Essay on ISRO
500 words essay on isro.
ISRO, the Indian Space Research Organization, is India’s national space agency that is located in the city of Bengaluru. Furthermore, the Department of Space Government of India controls the ISRO space agency. Let us learn more about this space agency with this essay on ISRO.

Essay On Isro

About the ISRO Space Agency
The formation of ISRO took place in the year 1969. Furthermore, the vision behind the establishment of ISRO was to develop and harness space technology in national development. Moreover, this development and harnessing of space technology were to take place while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.
ISRO is the successor of the Indian National Committee for Space Research whose establishment took place in the year 1962. ISRO now enjoys the reputation of being among the elite space agencies in the world.
As of now, ISRO is the primary Indian agency to perform activities related to the development of new technologies, space exploration, and space-based applications. Moreover, ISRO is among the only six government agencies that operate large fleets of artificial satellites, deploys cryogenic engines, undertakes extraterrestrial missions, and has full launch capabilities.
Throughout many years, ISRO incorporates space service for the benefit of the common man as well as the nation. Moreover, the maintenance of one of the largest fleets of communication satellites and remote sensing satellites takes place by ISRO. They serve the roles of fast and reliable communication as well as Earth observation.
Achievements of ISRO
The first Indian satellite that was built by ISRO was Aryabhata, whose launching took place on April 19 th , 1975. Furthermore, 1980 was another important year for ISRO because the launching of the Rohini satellite took place. Moreover, the successful placing of Rohini in the orbit took place by SLV-3.
In the year 2014 January, ISRO made use of an indigenously built cryogenic engine for GSLV-D5. Also, this was the launch of the GSAT-14 satellite . Most noteworthy, this made India one of the only six countries to develop a cryogenic technology.
Apart from technological capabilities, a lot of contribution has taken place by ISRO in the field of science. Furthermore, ISRO is in charge of its own Lunar and interplanetary missions. Moreover, ISRO controls various specific projects for the promotion of science education, and also to provide data to the scientific community.
The development of two rockets has taken place by ISRO, which are the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV). Moreover, ISRO sent Chandrayaan-1, a lunar orbiter, on October 22nd 2008, which made the spectacular discovery of lunar water in ice form.
The Mars Orbiter Mission was sent by ISRO on November 5th 2013, which made its entry into the orbit of Mars on September 24th 2014, thereby making India successful with its attempt to Mars.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on ISRO
There is no doubt that ISRO is really the pride of India. Furthermore, it has boosted the reputation of India in the world as a nation of scientific thought and development. Hopefully, ISRO will continue on its noble mission of space and technological exploration in the future.
FAQs For Essay on ISRO
Question 1: Mention some of the activities of ISRO?
Answer 1: Some of the activities of ISRO are the operation of large fleets of artificial satellites, deployment of cryogenic engines, undertaking extraterrestrial missions, and full launching capabilities.
Question 2: Mention any two satellites launched by ISRO?
Answer 2: Two satellites launched by ISRO are Aryabhata and Rohini. Furthermore, Aryabhata was the first Indian satellite that was built by ISRO. Moreover, Rohini was the first satellite whose placing took place in the orbit by SLV-3.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Indian Space Program: Phases and Achievements
Last updated on January 5, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

Indian Space Research Organization ( ISRO ) is the nodal agency and flag bearer in the Indian Space Program.
The Indian Space Program is guided by a probabilistic perspective. It is a regional development instrument. This built on an optical fibre network and wireless communication devices.
Learn more about this topic.
Also read: Aditya-L1 Mission
Table of Contents
Objectives of the Indian Space Program
ISRO has also contributed to science and science education in the country. The Department of Space oversees several dedicated research centers and independent organizations for remote sensing, astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences, and space sciences in general. the objectives of the Indian Space Program are twofold:
- Space discovery and exploration through space missions.
- Promotion of research and education related to space science in the country. E.g. Tele-education in remote areas in India.
Some of the other functions of the Indian Space Program are:
- Resource management such as mineral resources, agriculture, marine resources, etc.
- Environment conservation.
- Internal security and terrorism. E.g. use of IRNSS for regional security.
- Weather forecasting.
- Disaster Management.
Also read about SSLV , PSLV , and GSLV .
Communications satellites India
Communications satellites allow radio, television, and telephone transmissions to be sent live anywhere in the world. The purpose of communications satellites is to relay the signal around the curve of the Earth allowing communication between widely separated points. Communication Satellites use Microwaves and Radio waves for transmitting signals.
Indian National Satellite (INSAT) Series
- With nine operational communication satellites in Geo-stationary orbit, the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific area.
- INSAT System consists of 14 operational satellites, namely – INSAT-3A, 3C, 4A, 4B, 4CR, 3DR and GSAT-6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15 and 16.
- Educational TV Services
- Telemedicine Programme
- Satellite-Aided Search and Rescue
- Disaster management
- Helps in geopolitics like the SAARC satellite.
- Helps in the commercialization of space programs, like launching the communication satellites of Russia USA, etc.
Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS)
- ISRO has deployed numerous operational remote sensing satellites since IRS-1A in 1988. India now operates one of the largest constellations of remote-sensing satellites.
- IRS satellite consists of CARTOSAT, OCEANSAT & RISAT (Resource Sat) Satellites
Application of IRS satellites:
- Disaster Management Support
- BioResources and Environment survey and mapping e.g. RESOURCESAT
- Cartography e.g. CARTOSAT
- Agriculture & Soil
- Rural and Urban Development e.g. National Drinking Water mission
Important Milestones in the Indian Space Program
Phase I: 1960-70 (Incipient Stage)
- Dr. Vikram Sarabhai is regarded as a scientific visionary as well as the founding father of the Indian space programme.
- He recognized the potential of satellites after the launch of Sputnik in 1957. Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister, who considered scientific advancement as an important component of India’s future, placed space research under the jurisdiction of the Department of Atomic Energy in 1961.
- Homi Bhabha, the father of India’s atomic programme, then founded the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) in 1962, with Dr. Sarabhai as Chairman.
- The Indian space programme began establishing itself with the launch of sounding rockets in 1962, which was aided by India’s geographical proximity to the equator.
- Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) was built near Thiruvananthapuram in south Kerala.
- India developed an indigenous technology of sounding rockets called the Rohini Family of sounding rockets.
- The India Space Research Organisation (ISRO) was established in 1969, and the Department of Space was established in 1972.
Phase II: 1970-80
- Sarabhai had participated in an early NASA study on the viability of employing satellites for uses as diverse as direct television broadcasting.
- India began developing satellite technology in anticipation of future remote sensing and communication requirements.
- India’s first venture into space occurred in 1975, with the launch of their satellite Aryabhata by a Soviet launcher.
- By 1979, the SLV was ready to launch from the Sriharikota Rocket Launching Station, a newly created second launch site (SRLS).
- The first launch in 1979 failed due to a control malfunction in the second stage. This problem had been solved by 1980.
- The first indigenous satellite launched by India was called Rohini.
Phase III: 1980-90
- Following the success of the SLV, ISRO was eager to begin work on a satellite launch vehicle capable of placing a truly useful satellite into polar orbit.
- In 1987, the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV) was tested, but the launch failed. After modest adjustments, another launch attempt was made in 1988, which also failed.
Phase IV: 1990-2000
- It was not until 1992 that the first successful launch of the ASLV took place.
- Since its first successful launch in 1994, the PSLV has become the workhorse launch vehicle, launching both remote sensing and communications satellites into orbit, establishing the world’s largest cluster, and giving unique data to Indian industry and agriculture.
Developments after 2000
- In 2001, the first development flight of the GSLV took place.
- As the first attempt at exploring the solar system, India pursued a mission to send unmanned probes to the moon in 2008 namely Chandrayaan.
- ISRO has entered the lucrative industry of launching foreign payloads from Indian soil using its rockets.
- After 2010, ISRO embarked on the following programmes: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), and next-generation GSLV Mark-III launch vehicle missions are part of the launch vehicle development programme.
- The Earth Observation programme includes cutting-edge Indian remote sensing (IRS) satellites such as Resourcesat, Cartosat, Oceansat, Radar Imaging Satellite, Geo-Imaging Satellite, and weather/climate satellites such as INSAT-3DR missions.
- The satellite navigation programme consists of a constellation of seven Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) satellites and an associated ground segment designed to deliver accurate positional and timing information.
India’s Manned Mission to Space
- Three flights will be sent into orbit.
- There will be two unmanned flights and one human spaceflight.
- The Gaganyaan system module, known as the Orbital Module, would house three Indian astronauts, one of whom would be a woman.
- For 5-7 days, it will circle the Earth in a low-Earth orbit at an altitude of 300-400 km.
- In addition, to assure crew safety during the Gaganyaan mission, ISRO will perform two unmanned ‘Abort Missions’ in 2022.
Scramjet (Supersonic Combusting Ramjet) engine
- In August 2016, ISRO successfully conducted the Scramjet (Supersonic Combusting Ramjet) engine test.
- The Scramjet engine uses Hydrogen as fuel and Oxygen from the atmospheric air as the oxidizer.
- This test was the maiden short-duration experimental test of ISRO’s Scramjet engine with a hypersonic flight at Mach 6.
- ISRO’s Advanced Technology Vehicle (ATV), a futuristic-sounding rocket, served as the solid rocket booster for the supersonic testing of Scramjet engines.
- The new propulsion system will complement ISRO’s reusable launch vehicle that will have a longer flight duration.
- IN-SPACe was launched to provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- It serves as a single point of contact between the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and anyone interested in participating in space-related activities or utilizing India’s space resources.
NewSpace India Limited (NSIL):
- It is a Central Public Sector Enterprise of the Government of India that was founded in 2019 and is managed by the Department of Space.
- It is ISRO’s commercial arm, and its major purpose is to enable Indian enterprises to engage in high-technology space-related operations.
- It is headquartered in Bengaluru.
Indian Space Association (ISpA):
- ISpAaspires to be the collective voice of the Indian Space industry. ISpA will be represented by leading domestic and global corporations that have advanced capabilities in space and satellite technologies.
Amazonia-1:
- The 53 rd flight of PSLV-C51 marked the first dedicated mission for New Space India Ltd (NSIL), the commercial arm of ISRO.
- Amazonia-1, the National Institute for Space Research (INPE) optical earth observation satellite, would offer users remote sensing data for monitoring deforestation in the Amazon region and analyzing diverse agriculture across the Brazilian territory.
UNITYsat (three satellites):
- They have been deployed to provide Radio relay services.
- Satish Dhawan Satellite (SDSAT) is a nanosatellite intended to study the radiation levels/space weather and demonstrate long-range communication technologies.
Upcoming Missions:
- Chandrayaan-3 Mission: Chandrayaan-3 is likely to be launched during the third quarter of 2022.
- EOS-4 (Risat-1A) and EOS-6 (Oceansat-3) — will be launched using ISRO’s workhorse PSLV, and the third one, EOS-2 (Microsat) , will be launched in the first developmental flight of the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- These satellites will be launched in the first quarter of 2022.
- Shukrayaan Mission: The ISRO is also planning a mission to Venus, tentatively called Shukrayaan .
- Own Space Station : India is planning to launch its space station by 2030 , joining the league of the US, Russia, and China to an elite space club
- XpoSat: Space observatory, XpoSat, designed to study cosmic x-rays.
- There are five Lagrangian points between any two celestial bodies on the satellite where the gravitational attraction of both bodies is equivalent to the force required to keep the satellite in orbit without spending fuel, implying a parking area in space.
Also read: Space missions in 2024
Article Written by: Remya

