APA Research Paper Outline: Examples and Template
Table of contents
- 1 Why Is Research Paper Format Necessary?
- 2.1 Purpose of research paper outline
- 2.2 APA outline example
- 3.1 APA paper outline example
- 3.2 Introduction:
- 3.4 Conclusion:
- 4 The Basic APA Outline Format
- 5 APA Style Outline Template Breakdown
- 6.1 APA Research Paper Outline Example
- 6.2 APA Paper Outline Format Example
- 7.1 First Paragraph: Hook and Thesis
- 7.2 Main Body
- 7.3 Conclusion
- 7.4 Decimal APA outline format example
- 7.5 Decimal APA outline format layout
- 8.1 A definite goal
- 8.2 Division
- 8.3 Parallelism
- 8.4 Coordination
- 8.5 Subordination
- 8.6 Avoid Redundancy
- 8.7 Wrap it up in a good way
- 8.8 Conclusion
Formatting your paper in APA can be daunting if this is your first time. The American Psychological Association (APA) offers a guide or rules to follow when conducting projects in the social sciences or writing papers. The standard APA fromat a research paper outline includes a proper layout from the title page to the final reference pages. There are formatting samples to create outlines before writing a paper. Amongst other strategies, creating an outline is the easiest way to APA format outline template.

Why Is Research Paper Format Necessary?
Consistency in the sequence, structure, and format when writing a research paper encourages readers to concentrate on the substance of a paper rather than how it is presented. The requirements for paper format apply to student assignments and papers submitted for publication in a peer-reviewed publication. APA paper outline template style may be used to create a website, conference poster, or PowerPoint presentation . If you plan to use the style for other types of work like a website, conference poster, or even PowerPoint presentation, you must format your work accordingly to adjust to requirements. For example, you may need different line spacing and font sizes. Follow the formatting rules provided by your institution or publication to ensure its formatting standards are followed as closely as possible. However, to logically structure your document, you need a research paper outline in APA format. You may ask: why is it necessary to create an outline for an APA research paper?
Concept & Purposes of Research Paper Outline
A path, direction, or action plan! Writing short essays without a layout may seem easy, but not for 10,000 or more words. Yet, confusing a table of contents with an outline is a major issue. The table of contents is an orderly list of all the chapters’ front matter, primary, and back matter. It includes sections and, often, figures in your work, labeled by page number. On the other hand, a research APA-style paper outline is a proper structure to follow.
Purpose of research paper outline
An outline is a formalized essay in which you give your own argument to support your point of view. And when you write your apa outline template, you expand on what you already know about the topic. Academic writing papers examine an area of expertise to get the latest and most accurate information to work on that topic. It serves various purposes, including:
- APA paper outline discusses the study’s core concepts.
- The research paper outlines to define the link between your ideas and the thesis.
- It provides you with manageable portions that you can handle.
- The research paper’s APA outline enables the detection of structural faults or gaps.
- As shown in the example, it must clearly comprehend the subject at hand.
APA outline example

This research paper outline example will guide you in formatting the layout for a clear direction to work on. It eliminates the inconsistency along with lacking proper substance in the paper.
Understanding the APA Outline Format
It would not be wrong to say there is no standard outline format. The official publishing handbook does not give precise guidelines for preparing an outline. But, it requires certain basic guidelines to follow regarding typeface, font size, structure, margins, etc.
APA paper outline example
Moreover, the final shape of your work relies on your instructor’s specifications and your particular preferences for APA citation format. Though, it would be better to follow some standards for formatting your outline, for instance:
Times New Roman is a widely accessible standard typeface for an APA essay format in 12-point font. However, serif and sans serif fonts like Arial and Georgia are acceptable in font size 11pt.
The text of your paper format should be double-spaced.
The primary headlines use Roman and Arabic numerals to write an outline.
Headings & Subheadings
While writing an APA essay, there are particular standards for utilizing headings in your outline: I – Main headings are numbered by Roman numerals like I, II, III, IV A – Subheadings are numbered with Capital letters (A, B, C, D) 1 – The APA outline uses Arabic numerals (1-9 type numbers) within those subheadings. a – Below Arabic number subheadings, lower-case letters are used (a, b, a). [1] – Headings below those subheadings use Arabic numbers enclosed in parenthesis.
APA format offers a standard layout for each paper, such as
- 1-inch margins on the top, bottom, left, and right.
- The page number on the upper right corner.
The structure of writing an outline consists of three major sections:
- Introduction
Introduction:
This section highlights crucial background information.
Explain the primary points that support your ideas.
Conclusion:
- Summarize your key arguments.
- Explain how these concepts support your ultimate stance, as shown in APA outline example below.
An outline in APA has three common formats that vary in the numeric sequence of all. To make it easier for you, we have compiled all three templates. You can format your document using these examples for added coherence and structure.
The Basic APA Outline Format

APA Style Outline Template Breakdown
Numbering the APA style format follows five levels of headings that use different alphabets and numbers. For instance, I – Headings use Roman numerals like I, II, and III. A – CAPITAL ALPHABETS”, such as A, B, C, etc. 1 – Headings and subheadings use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3). a – If there are further headings (the fourth level), use lower-case alphabets. [1] – Headings below that (the fifth level) use Arabic numerals enclosed in parentheses, such as [1], [2], [3].
Full Sentence Outline Format
As the name specifies, the full-sentence style outline format requires every line to be a proper sentence. Full-sentence APA style outline is best recommended for essays and speeches. It gives your writing process an idea or a logical path to follow.
APA Research Paper Outline Example
If you are looking for how to write a research paper outline APA in Full Sentence Format, here is an example:
Full Sentence APA format heading utilizes Roman numerals I, II, and III. Every heading must be a full sentence. Here is an APA style paper outline template for the full-sentence format that will clear all your confusion on how to write an outline in full-sentence format.

