
- Education & Teaching
- Schools & Teaching

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery

Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Buy new: $13.99 $13.99 FREE delivery Wednesday, May 1 on orders shipped by Amazon over $35 Ships from: Amazon.com Sold by: Amazon.com
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used: $12.99
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service we offer sellers that lets them store their products in Amazon's fulfillment centers, and we directly pack, ship, and provide customer service for these products. Something we hope you'll especially enjoy: FBA items qualify for FREE Shipping and Amazon Prime.
If you're a seller, Fulfillment by Amazon can help you grow your business. Learn more about the program.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

How to Write a Thesis (Mit Press) Paperback – March 6, 2015
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Print length 256 pages
- Language English
- Publisher The MIT Press
- Publication date March 6, 2015
- Dimensions 5.5 x 0.55 x 8 inches
- ISBN-10 0262527138
- ISBN-13 978-0262527132
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Similar items that may deliver to you quickly

Editorial Reviews
How to Write a Thesis is full of friendly, no-bullshit, entry-level advice on what to do and how to do it, illustrated with lucid examples and—significantly—explanations of why, by one of the great researchers and writers in the post-war humanities … Best of all, the absolutely superb chapter on how to write is worth triple the price of admission on its own.
How to Write a Thesis remains valuable after all this time largely thanks to the spirit of Eco's advice. It is witty but sober, genial but demanding—and remarkably uncynical about the rewards of the thesis, both for the person writing it and for the enterprise of scholarship itself.... Some of Eco's advice is, if anything, even more valuable now, given the ubiquity and seeming omniscience of our digital tools.... Eco's humor never detracts from his serious intent. And anyway, even the sardonic pointers on cheating are instructive in their way.
Eco is a first-rate storyteller and unpretentious instructor who thrives on describing the twists and turns of research projects as well as how to avoid accusations of plagiarism.
The book's enduring appeal—the reason it might interest someone whose life no longer demands the writing of anything longer than an e-mail—has little to do with the rigors of undergraduate honors requirements. Instead, it's about what, in Eco's rhapsodic and often funny book, the thesis represents: a magical process of self-realization, a kind of careful, curious engagement with the world that need not end in one's early twenties. 'Your thesis,' Eco foretells, 'is like your first love: it will be difficult to forget.' By mastering the demands and protocols of the fusty old thesis, Eco passionately demonstrates, we become equipped for a world outside ourselves—a world of ideas, philosophies, and debates.
Well beyond the completion of the thesis, Eco's manual makes for pleasant reading and is deserving of a place on the desks of scholars and professional writers. Even sections such as that recommending the combinatory system of handwritten index cards, while outdated in the digital age, can propose a helpful exercise in critical thinking, and add a certain vintage appeal to the book.
How to Write a Thesis has become a classic.
About the Author
Product details.
- Publisher : The MIT Press; Translation edition (March 6, 2015)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 256 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0262527138
- ISBN-13 : 978-0262527132
- Item Weight : 2.31 pounds
- Dimensions : 5.5 x 0.55 x 8 inches
- #45 in Education Research (Books)
- #141 in Words, Language & Grammar Reference
- #2,348 in Motivational Self-Help (Books)
About the author
Umberto eco.
Umberto Eco (born 5 January 1932) is an Italian novelist, medievalist, semiotician, philosopher, and literary critic.
He is the author of several bestselling novels, The Name of The Rose, Foucault's Pendulum, The Island of The Day Before, and Baudolino. His collections of essays include Five Moral Pieces, Kant and the Platypus, Serendipities, Travels In Hyperreality, and How To Travel With a Salmon and Other Essays.
He has also written academic texts and children's books.
Photography (c) Università Reggio Calabria
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
Reviews with images

- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
How to Write a Thesis, According to Umberto Eco
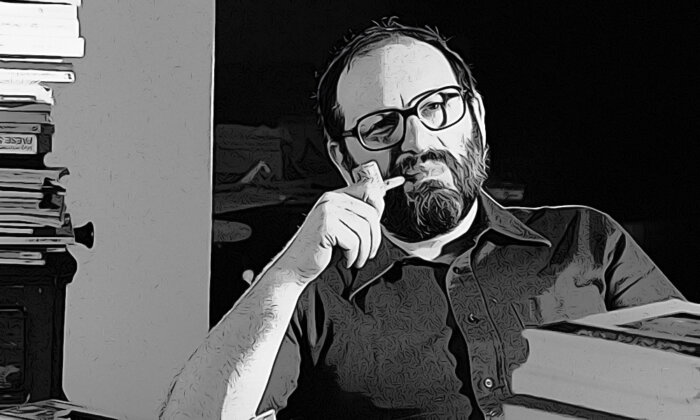

In 1977, three years before Umberto Eco’s groundbreaking novel “ The Name of the Rose ” catapulted him to international fame, the illustrious semiotician published a funny and unpretentious guide for his favorite audience: teachers and their students. Now translated into 17 languages (it finally appeared in English in 2015), “How to Write a Thesis” delivers not just practical advice for writing a thesis — from choosing the right topic (monograph or survey? ancient or contemporary?) to note-taking and mastering the final draft — but meaningful lessons that equip writers for a lifetime outside the walls of the classroom. “Your thesis is like your first love” Eco muses. “It will be difficult to forget. In the end, it will represent your first serious and rigorous academic work, and this is no small thing.”
