- How it works

How to Write a Research Design – Guide with Examples
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
A research design is a structure that combines different components of research. It involves the use of different data collection and data analysis techniques logically to answer the research questions .
It would be best to make some decisions about addressing the research questions adequately before starting the research process, which is achieved with the help of the research design.
Below are the key aspects of the decision-making process:
- Data type required for research
- Research resources
- Participants required for research
- Hypothesis based upon research question(s)
- Data analysis methodologies
- Variables (Independent, dependent, and confounding)
- The location and timescale for conducting the data
- The time period required for research
The research design provides the strategy of investigation for your project. Furthermore, it defines the parameters and criteria to compile the data to evaluate results and conclude.
Your project’s validity depends on the data collection and interpretation techniques. A strong research design reflects a strong dissertation , scientific paper, or research proposal .
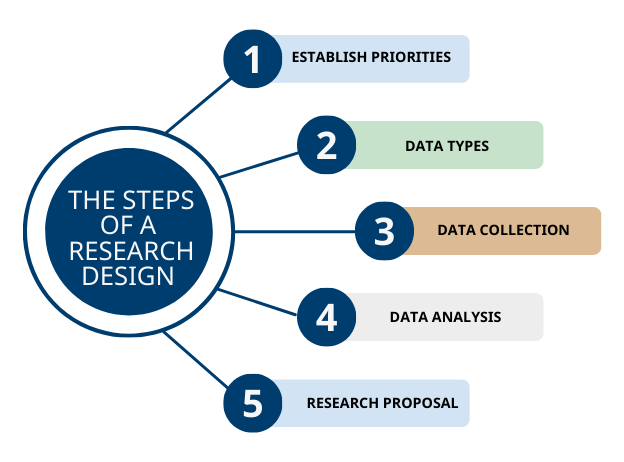
Step 1: Establish Priorities for Research Design
Before conducting any research study, you must address an important question: “how to create a research design.”
The research design depends on the researcher’s priorities and choices because every research has different priorities. For a complex research study involving multiple methods, you may choose to have more than one research design.
Multimethodology or multimethod research includes using more than one data collection method or research in a research study or set of related studies.
If one research design is weak in one area, then another research design can cover that weakness. For instance, a dissertation analyzing different situations or cases will have more than one research design.
For example:
- Experimental research involves experimental investigation and laboratory experience, but it does not accurately investigate the real world.
- Quantitative research is good for the statistical part of the project, but it may not provide an in-depth understanding of the topic .
- Also, correlational research will not provide experimental results because it is a technique that assesses the statistical relationship between two variables.
While scientific considerations are a fundamental aspect of the research design, It is equally important that the researcher think practically before deciding on its structure. Here are some questions that you should think of;
- Do you have enough time to gather data and complete the write-up?
- Will you be able to collect the necessary data by interviewing a specific person or visiting a specific location?
- Do you have in-depth knowledge about the different statistical analysis and data collection techniques to address the research questions or test the hypothesis ?
If you think that the chosen research design cannot answer the research questions properly, you can refine your research questions to gain better insight.
Step 2: Data Type you Need for Research
Decide on the type of data you need for your research. The type of data you need to collect depends on your research questions or research hypothesis. Two types of research data can be used to answer the research questions:
Primary Data Vs. Secondary Data
Qualitative vs. quantitative data.
Also, see; Research methods, design, and analysis .
Need help with a thesis chapter?
- Hire an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Statistical analysis, research methodology, discussion of the results or conclusion – our experts can help you no matter how complex the requirements are.
Step 3: Data Collection Techniques
Once you have selected the type of research to answer your research question, you need to decide where and how to collect the data.
It is time to determine your research method to address the research problem . Research methods involve procedures, techniques, materials, and tools used for the study.
For instance, a dissertation research design includes the different resources and data collection techniques and helps establish your dissertation’s structure .
The following table shows the characteristics of the most popularly employed research methods.
Research Methods
Step 4: Procedure of Data Analysis
Use of the correct data and statistical analysis technique is necessary for the validity of your research. Therefore, you need to be certain about the data type that would best address the research problem. Choosing an appropriate analysis method is the final step for the research design. It can be split into two main categories;
Quantitative Data Analysis
The quantitative data analysis technique involves analyzing the numerical data with the help of different applications such as; SPSS, STATA, Excel, origin lab, etc.
This data analysis strategy tests different variables such as spectrum, frequencies, averages, and more. The research question and the hypothesis must be established to identify the variables for testing.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis of figures, themes, and words allows for flexibility and the researcher’s subjective opinions. This means that the researcher’s primary focus will be interpreting patterns, tendencies, and accounts and understanding the implications and social framework.
You should be clear about your research objectives before starting to analyze the data. For example, you should ask yourself whether you need to explain respondents’ experiences and insights or do you also need to evaluate their responses with reference to a certain social framework.
Step 5: Write your Research Proposal
The research design is an important component of a research proposal because it plans the project’s execution. You can share it with the supervisor, who would evaluate the feasibility and capacity of the results and conclusion .
Read our guidelines to write a research proposal if you have already formulated your research design. The research proposal is written in the future tense because you are writing your proposal before conducting research.
The research methodology or research design, on the other hand, is generally written in the past tense.
How to Write a Research Design – Conclusion
A research design is the plan, structure, strategy of investigation conceived to answer the research question and test the hypothesis. The dissertation research design can be classified based on the type of data and the type of analysis.
Above mentioned five steps are the answer to how to write a research design. So, follow these steps to formulate the perfect research design for your dissertation .
ResearchProspect writers have years of experience creating research designs that align with the dissertation’s aim and objectives. If you are struggling with your dissertation methodology chapter, you might want to look at our dissertation part-writing service.
Our dissertation writers can also help you with the full dissertation paper . No matter how urgent or complex your need may be, ResearchProspect can help. We also offer PhD level research paper writing services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is research design.
Research design is a systematic plan that guides the research process, outlining the methodology and procedures for collecting and analysing data. It determines the structure of the study, ensuring the research question is answered effectively, reliably, and validly. It serves as the blueprint for the entire research project.
How to write a research design?
To write a research design, define your research question, identify the research method (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed), choose data collection techniques (e.g., surveys, interviews), determine the sample size and sampling method, outline data analysis procedures, and highlight potential limitations and ethical considerations for the study.
How to write the design section of a research paper?
In the design section of a research paper, describe the research methodology chosen and justify its selection. Outline the data collection methods, participants or samples, instruments used, and procedures followed. Detail any experimental controls, if applicable. Ensure clarity and precision to enable replication of the study by other researchers.
How to write a research design in methodology?
To write a research design in methodology, clearly outline the research strategy (e.g., experimental, survey, case study). Describe the sampling technique, participants, and data collection methods. Detail the procedures for data collection and analysis. Justify choices by linking them to research objectives, addressing reliability and validity.
You May Also Like
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Here's What You Need to Understand About Research Methodology

Table of Contents
Research methodology involves a systematic and well-structured approach to conducting scholarly or scientific inquiries. Knowing the significance of research methodology and its different components is crucial as it serves as the basis for any study.
Typically, your research topic will start as a broad idea you want to investigate more thoroughly. Once you’ve identified a research problem and created research questions , you must choose the appropriate methodology and frameworks to address those questions effectively.
What is the definition of a research methodology?
Research methodology is the process or the way you intend to execute your study. The methodology section of a research paper outlines how you plan to conduct your study. It covers various steps such as collecting data, statistical analysis, observing participants, and other procedures involved in the research process
The methods section should give a description of the process that will convert your idea into a study. Additionally, the outcomes of your process must provide valid and reliable results resonant with the aims and objectives of your research. This thumb rule holds complete validity, no matter whether your paper has inclinations for qualitative or quantitative usage.
Studying research methods used in related studies can provide helpful insights and direction for your own research. Now easily discover papers related to your topic on SciSpace and utilize our AI research assistant, Copilot , to quickly review the methodologies applied in different papers.