APA Paper Outline Format Example
I. Introduction
III. Conclusion
Decimal Outline Format
The decimal outline format for APA research papers differs from other formats. The decimal APA style is simple and uses paragraphs for structure. It contains three main paragraphs, introduction, main body, and conclusion.
First Paragraph: Hook and Thesis
- The first paragraph is a sentence or two that introduces the central concept of your article.
- Introduce your topic or subject of study where your research is applicable as a context for further research.
- Explain why the mentioned issue is essential or relevant to the audience.
- A thesis statement is a claim that you make throughout your whole essay.
- The topic phrase is the first point in any writing to support a thesis statement.
- Give an explanation or provide evidence to support your point.
- Provide verifiable facts, figures, and/or citations from credible sources in your writing. It helps in the substantiating assertion.
- Include as many supporting statements and related evidence in your decimal outline.
Finally, when you write an outline, provide a concluding remark to support your claims.
Decimal APA outline format example
1.0 The main heading 1.1 Subheading under the main heading 1.2 Second digit is represented by subheadings under the main headings 1.2.1 Further division adds another digit in decimal format 1.2.2 You can number them as per the number of paragraphs or points, or lines An easy way to write in decimal APA outline format is to remember the structure, i.e.; 1.1.1 = Heading.Paragraph.Sentence/point under paragraph.”
Decimal APA outline format layout
1.0 Main heading 1.1 First paragraph for first heading. 1.2 Second paragraph for first heading. 1.2.1 First point or sentence for the second paragraph. 2.0 Second heading 2.1 Second heading, first paragraph. 2.2 Second heading, second paragraph. 2.2.1 Second, heading, second paragraph, first sentence, or point. 3.0 Decimal working 3.1 You must remember that each digit represents a segment. 3.2 It is easier to remember the placement of numbers. 3.2.1 First digit represents the heading 3.2.2 Second digit represents the paragraph under the main heading <3.2.3 The third digit represents any point or sentence under the paragraph.
Tips for Writing an Outline: Organize Your Ideas
You may feel it is easier to write without outlines, but once you start writing, organizing your ideas or thoughts becomes hard. Even if you have some fantastic ideas, producing an engaging story is practically hard. If you are not first creating an outline or conceptual guides while writing a research paper, you may lose track. A well-written outline is essential in completing your paper and maintaining quality. Establishing your point in paper writing is easy if you create an outline first. You can find an APA research paper outline template that best suits your requirement. Moreover, these tips can help you polish your writing. These tips and sample papers can help you write outstanding outlines without making any hassle.
A definite goal
For better expression, make a list of primary objectives on a title page in a single phrase or less. Your goal should be specific and measurable. If it is too broad or imprecise, you will not achieve anything. If you are working on a large paper format that covers a variety of themes or topics, you may have a more general purpose in mind. But, if you plan to write an essay, the aim should be as specific and clear as possible to be effective.
Breaking things up rather than allowing them to become verbose is known as the division rule. Make sure that each subsection in the document corresponds to its parent heading. If it doesn’t compare to the section, removing it or moving it to another location is better.
Parallelism
It is mainly related to the consistency and structure of the document. It keeps your paper’s layout tidy and also ensures relevancy. For instance, if you begin one heading with a verb, make sure all other headings and subheadings also start with a verb.
Coordination
Having headings aligned is critical to creating a well-organized outline. This rule also applies to subheadings, which is a good thing. If one title is less important than another, consider changing your layout by incorporating it into a subsection instead.
Subordination
Subordination deals with maintaining a connection between your paper’s headings and subheadings. It helps in the proper sequencing of headings and subheadings. Headings should be broad at the outset. At the same time, the subheadings become more particular as they go further into the document.
Avoid Redundancy
While writing a paper outline, look through it many times and cross out any items that aren’t necessary or have no significance. While outlining, make sure to be specific and concise. It will prevent you from adding information that does not supporting your final essay. Remove all the extra information and points while c that weighs you down while you write.
Wrap it up in a good way
Creating an outline does not only help in writing a coherent term paper, but it also helps in ending with precise understanding. Be considerate of your audience’s time and effort when you write an outline in APA, and ensure it serves its purpose. If you still have any doubts about formatting your paper outline, you can use this APA-style research paper outline template to write your document. We have provided Outline Format Example for every style.
People find it hard to write an outline in APA, but if you are aware of the requirements and structure, it’s no breeze. Sometimes, your instructor may alter your paper format by introducing or removing existing sections. As a result, if you come across any templates for an outline in APA, pay close attention to them. If you are looking for a quick answer to how to outline an APA paper, here’s a standard logical sequence of typical parts to include when writing an outline in APA:
- Thesis statement
- Techniques employed
- Body of paper
- Conclusions section
- List of references
A well-written outline is an excellent tool for presenting an outstanding paper. Including the key components while writing an outline for a research paper is necessary.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Outline in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amanda Tust is a fact-checker, researcher, and writer with a Master of Science in Journalism from Northwestern University's Medill School of Journalism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Amanda-Tust-1000-ffe096be0137462fbfba1f0759e07eb9.jpg)
- Before Starting Your Outline
- How to Create an Outline
Writing a psychology paper can feel like an overwhelming task. From picking a topic to finding sources to cite, each step in the process comes with its own challenges. Luckily, there are strategies to make writing your paper easier—one of which is creating an outline using APA format .
Here we share what APA format entails and the basics of this writing style. Then we get into how to create a research paper outline using APA guidelines, giving you a strong foundation to start crafting your content.
At a Glance
APA format is the standard writing style used for psychology research papers. Creating an outline using APA format can help you develop and organize your paper's structure, also keeping you on task as you sit down to write the content.
APA Format Basics
Formatting dictates how papers are styled, which includes their organizational structure, page layout, and how information is presented. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA).
Learning the basics of APA format is necessary for writing effective psychology papers, whether for your school courses or if you're working in the field and want your research published in a professional journal. Here are some general APA rules to keep in mind when creating both your outline and the paper itself.
Font and Spacing
According to APA style, research papers are to be written in a legible and widely available font. Traditionally, Times New Roman is used with a 12-point font size. However, other serif and sans serif fonts like Arial or Georgia in 11-point font sizes are also acceptable.
APA format also dictates that the research paper be double-spaced. Each page has 1-inch margins on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right), and the page number is to be placed in the upper right corner of each page.
Both your psychology research paper and outline should include three key sections:
- Introduction : Highlights the main points and presents your hypothesis
- Body : Details the ideas and research that support your hypothesis
- Conclusion : Briefly reiterates your main points and clarifies support for your position
Headings and Subheadings
APA format provides specific guidelines for using headings and subheadings. They are:
- Main headings : Use Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV)
- Subheadings: Use capital letters (A, B, C, D)
If you need further subheadings within the initial subheadings, start with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3), then lowercase letters (a, b, c), then Arabic numerals inside parentheses [(1), (2), (3)]
Before Starting Your APA Format Outline
While APA format does not provide specific rules for creating an outline, you can still develop a strong roadmap for your paper using general APA style guidance. Prior to drafting your psychology research paper outline using APA writing style, taking a few important steps can help set you up for greater success.
Review Your Instructor's Requirements
Look over the instructions for your research paper. Your instructor may have provided some type of guidance or stated what they want. They may have even provided specific requirements for what to include in your outline or how it needs to be structured and formatted.
Some instructors require research paper outlines to use decimal format. This structure uses Arabic decimals instead of Roman numerals or letters. In this case, the main headings in an outline would be 1.0, 1.2, and 1.3, while the subheadings would be 1.2.1, 1.2.2, 1.2.3, and so on.
Consider Your Preferences
After reviewing your instructor's requirements, consider your own preferences for organizing your outline. Think about what makes the most sense for you, as well as what type of outline would be most helpful when you begin writing your research paper.
For example, you could choose to format your headings and subheadings as full sentences, or you might decide that you prefer shorter headings that summarize the content. You can also use different approaches to organizing the lettering and numbering in your outline's subheadings.
Whether you are creating your outline according to your instructor's guidelines or following your own organizational preferences, the most important thing is that you are consistent.
Formatting Tips
When getting ready to start your research paper outline using APA format, it's also helpful to consider how you will format it. Here are a few tips to help:
- Your outline should begin on a new page.
- Before you start writing the outline, check that your word processor does not automatically insert unwanted text or notations (such as letters, numbers, or bullet points) as you type. If it does, turn off auto-formatting.
- If your instructor requires you to specify your hypothesis in your outline, review your assignment instructions to find out where this should be placed. They may want it presented at the top of your outline, for example, or included as a subheading.
How to Create a Research Paper Outline Using APA
Understanding APA format basics can make writing psychology research papers much easier. While APA format does not provide specific rules for creating an outline, you can still develop a strong roadmap for your paper using general APA style guidance, your instructor's requirements, and your own personal organizational preferences.
Typically you won't need to turn your outline in with your final paper. But that doesn't mean you should skip creating one. A strong paper starts with a solid outline. Developing this outline can help you organize your writing and ensure that you effectively communicate your paper's main points and arguments. Here's how to create a research outline using APA format.
Start Your Research
While it may seem like you should create an outline before starting your research, the opposite is actually true. The information you find when researching your psychology research topic will start to reveal the information you'll want to include in your paper—and in your outline.
As you research, consider the main arguments you intend to make in your paper. Look for facts that support your hypothesis, keeping track of where you find these facts so you can cite them when writing your paper. The more organized you are when creating your outline, the easier it becomes to draft the paper itself.
If you are required to turn in your outline before you begin working on your paper, keep in mind that you may need to include a list of references that you plan to use.
Draft Your Outline Using APA Format
Once you have your initial research complete, you have enough information to create an outline. Start with the main headings (which are noted using Roman numerals I, II, III, etc.). Here's an example of the main headings you may use if you were writing an APA format outline for a research paper in support of using cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for anxiety :
- Introduction
- What CBT Is
- How CBT Helps Ease Anxiety
- Research Supporting CBT for Anxiety
- Potential Drawbacks of CBT for Anxiety and How to Overcome Them
Under each main heading, list your main points or key ideas using subheadings (as noted with A, B, C, etc.). Sticking with the same example, subheadings under "What CBT Is" may include:
- Basic CBT Principles
- How CBT Works
- Conditions CBT Has Been Found to Help Treat
You may also decide to include additional subheadings under your initial subheadings to add more information or clarify important points relevant to your hypothesis. Examples of additional subheadings (which are noted with 1, 2, 3, etc.) that could be included under "Basic CBT Principles" include:
- Is Goal-Oriented
- Focuses on Problem-Solving
- Includes Self-Monitoring
Begin Writing Your Research Paper
The reason this step is included when drafting your research paper outline using APA format is that you'll often find that your outline changes as you begin to dive deeper into your proposed topic. New ideas may emerge or you may decide to narrow your topic further, even sometimes changing your hypothesis altogether.
All of these factors can impact what you write about, ultimately changing your outline. When writing your paper, there are a few important points to keep in mind:
- Follow the structure that your instructor specifies.
- Present your strongest points first.
- Support your arguments with research and examples.
- Organize your ideas logically and in order of strength.
- Keep track of your sources.
- Present and debate possible counterarguments, and provide evidence that counters opposing arguments.
Update Your Final Outline
The final version of your outline should reflect your completed draft. Not only does updating your outline at this point help ensure that you've covered the topics you want in your paper, but it also gives you another opportunity to verify that your paper follows a logical sequence.
When reading through your APA-formatted outline, consider whether it flows naturally from one topic to the next. You wouldn't talk about how CBT works before discussing what CBT is, for example. Taking this final step can give you a more solid outline, and a more solid research paper.
American Psychological Association. About APA Style .
Purdue University Online Writing Lab. Types of outlines and samples .
Mississippi College. Writing Center: Outlines .
American Psychological Association. APA style: Style and Grammar Guidelines .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.) for Student Papers
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Powerpoint Presentations
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 2:30 PM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th

