CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry . These Assignments for Grade 10 Mathematics Trigonometry cover all important topics which can come in your standard 10 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 10 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry class 10 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Trigonometry assignments in Pdf for grade 10th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 10 important questions and answers for Mathematics Trigonometry as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 will be really helpful for standard 10th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 10th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics Trigonometry assignments for Grade 10, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics Trigonometry textbooks for Class 10 .
- All Mathematics Trigonometry assignments for Class 10 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Trigonometry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 10 Mathematics Trigonometry chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry in Grade 10, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Trigonometry Grade 10 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 10 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 10 Computers Assignments

Class 10 Social Science History Assignments

Class 10 Sanskrit Assignments
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 8 Class 10 Introduction to Trignometry
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
The chapter is updated according to the new NCERT, for 2023-2024 Board Exams.
Get NCERT Solutions with videos of all questions and examples of Chapter 8 Class 10 Trigonometry. Videos of all questions are made with step-by-step explanations. Check it out now.
Trigonometry means studying relationship between measures of triangle. Usually, we talk about right triangles when we study trigonometry,
In this chapter, we will study
- What is sin, cos, tan ( Sine, cosine, tangent) ... and how they are found in a triangle
- What is sec, cosec, cot, and how is it related to sin, cos, tan.
- (Sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec, cot are known as Trigonometric Ratios)
- Then, we study Trigonometric ratios of specific angles l ike 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90° ; and do some questions
- We study the formulas of sin (90 - θ) , cos (90 - θ), tan (90 - θ)
- And then we study Trigonometric Identities, and how other identities are derived from sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1
To study the answers of the NCERT Questions, click on an exercise or topic below.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 8: Introduction to Trigonometry
Trigonometry 8.1.
- Intro to the trigonometric ratios (Opens a modal)
- Solving for a side in right triangles with trigonometry (Opens a modal)
- Finding reciprocal trig ratios (Opens a modal)
- Introduction to Trigonometry 8.1 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
Trigonometry 8.2
- Special right triangles intro (part 1) (Opens a modal)
- Special right triangles intro (part 2) (Opens a modal)
- 30-60-90 triangle example problem (Opens a modal)
- Introduction to Trigonometry 8.2 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up!
Trigonometry 8.3
- Intro to Pythagorean trigonometric identities (Opens a modal)
- Converting between trigonometric ratios example: write all ratios in terms of sine (Opens a modal)
- Trigonometric identity example proof involving sec, sin, and cos (Opens a modal)
- Trigonometric identity example proof involving sin, cos, and tan (Opens a modal)
- Trigonometric identity example proof involving all the six ratios (Opens a modal)
- Introduction to Trigonometry 8.3 Get 5 of 6 questions to level up!
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
NCERT solutions for class 10 maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry builds on the concept of a right triangle and introduces students to the basics of trigonometry. The word ‘trigonometry’ is derived from the Greek words ‘tri’ (meaning three), ‘gon’ (meaning sides), and ‘metron’ (meaning measure). Trigonometry can be defined as the study of relationships between the sides and angles of a triangle. There are two main concepts that students will learn in this chapter, which are, trigonometric ratios and trigonometric identities. Most of the technologically advanced methods used in Engineering and Physical Sciences are based on trigonometric concepts making it an extremely important lesson. This is one of the most scoring topics in the board examinations provided they go through the topic with diligence and in an organized manner. These concepts are also used in sister topics of higher classes such as calculus and geometry.
NCERT solutions class 10 maths Chapter 8 helps students recognize the trigonometric functions that are used in an equation. There are 6 trigonometric ratios in a right-angled triangle. These are sine , cosine , tangent , cosecant , secant, and cotangent. These solutions will be the perfect guidelines that a student can use to build a very strong conceptual foundation of these ratios. They also enable kids to explore some practical applications of trigonometry. In this class 10 maths NCERT solutions Chapter 8, we will take a look at this lesson in detail and see how to effectively apply these concepts and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.4
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 PDF
A trigonometric ratio of an acute angle in a right triangle expresses the relationship between the angle and the length of its sides. The entire chapter of trigonometry is based on this simple concept. Throughout this lesson, there will be several important inferences drawn from theorems that will be useful in performing calculations. One such fact is that the values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the lengths of the sides of the triangle if the angle remains the same. To learn more, the NCERT solutions class 10 maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry can be downloaded for free in a scrollable PDF format using the links given below.
☛ Download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8
NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry covers all the basic concepts of trigonometry. This chapter also consists of many interesting formulas that can help solve questions related to real-life situations. Trigonometry is an essential concept for higher classes and competitive exams. As this is such a crucial lesson it is highly recommended to revise the important concepts outlined regularly. You can go through the detailed analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry mentioned below:
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.1 - 11 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.2 - 4 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.3 - 7 Questions
- Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.4 - 5 Questions
☛ Download Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: The topics covered in class 10 maths NCERT Solutions chapter 8 are trigonometric ratios , trigonometric identities , trigonometric ratios of specific angles , and trigonometric ratios of complementary angles . The discussion on trigonometric ratio and identities will be limited to acute angles only.
Total Questions: Class 10 maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry consists of 27 questions, of which 10 are straightforward, 10 are moderate, and 7 are long answer type problems. These sums have been distributed over 4 exercises.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 is a chapter based on formulas. It is advisable to create a formula chart as there are several formulas associated with trigonometry . Students must memorize all these formulas in order to produce satisfactory results and solve problems. As it can get confusing at times hence, practicing sums based on these formulas and identities is equally necessary. Kids can also go through the derivation of these formulas to develop a rock-solid foundation as well as understand the underlying concepts. Let us now go through some of the formulas covered in this chapter.
- sin A = Perpendicular/ Hypotenuse
- cos A = Base/ Hypotenuse
- tan A = Perpendicular/ Base
- cos 2 A + sin 2 A = 1
- 1 + tan 2 A = sec 2 A
- cot 2 A + 1 = cosec 2 A
Important Questions for Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8
Video solutions for class 10 maths ncert chapter 8, faqs on ncert solutions class 10 maths chapter 8, why are ncert solutions class 10 maths chapter 8 important.
NCERT solutions class 10 maths chapter 8 will help students establish a relationship between the sides and angle of a triangle. This topic is important for class 10 maths as it carries a huge weightage in exams and is very scoring. Chapter 8 lays a foundation for more complex trigonometry topics that will be taught in higher classes. This is considered to be the most essential subject matter that kids will be introduced to throughout their academic careers.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Given in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Introduction to Trigonometry?
Students should not miss out on any questions from NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Introduction to Trigonometry because each allows them to understand the topic at length and explore the formulas. A majority of questions are based on real-life examples thus, this topic becomes relatable and engaging. With the help of these problems, kids have the opportunity to score excellent results in their examinations.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8?
The NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 have a set of topics that give kids a holistic understanding of this lesson hence, all are equally important. Students must progress through this chapter very meticulously and with great focus. There are several tips and tricks outlined in this lesson that are helpful not only in acing the board exams but also in attempting challenging problems that appear in higher classes.
How many questions are there in Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8?
A total of 27 questions are included in NCERT solutions class 10 Maths Chapter 8 divided amongst 4 exercises. These sums cover different aspects of trigonometry including trigonometric ratios and identities. It is advisable for students to go through the chapter summary and solved examples before attempting these exercises.
What are the Important Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8?
One can find a variety of formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8. Some of the important formulas are reciprocal functions, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, the value of sin, cos, and many more. One has to master the formulas in order to crack all the questions of this chapter. Students can make formula charts to remember all the important formulas and revise them when required.
How can CBSE Students utilize NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 effectively?
CBSE students can utilize NCERT solutions class 10 maths chapter 8 effectively by solving each and every question. In case they get stuck on any problem, kids must check the detailed solutions to that sum. They can also go through the derivation of certain formulas to get a better idea of how to apply them to problems efficiently. It is necessary to go through all the theories before attempting the sums in order to get the most out of these solutions.
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments For Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry
Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry have been developed for Standard 10 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry from our website as we have provided all topic wise assignments free in PDF format which can be downloaded easily. Students are recommended to do these assignments daily by taking printouts and going through the questions and answers for Grade 10 Mathematics Trigonometry. You should try to do these test assignments on a daily basis so that you are able to understand the concepts and details of each chapter in your Mathematics Trigonometry book and get good marks in class 10 exams.
Question. If xcosθ – ycosθ = a, xsinθ + ycosθ = b , then x 2 + y 2 = ? A) a+b B) a 2 +b 2 C) a 2 – b 2 D) a-b
Question If sec2θ + cosec2θ can never be less than A) 1 B) 0 C) -1 D) 2
Question. If sin = 1/2 then 3cosθ – 4cos θ A) 0 B) 1 C) -1 D) 2
Question. sec Φ + tan Φ = p, sin Φ = ? A) (P+1) /P 2 -1 B) P 2 +1 /2P 2 -1 C) P 2 -1 /P 2 +1 D) None of these
Question. If 1– tanΘ/ 1–tanΘ = √(3 – 1) /√(3 + 1) then sinΘ /cos2Θ ? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3
Question. If 2x =secΘ and 2/x tanΘ , then find the value of 2 ( x2 – 1/x 2 ) A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3
Question. If 7sin2 θ + 3cos2θ = 4 then tanθ ? A) 2/√3 B) 1/√3 C)-2/√3 D) 4/√3
Question. If cos Φ + sin Φ = √2 cos Φ then cos Φ – sin Φ A) 2sin Φ B) 2cos Φ C) 2 sin Φ D) 2 cos Φ
Question. If tan A+sin A = m and tan A-sin A = n then m 2 – n 2 ? A) 4mn B) 4 √mn C) 2mn D) 2√mn
Question. If secA = x+1/4x then sec A + tanA= ? A) xor (1/X) B) 2xor (1/2X) C) 3xor (1/X) D) 3xor (1/3X)
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. The tops of two poles with heights 25 m and 35 m are connected by a wire, which makes an angle of elevation 30° at the top of 25 m pole. What is the length of the wire?
Question. A circus artist is climbing 24 m long rope, which is tightly stretched from the top of a vertical pole on the ground. If angle of elevation of the rope to the ground is 30°, what is the height of the pole?
Question. A tree breaks due to storm and the broken part bends so that the top of the tree touches the ground making an angle 30° with it. The distance between the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is 8 m. Find the height of the tree.
8 √3 m
Question. In figure, An object A is observed from two light houses P and Q. What are the angles of depression from the observing light houses?
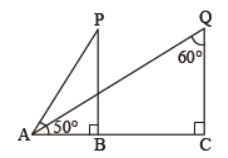
50° and 30° respectively
Question. In figure, what is the length of BC.
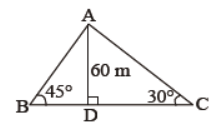
60 ( √3 +1) m
Question. A person standing on the bank of a river observe the angle of elevation of tree is 60°. When he moves 40 m away, the angle of elevation becomes 30°. At what distance is he now standing away from tree?
Question. In figure, the pole AB is 10 m away from a point C on the ground. What is the height of the pole?
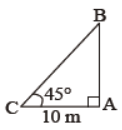
Question. A girl of height 170 cm stands in front of a lamp-post and casts a shadow of length 170 √3 cm on the ground. Find the angle of elevation of the top of the lamp-post.
Question. The ratio of the length of a rod and its shadow is √3 :1. Find the angle of elevation of the sun.
Question. If the steel wire tied to the top of the tower, makes an angle of 60° with the ground, then what is the length of the wire, if height of the tower is 18 m.
Trigonometric Ratios
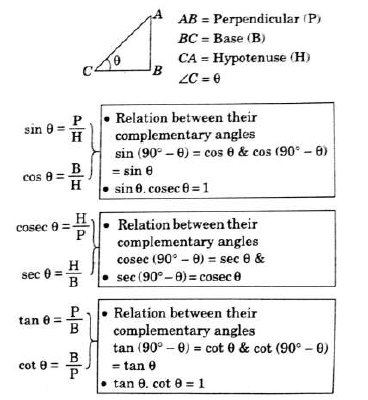
Trigonometric Identities Relationship between trigonometric ratio that holds true for any value of θ
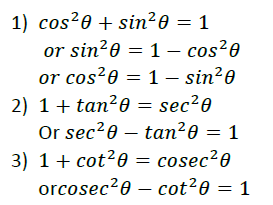
Question. If sec 2 θ (1 + sinθ)(1 – sinθ) = k, then find the value of k. Sol. sec 2 θ (1 +sinθ)(1 -sinθ) = sec2θ (1 -sin2θ) [(a + b)(a – b) = a 2 – b 2 ] = sec2θ .cos2θ [ ∴ cos2θ+sin 2 θ =1] = 1 ∴ k =1.
Question . If sin A = 3/4 calculate cos A and tan A.
Question. If sin A +sin 2 A =1, then cos 2 A +cos4 A =1. Sol. True, sin A +sin 2 A =1 ⇒ sin A =1 -sin 2 A = cos 2 A ∴ cos 2 A +cos 4 A = sin A +sin 2 A =1.
Question . If cot θ= 7/8 evaluate: (i) (1+sinθ) (1-sinθ)/(1+cosq) (1-cosθ), (ii) cot 2 θ
Sol. Let us draw a right triangle ABC in which ∠B = 90° and ∠C = θ. We have