The need for a good research methodology
While deciding on your approach towards your research, the reason or factors you weighed in choosing a particular problem and formulating a research topic need to be validated and explained. A research methodology helps you do exactly that. Moreover, a good research methodology lets you build your argument to validate your research work performed through various data collection methods, analytical methods, and other essential points.
Just imagine it as a strategy documented to provide an overview of what you intend to do.
While undertaking any research writing or performing the research itself, you may get drifted in not something of much importance. In such a case, a research methodology helps you to get back to your outlined work methodology.
A research methodology helps in keeping you accountable for your work. Additionally, it can help you evaluate whether your work is in sync with your original aims and objectives or not. Besides, a good research methodology enables you to navigate your research process smoothly and swiftly while providing effective planning to achieve your desired results.
What is the basic structure of a research methodology?
Usually, you must ensure to include the following stated aspects while deciding over the basic structure of your research methodology:
1. Your research procedure
Explain what research methods you’re going to use. Whether you intend to proceed with quantitative or qualitative, or a composite of both approaches, you need to state that explicitly. The option among the three depends on your research’s aim, objectives, and scope.
2. Provide the rationality behind your chosen approach
Based on logic and reason, let your readers know why you have chosen said research methodologies. Additionally, you have to build strong arguments supporting why your chosen research method is the best way to achieve the desired outcome.
3. Explain your mechanism
The mechanism encompasses the research methods or instruments you will use to develop your research methodology. It usually refers to your data collection methods. You can use interviews, surveys, physical questionnaires, etc., of the many available mechanisms as research methodology instruments. The data collection method is determined by the type of research and whether the data is quantitative data(includes numerical data) or qualitative data (perception, morale, etc.) Moreover, you need to put logical reasoning behind choosing a particular instrument.
4. Significance of outcomes
The results will be available once you have finished experimenting. However, you should also explain how you plan to use the data to interpret the findings. This section also aids in understanding the problem from within, breaking it down into pieces, and viewing the research problem from various perspectives.
5. Reader’s advice
Anything that you feel must be explained to spread more awareness among readers and focus groups must be included and described in detail. You should not just specify your research methodology on the assumption that a reader is aware of the topic.
All the relevant information that explains and simplifies your research paper must be included in the methodology section. If you are conducting your research in a non-traditional manner, give a logical justification and list its benefits.
6. Explain your sample space
Include information about the sample and sample space in the methodology section. The term "sample" refers to a smaller set of data that a researcher selects or chooses from a larger group of people or focus groups using a predetermined selection method. Let your readers know how you are going to distinguish between relevant and non-relevant samples. How you figured out those exact numbers to back your research methodology, i.e. the sample spacing of instruments, must be discussed thoroughly.
For example, if you are going to conduct a survey or interview, then by what procedure will you select the interviewees (or sample size in case of surveys), and how exactly will the interview or survey be conducted.
7. Challenges and limitations
This part, which is frequently assumed to be unnecessary, is actually very important. The challenges and limitations that your chosen strategy inherently possesses must be specified while you are conducting different types of research.
The importance of a good research methodology
You must have observed that all research papers, dissertations, or theses carry a chapter entirely dedicated to research methodology. This section helps maintain your credibility as a better interpreter of results rather than a manipulator.
A good research methodology always explains the procedure, data collection methods and techniques, aim, and scope of the research. In a research study, it leads to a well-organized, rationality-based approach, while the paper lacking it is often observed as messy or disorganized.
You should pay special attention to validating your chosen way towards the research methodology. This becomes extremely important in case you select an unconventional or a distinct method of execution.
Curating and developing a strong, effective research methodology can assist you in addressing a variety of situations, such as:
- When someone tries to duplicate or expand upon your research after few years.
- If a contradiction or conflict of facts occurs at a later time. This gives you the security you need to deal with these contradictions while still being able to defend your approach.
- Gaining a tactical approach in getting your research completed in time. Just ensure you are using the right approach while drafting your research methodology, and it can help you achieve your desired outcomes. Additionally, it provides a better explanation and understanding of the research question itself.
- Documenting the results so that the final outcome of the research stays as you intended it to be while starting.
Instruments you could use while writing a good research methodology
As a researcher, you must choose which tools or data collection methods that fit best in terms of the relevance of your research. This decision has to be wise.
There exists many research equipments or tools that you can use to carry out your research process. These are classified as:
a. Interviews (One-on-One or a Group)
An interview aimed to get your desired research outcomes can be undertaken in many different ways. For example, you can design your interview as structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. What sets them apart is the degree of formality in the questions. On the other hand, in a group interview, your aim should be to collect more opinions and group perceptions from the focus groups on a certain topic rather than looking out for some formal answers.
In surveys, you are in better control if you specifically draft the questions you seek the response for. For example, you may choose to include free-style questions that can be answered descriptively, or you may provide a multiple-choice type response for questions. Besides, you can also opt to choose both ways, deciding what suits your research process and purpose better.
c. Sample Groups
Similar to the group interviews, here, you can select a group of individuals and assign them a topic to discuss or freely express their opinions over that. You can simultaneously note down the answers and later draft them appropriately, deciding on the relevance of every response.
d. Observations
If your research domain is humanities or sociology, observations are the best-proven method to draw your research methodology. Of course, you can always include studying the spontaneous response of the participants towards a situation or conducting the same but in a more structured manner. A structured observation means putting the participants in a situation at a previously decided time and then studying their responses.
Of all the tools described above, it is you who should wisely choose the instruments and decide what’s the best fit for your research. You must not restrict yourself from multiple methods or a combination of a few instruments if appropriate in drafting a good research methodology.
Types of research methodology
A research methodology exists in various forms. Depending upon their approach, whether centered around words, numbers, or both, methodologies are distinguished as qualitative, quantitative, or an amalgamation of both.
1. Qualitative research methodology
When a research methodology primarily focuses on words and textual data, then it is generally referred to as qualitative research methodology. This type is usually preferred among researchers when the aim and scope of the research are mainly theoretical and explanatory.
The instruments used are observations, interviews, and sample groups. You can use this methodology if you are trying to study human behavior or response in some situations. Generally, qualitative research methodology is widely used in sociology, psychology, and other related domains.
2. Quantitative research methodology
If your research is majorly centered on data, figures, and stats, then analyzing these numerical data is often referred to as quantitative research methodology. You can use quantitative research methodology if your research requires you to validate or justify the obtained results.
In quantitative methods, surveys, tests, experiments, and evaluations of current databases can be advantageously used as instruments If your research involves testing some hypothesis, then use this methodology.
3. Amalgam methodology
As the name suggests, the amalgam methodology uses both quantitative and qualitative approaches. This methodology is used when a part of the research requires you to verify the facts and figures, whereas the other part demands you to discover the theoretical and explanatory nature of the research question.
The instruments for the amalgam methodology require you to conduct interviews and surveys, including tests and experiments. The outcome of this methodology can be insightful and valuable as it provides precise test results in line with theoretical explanations and reasoning.
The amalgam method, makes your work both factual and rational at the same time.
Final words: How to decide which is the best research methodology?
If you have kept your sincerity and awareness intact with the aims and scope of research well enough, you must have got an idea of which research methodology suits your work best.
Before deciding which research methodology answers your research question, you must invest significant time in reading and doing your homework for that. Taking references that yield relevant results should be your first approach to establishing a research methodology.
Moreover, you should never refrain from exploring other options. Before setting your work in stone, you must try all the available options as it explains why the choice of research methodology that you finally make is more appropriate than the other available options.
You should always go for a quantitative research methodology if your research requires gathering large amounts of data, figures, and statistics. This research methodology will provide you with results if your research paper involves the validation of some hypothesis.
Whereas, if you are looking for more explanations, reasons, opinions, and public perceptions around a theory, you must use qualitative research methodology.The choice of an appropriate research methodology ultimately depends on what you want to achieve through your research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Research Methodology
1. how to write a research methodology.
You can always provide a separate section for research methodology where you should specify details about the methods and instruments used during the research, discussions on result analysis, including insights into the background information, and conveying the research limitations.
2. What are the types of research methodology?
There generally exists four types of research methodology i.e.
- Observation
- Experimental
- Derivational
3. What is the true meaning of research methodology?
The set of techniques or procedures followed to discover and analyze the information gathered to validate or justify a research outcome is generally called Research Methodology.
4. Where lies the importance of research methodology?
Your research methodology directly reflects the validity of your research outcomes and how well-informed your research work is. Moreover, it can help future researchers cite or refer to your research if they plan to use a similar research methodology.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Using AI for research: A beginner’s guide

Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
Grounded Theory Research Design
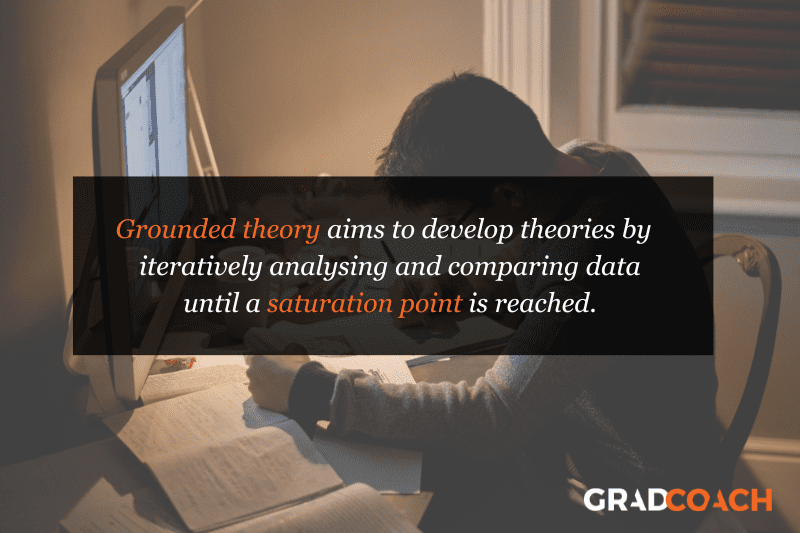
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
Case Study Design
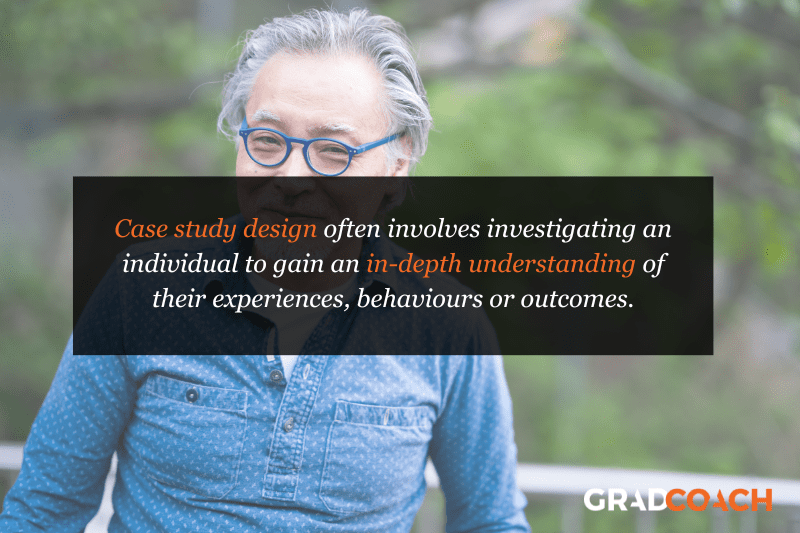
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.

Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.
Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Research Design & Method
Research Methods Guide: Research Design & Method
- Introduction
- Survey Research
- Interview Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Research Design & Method
Research Methods (sociology-focused)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (intro)
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods (advanced)

FAQ: Research Design & Method
What is the difference between Research Design and Research Method?
Research design is a plan to answer your research question. A research method is a strategy used to implement that plan. Research design and methods are different but closely related, because good research design ensures that the data you obtain will help you answer your research question more effectively.
Which research method should I choose ?
It depends on your research goal. It depends on what subjects (and who) you want to study. Let's say you are interested in studying what makes people happy, or why some students are more conscious about recycling on campus. To answer these questions, you need to make a decision about how to collect your data. Most frequently used methods include:
- Observation / Participant Observation
- Focus Groups
- Experiments
- Secondary Data Analysis / Archival Study
- Mixed Methods (combination of some of the above)
One particular method could be better suited to your research goal than others, because the data you collect from different methods will be different in quality and quantity. For instance, surveys are usually designed to produce relatively short answers, rather than the extensive responses expected in qualitative interviews.
What other factors should I consider when choosing one method over another?
Time for data collection and analysis is something you want to consider. An observation or interview method, so-called qualitative approach, helps you collect richer information, but it takes time. Using a survey helps you collect more data quickly, yet it may lack details. So, you will need to consider the time you have for research and the balance between strengths and weaknesses associated with each method (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative).
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Survey Research >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM
What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Why is research methodology important?
Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.
Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for....
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write Research Methodology
Last Updated: May 21, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 516,128 times.
The research methodology section of any academic research paper gives you the opportunity to convince your readers that your research is useful and will contribute to your field of study. An effective research methodology is grounded in your overall approach – whether qualitative or quantitative – and adequately describes the methods you used. Justify why you chose those methods over others, then explain how those methods will provide answers to your research questions. [1] X Research source
Describing Your Methods

- In your restatement, include any underlying assumptions that you're making or conditions that you're taking for granted. These assumptions will also inform the research methods you've chosen.
- Generally, state the variables you'll test and the other conditions you're controlling or assuming are equal.

- If you want to research and document measurable social trends, or evaluate the impact of a particular policy on various variables, use a quantitative approach focused on data collection and statistical analysis.
- If you want to evaluate people's views or understanding of a particular issue, choose a more qualitative approach.
- You can also combine the two. For example, you might look primarily at a measurable social trend, but also interview people and get their opinions on how that trend is affecting their lives.

- For example, if you conducted a survey, you would describe the questions included in the survey, where and how the survey was conducted (such as in person, online, over the phone), how many surveys were distributed, and how long your respondents had to complete the survey.
- Include enough detail that your study can be replicated by others in your field, even if they may not get the same results you did. [4] X Research source

- Qualitative research methods typically require more detailed explanation than quantitative methods.
- Basic investigative procedures don't need to be explained in detail. Generally, you can assume that your readers have a general understanding of common research methods that social scientists use, such as surveys or focus groups.

- For example, suppose you conducted a survey and used a couple of other research papers to help construct the questions on your survey. You would mention those as contributing sources.
Justifying Your Choice of Methods

- Describe study participants specifically, and list any inclusion or exclusion criteria you used when forming your group of participants.
- Justify the size of your sample, if applicable, and describe how this affects whether your study can be generalized to larger populations. For example, if you conducted a survey of 30 percent of the student population of a university, you could potentially apply those results to the student body as a whole, but maybe not to students at other universities.