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2025 (Online)
₹95000 ₹59000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2026 (Online)
₹115000 ₹69000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2027 (Online)
₹125000 ₹79000

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...

Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Achievements & Challenges
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), is the Indian space agency of the Department of Space, based in Bengaluru, Karnataka. Read all about ISRO, History, Achievements, Challenges for UPSC Exam.

Table of Contents
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, is the country of India’s space agency. It was established in 1969 to support the creation of an indigenous space project in India. The Department of Space of the Government of India oversees ISRO, a space agency with headquarters in Bengaluru, Karnataka. Its goal is to pursue planetary exploration, space science research, and national development via space technology. Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), the marketing division of ISRO, is in charge of commercialising space products, providing technical consulting services, and transferring innovations created by ISRO.
Currently, ISRO is among the top six space agencies in the world. Through a network of centres, offices, and research institutes dispersed around the nation, ISRO serves the needs of the country by maintaining one of the largest fleets of remote sensing (IRS) and communication (INSAT) satellites in the world. Broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster management, geographic information systems, navigation, cartography (maps), telemedicine, remote education satellites, and other services are all provided by ISRO.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface. LVM3 M4 vehicle successfully launched Chandrayaan-3 into orbit on July 14, 2023. Chandrayaan-3 successfully soft-landed on the south pole of the moon’s surface on August 23, 2023, and the Pragyaan Rover ramped down from the Vikram Lander and India took a walk on the moon on August 24, 2023. For detailed information about Chandrayaan-3 Mission click here.
Upcoming Missions of ISRO
The following are some of the upcoming ISRO Missions:
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Background
Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, the man responsible for launching India’s space project in the 1960s, started space research activities there. Three main elements have been a part of the Indian space project from the beginning: communication and remote sensing satellites, the space transportation system, and application programmes.
Dr. Ramanathan and Dr. Sarabhai established INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research). SITE, or Satellite Instructional Television Experiment, was run in 1975–1976. It was referred to as “the largest sociological experiment ever.” Following it was the “Kheda Communications Project (KCP),” which acted as a field laboratory for need-based and location-specific programme transmission in Gujarat.
The Department of Space was founded in 1972, although INCOSPAR was renamed the Indian Space Research Organisation in 1969 (now, ISRO is a division of the Department of Science). The following are the pivotal moments in ISRO history:
- The greatest sociological experiment ever done, SITE (Satellite Instructional Television Experiment), took place in 1975–1976.
- Gujarat is where the Kheda Communications Project was founded. The undertaking served as a field lab.
- In addition, ISRO created and launched Aryabhata, the first Indian spacecraft, utilising a Soviet launch vehicle.
- In 1980, SLV-3 made its maiden successful flight.
- Apple introduced the first satellite-based communication system.
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL), the ISRO’s marketing division, was established to advance and sell the use of space products.
- ISRO built a few specialised centres. These include the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) and the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, as well as the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) in Hyderabad, the Space Applications Centre (SAC) in Ahmedabad, and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR) in Sriharikota.
ISRO Achievements
Since the Indian Space Research Organisation was founded, its employees have worked very hard to accomplish its goals. The following missions were successfully launched by ISRO:

