Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review
Systematic literature reviews may seem daunting at first, but they offer substantial benefits, especially in enhancing the theoretical framework for your research! Learn more about systematic literature reviews and their benefits. And have a look at a simple step-by-step guide that breaks down the daunting task of conducting a systematic literature review into simple, actionable steps.

What is a systematic literature review?
The difference between a systematic and a regular literature review, the difference between a systematic literature review and a meta-analysis, benefits of conducting a systematic literature review, google scholar to conduct a systematic literature review, web of science to conduct a systematic literature review, scopus to conduct a systematic literature review, step-by-step guide for conducting a systematic literature review.
Systematic literature reviews are a means to rigorously review existing literature on a specific topic. They collect and analyze existing literature in a systematic and replicable way.
Following the definition of a topic of interest and concrete research question, a systematic literature review starts by defining several keywords. Then, academic citation databases are used to retrieve all articles that include these keywords.
Furthermore, inclusion and exclusion criteria for sorting through the existing literature are set up. Think of a time frame, the type of publication (articles, books etc.), a geographic focus, and a disciplinary background. You name it.
Systematic literature reviews are a means to rigorously review existing literature on a specific topic. They collect and analyse existing literature in a systematic and replicable way.
While systematic literature reviews require a lot of work, they can convincingly draw conclusions on the state of the art of existing knowledge, uncover research gaps, and support the creation of new theoretical and conceptual frameworks.
In a systematic literature review, inclusion and exclusion criteria for sorting through the existing literature are set up. Think of a time frame, the type of publication (articles, books etc.), a geographic focus, and a disciplinary background.
Therefore, systematic literature reviews are crystal clear about the process of collecting and analyzing literature, which makes them replicable.
Before starting to consider whether a systematic literature review is right for you, it is important to be aware of the main differences between systematic and regular literature reviews.
The main differences between a systematic and a regular literature review are the process of collecting and analyzing literature, the accuracy of claims, the scope and replicability.
In a regular literature review, authors select articles or other publications ad hoc, to support the arguments of their work. Authors make claims about the state of the art of academic knowledge on a specific topic, but do not necessarily provide systematic evidence to support their claims.
Therefore, the level of accuracy differs in systematic and regular literature reviews.
Furthermore, authors doing regular literature reviews generally do not explain how they conducted their review, and how they selected relevant literature. Therefore, regular literature reviews are usually not replicable, whereas systematic ones are.
Additionally, the scope of a review differs immensely between systematic and regular literature reviews.
Systematic literature reviews tend to methodically analyze hundreds of articles, whereas regular literature reviews are much more limited in scope and highly selective in their choice of publications that are included.
Systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses are frequently confused or used interchangeably, but it’s important to understand that they are distinct methodologies.
While a meta-analysis focuses on synthesizing data and drawing broad conclusions from multiple studies, a systematic literature review is geared towards answering a well-defined research question with a comprehensive and methodical approach.
A meta-analysis involves the comprehensive analysis of results from multiple studies on a particular topic, aiming to identify patterns and draw generalized conclusions. These analyses often rely on statistical methods to combine data from various sources.
On the other hand, systematic literature reviews can take either a qualitative or quantitative approach. They are designed to address a specific and often novel research question, going beyond a mere summary of existing studies.
Conducting a ‘regular’ literature review is perfectly valid, but there are compelling reasons to consider a systematic literature review for certain research endeavors.
One primary advantage of a systematic review is its ability to address the overwhelming volume of relevant literature that can leave researchers, particularly master’s and PhD students, feeling daunted and unsure of when to stop searching for more material.
By conducting a systematic review, all pertinent literature can be analyzed within specific parameters, alleviating concerns about potentially missing critical information.
Moreover, a systematic literature review offers the advantage of identifying and showcasing research gaps, bolstering the academic significance of one’s work. This comprehensive approach to reviewing existing literature contributes to a stronger foundation for the research and its potential impact.
Additionally, by being transparent and explicit about the methodology employed in collecting and analyzing the literature, researchers enhance the credibility and reliability of their statements and arguments. This explicitness reinforces the trustworthiness of the research findings, which is crucial in the academic world.
Academic citation databases suitable for systematic literature reviews
To conduct systematic literature reviews, it is recommended to utilize a citation database that provides built-in features to refine search queries effectively.
Google Scholar is a widely used search engine among scholars, but its sidebar for limiting search queries is relatively basic. Despite this limitation, the advantage of using Google Scholar is that it is freely accessible to all users, including those without institutional affiliations.
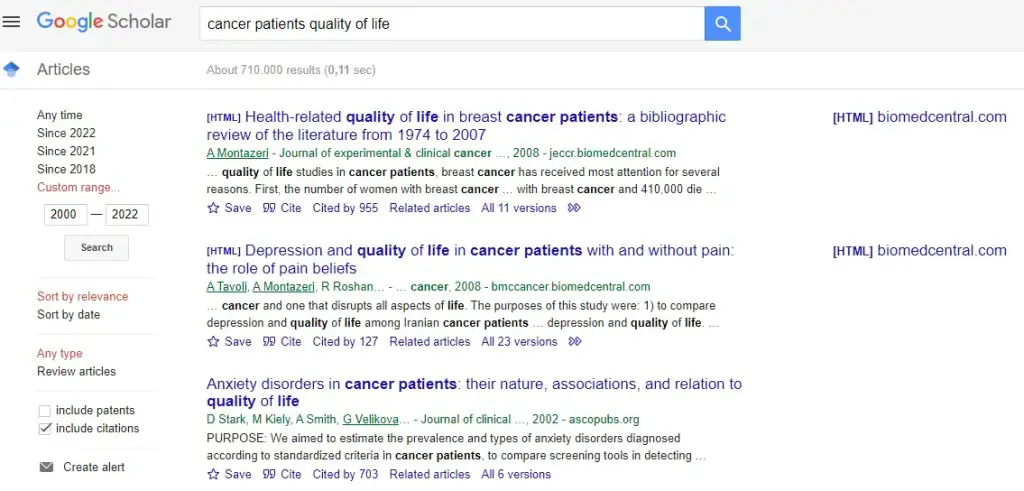
Web of Science has very elaborate search options. The search engine allows you to choose from various databases and indexes, such as the Science Citation Index or the Social Science Citation Index. Additionally, it enables you to search for keywords within topics or titles, as well as author names, affiliations, publication years, and more.
Web of Science provides a wide range of Booleans (depicted in the image below on the right) that you can utilize to precisely specify your search criteria. Booleans are a system of logic employed in programming and computer sciences, featuring operators like “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT.” By using these operators, you can fine-tune your search queries and filter results to precisely match what you are looking for.
After obtaining search results on Web of Science, you have the option to further refine and organize them based on various criteria, such as research areas, disciplines, languages, regions, document types, and more.
Although it may require some time and practice to become proficient in developing precise search queries on Web of Science, the database offers tremendous opportunities for conducting systematic literature reviews. Its extensive filtering and organizing features empower researchers to gather comprehensive and relevant literature on specific topics.
Scopus the citation database by publisher Elsevier, boasts access to over 36,000 journals. Its layout and search options closely resemble those of Web of Science, making it a highly recommended platform to explore for research purposes. If you are familiar with Web of Science, you will find Scopus user-friendly and worthwhile to explore for comprehensive academic content.
Citation databases can be utilized in combination for more comprehensive research. It is recommended to begin with popular ones like Web of Science and Scopus, as they provide extensive coverage. However, using additional databases can serve as a valuable double-check to ensure no relevant entries are overlooked. Employing multiple databases enhances the likelihood of capturing a comprehensive range of scholarly materials for your research.
While each systematic literature review is unique, there are commonly followed steps that serve as a foundation for the process:
- Clearly define a focused and narrow research question.
- Identify relevant keywords to lead you to articles that can potentially answer your research question.
- Choose a suitable citation database and establish inclusion and exclusion criteria, considering factors like timeframe, discipline, journal, research area, and geographical context.
- Download all pertinent results, which may amount to hundreds of articles.
- Systematically screen all titles and abstracts, manually excluding irrelevant articles based on your criteria.
- Create your own database, such as using Excel, to store the remaining entries and read them more thoroughly.
- Categorize the entries and/or their content in a way that provides meaningful insights to answer your research question.
- Develop visual representations like graphs and tables to present your results.
- Write a concise and engaging presentation of your findings, summarizing the key outcomes of the systematic review.
Following these steps will help you conduct a thorough and well-organized systematic literature review.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
Getting the most out of thesis supervision meetings
Separating your self-worth from your phd work, related articles.

25 short graduation quotes: Inspiration in four words or less

Journal vs conference papers: Key differences & advice

The 11 best AI tools for academic writing

How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Doing a Systematic Review: A Student's Guide
Student resources, chapter 1. carrying out a systematic review as a master's thesis.
Here are some other helpful materials for you to read through.
Centre for Review and Dissemination’s guidance for undertaking systematic reviews in health care
www.york.ac.uk/crd/guidance

Writing your thesis and conducting a literature review
- Writing your thesis
Your literature review
- Defining a research question
- Choosing where to search
- Search strings
- Limiters and filters
- Developing inclusion/exclusion criteria
- Managing your search results
- Screening, evaluating and recording
- Snowballing and grey literature
- Further information and resources
Most PhD and masters’ theses contain some form of literature review to provide the background for the research. The literature review is an essential step in the research process. A successful literature review will offer a coherent presentation and analysis of the existing research in your field, demonstrating:
- Your understanding of the subject area
- Gaps in current knowledge (that may in turn influence the direction of your research)
- Relevant methodologies
There are different approaches and methods to literature reviews, and you may have heard of terms like systematic, structured, scoping or meta-analysis. This is when the literature review becomes the research methodology in its own right, instead of forming part of the research process.