- Reading other research papers is a good way to identify potential problems that commonly arise with various methods. State whether you actually encountered any of these common problems during your research.

- If you encountered any problems as you collected data, explain clearly the steps you took to minimize the effect that problem would have on your results.

- In some cases, this may be as simple as stating that while there were numerous studies using one method, there weren't any using your method, which caused a gap in understanding of the issue.
- For example, there may be multiple papers providing quantitative analysis of a particular social trend. However, none of these papers looked closely at how this trend was affecting the lives of people.
Connecting Your Methods to Your Research Goals

- Depending on your research questions, you may be mixing quantitative and qualitative analysis – just as you could potentially use both approaches. For example, you might do a statistical analysis, and then interpret those statistics through a particular theoretical lens.

- For example, suppose you're researching the effect of college education on family farms in rural America. While you could do interviews of college-educated people who grew up on a family farm, that would not give you a picture of the overall effect. A quantitative approach and statistical analysis would give you a bigger picture.

- If in answering your research questions, your findings have raised other questions that may require further research, state these briefly.
- You can also include here any limitations to your methods, or questions that weren't answered through your research.

- Generalization is more typically used in quantitative research. If you have a well-designed sample, you can statistically apply your results to the larger population your sample belongs to.
Template to Write Research Methodology

Community Q&A
- Organize your methodology section chronologically, starting with how you prepared to conduct your research methods, how you gathered data, and how you analyzed that data. [13] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Write your research methodology section in past tense, unless you're submitting the methodology section before the research described has been carried out. [14] X Research source Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- Discuss your plans in detail with your advisor or supervisor before committing to a particular methodology. They can help identify possible flaws in your study. [15] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://expertjournals.com/how-to-write-a-research-methodology-for-your-academic-article/
- ↑ http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/methodology
- ↑ https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/dissertation-methodology.html
- ↑ https://uir.unisa.ac.za/bitstream/handle/10500/4245/05Chap%204_Research%20methodology%20and%20design.pdf
- ↑ https://elc.polyu.edu.hk/FYP/html/method.htm
About This Article

To write a research methodology, start with a section that outlines the problems or questions you'll be studying, including your hypotheses or whatever it is you're setting out to prove. Then, briefly explain why you chose to use either a qualitative or quantitative approach for your study. Next, go over when and where you conducted your research and what parameters you used to ensure you were objective. Finally, cite any sources you used to decide on the methodology for your research. To learn how to justify your choice of methods in your research methodology, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prof. Dr. Ahmed Askar
Apr 18, 2020
Did this article help you?

