
The Research Gap (Literature Gap)
Everything you need to know to find a quality research gap
By: Ethar Al-Saraf (PhD) | Expert Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | November 2022
If you’re just starting out in research, chances are you’ve heard about the elusive research gap (also called a literature gap). In this post, we’ll explore the tricky topic of research gaps. We’ll explain what a research gap is, look at the four most common types of research gaps, and unpack how you can go about finding a suitable research gap for your dissertation, thesis or research project.
Overview: Research Gap 101
- What is a research gap
- Four common types of research gaps
- Practical examples
- How to find research gaps
- Recap & key takeaways
What (exactly) is a research gap?
Well, at the simplest level, a research gap is essentially an unanswered question or unresolved problem in a field, which reflects a lack of existing research in that space. Alternatively, a research gap can also exist when there’s already a fair deal of existing research, but where the findings of the studies pull in different directions , making it difficult to draw firm conclusions.
For example, let’s say your research aims to identify the cause (or causes) of a particular disease. Upon reviewing the literature, you may find that there’s a body of research that points toward cigarette smoking as a key factor – but at the same time, a large body of research that finds no link between smoking and the disease. In that case, you may have something of a research gap that warrants further investigation.
Now that we’ve defined what a research gap is – an unanswered question or unresolved problem – let’s look at a few different types of research gaps.

Types of research gaps
While there are many different types of research gaps, the four most common ones we encounter when helping students at Grad Coach are as follows:
- The classic literature gap
- The disagreement gap
- The contextual gap, and
- The methodological gap
Need a helping hand?
1. The Classic Literature Gap
First up is the classic literature gap. This type of research gap emerges when there’s a new concept or phenomenon that hasn’t been studied much, or at all. For example, when a social media platform is launched, there’s an opportunity to explore its impacts on users, how it could be leveraged for marketing, its impact on society, and so on. The same applies for new technologies, new modes of communication, transportation, etc.
Classic literature gaps can present exciting research opportunities , but a drawback you need to be aware of is that with this type of research gap, you’ll be exploring completely new territory . This means you’ll have to draw on adjacent literature (that is, research in adjacent fields) to build your literature review, as there naturally won’t be very many existing studies that directly relate to the topic. While this is manageable, it can be challenging for first-time researchers, so be careful not to bite off more than you can chew.

2. The Disagreement Gap
As the name suggests, the disagreement gap emerges when there are contrasting or contradictory findings in the existing research regarding a specific research question (or set of questions). The hypothetical example we looked at earlier regarding the causes of a disease reflects a disagreement gap.
Importantly, for this type of research gap, there needs to be a relatively balanced set of opposing findings . In other words, a situation where 95% of studies find one result and 5% find the opposite result wouldn’t quite constitute a disagreement in the literature. Of course, it’s hard to quantify exactly how much weight to give to each study, but you’ll need to at least show that the opposing findings aren’t simply a corner-case anomaly .

3. The Contextual Gap
The third type of research gap is the contextual gap. Simply put, a contextual gap exists when there’s already a decent body of existing research on a particular topic, but an absence of research in specific contexts .
For example, there could be a lack of research on:
- A specific population – perhaps a certain age group, gender or ethnicity
- A geographic area – for example, a city, country or region
- A certain time period – perhaps the bulk of the studies took place many years or even decades ago and the landscape has changed.
The contextual gap is a popular option for dissertations and theses, especially for first-time researchers, as it allows you to develop your research on a solid foundation of existing literature and potentially even use existing survey measures.
Importantly, if you’re gonna go this route, you need to ensure that there’s a plausible reason why you’d expect potential differences in the specific context you choose. If there’s no reason to expect different results between existing and new contexts, the research gap wouldn’t be well justified. So, make sure that you can clearly articulate why your chosen context is “different” from existing studies and why that might reasonably result in different findings.

4. The Methodological Gap
Last but not least, we have the methodological gap. As the name suggests, this type of research gap emerges as a result of the research methodology or design of existing studies. With this approach, you’d argue that the methodology of existing studies is lacking in some way , or that they’re missing a certain perspective.
For example, you might argue that the bulk of the existing research has taken a quantitative approach, and therefore there is a lack of rich insight and texture that a qualitative study could provide. Similarly, you might argue that existing studies have primarily taken a cross-sectional approach , and as a result, have only provided a snapshot view of the situation – whereas a longitudinal approach could help uncover how constructs or variables have evolved over time.

Practical Examples
Let’s take a look at some practical examples so that you can see how research gaps are typically expressed in written form. Keep in mind that these are just examples – not actual current gaps (we’ll show you how to find these a little later!).
Context: Healthcare
Despite extensive research on diabetes management, there’s a research gap in terms of understanding the effectiveness of digital health interventions in rural populations (compared to urban ones) within Eastern Europe.
Context: Environmental Science
While a wealth of research exists regarding plastic pollution in oceans, there is significantly less understanding of microplastic accumulation in freshwater ecosystems like rivers and lakes, particularly within Southern Africa.
Context: Education
While empirical research surrounding online learning has grown over the past five years, there remains a lack of comprehensive studies regarding the effectiveness of online learning for students with special educational needs.
As you can see in each of these examples, the author begins by clearly acknowledging the existing research and then proceeds to explain where the current area of lack (i.e., the research gap) exists.

How To Find A Research Gap
Now that you’ve got a clearer picture of the different types of research gaps, the next question is of course, “how do you find these research gaps?” .
Well, we cover the process of how to find original, high-value research gaps in a separate post . But, for now, I’ll share a basic two-step strategy here to help you find potential research gaps.
As a starting point, you should find as many literature reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses as you can, covering your area of interest. Additionally, you should dig into the most recent journal articles to wrap your head around the current state of knowledge. It’s also a good idea to look at recent dissertations and theses (especially doctoral-level ones). Dissertation databases such as ProQuest, EBSCO and Open Access are a goldmine for this sort of thing. Importantly, make sure that you’re looking at recent resources (ideally those published in the last year or two), or the gaps you find might have already been plugged by other researchers.
Once you’ve gathered a meaty collection of resources, the section that you really want to focus on is the one titled “ further research opportunities ” or “further research is needed”. In this section, the researchers will explicitly state where more studies are required – in other words, where potential research gaps may exist. You can also look at the “ limitations ” section of the studies, as this will often spur ideas for methodology-based research gaps.
By following this process, you’ll orient yourself with the current state of research , which will lay the foundation for you to identify potential research gaps. You can then start drawing up a shortlist of ideas and evaluating them as candidate topics . But remember, make sure you’re looking at recent articles – there’s no use going down a rabbit hole only to find that someone’s already filled the gap 🙂
Let’s Recap
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this post. Here are the key takeaways:
- A research gap is an unanswered question or unresolved problem in a field, which reflects a lack of existing research in that space.
- The four most common types of research gaps are the classic literature gap, the disagreement gap, the contextual gap and the methodological gap.
- To find potential research gaps, start by reviewing recent journal articles in your area of interest, paying particular attention to the FRIN section .
If you’re keen to learn more about research gaps and research topic ideation in general, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . Alternatively, if you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your dissertation, thesis or research project, be sure to check out our private coaching service .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

29 Comments
This post is REALLY more than useful, Thank you very very much
Very helpful specialy, for those who are new for writing a research! So thank you very much!!
I found it very helpful article. Thank you.
Just at the time when I needed it, really helpful.
Very helpful and well-explained. Thank you
VERY HELPFUL
We’re very grateful for your guidance, indeed we have been learning a lot from you , so thank you abundantly once again.
hello brother could you explain to me this question explain the gaps that researchers are coming up with ?
Am just starting to write my research paper. your publication is very helpful. Thanks so much
How to cite the author of this?
your explanation very help me for research paper. thank you
Very important presentation. Thanks.
Best Ideas. Thank you.
I found it’s an excellent blog to get more insights about the Research Gap. I appreciate it!
Kindly explain to me how to generate good research objectives.
This is very helpful, thank you
Very helpful, thank you.
Thanks a lot for this great insight!
This is really helpful indeed!
This article is really helpfull in discussing how will we be able to define better a research problem of our interest. Thanks so much.
Reading this just in good time as i prepare the proposal for my PhD topic defense.
Very helpful Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much
This was very timely. Kudos
Great one! Thank you all.
Thank you very much.
This is so enlightening. Disagreement gap. Thanks for the insight.
How do I Cite this document please?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify
Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify
Table of Contents

Research Gap
Definition:
Research gap refers to an area or topic within a field of study that has not yet been extensively researched or is yet to be explored. It is a question, problem or issue that has not been addressed or resolved by previous research.
How to Identify Research Gap
Identifying a research gap is an essential step in conducting research that adds value and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. Research gap requires critical thinking, creativity, and a thorough understanding of the existing literature . It is an iterative process that may require revisiting and refining your research questions and ideas multiple times.
Here are some steps that can help you identify a research gap:
- Review existing literature: Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in your research area. This will help you identify what has already been studied and what gaps still exist.
- Identify a research problem: Identify a specific research problem or question that you want to address.
- Analyze existing research: Analyze the existing research related to your research problem. This will help you identify areas that have not been studied, inconsistencies in the findings, or limitations of the previous research.
- Brainstorm potential research ideas : Based on your analysis, brainstorm potential research ideas that address the identified gaps.
- Consult with experts: Consult with experts in your research area to get their opinions on potential research ideas and to identify any additional gaps that you may have missed.
- Refine research questions: Refine your research questions and hypotheses based on the identified gaps and potential research ideas.
- Develop a research proposal: Develop a research proposal that outlines your research questions, objectives, and methods to address the identified research gap.
Types of Research Gap
There are different types of research gaps that can be identified, and each type is associated with a specific situation or problem. Here are the main types of research gaps and their explanations:
Theoretical Gap
This type of research gap refers to a lack of theoretical understanding or knowledge in a particular area. It can occur when there is a discrepancy between existing theories and empirical evidence or when there is no theory that can explain a particular phenomenon. Identifying theoretical gaps can lead to the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones.
Empirical Gap
An empirical gap occurs when there is a lack of empirical evidence or data in a particular area. It can happen when there is a lack of research on a specific topic or when existing research is inadequate or inconclusive. Identifying empirical gaps can lead to the development of new research studies to collect data or the refinement of existing research methods to improve the quality of data collected.
Methodological Gap
This type of research gap refers to a lack of appropriate research methods or techniques to answer a research question. It can occur when existing methods are inadequate, outdated, or inappropriate for the research question. Identifying methodological gaps can lead to the development of new research methods or the modification of existing ones to better address the research question.
Practical Gap
A practical gap occurs when there is a lack of practical applications or implementation of research findings. It can occur when research findings are not implemented due to financial, political, or social constraints. Identifying practical gaps can lead to the development of strategies for the effective implementation of research findings in practice.
Knowledge Gap
This type of research gap occurs when there is a lack of knowledge or information on a particular topic. It can happen when a new area of research is emerging, or when research is conducted in a different context or population. Identifying knowledge gaps can lead to the development of new research studies or the extension of existing research to fill the gap.
Examples of Research Gap
Here are some examples of research gaps that researchers might identify:
- Theoretical Gap Example : In the field of psychology, there might be a theoretical gap related to the lack of understanding of the relationship between social media use and mental health. Although there is existing research on the topic, there might be a lack of consensus on the mechanisms that link social media use to mental health outcomes.
- Empirical Gap Example : In the field of environmental science, there might be an empirical gap related to the lack of data on the long-term effects of climate change on biodiversity in specific regions. Although there might be some studies on the topic, there might be a lack of data on the long-term effects of climate change on specific species or ecosystems.
- Methodological Gap Example : In the field of education, there might be a methodological gap related to the lack of appropriate research methods to assess the impact of online learning on student outcomes. Although there might be some studies on the topic, existing research methods might not be appropriate to assess the complex relationships between online learning and student outcomes.
- Practical Gap Example: In the field of healthcare, there might be a practical gap related to the lack of effective strategies to implement evidence-based practices in clinical settings. Although there might be existing research on the effectiveness of certain practices, they might not be implemented in practice due to various barriers, such as financial constraints or lack of resources.
- Knowledge Gap Example: In the field of anthropology, there might be a knowledge gap related to the lack of understanding of the cultural practices of indigenous communities in certain regions. Although there might be some research on the topic, there might be a lack of knowledge about specific cultural practices or beliefs that are unique to those communities.
Examples of Research Gap In Literature Review, Thesis, and Research Paper might be:
- Literature review : A literature review on the topic of machine learning and healthcare might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the use of machine learning for early detection of rare diseases.
- Thesis : A thesis on the topic of cybersecurity might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the effectiveness of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing cyber attacks.
- Research paper : A research paper on the topic of natural language processing might identify a research gap in the lack of studies that investigate the use of natural language processing techniques for sentiment analysis in non-English languages.
How to Write Research Gap
By following these steps, you can effectively write about research gaps in your paper and clearly articulate the contribution that your study will make to the existing body of knowledge.
Here are some steps to follow when writing about research gaps in your paper:
- Identify the research question : Before writing about research gaps, you need to identify your research question or problem. This will help you to understand the scope of your research and identify areas where additional research is needed.
- Review the literature: Conduct a thorough review of the literature related to your research question. This will help you to identify the current state of knowledge in the field and the gaps that exist.
- Identify the research gap: Based on your review of the literature, identify the specific research gap that your study will address. This could be a theoretical, empirical, methodological, practical, or knowledge gap.
- Provide evidence: Provide evidence to support your claim that the research gap exists. This could include a summary of the existing literature, a discussion of the limitations of previous studies, or an analysis of the current state of knowledge in the field.
- Explain the importance: Explain why it is important to fill the research gap. This could include a discussion of the potential implications of filling the gap, the significance of the research for the field, or the potential benefits to society.
- State your research objectives: State your research objectives, which should be aligned with the research gap you have identified. This will help you to clearly articulate the purpose of your study and how it will address the research gap.
Importance of Research Gap
The importance of research gaps can be summarized as follows:
- Advancing knowledge: Identifying research gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge in a particular field. By identifying areas where additional research is needed, researchers can fill gaps in the existing body of knowledge and contribute to the development of new theories and practices.
- Guiding research: Research gaps can guide researchers in designing studies that fill those gaps. By identifying research gaps, researchers can develop research questions and objectives that are aligned with the needs of the field and contribute to the development of new knowledge.
- Enhancing research quality: By identifying research gaps, researchers can avoid duplicating previous research and instead focus on developing innovative research that fills gaps in the existing body of knowledge. This can lead to more impactful research and higher-quality research outputs.
- Informing policy and practice: Research gaps can inform policy and practice by highlighting areas where additional research is needed to inform decision-making. By filling research gaps, researchers can provide evidence-based recommendations that have the potential to improve policy and practice in a particular field.
Applications of Research Gap
Here are some potential applications of research gap:
- Informing research priorities: Research gaps can help guide research funding agencies and researchers to prioritize research areas that require more attention and resources.
- Identifying practical implications: Identifying gaps in knowledge can help identify practical applications of research that are still unexplored or underdeveloped.
- Stimulating innovation: Research gaps can encourage innovation and the development of new approaches or methodologies to address unexplored areas.
- Improving policy-making: Research gaps can inform policy-making decisions by highlighting areas where more research is needed to make informed policy decisions.
- Enhancing academic discourse: Research gaps can lead to new and constructive debates and discussions within academic communities, leading to more robust and comprehensive research.
Advantages of Research Gap
Here are some of the advantages of research gap:
- Identifies new research opportunities: Identifying research gaps can help researchers identify areas that require further exploration, which can lead to new research opportunities.
- Improves the quality of research: By identifying gaps in current research, researchers can focus their efforts on addressing unanswered questions, which can improve the overall quality of research.
- Enhances the relevance of research: Research that addresses existing gaps can have significant implications for the development of theories, policies, and practices, and can therefore increase the relevance and impact of research.
- Helps avoid duplication of effort: Identifying existing research can help researchers avoid duplicating efforts, saving time and resources.
- Helps to refine research questions: Research gaps can help researchers refine their research questions, making them more focused and relevant to the needs of the field.
- Promotes collaboration: By identifying areas of research that require further investigation, researchers can collaborate with others to conduct research that addresses these gaps, which can lead to more comprehensive and impactful research outcomes.
Disadvantages of Research Gap
While research gaps can be advantageous, there are also some potential disadvantages that should be considered:
- Difficulty in identifying gaps: Identifying gaps in existing research can be challenging, particularly in fields where there is a large volume of research or where research findings are scattered across different disciplines.
- Lack of funding: Addressing research gaps may require significant resources, and researchers may struggle to secure funding for their work if it is perceived as too risky or uncertain.
- Time-consuming: Conducting research to address gaps can be time-consuming, particularly if the research involves collecting new data or developing new methods.
- Risk of oversimplification: Addressing research gaps may require researchers to simplify complex problems, which can lead to oversimplification and a failure to capture the complexity of the issues.
- Bias : Identifying research gaps can be influenced by researchers’ personal biases or perspectives, which can lead to a skewed understanding of the field.
- Potential for disagreement: Identifying research gaps can be subjective, and different researchers may have different views on what constitutes a gap in the field, leading to disagreements and debate.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: What is a research gap and how do I find one?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 64 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 27 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 26 Circulation
- 129 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 311 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 25 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 216 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Jun 27, 2023 Views: 463835
What is a research gap.
A research gap is a question or a problem that has not been answered by any of the existing studies or research within your field. Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn't been studied at all. Sometimes you'll find a research gap if all the existing research is outdated and in need of new/updated research (studies on Internet use in 2001, for example). Or, perhaps a specific population has not been well studied (perhaps there are plenty of studies on teenagers and video games, but not enough studies on toddlers and video games, for example). These are just a few examples, but any research gap you find is an area where more studies and more research need to be conducted. Please view this video clip from our Sage Research Methods database for more helpful information: How Do You Identify Gaps in Literature?
How do I find one?
It will take a lot of research and reading. You'll need to be very familiar with all the studies that have already been done, and what those studies contributed to the overall body of knowledge about that topic. Make a list of any questions you have about your topic and then do some research to see if those questions have already been answered satisfactorily. If they haven't, perhaps you've discovered a gap! Here are some strategies you can use to make the most of your time:
- One useful trick is to look at the “suggestions for future research” or conclusion section of existing studies on your topic. Many times, the authors will identify areas where they think a research gap exists, and what studies they think need to be done in the future.
- As you are researching, you will most likely come across citations for seminal works in your research field. These are the research studies that you see mentioned again and again in the literature. In addition to finding those and reading them, you can use a database like Web of Science to follow the research trail and discover all the other articles that have cited these. See the FAQ: I found the perfect article for my paper. How do I find other articles and books that have cited it? on how to do this. One way to quickly track down these seminal works is to use a database like SAGE Navigator, a social sciences literature review tool. It is one of the products available via our SAGE Knowledge database.
- In the PsycINFO and PsycARTICLES databases, you can select literature review, systematic review, and meta analysis under the Methodology section in the advanced search to quickly locate these. See the FAQ: Where can I find a qualitative or quantitative study? for more information on how to find the Methodology section in these two databases.
- In CINAHL , you can select Systematic review under the Publication Type field in the advanced search.
- In Web of Science , check the box beside Review under the Document Type heading in the “Refine Results” sidebar to the right of the list of search hits.
- If the database you are searching does not offer a way to filter your results by document type, publication type, or methodology in the advanced search, you can include these phrases (“literature reviews,” meta-analyses, or “systematic reviews”) in your search string. For example, “video games” AND “literature reviews” could be a possible search that you could try.
Please give these suggestions a try and contact a librarian for additional assistance.
Content authored by: GS
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 374 No 152
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Identify a Research Gap

