Reviewer comments: examples for common peer review decisions
Peer-reviewing an academic manuscript is not an easy task. Especially if you are unsure about how to formulate your feedback. Examples of reviewer comment s can help! Here you can find an overview of sample comments and examples for the most common review decisions: ‘minor revisions’, ‘major revisions’, ‘revise and resubmit’ and ‘reject’ decisions.

Examples of ‘minor revisions’ reviewer comments
Examples of ‘major revisions’ reviewer comments, examples of ‘revise and resubmit’ reviewer comments, examples of ‘reject’ reviewer comments.
- “This is a well-written manuscript that only needs to undergo a few minor changes. First, …”
- “The manuscript is based on impressive empirical evidence and makes an original contribution. Only minor revisions are needed before it can be published.”
- “I thoroughly enjoyed reviewing this manuscript and only have some minor requests for revision.”
- “The authors develop a unique theoretical framework, and I believe that they should highlight their originality much more.”
- “The authors conduct very relevant research, but fail to emphasise the relevance in their introduction.”
- “The authors draw on extensive empirical evidence. I believe that they can put forward their arguments much more confidently.”
- “The authors adequately addressed my feedback from the first round of peer review. I only have some minor comments for final improvements.”
- “To improve the readability of the paper, I suggest dividing the analysis into several subsections.”
- “Figure 3 is difficult to read and should be adjusted.”
- “Table 1 and 2 can be combined to create a better overview.”
- “The abstract is too long and should be shortened.”
- “I had difficulties understanding the first paragraph on page 5, and suggest that the authors reformulate and simplify it.”
- “The manuscript contains an elaborate literature review, but definitions of the key concepts are needed in the introduction.”
- “Throughout the manuscript, there are several language mistakes. Therefore, I recommend a professional round of language editing before the paper is published.”
- “The paper should undergo professional language editing before it can be published.”
If you want to learn more about common reasons for a ‘minor revisions’ decision and see examples of how an actual peer review might look like, check out this post on ‘minor revisions’ .
- “The manuscript shows a lot of promise, but some major issues need to be addressed before it can be published.”
- “This manuscript addresses a timely topic and makes a relevant contribution to the field. However, some major revisions are needed before it can be published.”
- “I enjoyed reading this manuscript, and believe that it is very promising. At the same time, I identified several issues that require the authors’ attention.”
- “The manuscript sheds light on an interesting phenomenon. However, it also has several shortcomings. I strongly encourage the authors to address the following points.”
- “The authors of this manuscript have an ambitious objective and draw on an interesting dataset. However, their main argument is unclear.”
- “The key argument needs to be worked out and formulated much more clearly.”
- “The theoretical framework is promising but incomplete. In my opinion, the authors cannot make their current claims without considering writings on… “
- “The literature review is promising, but disregards recent publications in the field of…”
- “The empirical evidence is at times insufficient to support the authors’ claims. For instance, in section…”
- “I encourage the authors to provide more in-depth evidence. For instance, I would like to see more interview quotes and a more transparent statistical analysis.”
- “The authors work with an interesting dataset. However, I was missing more detailed insights in the actual results. I believe that several additional tables and figures can improve the authors’ argumentation. “
- “I believe that the manuscript addresses a relevant topic and includes a timely discussion. However, I struggled to understand section 3.1.”
- “I think that the manuscript can be improved by removing section 4 and integrating it into section 5.”
- “The discussion and conclusions are difficult to follow and need to be rewritten to highlight the key contributions of this manuscript.”
- “The line of argumentation should be improved by dividing the manuscript into clear sections with subheadings.”
If you want to learn more about common reasons for a ‘major revisions’ decision and see examples of how an actual peer review might look like, check out this post on ‘major revisions’ .
- “I encourage the authors to revise their manuscript and to resubmit it to the journal.”
- “In its current form, this paper cannot be considered for publication. However, I see value in the research approach and encourage the authors to revise and resubmit their manuscript.”
- “ With the right changes, I believe that this manuscript can make a valuable contribution to the field of …”
- “The paper addresses a valuable topic and raises interesting questions. However, the logic of the argument is difficult to follow. “
- “The manuscript tries to achieve too many things at the same time. The authors need to narrow down their research focus.”
- “The authors raise many interesting points, which makes it difficult for the reader to follow their main argument. I recommend that the authors determine what their main argument is, and structure their manuscript accordingly.”
- “The literature review raises interesting theoretical debates. However, in its current form, it does not provide a good framework for the empirical analysis.”
- “A clearer theoretical stance will increase the quality of the paper.”
- “The manuscript draws on impressive data, as described in the methodology. However, the wealth of data does not come across in the analysis. My recommendation is to increase the number of interview quotes, figures and statistics in the empirical analysis.”
- “The authors draw several conclusions which are hard to connect to their empirical findings. “
- The authors are advised to critically reflect on the generalizability of their research findings.”
- “The manuscript needs to better emphasise the research relevance and its practical implications.”
- “It is unclear what the authors consider their main contribution to the academic literature, and what they envisage in terms of recommendations for further research.”
If you want to learn more about common reasons for a ‘revise and resubmit’ decision and see examples of how an actual peer review might look like, check out this post on ‘revise and resubmit’ .
- “I do not believe that this journal is a good fit for this paper.”
- “While the paper addresses an interesting issue, it is not publishable in its current form.”
- “In its current state, I do not recommend accepting this paper.”
- “Unfortunately, the literature review is inadequate. It lacks..”
- “The paper lacks a convincing theoretical framework , which is necessary to be considered for publication.”
- “Unfortunately, the empirical data does not meet disciplinary standards.”
- “While I applaud the authors’ efforts, the paper does not provide sufficient empirical evidence.”
- “The empirical material is too underdeveloped to consider this paper for publication.”
- “The paper has too many structural issues, which makes it hard to follow the argument.”
- “There is a strong mismatch between the literature review and the empirical analysis.”
- “The main contribution of this paper is unclear.”
- “It is unclear what the paper contributes to the existing academic literature.”
- “The originality of this paper needs to be worked out before it can be considered for publication.”
- “Unfortunately, the language and sentence structures of this manuscript are at times incomprehensible. The paper needs rewriting and thorough language editing to allow for a proper peer review.”
If you want to learn more about common reasons for a ‘reject’ decision and see examples of how an actual peer review might look like, check out this post on ‘reject’ decisions .
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
Minor revisions: Sample peer review comments and examples
5 proven ways to become an academic peer reviewer, related articles.

The different stages in the manuscript publication process

How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)

How to write effective cover letters for a paper submission

Dealing with failure as a PhD student
What the examiners said
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Examiners’ Comments on the Introduction Chapter in Theses ( a presentation)