Question. tan47°/cot73°=1 Sol. True, tan47°/cot73°=tan(90°-43° )/cot43°= cot43°/cot43°
Question . In ΔPQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
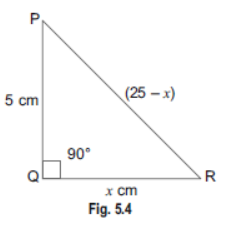
Sol. We have a right-angled ΔPQR in which ∠Q = 90°. Let QR = x cm Therefore, PR = (25 – x) cm By Pythagoras Theorem, we have PR 2 = PQ 2 + QR 2 (25 – x) 2 = 5 2 + x 2 ⇒ (25 – x) 2 – x 2 = 5 2 ⇒ (25 – x – x) (25 – x + x) = 25 ⇒ (25 – 2x) 25 = 25 Þ 25 – 2x =1 ⇒ 25 -1 = 2x ⇒ 24 = 2x ∴ x =12 cm. Hence, QR =12 cm PR = (25 – x) cm = 25 -12 =13 cm PQ = 5 cm
Question. If A + B = 90° and tan A = 3/4 , what is cot B ? Sol. cot B = cot (90°-A) ( ∴ A + B = 90°) = tan A ( ∴ cot (90° -θ) = tanθ) = 3/4.
Question . Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
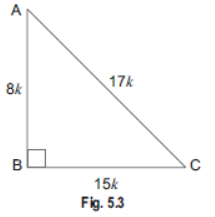
Sol. Let us first draw a right ΔABC, in which ∠B = 90°. Now, we have, 15 cot A = 8
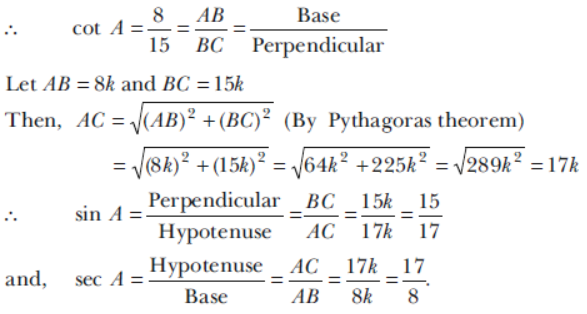
Question. The value of the expression (cos80° -sin80°) is negative. Sol. True, for θ > 45° , sinθ > cosθ, so cos80° -sin80° has a negative value.
Question. If 3 cot A = 4, check whether 1-tan 2 A/1+tan 2 A=cos 2 Asin 2 A or not.
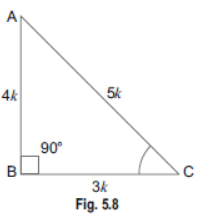
Sol. Let us consider a right triangle ABC in which ∠B= 90°.

Question. Write the acute angle θ satisfying 3 sinθ = cosθ. Sol. 3 sinθ = cosθ ⇒ sinθ/cosθ 1/3 ⇒ tanθ = 1/3 ⇒ θ = 30°.
Question. (tanθ +2)(2tanθ +1) = 5tanθ +sec 2 θ. Sol. False, (tanθ +2)(2tanθ +1) = 2tan 2 θ +5tanθ +2 = 5tanθ +2(1+tan 2 θ) = 5tanθ +2sec 2 θ.
Question. Write the value of cot 2 θ=1/sin 2 θ Sol. cot 2 θ=1/sin 2 θ= cot 2 θ-cosec2θ =1.
Question . If sinθ = 1/3 , then find the value of 2cot 2 θ+2. Sol.
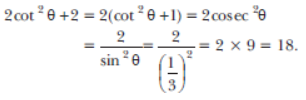
Question. Express the trigonometric ratios sin A, sec A and tan A in terms of cot A.
Sol. Let us consider a right-angled ΔABC in which ∠B = 90°. For ∠A, we have Base = AB Perpendicular = BC and Hypotenuse = AC
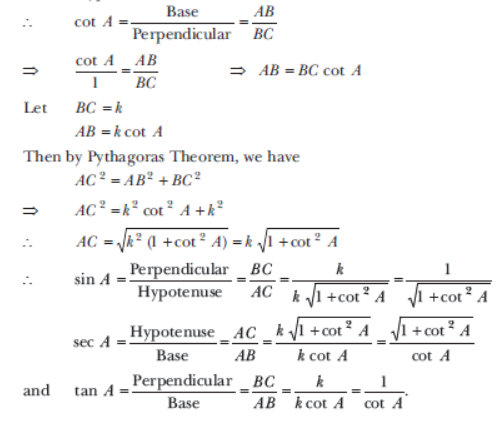
Question . Write all the other trigonometric ratios of ∠A in terms of sec A.
Sol. Let us consider a right-angled ΔABC, in which ∠B = 90°. For ∠A, we have Base = AB, Perpendicular = BC and Hypotenuse = AC

Question. Evaluate : 5cos 2 60° + 4sec 2 30° – tan 2 45°/sin2 30° + cos2 30° Solution.
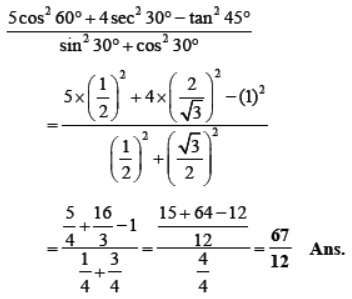
Question. If tan (A + B) = √3 and tan (A – B) = 1/√3 ; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°; A > B, find A and B. Solution. tan (A + B) = √3 = tan 60° ⇒ A + B = 60° and, tan (A B) = 1/√3 = tan 30° ⇒ A – B = 30° On adding (1) and (2), we get, 2A = 90° ⇒ A = 45° subtracting (2) from (1), we get, 2B = 30° ⇒ B = 15° So, A = 45° and B = 15° Ans.
Question. Given : cotθ = 20/21 , find all other trigonometric ratios. Solution.

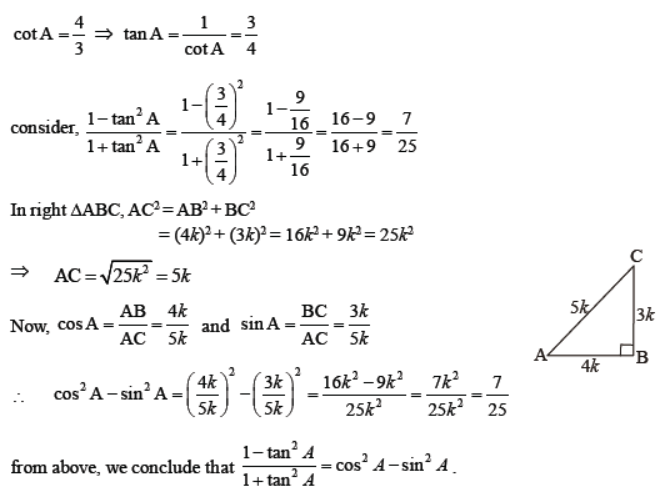
Question. If 3 cot A = 4, check whether 1 – tan 2 A /1 + tan 2 A = cos 2 A – sin 2 A or not. Solution.
Question. If A, B, C are the interior angles of a triangle ABC, show that sin(B + C)/2 = cos A/2 . Solution. We know, in any ΔABC, A + B + C = 180° ⇒ B + C = 180° – A
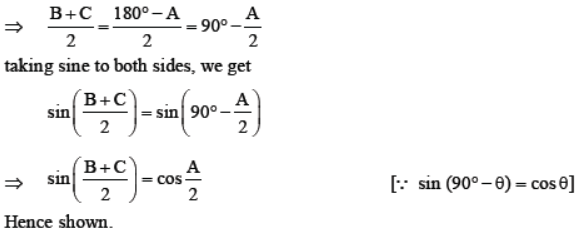
Question. Prove the following Trigonometric identities :
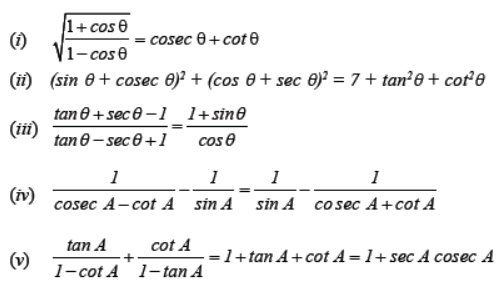
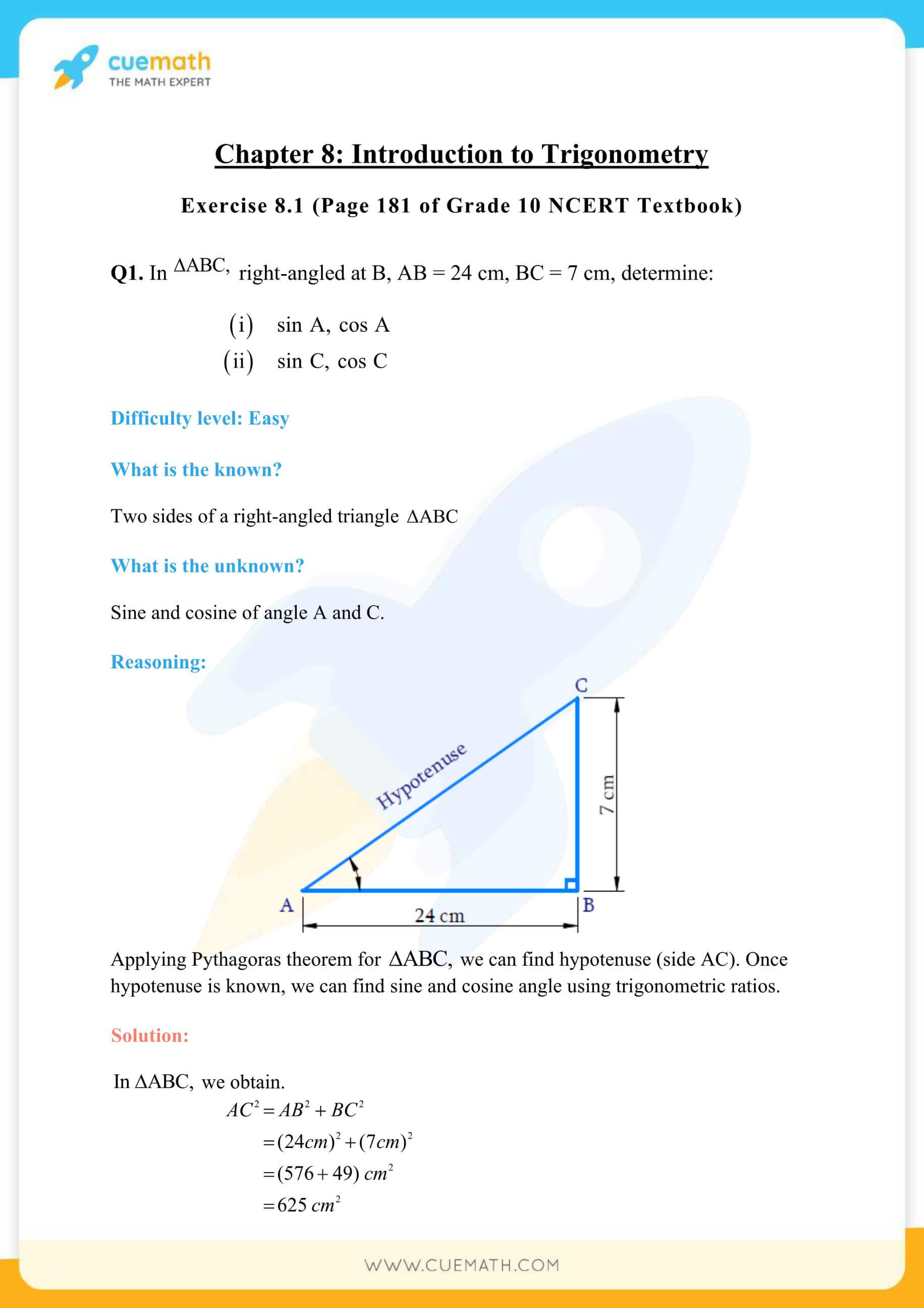
Question. In ΔABC, right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine : (i) sin A, cos A (ii) sin C, cos C Solution. In right angled ΔABC, we have AC 2 = AB 2 + BC 2 ⇒ AC 2 = (24) 2 + (7) 2 ⇒ AC 2 = 576 + 49 ⇒ AC 2 = 625 ⇒ AC = 25