This table shows the differences between a traditional literature review and a structured or systematic literature review.
Structured vs traditional literature reviews
What is a traditional literature review?
A traditional literature review is a critical review of the literature on a particular topic. The aim of this type of literature review is to identify any background research on your topic and to evaluate the quality and relevance of the literature. You will use your literature review to understand what has already been researched, help develop your research questions and the methodology that you should follow to collect and to identify any areas that your research can explore. You want your research to be unique so you will use a literature review to prevent you duplicating any previous research but also identifying any errors or mistakes that you would want to avoid.
A literature review is aimed at Masters (MSc students) and research level.
What is a structured literature review?
A structured literature review involves bringing many research studies together to use them as the data to determine findings (known as secondary research). There is no other form of data collection involved such as creating your own surveys and questionnaires (primary research). This approach allows you to look beyond one dataset and synthesise the findings of many studies to answer your clearly formulated research question.
Sometimes a structured review can be described as being a systematic literature review. A structured review typically does not fulfil all of the criteria for a full systematic review but may take a similar approach by taking a systematic, step by step method to find literature. They tend to follow a set protocol for determining the research studies to be included and every stage is documented.
To help you prepare for your structured literature review please complete this interactive workbook.
For Logistics students only
To help you prepare for your systematic literature review please complete this interactive workbook.
What is a systematic literature review?
A systematic literature review is a specific research methodology to identify, select, evaluate, and synthesise relevant published and unpublished literature to answer a particular research question. The systematic literature review should be transparent and replicable, you should follow a predetermined set of inclusion and exclusion criteria to select studies and help minimise bias. A systematic literature review may be registered, so that others can discover and minimise duplication, and can take several years to complete.
The systematic literature review is aimed at research (PhD students) level.
Useful background reading
Cranfield Libraries have several books offering guidance on how to approach and conduct literature reviews, and structured or systematic literature reviews:
- Reading list for literature review and study skills
- Reading list of items to support a structured or systematic literature review
Looking at previous structured and systematic literature reviews is an effective way to understand what is required and how they should be structured and written up. Structured literature reviews can be found in the Masters Thesis Archive (MTA) and systematic literature reviews can be found in the Cranfield University institutional Repository, CERES. Check out the Theses link.
- << Previous: Writing your thesis
- Next: Defining a research question >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://library.cranfield.ac.uk/writing-your-thesis
Press ESC to close
A roadmap for writing a literature review in a master’s thesis: Examples and guidelines
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- December 27, 2023

writing a literature review is an essential part of any master’s thesis. IT involves critically evaluating and synthesizing existing research to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-written literature review demonstrates your understanding of the scholarly conversation surrounding your research topic and helps to contextualize your own work within the broader academic landscape.
1. Understand the purpose of a literature review
Before you begin writing your literature review, IT ‘s important to understand its purpose. A literature review serves several key functions, including:
- Providing a comprehensive overview of existing research in your field.
- Critically evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of previous studies.
- Identifying gaps in the literature and highlighting areas for future research.
- Contextualizing your own research within the broader academic discourse.
By clearly understanding the purpose of your literature review, you can ensure that your writing is focused and relevant to your thesis.
2. Conduct a comprehensive literature search
Once you have a clear understanding of the purpose of your literature review, the next step is to conduct a comprehensive search for relevant academic sources. This involves searching for peer-reviewed journal articles, books, conference proceedings, and other scholarly publications related to your research topic.
IT ‘s important to use a variety of search strategies, including keyword searches, citation tracking, and database searches, to ensure that you are capturing all relevant literature. Additionally, consider using citation management software to organize and manage your references.
For example, if your master’s thesis is about the impact of social media on mental health, you would want to search for literature that examines the relationship between social media use and psychological well-being. This might include studies on social media usage patterns, the prevalence of mental health issues among social media users, and the potential benefits and drawbacks of social media use.
3. Analyze and synthesize the literature
Once you have gathered a comprehensive collection of literature related to your research topic, the next step is to analyze and synthesize the information. This involves critically evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each study, identifying key themes and patterns across the literature, and synthesizing the findings into a coherent narrative.
When analyzing and synthesizing the literature, consider the following questions:
- What are the main findings and arguments of each source?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of each study?
- What key themes and patterns emerge across the literature?
Using the example of the impact of social media on mental health, you might identify several key themes that emerge across the literature, such as the relationship between social media use and depression, the role of cyberbullying in affecting mental well-being, and the potential benefits of online peer support networks.
4. Write the literature review
With a clear understanding of the purpose of your literature review, a comprehensive collection of relevant literature, and a synthesized analysis of the existing research, you are now ready to write your literature review. When writing your literature review, consider the following guidelines:
- Provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the existing literature in your field.
- Critically evaluate and synthesize the key findings and arguments of each source.
- Organize the literature thematically or chronologically to highlight key patterns and developments in the research.
- Keep the focus on how each source relates to your research topic and thesis.
Continuing with the example of the impact of social media on mental health, your literature review might be organized into sections that correspond to the key themes you identified during your analysis. Each section could summarize and evaluate the existing literature on a specific aspect of the relationship between social media use and mental well-being, providing a clear overview of the current state of knowledge in the field.
5. Conclusion
Overall, writing a literature review for your master’s thesis involves understanding the purpose of the literature review, conducting a comprehensive literature search, analyzing and synthesizing the literature, and writing a well-organized and critical review of the existing research. By following these guidelines and examples, you can ensure that your literature review effectively contextualizes your own research within the broader academic discourse.
Q: How long should a literature review be?
A: The length of a literature review can vary depending on the requirements of your master’s thesis and the depth and breadth of the existing literature. In general, a literature review for a master’s thesis is typically around 3000-5000 words, but this can vary based on the specific expectations of your program or advisor.
Q: How many sources should I include in my literature review?
A: The number of sources you include in your literature review will depend on the scope of your research topic and the expectations of your program or advisor. In general, a literature review for a master’s thesis should include a comprehensive collection of relevant sources, typically ranging from 20-50 academic articles, books, and other scholarly publications.
Top 10 Recording Software for Professional Sound Engineering
Designing a professional website with a web hosting wordpress theme.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

Unlocking the Secrets to Boosting Your Alexa Rank, Google Pagerank, and Domain Age – See How You Can Dominate the Web!

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!

10 Tips for Creating a Stunning WordPress Theme
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
Structured literature reviews – A guide for students
This is a step-by-step guide aimed at Master's students undertaking a structured literature review as part of their Master's thesis.
There are several different kinds of literature reviews, but any literature review typically includes an extensive literature search. Whenever a systematic approach is used, the literature search features a methodical step-by-step procedure. However, as a Master's student, it might not be possible to fulfill all the criteria of a systematic review when writing a literature review-based thesis; you should rather do a structured literature review, which will include only certain aspects of the systematic review methodology.
In this guide we will go through the different steps of a structured literature review and provide tips on how to make your search strategy more structured and extensive. Additionally, make sure to follow any programme and course specific requirements.
Step 1: Formulate and delimit your research question
- It will be much easier for you to perform a structured information search if you first define and delimit your research question in a clear way.
- One way to define and structure your question is to break it down into different parts .
- PICO and PEO are two different frameworks that can be used for breaking down a research question into different parts.
- You also need to define the most important key concepts of your research question.
The formulation of your research question is partly connected to what kind of literature review you are doing. This article by Maria J. Grant and Andrew Booth usefully compares different kinds of reviews . While a systematic literature review is usually grounded in a clearly delimited and structured question, a scoping review may, for instance, feature a wider problem formulation. The wider a research question is, the larger number of search hits it tends to generate.
To be able to perform a literature review, you need to consider a subject area in which there seems to be a sufficiently large number of original research studies. Therefore, it may be a good idea to test search a database for previous research on the subject while you are trying to formulate and delimit your research question.
One way to structure your research question is to break it down into different parts. A well-delimited question often consists of three to four different parts. PICO and PEO are two examples of frameworks that can help you identify and define your research question.
- PICO ( P opulation, I ntervention, C omparison, O utcome) is primarily used for quantitative research questions.
- PEO ( P opulation, E xposure, O utcome) is primarily used for qualitative research questions.
Structuring your research question in accordance with a framework, such as PICO or PEO, will also help you decide on the inclusion and exclusion criteria of your literature review.
PICO & PEO
After you have delimited your research question, you also need to identify the key concepts that make up your question. Based on these key concepts, you will create " search blocks " that you will use to organise your search terms.
Step 2: Find search terms and create search blocks
- Test searching is a good way to investigate the terminology of a subject area and find search terms.
- Reading key articles can help you gather additional search terms for your final search strategy.
- Find subject headings for PubMed with the help of the US National Library of Medicine's MeSH database.
- Find& free-text search terms by investigating what words that occur in the title and abstract of relevant articles.
- A good way of achieving a structured final search query is to arrange your search terms into search blocks ; these blocks should arise from the key concepts of your research question.