Related Papers
Australian Journal of Educational and Developmental Psychology
Terence Lovat
Vernon Trafford
This paper contains accounts of what transpired in one doctoral viva by the five participants ~ candoidate, supervisor, internal and external examiner plus the independent Chair. It presents an analysis of the questions asked, the answers given and the interperonal transactions.
International Journal of Social Science and Human Research
JOSEPH BENJAMIN ARCHIBALD AFFUL
The thesis examiner’s report is an evaluation of a thesis, which includes dialogic and evaluative elements. The purpose of the study was to investigate the roles that examiners adopt for themselves and the language use in examiners’ reports on MPhil theses submitted to the School of Graduate Studies, University of Cape Coast. The study purposively selected 100 theses examiners reports from four disciplines. The study revealed that examiners adopted eight different roles in the reports. Another key finding of the study was that evaluator role was most frequent, and the least frequently occurring role was Institutional role. Again, examiners employed imperatives, personal pronouns, and adjectives in their adopted roles. The findings of the study serve to create an awareness for explicit guidelines for both fresh and experienced examiners in the task of postgraduate thesis examination.
The Australian Universities' review
Kerry Dally
Doctoral thesis examination is the litmus test for doctoral quality. Of those candidates who reach examination, most are notified they have more work to do on their thesis. Receiving and responding to feedback are integral parts of a formal learning process that continues until the final thesis is submitted. However, little is known about what happens after examiner reports are received by an institution, how recommendations and feedback are filtered through institutional processes to influence thesis outcomes, or about the roles that candidates and supervisors play in determining and giving action to thesis revisions. This article reports the findings from a desktop review of institutional protocols and policies governing doctoral thesis examination in Australian universities. Given that the PhD Viva, or oral examination, is rare in Australian universities, the authors question whether current examination processes allow adequate opportunities for candidates to actively engage with...
Journal of English for Academic Purposes
Elke Stracke
This paper outlines the procedures used in the textual analysis of examiner reports for 101 PhD candidates across disciplines in one Australian University. The method involves the use of QSR software2. Three levels of findings are outlined. The first level is the coding categories that emerged out of reading the report text. There are five broad categories of codes that capture: the structure of the reports, the ways in which examiners communicate, the subject matter of the thesis, the characteristics of examiners' evaluative comment and their comments on their role and the examination process. The second level of findings concerns the frequency of different categories of comment and the prevalence of comment on the analysis and interpretation of the candidate's results. The third extends beyond the individual categories to what we can learn about the utilization of the report. One key finding is that the examiners took on specific roles: mentor-colleague, supervisor-instr...
Sue Starfield
Melbourne Studies in Education
Ansie Lessing
Clive Palmer (National Teaching Fellow)
Introduction This workshop is intended for supervisors preparing their students for viva-voce examination. Practical issues such as timing in the lead up to submission, selecting examiners, thesis preparation and mock viva, will inform discussions about managing the viva-voce on the day. Informing this workshop also are aspects of examiner expectations of a doctoral thesis, setting assessment/modification outcomes, understanding the Independent Chair role. Please be prepared to discuss and contribute example to the workshop.
RELATED PAPERS
David George Beckett
International Journal of Dental Science and Innovative Research (IJDSIR)
Dr. Suman Madan
Anales de Medicina Interna
Astor Grumann
Bioengineering
Andrea Silenzi
Fortune Journals
Jaime Chung
Abdellatif Mnassri
Studia z Teorii Wychowania
Maria Czerepaniak-Walczak
GLAUCIA NASCIMENTO QUEIROGA
African health sciences
MOSES KAMYA
Archives of Medical Research
JOSE MIGUEL MENA VIGIL
Toxicology Letters
Angela Castro
Agricultural Biotechnology Journal
Agora-estudos Classicos Em Debate
Jacyntho Brandão
Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science
Dr. Shery Jacob
arXiv (Cornell University)
Kenan Morani
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental
Cristhian Fernando Jiménez Carrillo 23 23
Cornelia Janke
Journal of Translational Medicine
Dr. Paulo Gentil
Democracia, vivências políticas e os limites da liberdade
Arthur A S De Oliveira
Journal of Northwest Anthropology, Special Publication #7
Rick McClure
Zulfa Zaidon
Èksperimentalʹnaâ psihologiâ
Valery Nosulenko
Transplantation Reviews
Vinod Nargund
somayeh bahrami
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
45+ SAMPLE Thesis Evaluation in PDF | MS Word
Thesis evaluation | ms word, 45+ sample thesis evaluation, what is a thesis evaluation, different types of thesis evaluation, benefits of writing a thesis evaluation, basic elements of a thesis evaluation, how to write a thesis evaluation, what are some examples of thesis, what is the purpose of a thesis evaluation, what are the essential steps in writing a thesis evaluation, how to write a good thesis introduction.

Master Thesis Written Evaluation Form

Honors Critical Thesis Evaluation
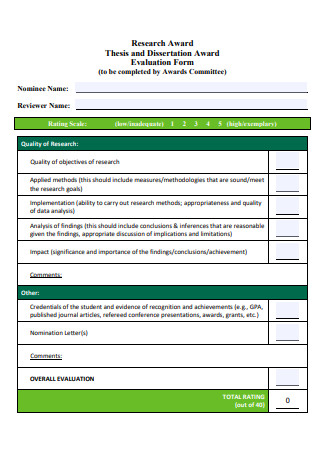
Thesis and Dissertation Award Evaluation Report Form
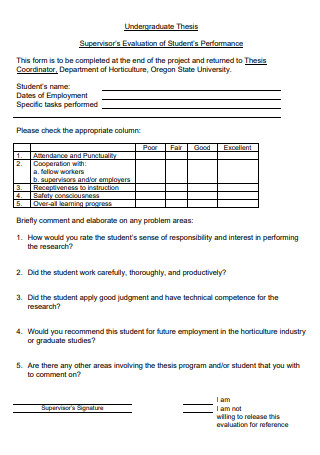
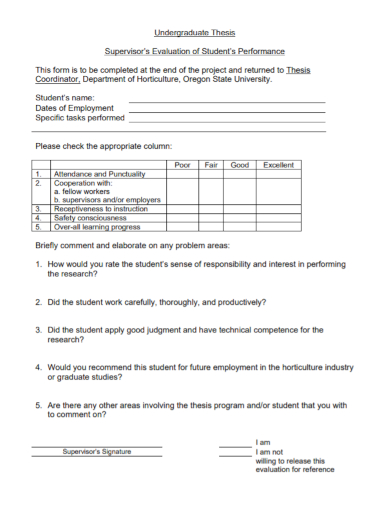
Undergraduate Thesis Supervisor Evaluation Assessment Form
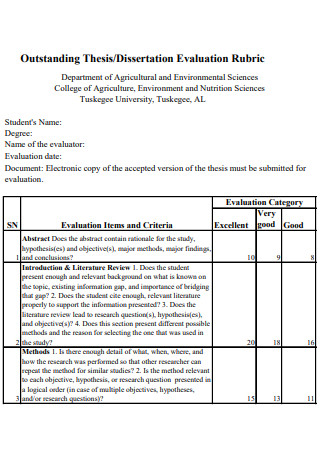
Outstanding Thesis Dissertation External Examiner Evaluation

Senior Honors Thesis Defense Evaluation Criteria Form
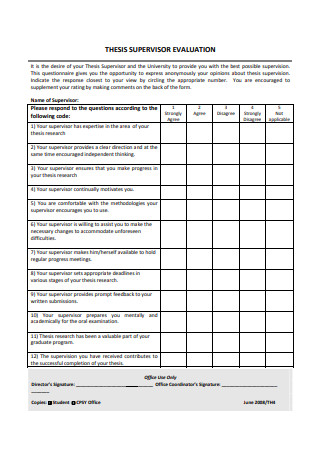
PhD Thesis Supervisor Evaluation

Undergraduate Thesis Evaluation Sheet
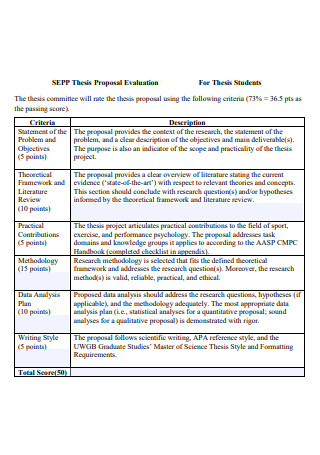
Thesis Proposal Evaluation For Students
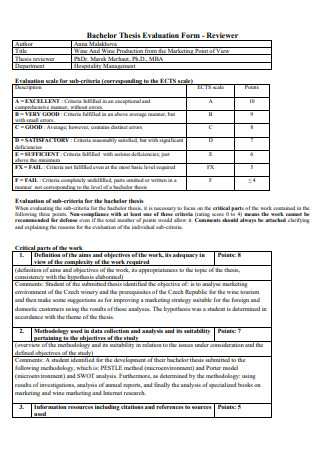
Bachelor Thesis Evaluation Form
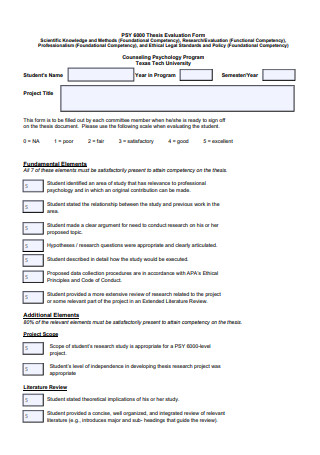
Thesis Evaluation Form
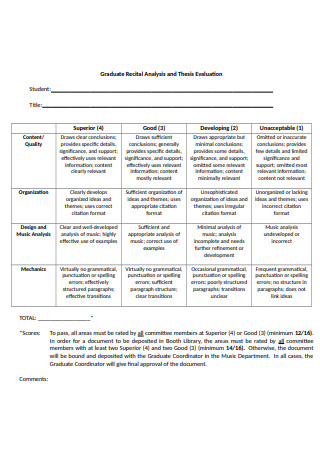
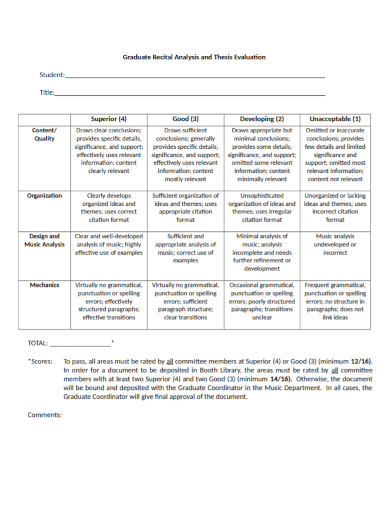
Graduate Recital Analysis and Thesis Evaluation

