

50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
In this useful lesson, we’ll explore direct and indirect speech through 50 simple examples. These two ways of speaking help us share what someone else said. Think of direct speech as using the speaker’s exact words, like quoting a friend. Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves changing the original words a bit, as if you’re telling a story about what was said. This lesson is great for anyone looking to get better at English, offering clear examples to make learning easier.
Rules to Make Direct and Indirect Speech
When converting direct speech into indirect speech, it’s important to follow specific rules to ensure the sentence still conveys the original meaning. Here are the key rules:
- Change in Pronouns : Pronouns often need to be changed according to the context and the point of view of the reporting verb. For example, “ I am going ” (direct) might become “ He said he was going ” (indirect).
- Tense Shifts : The tense of the verb in direct speech usually changes when converting to indirect speech. If the reporting verb is in the past tense , the tense in the reported speech shifts back as well. For instance, “ She said, ‘I am eating ‘” changes to “ She said she was eating “.
- Time and Place Words : Words indicating time and place in direct speech are often adjusted in indirect speech. “Here” may change to “there,” “today” to “ that day ,” “tomorrow” to “ the next day ,” etc.
- Question Form : If the direct speech is a question, the indirect form does not use a question format. Instead, it integrates the question into a statement, often using “if” or “whether” for yes/no questions, and ‘wh’ words ( what, when, where, why, who ) for questions that require more detailed answers. For example, “ He asked, ‘Are you coming? ‘” becomes “ He asked if I was coming .”
- No Quotes : In indirect speech, quotation marks are not used. The sentence is integrated into a larger statement, which often starts with verbs like said, asked, or told.
- Exclamations and Commands : Exclamatory sentences and commands in direct speech are transformed into statements or requests in indirect speech. For instance, “He said, ‘How beautiful!'” becomes “He exclaimed that it was beautiful.” Commands like “He said, ‘Sit down!'” change to “He ordered me to sit down.”
- Modal Verbs : Modal verbs can also change in indirect speech, especially might, could, would, and should, depending on the context and the necessity to maintain the original sentence’s meaning.
Remember, the goal of these changes is to maintain the essence of the original statement while adapting it to the grammatical and contextual framework of indirect speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
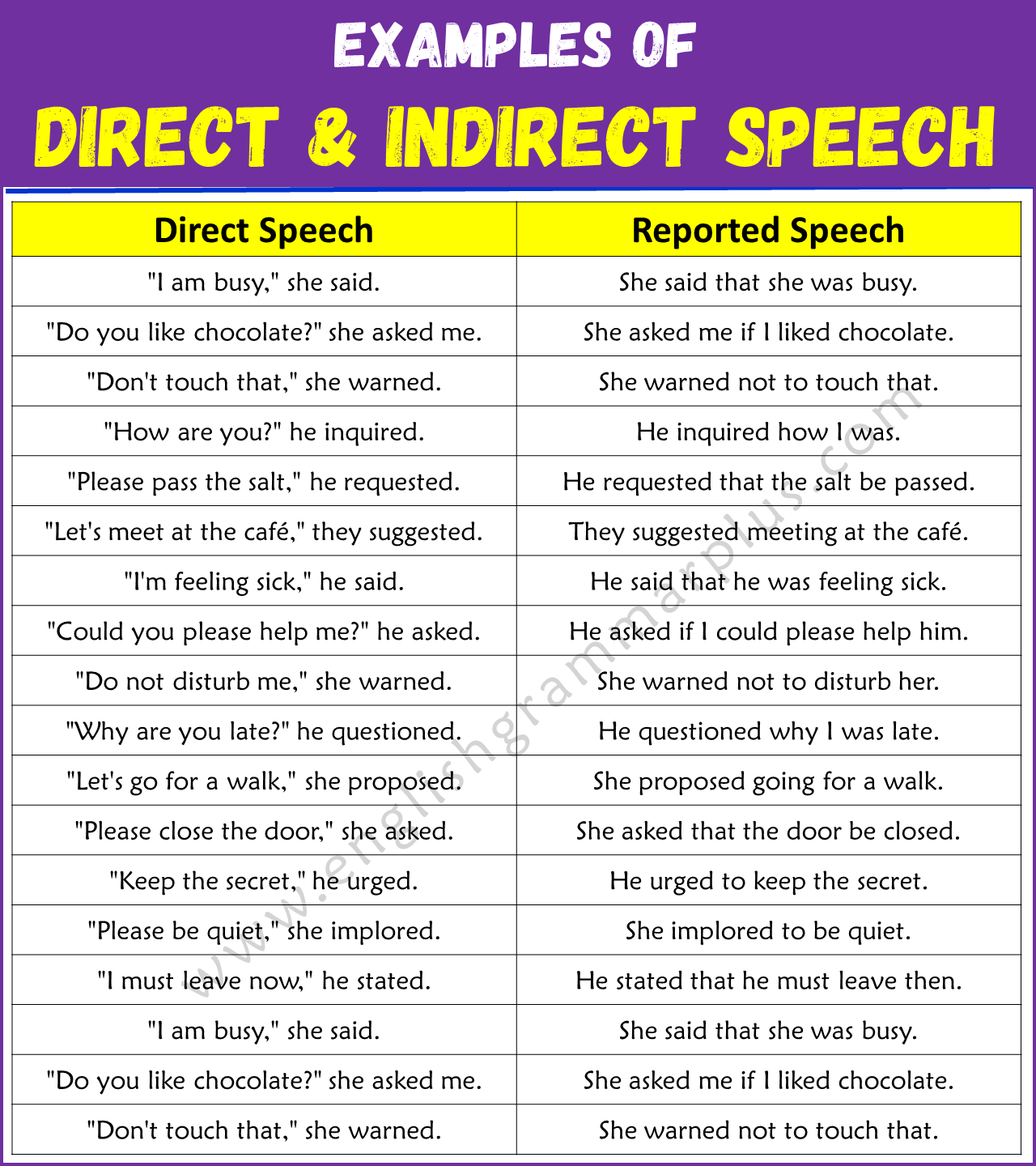