APA Style (7th ed.)
- Cite: Why? When?
- Book, eBook, Dissertation
- Article or Report
- Business Sources
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- In-Text Citation
- Format Your Paper
Format Your Paper
Download and use the editable templates for student papers below: .
- APA 7th ed. Template Document This is an APA format template document in Google Docs. Click on the link -- it will ask for you to make a new copy of the document, which you can save in your own Google Drive with your preferred privacy settings.
- APA 7th ed. Template Document A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly according to APA 7th edition.
- APA 7th ed. Annotated Bibliography template A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly for an annotated bibliography.
Or, view the directions for specific sections below:
Order of sections (section 2.17).
- Title page including Title, Author, University and Department, Class, Instructor, and Date
- Body (including introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion)
- Appendices (including tables & figures)
Margins & Page Numbers (sections 2.22-2.24)
- 1 inch at top, bottom, and both sides
- Left aligned paragraphs and leave the right edge ragged (not "right justified")
- Indent first line of each paragraph 1/2 inch from left margin
- Use page numbers, including on the title page, 1/2 inch from top and flush with right margin

Text Format (section 2.19)
- Times New Roman, 12 point
- Calibri, 11 point
- Arial, 11 point
- Lucinda Sans Unicode, 10 point
- Georgia, 11 point
- Double-space and align text to the left
- Use active voice
- Don't overuse technical jargon
- No periods after a web address or DOI in the References list.
Tables and Figures In-Text (chapter 7)
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1)
- Give each table column a heading and use separating lines only when necessary
- Design the table and figure so that it can be understood on its own, i.e. it does not require reference to the surrounding text to understand it
- Notes go below tables and figures
Title Page (section 2.3)
- Include the title, your name, the class name , and the college's name
- Title should be 12 words or less and summarize the paper's main idea
- No periods or abbreviations
- Do not italicize or underline
- No quotation marks, all capital letters, or bold
- Center horizontally in upper half of the page
Body (section 2.11)
- Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line
- Double-space
- As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold , and in Sentence Case Capitalization
- Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific organization will depend on the paper type
- Spell out long organization names and add the abbreviation in parenthesis, then just use the abbreviation
- Spell out numbers one through nine and use a number for 10 or more
- Use a number for units of measurement, in tables, to represent statistical or math functions, and dates or times
Headings (section 2.26-2.27)
- Level 1: Center, bold , Title Case
- Level 2: Align left, bold , Title Case
- Level 3: Alight left, bold italics , Title Case
- Level 4: Indented 1/2", bold , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.
- Level 5: Indented 1/2", bold italics , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.

Quotations (sections 8.26-8.33)
- Include short quotations (40 words or less) in-text with quotation marks
- For quotes more than 40 words, indent the entire quote a half inch from the left margin and double-space it with no quotation marks
- When quoting two or more paragraphs from an original source, indent the first line of each paragraph a half inch from the left margin
- Use ellipsis (...) when omitting sections from a quote and use four periods (....) if omitting the end section of a quote
References (section 2.12)
Begins on a new page following the text of your paper and includes complete citations for the resources you've used in your writing.
- References should be centered and bolded at the top of a new page
- Double-space and use hanging indents (where the first line is on the left margin and the following lines are indented a half inch from the left)
- List authors' last name first followed by the first and middle initials (ex. Skinner, B. F.)
- Alphabetize the list by the first author's last name of of each citation (see sections 9.44-9.49)
- Capitalize only the first word, the first after a colon or em dash, and proper nouns
- Don't capitalize the second word of a hyphenated compound
- No quotation marks around titles of articles
Appendices with Tables, Figures, & Illustrations (section 2.14, and chapter 7)
- Include appendices only to help the reader understand, evaluate, or replicate the study or argument
- Put each appendix on a separate page and align left
- For text, do not indent the first paragraph, but do indent the rest
- If you have only one appendix, label it "Appendix"
- If you have two or more appendices, label them "Appendix A", "Appendix B" and so forth as they appear in the body of your paper
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1, or Table B1 and Table B2 if Appendix B has two tables) and describe them within the text of the appendix
- Notes go below tables and figures (see samples on p. 210-226)
Annotated Bibliography
Double-space the entire bibliography. give each entry a hanging indent. in the following annotation, indent the entire paragraph a half inch from the left margin and give the first line of each paragraph a half inch indent. see the template document at the top of this page..
- Check with your professor for the length of the annotation and which elements you should evaluate.
These elements are optional, if your professor or field requires them, but they are not required for student papers:
Abstract (section 2.9).
- Abstract gets its own page
- Center "Abstract" heading and do not indent the first line of the text
- Summarize the main points and purpose of the paper in 150-250 words maximum
- Define abbreviations and acronyms used in the paper
Running Head (section 2.8 )
- Shorten title to 50 characters or less (counting spaces and punctuation) for the running head
- In the top margin, the running head is aligned left, with the page number aligned on the right
- On every page, put (without the brackets): [SHORTENED TITLE OF YOUR PAPER IN ALL CAPS] [page number]
More questions? Check out the authoritative source: APA style blog
- << Previous: In-Text Citation
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 3:02 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/apa