Question. (i) If tan θ + sin θ = m and tan θ – sin θ = n, show that m 2 – n 2 = 4 √mn. (ii) If sec θ + tan θ = p, show that p 2 – 1/p 2 + 1 = sinθ Solution. (i) We have, LHS = m 2 – n 2 = (tan θ + sin θ) 2 – (tan θ – sin θ) 2 = (tan 2 θ + sin 2 θ + 2tan θ . sin θ)– (tan 2 θ + sin 2 θ – 2 tan θ sin θ) = 4 tan θ sin θ
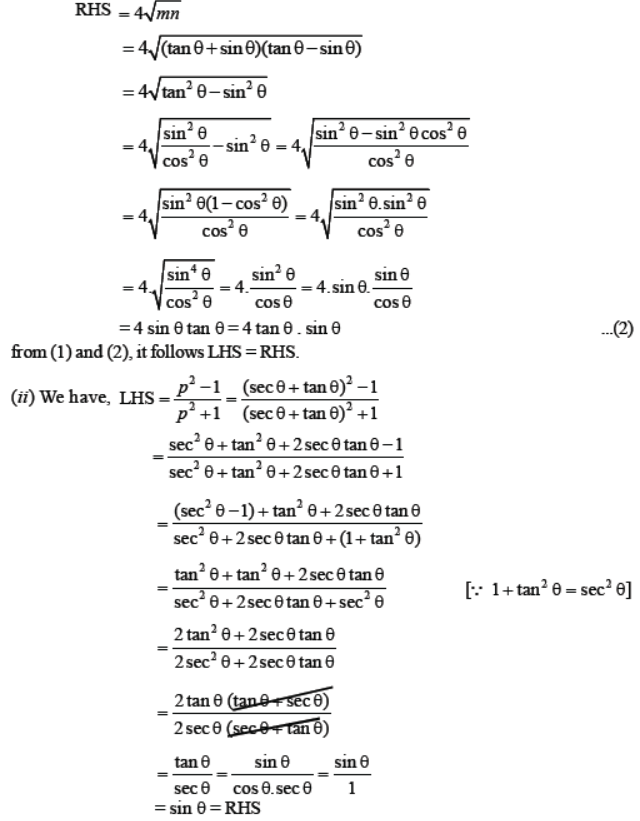
Question. Evaluate :
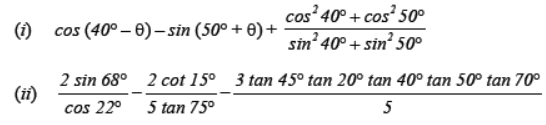
Question. If tan 2 A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle, find the value of A. Solution. We have, tan 2 A = cot (A – 18°) = tan [90° – (A – 18°)] [∴ cot θ = tan (90° – θ)] = tan (108° – A) ⇒ 2A = 108° – A ⇒ 3A = 108° ⇒ A = 108°/3 ⇒ A = 36°Ans.
PRACTICE EXERCISE
Question. A person standing on the bank of a river observes that the angle of elevation of the top of a tree standing on the opposite bank is 60°. When he moves 40 meters away from the bank, he finds the angle of elevation to be 30°. Find the height of the tree and the width of the river. Solution. height of tree = 34.64 m, width of river = 20 m
Question. A boy standing on a horizontal plane finds a bird flying at a distance of 100 m from him at an elevation of 30°. A girl standing on the roof of 20 metre high building, finds the angle of elevation of the same bird to be 45°. Both the boy and the girl are on opposite sides of the bird. Find the distance of bird from the girl. Solution. 30 √2 m
Question. Two men on either side of a cliff 80 m high observe the angles of elevation of top of the cliff to be 30° and 60° respectively. Find the distance between the two men. Solution. 184.64 m
Question. An aeroplane, when 1500 m high passes vertically above another aeroplane at an instance when the angles of the two aeroplanes from the same point on the ground are 60° and 45° respectively. Find the vertical distance between the two aeroplanes. Solution. 634 m
Question. The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points on the ground at distances 9m and 4m from the base of the tower are in the same straight line with it are complementary. Find the height of the tower. Solution. 6 m
Question. A flagstaff stands on the top of a 5 m high tower. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the flag-staff is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 45°. Find the height of the flag-staff. Solution. 3.65 m
Question. Two men are on the opposite sides of a tower. They measure the angles of elevation of the top of the towers as 30° and 45°. If the height of the tower is 60 m, find the distance between them. Solution. 163.92 m
Question. An aeroplane, at an altitude of 200 m, observes the angles of depression of opposite points on the two banks of a river to be 45° and 60°. Find the width of the river. Solution. 315.46 m
Question. From the top of a building 15 m high the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is found to be 30°. From the bottom of the same building, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is found to be 60°. Find the height of the tower and the distance between the tower and the building. Solution. Height = 22.5 m, Distance = 12.975 m
Question. At a point on the level ground the angle of elevation of a vertical tower is found to be such that its tangent is 5/12 . On walking 192 m towards the tower, the tangent of the angle is found to be 3/4 . Find the height of the tower. Solution. 180 m
Question. The angles of depression of two ships from the top of a light house are 45° and 30°. If the ships are 200 m apart, find the height of the light house. Solution. 273.2 m
Question. A man is standing on the deck of the a ship, which is 8 m above water level. He observes the angle of elevation of the top of the hill as 60° and the angle of depression of the base of the hill as 30°. Find the distance of the hill from the ship and the height of the hill. Solution. 32 m and 8 √3 m
Question. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point A on the ground is 30°. On moving a distance of 20 metres towards the foot of the tower to a point B, the angle of elevation increases to 60°. Find the height of the tower and the distance of the tower from the point A. Solution. Height = 17.32 m, Distance = 30 m
Question. From the top of a hill, the angle of depression of two consecutive milestones due east are found to be 30° and 45°. Find the height of the hill. Solution. √3 +1/2 miles
Question. The shadow of a tower, when the angle of elevation of the sun is 45°, is found to be 10 m longer than when it was 60°. Find the height of the tower. Solution. 23.66 m
Question. The horizontal distance between two towers is 140 m. The angle of elevation of the top of the first tower when seen from the top of the second tower is 30°. If the height of the second tower is 60 m, find the height of the first tower. Solution. 140.73 m
Question. The angle of elevation of a jet plane from a point A on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to 30°. If the jet plane is flying at a constant height of 1500 √3 m, find the speed of the jet plane. Solution. 720 km/hr = 200 m/s
Question. The angle of elevation of the top of a hill at the foot of the tower is 60° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the hill is 30°. If the tower is 50 m high, what is the height of the hill? Solution. 150 m
Question. An observer in a lighthouse 100 m above the sea-level is watching the ship sailing towards the lighthouse. The angle of depression of the ship from the observer is 30°. How far is the ship from the lighthouse? Solution. 100 √3 m
Question. On a horizontal plane there is a vertical tower with a flag pole on the top of the tower. At a point 9 metres away from the foot of the tower the angle of elevation of the top and bottom of the flag pole are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the tower and the flag pole mounted on it. Solution. 3√3 m, 6√3 m
Question. From a point 30 m away from the foot the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30°. Find the height of the tower. Solution. 17.32 m
Question. An aeroplane flying horizontally 1 km above the ground is observed at an elevation of 60°. After 10 seconds, its elevation is observed to be 30°. Find the speed of the aeroplane in km/hr. Solution. 415.66 km/hr
Question. As observed from the top of a light-house, 100 m above sea level, the angle of depression of a ship sailing directly towards it, changes from 30° to 45°. Determine the distance travelled by the ship during the period of observation. Solution. 73.2 m
Question. An observer, 1.5 m tall, is 28.5 m away from a tower 30 m high. Find the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from his eyes. Solution. 45°
Question. Find the sun’s altitude when the height of a tower is √3 times of the length of its shadow. Solution. 60°
Question. A 7 m long flagstaff is fixed on the top of a tower on the horizontal plane. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top and the bottom of the flagstaff are 45° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the tower correct to one place of decimal. Solution. 9.6 m
Question. A man on the roof of a house which is 10 m high observes the angle of elevation of the top of a building as 45° and the angle of depression of the base of the building as 30°. Find the height of the building and its distance from the house. Solution. Height of the building = 10 ( √3 +1) m, Distance of the building from house = 10 √3 m
Question. There is a small island in a 100 m wide river and a tall tree stands on the island. P and Q are points directly opposite to each other on the two banks and in the line with the tree. If the angles of elevation of the top of the tree from P and Q are 30° and 45° respectively, find the height of the tree. Solution. 36.5 m
Question. From the top of a cliff 50 m high, the angles of depression of the top and bottom of a tower are observed to be 30° and 45° respectively. Find the height of the tower. Solution. 21.17 m
Question. The angles of elevation and depression of the top and bottom of a light-house from the top of a building 60 m high, are 30° and 60° respectively. Find (i) the difference between the heights of the light-house and the building. (ii) distance between the light-house and the building. Solution. (i) 20 m (ii) 34.64 m
Question. The horizontal distance between two towers is 75 m and the angle of depression of the top of the first tower as seen from the top of the second tower, which is 160 m high, is 45°. Find the height of the first tower. Solution. 85 m
Question. The angle of elevation of a tower at a point is 45°. After going 40 m towards the foot of the tower, its angle of elevation becomes 60°. Find the height of the tower. Solution. 94.64 m
Question. The angle of elevation θ of the top of a light house, as seen by a person on the ground is such that tanθ = 5/12 . When the person moves a distance of 240 m towards the light house, the angle of elevation becomes φ such that tan φ = 3/4 . Find the height of the light house. Solution. 225 m
Question. A man on the top of a vertical tower observes a car moving at a uniform speed coming directly towards it. If it takes 12 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 45°, how soon after this will the car reach the observation tower? Solution. 16 minutes 23 seconds
Question. A bird is sitting on the top of a tree, which is 80 m high. The angle of elevation of the bird from a point on the ground is 45°. The bird flies away from the point of observation horizontally and remains at a constant height. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the point of observation becomes 30°. Find the speed of the flying bird. Solution. 29.28 m/s
Question. The upper part of a tree is broken by the action of wind. The top of the tree makes an angle of 45° with the horizontal ground. The distance between the base of the tree and the point where it touches the ground is 12 m. Find the height of the tree. Solution. 28.92 m
Question. The angle of elevation of the top of an unfinished tower at a point distant 120 m from its base is 45°, how much higher must the tower be raised so that its angle of elevation at the same point may be 60°? Solution. 87.84 m
Question. From a point on the ground the angles of elevation of the bottom and top of a water tank kept at the top of 20 m high tower are 45° and 60°. Find the height of the water tank. Solution. 14.60 m
Question. The angles of depression of the top and the bottom of a building, 50 metres high, as observed from the top of a tower are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower and also the horizontal distance between the building and the tower. Solution. 43.25 m and 75 m
Question. Standing on the top of a tower 100 m high, Abhishek observes two cars on the opposite sides of the tower. If their angles of depression are 60° and 45°, find the distance between the two cars. Solution. 157.74 m
Question. A surveyor wants to find the height of the top of a hill. He observes that the angles of elevation of the top of the hill at points C and D, 300 m apart, lying on the base of the hill and on the same side of the hill are 30° and 45° respectively. What is the height of the hill. Solution. 150( √3 +1) m
Question. An aeroplane flying horizontally 1 km above the ground is observed at an elevation of 60°. After 10 seconds, its elevation is observed to be 30°. Find the speed of the aeroplane in km/hr. Solution. 415.2 km/hr (approx)
Question. A statue 1.6 m tall stands on the top of pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 45°. Find the height of the pedestal. Solution. 2.184 m
Question. The angle of elevation of the top of a hill at the foot of a tower is 60° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the hill is 30°. If the tower is 65 m high, what is the height of the hill? Solution. 195 m
Question. On the same side of the tower, two objects are located. Observed from the top of the tower, their angles of depressions are 45° and 60°. If the height of the tower is 150 m, find the distance between the objects. Solution. 63.4 m
Question. The horizontal distance between two trees of different heights is 90 m. The angle of depression of the top of the first tree when seen from the top of the second tree is 30°. If the height of the second tree is 72 m, find the height of the first tree. Solution. 20.04 m
Question. From a building 60 m high, the angle of depression of the top and bottom of a lamp post are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the distance between the lamp post and building. Also find the difference of height between lamp post and building. Solution. 20 √3 m and 20 m
Question. The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 200 m above the lake is 30° and the angle of depression of its reflection in the lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud. Solution. 400 m
Question. A boy is standing on the ground and is flying a kite with 100 m of string at an elevation of 30°. Another boy is standing on the roof of a 10 m high building and is flying his kite at an elevation of 45°. Both the boys are on opposite sides of the kites. Find the length of the string that the second boy must have so that the two kites meet. Solution. 40 √2 m
Question. A bridge across a river makes an angle of 30° with the river bank. If the length of the bridge across the river is 60 m, find the width of the river. Solution. 40 m
Question. From the top of a tower 100 m, the angles of depression of the top and bottom of a pole standing on the same plane as the tower are observed to be 30° and 45° respectively. Find the height of the pole. Solution. 42.26 m
Question. Two ships are sailing in the sea on the either side of the light-house, the angles of depression of two ships as observed from the top of the light-house are 60° and 45° respectively. If the distance between the ships is 200 (√3 + 1/√3) metres, find the height of the light-house. Solution. 200 m
Question. A ladder is placed along a wall such that its upper end is touching the top of the wall. The foot of the ladder is 2m away from the wall and the ladder is making an angle of 60° with the level ground. Find the height of the wall. Solution. 3.46 m
Question. The length of the shadow of a tower at a particular time is one-third of its shadow, when the sun’s rays meet the ground at an angle of 30°. Find the angle between the sun’s rays and the ground at the time of shorter shadow. Solution. 60°
Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry as per CBSE NCERT pattern
All students studying in Grade 10 Mathematics Trigonometry should download the assignments provided here and use them for their daily routine practice. This will help them to get better grades in Mathematics Trigonometry exam for standard 10. We have made sure that all topics given in your textbook for Mathematics Trigonometry which is suggested in Class 10 have been covered ad we have made assignments and test papers for all topics which your teacher has been teaching in your class. All chapter wise assignments have been made by our teachers after full research of each important topic in the textbooks so that you have enough questions and their solutions to help them practice so that they are able to get full practice and understanding of all important topics. Our teachers at https://www.assignmentsbag.com have made sure that all test papers have been designed as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern. These question banks have been recommended in various schools and have supported many students to practice and further enhance their scores in school and have also assisted them to appear in other school level tests and examinations. Its easy to take print of thee assignments as all are available in PDF format.
Some advantages of Free Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry
- Solving Assignments for Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 helps to further enhance understanding of the topics given in your text book which will help you to get better marks
- By solving one assignments given in your class by Mathematics Trigonometry teacher for class 10 will help you to keep in touch with the topic thus reducing dependence on last minute studies
- You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected in your Mathematics Trigonometry class test
- You will be able to revise all topics given in the ebook for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry as all questions have been provided in the question banks
- NCERT Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Workbooks will surely help you to make your concepts stronger and better than anyone else in your class.
- Parents will be able to take print out of the assignments and give to their child easily.
All free Printable practice assignments are in PDF single lick download format and have been prepared by Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry teachers after full study of all topics which have been given in each chapter so that the students are able to take complete benefit from the worksheets. The Chapter wise question bank and revision assignments can be accessed free and anywhere. Go ahead and click on the links above to download free CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry Assignments PDF.
Free PDF download of Trigonometry Assignment Class 10 with Answers created by master educators from the latest syllabus of CBSE Boards. By practicing this Class 10 Trigonometry Assignments will help you to score more marks in your CBSE Board Examinations. We also give free NCERT Solutions and other study materials for students to make their preparation better.
Students who are searching for better solutions can download the Trigonometry Assignment Class 10 with answers to assist you with revising the whole syllabus and score higher marks in your exam.
This Trigonometry Assignment Class 10 with answers shows up with an answer key with step-by-step answers for students to comprehend the problem at each level and not retain it.