1. Direct: “I am busy,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she was busy.
2. Direct: “We will go tomorrow,” they said.
Indirect: They said that they would go the next day.
3. Direct: “He can play the guitar,” Mike said.
Indirect: Mike said that he could play the guitar.
4. Direct: “Do you like chocolate?” she asked me.
Indirect: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
5. Direct: “Please open the window,” John requested.
Indirect: John requested that the window be opened.
6. Direct: “I have finished my homework,” he announced.
Indirect: He announced that he had finished his homework.
7. Direct: “Don’t touch that,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to touch that.
8. Direct: “How are you?” he inquired.
Indirect: He inquired how I was.
9. Direct: “I will help you,” she promised.
Indirect: She promised that she would help me.
10. Direct: “I didn’t see him yesterday,” Tom confessed.
Indirect: Tom confessed that he hadn’t seen him the day before.
11. Direct: “I am going to the market,” Alex said.
Indirect: Alex said that he was going to the market.
12. Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they told me.
Indirect: They told me that they had seen a movie the night before.
13. Direct: “Can you drive a car?” she questioned.
Indirect: She questioned whether I could drive a car.
14. Direct: “Please pass the salt,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that the salt be passed.
15. Direct: “I have been to Spain,” she mentioned.
Indirect: She mentioned that she had been to Spain.
16. Direct: “Stay away from the dog,” he cautioned.
Indirect: He cautioned to stay away from the dog.
17. Direct: “Where did you buy this?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where I had bought that.
18. Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would call me that night.
19. Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” Sarah insisted.
Indirect: Sarah insisted that she hadn’t taken my book.
20. Direct: “Let’s meet at the café,” they suggested.
Indirect: They suggested meeting at the café.
21. Direct: “I’m feeling sick,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he was feeling sick.
22. Direct: “I won the match,” she exclaimed.
Indirect: She exclaimed that she had won the match.
23. Direct: “Could you please help me?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked if I could please help him.
24. Direct: “Turn off the lights,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded that the lights be turned off.
25. Direct: “I’ll see you tomorrow,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he would see me the next day.
26. Direct: “We’re moving to a new city,” they announced.
Indirect: They announced that they were moving to a new city.