While working on a literature review-based thesis, you will need to search for articles on several occasions. In the beginning of your project, it is often good to do a couple of unstructured and simple search queries, so-called test searches, in academic databases. This way you are off to a good start, as test searching helps you investigate the terminology of your subject area and find relevant search terms. While the final search strategy is typically reported in full, you don't need to present your test queries in your thesis.
Try to find a couple of key articles, that is, articles that correspond to the type of studies that you are planning to include in your review. Use key articles to gather additional search terms for your final search strategy. Analyse the terminology of your key articles by examining what subject headings (MeSH terms, etc.) that the articles have been tagged with and what words that occur in the titles and abstracts.
Test search - find keywords and narrow down your topic
Test search in pubmed & cinahl.
To retrieve as many relevant studies as possible, you will need to include free-text search terms as well as subject headings in your final search strategy. Free-text search terms are words that occur in the article's title and abstract – words used by the authors themselves. Subject headings are subject-related words that an article is tagged with when the article is added to the database.
- In PubMed , articles are tagged with MeSH terms ( Me dical S ubject H eadings). You can look up and browse MeSH terms in the US National Library of Medicine's MeSH database .
- Databases such as CINAHL , PsycInfo , ERIC , and Sociological Abstracts have their own subject heading lists; look up subject headings in each database's subject heading list.
- There are also so-called free-text databases, such as Web of Science . These databases lack subject heading lists. Hence, when searching a free-text database, you can only use free-text search terms.
Find subject headings
An effective way to increase the structure of your final search strategy is to arrange your search terms in so-called search blocks . Create your search blocks based on the key concepts of your research question.
Create search blocks
This search strategy worksheet might help you document and organise your search terms.
Download worksheet
- Worksheet for search terms (Word, 30.54 KB)
Step 3: Search in a structured way
- To get a comprehensive search result, you will need to search for articles in several different databases .
- Your search strategy should be as uniform as possible in every database, but you may have to adapt your use of subject headings .
- As you search the databases, combine your search terms and blocks with the help of AND and OR .
- Save time by documenting your search queries .
When doing a literature review-based thesis it is often wise to use at least two different databases. Many databases overlap, but may also contain unique content. At KI it is common for Master's students to use PubMed and Web of Science when doing a structured literature review as part of their Master's thesis. Depending on your research question, other databases may also be appropriate and useful. Read more about the most frequently used databases at KI .
Your search strategy should be as uniform as possible in every database. However, as mentioned in Step 2, databases may use different subject headings, and some databases only let you use free-text search terms. This means that you need to adapt your use of subject headings depending on the database.
Example: How subject headings may differ between databases
If you want to search for articles about day surgery in PubMed, you should use the MeSH term Ambulatory Surgical Procedures . However, if you also want to perform your search in a database such as CINAHL, you need to use the corresponding CINAHL Headings term instead: Ambulatory Surgery .
There are many different ways of searching databases. Most databases have one simple, basic Google-like search box and one advanced search form. One advantage of the latter is that combining search terms with AND and OR is usually easier in an advanced search form, especially if you will be using both AND and OR within the same search query. However, you can often combine search terms with AND and OR in a basic search box too, and in that case, you often isolate your different search blocks from each other by enclosing each block in parentheses.
Example: A search query that contains AND, OR, and parentheses
( inflammatory bowel diseases OR ulcerative colitis OR crohn disease) AND (adolescent OR child OR young adult OR teenager) AND (self-management OR self care OR self efficacy )
By choosing the advanced search form you will also be able to exert more control over your search process. The advanced search form lets you specify more closely and decide exactly how you want the database to interpret your search terms; this way you can make your search query more precise.
You should always document your search strategy in order to remember what search terms you have used, how these search terms have been combined, and whether you have applied any limits to your search. The easiest way to do this is to copy and paste your search history from the database into a text document. Also, academic databases often let you create a personal account, so that you may save your searches online.
How to do a structured search in PubMed
Step 4: narrowing or broadening your search.
- Briefly examine your search results to see if you need to narrow or broaden your search query.
- Investigate whether your key articles are present in the search results.
- By using the advanced search form you can improve your search.
Prepare yourself for having to modify and redo your search query several times, before deciding on your final search strategy. After you have combined all your search terms and made your very first database search, you should examine the search results and analyse whether your search query is able to generate the type of search hits that you are looking for.
Analyse your search results
- Are all your key articles present in the search results, or are there some key articles that your search query is unable to retrieve?
- Are you getting too few search hits ? Investigate why. Perhaps you need to remove one of your search blocks, add one or several synonyms within a search block, or search for parts of words by truncating one or several of your free-text search terms, in order to broaden your search ?
- Does your search strategy generate too many non-relevant search hits that have nothing to do with your research question? Investigate why. Perhaps you need to add another search block, remove one of the synonyms from one of your search blocks, or search for phrases by enclosing one or several of your free-text terms in quotation marks, in order to narrow your search ?
- More tips on how to improve your search strategy .
It is important to remember that there is nothing wrong, per se, if your search query generates irrelevant hits. This is quite normal when performing a structured literature search. What's important is that your search strategy is able to retrieve the type of articles that you are looking for, and that you are not overwhelmed by the total number of hits (given the time frame of your thesis project).
We recommend that you use the advanced search form when improving your search strategy. By using the advanced search form, you will for example be able to specify which search fields your search terms must be present in.
Narrowing your search
Broaden your search, how to specify the field you would like to search in pubmed, step 5: select and review articles.
- After you have completed your search, you will need to go through all your search hits and select which articles to include in your review.
- When selecting articles, read through the titles and abstracts of each article to decide its relevancy .
- Check the quality of each study that you include in your review.
- When checking the quality of articles, it is common to use critical appraisal worksheets or checklists .
Selecting articles
When you have completed and feel satisfied with your search, it is time to go through all the search hits and select which studies to include in your review. All relevant studies, that is, those studies that correspond to your research question and your previously set inclusion criteria, should be included. You decide on the relevancy of a study primarily by reading through the title and abstract. If you feel unsure, go through the whole article. You can describe your selection process with the help of a flow chart, such as the frequently used PRISMA flow diagram .
One of the challenges of systematic literature searches is that the search strategy should be exhaustive, but at the same time the number of search hits also needs to be kept within reasonable boundaries. A search query needs to be broad enough to retrieve all relevant studies, but on the other hand, this also means that a large portion of the search results will be irrelevant. Hence, even though your search strategy may have generated hundreds of hits, it is fine to only include ten to twenty articles in your review in the end.
Saving articles
If you create a personal account in a database it will be easier for you to save any references that you may find there. Another way of saving and organising article references is to use reference management software. There are several different reference management software, for example Endnote Online and Zotero.
Read more about reference management and see software guides.
Reviewing articles
When you have made your selection, you should critically examine the quality of all articles included in your review. The assessment is typically performed with the help of a critical appraisal guide or checklist. The purpose is to assess the reliability of the study results and whether there are any methodological flaws that may have impacted the results. Qualitative research articles are often reviewed with a focus on authenticity, credibility, and validity.
There are many different critical appraisal worksheets and checklists. Some examples are the SBU checklists for assessing the quality of randomized studies, observational studies, and qualitative research. In the course book How to do a systematic review in nursing there is a review guide that can be used for assessing different kinds of studies (both qualitative and quantitative); the original source is Caldwell, Henshaw & Taylor, 2011 .
Review worksheets and checklists contain criteria and questions that may help you identify flaws, errors, or bias. Sometimes different aspects of the study are scored separately. Later, all scores make up a final score that indicates whether the study is of high, medium, or low quality.
Many programmes and courses provide instructions on which checklists to use when reviewing articles, so check your course guidelines.
Step 6: Report your search strategy
- Describe your search strategy in a manner that makes it possible for your readers to replicate the search and get the same results.
- The search strategy is often presented in the form of a table .
- Look at the search history to see what words and limits that you have used when searching a database.
An important aspect of doing a structured literature review is transparency. It has to be easy for your readers to follow what you did when you searched and selected the articles that you have included in your review. In the method section of your literature review you should describe how you searched different databases. This is also where you describe any manual searches that you did. Search strategies are commonly reported in the form of tables. Present one table for each database.
You can examine your search terms and any limits you have applied when searching a database by visiting its search history.
Read more about how to report your search strategy and view examples.

Checklist for search strategies
Here is a checklist to help you review your own or someone else's search strategy.
If you would like us to get back to you, please submit your contact information in the form below along with your feeback.
- Open access
- Published: 12 December 2017
Acceptance of a systematic review as a thesis: survey of biomedical doctoral programs in Europe
- Livia Puljak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8467-6061 1 , 2 , 3 &
- Damir Sapunar 3
Systematic Reviews volume 6 , Article number: 253 ( 2017 ) Cite this article
15k Accesses
21 Citations
66 Altmetric
Metrics details
Systematic reviews (SRs) have been proposed as a type of research methodology that should be acceptable for a graduate research thesis. The aim of this study was to analyse whether PhD theses in European biomedical graduate programs can be partly or entirely based on SRs.
In 2016, we surveyed individuals in charge of European PhD programs from 105 institutions. The survey asked about acceptance of SRs as the partial or entire basis for a PhD thesis, their attitude towards such a model for PhD theses, and their knowledge about SR methodology.