- 5-minute read
- 10th January 2024
If you’ve been tasked with producing a thesis or dissertation, one of your first steps will be identifying a research gap. Although finding a research gap may sound daunting, don’t fret! In this post, we will define a research gap, discuss its importance, and offer a step-by-step guide that will provide you with the essential know-how to complete this critical step and move on to the rest of your research project.
What Is a Research Gap?
Simply put, a research gap is an area that hasn’t been explored in the existing literature. This could be an unexplored population, an untested method, or a condition that hasn’t been investigated yet.
Why Is Identifying a Research Gap Important?
Identifying a research gap is a foundational step in the research process. It ensures that your research is significant and has the ability to advance knowledge within a specific area. It also helps you align your work with the current needs and challenges of your field. Identifying a research gap has many potential benefits.
1. Avoid Redundancy in Your Research
Understanding the existing literature helps researchers avoid duplication. This means you can steer clear of topics that have already been extensively studied. This ensures your work is novel and contributes something new to the field.
2. Guide the Research Design
Identifying a research gap helps shape your research design and questions. You can tailor your studies to specifically address the identified gap. This ensures that your work directly contributes to filling the void in knowledge.
3. Practical Applications
Research that addresses a gap is more likely to have practical applications and contributions. Whether in academia, industry, or policymaking, research that fills a gap in knowledge is often more applicable and can inform decision-making and practices in real-world contexts.
4. Field Advancements
Addressing a research gap can lead to advancements in the field . It may result in the development of new theories, methodologies, or technologies that push the boundaries of current understanding.
5. Strategic Research Planning
Identifying a research gap is crucial for strategic planning . It helps researchers and institutions prioritize areas that need attention so they can allocate resources effectively. This ensures that efforts are directed toward the most critical gaps in knowledge.
6. Academic and Professional Recognition
Researchers who successfully address significant research gaps often receive peer recognition within their academic and professional communities. This recognition can lead to opportunities for collaboration, funding, and career advancement.
How Do I Identify a Research Gap?
1. clearly define your research topic .
Begin by clearly defining your research topic. A well-scoped topic serves as the foundation for your studies. Make sure it’s not too broad or too narrow; striking the right balance will make it easier to identify gaps in existing literature.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
2. Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
A comprehensive literature review is a vital step in any research. Dive deep into the existing research related to your topic. Look for patterns, recurring themes, and consensus among scholars. Pay attention to areas where conflicting opinions or gaps in understanding emerge.
3. Evaluate Existing Studies
Critically evaluate the studies you encounter during your literature review. Assess the paradigms , methodologies, findings, and limitations of each. Note any discrepancies, unanswered questions, or areas where further investigation is warranted. These are potential indicators of research gaps.
4. Identify Unexplored Perspectives
Consider the perspectives presented in the existing literature. Are there alternative viewpoints or marginalized voices that haven’t been adequately explored? Identifying and incorporating diverse perspectives can often lead to uncharted territory and help you pinpoint a unique research gap.
Additional Tips
Stay up to date with emerging trends.
The field of research is dynamic, with new developments and emerging trends constantly shaping the landscape. Stay up to date with the latest publications, conferences, and discussions in your field and make sure to regularly check relevant academic search engines . Often, identifying a research gap involves being at the forefront of current debates and discussions.
Seek Guidance From Experts
Don’t hesitate to reach out to experts in your field for guidance. Attend conferences, workshops, or seminars where you can interact with seasoned researchers. Their insights and experience can provide valuable perspectives on potential research gaps that you may have overlooked. You can also seek advice from your academic advisor .
Use Research Tools and Analytics
Leverage tech tools to analyze patterns and trends in the existing literature. Tools like citation analysis, keyword mapping, and data visualization can help you identify gaps and areas with limited exploration.
Identifying a research gap is a skill that evolves with experience and dedication. By defining your research topic, meticulously navigating the existing literature, critically evaluating studies, and recognizing unexplored perspectives, you’ll be on your way to identifying a research gap that will serve as the foundation for your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
If you need any help with proofreading your research paper , we can help with our research paper editing services . You can even try a sample of our services for free . Good luck with all your research!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Identifying Research Gaps to Pursue Innovative Research
This article is an excerpt from a lecture given by my Ph.D. guide, a researcher in public health. She advised us on how to identify research gaps to pursue innovative research in our fields.
What is a Research Gap?
Today we are talking about the research gap: what is it, how to identify it, and how to make use of it so that you can pursue innovative research. Now, how many of you have ever felt you had discovered a new and exciting research question , only to find that it had already been written about? I have experienced this more times than I can count. Graduate studies come with pressure to add new knowledge to the field. We can contribute to the progress and knowledge of humanity. To do this, we need to first learn to identify research gaps in the existing literature.
A research gap is, simply, a topic or area for which missing or insufficient information limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question. It should not be confused with a research question, however. For example, if we ask the research question of what the healthiest diet for humans is, we would find many studies and possible answers to this question. On the other hand, if we were to ask the research question of what are the effects of antidepressants on pregnant women, we would not find much-existing data. This is a research gap. When we identify a research gap, we identify a direction for potentially new and exciting research.

How to Identify Research Gap?
Considering the volume of existing research, identifying research gaps can seem overwhelming or even impossible. I don’t have time to read every paper published on public health. Similarly, you guys don’t have time to read every paper. So how can you identify a research gap?
There are different techniques in various disciplines, but we can reduce most of them down to a few steps, which are:
- Identify your key motivating issue/question
- Identify key terms associated with this issue
- Review the literature, searching for these key terms and identifying relevant publications
- Review the literature cited by the key publications which you located in the above step
- Identify issues not addressed by the literature relating to your critical motivating issue
It is the last step which we all find the most challenging. It can be difficult to figure out what an article is not saying. I like to keep a list of notes of biased or inconsistent information. You could also track what authors write as “directions for future research,” which often can point us towards the existing gaps.
Different Types of Research Gaps
Identifying research gaps is an essential step in conducting research, as it helps researchers to refine their research questions and to focus their research efforts on areas where there is a need for more knowledge or understanding.
1. Knowledge gaps
These are gaps in knowledge or understanding of a subject, where more research is needed to fill the gaps. For example, there may be a lack of understanding of the mechanisms behind a particular disease or how a specific technology works.
2. Conceptual gaps
These are gaps in the conceptual framework or theoretical understanding of a subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand the relationship between two concepts or to refine a theoretical framework.
3. Methodological gaps
These are gaps in the methods used to study a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to develop new research methods or to refine existing methods to address specific research questions.
4. Data gaps
These are gaps in the data available on a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to collect data on a specific population or to develop new measures to collect data on a particular construct.
5. Practical gaps
These are gaps in the application of research findings to practical situations. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand how to implement evidence-based practices in real-world settings or to identify barriers to implementing such practices.
Examples of Research Gap
Limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms of a disease:.
Despite significant research on a particular disease, there may be a lack of understanding of the underlying mechanisms of the disease. For example, although much research has been done on Alzheimer’s disease, the exact mechanisms that lead to the disease are not yet fully understood.
Inconsistencies in the findings of previous research:
When previous research on a particular topic has inconsistent findings, there may be a need for further research to clarify or resolve these inconsistencies. For example, previous research on the effectiveness of a particular treatment for a medical condition may have produced inconsistent findings, indicating a need for further research to determine the true effectiveness of the treatment.
Limited research on emerging technologies:
As new technologies emerge, there may be limited research on their applications, benefits, and potential drawbacks. For example, with the increasing use of artificial intelligence in various industries, there is a need for further research on the ethical, legal, and social implications of AI.
How to Deal with Literature Gap?
Once you have identified the literature gaps, it is critical to prioritize. You may find many questions which remain to be answered in the literature. Often one question must be answered before the next can be addressed. In prioritizing the gaps, you have identified, you should consider your funding agency or stakeholders, the needs of the field, and the relevance of your questions to what is currently being studied. Also, consider your own resources and ability to conduct the research you’re considering. Once you have done this, you can narrow your search down to an appropriate question.
Tools to Help Your Search
There are thousands of new articles published every day, and staying up to date on the literature can be overwhelming. You should take advantage of the technology that is available. Some services include PubCrawler , Feedly , Google Scholar , and PubMed updates. Stay up to date on social media forums where scholars share new discoveries, such as Twitter. Reference managers such as Mendeley can help you keep your references well-organized. I personally have had success using Google Scholar and PubMed to stay current on new developments and track which gaps remain in my personal areas of interest.
The most important thing I want to impress upon you today is that you will struggle to choose a research topic that is innovative and exciting if you don’t know the existing literature well. This is why identifying research gaps starts with an extensive and thorough literature review . But give yourself some boundaries. You don’t need to read every paper that has ever been written on a topic. You may find yourself thinking you’re on the right track and then suddenly coming across a paper that you had intended to write! It happens to everyone- it happens to me quite often. Don’t give up- keep reading and you’ll find what you’re looking for.
Class dismissed!
How do you identify research gaps? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research gap can be identified by looking for a topic or area with missing or insufficient information that limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Identifying a research gap is important as it provides a direction for potentially new research or helps bridge the gap in existing literature.
Gap in research is a topic or area with missing or insufficient information. A research gap limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Thank u for your suggestion.
Very useful tips specially for a beginner
Thank you. This is helpful. I find that I’m overwhelmed with literatures. As I read on a particular topic, and in a particular direction I find that other conflicting issues, topic a and ideas keep popping up, making me more confused.
I am very grateful for your advice. It’s just on point.
The clearest, exhaustive, and brief explanation I have ever read.
Thanks for sharing
Thank you very much.The work is brief and understandable
Thank you it is very informative
Thanks for sharing this educative article
Thank you for such informative explanation.
Great job smart guy! Really outdid yourself!
Nice one! I thank you for this as it is just what I was looking for!😃🤟
Thank you so much for this. Much appreciated
Thank you so much.
Thankyou for ur briefing…its so helpful
Thank you so much .I’ved learn a lot from this.❤️
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

- Research Process
What is a Research Gap
- 3 minute read
- 282.6K views
Table of Contents
If you are a young researcher, or even still finishing your studies, you’ll probably notice that your academic environment revolves around certain research topics, probably linked to your department or to the interest of your mentor and direct colleagues. For example, if your department is currently doing research in nanotechnology applied to medicine, it is only natural that you feel compelled to follow this line of research. Hopefully, it’s something you feel familiar with and interested in – although you might take your own twists and turns along your career.
Many scientists end up continuing their academic legacy during their professional careers, writing about their own practical experiences in the field and adapting classic methodologies to a present context. However, each and every researcher dreams about being a pioneer in a subject one day, by discovering a topic that hasn’t been approached before by any other scientist. This is a research gap.
Research gaps are particularly useful for the advance of science, in general. Finding a research gap and having the means to develop a complete and sustained study on it can be very rewarding for the scientist (or team of scientists), not to mention how its new findings can positively impact our whole society.
How to Find a Gap in Research
How many times have you felt that you have finally formulated THAT new and exciting question, only to find out later that it had been addressed before? Probably more times than you can count.
There are some steps you can take to help identify research gaps, since it is impossible to go through all the information and research available nowadays:
- Select a topic or question that motivates you: Research can take a long time and surely a large amount of physical, intellectual and emotional effort, therefore choose a topic that can keep you motivated throughout the process.
- Find keywords and related terms to your selected topic: Besides synthesizing the topic to its essential core, this will help you in the next step.
- Use the identified keywords to search literature: From your findings in the above step, identify relevant publications and cited literature in those publications.
- Look for topics or issues that are missing or not addressed within (or related to) your main topic.
- Read systematic reviews: These documents plunge deeply into scholarly literature and identify trends and paradigm shifts in fields of study. Sometimes they reveal areas or topics that need more attention from researchers and scientists.

Keeping track of all the new literature being published every day is an impossible mission. Remember that there is technology to make your daily tasks easier, and reviewing literature can be one of them. Some online databases offer up-to-date publication lists with quite effective search features:
- Elsevier’s Scope
- Google Scholar
Of course, these tools may be more or less effective depending on knowledge fields. There might be even better ones for your specific topic of research; you can learn about them from more experienced colleagues or mentors.
Find out how FINER research framework can help you formulate your research question.
Literature Gap
The expression “literature gap” is used with the same intention as “research gap.” When there is a gap in the research itself, there will also naturally be a gap in the literature. Nevertheless, it is important to stress out the importance of language or text formulations that can help identify a research/literature gap or, on the other hand, making clear that a research gap is being addressed.
When looking for research gaps across publications you may have noticed sentences like:
…has/have not been… (studied/reported/elucidated) …is required/needed… …the key question is/remains… …it is important to address…
These expressions often indicate gaps; issues or topics related to the main question that still hasn’t been subject to a scientific study. Therefore, it is important to take notice of them: who knows if one of these sentences is hiding your way to fame.
Language Editing Services by Elsevier Author Services:

- Manuscript Review
Systematic Review VS Meta-Analysis


Literature Review in Research Writing
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
How to identify research gaps

Anthony Newman
About this video
Researching is an ongoing task, as it requires you to think of something nobody else has thought of before. This is where the research gap comes into play.
We will explain what a research gap is, provide you with steps on how to identify these research gaps, as well as provide you several tools that can help you identify them.
About the presenter

Senior Publisher, Life Sciences, Elsevier
Anthony Newman is a Senior Publisher with Elsevier and is based in Amsterdam. Each year he presents numerous Author Workshops and other similar trainings worldwide. He is currently responsible for fifteen biochemistry and laboratory medicine journals, he joined Elsevier over thirty years ago and has been Publisher for more than twenty of those years. Before then he was the marketing communications manager for the biochemistry journals of Elsevier. By training he is a polymer chemist and was active in the surface coating industry before leaving London and moving to Amsterdam in 1987 to join Elsevier.

How to integrate sex, gender, and intersectional analysis into research

How to enhance your chances of serendipitous research discovery

Data Repositories to store your data

Make your data findable- It's Not FAIR! Improving Data Publishing Practices in Research

Make your data accessible -It's Not FAIR! Improving Data Publishing Practices in Research
Researcher Academy on Twitter

What is a Research Gap? How to Identify it?
“ Choosing a topic, research or subject that has not been answered or explored yet by any other scientists is referred to as a research gap.”
Unfortunately, it’s difficult to find one!
When you start reading literature, initially you may notice that nothing is left to study! That everyone feels, even me too when I was in my initial days of PhD. But when you get enough research experience, you can find gaps in research easily.
“Every research is incomplete.”
Indeed, a research work completes when it states a gap or unexplored area with the final conclusion, so that future research will get direction.
The process of research or doctorate starts (immediately after you get admission) by initiating searching a research gap which leads to postulating a research question.
A research question is your title or statement of thesis using which you will find your thesis objectives and address a particular question. It can be stated only by finding a research or literature gap.
And as I said, it’s quite difficult for PhD students.
So in this blog post, I will explain to you what a research or literature gap is and how you can identify it.
How to appear in the PhD Interview?
What is a research or literature gap?
Firstly, a research/ knowledge gap or literature gap is though different terms but has a similar meaning. The reason is that a research problem can be addressed either by experimental research and literature review.
Definition:
A research or literature gap is a problem or unexplored/ underexplored area of the existing research.
Choosing a topic, research or subject that has not been answered or explored yet by any other scientist is referred to as a research gap.
Let us start with an example;
Take a look at the hypothetical closing sentence.
“3 common mutations IVS1-5, IVS1-1 and CD8/9 have been selected for the present to screen thalassemia patients. A common mutation IVS1-5 has been identified in 2 out of 70 unrelated thalassemia patients using the conventional PCR technique.”
Let’s say you want to do research on the Genetics of Thalassemia. Suppose this one is the closing paragraph of some research article and is a final conclusion. How can you find a research gap here?
I find many gaps, Let us find out some of them;
- The sample size is too small.
- There are 12 common mutations in beta-thalassemia which are present in almost 80% of cases. Only three are selected in the present study.
- The present study is geologically restricted.
- The author has used a single conventional PCR technique. More techniques like DNA sequencing can be used to address the same problem, which possibly provides more knowledge and can identify novel mutations as well.
- The author hasn’t clarified which type of thalassemia patients they have included in the present study.
These are some of the possible gaps in the present research. Let’s look at other closing statements for the same.
“3 common mutations IVS1-5, IVS1-1 and CD8/9 have been selected for the present to screen thalassemia patients. A common mutation IVS1-5 has been identified in 2 out of 70 unrelated thalassemia patients using the conventional PCR technique. The present study can be strengthened by increasing sample size, diversifying geological studies, increasing the number of common mutations and using other techniques for thalassemia.”
“Major limitations of the present study are small sample size, number of mutations and technique selected for the study.
All these closing statements posit the same type of research gaps. You can use these to prepare your thesis statement. Take a look at the one.
“Identifying common Beta-thalassemia mutations by DNA sequencing from south India.”

