Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Researching and writing for Economics students
4 literature review and citations/references.

Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references
Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper’s introduction. (See organising for a standard format.)
Some disambiguation:
A ‘Literature survey’ paper: Some academic papers are called ‘literature surveys’. These try to summarise and discuss the existing work that has been done on a particular topic, and can be very useful. See, for example, works in The Journal of Economic Perspectives, the Journal of Economic Literature, the “Handbook of [XXX] Economics”
Many student projects and undergraduate dissertations are mainly literature surveys.
4.1 What is the point of a literature survey?
Your literature review should explain:
what has been done already to address your topic and related questions, putting your work in perspective, and
what techniques others have used, what are their strengths and weaknesses, and how might they be relevant tools for your own analysis.

Figure 4.2: Take notes on this as you read, and write them up.
4.2 What previous work is relevant?
Focus on literature that is relevant to your topic only.
But do not focus only on articles about your exact topic ! For example, if your paper is about the relative price of cars in the UK, you might cite papers (i) about the global automobile market, (ii) about the theory and evidence on competition in markets with similar features and (iii) using econometric techniques such as “hedonic regression” to estimate “price premia” in other markets and in other countries.
Consider: If you were Colchester a doctor and wanted to know whether a medicine would be effective for your patients, would you only consider medical studies that ran tests on Colchester residents, or would you consider more general national and international investigations?
4.3 What are “good” economics journal articles?
You should aim to read and cite peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals. (Journals in other fields such as Finance, Marketing and Political Science may also be useful.) These papers have a certain credibility as they have been checked by several referees and one or more editors before being published. (In fact, the publication process in Economics is extremely lengthy and difficult.)
Which journals are “reputable”? Economists spend a lot of time thinking about how to rank and compare journals (there are so many papers written about this topic that they someone could start a “Journal of Ranking Economics Journals”. For example, “ REPEC ” has one ranking, and SCIMAGO/SCOPUS has another one. You may want to focus on journals ranked in the top 100 or top 200 of these rankings. If you find it very interesting and relevant paper published somewhere that is ranked below this, is okay to cite it, but you may want to be a bit more skeptical of its findings.
Any journal you find on JSTOR is respectable, and if you look in the back of your textbooks, there will be references to articles in journals, most of which are decent.
You may also find unpublished “working papers”; these may also be useful as references. However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of these, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing.
Unpublished “working papers”
You may also find unpublished “working papers” or ‘mimeos’; these may also be useful as references. In fact, the publication process in Economics is so slow (six years from first working paper to publication is not uncommon) that not consulting working papers often means not being current.
However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of this ‘grey literature’, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing. Some working paper series are vetted, such as NBER; in terms of credibility, these might be seen as something in between a working paper and a publication.
Which of the following are “peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals”? Which of the following may be appropriate to cite in your literature review and in your final project? 8
Klein, G, J. (2011) “Cartel Destabilization and Leniency Programs – Empirical Evidence.” ZEW - Centre for European Economic Research Discussion Paper No. 10-107
Spencer, B. and Brander, J.A. (1983) “International R&D Rivalry and Industrial Strategy”, Review of Economic Studies Vol. 50, 707-722
Troisi, Jordan D., Andrew N. Christopher, and Pam Marek. “Materialism and money spending disposition as predictors of economic and personality variables.” North American Journal of Psychology 8.3 (2006): 421.
The Economist,. ‘Good, Bad And Ugly’. Web. 11 Apr. 2015. [accessed on…]
Mecaj, Arjola, and María Isabel González Bravo. “CSR Actions and Financial Distress: Do Firms Change Their CSR Behavior When Signals of Financial Distress Are Identified?.” Modern Economy 2014 (2014).
Universities, U. K. “Creating Prosperity: the role of higher education in driving the UK’s creative economy.” London Universities UK (2010).
4.4 How to find and access articles
You should be able to find and access all the relevant articles online. Leafing through bound volumes and photocopying should not be neededs. (Having been a student in the late 90’s and 2000’s, I wish I could get those hours back.)