“Full of friendly, no-bullshit, entry-level advice on what to do and how to do it,” praised one critic, “the absolutely superb chapter on how to write is worth triple the price of admission on its own.” An excerpt from that chapter can be read below.
Once we have decided to whom to write (to humanity, not to the advisor), we must decide how to write, and this is quite a difficult question. If there were exhaustive rules, we would all be great writers. I could at least recommend that you rewrite your thesis many times, or that you take on other writing projects before embarking on your thesis, because writing is also a question of training. In any case, I will provide some general suggestions:
You are not Proust. Do not write long sentences. If they come into your head, write them, but then break them down. Do not be afraid to repeat the subject twice, and stay away from too many pronouns and subordinate clauses. Do not write,
The pianist Wittgenstein, brother of the well-known philosopher who wrote the Tractatus Logico-Philosophicusthat today many consider the masterpiece of contemporary philosophy, happened to have Ravel write for him a concerto for the left hand, since he had lost the right one in the war.
Write instead,
The pianist Paul Wittgenstein was the brother of the philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein. Since Paul was maimed of his right hand, the composer Maurice Ravel wrote a concerto for him that required only the left hand.
The pianist Paul Wittgenstein was the brother of the famous philosopher, author of the Tractatus. The pianist had lost his right hand in the war. For this reason the composer Maurice Ravel wrote a concerto for him that required only the left hand.
Do not write,
The Irish writer had renounced family, country, and church, and stuck to his plans. It can hardly be said of him that he was a politically committed writer, even if some have mentioned Fabian and “socialist” inclinations with respect to him. When World War II erupted, he tended to deliberately ignore the tragedy that shook Europe, and he was preoccupied solely with the writing of his last work.
Rather write,
Joyce had renounced family, country, and church. He stuck to his plans. We cannot say that Joyce was a “politically committed” writer even if some have gone so far as describing a Fabian and “socialist” Joyce. When World War II erupted, Joyce deliberately ignored the tragedy that shook Europe. His sole preoccupation was the writing of Finnegans Wake.
Even if it seems “literary,” please do not write,
When Stockhausen speaks of “clusters,” he does not have in mind Schoenberg’s series, or Webern’s series. If confronted, the German musician would not accept the requirement to avoid repeating any of the twelve notes before the series has ended. The notion of the cluster itself is structurally more unconventional than that of the series. On the other hand Webern followed the strict principles of the author of A Survivor from Warsaw. Now, the author of Mantra goes well beyond. And as for the former, it is necessary to distinguish between the various phases of his oeuvre. Berio agrees: it is not possible to consider this author as a dogmatic serialist.
You will notice that, at some point, you can no longer tell who is who. In addition, defining an author through one of his works is logically incorrect. It is true that lesser critics refer to Alessandro Manzoni simply as “the author of the Betrothed,” perhaps for fear of repeating his name too many times. (This is something manuals on formal writing apparently advise against.) But the author of The Betrothed is not the biographical character Manzoni in his totality. In fact, in a certain context we could say that there is a notable difference between the author of The Betrothed and the author of Adelchi , even if they are one and the same biographically speaking and according to their birth certificate. For this reason, I would rewrite the above passage as follows:
When Stockhausen speaks of a “cluster,” he does not have in mind either the series of Schoenberg or that of Webern. If confronted, Stockhausen would not accept the requirement to avoid repeating any of the twelve notes before the end of the series. The notion of the cluster itself is structurally more unconventional than that of the series. Webern, by contrast, followed the strict principles of Schoenberg, but Stockhausen goes well beyond. And even for Webern, it is necessary to distinguish among the various phases of his oeuvre. Berio also asserts that it is not possible to think of Webern as a dogmatic serialist.

You are not e. e. cummings. Cummings was an American avant-garde poet who is known for having signed his name with lower-case initials. Naturally he used commas and periods with great thriftiness, he broke his lines into small pieces, and in short he did all the things that an avant-garde poet can and should do. But you are not an avant-garde poet. Not even if your thesis is on avant-garde poetry. If you write a thesis on Caravaggio, are you then a painter? And if you write a thesis on the style of the futurists, please do not write as a futurist writes. This is important advice because nowadays many tend to write “alternative” theses, in which the rules of critical discourse are not respected. But the language of the thesis is a metalanguage , that is, a language that speaks of other languages. A psychiatrist who describes the mentally ill does not express himself in the manner of his patients. I am not saying that it is wrong to express oneself in the manner of the so-called mentally ill. In fact, you could reasonably argue that they are the only ones who express themselves the way one should. But here you have two choices: either you do not write a thesis, and you manifest your desire to break with tradition by refusing to earn your degree, perhaps learning to play the guitar instead; or you write your thesis, but then you must explain to everyone why the language of the mentally ill is not a “crazy” language, and to do it you must use a metalanguage intelligible to all. The pseudo-poet who writes his thesis in poetry is a pitiful writer (and probably a bad poet). From Dante to Eliot and from Eliot to Sanguineti, when avant-garde poets wanted to talk about their poetry, they wrote in clear prose. And when Marx wanted to talk about workers, he did not write as a worker of his time, but as a philosopher. Then, when he wrote The Communist Manifesto with Engels in 1848, he used a fragmented journalistic style that was provocative and quite effective. Yet again, The Communist Manifesto is not written in the style of Capital, a text addressed to economists and politicians. Do not pretend to be Dante by saying that the poetic fury “dictates deep within,” and that you cannot surrender to the flat and pedestrian metalanguage of literary criticism. Are you a poet? Then do not pursue a university degree. Twentieth-century Italian poet Eugenio Montale does not have a degree, and he is a great poet nonetheless. His contemporary Carlo Emilio Gadda (who held a degree in engineering) wrote fiction in a unique style, full of dialects and stylistic idiosyncrasies; but when he wrote a manual for radio news writers, he wrote a clever, sharp, and lucid “recipe book” full of clear and accessible prose. And when Montale writes a critical article, he writes so that all can understand him, including those who do not understand his poems.