27. Direct: “Do not disturb me,” she warned.
Indirect: She warned not to disturb her.
28. Direct: “Why are you late?” he questioned.
Indirect: He questioned why I was late.
29. Direct: “I’ll handle the situation,” she assured.
Indirect: She assured that she would handle the situation.
30. Direct: “I’ve never been to Asia,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he had never been to Asia.
31. Direct: “Let’s go for a walk,” she proposed.
Indirect: She proposed going for a walk.
32. Direct: “I am learning Spanish,” he mentioned.
Indirect: He mentioned that he was learning Spanish.
33. Direct: “Please close the door,” she asked.
Indirect: She asked that the door be closed.
34. Direct: “I will join you later,” he promised.
Indirect: He promised that he would join me later.
35. Direct: “I lost my wallet,” she declared.
Indirect: She declared that she had lost her wallet.
36. Direct: “Keep the secret,” he urged.
Indirect: He urged to keep the secret.
37. Direct: “Where is the nearest bank?” she inquired.
Indirect: She inquired where the nearest bank was.
38. Direct: “I might go to the concert,” he speculated.
Indirect: He speculated that he might go to the concert.
39. Direct: “Please be quiet,” she implored.
Indirect: She implored to be quiet.
40. Direct: “I will finish the project by Monday,” he assured.
Indirect: He assured that he would finish the project by Monday.
41. Direct: “Don’t forget to lock the door,” she reminded.
Indirect: She reminded to not forget to lock the door.
42. Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” he pondered.
Indirect: He pondered how to solve that problem.
43. Direct: “I can’t believe I won!” he exclaimed.
Indirect: He exclaimed that he couldn’t believe he had won.
44. Direct: “Would you like some coffee?” she offered.
Indirect: She offered if I would like some coffee.
45. Direct: “I must leave now,” he stated.
Indirect: He stated that he must leave then.
46. Direct: “We’re adopting a puppy,” they shared.
Indirect: They shared that they were adopting a puppy.
47. Direct: “Never speak to me again,” she commanded.
Indirect: She commanded never to speak to her again.
48. Direct: “When will you return the book?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked when I would return the book.
49. Direct: “I’ll think about your offer,” she considered.
Indirect: She considered that she would think about the offer.
50. Direct: “Please bring me a glass of water,” he requested.
Indirect: He requested that a glass of water be brought to him.
Post navigation
Previous post.
No comments yet. Why don’t you start the discussion?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Direct and Indirect Speech: The Ultimate Guide
Direct and Indirect Speech are the two ways of reporting what someone said. The use of both direct and indirect speech is crucial in effective communication and writing. Understanding the basics of direct and indirect speech is important, but mastering the advanced techniques of these two forms of speech can take your writing to the next level. In this article, we will explore direct and indirect speech in detail and provide you with a comprehensive guide that covers everything you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is Direct Speech?
Direct speech is a way of reporting what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is typically enclosed in quotation marks to distinguish it from the writer’s own words. Here are some examples of direct speech:
- “I am going to the store,” said John.
- “I love ice cream,” exclaimed Mary.
- “The weather is beautiful today,” said Sarah.
In direct speech, the exact words spoken by the speaker are used, and the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained. Punctuation is also important in direct speech. Commas are used to separate the quote from the reporting verb, and full stops, question marks, or exclamation marks are used at the end of the quote, depending on the tone of the statement.
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is a way of reporting what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. In indirect speech, the writer rephrases the speaker’s words and incorporates them into the sentence. Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- John said that he was going to the store.
- Mary exclaimed that she loved ice cream.
- Sarah said that the weather was beautiful that day.
In indirect speech, the tense and pronouns may change, depending on the context of the sentence. Indirect speech is not enclosed in quotation marks, and the use of reporting verbs is important.
Differences Between Direct and Indirect Speech
The structure of direct and indirect speech is different. Direct speech is presented in quotation marks, whereas indirect speech is incorporated into the sentence without quotation marks. The tenses and pronouns used in direct and indirect speech also differ. In direct speech, the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained, whereas, in indirect speech, they may change depending on the context of the sentence. Reporting verbs are also used differently in direct and indirect speech. In direct speech, they are used to introduce the quote, while in indirect speech, they are used to report what was said.