Thesis Defense Evaluation
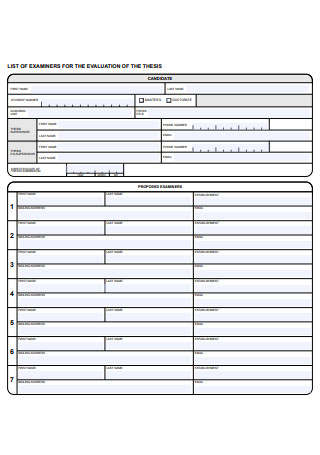
Thesis Evaluation of Examiners

Thesis Evaluation Report
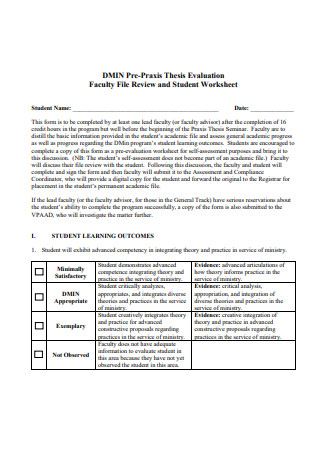
Thesis Evaluation and Student Worksheet

Thesis Evaluation Status Form

Thesis Prospectus Evaluation Form

Thesis Evaluation Matrix

Department of Mathematics and Statistics Thesis Evaluation Form

Thesis Evaluation Form For Master of Science in Biology
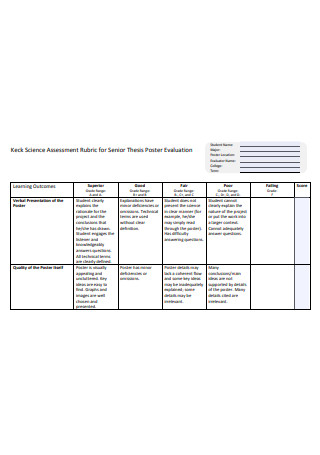
Senior Thesis Evaluation

Basic Thesis Evaluation

Thesis Committee Evaluation
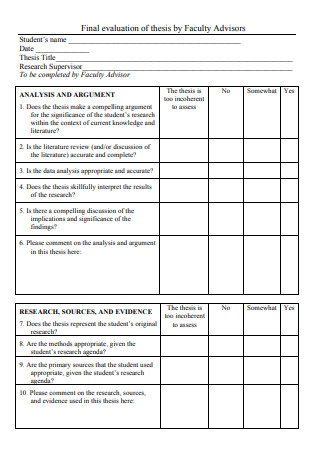
Faculty Thesis Final Evaluation
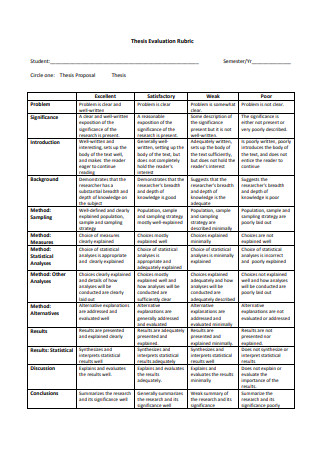
Thesis Evaluation in PDF

Thesis Dissertation Project Defense Evaluation
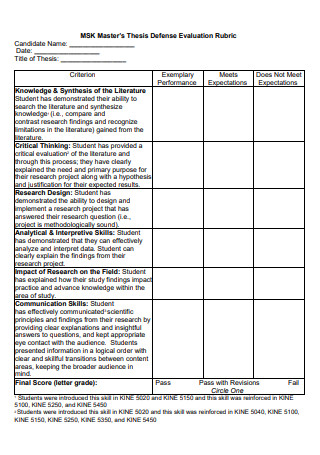
Master Thesis Defense Evaluation

Honors College Thesis Evaluation
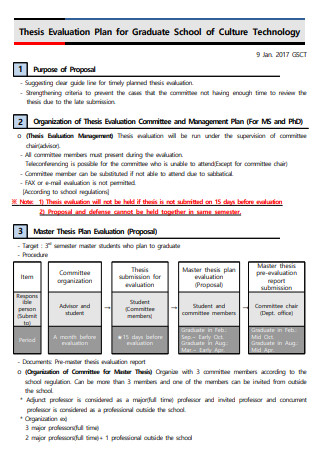
Thesis Evaluation Plan
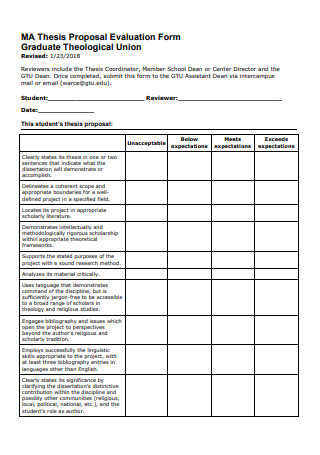
Thesis Proposal Evaluation Form

Doctoral Thesis Evaluation Form
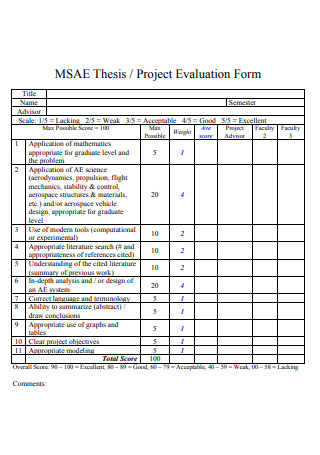
Thesis Project Evaluation Form
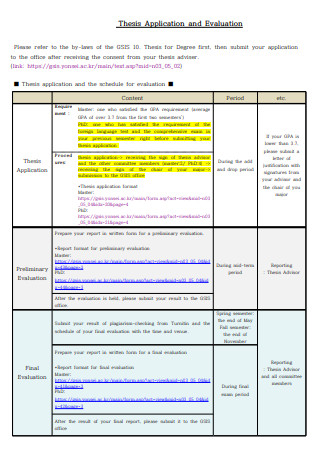
Thesis Application and Evaluation

Humanities Exit Assessment Thesis Evaluation

Thesis Committee Meeting Evaluation
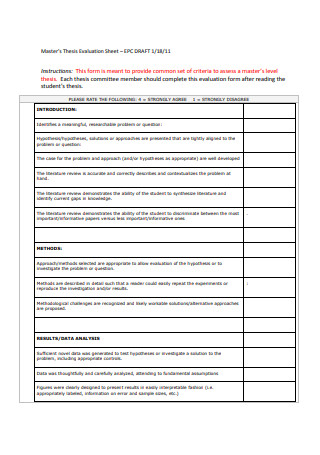
Master Thesis Evaluation Sheet
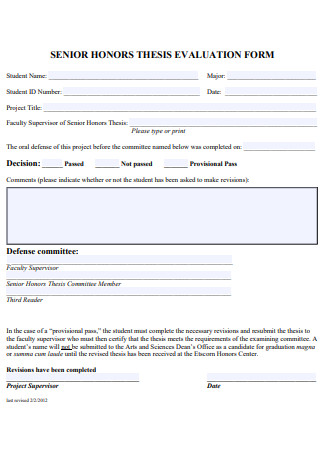
Senior Honors Thesis Evaluation Form


Master Thesis Evaluation and Score Assignment

Thesis Evaluation Example
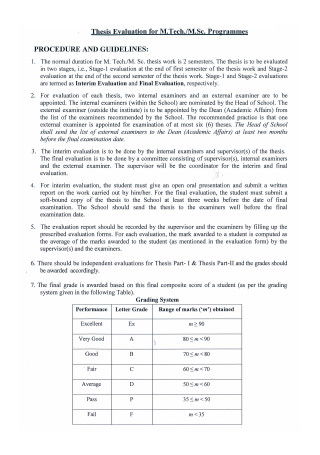
Programmes Thesis Evaluation

Supervisor Thesis Evaluation

Master Thesis Preliminary Evaluation

Thesis Review Evaluation Form

Graduate Thesis Evaluation
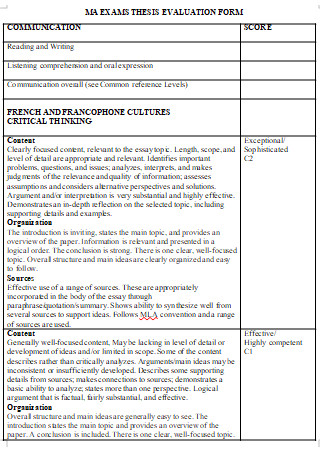
Exams Thesis Evaluation Form
1. bachelor thesis evaluation, 2. master thesis evaluation, 3. doctoral thesis evaluation, 1. maintains a clear analysis of thesis work, 2. facilitates organized decision making, 3. aims on a student’s overall performance, 4. provides summative comments , step 3: search for possible errors in a balanced way, what are some examples of thesis evaluation , share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 50+ sample internship evaluation in pdf | ms word.