Begin new paragraphs often. Do so when logically necessary, and when the pace of the text requires it, but the more you do it, the better.
Write everything that comes into your head , but only in the first draft. You may notice that you get carried away with your inspiration, and you lose track of the center of your topic. In this case, you can remove the parenthetical sentences and the digressions, or you can put each in a note or an appendix. Your thesis exists to prove the hypothesis that you devised at the outset, not to show the breadth of your knowledge.
Use the advisor as a guinea pig. You must ensure that the advisor reads the first chapters (and eventually, all the chapters) far in advance of the deadline. His reactions may be useful to you. If the advisor is busy (or lazy), ask a friend. Ask if he understands what you are writing. Do not play the solitary genius.
Do not insist on beginning with the first chapter . Perhaps you have more documentation on chapter 4. Start there, with the nonchalance of someone who has already worked out the previous chapters. You will gain confidence. Naturally your working table of contents will anchor you, and will serve as a hypothesis that guides you.
Do not use ellipsis and exclamation points, and do not explain ironies . It is possible to use language that is referential or language that is figurative . By referential language, I mean a language that is recognized by all, in which all things are called by their most common name, and that does not lend itself to misunderstandings. “The Venice-Milan train” indicates in a referential way the same object that “The Arrow of the Lagoon” indicates figuratively. This example illustrates that “everyday” communication is possible with partially figurative language. Ideally, a critical essay or a scholarly text should be written referentially (with all terms well defined and univocal), but it can also be useful to use metaphor, irony, or litotes. Here is a referential text, followed by its transcription in figurative terms that are at least tolerable:
[ Referential version :] Krasnapolsky is not a very sharp critic of Danieli’s work. His interpretation draws meaning from the author’s text that the author probably did not intend. Consider the line, “in the evening gazing at the clouds.” Ritz interprets this as a normal geographical annotation, whereas Krasnapolsky sees a symbolic expression that alludes to poetic activity. One should not trust Ritz’s critical acumen, and one should also distrust Krasnapolsky. Hilton observes that, “if Ritz’s writing seems like a tourist brochure, Krasnapolsky’s criticism reads like a Lenten sermon.” And he adds, “Truly, two perfect critics.”
[ Figurative version :] We are not convinced that Krasnapolsky is the sharpest critic of Danieli’s work. In reading his author, Krasnapolsky gives the impression that he is putting words into Danieli’s mouth. Consider the line, “in the evening gazing at the clouds.” Ritz interprets it as a normal geographical annotation, whereas Krasnapolsky plays the symbolism card and sees an allusion to poetic activity. Ritz is not a prodigy of critical insight, but Krasnapolsky should also be handled with care. As Hilton observes, “if Ritz’s writing seems like a tourist brochure, Krasnapolsky’s criticism reads like a Lenten sermon. Truly, two perfect critics.”
You can see that the figurative version uses various rhetorical devices. First of all, the litotes: saying that you are not convinced that someone is a sharp critic means that you are convinced that he is not a sharp critic. Also, the statement “Ritz is not a prodigy of critical insight” means that he is a modest critic. Then there are the metaphors : putting words into someone’s mouth, and playing the symbolism card. The tourist brochure and the Lenten sermon are two similes , while the observation that the two authors are perfect critics is an example of irony : saying one thing to signify its opposite.
