic and organize your essay. Let's dive in and learn how to turn scattered facts into powerful essays that really stand out.
What Is a Synthesis Essay
The synthesis essay is a powerful tool in writing. It's not just about gathering facts but about connecting them to make a clear and strong argument.
Writing a synthesis essay allows you to dive deep into ideas. You have to find similarities between different sources—like articles, studies, or arguments—and use them to tell a convincing story.
In today's world, where we're bombarded with information, synthesis essays are more important than ever. They let us explore how different ideas fit together and help us express our thoughts on complex topics. Whether you're writing about literature, science, history, or current events, a synthesis essay shows off your ability to analyze and understand a topic from all angles. And if you're struggling with this task, just ask us to ' write paper for me ,' and we'll handle your assignment for you.
Explanatory vs. Argumentative Synthesis Essays
In synthesis writing, there are two main types: explanatory and argumentative. Understanding these categories is key because they shape how you approach your essay.
Explanatory:
An explanatory synthesis essay does just what it says—it explains. These essays aim to give a balanced view of a topic by gathering information from different sources and presenting it clearly. They don't try to persuade; instead, they focus on providing information and making things easier to understand. They're like comprehensive summaries, breaking down complex ideas for a broader audience. These essays rely heavily on facts and expert opinions, avoiding personal bias.
Argumentative:
On the flip side, argumentative synthesis essays are all about persuasion. Their main goal is to take a stance on an issue and convince the reader. They gather information from various sources not only to present different views but also to build a strong argument. Argumentative essays aim to sway the reader's opinion by using gathered information as evidence. These essays express opinions and use rhetorical strategies to persuade.
And if you're keen on knowing how to write an informative essay , we've got you covered on that, too!
Synthesis Essay Structure
To craft a strong synthesis essay, you need a solid foundation. Here's a structured approach to help you nail it:
Introductory Paragraph:
- To kick things off, grab your reader's attention with a catchy hook or interesting fact. Give a bit of background info about your topic and the sources you'll be using, as it can help readers understand your topic better! Then, lay out your main argument in a clear thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs:
- Each paragraph should focus on a different aspect of your topic or source. Start with a topic sentence that links back to your thesis. Introduce the source you're discussing and highlight its main points. Also, using quotes, paraphrases, or summaries from your sources can make your arguments stronger.
Synthesis :
- This part is where your essay comes together. Look for common themes or differences among your sources. Use your analysis to build a strong argument. Don't forget to address any opposing viewpoints if they're relevant!
Conclusion :
- Wrap things up by restating your thesis and summarizing your main points. Explain why your argument is important and what it means in the bigger picture. End with a thought-provoking statement to leave a lasting impression.
References :
- Finally, don't forget to list all your sources properly using the right citation style, like MLA or APA. Do you know that different citation styles have different rules? So, make sure you follow the right one!
Choosing a Synthesis Essay Topic
Picking essay topics is just the beginning. To write a great synthesis essay, you need to carefully evaluate and connect different sources to build a strong argument or viewpoint. Here's a step-by-step infographic guide to help you choose the right synthesis essay topics wisely.

How to Write a Synthesis Essay with Easy Steps
Writing a synthesis essay is similar to a compare and contrast essay . It requires a methodical approach to blend information from different sources into a strong and persuasive argument. Here are some crucial steps and tips to help you along the way.
- Clarify Your Purpose: First, decide if you're writing an explanatory or argumentative synthesis essay. This choice will set the tone and direction for your essay.
- Source Selection and Analysis: Choose credible and relevant sources for your topic, balancing different types like articles, books, and websites. Analyze each source carefully, noting the main ideas and evidence presented.
- Formulate a Strong Thesis Statement: Create a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your essay. It should express your main argument or perspective.
- Structure Your Essay: Organize your essay with a clear synthesis essay outline, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of your topic.
- Employ Effective Transition Sentences: Use transition sentences to connect your ideas and paragraphs smoothly, ensuring a cohesive flow in your essay.
- Synthesize Information: Blend information from your sources within your paragraphs. Discuss how each source contributes to your thesis and highlight common themes or differences.
- Avoid Simple Summarization: Don't just summarize your sources—analyze them critically and use them to build your argument.
- Address Counterarguments (if applicable): Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counter them with well-supported arguments, showing a deep understanding of the topic.
- Craft a Resolute Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in the conclusion. Emphasize the importance of your argument or insights, and end with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
- Revise and Proofread: Check your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammar mistakes. Ensure your citations are correct and follow the chosen citation style, like MLA or APA.
Ready to Transform Your Synthesis Essay from Bland to Grand?
Let's tap into the magic of our expert wordsmiths, who will create an essay that dances with ideas and dazzles with creativity!
Synthesis Essay Format
Choosing the right citation style can enhance the credibility and professionalism of your paper. The format of your synthesis paper depends on the specific guidelines given by your instructor. They usually fall into one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago, each used in different academic fields.

1. MLA (Modern Language Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and page number.
- Includes a 'Works Cited' page at the end listing all sources.
- Focuses on the author and publication date.
- Often used in humanities essays, research papers, and literary analyses.
2. APA (American Psychological Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and publication date in parentheses.
- Includes a 'References' page listing all sources alphabetically.
- Emphasizes the publication date and scientific precision.
- Commonly used in research papers, scholarly articles, and scientific studies.
3. Chicago Style:
- Offers two documentation styles: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date.
- Notes-Bibliography uses footnotes or endnotes for citations, while Author-Date uses in-text citations with a reference list.
- Suitable for various academic writing, including research papers and historical studies.
- Provides flexibility in formatting and citation methods, making it adaptable to different disciplines.
Synthesis Essay Example
Here are two examples of synthesis essays that demonstrate how to apply the synthesis process in real life. They explore interesting topics and offer practical guidance for mastering the art of writing this type of paper.
Synthesis Essay Tips
Crafting a strong synthesis essay requires careful planning and effective techniques. Here are five essential tips to help you write your best paper:
- Diverse Source Selection : Choose a range of reliable sources that offer different viewpoints on your topic. Make sure they're recent and relevant to your subject.
- Seamless Source Integration : Avoid just summarizing your sources. Instead, blend them into your essay by analyzing and comparing their ideas. Show how they connect to build your argument.
- Balanced Tone : Maintain an impartial tone in your writing, even if you have personal opinions. Synthesis essays require objectivity, so they present different viewpoints without bias.
- Focus on Synthesis : Remember, synthesis essays are about linking ideas, not just summarizing sources. Explore how your sources relate to each other to create a cohesive argument.
- Address Counterarguments : Like in persuasive essays topics , acknowledge opposing viewpoints and explain why your perspective is stronger. This demonstrates your understanding of the topic and adds depth to your argument.
Concluding Thoughts
When writing a synthesis essay, it's essential to pick trustworthy sources, blend them effectively to build your argument and stay objective. Use smooth transitions, address counterarguments thoughtfully, and focus on analyzing rather than just summarizing. By following these steps, you'll create essays that inform, persuade, and engage your readers!
Want an Essay that Sings, Sparkles, and Stuns?
Fear not! Our expert wordsmiths are here to turn your thoughts into a symphony of ideas!
How Should You Conclude a Synthesis Essay?
Related articles.
.webp)
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center Write to Synthesize: The Research Essay
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
In a synthesis, you bring things together. This combination, integration, or merging creates something new--your synthesis. The action of synthesis is basic to our world. Take, for example, what happens when a single oxygen molecule is combined with two hydrogen molecules. Water is created or synthesized. Hard to get more basic than that.
You also use synthesis to make personal decisions. If two instructors are teaching a class you must take, you may synthesize your past experiences with the teachers to choose the best class for you.
Research Essays:
Thesis driven.
In school, when writing a synthesis from your research, your sources may come from the school's library, a textbook, or the Internet. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
First, regardless of where your sources come from or how many you have, what you write should be driven by a thesis that you devise. After reading and studying your sources, you should form a personal point of view, a slant to connect your sources.
Here's a quick example--Let's say you've read three folktales: Goldilocks and the Three Bears, Little Red Riding Hood, and the Pied Piper--and now you must write a synthesis of them. As you study the three sources, you think about links between them and come up with this thesis:
Folktales use fear to teach children lessons.
Then you use this thesis to synthesize your three sources as you support your point of view. You combine elements from the three sources to prove and illustrate this thesis. Your support points could focus on the lessons for children:
- Lesson 1 : Never talk to strangers.
- Lesson 2 : Don't wander from home.
- Lesson 3 : Appearances can deceive us.
This step of outlining your thesis and main points is a crucial one when writing a synthesis. If your goal in writing a research essay is to provide readers a unified perspective based on sources, the unified perspective must be clear before the writing begins.
Once the writing begins, your point of view is then carried through to the paragraph and sentence levels. Let's examine some techniques for achieving the unity that a good synthesis requires. First, here’s an example of an unsuccessful attempt at synthesizing sources:
Many sources agree that capital punishment is not a crime deterrent. [This is the idea around which the sources should be unified. Now comes the sources] According to Judy Pennington in an interview with Helen Prejean, crime rates in New Orleans rise for at least eight weeks following executions (110). Jimmy Dunne notes that crime rates often go up in the first two or three months following an execution. “Death in the Americas” argues that America’s crime rate as a whole has increased drastically since the re-instatement of the death penalty in the 1960s. The article notes that 700 crimes are committed for every 100,000 Americans (2). Helen Prejean cites Ellis in her book to note that in 1980, 500,000 people were behind bars and in 1990 that figure rose to 1.1 million (112).
Sample student paragraph adapted from "Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources." Retrieved 2011 from https://scholarworks.iupui.edu/items/7dda80e7-b0b3-477c-a972-283b48cfdf5c
This paragraph certainly uses a number of sources. However, the sources are presented in a random, grocery list fashion. Besides the main point at the beginning, there is no further attempt to synthesize. The sources seem tossed in, like ingredients in a salad. Let's examine a possible revision of that paragraph and how an adequate synthesis might be achieved:
Major studies suggest that capital punishment fails to deter crime. Helen Prejean, in "Deadman Walking," reviews decades of statistics that indicate capital punishment does little to lower crime. [Key idea from topic sentence—"capital punishment fails to deter crime"— echoed in sentence about source–"capital punishment does little to lower crime." Repetition links source to main idea.] Based on this evidence, Prejean concludes “Executions do not deter crime . . . the U.S. murder rate is no higher in states that do not have the death penalty than those who do” (110). ["Based on this evidence" forces reader to refer back to "statistics" in previous sentence.] Prejean’s point is reiterated from a historical perspective in Dunne's article “Death in the Americas.” [This sentence provides a thought bridge between two sources.] Dunne first points out that, despite the social and economic upheavals from 1930 to 1960, crime rates were unchanged (2). [Linking phrase:"Dunne first points out"] However, after the reinstatement of the death penalty in the 1960s, “crime rates soared” (2). [Linking phase "However, Dunne notes."]
The result is a matrix of connective devices that unifies the sources around a key idea stated at the beginning. Although this matrix seems complex, it is actually built on a simple three-point strategy.
- Stay in charge . You the writer must control the sources, using them to serve your purpose. In good synthesis writing, sources are used to support what you, the writer, have already said in your own words.
- Stay focused . Your main point is not merely stated once and left to wilt. Your main idea is repeated and echoed throughout as a way to link the sources, to weave them together into a strong fabric of meaning.
- Stay strategic . Notice the "source sandwich" strategy at work. First, the author sets up the source with its background and relevance to the point. After the source comes a follows up in his/her own words as a way to bridge or link to the next part. In other words, the writer's own words are used like two slices of bread, with the source in the middle.
Follow these simple principles when using sources in your writing and you will achieve the most important goal of synthesis writing--to create a whole greater than its parts.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
27 How do I Write a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is a type of essay that gathers information from a variety of sources to form a new idea, question, or argumentative thesis. Writers composing a synthesis essay will discuss ideas, data, and evidence from a series of sources to either explain or argue something original.
Explanatory vs. Argumentative Synthesis Essays: How Are They Different?
Though the formatting is largely the same, there are two main types of synthesis essays: explanatory and argumentative.
- 1. Explanatory : The purpose of an explanatory synthesis essay is to use different sources to explain a particular point of view. These synthesis papers objectively examine the similarities and differences between ideas but don’t necessarily choose a side or attempt to sway the reader in any direction.
- 2. Argumentative : An argumentative synthesis essay follows the same structure as a typical argumentative essay. The thesis of an argumentative essay will argue one specific point.
Synthesis Essay Structure
Synthesis essays typically adhere to the five-paragraph essay structure, but there are slight nuances to structuring this type of essay. Here is how a synthesis essay is structured.
- Introduction : The foundational ideas of your essay are expressed in the introductory paragraph. You will address the general landscape of ideas around your topic, introducing some of your sources. You will also introduce the argument to be made through a thesis statement, which succinctly states your primary argument in a sentence or two. The thesis statement typically comes at the very end of your introductory paragraph.
- Body : The body of your synthesis essay is usually about three paragraphs long. This typically includes two paragraphs synthesizing your sources in a way that supports your argument, and one paragraph that acknowledges opposing arguments.
- Conclusion : The conclusion of your synthesis essay reiterates the argument that you’ve made throughout your essay. It may emphasize how each of the points you made and the sources you’ve cited substantiate your point.
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
A great synthesis essay walks readers through a series of ideas and sources to prove or explain a larger point.
Follow this step-by-step guide for writing your essay:
- Choose a topic you’re curious about . Brainstorm a few ideas for your synthesis essay topic, prioritizing the subjects you feel passionate about.
- Do your research . Once you’ve decided on a topic, use the internet, library, and other sources to perform extensive research. You can turn to academic primary sources to find quotes from scholars and experts, or look up statistics or scientific studies relevant to your topic. This research will help you develop a point of view that is backed up by concrete information. Use credible sources that are unbiased.
- Outline your point . Your entire essay should focus on either explaining a certain perspective or making an argument. Outline how each of your sources relates to your theme and support your idea.
- Write your introduction . An introduction is the first paragraph of a paper. Its main purpose is to present the general premise of the paper, provide any necessary background information, and hopefully, capture the reader’s attention. The introductory paragraph to your synthesis essay should be where you include a strong thesis statement. This is where you will state the point of view that you’re exploring or the argument you’re making.
- Include your body paragraphs . Synthesis essays will typically contain three body paragraphs. A good body paragraph contains three main sections: a topic sentence (or key sentence), relevant supporting sentences, and a closing (or transition)
- sentence. This structure keeps your paragraph focused on the main idea, providing clear, concise information. Each body paragraph should discuss different elements and supporting arguments of your thesis, along with evidence drawn from each source. Explain the common theme between your resources, as well as how they are relevant to your text. Include counterarguments as well as how your source material can discredit those claims and support your own idea.
- Wrap it up with a strong conclusion . A conclusion is a final piece of writing in a research paper, essay, or article that summarizes the entire work. The concluding paragraph of your synthesis essay will restate your thesis, summarize the key supporting ideas you discussed throughout the work, and offer your final impression of the central idea.
- Proofread . Always proofread your writing a few times before submitting or presenting it. A few missed words or grammatical errors can sometimes change or discredit the entire crux of an argument or opinion. Make sure that your grammar, syntax, and flow are as accurate and clear as possible. This will help you come across as a credible source.
College Reading & Writing: A Handbook for ENGL- 090/095 Students Copyright © by Yvonne Kane; Krista O'Brien; and Angela Wood. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