Providing invaluable professional experience can be made through facilitating internships to potential individuals, allowing college and undergraduate students to test the concepts and theories that they learned throughout their…
39+ SAMPLE Probationary Evaluation in PDF | MS Word

It is hard to find a job these days. There is a 5.6% unemployment rate in the US this year. Though Trade Economics has predicted that it would go…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Chat With Us
Call us +1 888 211 8005
- Our Services
- Testimonials
- Resources Blog Thesis topics What is Writing tips Facts
Chat With Us 1(888)958-6528
How to write Evaluative Thesis

September 5 2023 03:02 PM
- Next >>
In the realm of academic writing, the thesis statement reigns supreme. It serves as the North Star, guiding writers and readers through the complex terrain of ideas and arguments. A well-crafted thesis statement can distinguish between a compelling, thought-provoking essay and one that leaves the audience bewildered or unengaged. Among the various types of thesis statements, the evaluative thesis is a testament to the writer's ability to critically assess and form judgments on a subject.
In this article, we explore evaluative theses, exploring what they are, why they matter, and how to craft them effectively. Whether you're a seasoned academic or a budding writer seeking to hone your skills, understanding evaluative theses will undoubtedly enhance your ability to communicate and persuade through the written word.
Definition of an Evaluative Thesis
Before we delve deeper into the nuances of evaluative theses, let's establish a clear understanding of what they entail. An evaluative thesis is a concise, arguable statement that expresses a judgment or assessment about a particular subject, backed by evidence and analysis. Unlike informative theses that merely inform the reader about a topic or argumentative theses that take a position on an issue, evaluative theses go further. They require writers to critically examine a subject and provide a well-reasoned evaluation, offering insight into its quality, significance, or effectiveness.
Imagine you're a film critic tasked with reviewing a recently released movie. Your evaluative thesis would serve as the core of your review, encapsulating your overall assessment of the film's merits or shortcomings. This thesis statement sets the tone for your review and informs readers about the lens through which you'll analyze the movie's various elements - plot, acting, cinematography, and more.
The Importance of Having a Clear Thesis Statement
In the vast sea of words that constitute the world of writing, a thesis statement is a lighthouse, guiding both the writer and the reader toward a focused, well-structured narrative. Without a strong thesis, an essay can meander aimlessly, leaving the reader uncertain about the writer's intentions or conclusions. Conversely, a well-crafted thesis provides a roadmap for the writer, ensuring that every subsequent paragraph and sentence contributes to the overarching argument or evaluation.
A clear statement is particularly crucial in an evaluative thesis. It sets the stage for your evaluation and helps readers understand how you view the subject. Are you assessing a work of literature for its thematic depth, a scientific theory for its empirical support, or a product for its market viability? Your evaluative thesis tells your audience what to expect and why they should care.
Understanding the Basics
We must start with a solid foundation to unravel the intricacies of evaluative theses. In this chapter, we will explore the fundamental concepts that underpin the art of evaluative thesis writing. We will define a thesis statement, distinguish between different types of theses, and elucidate the unique role of evaluative theses in academic discourse.
What is a Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence or two that briefly and clearly expresses the main point or argument of an essay, research paper, or any written work. Think of it as the compass guiding the writer and the reader through the text's intricate terrain. It serves as a promise to your audience, indicating the direction your writing will take and the purpose it aims to fulfill.
The Essence of a Thesis Statement:
- Clarity : A good thesis statement is unambiguous and leaves no room for ambiguity. It provides a clear and specific focus for the entire piece of writing.
- Conciseness : A thesis statement should be brief and to the point, capturing the essence of your argument without unnecessary jargon.
- Arguability : An effective thesis statement is debatable. It presents an assertion that can be challenged, discussed, or supported with evidence and analysis.
- Relevance : A thesis statement must be directly relevant to the topic and align with the subject of your writing.
Different Types of Thesis Statements
Not all thesis statements are created equal. Depending on the writer's objectives, different types of thesis statements can be employed. It's important to recognize the distinctions between these types to choose the most appropriate one for your writing task. The three primary types of thesis statements are:
- Informative Thesis
An informative thesis statement merely informs the reader about a topic, presenting facts straightforwardly. It does not take a position, make an argument, or provide an evaluation. Informative theses are commonly used in expository and descriptive essays.
Example: "The history of the Great Wall of China spans over 2,000 years."
- Argumentative Thesis
An argumentative thesis statement takes a clear position on a specific issue or topic and presents an argument the writer intends to prove or defend. It is the cornerstone of persuasive essays and research papers, where the writer seeks to persuade the audience of a particular viewpoint.
Example: "The government should implement stricter regulations on carbon emissions to combat climate change."
- Evaluative Thesis
Example: "The novel 'To Kill a Mockingbird' by Harper Lee is a timeless masterpiece due to its profound exploration of social injustice and moral growth."
The Role of an Evaluative Thesis in Academic Writing
Evaluative theses are a distinctive breed among thesis statements. They play a crucial role in academic writing by requiring writers to assert their position and critically analyze and evaluate a subject's merits or shortcomings. Here are some key aspects that highlight the significance of evaluative theses in academic discourse:
- Critical Thinking : Evaluative theses demand rigorous critical thinking. Writers must weigh evidence, consider multiple perspectives, and make informed judgments.
- Depth of Analysis : They require in-depth analysis and exploration of a subject, often delving into various facets such as quality, significance, effectiveness, or impact.
- Nuanced Perspective : Evaluative theses foster a nuanced perspective. Writers must distinguish between objectivity and subjectivity, avoiding overly biased or unsubstantiated claims.
With these foundational concepts in mind, we are now equipped to explore the unique characteristics of evaluative theses in greater detail. In the following chapters, we will delve into the art of crafting evaluative thesis statements, selecting appropriate topics for evaluation, and providing robust evidence and analysis to support your judgments.
Characteristics of an Evaluative Thesis
In exploring evaluative theses, one must grasp the distinctive features that set them apart from other thesis statements. Evaluative theses are the analytical bedrock of critical essays and reviews, demanding writers' specific approaches and mindsets. In this chapter, we will delve into the key characteristics that define an evaluative thesis.
- Objective Evaluation vs. Subjective Opinion
One of the defining characteristics of an evaluative thesis is its emphasis on objective evaluation rather than subjective opinion. While evaluative theses involve making judgments, these judgments must be grounded in evidence, analysis, and established criteria.
Objective Evaluation : In an evaluative thesis, objectivity is paramount. Writers should strive to evaluate a subject based on universally accepted standards, established criteria, or commonly recognized principles. The goal is to provide an assessment that others can reasonably agree or disagree with, regardless of personal preferences.
Subjective Opinion : In contrast, subjective opinions are based on personal feelings, tastes, or preferences and may not be universally applicable. An evaluative thesis should avoid being overly reliant on the writer's personal biases or emotions.
- The Need for Evidence and Analysis
Evaluative theses are not mere declarations of judgment; they require robust support through evidence and analysis. This support serves two essential purposes:
Substantiating the Judgment : To make a convincing evaluation, writers must present credible evidence that supports their judgment. This can include facts, statistics, examples, or expert opinions.
Demonstrating Critical Thinking : Evaluation demands critical thinking and analysis. Writers must present evidence and analyze it in the context of the subject and criteria. This analysis forms the backbone of a well-constructed evaluative thesis.
- Expressing a Judgment or Assessment
At the heart of an evaluative thesis lies judgment or assessment. This judgment can take various forms, depending on the nature of the subject and the writer's purpose:
Positive Evaluation : An evaluative thesis may express a positive judgment, highlighting the subject's merits, strengths, or positive attributes. This type of evaluation often seeks to persuade the audience of the subject's value or significance.
Example: "The innovative use of symbolism in F. Scott Fitzgerald's 'The Great Gatsby' enhances the novel's thematic depth and literary brilliance."
Negative Evaluation : Conversely, an evaluative thesis may convey a negative judgment, focusing on the subject's flaws, weaknesses, or shortcomings. This type of evaluation aims to critique or discourage engagement with the subject.
Example: "The film's weak character development and clichéd plot detract from its overall quality, disappointing it."
Balanced Evaluation : In some cases, evaluative theses may strike a balanced tone, acknowledging the subject's strengths and weaknesses. This approach fosters a nuanced perspective and may be particularly relevant for complex or multifaceted subjects.
Example: "While the smartphone offers cutting-edge technology and convenience, its high cost and potential privacy concerns should not be overlooked."
Selecting Your Topic
The choice of topic is a crucial starting point in crafting an evaluative thesis. A well-chosen topic not only sets the stage for a meaningful evaluation but also determines the relevance and engagement of your essay. In this chapter, we will explore the intricacies of selecting a suitable topic for evaluation.