Where to find a literature gap?
Some research clearly indicates gaps in their studies whereas some don’t. And that’s why it’s difficult for students to discover one. Notedly, by looking into variables used in the study, gaps can be recognized.
- Samples- size, types, collection method, transportation conditions.
- Research technique- single, two or multiple; significance, efficiency and accuracy of the techniques used.
- Geological location and condition of the study conducted.
- Objectives selected for the study.
- Data obtained and research discussions.
You have to read tons of literature to actually determine possible gaps in the research. A research gap has been indicated in the conclusion section, final interpretation, future direction or suggestions part of a research paper.
Besides, when you came across some phrases used in the literature such as,
The present study has not been covered…..
………… excluded from the present study.
………… is important to address in future research.
…………. Techniques can be fruitful for future research.
……………. have/has not been studied/ reported/ evaluated in the present study.
Keep in mind that this indicates a gap, problem or scopes of improvement in the study.
Read more: Which factors decide a PhD Salary?
How to find a research gap?
As I said, it’s not an easy process to find a problem or gap in the research, though by following some steps that I will mention here, you can find one and can go with it.
Select a topic that you like and that motivates you:
Research interest is important because you have to do the same work for at least 4 to 5 years. Research takes a tremendous amount of physical, mental, economical and intellectual effort. Meaning you have to select a topic that likely motivates you. You should not get tired of doing that!
Find lucrative keywords to go ahead:
You can’t go through the whole topic or subject, right! you have to select one or a few. Means, make things more narrow. Take a look at the process, I have explained with an example.
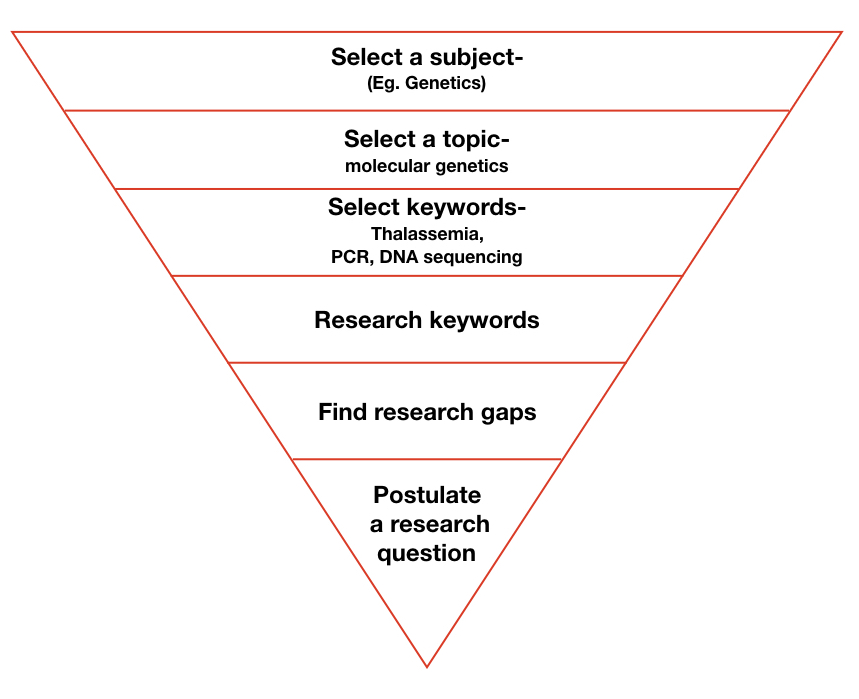
Find a keyword that is relevant to the topic you like or are interested in and go ahead with it.
Find relevant resources and literature:
Now next in the process, type your keyword or group of keywords in the Google search box and try identifying literature, reviews and research associated with it.
Find reviews, read them and try to find gaps in studies. Keep in mind that it will remain in your interest circle.
Read peer-reviewed articles and find gaps in the research:
Try to read every fresh research and review article around your topic, go through the technique and sample collection process used in each research and discover discordance or space there.
You can make a comparative analysis table as well. Take a look at the table below,
When you make a comparative analysis of a few studies you will get an idea about the research gap, gap in sample collection, scope to use other techniques, improvisation or new research areas to include in the study.
Choosing one from many:
When you complete the process, you may find many unanswered questions or research gaps (if you have done things in this manner) and you get stuck with many, which to choose and which to leave.
For PhD, it’s important to weightage a research work accurately; not more, not less. An imbalance will create an unnecessary burden and create problems in the future.
Henceforth, prioritizing and narrowing down the research gap is crucial.
In this case, you can take your supervisor’s help. Postulate an amazing research question that would be suitable for PhD, as per your interest, under your budget and fulfill your supervisor’s need.
Expected outcomes:
This is confusing for you surely!
You may wonder by only identifying a gap and postulating a research question, how can we expect anything as outcomes?
Expected outcomes of the research have significant value and importance in the PhD, PhD research proposal and your final report. You or your guide has to explain the possible results of the study.
It’s mandatory and will give you direction for research. Expected outcomes can be considered as a path on which you will have to walk.
Take an example of the research question we just postulated, “Identifying common Beta-thalassemia mutations by DNA sequencing from south India.”
What will be the expected results?
- You will get some common mutations.
- You will probably get some new mutations or variations.
- Or you will get nothing, which means, no mutations in any samples.
In either case, you have definite outcomes, and your final results will be around it, perhaps. You will definitely not get any information regarding the globin protein because that’s not included in the study.
Right!
You are just doing mutational analysis and want to find some common mutations in the selected population. So what research gap you will identify will surely give some expected outcomes.
Wrapping up:
Research gap/ knowledge gap or literature gap all terms leads us to the same direction and help us to propose a research question. Although as we said, expected outcomes are also an important consideration to fill the gap.
If you are new to PhD or just started this article is the best place for you to start, and will definitely assist you to find a mission piece of link in the research.
I hope you like this article. Please do visit other articles on this blog.

Dr. Tushar Chauhan is a Scientist, Blogger and Scientific-writer. He has completed PhD in Genetics. Dr. Chauhan is a PhD coach and tutor.
Share this:

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Linkedin
- Share via Email
About The Author

Dr Tushar Chauhan
Related posts.
What is PhD?- History, Definition, Origin, Requirement, Fees, Duration and Process

How to write a PhD thesis?
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
- Library databases
- Library website
Library Guide to Capstone Literature Reviews: Find a Research Gap
Find a research gap: tips to get started.
Finding a research gap is not an easy process and there is no one linear path. These tips and suggestions are just examples of possible ways to begin.
In Ph.D. dissertations, students identify a gap in research. In other programs, students identify a gap in practice. The literature review for a gap in practice will show the context of the problem and the current state of the research.
Research gap definition
A research gap exists when:
- a question or problem has not been answered by existing studies/research in the field
- a concept or new idea has not been studied at all
- all the existing literature on a topic is outdated
- a specific population/location/age group etc has not been studied
A research gap should be:
- grounded in the literature
- amenable to scientific study
- Litmus Test for a Doctoral-Level Research Problem (Word) This tool helps students determine if they have identified a doctoral level research problem.
Identify a research gap
To find a gap you must become very familiar with a particular field of study. This will involve a lot of research and reading, because a gap is defined by what does (and does not) surround it.
- Search the research literature and dissertations (search all university dissertations, not just Walden!).
- Understand your topic! Review background information in books and encyclopedias .
- Look for literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
- Take notes on concepts, themes, and subject terms .
- Look closely at each article's limitations, conclusions, and recommendations for future research.
- Organize, analyze, and repeat!
- Quick Answer: How do I find dissertations on a topic?
Start with broad searches
Use the Library Search (formerly Thoreau) to do a broad search with just one concept at a time . Broad searches give you an idea of the academic conversation surrounding your topic.
- Try the terms you know (keywords) first.
- Look at the Subject Terms (controlled language) to brainstorm terms.
- Subject terms help you understand what terms are most used, and what other terms to try.
- No matter what your topic is, not every researcher will be using the same terms. Keep an eye open for additional ways to describe your topic.
- Guide: Subject Terms & Index Searches: Index Overview
Keep a list of terms
- Create a list of terms
- Example list of terms
This list will be a record of what terms are:
- related to or represent your topic
- synonyms or antonyms
- more or less commonly used
- keywords (natural language) or subject terms (controlled language)
- Synonyms & antonyms (database search skills)
- Turn keywords into subject terms
Term I started with:
culturally aware
Subject terms I discovered:
cultural awareness (SU)
cultural sensitivity (SU)
cultural competence (SU)
Search with different combinations of terms
- Combine search terms list
- Combine search terms table
- Video: Search by Themes
Since a research gap is defined by the absence of research on a topic, you will search for articles on everything that relates to your topic.
- List out all the themes related to your gap.
- Search different combinations of the themes as you discover them (include search by theme video at bottom)
For example, suppose your research gap is on the work-life balance of tenured and tenure-track women in engineering professions. In that case, you might try searching different combinations of concepts, such as:
- women and STEM
- STEM or science or technology or engineering or mathematics
- female engineering professors
- tenure-track women in STEM
- work-life balance and women in STEM
- work-life balance and women professors
- work-life balance and tenure
Topic adapted from one of the award winning Walden dissertations.
- Walden University Award Winning Dissertations
- Gossage, Lily Giang-Tien, "Work-Life Balance of Tenured and Tenure-Track Women Engineering Professors" (2019). Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies. 6435.
Break your topic into themes and try combining the terms from different themes in different ways. For example:
Theme 1 and Theme 4
Theme 2 and Theme 1
Theme 3 and Theme 4
Video: Search by Themes (YouTube)
(2 min 40 sec) Recorded April 2014 Transcript
Track where more research is needed
Most research articles will identify where more research is needed. To identify research trends, use the literature review matrix to track where further research is needed.
- Download or create your own Literature Review Matrix (examples in links below).
- Do some general database searches on broad topics.
- Find an article that looks interesting.
- When you read the article, pay attention to the conclusions and limitations sections.
- Use the Literature Review Matrix to track where 'more research is needed' or 'further research needed'. NOTE: you might need to add a column to the template.
- As you fill in the matrix you should see trends where more research is needed.
There is no consistent section in research articles where the authors identify where more research is needed. Pay attention to these sections:
- limitations
- conclusions
- recommendations for future research
- Literature Review Matrix Templates: learn how to keep a record of what you have read
- Literature Review Matrix (Excel) with color coding Sample template for organizing and synthesizing your research
- Previous Page: Scope
- Next Page: Get & Stay Organized
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
info This is a space for the teal alert bar.
notifications This is a space for the yellow alert bar.

Research Process
- Brainstorming
- Explore Google This link opens in a new window
- Explore Web Resources
- Explore Background Information
- Explore Books
- Explore Scholarly Articles
- Narrowing a Topic
- Primary and Secondary Resources
- Academic, Popular & Trade Publications
- Scholarly and Peer-Reviewed Journals
- Grey Literature
- Clinical Trials
- Evidence Based Treatment
- Scholarly Research
- Database Research Log
- Search Limits
- Keyword Searching
- Boolean Operators
- Phrase Searching
- Truncation & Wildcard Symbols
- Proximity Searching
- Field Codes
- Subject Terms and Database Thesauri
- Reading a Scientific Article
- Website Evaluation
- Article Keywords and Subject Terms
- Cited References
- Citing Articles
- Related Results
- Search Within Publication
- Database Alerts & RSS Feeds
- Personal Database Accounts
- Persistent URLs
- Literature Gap and Future Research
- Web of Knowledge
- Annual Reviews
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- Finding Seminal Works
- Exhausting the Literature
- Finding Dissertations
- Researching Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology & Design
- Tests and Measurements
- Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Scholarly Publication
- Learn the Library This link opens in a new window
Research Articles
These examples below illustrate how researchers from different disciplines identified gaps in existing literature. For additional examples, try a NavigatorSearch using this search string: ("Literature review") AND (gap*)
- Addressing the Recent Developments and Potential Gaps in the Literature of Corporate Sustainability
- Applications of Psychological Science to Teaching and Learning: Gaps in the Literature
- Attitudes, Risk Factors, and Behaviours of Gambling Among Adolescents and Young People: A Literature Review and Gap Analysis
- Do Psychological Diversity Climate, HRM Practices, and Personality Traits (Big Five) Influence Multicultural Workforce Job Satisfaction and Performance? Current Scenario, Literature Gap, and Future Research Directions
- Entrepreneurship Education: A Systematic Literature Review and Identification of an Existing Gap in the Field
- Evidence and Gaps in the Literature on HIV/STI Prevention Interventions Targeting Migrants in Receiving Countries: A Scoping Review
- Homeless Indigenous Veterans and the Current Gaps in Knowledge: The State of the Literature
- A Literature Review and Gap Analysis of Emerging Technologies and New Trends in Gambling
- A Review of Higher Education Image and Reputation Literature: Knowledge Gaps and a Research Agenda
- Trends and Gaps in Empirical Research on Open Educational Resources (OER): A Systematic Mapping of the Literature from 2015 to 2019
- Where Should We Go From Here? Identified Gaps in the Literature in Psychosocial Interventions for Youth With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Comorbid Anxiety
What is a ‘gap in the literature’?
The gap, also considered the missing piece or pieces in the research literature, is the area that has not yet been explored or is under-explored. This could be a population or sample (size, type, location, etc.), research method, data collection and/or analysis, or other research variables or conditions.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that just because you identify a gap in the research, it doesn't necessarily mean that your research question is worthy of exploration. You will want to make sure that your research will have valuable practical and/or theoretical implications. In other words, answering the research question could either improve existing practice and/or inform professional decision-making (Applied Degree), or it could revise, build upon, or create theoretical frameworks informing research design and practice (Ph.D Degree). See the Dissertation Center for additional information about dissertation criteria at NU.
For a additional information on gap statements, see the following:
- How to Find a Gap in the Literature
- Write Like a Scientist: Gap Statements
How do you identify the gaps?
Conducting an exhaustive literature review is your first step. As you search for journal articles, you will need to read critically across the breadth of the literature to identify these gaps. You goal should be to find a ‘space’ or opening for contributing new research. The first step is gathering a broad range of research articles on your topic. You may want to look for research that approaches the topic from a variety of methods – qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods.
See the videos below for further instruction on identifying a gap in the literature.
Identifying a Gap in the Literature - Dr. Laurie Bedford
How Do You Identify Gaps in Literature? - SAGE Research Methods
Literature Gap & Future Research - Library Workshop
This workshop presents effective search techniques for identifying a gap in the literature and recommendations for future research.
Where can you locate research gaps?
As you begin to gather the literature, you will want to critically read for what has, and has not, been learned from the research. Use the Discussion and Future Research sections of the articles to understand what the researchers have found and where they point out future or additional research areas. This is similar to identifying a gap in the literature, however, future research statements come from a single study rather than an exhaustive search. You will want to check the literature to see if those research questions have already been answered.

Roadrunner Search
Identifying the gap in the research relies on an exhaustive review of the literature. Remember, researchers may not explicitly state that a gap in the literature exists; you may need to thoroughly review and assess the research to make that determination yourself.
However, there are techniques that you can use when searching in NavigatorSearch to help identify gaps in the literature. You may use search terms such as "literature gap " or "future research" "along with your subject keywords to pinpoint articles that include these types of statements.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Resources for a Literature Review
- Next: Web of Knowledge >>
- Last Updated: Mar 31, 2024 4:57 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchprocess

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Research Gap and Research Problem
What is the Difference Between Research Gap and Research Problem
The main difference between research gap and research problem is that a research gap identifies a gap in knowledge about a subject, whereas a research problem identifies and articulates the need for research .
Research gap and research problem are two very similar elements of a research study. They are closely related and play a crucial role in research. In fact, a researcher cannot identify a research problem without a research gap, and it’s impossible to conduct a research study without both. A researcher first identifies a research gap (an area that has not been explored in previous literature on the subject) after conducting a thorough literature review . Then he/she formulates a clear research problem from this research gap.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is a Research Gap – Definition, Features, Function 2. What is a Research Problem – Definition, Features, Function 3. Difference Between Research Gap and Research Problem – Comparison of Key Differences
Research Gap, Research Problem

What is a Research Gap
A research gap is a key element in any research study. It’s the center of a research project and determines the area that lacks crucial information. We can define a research gap as a question that has not been addressed or an area of interest that has not been explored in previous literature on the subject. For example, a researcher in the field of health or medicine can research the long-term effects of Covid-19 vaccines, which is a research gap in the existing literature on the subject. To identify the research gap, the researcher has to gather and study all relevant books, reports, and journal articles on the subject. Researchers can usually decide on their research gap once they have conducted their literature review.
A research gap can exist when there are no studies on a new concept or idea. Sometimes, researchers can also find a research gap if the existing research is not up to date and needs modification or updates. For example, research on internet use in 2002 is no longer valid today, and the data needs modification. A researcher can also choose a specific population that has not been studied well.

What is a Research Problem
A research problem is a question(s) the researcher wants to answer through his study. Research problems introduce the readers to the topic that is being discussed. It also places the problem in a particular context, defining the parameters of the investigation. Finally, it provides the framework for reporting the results of the research, reveals what is necessary to conduct the research, and explains how the information will be presented.
A research problem must cover the essential issues at hand and be specific. Moreover, the researcher must present it logically and clearly. The research problem must also ensure that the research is based on actual facts and evidence and not on beliefs and opinions.
There are four general types of research problems:
- Casuist Research Problem – involves the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience
- Difference Research Problem – compares and contrasts two or more phenomena
- Descriptive Research Problem – describes the significance of a state, situation, phenomenon
- Relational Research Problem – indicates a relationship between two or more variables
Without a well-defined research problem, a researcher will be more likely to end up with an unfocused and unmanageable research study.
Difference Between Research Gap and Research Problem
A research gap is an area of interest that has not been explored in previous literature on the subject, while a research problem is a definite or clear statement about an area of concern that points to a need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation.
First, the researcher has to identify a research gap in the area of interest and then form his/her research problem.
A research gap identifies a gap in knowledge about a subject, whereas a research problem identifies and articulates the need for research.
A researcher identifies a research gap after conducting a thorough literature review. Then he/she formulates a clear research problem from this research gap. Therefore, the difference between research gap and research problem is the order of sequence. A research gap further justifies the research problem.
1. “ FAQ: What is a research gap and how do I find one? ” Shapiro Library. Southern New Hampshire University. 2. McCombes, Shona. “ How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples ” Scribber.
Image Courtesy:
1. “ Concept-man-papers-person-plan ” (CC0) via Pixabay
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Methodological research gap: definition, identification and examples
On this page, types of methodological research gaps.
What is methodological Research gap?
1.1 Definition
Methodological research gap is the missing gap of knowledge on a more appropriate underlying method(s) which can be used in research instead of the previously one. This implies that the researcher or you as a postgraduate student may propose a method in research to address a particular aspect in life or research which is more fitting to realize improved research findings than before.
Remember that in research, there are diverse methods utilized to arrive at valid research findings. That is, from the stage of formulating a research problem up to presentation of research findings, there are several methods that a researcher can adopt to come up with better and more reliable research results. Therefore, in each stage of research process, a researcher such as you and me is expected to identify methodological knowledge gap which should result to more reliable research outcome as aforementioned. This calls for two things;
One, identification of the applicable type of method at each stage in the research process and
Two, devising steps to be followed by the researcher to establish the methodological knowledge gap to be filled in the current study as compared to the one used by your predecessors as per past studies.
To achieve the two objectives above, Table 1.1 below summarizes the common stages in research and the corresponding aspects of methods utilized by the researchers and the examples of those methods and then a detailed explanation on how to identify the specific methodological knowledge gap follow suit.
From Table 1.1 above, we can identify the different types of methodological knowledge gaps that are found in research and that you as a researcher/ postgraduate student need to be familiar with and also apply.
STAGE 1: RESEARCH PROBLEM
In research process, the first step is the formulation of a research problem which is the critical matter at hand to the researcher. It is the question that the researcher need to get an answer through scientific investigation or inquiry.
NOTE-that when writing an academic research proposal or dissertation, this is the aspect we indicate mostly in chapter three under research methodology. Yes, down the line as we carry out our research assignment, there are many methods that cut across all the stages. But when we are addressing chapter three of our research proposal, the sub-title on research design refers to the method we consider when identifying the research problem. It is then at this point based on the nature of the research question to be answered that a particular method is selected to answer the question at hand. The relevant methods at this stage are;
2.1.1 Descriptive Research Design
If the researcher adopts a descriptive research design, the aim is to answer research questions of “what” nature which pertain to the respondent who is expected to provide data for the study.
NB: To describe the characteristics of the study variables, the researcher use statistic tools such as mean, standard deviation, variance, minimum and maximum values, frequency and percentages. It is also common in research to use likert scale approach where opinion of the respondent is ranked as SA=Strongly Agree; A=Agree; N=Neutral; D=Disagree and SD=Strongly Disagree or any other connotation is also applicable.
Applicability
Used when answering research questions of ‘ What’ nature of the respondents.
Used where the researcher want to describe or label characteristics of the study variable.
Used where the researcher does not manipulate the study variables-He/she just does physical observations. E.g. variables such as age , sex , education level e.t.c which are all demographic characteristics and you cannot alter or twist them.
Used where primary data is collected for the study using a questionnaire or interview schedule.
Used where the research problem is clear.
The following are extracts of past studies where the descriptive method was used to enquire on the characteristics of the study variables.
Description of Demographic Characteristics of firms
Table 1: Ownership Structure of firms