You can download free assignments for class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry from https://www.assignmentsbag.com
You can get free PDF downloadable assignments for Grade 10 Mathematics Trigonometry from our website which has been developed by teachers after doing extensive research in each topic.
On our website we have provided assignments for all subjects in Grade 10, all topic wise test sheets have been provided in a logical manner so that you can scroll through the topics and download the worksheet that you want.
You can easily get question banks, topic wise notes and questions and other useful study material from https://www.assignmentsbag.com without any charge
Yes all test papers for Mathematics Trigonometry Class 10 are available for free, no charge has been put so that the students can benefit from it. And offcourse all is available for download in PDF format and with a single click you can download all assignments.
https://www.assignmentsbag.com is the best portal to download all assignments for all classes without any charges.
Related Posts

Assignments For Class 12 Economics

Assignments For Class 9 Mathematics Herons Formula

Assignments For Class 10 Chemistry
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 - Some Applications Of Trigonometry
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry - Free PDF Download
Chapter 9 of the class 10 maths syllabus is on Applications of Trigonometry. It is an important chapter that is covered in class 10 and is divided into 3 major sections. We recommend that students take time to read through these topics very carefully so that they do not miss out on any important information that is provided in our solutions. Our expert teachers have invested their time in curating these exam-appropriate solutions to best suit the needs of the students to aid them in scoring well in their examinations.
The following table has been provided to give the students a glimpse at the subtopics under the chapter on Applications of Trigonometry.
Importance of Applications of Trigonometry
The branch of mathematics that deals with relations of the sides and angles of triangles and the related functions of angles of triangles is known as Trigonometry.
The application of trigonometry is an important area that students in class 10 should concentrate on. These applications will not just help in solving sums based on trigonometry in exams but will also aid in real-world calculations and measurements.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry gives a detailed explanation of all the questions given in the NCERT textbook. NCERT Solutions help you to score high marks in 10th CBSE board exams as well as increase your confidence level as all the trigonometry related concepts are well-explained in a structured way. The Vedantu expert teachers have prepared the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 some applications of trigonometry free pdfs as per the NCERT syllabus and guidelines given by the CBSE board. NCERT Solution is always beneficial in your exam preparation and revision. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Also, you can revise and download Class 10 Science Solutions for Exam 2023-2024, using the updated CBSE textbook solutions provided by us.
Key Features for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
The key features of Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions for Ch-9 Some Applications of Trigonometry are listed below.
Provides a comprehensive explanation of the applications of trigonometry
Available as free downloadable PDF files
Easy to access on the Vedantu mobile app and website
Step-by-step solutions for all sums
Supporting explanations for self-study
Solved by experts as per the updated CBSE syllabus and guidelines