Choosing a Subject for Evaluation
Selecting the right subject is the cornerstone of crafting a compelling evaluative thesis. Here are some considerations to guide you in the process:
- Relevance and Interest : Choose a subject that is relevant to your audience and aligns with your interests. An engaging topic will capture your reader's attention and motivate you throughout the writing process.
- Clarity and Specificity : Opt for a subject that can be clearly defined and evaluated within the scope of your essay. Avoid overly broad or vague topics that may lead to unfocused writing.
- Availability of Information : Ensure you can access sufficient information, evidence, or examples to support your evaluation. A lack of credible sources or data can hinder your ability to make a convincing argument.
- Significance : Consider the importance of the subject within its relevant context. Evaluating a topic that holds significance in academia, society, or a specific field can add depth and relevance to your writing.
- Controversy or Complexity : Topics that are controversial or multifaceted often provide rich material for evaluation. They invite critical thinking and analysis, leading to more robust evaluative theses.
Narrowing Down Your Focus
Once you have identified a general subject for evaluation, the next step is to narrow down your focus. This involves defining the specific aspect or dimension of the subject you intend to evaluate. Consider the following strategies:
- Establish Criteria : Determine the criteria or standards against which you will evaluate the subject. These criteria will serve as the basis for your judgment. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, your criteria might include food quality, service, ambiance, and value for money.
- Focus on Specific Elements : Choose specific elements or components of the subject to evaluate. For instance, if you are evaluating a book, you might focus on its characterization, plot development, or thematic depth.
- Identify a Research Question : Formulate a research question that encapsulates the core of your evaluation. This question should guide your analysis and help you stay on track as you gather evidence and develop your thesis.
- Consider Audience Expectations : Consider your audience. What aspects of the subject are likely to interest or concern your readers? Tailor your evaluation accordingly.
The Relevance of Your Topic to Your Audience
While your evaluative thesis primarily reflects your assessment, it is essential to consider the relevance of your chosen topic to your audience. Consider why your readers should care about your evaluation and how it might impact them. Aligning your evaluation with your audience's interests or concerns can enhance the significance of your writing.
In the next chapter, we will delve into the process of crafting your evaluative thesis statement, which will serve as the compass guiding your evaluation. Selecting a relevant and well-defined topic lays the foundation for a compelling and persuasive evaluative thesis.
Crafting Your Evaluative Thesis
As we continue our journey into evaluative theses, we arrive at a critical juncture: crafting the very heart of your evaluation - the evaluative thesis statement. This chapter will explore the art of formulating clear, concise, and compelling evaluative thesis statements that will guide your entire essay.
Developing a Clear and Concise Thesis Statement
The evaluative thesis statement is the anchor of your essay, encapsulating your central judgment and providing a roadmap for your readers. Here's how to craft a clear and concise evaluative thesis statement:
1. Be Specific: Your thesis should focus on the subject of evaluation and the criteria by which you will judge it. Avoid vague or overly general statements.
Vague Statement: "This restaurant has its pros and cons."
Specific Statement: "The restaurant's exceptional food quality and attentive service outweigh its high prices."
2. Express a Judgment: Clearly express your judgment or assessment of the subject. Whether positive, negative, or balanced, your thesis should leave no doubt about your stance.
Positive Evaluation: "The documentary 'Planet Earth' is a stunning achievement in wildlife filmmaking."
Negative Evaluation: "The smartphone's sleek design is overshadowed by its short battery life."
Balanced Evaluation: "While the novel '1984' has enduring relevance, its pacing can be challenging for modern readers."
3. Include Criteria: Indicate the criteria or standards by which you are evaluating the subject. This provides context for your judgment and guides your analysis.
"The film's captivating cinematography and powerful performances make it a must-see."
4. Avoid Ambiguity: Ensure that your thesis statement is unambiguous. Readers should immediately understand the essence of your evaluation and the direction of your essay.
Ambiguous Statement: "The latest software update has pros and cons."
Clear Statement: "The latest software update enhances user interface functionality but introduces stability issues."
Including the Subject of Evaluation and the Criteria
A well-constructed evaluative thesis statement typically comprises two essential components: the subject of evaluation and the criteria by which you are evaluating it. These components work in tandem to provide clarity and focus. Consider the following example:
Evaluative Thesis: "The novel 'To Kill a Mockingbird' by Harper Lee is a timeless masterpiece due to its profound exploration of social injustice and moral growth."
The subject of Evaluation: "The novel 'To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee."
Criteria for Evaluation: "Profound exploration of social injustice and moral growth."
By including both the subject and criteria, your evaluative thesis sets the stage for your essay's subsequent analysis and discussion.
Avoiding Vague or Overly Broad Statements
Vague or overly broad evaluative thesis statements can lead to unfocused and ineffective essays. Consider these strategies to avoid common pitfalls:
- Vague Statements: Statements that lack specificity and fail to convey a clear judgment can confuse readers.
"This movie has its good and bad aspects."
- Overly Broad Statements: Overgeneralized statements may be too broad to address effectively in one essay.
"Technology has both positive and negative effects on society."
- Lack of Criteria: Ensure that your thesis includes specific criteria for evaluation, as this forms the basis for your judgment.
"The book 'The Great Gatsby' has strengths and weaknesses."
Providing Evidence and Support
A compelling evaluative thesis statement is just the beginning of your journey in crafting a persuasive evaluation. You must provide robust evidence and support to substantiate your judgment and convince your readers. This chapter will explore the critical role of evidence and analysis in bolstering your evaluative thesis.
- Gathering Relevant Evidence and Examples
Effective evaluation relies on credible evidence and concrete examples that illustrate the merits or shortcomings of your subject. Here's how to gather relevant evidence:
Research: Conduct thorough research to gather facts, data, and expert opinions about your subject. Look for reputable sources, such as scholarly articles, books, websites, or expert interviews.
Direct Observation: If applicable, use direct observation or personal experiences to collect firsthand information about your subject. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, visit it and make detailed observations.
Case Studies: Seek out case studies, real-world examples, or case-specific evidence that support your judgment. These can provide powerful illustrations of your evaluation.
Historical Context: Consider your subject's historical context or background, as it can shed light on its significance or evolution over time.
- Citing Credible Sources
When incorporating evidence into your evaluative essay, it's essential to cite credible sources transparently. Proper citation serves two crucial purposes:
Establishing Credibility: Citing reputable sources lends credibility to your evaluation. It shows that expert opinions or well-documented facts inform your judgment.
Providing a Reference: Citations provide a reference point for readers who wish to explore the evidence further or verify your claims.
Follow the citation style specified by your academic institution or publication guidelines (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Demonstrating Critical Thinking and Analysis
The mere presentation of evidence is insufficient; you must also engage in critical thinking and analysis. Here's how to effectively analyze and interpret your evidence:
Interpretation: Explain the significance of the evidence in the context of your evaluation. Describe how it supports or challenges your thesis statement.
Comparative Analysis: Compare and contrast different pieces of evidence or examples to highlight patterns or trends. This can add depth to your evaluation.
Consider Counterarguments: Acknowledge and address counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Demonstrating awareness of different perspectives adds credibility to your evaluation.
Cause and Effect: Analyze the cause-and-effect relationships between your evidence and the subject of evaluation. How do specific aspects of your subject lead to your judgments?
Critically analyzing your evidence strengthens your argument and demonstrates your ability to think deeply and objectively about the subject.
- Maintaining a Balanced Approach
Balancing your evaluation is essential, especially when dealing with complex or multifaceted subjects. While providing evidence that supports your judgment is crucial, avoid cherry-picking evidence that only confirms your preconceived notions. Embrace a balanced approach that acknowledges both strengths and weaknesses.
- Presenting Evidence Effectively
The presentation of evidence in your evaluative essay should be clear and logically organized. Consider the following strategies:
Use of Examples: Incorporate illustrative examples or anecdotes to make your evidence relatable and memorable for your readers.
Organization: Structure your essay logically, each paragraph focusing on a specific evidence or aspect of your evaluation.
Transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to guide readers from one piece of evidence to the next, creating a seamless flow of ideas.
Structuring Your Essay
A well-structured essay is the canvas on which your evaluative thesis comes to life. In this chapter, we will explore the structural components of your evaluative essay, from the introduction that hooks your readers to the conclusion that reinforces your thesis.
- Introduction with the Evaluative Thesis Statement
Hook Your Readers: Begin your essay with a compelling hook that grabs your reader's attention and introduces the subject of evaluation. This can be a thought-provoking question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an engaging anecdote.