We received responses from 86 individuals running PhD programs in 68 institutions (institutional response rate of 65%). In 47% of the programs, SRs were an acceptable study design for a PhD thesis. However, only 20% of participants expressed a personal opinion that SRs meet the criteria for a PhD thesis. The most common reasons for not accepting SRs as the basis for PhD theses were that SRs are ‘not a result of a PhD candidate’s independent work, but more of a team effort’ and that SRs ‘do not produce enough new knowledge for a dissertation’. The majority of participants were not familiar with basic concepts related to SRs; questions about meta-analyses and the type of plots frequently used in SRs were correctly answered by only one third of the participants.
Conclusions
Raising awareness about the importance of SRs and their methodology could contribute to higher acceptance of SRs as a type of research that forms the basis of a PhD thesis.
Peer Review reports
Systematic reviews (SRs) are a type of secondary research, which refers to the analysis of data that have already been collected through primary research [ 1 ]. Even though SRs are a secondary type of research, a SR needs to start with a clearly defined research question and must follow rigorous research methodology, including definition of the study design a priori, data collection, appraisal of study quality, numerical analyses in the form of meta-analyses and other analyses when relevant and formulation of results and conclusions. Aveyard and Sharp defined SRs as ‘original empirical research’ because they ‘review, evaluate and synthesise all the available primary data, which can be either quantitative or qualitative’ [ 2 ]. Therefore, a SR represents a new research contribution to society and is considered the highest level in the hierarchy of evidence in medicine [ 3 ].
SRs have been proposed as a type of research methodology that should be acceptable as the basis for a graduate research thesis [ 4 , 5 ]. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the acceptance of SRs as the basis for PhD theses. A recent review addressed potential advantages and disadvantages of such a thesis type and presented opposing arguments about the issue [ 5 ]. However, there were no actual data that would indicate how prevalent one opinion is over another with regard to the acceptance of a SR as the primary research methodology for a PhD thesis. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess whether a PhD thesis in European biomedical graduate programs can be partly or entirely based on a SR, as well as to explore the attitudes and knowledge of individuals in charge of PhD programs with regard to a thesis of this type.
Participants
The Organization of PhD Education in Biomedicine and Health Sciences in the European System (ORPHEUS) includes 105 institutional members from 40 countries and six associate members from Canada, Georgia, Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan and the USA [ 6 ]. The ORPHEUS encompasses a network of higher education institutions committed to developing and disseminating best practice within PhD training programs in biomedicine, health sciences and public health. ORPHEUS approved the use of their mailing list for the purpose of this study. The mailing list had 1049 contacts. The study authors were not given the mailing list due to data protection and privacy. Instead, it was agreed that ORPHEUS officials would send the survey via email to the mailing list. The General Secretary of the ORPHEUS contacted individuals responsible for PhD programs (directors or deputy directors) among the institutional members, via e-mail, on 5th of July 2016. These individuals were sent an invitation to complete an online survey about SRs as the basis for PhD theses. We invited only individuals responsible for PhD programs (e.g., directors, deputy directors, head of graduate school, vice deans for graduate school or similar). We also asked them to communicate with other individuals in charge of their program to make sure that only one person per PhD program filled out the survey. If there were several PhD programs within one institution, we asked for participation of one senior person per program.
The survey was administered via Survey Monkey (Portland, OR, USA). The survey took 5–10 min to complete. One reminder was sent to the targeted participants 1 month after the first mail.
The ethics committee of the University of Split School of Medicine approved this study, which formed part of the Croatian Science Foundation grant no. IP-2014-09-7672 ‘Professionalism in Health Care’.
Questionnaire
The 20-item questionnaire, designed specifically for this study by both authors (LP and DS), was first tested for face validity and clarity among five individuals in charge of PhD programs. The questionnaire was then modified according to their feedback. The questionnaire included questions about their PhD program; whether PhD candidates are required to publish manuscript(s) before thesis defence; the minimum number of required manuscripts for defending a PhD thesis; the authorship requirements for a PhD candidate with regard to published manuscript(s); whether there is a requirement for a PhD candidate to publish manuscript(s) in journals indexed in certain databases or journals of certain quality, and how the quality is defined; the description about other requirements for defending a PhD thesis; whether a SR partly or fully meets requirements for approval of a PhD thesis in their graduate program; what are the rules related to the use of a SR as the basis for a PhD thesis; and the number of PhD theses based on SRs relative to other types of research methods.
Participants were also asked about their opinion with regard to the main reasons that SRs are not recognised in some institutions as the basis for a doctoral dissertation, and their opinion about literature reviews, using a four-item Likert scale, ranging from ‘agree’ to ‘disagree’, including an option for ‘don’t know’. In the last question, the participants’ knowledge about SR methodology was examined using nine statements; participants had to rate each statement as either ‘correct’, ‘incorrect’, ‘unsure’ or ‘I don’t know’. Finally, participants were invited to leave their email address if they wanted to receive survey results. The survey sent to the study participants can be found in an additional file (Additional file 1 ).
Data analysis
Survey responses were entered into a spreadsheet, checked by both authors and analysed using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Inc., Redmond, WA, USA). Descriptive data are presented as frequencies and percentages. All raw data and analysed data sets used in the manuscript are available from authors on request. A point-biserial correlation (SPSS, IBM, Chicago, IL, USA) was used to measure the strength of the association between results on the knowledge test (continuous variable) and the attitude towards SRs as the basis for dissertations (dichotomous variable; we used the answer to the following question as this measure: ‘Do you agree that a systematic review, in whole or in part, meets the criteria for a publication on which a doctoral dissertation can be based?’).
Study participants
There are 105 institutions included in the ORPHEUS network. We received a response from 86 individuals representing 68 institutions from 37 countries (65% institutional response rate). There were more respondents than institutions because some institutions have several PhD programs and thus several program directors. Those responders were used as a unit of analysis in the analysis of attitudes and knowledge; institutions were the unit of analysis when analysing criteria for theses. Some of the questionnaires ( n = 15) were only partly completed. In most cases, the missing data were related to knowledge about SR methodology.
Overview of requirements for a dissertation
Based on the information provided by the graduate program directors, in the majority of the included PhD programs, students were required to publish a research manuscript prepared within their PhD thesis prior to their thesis defence (83%; n = 64). Among 13 programs (17%) that did not have this requirement, five respondents (38%) indicated that in their opinion their school’s rules related to a PhD thesis should be changed such as to specify that each thesis should be based on work that is already published in a journal.
The minimum number of published manuscripts necessary for the PhD thesis defence was prespecified in 94% ( n = 60) of the programs that required publication of research manuscripts prior to the thesis defence. In most of the programs (37%; n = 22), the number of required manuscripts was three or more. Two manuscripts were required in 30% ( n = 18) and one was required in 33% ( n = 20) of the programs. In four programs, there was no formal policy on this matter, but there was a strong expectation that the student will have contributed substantially to several manuscripts in peer-reviewed journals.
In most cases, the PhD candidates’ contribution to published manuscripts within the PhD thesis was determined through first authorship. A requirement that a PhD candidate should be the first author on a manuscript(s) that constitutes a PhD thesis was reported in 82% ( n = 64) of the graduate programs.
In 60% ( n = 52) of the graduate programs, the quality of the journals where a PhD candidate has to publish research manuscripts as a part of a PhD thesis was defined by the database in which these journals are indexed. The most commonly specified databases were Web of Science (41%; n = 35) and MEDLINE/PubMed (13%; n = 11), followed by Science Citation Index, Scopus, Current Contents, a combination of several databases or, in two cases, a combination of journals from a list defined by some governing body.
Systematic reviews as a PhD thesis
SRs, in whole or in part, met the criteria for acceptable research methodology for a PhD thesis in 47% ( n = 40) of programs, whereas 53% ( n = 46) of programs specifically stated that they did not accept SRs in this context (Fig. 1 a, b). Among the programs that accepted SRs, theses could be exclusively based on a SR in 42% ( n = 17) of programs, while in the remaining programs, SRs were acceptable as one publication among others in a dissertation.
a European PhD programs that recognise a systematic review as a PhD thesis (green dot) and those that do not (red dot). Half red and half green dots indicate the five universities with institutions that have opposite rules regarding recognition of a systematic review as a PhD thesis. The pie chart presents b the percentage of the programs in which systematic reviews, in whole or in part, meet the criteria for a dissertation and c the opinion of participants about whether systematic reviews should form the basis of a publication within a PhD dissertation
The majority of participants (80%; n = 69) indicated that SRs did not meet criteria for a publication on which a PhD dissertation should be based (Fig. 1 c). The main arguments for not recognising a SR as the basis for a PhD thesis are listed in Table 1 . The majority of respondents were neutral regarding the idea that scoping reviews or SRs should replace traditional narrative reviews preceding the results of clinical and basic studies in doctoral theses. Most of the respondents agreed that narrative or critical/discursive literature reviews preceding clinical studies planned as part of a dissertation should be replaced with systematic reviews (Table 2 ).
Most of the programs that accepted SRs as a research methodology acceptable for PhD theses had defined rules related to the use of an SR as part of a PhD thesis (Fig. 2 ). The most common rule was that a SR can be one publication among others within a PhD thesis. Some of the respondents indicated that empty (reviews that did not find a single study that should be included after literature search) or updated reviews could also be used for a PhD thesis (Fig. 2 ).