Figure 4.3: The old way!
Good online tools include Jstor (jstor.org) and Google Scholar (scholar.google.co.uk). Your university should have access to Jstor, and Google is accessible to all (although the linked articles may require special access). You will usually have the ‘most access’ when logged into your university or library computing system.If you cannot access a paper, you may want to consult a reference librarian.
It is also ok, if you cannot access the journal article itself, to use the last working paper version (on Google scholar find this in the tab that says “all X versions”, where X is some number, and look for a PDF). However, authors do not always put up the most polished versions, although they should do to promote open-access. As a very last resort, you can e-mail the author and ask him or her to send you the paper.
When looking for references, try to find ones published in respected refereed economics journals (see above ).
4.5 Good starting points: Survey article, course notes, and textbooks
A “survey article” is a good place to start; this is a paper that is largely a categorization and discussion of previous work on a particular topic. You can often find such papers in journals such as
- the Journal of Economic Perspectives,
- the Journal of Economic Surveys,
- and the Journal of Economic Literature.
These will be useful as a “catalog” of papers to read and considers citing. They are also typically very readable and offer a decent introduction to the issue or the field.
It is also helpful to consult module (course) notes and syllabi from the relevant field. Do not only limit yourself to the ones at your own university; many of universities make their course materials publicly accessible online. These will not only typically contain reading lists with well-respected and useful references, they may also contain slides and other material that will help you better understand your topic and the relevant issues.
However, be careful not to take material from course notes without properly citing it. (Better yet, try to find the original paper that the course notes are referring to.)
Textbooks serve as another extremely useful jumping off point. Look through your own textbooks and other textbooks in the right fields. Textbooks draw from, and cite a range of relevant articles and papers. (You may also want to go back to textbooks when you are finding the articles you are reading too difficult. Textbooks may present a simpler version of the material presented in an article, and explain the concepts better.)
4.6 Backwards and forwards with references
When you find a useful paper, look for its “family.” You may want to go back to earlier, more fundamental references, by looking at the articles that this paper cited. See what is listed as “keywords” (these are usually given at the top of the paper), and “JEL codes”. Check what papers this paper cites, and check what other papers cited this paper. On Google scholar you can follow this with a link “Cited by…” below the listed article. “Related articles” is also a useful link.
4.7 Citations
Keep track of all references and citations
You may find it helpful to use software to help you manage your citations
A storage “database” of citations (e.g., Jabref, Zotero, Endnote, Mendeley); these interface well with Google Scholar and Jstor
An automatic “insert citation” and “insert bibliography” in your word processing software
Use a tool like Endnote to manage and insert the bibliographies, or use a bibliography manager software such as Zotero or Jabref,
Further discussion: Citation management tools
List of works cited
Put your list of references in alphabetical order by author’s last name (surname).
Include all articles and works that you cite in your paper; do not include any that you don’t cite.
Avoiding plagiarism and academic offenses**
Here is a definition of plagiarism
The main point is that you need to cite everything that is not your own work. Furthermore, be clear to distinguish what is your own work and your own language and what is from somewhere/someone else.
Why cite? Not just to give credit to others but to make it clear that the remaining uncited content is your own.
Here are some basic rules:
(Rephrased from University of Essex material, as seen in Department of Economics, EC100 Economics for Business Handbook 2017-18, https://www1.essex.ac.uk/economics/documents/EC100-Booklet_2017.pdf accessed on 20 July 2019, pp. 15-16)
Do not submit anything that is not your own work.
Never copy from friends.
Do not copy your own work or previously submitted work. (Caveat: If you are submitting a draft or a ‘literature review and project plan’ at an earlier stage, this can be incorporated into your final submission.
Don’t copy text directly into your work, unless:
- you put all passages in quotation marks: beginning with ’ and ending with ’, or clearly offset from the main text
- you cite the source of this text.
It is not sufficient merely to add a citation for the source of copied material following the copied material (typically the end of a paragraph). You must include the copied material in quotation marks. … Ignorance … is no defence.’ (ibid, pp. 15 )
(‘Ibid’ means ‘same as the previous citation’.)
Your university may use sophisticated plagiarism-detection software. Markers may also report if the paper looks suspect
Before final submission, they may ask you to go over your draft and sign that you understand the contents and you have demonstrated that the work is your own.
Not being in touch with your supervisor may put you under suspicion.
Your university may give a Viva Voce oral exam if your work is under suspicion. It is a cool-sounding word but probably something you want to avoid.
Your university may store your work in its our database, and can pursue disciplinary action, even after you have graduated.
Penalties may be severe, including failure with no opportunity to retake the module (course). You may even risk your degree!
Comprehension questions; answers in footnotes
True or false: “If you do not directly quote a paper you do not need to cite it” 9
You should read and cite a paper (choose all that are correct)… 10
- If it motivates ‘why your question is interesting’ and how it can be modeled economically
- Only if it asks the same question as your paper
- Only if it is dealing with the same country/industry/etc as you are addressing
- If it has any connection to your topic, question, or related matters
- If it answers a similar question as your paper
- If it uses and discusses techniques that inform those you are using
4.8 How to write about previous authors’ analysis and findings
Use the right terminology.
“Johnson et al. (2000) provide an analytical framework that sheds substantial doubt on that belief. When trying to obtain a correlation between institutional efficiency and wealth per capita, they are left with largely inconclusive results.”
They are not trying to “obtain a correlation”; they are trying to measure the relationship and test hypotheses.
“Findings”: Critically examine sources
Don’t take everything that is in print (or written online) as gospel truth. Be skeptical and carefully evaluate the arguments and evidence presented. Try to really survey what has been written, to consider the range of opinions and the preponderance of the evidence. You also need to be careful to distinguish between “real research” and propaganda or press releases.
The returns to higher education in Atlantis are extremely high. For the majority of Atlanian students a university degree has increased their lifetime income by over 50%, as reported in the “Benefits of Higher Education” report put out by the Association of Atlantian Universities (2016).
But don’t be harsh without explanation:
Smith (2014) found a return to education in Atlantis exceeding 50%. This result is unlikely to be true because the study was not a very good one.
“Findings:” “They Proved”
A theoretical economic model can not really prove anything about the real world; they typically rely on strong simplifying assumptions.
Through their economic model, they prove that as long as elites have incentives to invest in de facto power, through lobbying or corruption for example, they will invest as much as possible in order to gain favourable conditions in the future for their businesses.
In their two period model, which assumes \[details of key assumptions here\] , they find that when an elite Agent has an incentive to invest in de facto power, he invests a strictly positive amount, up to the point where marginal benefit equals marginal cost”
Empirical work does not “prove” anything (nor does it claim to).
It relies on statistical inference under specific assumptions, and an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“As Smith et al (1999) proved using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange, equity prices always increase in response to reductions in corporate tax rates.”
“Smith et al (199) estimated a VAR regression for a dynamic CAP model using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange. They found a strongly statistically significant negative coefficient on corporate tax rates. This suggests that such taxes may have a negative effect on publicly traded securities. However, as their data was from a limited period with several simultaneous changes in policy, and their results are not robust to \[something here\] , further evidence is needed on this question.”
Use the language of classical 11 statistics:
Hypothesis testing, statistical significance, robustness checks, magnitudes of effects, confidence intervals.
Note that generalisation outside the data depends on an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“Findings”: How do you (or the cited paper) claim to identify a causal relationship?
This policy was explained by Smith and Johnson (2002) in their research on subsidies and redistribution in higher education. Their results showed that people with higher degree have higher salaries and so pay higher taxes. Thus subsidizing higher education leads to a large social gain.
The results the student discusses seem to show an association between higher degrees and higher salaries. The student seems to imply that the education itself led to higher salaries. This has not been shown by the cited paper. Perhaps people who were able to get into higher education would earn higher salaries anyway. There are ways economists used to try to identify a “causal effect” (by the way, this widely used term is redundant as all effects must have a cause), but a mere association between two variables is not enough
As inflation was systematically lower during periods of recession, we see that too low a level of inflation increases unemployment.
Economists have long debated the nature of this “Phillips curve” relationship. There is much work trying to determine whether the association (to the extent it exists) is a causal one. We could not rule out reverse causality, or third factor that might cause changes in both variables.
4.9 …Stating empirical results
Don’t write: “I accept the null hypothesis.”
Do write: “The results fail to reject the null hypothesis, in spite of a large sample size and an estimate with small standard errors” (if this is the case)
Note: The question of what to infer from acceptance/rejection of null hypotheses is a complex difficult one in Classical (as opposed to Bayesian) statistics. This difficulty is in part philosophical: classical hypothesis testing is deductive , while inference is necessarily inductive.
4.10 What to report
You need to read this paper more clearly; it is not clear what they conclude nor what their evidence is.
4.11 Organising your literature review
A common marking comment:
These papers seem to be discussed in random order – you need some structure organising these papers thematically, by finding, by technique, or chronologically perhaps.
How should you organise it? In what order?
Thematically (usually better)
By method, by theoretical framework, by results or assumptions, by field
Chronologically (perhaps within themes)
Exercise: Compare how the literature review section is organized in papers you are reading.

Figure 4.4: Organising a set of references
Q: What sort of structure am I using in the above outline?
It may also be helpful to make a ‘table’ of the relevant literature, as in the figure below. This will help you get a sense of the methods and results, and how the papers relate, and how to assess the evidence. You may end up putting this in the actual paper.