Evaluative Thesis Statement: In the introductory paragraph, present your evaluative thesis statement clearly and concisely. Ensure it includes the subject of evaluation and the criteria by which you will judge it. The thesis should serve as the guiding beacon for your entire essay.
Contextual Background: Provide some background information about the subject of evaluation, especially if it's not widely known or understood. This helps readers understand its significance.
Body Paragraphs Presenting Evidence and Analysis
The body of your essay is where you present your evidence, analysis, and discussion. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific piece of evidence or aspect of your evaluation:
Topic Sentence: Begin each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the paragraph's main point. This should connect to your evaluative thesis.
Evidence Presentation: Present your evidence or examples logically and organized. Use descriptive language and context to help readers understand the relevance of the evidence.
Analysis: After presenting evidence, engage in critical analysis. Explain how the evidence supports or challenges your evaluative thesis. Address questions like "Why is this evidence significant?" and "How does it relate to the criteria?"
Transitions: Use transitional phrases and sentences to smoothly transition from one body paragraph to the next. This creates a coherent flow of ideas and arguments throughout your essay.
- Conclusion Summarizing the Evaluation
The conclusion is where you tie everything together and leave a lasting impression on your readers:
Restate Your Thesis: Begin your conclusion by restating your evaluative thesis statement. This reinforces your central judgment.
Summarize Key Points: Summarize the key points you've discussed in your essay. Highlight the most significant evidence and analysis that support your evaluation.
Final Thoughts: Offer some final thoughts or insights that encapsulate the essence of your evaluation. Reflect on the broader implications or significance of your judgment.
Call to Action or Consideration: Depending on your essay's purpose, you might include a call to action, a thought-provoking question, or an invitation for further consideration of the subject.
Tips for Effective Writing
While mastering the art of crafting evaluative theses is essential, effective writing goes beyond thesis statements. It encompasses the entire process, from brainstorming ideas to polishing your final draft. This chapter will explore tips and strategies for enhancing your writing skills and producing compelling evaluative essays.
Use of Language and Tone
Clarity is Key: Strive for clarity in your writing. Use clear and straightforward language to convey your ideas. Avoid convoluted sentences or overly complex vocabulary that may confuse your readers.
Formal Tone: Maintain a formal and professional tone in academic writing. Avoid overly informal language, slang, or colloquialisms.
Precision: Choose words and phrases that convey your intended meaning precisely. Avoid vague or ambiguous language.
Transitions: Use transitional words and phrases to guide your readers through your essay. This helps create a seamless flow of ideas.
- Avoiding Bias and Maintaining Objectivity
Balance Perspectives: When presenting evidence or discussing your evaluation, strive for balance. Acknowledge the subject's strengths and weaknesses, even if your overall evaluation leans in one direction.
Avoid Personal Pronouns: Minimize using personal pronouns like "I" or "you." Instead, opt for a more objective third-person perspective.
Cite Expert Opinions: Incorporate expert opinions or scholarly sources to support your arguments. This demonstrates that your evaluation is grounded in authoritative perspectives.
Objective Language: When presenting evidence or analysis, use objective language. Avoid emotionally charged or judgmental language that may bias your readers.
- Revision and Proofreading
Multiple Drafts: Never settle for your first draft. Writing is a process, and revision is where your work truly shines. Review and revise your essay multiple times to refine your arguments and improve clarity.
Fresh Eyes: Take breaks between writing and revising sessions. Returning to your work with fresh eyes allows you to spot errors or areas that need improvement more effectively.
Peer Review: Consider seeking peer, mentor, or writing tutor feedback. Fresh perspectives can provide valuable insights and suggestions for improvement.
Grammar and Mechanics: Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Errors in these areas can detract from your writing's professionalism and credibility.
- Conciseness and Efficiency
Avoid Repetition: Eliminate unnecessary repetition of ideas or words. Each sentence and paragraph should contribute something new to your argument.
Cut Unnecessary Words: Trim excessive words or phrases that do not add value to your writing. Be concise while retaining clarity.
Active Voice: Use the active voice to make your writing more direct and engaging. Passive voice can sometimes make sentences more convoluted.
- Seek Feedback and Revise
Welcome Feedback: Embrace feedback from others as an opportunity to improve your writing. Constructive criticism helps you grow as a writer.
Multiple Revisions: Don't be afraid to revise your work extensively. The best writing often comes after multiple revisions and refinements.
Read Aloud: Reading your essay aloud can help you catch awkward phrasing, unclear sentences, or errors you might miss when reading silently.
- Follow Guidelines and Requirements
Adhere to Guidelines: Follow any specific guidelines or requirements from your instructor or publication. This includes formatting, citation styles, and word count.
Meet Deadlines: Submit your essay on time. Effective time management is crucial for producing high-quality work.
Examples of Evaluative Theses
Example 1: Film Evaluation
Evaluative Thesis: "Christopher Nolan's 'Inception' is a cinematic masterpiece due to its innovative narrative structure, breathtaking visual effects, and thought-provoking exploration of dreams and reality."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis provides a clear judgment (positive) and presents the subject ("Inception") along with specific criteria for evaluation (narrative structure, visual effects, exploration of dreams and reality). The criteria offer insight into why the film is deemed a masterpiece.
Example 2: Book Evaluation
Evaluative Thesis: "Jane Austen's 'Pride and Prejudice' remains a timeless classic because of its sharp social commentary, memorable characters, and enduring relevance in exploring themes of love and societal expectations."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis takes a positive stance on the novel and presents the subject ("Pride and Prejudice") along with specific criteria for evaluation (social commentary, characters, exploration of themes). The thesis highlights the novel's timeless qualities.
Example 3: Restaurant Review
Evaluative Thesis: "The 'Mediterraneo' restaurant provides a delightful dining experience with its flavorful cuisine, attentive service, and inviting ambiance, making it a must-visit for food enthusiasts."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis expresses a positive judgment and introduces the subject ("Mediterraneo" restaurant) along with the evaluation criteria (cuisine, service, ambiance). The thesis highlights the restaurant's appeal to food enthusiasts.
Example 4: Technology Assessment
Evaluative Thesis: "The latest smartphone model, while offering innovative features and enhanced performance, falls short in battery life, significantly impacting its overall user experience."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis conveys a balanced evaluation, acknowledging the smartphone's positive and negative aspects. The subject ("latest smartphone model") and evaluation criteria (features, performance, battery life) are clearly outlined.
Example 5: Film Critique
Evaluative Thesis: "While 'Avatar' is visually stunning and groundbreaking in its use of technology, its reliance on a familiar storyline and one-dimensional characters diminishes its overall impact as a cinematic experience."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis presents a balanced judgment, recognizing both the film's strengths and weaknesses. The subject ("Avatar") and evaluation criteria (visuals, technology, storyline, characters) are explicitly mentioned.
Example 6: Product Review
Evaluative Thesis: "The 'EcoClean' laundry detergent offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional detergents, effectively removing stains and reducing environmental impact, making it an ideal choice for environmentally conscious consumers."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis takes a positive stance and introduces the subject ("EcoClean" laundry detergent) along with criteria for evaluation (efficacy in stain removal, eco-friendliness). The thesis caters to environmentally conscious consumers.
Example 7: Literary Analysis
Evaluative Thesis: "Shakespeare's 'Hamlet' stands as a profound exploration of human nature, with its intricate characters, moral dilemmas, and timeless themes of revenge and madness."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis expresses a positive judgment and presents the subject ("Hamlet") along with evaluation criteria (characters, moral dilemmas, exploration of themes). The thesis underscores the play's enduring significance.
Example 8: Art Critique
Evaluative Thesis: "Van Gogh's 'Starry Night' is a masterpiece of post-impressionist art, captivating viewers with its vivid colors, expressive brushwork, and emotional depth."
Analysis: This evaluative thesis takes a positive stance and introduces the subject ("Starry Night" by Van Gogh) along with criteria for evaluation (colors, brushwork, emotional depth). The thesis emphasizes the artwork's artistic merits.
By examining these diverse examples of evaluative thesis statements, you can discern common elements, such as clear judgment, subject identification, and evaluation criteria. These examples illustrate the versatility of evaluative theses across different domains, from literature and art to technology and dining experiences.
Our exploration of evaluative theses is foundational in developing strong critical analysis and persuasive writing skills. As you continue to hone your abilities, remember that evaluative theses are powerful tools for engaging, informing, and persuading your readers.
In conclusion, evaluative theses are not just statements but catalysts of insightful analysis and persuasive communication. By mastering the art of crafting evaluative thesis statements and refining your writing skills, you can influence, inform, and engage with the world through critical evaluation.
Thank you for joining us on this journey of discovery. We wish you success in your future endeavors as a critical thinker and persuasive writer.