How to Write a Synthesis Essay
it requires researching several sources to come up with your idea, but it isn’t very different than a research essay or other academic writing assignments that students will be familiar with. This article will guide you through all the elements of a synthesis essay, including the various types, formats, citation styles, outlines, topics, guides, and tips.
At Studyfy, we understand that writing a synthesis essay can be a challenging task. That's why we offer a custom essay writing service to assist students with their assignments. Our team of expert writers has experience in writing various types of essays, including synthesis essays, and can help you with your assignment. With our online paper writing service , you can be sure that your paper will be well-researched, properly formatted, and tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today and let us help you write a top-quality synthesis essay that meets all your requirements.
What is a Synthesis Essay?
At its core, a synthesis essay asks the writer to analyze several sources and come up with their own opinion on a subject. Think of it as creating your thesis statement based on the information you have collected from several places. It’s actually not unlike any other essay. Synthesis means combining elements of separate materials or abstract entities into a single or unified entity, and that’s what a synthesis essay does.
Types of Synthesis Essay
There are three main types of synthesis essays:
A Review Essay
A review essay collects available information about a topic to suggest what further research needs to be done. It focuses on analyzing available sources rather than making a point of its own.
An Argument Essay
These types of essays use multiple sources to back up a claim or argument. Like a typical argumentative essay, the goal is to convince the reader that your viewpoint on an issue is correct providing evidence from research.
An Explanatory Essay
The goal of this type of essay is to present information about a specific topic from various perspectives. Do not make an argument, just explain the topic with every point of information backed by research.
Synthesis Essay Structure
A synthesis essay follows the traditional structure of a 5 paragraph essay but with a few modifications. An outline is always helpful to plan any form of writing, but it is especially useful when writing this type of essay because of the many sources and various arguments to keep track of. An outline helps plan an essay and ensures that all the major points are covered as well as helps develop a flow to the paper.
The basic synthesis essay structure follows the 5 paragraph essay format.
Introduction - Briefly describe what the paper will be about. Start with a hook to engage the reader from the very beginning, followed by a brief description, and make sure to include your thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs - The first body paragraph typically contains a counterargument to your thesis. Comprehensive research and proper analysis of a subject requires understanding the issue from the opposing viewpoint as well. By presenting the most popular counterargument and debunking it, you make your overall case stronger. The next body paragraphs should present information supporting your thesis.
Conclusion - The conclusion wraps up your paper by summarizing the main points and stating how you proved your thesis with facts.
Synthesis Essay Outline
Here’s an outline template for you to use. As you do your research and come up with arguments, fill this template with information.
Introduction
- Background information
- The importance of the issue
- Thesis statement
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic sentence with a counterargument
- Evidence for the counterargument
- Invalidate the counterargument
- Evidence and facts backing your claim
Conclusion
- Transition to body paragraph 2
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic sentence supporting your thesis
- Quote a source
- Evidence for your claim
- Analysis of your claim
- How it connects to and supports your claim
- One sentence summary
- Transition to body paragraph 3
Body Paragraph 3
- Quote a different source
- How it connects to and supports your claim
- One sentence summary
- Connect all research backing your claim
- Transition to the conclusion
- Summary of the main points made in the essay
- Restate your thesis
- Your main argument and the most important evidence
- One sentence about why our view is important
Struggling with your Synthesis Essay Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
How to Write a Synthesis Paper
Now that you know what a synthesis essay is, what the structure should be, and have an outline to fill, let’s get to how to write a synthesis essay!
How to Start a Synthesis Essay
The first thing you need to do is come up with an appropriate topic. If you’ve been given a prompt, make sure to read it carefully and follow all the instructions.
If you have to choose your own topic make sure that the issue you choose has opposing views so that you can find research backing both sides.
Find the sweet spot between a topic that’s too broad, which can be difficult to address fully, and a topic that’s too marrow, which might not have enough available information.
Explore our lists of possible essay topics to get an idea of what you may want to write about and read some example essays to become familiar with the structure and style.
Once you have a topic in mind, find at least 3 sources and read them thoroughly while taking notes on specific facts to help build your thesis statement.
Writing a Synthesis Essay Thesis
After you’ve found a topic you find interesting and that complies with the prompt, your research should guide your thesis statement. What does your research say about the topic you’ve chosen? Your thesis is the main claim you are making in the essay. This doesn’t have to mean that you follow what a majority of the research says, just make sure you have enough evidence to back up your perspective as well as evidence to refute the main counter-arguments.
Your thesis statement should be written as a complete sentence, identifying the subject and stating your viewpoint on it. This will be the guiding idea and the main point you will try and prove through the body paragraphs.
Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs are the main text of your essay. This is where you will present your research, support your thesis, and build your case.
The first body paragraph usually describes a major argument against your thesis to show why the argument is wrong, or why your argument is better. There are several different approaches you can take to achieve this.
The straw man technique involves presenting the main counterargument and then destroying it with evidence showing its flaws. It can be a powerful way to strengthen your claim and it shows that you have researched opposing views. End a body paragraph using this technique with a transition sentence that introduces your main statement supporting your thesis.
The concession technique can be thought of as a softer version of the straw man. You present evidence that goes against your thesis and acknowledges that it makes sense, but show that your argument is stronger. This technique is useful for convincing people that hold the opposing view to what you believe. By agreeing with and accepting that the opposing viewpoints have some merits, it put the reader in a less hostile frame of mind.
The comparison and contrast technique presents a nuanced analysis of both sides. This is the most difficult technique because it requires a deep understanding of the issue as well as careful analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of both sides of the argument. When pulled off successfully though, it is incredibly powerful and shows an in-depth understanding of the issue.
The body paragraphs after the first should provide evidence supporting your thesis. These can contain direct quotes from your sources. Your analysis should be clear and flow logically from the research. Towards the end of each paragraph connect the evidence directly to the thesis statement to build a strong case for your claim.
Your conclusion should state all the main points of the essay as well as the main takeaways. Summarize the evidence that backs your claim and reiterate your thesis statement. Make sure to acknowledge the opposing viewpoint and state why your perspective is either correct or stronger.
Synthesis Essay Format
Citation is important for any paper, but especially for one that is research-driven. The three main citation styles are MLA, APA, and Chicago. Each one has its own synthesis essay format and conventions described below.
MLA stands for Modern Language Association and is a citation style used for papers in the Humanities like art, literature, and philology. These are the key formatting rules for MLA:
- Font should be Times New Roman
- Font size should be 12
- The entire paper should be double-spaced
- Margins should be 1 inch
- Titles should be centered
- Include your last name and the page number on each page
- The header should contain your name, your professor’s name, the date, and the course code
- The research page at the end should be titled “Works Cited”
- Journal Citation Format: Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper (Print) Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Newspaper, Date of Publication, p. Page Number.
- Newspaper (Online) Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Title of Website, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
- Website Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
APA stands for American Psychological Association and is a citation style used for science, education, and psychology. These are the key formatting rules for APA:
- Include a Title Page
- Include an Abstract
- Include the page number on each page
- The header should contain the page number and the paper’s title
- The research page at the end should be titled “References”
- Journal Citation Format: Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Article title. Journal Name, Volume (Issue), page number(s).
- Newspaper Print Citation Format: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. Xx-xx.
- Newspaper Online Citation Format: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, Retrieved from newspaper homepage URL
- Website Citation Format: Author’s last name, Initial(s). (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of work. Website. https://URL
The Chicago style is used for history, business, and the fine arts. These are the key formatting rules for the Chicago style:
- The space between lines should be double-spaced
- Use half-inch indents for the beginning of every paragraph
- Use the full names of people and organizations
- The research page at the end should be titled “Bibliography”
- There are 2 main ways of citing sources, Author-Dates and Notes-Bibliography
- Author-Dates uses parenthetical citations in the text referencing the source's author's last name and the year of publication.
- Notes-Bibliography uses numbered footnotes in the text to direct readers to a short citation at the bottom of the page.
- Both styles have a full bibliography as well
- Full source citations are in alphabetical order
Did you like our inspiring Synthesis Essay Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Synthesis Essay Topics
Here are 30 topics to inspire you. You can think of these as brief synthesis essay thesis examples.
What is the impact of culture on academic success?
How does social media influence feelings of loneliness?
How does human crated sound pollution impact urban wildlife?
What will the impact of self-driving cars be on the trucking industry?
Were superheroes better role models in the past as compared to now?
How can private drones be policed?
Will machine learning ever be able to make human artists obsolete?
Does privatization of infrastructure make sense for developing countries?
What would be the best way to communicate with aliens?
Are there negative aspects of meditation?
What is the biggest potential reason for a potential World War III?
Do tall people make better leaders?
Self-fulfilling prophecies and confirmation bias explain why some predictions come true.
What can we learn from interactions with indigenous tribes?
What are the key steps developed countries must take to manage future pandemics?
How have volcanos shaped the Earth’s climate?
What is the impact of snow on overall mood?
Is it possible to reduce the wage gap fairly?
Does having pets enhance the quality of life?
Has the rise of visual media killed imagination?
Which societies in the past have been matriarchal?
How can video games help those with mental disorders?
Which is the worst seven deadly sin?
Why Anime is better than western animation
Is honor beneficial or detrimental in sports?
What are the problems with social Darwinism?
Can anyone become a model now?
What does it take to be considered an expert?
Where is the line between advertising and manipulation?
Is there an objective idea of ethical behavior?
Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing your essay.
- Write in the third person
- Make sure your research comes from credible sources
- Cite every fact
- Write multiple drafts of your essay
- Spend time editing and proofreading
- Organize your arguments clearly
- Think about your audience
- Use technical terms
- Use paragraph transitions
- Use a synthesis essay outline template
- Use present tense for MLA
- Use past tense for APA
What Not To Do
- Use informal language
- Rely only on opinion
- Use the passive voice
- Stick to the outline template exactly
- Use fewer than three sources
- Use more than five sources
- Submit the first draft
A synthesis essay might be more technical than the types of writing you’re used to, but don’t stress too much. If you think about it as any other essay, but just a little more research-intensive, it’ll be easy to write. Choose a topic that you are interested in to make the research more fun. If you know about the topic, it will guide your research and make the writing flow more smoothly as well. Citations may seem daunting, but using a citation generator will make it a cinch!
If you need assistance with writing a synthesis essay, Studyfy has a team of qualified coursework writers who can provide you with high-quality, custom essays. Whether you need to order an essay online, or require help with essay editing or proofreading, our experts are available to assist you. Don't hesitate to contact us and say " write my essay for me " if you need any kind of academic assistance.
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay

ESL004: Advanced English as a Second Language
Synthesis essay example and rubric.
In the next section, you will write a synthesis essay in which you will include your ideas on a topic. Here, you will find a sample synthesis essay that will guide you and the rubric that will point out the elements considered in assessing your essay. Carefully examine the information on this page prior to writing your essay.
This essay example discusses the topic: "Is The Future Paperless?". It synthesizes a variety of viewpoints into a coherent, well-written essay. Notice how the author includes his/her own point of view in paragraph 2? Use this example as a guide to writing a good synthesis essay of your own. Remind yourself that a synthesis is NOT a summary.
Is going paperless the future? For schools, the answer is likely no, or not for some time. Paper documentation is still critical in the school environment, especially in administration. Student records contain sensitive information, and if online, in a paperless system, these records can be vulnerable to hacking. And while the idea of a school's records being hacked might seem alarmist, recall the recent hack of the United States Office of Personnel Management's hack. Schools might contain similar identifying information and might therefore be tempting to hackers.
Besides hacking, paper documents continue to have an advantage in established workplaces like schools. There, workflows already incorporate paper documents, and online systems operate only with significant investment in retraining. Students, too, rely on paper. For me, it is easier to get the full picture of an assignment from reading text written on a piece of paper rather than looking at a screen. True that some schools have initiatives in getting iPads and laptops for their students, but these expensive technologies are not as customizable by teachers as paper handouts, so their use is limited. Also, most people would like to have a paper backup in case something happens to their digital device. Paper and document technology are crucial to the current school environment, both in administration and students' own lives. As a company, H.G. Bissinger Office Technology is especially attuned to the significance of paper for education. They recently promoted one of their customer service managers to a new task force on meeting the document technology needs for education. That manager, Lyla Garrity, had created a uniquely strong collaborative relationship with Permian College. Through their work together, she realized that educational document services are an area that specialists could greatly improve, compared to unspecialized, general service that most schools suffer through. H.G. Bissinger Office Technology leases 10 copiers to the Northwest Local School District, along with technical support and copier supplies, excluding paper. For a school, the large investment in a machine is shadowed by the uncertainty of how far from obsolescence a machine might be. Also, purchasing a copier outright will leave the school or business to handle service on its own. Additionally, in these financially limited times, the initial investment of a large sum can be difficult to justify or approve. For schools, uncertainty over future budgets often makes a lease a more flexible option. Most copier leases deal with equipment costs by including provisions in which the client must purchase the machine at the end of the lease. More recently, lease companies like H.G. Bissinger Office Technology are offering leases that are more like rentals. After the monthly fee is paid, the company will take the machine back.
Each of the five items below is worth from 2 to 8 points. To calculate your composite score for your rough draft, add together your scores for all five rubric items below. The maximum score for your final draft is 40 points.
1. Evidential Support
- Excellent (8 points): I have clearly synthesized the content from the article, paraphrasing the ideas and connecting them to opinions to demonstrate comprehension. All of the main claims in my essay are supported by reasons based on accurate factual evidence derived from the article or a properly-formatted quotation, paraphrase, and/or summary of the assigned text.
- Proficient (6 points): I have clearly synthesized the content from the article, paraphrasing the ideas and related topics to demonstrate comprehension; however, my essay does not clearly reflect my opinion on the topic. The majority of the main claims in my essay are backed up by specific factual evidence, although a small number of my claims may be unsubstantiated statements or broad generalizations. When quoting or paraphrasing the assigned reading, I may occasionally misrepresent it or take it out of context.
- Adequate (4 points): I have synthesized the content from the article, paraphrasing the ideas and related topics to demonstrate comprehension, but my essay does not mention my point of view on the topic. At least half of the main claims in my essay are based on factual evidence or properly cited passages from the assigned reading. The other half of my claims may be unreasonable, lack quoted or factual support, may be based on misinformation or misreading, may consist of broad generalizations, or may distort and incorrectly format the assigned text.
- Not Yet Adequate (2 points): I have synthesized some of the content from the article, but my paraphrasing demonstrates limited comprehension of the topic, and my opinion on the topic is not addressed. On balance, most of the claims in my essay are unsubstantiated or based on distortions (or misreadings) of the assigned text.
- No Points Awarded (0 points): I have demonstrated minimal synthesis of the topic. My essay does not support its claims with evidence of any kind; my essay does not make claims in response to the prompt.
2. Persuasive Appeals
- Excellent (8 points): My essay uses a variety of persuasive appeals (emotion, logic, and credibility) to support its claims.
- Proficient (6 points): My essay uses some of the strategies effectively (as above) some of the time.
- Adequate (4 points): My essay uses at least one persuasive appeal correctly, but may sometimes use them unfairly or unconvincingly.
- Not Yet Adequate (2 points): If my essay uses persuasive appeals at all, it does so unfairly or unconvincingly.
- No Points Awarded (0 points): My essay uses none of the standard persuasive appeals discussed in this course.
3. Rhetorical Strategies
- Comparison and Contrast
- Definition of Terms
- Cause and Effect Analysis
- Proficient (6 points): My essay uses some of the rhetorical strategies employed by an excellent essay (above); my essay usually uses these strategies with a clear purpose, but may sometimes (for example) define a term without putting it to use, or draw a contrast without showing what it signifies.
- Adequate (4 points): My essay makes little use of the rhetorical strategies employed by an excellent essay, and may often do so without clear purpose and without using these techniques to persuade my reader; my essay may sometimes use these techniques incorrectly (for example, by providing inaccurate definitions of terms, or by confusing cause and effect).
- Not Yet Adequate (2 points): My essay incorporates few or no rhetorical appeals, and when it does, it does not use them correctly or persuasively.
- No Score Awarded (0 points): My essay does not use any of the rhetorical appeals used by an excellent essay (listed above).
- Excellent (8 points): The grammar errors on the list below, singly or in combination, occur no more than once per 250 words; no persistent patterns of grammar errors are present in the paper; errors do not distract the reader.
- Proficient (6 points): The errors on the list below, singly or in combination, occur no more than two times per 250 words; single errors from the list below may begin to recur and form a pattern of error; grammar errors are occasionally distracting to the reader.
- Close to Proficient (4 points): The errors on the list below, singly or in combination, occur on average three times per 250 words; single errors from the list below may recur and form a distinct pattern of error; errors of haste or lack of proofreading are present; grammar errors are persistently distracting to the reader.
- Not Yet Adequate (2 points): Grammar errors are numerous and impede the reader's comprehension of my essay; my essay reflects a lack of proofreading.
Common Grammatical Errors:
Each error type you have studied is shown next to an example of the error.
- Inappropriate Punctuation
- Faulty Parallel Structure
- Excessive or Inappropriate Use of the Passive Voice
- Use of weak "to be" verbs rather than strong, active verbs
- Failure to maintain a formal, rational, objective, unbiased, and academic tone that is directed at an educated audience
- Proficient (6 points): My essay reads clearly, but may occasionally exhibit one or two of the stylistic errors avoided by an excellent essay (above).
- Adequate (4 points): Not always, but distractingly often, my essay does not read smoothly because it repeats singly or in combination with the stylistic errors listed above.
- Not Yet Adequate (2 points): My essay exhibits the stylistic errors above so frequently that it is very difficult to read.
Use this checklist to review each of your sentences for errors:
- Read each sentence out loud. Do they sound correct? Is anything missing? You can add to your sentences if you want to explain more about your topic.
- Spelling – Is every word spelled correctly?
- Correct words – Did you use the right word? Many words in English look similar but have different meanings (for example, like and lick). Check each word to make sure it's the right one.
- Timeline order – Are your events in the correct order? Make sure your sentences don't jump around.
- Past tense – Are the verbs in each sentence conjugated in past tense? Go back and review verb endings if you're not sure.
- Describing words – Do each of your sentences include at least one adjective or one adverb?
- Capitalization – The first word in every sentence should be capitalized. After the first word, only proper nouns (like people's names) should be capitalized. Everything else should be lower case.
- Punctuation – Does each sentence end with a period? Questions may end with a question mark (?), and exclamations may end with an exclamation mark (!), but most of your sentences should end with a period (.).


273 Strong Verbs That’ll Spice Up Your Writing
Do you ever wonder why a grammatically correct sentence you’ve written just lies there like a dead fish?
I sure have.
Your sentence might even be full of those adjectives and adverbs your teachers and loved ones so admired in your writing when you were a kid.
But still the sentence doesn’t work.
Something simple I learned from The Elements of Style years ago changed the way I write and added verve to my prose. The authors of that little bible of style said: “Write with nouns and verbs, not with adjectives and adverbs.”
Even Mark Twain was quoted, regarding adjectives: “When in doubt, strike it out.”
That’s not to say there’s no place for adjectives. I used three in the title and first paragraph of this post alone.
The point is that good writing is more about well-chosen nouns and strong verbs than it is about adjectives and adverbs, regardless what you were told as a kid.
There’s no quicker win for you and your manuscript than ferreting out and eliminating flabby verbs and replacing them with vibrant ones.
- How To Know Which Verbs Need Replacing
Your first hint is your own discomfort with a sentence. Odds are it features a snooze-inducing verb.
As you hone your ferocious self-editing skills , train yourself to exploit opportunities to replace a weak verb for a strong one.
At the end of this post I suggest a list of 273 vivid verbs you can experiment with to replace tired ones.
Want to download a copy of this strong verbs list to reference whenever you write? Click here. What constitutes a tired verb? Here’s what to look for:
- 3 Types of Verbs to Beware of in Your Prose
1. State-of-being verbs
These are passive as opposed to powerful:
Am I saying these should never appear in your writing? Of course not. You’ll find them in this piece. But when a sentence lies limp, you can bet it contains at least one of these. Determining when a state-of-being verb is the culprit creates a problem—and finding a better, more powerful verb to replace it— is what makes us writers. [Note how I replaced the state-of-being verbs in this paragraph.]
Resist the urge to consult a thesaurus for the most exotic verb you can find. I consult such references only for the normal word that carries power but refuses to come to mind.
I would suggest even that you consult my list of powerful verbs only after you have exhaust ed all efforts to come up with one on your own. You want Make your prose to be your own creation, not yours plus Roget or Webster or Jenkins. [See how easy they are to spot and fix?]
Impotent: The man was walking on the platform.
Powerful: The man strode along the platform.
Impotent: Jim is a lover of country living.
Powerful: Jim treasures country living.
Impotent: There are three things that make me feel the way I do…
Powerful: Three things convince me…
2. Verbs that rely on adverbs
Powerful verbs are strong enough to stand alone.
The fox ran quickly dashed through the forest.
She menacingly looked glared at her rival.
He secretly listened eavesdropped while they discussed their plans.
3. Verbs with -ing suffixes
Before: He was walking…
After: He walked…
Before: She was loving the idea of…
After: She loved the idea of…
Before: The family was starting to gather…
After: The family started to gather…
- The Strong Verbs List
- Disillusion
- Reverberate
- Revolutionize
- Supercharge
- Transfigure

Are You Making This #1 Amateur Writing Mistake?

Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

Before you go, be sure to grab my FREE guide:
How to Write a Book: Everything You Need to Know in 20 Steps
Just tell me where to send it:

Great!
Where should i send your free pdf.

We have sent you an email with a 6 digit code to:
Didn't receive an email? Check your spam folder and mark the email as not spam!. If you Skip this step, you won't be able to receive order-related updates via email.
Understanding and Writing a Synthesis Essay

Writing a synthesis essay can seem like a daunting task. After all, your goal is to synthesize and evaluate a variety of sources in order to create an insightful and impactful essay. Be at ease, though! You can become an expert at writing this kind of essay with time and practice. In this post, we'll define essays, offer advice on how to write an essay, and present a sample synthesis essay for your review. Additionally, we'll give you some resources to get the writing process going. Continue reading to find out more about what constitutes a strong synthesis essay—then put what you've learned to use! If you encounter any difficulty, you can get the assistance of professional analytical essay writers at Nerdpapers.
Steps to Writing a Brilliant Synthesis Essay
1. choosing a synthesis essay topic.
Although it can be difficult, writing an essay can also be immensely fulfilling. You must choose a topic, though, before you start writing the essay. If your teacher doesn't provide you with a specific topic to write on, then you'll have to choose one on your own. There are a few essential factors to take into account while selecting a synthesis essay topic. To begin with, you must ensure that the topic you choose is pertinent to both your English language and writing course and the materials you'll be employing for your essay. Additionally, there must be enough data available for you to use in order to provide focused proof to support the thesis. Last, but not least, think about the readers of this essay and their potential responses. A good synthesis essay topic should be intriguing enough to pique readers' interest and also appeal to them on a personal or public level, causing them to reflect critically on the topic at hand.
☑️Reading suggestion: “ How to write an AP Lang synthesis essay ”
2. Developing a Thesis Statement for Your Synthesis Essay
Read the relevant source material after deciding on your essay's topic. Understanding the knowledge and applying critical thought to it should be your objectives. Form your own thoughts about the topic as you read and weigh the various sources. Take notes as you go along, noting any quotes, information, or examples that can assist you to support your position and develop a strong thesis statement. When writing an essay, coming up with a thesis statement is the most crucial step in the writing process. Readers should be able to deduce from this statement both the topic of your work and the argument you are making. Do not forget that a quality thesis should be concise, specific, and arguable. Make sure to include material from all sources in your essay if they're relevant to your argument and summarize them. Your goal is for readers to understand why you chose the material for your synthesis essay topic and how you plan on presenting it in support of your argument or position.
3. Finding and Reading Source Materials for Evidence
It's time to delve deeper into the sources and uncover the precise evidence your argument requires. You should make notes on significant ideas from each source, keeping track of important details, quotes, and figures that you might utilize in your academic writing . As you read, remember to focus on how each of the sources ties in with your topic and contributes to your argument. Here are some tips to help you as you read:
- Look for key phrases or words that address the essay topic so you can quickly identify material related to it
- Jot down notes in the margins or highlight pertinent information as a reference when writing your essay
- Summarize those major points afterwards so they're fresh in your mind while writing
- Search for different perspectives related to your topic. This will help when forming an argument and refuting any opposing viewpoints
- If a source is not relevant or doesn't contain enough substantial evidence, discard it
- Ask yourself specific questions about each source as you read, such as “What kind of evidence does this provide?”.
By reading through the source materials ahead of time and taking detailed notes, you can come up with more organized thoughts for a smoother writing process. Wondering how to organize your sources effectively? Consider creating an annotated bibliography to keep track of your findings.
4. Outlining and Organizing Your Synthesis Essay
Writing a good essay starts with outlining and organizing the essay. Making an outline for your paper comes next after gathering all of your sources and reading them thoroughly. You'll be able to better plan your ideas and decide how to convey your information by doing this.
There are some fundamental elements that must be covered in the outline of a synthesis essay:
- Introduction: Where you introduce the thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each body paragraph should include a topic sentence and two or three pieces of specific evidence from one or two different sources that support your argument.
- Conclusion: Here, you will review the main points of your essay and offer any insights or observations gained from the process of writing it.
When organizing these basic components into an outline, it's important to make sure they flow logically from one point to another, while also linking all of your points back to the original thesis statement. Additionally, make sure that you are citing all of your sources correctly throughout the paper—English language and composition teachers are often very specific about this requirement! Understanding how to accurately cite sources is an essential part of writing a good synthesis essay.
5. The Writing Process: Drafting Body Paragraphs with Specific Evidence
When it comes to writing an essay, the writing process is key. Once you have read the sources and written a thesis statement, it's time to start drafting your essay. You want to make sure that each body paragraph supports your thesis with specific evidence from the source material.
a. Provide Context
Each body paragraph should introduce one point from your thesis statement and provide context for the evidence you're about to cite. It's also important to note that when you do cite evidence, make sure it is relevant and related to that particular point and argument.
b. Provide Specific Evidence & Explain How It Supports Your Argument
Now that you have provided relevant context, provide evidence from one or more sources while explaining how it connects back to the point and argument of your essay. Before moving on to the next piece of evidence, make sure that the previous one has been thoroughly explained. Instead of simply summarizing the sources, make sure to explain how the data supports your thesis and why it does so well.
c. Conclude Paragraph with Summary Statement
Finally, conclude each body paragraph with a summary statement that ties back in with either other parts of this same paragraph or other paragraphs from earlier in your essay. The connective thread between paragraphs will help readers see how all of these points come together as part of a cohesive argument in support of your thesis statement.
6. Proofreading and Editing Your Synthesis Essay
Once you've written your synthesis essay, it's time to proofread and edit it. This is a crucial step as it's your chance to make sure that your essay flows logically, uses up-to-date sources, is error-free, and clearly expresses your idea or thesis statement.
a. Check Your Thesis Statement
Make sure the thesis statement or main argument of your essay stands out clearly and confidently. It's important to check the wording here—is it supported by specific evidence in the body of the essay? Have you made any sweeping generalizations?
b. Read Aloud and Listen for Errors
Reading aloud helps you slow down and pay more attention to punctuation details such as commas in a series, colons, apostrophes, etc. You can also use text-to-speech programs if you're more comfortable listening than reading.
c. Check the Structure, Flow, and Transitions
Your essay should have a clear structure that follows logically from one point to the next so that readers know what to expect next. Also, check for smooth transitions between paragraphs so that there is a clear connection between them all.
d. Track Your Citations
Make sure all sources are credited correctly—both within the text as well as on the references page. Any source material that’s not cited correctly can be interpreted as plagiarism! Use formatting guidelines specified by your professor (e.g., APA or MLA ). Finally, don't forget to proofread like an editor would: read each sentence carefully with an eye for errors in spelling, grammar, syntax, or punctuation. If possible, run spell-check programs such as Grammarly after reading.
Writing a synthesis essay can seem daunting, but with the right process and understanding of the topic, it can be an informative and engaging experience. Starting out with copying keywords and sources onto a page can help you organize your ideas and give you a place to start. Knowing the task and how to develop your thesis statement, as well as how to pick and analyze specific evidence, is also important for forming your written argument. Finally, the writing process involves making sense of the topic and developing connections between your sources to build a stronger essay. With the right essay writing tips , writing a synthesis essay can be a smooth and enjoyable process.
Table of Contents
Persuasive essay topics – how to choose one for you, how to write a persuasive essay- expert tips.
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Examples, Topics, & Outline
A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place!
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this guide by our custom writing team, you will find:
- a step-by-step writing guide;
- a list of 34 synthesis essay topics;
- a full essay sample in MLA format.
- 📚 Synthesis Essay Definition
- 📝 Essay Types
- ✅ Step-by-Step Guide
- ✍️ Topics & Prompts
- 📑 Example & Formatting Tips
📚 What Is a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is an assignment that requires a unique interpretation of a particular topic using several reliable sources. To write it, you need to understand, analyze, and synthesize information. That is why this type of essay is used in the AP Lang exam to assess students’ reasoning skills.
The key features of the synthesis essay are:
- Debatable topic . If your goal is to write a good synthesis essay, it’s necessary to choose an arguable topic. It’s best to choose something that people have different opinions about. This will allow you to use many sources with various viewpoints for your synthesis.
- Clear thesis statement. It’s a sentence that briefly describes the main idea of your essay.
- Reliable sources to prove your thesis . For a synthesis essay, your opinion is not enough. You also need to find the evidence. Keep in mind that simply reading an online encyclopedia won’t do; make sure to choose only reliable sources.
What Does It Mean to Synthesize Information?
Synthesis is a process that has huge importance in nature, science, and our everyday life. The word stems from Ancient Greek “synthesis,” which means “putting together.” In general, synthesis is the combination of components to form a connected whole.

In everyday life, we usually resort to it to synthesize information . This means taking the data from different sources and bringing it together. This process is the opposite of analyzing:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
- For an analysis , you break problems into pieces,
- For a synthesis , you combine separate elements into a whole.
We use synthesis for analysis papers, research papers, argument papers, and business reports.

What Does Synthesis Mean in Writing?
Synthesis in writing means summarizing and connecting different sources considering a particular topic. Although synthesis and analysis are two opposite things, they usually go together in synthesis essays. The process consists of 2 stages:
- Conduct the analysis. For that, you break down a problem into parts and analyze the sources. It’s helpful to highlight everything regarding your topic while reading.
- Carry out the synthesis. The next step is to formulate an opinion and combine the highlighted information from the sources.
Synthesis is not only used in writing but also in reading comprehension . It’s useful to do this kind of reading while studying your sources. There are three reading comprehension stages:
- Your previous knowledge about the topic.
- Expansion of your knowledge while you are reading.
- Understanding of the problem when you have finished reading.
So, synthesized reading comprehension means combining three stages in one and formulating one statement.
Synthesis vs Summary: What Is the Difference?
A summary is a paraphrasing of the written source in your own words. For a good summary, it’s necessary to include all of the text’s key elements. Meanwhile, synthesis means combining different ideas from different sources. You don’t have to include all the key points; just choose everything related to your topic.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!