Figure 4.5: Organisational table from Reinstein and Riener, 2012b
4.12 What if you have trouble reading and understanding a paper?
Consult a survey paper, textbook, or lecture notes that discuss this paper and this topic
Try to find an easier related paper
Ask your supervisor for help; if he or she can
Try to understand what you can; do not try to “fake it”
4.13 Some literature survey do’s and don’ts
Do not cite irrelevant literature.
Do not merely list all the papers you could find.
Discuss them, and their relevance to your paper.
What are their strengths and weaknesses? What techniques do they use, and what assumptions do they rely on? How do they relate to each other?
Use correct citation formats.
Try to find original sources (don’t just cite a web link).
Don’t just cut and paste from other sources. And make sure to attribute every source and every quote. Be clear: which part of your paper is your own work and what is cited from others? The penalties for plagiarism can be severe!
- Critically examine the sources, arguments, and methods
4.14 Comprehension questions: literature review
How to discuss empirical results: “Causal” estimation, e.g., with Instrumental Variables
Which is the best way to state it? 12
“As I prove in table 2, more lawyers lead to slower growth (as demonstrated by the regression analysis evidence).”
“Table 2 provides evidence that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population leads to slower growth.”
3.“Table 2 shows that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population is correlated with slower growth.”
Which is better? 13
- “However, when a set of observable determinants of city growth (such as Census Region growth) are accounted for, the estimate of this effect becomes less precise.”
- “In the correct regression I control for all determinants of city growth and find that there is no effect of lawyers on growth”
Stating empirical results: descriptive
“Using the US data from 1850-1950, I find that inflation is lower during periods of recession. This is statistically significant in a t-test [or whatever test] at the 99% level, and the difference is economically meaningful. This is consistent with the theory of …, which predicts that lower inflation increases unemployment. However, other explanations are possible, including reverse causality, and unmeasured covarying lags and trends.”
“I find a significantly lower level of inflation during periods of recession, and the difference is economically meaningful. This relationship is statistically significant and the data is accurately measured. Thus I find that inflation increases unemployment.”
Some tips on writing a good paper– relevant to literature reviews
- Answer the question
- Provide clear structure and signposting
- Demonstrate an ability for critical analysis
- Refer to your sources
- Produce a coherent, clear argument
- Take time to proofread for style and expresssion
- Source “Assignment Writing Skills EBS 3rd year 2012”"
Answer: only b is a ‘peer reviewed article in a reputable economics journal’. All of these might be useful to cite, however. ↩
False. You need to cite any content and ideas that are not your own. ↩
Answers: 1, 5, and 6. Note that 2 and 3 are too narrow criteria, and 4 is too broad. ↩
or Bayesian if you like ↩
The second one; if this is really causal evidence. ↩
The first one. There is no ‘correct regression’. It is also not really correct in classical statistics to ‘find no effect’. ↩
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 4. Manage Your References
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
Manage your references
Why do i have to cite my sources, citation styles, major citation styles - official and credible guidance.
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
Citation Management Tools
Citation managers help you collect, organize, cite, and share research. Click on the links below for guidance on using these tools.

Learning Opportunities
For help learning these tools, contact an expert listed on the tool's guide or sign up for one of our workshops:
- Sign up for UO Libraries workshops here!

As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information.
Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these:
- APA (American Psychological Association)
- Chicago Manual of Style
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
University Library provides an online guide to help you cite your sources correctly in multiple styles.
Citation styles
In academic writing, there are many different formats for citing the sources you use in your research. Here are a few of the most common, and their related disciplines.
Accessibility note: Below is a chart with two columns for format and discipline.
Note: Regardless of which format you use, you must include the same basic bibliographic information when citing a source.
Official Style Manuals
There are many different types of academic and professional writing styles. The four guidebooks below represent some of the major ones. Use these guides to learn how professional researchers and writers prepare their manuscripts for publication or sharing.
Online Style Resources
Although these resources are not official, they are still credible and very useful! If one of these websites doesn't answer your question, check out the official style guide or contact a librarian for help!

UO Research Guides
These helpful guided from UO Libraries provide information on various citation styles.
- Citation and Plagiarism by Genifer Snipes Last Updated Mar 29, 2024 1540 views this year
- Introductory How-To Tutorials for MLA and APA Styles from UO Libraries by Genifer Snipes Last Updated Jul 17, 2023 32 views this year
- << Previous: When to Stop Searching
- Next: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Boatwright Memorial Library
Citing sources research guide: literature reviews.
- Quick Citing in Databases
- Chicago/Turabian
- ASA & AAA (Soc/Ant)
- ACS (Chemistry)
- AP (Associated Press)
- APSA (Political Science)
- SBL (Society of Biblical Literature)
- Harvard Style
- MS Word Help
- DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers)
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- EndNote Web
- Citation exercises This link opens in a new window
Literature Reviews: Overview
This video from NCSU Libraries gives a helpful overview of literature reviews. Even though it says it's "for graduate students," the principles are the same for undergraduate students too!
Reading a Scholarly Article
- Reading a Scholarly Article or Literature Review Highlights sections of a scholarly article to identify structure of a literature review.
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Article (NCSU Libraries) Interactive tutorial that describes parts of a scholarly article typical of a Sciences or Social Sciences research article.
- Evaluating Information | Reading a Scholarly Article (Brown University Library) Provides examples and tips across disciplines for reading academic articles.
- Reading Academic Articles for Research [LIBRE Project] Gabriel Winer & Elizabeth Wadell (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative (OERI))
Literature Review Examples
What is a Literature Review?
The literature review is a written explanation by you, the author, of the research already done on the topic, question or issue at hand. What do we know (or not know) about this issue/topic/question?
- A literature review provides a thorough background of the topic by giving your reader a guided overview of major findings and current gaps in what is known so far about the topic.
- The literature review is not a list (like an annotated bibliography) -- it is a narrative helping your reader understand the topic and where you will "stand" in the debate between scholars regarding the interpretation of meaning and understanding why things happen. Your literature review helps your reader start to see the "camps" or "sides" within a debate, plus who studies the topic and their arguments.
- A good literature review should help the reader sense how you will answer your research question and should highlight the preceding arguments and evidence you think are most helpful in moving the topic forward.
- The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought and arguments, using your research question as an anchor. If you find something that doesn't help answer your question, you don't have to read (or include) it. That's the power of the question format: it helps you filter what to read and include in your literature review, and what to ignore.
How Do I Start?
Essentially you will need to:
- Identify and evaluate relevant literature (books, journal articles, etc.) on your topic/question.
- Figure out how to classify what you've gathered. You could do this by schools of thought, different answers to a question, the authors' disciplinary approaches, the research methods used, or many other ways.
- Use those groupings to craft a narrative, or story, about the relevant literature on this topic.
- Remember to cite your sources properly!
- Research: Getting Started Visit this guide to learn more about finding and evaluating resources.
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources (IUPUI Writing Center) An in-depth guide on organizing and synthesizing what you've read into a literature review.
- Guide to Using a Synthesis Matrix (NCSU Writing and Speaking Tutorial Service) Overview of using a tool called a Synthesis Matrix to organize your literature review.
- Synthesis Matrix Template (VCU Libraries) A word document from VCU Libraries that will help you create your own Synthesis Matrix.
Additional Tutorials and Resources
- UR Writer's Web: Using Sources Guidance from the UR Writing Center on how to effectively use sources in your writing (which is what you're doing in your literature review!).
- Write a Literature Review (VCU Libraries) "Lit Reviews 101" with links to helpful tools and resources, including powerpoint slides from a literature review workshop.
- Literature Reviews (UNC Writing Center) Overview of the literature review process, including examples of different ways to organize a lit review.
- “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” Pautasso, Marco. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” PLOS Computational Biology, vol. 9, no. 7, July 2013, p. e1003149.
- Writing the Literature Review Part I (University of Maryland University College) Video that explains more about what a literature review is and is not. Run time: 5:21.
- Writing the Literature Review Part II (University of Maryland University College) Video about organizing your sources and the writing process. Run time: 7:40.
- Writing a Literature Review (OWL @ Purdue)
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Zotero >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 9:09 AM
- URL: https://libguides.richmond.edu/citingsources