So you see, the researcher is able to describe the characteristics of the study variable, namely ownership structure of firms without any manipulations. That is, the fact remains that if it is sole ownership, it was observed to be 102 out of 223 and the percentage was 46%. Same with description of the other aspects of ownership structure.
Description of Characteristics of Firm Performance (The Variable)
Table 2: Financial Performance of a firms
So the question is, how do we identify the methodological knowledge gap at this stage of research question? This is explained below
Identification of Methodological Knowledge Gaps
Under descriptive research design , the researcher need to consider the following steps
Step 1: Confirm if the research question is of “WHAT” nature
The researcher need to ensure that the research question at hand is clear and that it is aimed at answering the WHAT kind of perspective
Step 2: Review of past studies
The researcher need to consider similar studies undertaken by other researchers to find out the nature or type of the study variables used in the concept under investigation. The aim being to find out how the study variables were described. For instance, did past studies use mean, standard deviation, variance, minimum and maximum values or they used range to describe the study variable.
Step 3: Assess the appropriateness of the statistics used to describe the characteristics of the study variables.
At this step, do your own critique on the statistics used to justify or disqualify why they were used to describe the characteristics of the study variables.
Step 4: Develop a Descriptive Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
At step 4, you should pinpoint or rather build up the methodological knowledge gap. This can be achieved by;
-Evaluate if the WHAT question in the past studies was effectively answered or not.
-Find out if the research design adopted is qualitative or not. In other words, is the data source primary or secondary?
-Assessing if past studies used appropriate statistics to describe the study variables in a manner that it is clear as pertain their characteristics being described.
-Find out if the descriptive research design used resulted to the appropriate sampling method or and data collection method in the past studies.
Now, based on those indicators and any other strategy which is appropriate, you as a researcher/or postgraduate student should pinpoint the gaps thereof and suggest a more appropriate method of describing the study variables to be able to answer the research question more correctly.
Illustration1
Researchers in the past literature may have used mean, standard deviation, minimum and maximum values, range and variance to describe the study variables. This can be problematic for apart from mean which is a measure of central tendency, the rest of the statistics are measures of dispersion. That is standard deviation, minimum and maximum values, range and variance are all measures of dispersion and serve the same purpose.
Therefore, in your current study, you can portray the methodological knowledge gap of descriptive nature by using standard deviation only instead of incorporating all the other measures of dispersion. You can then justify your new methodology by arguing that, one; all the other statistics serve the same purpose like standard deviation . Two, use of standard deviation help in avoiding all the other measures of dispersion which eliminates congestion in your write up. Three, the approach/methodology is economical for less time and financial resources are utilized for data to be collected will be for only standard deviation and not for all statistics as in the past studies.
2.1.2 Exploratory Research Design
If the researcher adopts exploratory research design, the aim is to answer research questions of;
Why a research study has been undertaken,
How the research problem has been defined,
What way and why the hypothesis has been formulated,
What data have been collected and
What particular method has been adopted and
Why particular technique of analyzing data has been used and a spectrum of related other enquiries are usually answered.
Used where the research question is not clear.
Used where the area of study is a new one and the researcher is trying to answer questions such as;
What is the problem?
What is the purpose of the study?
What topics could be studied?
Used where generally there is no prior research done or the existing ones do not answer the problem in a more satisfying manner.
Used where there are no set of rules to carry out the research as such, so they are stretchy/more open ended or wide-ranging.
Used where the research is of great importance or value.
Used where there are few theories which can support its findings.
Used where qualitative data is available and can be collected using data collection tools such as interview schedules or questionnaires.
Identification of Methodological knowledge gaps
Under exploratory research design , the researcher is investigating on a new field and past studies are missing. So in this case, it is not easy to identify the methodological knowledge gap for the findings gotten are inconclusive.
However, still the researcher may have a loophole to take advantage of and identify the exploratory based methodological knowledge gap at the initial stages of research process. How can this be done? Very simple;
Illustration 2
A researcher starts with a general idea and uses this research as intermediary to identify issues that can be the focus for future research. If then the researcher(s) from the past exploratory research did not identify a solid rock that further studies in future may be anchored on, then this represents a methodological knowledge gap that can be filled. You as a researcher can pinpoint the weaknesses of the base set by your predecessor researchers and re-do a similar exploratory to provide a better research anchorage in the future.
2.1.3 Explanatory Research Design
Explanatory research design sounds like Exploratory research design as discussed in 2.1.2 above, but they are distinctly dissimilar.
An explanatory research design aims at “exploring a new” on existing phenomena, which is not well explained due to lack of previous research on it. It is a design which is helpful for furtherance of research on the same area or phenomenon for its main purpose is to discover the why and what of a subject under investigation. In short, it is a type of research design which is responsible for finding the why of the events through the establishment of cause-effect relationships.
Used where the researcher want to further substantiate an already existing relationship by providing the cause-effect perspective.
Used where there is lack of or there is less information pertaining the relationship at hand.
Used where the researcher has to justify why relationship is of a certain nature.
Used when it is necessary to lay a foundational source of information for the phenomena under investigation.
Identification of Methodological knowledge gaps.
Under explanatory research design , the researcher need to consider the following steps
Step 1: Identify the immediate cause factors.
As a researcher be concerned with the express characteristics and existing social problems, by endeavoring to find out association between direct causes of an outcome.
Step 2: Establish research Problem.
Design an accurate research problem translating to appropriate research objective(s) so as to precisely state the principal areas of investigation to be properly linked.
Step 3: Develop a research hypothesis
In this step, establish a hypothesis with consideration of the most suspected causing study variables, which will be used in hypothesis testing to approve or disapprove the cause of the problem.
Step 4: Data collection.
In this step actual data collection process is undertaken so as to create more information to support the suggested hypothesis.
Step 5: Develop an Explanatory Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
Step 5, is the point where you should pinpoint the methodological knowledge gap. This can be achieved by;
-Evaluating past studies to identify the exiting conceptual framework established by scholars or/researchers.
-Check the level of plausibility of the variables previously used in the aforementioned conceptual framework.
-Critique positively the research findings from past studies pertaining that particular conceptual framework by highlighting the most probable factors further explaining the changes in the outcome variable. And hence suggest your own way of approach.
Illustration 3
Researchers in the past literature may have ignored critical study variables. Therefore, in your current study, you can portray the methodological knowledge gap of explanatory nature by using more critical or specific factors that can explain the changes in outcome variable (ie dependent variable) of the matter at hand. This will represent a methodological knowledge gap to your study.
From economics point of view, the quantity demanded is determined by the changes in price levels. Hence the relationship between the price and quantity demanded of the commodity is negatively related for a normal good. Holding other factors constant. Graphically, the demand curve is up down slopping. This shows that price dictate the changes in quantity demanded.
The conceptual framework is as follows;

In Economics, it is further proven that price of the commodity may not necessary be the direct cause of change in quantity demanded of a commodity but the Utility or level of satisfaction derived from the product by the consumer may be more predicting than just a decreasing price level. Therefore, an explanatory research design can be adopted to explain the reason as to why demand of a commodity is more tied to the utility derived by the customer and not necessarily the price per se’ . This presents an explanatory methodological knowledge gap for the current study to fill.
The new conceptual framework turns to be as follows;