Both of these techniques are used for the synthesis essay:
- The summary goes in the conclusion. You briefly sum up your paper’s main ideas.
- Synthesis goes in the body paragraphs. Here, you combine multiple sources to prove a point.
📝 Synthesis Essay Types
There are two main types of a synthesis essay: argument and explanatory synthesis.
Both of them require working with multiple reliable sources and analyzing information. The only difference is that an argument synthesis essay requires your own opinion, while an explanatory synthesis essay does not.
Argument Synthesis Essay: Outline and Definition
As you already know, an argument synthesis essay requires you to state your own opinion about the given topic and back it up with several reliable sources. The purpose of such an essay is to persuade the reader that your point is correct.
Here’s what an argument synthesis essay consists of:
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Explanatory Synthesis Essay: Definition and How to Write
An explanatory informative synthesis essay requires you to stay neutral towards the problem you are discussing. This means you cannot express your own opinion considering the given question or a problem. Your task is just to inform the reader. That’s why this essay type is also called informative synthesis.
Check out this explanatory essay outline:
✅ How to Write a Synthesis Essay Step by Step
When it comes to the synthesis essay outline, it’s not too different from other assignments. Have a look at this template:

How to Synthesize: Working with Sources
After you’ve decided on your topic, it’s time to figure out how to synthesize articles into one text. This is how you do it:
- Choose reliable sources: the ones printed in journals or published on academic websites.
- Become familiar with them and see if they fit into your essay.
- Try to find a few sources for each point. It will increase your essay’s reliability.
- Relate each source to your arguments and see similarities between them.
- Don’t forget to list every source in the references.
When you are done with a comprehensive analysis of related literature, try to step back and imagine a person who has a different opinion on this topic. Think of some arguments that they can provide to prove their opinion. After you have the list of arguments, find the written evidence of why they are wrong and put them in your essay.
Analyzing and organizing sources is the first and very important step for the synthesis essay. So make sure you do understand what the text means before using it as a reference.
Synthesis Essay Outline: How to Write
For structuring your essay, it’s useful to try mapping . This technique means combining the information from different sources and rearranging it to create a new direction. To do it, you need to analyze the authors’ ideas and come up with your own conclusions.
The best way to do that is called synthesis matrix or graphic organizer. It’s a chart that you can make when you start working on your essay. Here you have a horizontal column that states the main ideas and a few vertical columns that present sources. Your task is to take sources you have chosen and write down the main ideas from them.
Here’s an example of a matrix chart:
While doing that, you will see how many sources contain the same ideas. When you analyze them, you will be able to formulate your thesis backed up with evidence. The synthesis matrix also helps to see new arguments you can cover in your synthesis paper.
How to Write an Introduction for a Synthesis Essay
Now it’s time to start writing the paper. In the introductory part of the essay, you can include:
- A short yet catchy sentence or a quotation that would present the topic. The start of your essay should make people interested. It’s best to make the first sentence not only informative but also easy to understand.
- The texts that are used for the essay. Provide the titles and the authors’ names (use the appropriate guidelines depending on the writing style.)
- The background information which is needed to understand your essay. Definitions of terms or unknown words considering the topic can be included in this part. Otherwise, people may find it hard to understand what they are reading about.
How to Write a Thesis for a Synthesis Essay
A thesis statement is a point of view on a certain problem that you will defend in your essay. It should contain the key points that you want to include in your paper. Here’s how to create a perfect thesis statement:
- Find several central ideas in the chart.
- Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay.
- Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points.
- Make a draft of the thesis statement. Try to formulate the main idea you want to present in your essay.
- Elaborate on this idea. Add some details and expand it a bit further.
If the whole picture is coherent, and it conveys exactly what you wanted, then this is your perfect thesis statement. See the example below:
Gender inequality still exists at the workplace: women are less likely to get the most responsible positions, easily lose careers due to maternity leave, and often receive less pay for the same amount of work.
How to Write Synthesis Paragraphs for the Main Body
Your essay’s main body consists of a few paragraphs. Each of them presents a different argument considering the topic. When you start a paragraph, make sure to begin with a topic sentence, which informs the reader about the paragraph’s main idea. Then, include the synthesized sources and elaborate on them.
Here’s what you should and shouldn’t do when writing the main body:
You can use the following words to present the ideas from your sources. They will help you reflect the authors’ tone:
How to Conclude a Synthesis Essay
There are quite a few ways to conclude the synthesis paper. Have a look at some of the options:
- Paraphrase the thesis. As you remember, the thesis is the main idea of your essay. The conclusion is a good place to remind your readers about it. When they are done with the reading, they remember the most important thing from your essay.
- Synthesize the arguments. There is no need to repeat everything you wrote in your essay. Just briefly summarize the most crucial points.
- Answer the “So what” question. Tell the readers why this topic matters, why you’ve chosen it, and why it’s valuable for the reader.
- Provide a closure. It’s an effective strategy when you want to make the reader think. Leave them with a strong statement at the end of your essay.
Synthesis Paper Proofreading Tips
When you have finally written your paper, there is still one important thing left to do. You need to check your paper for any grammatical and contextual mistakes. You certainly can do it yourself, but it would be perfect if you could ask somebody else to read it.
The first thing you need to check grammar-wise is the tense you are using. There is no single tense you need to use for the synthesis essay. It depends on the format:
- If you’re writing in MLA format, use the present tense;
- For APA essays, you use the past tense.
The next step is to check whether your synthesis essay has everything that’s required. For that, we have prepared the checklist of questions you can ask yourself to proofread your essays.
- Is there a clear thesis statement?
- Did you include all of the key points from the synthesis?
- Are there clear transitions between paragraphs?
- Did you organize a paragraph around a single idea?
- Did you use reliable and up-to-date sources?
- Did you analyze sources rather than just summarize them?
- Did you mention every source you’ve used?
If you’ve answered “yes” to all the questions—congratulations, you are done with the essay! Otherwise, you need to come back and fix everything that you’ve answered “no” to.
✍️ Synthesis Essay Topics and Prompts
Sometimes, when you don’t have a topic , it is tough to come up with a suitable idea. That is why we have prepared two lists of topics that you can use for any synthesis essay type.
Explanatory Synthesis Essay Topics
The topics below are suitable for an explanatory synthesis essay:
- The beginning of Hollywood cinema . Cinema is a huge industry in the USA. Tell the readers about its history. Describe what it was like in the beginning, which movie was the first one, and who started this industry.
- Tactics on dealing with noisy children. Sometimes kids can be very loud, especially in public places. Write about different tactics that can help with this issue.
- The effects of climate change on the water cycle. Climate change has affected the water cycle significantly. Your task is to explain how.
- The best American cities to live in. Provide the list of the best cities and explain why you’ve included them.
- The importance of a healthy diet . Keeping a healthy diet is beneficial in many ways. Write about all the advantages it brings.
- Who can become an entrepreneur? Entrepreneurship is not for everybody. In this essay, you can describe the qualities needed for having your own business.
- The correlation between overpopulation and poverty . Describe how overpopulation leads to poverty and vice versa.
- The advantages of taking an active vacation.
- Cultural shock as a part of moving to a different country.
- The consequences of the first wave of feminism .
- Synthesis of Tan and Rodriguez’ essays ideas.
- Difficulties you may encounter during the job interview.
- How does reading prevent Alzheimer’s disease ?
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on businesses .
- The connection between religion and politics in ruling the country.
- What can non-verbal signals tell you about a person ?
- The psychology of leadership .
- The origins of the most common stereotypes about Americans.
- Role of social media in business communication .
- The synthesis of personal nursing philosophy concept.
- Behavioral components of schizophrenia and psychosis.
- Main components of successful entrepreneurship.
- Critical components of scientific research.
- Change in religion and human beliefs throughout history.
- The effect of global warming on modern life.
Argument Synthesis Paper Topics
The list of topics for the Argument Synthesis Essay:
- Vaping is better than smoking . People are starting to exchange cigarettes for vapes and e-cigarettes. In what ways are they less harmful?
- Rich people should pay higher taxes. The same percentage of money doesn’t equal for rich and poor people. Explain why the ones who can afford more should share with others.
- Depression is a disease . Prove that psychological problems must be recognized as real health issues that should be cured and not ignored.
- Social media affects young people’s lives. Social media has a massive influence on people. In this essay, you can discuss which life spheres are the most affected.
- Beauty pageants should be banned. Provide the reasons why they should be banned and tell the reader about psychological problems they can cause.
- People should cut meat from their diet to stop global warming . Describe how the meat industry influences climate change.
- The voting age should be 25+. Your task is to show the reasons why the votes of people under 25 should not be taken into account during elections.
- A healthy lifestyle requires a lot of money.
- Each healthy man should serve in the military.
- School bullying should be punished by immediate exclusion.
- Does friendship exist between men and women?
- Drinking coffee is a bad habit.
- Working hard is more important than being talented.
- Everybody should visit a therapist at least once.
- Should universities be free ?
- Artificial intelligence will cause huge unemployment rates.
- Gaming should not be allowed to children under 18.
- Components and strategies of social responsibility
- Integration of relevant ethical theory and conceptual principles in health care
- Children under 10 should be banned from gadgets .
- Social media platforms facilitate cyberbullying.
- Issues of distance education .
- Social media addiction is a serious disease.
- Deforestation critically contributes to global warming.
- Healthcare should be free for everyone.
📑 Synthesis Essay Example & Synthesis Essay Format Tips
Now let’s talk about formatting. There are two writing styles you can use for a synthesis essay: APA or MLA. You need to choose the one that is required for your assignment.
We will start with the paper in APA format. It is usually used in science and education.
And these are MLA formatting rules:
Finally, we’ve prepared a synthesis essay sample for you to check out. Feel free to download the PDF file below:
First introduced in the Civil Rights Act of 1964, affirmative action policies aim to mitigate the discrepancy in opportunities available for underrepresented social groups by taking into account one’s minority background. The policies have become a pressing public issue that obstructs previously marginalized individuals, particularly in the educational environment.
Thank you for reading the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing. We hope you found it helpful. Don’t forget to share it with your friends. Good luck with your assignments!
🔍 References
- Writing a Synthesis Essay: Bowling Green State University
- What Is Synthesis: University of Manitoba
- Synthesis: Biology Online
- Reading Strategies: Difference Summarizing and Synthesizing: WordPress
- Summary, Analysis, Synthesis Definitions: University of Utah
- Argumentative Synthesis: University of Arkansas
- How to Synthesize Written Information: Simply Psychology
- Mapping of Synthesis Essay: University of Nevada, Reno
- Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix: Florida International University
- Synthesis Essay: Cleveland State University
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources: Louisiana State University
- Writing a Conclusion: Texas Women’s University
- General APA Guidelines: Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![strong verbs for synthesis essay Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
Last Updated: April 7, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,121,128 times.
Writing a synthesis essay requires the ability to digest information and present it in an organized fashion. While this skill is developed in high school and college classes, it translates to the business and advertising world as well. Scroll down to Step 1 to begin learning how to write a synthesis essay.
Examining Your Topic

- Argument synthesis: This type of essay has a strong thesis statement that presents the writer's point of view. It organizes relevant information gathered from research in a logical manner to support the thesis' point of view. Business white papers known as position papers often take this form. This is the type of synthesis essay that students will write during the AP test.
- Review: Often written as a preliminary essay to an argument synthesis, a review essay is a discussion of what has been written previously on a topic, with a critical analysis of the sources covered. Its unstated thesis is usually that more research needs to be done in that area or that the topic problem has not been adequately addressed. This type of paper is common in social science classes and in medicine.
- Explanatory/background synthesis: This type of essay helps readers understand a topic by categorizing facts and presenting them to further the reader's understanding. It does not advocate a particular point of view, and if it has a thesis statement, the thesis is a weak one. Some business white papers take this form, although they are more likely to have a point of view, if understated.

- Example of a broad topic narrowed down into a reasonable synthesis essay topic: Instead of the broad topic of Social Media, you could discuss your view on the effects texting has had on the English language.
- If you've been assigned a topic as part of a class, make sure you read the prompt carefully and fully understand it.

- Keep in mind that it's better to do three sources well than to do five sources incompletely.
- Annotate each source by writing notes in the margins. This allows you to keep track of your train of thought, developing ideas, etc.

- Example: Texting has had a positive impact on the English language as it has helped the millennial generation create their own form of the language.

- If you wish to take on a claim by an opponent of your idea, and to poke holes in it, you should also find some ideas or quotes that go against your thesis statement, and plan ways to disprove them. This is called a concession, refutation, or rebuttal, which can strengthen your argument if you do it well.
- Example : For the thesis statement listed above, excellent sources would include quotes from linguists discussing the new words that have developed through 'text-speak', statistics that show the English language has evolved with almost every generation, and facts that show students still have the ability to write with the use of grammar and spelling (which your opponents would bring up as the main reason texting has had a negative effect on the English language).
Outlining Your Essay

- The introductory paragraph: 1. An introductory sentence that acts as a hook, capturing the reader's interest. 2. Identification of the issue you will be discussing. 3. Your thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs: 1. Topic sentence that gives one reason to support your thesis. 2. Your explanation and opinion of the topic sentence. 3. Support from your sources that backs up the claim you just made. 4. Explanation of the significance of the source(s).
- The conclusion paragraph: 1. State further significance of your topic from the evidence and reasons you discussed in the essay. 2. A profound thought or thoughtful ending for your paper.