How to Format Your Research Paper
Writing your paper: apa 7th edition, apa style papers 7th edition.
- MLA Paper Format
- Chicago Paper Format
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
APA 7th Edition Resources
- APA Style Blog The style and grammar guidelines pages present information about APA Style as described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition.
- Purdue OWL: APA Style Guide This Purdue OWL style guide will help you in citing your sources in the APA Style commonly used to cite sources within the area of social sciences.
Printable APA 7th Edition Guides
Creating citations using APA 7th Edition:
- APA 7th Edition Citations - PDF
- APA 7th Edition Citations - Word
Creating in-text citations using APA 7th Edition:
- APA 7th In-Text Citations - PDF
- APA 7th In-Text Citations - Word
Integrating sources into the text of your paper using signal phrases:
- Integrating Sources - PDF
- Integrating Sources - Word
Things to know before you begin:
- Sans serif fonts: Arial (11-point), Calibri (11-point), or Lucinda Sans Unicode (10-point)
- Serif fonts: Times New Roman (12-point), Georgia (11-point), or Computer Modern (10-point)
- Margins: 1 inch on all sides
- Paragraphs: All paragraphs (except in the Abstract) should be indented
- Spacing: All of the text in your paper should be double-spaced (title page included)
Typical APA style papers have four main sections:
See the tabs below for a breakdown of how each portion should be formatted.
- Paper Templates
- Sample Papers
- APA 7 Citations
Below you will find templates for APA Style papers. Click the link to make a copy of the file.
- Google Docs : To make a copy of these templates you must first sign in to your Google account. After you’re signed in, click "File" and then click “Make a Copy.”
- Microsoft Word : To make a copy of these templates download the file.
- APA Style Student Paper Template (7th Edition) - Word Download a copy of this Word Doc and change the pre-filled information to your own.
APA Style Report Templates: These templates include multiple heading levels and should be used for report style papers.
- APA Style Student Report Template (7th Edition) - Word Download a copy of this Word Doc and change the pre-filled information to your own.
Below you will find an example of an accurately formatted APA Style student paper.
- APA Style Student Paper Sample (7th Edition) - PDF Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted APA style student paper.
- APA Style Student Paper Sample (7th Edition) - Word Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted APA style student paper.

Place only page numbers in the header.
Your paper should have the full title in bold. Place an extra space beneath the title and before your name.
Your name, your affiliation, the course title, professor’s name, and due date should be double spaced beneath the title.
All of this should be in the center of the title page.

- Put the word “Abstract” on the top of the page. Be sure it is center-aligned and in bold.
- Do not indent any paragraphs on this page.
Indent all other paragraphs throughout the body of the paper.

- Place the entire title of your paper in Title Case on the top line of a new page.
- Be sure it is center-aligned and in bold.

- Center-align the word “References” on the first line of a new page, be sure that it is in bold.
- Your citations should be alphabetized.
- Entries are double-spaced with no extra lines between them.
- Be sure to use a hanging indent for any citations that require more than one line.
Need help formatting your APA style citations using the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association ? Click the image or link below to go to the citation guide.

- APA 7th Edition Citations
Need help learning what hanging indents are and how to create them using Google Docs or Microsoft Word?