In conclusion, you can see utility is the predictor which explains more of the phenomenon of changes in demand amongst consumers than the price of the commodity.
2.1.4 Correlational Research Design
If the researcher adopts a correlational research design, the aim is to answer research questions of “How” nature which pertain to determination of how two variables relate with one another.
Used when answering research questions of the level of strength of a relationship
Used where one wish to determine the direction of a relationship
Used where the researcher does not control the study variables
Used where the research problem is clear
Used where the relationship being tested is at a natural state
NB: A coefficient of between -1 up to +1 is used to describe the strength of the relationship.
The following are extracts of past studies where the correlation method was used to demonstrate the relationship between variables.
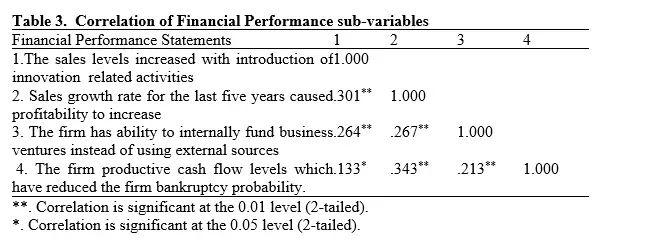
So the question that you have is, how do we identify the correlational methodological knowledge gap at this stage of research question? This is explained in below
Identification of Methodological Knowledge Gaps
Under correlational research design, the researcher need to consider the following steps.
Step 1: Confirm if the research question is of “HOW” nature
The researcher need to ensure that the research question at hand is clear and that it is aimed at answering the HOW kind of perspective.
The researcher need to consider similar studies undertaken by other researchers to find out the level of correlational strength or weakness between the study variables under investigation. For instance, if the correlation between the two variables is weak, average or strong.
Step 3: Assess the appropriateness of the concept or conceptual framework used
At this step, do your own critique on the level of correlating between study variables so as to know whether there are high chances of one variable causing the other.
Step 4: Develop a Correlational Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
In step 4, you should pinpoint the methodological knowledge gap. This can be achieved by;
-Evaluating if the HOW question in the past studies was effectively answered or not.
-Find out if the research design adopted is quantitative or not. In other words, is the data source primary or secondary?
-Assessing if past studies used right concept by selecting study variables that are fairly highly correlated (orthogonal).
-Find out if the correlation strength guarantees the researcher to further carry out regression analysis to test the hypothesis thereof.
Now, based on those indicators and any other strategy which is appropriate, you as a researcher/or postgraduate student should pinpoint the gaps thereof.
Illustration 4
Researchers in the past studies may have found no correlation (ie coefficient=0.00) between two variables. This may imply that wrong variables were chosen for the study and hence you as a researcher need to consider other more suitable variables to represent the concept of your focus. This can be achieved if the ones chosen portrays plausibility or logical relationship. This will represent a methodological knowledge gap.
Also, equally, past studies may portray a very high correlation . If that be the case, it means the variables are suffering from a multicollinearity problem and this calls for a replacement of the variables of concern. That is you as a researcher can use less number of the variables previously used by eliminating the ones which are highly correlated or replace the highly correlated variables with others with fair correlation. This again will represent a methodological knowledge gap.
Lastly and not the least, as a researcher, you can consider classification of level of strength or weakness of the correlation between two variables. From past studies, the researchers or scholars could have ignored that perspective. In your case, you can consider the proposition of Cohen of 1988 who suggested that for the purposes of interpreting the magnitude of a correlation, as well as estimating power; r = 0.10, r = 0.30, and r = 0.50 were recommended to be considered small, medium , and large in magnitude, respectively. You can rely on the same argument for sometimes past research findings have similar correlations of 0.10 up to 0.50 which is termed as weak. But you see, this could have been due to use of a small sample. This becomes a methodological knowledge gap for the end results will entail appreciation of the fact that data may be scarce in some cases and this cannot stop one from carrying out a study on a particular field.
2.1.5 Experimental Research Design
An experimental research design, is a scientific method of establishing changes in the variable being studied when another variable is manipulated. The manipulated variable is referred to as the predictor or predator or independent variable.
Used when two or more variables are used in the study
Used where the researcher uses quantitative data
Used where the researcher is in control of one variable, namely the independent variable
Used where cause-effect relationship between or amongst several variables exist
The following are extracts of past studies where the experimental method was used to enquire on the study variables.
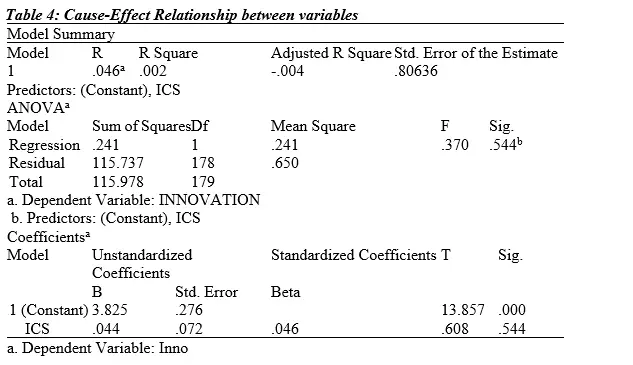
So you see, the researcher is able to portray the cause-effect relationship between the independent variable(s) and the outcome or response variable. This is achieved by manipulating the predictor variable so as to determine the value change in the dependent variable.
Under experimental research design also referred to as causal-effect relationship, the researcher need to consider the following steps so as to develop the gap thereof.
Step 1: Review of past studies
The researcher need to consider similar studies undertaken by other researchers to find out the hypothesis which was tested and the research findings thereof.
Step 2: Re-hypothesize the research problem if in step 1 you realized that the cause-effect relationship was not statistically significant
In experimental research design, the aim is to test the degree of statistical significance one variable referred to as independent variable influence another variable referred to as response/outcome variable. Therefore, if the stated hypothesis was empirically disapproved due to the relationship not being statistically significant, then it means that the concept lacked plausibility or logical sense. This calls for re-defining the research problem and of course re-defining the research hypothesis.
Step 3: Develop Experimental Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
In step 3, you should pinpoint the methodological knowledge gap. This can be achieved by;
-Considering similar conceptual framework from past studies to find out the significant level of the relationship between and or amongst study variables used.
-Investigate further on the sample size used in comparison to the population size . This will guide you to conclude if the sample size was a true representation of the population or not. For if it is not a true representation, this may be the cause of research findings with no statistical significance.
-Interrogate on the perspective of plausibility of the study variables used-if they do not represent logic in their natural/physical relationship, then the regression results will not portray statistically significant relationship.
Illustration 5
Past literature may lack study variables with plausibility or logical relationship-the researcher then can further consider other variables which have a relationship in the natural phenomenon.
Past studies could have used small sample size hence adversely affecting the level of cause-effect relationship. You as a researcher need to consider a large ‘in quotes’ sample size that truly represent the entire population.
2.1.6 Diagnostic Research Design
Diagnostic research is a type of design that aims to examine the original cause of a certain circumstances or occurrence. That is the design can help you to discover more on an issue at hand. For example, the number of “return” customers as compared to new ones could have been reducing for the last three months. The question is, what other causes could be contributing to this trend or what could be the root cause of this? In other words, the diagnostic research design is helpful in identifying where the rains started beating you if it is a case of undesirable results.
It is a research design composed of three research stages, namely;
(1) Problem Inception,
(2) Problem Diagnosis, &
(3) Problem Solution.
So if the researcher adopts a diagnostic research design, the aim is to answer research questions of;
Origin of the issue – When did the matter crop up? Where do we get more evident on the matter?
Diagnosis of the problem – What is the underlying cause of the issue? In other words, what other factors could be worsening the situation?
Solution for the Matter – What is more practical/logical in solving the matter at hand?
Used where the researcher is more concerned of the specific cause of the problem at hand.
Used where specific data need to be collected to solve an immediate need.
Used where the research problem needs more clarification.
Under diagnostic research design , the researcher need to consider the following steps
Step 1: Identify the immediate cause factors
Step 2: Establish research Problem
Step 3: Develop a hypothesis
In this step 3, establish a hypothesis with consideration of the most suspected causing study variables, which will be used in hypothesis testing to approve or disapprove the cause of the problem.
Step 4: Data collection
Step 5: Develop a Diagnostic Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
In step 5, you should pinpoint the methodological knowledge gap. This can be achieved by;
-Evaluate if past studies had identified any specific factor acting as the key cause of the matter at hand
-Check the level of plausibility of the variables previously used in similar study to the one at hand
-Critique the research findings from past studies and suggest your own way of approach
Illustration 6
Researchers in the past literature may have ignored critical study variables. Therefore, in your current study, you can portray the methodological knowledge gap of diagnostic nature by using more critical or specific factors that can explain the immediate cause of the matter at hand. This will represent a methodological knowledge gap to your study.
STAGE 2: OPERATIONALIZATION
Operationalization is the process of assigning a measurable indicator or proxy on a specific fuzzy characteristic to make it possible to measure it through observation. This approach make it possible for the researcher to systematically collect and evaluate phenomena that can't be observed directly.
Fuzzy characteristic is that kind of behavioral element portrayed by the unit of observation which is vague and not easily measurable. In other words it is not definitely expressible in fixed terms and its measurability depends on context or conditions, and therefore a precise meaning is lacking . The idea of operationalization is in addition to the well-known methodologies of measuring of study variables. That is use of measurement scales which are used to qualify or quantify data variables in statistics and they are usually four in number. That is;
Nominal Scale
Ordinal Scale
Interval Scale
Ratio Scale.
NB: That, qualitative data is measured using nominal and ordinal scale while quantitative data is measured using interval and ratio scales.
Operationalization Methodological Knowledge Gaps
How do we identify methodological gap on the basis of measurement or operationalization of a variable/construct? To achieve this objective, you, the researcher need to use the following guidelines as portrayed by these steps below
Step 1: Review Past Studies
In this step, the researcher will aim at finding out how the similar variable was measured by his/her predecessor researchers. Remember that you cannot re-invent the wheel and come up with your own way of measuring a variable. Also, for a variable to be useful in a study, it must be measurable. As we have let you know in our other articles, “ if a variable is not measurable then it does not exist”.
So in this step one, you as a researcher need to find out if a universally authentic method has been used to gauge the variable.
Step 2: Assess the Appropriateness of the Method of Measurement Used
In this step, the researcher need to assess whether the proxy used to gauge the variable is correct. The extent of correctness or fitting will be assessed against some set thresholds such as:-
Contextual environment
Targeted group in the study
Generally accepted/universal method used
Technological advancements
Step 3: Positively critique to highlight areas of improvement in measurement
At this point, pinpoint the weaknesses of using the measurements used by other scholars/researchers on similar variable(s) in the past studies. This should be done with justification without necessarily critiquing in the wrong way . For example, I have witnessed postgraduate students suggesting that the past studies failed to use a certain method in measuring a particular variable.
For example, one will say that the study of X and Z failed to use ROE to measure profitability of the firm for in their case they used market share instead. So this is the reason why the current researcher want to use ROE!
This is wrong approach in creating methodological knowledge gap. The reason being that, may be as per those researchers, the research problem at hand dictated use of a certain proxy or measurement to gauge the study variables thereof. So as per their study, it was appropriate!. So the current researcher has no right to negatively critique or demonize his/her predecessor researcher’s work!
Step 4: Develop an Operational/Measurement Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
The following illustration will take care of the best way to create such gaps.
Illustration 1
Let me assume I am writing a research to investigate on the factors that influence financial performance of firms listed at the stock exchange. The factors I have proposed are X. Y and Z which are the independent variables whereas, financial performance is the criteria variable (Response variable) and is measured using Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
The corresponding conceptual framework will be as demonstrated by Figure 1.1 below;
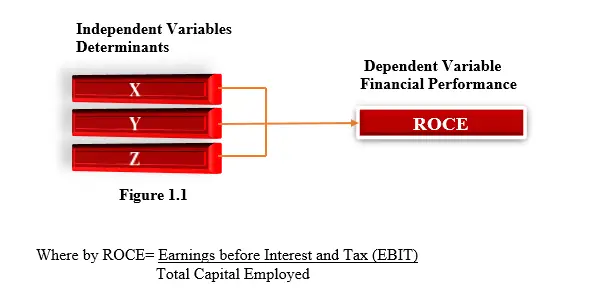
If the research findings portray that there is statistically significant influence of the three factors taken together, namely X, Y and Z on financial performance of those firms listed at the stock market, this currently represents the body of existing knowledge.
From contextual point of view (users of the research report), a methodological knowledge gap based on measurement/operationalization can be established. For instance, suppose another researcher wanted to establish the influence of the same factors, namely X, Y and Z on financial performance with an aim of advising the owners of the companies as far as their Earnings per Share (EPS) is concerned. Then the method used to measure financial performance will change to EPS. This will represent a better way of informing the owners on their expectations as far as their returns are concerned. This is because it is more specific on returns originating from equity invested in the firm other than ROCE which is returns associated with all the investors, hence a general proxy. In other words, we are not saying that the previous way of measuring financial performance, i.e. ROCE was wrong for it fitted the purpose expressing performance of the firm in general.
Therefore, the more appropriate conceptual framework will be as follows as per Figure 1.2;
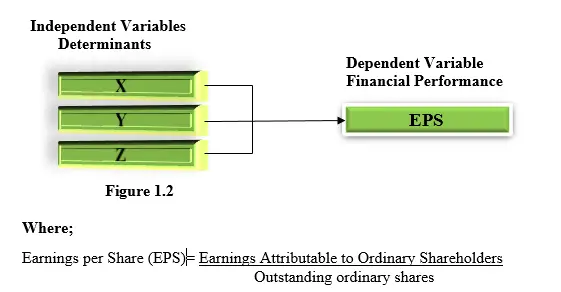
So note that although both studies are similar in every other way, the use of a different measurement of the financial performance of the firms to suit a particular purpose, represents a operational/measurement methodological knowledge gap. This is paramount for appropriateness of measurement is key in ensuring that no confusion in defining a variable and also there is clarity on decision making by the management.
Suppose in another study, the researcher investigated on the factors influencing financial performance of firms listed at the security exchange and financial performance was measured in three ways, namely; Return on Equity (ROE), Return On Assets (ROA) and Return On Invest
ment(ROI) as shown in Figure 1.3 below
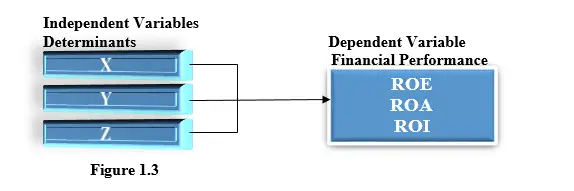
From Corporate Finance perspective, the three measures of financial performance are similar/same for ROI=ROA=ROE. This implies that the research findings will be similar and number two, the data for ROA,ROE and ROI is highly correlated and incase of carrying out multicollinearity test, the relationship will prove to be so. Therefore, there arises a need to eliminate some of dependent variables so as to;
One, avoid multicollinearity problem and
Two , avoid waste of resources for data will be required for the three measures of financial performance which represent the same outcome. This represents a methodological knowledge gap based on the measurement adopted by the researcher.
For an improved study, one can incorporate only one measurement of financial performance, such as either ROE or ROI or ROA but not all. See Figure 1.4 below
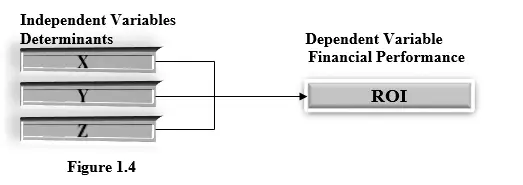
NOTE: That, in the three illustrations, we have only focused on the measurement of the dependent variable. This was only made for simplicity of understanding the concept. Otherwise, dissimilar methodologies can be used to measure all study variables as long as one can justify why he/she has gauged a variable in a particular manner. Also, for all the other measuring scale, the right applicability in measuring a characteristics should be considered. If not so, then a researcher can suggest a better method.
STAGE 3: SAMPLING
At the sampling stage in research process, there exists an opportunity to portray methodological knowledge gap also. How does this occur? As we appreciate that most of the time research data is collected from a sample and not the entire population, this increases the chances of pinpointing weaknesses on the sampling techniques used in similar studies hence suggest a better or more appropriate sampling method. The following steps is of paramount importance to you as a scholar or researcher in identifying sampling methodological knowledge gaps
This step will help you as a researcher to compare the research method and the sampling method(s) used by researchers/scholars in past literature similar to your study. The aim is to assess the matching for each research design has a corresponding appropriate sampling technique that guide towards establishment of the right sample size .
Step 2: Identify the Sample Size used in each Past Study Reviewed
Step 2 is a furtherance of step one, which aims at checking the appropriateness of the sample used. The sample size should always be a true representation of the population. Then it means that if the past studies similar to yours has wrong sample size, it is at this juncture that you should raise a red flag for this implies that the data used in those studies could have resulted to biased research findings which have no validity.
Step 3: Critique Past studies
This is done by suggesting the most appropriate sampling methods(s) to use in your study. Either portray why the sampling method used earlier on is not suitable in the similar current study or why another method is more suitable than those used in similar studies.
Your justification points/strengths may include and not limited to;
i). Type of sampling Method used
You can argue that the sampling method used did not give all the units of observation equal chances of being selected to participate in data collection process hence may be the results were bias. For example, you see there are two types of sampling methods; probabilistic sampling which gives all units of observation equal chance to participate in data collection and this assures us of unbiased and valid research findings. Then there is non-probabilistic sampling techniques which may result to biased research findings although to some extent they can be appropriate based on the context or objective under consideration.
ii.) Mismatch between Research Method and Sampling Method
Each research method used in a study dictates the sampling technique to adopt, the type of data to collect, sample size and other many aspects. Then this calls for interrogation of the matching done by researchers in past studies to see the appropriateness of the matching, which may result to a shortcoming in the process of sampling
iii). Nature of the population
The nature of population may assume manifold aspects such as its characteristics, distribution patterns and so on and so on. This may dictate use of specifically a certain type of sampling. For instance, when data is not equally distributed such as unbalanced data panel.
Step 4 : Develop a Sampling Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
Build your case of the methodological knowledge gap by highlighting issues of your concern in the past studies.
In a study where the population is in form of strata, then stratified random sampling method can be adopted to establish a sample size which is a true representative of the entire population. For example, data to be collected for public hospitals in Kenya. In this case, we can consider only the level five category from the 47 counties. The counties will be representing the stratus and then further random selection can be done to pick the right sample for data collection purposes. In this case, the results are unbiased and validity is assured. Note that this is just a simple approach, for we have left out the key details. So in this case, a random sampling method is more suitable.
In a study where the researcher has an aim of discriminatively looking for certain specific data to meet a specific objective, then a non-probabilistic sampling method can be more appropriate. For instance, when I was doing my PhD, my concern was data for firms listed at the Nairobi Securities Exchange. Since some of my variables would produce contradicting research findings such as cashholdings, I discriminated all financial such as banks and insurance institutions whose liquidity rule and regulations require them to keep a certain level of cash reserves which is almost composed of elements of cashholdings. Hence I went for non-financial firms for convenience purposes. Also some of the firms did not portray some of the study variables I was using in my study so I conveniently selected those firms with all the study variables I had incorporated in my study. This called for use of convenient sampling which is non-probabilistic in nature.
Look at this EXTRACT from my PhD thesis;
(“ The total number of registered organizations at the Nairobi Securities Exchange by 2015 was 63 in total (NSE, 2015). Commercial banks and insurance firms were excluded in this study because they are heavily regulated than non-financial firms and have a unique capital structure (which is similar amongst themselves) from other firms (Berkman & Bradbury, 2001). NSE facilitates its member firms hence it is unique in its operations as compared to the targeted firms for the study. To ensure that the firms used in the study are uniform, such unique firm attributes were put under consideration and discriminatively selected some firms for the study. Therefore, the target population comprised of 47 firms.
Convenience sampling technique was used to collect a more representative sample for the study. Hence, the relevant observation items that enabled achievement of the research objectives were considered and therefore firms with incomplete data were left out. This implies that companies which did not have a full set of data on variables mentioned in the study were excluded. Therefore a sample size of 31 organizations registered at the NSE for the period of eleven years was selected out of the targeted population of 47 firms as shown in Table 3.1 below
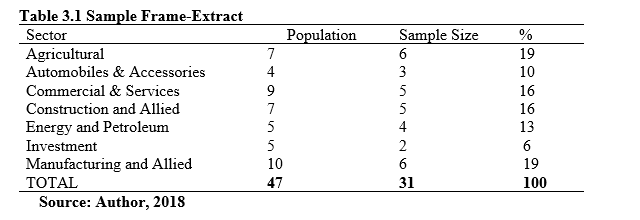
Sometimes, past studies may use sample size which is large but not scientifically determined. That is, as one arrives at a particular sample size, a scientific method should have been used so as to justify the authenticity of the sample size and its usability in the study. Therefore, in the current study, the researcher need to justify why such a “ sample size determination formula” has been used.
For example, the following extract is from a past study where Yamane (Formula) was used to determine the sample size
Sample Size
The appropriate sample for this study was 265 SMEs drawn from a target population of 5311 SMEs operating in Machakos County using Yamane formula (1967). This formula was used to determine the sample size (n) which is the number of subjects to be randomly selected from each category of SME projects in Machakos County.
Sampling Procedure
The procedure of how the 265 firms was selected out of the total population of 5311 was summarized in Table 3.2
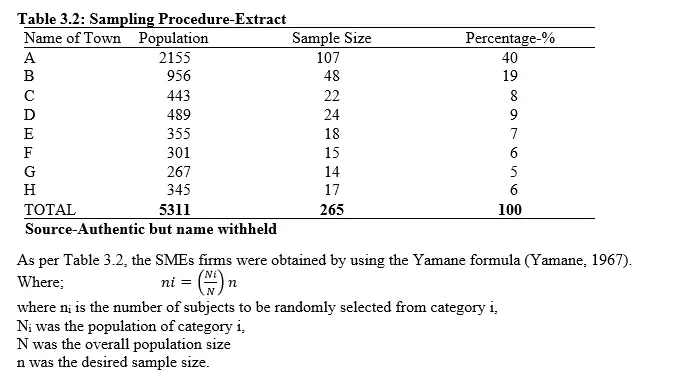
NB: The researcher has to justify why such a formula is used in such a study. Of course there are other sample size determination formulas and if used by the researcher, then again justification is necessary. All these sampling concerns portray sampling methodological knowledge gaps.
STAGE 4: DATA COLLECTION
After sample size or population has been determined in stage 3, then actual data is collected. This process also just like the other stages of research process presents to you as a researcher another chance to demonstrate the data collection methodological gaps in existence as per past studies.
Remember that data collection is a sensitive procedure and if the appropriate data collection method is not used, then biasness dominates the data collected and the data analysis process will bring forth results which are not admirable. Data collection utilizes three data collection research designs as explained in our research Hub, namely;
Cross sectional Research design- A cross-sectional study design is a type of research design in which data is collected from many unit of observations/respondents at a single point in time.
Longitudinal Research design- A longitudinal study design, is a type of research design whereby researchers repeatedly examine the same unit of observations/respondents to detect any changes that might occur over time (ie at different points in time) without trying to influence those variables.
Time series Research design- Time series designs are a sub-set of longitudinal research design which its analysis focus is on “large series of observations made on the same variable consecutively over different point in time.
The following steps will guide you to establish the data collection methodological knowledge gap
From past studies, identify the data collection research design used to assess its appropriateness in that study(ies). Based on the research problem at hand, one is able to tell the most suitable data collection research design.
Step 2: Assess the nature of population or sample to collect data from
This aspect represents the source of data which can either be primary data or secondary data
If primary data for several variables -then cross sectional research design is useful
If secondary data for several variables -then longitudinal research design is helpful
If secondary data for only one variable-then time series research design is helpful
From past studies, demonstrate that the methods of data collection are unsuitable to your current study. This can be achieved by positively proving that the data collection research design is only suitable in the past similar studies but not the current one. This can be achieved by suggesting the appropriate method of collecting data based on the aforementioned data collection research design which is well fitting.
Step 4: Development of Data Collection Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
At this point show the suitability of the current methods of data collection by justifying that the methods will meet objectives such as;
Right data collection method ensures data validity which translate in to unbiased research findings.
Right data collection method saves time.
Right data collection method translates to reliable data analysis methods etc etc.
Suppose you are carrying a study on the relationship between time taken to coach undergraduate students and academic performance for the last 5 years from 2016 up to 2020.
The data to be collected is primary data and will be collected through questionnaires issued at the year 2020
This is data collection at one data point to represent performance information of students for 5 years
Data is collected from more than one unit of observation
Therefore, cross sectional data collection method will apply.
Suppose you are carrying another study on the relationship between time taken to coach a particular undergraduate student by the name James and his Mathematics performance for the last 5 years from 2016 up to 2020.
One; the data to be collected is secondary data and will be collected through using secondary source such as James academic reports from the year 2016 up to 2020.
This is data collection at 5 different data points, that is 2016; 2017;2018;2019 and 2020.
Two; data is collected for one unit of observation, ie James who is a student.
Therefore, longitudinal data collection method will apply. This will be a new approach of collecting data hence a dissimilar data collection methodological knowledge gap is realized.
STAGE 5: DATA ANALYSIS
This is the last stage in research process whose end result is the research findings which in turn are used for making conclusions. In this stage there are diverse data analysis approaches that are useful to the researcher based on the objectives to be achieved.
Since the methods are several, (visit STATA, E-VIEWs, SPSS program) I will demonstrate the steps to follow when creating data analysis methodological knowledge.
The following steps matter
Revisit past studies similar to your topic to evaluate the data analysis method utilized and the justifications the authors have provided.
Step 2: Identify both the research question and the specific objectives of the study.
From the past studies you review, you will notice that at least one or two methods of data analysis has been utilized. At this point, equally identify the corresponding research questions and the research specific objectives which obviously should emanate from the research question.
Step 3: Identify the research design used by the researcher in that past study.
With the research question and the specific objectives at hand, further identify the research design used and evaluate its suitability in answering the research question at hand and achieving the study specific objectives. Ask yourself, whether with such a research design, the two aspects were fulfilled to satisfaction.
NB: For your information, the right matching should be for instance, if the research problem was descriptive in nature, the research question will be descriptive and specific objective as well. Then, descriptive research methodology will be used, followed by descriptive research methods and descriptive data analysis. Similarly, the same applies in all other research designs.
Step 4: Benchmark the data analysis method used and the researcher’s research question
Again consider the matching of the research design chosen with the data analysis method used if it is correlated in any way. Of course, you know that the research design chosen dictates the data analysis method used. And the data analysis used is meant to answer the research question. If this is the case as per the past study research findings, then it’s ok. But if not, this becomes a case to raise some questions on how best the data analysis should have been done.
Step 5: Benchmark the data analysis method used and the researcher’s specific objectives
Repeat step 4 to step 5 and consider the matching of the data analysis method and the extent to which the tool has helped in achieving the set specific objectives of the past study. Of course, you know that the data analysis method chosen dictates the extent to which the specific objectives are achieved. If with the data analysis used, the specific objectives are fully achieved, ok. But if not, this becomes a case to raise some questions on how best such objectives should have been achieved. This calls for identification of areas for further research as indicated in most of the academic papers in chapter five or six of the project paper.
Step 6: Critique the data analysis approach used in the past studies
In step 6, you highlight the appropriate data methodology to use in your current study by pinpointing either weaknesses or strengths of the methods used earlier on by your predecessors in the similar studies you have reviewed.
Show how more suitable or appropriate your methodology is and how it will sufficiently be able to answer the question at hand and meet the specific objectives of the study.
NB: As you review past studies to interrogate the data analysis method used, you need to be careful of the specific objectives which that particular researcher wanted to achieve.
Step 7: Development of Data Analysis Based Methodological Knowledge Gap
Pegged on the hypotheses set, demonstrate how the data analysis has proven or disapproved the hypotheses.
Assess the level of hypothesis test statistical significance to determine whether to fail to accept the null hypothesis (ie reject the null hypothesis) or fail to reject the null hypothesis (ie accept the null hypothesis).
State the data analysis methodological knowledge gap thereof. So in the following illustrations, we will consider different scenarios with different researchers as portrayed below;
Assume that researcher one carried out a study on the relationship between P and M .
So in this case, the research question he wanted to answer was;
Research Question : Does variable P have a strong association with M ?
The corresponding;
Specific Objective was; To determine the relationship between P and M
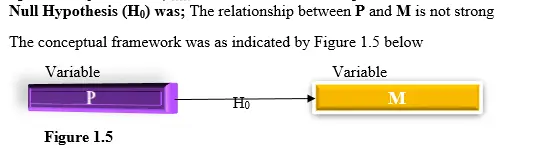
NOTE the following;
The specific objective to be achieved is to establish the relationship between P and M variables.
In the conceptual framework, we do not indicate the role of the variables for we are concerned about the relationship and not which variable influence the other. So no predictor or response variable classification.
The researcher incorporated correlation data analysis method to find out the association between P and M variables. Pearson Product Moment correlation model was used.
Research findings revealed that there exists a strong positive relationship between P and M .
Now, let us assume that illustration one will represent the “existing body of knowledge” that there exists a strong positive correlation between P and M. This assumption will help us understand how to develop data analysis methodology knowledge gaps that can arise from this first case.
So let’s move on….
From past literature, researcher two came across a study by researcher one (refer to researcher one research findings) whereby the research findings showed that there exists a strong positive relationship between P and M .
However, according to researcher two, there exists some data analysis methodological knowledge gap as per the past study undertaken by researcher one if regression analysis is incorporated.
One; researcher one focused on correlation of P and M variables while the current study of researcher two is on the influence of P on M hence need to carry out regression analysis and not correlation analysis
Two; the previous study of researcher one was on determining the level of strength of the relationship between P and M while in the case of researcher two, the focus was to establish the level of significance influence of P on M.
Three; both the research questions and specific objectives of the two researchers were dissimilar .
Point of correction -when creating the methodological gap of whichever nature, its common amongst researchers even I have witnessed my postgraduate students, even others during postgraduate academic defenses state that “ researchers as per past literature failed to use either multiple regression or correlation analysis method and that is why there is a methodological gap. ”
No, you cannot afford to say that because past literature had different research question, different specific objective and of course different hypothesis and so the method used was appropriate as far as that case was concerned. So, no one has a right to negatively critique that researcher(s)!
Therefore, Researcher two further carried out a research on the influence of P on M . This means that, he sought to investigate the level of significance that P has on M .
Now, in this case the research question was,
Research Question: Does variable P have statistically significant influence on M ?
Specific Objective was; to establish the influence of P on M
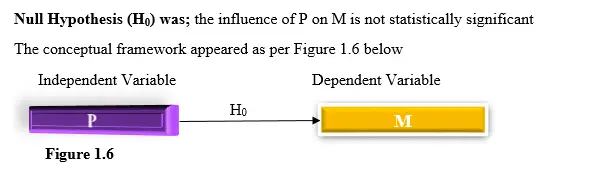
1. The specific objective to be achieved is to establish the influence of variable P on variable M.
2. In the conceptual framework, we indicate the role of the variables for we are concerned about the influence that one variable (independent variable) has on another variable (dependent variable). So P is taken to be the predictor variable and M is the response variable as indicated in the conceptual framework unlike in the correlation case were there was no classification of the same two variables.
Therefore, from illustration two, there exists some data analysis methodological knowledge gap for researcher one used correlation data analysis method which was and is for sure appropriate for determining the strength of a relationship. But it cannot apply for testing the level of significance of influence of one factor on another. Hence researcher two has to point out that instead of using correlation, simple regression method is more applicable. This way, the knowledge gap is filled and this justifies why researcher two is undertaking a similar study to that of researcher one for there is new knowledge added to the already existing body of knowledge.
Research findings -it was established that there was statistically significant influence of P on M. Therefore, the researcher failed to accept the null hypothesis. Ie rejected the Null Hypothesis so as the accept the Alternative Hypothesis (HA) That variable P has statistically significant influence on P.
Let us assume that both illustration one and two now represent the “existing body of knowledge” that there exists a strong positive correlation between P and M and also P has statistical significant influence on M. This assumption further will help us understand how to develop data analysis methodology knowledge gaps that can arise from these two cases.
So let’s move on again..
From past literature, researcher three came across studies by researcher one and researcher two whereby although both studies focused on P and M variables, there still existed some data analysis methodological knowledge gap as per those past studies.
One; although both researcher one and two focused on the P and M linkage, one was looking at the correlation of P and M while researcher two considered the influence of P on M and as a result, one used correlation analysis and the other simple regression analysis.
Two; although researcher two work was an improved study of researcher one, he only focused on a Bivariate model where by only one independent variable was considered in predicting the changes in
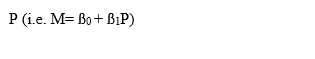
Three; use of one predictor variable may not be good enough to estimate the changes observed in the response (dependent variable). This is because in normal circumstances, changes that occur on the dependent variable (outcome variable) may not originate from only one predictor/factor. So the simple regression model cannot be the most appropriate estimator of the dependent variable.
Therefore, there exists some data analysis methodological knowledge gap for researcher one used correlation data analysis method which was and is for sure appropriate for determining the strength of a relationship. But it cannot apply for testing the level of significance of influence of one factor on another.
Similarly, the research findings of researcher two of P having statistically significant influence on M was ok. However, use of Bivariate model is not good enough to conclude that P is only influenced by P alone. Hence researcher three has to point out that instead of using simple regression method, multiple regression analysis is far much better for more than one predictor/independent variable is used to predict the outcome variable. This way the knowledge gap is filled and this justifies why researcher three is undertaking a similar study to researcher one and two for there is new knowledge added to the already existing body of knowledge.
NB: That, in Multiple regression data analysis method, Ordinary Least Square (OLS) tool or model is used to analyze the end results.
Therefore, Researcher three carried out a study to determine the factors that influence M. She sought to determine the influence of two variables, namely P and Q which were classified as the independent variables on M.
Research Question:
Does variable P and Q have statistically significant influence on M?
Specific Objective was ;
To establish the influence of P and Q on M
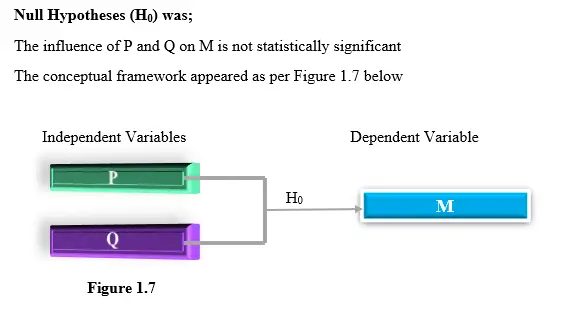
1. The specific objective to be achieved is to establish the influence of two variables, P and Q on variable M.
2. In the conceptual framework, we indicate the role of ALL the variables for we are concerned about the influence that two variables (independent variables) have on another variable (dependent variable). So both P and Q are taken to be the predictor variables and M is the response variable as indicated in the conceptual framework.
3. Although the two independent variables appear separately in the conceptual framework, this does not represent a corresponding two research questions, two research objectives and two hypotheses as witnessed in most academic research proposals/projects. CONCEPTUALLY or THEORETICALLY, the conceptual framework represent only one theory of the joint influence of P and Q on M.
Research findings- it was established that there was statistically significant influence of P and Q on M. Therefore, the researcher failed to accept both null hypotheses. I.e. rejected the Null Hypotheses so as to accept the Alternative Hypothesis (HA) that variable P and Q has statistically significant influence on M.
Similarly, let us assume that the THREE illustrations represent a wider existing body of knowledge so far. This assumption further will help us understand how to develop data analysis methodology knowledge gaps that can arise from these three cases.
So let’s move on further..
Again, from past literature, researcher four came across studies by researcher one, two and three which formed the existing body of knowledge. But still researcher four is able to incorporate new data analysis methodological knowledge gap as per the past studies undertaken by the three researchers so far.
One; some studies considered correlation, others simple regression and others multiple regression analysis methods as witnessed in the case of researcher one to three
Two; some studies used bivariate models with one predictor variable while others like researcher three used multivariate model with two predictor variables
Three; although use of multivariate model with two predictor variables is better and more appropriate in estimating changes in the dependent variable, there still exists some data analysis methodological knowledge gap for researcher three performed multiple regression whereby she ran all the two predictor variables at once either using SPSS or STATA computer program. This approach/method did not give her room to evaluate the prediction power of every incremental predictor variable considered.
Therefore, researcher four carried out a similar study like the rest but incorporate Hierarchical multiple regression model instead of just using multiple regression. This methodology has an option of portraying which predictor variable has more power to estimate the response variable for there is an option in the computer program to command significant change . In addition, use of four predictor variable is more accurate in estimating the dependent variable changes.
NB: That, in Hierarchical Multiple regression data analysis method, Ordinary Least Square (OLS) tool or model is used to analyze the end results.
Researcher four therefore aimed at interrogating on the factors influencing variable M as it was in the cases of researcher one, two and three. But researcher four feels that there are more factors than just two that influence variable M. For this matter, he proposed four variables, namely; P , Q , R and S as the predictor variables.
Does variable P, Q, R and S have statistically significant influence on M?
Specific Objective was;
To establish the influence of P, Q, R and S on M
The influence of P, Q, R and S on M is not statistically significant
The conceptual framework appeared as per Figure 1.8 below
1. The specific objective to be achieved is to establish the influence of four variables, P, Q, R and S on variable M.
2. In the conceptual framework, we indicate the role of ALL the variables for we are concerned about the influence that the four variables (independent variables) have on another variable (dependent variable). So all variables P, Q, R and S are proposed to be the predictor variables on M which is the response variable as indicated in the conceptual framework.
3. Although the four independent variables appear separately in the conceptual framework, this does not represent corresponding four research questions, four research objectives and four hypotheses as witnessed in most academic research proposals/projects. CONCEPTUALLY or THEORETICALLY, the conceptual framework represent only one theory of the joint influence of P, Q, R and S on M.
Research findings-it was established that there was statistically significant influence of P, Q, R and S taken together on M. Therefore, the researcher failed to accept the null hypothesis i.e. rejected the Null Hypothesis so as to accept the Alternative Hypothesis (HA) that variable P, Q, R and S has statistically significant influence on M.
In conclusion, under methodological knowledge gap perspective, there are many ways of the researcher like you and me to argue any case at hand and succeed. This will further be discussed in oncoming online tutorials.