M. Mahmood Shah Khan
Mar 17, 2020
Shimola Makondo
Jul 20, 2019
Zain Sharif Mohammed Alnadhery
Jan 7, 2019
Lundi Dukashe
Feb 17, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Language: English | German
How to Construct a Mixed Methods Research Design
Wie man ein mixed methods-forschungs-design konstruiert, judith schoonenboom.
1 Institut für Bildungswissenschaft, Universität Wien, Sensengasse 3a, 1090 Wien, Austria
R. Burke Johnson
2 Department of Professional Studies, University of South Alabama, UCOM 3700, 36688-0002 Mobile, AL USA
This article provides researchers with knowledge of how to design a high quality mixed methods research study. To design a mixed study, researchers must understand and carefully consider each of the dimensions of mixed methods design, and always keep an eye on the issue of validity. We explain the seven major design dimensions: purpose, theoretical drive, timing (simultaneity and dependency), point of integration, typological versus interactive design approaches, planned versus emergent design, and design complexity. There also are multiple secondary dimensions that need to be considered during the design process. We explain ten secondary dimensions of design to be considered for each research study. We also provide two case studies showing how the mixed designs were constructed.
Zusammenfassung
Der Beitrag gibt einen Überblick darüber, wie das Forschungsdesign bei Mixed Methods-Studien angelegt sein sollte. Um ein Mixed Methods-Forschungsdesign aufzustellen, müssen Forschende sorgfältig alle Dimensionen von Methodenkombinationen abwägen und von Anfang an auf die Güte und damit verbundene etwaige Probleme achten. Wir erklären und diskutieren die für Forschungsdesigns relevanten sieben Dimensionen von Methodenkombinationen: Untersuchungsziel, Rolle von Theorie im Forschungsprozess, Timing (Simultanität und Abhängigkeit), Schnittstellen, an denen Integration stattfindet, systematische vs. interaktive Design-Ansätze, geplante vs. emergente Designs und Komplexität des Designs. Es gibt außerdem zahlreiche sekundäre Dimensionen, die bei der Aufstellung des Forschungsdesigns berücksichtigt werden müssen, von denen wir zehn erklären. Der Beitrag schließt mit zwei Fallbeispielen ab, anhand derer konkret gezeigt wird, wie Mixed Methods-Forschungsdesigns aufgestellt werden können.
What is a mixed methods design?
This article addresses the process of selecting and constructing mixed methods research (MMR) designs. The word “design” has at least two distinct meanings in mixed methods research (Maxwell 2013 ). One meaning focuses on the process of design; in this meaning, design is often used as a verb. Someone can be engaged in designing a study (in German: “eine Studie konzipieren” or “eine Studie designen”). Another meaning is that of a product, namely the result of designing. The result of designing as a verb is a mixed methods design as a noun (in German: “das Forschungsdesign” or “Design”), as it has, for example, been described in a journal article. In mixed methods design, both meanings are relevant. To obtain a strong design as a product, one needs to carefully consider a number of rules for designing as an activity. Obeying these rules is not a guarantee of a strong design, but it does contribute to it. A mixed methods design is characterized by the combination of at least one qualitative and one quantitative research component. For the purpose of this article, we use the following definition of mixed methods research (Johnson et al. 2007 , p. 123):
Mixed methods research is the type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e. g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purposes of breadth and depth of understanding and corroboration.
Mixed methods research (“Mixed Methods” or “MM”) is the sibling of multimethod research (“Methodenkombination”) in which either solely multiple qualitative approaches or solely multiple quantitative approaches are combined.
In a commonly used mixed methods notation system (Morse 1991 ), the components are indicated as qual and quan (or QUAL and QUAN to emphasize primacy), respectively, for qualitative and quantitative research. As discussed below, plus (+) signs refer to concurrent implementation of components (“gleichzeitige Durchführung der Teilstudien” or “paralleles Mixed Methods-Design”) and arrows (→) refer to sequential implementation (“Sequenzielle Durchführung der Teilstudien” or “sequenzielles Mixed Methods-Design”) of components. Note that each research tradition receives an equal number of letters (four) in its abbreviation for equity. In this article, this notation system is used in some depth.
A mixed methods design as a product has several primary characteristics that should be considered during the design process. As shown in Table 1 , the following primary design “dimensions” are emphasized in this article: purpose of mixing, theoretical drive, timing, point of integration, typological use, and degree of complexity. These characteristics are discussed below. We also provide some secondary dimensions to consider when constructing a mixed methods design (Johnson and Christensen 2017 ).
List of Primary and Secondary Design Dimensions
On the basis of these dimensions, mixed methods designs can be classified into a mixed methods typology or taxonomy. In the mixed methods literature, various typologies of mixed methods designs have been proposed (for an overview see Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 , p. 69–72).
The overall goal of mixed methods research, of combining qualitative and quantitative research components, is to expand and strengthen a study’s conclusions and, therefore, contribute to the published literature. In all studies, the use of mixed methods should contribute to answering one’s research questions.
Ultimately, mixed methods research is about heightened knowledge and validity. The design as a product should be of sufficient quality to achieve multiple validities legitimation (Johnson and Christensen 2017 ; Onwuegbuzie and Johnson 2006 ), which refers to the mixed methods research study meeting the relevant combination or set of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods validities in each research study.
Given this goal of answering the research question(s) with validity, a researcher can nevertheless have various reasons or purposes for wanting to strengthen the research study and its conclusions. Following is the first design dimension for one to consider when designing a study: Given the research question(s), what is the purpose of the mixed methods study?
A popular classification of purposes of mixed methods research was first introduced in 1989 by Greene, Caracelli, and Graham, based on an analysis of published mixed methods studies. This classification is still in use (Greene 2007 ). Greene et al. ( 1989 , p. 259) distinguished the following five purposes for mixing in mixed methods research:
1. Triangulation seeks convergence, corroboration, correspondence of results from different methods; 2. Complementarity seeks elaboration, enhancement, illustration, clarification of the results from one method with the results from the other method; 3. Development seeks to use the results from one method to help develop or inform the other method, where development is broadly construed to include sampling and implementation, as well as measurement decisions; 4. Initiation seeks the discovery of paradox and contradiction, new perspectives of frameworks, the recasting of questions or results from one method with questions or results from the other method; 5. Expansion seeks to extend the breadth and range of inquiry by using different methods for different inquiry components.
In the past 28 years, this classification has been supplemented by several others. On the basis of a review of the reasons for combining qualitative and quantitative research mentioned by the authors of mixed methods studies, Bryman ( 2006 ) formulated a list of more concrete rationales for performing mixed methods research (see Appendix). Bryman’s classification breaks down Greene et al.’s ( 1989 ) categories into several aspects, and he adds a number of additional aspects, such as the following:
(a) Credibility – refers to suggestions that employing both approaches enhances the integrity of findings. (b) Context – refers to cases in which the combination is justified in terms of qualitative research providing contextual understanding coupled with either generalizable, externally valid findings or broad relationships among variables uncovered through a survey. (c) Illustration – refers to the use of qualitative data to illustrate quantitative findings, often referred to as putting “meat on the bones” of “dry” quantitative findings. (d) Utility or improving the usefulness of findings – refers to a suggestion, which is more likely to be prominent among articles with an applied focus, that combining the two approaches will be more useful to practitioners and others. (e) Confirm and discover – this entails using qualitative data to generate hypotheses and using quantitative research to test them within a single project. (f) Diversity of views – this includes two slightly different rationales – namely, combining researchers’ and participants’ perspectives through quantitative and qualitative research respectively, and uncovering relationships between variables through quantitative research while also revealing meanings among research participants through qualitative research. (Bryman, p. 106)
Views can be diverse (f) in various ways. Some examples of mixed methods design that include a diversity of views are:
- Iteratively/sequentially connecting local/idiographic knowledge with national/general/nomothetic knowledge;
- Learning from different perspectives on teams and in the field and literature;
- Achieving multiple participation, social justice, and action;
- Determining what works for whom and the relevance/importance of context;
- Producing interdisciplinary substantive theory, including/comparing multiple perspectives and data regarding a phenomenon;
- Juxtaposition-dialogue/comparison-synthesis;
- Breaking down binaries/dualisms (some of both);
- Explaining interaction between/among natural and human systems;
- Explaining complexity.
The number of possible purposes for mixing is very large and is increasing; hence, it is not possible to provide an exhaustive list. Greene et al.’s ( 1989 ) purposes, Bryman’s ( 2006 ) rationales, and our examples of a diversity of views were formulated as classifications on the basis of examination of many existing research studies. They indicate how the qualitative and quantitative research components of a study relate to each other. These purposes can be used post hoc to classify research or a priori in the design of a new study. When designing a mixed methods study, it is sometimes helpful to list the purpose in the title of the study design.
The key point of this section is for the researcher to begin a study with at least one research question and then carefully consider what the purposes for mixing are. One can use mixed methods to examine different aspects of a single research question, or one can use separate but related qualitative and quantitative research questions. In all cases, the mixing of methods, methodologies, and/or paradigms will help answer the research questions and make improvements over a more basic study design. Fuller and richer information will be obtained in the mixed methods study.
Theoretical drive
In addition to a mixing purpose, a mixed methods research study might have an overall “theoretical drive” (Morse and Niehaus 2009 ). When designing a mixed methods study, it is occasionally helpful to list the theoretical drive in the title of the study design. An investigation, in Morse and Niehaus’s ( 2009 ) view, is focused primarily on either exploration-and-description or on testing-and-prediction. In the first case, the theoretical drive is called “inductive” or “qualitative”; in the second case, it is called “deductive” or “quantitative”. In the case of mixed methods, the component that corresponds to the theoretical drive is referred to as the “core” component (“Kernkomponente”), and the other component is called the “supplemental” component (“ergänzende Komponente”). In Morse’s notation system, the core component is written in capitals and the supplemental component is written in lowercase letters. For example, in a QUAL → quan design, more weight is attached to the data coming from the core qualitative component. Due to the decisive character of the core component, the core component must be able to stand on its own, and should be implemented rigorously. The supplemental component does not have to stand on its own.
Although this distinction is useful in some circumstances, we do not advise to apply it to every mixed methods design. First, Morse and Niehaus contend that the supplemental component can be done “less rigorously” but do not explain which aspects of rigor can be dropped. In addition, the idea of decreased rigor is in conflict with one key theme of the present article, namely that mixed methods designs should always meet the criterion of multiple validities legitimation (Onwuegbuzie and Johnson 2006 ).
The idea of theoretical drive as explicated by Morse and Niehaus has been criticized. For example, we view a theoretical drive as a feature not of a whole study, but of a research question, or, more precisely, of an interpretation of a research question. For example, if one study includes multiple research questions, it might include several theoretical drives (Schoonenboom 2016 ).
Another criticism of Morse and Niehaus’ conceptualization of theoretical drive is that it does not allow for equal-status mixed methods research (“Mixed Methods Forschung, bei der qualitative und quantitative Methoden die gleiche Bedeutung haben” or “gleichrangige Mixed Methods-Designs”), in which both the qualitative and quantitative component are of equal value and weight; this same criticism applies to Morgan’s ( 2014 ) set of designs. We agree with Greene ( 2015 ) that mixed methods research can be integrated at the levels of method, methodology, and paradigm. In this view, equal-status mixed methods research designs are possible, and they result when both the qualitative and the quantitative components, approaches, and thinking are of equal value, they take control over the research process in alternation, they are in constant interaction, and the outcomes they produce are integrated during and at the end of the research process. Therefore, equal-status mixed methods research (that we often advocate) is also called “interactive mixed methods research”.
Mixed methods research can have three different drives, as formulated by Johnson et al. ( 2007 , p. 123):
Qualitative dominant [or qualitatively driven] mixed methods research is the type of mixed research in which one relies on a qualitative, constructivist-poststructuralist-critical view of the research process, while concurrently recognizing that the addition of quantitative data and approaches are likely to benefit most research projects. Quantitative dominant [or quantitatively driven] mixed methods research is the type of mixed research in which one relies on a quantitative, postpositivist view of the research process, while concurrently recognizing that the addition of qualitative data and approaches are likely to benefit most research projects. (p. 124) The area around the center of the [qualitative-quantitative] continuum, equal status , is the home for the person that self-identifies as a mixed methods researcher. This researcher takes as his or her starting point the logic and philosophy of mixed methods research. These mixed methods researchers are likely to believe that qualitative and quantitative data and approaches will add insights as one considers most, if not all, research questions.
We leave it to the reader to decide if he or she desires to conduct a qualitatively driven study, a quantitatively driven study, or an equal-status/“interactive” study. According to the philosophies of pragmatism (Johnson and Onwuegbuzie 2004 ) and dialectical pluralism (Johnson 2017 ), interactive mixed methods research is very much a possibility. By successfully conducting an equal-status study, the pragmatist researcher shows that paradigms can be mixed or combined, and that the incompatibility thesis does not always apply to research practice. Equal status research is most easily conducted when a research team is composed of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed researchers, interacts continually, and conducts a study to address one superordinate goal.
Timing: simultaneity and dependence
Another important distinction when designing a mixed methods study relates to the timing of the two (or more) components. When designing a mixed methods study, it is usually helpful to include the word “concurrent” (“parallel”) or “sequential” (“sequenziell”) in the title of the study design; a complex design can be partially concurrent and partially sequential. Timing has two aspects: simultaneity and dependence (Guest 2013 ).
Simultaneity (“Simultanität”) forms the basis of the distinction between concurrent and sequential designs. In a sequential design , the quantitative component precedes the qualitative component, or vice versa. In a concurrent design , both components are executed (almost) simultaneously. In the notation of Morse ( 1991 ), concurrence is indicated by a “+” between components (e. g., QUAL + quan), while sequentiality is indicated with a “→” (QUAL → quan). Note that the use of capital letters for one component and lower case letters for another component in the same design suggest that one component is primary and the other is secondary or supplemental.
Some designs are sequential by nature. For example, in a conversion design, qualitative categories and themes might be first obtained by collection and analysis of qualitative data, and then subsequently quantitized (Teddlie and Tashakkori 2009 ). Likewise, with Greene et al.’s ( 1989 ) initiation purpose, the initiation strand follows the unexpected results that it is supposed to explain. In other cases, the researcher has a choice. It is possible, e. g., to collect interview data and survey data of one inquiry simultaneously; in that case, the research activities would be concurrent. It is also possible to conduct the interviews after the survey data have been collected (or vice versa); in that case, research activities are performed sequentially. Similarly, a study with the purpose of expansion can be designed in which data on an effect and the intervention process are collected simultaneously, or they can be collected sequentially.
A second aspect of timing is dependence (“Abhängigkeit”) . We call two research components dependent if the implementation of the second component depends on the results of data analysis in the first component. Two research components are independent , if their implementation does not depend on the results of data analysis in the other component. Often, a researcher has a choice to perform data analysis independently or not. A researcher could analyze interview data and questionnaire data of one inquiry independently; in that case, the research activities would be independent. It is also possible to let the interview questions depend upon the outcomes of the analysis of the questionnaire data (or vice versa); in that case, research activities are performed dependently. Similarly, the empirical outcome/effect and process in a study with the purpose of expansion might be investigated independently, or the process study might take the effect/outcome as given (dependent).
In the mixed methods literature, the distinction between sequential and concurrent usually refers to the combination of concurrent/independent and sequential/dependent, and to the combination of data collection and data analysis. It is said that in a concurrent design, the data collection and data analysis of both components occurs (almost) simultaneously and independently, while in a sequential design, the data collection and data analysis of one component take place after the data collection and data analysis of the other component and depends on the outcomes of the other component.
In our opinion, simultaneity and dependence are two separate dimensions. Simultaneity indicates whether data collection is done concurrent or sequentially. Dependence indicates whether the implementation of one component depends upon the results of data analysis of the other component. As we will see in the example case studies, a concurrent design could include dependent data analysis, and a sequential design could include independent data analysis. It is conceivable that one simultaneously conducts interviews and collects questionnaire data (concurrent), while allowing the analysis focus of the interviews to depend on what emerges from the survey data (dependence).
Dependent research activities include a redirection of subsequent research inquiry. Using the outcomes of the first research component, the researcher decides what to do in the second component. Depending on the outcomes of the first research component, the researcher will do something else in the second component. If this is so, the research activities involved are said to be sequential-dependent, and any component preceded by another component should appropriately build on the previous component (see sequential validity legitimation ; Johnson and Christensen 2017 ; Onwuegbuzie and Johnson 2006 ).
It is under the purposive discretion of the researcher to determine whether a concurrent-dependent design, a concurrent-independent design, a sequential-dependent design, or a sequential-dependent design is needed to answer a particular research question or set of research questions in a given situation.
Point of integration
Each true mixed methods study has at least one “point of integration” – called the “point of interface” by Morse and Niehaus ( 2009 ) and Guest ( 2013 ) –, at which the qualitative and quantitative components are brought together. Having one or more points of integration is the distinguishing feature of a design based on multiple components. It is at this point that the components are “mixed”, hence the label “mixed methods designs”. The term “mixing”, however, is misleading, as the components are not simply mixed, but have to be integrated very carefully.
Determining where the point of integration will be, and how the results will be integrated, is an important, if not the most important, decision in the design of mixed methods research. Morse and Niehaus ( 2009 ) identify two possible points of integration: the results point of integration and the analytical point of integration.
Most commonly, integration takes place in the results point of integration . At some point in writing down the results of the first component, the results of the second component are added and integrated. A joint display (listing the qualitative and quantitative findings and an integrative statement) might be used to facilitate this process.
In the case of an analytical point of integration , a first analytical stage of a qualitative component is followed by a second analytical stage, in which the topics identified in the first analytical stage are quantitized. The results of the qualitative component ultimately, and before writing down the results of the analytical phase as a whole, become quantitative; qualitizing also is a possible strategy, which would be the converse of this.
Other authors assume more than two possible points of integration. Teddlie and Tashakkori ( 2009 ) distinguish four different stages of an investigation: the conceptualization stage, the methodological experimental stage (data collection), the analytical experimental stage (data analysis), and the inferential stage. According to these authors, in all four stages, mixing is possible, and thus all four stages are potential points or integration.
However, the four possible points of integration used by Teddlie and Tashakkori ( 2009 ) are still too coarse to distinguish some types of mixing. Mixing in the experiential stage can take many different forms, for example the use of cognitive interviews to improve a questionnaire (tool development), or selecting people for an interview on the basis of the results of a questionnaire (sampling). Extending the definition by Guest ( 2013 ), we define the point of integration as “any point in a study where two or more research components are mixed or connected in some way”. Then, the point of integration in the two examples of this paragraph can be defined more accurately as “instrument development”, and “development of the sample”.
It is at the point of integration that qualitative and quantitative components are integrated. Some primary ways that the components can be connected to each other are as follows:
(1) merging the two data sets, (2) connecting from the analysis of one set of data to the collection of a second set of data, (3) embedding of one form of data within a larger design or procedure, and (4) using a framework (theoretical or program) to bind together the data sets (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 , p. 76).
More generally, one can consider mixing at any or all of the following research components: purposes, research questions, theoretical drive, methods, methodology, paradigm, data, analysis, and results. One can also include mixing views of different researchers, participants, or stakeholders. The creativity of the mixed methods researcher designing a study is extensive.