Frequency of different rules that define the use of systematic reviews as a part of a PhD thesis in European biomedical graduate programs
The results of the survey regarding knowledge about SR methodology indicated that the majority of respondents were not familiar with this methodology. Only three out of nine questions were correctly answered by more than 80% of the participants, and questions about meta-analyses and the type of plots frequently used in a SR were correctly answered by only one third of the participants (Table 3 ). The association between participants’ results on the knowledge test and attitudes towards SRs was tested using a point-biserial correlation; this revealed that lack of knowledge was not correlated with negative attitudes towards SRs ( r pb = 0.011; P = 0.94).
In this study conducted among individuals in charge of biomedical graduate programs in Europe, we found that 47% of programs accepted SRs as research methodology that can partly or fully fulfil the criteria for a PhD thesis. However, most of the participants had negative attitudes about such a model for a PhD thesis, and most had insufficient knowledge about the basic aspects of SR methodology. These negative attitudes and lack of knowledge likely contribute to low acceptance of SRs as an acceptable study design to include in a PhD thesis.
A limitation of this study was that we relied on participants’ responses and not on assessments of formal rules of PhD programs. Due to a lack of familiarity with SRs, it is possible that the respondents gave incorrect answers. We believe that this might be the case since we received answers from different programs in the same university, where one person claimed that SRs were accepted in their program, and the other person claimed that they were not accepted in the other program. We had five such cases, so it is possible that institutions within the same university have different rules related to accepted research methodology in graduate PhD programs. This study may not be generalisable to different PhD programs worldwide that were not surveyed. The study is also not generalisable to Europe, as there are no universal criteria or expectations for PhD theses in Europe. Even in the same country, there may be different models and expectations for a PhD in different higher education institutions.
A recent study indicated a number of opposing views and disadvantages related to SRs as research methodology for graduate theses, including lack of knowledge and understanding by potential supervisors, which may prevent them from being mentors and assisting students to complete such a study [ 5 ]. This same manuscript emphasised that there may be constraints if the study is conducted in a resource-limited environment without access to electronic databases, that there may be a very high or very low number of relevant studies that can impact the review process, that methods may not be well developed for certain types of research syntheses and that it may be difficult to publish SRs [ 5 ].
Some individuals believe that a SR is not original research. Indeed, it has been suggested that SRs as ‘secondary research’ are different than ‘primary or original research’, implying that they are inferior and lacking in novelty and methodological rigour as compared to studies that are considered primary research. In 1995, Feinstein suggested that such studies are ‘statistical alchemy for the 21st century’ and that a meta-analysis removes or destructs ‘scientific requirements that have been so carefully developed and established during the 19th and 20th centuries’ [ 7 ]. There is little research about this methodological issue. Meerpohl et al. surveyed journal editors and asked whether they consider SRs to be original studies. The majority of the editors indicated that they do think that SRs are original scientific contributions (71%) and almost all journals (93%) published SRs. That study also highlighted that the definition of original research may be a grey area [ 8 ]. They argued that, in an ideal situation, ‘the research community would accept systematic reviews as a research category of its own, which is defined by methodological criteria, as is the case for other types of research’ [ 8 ]. Biondi-Zoccai et al. pointed out that the main criteria to judge a SR should be its novelty and usefulness, and not whether it is original/primary or secondary research [ 9 ].
In our study, 80% of the participants reported negative attitudes, and more than half of the respondents agreed with a statement that SRs are ‘not a result of the candidate’s independent work since systematic reviews tend to be conducted by a team’. This opinion is surprising since other types of research are also conducted within a team, and single authorship is very rare in publications that are published within a PhD thesis. On the contrary, the mean number of authors of research manuscripts is continuously increasing [ 10 ]. At the very least, the authors of manuscripts within a PhD will include the PhD candidate and a mentor, which is a team in and of itself. Therefore, it is unclear why somebody would consider it a problem that a SR is conducted within a team.
The second most commonly chosen argument against such a thesis was that SRs ‘do not produce enough new knowledge for a dissertation’. The volume of a SR largely depends on the number of included studies and the available data for numerical analyses. Therefore, it is unfair to label a SR as a priori lacking in new knowledge. There are SRs with tens or hundreds of included studies, and some of them not only include meta-analyses, but also network meta-analyses, which are highly sophisticated statistical methods. However, limiting SRs within a thesis only to those with meta-analysis would be unfair because sometimes meta-analysis is not justified due to clinical or statistical heterogeneity [ 11 ] and the presence or absence of a meta-analysis is not an indicator of the quality of a SR. Instead, there are relevant checklists for appraising methodological and reporting quality of a SR [ 12 , 13 ].
The third most commonly chosen argument against SRs within PhD theses was ‘lack of adequate training of candidates in methodology of systematic reviews’. This could refer to either insufficient formal training or insufficient mentoring. The graduate program and the mentor need to ensure that a PhD candidate receives sufficient knowledge to complete the proposed thesis topic. Successful mentoring in academic medicine requires not only commitment and interpersonal skills from both the mentor and mentee, but also a facilitating institutional environment [ 14 ]. This finding could be a result of a lack of capacity and knowledge for conducting SRs in the particular institutions where the survey was conducted, and not general opinion related to learning a research method when conducting a PhD study. Formal training in skills related to SRs and research synthesis methods [ 15 , 16 ], as well as establishing research collaborations with researchers experienced in this methodology, could alleviate this concern.
One third of the participants indicated a ‘lack of appreciation of systematic review methodology among faculty members’ as a reason against such a thesis model. This argument, as well as the prevalent negative attitude towards SRs as PhD theses, perhaps can be traced to a lack of knowledge about SR methodology; however, although the level of knowledge was quite low in our study, there was no statistically significant correlation between knowledge and negative attitudes. Of the nine questions about SR research methodology, only three questions were correctly answered by more than half of the participants. This could be a cause for concern because it has been argued that any health research should begin with a SR of the literature [ 17 ]. It has also been argued that the absence of SRs in the context of research training might severely hamper research trainees and may negatively impact the research conducted [ 18 ]. Thus, it has been recommended that SRs should be included ‘whenever appropriate, as a mandatory part of any PhD program or candidature’ [ 18 ].
It has recently been suggested that the overwhelming majority of investment in research represents an ‘avoidable waste’ [ 19 ]. Research that is not necessary harms both the public and patients, because funds are not invested where they are really necessary, and necessary research may not be conducted [ 17 ]. This is valid not only for clinical trials, but also for other types of animal and human experiments [ 20 ]. SRs can help improve the design of new experiments by relying on current evidence in the field and by helping to clarify which questions still need to be addressed. SRs can be instrumental in improving methodological quality of new experiments, providing evidence-based recommendations for research models, reducing avoidable waste, and enabling evidence-based translational research [ 20 ].
Four respondents from three institutions indicated that empty SRs are accepted as a PhD thesis. While it makes sense to include such a SR as a part of the thesis to indicate lack of evidence in a certain field, it is highly unlikely that an entire thesis can be based on an empty SR, without a single included study.
There are many advantages of a SR as a graduate thesis [ 4 , 5 ], especially as a research methodology suitable for low-resource settings. A PhD candidate can prepare a Cochrane SR as a part of the PhD thesis, yielding a high-impact publication [ 4 ]. Non-Cochrane SRs can also be published in high-impact journals. A PhD candidate involved in producing a SR within a PhD thesis goes through the same research process as those conducting primary research, from setting up a hypothesis and a research question, to development of a protocol, data collection, data analysis and appraisal, and formulation of conclusions. Graduate programs can set limits, such as the prevention of empty reviews and the recognition of updated reviews as valid for a PhD thesis, and engage experienced researchers as advisors and within thesis evaluation committees, to ensure that a candidate will conduct a high-quality SR [ 4 ]. Conducting a SR should not be mandatory, but candidates and mentors willing to produce such research within a graduate program should be allowed to do so.
Further studies in this field could provide better insight into attitudes related to SRs as graduate theses and explore interventions that can be used to change negative attitudes and improve knowledge of SRs among decision-makers in graduate education.
Raising awareness about the importance of SRs in biomedicine, the basic aspects of SR methodology and the status of SRs as original secondary research could contribute to greater acceptance of SRs as potential PhD theses. Our results can be used to create strategies that will enhance acceptance of SRs among graduate education program directors.
Gopalakrishnan S, Ganeshkumar P. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: understanding the best evidence in primary healthcare. J. Fam. Med Prim Care. 2013;2(1):9–14.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Aveyard H, Sharp P. A beginner’s guide to evidence-based practice in health and social care. Glasgow: McGraw Open Press University; 2011.
Google Scholar
Cook DJ, Mulrow CD, Haynes RB. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126(5):376–80.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Puljak L, Sambunjak D. Cochrane systematic review as a PhD thesis: an alternative with numerous advantages. Biochemia Medica. 2010;20(3):319–2.
ten Ham-Baloyi W, Jordan P. Systematic review as a research method in post-graduate nursing education. Health SA Gesondheid. 2016;21:120–8.
Article Google Scholar
Organisation for PhD Education in Biomedicine and Health Sciences in the European System (ORPHEUS). Available at: http://www.orpheus-med.org/ .
Feinstein AR. Meta-analysis: statistical alchemy for the 21st century. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995;48(1):71–9.
Meerpohl JJ, Herrle F, Reinders S, Antes G, von Elm E. Scientific value of systematic reviews: survey of editors of core clinical journals. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35732.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Biondi-Zoccai G, Lotrionte M, Landoni G, Modena MG. The rough guide to systematic reviews and meta-analyses. HSR proc intensive care cardiovascular anesth. 2011;3(3):161–73.