Now, we either use rhetorical figures effectively, or we do not use them at all. If we use them it is because we presume our reader is capable of catching them, and because we believe that we will appear more incisive and convincing. In this case, we should not be ashamed of them, and we should not explain them . If we think that our reader is an idiot, we should not use rhetorical figures, but if we use them and feel the need to explain them, we are essentially calling the reader an idiot. In turn, he will take revenge by calling the author an idiot. Here is how a timid writer might intervene to neutralize and excuse the rhetorical figures he uses:
[ Figurative version with reservations :] We are not convinced that Krasnapolsky is the “sharpest” critic of Danieli’s work. In reading his author, Krasnapolsky gives the impression that he is “putting words into Danieli’s mouth.” Consider Danieli’s line, “in the evening gazing at the clouds.” Ritz interprets this as a normal geographical annotation, whereas Krasnapolsky “plays the symbolism card” and sees an allusion to poetic activity. Ritz is not a “prodigy of critical insight,” but Krasnapolsky should also be “handled with care”! As Hilton ironically observes, “if Ritz’s writing seems like a vacation brochure, Krasnapolsky’s criticism reads like a Lenten sermon.” And he defines them (again with irony!) as two models of critical perfection. But all joking aside …
I am convinced that nobody could be so intellectually petit bourgeois as to conceive a passage so studded with shyness and apologetic little smiles. Of course I exaggerated in this example, and here I say that I exaggerated because it is didactically important that the parody be understood as such. In fact, many bad habits of the amateur writer are condensed into this third example. First of all, the use of quotation marks to warn the reader, “Pay attention because I am about to say something big!” Puerile. Quotation marks are generally only used to designate a direct quotation or the title of an essay or short work; to indicate that a term is jargon or slang; or that a term is being discussed in the text as a word, rather than used functionally within the sentence. Secondly, the use of the exclamation point to emphasize a statement. This is not appropriate in a critical essay. If you check the book you are reading, you will notice that I have used the exclamation mark only once or twice. It is allowed once or twice, if the purpose is to make the reader jump in his seat and call his attention to a vehement statement like, “Pay attention, never make this mistake!” But it is a good rule to speak softly. The effect will be stronger if you simply say important things. Finally, the author of the third passage draws attention to the ironies, and apologizes for using them (even if they are someone else’s). Surely, if you think that Hilton’s irony is too subtle, you can write, “Hilton states with subtle irony that we are in the presence of two perfect critics.” But the irony must be really subtle to merit such a statement. In the quoted text, after Hilton has mentioned the vacation brochure and the Lenten sermon, the irony was already evident and needed no further explanation. The same applies to the statement, “But all joking aside.” Sometimes a statement like this can be useful to abruptly change the tone of the argument, but only if you were really joking before. In this case, the author was not joking. He was attempting to use irony and metaphor, but these are serious rhetorical devices and not jokes.
You may observe that, more than once in this book, I have expressed a paradox and then warned that it was a paradox. For example, in section 2.6.1, I proposed the existence of the mythical centaur for the purpose of explaining the concept of scientific research. But I warned you of this paradox not because I thought you would have believed this proposition. On the contrary, I warned you because I was afraid that you would have doubted too much, and hence dismissed the paradox. Therefore I insisted that, despite its paradoxical form, my statement contained an important truth: that research must clearly define its object so that others can identify it, even if this object is mythical. And I made this absolutely clear because this is a didactic book in which I care more that everyone understands what I want to say than about a beautiful literary style. Had I been writing an essay, I would have pronounced the paradox without denouncing it later.
Always define a term when you introduce it for the first time . If you do not know the definition of a term, avoid using it. If it is one of the principal terms of your thesis and you are not able to define it, call it quits. You have chosen the wrong thesis (or, if you were planning to pursue further research, the wrong career).
Umberto Eco was an Italian novelist, literary critic, philosopher, semiotician, and university professor. This article is excerpted from his book “ How to Write a Thesis .”
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
How to Write a Master's Thesis
- Yvonne N. Bui - San Francisco State University, USA
- Description
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
“Yvonne Bui’s How to Write a Master’s Thesis should be mandatory for all thesis track master’s students. It steers students away from the shortcuts students may be tempted to use that would be costly in the long run. The step by step intentional approach is what I like best about this book.”
“This is the best textbook about writing an M.A. thesis available in the market.”
“This is the type of textbook that students keep and refer to after the class.”
Excellent book. Thorough, yet concise, information for students writing their Master's Thesis who may not have had a strong background in research.
Clear, Concise, easy for students to access and understand. Contains all the elements for a successful thesis.
I loved the ease of this book. It was clear without extra nonsense that would just confuse the students.
Clear, concise, easily accessible. Students find it of great value.
NEW TO THIS EDITION:
- Concrete instruction and guides for conceptualizing the literature review help students navigate through the most challenging topics.
- Step-by-step instructions and more screenshots give students the guidance they need to write the foundational chapter, along with the latest online resources and general library information.
- Additional coverage of single case designs and mixed methods help students gain a more comprehensive understanding of research methods.
- Expanded explanation of unintentional plagiarism within the ethics chapter shows students the path to successful and professional writing.
- Detailed information on conference presentation as a way to disseminate research , in addition to getting published, help students understand all of the tools needed to write a master’s thesis.
KEY FEATURES:
- An advanced chapter organizer provides an up-front checklist of what to expect in the chapter and serves as a project planner, so that students can immediately prepare and work alongside the chapter as they begin to develop their thesis.
- Full guidance on conducting successful literature reviews includes up-to-date information on electronic databases and Internet tools complete with numerous figures and captured screen shots from relevant web sites, electronic databases, and SPSS software, all integrated with the text.
- Excerpts from research articles and samples from exemplary students' master's theses relate specifically to the content of each chapter and provide the reader with a real-world context.
- Detailed explanations of the various components of the master's thesis and concrete strategies on how to conduct a literature review help students write each chapter of the master's thesis, and apply the American Psychological Association (APA) editorial style.
- A comprehensive Resources section features "Try It!" boxes which lead students through a sample problem or writing exercise based on a piece of the thesis to reinforce prior course learning and the writing objectives at hand. Reflection/discussion questions in the same section are designed to help students work through the thesis process.
Sample Materials & Chapters
1: Overview of the Master's Degree and Thesis
3: Using the Literature to Research Your Problem
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, related products.