- 300 or 600 words per page
- Over 1000 PhD writers
- Direct communication with a writer
- Free editing of your paper
- The largest source database
Get a price
Best Thesis Statement Examples with Expert Comments
“Where is your thesis statement?” asks your teacher in a dramatic tone. “Where is my what?” you want to reply, but instead, you quickly point your finger at a random sentence in your paper, saying, “Here it is…”
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
To avoid this sad situation (which is usually followed by a bad mark), you should clearly understand what a thesis sentence is and how to make it stronger. Discover the best and worst thesis statement examples for research papers with expert comments on them in the sections below (or simply try Custom-writing.org , and you will never have a headache with any assignments).
❓ What Is a Thesis Statement?
- ✅ Thesis Checklist
- 😃 Essay Thesis Examples
- 👨🎓️ Research Paper Thesis Examples
🔗 References
What is a thesis statement, after all? A thesis statement is a logical center and a roadmap of your paper, clearly and concisely expressed in the introduction. It aims to convince your reader of the point you are making in your research. The thesis statement summarizes your argument in one sentence.
✅ Thesis Statement Checklist
Below is a thesis statement checklist. It is a good idea to use it any time after you’ve made your statement. Make sure that it is specific, arguable, and meaningful!

😃 Thesis Statement Examples for an Essay
Find good and bad examples of essay thesis statements with comments below!
👨🎓️ Examples of Thesis Statements for Research Papers
The situation is somewhat different with thesis sentences for research papers . Expressing your personal position is not enough for a good research paper. You should find truly weighty arguments and include them in your thesis statement.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Take a look at the same checklist to differentiate between the worst and best thesis statement samples for research papers.
Now you can see the difference between good and bad thesis statements. This will help you create a marvelous thesis statement example of your own!
- Thesis Statements – UNC Writing Center
- Developing A Thesis | – Harvard College Writing Center
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Indiana State University
- Creating a Thesis Statement, Thesis Statement Tips // Purdue OWL
- Guide to Writing Thesis Statements – University of Washington
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
Yes, thanks
Always keep your Thesis Statement under 30 words. If you do go over, you are accidentaly writing a run-on sentence.

- {{ service.text }}
PhD Thesis Evaluation Report Writing
Thesis writing plays a vital role in completing your academic study in any research area. In this thesis, among all the chapters, the evaluation is important that is illustrated in this blog.
Our technical team is available 24/7 for research assistance
Send your techinical enquiries directly to our technical team via mail - [email protected] or you can send it to support team via WhatsApp
PhD Thesis Evaluation Report is a blog that gives you information about an evaluation report in the thesis. The significance of evaluation in the thesis is illustrated, start to read this blog.
What is a Thesis?
The thesis is a technical write-up of research work as a single strength from the introduction to the conclusion. A thesis consists of sequential chapters to give a deep understanding of the concept. In simple, a thesis is a report of research to illustrate methods and their results in detail.
Importance of Evaluation in Thesis
- At first, the metrics for evaluation in a research concept need to be relevant to the objectives of the work.
- It depicts the efficiency of the proposed methodologies and their best on that system.
- The comparison to previous methodologies and algorithms will make sure that the proposed method operates at higher performances.
- The result evaluation in the thesis depicts tabulated values and graphical plotted values.
The evaluation is not only important in a thesis, in basic it is used to identify the performance of the proposed research. The improvement in the research reflects in the evaluation report. We have experts to write PhD Thesis Evaluation Report in any research field. The research fields in PhD for thesis are given below.
Fields in PhD Thesis Writing
- Network and Communication
- Processing of Images
- Mining different types of Data
- Management of all Data
- Analysis of Banking Records
In this way, there are many other research fields of study to write a thesis. According to the major course, the research field depends upon. We offer support for writing only evaluation reports for the thesis. It is a special opportunity for all scholars and doctorates. We are here to assist you in completing your PhD thesis on time.
Did you find it helpful ?
Leave a reply.

Free Base papers and Topics for your Research

PhD services using Research Domain with important areas

Cloud Computing with Blockchain technology for Security in PhD

Image Processing Integrates with Blockchain Technology for Security

Security by Blockchain and Proof of Blocks for PhD Thesis Writing
- Business Templates
- Sample Evaluations
FREE 10+ Thesis Evaluation Samples [ Master, Defense, Project ]

A thesis, also known as a dissertation , is a type of document that supports any specific candidature for a particular degree or professional and academic qualification that enables authors to present their research and findings . It is composed mainly of a long piece of an academic writing that has an overview of your research. One of the main highlights in this type of document is the discussion of the results together with its implications and the conclusion that allows you to know about the contribution of your research to the society. In this article, you will be able to know more about how you are going to effectively evaluate a thesis.
Thesis Evaluation
10+ thesis evaluation samples, 1. masters thesis evaluation, 2. thesis dissertation evaluation, 3. thesis evaluation form, 4. thesis evaluation, 5. thesis defense final evaluation, 6. thesis supervisor evaluation, 7. research thesis award evaluation, 8. psychology thesis evaluation, 9. masters thesis evaluation form, 10. graduate recital analysis thesis evaluation, 11. external examiner thesis evaluation, how do you write a thesis comment, how are you going to respond to the examiners.

Size: 65 KB
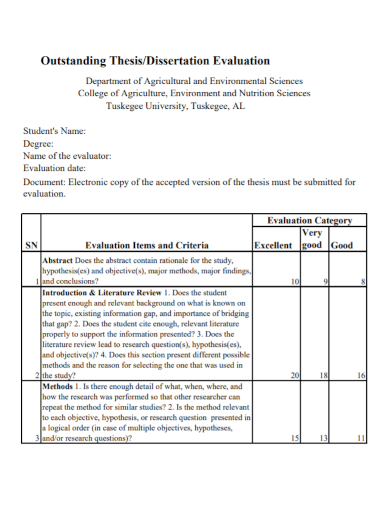
Size: 89 KB

Size: 116 KB
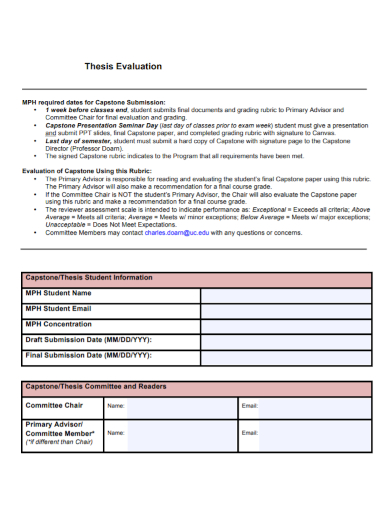
Size: 324 KB
Every thesis should have a good amount of original research. Universities have the ability to grant the degree especially if they undergo evaluations to assess how suitable a candidate must be for an award. Requirements may vary depending on what university you are in. The purpose of this evaluation is to assess if the student’s knowledge pertaining to the subject matter is in lined with their research capabilities.
There is an equivalent amount of importance when it comes to the sensitivity of the researches that are being conducted in different fields including medical sciences and the like. These fields require a specific level of expertise that includes highly skilled and highly intellectual researchers. In addition to the aspect of teaching, they know that professors in most universities have to make some time in mentoring the next generation of researchers. In order to make sure that the candidates who are taking the position are competent with their jobs.