Substantively, it can be useful to think of integration or mixing as comparing and bringing together two (or more) components on the basis of one or more of the purposes set out in the first section of this article. For example, it is possible to use qualitative data to illustrate a quantitative effect, or to determine whether the qualitative and the quantitative component yield convergent results ( triangulation ). An integrated result could also consist of a combination of a quantitatively established effect and a qualitative description of the underlying process . In the case of development, integration consists of an adjustment of an, often quantitative, for example, instrument or model or interpretation, based on qualitative assessments by members of the target group.
A special case is the integration of divergent results. The power of mixed methods research is its ability to deal with diversity and divergence. In the literature, we find two kinds of strategies for dealing with divergent results. A first set of strategies takes the detected divergence as the starting point for further analysis, with the aim to resolve the divergence. One possibility is to carry out further research (Cook 1985 ; Greene and Hall 2010 ). Further research is not always necessary. One can also look for a more comprehensive theory, which is able to account for both the results of the first component and the deviating results of the second component. This is a form of abduction (Erzberger and Prein 1997 ).
A fruitful starting point in trying to resolve divergence through abduction is to determine which component has resulted in a finding that is somehow expected, logical, and/or in line with existing research. The results of this research component, called the “sense” (“Lesart”), are subsequently compared to the results of the other component, called the “anti-sense” (“alternative Lesart”), which are considered dissonant, unexpected, and/or contrary to what had been found in the literature. The aim is to develop an overall explanation that fits both the sense and the anti-sense (Bazeley and Kemp 2012 ; Mendlinger and Cwikel 2008 ). Finally, a reanalysis of the data can sometimes lead to resolving divergence (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ).
Alternatively, one can question the existence of the encountered divergence. In this regard, Mathison ( 1988 ) recommends determining whether deviating results shown by the data can be explained by knowledge about the research and/or knowledge of the social world. Differences between results from different data sources could also be the result of properties of the methods involved, rather than reflect differences in reality (Yanchar and Williams 2006 ). In general, the conclusions of the individual components can be subjected to an inference quality audit (Teddlie and Tashakkori 2009 ), in which the researcher investigates the strength of each of the divergent conclusions. We recommend that researchers first determine whether there is “real” divergence, according to the strategies mentioned in the last paragraph. Next, an attempt can be made to resolve cases of “true” divergence, using one or more of the methods mentioned in this paragraph.
Design typology utilization
As already mentioned in Sect. 1, mixed methods designs can be classified into a mixed methods typology or taxonomy. A typology serves several purposes, including the following: guiding practice, legitimizing the field, generating new possibilities, and serving as a useful pedagogical tool (Teddlie and Tashakkori 2009 ). Note, however, that not all types of typologies are equally suitable for all purposes. For generating new possibilities, one will need a more exhaustive typology, while a useful pedagogical tool might be better served by a non-exhaustive overview of the most common mixed methods designs. Although some of the current MM design typologies include more designs than others, none of the current typologies is fully exhaustive. When designing a mixed methods study, it is often useful to borrow its name from an existing typology, or to construct a superior and nuanced clear name when your design is based on a modification of one or more of the designs.
Various typologies of mixed methods designs have been proposed. Creswell and Plano Clark’s ( 2011 ) typology of some “commonly used designs” includes six “major mixed methods designs”. Our summary of these designs runs as follows:
- Convergent parallel design (“paralleles Design”) (the quantitative and qualitative strands of the research are performed independently, and their results are brought together in the overall interpretation),
- Explanatory sequential design (“explanatives Design”) (a first phase of quantitative data collection and analysis is followed by the collection of qualitative data, which are used to explain the initial quantitative results),
- Exploratory sequential design (“exploratives Design”) (a first phase of qualitative data collection and analysis is followed by the collection of quantitative data to test or generalize the initial qualitative results),
- Embedded design (“Einbettungs-Design”) (in a traditional qualitative or quantitative design, a strand of the other type is added to enhance the overall design),
- Transformative design (“politisch-transformatives Design”) (a transformative theoretical framework, e. g. feminism or critical race theory, shapes the interaction, priority, timing and mixing of the qualitative and quantitative strand),
- Multiphase design (“Mehrphasen-Design”) (more than two phases or both sequential and concurrent strands are combined over a period of time within a program of study addressing an overall program objective).
Most of their designs presuppose a specific juxtaposition of the qualitative and quantitative component. Note that the last design is a complex type that is required in many mixed methods studies.
The following are our adapted definitions of Teddlie and Tashakkori’s ( 2009 ) five sets of mixed methods research designs (adapted from Teddlie and Tashakkori 2009 , p. 151):
- Parallel mixed designs (“paralleles Mixed-Methods-Design”) – In these designs, one has two or more parallel quantitative and qualitative strands, either with some minimal time lapse or simultaneously; the strand results are integrated into meta-inferences after separate analysis are conducted; related QUAN and QUAL research questions are answered or aspects of the same mixed research question is addressed.
- Sequential mixed designs (“sequenzielles Mixed-Methods-Design”) – In these designs, QUAL and QUAN strands occur across chronological phases, and the procedures/questions from the later strand emerge/depend/build on on the previous strand; the research questions are interrelated and sometimes evolve during the study.
- Conversion mixed designs (“Transfer-Design” or “Konversionsdesign”) – In these parallel designs, mixing occurs when one type of data is transformed to the other type and then analyzed, and the additional findings are added to the results; this design answers related aspects of the same research question,
- Multilevel mixed designs (“Mehrebenen-Mixed-Methods-Design”) – In these parallel or sequential designs, mixing occurs across multiple levels of analysis, as QUAN and QUAL data are analyzed and integrated to answer related aspects of the same research question or related questions.
- Fully integrated mixed designs (“voll integriertes Mixed-Methods-Design”) – In these designs, mixing occurs in an interactive manner at all stages of the study. At each stage, one approach affects the formulation of the other, and multiple types of implementation processes can occur. For example, rather than including integration only at the findings/results stage, or only across phases in a sequential design, mixing might occur at the conceptualization stage, the methodological stage, the analysis stage, and the inferential stage.
We recommend adding to Teddlie and Tashakkori’s typology a sixth design type, specifically, a “hybrid” design type to include complex combinations of two or more of the other design types. We expect that many published MM designs will fall into the hybrid design type.
Morse and Niehaus ( 2009 ) listed eight mixed methods designs in their book (and suggested that authors create more complex combinations when needed). Our shorthand labels and descriptions (adapted from Morse and Niehaus 2009 , p. 25) run as follows:
- QUAL + quan (inductive-simultaneous design where, the core component is qualitative and the supplemental component is quantitative)
- QUAL → quan (inductive-sequential design, where the core component is qualitative and the supplemental component is quantitative)
- QUAN + qual (deductive-simultaneous design where, the core component is quantitative and the supplemental component is qualitative)
- QUAN → qual (deductive-sequential design, where the core component is quantitative and the supplemental component is qualitative)
- QUAL + qual (inductive-simultaneous design, where both components are qualitative; this is a multimethod design rather than a mixed methods design)
- QUAL → qual (inductive-sequential design, where both components are qualitative; this is a multimethod design rather than a mixed methods design)
- QUAN + quan (deductive-simultaneous design, where both components are quantitative; this is a multimethod design rather than a mixed methods design)
- QUAN → quan (deductive-sequential design, where both components are quantitative; this is a multimethod design rather than a mixed methods design).
Notice that Morse and Niehaus ( 2009 ) included four mixed methods designs (the first four designs shown above) and four multimethod designs (the second set of four designs shown above) in their typology. The reader can, therefore, see that the design notation also works quite well for multimethod research designs. Notably absent from Morse and Niehaus’s book are equal-status or interactive designs. In addition, they assume that the core component should always be performed either concurrent with or before the supplemental component.
Johnson, Christensen, and Onwuegbuzie constructed a set of mixed methods designs without these limitations. The resulting mixed methods design matrix (see Johnson and Christensen 2017 , p. 478) contains nine designs, which we can label as follows (adapted from Johnson and Christensen 2017 , p. 478):
- QUAL + QUAN (equal-status concurrent design),
- QUAL + quan (qualitatively driven concurrent design),
- QUAN + qual (quantitatively driven concurrent design),
- QUAL → QUAN (equal-status sequential design),
- QUAN → QUAL (equal-status sequential design),
- QUAL → quan (qualitatively driven sequential design),
- qual → QUAN (quantitatively driven sequential design),
- QUAN → qual (quantitatively driven sequential design), and
- quan → QUAL (qualitatively driven sequential design).
The above set of nine designs assumed only one qualitative and one quantitative component. However, this simplistic assumption can be relaxed in practice, allowing the reader to construct more complex designs. The Morse notation system is very powerful. For example, here is a three-stage equal-status concurrent-sequential design:
The key point here is that the Morse notation provides researchers with a powerful language for depicting and communicating the design constructed for a specific research study.
When designing a mixed methods study, it is sometimes helpful to include the mixing purpose (or characteristic on one of the other dimensions shown in Table 1 ) in the title of the study design (e. g., an explanatory sequential MM design, an exploratory-confirmatory MM design, a developmental MM design). Much more important, however, than a design name is for the author to provide an accurate description of what was done in the research study, so the reader will know exactly how the study was conducted. A design classification label can never replace such a description.
The common complexity of mixed methods design poses a problem to the above typologies of mixed methods research. The typologies were designed to classify whole mixed methods studies, and they are basically based on a classification of simple designs. In practice, many/most designs are complex. Complex designs are sometimes labeled “complex design”, “multiphase design”, “fully integrated design”, “hybrid design” and the like. Because complex designs occur very often in practice, the above typologies are not able to classify a large part of existing mixed methods research any further than by labeling them “complex”, which in itself is not very informative about the particular design. This problem does not fully apply to Morse’s notation system, which can be used to symbolize some more complex designs.
Something similar applies to the classification of the purposes of mixed methods research. The classifications of purposes mentioned in the “Purpose”-section, again, are basically meant for the classification of whole mixed methods studies. In practice, however, one single study often serves more than one purpose (Schoonenboom et al. 2017 ). The more purposes that are included in one study, the more difficult it becomes to select a design on the basis of the purpose of the investigation, as advised by Greene ( 2007 ). Of all purposes involved, then, which one should be the primary basis for the design? Or should the design be based upon all purposes included? And if so, how? For more information on how to articulate design complexity based on multiple purposes of mixing, see Schoonenboom et al. ( 2017 ).
It should be clear to the reader that, although much progress has been made in the area of mixed methods design typologies, the problem remains in developing a single typology that is effective in comprehensively listing a set of designs for mixed methods research. This is why we emphasize in this article the importance of learning to build on simple designs and construct one’s own design for one’s research questions. This will often result in a combination or “hybrid” design that goes beyond basic designs found in typologies, and a methodology section that provides much more information than a design name.
Typological versus interactive approaches to design
In the introduction, we made a distinction between design as a product and design as a process. Related to this, two different approaches to design can be distinguished: typological/taxonomic approaches (“systematische Ansätze”), such as those in the previous section, and interactive approaches (“interaktive Ansätze”) (the latter were called “dynamic” approaches by Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ). Whereas typological/taxonomic approaches view designs as a sort of mold, in which the inquiry can be fit, interactive approaches (Maxwell 2013 ) view design as a process, in which a certain design-as-a-product might be the outcome of the process, but not its input.
The most frequently mentioned interactive approach to mixed methods research is the approach by Maxwell and Loomis ( 2003 ). Maxwell and Loomis distinguish the following components of a design: goals, conceptual framework, research question, methods, and validity. They argue convincingly that the most important task of the researcher is to deliver as the end product of the design process a design in which these five components fit together properly. During the design process, the researcher works alternately on the individual components, and as a result, their initial fit, if it existed, tends to get lost. The researcher should therefore regularly check during the research and continuing design process whether the components still fit together, and, if not, should adapt one or the other component to restore the fit between them. In an interactive approach, unlike the typological approach, design is viewed as an interactive process in which the components are continually compared during the research study to each other and adapted to each other.
Typological and interactive approaches to mixed methods research have been presented as mutually exclusive alternatives. In our view, however, they are not mutually exclusive. The interactive approach of Maxwell is a very powerful tool for conducting research, yet this approach is not specific to mixed methods research. Maxwell’s interactive approach emphasizes that the researcher should keep and monitor a close fit between the five components of research design. However, it does not indicate how one should combine qualitative and quantitative subcomponents within one of Maxwell’s five components (e. g., how one should combine a qualitative and a quantitative method, or a qualitative and a quantitative research question). Essential elements of the design process, such as timing and the point of integration are not covered by Maxwell’s approach. This is not a shortcoming of Maxwell’s approach, but it indicates that to support the design of mixed methods research, more is needed than Maxwell’s model currently has to offer.
Some authors state that design typologies are particularly useful for beginning researchers and interactive approaches are suited for experienced researchers (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ). However, like an experienced researcher, a research novice needs to align the components of his or her design properly with each other, and, like a beginning researcher, an advanced researcher should indicate how qualitative and quantitative components are combined with each other. This makes an interactive approach desirable, also for beginning researchers.
We see two merits of the typological/taxonomic approach . We agree with Greene ( 2007 ), who states that the value of the typological approach mainly lies in the different dimensions of mixed methods that result from its classifications. In this article, the primary dimensions include purpose, theoretical drive, timing, point of integration, typological vs. interactive approaches, planned vs. emergent designs, and complexity (also see secondary dimensions in Table 1 ). Unfortunately, all of these dimensions are not reflected in any single design typology reviewed here. A second merit of the typological approach is the provision of common mixed methods research designs, of common ways in which qualitative and quantitative research can be combined, as is done for example in the major designs of Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2011 ). Contrary to other authors, however, we do not consider these designs as a feature of a whole study, but rather, in line with Guest ( 2013 ), as a feature of one part of a design in which one qualitative and one quantitative component are combined. Although one study could have only one purpose, one point of integration, et cetera, we believe that combining “designs” is the rule and not the exception. Therefore, complex designs need to be constructed and modified as needed, and during the writing phase the design should be described in detail and perhaps given a creative and descriptive name.
Planned versus emergent designs
A mixed methods design can be thought out in advance, but can also arise during the course of the conduct of the study; the latter is called an “emergent” design (Creswell and Plano Clark 2011 ). Emergent designs arise, for example, when the researcher discovers during the study that one of the components is inadequate (Morse and Niehaus 2009 ). Addition of a component of the other type can sometimes remedy such an inadequacy. Some designs contain an emergent component by their nature. Initiation, for example, is the further exploration of unexpected outcomes. Unexpected outcomes are by definition not foreseen, and therefore cannot be included in the design in advance.
The question arises whether researchers should plan all these decisions beforehand, or whether they can make them during, and depending on the course of, the research process. The answer to this question is twofold. On the one hand, a researcher should decide beforehand which research components to include in the design, such that the conclusion that will be drawn will be robust. On the other hand, developments during research execution will sometimes prompt the researcher to decide to add additional components. In general, the advice is to be prepared for the unexpected. When one is able to plan for emergence, one should not refrain from doing so.
Dimension of complexity
Next, mixed methods designs are characterized by their complexity. In the literature, simple and complex designs are distinguished in various ways. A common distinction is between simple investigations with a single point of integration versus complex investigations with multiple points of integration (Guest 2013 ). When designing a mixed methods study, it can be useful to mention in the title whether the design of the study is simple or complex. The primary message of this section is as follows: It is the responsibility of the researcher to create more complex designs when needed to answer his or her research question(s) .
Teddlie and Tashakkori’s ( 2009 ) multilevel mixed designs and fully integrated mixed designs are both complex designs, but for different reasons. A multilevel mixed design is more complex ontologically, because it involves multiple levels of reality. For example, data might be collected both at the levels of schools and students, neighborhood and households, companies and employees, communities and inhabitants, or medical practices and patients (Yin 2013 ). Integration of these data does not only involve the integration of qualitative and quantitative data, but also the integration of data originating from different sources and existing at different levels. Little if any published research has discussed the possible ways of integrating data obtained in a multilevel mixed design (see Schoonenboom 2016 ). This is an area in need of additional research.
The fully-integrated mixed design is more complex because it contains multiple points of integration. As formulated by Teddlie and Tashakkori ( 2009 , p. 151):
In these designs, mixing occurs in an interactive manner at all stages of the study. At each stage, one approach affects the formulation of the other, and multiple types of implementation processes can occur.
Complexity, then, not only depends on the number of components, but also on the extent to which they depend on each other (e. g., “one approach affects the formulation of the other”).
Many of our design dimensions ultimately refer to different ways in which the qualitative and quantitative research components are interdependent. Different purposes of mixing ultimately differ in the way one component relates to, and depends upon, the other component. For example, these purposes include dependencies, such as “x illustrates y” and “x explains y”. Dependencies in the implementation of x and y occur to the extent that the design of y depends on the results of x (sequentiality). The theoretical drive creates dependencies, because the supplemental component y is performed and interpreted within the context and the theoretical drive of core component x. As a general rule in designing mixed methods research, one should examine and plan carefully the ways in which and the extent to which the various components depend on each other.
The dependence among components, which may or may not be present, has been summarized by Greene ( 2007 ). It is seen in the distinction between component designs (“Komponenten-Designs”), in which the components are independent of each other, and integrated designs (“integrierte Designs”), in which the components are interdependent. Of these two design categories, integrated designs are the more complex designs.
Secondary design considerations
The primary design dimensions explained above have been the focus of this article. There are a number of secondary considerations for researchers to also think about when they design their studies (Johnson and Christensen 2017 ). Now we list some secondary design issues and questions that should be thoughtfully considered during the construction of a strong mixed methods research design.
- Phenomenon: Will the study be addressing (a) the same part or different parts of one phenomenon? (b) different phenomena?, or (c) the phenomenon/phenomena from different perspectives? Is the phenomenon (a) expected to be unique (e. g., historical event, particular group)?, (b) something expected to be part of a more regular and predictable phenomenon, or (c) a complex mixture of these?
- Social scientific theory: Will the study generate a new substantive theory, test an already constructed theory, or achieve both in a sequential arrangement? Or is the researcher not interested in substantive theory based on empirical data?
- Ideological drive: Will the study have an explicitly articulated ideological drive (e. g., feminism, critical race paradigm, transformative paradigm)?
- Combination of sampling methods: What specific quantitative sampling method(s) will be used? What specific qualitative sampling methods(s) will be used? How will these be combined or related?
- Degree to which the research participants will be similar or different: For example, participants or stakeholders with known differences of perspective would provide participants that are quite different.
- Degree to which the researchers on the research team will be similar or different: For example, an experiment conducted by one researcher would be high on similarity, but the use of a heterogeneous and participatory research team would include many differences.