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Citation Styles
- Chicago Style
- Annotated Bibliographies
What is a Lit Review?
How to write a lit review.
- Video Introduction to Lit Reviews
Main Objectives
Examples of lit reviews, additional resources.
- Zotero (Citation Management)
What is a literature review?
- Either a complete piece of writing unto itself or a section of a larger piece of writing like a book or article
- A thorough and critical look at the information and perspectives that other experts and scholars have written about a specific topic
- A way to give historical perspective on an issue and show how other researchers have addressed a problem
- An analysis of sources based on your own perspective on the topic
- Based on the most pertinent and significant research conducted in the field, both new and old

- A descriptive list or collection of summaries of other research without synthesis or analysis
- An annotated bibliography
- A literary review (a brief, critical discussion about the merits and weaknesses of a literary work such as a play, novel or a book of poems)
- Exhaustive; the objective is not to list as many relevant books, articles, reports as possible
- To convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic
- To explain what the strengths and weaknesses of that knowledge and those ideas might be
- To learn how others have defined and measured key concepts
- To keep the writer/reader up to date with current developments and historical trends in a particular field or discipline
- To establish context for the argument explored in the rest of a paper
- To provide evidence that may be used to support your own findings
- To demonstrate your understanding and your ability to critically evaluate research in the field
- To suggest previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, and quantitative and qualitative strategies
- To identify gaps in previous studies and flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches in order to avoid replication of mistakes
- To help the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research
- To suggest unexplored populations
- To determine whether past studies agree or disagree and identify strengths and weaknesses on both sides of a controversy in the literature

- Choose a topic that is interesting to you; this makes the research and writing process more enjoyable and rewarding.
- For a literature review, you'll also want to make sure that the topic you choose is one that other researchers have explored before so that you'll be able to find plenty of relevant sources to review.

- Your research doesn't need to be exhaustive. Pay careful attention to bibliographies. Focus on the most frequently cited literature about your topic and literature from the best known scholars in your field. Ask yourself: "Does this source make a significant contribution to the understanding of my topic?"
- Reading other literature reviews from your field may help you get ideas for themes to look for in your research. You can usually find some of these through the library databases by adding literature review as a keyword in your search.
- Start with the most recent publications and work backwards. This way, you ensure you have the most current information, and it becomes easier to identify the most seminal earlier sources by reviewing the material that current researchers are citing.
The organization of your lit review should be determined based on what you'd like to highlight from your research. Here are a few suggestions:
- Chronology : Discuss literature in chronological order of its writing/publication to demonstrate a change in trends over time or to detail a history of controversy in the field or of developments in the understanding of your topic.
- Theme: Group your sources by subject or theme to show the variety of angles from which your topic has been studied. This works well if, for example, your goal is to identify an angle or subtopic that has so far been overlooked by researchers.
- Methodology: Grouping your sources by methodology (for example, dividing the literature into qualitative vs. quantitative studies or grouping sources according to the populations studied) is useful for illustrating an overlooked population, an unused or underused methodology, or a flawed experimental technique.

- Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review.
- Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review.
- Synthesize your sources. Your goal is not to make a list of summaries of each source but to show how the sources relate to one another and to your own work.
- Make sure that your own voice and perspective remains front and center. Don't rely too heavily on summary or paraphrasing. For each source, draw a conclusion about how it relates to your own work or to the other literature on your topic.
- Be objective. When you identify a disagreement in the literature, be sure to represent both sides. Don't exclude a source simply on the basis that it does not support your own research hypothesis.
- At the end of your lit review, make suggestions for future research. What subjects, populations, methodologies, or theoretical lenses warrant further exploration? What common flaws or biases did you identify that could be corrected in future studies?

- Double check that you've correctly cited each of the sources you've used in the citation style requested by your professor (APA, MLA, etc.) and that your lit review is formatted according to the guidelines for that style.
Your literature review should:
- Be focused on and organized around your topic.
- Synthesize your research into a summary of what is and is not known about your topic.
- Identify any gaps or areas of controversy in the literature related to your topic.
- Suggest questions that require further research.
- Have your voice and perspective at the forefront rather than merely summarizing others' work.
- Cyberbullying: How Physical Intimidation Influences the Way People are Bullied
- Use of Propofol and Emergence Agitation in Children
- Eternity and Immortality in Spinoza's 'Ethics'
- Literature Review Tutorials and Samples - Wilson Library at University of La Verne
- Literature Reviews: Introduction - University Library at Georgia State
- Literature Reviews - The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review - Boston College Libraries
- Write a Literature Review - University Library at UC Santa Cruz
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Zotero (Citation Management) >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 2:47 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.elac.edu/Citation
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.