How to Write a Thesis
Umberto Eco was an Italian semiotician, philosopher, literary critic, and novelist. He is the author of The Name of the Rose, Foucault's Pendulum , and The Prague Cemetery , all bestsellers in many languages, as well as a number of influential scholarly works.
Umberto Eco's wise and witty guide to researching and writing a thesis, published in English for the first time.
By the time Umberto Eco published his best-selling novel The Name of the Rose , he was one of Italy's most celebrated intellectuals, a distinguished academic and the author of influential works on semiotics. Some years before that, in 1977, Eco published a little book for his students, How to Write a Thesis , in which he offered useful advice on all the steps involved in researching and writing a thesis—from choosing a topic to organizing a work schedule to writing the final draft. Now in its twenty-third edition in Italy and translated into seventeen languages, How to Write a Thesis has become a classic. Remarkably, this is its first, long overdue publication in English.
Eco's approach is anything but dry and academic. He not only offers practical advice but also considers larger questions about the value of the thesis-writing exercise. How to Write a Thesis is unlike any other writing manual. It reads like a novel. It is opinionated. It is frequently irreverent, sometimes polemical, and often hilarious. Eco advises students how to avoid “thesis neurosis” and he answers the important question “Must You Read Books?” He reminds students “You are not Proust” and “Write everything that comes into your head, but only in the first draft.” Of course, there was no Internet in 1977, but Eco's index card research system offers important lessons about critical thinking and information curating for students of today who may be burdened by Big Data.
How to Write a Thesis belongs on the bookshelves of students, teachers, writers, and Eco fans everywhere. Already a classic, it would fit nicely between two other classics: Strunk and White and The Name of the Rose .
Contents The Definition and Purpose of a Thesis • Choosing the Topic • Conducting Research • The Work Plan and the Index Cards • Writing the Thesis • The Final Draft
- Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
How to Write a Thesis By: Umberto Eco, Caterina Mongiat Farina, Geoff Farina https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.001.0001 ISBN (electronic): 9780262328753 Publisher: The MIT Press Published: 2015
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager

Table of Contents
- [ Front Matter ] Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0013 Open the PDF Link PDF for [ Front Matter ] in another window
- Foreword By Francesco Erspamer Francesco Erspamer Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0001 Open the PDF Link PDF for Foreword in another window
- Translators' Foreword By Caterina Mongiat Farina , Caterina Mongiat Farina Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Geoff Farina Geoff Farina Search for other works by this author on: This Site Google Scholar Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0002 Open the PDF Link PDF for Translators' Foreword in another window
- Introduction to the Original 1977 Edition Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0003 Open the PDF Link PDF for Introduction to the Original 1977 Edition in another window
- Introduction to the 1985 Edition Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0004 Open the PDF Link PDF for Introduction to the 1985 Edition in another window
- 1: The Definition and Purpose of the Thesis Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0005 Open the PDF Link PDF for 1: The Definition and Purpose of the Thesis in another window
- 2: Choosing the Topic Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0006 Open the PDF Link PDF for 2: Choosing the Topic in another window
- 3: Conducting Research Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0007 Open the PDF Link PDF for 3: Conducting Research in another window
- 4: The Work Plan and the Index Cards Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0008 Open the PDF Link PDF for 4: The Work Plan and the Index Cards in another window
- 5: Writing the Thesis Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0009 Open the PDF Link PDF for 5: Writing the Thesis in another window
- 6: The Final Draft Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0010 Open the PDF Link PDF for 6: The Final Draft in another window
- 7: Conclusions Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0011 Open the PDF Link PDF for 7: Conclusions in another window
- Notes Doi: https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/10029.003.0012 Open the PDF Link PDF for Notes in another window
- Open Access
A product of The MIT Press
Mit press direct.
- About MIT Press Direct
Information
- Accessibility
- For Authors
- For Customers
- For Librarians
- Direct to Open
- Media Inquiries
- Rights and Permissions
- For Advertisers
- About the MIT Press
- The MIT Press Reader
- MIT Press Blog
- Seasonal Catalogs
- MIT Press Home
- Give to the MIT Press
- Direct Service Desk
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Statement
- Crossref Member
- COUNTER Member
- The MIT Press colophon is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Find anything you save across the site in your account
A Guide to Thesis Writing That Is a Guide to Life
“How to Write a Thesis,” by Umberto Eco, first appeared on Italian bookshelves in 1977. For Eco, the playful philosopher and novelist best known for his work on semiotics, there was a practical reason for writing it. Up until 1999, a thesis of original research was required of every student pursuing the Italian equivalent of a bachelor’s degree. Collecting his thoughts on the thesis process would save him the trouble of reciting the same advice to students each year. Since its publication, “How to Write a Thesis” has gone through twenty-three editions in Italy and has been translated into at least seventeen languages. Its first English edition is only now available, in a translation by Caterina Mongiat Farina and Geoff Farina.
We in the English-speaking world have survived thirty-seven years without “How to Write a Thesis.” Why bother with it now? After all, Eco wrote his thesis-writing manual before the advent of widespread word processing and the Internet. There are long passages devoted to quaint technologies such as note cards and address books, careful strategies for how to overcome the limitations of your local library. But the book’s enduring appeal—the reason it might interest someone whose life no longer demands the writing of anything longer than an e-mail—has little to do with the rigors of undergraduate honors requirements. Instead, it’s about what, in Eco’s rhapsodic and often funny book, the thesis represents: a magical process of self-realization, a kind of careful, curious engagement with the world that need not end in one’s early twenties. “Your thesis,” Eco foretells, “is like your first love: it will be difficult to forget.” By mastering the demands and protocols of the fusty old thesis, Eco passionately demonstrates, we become equipped for a world outside ourselves—a world of ideas, philosophies, and debates.