Communication Satellites
With nine operational communication satellites in Geostationary orbit launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system, which went into service in 1983 with the commissioning of INSAT-1B, is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific region.
The communications market in India underwent a significant transition as a result, which it sustained throughout time. The INSAT system supports telecommunications, satellite news gathering, television transmission, societal applications, weather forecasting, disaster warning, and search and rescue activities. Here are some of ISRO’s key communication satellites:
Earth Observation Satellites
Since the launch of IRS-1A in 1988, ISRO has launched a number of operational remote-sensing satellites. One of the largest satellite constellations for remote sensing is now run by India. Different instruments have been constructed and flown onboard to serve various national and international purposes in order to deliver the essential data at diversified temporal, spectral, and geographical resolutions. These satellites’ data are then utilised by ISRO for a variety of purposes, including disaster management, the management of ocean resources, forestry, environmental protection, mineral prospecting, rural development, urban planning, water resources, and agriculture.
The table below includes a list of ISRO’s significant Earth observation satellites, together with information about their launch vehicle and the date of launch:
Navigation Satellites
The Airport Authority of India (AAI) and ISRO are collaborating to build the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system in order to meet the requirements of Civil Aviation. Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) is a regional satellite navigation system being established by ISRO in order to satisfy customer requirements for positioning, navigation, and timing services based on indigenous technology.
Experimental Satellites
Many small satellites, usually for research, have been launched by ISRO. This experiment makes use of payload development, orbit controls, atmospheric research, remote sensing, and recovery technology. The following is a list of the key experimental satellites that ISRO has launched:
Small Satellites
The small satellite project will soon offer a platform for standalone payloads for science and earth imaging missions. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has developed two different bus types, the Indian Mini Satellite -1 (IMS-1) and Indian Mini Satellite – 2 (IMS-2), to offer a versatile platform for different payloads.
Here is a list of the small satellites that ISRO has launched:
Space Science & Exploration Satellites
Satellites fall within this group: The first dedicated Indian astronomy mission, AstroSat, studies celestial sources simultaneously in the X, optical, and UV spectral bands. The true first interplanetary mission of ISRO, the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), was launched on November 5, 2013. Both Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2, India’s first and second moon missions, included an orbiter, a lander, a rover, and other components.
Academic Institute Satellites
Educational institutions have been impacted by ISRO operations, such as the development of connectivity, remote sensing, and astronomy satellites. Universities and other organisations have been more interested in creating experimental student satellites as a result of the Chandrayaan-1 launch.
Here is a table listing the ISRO-launched academic institute satellites:
Scramjet (Supersonic Combusting Ramjet) Engine
The Supersonic Combusting Ramjet Engine Test, or Scramjet, was successfully completed by ISRO in August 2016. The fuel for the Scramjet engine is hydrogen, while the oxidizer is oxygen from the surrounding air. With a longer flight time, the new propulsion system will enhance ISRO’s reusable launch vehicle.
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Objective
ISRO has the ambition to develop space technology for the benefit of the country and to conduct planetary exploration and space science research. The following are the main goals of ISRO:
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), and Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) operational flights.
- To plan, create, and launch communication and earth observation satellites.
- Designing and developing fresh approaches to space transportation is another important goal of ISRO.
- To create satellites for planetary exploration and space science, as well as satellite navigation systems.
- To create tools for more accurate earth observation.
- To develop a system based on space for use in society.
- Developing proper training, education, and capacity-building programmes for students interested in space technology is one of ISRO’s main goals.
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) Challenges and Opportunities
Even though ISRO’s success stories are celebrated all over the world, the organisation still faces obstacles in accomplishing its objectives. The Indian Space Programme has the following problems and opportunities:
- India is not in a situation where it is facing specific security and development concerns since it is a developing nation. For instance, ISRO is called into question and forced to defend the funding for missions that need a lot of work but have little to do with development.
- Since China tested an anti-satellite missile (ASAT) in 2007, the country has upped the threat level. In addition to the one on the ground, it can start in space. There have been military weaknesses since India relied on satellites like MOM.
- The US or other nations must cooperate with the DRDO while it develops a missile.
- China launched the satellite in 2011 and 2012 to target Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) UPSC
One of the most significant scientific institutions in the nation and a recent boon to India is ISRO. The ISRO-launched satellites have been successful in gathering the needed information, making them a crucial component of India’s development. Being so important for the nation, it is also a key subject for UPSC hopefuls because many questions from the ISRO UPSC notes are asked in the IAS Exam.
Sharing is caring!
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) FAQs
What does isro stands for.
The Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, is the country's space agency and is located in Bengaluru, Karnataka. The ISRO's goal is to perform planetary exploration and space science research while using space technologies to advance national development.
Is Chandrayaan-3 successful?
"India successfully launches Chandrayaan-3 marking another significant milestone in space exploration.
How many centres are there in ISRO?
There are six main centres within ISRO. These include the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), the Space Applications Centre (SAC), the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR), and the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) in Hyderabad.
When was ISRO Formed?
On August 15, 1969, Dr. Vikram A. Sarabhai founded ISRO. The Indian government did, however, create the Department of Science and the Space Commission in 1972. ISRO was established under the Department of Science on June 1st, 1972.
What is main Objective of ISRO?
The Indian Space Research Organization's main goal is to create space technology in order to meet various national demands. To accomplish this, ISRO has created INSAT and the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite System.
- science and tech