How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
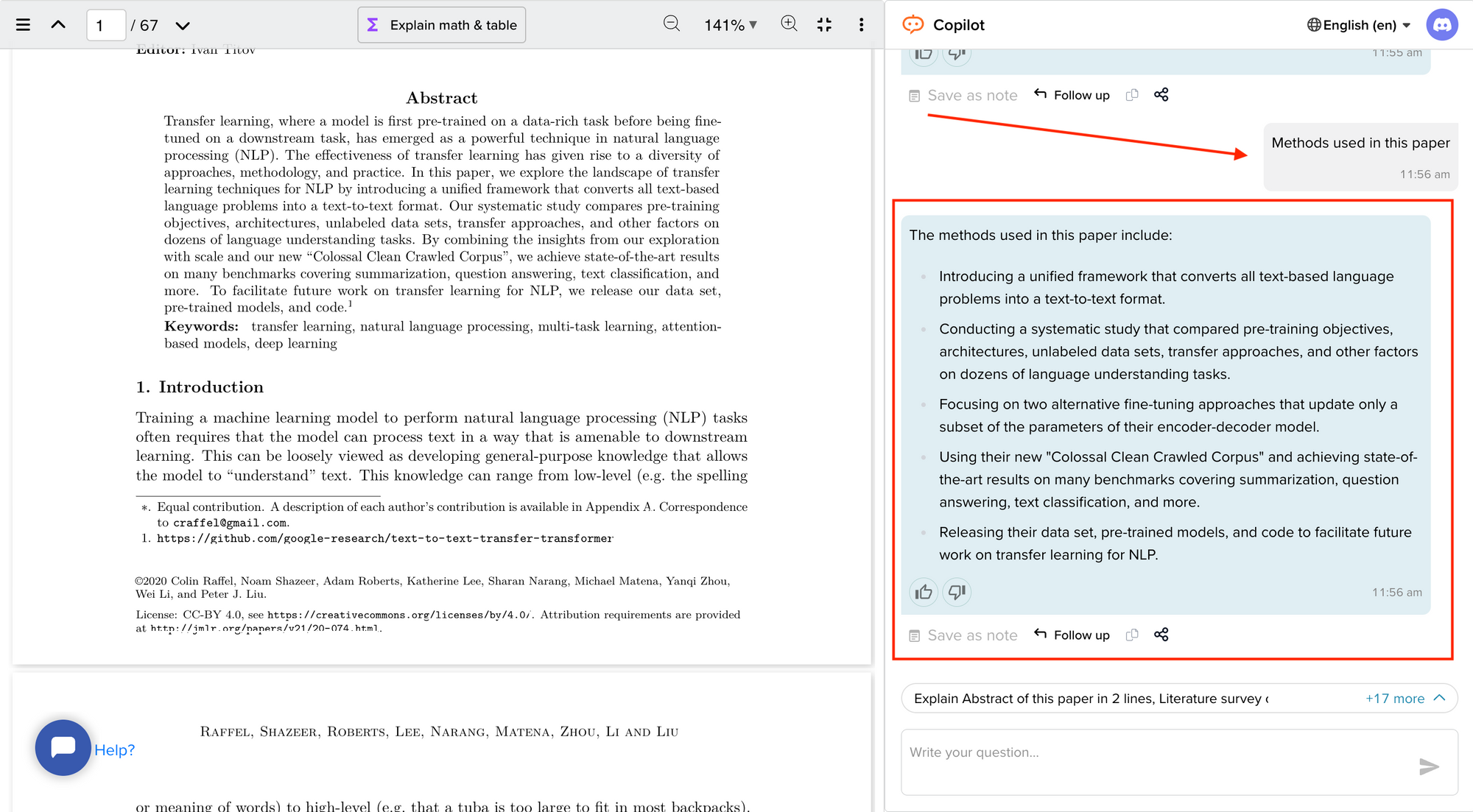
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 1:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Chester Fritz Library
- Library of the Health Sciences
- Thormodsgard Law Library
Literature Reviews
- Get started
- What is a Literature Review?
- Finding Literature Reviews
- Your Literature Search
- Library Books
- How to Videos
- Communicating & Citing Research
References & Further Reading
Manuals & guidelines, print books.
- Beyond PICO: the SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis Cooke, A., Smith, D., & Booth, A. (2012). Qualitative Health Research, 22(10), 1435-1443.
- Checking reference lists to find additional studies for systematic reviews Horsley, T., Dingwall, O., & Sampson, M. (2011). The Cochrane Library, 8.
- Domain Definition and Search Techniques in Meta-analyses of L2 Research (Or why 18 meta-analyses of feedback have different results) Plonsky, L., & Brown, D. (2015). Second Language Research, 31(2), 267–278.
- Effectiveness and Efficiency of Search Methods in Systematic Reviews of Complex Evidence: Audit of Primary Sources Greenhalgh, T., & Peacock, R. (2005). BMJ, 331(7524), 1064-1065. Only 30% of sources were obtained from the protocol defined at the outset of the study (that is, from the database and hand searches). Fifty one per cent were identified by “snowballing” (such as pursuing references of references), and 24% by personal knowledge or personal contacts. Conclusion: Systematic reviews of complex evidence cannot rely solely on protocol-driven search strategies.
- An Empirical Assessment of A Systematic Search Process for Systematic Reviews Zhang, H., Babar, M. A., Bai, X., Li, J., & Huang, L. (2011, April). In Evaluation & Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE 2011), 15th Annual Conference on (pp. 56-65). IET.
- The Impact of Limited Search Procedures for Systematic Literature Reviews – A Participant-Observer Case Study Kitchenham, B., Brereton, P., Turner, M., Niazi, M., Linkman, S., Pretorius, R., & Budgen, D. (2009, October). In Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement, 2009. ESEM 2009. 3rd International Symposium on (pp. 336-345). IEEE.
- Information retrieval in systematic reviews: Challenges in the public health arena Beahler, C. C., Sundheim, J. J., & Trapp, N. I. (2000). American Journal of Preventive Medicine, (18)4, 6-10.
- Literature Searching for Social Science Systematic Reviews: Consideration of a range of search techniques. Papaioannou, D. , Sutton, A. , Carroll, C. , Booth, A. and Wong, R. (2010). Health Information & Libraries Journal, 27, 114-122.
- Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge‐building and theory‐generating qualitative systematic reviews Finfgeld‐Connett, D., & Johnson, E. D. (2013). Journal of Advanced Nursing, 69(1), 194-204.
- Performing a Literature Review. Reed, L. E. (1998, November). In fie (pp. 380-383). IEEE.
- Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in Systematic Reviews: A Structured Methodological Review Booth, A. (2016). Systematic Reviews, (5)74, 1-23.
- Should We Exclude Inadequately Reported Studies From Qualitative Systematic Reviews? An Evaluation of Sensitivity Analyses in Two Case Study Reviews Carroll, C., Booth, A., & Lloyd-Jones, M. (2012). Qualitative Health Research, 22(10), 1425-1434.
- Systematic Literature Studies: Database Searches vs. Backward Snowballing Jalali, S., & Wohlin, C. (2012, September). In Proceedings of the ACM-IEEE international symposium on Empirical software engineering and measurement (pp. 29-38). ACM.
- Text-Mining Techniques and Tools for Systematic Literature Reviews: A Systematic Literature Review Feng, L., Chiam, Y. K., & Lo, S. K. (2017, December). In Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC), 2017 24th (pp. 41-50). IEEE. Also available open access: http://eprints.um.edu.my/18515/1/All.pdf
- Use of information-seeking strategies for developing systematic reviews and engaging in evidence-based practice: the application of traditional and comprehensive Pearl Growing. A review Schlosser, R. W., Wendt, O., Bhavnani, S., & Nail‐Chiwetalu, B. (2006). International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 41(5), 567-582.
- What is your research question? An introduction to the PICOT format for clinicians. Riva, J. J., Malik, K. M., Burnie, S. J., Endicott, A. R., & Busse, J. W. (2012). The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, 56(3), 167-71.
- Writing a Literature Review
- ECO 495: Senior Economic Project: Literature Review
- Ethical use of Sources and Writing
For Conducting a Systematic Review or Meta-analysis
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Version 5.1.0) Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Annals of Internal Medicine, 151(4), 264-269.
- Standards for Systematic Reviews (Report) The National Academies of Science, Engineering, Medicine. Released 3/23/2011. Copyright © 2018 National Academy of Sciences.
- Systematic Reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking reviews in health care Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York (2008). York, UK: York Publishing Services Ltd.
- Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews Kitchenham, B. (2004). Keele University, 33(2004), 1-26. Software Engineering Group, Department of Computer Science, Keele, UK.
- A Roadmap for Systematic Reviews & Meta-analyses Adapted from: Pai, M. et al. (2004). The National Medical Journal of India, 17(2):86-95.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses: An Illustrated, Step-By-Step Guide. Pai, M., McCulloch, M., Gorman, J. D., Pai, N., Enanoria, W., Kennedy, G., ... & Colford, J. J. (2004). The National Medical Journal of India, 17(2), 86-95.
- Systematic Reviews of Health Promotion and Public Health Interventions (Version 2) July 2007. Armstrong, R., & Waters, E. on behalf of the Guidelines for Systematic Reviews in Health Promotion and Public Health Taskforce.
- A Guideline for Applying Systematic Reviews to Child Language Intervention Hargrove, P., Lund, B., & Griffer, M. (2005). Communication Disorders Quarterly, 26(4), 226–235.
- A Tutorial on Conducting Meta-Analyses of Clinical Outcome Research Robey, R. R., & Dalebout, S. D. (1998). Journal of Speech, Language & Hearing Research, 41(6), 1227-1241.
- Handbook of Meta-analysis in Ecology and Evolution Koricheva J., Gurevitch J., & Mengersen K. (Eds.). (2013). Princeton University Press.
Across Disciplines
- Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). The Qualitative Report, 13(4), 544-559. Discusses differences between exploratory and other types of case studies.
- Research Methods for Postgraduates Greenfield, Tony, and Sue Greener. Research Methods for Postgraduates. Third ed. 2016. Print.
- Case Study Research and Applications: Design and methods (3rd ed.). Summary Yin, R. K. (1994). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Summary only. 6th edition (2018) available in Chester Fritz Library. Discusses exploratory and other types of case studies.
- The Book Review: Scholarly and Editorial Responsibility Felber, L. (2002). Journal of Scholarly Publishing, 33(3), 166.
- Special Section on the Value of Scholarly Book Reviews. Gump, S. E. (2018). Journal of Scholarly Publishing, 50(1), 1-7. University of Toronto Press.
- Use of Scholarly Book Reviews: Implications for Electronic Publishing and Scholarly Communication Spink, A., Robins, D., & Schamber, L. (1998). Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 49(4), 364-374.
- What Synthesis Methodology Should I Use? A Review and Analysis of Approaches to Research Synthesis Schick-Makaroff, K., MacDonald, M., Plummer, M., Burgess, J., Neander, W. (2016). AIMS Public Health, 3(1), 172–215. From health and social sciences perspectives.
- Use of Content Analysis to Conduct Knowledge-Building and Theory-Generating Qualitative Systematic Reviews Finfgeld-Connett, D. (2014). Qualitative Research, 14(3), 341-352.