How to Convert Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
Converting direct speech to indirect speech involves changing the tense, pronouns, and reporting verb. Here are the steps involved in converting direct speech to indirect speech:
- Remove the quotation marks.
- Use a reporting verb to introduce the indirect speech.
- Change the tense of the verb in the quote if necessary.
- Change the pronouns if necessary.
- Use the appropriate conjunction if necessary.
Here is an example of converting direct speech to indirect speech:
Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
How to Convert Indirect Speech to Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech to direct speech involves using the same tense, pronouns, and reporting verb as the original quote. Here are the steps involved in converting indirect speech to direct speech:
- Remove the reporting verb.
- Use quotation marks to enclose the direct speech.
- Maintain the tense of the verb in the quote.
- Use the same pronouns as the original quote.
Here is an example of converting indirect speech to direct speech:
Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store. Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.

Advanced Techniques for Using Direct and Indirect Speech
Using direct and indirect speech effectively can add depth and complexity to your writing. Here are some advanced techniques for using direct and indirect speech:
Blending Direct and Indirect Speech
Blending direct and indirect speech involves using both forms of speech in a single sentence or paragraph. This technique can create a more engaging and realistic narrative. Here is an example:
“Sarah said, ‘I can’t believe it’s already winter.’ Her friend replied that she loved the cold weather and was excited about the snowboarding season.”
In this example, direct speech is used to convey Sarah’s words, and indirect speech is used to convey her friend’s response.
Using Reported Questions
Reported questions are a form of indirect speech that convey a question someone asked without using quotation marks. Reported questions often use reporting verbs like “asked” or “wondered.” Here is an example:
“John asked if I had seen the movie last night.”
In this example, the question “Have you seen the movie last night?” is reported indirectly without using quotation marks.
Using Direct Speech to Convey Emotion
Direct speech can be used to convey emotion more effectively than indirect speech. When using direct speech to convey emotion, it’s important to choose the right tone and emphasis. Here is an example:
“She screamed, ‘I hate you!’ as she slammed the door.”
In this example, the use of direct speech and the exclamation mark convey the intense emotion of the moment.
- When should I use direct speech?
- Direct speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is appropriate when you want to convey the speaker’s tone, emphasis, and emotion.
- When should I use indirect speech?
- Indirect speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. Indirect speech is appropriate when you want to provide information without conveying the speaker’s tone, emphasis, or emotion.
- What are some common reporting verbs?
- Some common reporting verbs include “said,” “asked,” “exclaimed,” “whispered,” “wondered,” and “suggested.”
Direct and indirect speech are important tools for effective communication and writing. Understanding the differences between these two forms of speech and knowing how to use them effectively can take your writing to the next level. By using advanced techniques like blending direct and indirect speech and using direct speech to convey emotion, you can create engaging and realistic narratives that resonate with your readers.
Related Posts
Active Passive Voice: Difference, Usage, and Examples
100 Question Tags Examples with Answers
List of Contractions in English With Examples
What Is The Parts of Speech? Definitions, Types & Examples
Rules Articles: a, an, the With Examples
14 Punctuation Marks With Examples
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
10 Example of Direct and Indirect speech - Easy English Lessons 1. John said, 'I want to become a lawyer.'(Direct Speech) John said that he wanted to become a lawyer. (Indirect speech) 2. The girl said, 'I like sweets.' (Direct Speech) The girl said that she liked sweets. (Indirect speech) 3. She said, ' I am buying a new car.' (Direct Speech) She said that she was buying a new car. .
Direct Speech - the reporting of speech by repeating the actual words of a speaker, for example "I'm going," she said. Explanation: Examples: "I'll be going now" They said. "You have to give me another chance" They pleaded. "If you don't finish that assignment, I am telling your mother" They said. "Why are you watching that?" They asked.