CAS Google Scholar
Baethge C. Publish together or perish: the increasing number of authors per article in academic journals is the consequence of a changing scientific culture. Some researchers define authorship quite loosely. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2008;105(20):380–3.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statist Med. 2002;21:1539–58.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000100.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, Porter AC, Tugwell P, Moher D, Bouter LM. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:10.
Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusic A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Balajic K, Barac-Latas V, Drenjancevic I, Ostojic M, Fabijanic D, Puljak L. Influence of a vertical subject on research in biomedicine and activities of the Cochrane collaboration branch on medical students’ knowledge and attitudes toward evidence-based medicine. Croat Med J. 2012;53(4):367–73.
Marusic A, Sambunjak D, Jeroncic A, Malicki M, Marusic M. No health research without education for research—experience from an integrated course in undergraduate medical curriculum. Med Teach. 2013;35(7):609.
Mahtani KR. All health researchers should begin their training by preparing at least one systematic review. J R Soc Med. 2016;109(7):264–8.
Olsson C, Ringner A, Borglin G. Including systematic reviews in PhD programmes and candidatures in nursing - ‘Hobson’s choice’? Nurse Educ Pract. 2014;14(2):102–5.
Chalmers I, Glasziou P. Avoidable waste in the production and reporting of research evidence. Lancet. 2009;374(9683):86–9.
de Vries RB, Wever KE, Avey MT, Stephens ML, Sena ES, Leenaars M. The usefulness of systematic reviews of animal experiments for the design of preclinical and clinical studies. ILAR J. 2014;55(3):427–37.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the ORPHEUS secretariat for administering the survey and the study participants for taking time to participate in the survey. We are grateful to Prof. Ana Marušić for the critical reading of the manuscript.
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation, grant no. IP-2014-09-7672 ‘Professionalism in Health Care’. The funder had no role in the design of this study or its execution and data interpretation.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed for the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Cochrane Croatia, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2, 21000, Split, Croatia
Livia Puljak
Department for Development, Research and Health Technology Assessment, Agency for Quality and Accreditation in Health Care and Social Welfare, Planinska 13, 10000, Zagreb, Croatia
Laboratory for Pain Research, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2, 21000, Split, Croatia
Livia Puljak & Damir Sapunar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors participated in the study design, data collection and analysis and writing of the manuscript, and both read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Livia Puljak .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The Ethics Committee of the University of Split School of Medicine approved the study. All respondents consented to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:.
Online survey used in the study. Full online survey that was sent to the study participants. (PDF 293 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Puljak, L., Sapunar, D. Acceptance of a systematic review as a thesis: survey of biomedical doctoral programs in Europe. Syst Rev 6 , 253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0653-x
Download citation
Received : 29 August 2017
Accepted : 30 November 2017
Published : 12 December 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0653-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Systematic review
- PhD program
- Biomedicine
- Study design
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Acceptance of a systematic review as a thesis: survey of biomedical doctoral programs in Europe
Livia puljak.
1 Cochrane Croatia, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2, 21000 Split, Croatia
2 Department for Development, Research and Health Technology Assessment, Agency for Quality and Accreditation in Health Care and Social Welfare, Planinska 13, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia
3 Laboratory for Pain Research, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2, 21000 Split, Croatia
Damir Sapunar
Associated data.
The datasets used and/or analysed for the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Systematic reviews (SRs) have been proposed as a type of research methodology that should be acceptable for a graduate research thesis. The aim of this study was to analyse whether PhD theses in European biomedical graduate programs can be partly or entirely based on SRs.
In 2016, we surveyed individuals in charge of European PhD programs from 105 institutions. The survey asked about acceptance of SRs as the partial or entire basis for a PhD thesis, their attitude towards such a model for PhD theses, and their knowledge about SR methodology.
We received responses from 86 individuals running PhD programs in 68 institutions (institutional response rate of 65%). In 47% of the programs, SRs were an acceptable study design for a PhD thesis. However, only 20% of participants expressed a personal opinion that SRs meet the criteria for a PhD thesis. The most common reasons for not accepting SRs as the basis for PhD theses were that SRs are ‘not a result of a PhD candidate’s independent work, but more of a team effort’ and that SRs ‘do not produce enough new knowledge for a dissertation’. The majority of participants were not familiar with basic concepts related to SRs; questions about meta-analyses and the type of plots frequently used in SRs were correctly answered by only one third of the participants.
Conclusions
Raising awareness about the importance of SRs and their methodology could contribute to higher acceptance of SRs as a type of research that forms the basis of a PhD thesis.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13643-017-0653-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Systematic reviews (SRs) are a type of secondary research, which refers to the analysis of data that have already been collected through primary research [ 1 ]. Even though SRs are a secondary type of research, a SR needs to start with a clearly defined research question and must follow rigorous research methodology, including definition of the study design a priori, data collection, appraisal of study quality, numerical analyses in the form of meta-analyses and other analyses when relevant and formulation of results and conclusions. Aveyard and Sharp defined SRs as ‘original empirical research’ because they ‘review, evaluate and synthesise all the available primary data, which can be either quantitative or qualitative’ [ 2 ]. Therefore, a SR represents a new research contribution to society and is considered the highest level in the hierarchy of evidence in medicine [ 3 ].
SRs have been proposed as a type of research methodology that should be acceptable as the basis for a graduate research thesis [ 4 , 5 ]. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the acceptance of SRs as the basis for PhD theses. A recent review addressed potential advantages and disadvantages of such a thesis type and presented opposing arguments about the issue [ 5 ]. However, there were no actual data that would indicate how prevalent one opinion is over another with regard to the acceptance of a SR as the primary research methodology for a PhD thesis. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess whether a PhD thesis in European biomedical graduate programs can be partly or entirely based on a SR, as well as to explore the attitudes and knowledge of individuals in charge of PhD programs with regard to a thesis of this type.
Participants
The Organization of PhD Education in Biomedicine and Health Sciences in the European System (ORPHEUS) includes 105 institutional members from 40 countries and six associate members from Canada, Georgia, Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan and the USA [ 6 ]. The ORPHEUS encompasses a network of higher education institutions committed to developing and disseminating best practice within PhD training programs in biomedicine, health sciences and public health. ORPHEUS approved the use of their mailing list for the purpose of this study. The mailing list had 1049 contacts. The study authors were not given the mailing list due to data protection and privacy. Instead, it was agreed that ORPHEUS officials would send the survey via email to the mailing list. The General Secretary of the ORPHEUS contacted individuals responsible for PhD programs (directors or deputy directors) among the institutional members, via e-mail, on 5th of July 2016. These individuals were sent an invitation to complete an online survey about SRs as the basis for PhD theses. We invited only individuals responsible for PhD programs (e.g., directors, deputy directors, head of graduate school, vice deans for graduate school or similar). We also asked them to communicate with other individuals in charge of their program to make sure that only one person per PhD program filled out the survey. If there were several PhD programs within one institution, we asked for participation of one senior person per program.
The survey was administered via Survey Monkey (Portland, OR, USA). The survey took 5–10 min to complete. One reminder was sent to the targeted participants 1 month after the first mail.
The ethics committee of the University of Split School of Medicine approved this study, which formed part of the Croatian Science Foundation grant no. IP-2014-09-7672 ‘Professionalism in Health Care’.
Questionnaire
The 20-item questionnaire, designed specifically for this study by both authors (LP and DS), was first tested for face validity and clarity among five individuals in charge of PhD programs. The questionnaire was then modified according to their feedback. The questionnaire included questions about their PhD program; whether PhD candidates are required to publish manuscript(s) before thesis defence; the minimum number of required manuscripts for defending a PhD thesis; the authorship requirements for a PhD candidate with regard to published manuscript(s); whether there is a requirement for a PhD candidate to publish manuscript(s) in journals indexed in certain databases or journals of certain quality, and how the quality is defined; the description about other requirements for defending a PhD thesis; whether a SR partly or fully meets requirements for approval of a PhD thesis in their graduate program; what are the rules related to the use of a SR as the basis for a PhD thesis; and the number of PhD theses based on SRs relative to other types of research methods.
Participants were also asked about their opinion with regard to the main reasons that SRs are not recognised in some institutions as the basis for a doctoral dissertation, and their opinion about literature reviews, using a four-item Likert scale, ranging from ‘agree’ to ‘disagree’, including an option for ‘don’t know’. In the last question, the participants’ knowledge about SR methodology was examined using nine statements; participants had to rate each statement as either ‘correct’, ‘incorrect’, ‘unsure’ or ‘I don’t know’. Finally, participants were invited to leave their email address if they wanted to receive survey results. The survey sent to the study participants can be found in an additional file (Additional file 1 ).
Data analysis
Survey responses were entered into a spreadsheet, checked by both authors and analysed using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Inc., Redmond, WA, USA). Descriptive data are presented as frequencies and percentages. All raw data and analysed data sets used in the manuscript are available from authors on request. A point-biserial correlation (SPSS, IBM, Chicago, IL, USA) was used to measure the strength of the association between results on the knowledge test (continuous variable) and the attitude towards SRs as the basis for dissertations (dichotomous variable; we used the answer to the following question as this measure: ‘Do you agree that a systematic review, in whole or in part, meets the criteria for a publication on which a doctoral dissertation can be based?’).