- HARKing: Hypothesizing After the Results are Known Kerr, N. L. (1998). Personality and Social Psychology Review, 2(3), 196–217.
- p-Curve and Effect Size: Correcting for Publication Bias Using Only Significant Results Simonsohn, U., Nelson, L. D., & Simmons, J. P. (2014). Perspectives on Psychological Science, 9(6), 666–681.
Medicine & Public Health
- How to Write a Scholarly Book Review for Publication in a Peer-reviewed Journal: A Review of the Literature Lee, A. D., Green, B. N., Johnson, C. D., & Nyquist, J. (2010). Journal of Chiropractic Education, 24(1), 57-69.
- Writing a Literature Review Steward, B. (2004). British Journal of Occupational Therapy, 67(11), 495–500.
- How to Read a Paper: Papers that Summarise other Papers: Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis. Greenalgh, T. (1997). British Medical Journal, 315, 672-675.
- A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies Grant, M. J., & Booth, A. (2009). Health Information And Libraries Journal, 26(2), 91–108.
- Five Steps to Conducting a Systematic Review Khan, K. S., Kunz, R., Kleijnen, J., & Antes, G. (2003). Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 96(3), 118-121.
- Criteria for the Systematic Review of Health Promotion and Public Health Interventions Jackson, N. & Waters, E. for the Guidelines for Systematic Reviews in Health Promotion and Public Health Taskforce. (2005). Health Promotion International, Volume 20, Issue 4(1), Pages 367–374.
- Qualitative Research in Systematic Reviews -- Has established a place for itself Dixon-Woods, M., & Fitzpatrick, R. (2001). BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 323(7316), 765-6.
- A Brief History of Research Synthesis Chalmers, I., Hedges, L. V., & Cooper, H. (2002). Evaluation & the Health Professions, 25(1), 12–37.
- Methods for the Thematic Synthesis of Qualitative Research in Systematic Reviews Thomas, J., & Harden, A. (2008). BMC Medical Research Methodology, 8(1), 45.
- The Mass Production of Redundant, Misleading, and Conflicted Systematic Reviews and Meta‐analyses Ioannidis, J. P. (2016). The Milbank Quarterly, 94(3), 485-514.
- Methodologic Issues in Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses Montori, V. M., Swiontkowski, M. F., & Cook, D. J. (2003). Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®, 413, 43-54.
- I Have the Answer, Now What's the Question?: Why Metaanalyses Do Not Provide Definitive Solutions Streiner, D. L. (2005). The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 50(13), 829–831.
Social Sciences
- Book Reviews and Scientist-Practitioner Currency: A Critical Lever. Jones RG, Fleenor JW, Summers L. (2004). The Industrial-Organizational Psychologist, 41, 22-25.
- All in the Family: Systematic Reviews, Rapid Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Realist Reviews, and More Moher, D., Stewart, L., & Shekelle, P. (2015). Systematic Reviews, 4(183), 1–2.
- Writing a Literature Review Baumeister, R. F. (2013). In M. J. Prinstein (Ed.), The Portable Mentor (pp. 119–132). New York, NY: Springer New York.
- Writing a Review Article for Psychological Bulletin Bem, D. J. (1995). Psychological Bulletin, 118(2), 172-177.
- Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide [Book Review] Suri, H. (2009). Evaluation Journal of Australaisa, 9(1), 62-63. Book Reviewed: Petticrew, M. & Roberts, H. (2006). Malden, MA: Blackwell. ISBN: 978-1-4051-2110-1 Book in library collection: https://odin-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com:443/und:all:ODIN_ALEPH008277698
- Using Logic Models to Capture Complexity in Systematic Reviews Anderson, L. M., Petticrew, M. , Rehfuess, E., Armstrong, R. , Ueffing, E. , Baker, P. , Francis, D. and Tugwell, P. (2011). Research Synthesis Methods, (2), 33-42.
- Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005). International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19-32.
- Face Validity of Meta-Analyses in Emotional or Behavioral Disorders. Mostert, M. (2004). Behavioral Disorders, 29(2), 89-118.
- Meta-analytic Decisions and Reliability: A Serendipitous Case of Three Independent Telecommuting Meta-analyses. Nieminen, L., Nicklin, J., McClure, T., & Chakrabarti, M. (2011). Journal of Business and Psychology, 26(1), 105-121.
- Research Transparency in Psychological Science: How & Why? Gernsbacher, M. A. (2018a, October 26. [Video File]. Presented at the Northern Lights Psychology Conference 2018, UND, Grand Forks, ND, https://commons.und.edu/nlp-conference/2018/
- Rewarding Research Transparency Gernsbacher, M. A. (2018). Trends in Cognitive Sciences.
- Writing Empirical Articles: Transparency, Reproducibility, Clarity, and Memorability Gernsbacher, M. A. (2018). Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 1, 403-414.
Education & Public Policy
- Teaching the Literature Review: A Practical Approach for College Instructors Cisco, J. (2014). Teaching & Learning Inquiry: The ISSOTL Journal, 2(2), 41-57.
- Producing Policy Relevant Systematic Reviews: Navigating the Policy-Research Interface Oliver, S., Bangpan, M., & Dickson, K. (2018). Evidence & Policy: A Journal of Research, Debate and Practice, 14(2), 197-220.
- Use and Impacts of Campbell Systematic Reviews on Policy, Practice, and Research Maynard, B. R. & Dell, N. A. (2018). Research on Social Work Practice, 28(1), 13 -18.
- The Relevance of Systematic Reviews to Educational Policy and Practice. Davies, P. (2000). Oxford Review of Education, 26(3/4), 365-378.
- The Place of Systematic Reviews in Education Research Andrews, R. (2005). British Journal of Educational Studies, 53(4), 399-416.
- The Relationship Between Sample Sizes and Effect Sizes in Systematic Reviews in Education Slavin, R., & Smith, D. (2009). Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 31(4), 500-506.
- Application of Systematic Reviews in Speech‐and‐Language Therapy Marshall, J. (2011). International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 46(3), 261 -272.
- A Review of Meta-Analyses in Education: Methodological Strengths and Weaknesses. Ahn, S., Ames, A., & Myers, N. (2012). Review of Educational Research, 82(4), 436-476.
- Deficiencies of Reporting in Meta-Analyses and Some Remedies. Harwell, M., & Maeda, Y. (2008). The Journal of Experimental Education, 76(4), 403-428.
- Effect Sizes and Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis in Higher Education. Bowman, N. (2012). Research in Higher Education, 53(3), 375-382.
- Meta-Analysis With Complex Research Designs: Dealing With Dependence From Multiple Measures and Multiple Group Comparisons. Scammacca, N., Roberts, G., & Stuebing, K. (2014). Review of Educational Research, 84(3), 328-364.
- Meta-Analysis in Higher Education: An Illustrative Example Using Hierarchical Linear Modeling Denson, N., & Seltzer, M. (2011). Research in Higher Education, 52(3), 215-244.
(Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics)
- The Evolving Practice of Scholarly Book Reviews. Jinfa Cai. (2015). Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 46(3), 250-252.
- Workshop in Conducting Integrative Literature Reviews Carliner, S. (2011, October). In Professional Communication Conference (IPCC), 2011 IEEE International (pp. 1-3). IEEE.
- Repeatability of Systematic Literature Reviews Kitchenham, B., Brereton, P., Li, Z., Budgen, D., & Burn, A. (2011). Proceedings of EASE 2011 (15th Annual Conference on Evaluation & Assessment in Software Engineering)
- Methodology for Systematic Literature Review Applied to Engineering and Education Torres-Carrión, P. V., González-González, C. S., Aciar, S., & Rodríguez-Morales, G. (2018, April). In Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), 2018 IEEE (pp. 1364-1373). IEEE.
- Identifying Barriers to the Systematic Literature Review Process Carver, J. C., Hassler, E., Hernandes, E., & Kraft, N. A. (2013, October). In Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement, 2013 ACM/IEEE International Symposium on (pp. 203-212). IEEE.