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.10(11); 2020

Original research
Key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences with defining, identifying and displaying gaps in health research: a qualitative study, linda nyanchoka.
1 Universite de Paris, Paris, Île-de-France, France
2 Institute of Translational Medicine, University of Liverpool Institute of Translational Medicine, Liverpool, UK
3 Hôpital Hôtel-Dieu, Center for Clinical Epidemiology, Paris, France
Catrin Tudur-Smith
Raphaël porcher.
4 Assistance Publique—Hopitaux de Paris, Paris, Île-de-France, France
5 University of Split Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Split, Croatia
Associated Data
bmjopen-2020-039932supp001.pdf
Introduction
Mapping the current body of evidence including what is missing helps provide a better understanding of what research is available, ongoing and needed and should be prioritised. Identifying research gaps can inform the design and conduct of health research by providing additional context information about the body of evidence in a given topic area. Despite the commonly used term ‘research gap’ in scientific literature, little is written on how to find a ‘research gap’ in the first place. Moreover, there is no clear methodological guidance to identify and display gaps.
This study aimed to explore how key stakeholders define research gaps and characterise methods/practices used to identify and display gaps in health research to further advance efforts in this area.
This was an exploratory qualitative study using semistructured in-depth interviews. The study sample included the following stakeholder groups: researchers, funders, healthcare providers, patients/public and policy-makers. Interview transcripts were subjected to thematic analysis.
Among the 20 interviews conducted (20 participants), a variety of research gap definitions were expressed (ie, five main themes, including gaps in information, knowledge/evidence gaps, uncertainties, quality and patient perspective). We identified three main themes for methods used to identify gaps (primary, secondary and both primary and secondary) and finally six main themes for the methods to display gaps (forest plots, diagrams/illustrations, evidence maps, mega maps, 3IE gap maps and info graphics).
This study provides insights into issues related to defining research gaps and methods used to identify and display gaps in health research from the perspectives of key stakeholders involved in the process. Findings will be used to inform methodological guidance on identifying research gaps.
Strengths and limitations of this study
- This study used qualitative methodology that provided an in-depth understanding of key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences in identifying, describing and displaying gaps in health research.
- The study benefited from having a variety of different stakeholders participating in semistructured interviews, which provided a wider scope of perspectives and experiences in identifying, describing and displaying gaps in health research.
- This study could have benefited from involving patient/public perspectives to inform the design of the study to improve the importance and relevance of the findings for this population.
Identifying research gaps can help inform the design and conduct of health research, practice and policies by providing a better understanding of the current body of evidence. Healthcare decisions for individual patients, public health policies and clinical guidelines should be informed by the best available research while taking into account research gaps.
The identification of research gaps has no well-defined process, although research gaps serve as the basis in developing a new research question and informing future research, healthcare delivery and health policies. In addition, research gaps in healthcare do not necessarily align directly with research needs. Hence, research gaps are critical in that knowledge gaps substantially inhibit the decision-making ability of stakeholders such as patients, healthcare providers and policy-makers, thus creating a need to fill the knowledge gap. 1
Moreover, identifying and characterising research gaps often highlight multiple competing gaps that are worthwhile to be explored. 1 Initiatives such as the James Lind Alliance (JLA), UK Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments, Cochrane Agenda and Priority Setting Methods Group, and Evidence-based Research Network are some examples of existing efforts to identify and prioritise research gaps in health. 2
The term ‘research gap’ is not well defined, and its meaning can differ depending on the researcher and research context. A recent scoping review of methods used to identify, prioritise and display gaps in health research reported 12 different definitions related to gaps in health research, each describing research gaps differently. 2 This finding shows the ambiguity of the term ‘research gap’ and the different practices it may relate to.
As a basis for further exploring and understanding ‘research gaps’, we start from the definition given by the National Collaborating Centre for Methods and Tools in Canada based on the work by Robinson et al , whereby a research gap is defined as a topic or area for which missing or insufficient information limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question. 3 Given the different meanings and definitions of research gaps identified in the scoping review, 2 we considered it important to further explore key stakeholders’ perspectives to better understand the topic area. Clearly defining the type of research gap can help determine how to better identify, characterise, prioritise and address research gaps.
Different methods for identifying research gaps reported include scoping reviews and umbrella reviews for mapping and summarising evidence. These methods have an explicit aim of identifying research gaps in a broad area compared with systematic reviews, which focus on answering a specific research question. 4–8 Furthermore, investigating experiences with practices/methods used to identify research gaps can inform explicit methodological approaches in identifying and describing research gaps. This investigation can enhance practices of different stakeholder groups (ie, health professionals, health commissioners, researchers, patients/public and decision-makers) when addressing areas of uncertainty within the research problem and topic area. 9
The specific objectives of the study were to (1) investigate key stakeholders’ knowledge and perceptions of and experiences with defining research gaps and (2) characterise methods/practices used to identify and display gaps in health research.
Methods and analysis
Qualitative study design.
We conducted an exploratory qualitative study using semistructured interviews. This method was selected to provide an in-depth understanding of key stakeholders’ perspectives, experiences and practices in defining, identifying and displaying research gaps. This method also ensured that we explored key stakeholders’ understanding and practices related to identifying research gaps through a variety of lenses from different stakeholder groups. In turn, this process provided multiple facets of research gap definitions and methodological practices to identify and display gaps. 10
Study sample and recruitment
We used purposive sampling to ensure that the perspectives of all identified stakeholder groups were represented. Purposive sampling is widely used in qualitative research to identify and select information-rich cases. The study sample included the following stakeholder groups: researchers, funders, healthcare providers, patients/public and policy-makers. The stakeholder groups were determined according to the findings of a previously conducted scoping review 2 and organised into three main categories focusing on the use of evidence to inform health policy, health practice and health research ( table 1 ). A detailed description of participant categories was given in the previously published study protocol. 11 Study participants were recruited via contacts and organisations identified in the scoping review, relevant scientific publications, existing professional networks (eg, H2020 International Training Network ‘Methods in Research on Research’) and contacts from conference attendance (eg, Evidence Live and Cochrane Colloquium).
Participant characteristics (n=20)
The main inclusion criteria for the study were as follows:
- Adults aged ≥18 years (researchers, funders, healthcare providers, patients/public and policy-makers).
- Experience with the use of evidence to inform health decisions/choices, policy, practice or research.
- Ability to converse in English.
- Consent for research.
The sample size for qualitative studies usually depends on the point when data saturation is reached (ie, the point when new data do not add to a better understanding of the studied phenomenon but rather repeat what was previously expressed 12 ). Considering that the point of saturation cannot be specified in advance, we planned to conduct between 14 and 28 interviews, owing to usual points of data saturation reported in qualitative studies. 11 The point of data saturation was determined based on the seven parameters identified by Hennink et al , 13 14 including the study purpose, population, sampling strategy, data quality, type of codes, code book and saturation goal, and focus retrieved from the study. These parameters were discussed throughout the study primarily between the lead researcher (LN) and the senior researcher (DH).
Data collection and recording
Semistructured interviews were used for this study. The main reason for selecting semi-structured interviews was to allow for specific areas to be addressed while giving the interviewees the opportunity to reflect on their experiences and perspectives related to defining, identifying and presenting research gaps that are relevant to them and that may not have been explored or anticipated by the researcher(s). 15
The guide was developed by focusing on exploring key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences with the following key areas:
- Participant background information.
- Definitions of research gaps.
- Knowledge and perceptions of and experiences with methods/practices used to identify and display gaps in health research to inform further health policy, practice and research.
These three categories were developed with information from the scoping review to guide the questions. The interview topic guide was piloted before data collection. It was also adapted according to key stakeholder groups to ensure that it was meaningful to their background and to gather more relevant information based on their experiences and knowledge. 16
The semistructured interview guide contained two levels of questions: main themes and follow‐up questions. The main themes covered the general content of the research gaps aimed at encouraging participants to speak freely about their perceptions, experiences and practices. The follow-up questions were used as prompts and probes aiming to follow respondents’ answers and to investigate the issues raised more in depth. The interview guide covered the main topics of the study, providing a focused structure for the discussion during the interview. 17
We conducted in-person, telephone and teleconference interviews. In-person interviews were conducted with participants residing or reachable in London, UK, and other participants were interviewed via telephone or teleconference (for the interview guide for both in-person and teleconference interviews, see online supplemental appendix ).
Supplementary data
All interviews were digitally recorded, transcribed verbatim and anonymised. The lead researcher (LN) transcribed two interviews to help inform the analytical process, and the other audio files were transcribed by a professional transcription agency licensed from the University of Liverpool.
Data analysis
We used analytical categories to describe and explain definitions, experiences and practices reported among the groups of participants. All data relevant to each category (defining research gaps, experiences with methods/practices used to identify and display gaps in health research) were identified and examined to ensure that each data item was checked accordingly.
Our approach was based on the thematic analysis outlined by Braun and Clarke. 18 The steps included the following: (1) transcription and checking transcripts with recordings for accuracy, (2) open coding from interview responses performed by two researchers independently (LN and DH), (3) agreement of initial codes discussed among the researchers and an initial codebook developed, (4) developing the code structure used for analysing the remaining responses with openness that included new codes and refined existing ones and (5) themes and subthemes identified from the final code structure and their relationships presented. 18
The initial coding framework for our analysis started from broad categories identified in the previous scoping review with which the interviews were structured. Within these broad categories (ie, defining research gaps, experiences with methods/practices used to identify and display gaps in health research), analytical categories were inductively derived from the data. In this sense, our approach includes both top-down and bottom-up development of analytical categories and themes.
QSR International’s NVivo V.12 qualitative data analysis software was used for data management and analysis.
Ensuring study quality
To further ensure rigour and trustworthiness, the study was guided by Lincoln and Guba ’s concepts for defining and investigating quality in qualitative research that can be considered parallel to quantitative research concepts of validity and reliability. 13 19 20 The concepts include credibility, transferability, dependability, confirmability, audit trails and reflexivity. They are interrelated, and thinking through them from the onset and incorporating them into a study improve the study’s rigour.
The main researcher’s (LN) past experience as a Public Health Advisor at a National Institute of Public Health in Europe influenced the conceptualisation and conduct of this study, including the interviews. Her previous role focused on knowledge production for the health sector and providing knowledge about the health status of the population, influencing factors and how the status can be improved. She recognised the need for evidence to inform research planning, implementation and evaluation. Therefore, the design and conduct of this study were informed by her previous role and influenced the development of the interview guide, and interpretation and reporting of study findings. Throughout the different steps of the study, she consulted a senior researcher (DH) to discuss all matters related to the study design, conduct and reporting.
Patient and public involvement
Patients and the public were not involved in the design or analysis of this study. However, we involved them as study participants and will disseminate the study findings that pertain to them using a patient/public online platform, peopleinresearch.org.
Among the 30 key stakeholders contacted, 20 agreed to participate in the study. Hence, we conducted 20 interviews with 20 participants involved in using evidence for informing health policy, practice or future research ( table 1 ).
Definitions of gaps in health research
We first explored what participants reported as gaps in health research. Given the nature of our interest, all participants’ answers were grouped under a single theme ‘Definitions of Gaps in Health Research’. However, the focus of the definitions differed, and within this main theme, we identified five subthemes related to gaps in health research described by the participants (ie, gaps in information, knowledge/evidence-related gaps, quality of evidence, uncertainties and patient-related gaps; summarised in figure 1 ). The discrepancies and similarities of terms used are further illustrated in the online supplemental appendix . Terms ranged from lack of information/insufficient information, known unknowns/unanswered research questions and evidence uncertainty to treatment uncertainty, among others.