Eco’s career has been defined by a desire to share the rarefied concerns of academia with a broader reading public. He wrote a novel that enacted literary theory (“The Name of the Rose”) and a children’s book about atoms conscientiously objecting to their fate as war machines (“The Bomb and the General”). “How to Write a Thesis” is sparked by the wish to give any student with the desire and a respect for the process the tools for producing a rigorous and meaningful piece of writing. “A more just society,” Eco writes at the book’s outset, would be one where anyone with “true aspirations” would be supported by the state, regardless of their background or resources. Our society does not quite work that way. It is the students of privilege, the beneficiaries of the best training available, who tend to initiate and then breeze through the thesis process.
Eco walks students through the craft and rewards of sustained research, the nuances of outlining, different systems for collating one’s research notes, what to do if—per Eco’s invocation of thesis-as-first-love—you fear that someone’s made all these moves before. There are broad strategies for laying out the project’s “center” and “periphery” as well as philosophical asides about originality and attribution. “Work on a contemporary author as if he were ancient, and an ancient one as if he were contemporary,” Eco wisely advises. “You will have more fun and write a better thesis.” Other suggestions may strike the modern student as anachronistic, such as the novel idea of using an address book to keep a log of one’s sources.
But there are also old-fashioned approaches that seem more useful than ever: he recommends, for instance, a system of sortable index cards to explore a project’s potential trajectories. Moments like these make “How to Write a Thesis” feel like an instruction manual for finding one’s center in a dizzying era of information overload. Consider Eco’s caution against “the alibi of photocopies”: “A student makes hundreds of pages of photocopies and takes them home, and the manual labor he exercises in doing so gives him the impression that he possesses the work. Owning the photocopies exempts the student from actually reading them. This sort of vertigo of accumulation, a neocapitalism of information, happens to many.” Many of us suffer from an accelerated version of this nowadays, as we effortlessly bookmark links or save articles to Instapaper, satisfied with our aspiration to hoard all this new information, unsure if we will ever get around to actually dealing with it. (Eco’s not-entirely-helpful solution: read everything as soon as possible.)
But the most alluring aspect of Eco’s book is the way he imagines the community that results from any honest intellectual endeavor—the conversations you enter into across time and space, across age or hierarchy, in the spirit of free-flowing, democratic conversation. He cautions students against losing themselves down a narcissistic rabbit hole: you are not a “defrauded genius” simply because someone else has happened upon the same set of research questions. “You must overcome any shyness and have a conversation with the librarian,” he writes, “because he can offer you reliable advice that will save you much time. You must consider that the librarian (if not overworked or neurotic) is happy when he can demonstrate two things: the quality of his memory and erudition and the richness of his library, especially if it is small. The more isolated and disregarded the library, the more the librarian is consumed with sorrow for its underestimation.”
Eco captures a basic set of experiences and anxieties familiar to anyone who has written a thesis, from finding a mentor (“How to Avoid Being Exploited By Your Advisor”) to fighting through episodes of self-doubt. Ultimately, it’s the process and struggle that make a thesis a formative experience. When everything else you learned in college is marooned in the past—when you happen upon an old notebook and wonder what you spent all your time doing, since you have no recollection whatsoever of a senior-year postmodernism seminar—it is the thesis that remains, providing the once-mastered scholarly foundation that continues to authorize, decades-later, barroom observations about the late-career works of William Faulker or the Hotelling effect. (Full disclosure: I doubt that anyone on Earth can rival my mastery of John Travolta’s White Man’s Burden, owing to an idyllic Berkeley spring spent studying awful movies about race.)
In his foreword to Eco’s book, the scholar Francesco Erspamer contends that “How to Write a Thesis” continues to resonate with readers because it gets at “the very essence of the humanities.” There are certainly reasons to believe that the current crisis of the humanities owes partly to the poor job they do of explaining and justifying themselves. As critics continue to assail the prohibitive cost and possible uselessness of college—and at a time when anything that takes more than a few minutes to skim is called a “longread”—it’s understandable that devoting a small chunk of one’s frisky twenties to writing a thesis can seem a waste of time, outlandishly quaint, maybe even selfish. And, as higher education continues to bend to the logic of consumption and marketable skills, platitudes about pursuing knowledge for its own sake can seem certifiably bananas. Even from the perspective of the collegiate bureaucracy, the thesis is useful primarily as another mode of assessment, a benchmark of student achievement that’s legible and quantifiable. It’s also a great parting reminder to parents that your senior learned and achieved something.
But “How to Write a Thesis” is ultimately about much more than the leisurely pursuits of college students. Writing and research manuals such as “The Elements of Style,” “The Craft of Research,” and Turabian offer a vision of our best selves. They are exacting and exhaustive, full of protocols and standards that might seem pretentious, even strange. Acknowledging these rules, Eco would argue, allows the average person entry into a veritable universe of argument and discussion. “How to Write a Thesis,” then, isn’t just about fulfilling a degree requirement. It’s also about engaging difference and attempting a project that is seemingly impossible, humbly reckoning with “the knowledge that anyone can teach us something.” It models a kind of self-actualization, a belief in the integrity of one’s own voice.