- Visualizing Systematic Literature Reviews to Identify New Areas of Research Godwin, A. (2016, October). In Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), 2016 IEEE (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Review: Power and Information Technology Research: A Metatriangulation Review Jasperson, J., Carte, T. A., Saunders, C. S., Butler, B. S., Croes, H. J. P., & Zheng, W. (2002). MIS Quarterly, 26(4), 397–459.
- Statistical Issues in Ecological Meta-Analyses Gurevitch, J., & Hedges, L. (1999). Ecology, 80(4), 1142-1149.
Business & Management
- Extending a Provocative Tradition: Book Reviews and Beyond at AMR Bartunek, J. M., & Ragins, B. R. (2015). The Academy of Management Review, 40(3), 474–479
- Compliments and Criticisms in Book Reviews About Business Communication Mackiewicz, J. (2007). Journal of Business & Technical Communication, 21(2), 188–215.
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples Torraco, R. J. (2005). Human Resource Development Review, 4(3), 356–367.
- Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence‐informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). British Journal of Management, 14(3), 207-222.
- Shades of Grey: Guidelines for Working with the Grey Literature in Systematic Reviews for Management and Organizational Studies Adams, R. J., Smart, P., & Huff, A. S. (2017). International Journal of Management Reviews, 19(4), 432–454.
- Meta-Analysis in Advertising Research. Eisend, M. (2017). Journal of Advertising, 46(1), 21–35.
- Meta-analyses in Sales Research. Johnson, J. S., & Jaramillo, F. (2017). Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 37(2), 134–152.
- Qualitative Inquiry in Management: Methodological Dilemmas and Concerns in Meta-Analysis. Point, S., Fendt, J., & Jonsen, K. (2017). European Management Review, 14(2), 185–204.
- The Suitability of Simulations and Meta-Analyses for Submissions to Academy of Management Journal Shaw, J. D., & Ertug, G. (2017). Academy of Management Journal, 60(6), 2045–2049. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2017.4006
- The Scholarly Book Review in the Humanities: An Academic Cinderella? East, J. W. (2011). Journal of Scholarly Publishing 43(1), 52-67. University of Toronto Press.
- H-Net Book Reviews: Enhancing Scholarly Communication with Technology McGrath, E. L., Metz, W. F., & Rutledge, J. B. (2005). College & Research Libraries, 66(1), 8-19.
- Literature Reviews and the Hermeneutic Circle Boell, S. K., & Cecez-Kecmanovic, D. (2010) Australian Academic & Research Libraries, (41)2, 129-144.
- Meta-analysis in Second Language Research: Choices and Challenges Annual Review of Applied Linguistics (2010), 30, 85–110
- Publication Practices in Motion: The Benefits of Open Access Publishing for the Humanities. Adema, J., & Ferwerda, E. (2014). In Dávidházi P. (Ed.), New Publication Cultures in the Humanities: Exploring the Paradigm Shift (pp. 131-146). Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
- Going Open Smith, S. (2016). In Manifesto for the Humanities: Transforming Doctoral Education in Good Enough Times (pp. 67-84). ANN ARBOR: University of Michigan Press.
- Qualitative Research
- Journal of Scholarly Publishing
- Systematic Reviews
- International Journal of Social Research Methodology
- Campbell Systematic Reviews
Hover over the title for a brief overview and click on the title to be taken to the listing in the catalog where you can find more information such as location and call number. If you want to find additional print books on literature reviews, send me an email or ask a librarian around the clock using our Ask Us 24/7 chat service!
Need a book that we don't have in the collection? Borrow it using our interlibrary loan service .
- << Previous: Communicating & Citing Research
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2023 8:31 PM
- URL: https://libguides.und.edu/literature-reviews
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and....
- Library Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Writing the Review
Literature Reviews: Writing the Review
Outline of review sections.
Your Literature Review should not be a summary and evaluation of each article, one after the other. Your sources should be integrated together to create a narrative on your topic.
Consider the following ways to organize your review:
- By themes, variables, or issues
- By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy
- Chronologically, to show how the topic and research have developed over time
Use an outline to organize your sources and ideas in a logical sequence. Identify main points and subpoints, and consider the flow of your review. Outlines can be revised as your ideas develop. They help guide your readers through your ideas and show the hierarchy of your thoughts. What do your readers need to understand first? Where might certain studies fit most naturally? These are the kinds of questions that an outline can clarify.
An example outline for a Literature Review might look like this:
Introduction
- Background information on the topic & definitions
- Purpose of the literature review
- Scope and limitations of the review (what is included /excluded)
- Historical background
- Overview of the existing research on the topic
- Principle question being asked
- Organization of the literature into categories or themes
- Evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of each study
- Combining the findings from multiple sources to identify patterns and trends
- Insight into the relationship between your central topic and a larger area of study
- Development of a new research question or hypothesis
- Summary of the key points and findings in the literature
- Discussion of gaps in the existing knowledge
- Implications for future research
Strategies for Writing
Annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography collects short descriptions of each source in one place. After you have read each source carefully, set aside some time to write a brief summary. Your summary might be simply informative (e.g. identify the main argument/hypothesis, methods, major findings, and/or conclusions), or it might be evaluative (e.g. state why the source is interesting or useful for your review, or why it is not).
This method is more narrative than the Literature Matrix talked about on the Documenting Your Search page.
Taking the time to write short informative and/or evaluative summaries of your sources while you are researching can help you transition into the drafting stage later on. By making a record of your sources’ contents and your reactions to them, you make it less likely that you will need to go back and re-read many sources while drafting, and you might also start to gain a clearer idea of the overarching shape of your review.
READ EXTANT LIT REVIEWS CLOSELY
As you conduct your research, you will likely read many sources that model the same kind of literature review that you are researching and writing. While your original intent in reading those sources is likely to learn from the studies’ content (e.g. their results and discussion), it will benefit you to re-read these articles rhetorically.
Reading rhetorically means paying attention to how a text is written—how it has been structured, how it presents its claims and analyses, how it employs transitional words and phrases to move from one idea to the next. You might also pay attention to an author’s stylistic choices, like the use of first-person pronouns, active and passive voice, or technical terminology.
See Finding Example Literature Reviews on the Developing a Research Question page for tips on finding reviews relevant to your topic.
MIND-MAPPING
Creating a mind-map is a form of brainstorming that lets you visualize how your ideas function and relate. Draw the diagram freehand or download software that lets you easily manipulate and group text, images, and shapes ( Coggle , FreeMind , MindMaple ).
Write down a central idea, then identify associated concepts, features, or questions around that idea. Make lines attaching various ideas, or arrows to signify directional relationships. Use different shapes, sizes, or colors to indicate commonalities, sequences, or relative importance.