Size: 409 KB
Size: 56 KB
Size: 74 KB
Size: 25 KB

Size: 111 KB
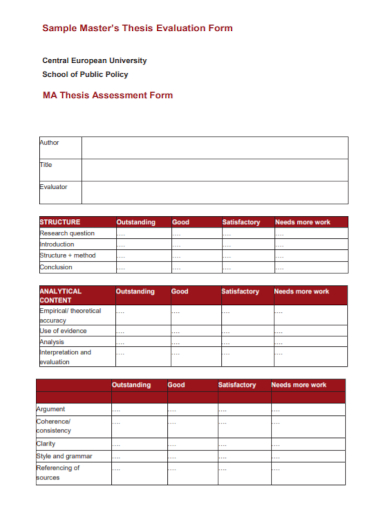
In the case of a master thesis, there is also an equivalent guidelines on how you are going to conduct the evaluation. The thesis itself will be evaluated based on the diploma policies implemented by the graduate school , the program and the laboratory category that the candidate belongs. Below is the criteria:
- The title should clearly identify the topic presented in a thesis statement .
- All parts should follow the standard thesis style including the introduction, methodology, discussion of the results, figures, tables and the references.
- The relevant research should be investigated thoroughly and being analyzed in the background and objective .
- The methods used should be described in a detailed manner. It should be explained clearly why they were being selected for the research.
- Data should be presented accurately using tables, figures, and other related visual organizers.
- Results should be interpreted and discussed critically.
- Your thesis should include original findings.
- The items on your reference list should be arranged and listed completely and accurately following the conditions under the rule of plagiarism and proper citation.
Certain examiners will be asked to evaluate a particular thesis based on the criteria for either a Master’s or Doctor’s thesis. These examiners should be able to determine if the thesis can be considered “Passed” or “Not Passed”. For students who are still in the masters degree, the evaluation will determine if the thesis is ready for the final submission regardless of the minor changes that are being recommended.
If the thesis met all the needed criteria and has been evaluated as “passed”, the examiners will be asked to provide a report that includes the recommendations regarding the minor changes. If it has been evaluated and didn’t passed the criteria, the examiners will need a new study or an additional research and the need to address the problem provided that it should be with a presentation of the work.
You should reflect back on the main point of the paper first then, discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the thesis. Focus on the large problem first before you are going to deal with the minor ones. Lastly, type your final comments.
Make any corrections or revisions in your thesis. The response should be given in the most systematic manner which would clearly indicate which comment you are giving your response to. If you have accepted the examiner’s criticism, then provide the changes indicating where they should go. If you think that their criticism is not valid, do not make any changes. Lastly, include a statement that would indicate that the grammar, spelling and other errors has been attended to.
Make sure that you will give sufficient feedback to the students. It is not enough to just say that they were perfectly written or not. You should also focus on giving them positive things pertaining to the thesis including those that they can revise. Providing a good feedback helps the students in improving their capabilities and skills as a researcher.
Related Posts
Free 10+ project management proposal samples, free 10+ research progress report samples, free 10+ self-introduction speech samples, free 10+ marketing research proposal samples, free 10+ sample project assessment, free 10+ marketing campaign evaluation samples, free 9+ argumentative essay samples, free 7+ sample supplier evaluations, free 7+ sample presentation evaluations, free 6+ sample presentation evaluations, free 54+ questionnaire samples, free 11+ essay samples, free 10+ research study plan samples, free 10+ academic research plan samples, free 10+ student assessment reports samples, free 5+ self-assessment essay samples, dos in writing your self-evaluation, free 15+ research flow chart samples, free 14+ sample employee self evaluation forms.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The thesis supervisor submits a written statement on the thesis with a proposal for a grade, i.e. an evaluation statement to the Degree Programme Committee. When preparing the report, the supervisor may also request statements from the advisor(s). In cases where the supervisor has proposed the grade '5' or '1' or 'fail', the Degree ...
Assessing a PhD thesis - The Examiner's Perspective . Dr Louise Johnson April 29, 2015 . ... the revealing of my name and usually agree as this enhances the value of the comments and the thesis outcome for the student if someone reasonably eminent has marked their work). I also know ... critical but respectful evaluation of theirwork).
Abstract. Throughout the dissertation process, the chair and commitee members provide feedback regarding quality to help the doctoral candidate to produce the highest-quality document and become an independent scholar. Nevertheless, results of previous research suggest that overall dissertation quality generally is poor.
Evaluation of a Written Thesis. Examiners are asked to evaluate the thesis in myThesis, according to the criteria in the respective thesis examiner report for a Master's or Doctoral thesis. For an example of the criteria, please see the forms: see: Master's Examiner report form; Doctoral Examiner report form (note these forms are now integrated ...
abstract. Traditionally, examiners 'reports on theses at the doctoral and Masters level consist of two. components: firstly, summative assessment where a judgement is made about whether. the ...
Examples of 'reject' reviewer comments. "I do not believe that this journal is a good fit for this paper.". "While the paper addresses an interesting issue, it is not publishable in its current form.". "In its current state, I do not recommend accepting this paper.". "Unfortunately, the literature review is inadequate.
What the examiners said. In Australia, a thesis must be submitted to three examiners: one in the University and two external, one of whom must be overseas. The comments are sent back to the examinations committee, who decide whether the candidate's thesis is. Acceptable as-is (uncommon) Acceptable with minor revisions (most common, and what I got)
thesis of some three and a half pages in length and a large number of different student variables), and to provide a firm superstructure for validation, theory building and testing. ... Editorial comments (3 5 2) 50 Evaluative Comment Positive summative comment (5 1 1) 80 Neutral summative comment ( 5 1 2) 52
This is a sample of an M. Sc. preliminary evaluation report. The report gives different comments that help student to upgrade his/her thesis before final delivery.
1. Evaluation of the Thesis: Complete the evaluation grid below and comment on the criteria in your written report. Criteria for Evaluation of Thesis Excellent Top 10% Very Good Good Satisfactory Unsatisfactory 1. Makes an original contribution to knowledge 2. Advances knowledge in the field 3.
A thesis examiner is an academic who reads the fin-ished thesis, and gives a report recommending a result. The aim of our review is to clarify what thesis examiners do as they examine a written thesis submitted for a research higher degree. In some countries, such as Australia, a thesis examination typically consists of two or three examiners ...
A doctoral thesis is the culmination of three years full time work. By definition, it should be publishable in whole or in part. This means that the candidate has mastered the thesis genre, has written an original evaluation of the relevant literature, innovatively collected and analysed data, and presented the work in
The thesis examiner's report is an evaluation of a thesis, which includes dialogic and evaluative elements. ... Conclusion 10.References 11.Appendices My talk focuses on 1. examiners' evaluation and comments on these genres/section. 2. Suggestions for how tackle these comments Topic Three 14 Thesis examination: procedures 15 The examination ...
as per above comments. Introduction: P1, L 23 -24: Please be more specific. Focus could be on the entire Southern Ocean (e.g. Saenz & Arrigo 2012, Arrigo 2014, Meiners et al. 2012) or Antarctic fast-ice ecosystems. Rysgaard is an older (and Arctic) reference. Maybe cite Mundy et al. 2007 and the recent papers of Campbell et al. 2014, 2015?
3.Thesis submission. Within 30 days of submission of synopsis the students submits soft copy (pdf) of the thesis for evaluation. A student can be asked to submit the hard copy of the thesis if required by the examiner. The format for preparation of Ph.D. thesis is placed at Annexure-II.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Step 5: Proofread, Revise, and Prepare the Final Thesis Evaluation Report. Check your entire thesis evaluation. Write all the crucial aspects in your thesis evaluation. If you notice that you overlook some sections that require sufficient points, we suggest that you proofread and revise the document.
Analysis: This evaluative thesis takes a positive stance on the novel and presents the subject ("Pride and Prejudice") along with specific criteria for evaluation (social commentary, characters, exploration of themes). The thesis highlights the novel's timeless qualities. Example 3: Restaurant Review.
A thesis statement is a logical center and a roadmap of your paper, clearly and concisely expressed in the introduction. It aims to convince your reader of the point you are making in your research. The thesis statement summarizes your argument in one sentence. Thesis Statement Checklist. Below is a thesis statement checklist.
The result evaluation in the thesis depicts tabulated values and graphical plotted values. The evaluation is not only important in a thesis, in basic it is used to identify the performance of the proposed research. The improvement in the research reflects in the evaluation report. We have experts to write PhD Thesis Evaluation Report in any ...
Awarded the degree subject to the major amendments specified elsewhere in this report being made in the thesis, and I do need to re-examine the amended thesis. Not awarded the degree but permitted to re-submit/re-defend the thesis in a revised form. Not awarded the degree. Comments to candidate (please attach a separate sheet, if needed):
Outline 2 1.Introduction 2.Thesis Structure 3.Thesis examination: procedures 4.Thesis evaluation forms: Examples 5.Comments on the Title 6.Comments on the Abstract 7.Comments on the Introduction Chapter 8.Conclusion
Research Thesis Award Evaluation. 8. Psychology Thesis Evaluation. 9. Masters Thesis Evaluation Form. 10. Graduate Recital Analysis Thesis Evaluation. 11. External Examiner Thesis Evaluation.