- Example/illustration. This may be a detailed recount, summary, or direct quote from your source material that provides major support for your point of view. You may use more than one example or illustration, if your paper calls for it. You should not, however, make your paper a series of examples at the expense of supporting your thesis.
- Straw man. With this technique, you present an argument opposed to the argument stated in your thesis, then show the weaknesses and flaws of the counter-argument. This format shows your awareness of the opposition and your readiness to answer it. You present the counter-argument right after your thesis, followed by the evidence to refute it, and end with a positive argument that supports your thesis. [5] X Research source
- Concession. Essays with concessions are structured similar to those using the straw man technique, but they acknowledge the validity of the counter-argument while showing that the original argument is stronger. This structure is good for presenting papers to readers who hold the opposing viewpoint.
- Comparison and contrast. This structure compares similarities and contrasts differences between two subjects or sources to show the facets of both. Writing an essay with this structure requires a careful reading of your source material to find both subtle and major points of similarity and difference. This kind of essay can present its arguments source-by-source or by points of similarity or difference.

- Summary. This structure presents summaries of each of your relevant sources, making a progressively stronger argument for your thesis. It provides specific evidence to support your point of view, but usually omits presenting your own opinions. It's most commonly used for background and review essays.
- List of reasons. This is a series of sub-points that flow from the main point of your paper as stated in its thesis. Each reason is supported with evidence. As with the summary method, reasons should become progressively more important, with the most important reason last.
Writing Your Essay

- Your essay should have an introductory paragraph that includes your thesis , a body to present evidence that supports your thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes your point of view.

- Lengthy quotes of three lines or more should generally be set off as block quotes to better call attention to them. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Finalizing Your Essay

- Ask someone else to proofread your paper. The saying “two heads are better than one” still holds true. Ask a friend or colleague what would they add or remove from the paper. Most importantly, does your argument make sense, and is it clearly supported by your sources?

- Read the paper aloud to guarantee that you don't accidentally add in or take out words when reading in your head.
- If you can, get a friend or classmate to proofread your essay as well.

- Example of citing in an AP synthesis essay: McPherson claims “texting has changed the English language in a positive way--it has given a new generation their own unique way to communicate” (Source E).
- For college essays, you'll most likely use MLA format. Whichever format you use, be consistent in its use. You may also be asked to use APA or Chicago style.

- Example title: : English and the iPhone: Exploring the Benefits of 'Text-Speak'
Outline Template

Community Q&A
- Just as your title should fit your essay instead of writing your essay to fit the title, your thesis, once chosen, should direct your subsequent research instead of subsequent research altering your thesis � unless you find you've adopted an unsupportable thesis. Thanks Helpful 21 Not Helpful 8

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://success.uark.edu/get-help/student-resources/synthesis-paper.php
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/mapping-a-synthesis-essay
- ↑ https://www.bgsu.edu/content/dam/BGSU/learning-commons/documents/writing/synthesis/planning-synthesis-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://writingcenterofprinceton.com/synthesis-essays-a-step-by-step-how-to-guide/
- ↑ https://owl.excelsior.edu/argument-and-critical-thinking/logical-fallacies/logical-fallacies-straw-man/
- ↑ https://writingcommons.org/section/rhetoric/rhetorical-stance/point-of-view/third-person-point-of-view/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://www.edhs.org/ourpages/auto/2010/5/17/41759867/Synthesis%20Essay%20Introduction.pdf
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
About This Article

To write a synthesis essay, start by coming up with a thesis statement that you can support using all of the sources you've read for your essay. For example, your thesis statement could be "Texting has had a positive impact on the English language." Once you've got your thesis, go through your sources to find specific quotes, facts, and statistics that back up your claim. Structure your essay so it has an introduction that includes your thesis statement, a body that includes your arguments and evidence, and a conclusion that wraps everything up. For more tips on structuring your synthesis essay, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Aug 8, 2016
Did this article help you?
Adrian Mastrocola
Sep 29, 2016
Emmanuel Amoatey Djaba
Nov 26, 2016
Anna VonLeader
Jun 6, 2016
May 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write a Synthesis Essay Like a Pro
.webp)
The definition of a synthesis entails a written discourse integrating support from multiple sources, each offering diverse perspectives.
Writing a synthesis essay demands the skill to comprehend information and structure it cohesively. This proficiency cultivated in academic settings also holds value in the realms of business and advertising. In this article, you will learn about the main types of this essay, writing steps, optimal structure, and hands-on writing hints. If you still require any help with any of the material, feel free to consult our essay writing service online .
What is a Synthesis Essay: Types and a Step-by-Step Writing Guide
The essence of how to write synthesis essay lies in forging insightful connections among various elements within a work or across multiple works, all with the overarching objective of formulating and substantiating a claim on a specific topic. Essentially, it's the art of researching a subject and discovering linkages that culminate in a well-supported perspective. It’s possible to name three types of synthesis essays:
.webp)
Argument Synthesis: Featuring a robust thesis statement, a synthesis argument essay articulates the writer's viewpoint. It systematically arranges relevant research findings to bolster the thesis, commonly seen in business white papers and AP test essays.
Review Synthesis: Often a precursor to an argument synthesis, this essay evaluates previous literature on a topic, offering a critical analysis. Typically, its implicit thesis suggests the need for further research or that the topic's problem remains unaddressed. It's prevalent in social sciences and medicine.
Explanatory/Background Synthesis: Focused on elucidating a topic, an explanatory synthesis essay categorizes facts to enhance the reader's comprehension. It refrains from advocating a particular perspective, and if it features a thesis, it tends to be relatively weak. Some business white papers adopt this approach, occasionally with a subtle viewpoint. Now, let’s find out how to start a synthesis essay.
Brainstorm Good Synthesis Essay Topics
Synthesis essay topics you choose should strike a balance – they must encompass a scope wide enough to unite various interconnected sources, yet not so expansive that they amalgamate vastly unrelated ones. If you are free to select your topic, conducting some initial research can guide your decision-making process. To illustrate, consider the transformation of a broad subject like "Social Media" into a more focused essay topic, such as exploring the impact of texting on the English language. When synthesis paper topics are assigned in a class, be sure to meticulously examine the prompts to ensure a thorough comprehension of their requirements.
Carefully Select and Double-Check Your Sources
For the AP test, your sources will be provided. For the purpose of learning what is synthesis essay, you should aim to choose a minimum of three sources for your essay. If time permits, study one or two additional sources, especially those directly relevant to your essay's purpose or argument.
Remember, it's more advantageous to analyze three sources than to superficially cover five thoroughly. While working on synthesis essay writing regarding sources, annotate them by jotting down notes in the margins. This practice will help you maintain a clear line of thought and develop your ideas effectively.
Write a Thesis Statement
After reviewing the assigned sources or conducting independent research, it's time to formulate a synthesis essay thesis on the topic. Your thesis serves as the central concept in your essay, encompassing the subject and articulating your perspective. It should be expressed as a complete sentence. In your essay, the thesis statement can function as either the opening sentence or the concluding sentence of the first paragraph, depending on the essay's structure. For instance, consider the following example: " Climate change is an urgent global crisis, and its mitigation requires a coordinated effort involving government policies, renewable energy adoption, and public awareness campaigns to combat its detrimental effects on our planet. ”
Revisit Your Source Material to Identify Supporting Elements for Your Thesis
When learning how to write a synthesis thesis, thoroughly review your sources and identify key quotes, statistics, ideas, and facts that align with and support your thesis. As you encounter these elements, document them for use throughout your essay.
If you intend to address opposing claims and challenge them, seek out ideas or quotes that contradict your thesis statement and devise strategies to refute them. This practice, known as a concession, refutation, or rebuttal, can significantly bolster your argument when executed effectively.
For example, with the provided thesis statement of an argumentative synthesis essay, valuable sources may encompass quotes from linguists discussing the emergence of new words in 'text-speak,' statistics showcasing the continuous evolution of the English language with each generation, and factual evidence demonstrating that students maintain the ability to write with proper grammar and spelling. These elements can serve to counter the arguments against the positive impact of texting on the English language.

Optimal Synthesis Essay Structure
You can choose to organize your approach formally with a synthesis paper outline or plan the structure in your head. But it's crucial to determine the most effective way to present your material. If you're composing this paper for the AP test, be aware that graders expect a specific structure of a synthesis essay thesis outline.
.webp)
Synthesis Essay Introduction:
- An attention-grabbing opening sentence to engage the reader.
- Clear identification of the issue under discussion.
- Presentation of your thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs:
- Start with a topic sentence that supports one aspect of your thesis.
- Provide your interpretation and viewpoint on the topic.
- Cite evidence from your sources to support your assertion.
- Explain the significance of the source(s) in the context of your argument.
Conclusion Paragraph:
- Reiterate the broader significance of your topic based on the evidence and reasons explored in the essay.
- Conclude with a profound insight or thoughtful ending for your paper.
Explore a More Imaginative Structure for Your Synthesis Essay
If you are learning how to write a synthesis essay AP lang, consider adopting a structure that was outlined earlier. In another case, approach a synthesis essay structure more creatively. You have the flexibility to employ one or more of the following creative approaches:
1. Example/Illustration: This approach involves providing detailed anecdotes, summaries, or direct quotes from your source material to offer substantial backing for your perspective. You can employ multiple examples or illustrations, but avoid making your essay solely a series of examples at the expense of supporting your thesis.
2. Straw Man: With this method, you mean to present an argument opposing the thesis in your argumentative synthesis essay, subsequently highlighting its weaknesses and flaws. By showcasing your understanding of the opposing viewpoint and your ability to counter it, you enhance the strength of your argument. In the beginning, present the counter-argument immediately after your thesis, follow with evidence to disprove it, and conclude with a compelling argument supporting your thesis.
3. Concession: Essays structured with concessions resemble those using the straw man technique. However, they acknowledge the validity of the counter-argument while demonstrating that the original argument holds more weight. This structure effectively presents your paper to readers who maintain opposing viewpoints.
4. Comparison and Contrast: This structure involves examining similarities and differences between two subjects or sources to showcase their various aspects. Crafting an essay using this structure necessitates a meticulous analysis of your source material to identify both subtle and significant points of similarity and contrast. You can present your arguments either source-by-source or by highlighting points of similarity or difference. We know that this information might sound tricky, so we would like to offer you to order essay writing from expert writers to save you the trouble.
Generate an Outline Tailored for a Background and Review Essays
While a synthesis paper primarily focuses on articulating and substantiating a thesis, background and review essays delve into the concepts and ideas contained within the sources rather than centering on the author's perspective. There are two fundamental approaches to structuring such essays:
1. Summary: This framework provides summaries of each relevant source, gradually constructing a more robust argument for your thesis. It offers specific evidence to bolster your viewpoint but typically refrains from expressing your personal opinions. This method is most commonly employed in background and review essays.
2. List of Reasons: This approach consists of a series of sub-points derived from the central thesis of your synthesis in English. Each reason is fortified with supporting evidence. Similar to the summary method, the reasons should progress in importance, with the most significant reason appearing last.
Writing Tips That Will Help You Score Better
One of the cornerstones of how to write a synthesis paragraph is to be ready to adjust your plan as needed, especially if you synthesize ideas and information in your source material that strengthens your thesis. If you're composing the synthesis for the AP test, remember that you won't have the luxury of multiple drafts, so manage your time wisely to ensure it reaches its utmost potential.
Synthesis essay writing should commence with an introductory paragraph that features your thesis, followed by a body that provides compelling evidence in support of your thesis. Conclude your essay with a summary of your perspective. Is everything clear so far? If not, simply say, ‘ Help me write my essay ,’ and our experts will get back to you with more practical assistance.
Write in the Third Person
If you are wondering how to write a synthesis paper correctly, remember that writing in the third person is recommended. It involves the use of pronouns like "he," "she," and "it," alongside crafting clear and comprehensive sentences. It's essential to provide sufficient information that demonstrates your expertise in the subject matter of your essay. Writing a synthesis essay, strive to maintain an active voice in your writing. However, passive voice can be employed when necessary, particularly when avoiding the use of first-person ("I") or second-person ("you").
Use Transitions
Transitions serve as effective tools for illustrating the intersections where your sources reinforce each other. For instance, you can highlight this synergy as follows: " Hallstrom's insights into market dynamics receive further validation from Anderson's comprehensive study, 'Market Trends Unveiled,' where he argues… "
For extensive quotations spanning three lines or more, it's advisable to set them apart as block quotes to emphasize their significance.
Self-Check List Before Handing Your Work In
Now is the moment to fortify your argumentative synthesis essay and enhance the flow between points and paragraphs. Strive for clarity and conciseness in your argumentation, making it easily comprehensible. Reading your essay aloud can be beneficial, as it reveals awkward sentences and incoherent arguments.
Consider enlisting a second set of eyes for proofreading; the phrase "two heads are better than one" remains relevant. Request feedback from a friend or colleague regarding potential additions or removals from your synthesis in English writing. Crucially, ascertain whether your argument is logically sound and well-supported by your sources.
Proofread Carefully
In the framework of how to write an academic essay , proofreading is absolutely key. Thoroughly review your paper to identify and rectify any grammar, punctuation, or spelling mistakes. Pay special attention to the accurate spelling of names and proper nouns. Check for run-on sentences or sentence fragments and make necessary corrections as you proceed.
To ensure accuracy, read your paper aloud, as this can help prevent accidental insertions or omissions that might occur when reading silently. Whenever possible, seek the assistance of a friend or classmate for additional proofreading to enhance the overall quality of your essay.
Acknowledge and Cite Your Source Material
The process of how to cite in a synthesis essay includes Incorporating footnotes to cite material within the body of your essay and compiling a bibliography of the cited works at the conclusion is the preferred method. Ensure that footnotes and in-text citations are employed whenever you quote, paraphrase, or reference any material. If you're composing this essay for the AP test, a specific citation style may not be required, but it is essential to identify the source after citing it.
For instance, in an AP essay, you might mention: “ Johnson posits, ‘The advent of texting has revolutionized the English language, offering a distinct mode of communication for the younger generation. ’"
In college essays, you'll typically adhere to MLA format, although you may be asked to use APA or Chicago style. Regardless of the format, maintain consistency in its application throughout your essay. To help you with this, we’ve prepared a guide on how to format an essay .
What Should Not Be Said in a Synthesis Essay?
In an argumentative synthesis essay, it's crucial to avoid expressing personal opinions or introducing new informative insights not supported by your cited sources. Steer clear of making sweeping generalizations or assumptions without proper evidence, and do not rely solely on personal anecdotes or anecdotes that aren't reinforced by reputable sources. Additionally, avoid simply summarizing sources without analyzing and documenting the information to build a cohesive argument. Your essay should focus on presenting a well-supported thesis derived from the integrated ideas of your sources rather than introducing personal viewpoints or extraneous information.
Should a Synthesis Paper Have a Title?
Yes, you can certainly have a title for a synthesis paper. A well-chosen title can provide readers with an initial understanding of the essay's topic or theme and can make your paper more engaging. The title should be relevant to the content and give readers a sense of what to expect from your essay. Make sure the title is concise, descriptive, and reflective of the main idea or argument in your paper.
What Is the Length of a Synthesis Paper?
When writing a synthesis paper, the length can vary significantly depending on the specific assignment or guidelines provided by your instructor. Typically, synthesis papers range from 2-5 pages for shorter assignments to longer papers of 10 or more pages for more extensive projects. The exact page count may also depend on the complexity of the topic and the number of sources you are required to integrate into your synthesis. It's essential to adhere to your instructor's instructions regarding the required length for your synthesis paper.
Is There a Difference Between Synthesis and Argument Essay?
A synthesis essay combines information from multiple sources to develop a balanced viewpoint on a topic, emphasizing objectivity. In contrast, an argument essay focuses on presenting and defending a particular perspective on a subject, often using reasons and evidence to persuade the audience. The use of sources and the tone differs, with synthesizing essays adopting a more objective tone and incorporating various perspectives. In contrast, argument essays take a persuasive approach with a clear thesis. In summary, the key distinction lies in their purpose, use of sources, and the tone and voice employed.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support