- Implementation setting: Will the phenomenon be studied naturalistically, experimentally, or through a combination of these?
- Degree to which the methods similar or different: For example, a structured interview and questionnaire are fairly similar but administration of a standardized test and participant observation in the field are quite different.
- Validity criteria and strategies: What validity criteria and strategies will be used to address the defensibility of the study and the conclusions that will be drawn from it (see Chapter 11 in Johnson and Christensen 2017 )?
- Full study: Will there be essentially one research study or more than one? How will the research report be structured?
Two case studies
The above design dimensions are now illustrated by examples. A nice collection of examples of mixed methods studies can be found in Hesse-Biber ( 2010 ), from which the following examples are taken. The description of the first case example is shown in Box 1.
Box 1
Summary of Roth ( 2006 ), research regarding the gender-wage gap within Wall Street securities firms. Adapted from Hesse-Biber ( 2010 , pp. 457–458)
Louise Marie Roth’s research, Selling Women Short: Gender and Money on Wall Street ( 2006 ), tackles gender inequality in the workplace. She was interested in understanding the gender-wage gap among highly performing Wall Street MBAs, who on the surface appeared to have the same “human capital” qualifications and were placed in high-ranking Wall Street securities firms as their first jobs. In addition, Roth wanted to understand the “structural factors” within the workplace setting that may contribute to the gender-wage gap and its persistence over time. […] Roth conducted semistructured interviews, nesting quantitative closed-ended questions into primarily qualitative in-depth interviews […] In analyzing the quantitative data from her sample, she statistically considered all those factors that might legitimately account for gendered differences such as number of hours worked, any human capital differences, and so on. Her analysis of the quantitative data revealed the presence of a significant gender gap in wages that remained unexplained after controlling for any legitimate factors that might otherwise make a difference. […] Quantitative findings showed the extent of the wage gap while providing numerical understanding of the disparity but did not provide her with an understanding of the specific processes within the workplace that might have contributed to the gender gap in wages. […] Her respondents’ lived experiences over time revealed the hidden inner structures of the workplace that consist of discriminatory organizational practices with regard to decision making in performance evaluations that are tightly tied to wage increases and promotion.
This example nicely illustrates the distinction we made between simultaneity and dependency. On the two aspects of the timing dimension, this study was a concurrent-dependent design answering a set of related research questions. The data collection in this example was conducted simultaneously, and was thus concurrent – the quantitative closed-ended questions were embedded into the qualitative in-depth interviews. In contrast, the analysis was dependent, as explained in the next paragraph.
One of the purposes of this study was explanation: The qualitative data were used to understand the processes underlying the quantitative outcomes. It is therefore an explanatory design, and might be labelled an “explanatory concurrent design”. Conceptually, explanatory designs are often dependent: The qualitative component is used to explain and clarify the outcomes of the quantitative component. In that sense, the qualitative analysis in the case study took the outcomes of the quantitative component (“the existence of the gender-wage gap” and “numerical understanding of the disparity”), and aimed at providing an explanation for that result of the quantitative data analysis , by relating it to the contextual circumstances in which the quantitative outcomes were produced. This purpose of mixing in the example corresponds to Bryman’s ( 2006 ) “contextual understanding”. On the other primary dimensions, (a) the design was ongoing over a three-year period but was not emergent, (b) the point of integration was results, and (c) the design was not complex with respect to the point of integration, as it had only one point of integration. Yet, it was complex in the sense of involving multiple levels; both the level of the individual and the organization were included. According to the approach of Johnson and Christensen ( 2017 ), this was a QUAL + quan design (that was qualitatively driven, explanatory, and concurrent). If we give this study design a name, perhaps it should focus on what was done in the study: “explaining an effect from the process by which it is produced”. Having said this, the name “explanatory concurrent design” could also be used.
The description of the second case example is shown in Box 2.
Box 2
Summary of McMahon’s ( 2007 ) explorative study of the meaning, role, and salience of rape myths within the subculture of college student athletes. Adapted from Hesse-Biber ( 2010 , pp. 461–462)
Sarah McMahon ( 2007 ) wanted to explore the subculture of college student athletes and specifically the meaning, role, and salience of rape myths within that culture. […] While she was looking for confirmation between the quantitative ([structured] survey) and qualitative (focus groups and individual interviews) findings, she entered this study skeptical of whether or not her quantitative and qualitative findings would mesh with one another. McMahon […] first administered a survey [instrument] to 205 sophomore and junior student athletes at one Northeast public university. […] The quantitative data revealed a very low acceptance of rape myths among this student population but revealed a higher acceptance of violence among men and individuals who did not know a survivor of sexual assault. In the second qualitative (QUAL) phase, “focus groups were conducted as semi-structured interviews” and facilitated by someone of the same gender as the participants (p. 360). […] She followed this up with a third qualitative component (QUAL), individual interviews, which were conducted to elaborate on themes discovered in the focus groups and determine any differences in students’ responses between situations (i. e., group setting vs. individual). The interview guide was designed specifically to address focus group topics that needed “more in-depth exploration” or clarification (p. 361). The qualitative findings from the focus groups and individual qualitative interviews revealed “subtle yet pervasive rape myths” that fell into four major themes: “the misunderstanding of consent, the belief in ‘accidental’ and fabricated rape, the contention that some women provoke rape, and the invulnerability of female athletes” (p. 363). She found that the survey’s finding of a “low acceptance of rape myths … was contradicted by the findings of the focus groups and individual interviews, which indicated the presence of subtle rape myths” (p. 362).
On the timing dimension, this is an example of a sequential-independent design. It is sequential, because the qualitative focus groups were conducted after the survey was administered. The analysis of the quantitative and qualitative data was independent: Both were analyzed independently, to see whether they yielded the same results (which they did not). This purpose, therefore, was triangulation. On the other primary dimensions, (a) the design was planned, (b) the point of integration was results, and (c) the design was not complex as it had only one point of integration, and involved only the level of the individual. The author called this a “sequential explanatory” design. We doubt, however, whether this is the most appropriate label, because the qualitative component did not provide an explanation for quantitative results that were taken as given. On the contrary, the qualitative results contradicted the quantitative results. Thus, a “sequential-independent” design, or a “sequential-triangulation” design or a “sequential-comparative” design would probably be a better name.
Notice further that the second case study had the same point of integration as the first case study. The two components were brought together in the results. Thus, although the case studies are very dissimilar in many respects, this does not become visible in their point of integration. It can therefore be helpful to determine whether their point of extension is different. A point of extension is the point in the research process at which the second (or later) component comes into play. In the first case study, two related, but different research questions were answered, namely the quantitative question “How large is the gender-wage gap among highly performing Wall Street MBAs after controlling for any legitimate factors that might otherwise make a difference?”, and the qualitative research question “How do structural factors within the workplace setting contribute to the gender-wage gap and its persistence over time?” This case study contains one qualitative research question and one quantitative research question. Therefore, the point of extension is the research question. In the second case study, both components answered the same research question. They differed in their data collection (and subsequently in their data analysis): qualitative focus groups and individual interviews versus a quantitative questionnaire. In this case study, the point of extension was data collection. Thus, the point of extension can be used to distinguish between the two case studies.
Summary and conclusions
The purpose of this article is to help researchers to understand how to design a mixed methods research study. Perhaps the simplest approach is to design is to look at a single book and select one from the few designs included in that book. We believe that is only useful as a starting point. Here we have shown that one often needs to construct a research design to fit one’s unique research situation and questions.
First, we showed that there are there are many purposes for which qualitative and quantitative methods, methodologies, and paradigms can be mixed. This must be determined in interaction with the research questions. Inclusion of a purpose in the design name can sometimes provide readers with useful information about the study design, as in, e. g., an “explanatory sequential design” or an “exploratory-confirmatory design”.
The second dimension is theoretical drive in the sense that Morse and Niehaus ( 2009 ) use this term. That is, will the study have an inductive or a deductive drive, or, we added, a combination of these. Related to this idea is whether one will conduct a qualitatively driven, a quantitatively driven, or an equal-status mixed methods study. This language is sometimes included in the design name to communicate this characteristic of the study design (e. g., a “quantitatively driven sequential mixed methods design”).
The third dimension is timing , which has two aspects: simultaneity and dependence. Simultaneity refers to whether the components are to be implemented concurrently, sequentially, or a combination of these in a multiphase design. Simultaneity is commonly used in the naming of a mixed methods design because it communicates key information. The second aspect of timing, dependence , refers to whether a later component depends on the results of an earlier component, e. g., Did phase two specifically build on phase one in the research study? The fourth design dimension is the point of integration, which is where the qualitative and quantitative components are brought together and integrated. This is an essential dimension, but it usually does not need to be incorporated into the design name.
The fifth design dimension is that of typological vs. interactive design approaches . That is, will one select a design from a typology or use a more interactive approach to construct one’s own design? There are many typologies of designs currently in the literature. Our recommendation is that readers examine multiple design typologies to better understand the design process in mixed methods research and to understand what designs have been identified as popular in the field. However, when a design that would follow from one’s research questions is not available, the researcher can and should (a) combine designs into new designs or (b) simply construct a new and unique design. One can go a long way in depicting a complex design with Morse’s ( 1991 ) notation when used to its full potential. We also recommend that researchers understand the process approach to design from Maxwell and Loomis ( 2003 ), and realize that research design is a process and it needs, oftentimes, to be flexible and interactive.
The sixth design dimension or consideration is whether a design will be fully specified during the planning of the research study or if the design (or part of the design) will be allowed to emerge during the research process, or a combination of these. The seventh design dimension is called complexity . One sort of complexity mentioned was multilevel designs, but there are many complexities that can enter designs. The key point is that good research often requires the use of complex designs to answer one’s research questions. This is not something to avoid. It is the responsibility of the researcher to learn how to construct and describe and name mixed methods research designs. Always remember that designs should follow from one’s research questions and purposes, rather than questions and purposes following from a few currently named designs.
In addition to the six primary design dimensions or considerations, we provided a set of additional or secondary dimensions/considerations or questions to ask when constructing a mixed methods study design. Our purpose throughout this article has been to show what factors must be considered to design a high quality mixed methods research study. The more one knows and thinks about the primary and secondary dimensions of mixed methods design the better equipped one will be to pursue mixed methods research.
Acknowledgments
Open access funding provided by University of Vienna.
Biographies
1965, Dr., Professor of Empirical Pedagogy at University of Vienna, Austria. Research Areas: Mixed Methods Design, Philosophy of Mixed Methods Research, Innovation in Higher Education, Design and Evaluation of Intervention Studies, Educational Technology. Publications: Mixed methods in early childhood education. In: M. Fleer & B. v. Oers (Eds.), International handbook on early childhood education (Vol. 1). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer 2017; The multilevel mixed intact group analysis: A mixed method to seek, detect, describe and explain differences between intact groups. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 10, 2016; The realist survey: How respondents’ voices can be used to test and revise correlational models. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 2015. Advance online publication.
1957, PhD, Professor of Professional Studies at University of South Alabama, Mobile, Alabama USA. Research Areas: Methods of Social Research, Program Evaluation, Quantitative, Qualitative and Mixed Methods, Philosophy of Social Science. Publications: Research methods, design and analysis. Boston, MA 2014 (with L. Christensen and L. Turner); Educational research: Quantitative, qualitative and mixed approaches. Los Angeles, CA 2017 (with L. Christensen); The Oxford handbook of multimethod and mixed methods research inquiry. New York, NY 2015 (with S. Hesse-Biber).
Bryman’s ( 2006 ) scheme of rationales for combining quantitative and qualitative research 1
- Triangulation or greater validity – refers to the traditional view that quantitative and qualitative research might be combined to triangulate findings in order that they may be mutually corroborated. If the term was used as a synonym for integrating quantitative and qualitative research, it was not coded as triangulation.
- Offset – refers to the suggestion that the research methods associated with both quantitative and qualitative research have their own strengths and weaknesses so that combining them allows the researcher to offset their weaknesses to draw on the strengths of both.
- Completeness – refers to the notion that the researcher can bring together a more comprehensive account of the area of enquiry in which he or she is interested if both quantitative and qualitative research are employed.
- Process – quantitative research provides an account of structures in social life but qualitative research provides sense of process.
- Different research questions – this is the argument that quantitative and qualitative research can each answer different research questions but this item was coded only if authors explicitly stated that they were doing this.
- Explanation – one is used to help explain findings generated by the other.
- Unexpected results – refers to the suggestion that quantitative and qualitative research can be fruitfully combined when one generates surprising results that can be understood by employing the other.
- Instrument development – refers to contexts in which qualitative research is employed to develop questionnaire and scale items – for example, so that better wording or more comprehensive closed answers can be generated.
- Sampling – refers to situations in which one approach is used to facilitate the sampling of respondents or cases.
- Credibility – refer s to suggestions that employing both approaches enhances the integrity of findings.
- Context – refers to cases in which the combination is rationalized in terms of qualitative research providing contextual understanding coupled with either generalizable, externally valid findings or broad relationships among variables uncovered through a survey.
- Illustration – refers to the use of qualitative data to illustrate quantitative findings, often referred to as putting “meat on the bones” of “dry” quantitative findings.
- Utility or improving the usefulness of findings – refers to a suggestion, which is more likely to be prominent among articles with an applied focus, that combining the two approaches will be more useful to practitioners and others.
- Confirm and discover – this entails using qualitative data to generate hypotheses and using quantitative research to test them within a single project.
- Diversity of views – this includes two slightly different rationales – namely, combining researchers’ and participants’ perspectives through quantitative and qualitative research respectively, and uncovering relationships between variables through quantitative research while also revealing meanings among research participants through qualitative research.
- Enhancement or building upon quantitative/qualitative findings – this entails a reference to making more of or augmenting either quantitative or qualitative findings by gathering data using a qualitative or quantitative research approach.
- Other/unclear.
- Not stated.
1 Reprinted with permission from “Integrating quantitative and qualitative research: How is it done?” by Alan Bryman ( 2006 ), Qualitative Research, 6, pp. 105–107.
Contributor Information
Judith Schoonenboom, Email: [email protected] .
R. Burke Johnson, Email: ude.amabalahtuos@nosnhojb .
- Bazeley, Pat, Lynn Kemp Mosaics, triangles, and DNA: Metaphors for integrated analysis in mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2012; 6 :55–72. doi: 10.1177/1558689811419514. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryman A. Integrating quantitative and qualitative research: how is it done? Qualitative Research. 2006; 6 :97–113. doi: 10.1177/1468794106058877. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook TD. Postpositivist critical multiplism. In: Shotland RL, Mark MM, editors. Social science and social policy. Beverly Hills: SAGE; 1985. pp. 21–62. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell JW, Plano Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. 2. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Erzberger C, Prein G. Triangulation: Validity and empirically-based hypothesis construction. Quality and Quantity. 1997; 31 :141–154. doi: 10.1023/A:1004249313062. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene JC. Mixed methods in social inquiry. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene JC. Preserving distinctions within the multimethod and mixed methods research merger. Sharlene Hesse-Biber and R. Burke Johnson. New York: Oxford University Press; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene JC, Valerie J, Caracelli, Graham WF. Toward a conceptual framework for mixed-method evaluation designs. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis. 1989; 11 :255–274. doi: 10.3102/01623737011003255. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene JC, Hall JN. Dialectics and pragmatism. In: Tashakkori A, Teddlie C, editors. SAGE handbook of mixed methods in social & behavioral research. 2. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2010. pp. 119–167. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guest, Greg Describing mixed methods research: An alternative to typologies. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2013; 7 :141–151. doi: 10.1177/1558689812461179. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hesse-Biber S. Qualitative approaches to mixed methods practice. Qualitative Inquiry. 2010; 16 :455–468. doi: 10.1177/1077800410364611. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson BR. Dialectical pluralism: A metaparadigm whose time has come. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2017; 11 :156–173. doi: 10.1177/1558689815607692. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson BR, Christensen LB. Educational research: Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed approaches. 6. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson BR, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Mixed methods research: a research paradigm whose time has come. Educational Researcher. 2004; 33 (7):14–26. doi: 10.3102/0013189X033007014. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson BR, Onwuegbuzie AJ, Turner LA. Toward a definition of mixed methods research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2007; 1 :112–133. doi: 10.1177/1558689806298224. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mathison S. Why triangulate? Educational Researcher. 1988; 17 :13–17. doi: 10.3102/0013189X017002013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maxwell JA. Qualitative research design: An interactive approach. 3. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maxwell, Joseph A., and Diane M. Loomis. 2003. Mixed methods design: An alternative approach. In Handbook of mixed methods in social & behavioral research , Eds. Abbas Tashakkori and Charles Teddlie, 241–271. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
- McMahon S. Understanding community-specific rape myths: Exploring student athlete culture. Affilia. 2007; 22 :357–370. doi: 10.1177/0886109907306331. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mendlinger S, Cwikel J. Spiraling between qualitative and quantitative data on women’s health behaviors: A double helix model for mixed methods. Qualitative Health Research. 2008; 18 :280–293. doi: 10.1177/1049732307312392. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan DL. Integrating qualitative and quantitative methods: a pragmatic approach. Los Angeles: Sage; 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse JM. Approaches to qualitative-quantitative methodological triangulation. Nursing Research. 1991; 40 :120–123. doi: 10.1097/00006199-199103000-00014. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse JM, Niehaus L. Mixed method design: Principles and procedures. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Onwuegbuzie AJ, Burke Johnson R. The “validity” issue in mixed research. Research in the Schools. 2006; 13 :48–63. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roth LM. Selling women short: Gender and money on Wall Street. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoonenboom J. The multilevel mixed intact group analysis: a mixed method to seek, detect, describe and explain differences between intact groups. Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 2016; 10 :129–146. doi: 10.1177/1558689814536283. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoonenboom, Judith, R. Burke Johnson, and Dominik E. Froehlich. 2017, in press. Combining multiple purposes of mixing within a mixed methods research design. International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches .
- Teddlie CB, Tashakkori A. Foundations of mixed methods research: Integrating quantitative and qualitative approaches in the social and behavioral sciences. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yanchar SC, Williams DD. Reconsidering the compatibility thesis and eclecticism: Five proposed guidelines for method use. Educational Researcher. 2006; 35 (9):3–12. doi: 10.3102/0013189X035009003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. Case study research: design and methods. 5. Los Angeles: SAGE; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]