Study participants
There are 105 institutions included in the ORPHEUS network. We received a response from 86 individuals representing 68 institutions from 37 countries (65% institutional response rate). There were more respondents than institutions because some institutions have several PhD programs and thus several program directors. Those responders were used as a unit of analysis in the analysis of attitudes and knowledge; institutions were the unit of analysis when analysing criteria for theses. Some of the questionnaires ( n = 15) were only partly completed. In most cases, the missing data were related to knowledge about SR methodology.
Overview of requirements for a dissertation
Based on the information provided by the graduate program directors, in the majority of the included PhD programs, students were required to publish a research manuscript prepared within their PhD thesis prior to their thesis defence (83%; n = 64). Among 13 programs (17%) that did not have this requirement, five respondents (38%) indicated that in their opinion their school’s rules related to a PhD thesis should be changed such as to specify that each thesis should be based on work that is already published in a journal.
The minimum number of published manuscripts necessary for the PhD thesis defence was prespecified in 94% ( n = 60) of the programs that required publication of research manuscripts prior to the thesis defence. In most of the programs (37%; n = 22), the number of required manuscripts was three or more. Two manuscripts were required in 30% ( n = 18) and one was required in 33% ( n = 20) of the programs. In four programs, there was no formal policy on this matter, but there was a strong expectation that the student will have contributed substantially to several manuscripts in peer-reviewed journals.
In most cases, the PhD candidates’ contribution to published manuscripts within the PhD thesis was determined through first authorship. A requirement that a PhD candidate should be the first author on a manuscript(s) that constitutes a PhD thesis was reported in 82% ( n = 64) of the graduate programs.
In 60% ( n = 52) of the graduate programs, the quality of the journals where a PhD candidate has to publish research manuscripts as a part of a PhD thesis was defined by the database in which these journals are indexed. The most commonly specified databases were Web of Science (41%; n = 35) and MEDLINE/PubMed (13%; n = 11), followed by Science Citation Index, Scopus, Current Contents, a combination of several databases or, in two cases, a combination of journals from a list defined by some governing body.
Systematic reviews as a PhD thesis
SRs, in whole or in part, met the criteria for acceptable research methodology for a PhD thesis in 47% ( n = 40) of programs, whereas 53% ( n = 46) of programs specifically stated that they did not accept SRs in this context (Fig. 1 a, b). Among the programs that accepted SRs, theses could be exclusively based on a SR in 42% ( n = 17) of programs, while in the remaining programs, SRs were acceptable as one publication among others in a dissertation.

a European PhD programs that recognise a systematic review as a PhD thesis (green dot) and those that do not (red dot). Half red and half green dots indicate the five universities with institutions that have opposite rules regarding recognition of a systematic review as a PhD thesis. The pie chart presents b the percentage of the programs in which systematic reviews, in whole or in part, meet the criteria for a dissertation and c the opinion of participants about whether systematic reviews should form the basis of a publication within a PhD dissertation
The majority of participants (80%; n = 69) indicated that SRs did not meet criteria for a publication on which a PhD dissertation should be based (Fig. 1 c). The main arguments for not recognising a SR as the basis for a PhD thesis are listed in Table 1 . The majority of respondents were neutral regarding the idea that scoping reviews or SRs should replace traditional narrative reviews preceding the results of clinical and basic studies in doctoral theses. Most of the respondents agreed that narrative or critical/discursive literature reviews preceding clinical studies planned as part of a dissertation should be replaced with systematic reviews (Table 2 ).
The main reasons for not recognising a systematic review as the basis for a PhD thesis in European biomedical graduate programs
Respondents’ opinions about literature reviews
Most of the programs that accepted SRs as a research methodology acceptable for PhD theses had defined rules related to the use of an SR as part of a PhD thesis (Fig. 2 ). The most common rule was that a SR can be one publication among others within a PhD thesis. Some of the respondents indicated that empty (reviews that did not find a single study that should be included after literature search) or updated reviews could also be used for a PhD thesis (Fig. 2 ).

Frequency of different rules that define the use of systematic reviews as a part of a PhD thesis in European biomedical graduate programs
The results of the survey regarding knowledge about SR methodology indicated that the majority of respondents were not familiar with this methodology. Only three out of nine questions were correctly answered by more than 80% of the participants, and questions about meta-analyses and the type of plots frequently used in a SR were correctly answered by only one third of the participants (Table 3 ). The association between participants’ results on the knowledge test and attitudes towards SRs was tested using a point-biserial correlation; this revealed that lack of knowledge was not correlated with negative attitudes towards SRs ( r pb = 0.011; P = 0.94).
Knowledge of systematic reviews among individuals in charge of European biomedical graduate programs
In this study conducted among individuals in charge of biomedical graduate programs in Europe, we found that 47% of programs accepted SRs as research methodology that can partly or fully fulfil the criteria for a PhD thesis. However, most of the participants had negative attitudes about such a model for a PhD thesis, and most had insufficient knowledge about the basic aspects of SR methodology. These negative attitudes and lack of knowledge likely contribute to low acceptance of SRs as an acceptable study design to include in a PhD thesis.
A limitation of this study was that we relied on participants’ responses and not on assessments of formal rules of PhD programs. Due to a lack of familiarity with SRs, it is possible that the respondents gave incorrect answers. We believe that this might be the case since we received answers from different programs in the same university, where one person claimed that SRs were accepted in their program, and the other person claimed that they were not accepted in the other program. We had five such cases, so it is possible that institutions within the same university have different rules related to accepted research methodology in graduate PhD programs. This study may not be generalisable to different PhD programs worldwide that were not surveyed. The study is also not generalisable to Europe, as there are no universal criteria or expectations for PhD theses in Europe. Even in the same country, there may be different models and expectations for a PhD in different higher education institutions.
A recent study indicated a number of opposing views and disadvantages related to SRs as research methodology for graduate theses, including lack of knowledge and understanding by potential supervisors, which may prevent them from being mentors and assisting students to complete such a study [ 5 ]. This same manuscript emphasised that there may be constraints if the study is conducted in a resource-limited environment without access to electronic databases, that there may be a very high or very low number of relevant studies that can impact the review process, that methods may not be well developed for certain types of research syntheses and that it may be difficult to publish SRs [ 5 ].
Some individuals believe that a SR is not original research. Indeed, it has been suggested that SRs as ‘secondary research’ are different than ‘primary or original research’, implying that they are inferior and lacking in novelty and methodological rigour as compared to studies that are considered primary research. In 1995, Feinstein suggested that such studies are ‘statistical alchemy for the 21st century’ and that a meta-analysis removes or destructs ‘scientific requirements that have been so carefully developed and established during the 19th and 20th centuries’ [ 7 ]. There is little research about this methodological issue. Meerpohl et al. surveyed journal editors and asked whether they consider SRs to be original studies. The majority of the editors indicated that they do think that SRs are original scientific contributions (71%) and almost all journals (93%) published SRs. That study also highlighted that the definition of original research may be a grey area [ 8 ]. They argued that, in an ideal situation, ‘the research community would accept systematic reviews as a research category of its own, which is defined by methodological criteria, as is the case for other types of research’ [ 8 ]. Biondi-Zoccai et al. pointed out that the main criteria to judge a SR should be its novelty and usefulness, and not whether it is original/primary or secondary research [ 9 ].
In our study, 80% of the participants reported negative attitudes, and more than half of the respondents agreed with a statement that SRs are ‘not a result of the candidate’s independent work since systematic reviews tend to be conducted by a team’. This opinion is surprising since other types of research are also conducted within a team, and single authorship is very rare in publications that are published within a PhD thesis. On the contrary, the mean number of authors of research manuscripts is continuously increasing [ 10 ]. At the very least, the authors of manuscripts within a PhD will include the PhD candidate and a mentor, which is a team in and of itself. Therefore, it is unclear why somebody would consider it a problem that a SR is conducted within a team.
The second most commonly chosen argument against such a thesis was that SRs ‘do not produce enough new knowledge for a dissertation’. The volume of a SR largely depends on the number of included studies and the available data for numerical analyses. Therefore, it is unfair to label a SR as a priori lacking in new knowledge. There are SRs with tens or hundreds of included studies, and some of them not only include meta-analyses, but also network meta-analyses, which are highly sophisticated statistical methods. However, limiting SRs within a thesis only to those with meta-analysis would be unfair because sometimes meta-analysis is not justified due to clinical or statistical heterogeneity [ 11 ] and the presence or absence of a meta-analysis is not an indicator of the quality of a SR. Instead, there are relevant checklists for appraising methodological and reporting quality of a SR [ 12 , 13 ].
The third most commonly chosen argument against SRs within PhD theses was ‘lack of adequate training of candidates in methodology of systematic reviews’. This could refer to either insufficient formal training or insufficient mentoring. The graduate program and the mentor need to ensure that a PhD candidate receives sufficient knowledge to complete the proposed thesis topic. Successful mentoring in academic medicine requires not only commitment and interpersonal skills from both the mentor and mentee, but also a facilitating institutional environment [ 14 ]. This finding could be a result of a lack of capacity and knowledge for conducting SRs in the particular institutions where the survey was conducted, and not general opinion related to learning a research method when conducting a PhD study. Formal training in skills related to SRs and research synthesis methods [ 15 , 16 ], as well as establishing research collaborations with researchers experienced in this methodology, could alleviate this concern.