This drafting technique allows you to generate ideas while thinking visually about how they function together. As you follow lines of thought, you can see which ideas can be connected, where certain pathways lead, and what the scope of your project might be. By drawing out a mind-map you may be able to see what elements of your review are underdeveloped and will benefit from more focused attention.
USE VISUALIZATION TOOLS
Attribution.
Thanks to Librarian Jamie Niehof at the University of Michigan for providing permission to reuse and remix this Literature Reviews guide.
Avoiding Bias
Reporting bias.
This occurs when you are summarizing the literature in an unbalanced, inconsistent or distorted way .
Ways to avoid:
- look for literature that supports multiple perspectives, viewpoints or theories
- ask multiple people to review your writing for bias
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 4:51 PM
- URL: https://info.library.okstate.edu/literaturereviews
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references. Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper's introduction.
As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information. Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these: APA (American Psychological Association) Chicago Manual of Style
The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought and arguments, using your research question as an anchor. If you find something that doesn't help answer your question, you don't have to read (or include) it. That's the power of the question format: it helps you ...
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
APA 7th Paper & Reference Examples & Guidelines. Reference Page Format ; Abstract and Keywords ; ... Also known as 'narrative literature review'. " Key takeaways from the Psi Chi webinar So You Need to Write a Literature Review via APA Style.org. Examples of Literature Reviews. Financial socialization: A decade in review (2021) ...
Step 4: Write. Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review. Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review. Synthesize your sources.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
3. Evaluate and select literature. 4. Analyze the literature. 5. Plan the structure of your literature review. 6. Write your literature review. Other resources to help you write a successful literature review.
Writing the literature review Using EndNote's Cite While You Write, you can instantly insert references and format citations and bibliographies while writing your review in Microsoft Word. 7,000+ styles are available, plus you can create your own. Collaborate with others by sharing your library. FIND AND SELECT CITATIONS and
Reference management. Clean and simple. 200,000+ happy users. Try Paperpile. at. rely on Paperpile every day. love Paperpile. Learn why. Try Paperpile. ... This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses. How to write a systematic ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question ...
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Organizing Your Literature Review. An APA style paper is organized in the author-date style. This means you cite the author's name and year of publication within the text with an in-text citation. You also include the page number, if appropriate. You then include the full information of that source in a reference list at the end of your paper.
5. Find the Patterns. As you read and analyze each source, look for key themes, patterns, and findings. Identify areas of agreement, disagreement, or controversy among the sources so you can use those in the body. This can be one of the most difficult components of knowing how to write a literature review.
An overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review. Division of works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative theses entirely)
WRITING A TARGETED LITERATURE REVIEW a targeted literature review is NOT: ¡ a sophisticated evaluation of the entire literature or literatures related to your topic ¡ a set of thinly connected summaries of important related works haphazardly selected from many subfields a targeted literature review IS: ¡ a carefully curated set of sources from a small number of subfield literatures
Plonsky, L., & Brown, D. (2015). Second Language Research, 31 (2), 267-278. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Search Methods in Systematic Reviews of Complex Evidence: Audit of Primary Sources. Greenhalgh, T., & Peacock, R. (2005). BMJ, 331 (7524), 1064-1065. Only 30% of sources were obtained from the protocol defined at the outset of the study ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
2. Decide the scope of your review: This depends on the nature of your study. Decide on the number of articles you want to read, the recentness of these articles, and how comprehensive these are. 3. Go for reliable data sources: An important step in writing a good literature review is collecting data.
Consider the following ways to organize your review: Use an outline to organize your sources and ideas in a logical sequence. Identify main points and subpoints, and consider the flow of your review. Outlines can be revised as your ideas develop. They help guide your readers through your ideas and show the hierarchy of your thoughts.
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
Literature review. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has dramatically altered the landscape of academic research, acting as a catalyst for both methodological innovation and broader shifts in scholarly paradigms (Pal, Citation 2023).Its transformative power is evident across multiple disciplines, enabling researchers to engage with complex datasets and questions at a scale previously unimaginable ...