Synthesis in Writing: What, Why, and How?
Synthesis in Writing
Scholarly writing requires the use of synthesis. Scholars take writing beyond the analysis level to the level where synthesis is evident; they add their ideas, interpretations, and voices to existing sources’ information and take it further ( Efron & Ravid, 2018).
What's the difference between Summarizing and Synthesis?
Summarizing requires an understanding of the material and identification of the major themes. No new information is being added to the information; it’s just being summed up. Although summarizing is necessary for the process of synthesis, synthesis goes beyond summarizing into the addition of information like interpretations or new conclusions ( Efron & Ravid, 2018).
Moving from Summarizing to Synthesis
Approach this in a step-by-step manner, starting with a summary of each source. The next step is to look for patterns and themes within each summary. After noting those, compare and contrast those patterns and themes between all sources. Find the relationships between the sources ( Efron & Ravid, 2018).
Synthesis occurs at the paragraph level when writers connect individual pieces of evidence from multiple sources to support a paragraph’s main idea and advance a paper’s thesis statement. Your paragraph includes a main idea, evidence from multiple sources, and the analysis of those multiple sources together.
Use strong verbs to integrate sources:
- The author affirms, states, mentions, warns, predicts, proposes, admits that..
- Finings emphasize, argue, reject the importance..
- Research revealed, verified, suggests that..
- Evidence indicates, confirms, denies, demonstrates ...
Here’s an example:

For additional support, a synthesis matrix will simplify this process.
Synthesis Matrix:

( Efron & Ravid, 2018).
Questions to consider:
Did all the authors make the same comments and interpretations? Did only the recent papers have the same conclusions? Is there a pattern of the same interpretations over time? Are all the author’s in agreement? Does one author extend the research of another? Where do sources overlap and where do they differ?
Reference: Efron , S. E., & Ravid, R . (2018). Writing the literature review: A practical guide . Guilford Publications.
More information on this topic:
Paraphrasing & Student Voice: What, Why, and How?
Writing the Literature Review : A Practical Guide by Sara Efrat Efron , and Ruth Ravid https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/ras/reader.action?docID=5522670&ppg=199
Judith Garrard. (2020). Health Sciences Literature Review Made Easy . Jones & Bartlett Learning. https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=nlebk&AN=2693815&site=ehost-live&scope=site&custid=s9076023&ebv=EK&ppid=Page-__-173
Hempel, S. (2019). Conducting your literature review . American Psychological Association. https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/ras/reader.action?docID=5899941&ppg=111
Clark, K. R., & Buckley, M. B. (2017). Using a Synthesis Matrix to Plan a Literature Review. Radiologic Technology , 88 (3), 354–357. https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&AuthType=ip,shib&db=mnh&AN=28298590&site=eds-live&custid=s9076023
- Reading and Writing
- Research and Library
- General Education & Other
- Research Papers
- Graduate Writing
- Graduate Education
- Last Updated May 02, 2023
- Answered By Tammy Hopps
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (0)
Hello! We're here to help! Please log in to ask your question.
Need an answer now? Search our FAQs !
How can I find my course textbook?
You can expect a prompt response, Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM-4:00 PM Central Time (by the next business day on weekends and holidays).
Questions may be answered by a Librarian, Learning Services Coordinator, Instructor, or Tutor.
280+ Strong Verbs: 3 Tips to Strengthen Your Verbs in Writing
by Joe Bunting | 0 comments
Free Book Planning Course! Sign up for our 3-part book planning course and make your book writing easy . It expires soon, though, so don’t wait. Sign up here before the deadline!
Strong verbs transform your writing from drab, monotonous, unclear, and amateurish to engaging, professional, and emotionally powerful.
Which is all to say, if you're not using strong verbs in your writing, you're missing one of the most important stylistic techniques.

Why listen to Joe? I've been a professional writer for more than a decade, writing in various different formats and styles. I've written formal nonfiction books, descriptive novels, humorous memoir chapters, and conversational but informative online articles (like this one!).
In short, I earn a living in part by writing (and revising) using strong verbs selected for each type of writing I work on. I hope you find the tips on verbs below useful! And if you want to skip straight to the verb list below, click here to see over 200 strong verbs.
Hemingway clung to a writing rule that said, “Use vigorous English.” In fact, Hemingway was more likely to use verbs than any other part of speech, far more than typical writing, according to LitCharts :