One third of the participants indicated a ‘lack of appreciation of systematic review methodology among faculty members’ as a reason against such a thesis model. This argument, as well as the prevalent negative attitude towards SRs as PhD theses, perhaps can be traced to a lack of knowledge about SR methodology; however, although the level of knowledge was quite low in our study, there was no statistically significant correlation between knowledge and negative attitudes. Of the nine questions about SR research methodology, only three questions were correctly answered by more than half of the participants. This could be a cause for concern because it has been argued that any health research should begin with a SR of the literature [ 17 ]. It has also been argued that the absence of SRs in the context of research training might severely hamper research trainees and may negatively impact the research conducted [ 18 ]. Thus, it has been recommended that SRs should be included ‘whenever appropriate, as a mandatory part of any PhD program or candidature’ [ 18 ].
It has recently been suggested that the overwhelming majority of investment in research represents an ‘avoidable waste’ [ 19 ]. Research that is not necessary harms both the public and patients, because funds are not invested where they are really necessary, and necessary research may not be conducted [ 17 ]. This is valid not only for clinical trials, but also for other types of animal and human experiments [ 20 ]. SRs can help improve the design of new experiments by relying on current evidence in the field and by helping to clarify which questions still need to be addressed. SRs can be instrumental in improving methodological quality of new experiments, providing evidence-based recommendations for research models, reducing avoidable waste, and enabling evidence-based translational research [ 20 ].
Four respondents from three institutions indicated that empty SRs are accepted as a PhD thesis. While it makes sense to include such a SR as a part of the thesis to indicate lack of evidence in a certain field, it is highly unlikely that an entire thesis can be based on an empty SR, without a single included study.
There are many advantages of a SR as a graduate thesis [ 4 , 5 ], especially as a research methodology suitable for low-resource settings. A PhD candidate can prepare a Cochrane SR as a part of the PhD thesis, yielding a high-impact publication [ 4 ]. Non-Cochrane SRs can also be published in high-impact journals. A PhD candidate involved in producing a SR within a PhD thesis goes through the same research process as those conducting primary research, from setting up a hypothesis and a research question, to development of a protocol, data collection, data analysis and appraisal, and formulation of conclusions. Graduate programs can set limits, such as the prevention of empty reviews and the recognition of updated reviews as valid for a PhD thesis, and engage experienced researchers as advisors and within thesis evaluation committees, to ensure that a candidate will conduct a high-quality SR [ 4 ]. Conducting a SR should not be mandatory, but candidates and mentors willing to produce such research within a graduate program should be allowed to do so.
Further studies in this field could provide better insight into attitudes related to SRs as graduate theses and explore interventions that can be used to change negative attitudes and improve knowledge of SRs among decision-makers in graduate education.
Raising awareness about the importance of SRs in biomedicine, the basic aspects of SR methodology and the status of SRs as original secondary research could contribute to greater acceptance of SRs as potential PhD theses. Our results can be used to create strategies that will enhance acceptance of SRs among graduate education program directors.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the ORPHEUS secretariat for administering the survey and the study participants for taking time to participate in the survey. We are grateful to Prof. Ana Marušić for the critical reading of the manuscript.
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation, grant no. IP-2014-09-7672 ‘Professionalism in Health Care’. The funder had no role in the design of this study or its execution and data interpretation.
Availability of data and materials
Additional file.
Online survey used in the study. Full online survey that was sent to the study participants. (PDF 293 kb)
Authors’ contributions
Both authors participated in the study design, data collection and analysis and writing of the manuscript, and both read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Ethics Committee of the University of Split School of Medicine approved the study. All respondents consented to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Livia Puljak, Phone: +385-21-557-807, Email: rh.tsfem@aivil , Email: [email protected] .
Damir Sapunar, Email: [email protected] .
Systematic Literature Review and Expert Interviews
- First Online: 04 September 2021
Cite this chapter

- Alexander G. W. Schröder 6
Part of the book series: Entrepreneurship ((ENTRE))
578 Accesses
We followed two successive procedures to identify relevant attributes that make IVC and CVC comparable.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
The expert interviews were conducted in the form of a Master Thesis, which was supervised and guided by the author of this dissertation. The interview transcripts are listed in the appendices of that thesis.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Berlin, Germany
Alexander G. W. Schröder
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alexander G. W. Schröder .
3.1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (ZIP 402 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Schröder, A.G.W. (2021). Systematic Literature Review and Expert Interviews. In: The Founder’s Investor Choice . Entrepreneurship. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-35345-2_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-35345-2_3
Published : 04 September 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-35347-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-35345-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
by Angela Boland, M. Gemma Cherry and Rumona Dickson. Chapter 1. Carrying Out a Systematic Review as a Master's Thesis. Explore the wealth of resources available across the web. Here are some good places to start. Link to the Campbell Collaboration, an organization that prepares, maintains and disseminates systematic reviews in education, crime ...
This Master of Science thesis uses a systematic literature review to identify the current research. The thesis presents a systematic literature review on agile project management, and conducts a classification of the studies. It provides a comprehensive study of planning, conducting and documenting the outcome of the APM review.
Systematic literature reviews are a means to rigorously review existing literature on a specific topic. They collect and analyze existing literature in a systematic and replicable way. Following the definition of a topic of interest and concrete research question, a systematic literature review starts by defining several keywords.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
by Angela Boland, M. Gemma Cherry and Rumona Dickson. Chapter 1. Carrying Out a Systematic Review as a Master's Thesis. Here are some other helpful materials for you to read through. Centre for Review and Dissemination's guidance for undertaking systematic reviews in health care.
Now, the term systematic review has a very clear definition, but unfortunately the term is used loosely even in academic settings. Students may be asked to write a 'systematic review,' meaning only that they should adopt a thorough and scholarly approach. All literature reviews should be that, but a systematic review has a
We suggest master's thesis and doctoral dissertation committees review students' literature review protocols as part of the proposal defense. Step 3: Search the Literature The quality of literature review is highly dependent on the literature collected for the review—"Garbage-in, garbage-out."
Method details Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12].An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a ...
A systematic literature review is a specific research methodology to identify, select, evaluate, and synthesise relevant published and unpublished literature to answer a particular research question. ... Structured literature reviews can be found in the Masters Thesis Archive (MTA) and systematic literature reviews can be found in the Cranfield ...
A literature review, though a systematic review with critique and suggestions to the field can be acceptable. A formal meta-analysis is acceptable in that it generates new knowledge. A group project, though the thesis may be part of a collaborative project, provided the student had the lead role in that part (original work).
A: The length of a literature review can vary depending on the requirements of your master's thesis and the depth and breadth of the existing literature. In general, a literature review for a master's thesis is typically around 3000-5000 words, but this can vary based on the specific expectations of your program or advisor.
This is a step-by-step guide aimed at Master's students undertaking a structured literature review as part of their Master's thesis. There are several different kinds of literature reviews, but any literature review typically includes an extensive literature search. Whenever a systematic approach is used, the literature search features a ...
At least in my Faculty (of Computer Science), a master thesis can be "just" a literature review. A literature review can be an important contribution, and is part of what is usually called secondary research.. However, you should consider performing a systematic literature review, which is a literature review comprising several analytic and precise steps to enhance the reliability of the study.
Title: : A Systematic Literature Review of Project Management Tools and Their Impact on Project Management Effectiveness. Committee Chair: Dr. Michael Dyrenfurth and Dr. Mitchell L. Springer This thesis was conducted to examine project effectiveness and the best methodologies to use for managing projects as supported by the literature.
Background Systematic reviews (SRs) have been proposed as a type of research methodology that should be acceptable for a graduate research thesis. The aim of this study was to analyse whether PhD theses in European biomedical graduate programs can be partly or entirely based on SRs. Methods In 2016, we surveyed individuals in charge of European PhD programs from 105 institutions. The survey ...
a European PhD programs that recognise a systematic review as a PhD thesis (green dot) and those that do not (red dot). Half red and half green dots indicate the five universities with institutions that have opposite rules regarding recognition of a systematic review as a PhD thesis. ... Narrative or critical/discursive literature reviews ...
These differences highlight shortcomings of the current literature on master's thesis supervision, which we further address in the avenues for future research. ... New perspectives in online doctoral supervision: A systematic literature review. Studies in Continuing Education, 41 (2) (2019), pp. 173-190, 10.1080/0158037X.2018.1532405.
1.2 Goal of this Thesis The method of solving the problem is a systematic literature review, which will include articles, books, researches and reviews about refactoring. In this review, we will try to cover the available information about the use of refactoring by developers and answer questions like when, why and how refactoring is used.
Report. 4. ii. Example for a Systematic Literature Review: In references 5 example for paper that use Systematic Literature Review (SlR) example: ( Event-Driven Process Chain for Modeling and ...
3.1 Specifics of Literature Review. The literature review is based on the approaches used by Josefy, Harrison, Sirmon, and Carnes (2017) and Su, Zhai, and Karlsson (2017). The former provide a literature review of firm survival and failure. The authors searched titles, abstracts, and keywords of eight top tier management and entrepreneurship ...
This thesis is closely related to the current research of the chair and includes a systematic literature review analyzing the development and current state of research on Mission Drift in organizations. The main tasks are: 1) identifying and collecting articles in influential peer-reviewed journals; 2) systematically reviewing and categorizing ...
Master Thesis "A systematic literature review of the field of Knowledge Management" Background Knowledge Management has become a critical factor in ensuring the long-term success of organizations. Therefore, as a discipline it has been at the center of several discussion repeatedly over the past few decades