Related Chapters
Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Exercise 9.1: This exercise covers four questions related to finding angles of elevation and depression. The questions involve finding the height, distance, or both of an object using trigonometric ratios. The solutions provided aim to help students understand the practical application of trigonometry in real-life situations.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 - Some Applications Of Trigonometry
Exercise- 9.1
1. A circus artist is climbing a \[20m\] long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \].
Ans: By observing the figure, \[AB\] is the pole.
In\[\Delta ABC\],
$\frac{\text{AB}}{\text{AC}}=\sin {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{20}=\frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{AB}=\frac{20}{2}=10$
Therefore, the height of the pole is$10m$.
2. A tree breaks due to storm and the broken part bends so that the top of the tree touches the ground making an angle \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \]with it. The distance between the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is \[\mathbf{8m}\]. Find the height of the tree.
Ans: Let \[AC\]was the original tree. Due to the storm, it was broken into two parts. The broken part \[AB\] is making 30° with the ground.
Let $\mathrm{AC}$ be the original tree. Due to the storm, it was broken into two parts. The broken part $\mathrm{A}^{\prime} \mathrm{B}$ is making ${{30}^{{}^\circ }}$ with the ground. In triangle${{\text{A}}^{\prime }}\text{BC}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{BC}{{{A}^{\prime }}C}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{BC}{8}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{BC}=\left( \frac{8}{\sqrt{3}} \right)\text{m}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{{{\text{A}}^{\prime }}\text{C}}{{{\text{A}}^{\prime }}\text{B}}=\cos 30$
$\Rightarrow \frac{8}{{{A}^{\prime }}B}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{A}^{\prime }}B=\left( \frac{16}{\sqrt{3}} \right)m$
Height of tree $=\mathrm{A}^{\prime} \mathrm{B}+\mathrm{BC}$
$=\left(\frac{16}{\sqrt{3}}+\frac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\right) \mathrm{m}=\frac{24}{\sqrt{3}} \mathrm{~m}$
$=8 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m}$
3. A contractor plans to install two slides for the children to play in a park. For the children below the age of $5$ years, she prefers to have a slide whose top is at a height of\[\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{5m}\], and is inclined at an angle of \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \] to the ground, whereas for the elder children she wants to have a steep slide at a height of\[\mathbf{3m}\], and inclined at an angle of \[60{}^\circ \] to the ground. What should be the length of the slide in each case?
Ans: It can be observed that $\text{AC}$ and $\text{PR}$ are the slides for younger and elder children respectively.
In $\vartriangle \text{ABC}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{AC}}=\sin 30$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1.5}{\text{AC}}=\frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{AC}=3~\text{m}$
In $\vartriangle \text{PQR}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{PQ}}{\text{PR}}=\sin {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3}{\text{PR}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{PR}=\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}=2\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$
Therefore, the lengths of these slides are $3~\text{m}$ and $2\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$.
4. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is\[\mathbf{30m}\] away from the foot of the tower is \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ .\] Find the height of the tower.
Ans: Let $\mathrm{AB}$ be the tower and the angle of elevation from point $\mathrm{C}$ (on ground) is $30^{\circ}$
In $\vartriangle \text{ABC}$ ,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BC}}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{30}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{AB}=\frac{30}{\sqrt{3}}=10\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $10\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$.
5. A kite is flying at a height of \[\mathbf{60m}\] above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ .\] Find the length of the string, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
Ans: Let $\text{K}$ be the kite and the string is tied to point $\text{P}$ on the ground.
In $\vartriangle \text{KLP}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{KL}}{\text{KP}}=\sin {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{60}{\text{KP}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{KP}=\frac{120}{\sqrt{3}}=40\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$
Hence, the length of the string is $40\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$.
6. A \[\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{5m}\] tall boy is standing at some distance from a \[\mathbf{30m}\] tall building. The angle of elevation from his eyes to the top of the building increases from \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \] to \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ \] as he walks towards the building. Find the distance he walked towards the building.
Ans : Let the boy was standing at point S initially. He walked towards the building and reached at point T.
$\text{PR}=\text{PQ}-\text{RQ}$
$=(30-1.5)=28.5~=\frac{57}{2}~$
In $\vartriangle \text{PAR}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{PR}}{\text{AR}}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{57}{2\text{AR}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{AR}=\left( \frac{57}{2}\sqrt{3} \right)\text{m}$
In $\vartriangle \text{PRB}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{PR}}{\text{BR}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{57}{2B\text{R}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{BR}=\frac{57}{2\sqrt{3}}\text{=}\frac{19\sqrt{3}}{2}m$
By observing the figure,
$=AR-BR=\left( \frac{57\sqrt{3}}{2}-\frac{19\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)$
$=\left( \frac{38\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)=19\sqrt{3}m$
Hence, he walked $19\sqrt{3}m$ towards the building.
7. From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and the top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a \[\mathbf{20m}\] high building are \[\mathbf{45}{}^\circ \] and \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ \] respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Ans: Let \[AB\] be the statue, \[BC\] be the pedestal, and \[D\] be the point on the ground from where the elevation angles are to be measured.
In $\Delta \text{BCD}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\tan {{45}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=1$
$\Rightarrow \text{BC}=\text{CD}$
In $\Delta A\text{CD}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}+\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}+\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\frac{AB+20}{20}=\sqrt{3}$
$AB=\left( 20\sqrt{3}-20 \right)m$
$=20\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)m$
8. A statue, \[\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{6m}\] tall, stands on a top of pedestal, from a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of statue is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ \] and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is \[\mathbf{45}{}^\circ .\] Find the height of the pedestal.
Let AB be the statue, BC be the pedestal, and D be the point on the ground from where the elevation angles are to be measured.
$\text{ In }\vartriangle \text{BCD,} $
$ \text{ }\frac{\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\tan 45 $
$ \frac{\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=1 $
$ \text{BC}=\text{CD }$
$ \text{In }\vartriangle \text{ACD, } $
$ \frac{\text{AB}+\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ \frac{\text{AB}+\text{BC}}{\text{CD}}=\sqrt{3}\text{ } $
$ 1.6+\text{BC}=\text{BC}\sqrt{3}\quad [\text{As}\,\,\text{CD}=\text{BC}]\,\, $
$ \text{BC}(\sqrt{3}-1)=1.6\,\,\, $
$ \text{BC}=\frac{(1.6)(\sqrt{3}+1)}{(\sqrt{3}-1)(\sqrt{3}+1)}\quad [\text{ByRationalization}]$
$ =\frac{1.6(\sqrt{3}+1)}{{{(\sqrt{3})}^{2}}-{{(1)}^{2}}}$
$=\frac{1.6\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{2}=0.8\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)m$
9. The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \] and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ .\] If the tower is \[\mathbf{50m}\] high, find the height of the building.
Ans: Let \[AB\]be the building and \[CD\]be the tower.
In $\Delta \text{CDB}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{CD}}{\text{BD}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{50}{\text{BD}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{BD}=\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}$
In $\Delta ABD$
$\Rightarrow \frac{AB}{BD}=\tan 30{}^\circ $
$\Rightarrow AB=\frac{50}{\sqrt{3}}\left( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\frac{50}{3}=16\frac{2}{3}$
Therefore, the height of the building is $16\frac{2}{3}$m.
10. Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is \[\mathbf{80m}\]wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ \]and \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \]respectively. Find the height of poles and the distance of the point from the poles.
Ans : Let \[AB\] and \[CD\] be the poles and \[O\] is the point from where the elevation angles are measured.
In $\Delta \mathrm{CDO}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BO}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BO}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{BO}=\frac{\text{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}$
In $\Delta \text{CDO}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{CD}}{\text{DO}}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{CD}}{80-\text{BO}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}\sqrt{3}=80-\text{BO}$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}\sqrt{3}=80-\frac{\text{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}\sqrt{3}+\frac{\text{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}=80$
Since the poles are of equal heights, $\text{CD}=\text{AB}$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}\left[ \sqrt{3}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right]=80$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}\left( \frac{3+1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=80$
$\Rightarrow \text{CD}=20\sqrt{3}~\text{m}$
$\Rightarrow BO=\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{CD}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{20\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=20m$
$\Rightarrow DO=BD-BO=80-20=60m$
Therefore, the height of poles is $20\sqrt{3}$ and the point is $20m$ and $60m$ far from these poles.
11. A TV tower stands vertically on a bank of a canal. From a point on the other bank directly opposite the tower the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ .\] From another point \[\mathbf{20m}\]away from this point on the line joining this point to the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ .\] Find the height of the tower and the width of the canal.
Ans: In $\Delta \text{ABC}$,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{AB}}{\text{BC}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{AB}}{\text{BO}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{BC}=\frac{\text{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}$…. (1)
In $\Delta ABD$,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{\text{BD}}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{BC+CD}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}+20}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB\sqrt{3}}{AB+20\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow 3AB=AB+20\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow 2AB=20\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow AB=10\sqrt{3}m$
Substitute $AB=10\sqrt{3}m$ in $\text{BC}=\dfrac{\text{AB}}{\sqrt{3}}$,
$\Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{10\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=10m$
Therefore, the height of the tower is $10\sqrt{3}m$ and the width of the canal is $10m$.
12. From the top of a \[\mathbf{7m}\] high building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ \] and the angle of depression of its foot is \[\mathbf{45}{}^\circ .\] Determine the height of the tower.
Ans: Let $AB$ be a building and $CD$ be a cable tower.
In $\Delta \text{ABD}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BD}}=\tan {{45}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{7}{\text{BD}}=1$
$\Rightarrow \text{BD=7m}$
In $\Delta \text{ACE}$, $AE=BD=7m$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{CE}}{AE}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{CE}}{7}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{CE=7}\sqrt{3}\text{m}$
$\Rightarrow CD=CE+ED=\left( 7\sqrt{3}+7 \right)=7\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)m$
Therefore, the height of the cable tower is $7\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)m$.
13. As observed from the top of a \[\mathbf{75m}\]high lighthouse from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ \]and \[\mathbf{45}{}^\circ .\]If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the lighthouse, find the distance between the two ships.
Ans: Let $AB$be the lighthouse and the two ships be at point $C$ and \[D\]respectively.
In $\Delta \text{ABC}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{\text{BC}}=\tan {{45}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{75}{\text{BC}}=1$
$\Rightarrow \text{BC=75m}$
In $\Delta \text{ABD}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{AB}{BD}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{75}{BC+CD}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{75}{75+CD}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow 75\sqrt{3}=75+CD$
$\Rightarrow 75\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)m=CD$
Therefore, the distance between the two ships is $75\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)m.$
14. A \[\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{2m}\] tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of \[\mathbf{88}.\mathbf{2m}\] from the ground. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the eyes of the girl at any instant is \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ .\] After some time, the angle of elevation reduces to \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ .\] Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval.
Ans: Let the initial position $A$ of balloon change to $B$ after some time and \[CD\] be the girl.
In $\Delta \text{ACE}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AE}}{\text{CE}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AF-EF}}{\text{CE}}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{88}\text{.2-1}\text{.2}}{\text{CE}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{87}}{\text{CE}}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow CE=\frac{87}{\sqrt{3}}=29\sqrt{3}m$
In $\Delta B\text{CG}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{BG}}{\text{CG}}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{BH-GH}}{\text{CG}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{88}\text{.2-1}\text{.2}}{\text{CG}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{87}\sqrt{3}=CG$
Distance travelled by balloon$=EG=CG-CE$
$ =\left( 87\sqrt{3}-29\sqrt{3} \right) $
$ =58\sqrt{3}m $
15. A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing at the top of the tower observes a car at an angle of depression of \[\mathbf{30}{}^\circ ,\] which is approaching the foot of the tower with a uniform speed. Six seconds later, the angle of depression of the car is found to be \[\mathbf{60}{}^\circ .\] Find the time taken by the car to reach the foot of the tower from this point.
Ans: Let \[AB\] be the tower. Initial position of the car is \[C\], which changes to \[D\] after six seconds.
In $\Delta \text{ADB}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{CB}=\tan {{60}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{DB}=\sqrt{3}$
$\Rightarrow DB=\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{BC}=\tan {{30}^{{}^\circ }}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AB}}{BD+DC}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\Rightarrow AB\sqrt{3}=BD+DC$
$\Rightarrow AB\sqrt{3}=\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}+DC$
$\Rightarrow DC=AB\sqrt{3}-\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}}=AB\left( \sqrt{3}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\frac{2AB}{\sqrt{3}}$
Time taken by the car to travel distance DC $\left( i.e\frac{2AB}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=6$ seconds.
Time taken by the car to travel distance DB $\left( ie.,\frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\frac{6}{\frac{2AB}{\sqrt{3}}}\left( \frac{AB}{\sqrt{3}} \right)=\frac{6}{2}=3$ seconds.
16. The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of \[4m\]and \[9m\]from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is\[6m\].
Ans: Let \[AQ\]be the tower and \[R,S\]are the points \[4m,\text{ }9m\]away from the base of the tower respectively. The angles are complementary. Therefore, if one angle is\[\theta \], the other will be \[90\text{ }-\text{ }\theta \]
(Image will be uploaded soon)
In $\Delta \text{AQR}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AQ}}{QR}=\tan \theta $
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AQ}}{4}=\tan \theta $ …. (i)
In $\Delta \text{AQS}$,
$\Rightarrow \frac{\text{AQ}}{SQ}=\tan (90-\theta )$
$\Rightarrow \frac{AQ}{9}=\cot \theta $ ….. (ii)
On multiplying equations (i) and (ii), we obtain
$\Rightarrow \left( \frac{AQ}{4} \right)\left( \frac{AQ}{9} \right)=\left( \tan \theta \right)\left( \cot \theta \right)$
$\Rightarrow \frac{A{{Q}^{2}}}{36}=1$
$\Rightarrow A{{Q}^{2}}=36$
$\Rightarrow AQ=\sqrt{36}=\pm 6$
However, height cannot be negative.
Therefore, the height of the tower is $6m$.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry - PDF Download
You can opt for Chapter 9 - Some Applications of Trigonometry NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths PDF for Upcoming Exams and also You can Find the Solutions of All the Maths Chapters below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
Chapter 2 - Polynomials
Chapter 3 - Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
Chapter 5 - Arithmetic Progressions
Chapter 6 - Triangles
Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 8 - Introduction to Trigonometry
Chapter 9 - Some Applications of Trigonometry
Chapter 10 - Circles
Chapter 11 - Constructions
Chapter 12 - Areas Related to Circles
Chapter 13 - Surface Areas and Volumes
Chapter 14 - Statistics
Chapter 15 - Probability
About the Chapter
In the Class 10 Maths Chapter 9, you will study about different ways in which trigonometry is used to find the height and distance of different objects without actually measuring them. This chapter is divided into 3 sections and one exercise. The first section is the basic introduction of trigonometry in which you will learn, how the need for the trigonometry arose and its application in different fields. The second section includes an introduction to height and distance, important terms related to the height and distance, conditions where the trigonometry concepts are used along with the examples, and last but not the least one exercise at the end. The questions asked in the exercise are based on the basic concepts of trigonometry and its application. The third section includes a summary of the chapter where some important terms given in the chapter are discussed.