- Hanging Indents This page gives a brief description of what they are, where to find information on when and how to properly use them, and also video tutorials on how to create them.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: MLA Paper Format >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 2:49 PM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.
APA Citation Style
- Citation Examples
- Paper Format
- Style and Grammar Guidelines
- Citation Management Tools
- What's New in the 7th Edition?
- Order of Pages
- Title Page Setup
- Page Header
- Line Spacing
- Paragraph Alignment & Indentation
- Sample Papers
- Accessibility
Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper’s content rather than its presentation.
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create another kind of work (e.g., a website, conference poster, or PowerPoint presentation), you may need to format your work differently in order to optimize its presentation, for example, by using different line spacing and font sizes. Follow the guidelines of your institution or publisher to adapt APA Style formatting guidelines as needed.
Paper format is covered in Chapter 2 of APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition
**All information taken from: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format
Order of pages is covered in Section 2.17 of the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition
All papers, including student papers, generally include a title page, text, and references. They may include additional elements such as tables and figures depending on the assignment. Student papers generally do not include an abstract unless requested.
Arrange the pages of an APA Style paper in the following order:
In general, start each section on a new page. However, the order of pages is flexible in the following cases:
- tables and figures: Embed tables and figures within the text after they are first mentioned (or “called out”), or place each table and then each figure on separate pages after the references. If an embedded table or figure appears on the same page as text, place it at either the top or the bottom of the page, and insert a blank double-spaced line to separate the table or figure from the adjacent text.
- footnotes: Use the footnotes function of your word-processing program to insert a footnote at the bottom of the page of text on which the footnote appears, or list footnotes together on a separate page after the references.;
Papers such as dissertations and theses may require additional elements not listed here. Follow the institutional or departmental guidelines of your university to order the pages of a dissertation or thesis.
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student Title Page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in the following example.
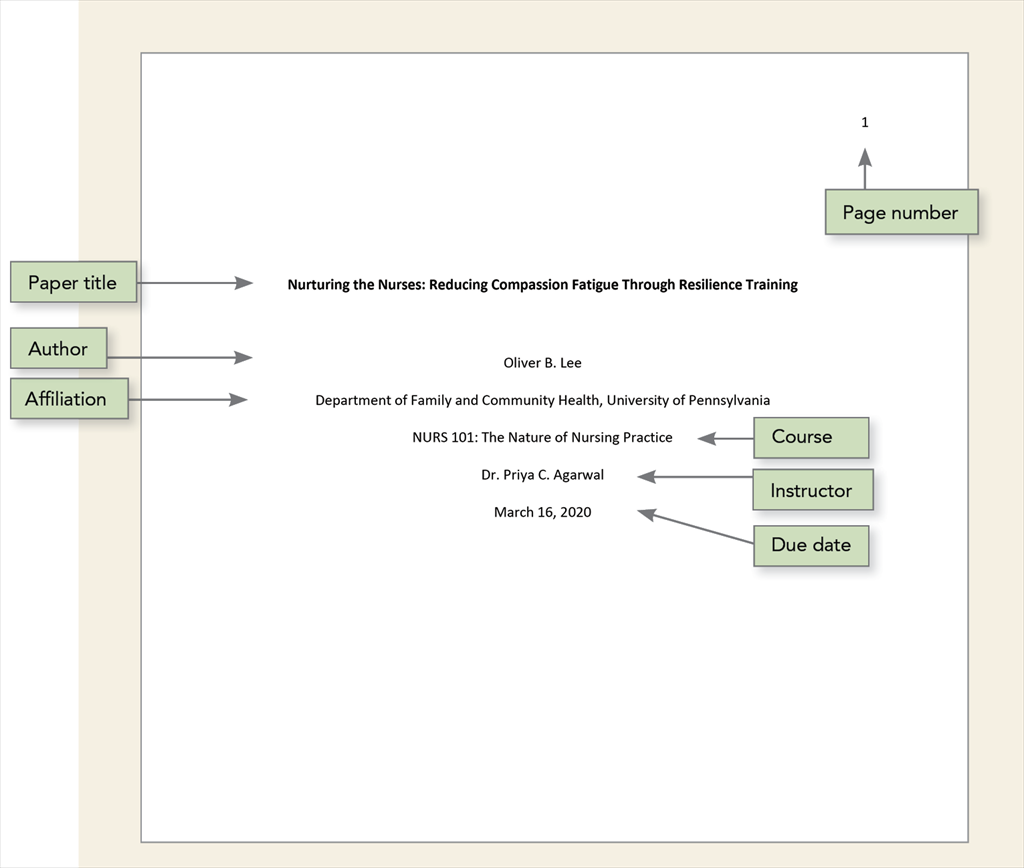
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
Professional Title Page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
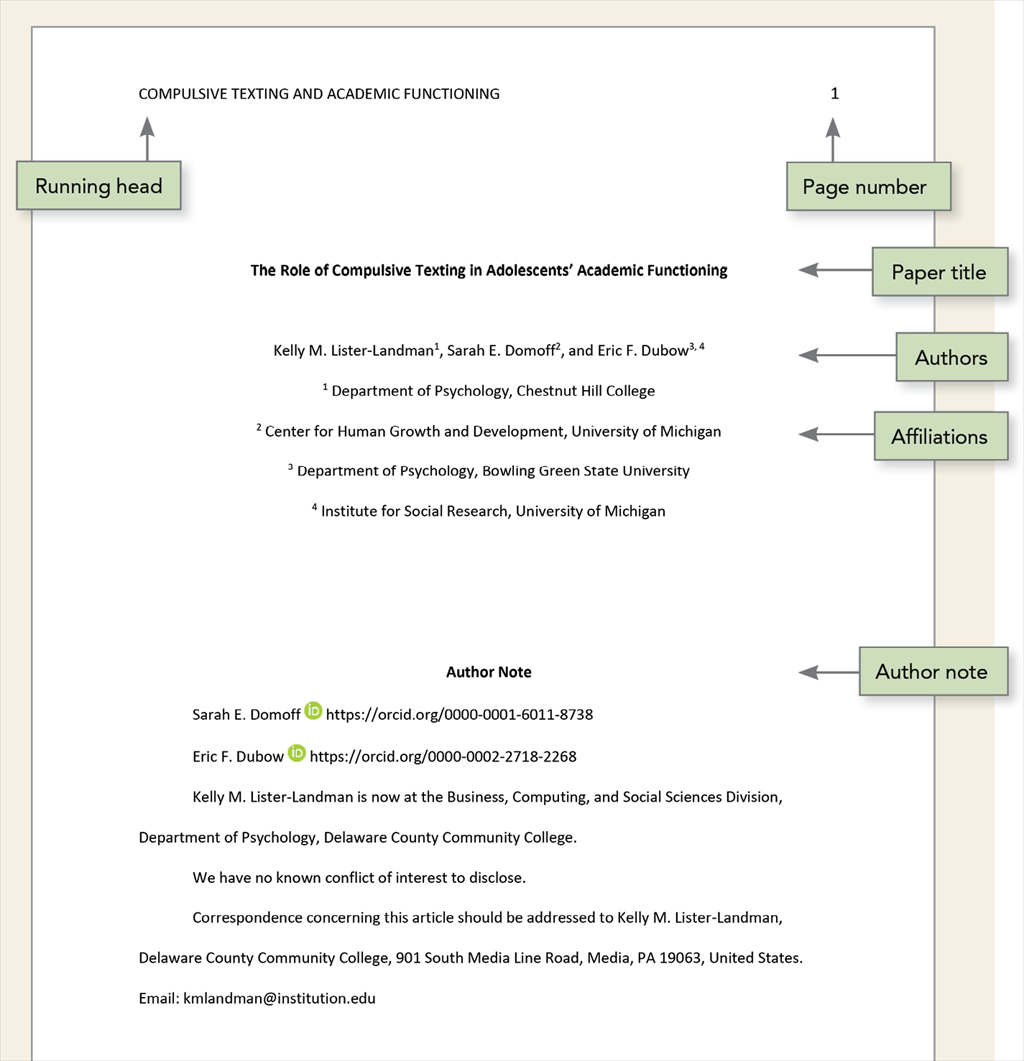
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
A variety of fonts are permitted in APA Style papers. Font options include the following:
- sans serif fonts such as 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode
- serif fonts such as 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or normal (10-point) Computer Modern (the default font for LaTeX)
We recommend these fonts because they are legible and widely available and because they include special characters such as math symbols and Greek letters. Historically, sans serif fonts have been preferred for online works and serif fonts for print works; however, modern screen resolutions can typically accommodate either type of font, and people who use assistive technologies can adjust font settings to their preferences. For more on how font relates to accessibility, visit the page on the accessibility of APA Style .
Use the same font throughout your paper, with the following exceptions:
- figures: Within figure images, use a sans serif font with a type size between 8 and 14 points.
- computer code: To present computer code, use a monospace font such as 10-point Lucida Console or 10-point Courier New.
- footnotes: When inserting footnotes with the footnotes function of your word-processing program, use the default font settings. The footnote font might be smaller than the text font (and have different line spacing), and it is not necessary to change it.
Instructors and publishers vary in how they specify length requirements. Different fonts take up different amounts of space on the page; thus, we recommend using word count rather than page count to gauge paper length if possible.
The page header appears within the top margin of every page of the paper.
- For student papers, the page header consists of the page number only.
- For professional papers, the page header consists of the page number and running head.
Page headers are covered in Section 2.18 of the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition
Page Numbers
Follow these guidelines to include page numbers in both student and professional APA Style papers:
- Use the page-numbering function of your word-processing program to insert page numbers.
- Insert page numbers in the top right corner. The page number should show on all pages.
- The title page carries page number 1.
Running Head
The running head is an abbreviated version of the title of your paper (or the full title if the title is already short). The running head is not required for student papers unless the instructor or institution requests it. Thus, typically only professional papers include a running head.
Follow these guidelines to include a running head in an APA Style paper:
- Type the running head in all-capital letters.
- Ensure the running head is no more than 50 characters, including spaces and punctuation.
- Avoid using abbreviations in the running head; however, the ampersand symbol (&) may be used rather than “and” if desired.
- The running head appears in the same format on every page, including the first page.
- Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head.
- Align the running head to the left margin of the page header, across from the right-aligned page number.
View the sample papers to see how the running head and page number appear in APA Style papers.
In general, double-space all parts of an APA Style paper, including the abstract; text; block quotations; table and figure numbers, titles, and notes; and reference list (including between and within entries). Do not add extra space before or after paragraphs.
Exceptions to double line spacing are as follows:
- title page: Insert a double-spaced blank line between the title and the byline on the title page . For professional papers, also include at least one double-spaced blank line above the author note (student papers do not include author notes). Double-space the rest of the title page.
- tables: The table body (cells) may be single-spaced, one-and-a-half-spaced, or double-spaced, depending on which is the most effective layout for the information. Double-space the table number, title, and notes.
- figures: Words within the image part of a figure may be single-spaced, one-and-a-half-spaced, or double-spaced, depending on which is the most effective layout for the information. Double-space the figure number, title, and notes.
- footnotes: When inserting footnotes with the footnotes function of your word-processing program, use the default font settings (usually single-spaced and a slightly smaller font than the text).
- displayed equations: It is permissible to apply triple- or quadruple-spacing in special circumstances, such as before and after a displayed equation.
These guidelines apply to APA Style student papers and to manuscripts being submitted for publication. If you are using APA Style in another context (e.g., on a website or in a formal publication), different line spacing and other formatting specifications may be appropriate.
Use 1-in. margins on every side of the page for an APA Style paper.
However, if you are writing a dissertation or thesis , your advisor or institution may specify different margins (e.g., a 1.5-in. left margin to accommodate binding).
APA Style includes guidelines for paragraph alignment and indentation to ensure that papers are formatted in a consistent and readable manner. All writers should follow these guidelines.
Paragraph Alignment
Align the text of an APA Style paper to the left margin. Leave the right margin uneven, or “ragged.” Do not use full justification for student papers or manuscripts being submitted for publication.
Do not insert hyphens (manual breaks) in words at the end of line. However, it is acceptable if your word-processing program automatically inserts breaks in long hyperlinks (such as in a DOI or URL in a reference list entry .
Paragraph Indentation
Indent the first line of each paragraph of text 0.5 in. from the left margin. Use the tab key or the automatic paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program to achieve the indentation (the default setting is likely already 0.5 in.). Do not use the space bar to create indentation.
Exceptions to these paragraph-formatting requirements are as follows:
- title page: For professional papers, the title (in bold), byline, and affiliations should be centered on the title page . For student papers, the title (in bold), byline, affiliations, course number and name, instructor, and assignment due date should be centered on the title page .
- section labels: Section labels (e.g., “Abstract,” “References”) should be centered (and bold).
- abstract: The first line of the abstract should be flush left (not indented).
- block quotations: Indent a whole block quotation 0.5 in. from the left margin. If the block quotation spans more than one paragraph, the first line of the second and any subsequent paragraphs of the block quotation should be indented another 0.5 in., such that those first lines are indented a total of 1 in.
- headings: Level 1 headings should be centered (and in bold), and Level 2 and 3 headings should be left-aligned (and in bold or bold italic, respectively). Level 4 and 5 headings are indented like regular paragraphs.
- tables and figures: Table and figure numbers (in bold), titles (in italics), and notes should be flush left.