Reported descriptions of gaps in health research.
We identified some similarities among the participants on how they defined research gaps, for example, researchers and oversight bodies mainly defined gaps in health research as a lack of information/insufficient information, known unknowns and no primary studies (more information can be found in online supplemental appendix ). Patient/public participants defined research gaps in a much more literal manner, for example, ‘The gap is to get more patients involved in doing … clinical trials; have [someone] at the beginning introduce me, [educate me], [provide] awareness [because] I didn’t know what [a clinical trial] was. I [didn’t] know what they’re talking about’ (patient/public person, PPI01) and ‘Get me involved in co-production. That is the gap that is missing in clinical research’ (patient/public person, PPI01). The most common description research participants provided was the absence of scientific information to answer a research question, for example,
An area where there is missing or … insufficient information. And because of this … you cannot reach a conclusion for a question. So … it is a field, it is an area, a question an issue to which you don’t have an appropriate answer because there is missing … information or the research that still needs to be done in that particular area. (Funding body, F01)
One participant related research gaps to quality of evidence by use of Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE), an approach for rating the quality of evidence and grading the strength of recommendations in healthcare. 21 Another participant emphasised the importance of public and community involvement in gap identification to ensure that it takes into account their perspectives and contributions to the research ecosystem:
existing knowledge but not documented is of key importance in understanding the current body of knowledge on a particular topic area …. Evidence gaps need to be defined not only by [the] research community but also according to the key stakeholders including community members. Community knowledge is of key importance to inform the evidence base. Further evaluation on research findings to characterise the nature of research gaps can be carried out by evaluating community perspectives and local evidence to confirm scientific evidence. (Health research PhD student, R01)
We identified variability in participant responses on how to define gaps in health research; this variability was mainly observed in individual responses for the three main categories (research, practice, and policy and funding).
Methods to identify gaps in health research
Participants reported a range of applicable methods to identify gaps in health research (eg, surveys, reviews, syntheses, priority-setting partnerships and assessments) as shown in figure 2 . The methods were also characterised by the different research methodologies used (ie, primary, secondary and both). Participants also expressed their difficulty in identifying research gaps, for example,

Methods used to identify gaps in health research.
It is really difficult to identify research gaps. Lots of people you know will try and use the discussion section from research, [whereas] other authors have asked for further research, but in my experience that has not been a very useful method because sometimes authors will write that you know without really seeing or understanding that there has been something similar done in that field. (Health research methodologist, R02)
The variety of identified methods reflected the state of the field in the sense of the wide array of methods currently used, in line with the variety of specific goals of studies on research gaps ( figure 1 ). The difficulty in identifying research gaps raised by participants, together with the plurality of definition of gaps and range of methodologies, may, however, also reflect a possible lack of consensus and guidance on what method would be best suited for a given objective.
Methods to display gaps in health research
Participants referred to a number of different methods used to display gaps in health research (ie, forest plots, diagrams/illustrations, evidence maps, mega maps, 3IE gap maps and info graphics) ( figure 3 ). Participant perspectives varied; one of the interviewees pointed out,

Methods used to display gaps in health research.
I think with the growth of technology, it is very important to use sophisticated methods to better communicate evidence for policy-making and decision-making. I think the availability of evidence is not enough on its own and finding different methods to communicate is important, not only the analysis and findings but also sharing it in different platforms online for a greater audience. (Health policy and guideline developer, P02)
Another participant highlighted that one of the key benefits of visually presenting research is being able to immediately see what information is available and missing.
The participants mainly expressed the importance of using data visualisation in research; there was a common understanding on the use of data visualisation as a whole, particularly with the growth of technology and the need to capitalise on it. The main challenges expressed were how to identify an appropriate visualisation to present the research and also how to effectively present data. We summarise these general experiences with data visualisation in health research in figure 3 and the online supplemental appendix .
This study provides insight into issues related to defining, identifying and displaying research gaps in health from the perspectives of key stakeholders. The findings indicate several definitions of gaps in health research and methods used to identify and display research gaps.
Our study confirmed the ambiguity in defining research gaps and methodological approaches to identify 3 22 and display research gaps. 2 The methods used to identify research gaps were closely linked to the definition of research gaps. For example, the JLA method of gap identification and setting priorities for research begins by clearly defining what the alliance refers to as evidence uncertainty, that is, there is no up-to-date, reliable systematic review of research evidence addressing the uncertainty or showing that uncertainty. 23 This step further informs the rest of the methodology used and is critical in identifying treatment uncertainties and determining future research priorities. This method combines both primary and secondary approaches and not only identifies research gaps but also verifies them across different relevant stakeholders, including researchers, patients, their carers and clinicians, to ensure the relevance and potential benefit to them. 23 This verification is important, given that some research gaps may be of key interest to researchers but have little relevance and importance to patients or the public, who should be the main beneficiaries of research to improve their health and well-being.
The overall method to identify research gaps involved primary, secondary or both approaches ( figure 2 ). Most of the participants mentioned the use of secondary research methods; this is in accordance with the research that has been conducted on research gaps, which has also primarily focused on the use of secondary research and developed frameworks for identifying research gaps. 2 3 8 24 25 The most commonly adopted framework involves identifying research gaps from systematic reviews using the Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome framework to characterise a research gap. 3 The other framework involves identifying research gaps in qualitative literature reviews. 25 In addition, the GRADE approach for rating the quality of evidence and grading the strength of recommendations in healthcare 21 presents the use of a prominent framework for evaluating the certainty of evidence that can inform the research gap and characterise it. 26 Moreover, scoping reviews are commonly used, and the definition includes aiming to identify research gaps by mapping the current body of evidence. These examples focus on the use of secondary research methods, but we lack studies that specifically explore the use of primary or both primary and secondary methods to identify research gaps, yet these methods equally exist and are being used. Additional exploration of applicable methods for identifying gaps can improve their usefulness and relevance in health research.
In summary, this study showed that research gaps need to be defined by researchers and confirmed by different research stakeholders such as patients and the public to ensure societal relevance and importance. 1 We also found that clearly defining research gaps can provide information on the most appropriate methodological approach to adopt in identifying and displaying gaps, for example, for exploring research gaps in a specific or broad area. For a specific area, a systematic review can be considered, and within a broad area, an umbrella review can be considered. The study also showed that the use of both primary and secondary methods (JLA method) to identify gaps is the most robust method for gap identification. The main reported advantage of this method is that it identifies gaps (treatment uncertainties) and involves different stakeholders, including patients and the public, to confirm and prioritise gaps. The main disadvantage is that it is labor-intensive (requires a team of different specialists) and expensive (administrative support, meeting rooms and catering, among others) compared with secondary methods (evidence synthesis) or primary methods (survey).
Participants mainly expressed the importance of data visualisation in communicating research; no specific methods or formats to present gaps were expressed. Thus, the use of data visualisation is desirable among different stakeholders, particularly researchers, when communicating research, although we found few examples of experiences with developing and using data visualisation. The participants mainly expressed their difficulty in finding the right tool to use to present research findings.
Finally, although scientific articles often refer to the existence of research gaps in studies, few respondents were able to define research gaps, unless contextualising them within a specific study or area, or methods of identification. Fully understanding research gaps in health research and adequately addressing them are difficult. In this study, we highlighted three key items on the topic: (1) clearly defining research gaps provides a context to understand better what the gaps are and what they are caused by; (2) a clear definition of research gaps can inform the methods used to identify research gaps, similar to how a clear research question can inform the research study methodology; and (3) on adopting the most appropriate methods to identify research gaps, finding the right visualisation to communicate them effectively is important. Last but not least, public involvement, when applicable, is needed to verify that gaps are important and relevant to the public.
To conclude, our study found that various methods can be used to identify gaps (ie, primary, secondary and both primary and secondary). Of all the methods used to identify gaps, secondary methods are the most common, specifically systematic reviews, which are considered the gold standard in that they address a highly focused question related to the existing evidence and thus present difficulties for explicitly identifying research gaps in a general area. 3 8 27 Other secondary research methods reported were overviews of reviews, also known as umbrella reviews, scoping reviews and evidence mapping. Overviews of reviews focus on a much broader area, compiling evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document and highlighting other reviews within the specified topic area. 28 29 Given the resource requirements of formal evidence reviews, topic prioritisation is needed to best allocate resources to those areas deemed the most relevant for the health system. Regardless of the topic, the prioritisation process is likely to be stakeholder-dependent. Priorities for evidence synthesis will vary depending on the mission of the healthcare system and the local needs of the healthcare stakeholders. 1 Hence, using both primary and secondary methods is the most robust because it involves the participation of patients, caregivers and healthcare and social care professionals in identifying research questions and then prioritising them using a combination of primary and secondary research. 30–49
To advance efforts in identifying research gaps, further work and different study designs are needed to take this work to the next step, to find consensus on definitions and different practices for methods in identifying research gaps. Subsequently, also assessing the best methods according to different stakeholders will be informative and important.
One of the main challenges of this study was that because the topic area is still very vague and unclear, the recruitment and interview process was challenging. Therefore, this study was primarily limited to what participants were familiar with and not necessarily representative of the full scope of the status of health researchers, health practitioners, oversight bodies and patients/public. A more generalisable understanding of this topic area would require a larger sample of participants and methodology, such as a Delphi survey, and/or a priority-setting partnership with representatives using evidence to inform policy, practice and research. This study would also have benefited from widening the scope of the stakeholder categories (use of evidence to inform health policy, health practice and health research). 2 This would have enriched our study findings and provided a wider view of stakeholder experiences outside our categories. Another limitation of this study is not including patients/public in designing the study. Including patient/public perspectives would have benefited the study design by being able to improve the importance and relevance of the findings for this population.
One of the main strengths of the study is improving the definition of research gaps and subsequently improving the accurate reporting of research gaps to elucidate the characteristics, which can help in evidence-based decisions. For example, a decision based on a research gap contributing to lack of primary research on a specific health problem can differ from the one based on a research gap related to lack of secondary research summarising the research. Hence, all these factors regarding research gaps need to be highlighted if they are known and made explicit when disseminating and communicating research. In addition, providing more information on what the gap represents may inform users of evidence of more specific information about the research gap and how it can be addressed more accurately.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
The authors thank the interviewees for their time and input. They also thank Laura Smales (BioMedEditing, Toronto, ON) for editing the manuscript.
Twitter: @LindaNyanchoka
Contributors: LN and DH conceived the study with guidance and feedback from RP and CT-S. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This project is a part of an MiRoR (Methods in Research on Research)-funded PhD undertaken by LN. MiRoR received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under a Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant (agreement no. 676207).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Ethics approval: Informed consent was obtained in accordance with the University of Liverpool Ethics Committee board requirements. Verbal consent was sought for phone interviews and written consent for in-person interviews. Confidentiality and data protection will be ensured in accordance with the University of Liverpool Ethics Committee board. All participant information will be anonymised, and hard-copy data will be stored in a locked unit. Soft-copy material will be stored in a password-protected file. On completion of the study and publication of the study results, all study material will be stored and disposed of according to the rules and regulations of the University of Liverpool. The study protocol was stored in the data repository Zenodo. The research obtained ethical approval from the University of Liverpool, UK. This research project is part of a doctoral thesis of the PhD fellow (LN).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement: All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplemental information. Supporting data items can be found on Zenodo, https://zenodo.org/record/3664981%23.X4g7otAzY2y .
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
At the heart of this cozy coffee shop lies a big sister's love for her little brother

Yuki Noguchi

Sibling Coffee Roasters owner Libby Powell poses with her brother, Benjamin Withem, outside her West Virginia coffee shop. In her hand is an early photo of the pair — one they are trying to re-create. Susana Raab/for NPR hide caption
Sibling Coffee Roasters owner Libby Powell poses with her brother, Benjamin Withem, outside her West Virginia coffee shop. In her hand is an early photo of the pair — one they are trying to re-create.
The Science of Siblings is a new series exploring the ways our siblings can influence us, from our money and our mental health all the way down to our very molecules. We'll be sharing these stories over the next several weeks.
There's a coffee shop in the historic center of Charles Town, W.Va., where Libby Powell's family memorabilia hang from the exposed brick walls.
On one shelf, there's a photo of Libby posing with her towheaded baby brother. A jar of oatmeal-and-butterscotch cookies called Salty Siblings perches by the cash register. An elegant copper roaster parked in the shop's front bay window churns out the store's custom blends, including a popular one with Ethiopian beans named after that baby brother: The Benjamin.
Powell named this place Sibling Coffee Roasters — and it stands as a testament to one of her most cherished relationships.
Powell was already 14 and in high school when her brother, Benjamin Withem, was born 34 years ago. By that time she'd already thought a lot about the significance of having a sibling in her life. She knew, through intuition and experience, what the scientific research now shows: That this connection can deeply affect our mental and physical health over the course of our lives , for good or for ill.

Libby Powell was 14 years old and a high school student when her brother, Benjamin, was born. Susan Raab for NPR hide caption
"We have a human need to bond," she says. "Your friends are going to come and go. But when it's family, if your sibling is your friend, they're going to be there forever."
About 80% of children in the United States grow up with a sibling. It's a relationship that usually comes with shared experiences of family and childhood — and maybe also shared bedrooms and rivalries. Research about siblings' influence on our development and psychology is a relatively new field . But scientific studies show those relationships shape us in myriad ways, seen and unseen. And the impact of those relationships — good or bad — endures well beyond childhood, into middle age and beyond.

Special Series
The science of siblings.
In adolescence, siblings are very influential when it comes to risk-taking behaviors that can include things like sex or substance abuse . Even in middle age, being on good terms with our siblings continues to strongly correlate with our mental and physical well-being, especially during life transitions like a divorce or caring for ailing parents. Late in life, siblings can help support one another to maintain their health and companionship, and recounting shared memories can be a powerful antidote to loneliness .
"Siblings matter. They matter above and beyond our parents. They matter above and beyond our peers," says Shawn Whiteman, who studies human development at Utah State University.
A sibling worth waiting for
On this bustling Saturday morning, Powell picks up a bag of The Benjamin off the shelves by the cash register and reads its label: "Sibling's brotherly love blend." It is mild, in keeping with her brother's personality, with a blueberry-like flavor. "I definitely wanted that to encompass what his taste for coffee is," she says.
Powell says she once experimented with a dark roast she called "The Sibling Rivalry," but it didn't fit any part of her ethos.
"I hated it," she says. "And I don't like to fight with my brother, so I decided — we're not going to carry a dark roast."
As a girl, Powell — a Baptist preacher's daughter — yearned to have a brother or sister, and her parents, Mike and Naysa Withem, tried to have more children.

Sibling Coffee Roasters features a variety of house-made baked goods including a "Salty Sibling" cookie. Susana Raab for NPR hide caption
When Libby Powell was about 2, they started taking in foster children. Those experiences were inevitably marked by disappointment, because for one reason or another they could not stay, says Naysa Withem.
The last foster child, an older boy named James, stayed for seven years, and Powell grew up thinking of him as her actual big brother, complete with all the skirmishes and antics that come with traditional siblings.
"I remember the arguments, and getting into trouble with him, and doing things with him that were sneaky," Powell says.
But when he was 16, her foster brother chose to leave the family, a decision that left a 10-year-old Powell devastated: "I was alone. It was like all eyes were back on me, and I didn't know what that felt like because I don't think I remember being an only child." His absence, and the sense of isolation, fed her desire for siblings.
Her parents, meanwhile, were trying to have another child. "I remember my mom had gotten pregnant and I was so excited," Powell recalls. "I remember that feeling and thinking, 'I'm gonna be a big sister.'"
It was not to be: Powell was with her mother when she miscarried. "That was traumatic," says Naysa Withem.

Powell and her mother, Naysa Withem, load a display case with baked goods. Pierre Kattar/NPR hide caption
So when Baby Benjamin arrived two years later, his sister was waiting with open arms.
"I just remember just thinking: 'This is the prettiest baby I've ever seen in my life,'" she says, her voice rising with emotion. Her brother shuffles from around the counter in the shop's back kitchen and pulls her in for a tight hug.
Awash with gratitude that he was born alive and healthy, Powell says she doted on her brother like a doll, lathering him with lotions and changing his diapers and clothes.
Around the time Benjamin Withem was potty trained, Powell headed to college. Even though the time they overlapped in the same house was limited, her brother says he had developed a close connection with her that endured: "It's nice to always be reminded that you have these shared experiences that are constantly pulling you back together."

Sibling Coffee Roasters is a family affair; brother Benjamin Withem will stop by to indulge in a cold brew and chat with mother Naysa Withem, father Michael Withem, and sister and owner Libby Powell. Here, they pose in front of a quilt Naysa made for the shop. Susana Raab for NPR hide caption
An evolving relationship
The study of sibling relationships and their influence on how we think or act hasn't been as studied as other family relationships — like those between mothers and children, for example. Researching siblings also isn't easy, because no two families are alike. Variations like gender, age gap, or the number of siblings can really matter, making comparisons between families difficult and conclusions harder to draw.
One classic example where that can get complicated is birth order — something popularly believed to have a great deal of influence on our personalities. While some earlier studies suggested it might have some impact, most research doesn't bear out the idea that birth order has any lasting significance on who we become, says Utah State's Whiteman.
Still, siblings are overall very influential because they're usually our first peers. We might idolize them or battle them, but either way, through them we learn how to relate to others.
"Peers, if you have too many conflicts with them, they are just not going to be your friend anymore, but siblings really can't get away from it," says Nicole Campione-Barr, a psychologist who researches family dynamics at the University of Missouri. "So it's really one of our only training grounds socially to understand how to handle conflict in effective ways."

Powell says hello to her brother, Benjamin Withem, at her coffee shop. Susana Raab for NPR hide caption
Powell says hello to her brother, Benjamin Withem, at her coffee shop.
Libby Powell, for example, recalls how her brother used her as a sounding board — especially in his teen years, and especially after he'd made a mistake.
"If he was going to be in trouble or if he made a bad decision, he came to me first — and he was feeling out what my reaction would be," she says.
"I think he was testing the waters," she says, before having to tell their parents.
Naysa Withem, who's been watching her two children reminisce as she cleans the shop's kitchen, chimes in with a correction: "He was hoping you would cushion that with mom and dad," she says with a laugh.
The dynamics between siblings often change in young adulthood, as they explore independent paths. That was true also for Ben Withem who, after college, took a cybersecurity job in the Middle East — a world away from his sister in Charles Town.

Have a story about your sibling? Share it with us!
"That was definitely the most distance we've experienced," he says. And being that far was "almost like hitting the reset button" on their relationship, he says.
Powell found that "reset" difficult and says she felt angry. "I felt those same feelings when James left — when my foster brother left," she explains. At the same time, her brother had recently married, which meant Powell had to adjust to make room for another important person in his life. "That was hard for me because I'm sharing my little brother, who I thought that I had a little control over."

Libby Powell says that she and her brother were always close and have hardly ever fought. Susana Raab for NPR hide caption
It was the only time they remember any tension existing between them. They had one fight, which culminated with Powell accepting her brother as an adult peer.
"He was taking a stand as an adult for the first time ... and I was put exactly where I needed to be put," Powell recalls, nodding approvingly toward her brother. Benjamin Withem, the more introverted sibling, agrees silently, deferring to her memory.
Through their adult lives, coffee played a big role in keeping them connected. Withem loved good coffee, and Powell says she relied on bad coffee for decades to get her through working overnight shifts as a nurse. He tried roasting beans in his popcorn popper; she eventually began following her younger brother's lead and upgraded to their current, kitchen-table-size industrial roaster.
Powell discovered she loved the taste of her own freshly roasted beans, as well as the coffee culture and social life that surrounded it.