Some Applications of Trigonometry
List of topics and exercise covered in Class 10 Chapter 9 Some applications of trigonometry.
Section 9.1: Introduction to some applications of trigonometry
Section 9.2: Height and Distance
Exercise 9.1: Questions related to some applications of trigonometry. This exercise included 16 questions.
Section 9.3: Summary of the chapter
In the ch 9 Maths class 10, we will be learning about trigonometry, some application of trigonometry, and the entire summary of the chapter.
Overview of the Exercises Covered in the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Ch-9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
The sums of Chapter 9 Class 10 Maths are based on the concepts of trigonometry and their applications. Students are advised to learn and revise all the important formulas and theories of trigonometry to have a better grasp of these NCERT Solutions. The sums mostly involve computing various heights and distances using trigonometric ratios. Students should revise the values of some trigonometric ratios like sin, cos, tan, cot, cosec, and sec for the commonly used measures of theta.
Hence, by practising and referring to the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry, students will get an overview of how the trigonometric ratios are employed in day-to-day real-world scenarios. For example, the sums that involve using the trigonometric ratios to calculate the heights and angles for poles, buildings, towers, etc., are going to provide them with this kind of knowledge.
What is Trigonometry?
Trigonometry is one of the most historical subjects studied by different scholars throughout the world. As you have read in Chapter 8 that trigonometry was introduced because its requirement arose to astronomy. Since then trigonometry is used to calculate the distance from the Earth to the stars and the planets. The most important use of trigonometry is to find out the height of the highest mountain in the world i.e. Mount Everest which is named after Sir George Everest. It is also widely used in Geography and navigation. The knowledge of trigonometry enables us to construct maps, evaluate the position of an island concerning the longitudes and latitudes.
Historical Facts. Let us Turn to the History of Trigonometry
The trigonometry was used by surveyors for centuries. One of the notable and the largest surveying projects of the nineteenth century was the “ Great Trigonometric Survey" of British India for which the two largest theodolites were constructed. The highest mountain in the world was discovered during the survey in 1852. From a distance of over 160 km, this peak was seen from 6 distinct stations. This peak was named after Sir George Everest who had first used the theodolites. Theodolites are now exhibited in the museum of the surveys of Dehradun.
Theodolites
Surveying instrument, which is used for measuring angles with a rotating telescope
Height and Distance
In this topic, you will study about the line of sight, angle of elevation, horizontal level, and angle of depression. All these terms are explained in a detailed form along with some solved examples based on it. These solved examples based on the terms line of sight, angle of elevation and angle of depression will help you to understand the concepts thoroughly.
How to Calculate Height and Distance?
Trigonometric ratios are used to find out the height and the distance of the object. For example: In figure 1, you can see a boy looking at the top of the lampost. AB is considered as the horizontal level. This level is stated as the line parallel to the ground passing through the viewer's eyes. AC is considered as the line of sight. ∠A is known as the angle of elevation. Similarly, in figure 2, you can see PQ is the line of sight, PR is the horizontal level and ∠P is known as the angle of elevation.
An inclinometer or Clinometer is a device usually used for measuring the angle of elevation and the angle of depression.
Let us recall some trigonometric ratios which help to solve the questions based on class 10 maths Chapter 9.
Trigonometry Ratios
The ratio of the sides of a right-angle triangle in terms of any of its acute angle triangle is known as the trigonometric ratio of that specific angle.
In terms of ∠C, the ratio of trigonometry are given as:
Sine - The sine of an angle is stated as the ratio of the opposite side ( perpendicular side) to that angle to the hypotenuse side.
Hence, Sine C = Opposite side/Hypotenuse side
Cosine- The cosine of an angle is stated as the ratio of the adjacent side to that angle to the hypotenuse side.
Hence, Cosine C = Adjacent side /Hypotenuse side
Tangent - The tan of an angle is stated as the ratio of the opposite side (perpendicular side) to that angle to the side adjacent to that angle.
Hence, Tan C = Opposite side/Adjacent side
Cosecant- It is the reciprocal of sine.
Hence, Cosec C = Hypotenuse side/Opposite side
Secant- It is the reciprocal of cosine.
Hence, Sec C= Hypotenuse side/Adjacent side
Cotangent- It is the reciprocal of tangent.
Hence, Cot C = Adjacent side/Opposite side
The following trigonometry ratio table is used to calculate the questions based on applications of trigonometry class 10 NCERT solutions.
Trigonometric Ratio Table
Now, you must have understood all the important topics and terms covered in each section of class 10 maths chapter 9. Perfect understanding of NCERT class 10 chapter 9 Introduction helps you to focus on some points such as the weightage of the chapter, important questions that can be asked in the examination, types of questions that can be appeared in your, etc. This will help you to solve the exam more confidently and also ensures you that you can finish your exam within a time-duration.
As, there is a proverb that says "Practice makes the men perfect". It tells us the importance of practicing continuously in any subject to learn anything. Continuous practice is a must to learn any of the subjects. Practicing class 10 maths Chapter 9 NCERT solutions designed by Vedantu experts will bring accuracy and confidence in you as they are designed according to the caliber of the students. It helps you to increase the speed of solving your problems and also bring more accuracy in you. With practicing NCERT questions more and more, you will be aware of the types of questions that can be asked in the examination. This will help you to solve your exam paper more confidently. Practicing not merely enhances your conceptual understanding but also enhances your logical reasoning. Most of the time the questions asked in the examination are repeated and solving the previous questions helps you to solve the questions speedily and accurately in the exam. By following the above-mentioned points, you can surely score above 90% in your board exam.
Important features of the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9- Some Applications of Trigonometry
The solutions are designed by the subject experts of Vedantu.
Chapter-wise questions and solutions are easily accessible.
Special guidance for the students preparing for their board examinations.
Exercise questions are easily accessible.
The solutions are well-explained in the comprehensive method.
How Vedantu NCERT Solutions for class 10 maths Chapter 9 -Some applications of trigonometry will help you to score good marks in your board exams?
NCERT Solution for class 10 plays an important role in shaping the future of the students as the grades which the students will score will shape the future of the student. The NCERT solution prepared by the professionals of Vedantu is a one-stop solution for all your queries related to class 10 maths chapter 9. Detailed explanation and stepwise solutions for each question prepared by the experts will help you to understand the concept in a better way. The NCERT solutions prepared by the experts of Vedantu provides excellent material for the student to practice and make the learning process more effective.
The importance of the Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9-Some applications of trigonometry are:
Solutions are framed keeping in mind the age of the students.
The content of the topic is pointed, brief, and straightforward.
Complex questions are divided into small parts and well-explained to save the students from taking the unnecessary strain.
Every question is explained with the relevant image to understand the question precisely.
The solutions are designed under the latest syllabus and CBSE guidelines.
Vedantu experts tried their level best to provide your NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9. The aim to provide the solution is to help the students to solve each question given in the board exams in no time.
Why are Some Applications of Trigonometry Important?
Class 10 Chapter 9 some application of trigonometry is an important topic to discuss as it tells how trigonometry is used to find the height and distance of different objects such as the height of the building, the distance between the Earth and Planet and Stars, the height of the highest mountain Mount Everest, etc.
To solve the questions based on some applications of trigonometry class 10, it is necessary to remember trigonometry formulas, trigonometric relations, and values of some trigonometric angles. The following are the concepts covered in the 'height and distance' Some applications of trigonometry.
To measure the height of big towers or big mountains
To determine the distance of the shore from the sea.
To find out the distance between two celestial bodies.
This chapter has a weightage of 12 marks in class 10 Maths Cbse (board) exams.
One question can be expected from this chapter. Class 10 Maths CBSE paper is divided into 4 parts and each question comes with different marks. The questions will be allocated with 1 mark, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
Discussion about the sections, exercise, and type of questions given in the exercise.
The important topic “ Height and Distance" covered in Some applications of trigonometry class 10 is followed by one exercise with 16 questions. The exercise aims to test your knowledge and how deeply you understood each formula and concept of the topic. The numerical questions given in this chapter are based on some applications of trigonometry.
To make you understand the topic and related concept, solved numerical problems are also given. Stepwise solutions are given for each of the solved examples. It will help you to understand which concept and formula will be used to solve the given questions accurately.
Section 9.1 - Introduction
This section gives an introduction to some applications of trigonometry. It tells you how trigonometry is used by different scholars throughout the world and its uses in different fields. It also tells you the way trigonometry is used to find the height and distance of different objects without actually measuring them.
In this section, some important terms such as a line of sight, horizontal level, angle of elevation, and angle of depression are discussed. All these important terms are discussed along with the solved examples based on them which will clear your concepts thoroughly and also helps you to solve the questions given in the exercise.
Exercise 9.1: “Height and Distance”
This exercise includes a total of 16 questions. Each question asked in the exercise are based on the concept of “Height and Distance”.
Description of the Questions Asked in Exercise 9.1
Section 9.3: summary.
The summary at the end of the chapter details a brief explanation of all the topics you covered in this chapter.
Important Terms to Remember in Height and Distance
Line of Sight - It is a line that is drawn from the eye of an observer to the point on the object viewed by the observer.
The Angle of Elevation - It is defined as an angle that is formed between the horizontal line and line of sight. If the line of sight lies upward from the horizontal line, then the angle formed will be termed as an angle of elevation.
Let us take another situation when a boy is standing on the ground and he is looking at the object from the top of the building. The line joining the eye of the man with the top of the building is known as the line of sight and the angle drawn by the line of sight with the horizontal line is known as angle of elevation.
In the above figure line of sight is forming an angle θ through the horizontal line.This angle is known as the angle of elevation.
The Angle of Depression - It is defined as an angle drawn between the horizontal line and line of sight. If the line of sight lies downward from the horizontal line, then the angle formed will be termed as an angle of depression.
Let us take a situation when a boy is standing at some height concerning the object he is looking at. In this case, the line joining the eye of the man with the bottom of the building is known as the line of sight and the angle drawn by the line of sight with the horizontal line is known as angle of depression.
In the above figure angle, θ is considered as the angle of depression
Note: Angle of elevation is always equal to the angle of depression
The important Point to Remember
The distance of the object is also considered as the base of the right angle triangle drawn through the height of the object and the line of sight.
The length of the horizontal level is also known as the distance of the object it forms the base of the triangle.
Line of sight is considered as a hypotenuse of the right-angle triangle. Hypotenuse side is calculated using Pythagorean Theorem if the height and distance of the object are given.
Important Features of the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9- Some Applications of Trigonometry
Benefits of ncert solutions for class 10 maths.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 offer clear explanations, simplifying intricate concepts. Focusing on practical applications, they enhance problem-solving skills and real-world understanding. With step-by-step guidance, these solutions aid self-study and boost confidence in tackling trigonometry questions during exams. Other points of interest:
CBSE Guideline Adherence: Answers align with CBSE guidelines for clarity and accuracy.
Free PDF Availability: NCERT Solutions PDF is freely downloadable for convenient access.
Concise and Organized Content: Solutions are short, self-explanatory, and well-organized.
Visual Enhancements: Relevant infographics and images are incorporated for better topic understanding.
Revision Aid: Acts as a useful note during test revisions.
Simplified Solutions: Aimed at facilitating maximum question-solving for better chapter command.
Chapter Specificity: Tailored for Linear Equations in Two Variables chapter to address potential difficulties.
Expert Craftsmanship: Ensured by experts to guarantee easy comprehension.
Comprehensive Coverage: Covers the entire syllabus and theory within the solutions.
Other study materials are available on the Vedantu app and website, in addition to NCERT Solutions. Chapter-wise solutions for different subjects are also available for the convenience of students.
Engaging with NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 , "Some Applications of Trigonometry," is key to excelling in the CBSE Term 2 Mathematics exam. These solutions focus on calculating heights and distances using trigonometric ratios, offering valuable insights into their practical application. For students preparing for the Class 10 Term 2 Maths paper, free access to these NCERT Solutions ensures a comprehensive understanding, enhancing the likelihood of securing high grades in the exam. Download and reference to these solutions are highly recommended for effective preparation and success in the upcoming CBSE exam.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 - Some Applications Of Trigonometry
1. How downloading “NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry" PDF from Vedantu can help you to score better grades in exams?
Vedantu executed well-designed and reviewed applications of trigonometry class 10 ncert solutions which include the latest guidelines as recommended by CBSE board. The solutions are easily accessible from the Vedantiu online learning portal. It can be easily navigated as Vedantu retains a user-friendly network. The detailed solution of all the questions asked in the NCERT book will help you to understand the basic concepts of some applications of trigonometry class 10 thoroughly. Along with the NCERT solutions, the experts of Vedantu also provide various tips and techniques to solve the questions in the exam. Sign in to Vedantu and get access to the ncert solutions for class 10 maths chapter 9 some applications of trigonometry -Free pdf and you can download the updated solution of all the exercises given in the chapter.
2. What is the importance of trigonometry applications in real-life?
The application of trigonometry may not be directly used in solving practical issues but used in distinct fields. For example, trigonometry is used in developing computer music as you must be aware of the fact that sound travels in the form of waves and this wave pattern using sine and cosine functions helps to develop computer music. The following are some of the applications where the concepts of trigonometry and its functions are applicable.
It is used to measure the height and distance of a building or a mountain
It is used in the Aviation sector
It is used in criminology
It is used in Navigation
It is used in creating maps
It is used in satellite systems
The basic trigonometric functions such as sine and cosine are used to determine the sound and light waves.
It is used in oceanography to formulate the height of waves and tides in the ocean.
3. The distance from where the building can be viewed is 90ft from its base and the angle of elevation to the top of the building is 35°. Calculate the height of the building.