- reference list: Reference list entries should have a hanging indent of 0.5 in.
- appendices: Appendix labels and titles should be centered (and bold).
Headings identify the content within sections of a paper.
Make your headings descriptive and concise. Headings that are well formatted and clearly worded aid both visual and nonvisual readers of all abilities.
Levels of Heading
There are five levels of heading in APA Style. Level 1 is the highest or main level of heading, Level 2 is a subheading of Level 1, Level 3 is a subheading of Level 2, and so on through Levels 4 and 5.
The number of headings to use in a paper depends on the length and complexity of the work.
- If only one level of heading is needed, use Level 1.
- If two levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1 and 2.
- If three levels of heading are needed, use Levels 1, 2, and 3 (and so on).
Use only the number of headings necessary to differentiate distinct sections in your paper; short student papers may not require any headings. Furthermore, avoid these common errors related to headings:
- Avoid having only one subsection heading within a section, just like in an outline.
- Do not label headings with numbers or letters.
- Double-space headings; do not switch to single spacing within headings.
- Do not add blank lines above or below headings, even if a heading falls at the end of a page.
Format of Headings
The following table demonstrates how to format headings in APA Style.
Note. In title case , most words are capitalized.
Headings in the Introduction
Because the first paragraphs of a paper are understood to be introductory, the heading “Introduction” is not needed. Do not begin a paper with an “Introduction” heading; the paper title at the top of the first page of text acts as a de facto Level 1 heading.
It is possible (but not required) to use headings within the introduction. For subsections within the introduction, use Level 2 headings for the first level of subsection, Level 3 for subsections of any Level 2 headings, and so on. After the introduction (regardless of whether it includes headings), use a Level 1 heading for the next main section of the paper (e.g., Method).
Creating Accessible Headings
Writers who use APA Style may use the automatic headings function of their word-processing program to create headings. This not only simplifies the task of formatting headings but also ensures that headings are coded appropriately in any electronic version of the paper, which aids readers who use navigation tools and assistive technologies such as screen readers.
Here are some tips on how to create headings in some common word-processing programs:
- If you use Academic Writer to write your APA Style papers, the headings menu in the Writing Center will format headings for you in 7th edition APA Style.
- Follow these headings directions from Microsoft to customize the heading formats for your future use.
- To apply Level 4 and 5 headings (which are inline headings, meaning the heading appears on the same line as paragraph text), first type the heading and a few words of the text that follows. Then highlight the text that you want to be your heading and select the appropriate heading level from the Styles menu. Only the highlighted text will be formatted as the Level 4 or 5 heading
This page contains several sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style.
The following two sample papers were published in annotated format in the Publication Manual and are provided here for your ease of reference. The annotations draw attention to relevant content and formatting and provide users with the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.
- Annotated Student Sample Paper (PDF, 2MB)
- Annotated Professional Sample Paper (PDF, 3MB)
We also offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) file format without the annotations.
- Student Sample Paper (DOCX, 38KB )
- Professional Sample Paper (DOCX, 96KB)
Sample Papers in Real Life
Although published articles differ in format from manuscripts submitted for publication or student papers (e.g., different line spacing, font, margins, and column format), articles published in APA journals provide excellent demonstrations of APA Style in action.
APA journals will begin publishing papers in seventh edition APA Style in 2020. The transition to seventh edition style will occur over time and on a journal-by-journal basis until all APA journals use the new style. Professional authors should check the author submission guidelines for the journal to which they want to submit their paper to determine the appropriate style to follow.
The APA Style team worked with accessibility experts at David Berman Communications to ensure that APA Style guidelines as presented in the Publication Manual (7th ed.) are compliant with Web Content and Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 Level AA standards .
Accessible Typography
Here we are going to look at some myths and facts about accessible and usable typography as relevant to APA Style. The main takeaway is this: There do not have to be trade-offs—you can have great, expressive, nuanced typography that also meets or exceeds all regulatory and functional accessibility requirements. To paraphrase David Berman, when we style for the extremes and we do it well, everyone benefits.
Myth 1: Serif Fonts Are Not Accessible
It is a common misconception that serif fonts (e.g., Times New Roman) should be avoided because they are hard to read and that sans serif fonts (e.g., Calibri or Arial) are preferred. Historically, sans serif fonts have been preferred for online works and serif fonts for print works; however, modern screen resolutions can typically accommodate either type of font, and people who use assistive technologies can adjust font settings to their preferences.
Research supports the use of various fonts for different contexts. For example, there are studies that demonstrate how serif fonts are actually superior to sans serif in many long texts (Arditi & Cho, 2005; Tinker, 1963). And there are studies that support sans serif typefaces as superior for people living with certain disabilities (such as certain visual challenges and those who learn differently; Russell-Minda et al., 2007).
However, a skilled designer can create an accessible document that uses serif typefaces effectively, and if structured according to best practice standards, that same document can have its machine text presented in other ways for particular users. For example, a person living with severe dyslexia could choose to have the font swapped in real time with a typeface and spacing that works better for them—thus, there are no trade-offs for the typical user, and the typographic tone of voice that the designer intended for the message is retained.
Furthermore, typeface selection is only one part of the typographic solution for creating accessible typography. Designers must also make wise choices about other factors including size, color, justification, letter spacing, word spacing, line spacing, character thickness, screen resolution, print readiness, and other audience and media issues.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) set standards for online accessibility. WCAG 2.0 Level AA does not set any rules about typeface or type size. It does not specify which typefaces are better than others. There are effective and ineffective serif fonts, just as there are effective and ineffective sans serif fonts. If everyone were to strictly follow the Canadian National Institute for the Blind (CNIB) and the American Council of the Blind (ACB) guidelines for typography, all text would be in 12-point Arial black. Fortunately, you have the flexibility to choose from a variety of font types and identify which will best suit your work.
Furthermore, depending on your organization, there may be additional standards you have to follow to be in alignment with brand guidelines. And depending upon your jurisdiction, there may be additional regulations you need to follow (e.g., the European Union’s EN 301 549 calls for compliance with WCAG 2.1 Level AA, which includes specifics regarding line and character spacing).
Thus, a variety of typeface choices are permitted in APA Style. Also check with your publisher, instructor, or institution for any requirements regarding fonts. We recommend particular fonts in the Publication Manual because they are legible and widely available and because they include special characters such as math symbols and Greek letters. Other fonts can be used with APA Style provided that they also meet these criteria. Thus, users should be able to find a typographic solution that meets their needs.
Myth 2: All Caps Are Not Accessible
Many people have heard that is never accessible to present wording as all-capital lettering; however, this is another myth. Fear not! You can in fact use all caps in an accessible way.
It is true that presenting text in all caps will slow down all readers, especially those with certain types of visual and/or cognitive impairments. However, making sure you do not break the accessibility of wording by putting it in all caps is actually all about doing something no person reading it will see. Here’s how: Always type words with appropriate capitalization (capitals for the beginning of a sentence and proper nouns, etc., lowercase for other words). Then apply a style or text effect to create the appearance of all caps. Screen-reading devices will then announce the words correctly (as opposed to, e.g., trying to treat them as an initialism or acronym and reading out each word letter by letter). Other assistive technologies or conversions will also work correctly because they have the option to override your style to remove the all-caps style or effect. This puts the power exactly where we want it—in the hands of readers.
In APA Style papers, the running head is the only part of the paper that is written in all-capital letters. The running head appears only in professional papers. If the authors’ manuscript will appear online (e.g., as a preprint in PsyArXiv), authors should use a style or text effect as described here to format the running head in all caps.
Myth 3: Smart Quotes Are Not Needed