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024

Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
Indian Space Research Organisation [ISRO Notes for UPSC]
ISRO is an important body in India and spearheads research in space science in India, also playing a huge role in the development of the country through educational, agricultural, communication, and defence sector projects. Hence, it is an important segment of UPSC science and technology syllabus.
ISRO or Indian Space Research Organisation is India’s space agency founded in 1969 to help develop an indigenous Indian space program. It is one of the 6 largest space agencies in the world today. ISRO maintains one of the biggest fleets of remote sensing (IRS) and communication (INSAT) satellites catering to the needs of the nation through a network of centres, offices, and research institutes in different parts of the country. ISRO functions in the following areas: broadcasting, weather forecasting, disaster management, geographic information systems, navigation, cartography (maps), telemedicine, distance education satellites, etc.
ISRO – UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
ISRO is headquartered in Bengaluru.
ISRO Chairman: Dr K Sivan (who is also the Secretary of the Department of Space, GOI)
ISRO Latest News
The decommissioned weather satellite Megha-Tropiques-1 has been brought down by ISRO. Read more about this development here .
ISRO Formation
- The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1962 under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Eminent scientist Dr Vikram Sarabhai had a big role in this development. He understood the need for space research and was convinced of the role it can play in helping a nation develop.
- INCOSPAR set up the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) at Thumba, near Thiruvananthapuram at India’s southern tip. TERLS is a spaceport used to launch rockets.
- The INCOSPAR became ISRO in 1969.
- The Department of Space was created in 1972 and ISRO became a part of it and remains so till date. The Space Department reports directly to the Prime Minister of the country.
- During 1975-76, Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) was conducted. It was hailed as ‘the largest sociological experiment in the world’. It was followed by the ‘Kheda Communications Project (KCP)’, which worked as a field laboratory for need-based and locale-specific program transmission in the state of Gujarat State.
- During this phase, the first Indian spacecraft ‘Aryabhata’ was developed and was launched using a Soviet Launcher.
- Another major landmark was the development of the first launch vehicle SLV-3 with a capability to place 40 kg in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which had its first successful flight in 1980.
- ’80s was the experimental phase wherein, Bhaskara-I & II missions were pioneering steps in the remote sensing area whereas ‘Ariane Passenger Payload Experiment (APPLE)’ became the forerunner for the future communication satellite systems.
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL) is a Marketing arm of ISRO for promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
ISRO has many facilities each dedicated to a specialized field of study in space. A few of them are as follows:
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram – The space research activities were initiated in India under Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, the founding father of the Indian space program, during 1960s.
- Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), Thiruvananthapuram
- Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR), Sriharikota
- Space Applications Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad
- National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), Hyderabad
ISRO Milestones
- The first Indian-made sounding rocket was the RH-75 (Rohini-75). It was launched from TERLS in 1967. It weighed just 32 kg. Series of Rohini Sounding Rockets were developed by ISRO for atmospheric and meteorological studies.
- ISRO built its first satellite in 1975 and named it Aryabhata. This was launched by the Soviet Union.
- The first Indian-built launch vehicle was SLV-3 and it was used to launch the Rohini satellite in 1980.
- ISRO launched its first INSAT satellite in 1982. It was a communication satellite. It was named as INSAT-1A, which failed in orbit. The next communication satellite INSAT-1B was launched in 1983.
- Established in 1983 with commissioning of INSAT-1B, the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific region with nine operational communication satellites placed in Geostationary orbit. Details regarding INSAT – 1B are available on the linked page. The INSAT system provides services to telecommunications, television broadcasting, satellite newsgathering, societal applications, weather forecasting, disaster warning and Search and Rescue operations.
- ISRO also launched the first IRS (remote-sensing satellite) in 1988.
- ISRO has developed three types of launch vehicles (or rockets) namely, the PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle), the GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mark III or LVM). Further details on GSLV MK III are available on the link provided here.
- ISRO launched its first lunar mission Chandrayaan I in 2008.
- It also launched the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or the Mangalyaan in 2014. With this, India became the first country to achieve success in putting a satellite in the Mars orbit in its maiden attempt and the fourth space agency and the first space Asian agency to do so. Read the details on Mangalyaan Mission here.
- ISRO has launched many small satellites mainly for experimental purposes such as INS-1C, Aryabhatta, APPLE, Rohini Technology Payload, YOUTHSAT, etc. The experiment includes Remote Sensing, Atmospheric Studies, Payload Development, Orbit Controls, recovery technology and more.
- Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine – In August 2016, ISRO successfully conducted the Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) engine test. It uses Hydrogen as fuel and Oxygen from the atmospheric air as the oxidizer. ISRO’s Advanced Technology Vehicle (ATV), which is an advanced sounding rocket, was the solid rocket booster used for the test of Scramjet engines at supersonic conditions. This test was the maiden short duration experimental test of ISRO’s Scramjet engine with a hypersonic flight at Mach 6. The new propulsion system will complement ISRO’s reusable launch vehicle that would have a longer flight duration. Read in detail about the Advance Technology Vehicle of ISRO on the given link.
- In 2017, ISRO created another world record by launching 104 satellites in a single rocket. It launched its heaviest rocket yet, the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-Mark III and placed the GSAT 19 in orbit.
- India’s Manned Mission to Space also termed as Gaganyaan, this project is part of the government’s ambition to make India a global low-cost provider of services in space. The launch vehicle for this mission will carry heavy payloads into space. For this purpose, GSLV Mk-III is being developed with a cryogenic engine. ISRO has already tested the GSLV Mk-III with experimental crew module (Re-entry & Recovery technology) and Crew Escape System (CES). Detailed information on Gaganyaan Mission is available on the linked page.
Also read the List of Indian Satellite From 1975 to 2021 on the given link.
Candidates can go through a few more achievements of ISRO mentioned below –
- ISRO has launched many operational remote sensing satellites, starting with IRS-1A in 1988. Detailed information on IRS-1A – the first indigenous remote sensing satelite is available on the linked page. Today, India has one of the largest constellations of remote sensing satellites in operation. The data from these satellites are used for several applications covering agriculture, water resources, urban planning, rural development, mineral prospecting, environment, forestry, ocean resources and disaster management.
- Navigation services are necessary to meet the emerging demands of the Civil Aviation requirements and to meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation and timing based on the independent satellite navigation system. ISRO worked jointly with Airport Authority of India (AAI) in establishing the GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) system to meet the Civil Aviation requirements. Similarly, it established a regional satellite navigation system called the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) to meet the user requirements of the positioning, navigation and timing services. Know more on IRNSS-NAVIC on the linked page.
- ISRO has influenced educational institutions by its activities like making satellites for communication, remote sensing and astronomy. The launch of Chandrayaan-1 increased the interest of universities and institutions towards making experimental student satellites. Some important Academic Institute Satellite are – Kalamsat-V2, PRATHAM, SATHYABAMASAT, SWAYAM, Jugnu, etc.
Go through the information on Satellite Launch Vehicle Program on the linked page.
ISRO Vision & Objectives
ISRO’s vision is stated as “Harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.”
ISRO Mission
- Design and development of launch vehicles and related technologies for providing access to space.
- Design and development of satellites and related technologies for earth observation, communication, navigation, meteorology and space science.
- Indian National Satellite (INSAT) programme for meeting telecommunication, television broadcasting and developmental applications.
- Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) programme for management of natural resources and monitoring of environment using space-based imagery.
- Space-based Applications for Societal development.
- Research and Development in space science and planetary exploration.
FAQ about ISRO
Who is considered as the “founding father” of indian space programme, how the objectives od isro are met.
Related Links
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Essay on Isro the Pride of India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Isro the Pride of India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Isro the Pride of India
Introduction.
ISRO, or Indian Space Research Organisation, is India’s national space agency responsible for creating and launching Indian satellites.
ISRO has successfully launched several satellites like Aryabhata, INSAT and IRS, contributing to progress in various fields.
Spacecrafts
ISRO’s spacecrafts like PSLV and GSLV send these satellites into orbit, demonstrating India’s growing space capabilities.
Exploring the Moon
ISRO’s lunar missions, Chandrayaan-1, 2 and 3, significantly advanced moon research and exploration.
Beyond Earth
ISRO has dared to explore other planets with missions like Mangalyaan and Aditya-L1.
Human Spaceflight
ISRO’s Gaganyaan mission plans include astronaut space travel.
ISRO, indeed, is the pride of India.
250 Words Essay on Isro the Pride of India
Isro: india’s glory.
The Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, makes India shine brightly on the world stage. Established in 1969, it’s a place where India’s smartest scientists work on unveiling the mysteries of space.
Space Science Journey
ISRO started with small steps. In 1975, they sent Aryabhata, India’s first satellite, into space. Today, they have numerous satellites working for the country, from INSAT for communications to IRS for earth imaging and GSAT for internet connectivity. The IRNSS or NavIC helps with navigation and the RISAT series provide critical data on agriculture and disaster management.
Success with Launch Vehicles
ISRO has also shown proficiency in creating launch vehicles. They started with the SLV, India’s first launch vehicle, and have made considerable strides since then. The PSLV can transport multiple satellites into different orbits and the GSLV brings heavier satellites to geostationary orbits. Moreover, the GSLV Mk III, the heaviest vehicle, and SSLV for smaller satellites have also been created.
Lunar and Interplanetary Missions
The Chandrayaan missions showed us the moon like never before. While Chandrayaan-1 found evidence of water, Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed a rover on the moon’s south pole. ISRO’s journey to Mars was completed with the successful Mangalyaan mission. Another achievement was the Aditya-L1 mission to study the Sun.
ISRO has advanced towards human space exploration too. The ambitious Gaganyaan mission aims to send three astronauts into space. With all the developments and preparations underway, the mission is waiting for the right moment to launch.
In conclusion, ISRO’s hard work and innovative advancements in space research make it the pride of India.
500 Words Essay on Isro the Pride of India
A true gem in India’s crown, ISRO, the Indian Space Research Organisation, elevates India’s standing on the global stage. ISRO symbolizes the very spirit of India – innovative, resilient, and forward-looking.
What is ISRO?
ISRO is India’s national space agency. Its central job is to make and use space technology for the good of all Indian people. The Prime Minister of India oversees ISRO’s work, and it serves as the main arm for research and development for the Department of Space.
Achievements in Satellite Technology
ISRO has accomplished a lot in satellite technology. It started with launching Aryabhata, India’s first satellite in 1975. Then it built the INSAT and IRS systems. These systems help with communication, disaster warnings, and studying the Earth’s resources. Later, ISRO built the GSAT system for better internet and TV. It made the NavIC system to give us accurate location details and the RISAT system for all-weather imaging capability.
Launch Vehicle Technology
ISRO also shines in launch vehicle technology. It started with SLV, India’s first vehicle for launching satellites in 1980. Then, it made PSLV and GSLV, able to carry multiple satellites into different orbits. The GSLV Mk III, our most powerful vehicle, can carry heavier things into space. ISRO now is working on SSLV, a small vehicle for launching small satellites.
ISRO made the world sit up with its lunar missions, Chandrayaan-1, Chandrayaan-2, and Chandrayaan-3. They focused on studying the moon and, remarkably, found water. It also launched Mangalyaan, India’s first mission to Mars, and Aditya-L1, our first solar mission.
Human Spaceflight Programme
ISRO’s next big goal is the human spaceflight programme called Gaganyaan. The key aim is to send three astronauts to space by 2022. ISRO has made robust preparations for this, creating the tech and the facilities needed.
Impact on India
ISRO’s work doesn’t just bring us prestige. It helps us in tangible ways, aiding communication, studying the Earth, warning against disasters, and more. It has also opened up new opportunities in space research.
ISRO is truly India’s pride. Its amazing work has boosted India’s standing and given us a vision of a bright future. We can all draw inspiration from ISRO to keep learning, striving, and aiming high, in our own small ways, for our country.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Indian Villages
- Essay on Indian Judiciary System
- Essay on Indian Freedom Fighters
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
It’s not about the accomplishments if it is written so you mention in the essay
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- English News
ISRO’s 15 greatest achievements till date
- The first rocket launched by ISRO in 1963, from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launch Station (TERLS) later named as the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC).
- First Indian satellite named Aryabhata was launched from Kapustin Yar of Russia.
- In 2016, ISRO successful tested Reusable Launch Vehicle, Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD)