Research & Writing Help
What is research, methods & types of data, research prep & study design, selecting a method or data.
- Finding Literature & Using Sources
Need Research Help?
Book an appointment with a librarian by emailing [email protected] .
Book an appointment with a writing center tutor.
Ethical Research Review Board (ERRB)
The Ethical Research Review Board (ERRB) at COA reviews proposals by COA faculty, students, and staff that involve research with human subjects. In accordance with federal law, all “research with human subjects” that requires ERRB review must receive approval before the research can begin.
Visit coa.edu/academic-services/errb/ to learn more.
Research is a systematic investigation of a particular topic or phenomenon with the purpose of generating new knowledge, building on existing scholarly work, and solving many social and environmental issues we face. Not all research is about generating universal truths. In fact, it is often not possible because nature and humans are incredibly complex, but we are able to identify trends and patterns.
Research is a fundamental activity in all academic and scholarly disciplines. Areas of scholarly inquiry are typically divided into three interconnected areas: humanities (such as philosophy, language, performing arts, visual arts), social sciences (such as psychology, linguistics, communication, business, anthropology), and natural sciences (such as chemistry, biology, physics, engineering).
Examples of research questions and methods:
- This type of question might be answered through community/home observations, interviews, and other ethnographic work in the community depending on the purpose and context of the study. If it was a question about formal language instruction, classroom observations would be appropriate as well.
- This type of question can be answered through archival work by examining publicly available newspaper articles, books, and journals that have been archived by local libraries or official government archives and libraries. Many newspapers and magazines are not available digitally, and researchers use microfilm (or microform) to read old newspapers.
- This might be answered by examining popular music from various countries to examine the interactions and migration of hip hop. Methods could include discourse analysis of publicly available documents, analysis of lyrics, but also interviews with artists and different audiences from various geographical locations or digital spaces.
- This type of work would require the researcher to collect YA novels and document how young adults are described and conceptualized.
- Entertainment provides a window into how humans understand and conceptualize different identities. While fictional, they are grounded in human perceptions and understandings. Examining movies and television shows from multimodal discursive perspectives would provide insights into how conceptualizations of identities have shifted over time.
Research methods are often placed in two categories: quantitative and qualitative. The method you use depends on what your research questions are. Choose your method after you have identified your research questions rather than making the method fit a project. Common ways of collecting data and conducting research include:
- Archival research (examining and analyzing documents)
- Interviews and oral histories (these can be structured, semi-structure, or unstructured depending on the purpose)
- Observations (these take place in classrooms, hospitals, community sites and so on depending on the needs of the study)
- Ethnography (this is an immersive method where researchers spend a lot of time on-site. This method includes many ways of collecting data: observations, interviews, potential participation in activities in the community, archival work and so on)
- Surveys (these can range in scope in terms of location, e.g., these can be regional but also national and international)
- Experiments with control groups (for instance, testing out the effectiveness of a particular teaching method)
- Experiments in labs to examine (for instance, reactions and compounds)
Spoken and interactional data require the researcher to transcribe the interviews/interactions verbatim. Transcripts need to be as accurate as possible, not only in terms of what was uttered, but also how they were uttered to accurately represent the voices of the participants. Using software to organize the data is helpful when the data set is large or consists of many different components. Examples of software that can do this include NVivo and Atlas.ti, and R (this is a programming language, unlike the other programs that are mentioned). Note that these are tools to support the researcher. These programs do not analyze or interpret the data for researchers. This is particularly useful for coding purposes when the data set consists of different types of primary sources.
Having a well thought-out research plan is an essential part of the research process. A research matrix can help you design a solid plan. It helps researchers visualize what they will do and how they might need to pivot as their research progresses. Critical questions to answer prior to starting your study include:
- What will you do?
- How will you do it?
- Why are you doing it?
- When will you do it?
Having a plan is great, however, it is common (if not the norm) that an unplanned event happens that requires you to alter your plans. Learning how to pivot is part of the process. Research is messy and not a linear path from point A to B because it is an iterative process. Common challenges:
- During the early stages of a research project, it is very likely that your topic is too broad or too narrow. Shift your focus to one area. Narrow it down and revise your research question(s). You might also discover a more interesting aspect of your topic that you want to explore. This is okay!
- Stay flexible and always create alternative plans, just in case (e.g., political disruptions, global health crises, financial constraints, difficulty in recruiting participants and so on can all significantly shift research plans). Do you need to collect additional data? Do you need to find additional data sources and participants? Do you need to modify your analytical approach?
- Research Matrix This research matrix will help you start designing your research project
- Research project timeline This document helps you create a detailed timeline of the different phases of your project. You can modify the file to meet your needs