Given: Distance from where the building can be viewed is 90ft from its base and angle of elevation to the top of the building is stated as 35°
To calculate the height of the building, we will use the following trigonometry formula
Tan 35° = Opposite Side/ Adjacent Side
Tan 35° = H/90
H = 90 x Tan 35°
H = 90 x 0.7002
H = 63.018 feet
Hence, the height of the building is 63.018 feet.
4. From a 60 meter high tower, the angle of depression of the top and bottom of a house are ‘a and b’ respectively. Calculate the value of x, if the height of the house is [60 sin (β − α)]/ x.

H = d tan β and H- h = d tan α
60/60-h = tan β – tan α
h = [60 tan α – 60 tan β] / [tan β]
h= [60 sin (β – α)/ [(cos α cos β)] [(sin α sin β)]
x = cos α cos β
5. The top of the two different towers of height x and y, standing on the ground level subtended angle of 30° and 60° respectively at the center of the line joining their feet. Calculate x: y.
x/a = Tan 30°
y/a = Tan 60°
y/a = 3 → y = a x 3
x/a ÷ y/a = a/3÷ a3
x/a × y/a = a/3 × 1/a×3
6. What are the main points to study in Class 10 Maths NCERT Chapter 9?
The main points to study in Class 10 Maths NCERT Chapter 9 include:
Fundamental Basics Of Trigonometry Applications
The History Behind Trigonometry
Concepts On Height And Distance
The Study About The Line Of Sight
Angle Of Elevation, Horizontal Level
Angle Of Depression
The Calculation Methods For Heights And Distance
The Trigonometry Ratios And Angle Tables For The Ratios
A clear explanation for the solutions of the same can be found on the Vedantu website.
7. How many exercises are there in Chapter 9 of Class 10 Maths?
Chapter 9 of Class 10 Maths consists of one exercise that is Exercise 9.1 at the end of this chapter. This section of the chapter has 16 questions that are covered in the first two parts. The questions asked in the exercise are based on the basic concepts of trigonometry and its application, height distance etc. Following this, is a summary of the chapter.
8. How can I score full marks in Class 10 Chapter 9 Maths?
Maths is all about practice. If you practice your exercises regularly you will gradually lean towards perfection and accuracy. It will also increase your speed and hence you will be able to finish your paper on time, attempting all the questions, thereby scoring full marks in this subject. For this, you can refer to the Vedantu website or download the Vedantu app which will provide you with the best solutions at free of cost and help you fulfil your aim of scoring top grades in Maths.
9. Where can I get the best solutions for Maths chapter 9?
You can find the best solutions for NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 on Vedantu. Here, you will find the best possible trigonometry explanations and their solutions for respective exercises. These are provided in PDF format, which is totally free to download and you can study from it even in offline mode. For this:
Visit the page NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9.
Click on the download PDF option.
Once you’re redirected to a page you will be able to download it.
10. What is the advantage of using Vedantu?
Vedantu outshines all other learning apps and websites because it has the best team of experts who analyse and form the best answers for the students to learn and practice from. This has a complete chapter-wise explanation and their respective solutions. This also has options for parents to take weekly homely tests from Vedantu so that they can keep a check on their wards.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10
Search This Blog
Cbse mathematics.
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12. A complete resource centre of mathematics for students and teachers
Featured Posts
Maths assignment class viii | quadrilateral, math assignment class x ch-8 | trigonometry.
Math Assignment / Class X / Chapter 8 / Trigonometry
Extra questions of chapter 8 class 10 Trigonometric Functions with answer and hints to the difficult questions. Important and useful math assignment for the students of class 10

For better results
- Students should learn all the basic points of Trigonometry
- Student should revise NCERT book thoroughly with examples.
- Now revise this assignment. This assignment integrate the knowledge of the students.
ASSIGNMENT FOR 10 STANDARD TRIGONOMETRY
Post a Comment
Breaking news, popular post on this blog, lesson plan maths class 10 | for mathematics teacher.