Indian Space Research Organisation is one of the leading space agencies in the world that created a world record on February 15, 2017, with the successful launch of 104 nano satellites using PSLV C37. This was the 39th mission of the PSLV and is a path breaking solution for commercially efficient and low-cost satellite launch.
Since the first rocket launched on November 21, 1963, from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launch Station (TERLS) later named as the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) to the recent launch from Sriharikota, ISRO has made India proud with its remarkable achievements despite various hurdles.
Here are the 15 achievements of ISRO that has made every countryman proud.
1. In early 1970 under the leadership of APJ Abdul Kalam, the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) project was initiated. The aim of this project was to develop the necessary technology to launch satellites.
2. In 1975, first Indian satellite named Aryabhata was launched from Kapustin Yar of Russia. This satellite was built by ISRO to enhance its experience in building as well as operating a satellite in space.
3. In 1992, ISRO successfully launched Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV) carrying SROSS-C satellite. The same year also witnessed the successful launch of Insat – 2A, India’s first satellite of indigenously-built second generation Insat series.
4. In 2001, ISRO successfully launched heavy rocket Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) with GSAT-1 satellite.
5. In 2008, Chandrayaan, country’s first unmanned lunar probe was launched by ISRO. With this success, ISRO became joined the list of six space organisations who achieved this feat.
6. In 2009, ISRO launched the beta version of Bhuvan, a software application similar to Google Earth. Users can explore the 2D and 3D representation of earth surface using this app.
7. In the same year, ISRO scientists found three new bacteria species in the upper stratosphere of earth. These three bacteria are highly resistant to ultra-violet radiation and can’t be found on earth.
8. In 2012, ISRO successfully launched the 100th space mission using PSLV-C21 rocket and placed two foreign satellites into the orbit of the earth.
9. 2013 turned out to be a year of highest achievement for ISRO with the successful launch of the ₹450-crore Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called Mangalyaan by using PSLV-XL.
10. In 2014, the Mangalyaan successfully entered the Martian orbit, and India became the first country to complete a maiden Mars mission.
11. In 2015, ISRO launched its satellite-based air navigation services GAGAN (GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation Satellite System) and joined the elite group of US, Japan a and the European Union who have similar systems.
Also READ:
12. In June 2016, India set a record for itself with the successful launch of 20 satellites in one mission.
13. ISRO in 2016, also launched Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System for marine navigation, vehicle tracking, disaster management, fleet management and navigational aid for drivers.
Also CHECK:
14. The same year also saw the successful testing of Reusable Launch Vehicle, Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD) and it is called India’s space shuttle.
15. On February 15, 2017, India broke the record of Russia by successfully launching 104 satellites of seven countries in one mission. The success of this mission might forever change commercial satellite launch industry in space technology.
RELATED STORIES

WhatsApp update: Messaging app working on new feature to find favourite contacts faster

Apple announces ‘Let Loose’ launch event on May 7; Here's what you can expect

Good news for Apple fans in India: Tech giants to open stories in Bengaluru and Pune soon, says report

After fake SMS scam, Govt now warns against fake banking apps and fraudulent stock trading platforms

Tech giants TCS, Infosys and Wipro see combined headcount drop of 64,000 in FY24
Recent Stories

IPL 2024, DC vs MI Preview: Playoff race heats up as confident Delhi Capitals face struggling Mumbai Indians

Did Tamil star Simbu spend Rs 6 crore on Hansika Motwani while they were dating?

PM Modi asks Indians to 'never forget, forgive' Congress for looting, weakening security & mocking culture

IPL 2024: 'Aaj batting tera Jassi bhai karega!' MI's Jasprit Bumrah shows off skills ahead of DC clash (WATCH)
![Lok Sabha Elections 2024: Leaders, people cast their votes [PHOTOS] RKN Lok Sabha Elections 2024: Leaders, people cast their votes [PHOTOS] RKN](https://static-ai.asianetnews.com/images/01hwcv17qc3jpg7rmyfmqtjs6y/fotojet---2024-04-26t144533-261_180x120xt.jpg)
Lok Sabha Elections 2024: Leaders, people cast their votes [PHOTOS]
Recent Videos

Narendra Modi EXCLUSIVE! 'I cannot accuse Christians of not supporting BJP'

Narendra Modi EXCLUSIVE interview: 'I am not an astrologer, but I understand the vibrations' (WATCH)

EXCLUSIVE! PM Narendra Modi corrects 3 misconceptions about BJP (WATCH)

Rajeev Chandrasekhar Exclusive! 'People in Kerala are angry, fed up with Left and Congress' (WATCH)

Narendra Modi Exclusive! PM EXPOSES Left in Kerala; Congress and Communists two sides of the same coin'

Essay on ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization)