Always let your questions and purpose guide your choice, rather than forcing a method to fit your work.
- If you're interested in understanding how students develop their literacy in a second language in order to develop more supportive pedagogical practices, a qualitative approach that focuses on classroom observations, interviews, and the analysis of assignments would be more helpful as they provide you with deep insights into the connections of teaching and learning.
- If you're interested in a large group of students' experiences, you might want to use a survey to collect as much data as possible, and possibly combine it with a couple of interviews. Again, it depends on your research questions and purposes.
- Or maybe you want to try a specific teaching approach, then an experiment with control groups would be more suitable.
- Next: Finding Literature & Using Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.coa.edu/researchwritinghelp
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Step 2: Data Type you Need for Research. Decide on the type of data you need for your research. The type of data you need to collect depends on your research questions or research hypothesis. Two types of research data can be used to answer the research questions: Primary Data Vs. Secondary Data.
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Frequently asked questions.
Here are the steps to write a research methodology: Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it's important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods. Describe your research design: Explain the ...
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles.
Provide the rationality behind your chosen approach. Based on logic and reason, let your readers know why you have chosen said research methodologies. Additionally, you have to build strong arguments supporting why your chosen research method is the best way to achieve the desired outcome. 3. Explain your mechanism.
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
Saunders et al. (2007) proposed the concept of the research onion model to help researchers develop a methodology and construct research design techniques within the field of future studies. The characteristic of research onion model is illustrated by its six main layers, which serve as a step-by-step guide for researchers on how to write a ...
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data. Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive, correlational, experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs. Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
When to Write Research Design. Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem.
Learn how to write a strong methodology chapter that allows readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research. A good methodology chapter incl...
To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of "Participants," "Materials," and "Procedures.". These headings are not mandatory—aim to organize your methods section using subheadings that make sense for your specific study. Note that not all of these topics will necessarily be relevant for your study.
Most frequently used methods include: Observation / Participant Observation. Surveys. Interviews. Focus Groups. Experiments. Secondary Data Analysis / Archival Study. Mixed Methods (combination of some of the above) One particular method could be better suited to your research goal than others, because the data you collect from different ...
4: Research Design Overview This section outlines your overall research design/methodology. It includes the list of steps in carrying out your research from data collection through data analysis. The two sections that follow elaborate in greater detail on the methods of data collection and the process of data analysis. The narrative in
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9. Research design—should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory. Research method—this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
A quantitative approach and statistical analysis would give you a bigger picture. 3. Identify how your analysis answers your research questions. Relate your methodology back to your original research questions and present a proposed outcome based on your analysis.
Designing and writing a qualitative dissertation methodology chapter can be done! Qualitative Dissertation Methodology: A Guide for Research Design and Methods functions as a dissertation advisor to help students construct and write a qualitative methodological framework for their research. Drawing from the challenges author Nathan Durdella has ...
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
Chapter 3. Research Design and Methodology. Chapter 3 consists of three parts: (1) Purpose of the. study and research design, (2) Methods, and (3) Statistical. Data analysis procedure. Part one ...
The purpose of this article is to help researchers to understand how to design a mixed methods research study. Perhaps the simplest approach is to design is to look at a single book and select one from the few designs included in that book. We believe that is only useful as a starting point.
Step 1: Define your variables. You should begin with a specific research question. We will work with two research question examples, one from health sciences and one from ecology: Example question 1: Phone use and sleep. You want to know how phone use before bedtime affects sleep patterns.
Methods & Types of Data. Research methods are often placed in two categories: quantitative and qualitative. The method you use depends on what your research questions are. Choose your method after you have identified your research questions rather than making the method fit a project. Common ways of collecting data and conducting research include:
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".