But what are strong verbs? And how do you avoid weak ones?
In this post, you'll learn the three best techniques to find weak verbs in your writing and replace them with strong ones. We'll also look at a list of the strongest verbs for each type of writing, including the strongest verbs to use.
What are Strong Verbs?
Strong verbs, in a stylistic sense, are powerful verbs that are specific and vivid verbs. They are most often in active voice and communicate action precisely.
The Top 7 Strong Verbs
Here are the top 7 I found when I reviewed a couple of my favorite books. See if you agree and tell me in the comments.
Think about the vivid and specific image each of these strong verbs conjures. Each one asserts precision.
It's true that writers will use descriptive verbs that best fit their character, story, and style, but it's interesting to note trends.
For example, Hemingway most often used verbs like: galloped, punched, lashed, and baited. Each of these verbs evokes a specific motion, as well as a tone. Consider how Hemingway's verbs stack up against weaker counterparts:
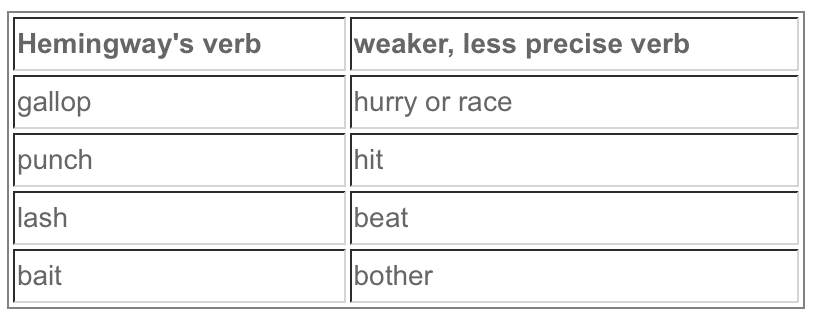
None of the weaker verbs are incorrect, but they don't pack the power of Hemingway's strong action verbs, especially for his story lines, characters, and style. These are verbs that are forward-moving and aggressive in tone. (Like his characters!)
Consider how those choices differ significantly than a few from Virginia Woolf's opening page of Mrs. Dalloway :
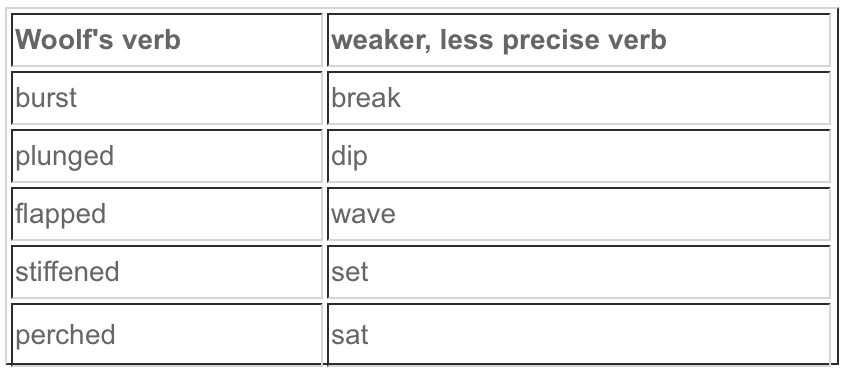
Notice how Woolf's choices create the vibrant, descriptive style that marks her experimental novel and its main character. Consider the difference between “perched” and “sat.” “Perched” suggests an image of a bird, balancing on a wire. Applied to people, it connotes an anxiousness or readiness to stand again. “Sat” is much less specific.
The strongest verbs for your own writing will depend on a few things: your story, the main character, the genre, and the style that is uniquely yours. How do you choose then? Let's look at three tips to edit out weak, boring verbs.
How to Edit for Strong Verbs FAST
So how do you root out those weak verbs and revise them quickly? Here are a few tips.
1. Search for Weak Verbs
All verbs can be strong if they're used in specific, detailed, and descriptive sentences.
The issue comes when verbs are overused, doing more work than they're intended for, watering down the writing.
Here are some verbs that tend to weaken your writing:
Did you notice that most of these are “to be” verbs? That's because “to be” verbs are linking verbs or state of being verbs. Their purpose is to describe conditions.
For example, in the sentence “They are happy,” the verb “are” is used to describe the state of the subject.
There's nothing particularly wrong with linking verbs. Writers who have a reputation for strong writing, like Ernest Hemingway or Cormac McCarthy, use linking verbs constantly.
The problem comes when you overuse them. Linking verbs tend to involve more telling vs. showing .
Strong verbs, on the other hand, are usually action verbs, like whack, said, ran, lassoed, and spit (see more in the list below).
The most important thing is to use the best verb for the context, while emphasizing specific, important details.
Take a look at the following example early into Hemingway's For Whom the Bell Tolls :
The young man, who was studying the country, took his glasses from the pocket of his faded, khaki flannel shirt, wiped the lenses with a handkerchief, screwed the eyepieces around until the boards of the mill showed suddenly clearly and he saw the wooden bench beside the door; the huge pile of sawdust that rose behind the open shed where the circular saw was , and a stretch of the flume that brought the logs down from the mountainside on the other bank of the stream.
I've highlighted all the verbs. You can see here that Hemingway does use the word “was,” but most of the verbs are action verbs, wiped, took, screwed, saw, etc. The result of this single sentence is that the audience pictures the scene with perfect clarity.
Here's another example from Naomi Novick's Deadly Education:
He was only a few steps from my desk chair, still hunched panting over the bubbling purplish smear of the soul-eater that was now steadily oozing into the narrow cracks between the floor tiles, the better to spread all over my room. The fading incandescence on his hands was illuminating his face, not an extraordinary face or anything: he had a big beaky nose that would maybe be dramatic one day when the rest of his face caught up, but for now was just too large, and his forehead was dripping sweat and plastered with his silver-grey hair that he hadn’t cut for three weeks too long.
Vivid right? You can see that again, she incorporates weaker verbs (was, had) into her writing, but the majority are highly descriptive action verbs like hunched, illuminating, spread, plastered, and dripping.
Don't be afraid of linking verbs, state verbs, or helping verbs, but emphasize action words to make your writing more powerful.
2. Remove Adverbs and Replace the Verbs to Make Them Stronger
Adverbs add more detail and qualifications to verbs or adjectives. You can spot them because they usually end in “-ly,” like the word “usually” in this sentence, or frequently, readily, happily, etc.
Adverbs get a bad rap from writers.
“I believe the road to hell is paved with adverbs,” Stephen King said.
“Adverbs are dead to me. They cannot excite me,” said Mark Twain .
“I was taught to distrust adjectives,” said Hemingway, “as I would later learn to distrust certain people in certain situations.”
Even Voltaire jumped in on the adverb dogpile, saying, “Adjectives are frequently the greatest enemy of the substantive.”
All of these writers, though, used adverbs when necessary. Still, the average writer uses them far more than they did.
Adverbs signal weak verbs. After all, why use two words, an adverb and a verb, when one strong verb can do.
Look at the following examples of adverbs with weak verbs replaced by stronger verbs:
- He ran quickly –> He sprinted
- She said loudly –> She shouted
- He ate hungrily –> He devoured his meal
- They talked quietly –> They whispered
Strive for simple, strong, clear language over padding your writing with more words.
You don't need to completely remove adverbs from your writing. Hemingway himself used them frequently. But cultivating a healthy distrust of adverbs seems to be a sign of wisdom among writers.
3. Stop Hedging and “Eliminate Weasel Words”
Amazon's third tip for writing for employees is “Eliminate Weasel Words,” and that advice applies to verbs too.
Instead of “nearly all customers,” say, “89 percent of customers.”
Instead of “significantly better,” say, “a 43 percent improvement.”
Weasel words are a form of hedging.
Hedging allows you to avoid commitment by using qualifiers such as “probably,” “maybe,” “sometimes,” “often,” “nearly always,” “I think,” “It seems,” and so on.
Hedge words or phrases soften the impact of a statement or to reduce the level of commitment to the statement's accuracy.
By eliminating hedging, you're forced to strengthen all your language, including verbs.
What do you really think about something? Don't say, “I think.” Stand by it. A thing is or isn't. You don't think it is or believe it is. You stand by it.
If you write courageously with strength of opinion, your verbs grow stronger as well.

Beware the Thesaurus: Strong Verbs are Simple Verbs
I caveat this advice with the advice to beware thesauruses.
Strong writing is almost always simple writing.
Writers who replace verbs like “was” and “get” with long, five-syllable verbs that mean the same thing as a simple, one-syllable verb don't actually communicate more clearly.
To prepare for this article, I studied the verb use in the first chapters of several books by my favorite authors, including Ernest Hemingway's For Whom the Bell Tolls and Naomi Novik's Deadly Education.
Hemingway has a bigger reputation as a stylist and a “great” writer, but I found that Novik's verb choice was just as strong and even slightly more varied.
Hemingway tended to use simpler, shorter verbs, though, often repeating verbs, whereas Novik's verbs were longer and often more varied.
I love both of these writers, but if you're measuring strength, simplicity will most often win.
In dialogue this is especially important . Writers sometimes try to find every synonym for the word, “said” to describe the exact timber and attitude of how a character is speaking.
This becomes a distraction from the dialogue itself. In dialogue, the words spoken should speak for themselves, not whatever synonym the writer has looked up for “said.”
Writers should use simple speaker tags like “said” and “asked” as a rule, only varying that occasionally when the situation warrants it.
270+ Strong Verbs List
We've argued strong verbs are detailed, descriptive, action verbs, and below, I list over 200 strong verbs to make your writing better.
I compiled this list directly from the first chapters of some of my favorite books, already mentioned previously, For Whom the Bell Tolls by Ernest Hemingway, Deadly Education by Naomi Novik, and The Undoing Project by Michael Lewis.
This is a necessarily simplified list, taken only from the first chapters of those books. There are thousands of strong verbs, usually action verbs, but these are a good start.
I've also sorted them alphabetically and put them into present tense.
- Collaborate
- Intellectualize
The Best Way to Learn to Use Strong Verbs
The above tips will help get you started using strong verbs, but the best way to learn how to grow as a writer with your verbs is through reading.
But not just reading, studying the work of your favorite writers carefully and then trying to emulate it, especially in the genre you write in.
As Cormac McCarthy, who passed away recently, said, “The unfortunate truth is that books are made from books.”
If you want to grow as a writer, start with the books you love. Then adapt your style from there.
Which tip will help you use more strong verbs in your writing today? Let me know in the comments.
Choose one of the following three practice exercises:
1. Study the verb use in the first chapter of one of your favorite books. Write down all of the verbs the author uses. Roughly what percentage are action verbs versus linking verbs? What else do you notice about their verb choice?
2. Free write for fifteen minutes using only action verbs and avoiding all “to be” verbs and adverbs.
3. Edit a piece that you've written, replacing the majority of linking verbs with action verbs and adverbs with stronger verbs.
Share your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop here , and give feedback to a few other writers.
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Active Verbs Note of Caution: Only use the verbs you're familiar with unless you take the time to examine the definition in the dictionary. This is NOT a list of synonyms. Each word has specific usage patterns that are unique to its meaning. Literary Essay Report or Persuasive Essay that refers to an expert's opinion or research studies
Synthesis Essay Tips. Crafting a strong synthesis essay requires careful planning and effective techniques. Here are five essential tips to help you write your best paper: Diverse Source Selection: Choose a range of reliable sources that offer different viewpoints on your topic. Make sure they're recent and relevant to your subject.
A synthesis essay uses a variety of sources to form a new idea, answer a question, or defend an argumentative thesis statement. A synthesis does not summarize but shows the connections among the different sources and the writers' ideas. A successful synthesis essay overviews research on the chosen topic, highlights the connections among ...
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
This step of outlining your thesis and main points is a crucial one when writing a synthesis. If your goal in writing a research essay is to provide readers a unified perspective based on sources, the unified perspective must be clear before the writing begins. Once the writing begins, your point of view is then carried through to the paragraph ...
3. Tips for an effective synthesis essay: • Establish your purpose to shape the way you want to argue and form your thesis. The thesis is the main claim or idea of your essay. • Select your sources and become familiar with them so that you can discuss them in relationship to your thesis and supporting argument(s).
Synthesis essays will typically contain three body paragraphs. A good body paragraph contains three main sections: a topic sentence (or key sentence), relevant supporting sentences, and a closing (or transition) sentence. This structure keeps your paragraph focused on the main idea, providing clear, concise information.
The basic synthesis essay structure follows the 5 paragraph essay format. Introduction - Briefly describe what the paper will be about. Start with a hook to engage the reader from the very beginning, followed by a brief description, and make sure to include your thesis statement. Body Paragraphs - The first body paragraph typically contains a ...
Use of weak "to be" verbs rather than strong, active verbs; Failure to maintain a formal, rational, objective, unbiased, and academic tone that is directed at an educated audience; Proficient (6 points): My essay reads clearly, but may occasionally exhibit one or two of the stylistic errors avoided by an excellent essay (above).
* Aspects of A Strong Synthesis Essay: ... As part of your revising process, take a marker and highlight all your verbs. Notice how you can use some of the strong verbs to strengthen your own academic voice. Ex.: Instead of, 'The author talks about the effects', you can write, 'The author argues that …., The author illustrates the need ...
Step 3: Crafting a strong thesis statement. A strong thesis statement has to capture the main idea of your synthesis essay. It should include a synthesis of information that you gathered during ...
Powerful: The man strode along the platform. Impotent: Jim is a lover of country living. Powerful: Jim treasures country living. Impotent: There are three things that make me feel the way I do…. Powerful: Three things convince me…. 2. Verbs that rely on adverbs. Powerful verbs are strong enough to stand alone. Examples.
If you have questions about synthesis, then refer to The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers, 7th edition. Synthesis is discussed on page 740. Also, refer to our handout "Introducing Sources (MLA Style)" for information on using sources and quotations correctly in an essay. "Verbs of Attribution" is a great handout too!
Powerful Verbs for Weaving Ideas in Essays The following verbs are helpful as a means of showing how an example or quote in literature Supports an idea or interpretation. Example + Verb + Explanation or Significance (CD) (CM) You may use the above in a sentence as a general formula that may need modified to fit each situation. verb
This is a crucial step as it's your chance to make sure that your essay flows logically, uses up-to-date sources, is error-free, and clearly expresses your idea or thesis statement. a. Check Your Thesis Statement. Make sure the thesis statement or main argument of your essay stands out clearly and confidently.
Find several central ideas in the chart. Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay. Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points. Make a draft of the thesis statement. Try to formulate the main idea you want to present in your essay.
Your essay should have an introductory paragraph that includes your thesis, a body to present evidence that supports your thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes your point of view. 2. Write in the third person. Writing in the third person means using "he," "she," "it", and using complete, unambiguous sentences.
The definition of a synthesis entails a written discourse integrating support from multiple sources, each offering diverse perspectives. Writing a synthesis essay demands the skill to comprehend information and structure it cohesively. This proficiency cultivated in academic settings also holds value in the realms of business and advertising.
with a strong analytical question that you will try to answer in your essay. Your answer to that question will be your essay's thesis. You may have many questions as you consider a source or set of sources, but not all of your questions will form the basis of a strong essay. For example, your initial questions
Synthesis occurs at the paragraph level when writers connect individual pieces of evidence from multiple sources to support a paragraph's main idea and advance a paper's thesis statement. Your paragraph includes a main idea, evidence from multiple sources, and the analysis of those multiple sources together. Use strong verbs to integrate ...
A synthesis paper is a written discussion that incorporates support from multiple sources to examine a variety of viewpoints related to a thesis. It is commonly used in various types of assignments such as analysis papers, research papers, argument papers, and business reports. To write an effective synthesis essay, it is crucial to establish a clear purpose, carefully select and evaluate ...
Tweet. 3. Stop Hedging and "Eliminate Weasel Words". Amazon's third tip for writing for employees is "Eliminate Weasel Words," and that advice applies to verbs too. Instead of "nearly all customers," say, "89 percent of customers.". Instead of "significantly better," say, "a 43 percent improvement.".