ISRO stands for Indian Space Research Organization; it is a space agency that comes under the Department of Space (DOS). ISRO is known for conducting economical programs and is responsible for managing space affairs in India. One of the main achievements is conducting a successful landing on Mars on the first attempt also being the least expensive Mars Mission in the world. ISRO is also responsible to carry out communication satellites and is supposed to work with DRDO to watch out for the security of India.
Short and Long Essay on ISRO in English
Here is a long essay mentioning the history and importance of ISRO to India.
10 Lines Essay on ISRO (100-120 Words)
1) The space-related affairs of India are managed by an agency known as ISRO.
2) ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) was set up on 15 August 1969.
3) The headquarters of ISRO reside in Bangalore.
4) ISRO’s current serving chairman is Shri S. Somanath (2022).
5) Aryabhatt is India’s first satellite developed by ISRO.
6) ISRO has discovered two moon missions.
7) DoS or the Department of Space is responsible for monitoring and managing ISRO.
8) Recently, ISRO has successfully completed Mars Mission.
9) IRS, INSAT, GAGAN, etc are some pride projects of ISRO.
10) ISRO holds 5 launch vehicles out of which three are operational launch vehicles.
Long Essay on Indian Space Research Organization – 1300 Words
Introduction
ISRO is also called Bhartiya Antariksh Anusandhan Sangathan in Hindi. It is directly seen by the Prime Minister of India. The current chairman, Dr. Kailasavadivoo Sivan also known as K Sivan is also an executive member of the Department of Space (DOS). ISRO holds the record for being one of the agencies with Full Launch capabilities, the ability to launch extraterrestrial missions and can operate a big cortege of artificial satellites.
ISRO boasts 5 launch vehicles namely Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV), Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV), Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) and Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV-MK III). Among those, 3 are operational launch vehicles which are mentioned below-
- PSLV – Stands for Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, it is a third generation launch vehicle and was first launched in the year 1994. Till 2017, it has launched 257 satellites in which 48 are Indian satellites and 209 are foreign. It is well known for its successful launch of Mars Orbiter Spacecraft in 2013 and Chandrayan-1 in2008.
- GSLV – Also known as Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle Mark II (MKII) was launched first on 18 th April 2001. Since then it has been in 13 missions and holds the record for having success in 4 missions consecutively.
- GSLV-MK III – Was chosen to launch the Chandrayan II and has the twice the capacity of GSLV MK II and was launched in the year 2014 for the first time.
History of ISRO
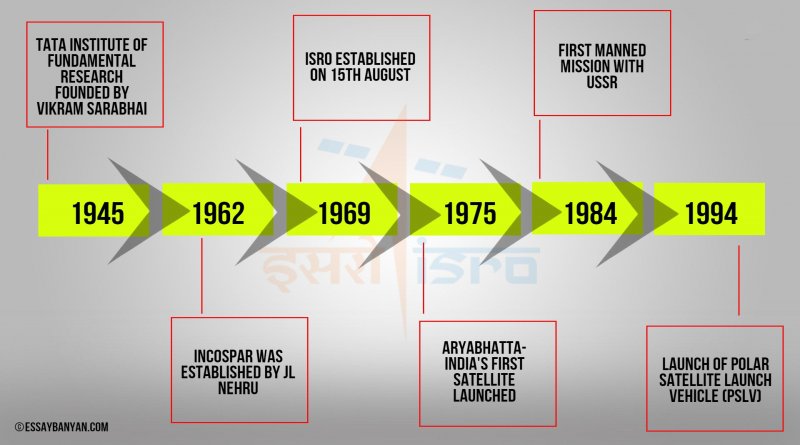
Earlier scientists like S.K. Mitra, C.V. Raman, and Meghnad Saha used to carry space programs. Later Vikram Sarabhai founded Physical Research Laboratory at Ahmedabad. Homi Bhabha established the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research in 1945.
In 1962, the urge of the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by PM Jawaharlal Nehru. Later in 1963 sounding rocket was launched from Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS). On 15th August 1969 Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) was established.
One of the biggest landmarks was seen when ISRO sent its first satellite ‘Aryabhatta’ with a Soviet Rocket in the year 1975. Later, in the year 1982, Indian National Satellite (INSAT-1A) was launched. ISRO collaborated with the Soviet Union to conduct the first manned mission in 1984 in which Rakesh Sharma was a part of it.
In 1994, ISRO conducted the launch of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the third generation of launch vehicles. Moving to 2001, ISRO managed to successfully launch GSLV D1. ISRO stepped on the moon in the year 2008 and in 2014 ISRO managed to land on Mars.
Role of ISRO in the Advancement of India
ISRO’s role in the Advancement of India cannot be forgotten from Aryabhatta to NavIC. Here are some of the projects that became a landmark and helped India in modernization.
- IRS – the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) is a series of Earth observation satellites from India. The IRS line provides remote sensing services and is the largest set of residential remote sensing satellites in use today in the world. They have a wide range of applications which are beneficial for different purposes.
- INSAT – The Indian National Satellite System (INSAT) is the Indian family of communication satellites. The project jointly includes DOS, DOT, MBI and Prasar Bharti. It is a multipurpose geostationary satellite helpful in different needs like telecommunications, broadcasting and research. These satellites have been put to good use by the Indian armed forces. GSAT9 or “SAARC Satellite” is a notable example of communication services to India’s small neighbors.
- GAGAN – GAGAN stands for GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation. It is a GPS Satellite Augmentation System working regionally; it has satellite communication and air traffic management plan for the aviation industry ‘civil Aviation. The Indian system SBAS, space Augmentation System.
Achievements of ISRO
India is prideful to have ISRO as it has given us many reasons to feel pride. ISRO has always delivered whenever India wanted to do something, ISRO never failed to surprise us. Be it the cheapest landing on Mars or finding water on Moon, ISRO has done many works. Here are some of the Achievements that ISRO must be proud of.
- Mars Orbital Mission (MOM) – The Mars Orbital Mission or Mangalyan is one of the biggest successes for ISRO. ISRO achieved the target of reaching Mars in the most economical way and became the first space agency to reach mars in the first attempt. The budget was 450 crores which is less than many Hollywood movies making India the 4 th country to reach on Mars. There is a movie made to highlight the landing of Mangalyan naming Mission Mangal.
- 104 satellites in 1 Mission – ISRO in 2017 created history as it launched 104 satellites in 1 goes. ISRO used its Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle to perform this target. Among 104 satellites, 101 were foreign and 3 were Indian.
- Water on Moon – India’s Chandrayan I mission was launched on 14 th November, 2008. It landed on the south pole of the moon and founded hydroxyl absorption lines on the surface. It was later confirmed by NASA, when M 3 sent data on 25 th September, 2009.
Budget Allocations
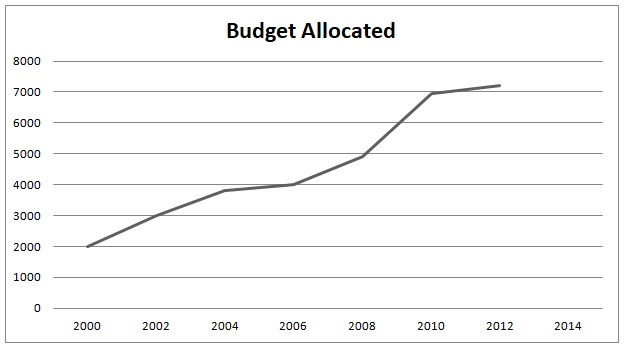
If an organization is this big that the world praises and hails its works, then it will definitely need a good amount of budget. Indian government never failed to provide that. Although, the Mars Orbital Mission was inexpensive but now the budget is not a big issue. The 8,228 Crore expenditure which was allocated for 2020-21, increased to 13,949 Crore for 2021-22. A new public sector named New Space India Limited (NSIL) got an allocation of Rs 700 crores for the same term.
ISRO – The Pride of India
Mentioning ISRO as a pride of India is no doubt a big statement. ISRO is something that India will always boast of. ISRO has been regarded as one of the fastest-growing space agencies in the world and can change the space race. Below mentioned points tell why India considers ISRO a pride.
- ISRO’s mars mission was so cheap that it took only Rs 7/km to reach mars.
- SUPARCO of Pakistan was established 8 years earlier than ISRO but the capabilities of launching satellite will be developed by 2040.
- ISRO is planning to launch Human Spaceflight program in 2023 which might make India the 4 th country to send humans in Space.
- ISRO works closely with Defence Research Development Organization for India’s defence and they have signed an MOU for the upcoming Gaganyan Mission.
- ISRO is also planning to launch its Space Station soon after the Gaganyan mission.
ISRO has always stunned everyone with its unbelievable achievements. However, they have failed many times but it didn’t affect them. ISRO has always learned from the setbacks and just as the diamond shines, it kept shining. The Indian government has also supported ISRO and past few years, the budget allocations are majorly focused. An Indian person sees ISRO scientists as supermen and respects them whenever they get to meet them. ISRO is supposed to compete with NASA in near future and it can be a matter of respect for all of us.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. ISRO is the National Space Agency which mainly focuses on space affairs in India.
Ans. ISRO stands for Indian Space Research Organization.
Ans. ISRO was established on 15th August 1969.
Ans. The chairman of ISRO is Dr. K. Sivan.
Related Posts
Essay on digital india, cashless india essay, essay on child is father of the man, essay on causes, effects and prevention of corona virus, essay on dr. sarvepalli radhakrishnan, durga puja essay, essay on summer vacation, essay on my plans for summer vacation, essay on holiday.
- Bihar Board
SRM University
- NBSE Result 2024
- MP Board 10th Result 2024
- MP Board 12th Result 2024
- TS Board Results 2024
- NBSE Board Result 2024
- UK Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- School Life
Essay on Aditya L1 for School Students: India’s First Solar Mission by ISRO
Essay on aditya l1 mission in english: isro has launched aditya l1 - india's first observatory class space based solar mission on september 2, 2023 at 11.50 am from sriharikota, andhra pradesh, india. get here a unique and easy essay in english along with all details regarding aditya l1 launch date, time, place, etc..