Using inch marks and foot marks (sometimes also called “straight quotes”) instead of proper left and right quotation marks (both double and single, including apostrophes) makes it harder for assistive technologies to understand your content. Imagine a screen reader announcing “inch” or “foot” rather than announcing the beginning or ending of a quotation.
Everyone deserves proper punctuation. So, in your word-processing program, turn on the option for “smart quotes” to help ensure that you are using the proper mark.
The following examples show the visual difference between straight quotes and proper left and right quotation marks, or smart quotes.
"Straight quotes" “Smart quotes”
Headings in a document identify the topic or purpose of the content within each section. Headings help all readers become familiar with how a document’s hierarchy is structured and how the content is organized, helping them easily find the information they seek. Headings that are formatted and worded well aid both visual and nonvisual readers of all abilities. Headings must be clearly distinguishable from body text.
How can one then create and use excellent headings (and related body text) for all users, including those using assistive technologies? Read on.
Purpose of Headings
The functional purpose of headings is to identify the topic of the content within each section. Treat your headings as if they are “landmarks” within the text, guiding readers to their desired destination. Headings allow readers searching for particular information to find it easily; readers looking to understand the scope of a work are able to do so at a glance.
Also, it is impossible to talk about presenting a truly great heading structure without crossing over into the wording within the headings. Headings should never contain content that is not within the text in the section described by the heading. In other words, if your heading is “How Many Designers Does It Take to Screw in a Lightbulb?” the text in that section must discuss designers and lightbulbs. In academic research papers, standard headings are often used, such as Method, Results, and Discussion. Standard headings allow readers to understand the structure and content of the research being reported. It is best practice to keep headings to 60 characters or less, and 80 at most. This is especially helpful to nonvisual users who could, for example, be using a dynamic Braille display that only presents 80 characters at a time.
When appropriate, headings can, accessibly, include intriguing wording intended to capture readers’ attention, as long as there is also a part of the heading that reveals what is actually present. Just like a book title can include both an intriguing phrase as well as an explanatory phrase (e.g., “Frustration Exemplified: How To Give a Cat a Pill”), you could do the same in a heading. However, context is important: For a “do it yourself” book, this might engage readers and enhance their reading pleasure. For a medical textbook, this might be distracting and even frustrating for readers trying to look up specific information.
In longer works (e.g., dissertations and theses, books), headings appear in a table of contents. The purpose of the table of contents is to give readers an overview of the entire contents of the text as well as to make them familiar with how the content is organized in sections and subsections. Especially for reference works, this is a vital part of the reader interaction. The table of contents, in essence, is a collection of the headings within the text. Readers use visual style and content to understand the importance of the heading (the hierarchy) and the topic or purpose of the content in the section labeled by the heading. Thus, if you have excellent headings (both in content and in visual style), you will generate an excellent table of contents. For electronic documents, excellent headings will help you generate an excellent navigational structure as well.
The Publication Manual does not set standards for tables of contents because journal articles and student papers do not contain tables of contents. For works that include a table of contents, such as dissertations and theses, APA recommends that you use the automatic table of contents function of your word-processing program to create the table of contents. Any of the automatic formats are acceptable. Typically the three highest levels of heading within each chapter or section are included in the table of contents; however, this can vary depending on the length and complexity of the work.
Are You Required to Use Heading Styles in Your Work?
Writers should use heading styles to format and electronically tag headings to help their audience of readers navigate and understand their work. Heading styles also help students create consistently formatted headings.
However, in some cases, using heading styles (vs. manually formatting body text to look like a heading) is optional. The most common case in which it is optional to use heading styles to format text is when authors are submitting a manuscript for publication. Regardless of whether the authors use heading styles in their manuscript, the typesetter will strip the work of all heading styles and implement the headings styles of the publisher. Thus, it is not required for authors to use headings styles in draft manuscripts, but they can if desired. For example, during review, heading styles may help editors and reviewers navigate the work, especially a longer work.
Likewise, students are not required to use heading styles to format their headings, but they can if desired. For example, if students submit a course assignment on paper, it will not matter whether they used heading styles or manual formatting to create the look of headings. However, if students submit an assignment electronically, it may be helpful to use heading styles to facilitate the instructor’s navigation of their work.
If writers are self-publishing their work online, it is helpful to use heading styles to assist readers in navigating the work. For further advice on how to use heading styles, particularly when publishing your work online, read more about accessible typography and style at David Berman Communications .
Inclusion of URLs in Reference Lists
WCAG 2.0 Level AA guidelines recommend that URLs in online works have descriptive text . For example, in the preceding sentence, the words “URLs in online works have descriptive text” are linked to the page at https://www.w3.org/TR/UNDERSTANDING-WCAG20/navigation-mechanisms-refs.html .
However, APA Style references include links with anchor text that is simply the destination DOI or URL (vs. anchor text that is natural, descriptive language)—does this mean that APA Style references are not accessible?
APA Style References Meet Accessibility Standards
To answer this question, the APA Style team consulted with accessibility experts at David Berman Communications to develop our strategy for seventh edition references. Although we considered creating references that included descriptive text links (e.g., linking the title of the work), we settled on the current approach for a few reasons:
- A reference list is not meant to be read from start to finish but rather consulted as needed if readers want more information on works cited in the text. Thus any reader—including a person using a screen reader—would not be expected to follow every link in a reference list. Even if the links in the reference list were beneath descriptive text, the list of links in the reference list would not be particularly helpful on its own because those links need the context of the in-text citation for readers to understand why the links are relevant.
- APA Style governs how manuscripts meant for publication and student papers are prepared. These papers might be read either in print or online. Thus, it is helpful to preserve the actual link address to account for the case in which the work is printed. This approach also produces one set of general guidelines rather than multiple sets, which simplifies writers’ task of understanding and implementing the APA Style reference system.
Because reference lists are not meant to be read from start to finish and because works in APA Style may be published either online or in print, our guidelines recommend that links show the DOI or URL of the work rather than be beneath descriptive text. Links in the text (which are relatively rare—they are only used for general mentions of websites) are treated in the same way; the URL should immediately follow the name of the page being linked to. To reduce the length of links, shortDOIs and shortened URLs are also acceptable.
Using Descriptive Links in APA Style
Although the Publication Manual addresses how to use APA Style for journal publication and student papers, APA Style is used in other contexts as well. Users who develop online-only resources should adapt APA Style to fit their needs. This adaption includes, but is not limited to, the use of descriptive links throughout texts and reference lists.
For example, on this very webpage and throughout the APA Style website, all links appear beneath descriptive text. Other users of APA Style in online contexts should follow this practice as well.
Likewise, in references, people creating online works in APA Style can put the DOI or URL beneath descriptive text. Some reference databases put DOIs or URLs beneath buttons labeled “Article.” Another approach is to link the title of the work to the work’s URL or DOI, as in the following examples.
American Psychological Association. (2019). Talking with your children about stress .
Warne, R. T., Astle, M. C., & Hill, J. C. (2018). What do undergraduates learn about human intelligence? An analysis of introductory psychology textbooks . Archives of Scientific Psychology, 6(1), 32–50.
Accessible Use of Color in Figures
The use of color also presents accessibility concerns. In APA Style, color is most commonly used within figures. It is important that color figures have adequate color contrast to allow users living with color-vision deficiencies (also called “color blindness”) to understand the material. For a thorough description of the accessible use of color, please visit the page on the accessible use of color in figures .
- << Previous: Citation Examples
- Next: Style and Grammar Guidelines >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 12:02 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/apa