Lesson Plan Math Class 10 (Ch-1) | Real Numbers

Lesson Plan Maths Class XII | For Maths Teacher

- Assignment 10 15
- Assignment 11 12
- Assignment 12 14
- Assignment 8 8
- Assignment 9 5
- Lesson plan 10 15
- Lesson Plan 12 13
- Lesson Plan 8 10
- Maths 10 20
- Maths 11 21
- Maths 12 17
SUBSCRIBE FOR NEW POSTS
Get new posts by email:.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet Class 10 PDF with Answers
These Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF can be helpful for both teachers and students. Teachers can track their student’s performance in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry. Students can easily identify their strong points and weak points by solving questions from the worksheet. Accordingly, students can work on both weak points and strong points.
All students studying in CBSE class 10th, need to practise a lot of questions for the chapter Applications of Trigonometry. Students can easily practise questions from the Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet PDF. By practising a lot of questions, students can improve their confidence level. With the help of confidence level, students can easily cover all the concepts included in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
Applications of Trigonometry Worksheets with Solutions
Solutions is the written reply for all questions included in the worksheet. With the help of Applications of Trigonometry worksheets with solutions, students can solve all doubts regarding questions. Students can have deep learning in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry by solving all their doubts. By solving doubts, students can also score well in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF
Worksheet is a sheet which includes many questions to solve for class 10th students. The Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF provides an opportunity for students to enhance their learning skills. Through these skills, students can easily score well in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry. Students can solve the portable document format (PDF) of the worksheet from their own comfort zone.
How to Download the Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF?
To solve questions from the Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF, students can easily go through the given steps. Those steps are-
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which can be seen in the navigation bar.
- Drop down menu will appear, select KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheet.
- A new page will appear, select class 10th from the given list of classes.
- Select Mathematics from the given list of subjects. Now click the chapter’s name that is Applications of Trigonometry.
Features of the Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF
Before starting to solve questions from the Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet PDF, students need to know everything about the worksheet. Those features are-
- Variety of questions are included: The Applications of Trigonometry Maths Worksheet for Class 10 includes varieties of questions. Those varieties of questions are- one mark questions, two mark questions, three mark questions, etc.
- Solutions are provided: Doubts regarding each question can be easily solved through the solutions given. Through solving questions, a student's comprehensive skill can be increased.
- All concepts are covered: By solving questions from the Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet, students can easily cover all the concepts included in the chapter.
- Created by Expert: These worksheets are personally created by the subject experts. These Applications of Trigonometry worksheet pdf are created with proper research.
- Provides plenty of questions: The Applications of Trigonometry worksheet provides plenty of questions to practise. Through good practice, students can get engaged in the learning process.
Benefits of the Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF
With the help of Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet PDF, students can easily track their performance. This is the most crucial benefit, other than this there are more benefits. Those benefits are-
- Builds a strong foundation: Regular solving questions from the worksheet can help students to build a strong foundation. Through the strong foundation, students can score well in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
- Improves speed and accuracy: While solving questions from the chapter Applications of Trigonometry, students need to maintain the speed and accuracy. Speed and accuracy can be easily maintained and improved by solving questions from the Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF.
- Acts as a guide: Applications of Trigonometry worksheets with solutions acts as guide for both the teachers and students. Through the worksheet, teachers can guide their students according to the answers given by them. Students can also analyse themselves with the help of answers and can improve accordingly.
- Enhances the learning process: Regular solving of questions from the worksheet can help students enhance their learning process. According to the learning skills, students can easily understand all topics and concepts included in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
- Improvisation of grades: Regular solving of questions from the worksheet can help students to improve their marks and grades. With the help of good marks and good grades, students can select their desired field further.
Tips to Score Good Marks in Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet
Students are requested to follow some tips to score good marks in the Applications of Trigonometry worksheet. Those tips are-
- Complete all the concepts: First and the most crucial step is to understand all the concepts included in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
- Practise questions: Next step is to practise questions from the Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet. Through this students can identify all types of questions: easy, moderate, difficult, etc.
- Note down the mistakes: After practising questions, students need to note down the wrong sums that have been done earlier.
- Rectify the mistakes: After noting down the mistakes, students need to rectify all the mistakes made.
- Maintain a positive attitude: Students are requested to maintain a positive attitude while solving worksheets. By maintaining a positive attitude, students can improve speed and accuracy while solving the worksheets.
- Remain focused: Students need to remain focused while solving questions from the Applications of Trigonometry problems worksheet pdf. As it helps students to solve the questions as fast as possible.
When should a student start solving the Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF?
Students studying in class 10 should start solving worksheets after covering each and every concept included in the chapter. Regular solving questions from the Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF, can help students to have a better understanding of the chapter. Better understanding of the chapter Applications of Trigonometry can help students to score well in the class 10th board exam.
Regular solving questions from the Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF can help students to build a strong foundation for the chapter Applications of Trigonometry. Strong foundation of the chapter Applications of Trigonometry can help students to understand further chapters.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- Math Article
Trigonometric Identities Class 10
Trigonometric identities class 10 includes basic identities of trigonometry. When we recall, an equation is considered identical, if the equations are true for all the values of variables involved. Similarly, the trigonometric equation, which involves trigonometry ratios of all the angles, is called a trigonometric identity if it is true for all values of the angles.
In Mathematics, trigonometry is one of the most important and prominent topics to learn. Trigonometry is basically the study of triangles. The term ‘Trigon’ means triangle and ‘metry’ means measurement. Trigonometric identities class 10 consists of trigonometry ratios such as sine, cosine and tangent in its equations. Even, trigonometry identities class 10 formulas are based on these ratios. These identities are used to solve various trigonometry problems.
By considering a right-angled triangle, trigonometry identities class 10 lists could be figured out. The trigonometric identities or equations are formed using trigonometry ratios for all the angles. Using trigonometry identities, we can express each trigonometric ratios in terms of other trigonometric ratios, and if any of the trigonometry ratios value is known to us, then we can find the values of other trigonometric ratios. We can also solve trigonometric identities class 10 questions, using these identities as well.
Trigonometric Identities for Class 10
Trigonometric identities are the equations that include the trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, tangent, etc., and are true for all values of angle θ. Here, θ is the reference angle taken for a right-angled triangle. In class 10th, there are basically three trigonometric identities, which we learn in the trigonometry chapter. They are:
- Cos 2 θ + Sin 2 θ = 1
- 1 + Tan 2 θ = Sec 2 θ
- 1 + Cot 2 θ = Cosec 2 θ
Here, we will prove one trigonometric identity and will use it to prove the other two. Take an example of a right-angled triangle ΔABC.

Proof of Trigonometric Identities Class 10
In a right-angled triangle, by the Pythagorean theorem , we know,
(Perpendicular) 2 + (Base) 2 = (Hypotenuse) 2
Therefore, in ΔABC, we have;
AB 2 + BC 2 = AC 2 ….. (1)
Dividing equation (1) by AC 2 , we get,
Cos 2 θ + Sin 2 θ = 1 …..(2)
If θ = 0, then,
- Cos 2 0 + Sin 2 0 = 1
- 1 2 + 0 2 = 1
And if we put θ = 90,then
- Cos 2 90 + Sin 2 90 = 1
- 0 2 + 1 2 = 1
For all angles, 0°≤ θ ≤ 90°, equation (2) is satisfied. Hence, equation (2) is a trigonometric identity.
Again, divide equation (1) by AB 2 , we get
1 + Tan 2 θ = Sec 2 θ …..(3)
If θ = 0, then,
- 1 + tan 2 0 = sec 2 0
- 1 + 0 2 = 1 2
- 1 + tan 2 90 = sec 2 90
As you can see, the values of both sides are equal. Therefore, it proves that for all the values between 0 0 and 90 0 , the equation (3) is satisfied. So, it is also a trigonometric identity.
Let’s see what we get if we divide equation (1) by BC 2 , we get,
Cot 2 θ + 1 = Cosec 2 θ ….(4)
Now let us prove this identity as well.
If θ = 0, then equation (4) can be written as;
- Cot 2 0 + 1 = Cosec 2 0
Both sides are equal.
And if θ = 90,then equation (4) can be written as;
- Cot 2 90 + 1 = Cosec 2 90
- 0 2 + 1 = 1 2
Thus, proved that equation (4) is a trigonometric identity.
Video Lesson on Trigonometry
More Formulas for Class 10
- Geometry Formulas For Class 10
- Algebra formulas for Class 10
- Maths Formulas For Class 10
- Mensuration Formulas Class 10
- Trigonometry Formulas For Class 10
Practice Questions From Class 10 Trigonometry Identities
- Prove √(sec θ – 1)/(sec θ + 1) = cosec θ – cot θ
- Prove (tan θ + sec θ – 1)/(tan θ – sec θ + 1) = (1 + sin θ)/cos θ
- Prove sec θ√(1 – sin 2 θ) = 1
- Given, √3 tan θ = 3 sin θ. Prove sin 2 θ – cos 2 θ = 1/3
- Evaluate cos 2 θ tan 2 θ + tan 2 θ sin 2 θ in terms of tan θ.
Practice Now: Important Questions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction Trigonometry
Learn more Maths formulas in BYJU’S and Download BYJU’S- The Learning App for interactive videos.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 10 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Trigonometry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf. Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Notes. The notes for trigonometry Class 10 Maths are provided here. In maths, trigonometry is one of the branches where we learn the relationships between angles and sides of a triangle. Trigonometry is derived from the Greek words 'tri' (means three), 'gon' (means sides) and ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 8 - Introduction to Trigonometry. For the Class 10 CBSE Maths examinations, out of the 80 marks (combined), 12 marks are assigned from the unit 5 "Trigonometry". The paper consists of 4 parts. Each part carries different marks and the questions have been assigned with 1 mark, two marks, 3 marks and 4 ...
Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Very Short Answer (1 Mark) Question 1. If tan θ + cot θ = 5, find the value of tan2θ + cotθ. (2012) Solution: tan θ + cot θ = 5 …. [Given. tan 2 θ + cot 2 θ + 2 tan θ cot θ = 25 …. [Squaring both sides. tan 2 θ + cot 2 θ + 2 = 25.
To study the answers of the NCERT Questions, click on an exercise or topic below. The chapter is updated according to thenew NCERT, for 2023-2024 Board Exams.Get NCERT Solutions with videos of all questions and examples of Chapter 8 Class 10 Trigonometry. Videos of all questions are made with step-by-step explanations.
Solution: Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4. Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A. Solution: Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5. Given sec θ = 1312 , calculate all other trigonometric ratios. Solution: Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 6. If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
Solving for a side in right triangles with trigonometry. Finding reciprocal trig ratios. Special right triangles intro (part 1) Special right triangles intro (part 2) 30-60-90 triangle example problem. Intro to Pythagorean trigonometric identities. Converting between trigonometric ratios example: write all ratios in terms of sine.
These concepts are also used in sister topics of higher classes such as calculus and geometry. NCERT solutions class 10 maths Chapter 8 helps students recognize the trigonometric functions that are used in an equation. There are 6 trigonometric ratios in a right-angled triangle. These are sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Important Questions and Answers. Below are the important trigonometry class 10 questions. Students can refer to the below-given class 10 trigonometry questions and they can practice these problems as well. Question. 1 : In ∆ ABC, right-angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Solution:
Assignments for Class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry have been developed for Standard 10 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 10 Mathematics Trigonometry from our website as we have provided all topic wise ...
Chapter 9 of Class 10 Maths consists of one exercise that is Exercise 9.1 at the end of this chapter. This section of the chapter has 16 questions that are covered in the first two parts. The questions asked in the exercise are based on the basic concepts of trigonometry and its application, height distance etc.
Extra questions of chapter 8 class 10 Trigonometric Functions with answer and hints to the difficult questions. Important and useful math assignment for the students of class 10. For better results. Students should learn all the basic points of Trigonometry ;
Even and Odd Trigonometric Functions. The trigonometric function can be described as being even or odd. Odd trigonometric functions: A trigonometric function is said to be an odd function if f(-x) = -f(x) and symmetric with respect to the origin. Even trigonometric functions: A trigonometric function is said to be an even function, if f(-x) = f(x) and symmetric to the y-axis.
Applications of Trigonometry Worksheet PDF. Worksheet is a sheet which includes many questions to solve for class 10th students. The Applications of Trigonometry worksheet PDF provides an opportunity for students to enhance their learning skills. Through these skills, students can easily score well in the chapter Applications of Trigonometry.
Applications of learning NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 are finding the height and distance of different objects without measuring. By learning these concepts students will be able to answer all the questions based on trigonometry, and it will also help in writing class tests and CBSE exams. Q3.
Trigonometry formulas for Class 10 are provided here for students. Trigonometry is the study of relationships between angles, lengths, and heights of triangles. It includes ratios, functions, identities, and formulas to solve problems based on it, especially for right-angled triangles.Applications of trigonometry
1 + Cot 2 θ = Cosec 2 θ. Here, we will prove one trigonometric identity and will use it to prove the other two. Take an example of a right-angled triangle ΔABC. Proof of Trigonometric Identities Class 10. In a right-angled triangle, by the Pythagorean theorem, we know, (Perpendicular) 2 + (Base) 2 = (Hypotenuse) 2. Therefore, in ΔABC, we have;