Essay on Aditya L1 Mission: Following the successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 and its commencement of lunar studies, ISRO is now embarking on an exploration mission to investigate the Sun's surface. ISRO has launched the PSLV Rocket from SriHarikota, Andhrs Pradesh, India at 11.50 am on 2nd September, 2023. The rocket will reach the Lagrange point L1 after about four months and will conduct its study from this point.
Essay on Aditya L1 in English
Details about aditya l1 mission.
- About Chandrayaan 3 Essay in English for School Students
- चंद्रयान 3 पर हिंदी निबंध और भाषण: Chandrayaan 3 Essay in Hindi for School Students
Why is ISRO’s Aditya L1 Mission So Unique?
- First time spatially resolved solar disk in the near UV band.
- CME dynamics close to the solar disk (~ from 1.05 solar radius) and thereby providing information in the acceleration regime of CME which is not observed consistently.
- On-board intelligence to detect CMEs and solar flares for optimised observations and data volume.
- Directional and energy anisotropy of solar wind using multi-direction observations.
Major Objectives of Aditya L1 Mission
- Understanding Coronal Heating and Solar Wind Acceleration.
- Understanding initiation of Coronal Mass Ejection (CME), flares and near-earth space weather.
- To understand coupling and dynamics of the solar atmosphere.
- To understand solar wind distribution and temperature anisotropy.
Our Sun, the nearest star and the largest object in our solar system, is approximately 4.5 billion years old. It consists of hot, glowing hydrogen and helium gases and is located about 150 million kilometers away from Earth. The Sun is the primary source of energy for our solar system, and life on Earth relies on this solar energy. Additionally, the Sun's gravitational force is responsible for holding all the objects in our solar system together.
The core of the Sun, situated at its central region, reaches incredibly high temperatures, around 15 million degrees Celsius, where a process known as nuclear fusion occurs, providing the Sun's power. In contrast, the visible surface of the Sun, called the photosphere, is relatively cooler, with a temperature of approximately 5,500°C.
Why Is It Important To Study The Sun?
Studying the Sun, our nearest star, offers a unique opportunity to gain insights into stars not only in our Milky Way but also in other galaxies. The Sun is a highly dynamic star, exhibiting eruptive phenomena and releasing vast amounts of energy into the solar system. These solar eruptions, if directed towards Earth, can disrupt near-Earth space environments, affecting spacecraft and communication systems. Early warning systems are crucial to mitigate these potential disturbances.
Furthermore, exposure to such explosive solar events poses risks to astronauts. The Sun's extreme thermal and magnetic phenomena provide a natural laboratory for studying processes that cannot be replicated in a controlled laboratory setting. Hence, studying the Sun serves both as a window into stellar behavior and as a means to understand extreme natural phenomena with practical implications for space exploration and communication.
Why Is It Important To Study The Sun From Space?
The Sun emits a wide range of radiation, including light across various wavelengths, energetic particles, and a magnetic field. Earth's atmosphere and magnetic field act as protective barriers, blocking many harmful radiations, particles, and fields from reaching the planet's surface. Consequently, instruments on Earth cannot detect these types of radiation, making it impossible to conduct solar studies based on them.
To overcome this limitation, scientists must conduct observations from outside Earth's atmosphere, specifically from space. This approach enables the study of solar radiations and other phenomena that are inaccessible from the Earth's surface. Additionally, to understand the behavior of solar wind particles and the Sun's magnetic field as they travel through interplanetary space, measurements need to be taken from a location far removed from the influence of Earth's magnetic field.
Is Aditya L1 A Complete Mission To Study The Sun?
The answer to whether Aditya-L1 or any space mission can fully address the study of various solar phenomena is a resounding 'NO.' This limitation arises from the constraints of spacecraft, including mass, power, and volume, which restrict the number and capacity of scientific instruments that can be sent into space. Aditya-L1, for instance, will conduct all its measurements from Lagrange point L1.
One significant limitation is that many solar phenomena, such as explosive eruptions, exhibit multi-directional characteristics, making it impossible for Aditya-L1 alone to study their directional distribution of energy. Another potential solution lies in Lagrange point L5, which offers a valuable perspective for studying Earth-directed CME events and assessing space weather.
Aditya L1 Payloads Details
ISRO’s first observatory class space based solar mission has a total of seven payloads on-board with four of them carrying out remote sensing of the Sun and three of them carrying in-situ observation.
- Aditya L1: India's Solar Mission - Space Education for Students
- Aditya L1: Technology and Working Principles behind India’s Solar Mission
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- What is the duration of Aditya-L1 mission? + The Aditya L1 rocket will take about 4 months to reach its destination - L1 point. The mission is expected to last for about five years. The satellite will spend its whole mission life orbiting around the L1 point conducting its study on the Sun.
- What is the budget of Aditya L1 mission? + The overall budget of ISRO's Aditya L1 is about Rs 400 Crore.
- What is the Aditya L1 Launch vehicle? + The launch vehicle for Aditya L1 is the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-XL.
- What is Aditya-L1 launch date? + The Aditya L1 mission by ISRO was launched on Saturday, 2 September 2023 at 11:50 am IST.
- Nagaland Board Result 2024
- Nagaland Board HSLC Result 2024
- NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Result 2024
- Nagaland Board HSSLC Result 2024
- nbsenl.edu.in NBSE Result 2024
- NBSE Toppers List 2024
- एमपी बोर्ड 10 वीं टॉपर लिस्ट 2024
- AP SSC Results 2024 Manabadi by Jagran Josh
- AP SSC Topper List 2024
Latest Education News
Lok Sabha Election 2024 Dates: अबकी बार 97 करोड़ वोटर्स करेंगे मतदान, फेज-वाइज फुल शेड्यूल यहां देखें
Can You Find The Missing Number In This Square Grid In 20 Seconds?
[Click Here] NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Result 2024 OUT: Download Nagaland 10th, 12th Class Results and Provisional Marksheet from NBSE Portal
[DIRECT LINK] Nagaland Board Result 2024: Check Class 10th, 12th with NBSE Result School Login, Roll Number, and Name
NBSE Result 2024 Released: Check Nagaland Board Class 10, 12 Results Online at nbsenl.edu.in by Roll Number, DOB and APP
Lok Sabha Elections 2024: 'आदर्श आचार संहिता', धारा-144 से कैसे है अलग चलिये समझें?
NBSE Toppers List 2024: Nagaland Board HSLC, HSSLC Subject-wise Toppers Name, Marks, District-wise School Name
Team-wise Most Consecutive Losses in IPL history till 2024
ISC Class 12 Environmental Science Syllabus 2024-25: Download Class 12th Environmental Science Syllabus PDF
Nagaland Board HSSLC Result 2024: NBSE 12th Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
Lok Sabha Elections 2024: यहां देखें दूसरे फेज के 5 सबसे अमीर उम्मीदवारों की संपत्ति, उड़ जायेंगे होश
Nagaland Board Result 2024: NBSE Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
ISC Class 11th Maths Syllabus 2024-25: Download Revised PDF for ISC Class 11 Maths
Nagaland Board HSLC Result 2024: NBSE 10th Result at Jagran Josh and nbsenl.edu.in
nbsenl.edu.in 2024 Result: Official Websites to Check Nagaland Board 10th, 12th Results Online and Jagran Josh
[Link Here] Nagaland Board Result 2024 Declared: Check NBSE HSLC, HSSLC Results at nbsenl.edu.in and Download Pass Certificate
BSEB Bihar Sakshamta Pariksha 2 Exam 2024 Notification OUT at bsebsakshamta.com, Apply Here
Class 10th JSP
Result HomePage JSP
Class12thJSP