A thesis represents an investment with an uncertain return, mostly because its life-changing aspects have to do with process. Maybe it’s the last time your most harebrained ideas will be taken seriously. Everyone deserves to feel this way. This is especially true given the stories from many college campuses about the comparatively lower number of women, first-generation students, and students of color who pursue optional thesis work. For these students, part of the challenge involves taking oneself seriously enough to ask for an unfamiliar and potentially path-altering kind of mentorship.
It’s worth thinking through Eco’s evocation of a “just society.” We might even think of the thesis, as Eco envisions it, as a formal version of the open-mindedness, care, rigor, and gusto with which we should greet every new day. It’s about committing oneself to a task that seems big and impossible. In the end, you won’t remember much beyond those final all-nighters, the gauche inside joke that sullies an acknowledgments page that only four human beings will ever read, the awkward photograph with your advisor at graduation. All that remains might be the sensation of handing your thesis to someone in the departmental office and then walking into a possibility-rich, almost-summer afternoon. It will be difficult to forget.
How To Write Your First Thesis
- © 2017
- Paul Gruba 0 ,
- Justin Zobel 1
School of Languages & Linguistics, University of Melbourne SLL, Babel Bldg 608, Melbourne, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
School of Computing & Information Systems, University of Melbourne Comp. Science & Software Engg., Carlton, VIC, Australia
- A practical guide for the entire process of producing a thesis for the first time
- Written by authors with many years of experience advising students
- Provides grounded advice to students who are new to writing extended original research, either undergraduate or graduate coursework
56k Accesses
3 Citations
10 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (9 chapters)
Front matter, transition to your first thesis.
- Paul Gruba, Justin Zobel
Getting Organized
The structure of a thesis, a strong beginning: the introduction, situating the study: the background, explaining the investigation: methods and innovations, presenting the outcome: the results, wrapping it up: discussion and conclusion, before you submit, back matter.
- research writing
- thesis preparation
- dissertation writing
- final project preparation
- thesis structure
- learning and instruction
About this book
Many courses and degrees require that students write a short thesis. This book guides students through their first experience of producing a thesis and undertaking original research. Written by experienced researchers and advisors, the book sets out signposts and tasks to help students to understand what is needed to succeed, including scoping a topic, managing references, interpreting data, and successful completion.
For students, the task of writing a thesis is a transition from structured coursework to becoming a researcher. The book provides advice on:
- What to expect from research and how to work with a supervisor
- Getting organized and approaching the work in a productive way
- Developing an overall thesis structure and avoidance of mistakes such as inadvertent plagiarism
- Producing each major component: a strong introduction, background chapters that are situated in the discipline, and an explanation ofmethods and results that are crucial to successful original research
- How to wrap up a complex project with an extended checklist of the many details needed to be checked before a final submission
Authors and Affiliations
School of languages & linguistics, university of melbourne sll, babel bldg 608, melbourne, australia, school of computing & information systems, university of melbourne comp. science & software engg., carlton, vic, australia.
Justin Zobel
About the authors
Paul Gruba is Associate Professor in the School of Languages and Linguistics, University of Melbourne.
Justin Zobel is Professor in the School of Computing & Information Systems, University of Melbourne.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : How To Write Your First Thesis
Authors : Paul Gruba, Justin Zobel
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61854-8
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Computer Science , Computer Science (R0)
Copyright Information : Springer International Publishing AG 2017
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-319-61853-1 Published: 06 September 2017
eBook ISBN : 978-3-319-61854-8 Published: 24 August 2017
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XIII, 95
Number of Illustrations : 8 b/w illustrations
Topics : Computer Science, general , Learning & Instruction , Natural Language Processing (NLP) , Popular Social Sciences , Science, Humanities and Social Sciences, multidisciplinary
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Library Subject Guides
4. writing up your research: books on thesis writing.
- Books on Thesis Writing
- Thesis Formatting (MS Word)
- Referencing
Other Research Support Guides 1. Plan (Design and Discover) your Research >> 2. Find & Manage Research Literature >> 3. Doing the Research >> 5. Publish & Share >> 6. Measure Impact
Your dissertation may be the longest piece of writing you have ever done, but there are ways to approach it that will help to make it less overwhelming.
Write up as you go along. It is much easier to keep track of how your ideas develop and writing helps clarify your thinking. It also saves having to churn out 1000s of words at the end.
You don't have to start with the introduction – start at the chapter that seems the easiest to write – this could be the literature review or methodology, for example.
Alternatively you may prefer to write the introduction first, so you can get your ideas straight. Decide what will suit your ways of working best - then do it.
Think of each chapter as an essay in itself – it should have a clear introduction and conclusion. Use the conclusion to link back to the overall research question.
Think of the main argument of your dissertation as a river, and each chapter is a tributary feeding into this. The individual chapters will contain their own arguments, and go their own way, but they all contribute to the main flow.
Write a chapter, read it and do a redraft - then move on. This stops you from getting bogged down in one chapter.
Write your references properly and in full from the beginning.