APA 7th Edition Style Guide
- Changes/updates
- The Concise APA Handbook: APA 7th Edition
- Article Examples
- Book Examples
- Internet Resources and Other Examples
- Media Examples
- Finding the DOI
- APA Reference Quick Guide
- Legal Cases
- Sample Annotated Student Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Handouts and Guides
Sample Annotated Paper - APA Style 7th Edition
- Annotated Student Sample Paper
- Annotated Professional Sample Paper
- Sample Student Paper (no annotations)
- << Previous: Statutes
- Next: Annotated Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 5:21 PM
- URL: https://libguides.eku.edu/apastyleguide
EO/AA Statement | Privacy Statement | 103 Libraries Complex Crabbe Library Richmond, KY 40475 | (859) 622-1790 ©
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Reference List: Textual Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Basic Format for Books
Edited book, no author, edited book with an author or authors, a translation.
Note : When you cite a republished work, like the one above, in your text, it should appear with both dates: Plato (385-378/1989)
Edition Other Than the First
Article or chapter in an edited book.
Note : When you list the pages of the chapter or essay in parentheses after the book title, use "pp." before the numbers: (pp. 1-21). This abbreviation, however, does not appear before the page numbers in periodical references, except for newspapers. List any edition number in the same set of parentheses as the page numbers, separated by a comma: (2nd ed., pp. 66-72).
Multivolume Work
Articles in periodicals.
APA style dictates that authors are named with their last name followed by their initials; publication year goes between parentheses, followed by a period. The title of the article is in sentence-case, meaning only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. The periodical title is run in title case, and is followed by the volume number which, with the title, is also italicized. If a DOI has been assigned to the article that you are using, you should include this after the page numbers for the article. If no DOI has been assigned and you are accessing the periodical online, use the URL of the website from which you are retrieving the periodical.
Article in Print Journal
Note: APA 7 advises writers to include a DOI (if available), even when using the print source. The example above assumes no DOI is available.
Article in Electronic Journal
Note : This content also appears on Reference List: Online Media .
As noted above, when citing an article in an electronic journal, include a DOI if one is associated with the article.
DOIs may not always be available. In these cases, use a URL. Many academic journals provide stable URLs that function similarly to DOIs. These are preferable to ordinary URLs copied and pasted from the browser's address bar.
Article in a Magazine
Article in a newspaper.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you are looking for how to write a research paper outline APA in Full Sentence Format, here is an example: A. For subheadings, you use capital alphabets A, B, C. B. Subheadings must complement, lead, or link to the paper's main idea. 1. Arabic numerals are used for headings under subheadings like 1, 2, and 3. 2.
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader. Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication).
How to Create a Research Paper Outline Using APA . Understanding APA format basics can make writing psychology research papers much easier. While APA format does not provide specific rules for creating an outline, you can still develop a strong roadmap for your paper using general APA style guidance, your instructor's requirements, and your own personal organizational preferences.
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats. Basic Rules Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the ...
APA_PM7_Ch2-BLueline.indd 51 8/1/19 7:01 PM Sample Papers • 51 Sample Professional Paper (continued) Level 2 heading in the introduction, 2.27, Table 2.3, Figure 2.4 narrative citation, 8.11; paraphrasing, 8.23 parenthetical citation of a work with one author, 8.17 parenthetical citation for works with the same author and same date, 8.19
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
While APA style rules do not specify how to properly format an outline, there are some helpful practices you should adhere to when creating one. This article will help you create an outline that you can use to write your next APA format paper. For help writing your essay, research paper, or other project, check out these writing tips.
APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials; Additional APA 7th Resources; Grammarly - your writing assistant; Writing ... Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper. APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl << Previous: Block Quotations; Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >> Last ...
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Writing an APA outline shouldn't be difficult. Learn how to format your ideal outline with these different examples, and make sure you have a strong backbone for your paper. ... A well-written outline is a valuable tool in crafting the best possible research paper. By building an outline, you establish a structure for what you will say and ...
Body (section 2.11) Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line; Double-space; As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold, and in Sentence Case Capitalization; Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific ...
Sample Student Paper paper title, 2.4, 2.27, Table 2.1, Figure 2.4 parenthetical citation of a work with two authors, 8.17 parenthetical citation of a work with one author, 8.17 group author, 9.11 use of first person, 4.16 italics to highlight a key term, 6.22 narrative citation in parenthetical running text, 8.11 repeated citation needed, 8.1
papers (a change from APA 6). Page numbers begin on the first page and follow on every subsequent page without interruption. No other information (e.g., authors' last names) is required. Note: your instructor may ask for a running head or your last name before the page number. You can look at the APA professional sample paper for guidelines on ...
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Get help formatting your research papers. Things to know before you begin: Font & Font Size: Be sure to use the same font throughout your entire paper.APA 7th Edition allows for the use of the fonts listed below.
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments. The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create ...
The authority on APA Style and the 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual. Find tutorials, the APA Style Blog, how to format papers in APA Style, and other resources to help you improve your writing, master APA Style, and learn the conventions of scholarly publishing.
How to Write APA Style Research Papers The Complete Paper from Title to References By Professor Emma Geller 1. What is the title of the paper? a. This should make the main idea or purpose of the research clear b. A title should not be more than 10-12 words c. You should also include a running head in the upper margin i.
The Concise APA Handbook: APA 7th Edition; Reference Components. Article Examples ; Book Examples ; Internet Resources and Other Examples ; Media Examples ; Finding the DOI ; APA Reference Quick Guide; Legal Citation--Reference Components. Legal Cases ; Statutes ; Sample Annotated Student Paper; Annotated Bibliography; Handouts and Guides; Need ...
Paper Format. Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper's content rather than its presentation. To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
Title of chapter. In E. E. Editor & F. F. Editor (Eds.), Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle (pp. pages of chapter). Publisher. Note: When you list the pages of the chapter or essay in parentheses after the book title, use "pp." before the numbers: (pp. 1-21). This abbreviation, however, does not appear before the page numbers in ...