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Achievements of ISRO. The first Indian satellite that was built by ISRO was Aryabhata, whose launching took place on April 19 th, 1975. Furthermore, 1980 was another important year for ISRO because the launching of the Rohini satellite took place. ... Conclusion of the Essay on ISRO. There is no doubt that ISRO is really the pride of India ...
It is a Central Public Sector Enterprise of the Government of India that was founded in 2019 and is managed by the Department of Space. It is ISRO's commercial arm, and its major purpose is to enable Indian enterprises to engage in high-technology space-related operations. It is headquartered in Bengaluru.
ISRO is the space agency under the Department of Space of Government of India, headquartered in the city of Bengaluru, Karnataka. Its vision is to harness space technology for national development, while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration. Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL) is a Marketing arm of ISRO for promotion and ...
Indian Space Research Organisation, or ISRO, is the country of India's space agency. It was established in 1969 to support the creation of an indigenous space project in India. The Department of Space of the Government of India oversees ISRO, a space agency with headquarters in Bengaluru, Karnataka. Its goal is to pursue planetary exploration ...
ISRO's first satellite, Aryabhata, was launched by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1975. Rohini, the first satellite to be placed in orbit by an Indian-made launch vehicle (the Satellite Launch Vehicle 3), was launched on July 18, 1980. ISRO has launched several space systems, including the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system for telecommunication, television broadcasting, meteorology ...
500 Words Essay on India's Achievements in Space Introduction. India's journey into space exploration began with small steps in the late 1960s and has since evolved into a fully-fledged space program that is recognized globally. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has been the pioneer and driving force behind this success.
Essay on ISRO: The Indian Space Research Organisation is the national space agency of India. It was founded in 1969 to develop an Indian space program. ISRO operates through a countrywide network of centres. ISRO is the primary agency that performs tasks related to space-based applications. ISRO has launched more than 50 satellites of other countries. […]
This essay will discuss how ISRO has demonstrated its excellence, innovation and leadership in various domains of space technology and exploration, such as satellite technology, launch vehicle technology, lunar missions, interplanetary missions and human spaceflight programme. ... ISRO's achievements are a source of inspiration and aspiration ...
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO / ˈ ɪ s r oʊ /) is the national space agency of India. It operates as the primary research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India while the Chairman of ISRO also acts as the executive of DoS. ISRO is primarily responsible for performing tasks related to space-based ...
ISRO has completed 115 spacecraft missions, 84 launch missions, and 13 student satellites. Major Accomplishments of ISRO. The first "Experimental Satellite Communication Earth Station (ESCES)" was set up in Ahmedabad in 1967. The ISRO developed a television program called "Krishi Darshan" to provide farmers with agricultural information.
Indian Space Programme - Achievements (May 2014 to April 2018) Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has completed 166 missions out of which 53 missions (23 Launch vehicle missions, 23 satellite missions & 7 technology demonstration missions) has been accomplished during the period May 2014 to April 2018. Launch Vehicles
ISRO's accomplishments showcase India's prowess in space technology. The agency's commitment to the betterment of the nation and humanity at large is commendable. As ISRO continues to break new ground, it fuels the aspirations of a nation and inspires future generations to dream big. 500 Words Essay on ISRO Introduction
The achievements are remarkable considering the frugal budget of the Indian Space Research Organisation, which has made a name for itself for low-cost, high-return space missions. 2) Achievements by ISRO Mangalyaan, 2014 a) India joined an exclusive global club when it successfully launched the Mars Orbiter Mission
Candidates can go through a few more achievements of ISRO mentioned below - ISRO has launched many operational remote sensing satellites, starting with IRS-1A in 1988. Detailed information on IRS-1A - the first indigenous remote sensing satelite is available on the linked page. Today, India has one of the largest constellations of remote ...
500 Words Essay on Isro the Pride of India. A true gem in India's crown, ISRO, the Indian Space Research Organisation, elevates India's standing on the global stage. ISRO symbolizes the very spirit of India - innovative, resilient, and forward-looking. ... Achievements in Satellite Technology. ISRO has accomplished a lot in satellite ...
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) - History, Achievements, ISRO UPSC Notes. ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation, is the space agency of the Indian government's Department of Space, based in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It was founded in 1969 and holds the mission to use space technology for national growth while conducting space ...
8. In 2012, ISRO successfully launched the 100th space mission using PSLV-C21 rocket and placed two foreign satellites into the orbit of the earth. 9. 2013 turned out to be a year of highest achievement for ISRO with the successful launch of the ₹450-crore Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called Mangalyaan by using PSLV-XL. 10.
10 Lines Essay on ISRO (100-120 Words) 1) The space-related affairs of India are managed by an agency known as ISRO. 2) ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) was set up on 15 August 1969. 3) The headquarters of ISRO reside in Bangalore. ... Achievements of ISRO.
A timeline of India's 75 major achievements of Space Programme. A timeline of India's 75 major achievements of Space ProgrammeHome/Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav. Description: A timeline of India's 75 major achievements of Space Programme. Format : MP4. File Size : 145 MB.
Essay on Aditya L1 Mission in English: ISRO has launched Aditya L1 - India's first observatory class space based solar mission on September 2, 2023 at 11.50 am from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh ...
PTI Photo / (ISRO), June 19, 2017. Launched on November 5, 2013, MOM was India's inaugural mission to Mars. The mission utilised the PSLV-C25 launch vehicle and had a total cost of $73 million.
Its vision is to "harness space technology for national development", while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration. The following are some of the major achievements of ISRO: Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, 2016: The seven-satellite system created India's very own satellite navigation system e- terrestrial and ...
ISRO is the best organization In India and all great and hardworking scientists giving their best performance. These scientists are playing their role honesty, responsibility and dedication in their work and giving new direction for ISRO. - Sanyog Varshney. Related Essay. Achievements of ISRO; ISRO-achievements essay
The proceedings of STD-2024, a compilation of innovative technical papers on satellite technology from various ISRO Centres were released as part of the celebrations. The event featured a video presentation showcasing the pioneering technological development by URSC for induction in future missions at SPOTLIGHT, a platform to demonstrate newer ...