Remember, the goal of these changes is to maintain the essence of the original statement while adapting it to the grammatical and contextual framework of indirect speech. Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech. 1. Direct: "I am busy," she said. Indirect: She said that she was busy. 2. Direct: "We will go tomorrow," they said.
Here are a few examples of direct speech changed to reported speech: 1. Direct speech: "I like pizza," she said. Reported speech: She said she liked pizza. 2. Direct speech: "We are going to the park," they said. Reported speech: They said they were going to the park. 3.
For example, if Jane says, 'I am going to the library', her exact words 'I am going to the library' is considered as direct speech. Direct speech is significant, particularly when you want to provide specific, concrete evidence to support a claim or an argument, such as verifying a statement made by a character in a book, a politician during a ...
Indirect speech: He told her that, she was trying to insult me. Direct speech: He said to her, "you are trying to insult me". Direct speech definition: Direct speech is quote actual words of the speaker. Indirect speech definition: Indirect speech reports the content said by the speaker without quoting exact words. This is "Reported speech".
Here are some examples of direct speech: "I am going to the store," said John. "I love ice cream," exclaimed Mary. "The weather is beautiful today," said Sarah. In direct speech, the exact words spoken by the speaker are used, and the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained. Punctuation is also important in direct speech.
For example: Direct speech: "We're quite cold in here." Indirect speech: They say (that) they're cold. Indirect Speech. Indirect speech is speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person's actual words: for example, 'They said you didn't like it', 'I asked her what her plans were', and ' Citizens complained about the ...
Find an answer to your question Example of direct speech and report speech: Example of direct speech and report speech: - brainly.com See what teachers have to say about Brainly's new learning tools!
Brainly App. Test Prep Soon. Brainly Tutor. For students. For teachers. For parents. Honor code. ... Speech is direct when it is written as it was said and punctuated correctly with inverted commas around the exact original words and is usually accompanied by a reporting clause ('he said', 'they said', 'said Julie'). ... Example: "You have to ...
Direct speech is a sentence in which the exact words spoken are reproduced in speech marks (also known as quotation marks or inverted commas). For example: "You'll never guess what I've just seen!" said Sam, excitedly. "What's that?" asked Louise. I should call my mother. He said he should call her mother. I might be late. He said he might be late.
Example of direct speech: >>> She said, "I am going to the store." Indirect speech. on the other hand, involves reporting what someone said without using their exact words. It often involves a change in tense, pronouns, and other grammatical elements to fit the reporting context. Example of indirect speech based on the above direct speech:
Find an answer to your question give me one example of an direct speech and indirect speech
Answer:For example: Direct speech: "I'm seeing my brother tomorrow." Indirect speech: She said she was seeing her brother the following day. pinky300 pinky300 21.01.2021 English Primary School answered Example of direct speech and indirect speech ... Get the Brainly App
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Examples for direct speech. aditiverma11feb2009 aditiverma11feb2009 29.10.2020 English Primary School answered Examples for direct speech. See answers Advertisement ... Get the Brainly App Download iOS App
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ example of direct speech
Read the following passage convert it into direct speech. My father once told me that I was not studying well. I replied him that I was focusing on my sports event which would be held any time. So my father was satisfied with me and asked if I could carry on both studies and sports.
What is the examples of direct speech See answers Advertisement Advertisement ...
write his her or its on the blank. •Grandmother Visits her grden every day. 2- Claudine is my classmate. Mrs Angelica Rose Is her Favorite teacher. 3. Psalm 27:1 can you explain me for this. 4.
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ change the direct speech into reported speech
Answer: hope you like . Explanation: •direct speech - she says,"i am ill." "i will study",mary said. indirect speech ; she says that she is ill. he said he bought a car. i was walking along the street
Find an answer to your question Change direct to indirect speech i say i am very honest. Shaan3692 Shaan3692 6 hours ago English Secondary School answered Change direct to indirect speech i say i am very honest See answer Advertisement ... Get the Brainly App Download iOS App
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Bring me that file"" turn to direct speech. Destroyer83511 Destroyer83511 6 hours ago English Secondary School Bring me that file"" turn to direct speech Advertisement Advertisement New questions in English ... Get the Brainly App