Keep your word count in mind – be ruthless and don't write anything that isn't relevant. It's often easier to add information, than have to cut down a long chapter that you've slaved over for hours.
Save your work! Remember to save your work frequently to somewhere you can access it easily. It's a good idea to at least save a copy to a cloud-based service like Google Docs or Dropbox so that you can access it from any computer - if you only save to your own PC, laptop or tablet, you could lose everything if you lose or break your device.
E-books on thesis writing
Who to Contact
Nick scullin, phone: +6433693904, find more books.
Try the following subject headings to search UC library catalogue for books on thesis writing
More books on writing theses
Dissertations, Academic
Dissertations, Academic -- Authorship
Dissertations, Academic -- Handbooks, manuals ,
Academic writing
Academic writing -- Handbooks, manuals ,
Report writing
Technical writing
Remember to save your work in different places
Save your work! Remember to save your work frequently to somewhere you can access it easily. It's a good idea to save your work in at least three places: on your computer, a flash drive and a copy to a cloud-based service like Google Docs or Dropbox .
Save each new file with the date in the file name as different files can get very confusing
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Thesis Formatting (MS Word) >>
- Last Updated: Feb 8, 2024 12:29 PM
- URL: https://canterbury.libguides.com/writingup

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The wise and witty guide to researching and writing a thesis, by the bestselling author of The Name of the Rose —now published in English for the first time. Learn the art of the thesis from a giant of Italian literature and philosophy—from choosing a topic to organizing a work schedule to writing the final draft.
Your thesis exists to prove the hypothesis that you devised at the outset, not to show the breadth of your knowledge. Use the advisor as a guinea pig. You must ensure that the advisor reads the first chapters (and eventually, all the chapters) far in advance of the deadline. His reactions may be useful to you.
From the book reviews: "After reading the book, you are left with no doubt as to what is required to write a thesis, as well as how to undertake the task using a systematic approach. … It should be mandatory reading for all postgraduate students embarking on a master's degree or higher academic qualification.
"This is the best textbook about writing an M.A. thesis available in the market." -Hsin-I Liu, University of the Incarnate Word The Third Edition of How to Write a Master's Thesis is a comprehensive manual on how to plan and write a five-chapter master's thesis, and a great resource for graduate students looking for concrete, applied guidance on how to successfully complete their ...
Murray, Rowena. McGraw-Hill Education (UK), May 1, 2011 - Education - 384 pages. How to Write a Thesis provides an invaluable resource to help students consider, plan and write their theses. The third edition of this best-selling and well loved book builds on the success of the second edition.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
How to Write a Thesis. by Umberto Eco. Translated by Caterina Mongiat Farina and Geoff Farina. Introduction by Francesco Erspamer. Paperback. $22.95. Paperback. ISBN: 9780262527132. Pub date: March 6, 2015.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
9780262328753. Publication date: 2015. Umberto Eco's wise and witty guide to researching and writing a thesis, published in English for the first time. By the time Umberto Eco published his best-selling novel The Name of the Rose, he was one of Italy's most celebrated intellectuals, a distinguished academic and the author of influential works ...
Umberto Eco's wise and witty guide to researching and writing a thesis, published in English for the first time. By the time Umberto Eco published his best-selling novel The Name of the Rose, he was one of Italy's most celebrated intellectuals, a distinguished academic and the author of influential works on semiotics.Some years before that, in 1977, Eco published a little book for his students ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
A Guide to Thesis Writing That Is a Guide to Life. By Hua Hsu. April 6, 2015. In "How to Write a Thesis," Umberto Eco walks students through the craft and rewards of sustained research ...
Umberto Eco. MIT Press, Feb 27, 2015 - Language Arts & Disciplines - 256 pages. The wise and witty guide to researching and writing a thesis, by the bestselling author of The Name of the Rose—now published in English for the first time. Learn the art of the thesis from a giant of Italian literature and philosophy—from choosing a topic to ...
are enough words in this book for you to read and there are enough words for you to ponder and digest as you walk through your PhD journey. Suffice to say, this book was born out of an intense passion to share, educate, guide and assist students. We've walked the same journey you're about to embark on (or have already embarked on).
Many courses and degrees require that students write a short thesis. This book guides students through their first experience of producing a thesis and undertaking original research. Written by experienced researchers and advisors, the book sets out signposts and tasks to help students to understand what is needed to succeed, including scoping ...
3.93. 4,130 ratings439 reviews. By the time Umberto Eco published his best-selling novel "The Name of the Rose," he was one of Italy's most celebrated intellectuals, a distinguished academic and the author of influential works on semiotics. Some years before that, in 1977, Eco published a little book for his students, "How to Write a Thesis ...
Read the following examples of strong thesis statements, from essays and book chapters, and see if you can identify the different elements of a strong thesis and of the MTS within them. Example 1: from "University Gothic, c. 1880-1910" by Minna Vuohelainen in Gothic Britain: Dark Places in the Provinces and Margins of the British Isles :
E-books on thesis writing. How to Write a Thesis by Umberto Eco; Geoff Farina; Francesco Erspamer; Caterina Mongiat Farina. ISBN: 0262527138. Publication Date: 2015-03-06. How to Write a Better Thesis by David Evans; Paul Gruba; Justin Zobel. ISBN: 3319042858. Publication Date: 2014-04-08.