Powell roasts her own coffee beans at her shop in West Virginia. Pierre Kattar/NPR hide caption
"I just found that coffee — the way that he would describe it — it wasn't just a drink, but it was a relationship," she says.
When she opened Sibling Coffee Roasters five years ago, Powell saw it as a kind of extension of that relationship, a chance to share the warmth and support she associates with siblinghood. She says the shop connects her to the community she's lived in her whole life, and it gives her an excuse to talk to people about their lives and their troubles.
"I always wanted to feel cared for, and I always have felt that way," she says, "and I know that there's just way too many people out there that don't."

Powell says the coffee shop is a kind of extension of her relationship with her brother, a chance to share the warmth and support she associates with siblinghood. Susana Raab for NPR hide caption
Powell says the coffee shop is a kind of extension of her relationship with her brother, a chance to share the warmth and support she associates with siblinghood.
Sibling Coffee Roasters also reflects the dream that Benjamin Withem will eventually open up another shop as they grow old together.
It's a sentiment he shares, he says. "I see the name she picked as the open invitation."
More from the Science of Siblings series:
- The order your siblings were born in may play a role in identity and sexuality
- In the womb, a brother's hormones can shape a sister's future
- These identical twins both grew up with autism, but took very different paths
- sibling relationships
- Science of Siblings
- family and relationships
- coffee culture
- healthy relationship
- broken relationships
Money latest: The age when the average Briton pays off their mortgage revealed
The average Briton is 61 when they pay off their mortgage - a drop of two years. Meanwhile, Spotify is raising prices again. Read about this and the rest of today's consumer and personal finance news in the Money blog, and leave a comment in the form below.
Thursday 11 April 2024 22:26, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Spotify to hike subscription price by up to £24 a year
- Minimum income for family visa rises by £10,000
- Italy mourns 'end of Italian waiters in London' as visa rule brought in
- Wendy's creating 400 jobs as part of UK expansion
- The age when the average Briton pays off their mortgage
- 'WTF is going on with the price of olive oil?'
- Could I build a home gym for less than my gym membership?
- Basically... Tax codes
- Cheap Eats : Great British Menu legend shares ultimate toastie recipe
Ask a question or make a comment
Fake flights and caravans are the two most common items being sold by fraudsters in relation to travel, Lloyds Bank's research has found.
As Britons head online to book deals for the upcoming bank holidays and summer, they have been urged to "remain vigilant", with the average holiday scam victim being conned out of £765.
Amid rising flight costs post-COVID, people have been flocking to social media and other lesser-known websites to secure cheaper deals.
A food delivery company claims to have created an "unshakeable bag" to avoid spillage in transit.
Bolt, which owns the Bolt Food delivery platform, said its design is based on gyroscope technology and will keep food stable "during the most abrupt movements".
In a post to its website, the firm said it would make the design available to its competitors as it is "too powerful to be owned by any one company".
"We believe everyone should enjoy a perfect meal, regardless of which app they order it from," it said.
Assaulting a shopworker is to be made a separate criminal offence after a government U-turn following pressure from campaigners.
The government previously said "more legislative change" was not needed to tackle the "intolerable violence and abuse" faced by shopworkers, arguing it did not think it was "required or will be most effective".
But Rishi Sunak is now set to announce his government will be amending the Criminal Justice Bill to bring in the new offence.
The drugmaker was on its knees when Sir Pascal Soriot took over in 2012.
But under his leadership it now does just about everything the UK wants from a business - creating high value-added jobs and developing products that improve people's lives.
The FTSE 100's performance has lagged that of many of its peers, both in the United States and Europe, more or less since the Brexit vote in 2016.
That poor performance has reflected the poor valuation of many UK-listed companies - resulting in numerous foreign takeovers of UK businesses in recent months and years.
It has also led to a scarcity in the number of companies floating on the London Stock Exchange, most notably the Cambridge-based chip designer ARM Holdings , which last year opted to list in the US instead.
The situation has alarmed the government, which has announced a number of reforms aimed at raising the UK's attractiveness .
An imminent shareholder vote on Sir Pascal's pay makes a particularly interesting test case because few would dispute that he has been the most outstanding FTSE 100 chief executive of his generation.
This rise could take his potential earnings to £18.5m this year - which critics say is excessive.
Read my full piece here ...
England's average house price has risen by £103,000 over the last decade, while the average annual wage has risen by £7,734.
But some areas have seen homeownership affordability decline more than others...
The London borough of Barking and Dagenham has seen the most significant fall, according to moving platform Getamover.
The platform found the area has seen house prices more than double to £380,000 in the last 10 years - but wages have only risen by £2,182.
Hillingdon in West London took the second spot, with the average property shooting up by £230,000 to £495,000, while the average income increased by just £143.
While London remains the most unaffordable region, the East Midlands has also seen a notable fall.
Oadby and Wigston in Leicestershire ranked fifth in the table, with the average house price increasing by £129,000 and the median annual income growing by £2,644.
Gedling ranks sixth among the areas of England where the affordability of buying a home has declined most.
The Nottinghamshire region has seen house prices soar by 84.8% to £231,000, while the average income has risen by just 13.11% to £33,454.
You can see how other areas fared in the table below...
Rishi Sunak's post-Brexit rules for foreign workers are getting tough press in Italy this week - with claims they could mark the end of Italian waiters in London.
April saw the minimum salary requirement for a skilled worker visa increase from £26,200 to £38,700 - a near 50% rise as the government tries to reduce immigration.
Italian daily newspaper La Repubblica published an article on its site headlined "Italians in London, the long goodbye" after the new rule was brought in this month.
There were an estimated 342,000 Italians living in the UK in 2021, according to the latest Office for National Statistics census data.
La Repubblica said the new rule change would lead to the "end of the story" of Italy's "ancient roots" in the capital, which was founded by the Romans in 43 AD.
Separately, Italian journalist Antonio Polito wrote in the Corriere della Sera newspaper that the new salary for skilled workers was "an amount that no young novice can realistically earn".
"Thus London gives up one of its great assets, the fact of being an offshore and cosmopolitan city," he said.
Mr Sunak's post-Brexit rule change has worried hospitality bosses who are still struggling to get to grips with a post-COVID reality and rising costs.
Conor Sheridan, founder of Nory and Mad Egg restaurant chain, previously told the Money blog that roughly 14% of his 15,000 UK employee base were on working visas that could be affected.
Trade body UKHospitality also said the changes would "further shrink the talent pool that the entire economy will be recruiting from".
As the migration law came in, Home Secretary James Cleverly said it was "time to turn off the taps and end the flow of cheap workers from abroad".
"We are refocusing our immigration system to prioritise the brightest and best who have the skills our economy needs, while reducing overall numbers," he said.
Several of the UK's biggest supermarkets closed their gender pay gap in the last year - while Morrisons saw the biggest rise, figures show.
Ocado and Lidl reduced their gap by the largest amounts in 2023-24 compared to the previous year, while Tesco, Asda, Aldi, Co-op, Iceland and Waitrose owner John Lewis also saw a reduction.
The data comes from the government's gender pay gap service and states the difference in hourly rates of pay.
In contrast to other big-name brands, Morrisons saw its mean pay gap widen to 12.5% from 7.6%. M&S also saw a slight increase from 12.5% to 12.6%.
The mean figure gives the best overall view of the gender pay gap but includes extreme values which could skew the average.
Of the 11 biggest UK supermarkets, Co-op has the largest pay gap with 13.2%, followed by M&S and Morrisons.
An M&S spokesperson said: "We're committed to driving equal opportunities and making M&S a great place to work for women. Encouragingly our median pay gap has decreased, and women now make up more than 50% of our UK store management population, but we know there is more to do.
"We're making progress with the launch of new initiatives, talent programmes, and policies, including our flexible working offer – Worklife, a Job Share Finder, and our industry-leading family leave offer."
A spokesperson for Co-op said: "We are committed to treating our colleague member owners fairly, and this includes driving equitable outcomes for female colleagues. We've seen a significant reduction in our gender pay gap since we started to report data in 2017, and this year's data shows further progress towards closing it.
"It's important to reiterate that we don't pay people differently based on their gender at Co-op. The gender pay gap is caused by us having fewer females in leadership role, where salaries are higher.
"Our focus on improving representation remains, as we know this is one of the key drivers causing the gender pay gap. Today, 40% of our leadership population are female - this is not enough, which is why we’ve launched a series of development programmes and have a coaching and mentoring offer to support women with career progression.
"We know there’s still much to do in this space and will hold ourselves to account and continue to strive for gender equality."
Morrisons has also been contacted for comment.
Every Thursday we look at a different savings option, explain the pros and cons, and reveal the best deals on the market (see table below for that). This week we're talking about the best notice accounts. Savings Champion founder Anna Bowes says this...
As with the rest of the savings market, the top notice account rates have started to fall. However, there are stalwarts like the Investec 90-day notice account that are holding steady and as a result offering savers an opportunity to earn a little more, while not having to tie up their cash for too long.
A relatively unused aspect of the savings market, notice accounts offer a bit of a halfway house, with the best rates available generally paying more than the top easy access rates, but will more flexibility of access than a fixed term bond.
Just as it sounds, these savings accounts require you to give notice in order to access your money without a penalty. The usual notice period ranges from 30 to 120 days, although there are some accounts on the market that require six months or even a year's notice.
By Sarah Taaffe-Maguire , business reporter
Another record month for Heathrow. Last month was the busiest ever March for the UK's biggest airport, the second record-breaking month in a row.
It was also the busiest Easter weekend as Good Friday became the busiest ever direct departure day, when 118,000 people began their journey at the airport.
It shows, despite cost of living pressures, lots of Britons were going on holiday.
More good news for Heathrow came earlier this week as planned strike action by 600 border force officers was called off to allow for negotiations in its dispute over working patterns.
Oil prices are still high, hanging around $90. A barrel of Brent crude oil, the benchmark for oil prices, costs $90.66. The last time prices were this high was in the wake of the 7 October attacks and fears of conflict spreading throughout the Middle East.
On the currency front, £1 buys $1.2538 and €1.1678.
How old is the average Briton when they buy their first home, or finish paying their mortgage, or retire?
These are some of the questions answered in a "Journeying Through Life" data dump from the Office for National Statistics.
Here are some of the key takeaways...
Home ownership - including the one life event that's happening earlier
People are buying homes later in life, perhaps unsurprisingly given how house prices have risen in the last decade or so.
In 2022, more than half of people owned their own home (either with a mortgage or outright) by the age of 36.
That's a significant increase on 2004's figures - which showed the average age for home ownership was 32.
This graph shows what proportion of people own homes at what age.
It isn't all doom and gloom on the homes front, however, with the age at which people own their home outright (ie mortgage paid off) dropping from 63 (in 2004) to 61 in 2020.
This is pretty much the only life event happening earlier, however.
Retiring later
Again, this probably won't come as a huge surprise, but people are retiring later.
The age where more than half of people were retired increased from 64 in 2011 to 66 in 2021.
There has been a bigger increase in average retirement age for women (from 61 years in 2011, to 66 years in 2021) than for men (from 65 in 2011 to 66 in 2021).
The ONS says this is because the state pension age for women was increased from 60 to 66 during this time to match men.
Gender pay gap shrinking but still present
The latest data shows that men are still, on the whole, being paid more than women - although the gender pay gap is shown to be shrinking.
For all employees, the gender pay gap was 14% in 2023 - compared with 20% in 2013.
Despite the gap shrinking, this graph shows that men's hourly wages are higher than women's at nearly all ages.
The grey shaded area represents the pay gap.
Another part of the data shows that males start work a touch earlier than women - with half of males in full-time employment by the age of 23 (compared with females at 24) in 2021.
That data could be explained by the fact that more women attend university - some 319,000 females compared with 285,000 males in 2022.
Moving out, marrying and having children
The age at which young people move out of their family homes is increasing, too.
In 2011, half of people were not living with their parents at the age of 21 - compared with 24 in 2022.
More men live with their parents than women, with 61% of adults living at home in 2021 were male.
When it comes to having children, the average age at which women have their first baby has risen to 29.
That's up from an average of just 23 in 1970.
And finally, marriage.
The median age at first marriage has been steadily increasing since the 1960s.
For opposite sex couples married in 2020, the median age was 32 years for men and 30 years for women. For those entering into same-sex marriage, the median age was older, at 36 years for men and 32 years for women.
As well as getting married older, fewer people are getting married. In 2019, marriage rates had fallen to their lowest on record. For men, there were 18.6 marriages per 1,000 never-married men; for women, there were 17.2 marriages per 1,000 never-married women.
Spotify has announced it is hiking its subscription prices by up to £24 a year.
It is the second time in less than a year that the music streaming giant has increased its prices.
Here's how the prices will change...
Individual: £11.99 a month (up from £10.99 a month)
Duo: £16.99 a month (up from £14.99 a month)
Family: £19.99 a month (up from £17.99 a month)
When will the change kick in?
The subscription price will change from May and if you are an existing customer Spotify will email you and give you one-month's notice of the change.
If you are on a free trial you will pay the old price for one month once your trial ends.
A Spotify spokesperson told Sky News: "So that we can keep innovating and delivering value to fans, the music industry, and creators on our platform, we occasionally update our prices.
"We've begun communicating with existing subscribers in the UK to explain what this means for their account."
American burger chain Wendy's will be recruiting for over 400 job roles as part of its expansion across the UK.
The chain returned to the UK in 2021 after a 20-year break and has since opened just over 30 sites, including drive-throughs in Colchester, Peterborough, Derby and Brampton Hut.
But the chain, which was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1969, plans to open a further nine sites this year in Liverpool, Middlesbrough, and a second location in Sheffield.
New locations will include Liverpool, Middlesbrough and a second site in Sheffield.
Wendy's franchisee GH Burgers will open a first restaurant in Wood Green, London, this year.
There will also be restaurants in Southend-on-Sea, Colchester, Cambridge and Newcastle.
Michael Clarke, UK managing director for the Wendy's Company, told The Caterer : "We've seen great momentum in building Wendy's fandom in the UK, and the love and excitement for this iconic brand grows stronger with each new restaurant opening."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research gap is an unanswered question or unresolved problem in a field, which reflects a lack of existing research in that space. The four most common types of research gaps are the classic literature gap, the disagreement gap, the contextual gap and the methodological gap.
Research Gap. Definition: Research gap refers to an area or topic within a field of study that has not yet been extensively researched or is yet to be explored. It is a question, problem or issue that has not been addressed or resolved by previous research. How to Identify Research Gap.
A research gap is a question or a problem that has not been answered by any of the existing studies or research within your field. Sometimes, a research gap exists when there is a concept or new idea that hasn't been studied at all. Sometimes you'll find a research gap if all the existing research is outdated and in need of new/updated research ...
Identifying a research gap has many potential benefits. 1. Avoid Redundancy in Your Research. Understanding the existing literature helps researchers avoid duplication. This means you can steer clear of topics that have already been extensively studied. This ensures your work is novel and contributes something new to the field.
These are gaps in the conceptual framework or theoretical understanding of a subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand the relationship between two concepts or to refine a theoretical framework. 3. Methodological gaps. These are gaps in the methods used to study a particular subject.
Literature Gap. The expression "literature gap" is used with the same intention as "research gap.". When there is a gap in the research itself, there will also naturally be a gap in the literature. Nevertheless, it is important to stress out the importance of language or text formulations that can help identify a research/literature gap ...
Learn what a research gap is, the different types of research gaps (including examples), and how to find a research gap for your dissertation, thesis or rese...
Research gaps are areas requiring more studies or research.1 They can be: an unsolved question or problem within your field. a case where inconclusive or contradictive results exist. a new concept or idea that hasn't been studied. a new/updated research to replace the outdated existing research.
About this video. Researching is an ongoing task, as it requires you to think of something nobody else has thought of before. This is where the research gap comes into play. We will explain what a research gap is, provide you with steps on how to identify these research gaps, as well as provide you several tools that can help you identify them.
BACKGROUND. Well-defined, systematic, and transparent methods to identify health research gaps, needs, and priorities are vital to ensuring that available funds target areas with the greatest potential for impact. 1, 2 As defined in the literature, 3, 4 research gaps are defined as areas or topics in which the ability to draw a conclusion for a given question is prevented by insufficient evidence.
The identification of gaps from systematic reviews is essential to the practice of "evidence-based research." Health care research should begin and end with a systematic review.1-3 A comprehensive and explicit consideration of the existing evidence is necessary for the identification and development of an unanswered and answerable question, for the design of a study most likely to answer ...
Though there is no well-defined process to find a gap in existing knowledge, your curiosity, creativity, imagination, and judgment can help you identify it. Here are 6 tips to identify research gaps: 1. Look for inspiration in published literature. Read books and articles on the topics that you like the most.
Firstly, a research/ knowledge gap or literature gap is though different terms but has a similar meaning. The reason is that a research problem can be addressed either by experimental research and literature review. Definition: A research or literature gap is a problem or unexplored/ underexplored area of the existing research. Or . Choosing a ...
A literature gap, or research gap, is an unexplored topic revealed during a literature search that has scope for research or further exploration. To identify literature gaps, you need to do a thorough review of existing literature in both the broad and specific areas of your topic. You could go through both the Introduction and Discussion ...
Research gap definition. A research gap exists when: a question or problem has not been answered by existing studies/research in the field ; ... Since a research gap is defined by the absence of research on a topic, you will search for articles on everything that relates to your topic.
A research gap refers to an unexplored or underexplored area within a particular field of study where there is a lack of existing research or a limited understanding of a specific topic or issue ...
The gap, also considered the missing piece or pieces in the research literature, is the area that has not yet been explored or is under-explored. This could be a population or sample (size, type, location, etc.), research method, data collection and/or analysis, or other research variables or conditions.
Research gaps prevent systematic reviewers from making conclusions and, ultimately, limit our ability to make informed health care decisions. While there are well-defined methods for conducting a systematic review, there has been no explicit process for the identification of research gaps from systematic reviews. In a prior project we developed a framework to facilitate the systematic ...
A researcher identifies a research gap after conducting a thorough literature review. Then he/she formulates a clear research problem from this research gap. Therefore, the difference between research gap and research problem is the order of sequence. A research gap further justifies the research problem. Reference: 1.
1.1 Definition. Methodological research gap is the missing gap of knowledge on a more appropriate underlying method(s) which can be used in research instead of the previously one. This implies that the researcher or you as a postgraduate student may propose a method in research to address a particular aspect in life or research which is more ...
A research gap, in a certain area of literature, is defined as a topic or subject for which. missing or insufficient existing body of knowledge limits the ability to reach a conclusion. It. may ...
The term 'research gap' is not well defined, and its meaning can differ depending on the researcher and research context. ... One of the main strengths of the study is improving the definition of research gaps and subsequently improving the accurate reporting of research gaps to elucidate the characteristics, which can help in evidence ...
The application of individual tree detection algorithms for assessing forest inventories and aiding decision-making in forestry has been a subject of research for more than two decades. Nevertheless, there is a notable research gap in the development of robust algorithms capable of automatically detecting trees of different species, ages, and varied crown sizes in dense forest environments.
Research about siblings' influence on our development and psychology is a relatively new field. But scientific studies show those relationships shape us in myriad ways, seen and unseen.
The mean figure gives the best overall view of the gender pay gap but includes extreme values which could skew the average. Of the 11 biggest UK supermarkets, Co-op has the largest pay gap with 13 ...